⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-02-11 更新
Graph Contrastive Learning for Connectome Classification
Authors:Martín Schmidt, Sara Silva, Federico Larroca, Gonzalo Mateos, Pablo Musé
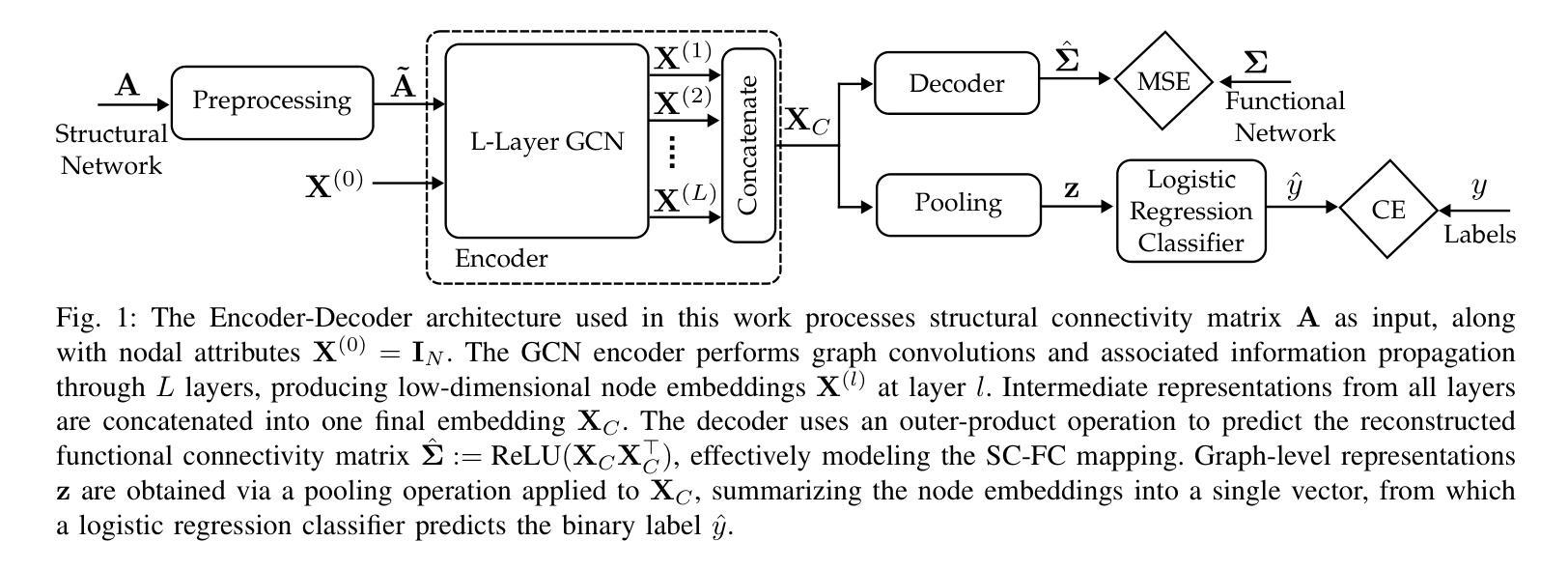
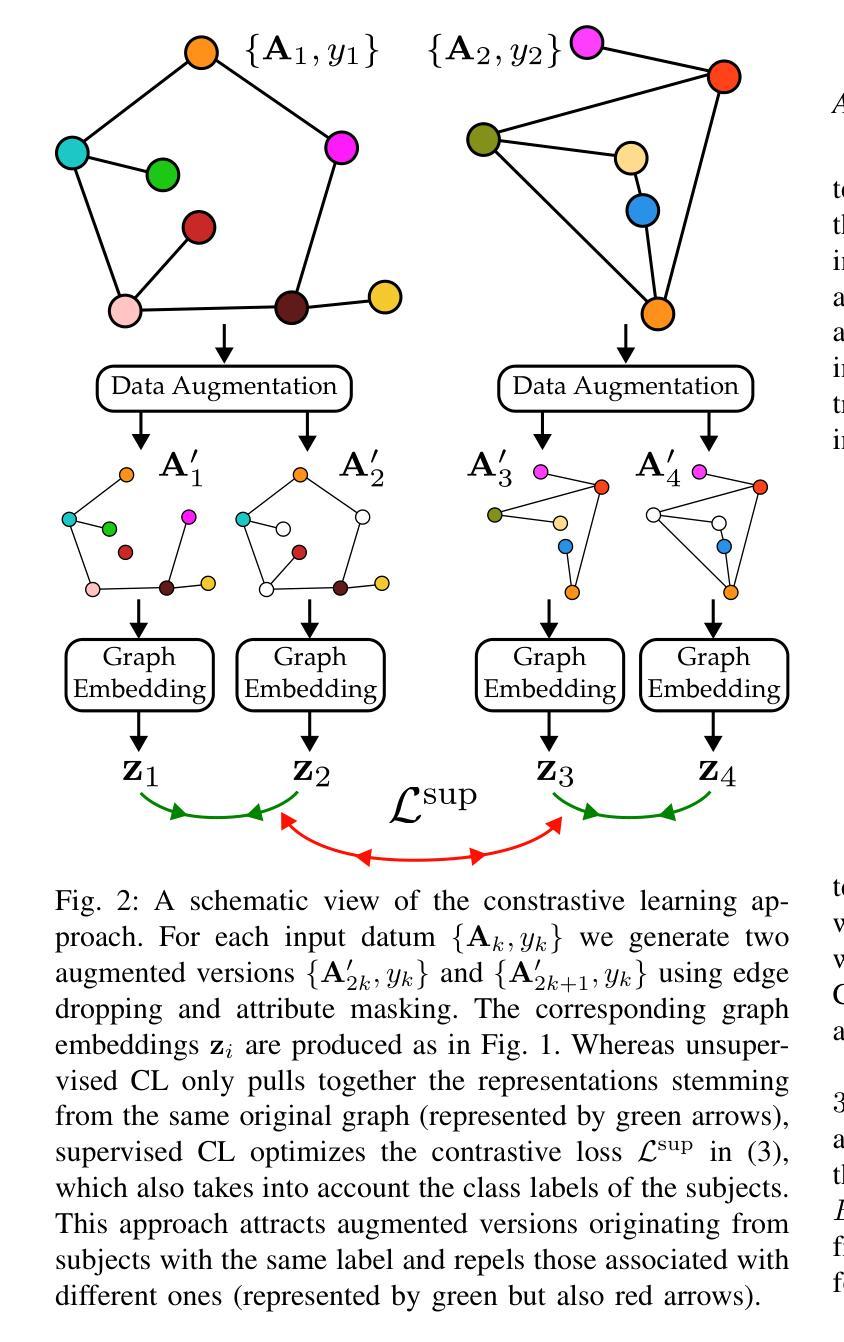
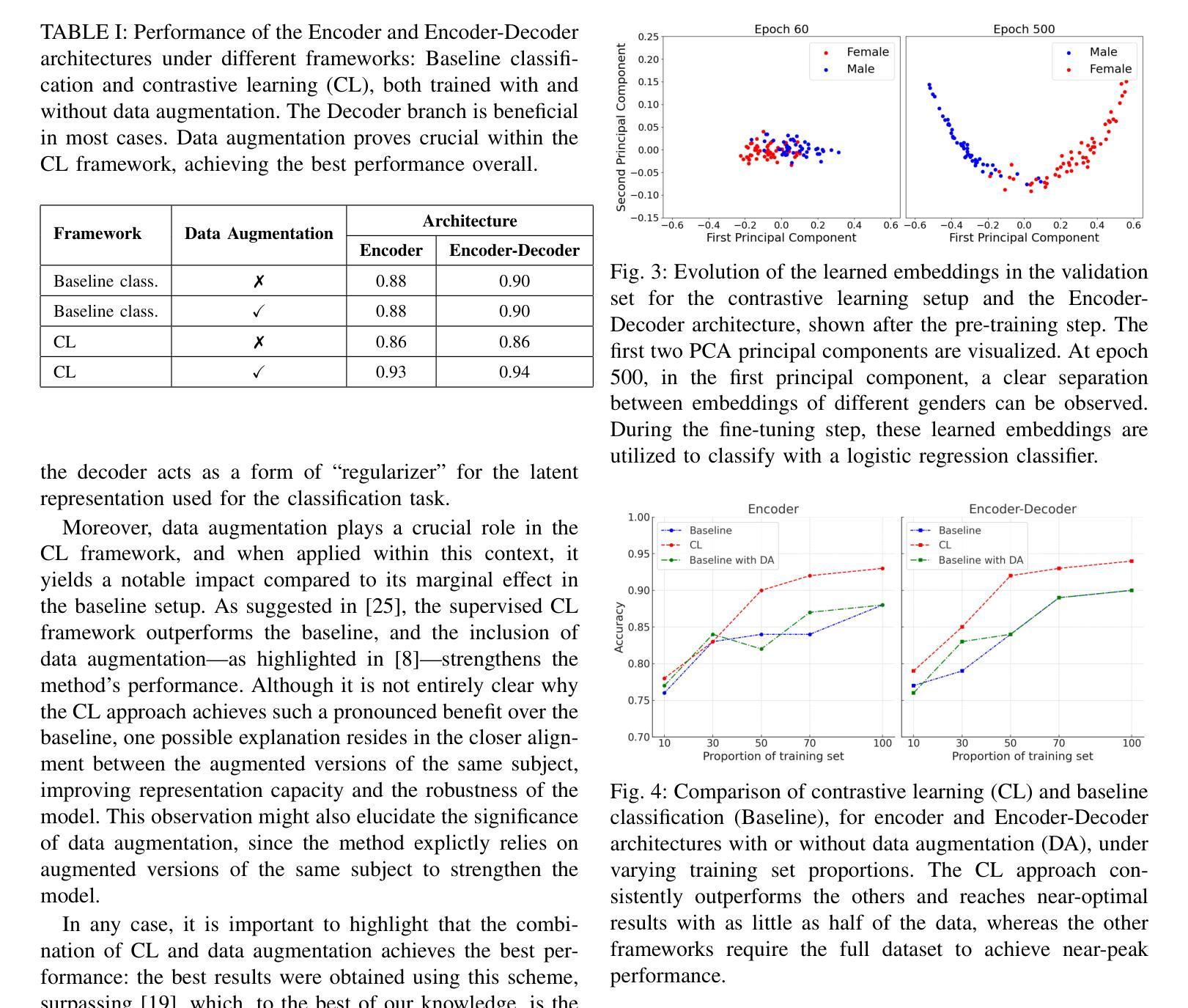
With recent advancements in non-invasive techniques for measuring brain activity, such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), the study of structural and functional brain networks through graph signal processing (GSP) has gained notable prominence. GSP stands as a key tool in unraveling the interplay between the brain’s function and structure, enabling the analysis of graphs defined by the connections between regions of interest – referred to as connectomes in this context. Our work represents a further step in this direction by exploring supervised contrastive learning methods within the realm of graph representation learning. The main objective of this approach is to generate subject-level (i.e., graph-level) vector representations that bring together subjects sharing the same label while separating those with different labels. These connectome embeddings are derived from a graph neural network Encoder-Decoder architecture, which jointly considers structural and functional connectivity. By leveraging data augmentation techniques, the proposed framework achieves state-of-the-art performance in a gender classification task using Human Connectome Project data. More broadly, our connectome-centric methodological advances support the promising prospect of using GSP to discover more about brain function, with potential impact to understanding heterogeneity in the neurodegeneration for precision medicine and diagnosis.
随着无创技术测量脑活动的最新进展,如磁共振成像(MRI),通过图信号处理(GSP)研究结构和功能脑网络已经变得尤为突出。图信号处理是揭示大脑功能结构相互作用的关键工具,能够分析由感兴趣区域之间连接所定义的图的分析,这在本文中被称为连接组。我们的工作是在这一方向上迈出了一步,通过探索图表示学习领域的监督对比学习方法。该方法的主要目标是生成主体级(即图级)的向量表示,这些表示能够将具有相同标签的主体聚集在一起,同时区分具有不同标签的主体。这些连接组嵌入来自图神经网络编码器-解码器架构,该架构同时考虑了结构和功能连接性。通过利用数据增强技术,所提出的框架在利用人类连接组项目数据的性别分类任务上达到了最先进的性能。更广泛地说,我们的以连接组为中心的方法论进展支持了使用GSP来了解大脑功能的希望前景,对精确医学和诊断中的神经变异的异质性理解具有潜在影响。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Submitted to EMBC ‘25
Summary
本文介绍了利用非侵入性技术(如磁共振成像)研究脑网络和图信号处理(GSP)的最新进展。文章重点介绍了一种基于图表示学习的有监督对比学习方法,旨在生成主题级别的向量表示,将同一标签的主题聚集在一起,同时区分不同标签的主题。通过利用数据增强技术,所提出的框架在人类连接组项目数据中实现了性别分类任务的卓越性能。此外,该研究为使用GSP深入了解大脑功能提供了前景,有望对神经退行性疾病的精确医学和诊断产生潜在影响。
Key Takeaways
- 非侵入性技术如磁共振成像(MRI)在研究脑网络方面扮演重要角色。
- 图信号处理(GSP)是揭示脑功能结构交互的关键工具。
- 通过对图表示学习的有监督对比学习方法的研究,可以生成主题级别的向量表示。
- 该方法通过数据增强技术实现了性别分类任务的卓越性能。
- 该研究利用GSP深入了解大脑功能,为神经科学领域带来新的视角。
- 此项研究在精确医学和诊断方面具有潜在的应用价值。
点此查看论文截图

Learning Street View Representations with Spatiotemporal Contrast
Authors:Yong Li, Yingjing Huang, Gengchen Mai, Fan Zhang
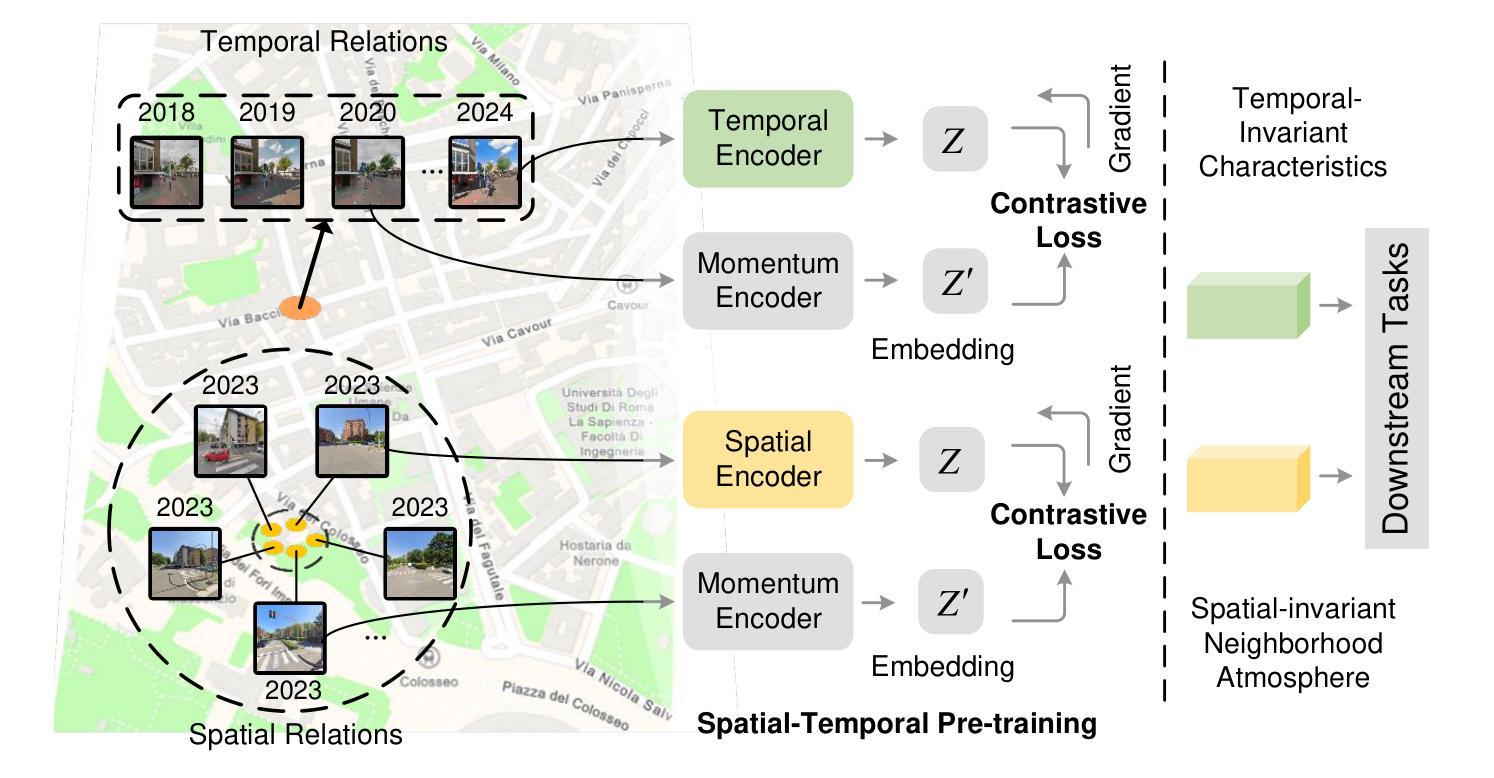
Street view imagery is extensively utilized in representation learning for urban visual environments, supporting various sustainable development tasks such as environmental perception and socio-economic assessment. However, it is challenging for existing image representations to specifically encode the dynamic urban environment (such as pedestrians, vehicles, and vegetation), the built environment (including buildings, roads, and urban infrastructure), and the environmental ambiance (such as the cultural and socioeconomic atmosphere) depicted in street view imagery to address downstream tasks related to the city. In this work, we propose an innovative self-supervised learning framework that leverages temporal and spatial attributes of street view imagery to learn image representations of the dynamic urban environment for diverse downstream tasks. By employing street view images captured at the same location over time and spatially nearby views at the same time, we construct contrastive learning tasks designed to learn the temporal-invariant characteristics of the built environment and the spatial-invariant neighborhood ambiance. Our approach significantly outperforms traditional supervised and unsupervised methods in tasks such as visual place recognition, socioeconomic estimation, and human-environment perception. Moreover, we demonstrate the varying behaviors of image representations learned through different contrastive learning objectives across various downstream tasks. This study systematically discusses representation learning strategies for urban studies based on street view images, providing a benchmark that enhances the applicability of visual data in urban science. The code is available at https://github.com/yonglleee/UrbanSTCL.
街景图像在城市视觉环境的表示学习中得到了广泛应用,支持各种可持续发展任务,如环境感知和社会经济评估。然而,现有图像表示在编码街景图像中描绘的动态城市环境(如行人、车辆和植被)、人工环境(包括建筑、道路和基础设施)和环境氛围(如文化和社会经济氛围)方面存在挑战,以应对与城市相关的下游任务。在这项工作中,我们提出了一种创新的自我监督学习框架,该框架利用街景图像的时空属性来学习动态城市环境的图像表示,以执行各种下游任务。我们通过采用在同一地点随时间捕获的街景图像和同一时间空间附近视图来构建对比学习任务,旨在学习人工环境的时序不变特性以及空间不变邻域氛围。我们的方法在视觉场所识别、社会经济估算、人与环境感知等任务中的表现均优于传统的监督和无监督方法。此外,我们展示了通过不同对比学习目标学到的图像表示在不同下游任务中的不同行为。本研究系统地讨论了基于街景图像的城市研究表示学习策略,提供了一个基准,增强了视觉数据在城市科学中的应用性。代码可用在https://github.com/yonglleee 可用访问。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种利用街道视角图像的时间与空间属性进行自监督学习的新框架,该框架能够学习动态城市环境的图像表示,适用于多种下游任务。通过在同一地点不同时间以及同一时间附近地点的街道视角图像,构建对比学习任务,学习建筑物的环境的时间不变特性和邻里氛围的空间不变性。该方法在视觉场所识别、社会经济估算以及人境感知等任务中的表现优于传统的监督和无监督方法。
Key Takeaways
- 街道视角图像在城市视觉环境表示学习中得到广泛应用,支持环境感知和社会经济评估等可持续发展任务。
- 当前图像表示难以编码街道视角图像中的动态城市环境、建筑环境和环境氛围,以应对与城市相关的下游任务。
- 提出一种自监督学习框架,利用街道视角图像的时间和空间属性来学习动态城市环境的图像表示。
- 通过在同一地点不同时间及同一时间附近地点的图像构建对比学习任务,学习建筑环境的时间不变特性和邻里氛围的空间不变性。
- 该方法在视觉场所识别、社会经济估算和人境感知等任务上的表现优于传统方法。
- 系统讨论基于街道视角图像的城市研究表示学习策略,为城市科学中视觉数据的应用提供基准。
点此查看论文截图

SLCGC: A lightweight Self-supervised Low-pass Contrastive Graph Clustering Network for Hyperspectral Images
Authors:Yao Ding, Zhili Zhang, Aitao Yang, Yaoming Cai, Xiongwu Xiao, Danfeng Hong, Junsong Yuan
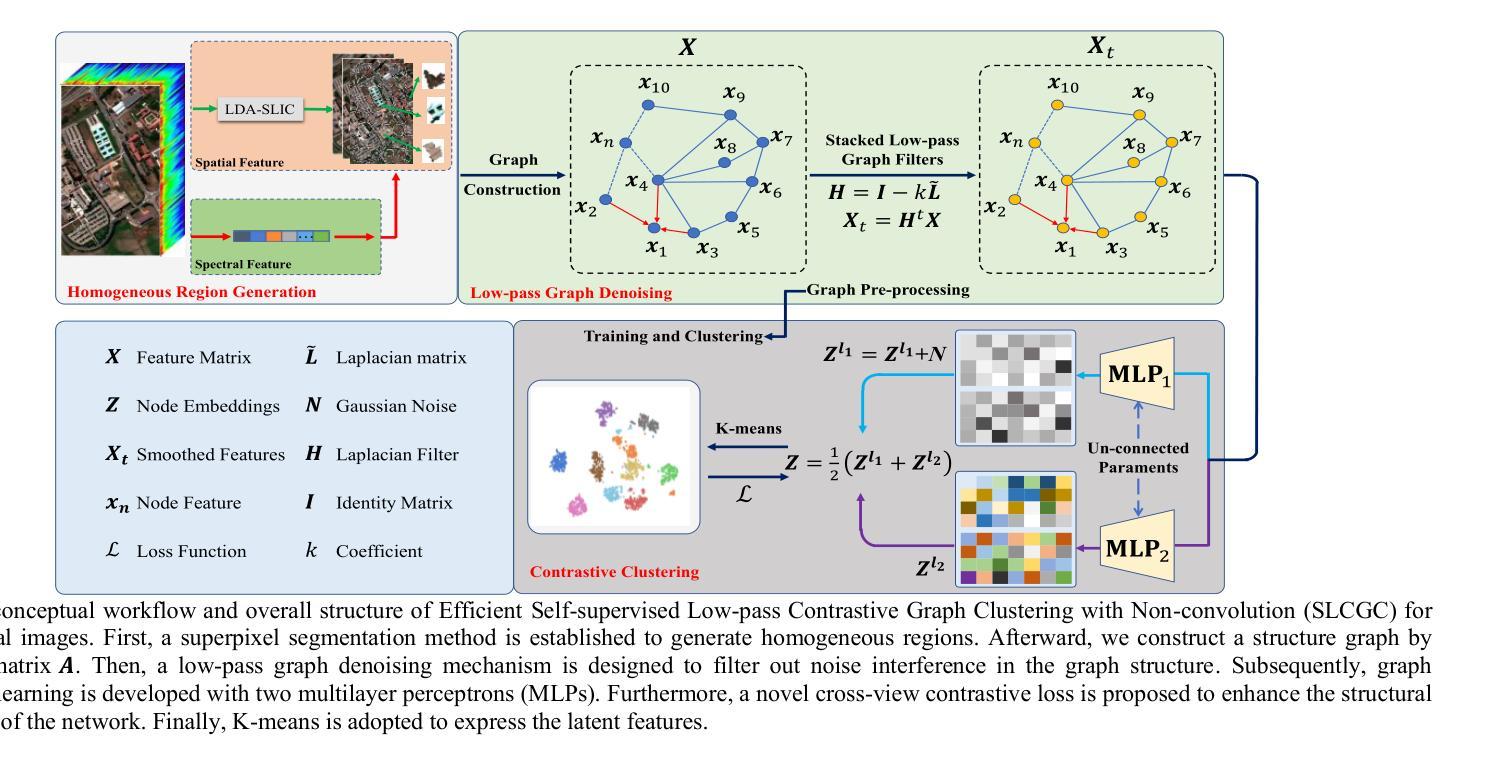
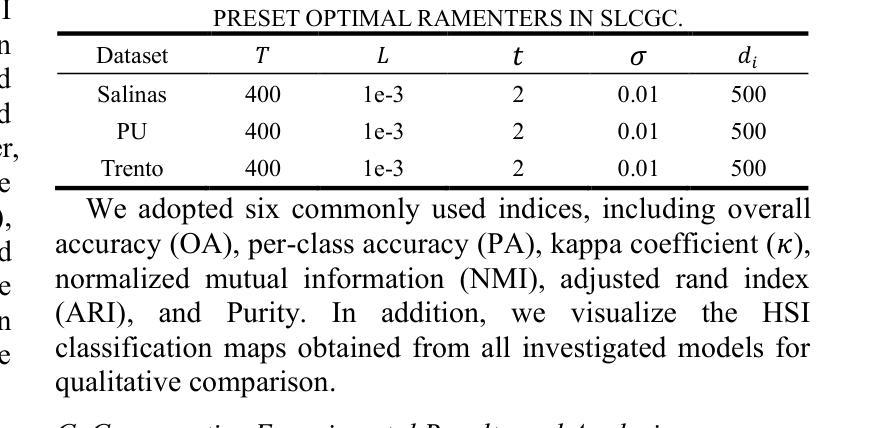
Self-supervised hyperspectral image (HSI) clustering remains a fundamental yet challenging task due to the absence of labeled data and the inherent complexity of spatial-spectral interactions. While recent advancements have explored innovative approaches, existing methods face critical limitations in clustering accuracy, feature discriminability, computational efficiency, and robustness to noise, hindering their practical deployment. In this paper, a self-supervised efficient low-pass contrastive graph clustering (SLCGC) is introduced for HSIs. Our approach begins with homogeneous region generation, which aggregates pixels into spectrally consistent regions to preserve local spatial-spectral coherence while drastically reducing graph complexity. We then construct a structural graph using an adjacency matrix A and introduce a low-pass graph denoising mechanism to suppress high-frequency noise in the graph topology, ensuring stable feature propagation. A dual-branch graph contrastive learning module is developed, where Gaussian noise perturbations generate augmented views through two multilayer perceptrons (MLPs), and a cross-view contrastive loss enforces structural consistency between views to learn noise-invariant representations. Finally, latent embeddings optimized by this process are clustered via K-means. Extensive experiments and repeated comparative analysis have verified that our SLCGC contains high clustering accuracy, low computational complexity, and strong robustness. The code source will be available at https://github.com/DY-HYX.
自监督型高光谱图像(HSI)聚类仍然是一项基础但具有挑战性的任务,原因在于缺乏标签数据以及空间光谱交互的内在复杂性。尽管最近有诸多进展和创新方法探索,现有方法在聚类精度、特征辨别力、计算效率以及对噪声的鲁棒性方面存在关键局限性,阻碍了其实践部署。本文介绍了一种用于HSI的自监督高效低通对比图聚类(SLCGC)。我们的方法首先从同质区域生成开始,将像素聚集成光谱一致的区域,以保留局部空间光谱一致性,同时大大降低图的复杂性。接着,我们使用邻接矩阵A构建结构图,并引入低通图去噪机制来抑制图拓扑中的高频噪声,以确保特征传播的稳定性。开发了一个双分支图对比学习模块,其中高斯噪声扰动通过两个多层感知器(MLP)生成增强视图,跨视图对比损失强制不同视图之间的结构一致性,以学习噪声不变表示。最后,通过此过程优化的潜在嵌入通过K-means进行聚类。广泛的实验和重复对比分析验证了我们的SLCGC具有高聚类精度、低计算复杂度和强鲁棒性。代码源将在https://github.com/DY-HYX处提供。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 12 pages, 9 figures
Summary:无监督的基于低通对比图的聚类策略,解决HSI聚类的难点问题,包含无标签数据和高频噪声干扰的问题。通过生成同质区域、构建结构图、引入低通图去噪机制和对比学习模块,实现高效稳定的聚类效果。代码将在GitHub上公开。
Key Takeaways:
- 自监督学习应用于高光谱图像聚类,解决无标签数据问题。
- 提出高效低通对比图聚类方法(SLCGC),通过生成同质区域降低图复杂性。
- 构建结构图并使用低通图去噪机制,确保特征传播稳定并抑制高频噪声干扰。
- 引入双分支对比学习模块,学习噪声不变特征表示。
- 优化后的潜在嵌入通过K-means进行聚类。
- 实验和比较分析显示SLCGC具有高的聚类精度、低的计算复杂度和强的鲁棒性。
点此查看论文截图


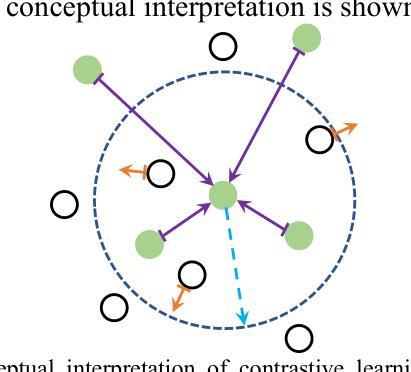


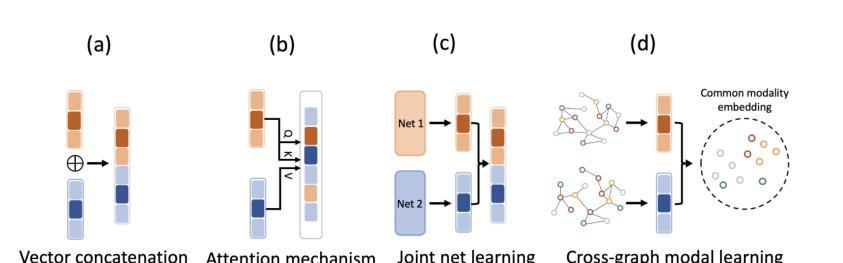
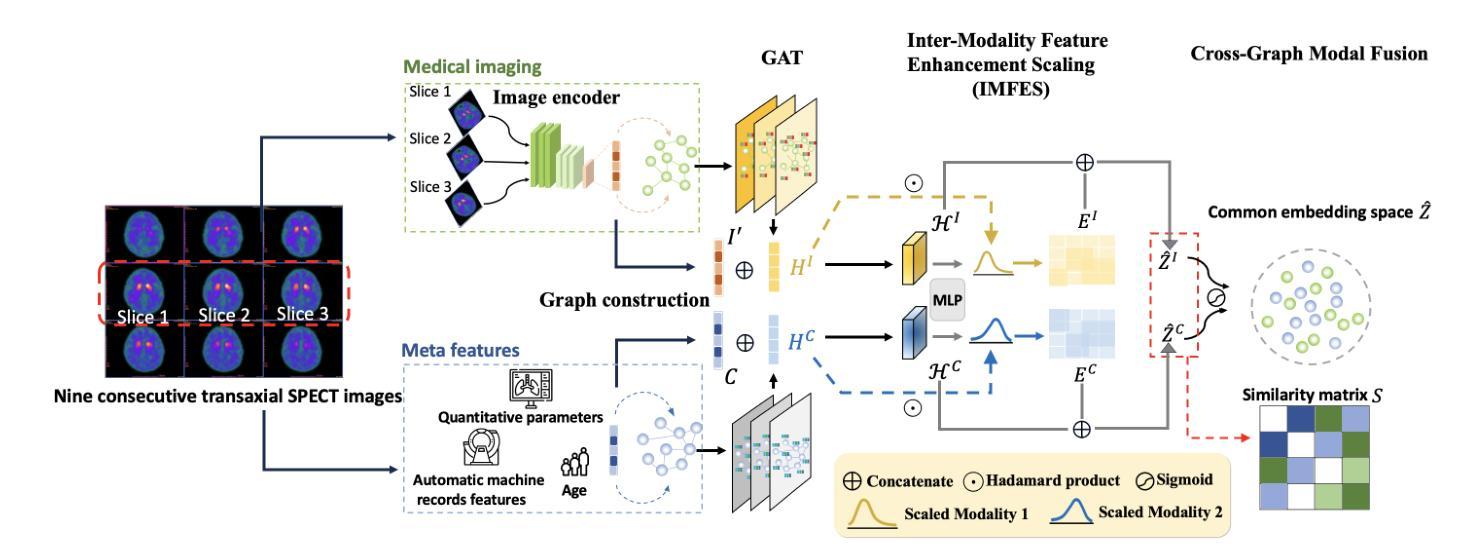
Enhancing Multimodal Medical Image Classification using Cross-Graph Modal Contrastive Learning
Authors:Jun-En Ding, Chien-Chin Hsu, Chi-Hsiang Chu, Shuqiang Wang, Feng Liu
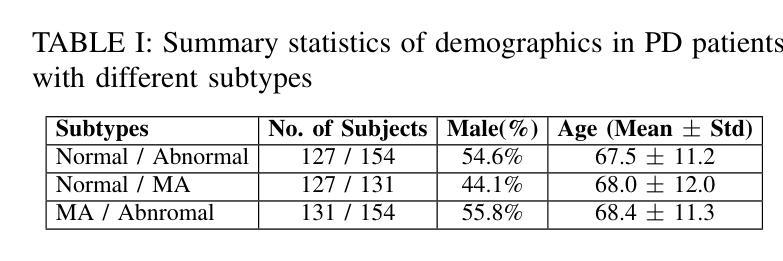
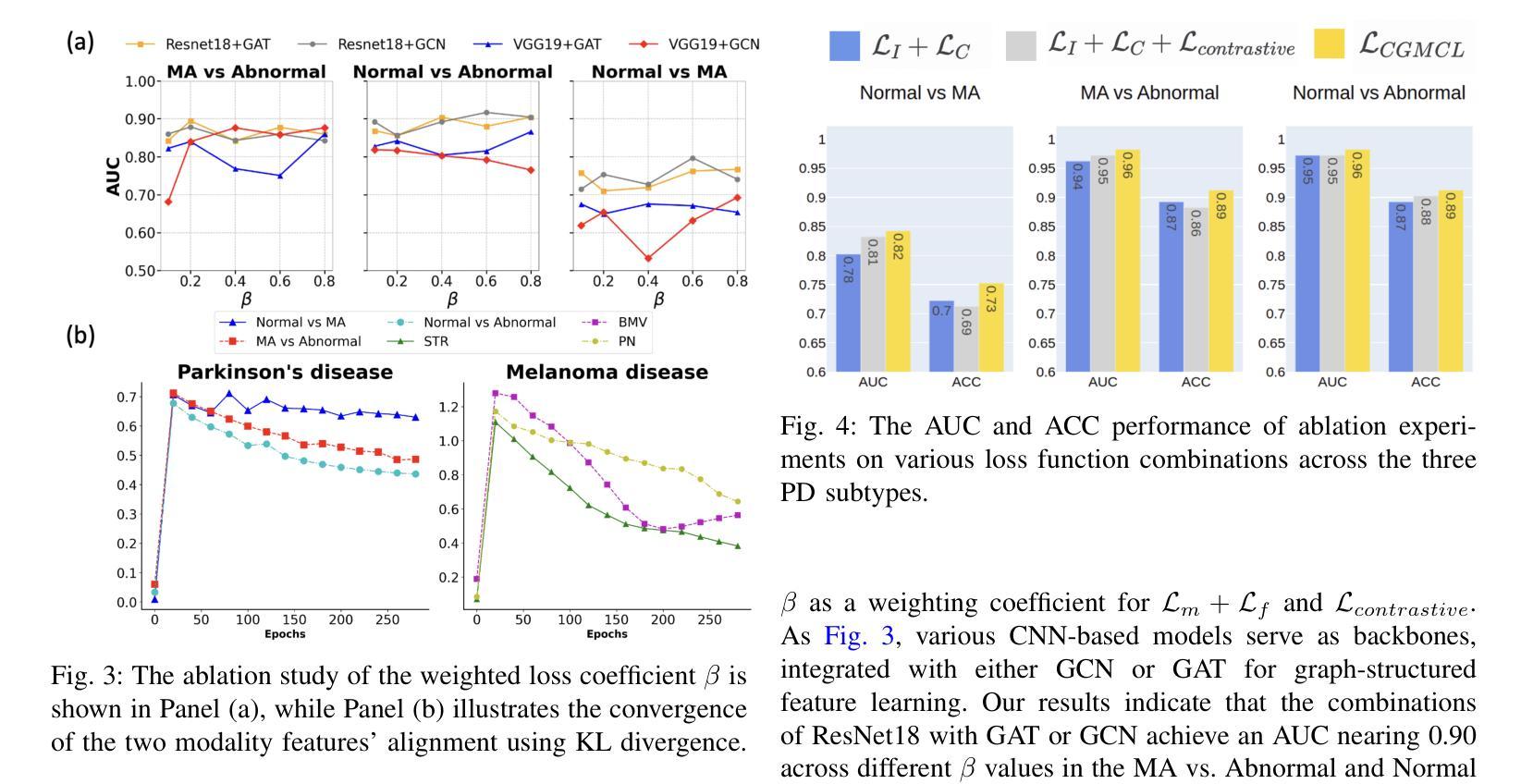
The classification of medical images is a pivotal aspect of disease diagnosis, often enhanced by deep learning techniques. However, traditional approaches typically focus on unimodal medical image data, neglecting the integration of diverse non-image patient data. This paper proposes a novel Cross-Graph Modal Contrastive Learning (CGMCL) framework for multimodal structured data from different data domains to improve medical image classification. The model effectively integrates both image and non-image data by constructing cross-modality graphs and leveraging contrastive learning to align multimodal features in a shared latent space. An inter-modality feature scaling module further optimizes the representation learning process by reducing the gap between heterogeneous modalities. The proposed approach is evaluated on two datasets: a Parkinson’s disease (PD) dataset and a public melanoma dataset. Results demonstrate that CGMCL outperforms conventional unimodal methods in accuracy, interpretability, and early disease prediction. Additionally, the method shows superior performance in multi-class melanoma classification. The CGMCL framework provides valuable insights into medical image classification while offering improved disease interpretability and predictive capabilities.
医疗图像分类是疾病诊断的关键环节,往往可以通过深度学习技术得到增强。然而,传统方法主要关注单模态医疗图像数据,忽视了不同非图像患者数据的整合。本文提出了一种新型的跨图模态对比学习(CGMCL)框架,用于从不同数据域的多模态结构化数据,以提高医疗图像分类的效果。该模型通过构建跨模态图并利用对比学习对齐多模态特征在共享潜在空间,有效地整合了图像和非图像数据。跨模态特征缩放模块进一步优化了表示学习过程,缩小了不同模态之间的差距。所提出的方法在两个数据集上进行了评估:帕金森病(PD)数据集和公共黑色素瘤数据集。结果表明,在准确性、可解释性和早期疾病预测方面,CGMCL优于传统单模态方法。此外,该方法在多类黑色素瘤分类方面也表现出卓越性能。CGMCL框架为医疗图像分类提供了有价值的见解,同时提高了疾病可解释性和预测能力。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
本文提出一种新型的跨图模态对比学习(CGMCL)框架,用于整合不同数据域的多元结构化数据,改善医学图像分类。该框架构建跨模态图并利用对比学习对齐多模态特征于共享潜在空间,通过跨模态特征缩放模块进一步优化表示学习过程,缩小异质模态之间的差距。在帕金森病数据集和公共黑色素瘤数据集上的评估结果表明,CGMCL在准确性、可解释性和早期疾病预测方面优于传统的单模态方法,并且在多类黑色素瘤分类中表现出卓越性能。
关键见解
- 医学图像分类是疾病诊断的重要方面,传统的做法主要关注于单一的医学图像数据,忽视了整合多元化的非图像患者数据。
- 本文提出了一种新型的跨图模态对比学习(CGMCL)框架,用于整合图像和非图像数据,通过构建跨模态图和利用对比学习来对齐多模态特征。
- CGMCL框架通过跨模态特征缩放模块优化表示学习过程,缩小异质模态之间的差距。
- 在帕金森病和黑色素瘤数据集上的实验结果表明,CGMCL框架在医学图像分类上的性能优于传统的单模态方法。
- CGMCL在准确性、可解释性和早期疾病预测方面展现出优势。
- CGMCL框架对于多类黑色素瘤分类表现出卓越性能。
点此查看论文截图

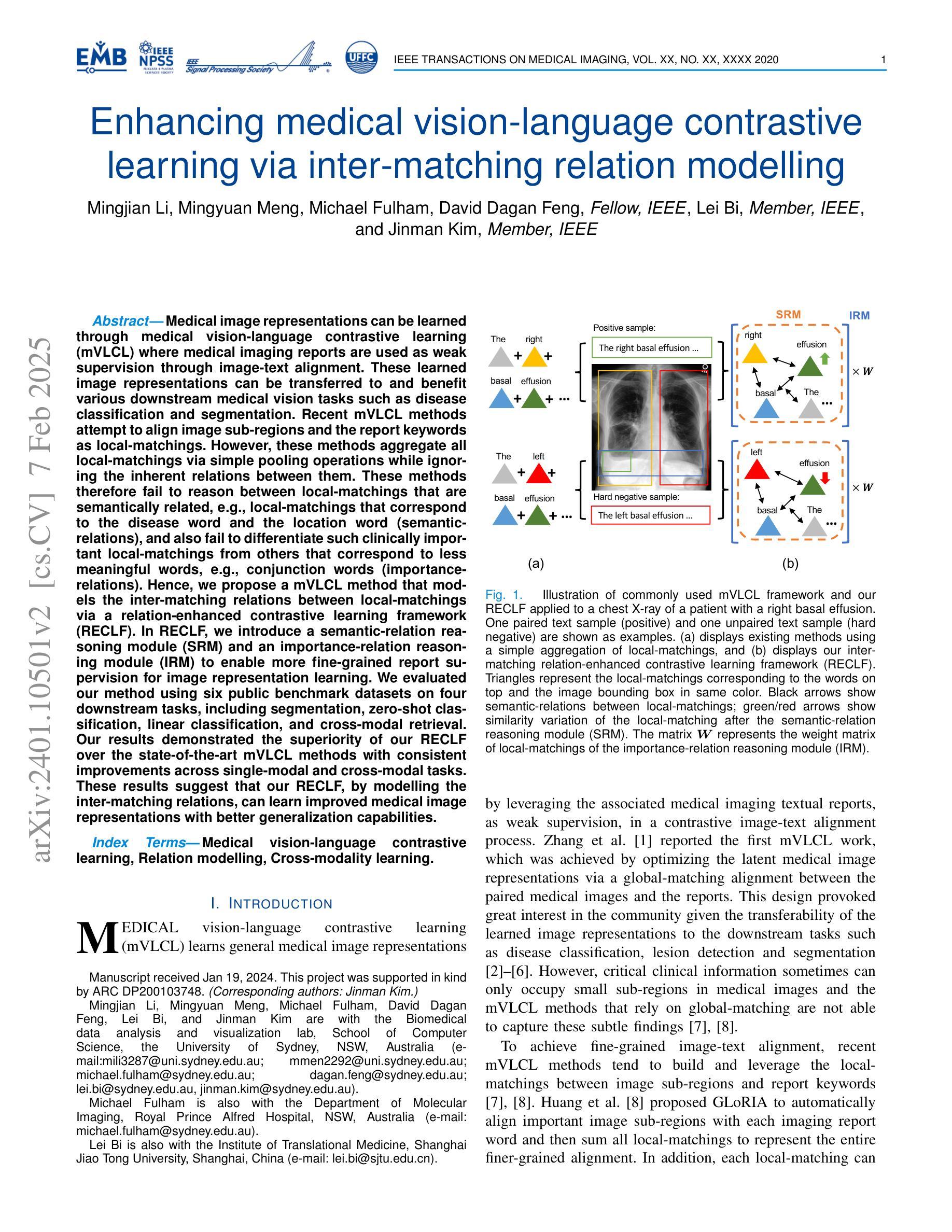
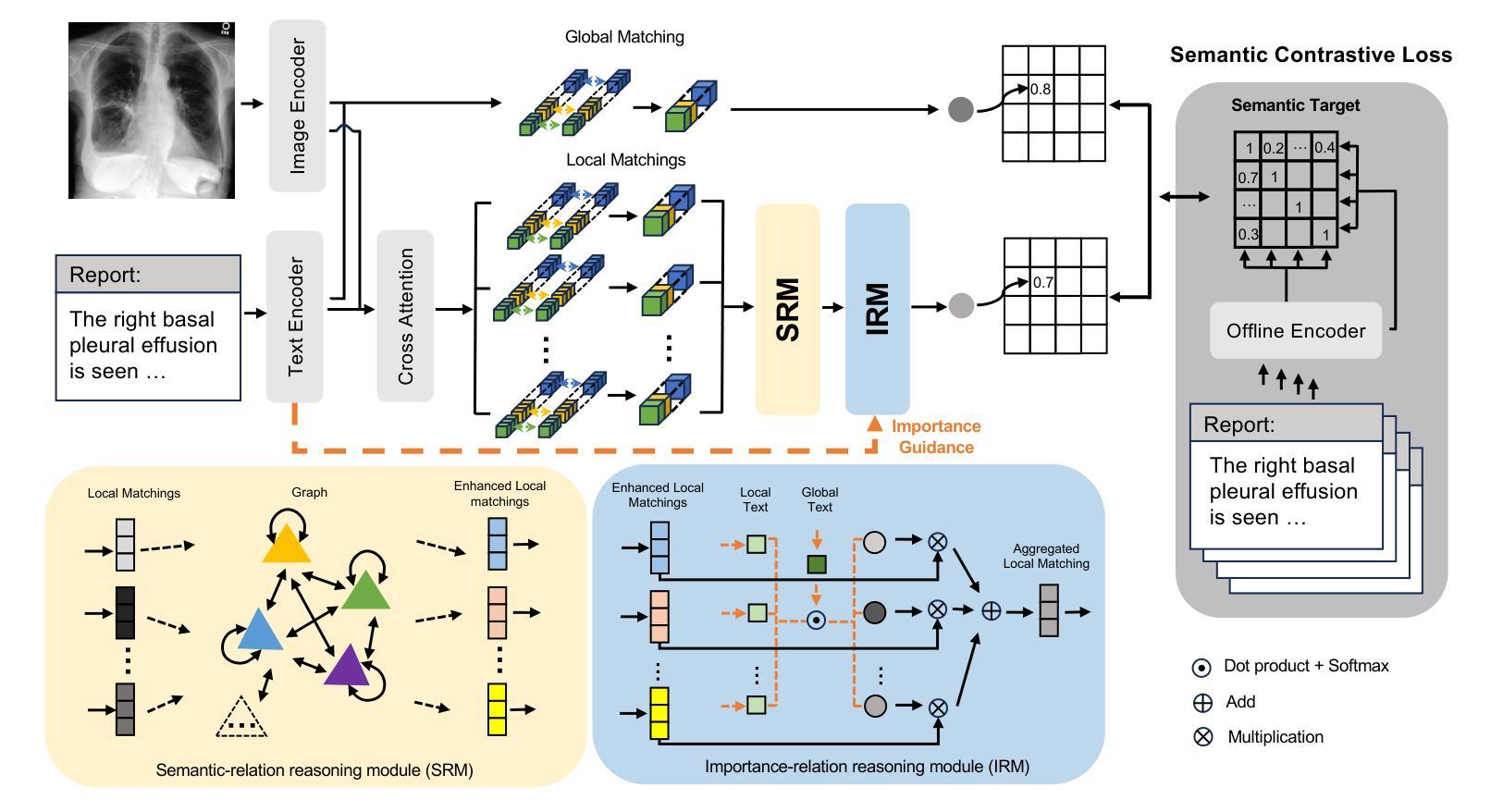
Enhancing medical vision-language contrastive learning via inter-matching relation modelling
Authors:Mingjian Li, Mingyuan Meng, Michael Fulham, David Dagan Feng, Lei Bi, Jinman Kim
Medical image representations can be learned through medical vision-language contrastive learning (mVLCL) where medical imaging reports are used as weak supervision through image-text alignment. These learned image representations can be transferred to and benefit various downstream medical vision tasks such as disease classification and segmentation. Recent mVLCL methods attempt to align image sub-regions and the report keywords as local-matchings. However, these methods aggregate all local-matchings via simple pooling operations while ignoring the inherent relations between them. These methods therefore fail to reason between local-matchings that are semantically related, e.g., local-matchings that correspond to the disease word and the location word (semantic-relations), and also fail to differentiate such clinically important local-matchings from others that correspond to less meaningful words, e.g., conjunction words (importance-relations). Hence, we propose a mVLCL method that models the inter-matching relations between local-matchings via a relation-enhanced contrastive learning framework (RECLF). In RECLF, we introduce a semantic-relation reasoning module (SRM) and an importance-relation reasoning module (IRM) to enable more fine-grained report supervision for image representation learning. We evaluated our method using six public benchmark datasets on four downstream tasks, including segmentation, zero-shot classification, linear classification, and cross-modal retrieval. Our results demonstrated the superiority of our RECLF over the state-of-the-art mVLCL methods with consistent improvements across single-modal and cross-modal tasks. These results suggest that our RECLF, by modelling the inter-matching relations, can learn improved medical image representations with better generalization capabilities.
通过医学视觉语言对比学习(mVLCL),可以利用医学影像学报告作为图像文本对齐的弱监督来学习医学图像表示。这些学习得到的图像表示可以转移到各种下游医学视觉任务中并为其带来益处,例如疾病分类和分割。最近的mVLCL方法试图将图像子区域和报告关键词对齐为局部匹配。然而,这些方法通过简单的池化操作聚合所有局部匹配,同时忽略了它们之间的内在关系。因此,这些方法无法推理语义相关的局部匹配,例如与疾病词和位置词对应的局部匹配(语义关系),也无法区分这样的临床重要的局部匹配与其他对应较少有意义的词(如连词)的局部匹配(重要性关系)。因此,我们提出了一种mVLCL方法,该方法通过关系增强对比学习框架(RECLF)对局部匹配之间的跨匹配关系进行建模。在RECLF中,我们引入了语义关系推理模块(SRM)和重要性关系推理模块(IRM),以实现更精细的报告监督用于图像表示学习。我们在四个下游任务、六个公共基准数据集上评估了我们的方法,包括分割、零样本分类、线性分类和跨模态检索。我们的结果证明了我们的RECLF在最新mVLCL方法上的优越性,在单模态和跨模态任务上都实现了持续的改进。这些结果表明,通过建模跨匹配关系,我们的RECLF可以学习改进的医疗图像表示,具有更好的泛化能力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Published at IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging
摘要
医疗影像资料通过医学视觉语言对比学习(mVLCL)学习表示,通过图像文本对齐利用医学影像报告作为弱监督。这些学习到的图像表示可以转移到各种下游医疗视觉任务中并带来益处,如疾病分类和分割等。最近的mVLCL方法尝试通过局部匹配对齐图像子区域和报告关键词。然而,这些方法通过简单的池化操作聚合所有局部匹配,而忽略了它们之间的内在关系。因此,这些方法无法推理出语义相关的局部匹配,例如与疾病词和位置词对应的局部匹配(语义关系),也无法区分这种临床上重要的局部匹配与其他对应较少意义词汇的匹配,例如连接词(重要性关系)。因此,我们提出了一种mVLCL方法,通过关系增强对比学习框架(RECLF)对局部匹配之间的跨匹配关系进行建模。在RECLF中,我们引入了语义关系推理模块(SRM)和重要性关系推理模块(IRM),以实现更精细的报告监督用于图像表示学习。我们在四个下游任务使用六个公共基准数据集对方法进行了评估,包括分割、零样本分类、线性分类和跨模态检索。结果表明,我们的RECLF在最新的mVLCL方法上具有优越性,在单模态和跨模态任务上均实现了持续的改进。这表明我们的RECLF通过建模跨匹配关系,可以学习改进的医疗图像表示,具有更好的泛化能力。
关键见解
- 医疗视觉语言对比学习(mVLCL)可通过医学图像报告作为弱监督来学习医疗图像表示。
- 现有mVLCL方法通过简单池化操作聚合局部匹配,忽略了局部匹配间的内在关系。
- 提出的关系增强对比学习框架(RECLF)包含语义关系推理模块(SRM)和重要性关系推理模块(IRM),实现更精细的报告监督。
- RECLF在多个公共数据集和下游任务上的表现优于现有mVLCL方法,包括分割、零样本分类、线性分类和跨模态检索。
- RECLF能够学习改进的医疗图像表示,具有更好的泛化能力。
- 通过建模局部匹配间的跨匹配关系,RECLF能够区分语义重要和不太重要的局部匹配。
点此查看论文截图