⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-02-11 更新
IPSeg: Image Posterior Mitigates Semantic Drift in Class-Incremental Segmentation
Authors:Xiao Yu, Yan Fang, Yao Zhao, Yunchao Wei
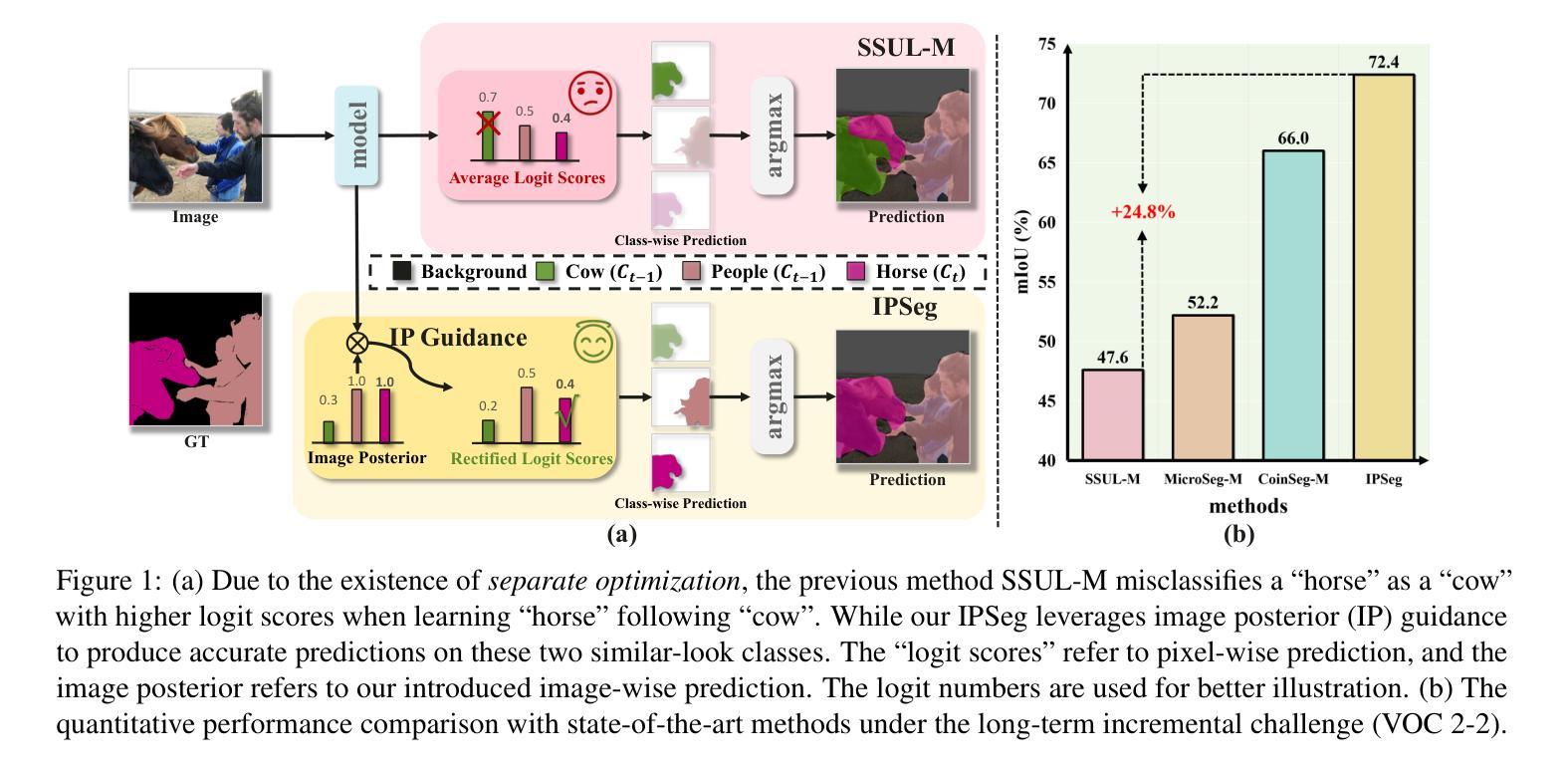
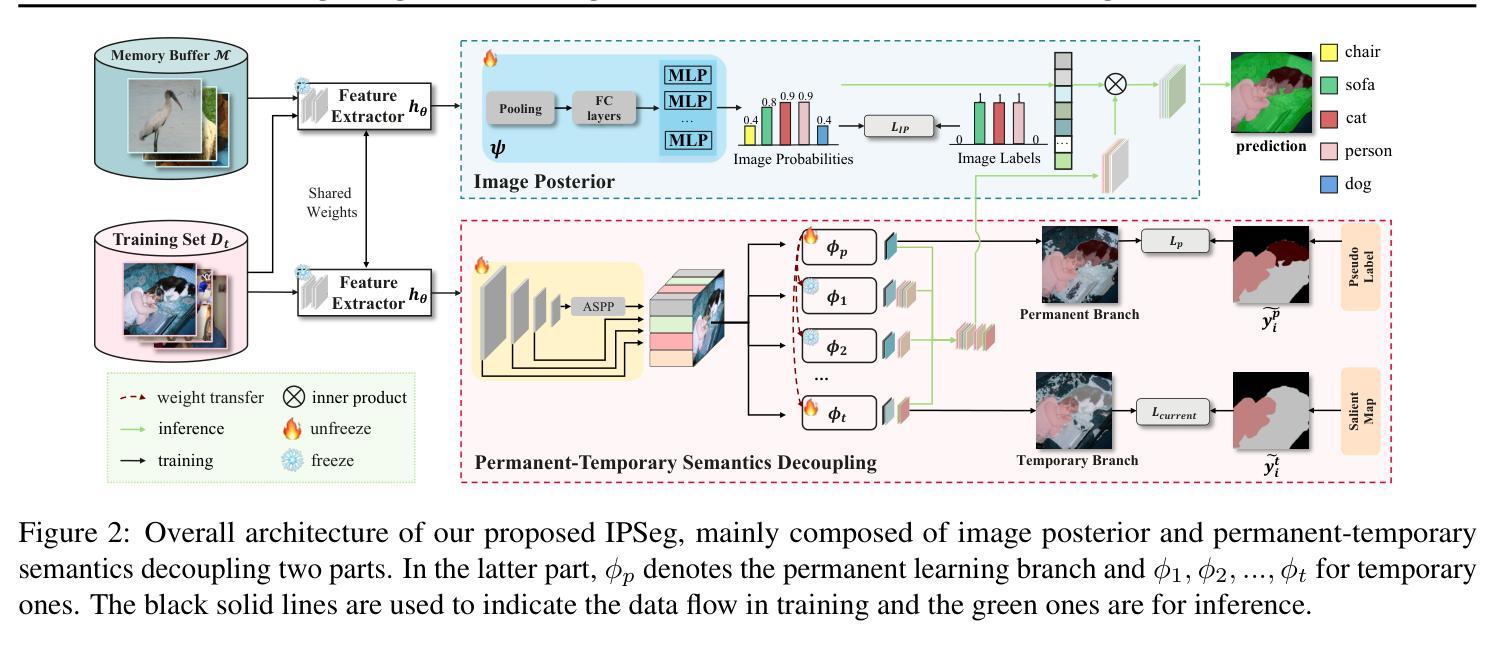
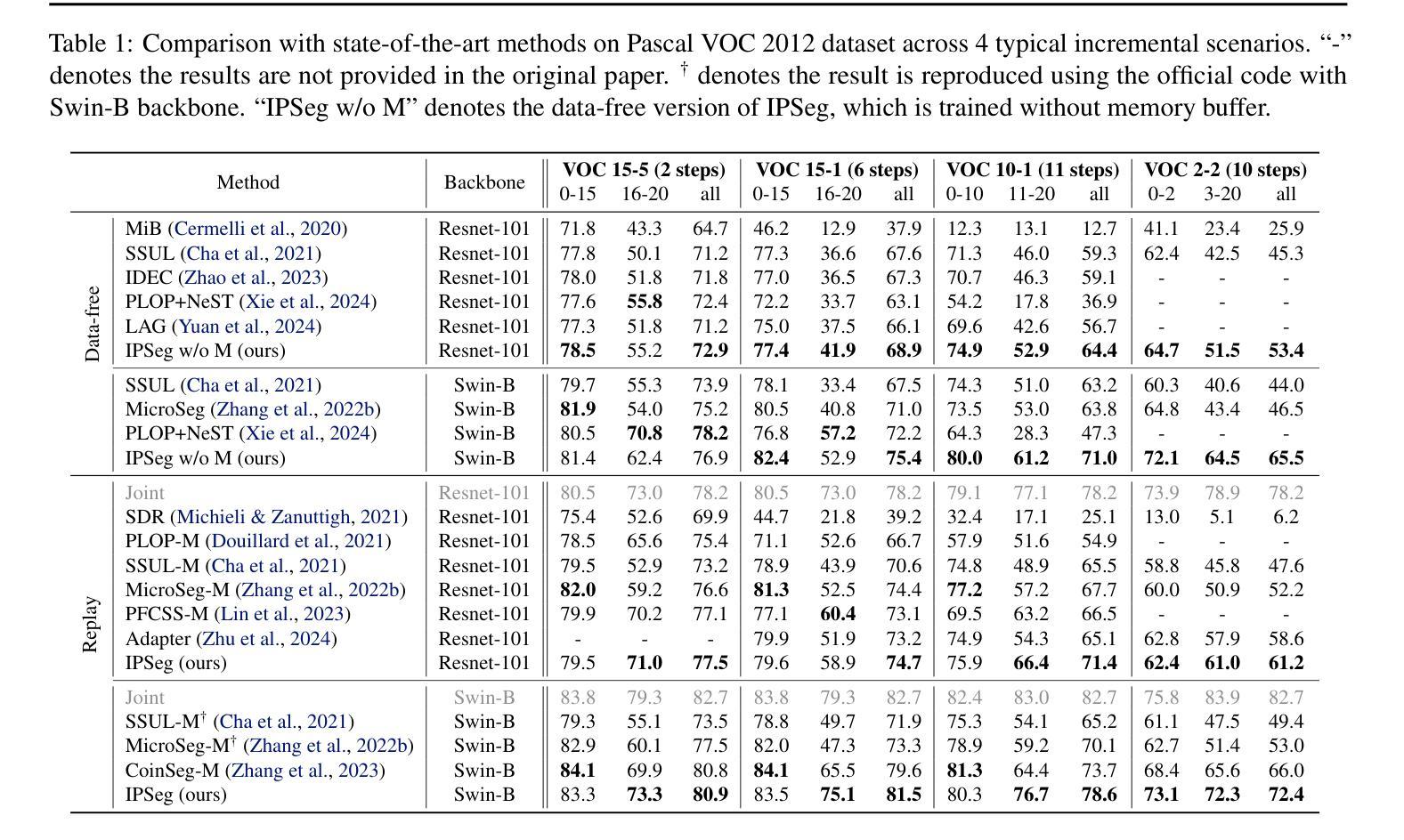
Class incremental learning aims to enable models to learn from sequential, non-stationary data streams across different tasks without catastrophic forgetting. In class incremental semantic segmentation (CISS), the semantic content of image pixels evolves over incremental phases, known as semantic drift. In this work, we identify two critical challenges in CISS that contribute to semantic drift and degrade performance. First, we highlight the issue of separate optimization, where different parts of the model are optimized in distinct incremental stages, leading to misaligned probability scales. Second, we identify noisy semantics arising from inappropriate pseudo-labeling, which results in sub-optimal results. To address these challenges, we propose a novel and effective approach, Image Posterior and Semantics Decoupling for Segmentation (IPSeg). IPSeg introduces two key mechanisms: (1) leveraging image posterior probabilities to align optimization across stages and mitigate the effects of separate optimization, and (2) employing semantics decoupling to handle noisy semantics and tailor learning strategies for different semantics. Extensive experiments on the Pascal VOC 2012 and ADE20K datasets demonstrate that IPSeg achieves superior performance compared to state-of-the-art methods, particularly in challenging long-term incremental scenarios.
类增量学习旨在使模型能够从不同任务的连续非平稳数据流中学习,而不会发生灾难性遗忘。在类增量语义分割(CISS)中,图像像素的语义内容会在增量阶段发生演变,这被称为语义漂移。在这项工作中,我们确定了CISS中的两个关键挑战,它们会导致语义漂移并降低性能。首先,我们强调了单独优化的问题,其中模型的不同部分在不同的增量阶段进行优化,从而导致概率尺度不匹配。其次,我们识别了由不适当的伪标签引起的嘈杂语义,这导致了次优结果。为了解决这些挑战,我们提出了一种新颖有效的方法,即分割的图像后验和语义解耦(IPSeg)。IPSeg引入了两个关键机制:(1)利用图像后验概率来对齐各阶段的优化,并减轻单独优化的影响;(2)采用语义解耦来处理嘈杂的语义,并为不同的语义量身定制学习策略。在Pascal VOC 2012和ADE20K数据集上的大量实验表明,IPSeg与最新技术相比实现了卓越的性能,特别是在具有挑战性的长期增量场景中。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 20 pages, 9 figures
Summary
这篇论文介绍了面向类别增量学习的语义分割方法。针对CISS中的语义漂移问题,论文指出了两个关键挑战:不同阶段的模型优化不一致导致概率尺度不匹配以及由于不恰当的伪标签引起的噪声语义问题。为解决这些问题,论文提出了一种名为IPSeg的新方法,它通过利用图像后验概率对齐不同阶段的优化和处理噪声语义来取得良好性能。
Key Takeaways
- 类别增量学习旨在使模型从非静态数据流中按顺序学习不同任务,而不会发生灾难性遗忘。
- 在类增量语义分割(CISS)中,图像像素的语义内容在增量阶段会发生演变,称为语义漂移。
- CISS面临两个关键挑战:不同阶段的模型优化不一致和由于不恰当的伪标签导致的噪声语义问题。
- IPSeg方法通过利用图像后验概率来对齐不同阶段的优化,并缓解单独优化的影响。
- IPSeg采用语义解耦来处理噪声语义,并为不同的语义定制学习策略。
- 在Pascal VOC 2012和ADE20K数据集上的广泛实验表明,IPSeg在具有挑战性的长期增量场景中实现了优于现有方法的性能。
点此查看论文截图

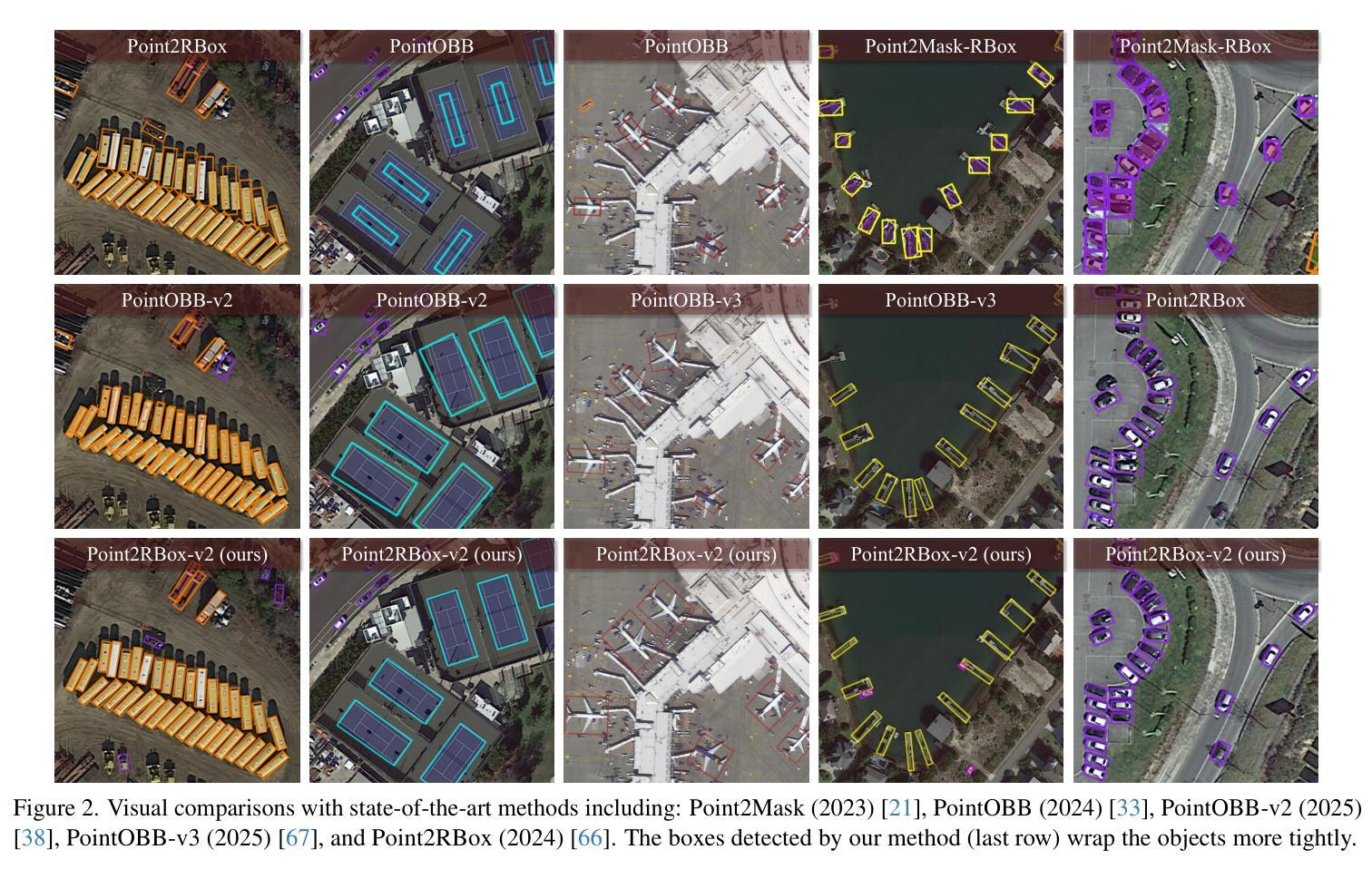
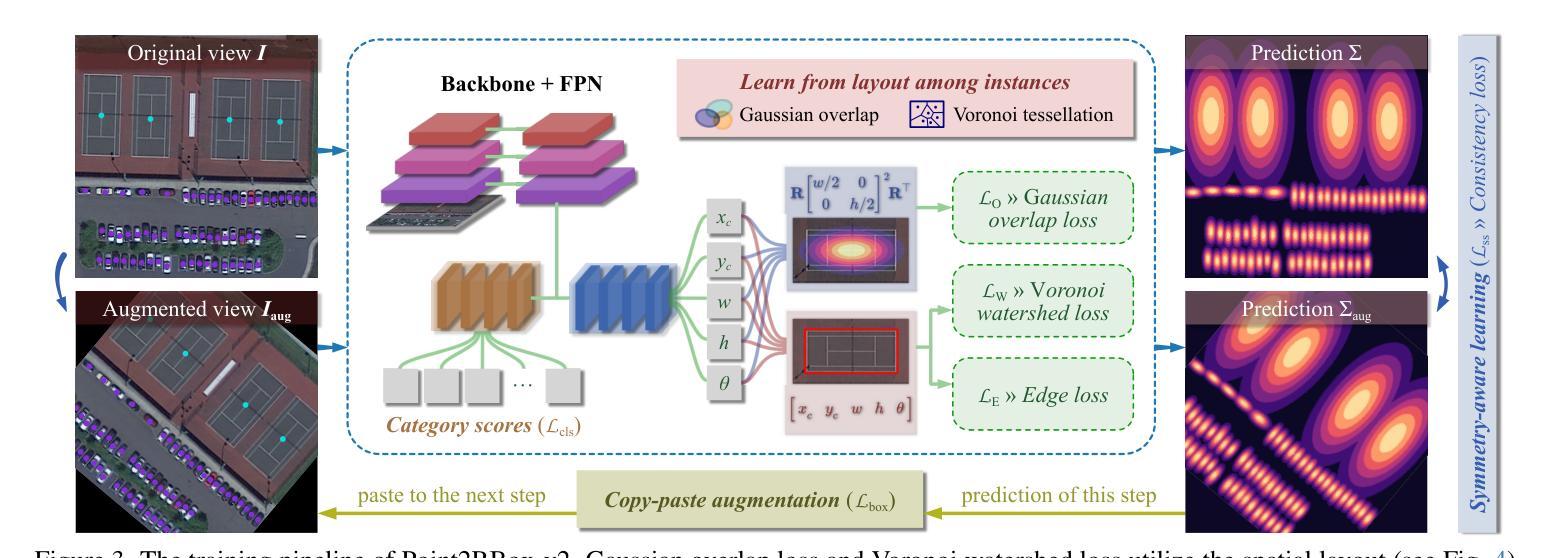
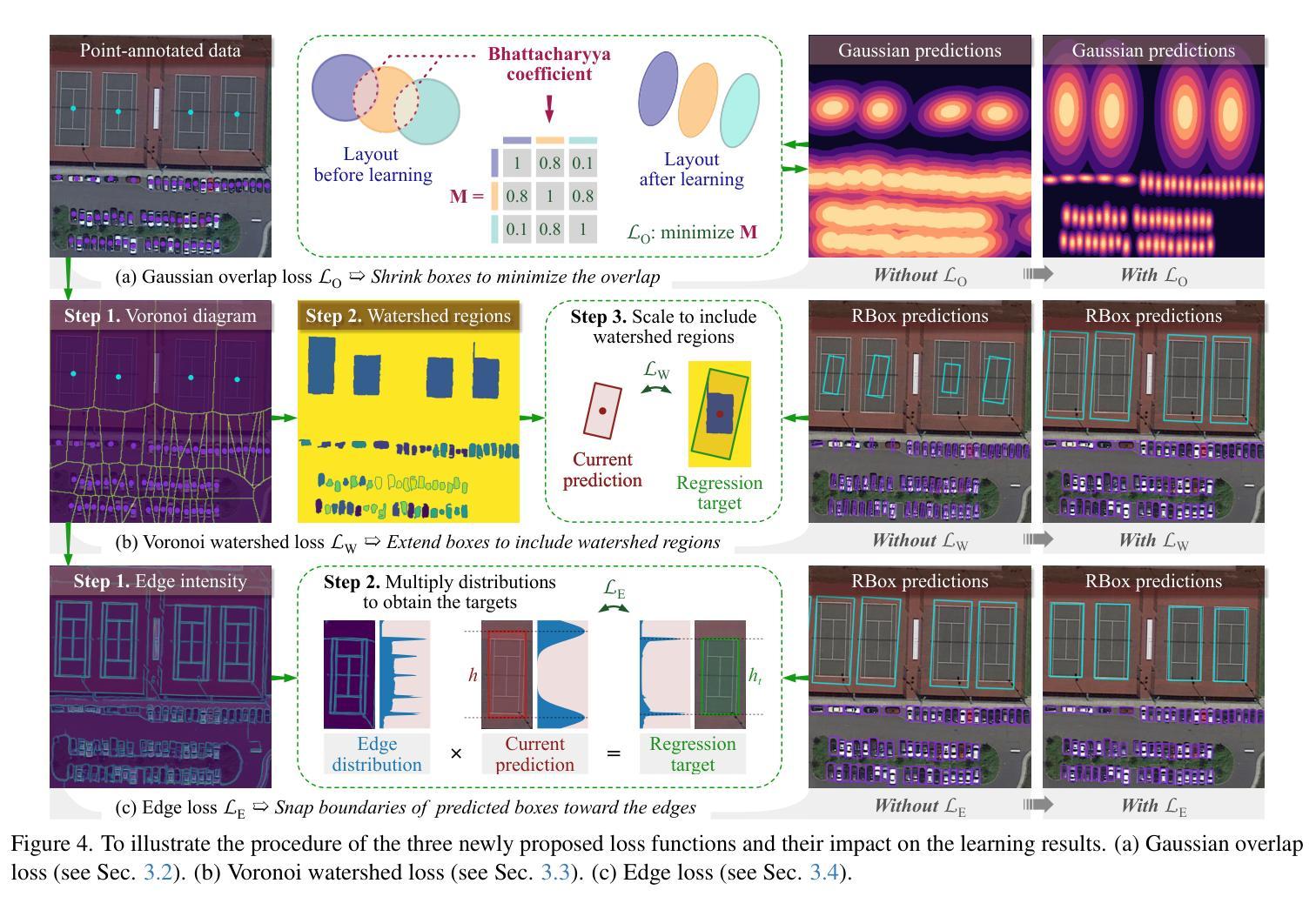
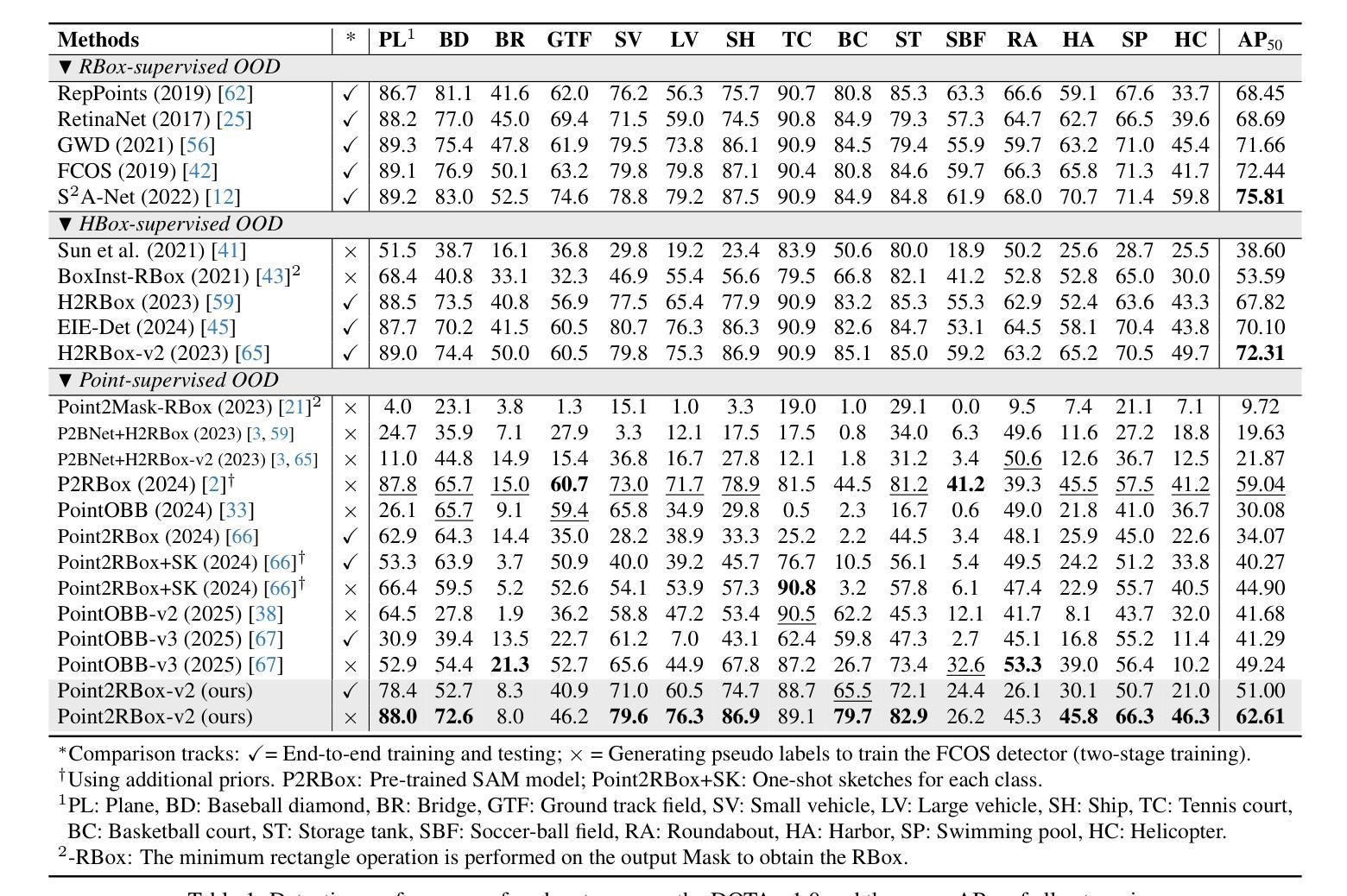
Point2RBox-v2: Rethinking Point-supervised Oriented Object Detection with Spatial Layout Among Instances
Authors:Yi Yu, Botao Ren, Peiyuan Zhang, Mingxin Liu, Junwei Luo, Shaofeng Zhang, Feipeng Da, Junchi Yan, Xue Yang
With the rapidly increasing demand for oriented object detection (OOD), recent research involving weakly-supervised detectors for learning OOD from point annotations has gained great attention. In this paper, we rethink this challenging task setting with the layout among instances and present Point2RBox-v2. At the core are three principles: 1) Gaussian overlap loss. It learns an upper bound for each instance by treating objects as 2D Gaussian distributions and minimizing their overlap. 2) Voronoi watershed loss. It learns a lower bound for each instance through watershed on Voronoi tessellation. 3) Consistency loss. It learns the size/rotation variation between two output sets with respect to an input image and its augmented view. Supplemented by a few devised techniques, e.g. edge loss and copy-paste, the detector is further enhanced. To our best knowledge, Point2RBox-v2 is the first approach to explore the spatial layout among instances for learning point-supervised OOD. Our solution is elegant and lightweight, yet it is expected to give a competitive performance especially in densely packed scenes: 62.61%/86.15%/34.71% on DOTA/HRSC/FAIR1M. Code is available at https://github.com/VisionXLab/point2rbox-v2.
随着面向对象检测(OOD)需求的快速增长,最近涉及使用点注释进行弱监督检测器学习的研究已引起广泛关注。在本文中,我们重新思考了这一具有挑战性的任务设置与实例之间的布局,并提出了Point2RBox-v2。其核心包含三个原则:1)高斯重叠损失。它将对象视为二维高斯分布,通过最小化其重叠来学习每个实例的上界。2)Voronoi水域损失。它通过Voronoi剖面上的水域来学习每个实例的下界。3)一致性损失。它学习输入图像及其增强视图对应的两个输出集之间的大小/旋转变化。通过补充一些设计的技术(如边缘损失和复制粘贴),进一步增强了检测器。据我们所知,Point2RBox-v2是首次探索实例之间空间布局以进行点监督OOD学习的方案。我们的解决方案优雅且轻量级,预计尤其在密集场景中具有竞争力:在DOTA/HRSC/FAIR1M上的性能分别为62.61%/86.15%/34.71%。代码可在https://github.com/VisionXLab/point2rbox-v2获得。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 11 pages, 5 figures, 10 tables
Summary:
近期研究关注弱监督检测器在点标注下对定向目标检测(OOD)的学习,本文重新思考了此挑战性任务的设置,提出了Point2RBox-v2模型。其核心包括三个原则:高斯重叠损失、Voronoi水域损失和一致性损失。此外,通过一些技术手段(如边缘损失和复制粘贴)增强了检测器性能。Point2RBox-v2是首个探索实例间空间布局的模型,用于学习点监督下的OOD,预期在密集场景中表现优异。
Key Takeaways:
- 研究关注弱监督检测器在点标注下的定向目标检测(OOD)学习。
- 提出Point2RBox-v2模型,通过三个核心原则:高斯重叠损失、Voronoi水域损失和一致性损失来处理OOD任务。
- 模型首次探索实例间的空间布局学习。
- 通过边缘损失和复制粘贴等技术增强检测器性能。
- 在DOTA、HRSC和FAIR1M等数据集上具有竞争力,代码已公开。
点此查看论文截图