⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-02-11 更新
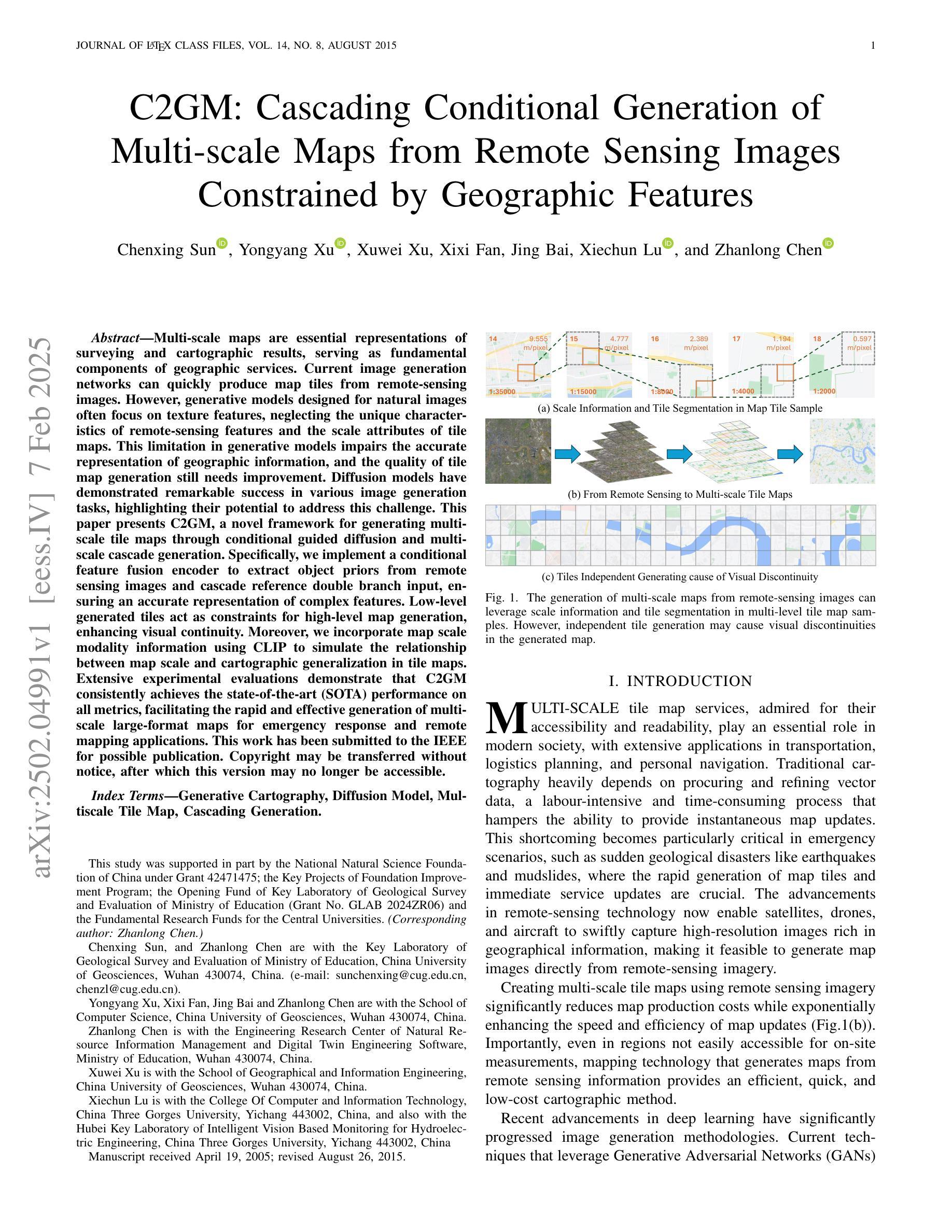
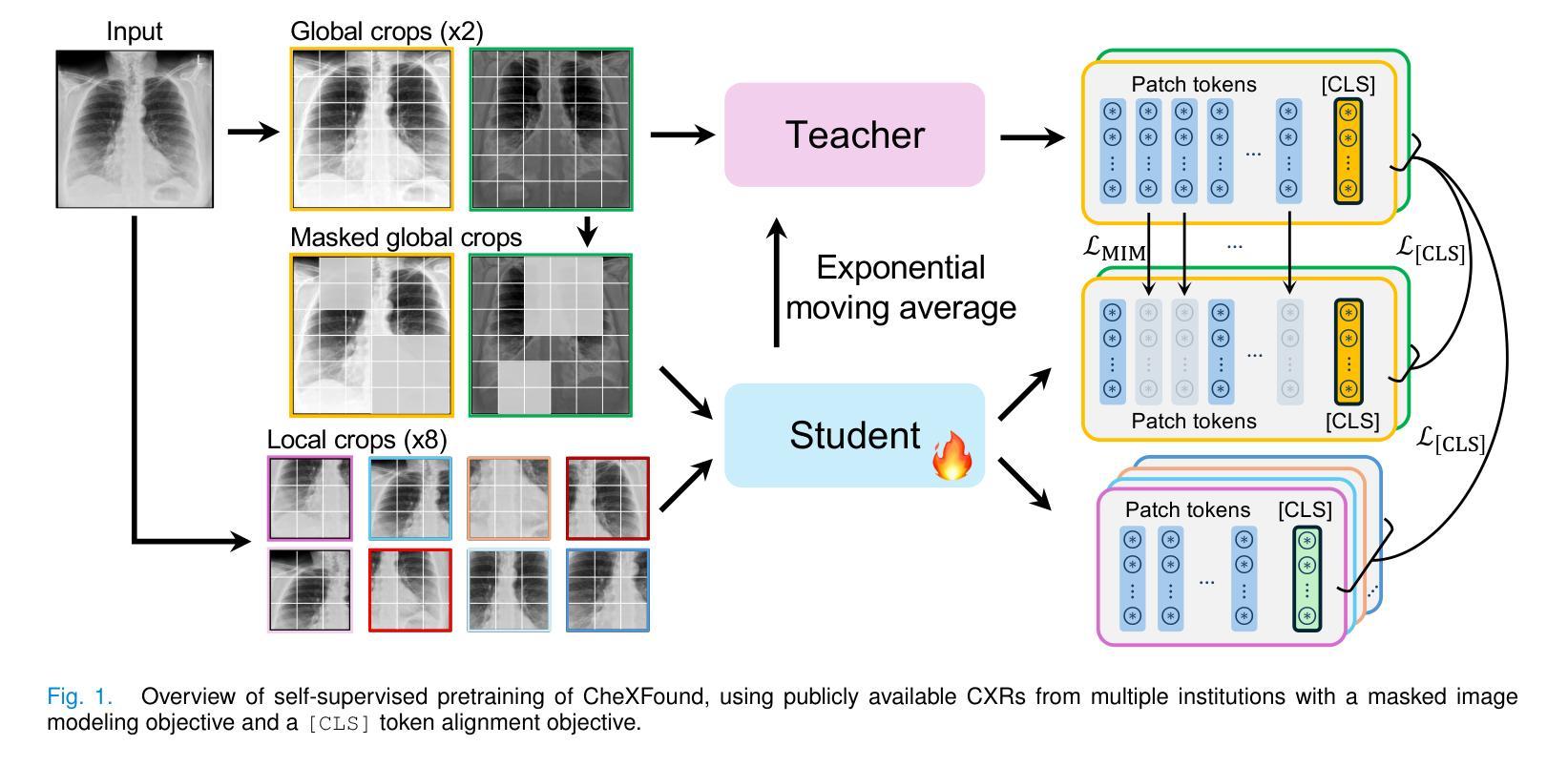
Chest X-ray Foundation Model with Global and Local Representations Integration
Authors:Zefan Yang, Xuanang Xu, Jiajin Zhang, Ge Wang, Mannudeep K. Kalra, Pingkun Yan
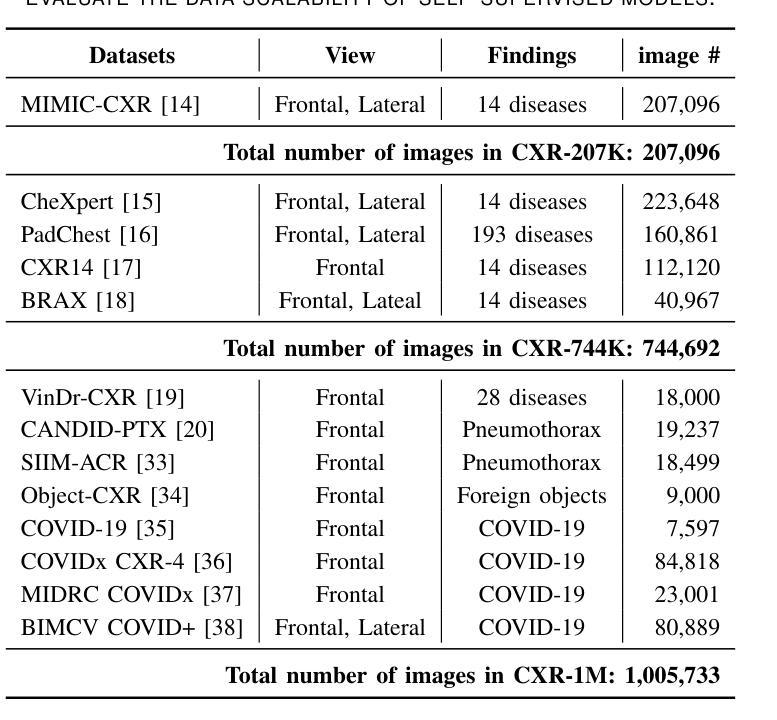
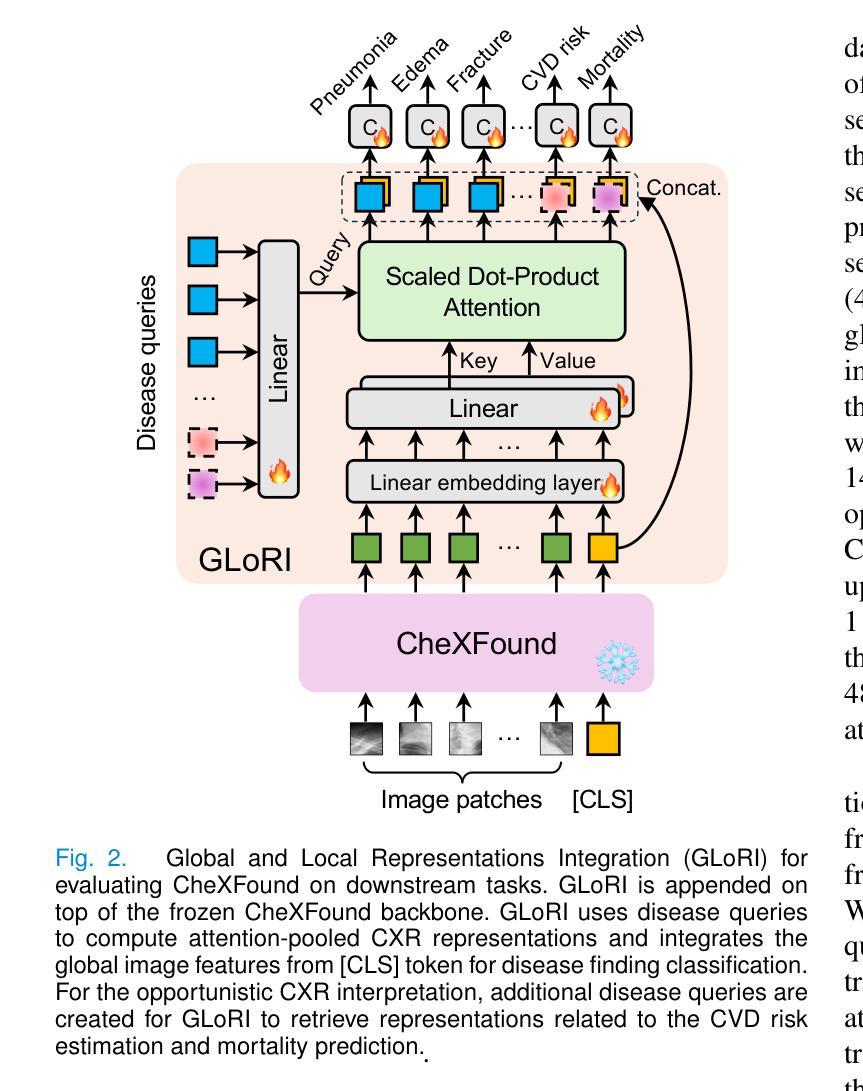
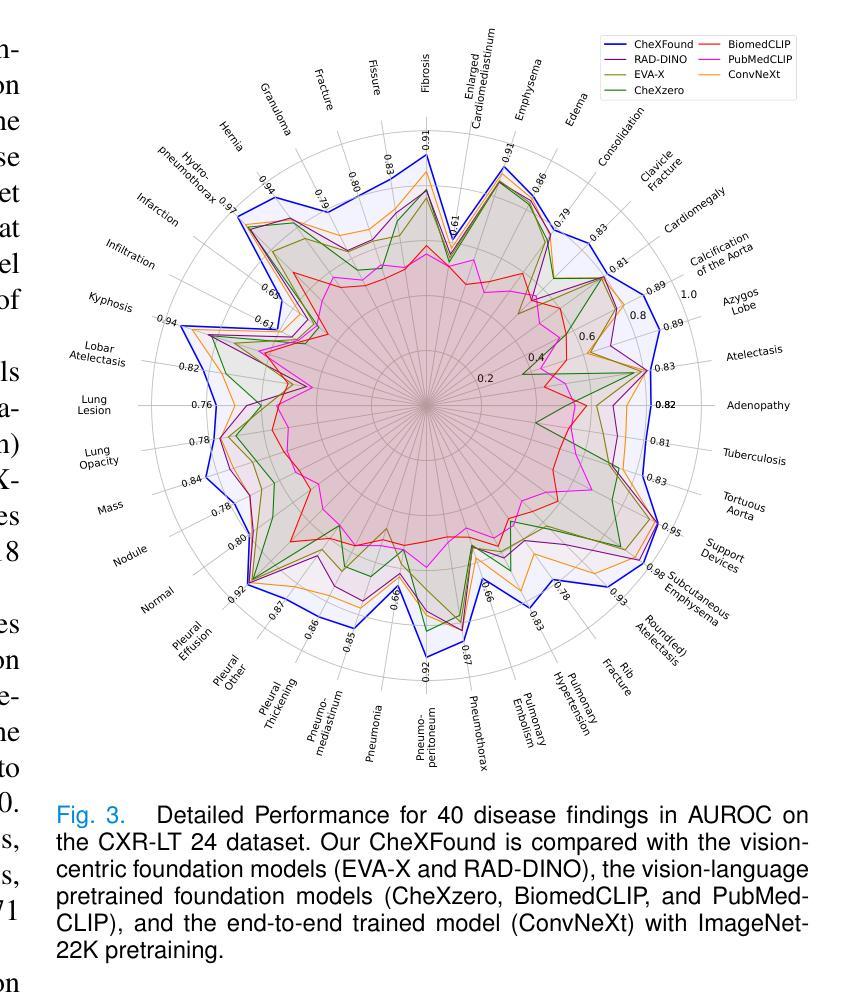
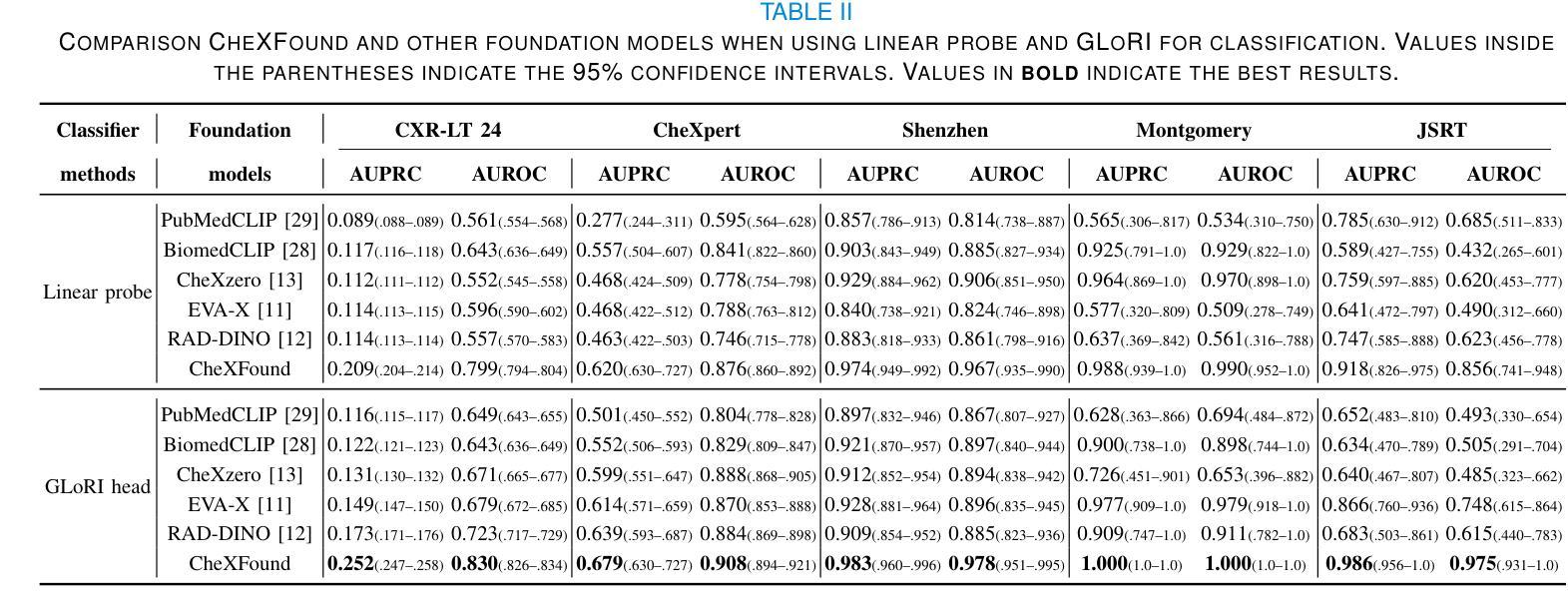
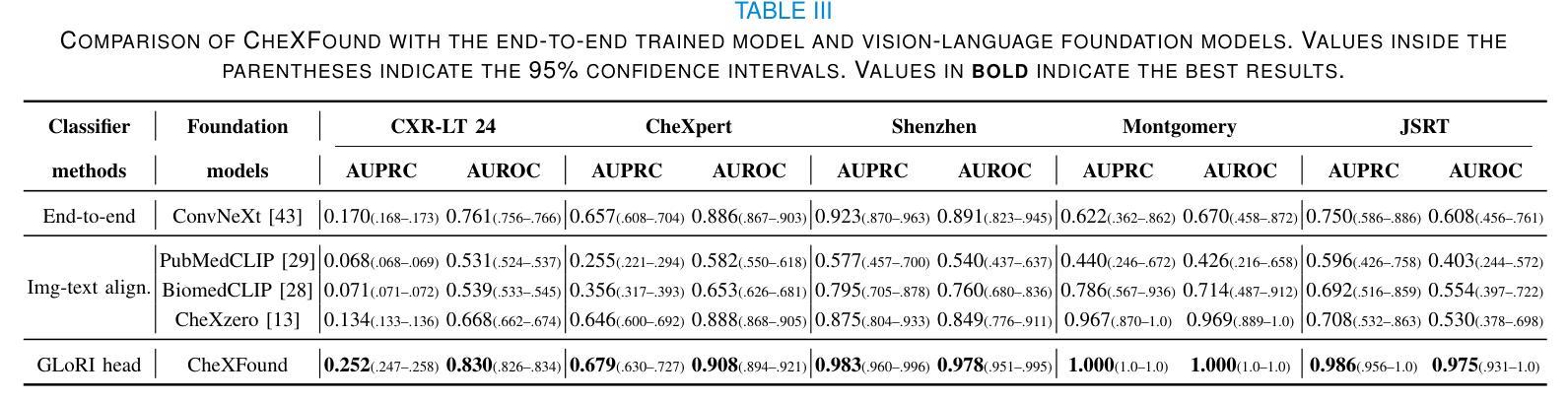
Chest X-ray (CXR) is the most frequently ordered imaging test, supporting diverse clinical tasks from thoracic disease detection to postoperative monitoring. However, task-specific classification models are limited in scope, require costly labeled data, and lack generalizability to out-of-distribution datasets. To address these challenges, we introduce CheXFound, a self-supervised vision foundation model that learns robust CXR representations and generalizes effectively across a wide range of downstream tasks. We pretrain CheXFound on a curated CXR-1M dataset, comprising over one million unique CXRs from publicly available sources. We propose a Global and Local Representations Integration (GLoRI) module for downstream adaptations, by incorporating disease-specific local features with global image features for enhanced performance in multilabel classification. Our experimental results show that CheXFound outperforms state-of-the-art models in classifying 40 disease findings across different prevalence levels on the CXR-LT 24 dataset and exhibits superior label efficiency on downstream tasks with limited training data. Additionally, CheXFound achieved significant improvements on new tasks with out-of-distribution datasets, including opportunistic cardiovascular disease risk estimation and mortality prediction. These results highlight CheXFound’s strong generalization capabilities, enabling diverse adaptations with improved label efficiency. The project source code is publicly available at https://github.com/RPIDIAL/CheXFound.
胸部X光(CXR)是最常进行的影像检查,支持从胸部疾病检测到术后监护的多种临床任务。然而,特定任务的分类模型在范围上有限,需要昂贵的标注数据,并且对超出分布范围的数据集缺乏通用性。为了应对这些挑战,我们引入了CheXFound,这是一种自我监督的视觉基础模型,能够学习稳健的CXR表示,并在广泛的下游任务中有效地进行推广。我们在定制的CXR-1M数据集上预训练CheXFound,该数据集包含来自公开来源的一百万多个独特的CXRs。我们提出了一个全局和局部表示集成(GLoRI)模块,用于下游适应,通过结合疾病特定的局部特征与全局图像特征,以提高多标签分类的性能。我们的实验结果表明,在CXR-LT 24数据集上,CheXFound在分类不同发病率的40种疾病发现方面优于最先进模型,并且在下游任务中表现出优越的标签效率,特别是在训练数据有限的情况下。此外,CheXFound在新任务上的表现也有显著改善,包括机会性心血管疾病风险评估和死亡率预测等超出分布范围的数据集。这些结果突显了CheXFound强大的通用性能力,能够实现多样化的适应并具有改进的标签效率。项目源代码可在https://github.com/RPIDIAL/CheXFound获取。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
CheXFound是一个基于自监督学习的通用医学图像基础模型,用于学习稳健的胸部X射线(CXR)表示,并广泛应用于多种下游任务。该模型在CXR-1M数据集上进行预训练,并通过结合全局图像特征和疾病特定的局部特征,使用一个名为Global and Local Representations Integration (GLoRI)的模块进行下游任务适配。实验结果表明,CheXFound在CXR-LT 24数据集上分类40种疾病的能力优于当前主流模型,并在具有有限训练数据的新任务上展现出出色的标签效率。此外,CheXFound在机会性心血管疾病风险评估和死亡率预测等离分布数据集的新任务上也取得了显著改进,证明了其强大的泛化能力。
Key Takeaways
- CheXFound是一个自监督的医学图像基础模型,用于学习稳健的胸部X射线(CXR)表示。
- CheXFound在广泛的下游任务中表现出强大的泛化能力。
- 通过预训练的CXR-1M数据集进行训练,包含超过一百万张独特的胸部X射线图像。
- 引入Global and Local Representations Integration (GLoRI)模块,结合全局图像特征和疾病特定的局部特征,提高下游任务的多标签分类性能。
- 在CXR-LT 24数据集上分类40种疾病的能力优于当前主流模型。
- 在具有有限训练数据的新任务上展现出出色的标签效率。
点此查看论文截图

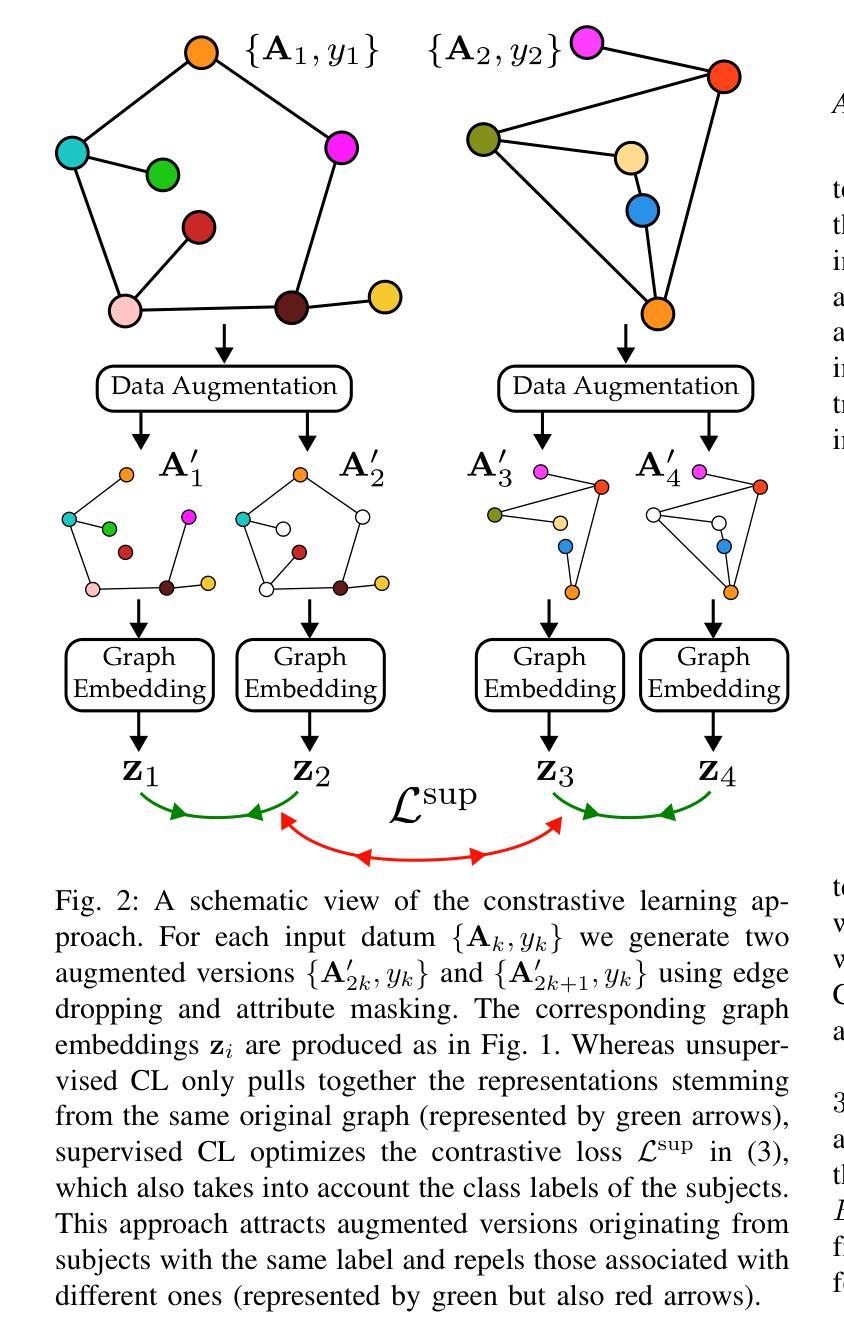
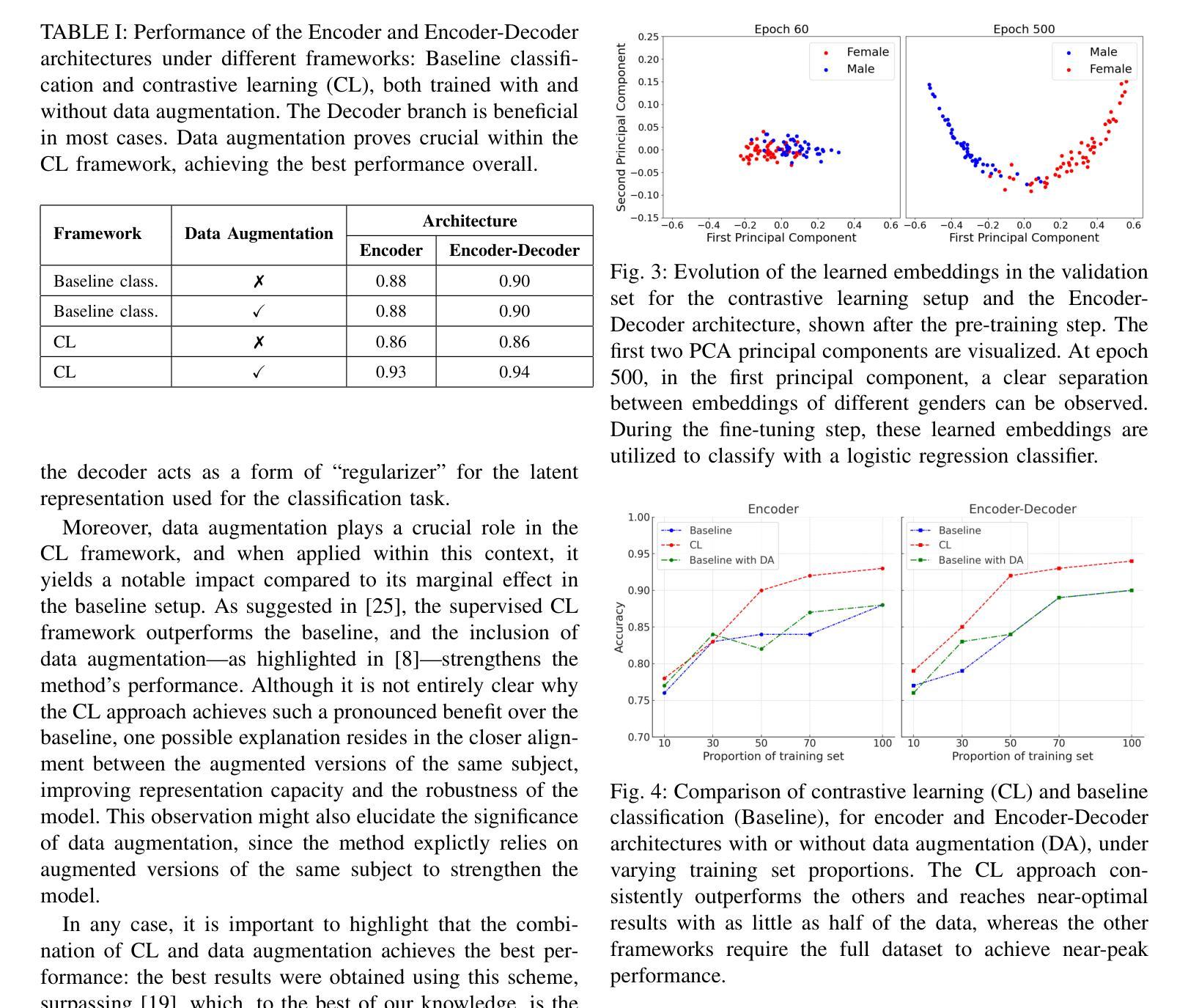
Graph Contrastive Learning for Connectome Classification
Authors:Martín Schmidt, Sara Silva, Federico Larroca, Gonzalo Mateos, Pablo Musé
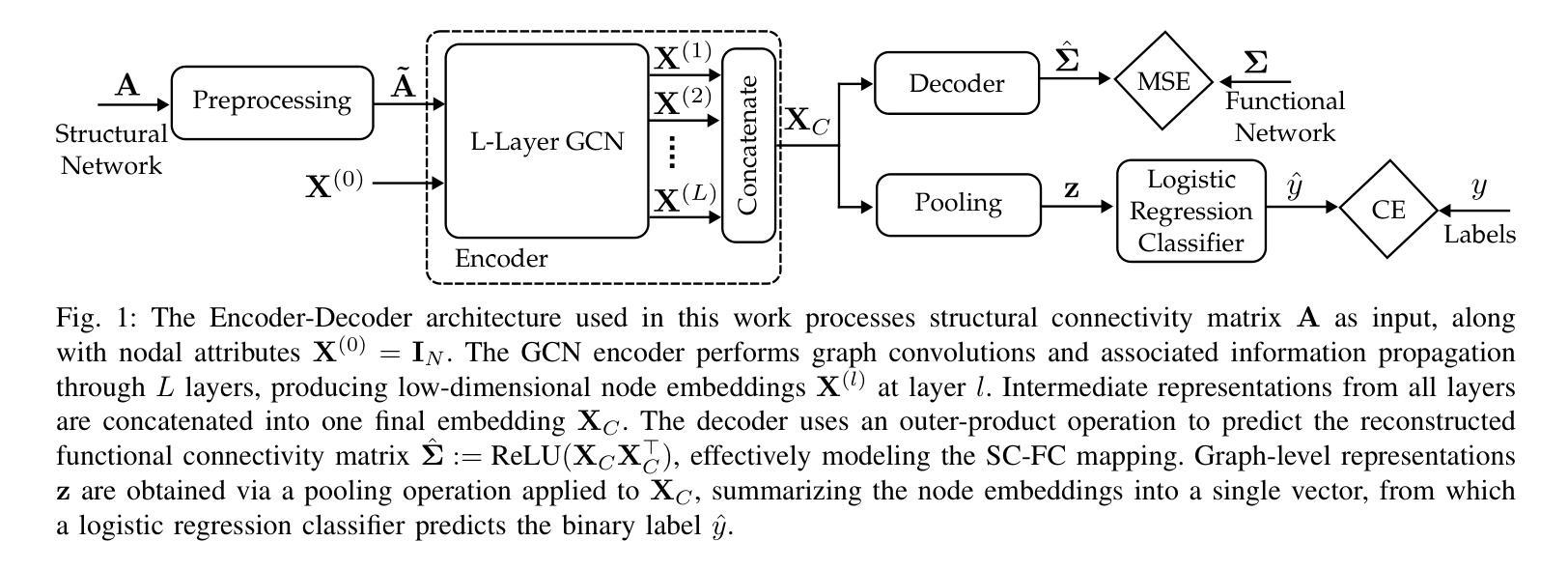
With recent advancements in non-invasive techniques for measuring brain activity, such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), the study of structural and functional brain networks through graph signal processing (GSP) has gained notable prominence. GSP stands as a key tool in unraveling the interplay between the brain’s function and structure, enabling the analysis of graphs defined by the connections between regions of interest – referred to as connectomes in this context. Our work represents a further step in this direction by exploring supervised contrastive learning methods within the realm of graph representation learning. The main objective of this approach is to generate subject-level (i.e., graph-level) vector representations that bring together subjects sharing the same label while separating those with different labels. These connectome embeddings are derived from a graph neural network Encoder-Decoder architecture, which jointly considers structural and functional connectivity. By leveraging data augmentation techniques, the proposed framework achieves state-of-the-art performance in a gender classification task using Human Connectome Project data. More broadly, our connectome-centric methodological advances support the promising prospect of using GSP to discover more about brain function, with potential impact to understanding heterogeneity in the neurodegeneration for precision medicine and diagnosis.
随着无创技术(如磁共振成像MRI)的最新发展,通过图形信号处理(GSP)研究脑的结构和功能网络已受到广泛关注。图形信号处理是揭示大脑功能和结构之间相互作用的关键工具,能够分析感兴趣区域之间连接所定义的图形,本文称之为连接组。我们的工作朝着这个方向迈出了一步,在图形表示学习的范围内探索了监督对比学习方法。这种方法的主要目标是生成主体级(即图级)的向量表示,这些表示能够将具有相同标签的主体聚集在一起,同时将具有不同标签的主体分开。这些连接组嵌入是从图形神经网络编码器-解码器架构中派生出来的,同时考虑了结构和功能连接。通过利用数据增强技术,所提出的框架在利用人类连接组项目数据的性别分类任务上达到了最先进的性能。更广泛地说,我们的以连接组为中心的方法论进步支持了使用图形信号处理来了解更多关于大脑功能的希望,这对精确医学和诊断中神经变异的异质性理解具有潜在影响。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Submitted to EMBC ‘25
Summary
医学图像研究领域近期借助非侵入技术(如磁共振成像MRI)的进步,通过图信号处理(GSP)研究脑结构和功能网络变得尤为突出。本研究旨在通过图表示学习中的监督对比学习方法,生成主体级别的向量表示,使相同标签的主体聚集,不同标签的主体分离。这些脑连接组嵌入来自图神经网络Encoder-Decoder架构,该架构联合考虑结构和功能连接。利用数据增强技术,该框架实现了人类连接组项目数据中的性别分类任务的最新性能。该研究的连接组为中心的方法论进步支持了GSP在了解大脑功能方面的前景,具有对神经变性的异质性的深入了解的潜力,有助于精准医疗和诊断。
Key Takeaways
- 利用非侵入技术(如MRI)进行脑结构和功能网络的研究成为当前焦点。
- 图信号处理(GSP)在解析脑功能结构交互中扮演重要角色。
- 监督对比学习方法用于生成主体级别的向量表示,实现相同标签主体的聚集和不同标签主体的分离。
- 脑连接组嵌入来源于图神经网络Encoder-Decoder架构,同时考虑结构和功能连接。
- 利用数据增强技术实现了性别分类任务的卓越性能。
- 研究方法在连接组为中心的图信号处理领域的进步对于深入了解大脑功能具有重要意义。
点此查看论文截图

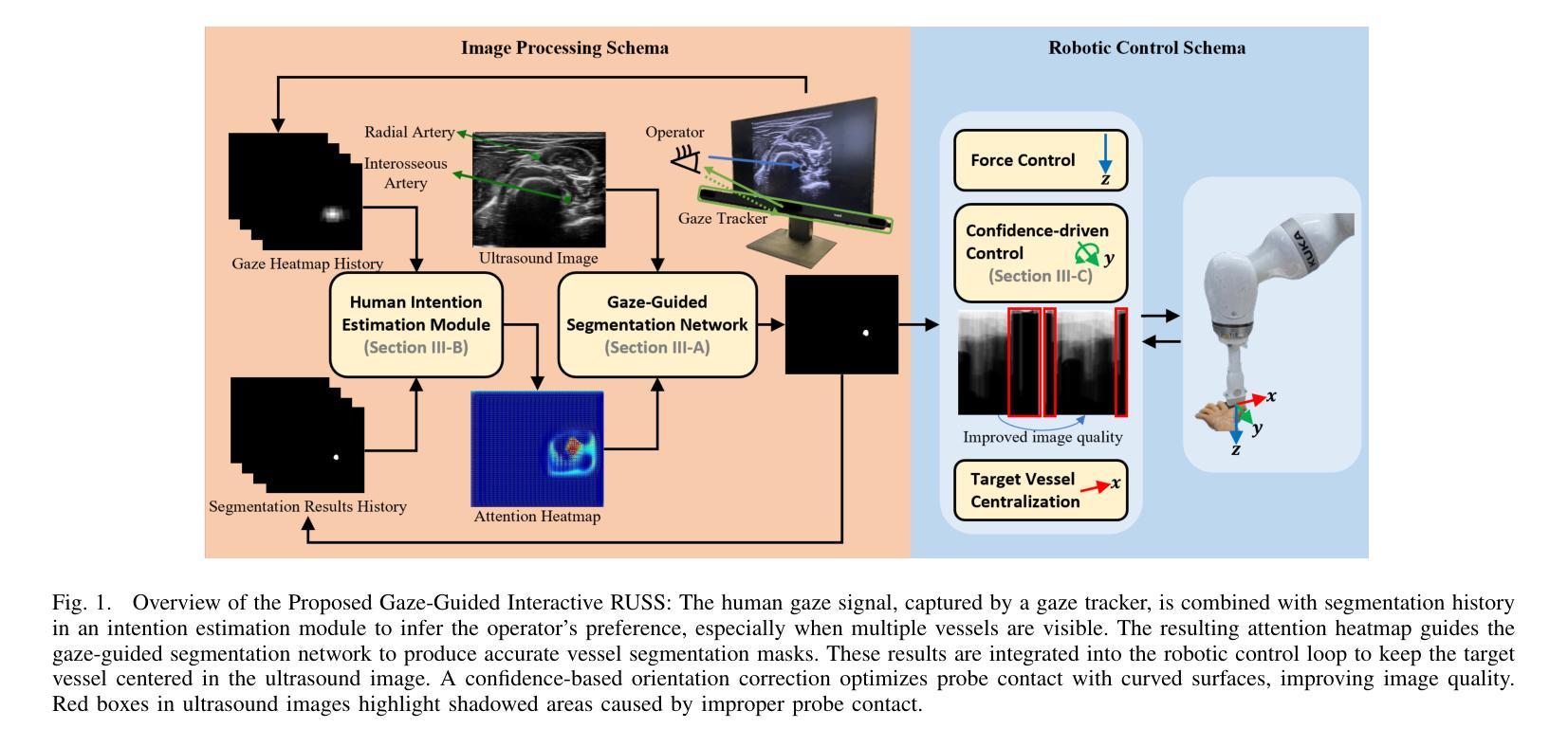
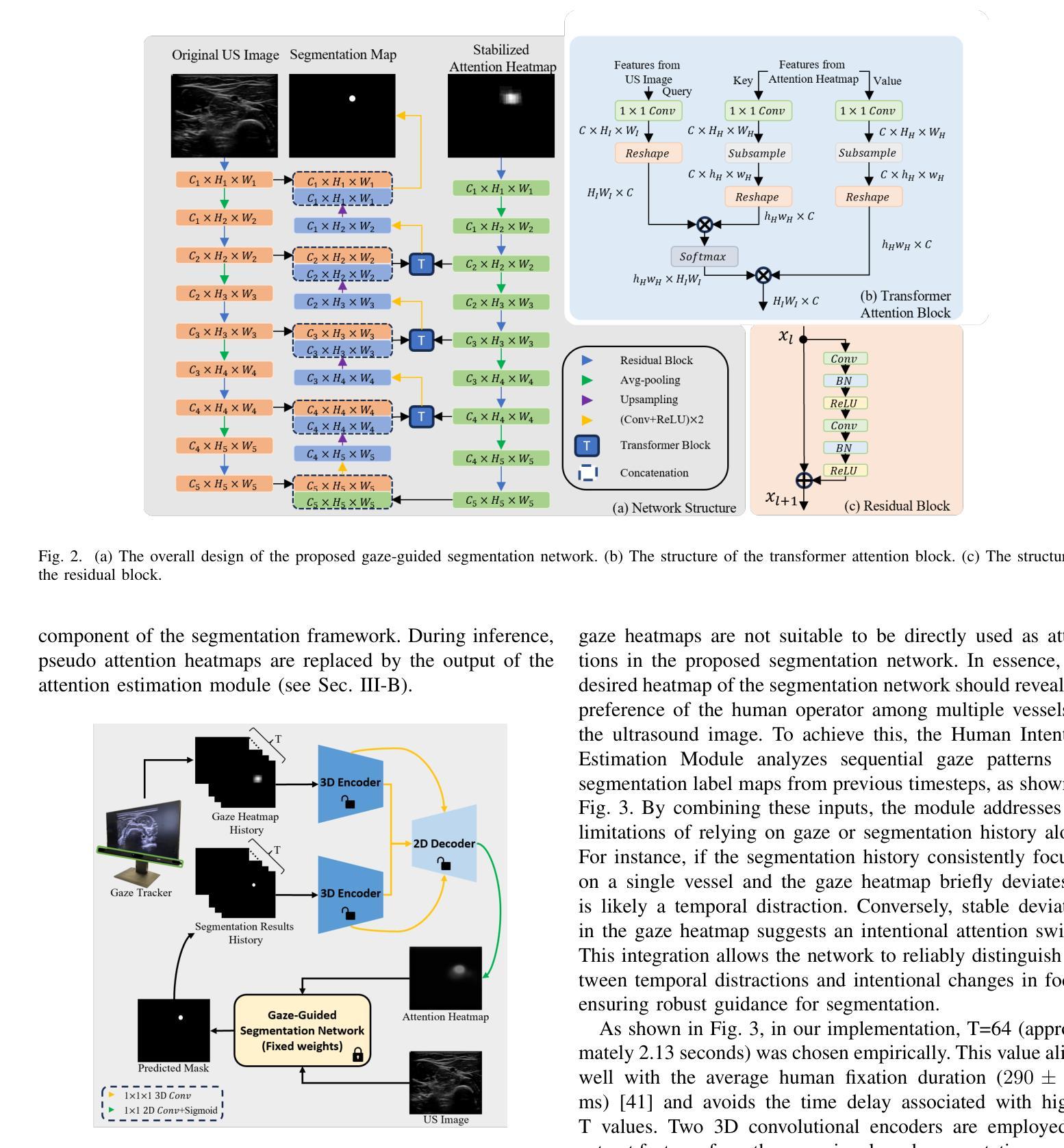
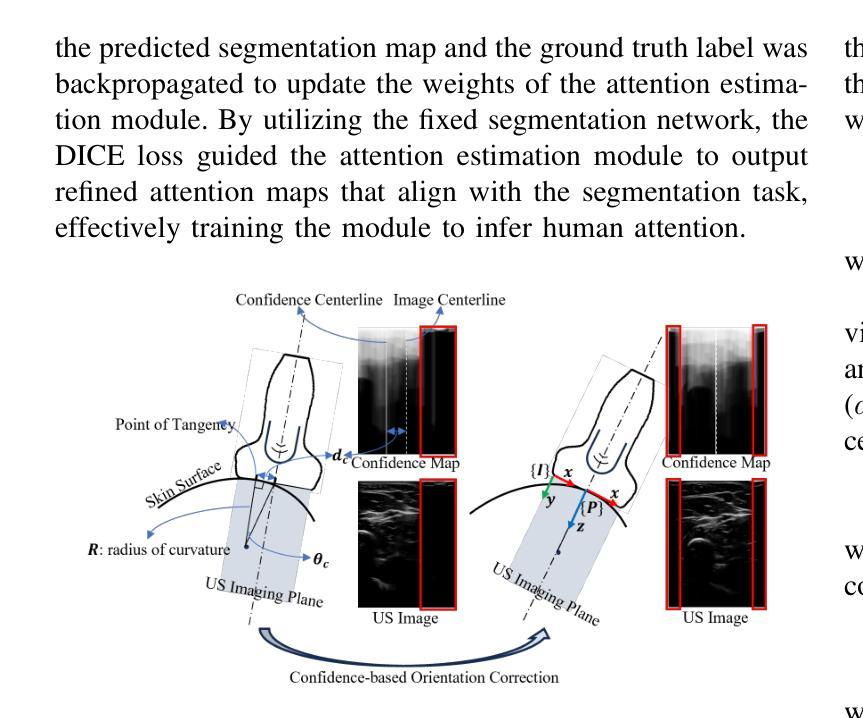
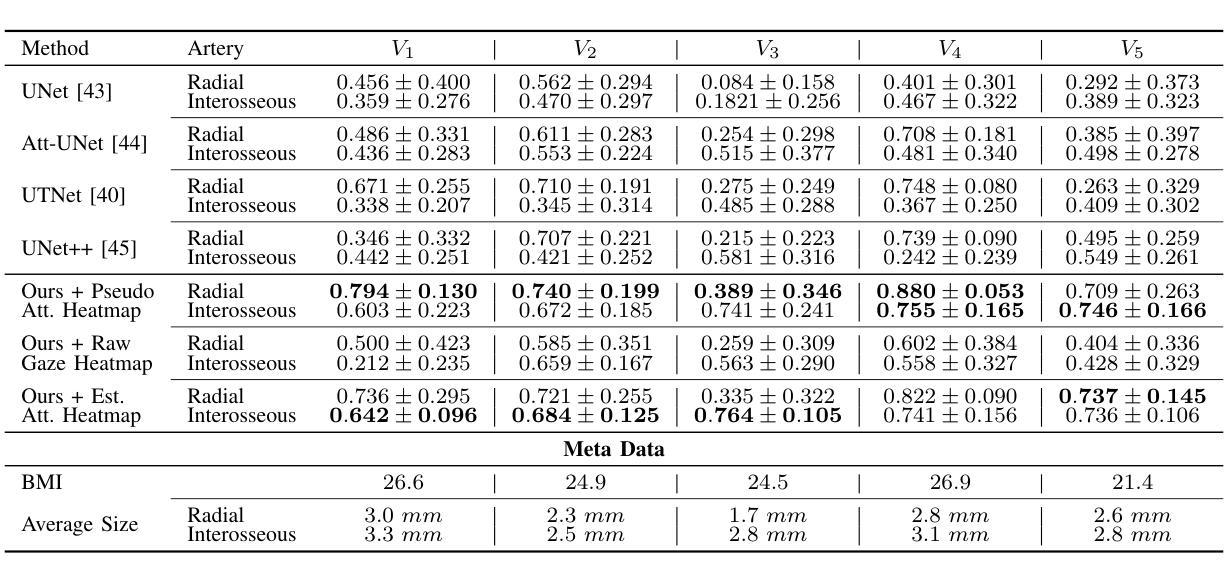
Gaze-Guided Robotic Vascular Ultrasound Leveraging Human Intention Estimation
Authors:Yuan Bi, Yang Su, Nassir Navab, Zhongliang Jiang
Medical ultrasound has been widely used to examine vascular structure in modern clinical practice. However, traditional ultrasound examination often faces challenges related to inter- and intra-operator variation. The robotic ultrasound system (RUSS) appears as a potential solution for such challenges because of its superiority in stability and reproducibility. Given the complex anatomy of human vasculature, multiple vessels often appear in ultrasound images, or a single vessel bifurcates into branches, complicating the examination process. To tackle this challenge, this work presents a gaze-guided RUSS for vascular applications. A gaze tracker captures the eye movements of the operator. The extracted gaze signal guides the RUSS to follow the correct vessel when it bifurcates. Additionally, a gaze-guided segmentation network is proposed to enhance segmentation robustness by exploiting gaze information. However, gaze signals are often noisy, requiring interpretation to accurately discern the operator’s true intentions. To this end, this study proposes a stabilization module to process raw gaze data. The inferred attention heatmap is utilized as a region proposal to aid segmentation and serve as a trigger signal when the operator needs to adjust the scanning target, such as when a bifurcation appears. To ensure appropriate contact between the probe and surface during scanning, an automatic ultrasound confidence-based orientation correction method is developed. In experiments, we demonstrated the efficiency of the proposed gaze-guided segmentation pipeline by comparing it with other methods. Besides, the performance of the proposed gaze-guided RUSS was also validated as a whole on a realistic arm phantom with an uneven surface.
现代医学实践中,医用超声已广泛应用于血管结构的检查。然而,传统超声检查常常面临操作者间和操作者内部的挑战。由于其在稳定性和可重复性方面的优势,机器人超声系统(RUSS)的出现为解决这些挑战提供了潜在解决方案。考虑到人类血管的复杂结构,超声图像中经常会出现多条血管,或者单个血管分叉成多个分支,使检查过程复杂化。为解决这一挑战,本研究提出了一种用于血管应用的目光引导型RUSS。目光追踪器捕捉操作员的眼球运动。提取的目光信号引导RUSS在血管分叉时追踪正确的血管。此外,本研究还提出了一种目光引导分割网络,利用目光信息提高分割的稳健性。然而,目光信号往往存在噪声,需要解读以准确判断操作员的真正意图。为此,本研究提出了一个稳定模块来处理原始的目光数据。推断出的注意力热图被用作区域提案,以辅助分割,并在操作员需要调整扫描目标(例如出现分叉时)时作为触发信号。为确保扫描过程中探头与表面之间的适当接触,开发了一种基于自动超声置信度的方向校正方法。通过与其他方法进行比较,我们验证了所提出的目光引导分割流程的效率。此外,在实际的手臂模型(具有不均匀表面)上,也对所提出目光引导型RUSS的整体性能进行了验证。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
医学超声广泛应用于现代临床实践中血管结构的检查,但传统超声检查常面临操作者间和操作者内部差异的挑战。机器人超声系统(RUSS)因其稳定性和可重复性优势,成为解决这些挑战的潜在方案。针对人类血管复杂结构,超声图像中常出现多条血管或单条血管分叉,使检查过程复杂化。本研究提出了一种用于血管应用的目光引导型RUSS。目光追踪器捕捉操作者的眼神动作,提取的目光信号引导RUSS在血管分叉时跟踪正确的血管。同时,提出一种目光引导分割网络,利用目光信息提高分割稳健性。然而,目光信号往往存在噪声,需要解读以准确判断操作者的真正意图。因此,本研究提出一种稳定模块来处理原始目光数据。推断出的注意力热图被用作区域提案,辅助分割,并在出现分叉等操作时触发信号,提醒操作者调整扫描目标。为确保扫描过程中探头与表面之间的适当接触,开发了一种基于自动超声置信度的方向校正方法。实验表明,与其他方法相比,所提出的目光引导分割管道的效率较高。此外,在具有不平表面的真实手臂幻影上验证了所提出目光引导型RUSS的性能。
关键见解
- 医学超声在血管结构检查中具有广泛应用,但传统超声检查面临操作者差异和血管结构复杂的挑战。
- 机器人超声系统(RUSS)因其稳定性和可重复性,被视为解决这些挑战的有潜力的方案。
- 提出一种目光引导型RUSS,通过捕捉操作者的眼动来指导机器人系统在复杂血管结构中的操作。
- 利用目光信号来增强图像分割的稳健性,并提出一种稳定模块来处理含有噪声的目光数据。
- 注意力热图作为区域提案,在血管分叉等情况下辅助分割并触发操作调整信号。
- 开发了一种自动超声置信度方法,以确保探头在扫描过程中的方向校正。
点此查看论文截图

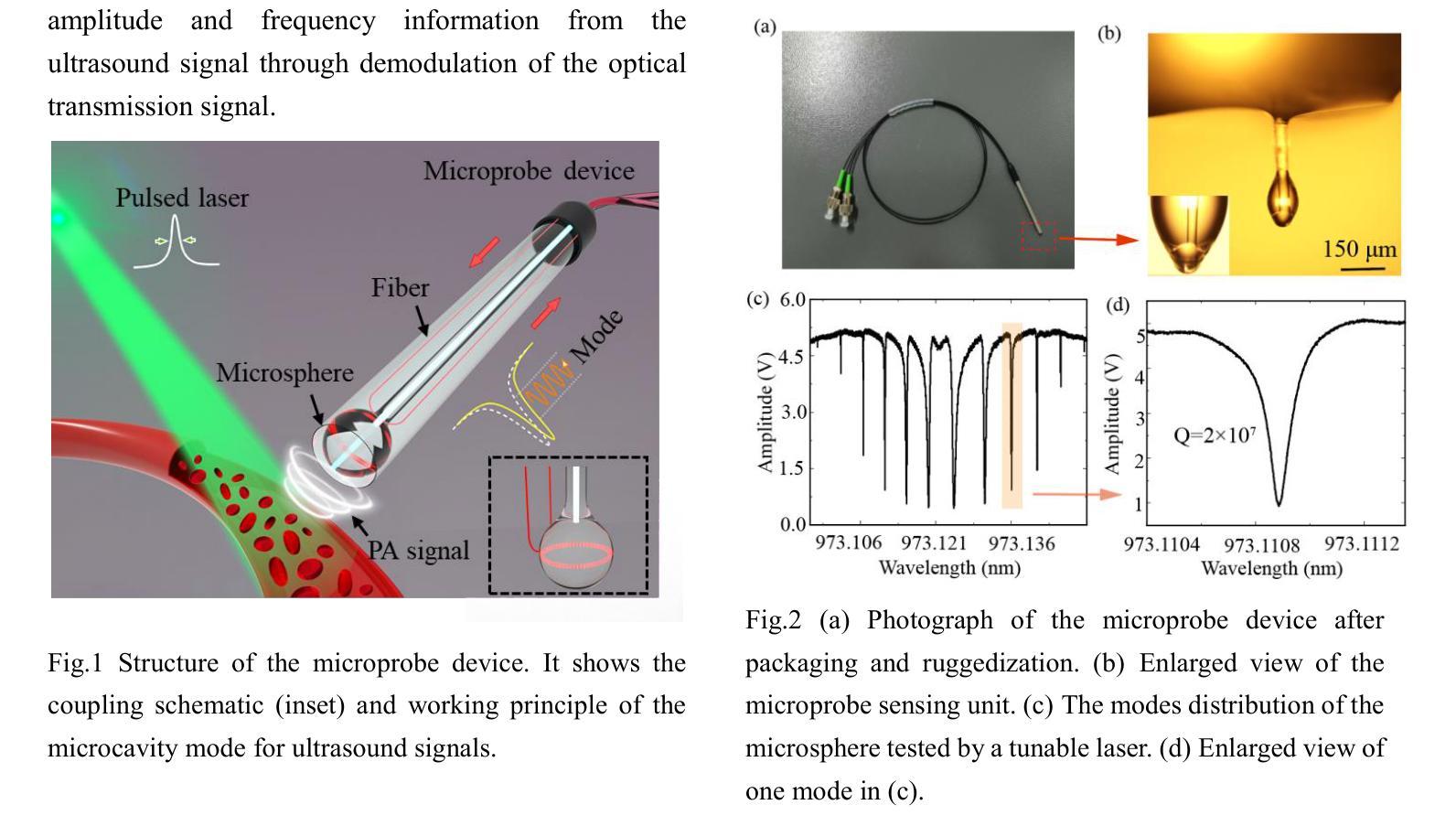
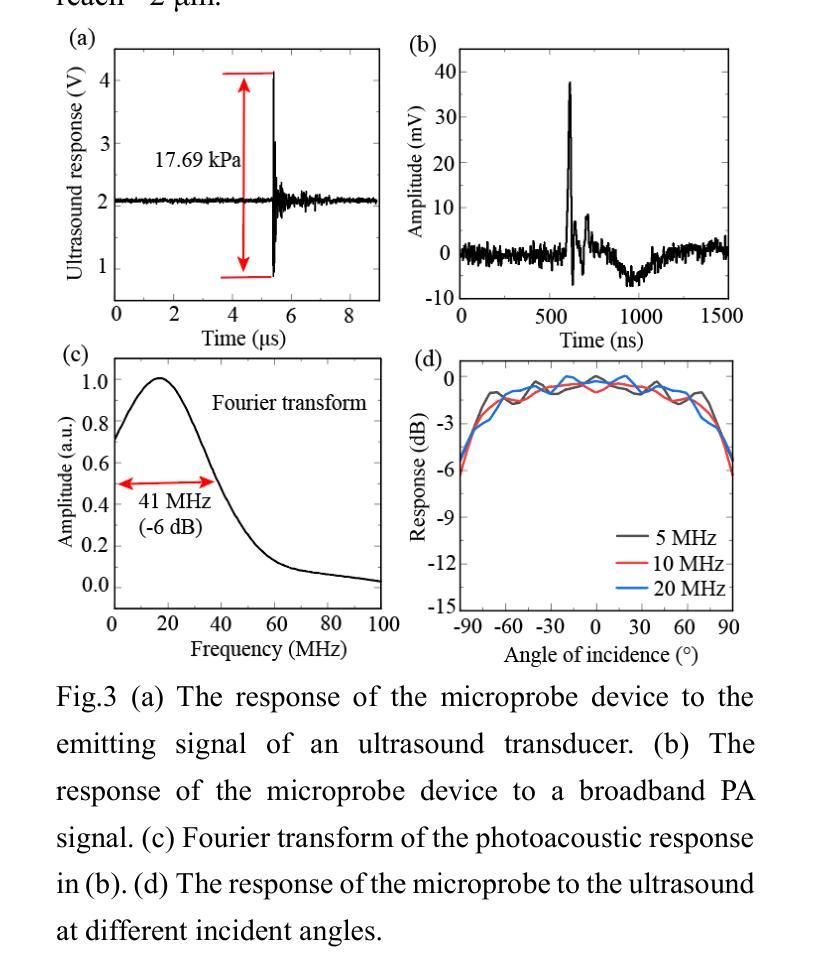
WGM microprobe device for high-sensitivity and broadband ultrasound detection
Authors:Jialve Sun, Shengnan Huangfu, Tinglan Chen, Zijing Cai, Bowen Ruan, Fangxing Zhang
Whispering-gallery-mode (WGM) microcavities have emerged as a promising alternative to traditional ultrasound probes, offering high sensitivity and wide bandwidth. In our research, we propose a novel silica WGM microprobe device, with impressive Q factors up to 10^7.The side-coupled approach and special encapsulation design make the device small, robust, and capable of utilizing in both gaseous and liquid environments.We have successfully conducted photoacoustic (PA) imaging on various samples using this device which demonstrates a high sensitivity of 5.4 mPa/sqrt(Hz) and a board bandwidth of 41 MHz at -6 dB for ultrasound. What’s more, it’s capable of capturing the vibration spectrum of microparticles up to a few hundred megahertz. Our compact and lightweight device exhibits significant application potential in PA endoscopic detection, near-field ultrasound sensing and other aspects.
低语型腔模式(WGM)微腔已经作为一种前景光明的超声探针替代方案出现,它提供了高灵敏度和宽带宽。在我们的研究中,我们提出了一种新型二氧化硅WGM微型探针设备,具有高达的Q因子(Q factor)达百万次方级。侧耦合方式和特殊的封装设计使得该设备体积小、稳定性高,能在气态和液态环境中都能应用自如。我们已经成功使用该设备对各种样本进行光声成像,证明了其灵敏度高达每赫兹的声压级为5.4米帕(mPa),超声波的带宽在-6分贝时达到41兆赫(MHz)。此外,它能够捕捉到高达数百兆赫兹的微粒子振动频谱。我们的紧凑且轻型的设备在光声内窥检测、近场超声感应等方面表现出显著的应用潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
微腔中的回音壁模式(WGM)微腔作为一种有前景的超声探针替代方案,具有高灵敏度和宽带宽的特点。研究中提出了一种新型二氧化硅WGM微探针设备,具有高达10^7的Q因子。该设备的侧耦合方式和特殊封装设计使其体积小、稳健,既可用于气体环境也可用于液体环境。使用此设备进行的光声成像实验表明,其灵敏度高达5.4 mPa/sqrt(Hz),在-6 dB时的超声波带宽为41 MHz,并能捕捉到高达数百兆赫兹的微粒子振动光谱。此紧凑轻便的设备在光声内窥检测、近场超声传感等方面具有显著的应用潜力。
Key Takeaways
- WGM微腔作为超声探针的替代方案,具有高灵敏度和宽带宽特性。
- 新型二氧化硅WGM微探针设备具有高达10^7的Q因子。
- 设备采用侧耦合方式和特殊封装设计,体积小、稳健,适用于气体和液体环境。
- 光声成像实验证明了设备的高灵敏度和宽带宽性能。
- 设备能捕捉到高达数百兆赫兹的微粒子振动光谱。
- 该设备具有广泛的应用潜力,特别是在光声内窥检测、近场超声传感等领域。
点此查看论文截图

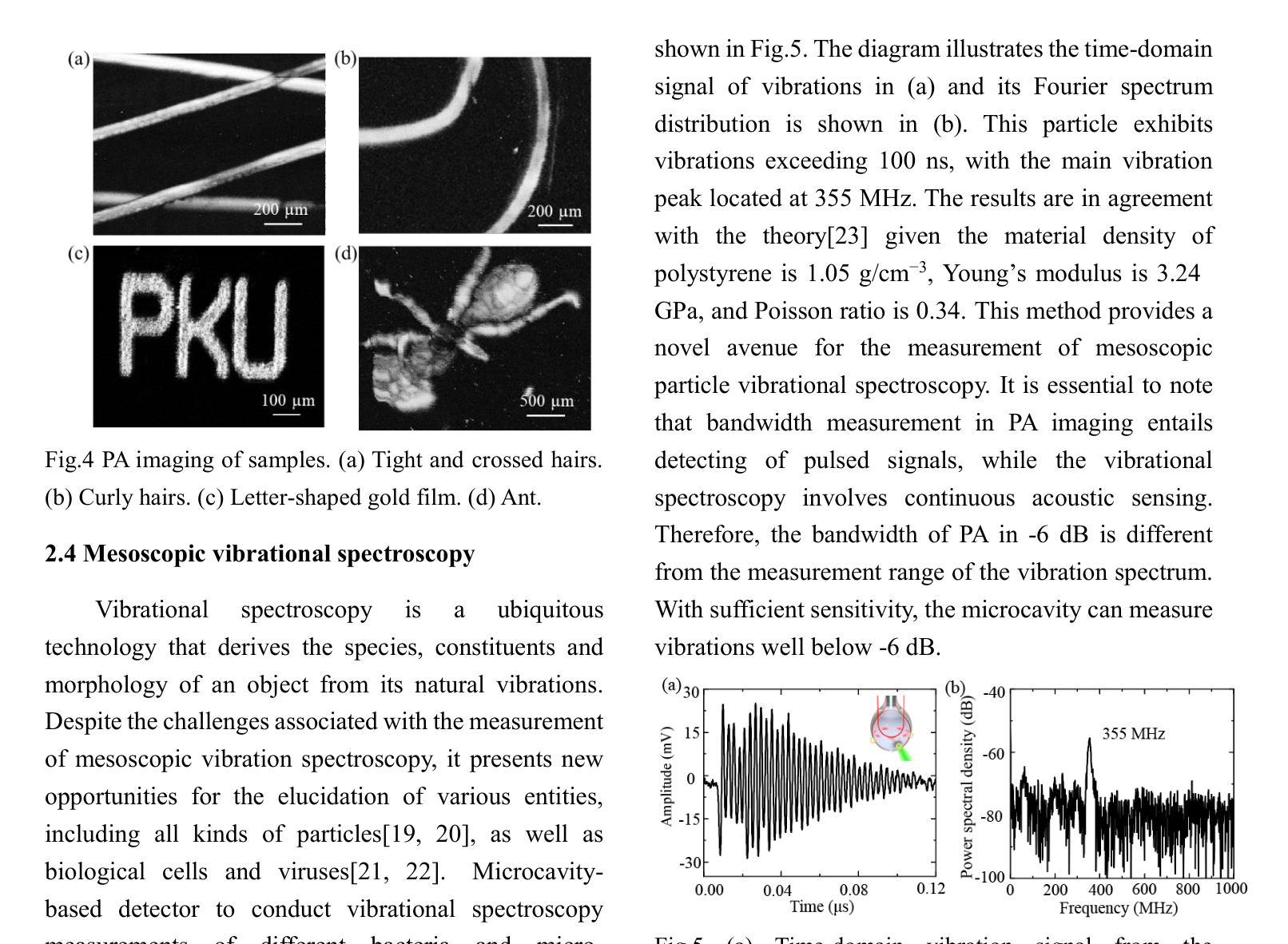
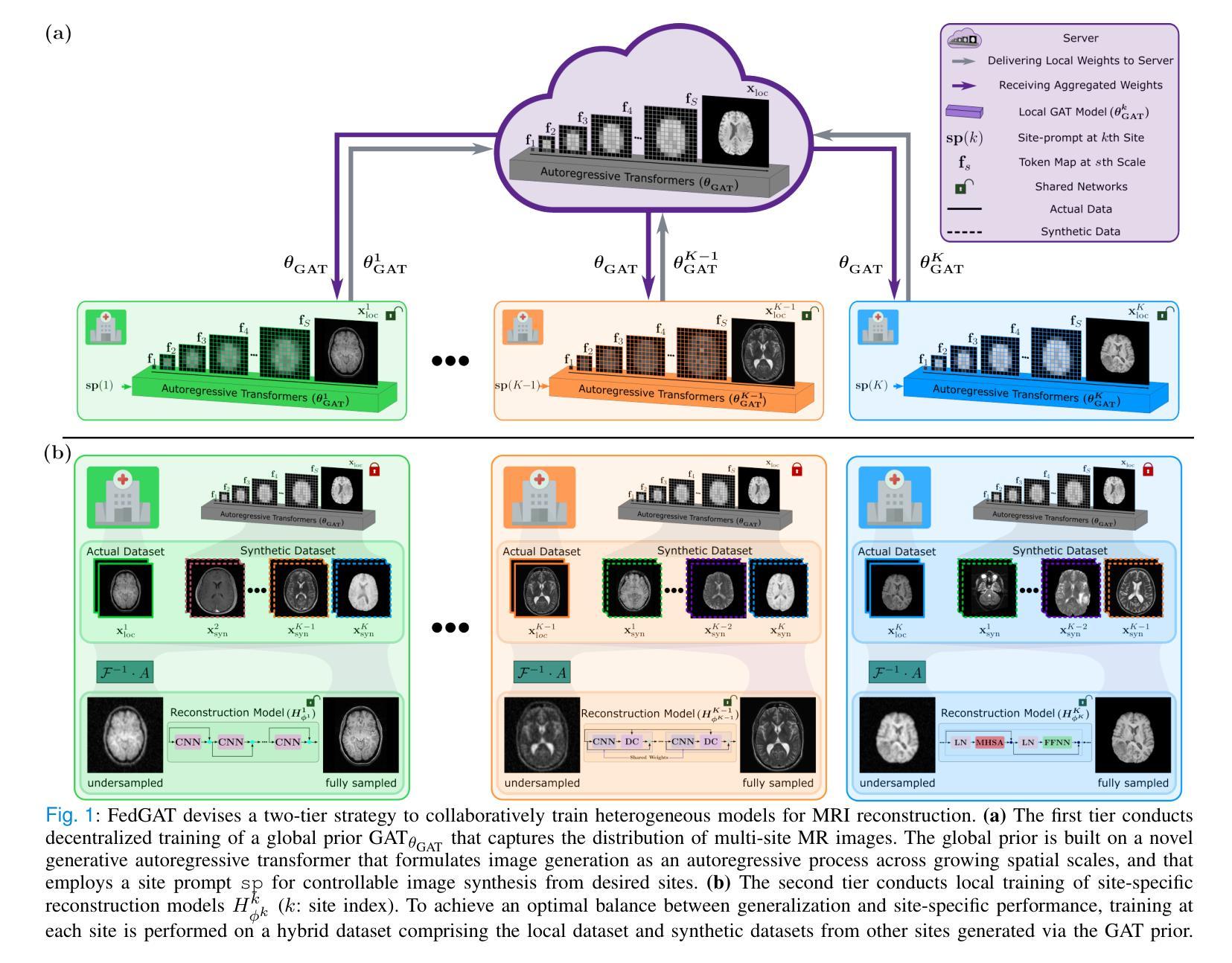
Generative Autoregressive Transformers for Model-Agnostic Federated MRI Reconstruction
Authors:Valiyeh A. Nezhad, Gokberk Elmas, Bilal Kabas, Fuat Arslan, Tolga Çukur
Although learning-based models hold great promise for MRI reconstruction, single-site models built on limited local datasets often suffer from poor generalization. This challenge has spurred interest in collaborative model training on multi-site datasets via federated learning (FL) – a privacy-preserving framework that aggregates model updates instead of sharing imaging data. Conventional FL builds a global model by aggregating locally trained model weights, inherently constraining all sites to a homogeneous model architecture. This rigid homogeneity requirement forces sites to forgo architectures tailored to their compute infrastructure and application-specific demands. Consequently, existing FL methods for MRI reconstruction fail to support model-heterogeneous settings, where individual sites are allowed to use distinct architectures. To overcome this fundamental limitation, here we introduce FedGAT, a novel model-agnostic FL technique based on generative autoregressive transformers. FedGAT decentralizes the training of a global generative prior that captures the distribution of multi-site MR images. For enhanced fidelity, we propose a novel site-prompted GAT prior that controllably synthesizes MR images from desired sites via autoregressive prediction across spatial scales. Each site then trains its site-specific reconstruction model – using its preferred architecture – on a hybrid dataset comprising the local MRI dataset and GAT-generated synthetic MRI datasets for other sites. Comprehensive experiments on multi-institutional datasets demonstrate that FedGAT supports flexible collaborations while enjoying superior within-site and across-site reconstruction performance compared to state-of-the-art FL baselines.
尽管基于学习的模型在MRI重建方面展现出巨大潜力,但仅依赖于有限本地数据集的单站点模型通常面临泛化能力差的挑战。这一挑战激发了对通过联邦学习(FL)进行多站点数据集协作模型训练的兴趣。联邦学习是一种隐私保护框架,它通过聚合模型更新而不是共享成像数据来进行训练。传统的联邦学习通过聚合本地训练的模型权重来构建全局模型,这固有地要求所有站点采用同质模型架构。这种刚性的同质化要求迫使站点放弃针对其计算基础设施和应用特定需求量身定制的架构。因此,现有的用于MRI重建的联邦学习方法无法支持模型异构设置,其中单个站点被允许使用不同的架构。为了克服这一基本限制,这里我们引入了FedGAT,这是一种基于生成自回归变压器的新型模型无关联邦学习技术。FedGAT去中心化全局生成先验的训练,该先验捕捉多站点MR图像的分布。为了提高保真度,我们提出了一种新型站点提示GAT先验,该先验可通过空间尺度的自回归预测,可控地合成来自所需站点的MR图像。然后,每个站点在其混合数据集(由本地MRI数据集和GAT生成的合成MRI数据集组成)上,使用其首选架构训练其特定的重建模型。在多机构数据集上的综合实验表明,FedGAT支持灵活的协作,同时在站内和跨站重建性能上优于最新的联邦学习基线。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于学习的模型在MRI重建中具有巨大潜力,但单一站点模型在有限的本地数据集上训练常常面临泛化性能不足的问题。为应对这一挑战,研究人员开始尝试使用联邦学习(FL)进行多站点数据集上的协同模型训练。然而,传统的联邦学习通过聚合本地训练的模型权重来建立全局模型,这要求所有站点必须使用相同架构,限制了站点的灵活性。本研究提出了一种新型的联邦学习技术——FedGAT,它基于生成式自回归转换器,打破了这一局限。FedGAT实现了生成式先验知识的去中心化训练,可以捕捉多站点MRI图像分布的特点。为提高图像质量,本研究还提出了一种新型的可控合成MRI图像的位点提示GAT先验技术。每个站点可以在本地数据集和GAT生成的合成MRI数据集组成的混合数据集上,使用其偏好的架构训练重建模型。在跨机构数据集上的综合实验表明,FedGAT在支持灵活协作的同时,其重建性能优于当前最先进的联邦学习基线方法。
Key Takeaways
- 学习型模型在MRI重建中有巨大潜力,但单一站点模型的泛化能力受限。
- 联邦学习(FL)通过多站点数据集协同模型训练解决此问题。
- 传统联邦学习方法要求所有站点使用相同模型架构,限制了灵活性。
- FedGAT是一种新型的联邦学习技术,基于生成式自回归转换器,支持模型异构设置。
- FedGAT实现了生成式先验知识的去中心化训练,捕捉多站点MRI图像分布特点。
- 提出了一种新型的可控合成MRI图像的位点提示GAT先验技术,提高图像质量。
点此查看论文截图

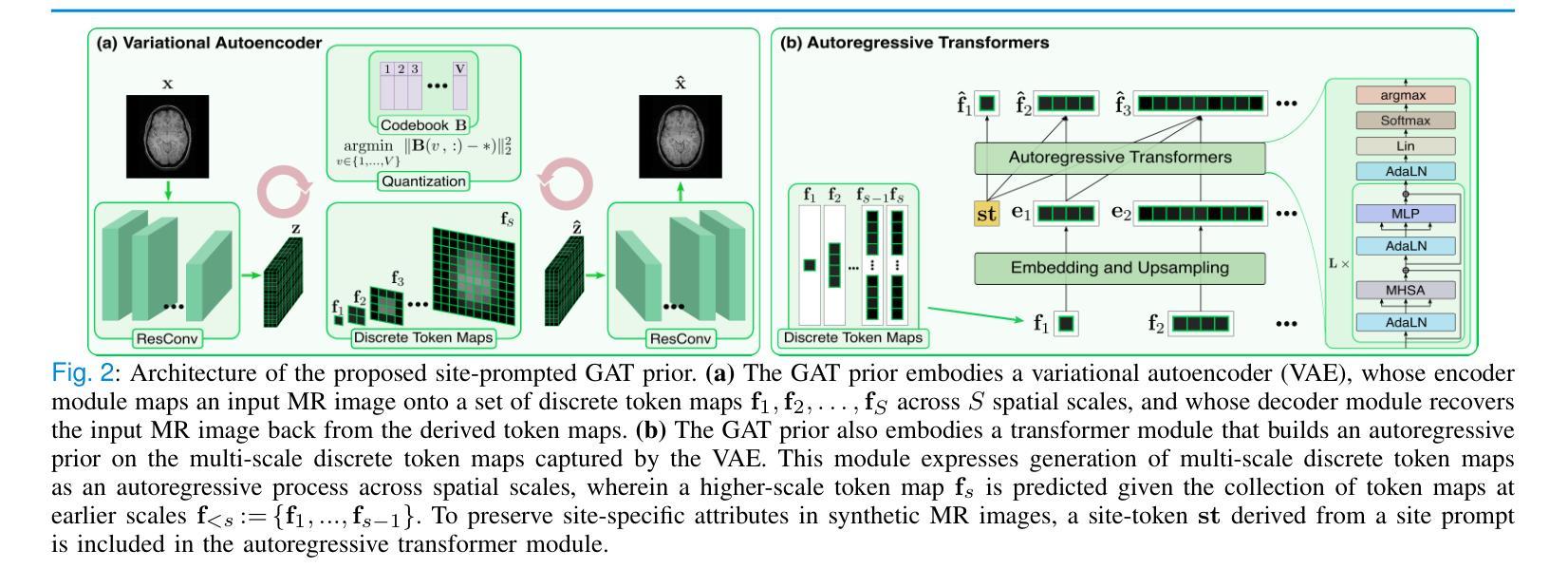
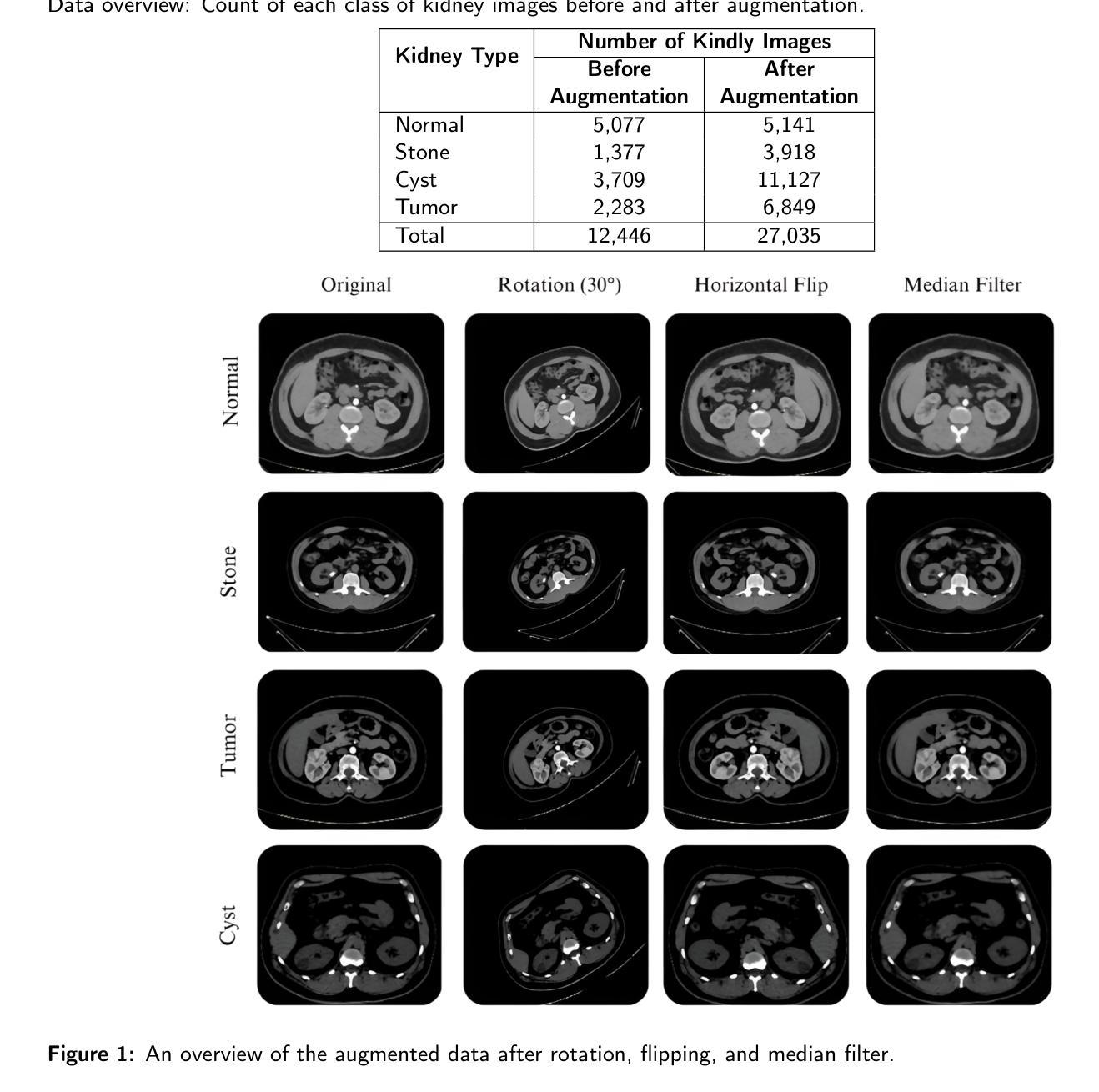
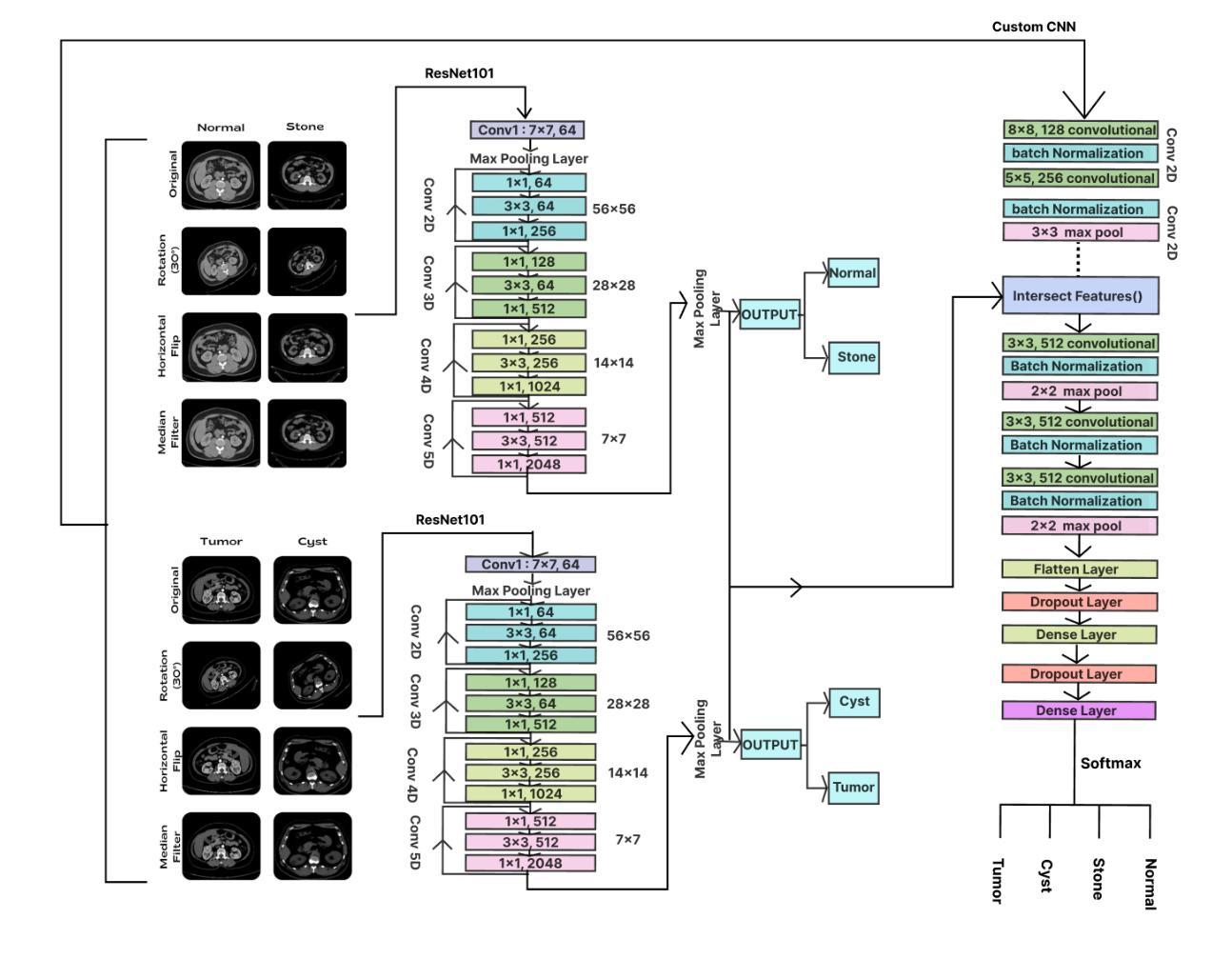
Hybrid Deep Learning Framework for Classification of Kidney CT Images: Diagnosis of Stones, Cysts, and Tumors
Authors:Kiran Sharma, Ziya Uddin, Adarsh Wadal, Dhruv Gupta
Medical image classification is a vital research area that utilizes advanced computational techniques to improve disease diagnosis and treatment planning. Deep learning models, especially Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs), have transformed this field by providing automated and precise analysis of complex medical images. This study introduces a hybrid deep learning model that integrates a pre-trained ResNet101 with a custom CNN to classify kidney CT images into four categories: normal, stone, cyst, and tumor. The proposed model leverages feature fusion to enhance classification accuracy, achieving 99.73% training accuracy and 100% testing accuracy. Using a dataset of 12,446 CT images and advanced feature mapping techniques, the hybrid CNN model outperforms standalone ResNet101. This architecture delivers a robust and efficient solution for automated kidney disease diagnosis, providing improved precision, recall, and reduced testing time, making it highly suitable for clinical applications.
医学图像分类是一个重要的研究领域,它利用先进的计算技术来改善疾病诊断和治疗计划的制定。深度学习模型,尤其是卷积神经网络(CNN),已经通过提供复杂医学图像的自动化和精确分析,使该领域发生了变革。本研究介绍了一种混合深度学习模型,它将预训练的ResNet101与自定义CNN相结合,将肾脏CT图像分类为正常、结石、囊肿和肿瘤四类。所提出的模型利用特征融合来提高分类精度,实现99.73%的训练精度和100%的测试精度。使用包含12446张CT图像的数据库和先进的特征映射技术,混合CNN模型的表现优于单独的ResNet101。该架构为自动化肾脏疾病诊断提供了稳健高效的解决方案,提高了精确度、召回率,并缩短了测试时间,非常适合临床应用。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
医学图像分类是运用先进计算技术促进疾病诊断和治疗计划的重要研究领域。本研究提出一种混合深度学习模型,结合预训练的ResNet101和自定义CNN,对肾脏CT图像进行正常、结石、囊肿和肿瘤四类分类。该模型利用特征融合提高分类精度,实现99.73%的训练精度和100%的测试精度。混合CNN模型优于单独的ResNet101,为肾脏疾病的自动诊断提供了精确、高效、快速的解决方案,非常适合临床应用。
Key Takeaways
- 医学图像分类在疾病诊断和治疗计划中起重要作用。
- 深度学习模型,尤其是卷积神经网络(CNNs),已经彻底改变了医学图像分析领域。
- 本研究提出了一种混合深度学习模型,结合了ResNet101和自定义CNN进行肾脏CT图像分类。
- 该模型通过特征融合提高了分类精度。
- 混合模型的训练精度达到99.73%,测试精度达到100%。
- 混合CNN模型优于单独的ResNet101模型。
点此查看论文截图


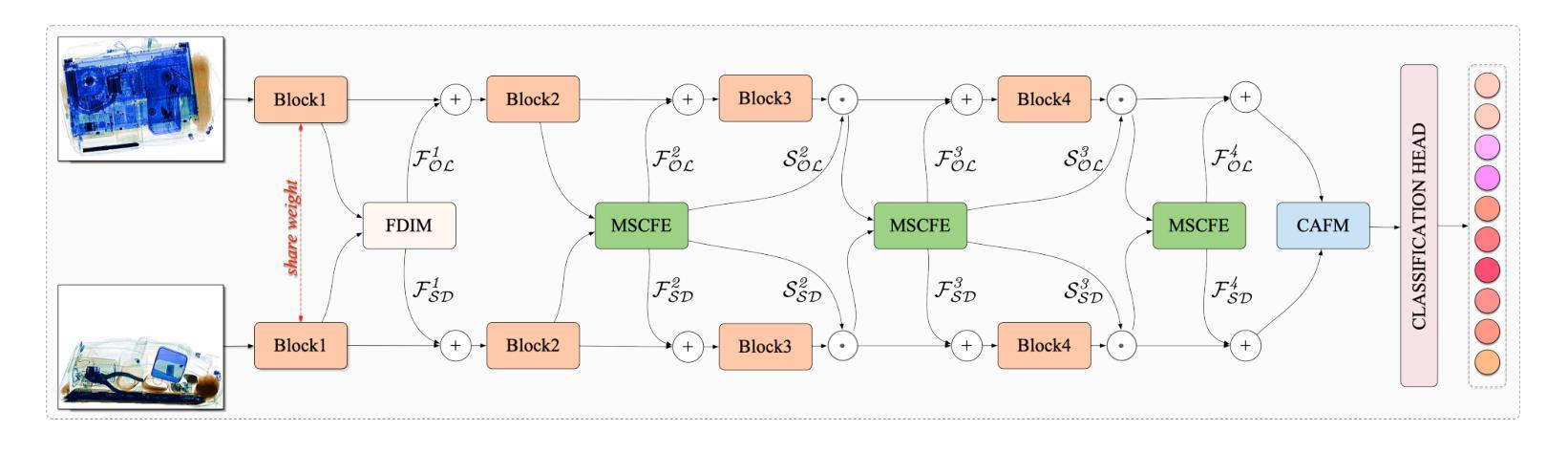
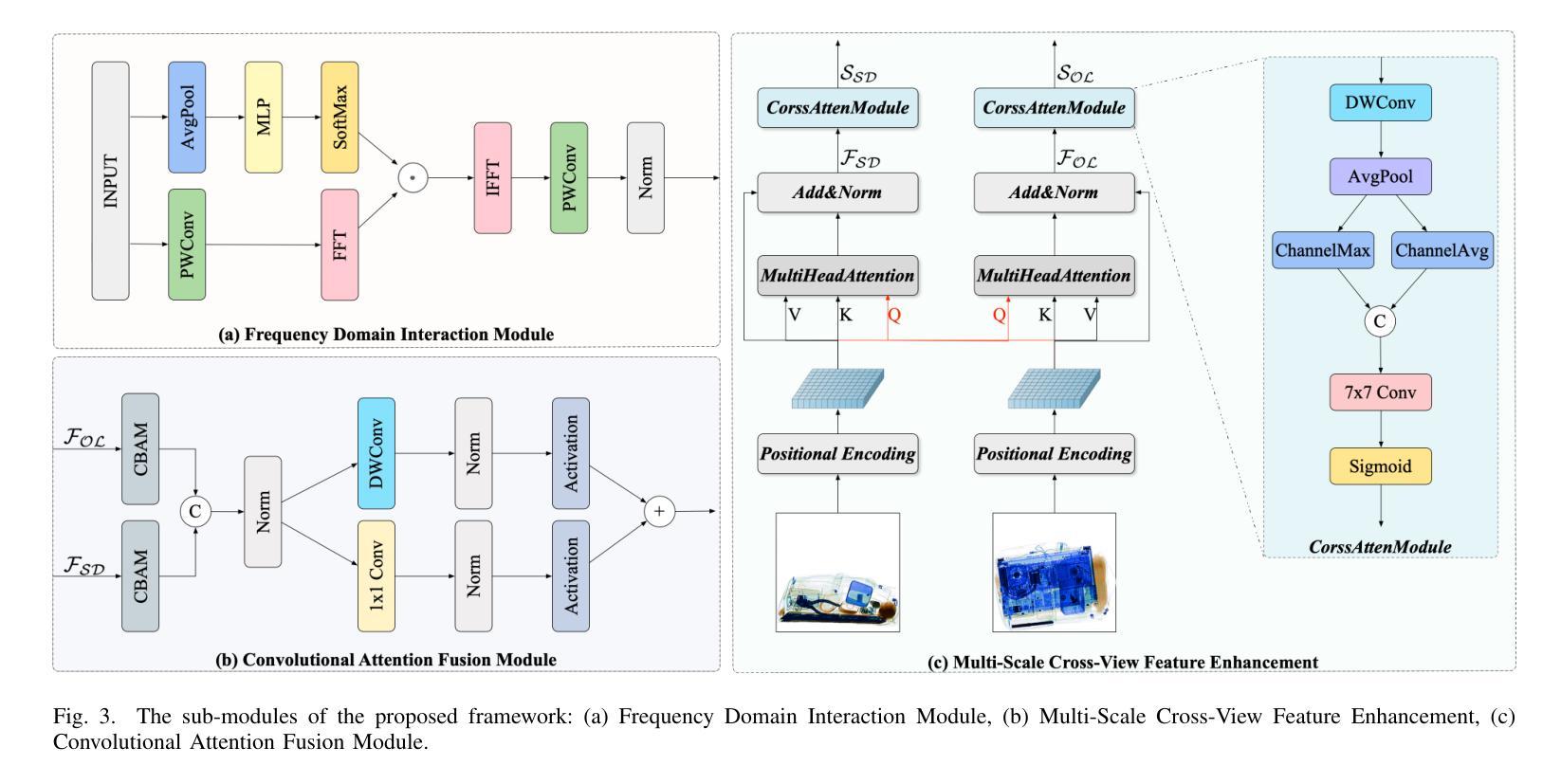
A Multi-Scale Feature Fusion Framework Integrating Frequency Domain and Cross-View Attention for Dual-View X-ray Security Inspections
Authors:Shilong Hong, Yanzhou Zhou, Weichao Xu
With the rapid development of modern transportation systems and the exponential growth of logistics volumes, intelligent X-ray-based security inspection systems play a crucial role in public safety. Although single-view X-ray equipment is widely deployed, it struggles to accurately identify contraband in complex stacking scenarios due to strong viewpoint dependency and inadequate feature representation. To address this, we propose an innovative multi-scale interactive feature fusion framework tailored for dual-view X-ray security inspection image classification. The framework comprises three core modules: the Frequency Domain Interaction Module (FDIM) enhances frequency-domain features through Fourier transform; the Multi-Scale Cross-View Feature Enhancement (MSCFE) leverages cross-view attention mechanisms to strengthen feature interactions; and the Convolutional Attention Fusion Module (CAFM) efficiently fuses features by integrating channel attention with depthwise-separable convolutions. Experimental results demonstrate that our method outperforms existing state-of-the-art approaches across multiple backbone architectures, particularly excelling in complex scenarios with occlusions and object stacking.
随着现代交通运输系统的快速发展和物流量的指数级增长,基于智能X射线的安全检查系统在公共安全中扮演着至关重要的角色。虽然单视图X射线设备已广泛部署,但由于其强烈的视角依赖性和特征表示的不足,它在复杂的堆叠场景中难以准确识别违禁品。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了一种针对双视图X射线安全检查图像分类的多尺度交互特征融合框架。该框架包括三个核心模块:频域交互模块(FDIM)通过傅里叶变换增强频域特征;多尺度跨视图特征增强(MSCFE)利用跨视图注意力机制加强特征交互;卷积注意力融合模块(CAFM)通过结合通道注意力和深度可分离卷积来有效地融合特征。实验结果表明,我们的方法在多种主干架构上超越了现有的最先进的方法,特别是在存在遮挡和物体堆叠的复杂场景中表现尤为出色。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
随着现代交通运输系统的快速发展和物流量的指数级增长,智能X光安全检测系统在公共安全中发挥着至关重要的作用。针对单视角X光设备在复杂堆叠场景中难以准确识别违禁品的问题,提出了一种多尺度交互式特征融合框架,用于双视角X光安全检测图像分类。该框架包括三个核心模块:频率域交互模块(FDIM)通过傅立叶变换增强频率域特征;多尺度跨视图特征增强(MSCFE)利用跨视图注意力机制加强特征交互;卷积注意力融合模块(CAFM)通过结合通道注意力和深度可分离卷积来有效地融合特征。实验结果表明,该方法在多种主干架构上优于现有最先进的方法,尤其在存在遮挡和物体堆叠的复杂场景中表现卓越。
Key Takeaways
- 智能X光安全检测系统在公共安全中扮演重要角色,特别是面对日益增长的物流量和复杂场景的挑战。
- 单视角X光设备在复杂堆叠场景中识别违禁品存在困难,需要更先进的图像分类技术。
- 提出的多尺度交互式特征融合框架包含三个核心模块,分别增强频率域特征、利用跨视图注意力机制和加强特征交互、以及有效地融合特征。
- 框架通过傅立叶变换增强频率域特征,通过跨视图注意力机制处理不同视角下的特征,并结合通道注意力和深度可分离卷积来融合特征。
- 实验结果表明,该框架在多种主干架构上的表现优于现有方法,特别是在复杂场景中。
- 该框架特别擅长处理存在遮挡和物体堆叠的情况,这是现有方法的一个重大改进。
- 框架的优异性能使其成为X光安全检测领域的一个有前途的研究方向。
点此查看论文截图

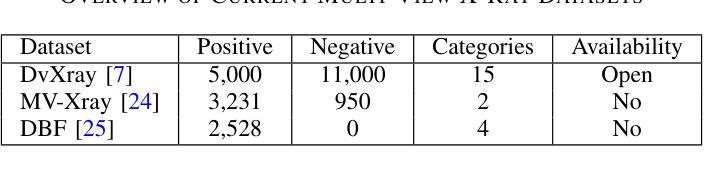
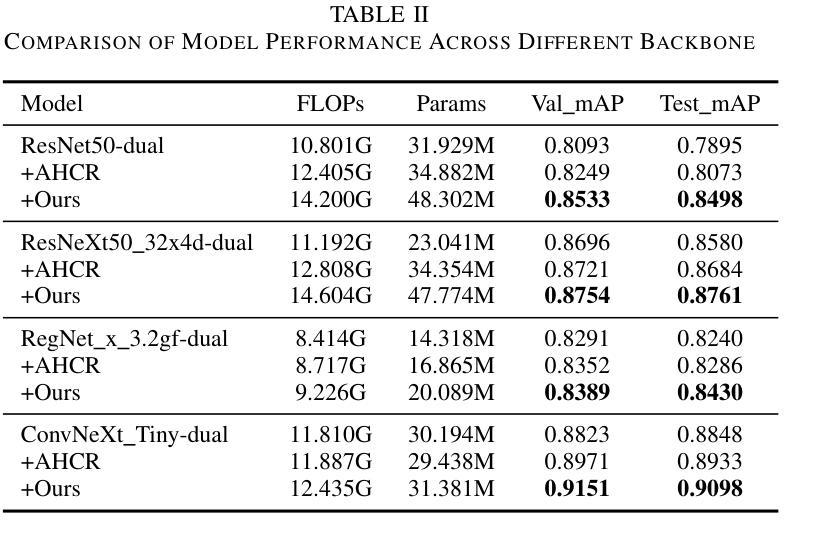
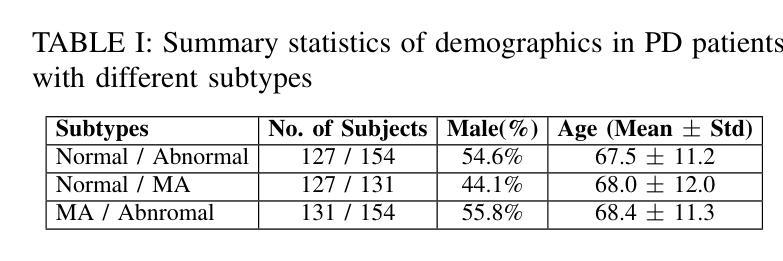
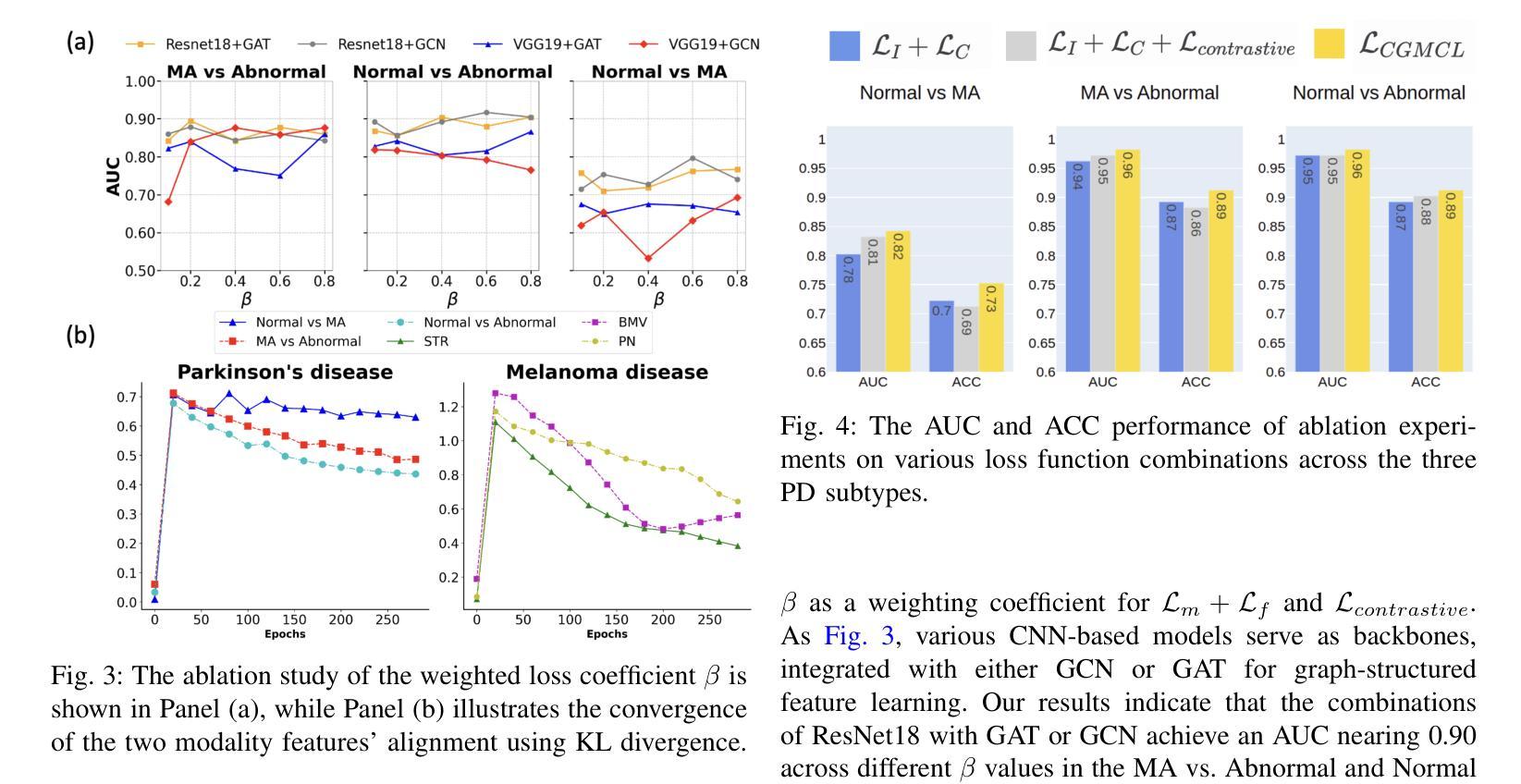
Enhancing Multimodal Medical Image Classification using Cross-Graph Modal Contrastive Learning
Authors:Jun-En Ding, Chien-Chin Hsu, Chi-Hsiang Chu, Shuqiang Wang, Feng Liu
The classification of medical images is a pivotal aspect of disease diagnosis, often enhanced by deep learning techniques. However, traditional approaches typically focus on unimodal medical image data, neglecting the integration of diverse non-image patient data. This paper proposes a novel Cross-Graph Modal Contrastive Learning (CGMCL) framework for multimodal structured data from different data domains to improve medical image classification. The model effectively integrates both image and non-image data by constructing cross-modality graphs and leveraging contrastive learning to align multimodal features in a shared latent space. An inter-modality feature scaling module further optimizes the representation learning process by reducing the gap between heterogeneous modalities. The proposed approach is evaluated on two datasets: a Parkinson’s disease (PD) dataset and a public melanoma dataset. Results demonstrate that CGMCL outperforms conventional unimodal methods in accuracy, interpretability, and early disease prediction. Additionally, the method shows superior performance in multi-class melanoma classification. The CGMCL framework provides valuable insights into medical image classification while offering improved disease interpretability and predictive capabilities.
医学图像分类是疾病诊断的重要方面,通常可以通过深度学习技术得到增强。然而,传统方法主要关注单模态医学图像数据,忽略了不同非图像患者数据的整合。本文提出了一种新颖的跨图模态对比学习(CGMCL)框架,用于不同数据域的多模态结构化数据,以改进医学图像分类。该模型通过构建跨模态图并利用对比学习来对齐多模态特征在共享潜在空间,从而有效地整合图像和非图像数据。跨模态特征缩放模块进一步优化了表示学习过程,缩小了不同模态之间的差距。所提出的方法在两个数据集上进行了评估:帕金森病(PD)数据集和公共黑色素瘤数据集。结果表明,在准确性、可解释性和早期疾病预测方面,CGMCL优于传统单模态方法。此外,该方法在多类黑色素瘤分类方面表现出卓越性能。CGMCL框架为医学图像分类提供了有价值的见解,同时提高了疾病可解释性和预测能力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
论文提出一种基于跨图模态对比学习(CGMCL)的多模态数据融合框架,用于医学图像分类。该框架能有效整合图像和非图像数据,通过构建跨模态图并利用对比学习对齐多模态特征,优化表示学习过程,缩小不同模态之间的差距。在帕金森病和公共黑色素瘤数据集上的实验结果表明,该框架在准确性、可解释性和早期疾病预测方面优于传统单模态方法,为多类黑色素瘤分类提供了卓越的性能。
Key Takeaways
- 医学图像分类是疾病诊断的关键环节,通常可通过深度学习技术加强。
- 传统方法主要关注单模态医学图像数据,忽略了非图像患者数据的整合。
- 论文提出了一种基于跨图模态对比学习(CGMCL)的多模态数据融合框架。
- CGMCL框架通过构建跨模态图,利用对比学习整合图像和非图像数据。
- 跨模态特征缩放模块缩小了不同模态之间的差距,优化了表示学习过程。
- 在帕金森病和黑色素瘤数据集上的实验验证了CGMCL框架的优越性。
点此查看论文截图

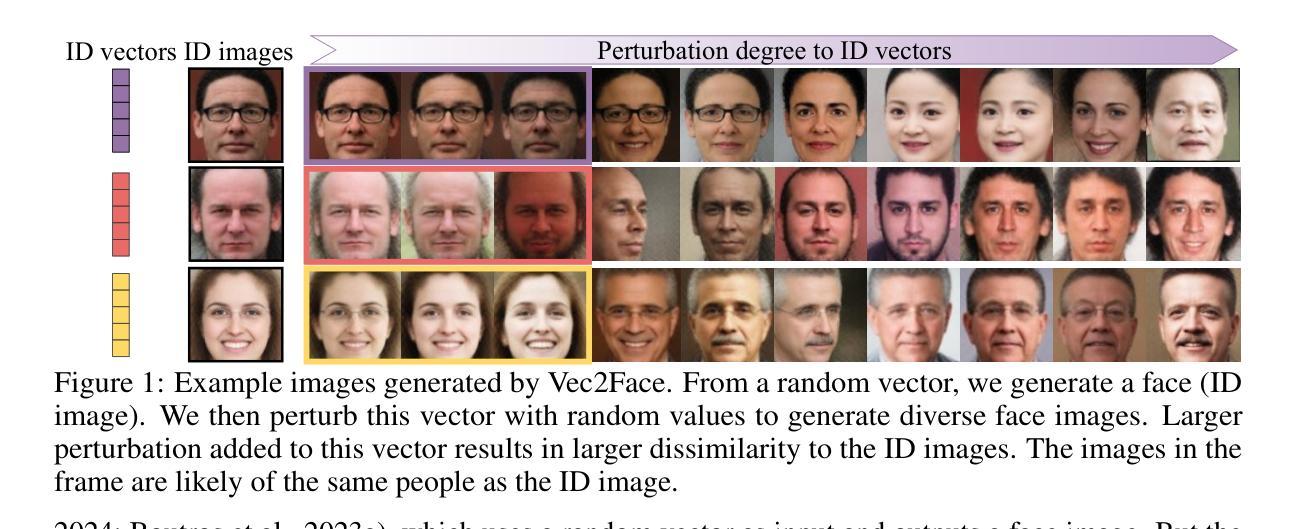
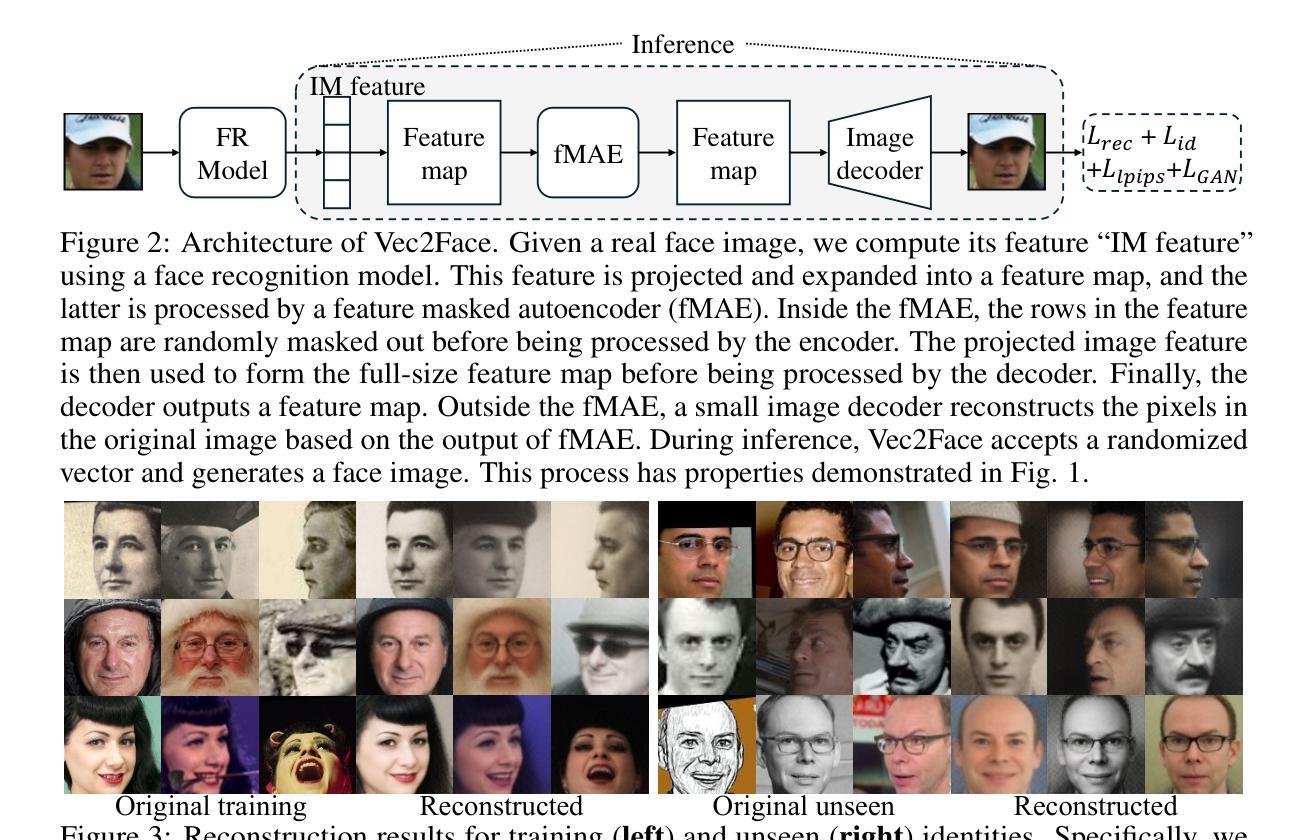
Vec2Face: Scaling Face Dataset Generation with Loosely Constrained Vectors
Authors:Haiyu Wu, Jaskirat Singh, Sicong Tian, Liang Zheng, Kevin W. Bowyer
This paper studies how to synthesize face images of non-existent persons, to create a dataset that allows effective training of face recognition (FR) models. Besides generating realistic face images, two other important goals are: 1) the ability to generate a large number of distinct identities (inter-class separation), and 2) a proper variation in appearance of the images for each identity (intra-class variation). However, existing works 1) are typically limited in how many well-separated identities can be generated and 2) either neglect or use an external model for attribute augmentation. We propose Vec2Face, a holistic model that uses only a sampled vector as input and can flexibly generate and control the identity of face images and their attributes. Composed of a feature masked autoencoder and an image decoder, Vec2Face is supervised by face image reconstruction and can be conveniently used in inference. Using vectors with low similarity among themselves as inputs, Vec2Face generates well-separated identities. Randomly perturbing an input identity vector within a small range allows Vec2Face to generate faces of the same identity with proper variation in face attributes. It is also possible to generate images with designated attributes by adjusting vector values with a gradient descent method. Vec2Face has efficiently synthesized as many as 300K identities, whereas 60K is the largest number of identities created in the previous works. As for performance, FR models trained with the generated HSFace datasets, from 10k to 300k identities, achieve state-of-the-art accuracy, from 92% to 93.52%, on five real-world test sets (\emph{i.e.}, LFW, CFP-FP, AgeDB-30, CALFW, and CPLFW). For the first time, the FR model trained using our synthetic training set achieves higher accuracy than that trained using a same-scale training set of real face images on the CALFW, IJBB, and IJBC test sets.
本文研究了如何合成不存在的人脸图像,以创建一个允许有效训练人脸识别(FR)模型的数据集。除了生成逼真的人脸图像外,另外两个重要目标是:1)能够生成大量不同的身份(类间分离),2)为每个身份的外观提供适当的变体(类内变化)。然而,现有工作1)通常可以生成的分离良好的身份数量有限,2)要么忽视要么使用外部模型进行属性增强。我们提出了Vec2Face,这是一个全面的模型,它只使用采样向量作为输入,可以灵活地生成和控制人脸图像的身份和属性。Vec2Face由特征掩码自动编码器和图像解码器组成,受到人脸图像重建的监督,可以方便地进行推理。使用彼此相似性低的向量作为输入,Vec2Face生成了分离良好的身份。在输入身份向量的小范围内进行随机扰动,允许Vec2Face生成具有适当变化面部属性的人脸图像。通过梯度下降法调整向量值,还可以生成具有指定属性的图像。Vec2Face已经有效地合成了多达30万个身份,而以前的工作最多只能创建6万个身份。在性能方面,使用生成的HSFace数据集训练的FR模型,从10k到30万身份,在五个真实世界测试集上达到了最先进的准确性,从92%到93.5%,即LFW、CFP-FP、AgeDB-30、CALFW和CPLFW测试集。首次尝试的是,使用我们合成训练集训练的FR模型在CALFW、IJBB和IJBC测试集上的准确性高于使用相同规模的现实人脸图像训练集训练的模型。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at ICLR2025
Summary
该论文旨在合成非真实人物的脸部图像,创建一个用于训练脸部识别模型的优质数据集。论文的目标包括生成逼真的脸部图像、生成大量不同的身份以及为每个身份提供适当的外观变化。提出了一种全新的模型Vec2Face,只需通过输入采样向量,就能灵活生成并控制脸部图像的身份及其属性。Vec2Face包括特征掩码自编码器和图像解码器,通过脸部图像重建进行监督,便于推理使用。Vec2Face能够生成具有良好分离度的身份,并使用随机扰动输入身份向量在较小的范围内生成具有适当属性变化的脸部图像。此外,通过调整向量值使用梯度下降法,可以生成具有指定属性的图像。Vec2Face已成功合成多达30万个身份,而之前的工作最多只能创建6万个身份。使用生成的HSFace数据集训练的面部识别模型在五个真实世界测试集上达到了最先进的准确性,在某些测试集上的准确性甚至超过了使用相同规模的真实面部图像训练集训练的模型。
Key Takeaways
- 该论文研究合成非真实人物脸部图像以创建数据集,用于训练脸部识别模型。
- 论文旨在生成大量不同的身份,同时保持良好的分离度,并为每个身份提供适当的外观变化。
- 论文提出了一种名为Vec2Face的模型,该模型使用采样向量作为输入,可以灵活生成和控制脸部图像的属性和身份。
- Vec2Face包括特征掩码自编码器和图像解码器,通过脸部图像重建进行监督。
- 通过随机扰动输入身份向量,Vec2Face可以生成具有适当属性变化的同一身份的脸部图像。
- Vec2Face能够生成具有指定属性的图像,这有助于在训练中引入更多变化和提高模型的泛化能力。
点此查看论文截图


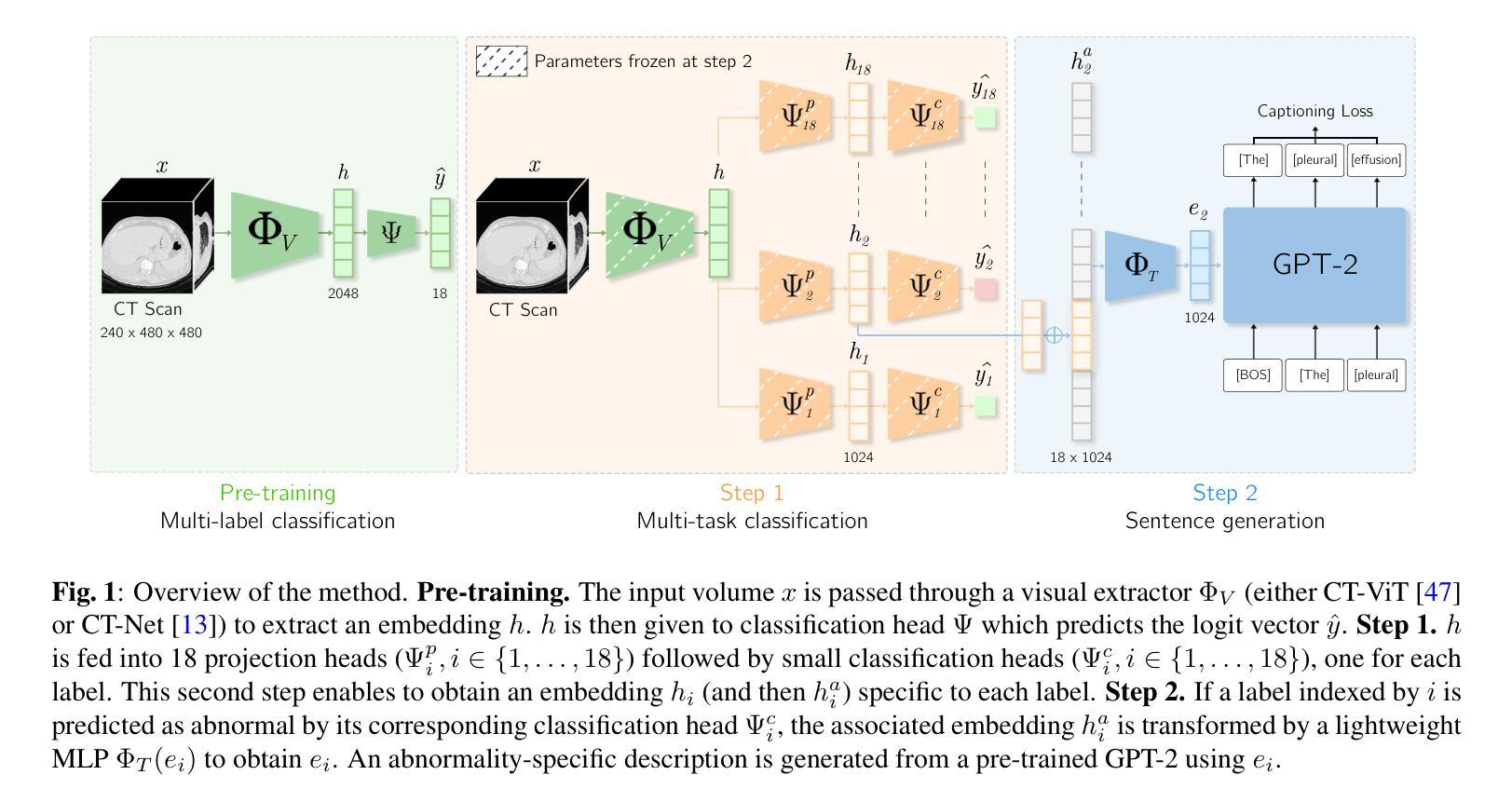
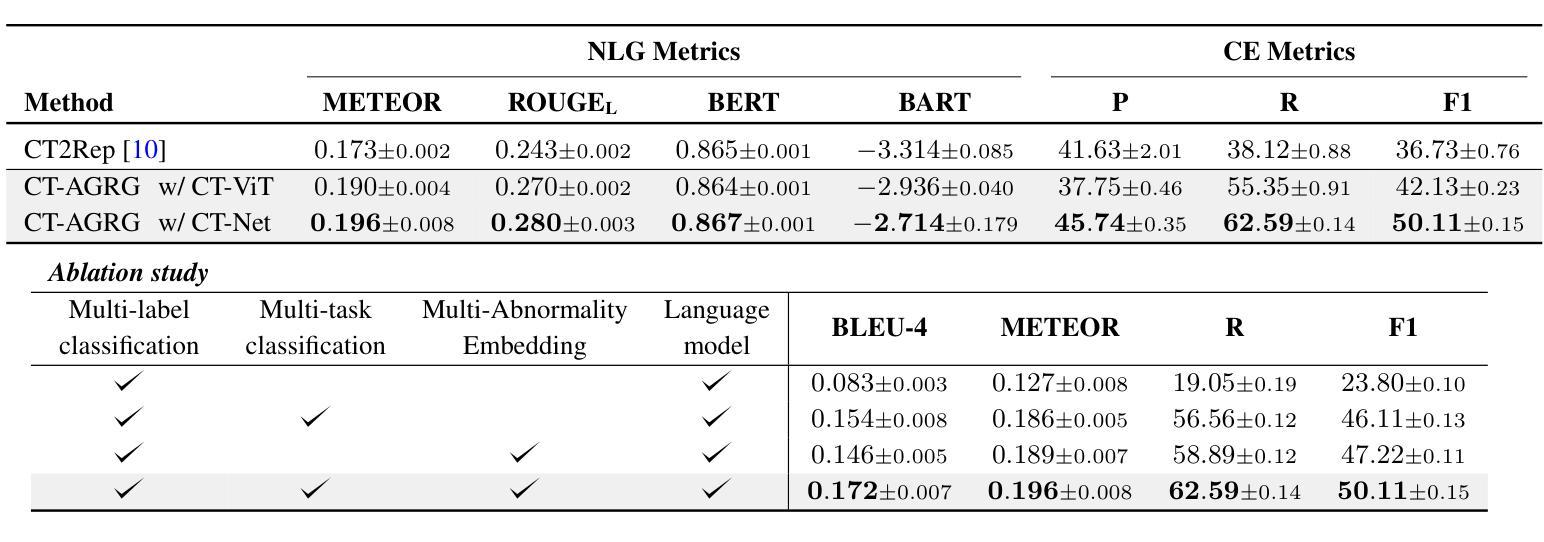
CT-AGRG: Automated Abnormality-Guided Report Generation from 3D Chest CT Volumes
Authors:Theo Di Piazza, Carole Lazarus, Olivier Nempont, Loic Boussel
The rapid increase of computed tomography (CT) scans and their time-consuming manual analysis have created an urgent need for robust automated analysis techniques in clinical settings. These aim to assist radiologists and help them managing their growing workload. Existing methods typically generate entire reports directly from 3D CT images, without explicitly focusing on observed abnormalities. This unguided approach often results in repetitive content or incomplete reports, failing to prioritize anomaly-specific descriptions. We propose a new anomaly-guided report generation model, which first predicts abnormalities and then generates targeted descriptions for each. Evaluation on a public dataset demonstrates significant improvements in report quality and clinical relevance. We extend our work by conducting an ablation study to demonstrate its effectiveness.
计算机断层扫描(CT)扫描的迅速增加及其耗时的手动分析,为临床环境中稳健的自动化分析技术创造了迫切的需求。这些技术的目标是协助放射科医生,并帮助他们应对日益增长的工作量。现有方法通常直接从3D CT图像生成整个报告,而没有明确关注观察到的异常。这种无导向的方法常常导致内容重复或报告不完整,无法优先提供异常特定的描述。我们提出了一种新的异常导向的报告生成模型,该模型首先预测异常,然后为每一个生成有针对性的描述。在公共数据集上的评估显示,该模型在报告质量和临床相关性方面有明显的改进。我们通过进行消融研究来进一步证明其有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Paper accepted to ISBI 2025
Summary
该文介绍了计算层析扫描(CT)扫描的快速增长及其耗时的人工分析所带来的问题,凸显了对临床环境中稳健自动化分析技术的迫切需求。现有方法通常直接从3D CT图像生成整个报告,没有特别强调观察到的异常。本文提出了一种新的异常引导报告生成模型,该模型首先预测异常,然后针对每个异常生成有针对性的描述。在公共数据集上的评估证明了该模型在提高报告质量和临床相关性方面的显著优势。通过进行消融研究进一步验证了其有效性。
Key Takeaways
- CT扫描的广泛应用及其耗时的人工分析凸显了对自动化分析技术的需求。
- 现有方法直接从3D CT图像生成报告,缺乏明确的异常识别。
- 新的异常引导报告生成模型先预测异常,再针对每个异常生成描述。
- 提出的模型在公共数据集上的评估显示,报告质量和临床相关性显著提高。
- 模型通过消融研究验证了其有效性。
- 该模型有助于减轻放射科医生的工作负担。
点此查看论文截图

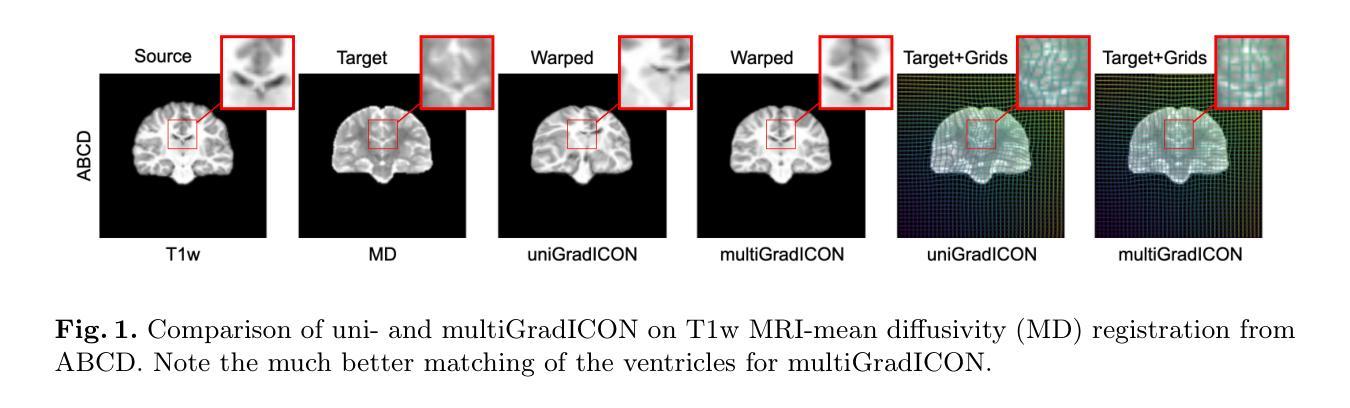
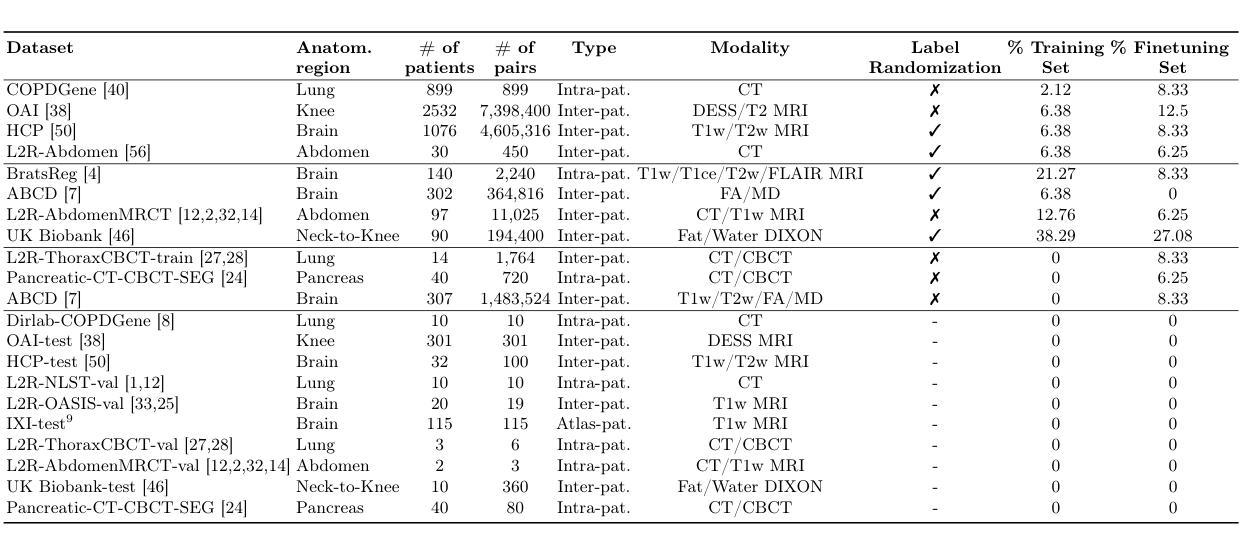
multiGradICON: A Foundation Model for Multimodal Medical Image Registration
Authors:Basar Demir, Lin Tian, Thomas Hastings Greer, Roland Kwitt, Francois-Xavier Vialard, Raul San Jose Estepar, Sylvain Bouix, Richard Jarrett Rushmore, Ebrahim Ebrahim, Marc Niethammer
Modern medical image registration approaches predict deformations using deep networks. These approaches achieve state-of-the-art (SOTA) registration accuracy and are generally fast. However, deep learning (DL) approaches are, in contrast to conventional non-deep-learning-based approaches, anatomy-specific. Recently, a universal deep registration approach, uniGradICON, has been proposed. However, uniGradICON focuses on monomodal image registration. In this work, we therefore develop multiGradICON as a first step towards universal multimodal medical image registration. Specifically, we show that 1) we can train a DL registration model that is suitable for monomodal and multimodal registration; 2) loss function randomization can increase multimodal registration accuracy; and 3) training a model with multimodal data helps multimodal generalization. Our code and the multiGradICON model are available at https://github.com/uncbiag/uniGradICON.
现代医学图像配准方法利用深度网络来预测变形。这些方法达到了最先进的配准精度,并且通常速度很快。然而,与传统的非深度学习方法相比,深度学习(DL)方法具有针对特定解剖结构的特点。最近,已经提出了一种通用的深度配准方法uniGradICON。然而,uniGradICON专注于单模态图像配准。因此,在这项工作中,我们开发了multiGradICON,作为通用多模态医学图像配准的第一步。具体来说,我们证明了以下几点:1)我们可以训练一个既适用于单模态又适用于多模态配准的深度学习配准模型;2)损失函数随机化可以提高多模态配准的精度;3)使用多模态数据进行模型训练有助于多模态泛化。我们的代码和multiGradICON模型可在https://github.com/uncbiag/uniGradICON获取。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
现代医疗图像配准方法使用深度网络预测变形,达到最新配准精度且通常快速。然而,深度学习方法与传统非深度学习方法相反,具有特定解剖结构的特点。最近提出了通用深度配准方法uniGradICON,但主要关注单模态图像配准。因此,我们开发了multiGradICON作为向通用多模态医学图像配准迈出的第一步。本工作证明了:1)我们可以训练一个适用于单模态和多模态配准的深度学习模型;2)损失函数随机化可以提高多模态配准精度;3)使用多模态数据进行模型训练有助于多模态泛化。我们的代码和multiGradICON模型可在以下网址获取:[链接地址]。
Key Takeaways
- 现代医疗图像配准方法使用深度网络提高配准精度和速度。
- 深度学习方法与传统方法不同,具有特定解剖结构的特点。
- uniGradICON方法主要关注单模态图像配准。
- multiGradICON作为通用多模态医学图像配准的第一步被开发出来。
- 本研究证明可以训练一个适用于单模态和多模态配准的深度学习模型。
- 损失函数随机化能提高多模态配准精度。
- 使用多模态数据进行模型训练有助于多模态泛化。
点此查看论文截图

Leveraging Bi-Focal Perspectives and Granular Feature Integration for Accurate Reliable Early Alzheimer’s Detection
Authors:Pandiyaraju V, Shravan Venkatraman, Abeshek A, Pavan Kumar S, Aravintakshan S A
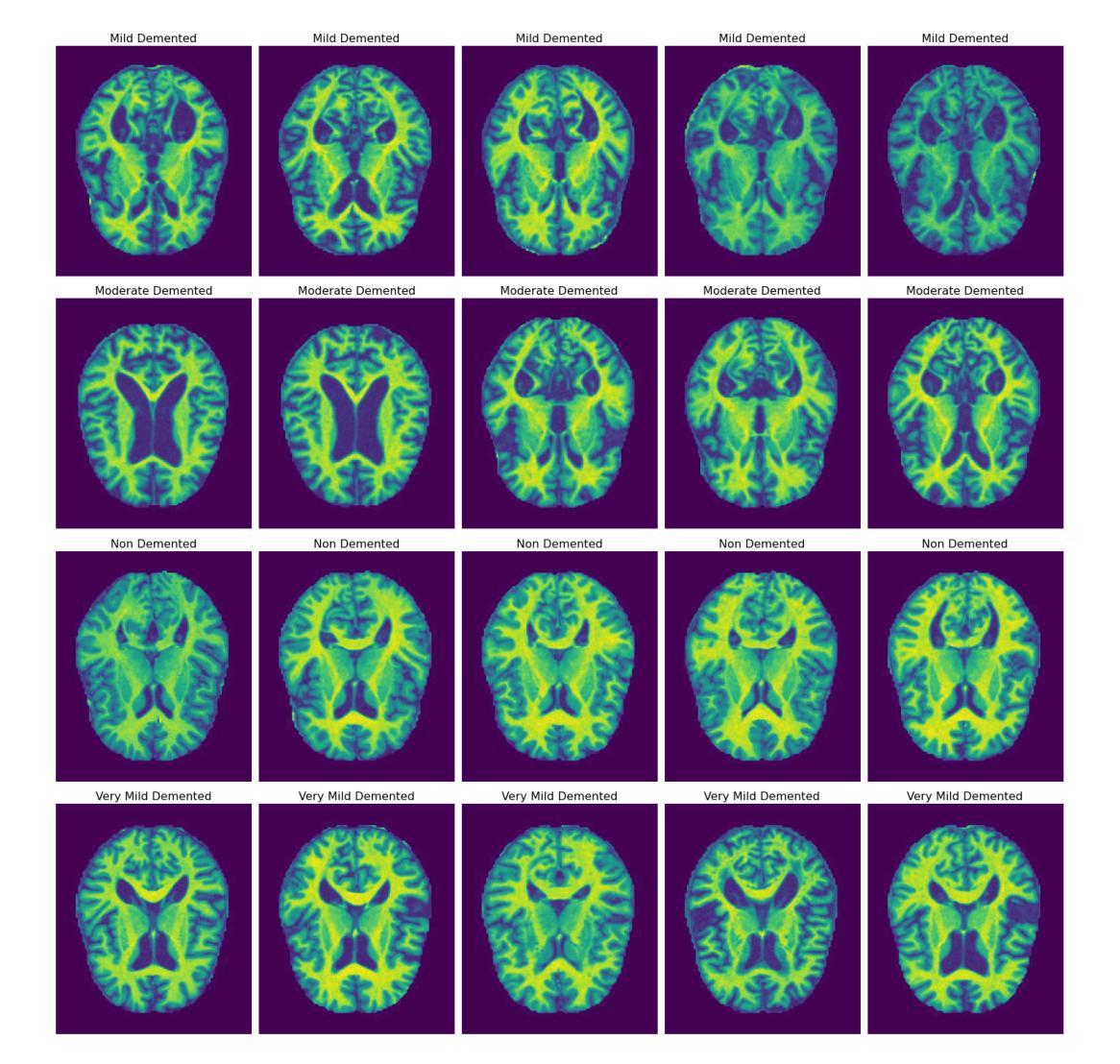
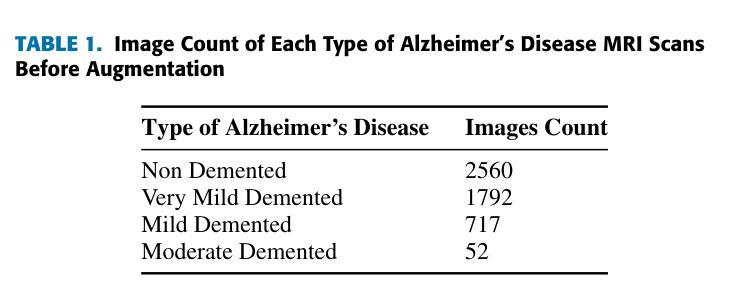
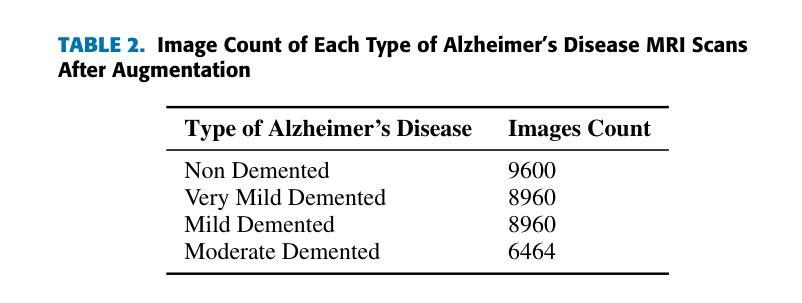
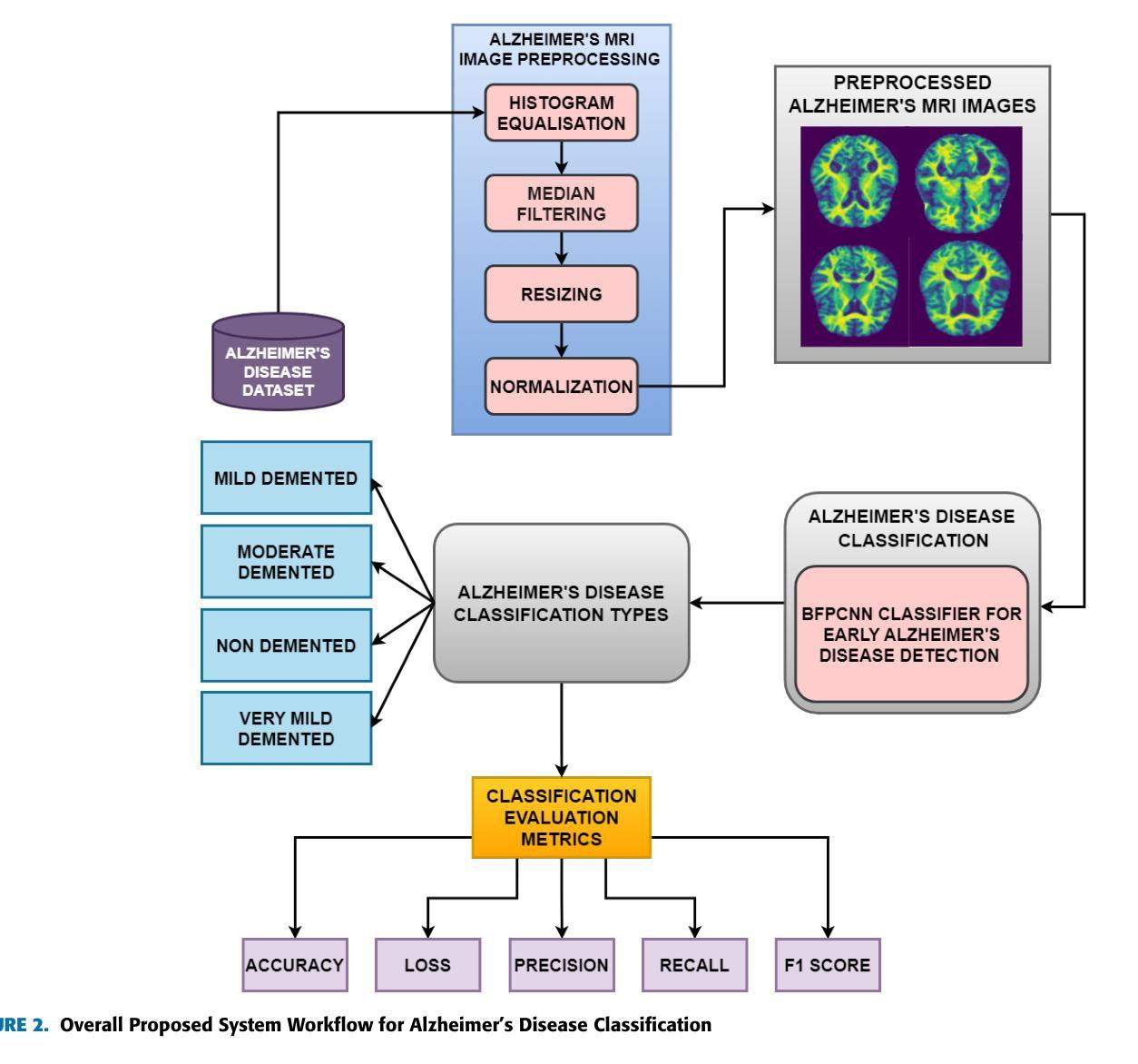
Being the most commonly known neurodegeneration, Alzheimer’s Disease (AD) is annually diagnosed in millions of patients. The present medical scenario still finds the exact diagnosis and classification of AD through neuroimaging data as a challenging task. Traditional CNNs can extract a good amount of low-level information in an image while failing to extract high-level minuscule particles, which is a significant challenge in detecting AD from MRI scans. To overcome this, we propose a novel Granular Feature Integration method to combine information extraction at different scales along with an efficient information flow, enabling the model to capture both broad and fine-grained features simultaneously. We also propose a Bi-Focal Perspective mechanism to highlight the subtle neurofibrillary tangles and amyloid plaques in the MRI scans, ensuring that critical pathological markers are accurately identified. Our model achieved an F1-Score of 99.31%, precision of 99.24%, and recall of 99.51%. These scores prove that our model is significantly better than the state-of-the-art (SOTA) CNNs in existence.
阿尔茨海默病(AD)是最常见的神经退行性疾病之一,每年有数百万患者被诊断出患有此病。当前医学界通过神经成像数据对阿尔茨海默病进行确切诊断和分类仍然是一项具有挑战性的任务。传统卷积神经网络(CNN)可以在图像中提取大量的低级信息,但无法提取高级微小颗粒,这对于从MRI扫描中检测阿尔茨海默病来说是一个巨大的挑战。为了克服这一问题,我们提出了一种新型的粒度特征集成方法,该方法能够结合不同尺度的信息提取和高效的信息流,使模型能够同时捕获广泛和精细的特征。我们还提出了一种双焦点透视机制,以突出MRI扫描中的神经原纤维缠结和淀粉样斑块等细微之处,确保准确识别关键病理标记物。我们的模型取得了F1分数为99.31%,精确度为99.24%,召回率为99.51%的成绩。这些分数证明我们的模型明显优于目前存在的最先进的CNN模型。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 14 pages, 12 figures, 6 tables
Summary
阿尔茨海默病(AD)的神经影像诊断仍具挑战。传统CNN难以提取高级微小颗粒信息,新型Granular Feature Integration方法结合不同尺度信息提取,同时捕捉广泛与精细特征。Bi-Focal Perspective机制能准确识别神经纤维缠结和淀粉样斑块等关键病理标记物。模型实现F1分数99.31%,精度99.24%,召回率99.51%,显著优于现有技术。
Key Takeaways
- 阿尔茨海默病(AD)的神经影像诊断仍是医学界的一大挑战。
- 传统CNN在提取高级微小颗粒信息方面存在困难。
- 新型Granular Feature Integration方法能够结合不同尺度的信息提取,提高诊断准确性。
- Bi-Focal Perspective机制能突出显示MRI扫描中的细微神经纤维缠结和淀粉样斑块。
- 该模型的F1分数达到99.31%,精度和召回率均超过99%,表现优异。
- 模型显著优于现有技术(SOTA)。
点此查看论文截图

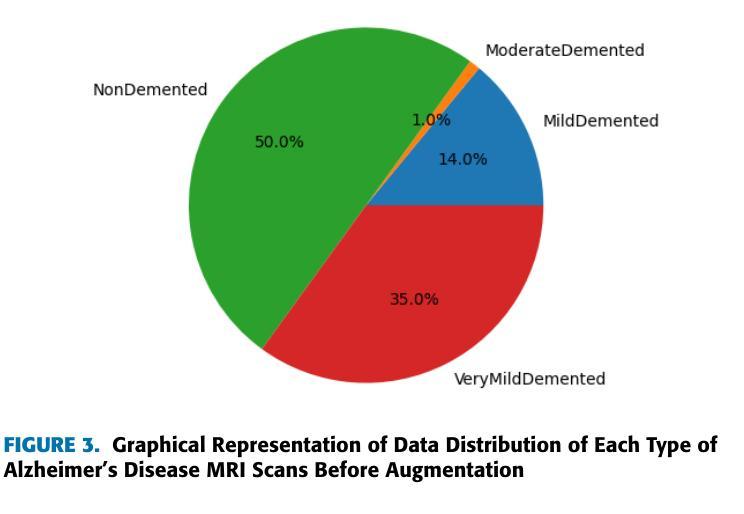
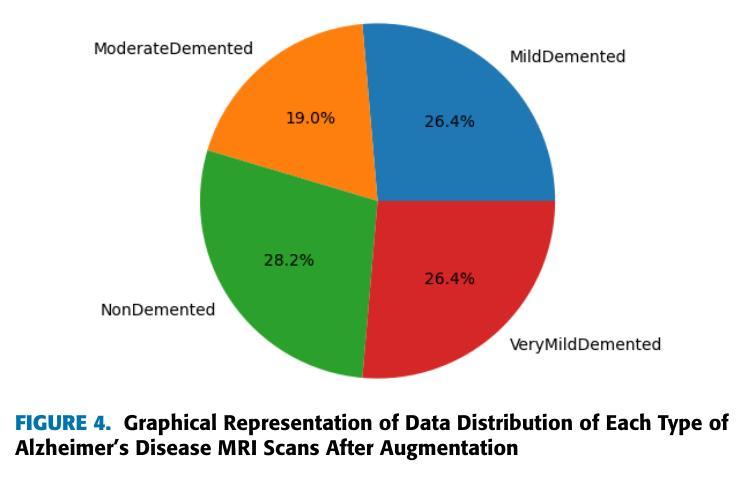
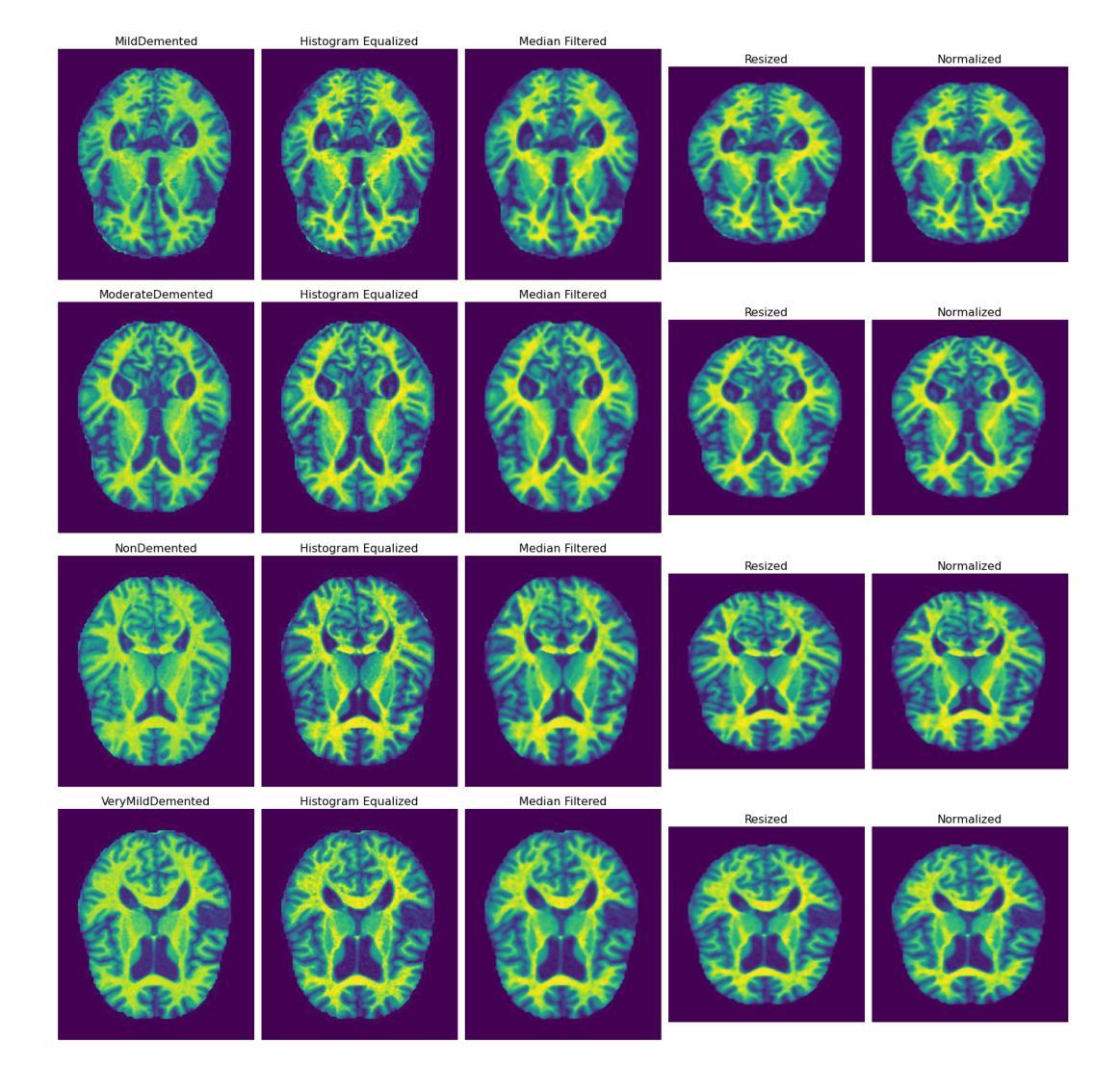
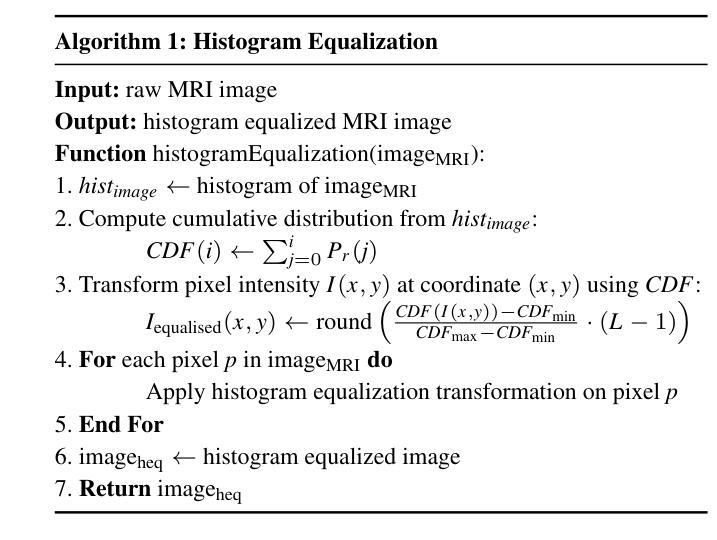
Exploring scalable medical image encoders beyond text supervision
Authors:Fernando Pérez-García, Harshita Sharma, Sam Bond-Taylor, Kenza Bouzid, Valentina Salvatelli, Maximilian Ilse, Shruthi Bannur, Daniel C. Castro, Anton Schwaighofer, Matthew P. Lungren, Maria Teodora Wetscherek, Noel Codella, Stephanie L. Hyland, Javier Alvarez-Valle, Ozan Oktay
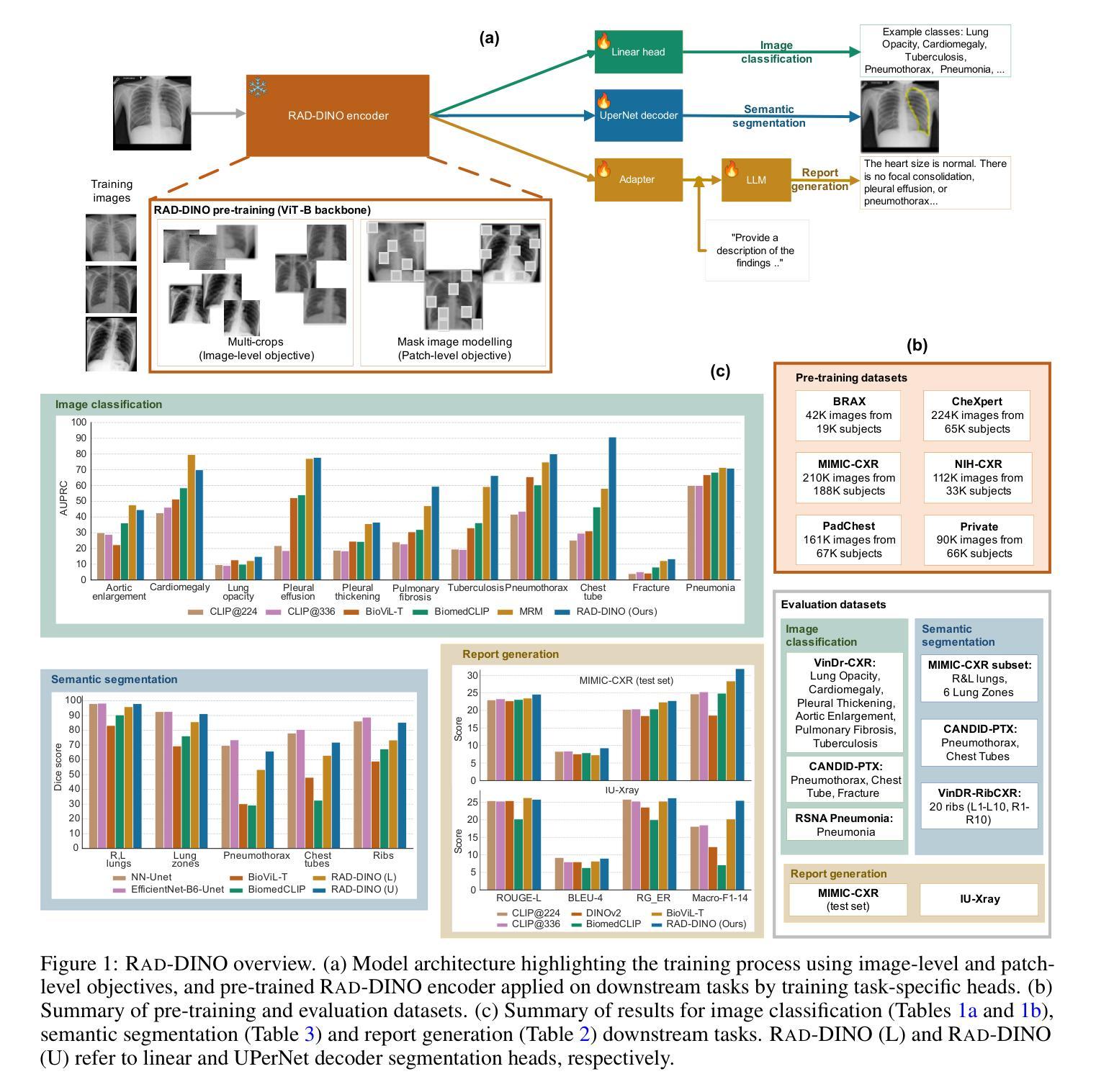
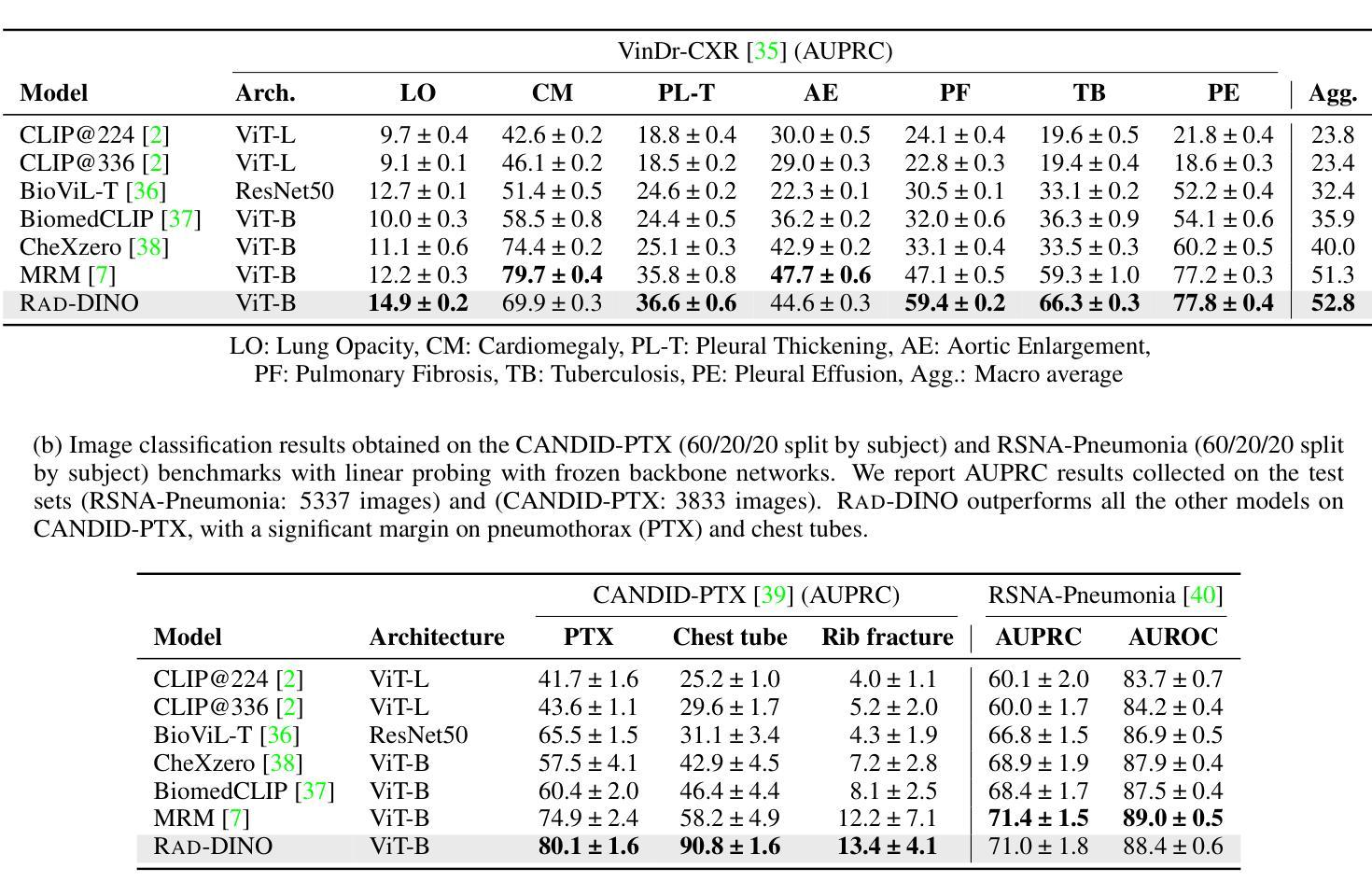
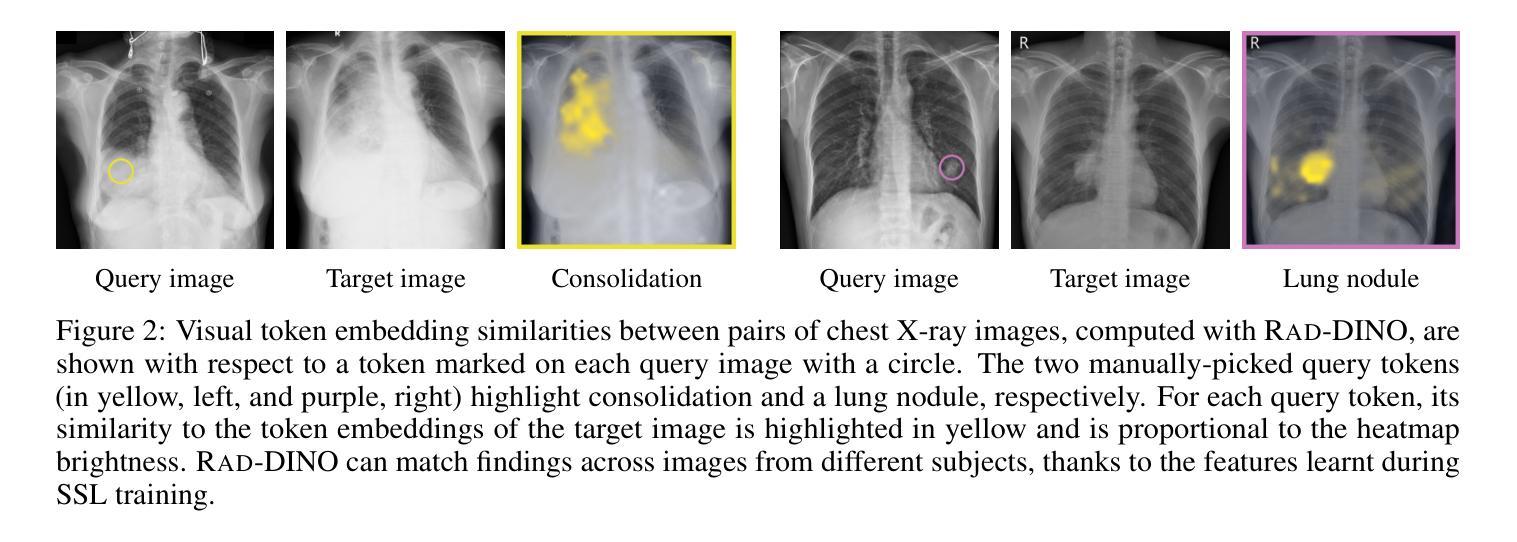
Language-supervised pre-training has proven to be a valuable method for extracting semantically meaningful features from images, serving as a foundational element in multimodal systems within the computer vision and medical imaging domains. However, the computed features are limited by the information contained in the text, which is particularly problematic in medical imaging, where the findings described by radiologists focus on specific observations. This challenge is compounded by the scarcity of paired imaging-text data due to concerns over leakage of personal health information. In this work, we fundamentally challenge the prevailing reliance on language supervision for learning general-purpose biomedical imaging encoders. We introduce RAD-DINO, a biomedical image encoder pre-trained solely on unimodal biomedical imaging data that obtains similar or greater performance than state-of-the-art biomedical language-supervised models on a diverse range of benchmarks. Specifically, the quality of learned representations is evaluated on standard imaging tasks (classification and semantic segmentation), and a vision-language alignment task (text report generation from images). To further demonstrate the drawback of language supervision, we show that features from RAD-DINO correlate with other medical records (e.g., sex or age) better than language-supervised models, which are generally not mentioned in radiology reports. Finally, we conduct a series of ablations determining the factors in RAD-DINO’s performance; notably, we observe that RAD-DINO’s downstream performance scales well with the quantity and diversity of training data, demonstrating that image-only supervision is a scalable approach for training a foundational biomedical image encoder. Model weights of RAD-DINO trained on publicly available datasets are available at https://huggingface.co/microsoft/rad-dino.
语言监督的预训练已被证明是从图像中提取语义上有意义的特征的一种有价值的方法,作为计算机视觉和医学成像领域中的多模态系统的基础元素。然而,计算出的特征受到文本中所包含信息的限制,这在医学成像中尤其成问题,因为放射科医生所描述的发现主要关注特定的观察结果。这一挑战还因配对成像-文本数据的稀缺而加剧,这主要是由于担心泄露个人健康信息。在这项工作中,我们从根本上质疑对语言监督的普遍依赖,以学习通用生物医学成像编码器。我们引入了RAD-DINO,这是一种仅在一维生物医学成像数据上进行预训练的生物医学图像编码器,它在多种基准测试上达到了或超越了最新生物医学语言监督模型的表现。具体来说,通过在标准成像任务(分类和语义分割)和视觉语言对齐任务(根据图像生成文本报告)上评估所学表示的质量。为了进一步证明语言监督的局限性,我们展示了RAD-DINO的特征与其他医疗记录(如性别或年龄)的相关性优于语言监督模型,这些通常不会在放射学报告中被提及。最后,我们进行了一系列确定RAD-DINO性能因素的实验;值得注意的是,我们观察到RAD-DINO的下游性能随着训练数据数量和多样性的增加而表现良好,这表明仅使用图像监督是一种可扩展的方法来训练基础生物医学图像编码器。RAD-DINO在公开数据集上训练的模型权重可在https://huggingface.co/microsoft/rad-dino 获得。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
该文本介绍了在医学图像领域,通过纯图像预训练方法(RAD-DINO)来提取图像特征,其性能可以达到甚至超越依赖于语言监督的预训练模型。RAD-DINO能够在标准成像任务(分类和语义分割)以及跨模态任务(从图像生成文本报告)中表现优秀。相较于语言监督模型,RAD-DINO的特征能更好地与其他医疗记录(如性别、年龄等)相关联。此外,RAD-DINO的训练性能可通过增加训练数据量和多样性来进一步提升,证明了纯图像监督是一种可扩展的医学图像基础编码器训练方法。
Key Takeaways
- 语言监督预训练在医学图像特征提取中存在局限性,尤其是在注重特定观察的医学成像领域。
- RAD-DINO是一个纯图像预训练的医学图像编码器,能在多种基准测试中达到或超越先进语言监督模型的表现。
- RAD-DINO学到的表示质量在标准成像任务(分类和语义分割)上得到评估,并展示了其在跨模态任务(从图像生成文本报告)中的有效性。
- 与语言监督模型相比,RAD-DINO的特征能更好地与其他医疗记录(如性别、年龄)关联。
- RAD-DINO的训练性能可通过增加训练数据量和多样性来提升,证明了纯图像监督的可扩展性。
- RAD-DINO模型权重可在公开数据集上进行训练,并可在huggingface.co/microsoft/rad-dino获取。
- 该研究通过一系列消融实验确定了RAD-DINO性能的关键因素。
点此查看论文截图