⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-02-11 更新
AuraFusion360: Augmented Unseen Region Alignment for Reference-based 360° Unbounded Scene Inpainting
Authors:Chung-Ho Wu, Yang-Jung Chen, Ying-Huan Chen, Jie-Ying Lee, Bo-Hsu Ke, Chun-Wei Tuan Mu, Yi-Chuan Huang, Chin-Yang Lin, Min-Hung Chen, Yen-Yu Lin, Yu-Lun Liu
Three-dimensional scene inpainting is crucial for applications from virtual reality to architectural visualization, yet existing methods struggle with view consistency and geometric accuracy in 360{\deg} unbounded scenes. We present AuraFusion360, a novel reference-based method that enables high-quality object removal and hole filling in 3D scenes represented by Gaussian Splatting. Our approach introduces (1) depth-aware unseen mask generation for accurate occlusion identification, (2) Adaptive Guided Depth Diffusion, a zero-shot method for accurate initial point placement without requiring additional training, and (3) SDEdit-based detail enhancement for multi-view coherence. We also introduce 360-USID, the first comprehensive dataset for 360{\deg} unbounded scene inpainting with ground truth. Extensive experiments demonstrate that AuraFusion360 significantly outperforms existing methods, achieving superior perceptual quality while maintaining geometric accuracy across dramatic viewpoint changes. See our project page for video results and the dataset at https://kkennethwu.github.io/aurafusion360/.
三维场景补全对于从虚拟现实到建筑可视化等应用至关重要,但现有方法在360°无界场景的视图一致性及几何精度方面存在困难。我们提出了AuraFusion360,这是一种基于参考的新方法,能够在高斯散斑表示的三维场景中进行高质量的对象移除和空洞填充。我们的方法引入了(1)深度感知未见掩模生成,用于准确识别遮挡,(2)自适应引导深度扩散,这是一种无需额外训练的零样本方法,可用于准确放置初始点,(3)基于SDEdit的细节增强,以实现多视图一致性。我们还引入了360-USID,这是首个针对360°无界场景补全的综合数据集,带有真实标签。大量实验表明,AuraFusion360在感知质量上显著优于现有方法,在剧烈视点变化时也能保持几何精度。视频结果和数据集请参见我们的项目页面:https://kkennethwu.github.io/aurafusion360/(链接地址请根据实际情况修改)。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project page: https://kkennethwu.github.io/aurafusion360/
Summary
本文介绍了一种名为AuraFusion360的新型基于参考的三维场景补全方法,适用于虚拟现实和建筑可视化等应用。该方法在Gaussian Splatting表示的3D场景中进行高质量的对象移除和空洞填充,具有深度感知的未见掩膜生成、自适应引导深度扩散和SDEdit细节增强等技术特点。同时,引入了首个全面的360°无界场景补全数据集360-USID,实验表明AuraFusion360在视觉质量和几何准确性方面显著优于现有方法。
Key Takeaways
- AuraFusion360是一种新型基于参考的三维场景补全方法,适用于多种应用如虚拟现实和建筑可视化。
- 该方法采用Gaussian Splatting表示3D场景,进行高质量的对象移除和空洞填充。
- 深度感知的未见掩膜生成技术,能准确识别遮挡区域。
- 引入自适应引导深度扩散技术,无需额外训练即可实现准确初始点放置。
- SDEdit细节增强技术,实现多视角一致性。
- 引入首个全面的360°无界场景补全数据集360-USID,提供真实场景数据。
点此查看论文截图




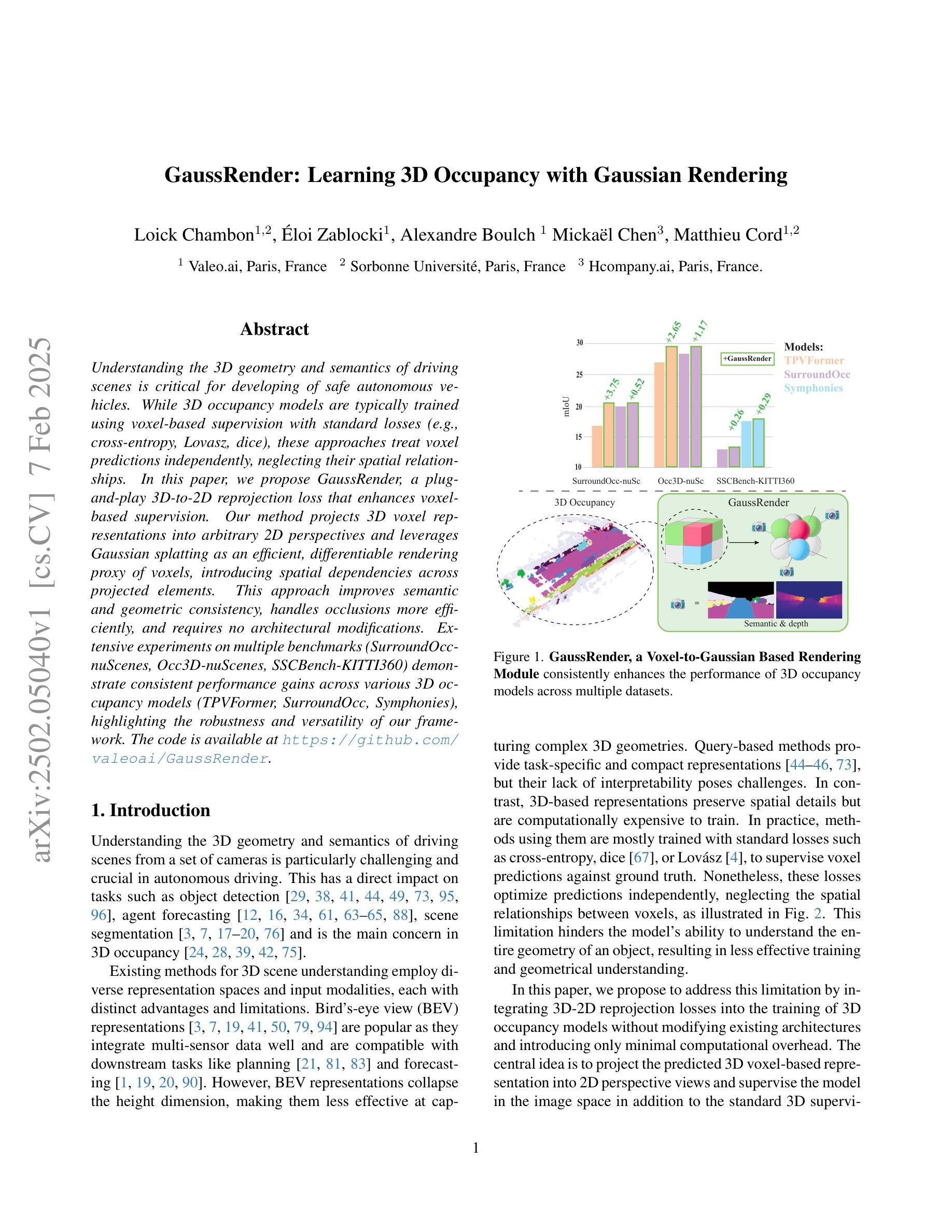
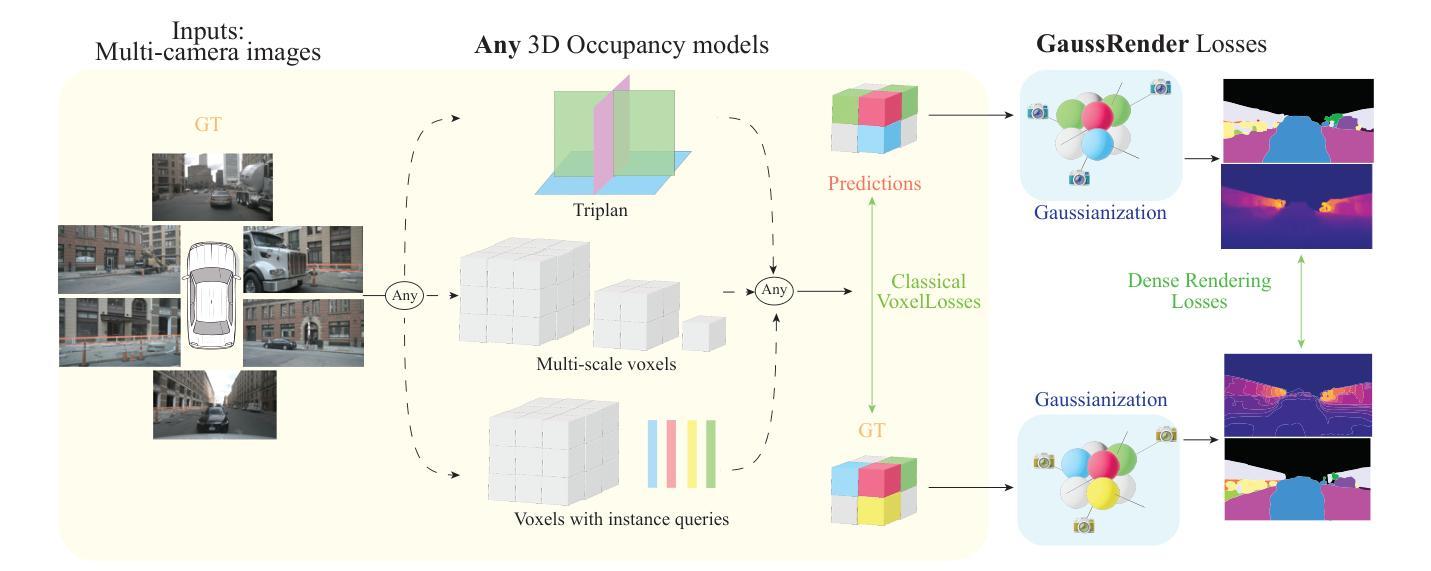
GaussRender: Learning 3D Occupancy with Gaussian Rendering
Authors:Loick Chambon, Eloi Zablocki, Alexandre Boulch, Mickael Chen, Matthieu Cord
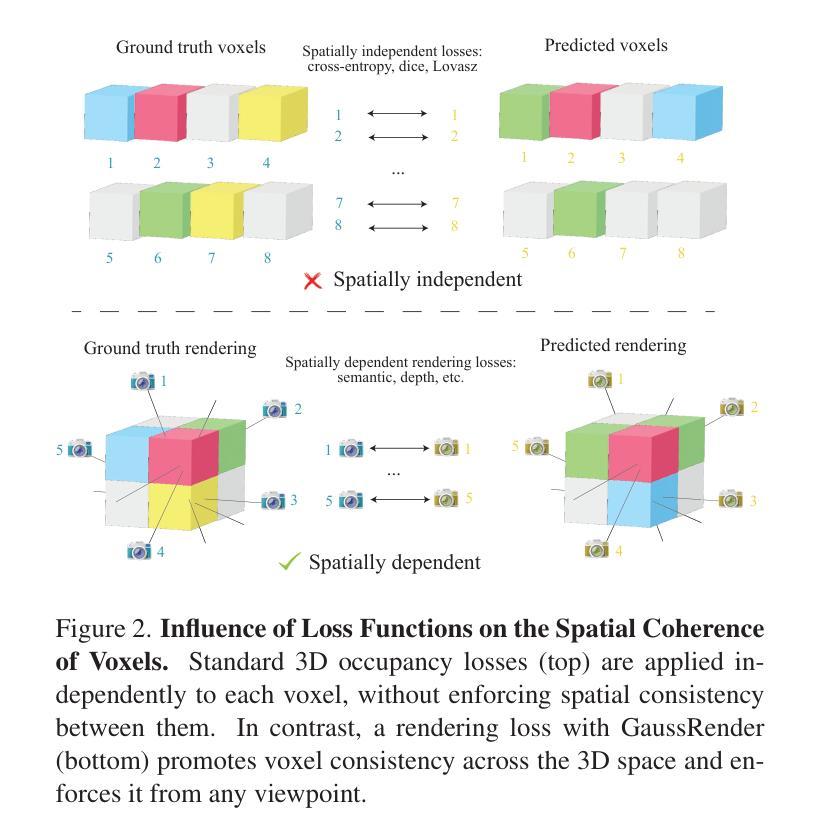
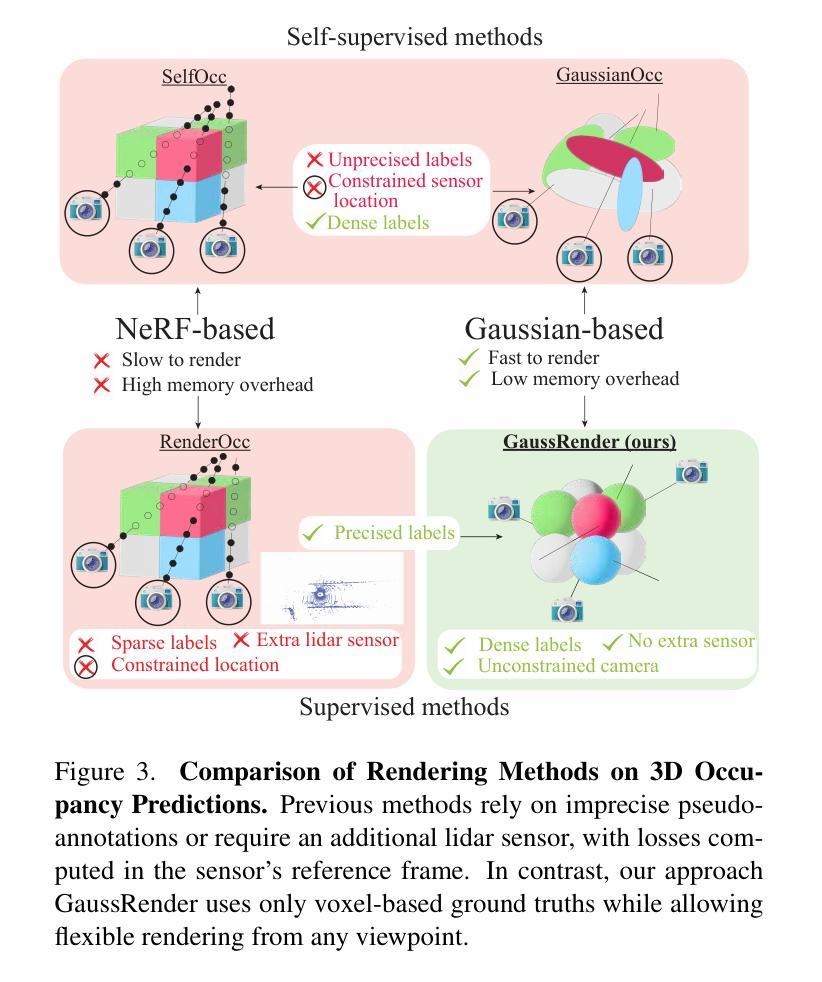
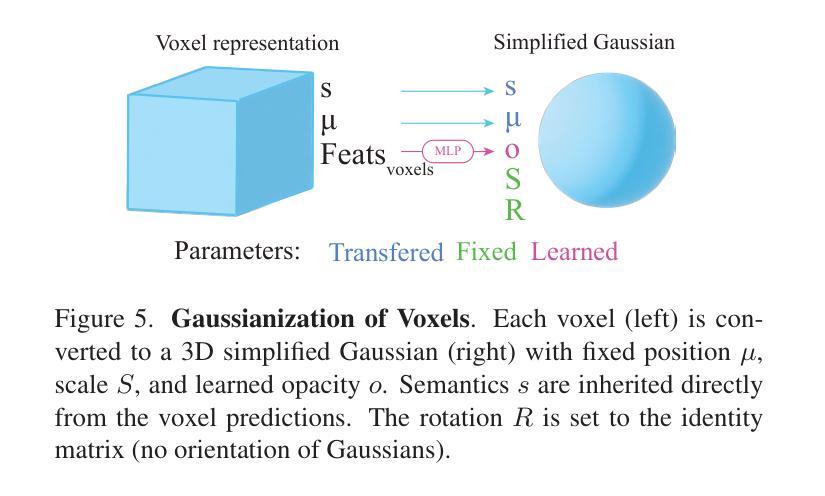
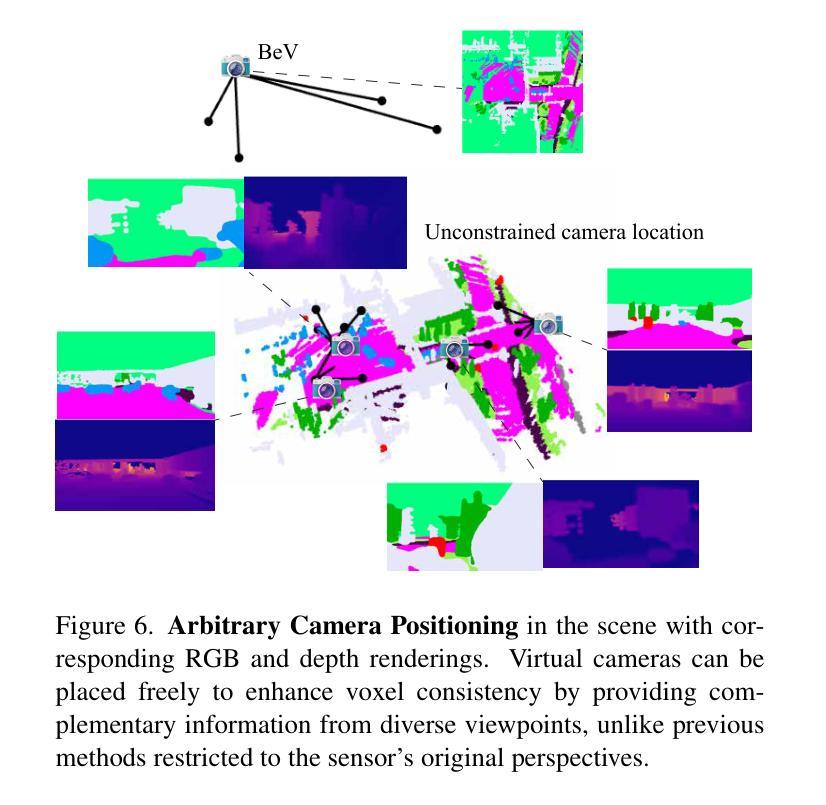
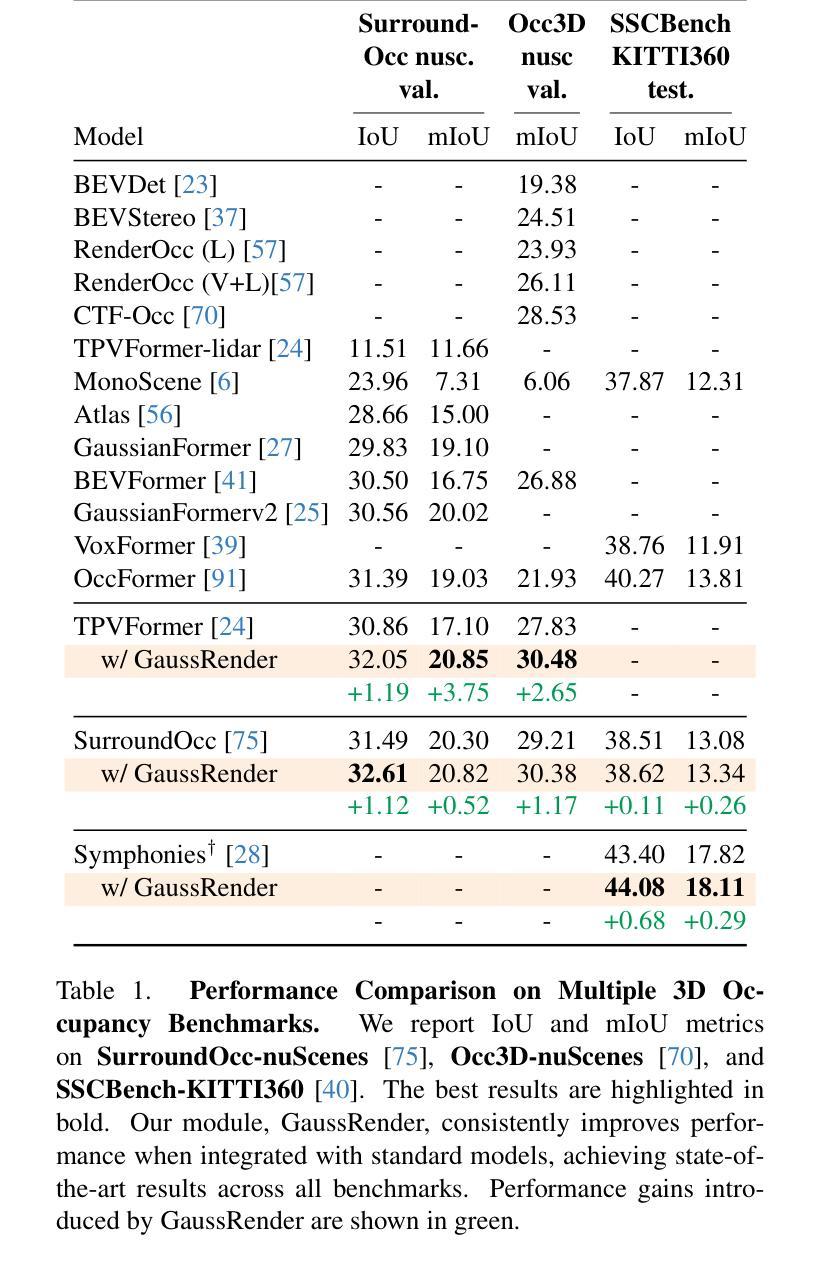
Understanding the 3D geometry and semantics of driving scenes is critical for developing of safe autonomous vehicles. While 3D occupancy models are typically trained using voxel-based supervision with standard losses (e.g., cross-entropy, Lovasz, dice), these approaches treat voxel predictions independently, neglecting their spatial relationships. In this paper, we propose GaussRender, a plug-and-play 3D-to-2D reprojection loss that enhances voxel-based supervision. Our method projects 3D voxel representations into arbitrary 2D perspectives and leverages Gaussian splatting as an efficient, differentiable rendering proxy of voxels, introducing spatial dependencies across projected elements. This approach improves semantic and geometric consistency, handles occlusions more efficiently, and requires no architectural modifications. Extensive experiments on multiple benchmarks (SurroundOcc-nuScenes, Occ3D-nuScenes, SSCBench-KITTI360) demonstrate consistent performance gains across various 3D occupancy models (TPVFormer, SurroundOcc, Symphonies), highlighting the robustness and versatility of our framework. The code is available at https://github.com/valeoai/GaussRender.
了解驾驶场景的3D几何和语义对于开发安全自动驾驶汽车至关重要。虽然3D占用模型通常使用基于体素的标准损失(例如交叉熵、Lovasz和dice)进行训练,但这些方法独立处理体素预测,忽略了它们的空间关系。在本文中,我们提出了一种即插即用的3D到2D重投影损失GaussRender,它增强了基于体素的监督方法。我们的方法将3D体素表示投影到任意二维视角,并利用高斯模板作为体素高效、可微分的渲染代理,在投影元素之间引入空间依赖性。这种方法提高了语义和几何一致性,能更有效地处理遮挡问题,且无需修改架构。在多个基准测试集(SurroundOcc-nuScenes、Occ3D-nuScenes、SSCBench-KITTI360)上的大量实验表明,在各种3D占用模型(TPVFormer、SurroundOcc、Symphonies)中都能获得稳定的性能提升,突显了我们框架的稳健性和通用性。代码可访问https://github.com/valeoai/GaussRender。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
本文提出一种名为GaussRender的3D到2D重投影损失方法,用于增强基于体素的监督训练,提高自主车辆对驾驶场景的理解能力。该方法将3D体素表示投影到任意2D视角,并利用高斯平铺作为体素的可微高效渲染代理,引入投影元素之间的空间依赖性。该方法提高了语义和几何一致性,更有效地处理遮挡问题,且无需修改架构。在多个基准测试集上的实验表明,该方法在各种3D占用模型上的性能均有所提升,凸显了其稳健性和通用性。代码已公开。
要点
- 自主车辆对驾驶场景的理解需依赖于3D几何和语义分析。
- 传统3D占用模型训练多采用基于体素的监督方法和标准损失函数,但忽略了空间关系。
- GaussRender是一种新型的3D到2D重投影损失方法,旨在增强基于体素的监督训练。
- GaussRender通过将3D体素表示投影到任意2D视角,并借助高斯平铺技术处理体素渲染,从而引入空间依赖性。
- 该方法提高了语义和几何一致性,更有效地处理遮挡问题。
- GaussRender具有广泛的适用性和稳健性,适用于多种3D占用模型,且在多个基准测试集上表现优异。
点此查看论文截图
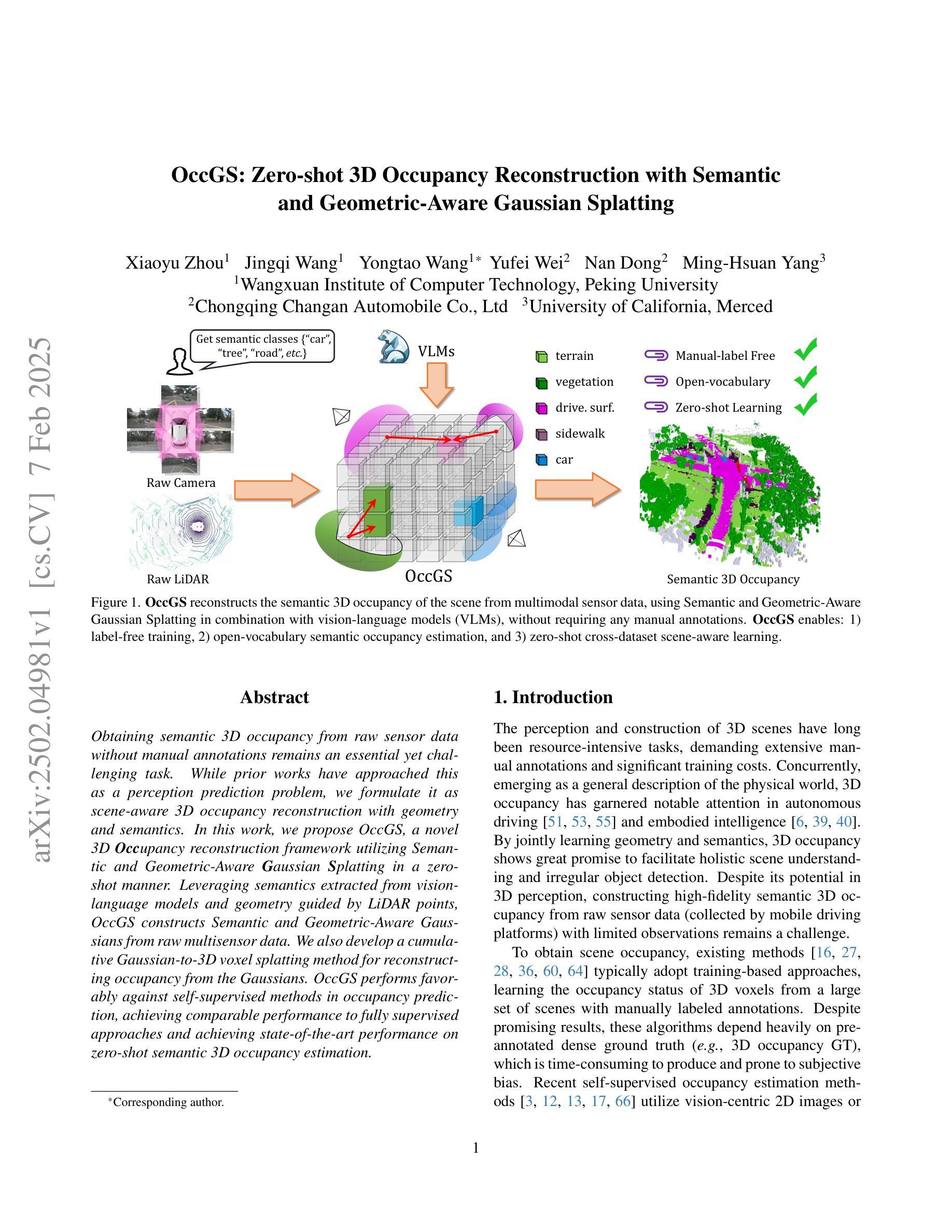
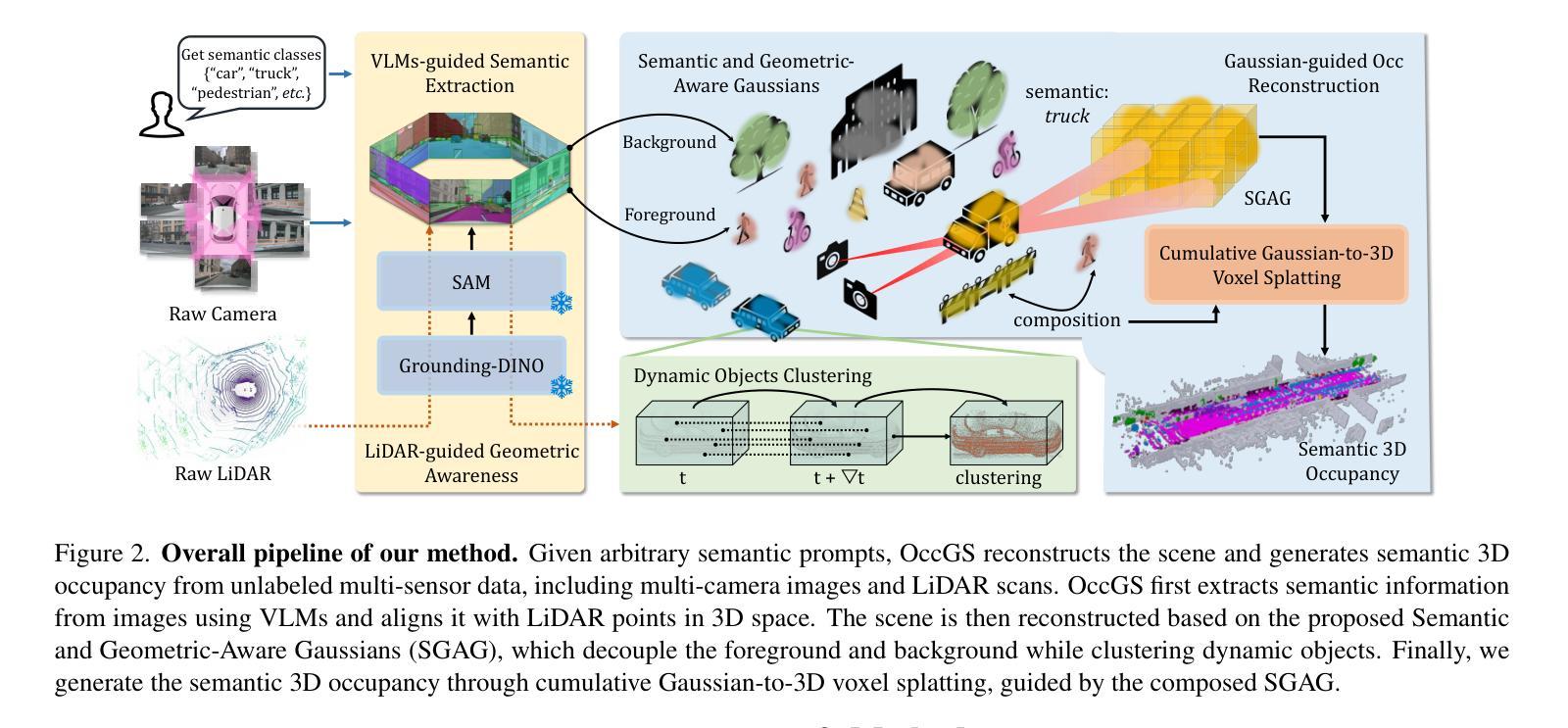
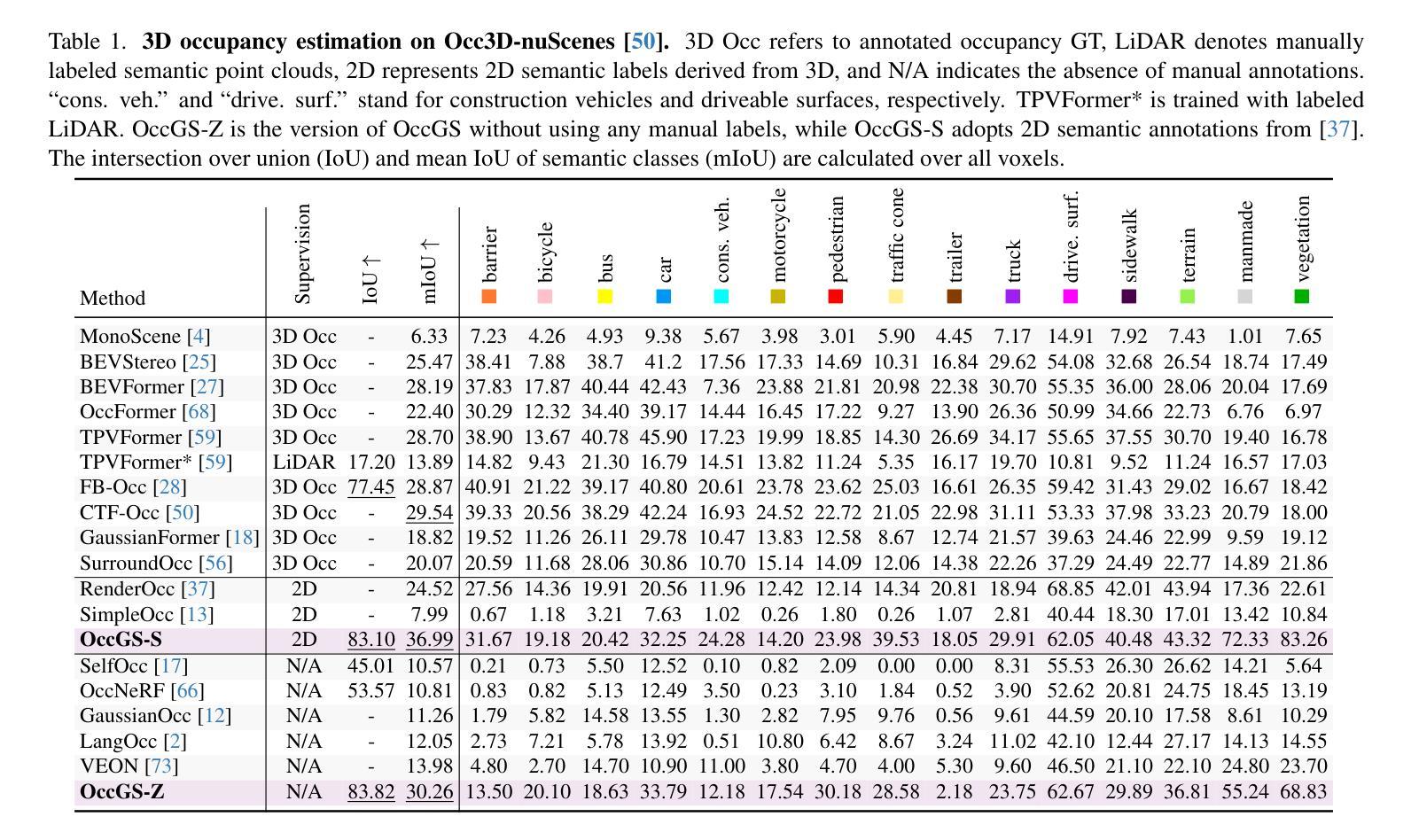
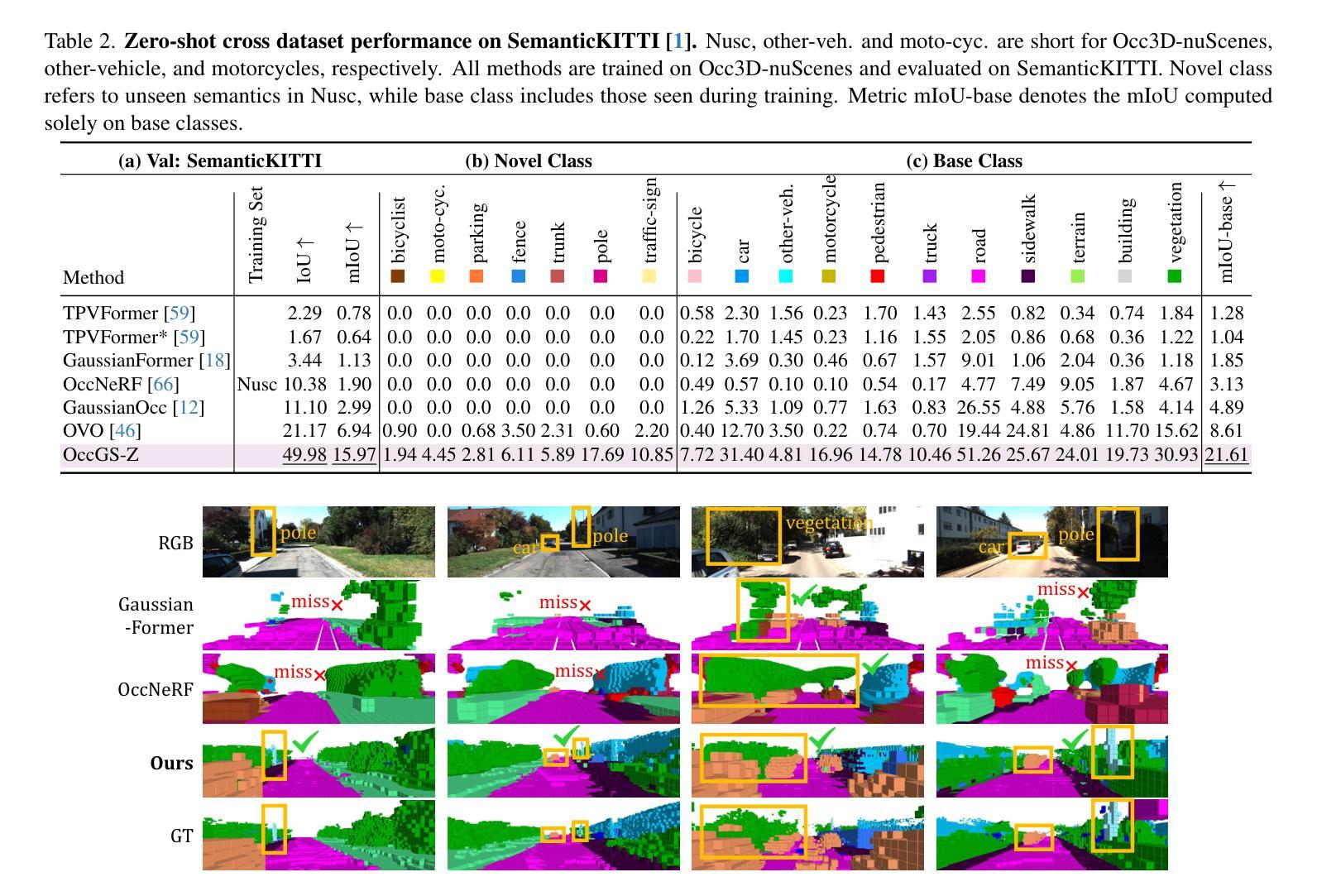
OccGS: Zero-shot 3D Occupancy Reconstruction with Semantic and Geometric-Aware Gaussian Splatting
Authors:Xiaoyu Zhou, Jingqi Wang, Yongtao Wang, Yufei Wei, Nan Dong, Ming-Hsuan Yang
Obtaining semantic 3D occupancy from raw sensor data without manual annotations remains an essential yet challenging task. While prior works have approached this as a perception prediction problem, we formulate it as scene-aware 3D occupancy reconstruction with geometry and semantics. In this work, we propose OccGS, a novel 3D Occupancy reconstruction framework utilizing Semantic and Geometric-Aware Gaussian Splatting in a zero-shot manner. Leveraging semantics extracted from vision-language models and geometry guided by LiDAR points, OccGS constructs Semantic and Geometric-Aware Gaussians from raw multisensor data. We also develop a cumulative Gaussian-to-3D voxel splatting method for reconstructing occupancy from the Gaussians. OccGS performs favorably against self-supervised methods in occupancy prediction, achieving comparable performance to fully supervised approaches and achieving state-of-the-art performance on zero-shot semantic 3D occupancy estimation.
从原始传感器数据获取语义3D占用信息,无需手动注释,仍然是一项重要而具有挑战性的任务。尽管以前的工作将其视为感知预测问题,但我们将其制定为场景感知的3D占用重建问题,涉及几何和语义。在这项工作中,我们提出OccGS,这是一种利用语义和几何感知的高斯点散作为零样本方式的三维占用重建框架。借助从视觉语言模型中提取的语义信息和激光雷达点引导的几何信息,OccGS从原始多传感器数据中构建语义和几何感知的高斯分布。我们还开发了一种累积高斯到三维体素点散方法,用于从高斯分布重建占用情况。在占用预测方面,OccGS的表现优于自监督方法,其性能与全监督方法相当,并在零样本语义3D占用估计方面达到了最先进的性能。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出了一项将语义和几何感知结合的新型三维占用重建框架OccGS,采用零样本方式从原始传感器数据中获取语义三维占用信息。利用视觉语言模型提取的语义信息和激光雷达点引导的几何信息,构建语义和几何感知高斯映射,再通过累积高斯到三维体素点迹法重建占用情况。相较于自监督方法,OccGS在占用预测上表现优越,甚至在零样本语义三维占用估计上达到了最先进的性能。
Key Takeaways
- 将语义三维占用重建任务从单纯的感知预测问题转化为场景感知问题,强调几何和语义的结合。
- 提出了新型框架OccGS,能够利用原始多传感器数据中的语义和几何信息。
- 采用零样本方式处理数据,无需手动标注。
- 利用视觉语言模型提取语义信息,并引入激光雷达点以指导几何信息的利用。
- 通过构建语义和几何感知高斯映射,提高了占用预测的精度。
- 采用累积高斯到三维体素点迹法重建占用情况,这一方法具有创新性。
点此查看论文截图
PoI: Pixel of Interest for Novel View Synthesis Assisted Scene Coordinate Regression
Authors:Feifei Li, Qi Song, Chi Zhang, Hui Shuai, Rui Huang
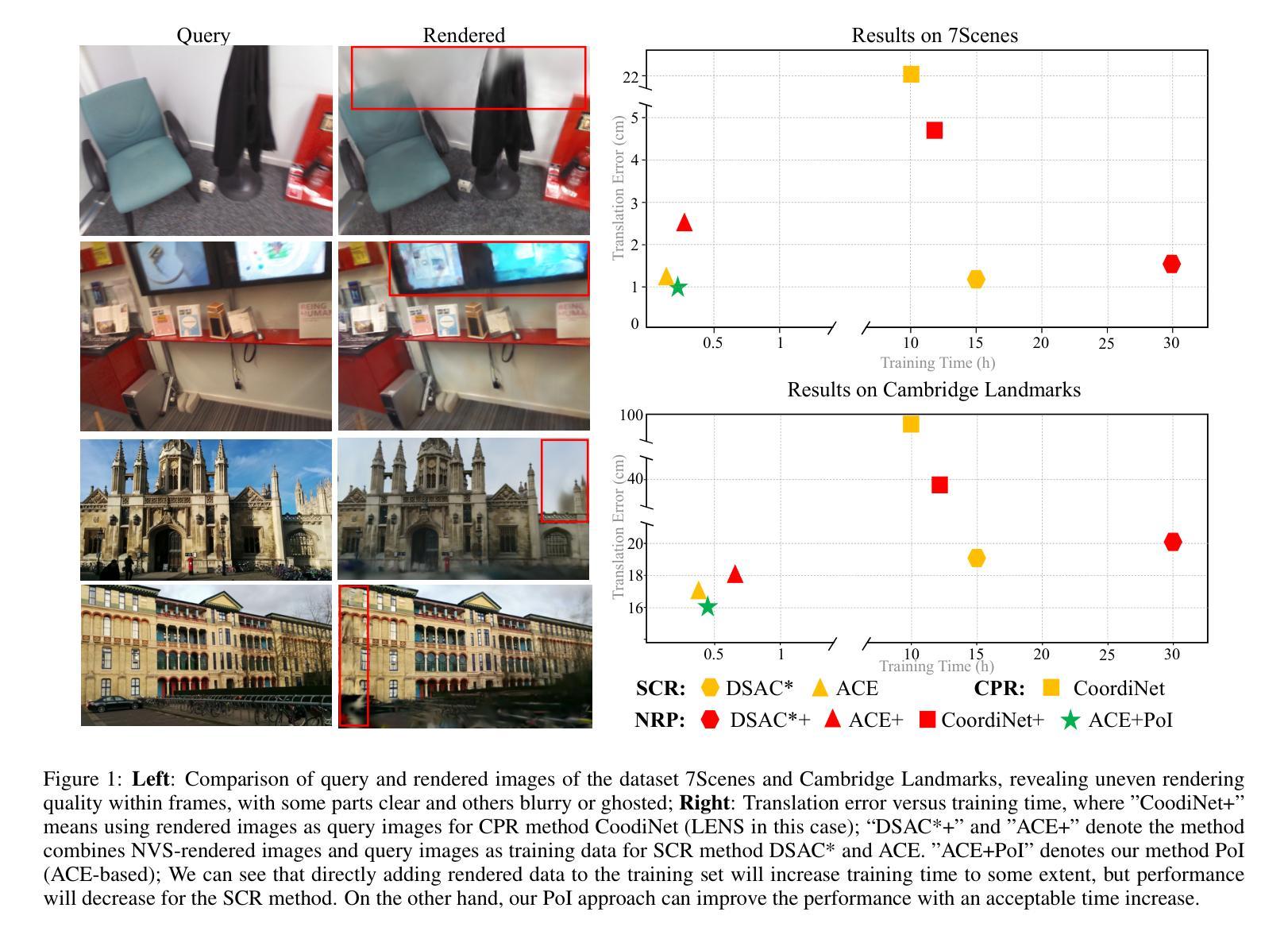
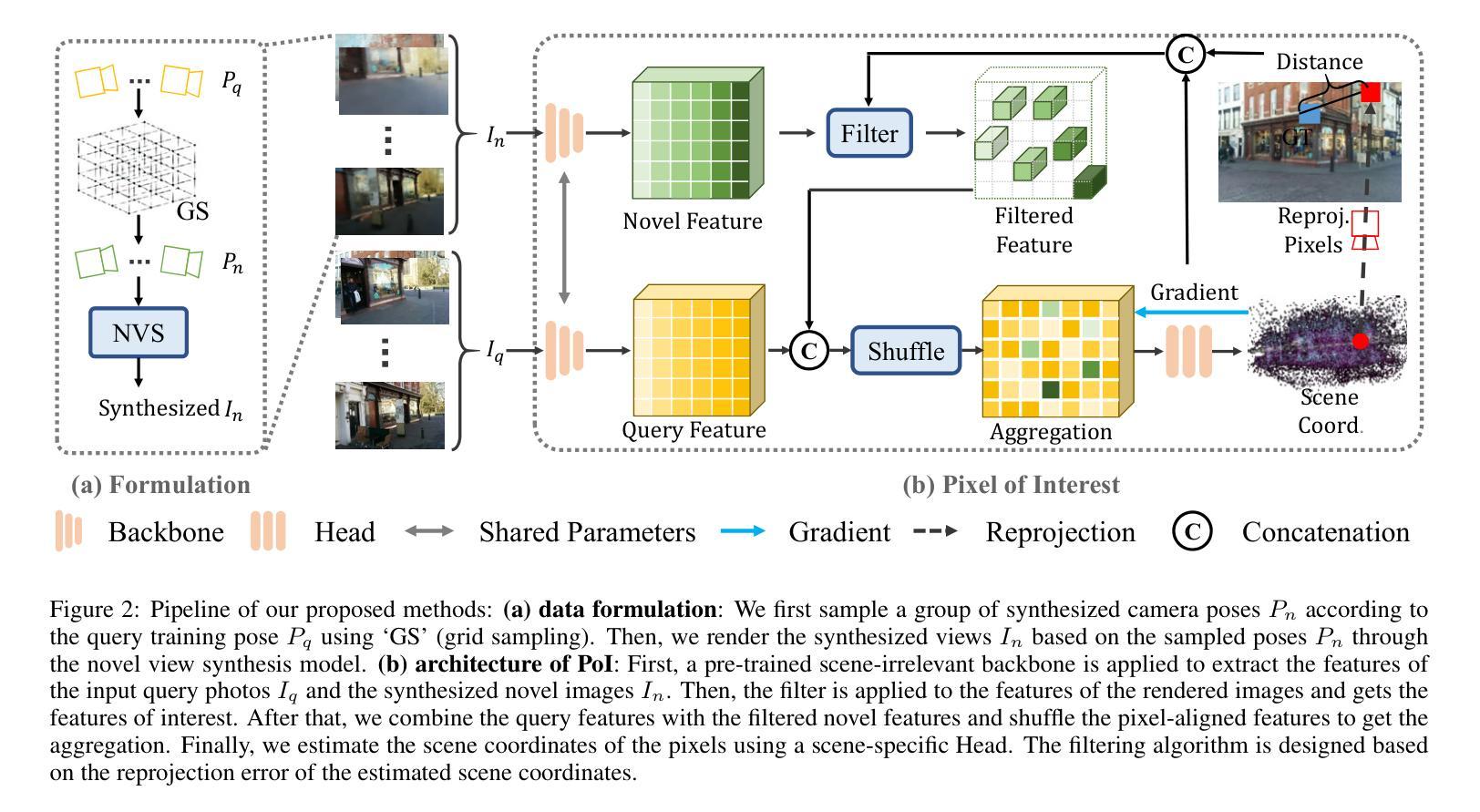
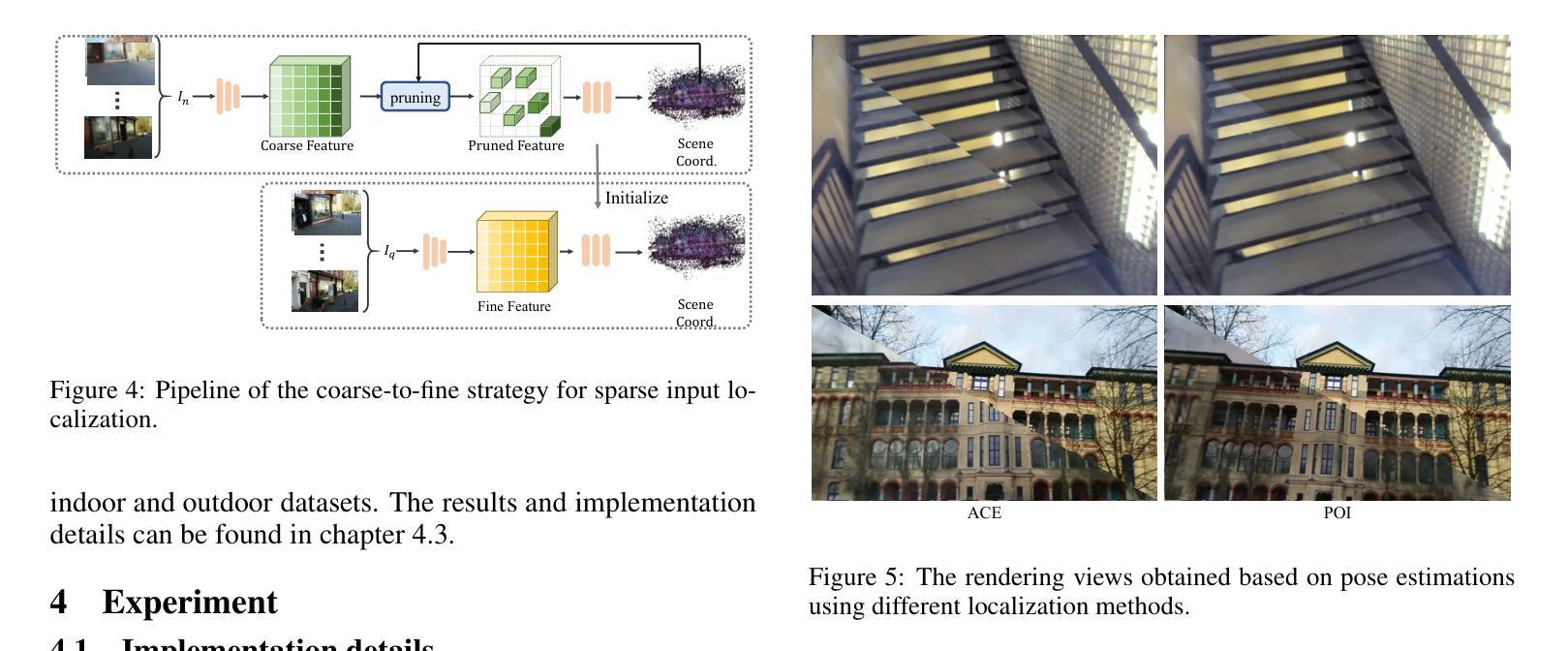
The task of estimating camera poses can be enhanced through novel view synthesis techniques such as NeRF and Gaussian Splatting to increase the diversity and extension of training data. However, these techniques often produce rendered images with issues like blurring and ghosting, which compromise their reliability. These issues become particularly pronounced for Scene Coordinate Regression (SCR) methods, which estimate 3D coordinates at the pixel level. To mitigate the problems associated with unreliable rendered images, we introduce a novel filtering approach, which selectively extracts well-rendered pixels while discarding the inferior ones. This filter simultaneously measures the SCR model’s real-time reprojection loss and gradient during training. Building on this filtering technique, we also develop a new strategy to improve scene coordinate regression using sparse inputs, drawing on successful applications of sparse input techniques in novel view synthesis. Our experimental results validate the effectiveness of our method, demonstrating state-of-the-art performance on indoor and outdoor datasets.
通过NeRF和Gaussian Splatting等新型视图合成技术,可以增强对相机姿态的估计任务,从而提高训练数据的多样性和扩展性。然而,这些技术往往产生的渲染图像存在模糊和重影等问题,从而影响了它们的可靠性。这些问题在场景坐标回归(SCR)方法中尤为突出,这些方法估计像素级别的3D坐标。为了缓解与不可靠的渲染图像相关的问题,我们引入了一种新型过滤方法,该方法能够有选择地提取渲染良好的像素,同时丢弃质量较差的像素。该过滤器在训练过程中实时测量SCR模型的再投影损失和梯度。基于这种过滤技术,我们还开发了一种利用稀疏输入改进场景坐标回归的新策略,这借鉴了稀疏输入技术在新型视图合成中的成功应用。我们的实验结果验证了该方法的有效性,在室内和室外数据集上均表现出卓越的性能。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
该文本探讨了如何通过新技术改进相机姿态估计任务,例如NeRF和高斯贴片技术可增加训练数据的多样性和扩展性。然而,这些技术生成的渲染图像常常存在模糊和重影等问题,影响可靠性。对于像素级估计的场景坐标回归(SCR)方法,这些问题尤为突出。为缓解不可靠渲染图像带来的问题,研究引入了新型过滤方法,能够选择性提取渲染良好的像素并舍弃质量较差的像素。该过滤器同时测量SCR模型的实时重投影损失和训练过程中的梯度。基于过滤技术,研究还开发出一种利用稀疏输入改进场景坐标回归的新策略,该方法借鉴了稀疏输入在新型视图合成中的成功应用。实验证明该方法的先进性,在室内和室外数据集上表现出最佳性能。
Key Takeaways
- 新视图合成技术如NeRF和高斯贴片能提高相机姿态估计任务的多样性和扩展性。
- 渲染图像常常存在模糊和重影问题,影响可靠性。
- 为解决上述问题,研究引入了新型过滤方法,选择性提取良好渲染的像素并舍弃质量差的像素。
- 该过滤技术同时测量场景坐标回归模型的实时重投影损失和训练过程中的梯度。
- 利用上述过滤技术,发展出使用稀疏输入改进场景坐标回归的新策略。
- 实验证明该方法的先进性,室内和室外数据集上表现最佳性能。
点此查看论文截图


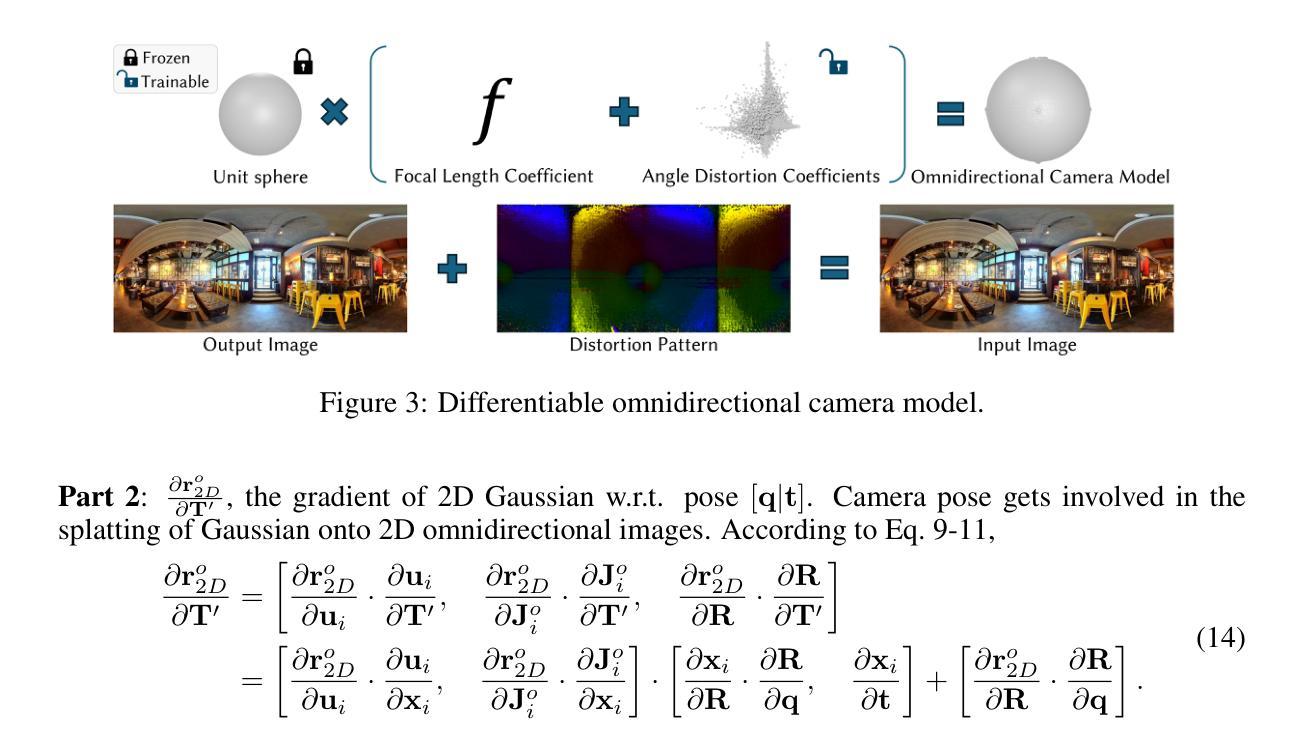
SC-OmniGS: Self-Calibrating Omnidirectional Gaussian Splatting
Authors:Huajian Huang, Yingshu Chen, Longwei Li, Hui Cheng, Tristan Braud, Yajie Zhao, Sai-Kit Yeung
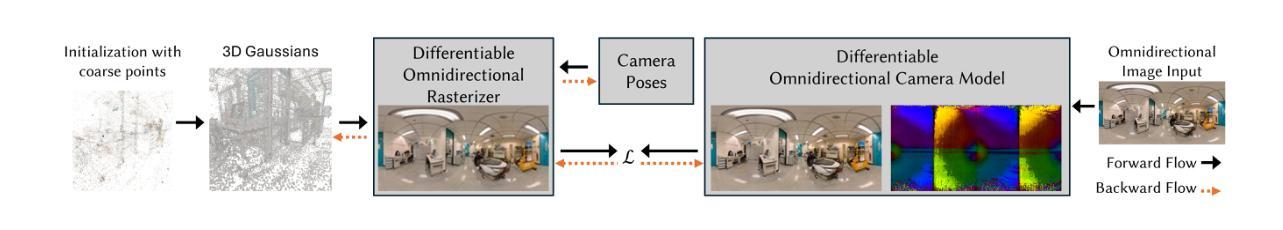
360-degree cameras streamline data collection for radiance field 3D reconstruction by capturing comprehensive scene data. However, traditional radiance field methods do not address the specific challenges inherent to 360-degree images. We present SC-OmniGS, a novel self-calibrating omnidirectional Gaussian splatting system for fast and accurate omnidirectional radiance field reconstruction using 360-degree images. Rather than converting 360-degree images to cube maps and performing perspective image calibration, we treat 360-degree images as a whole sphere and derive a mathematical framework that enables direct omnidirectional camera pose calibration accompanied by 3D Gaussians optimization. Furthermore, we introduce a differentiable omnidirectional camera model in order to rectify the distortion of real-world data for performance enhancement. Overall, the omnidirectional camera intrinsic model, extrinsic poses, and 3D Gaussians are jointly optimized by minimizing weighted spherical photometric loss. Extensive experiments have demonstrated that our proposed SC-OmniGS is able to recover a high-quality radiance field from noisy camera poses or even no pose prior in challenging scenarios characterized by wide baselines and non-object-centric configurations. The noticeable performance gain in the real-world dataset captured by consumer-grade omnidirectional cameras verifies the effectiveness of our general omnidirectional camera model in reducing the distortion of 360-degree images.
360度相机通过捕捉全面的场景数据,简化了辐射场3D重建的数据收集过程。然而,传统的辐射场方法并没有解决360度图像所特有的挑战。我们提出了SC-OmniGS,这是一种新型的自标定全向高斯喷溅系统,利用360度图像快速准确地重建全向辐射场。我们并不将360度图像转换为立方体地图并进行透视图像校准,而是将360度图像视为整个球体,并推导出一个数学框架,该框架能够实现直接的全向相机姿态校准,以及通过3D高斯进行优化。此外,我们引入了一个可区分的全向相机模型,以矫正真实世界数据的失真,从而提高性能。总体而言,通过最小化加权球面光度损失,对全向相机的内在模型、外在姿态和3D高斯进行联合优化。大量实验表明,我们提出的SC-OmniGS能够从具有挑战性的场景中恢复高质量辐射场,这些场景的特征是基线宽、非以对象为中心的配置、带有噪声的相机姿态,甚至在没有任何姿态先验的情况下也能如此。由消费级全向相机捕获的真实世界数据集的性能提升显著,这验证了我们的通用全向相机模型在减少360度图像失真方面的有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to ICLR 2025, Project Page: http://www.chenyingshu.com/sc-omnigs/
Summary
本文介绍了SC-OmniGS系统,该系统采用全景相机技术,通过优化全景相机模型实现对辐射场的重建。该方法无需将全景图像转换为立方体地图并进行透视图像校准,而是直接将全景图像视为整体球体,并采用数学模型直接进行全景相机姿态校准及优化三维高斯球体形态。另外还引入了可区分的全景相机模型以减少实际数据中的畸变并提升性能表现。系统通过对全景相机内在模型、外在姿态和三维高斯球体的联合优化,达到降低辐射场重建的难度和提高图像质量的目的。
Key Takeaways
- 全景相机技术用于简化辐射场重建的数据收集过程。
- SC-OmniGS系统是一种新型的自校准全景高斯球状系统,适用于快速准确的辐射场重建。
- 该方法无需将全景图像转换为立方体地图进行透视图像校准,而是直接将全景图像视为整体球体进行数学处理。
- 系统采用数学模型直接进行全景相机姿态校准和三维高斯球体优化。
- 系统引入可区分的全景相机模型,以提高性能表现并减少实际数据中的畸变。
- 通过联合优化全景相机的内在模型、外在姿态和三维高斯球体,系统可有效提高辐射场重建的质量。
- 实验证明SC-OmniGS在具有挑战性的场景中,如噪声相机姿态或没有姿态先验的情况下,仍能恢复高质量辐射场。
点此查看论文截图


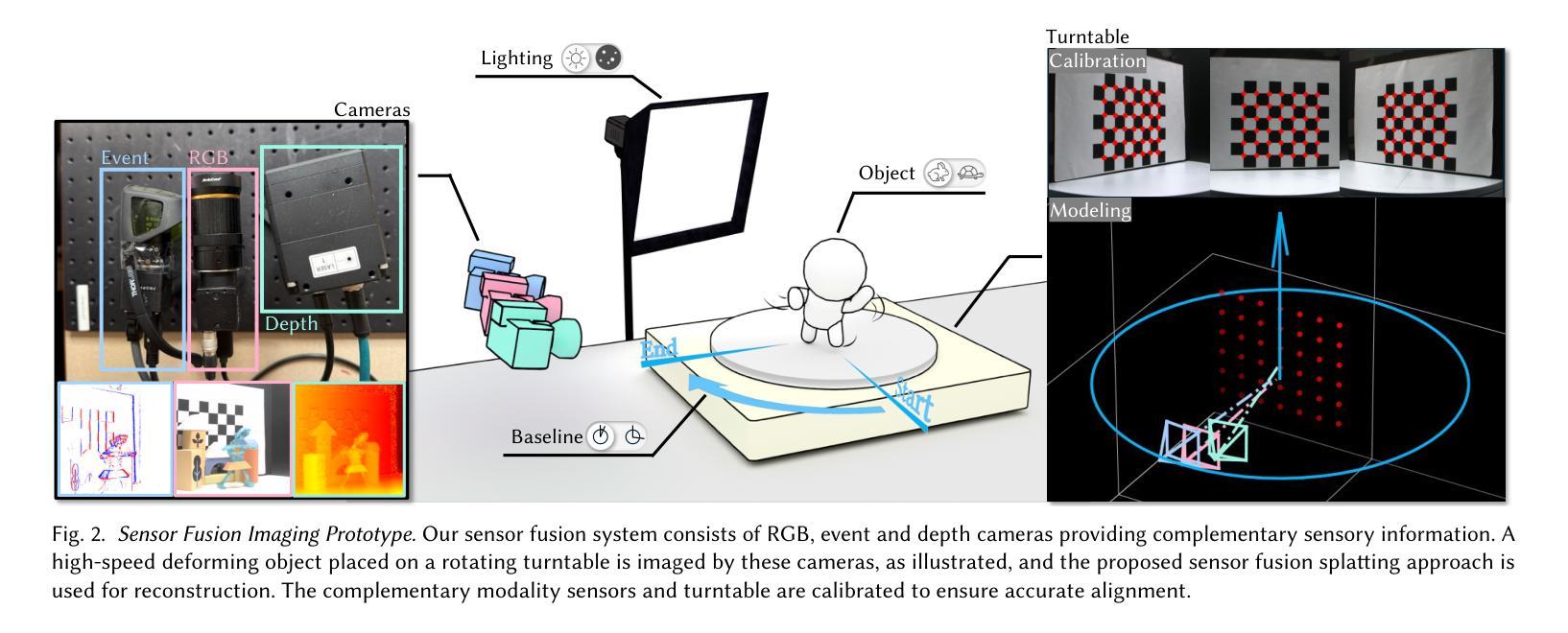
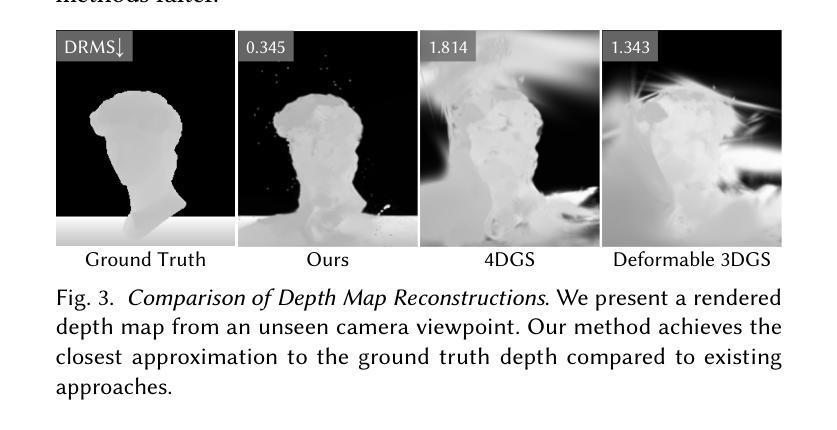
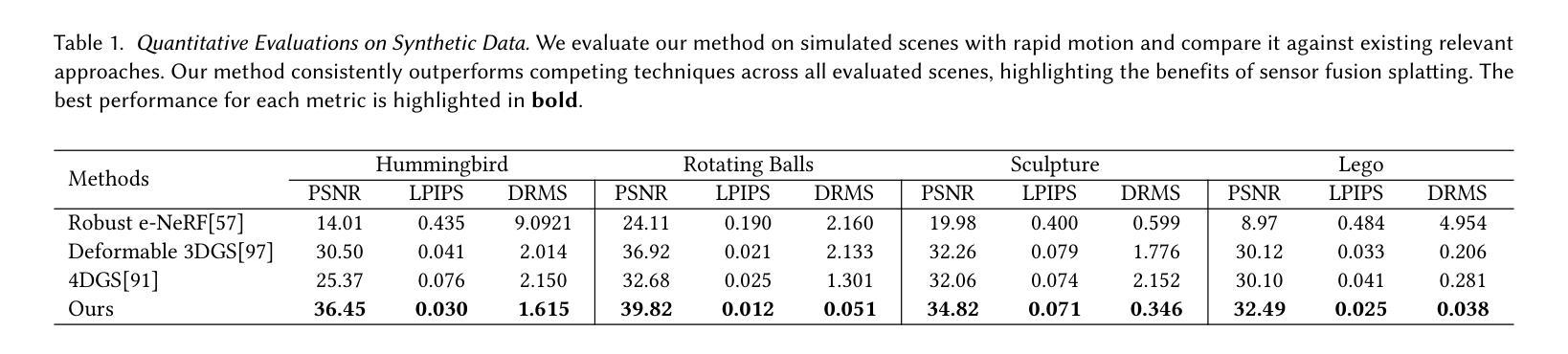
High-Speed Dynamic 3D Imaging with Sensor Fusion Splatting
Authors:Zihao Zou, Ziyuan Qu, Xi Peng, Vivek Boominathan, Adithya Pediredla, Praneeth Chakravarthula
Capturing and reconstructing high-speed dynamic 3D scenes has numerous applications in computer graphics, vision, and interdisciplinary fields such as robotics, aerodynamics, and evolutionary biology. However, achieving this using a single imaging modality remains challenging. For instance, traditional RGB cameras suffer from low frame rates, limited exposure times, and narrow baselines. To address this, we propose a novel sensor fusion approach using Gaussian splatting, which combines RGB, depth, and event cameras to capture and reconstruct deforming scenes at high speeds. The key insight of our method lies in leveraging the complementary strengths of these imaging modalities: RGB cameras capture detailed color information, event cameras record rapid scene changes with microsecond resolution, and depth cameras provide 3D scene geometry. To unify the underlying scene representation across these modalities, we represent the scene using deformable 3D Gaussians. To handle rapid scene movements, we jointly optimize the 3D Gaussian parameters and their temporal deformation fields by integrating data from all three sensor modalities. This fusion enables efficient, high-quality imaging of fast and complex scenes, even under challenging conditions such as low light, narrow baselines, or rapid motion. Experiments on synthetic and real datasets captured with our prototype sensor fusion setup demonstrate that our method significantly outperforms state-of-the-art techniques, achieving noticeable improvements in both rendering fidelity and structural accuracy.
捕捉和重建高速动态三维场景在计算机图形学、计算机视觉以及跨学科领域(如机器人技术、空气动力学和进化生物学)具有众多应用。然而,使用单一成像模式实现这一目标仍然具有挑战性。例如,传统RGB相机存在帧率较低、曝光时间有限和基线较窄等问题。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了一种新颖的传感器融合方法,采用高斯喷溅技术,结合RGB、深度和事件相机,以高速捕捉和重建变形场景。我们的方法的关键在于利用这些成像模式的互补优势:RGB相机捕捉详细的颜色信息,事件相机以微秒分辨率记录场景快速变化,深度相机提供三维场景几何结构。为了统一这些模式下的场景表示,我们使用可变形三维高斯来表示场景。为了处理场景的快速运动,我们通过整合所有三种传感器模式的数据,联合优化三维高斯参数及其时间变形场。这种融合即使在具有挑战性的条件下(例如低光、窄基线或快速运动)也能实现高效、高质量的快照和复杂场景的成像。在我们原型传感器融合设置上进行的合成和真实数据集的实验表明,我们的方法显著优于最先进的技术,在渲染保真度和结构准确性方面都取得了明显的改进。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种融合RGB、深度及事件相机的新型传感器融合方法,采用高斯平铺技术捕捉和重建高速动态3D场景。该方法利用各成像模式的长处,通过优化3D高斯参数及其时间变形场,实现高效、高质量的快照和复杂场景的成像,即使在低光、窄基线或快速运动等挑战条件下也表现优异。
Key Takeaways
- 传感器融合方法结合了RGB、深度及事件相机,以捕捉和重建高速动态3D场景。
- 方法的关键洞察在于利用各成像模式(RGB、事件和深度相机)的互补优势。
- 通过使用变形3D高斯来统一不同模式的场景表示。
- 联合优化3D高斯参数及其时间变形场,以处理快速场景移动。
- 该融合方法在合成和真实数据集上的实验表现显著优于现有技术。
- 即使在挑战条件下(如低光、窄基线或快速运动),该方法也能实现高质量成像。
点此查看论文截图

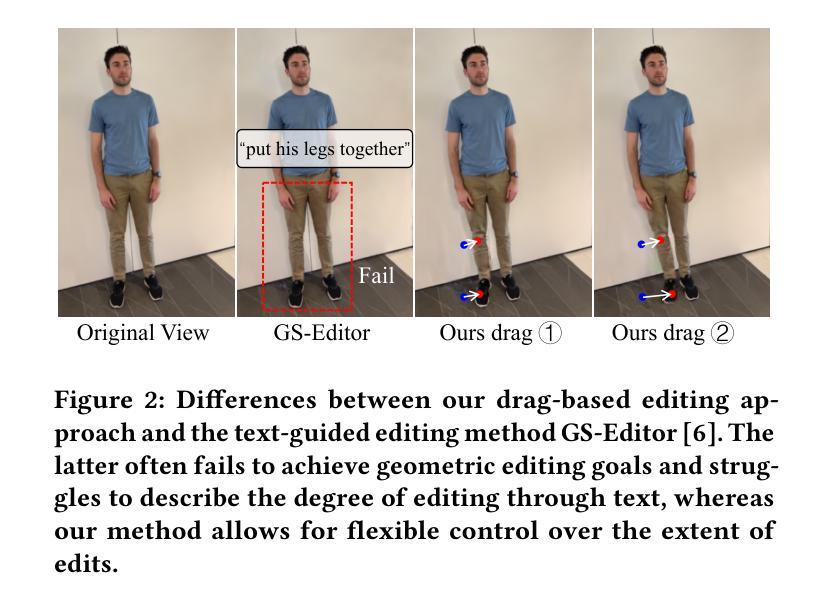
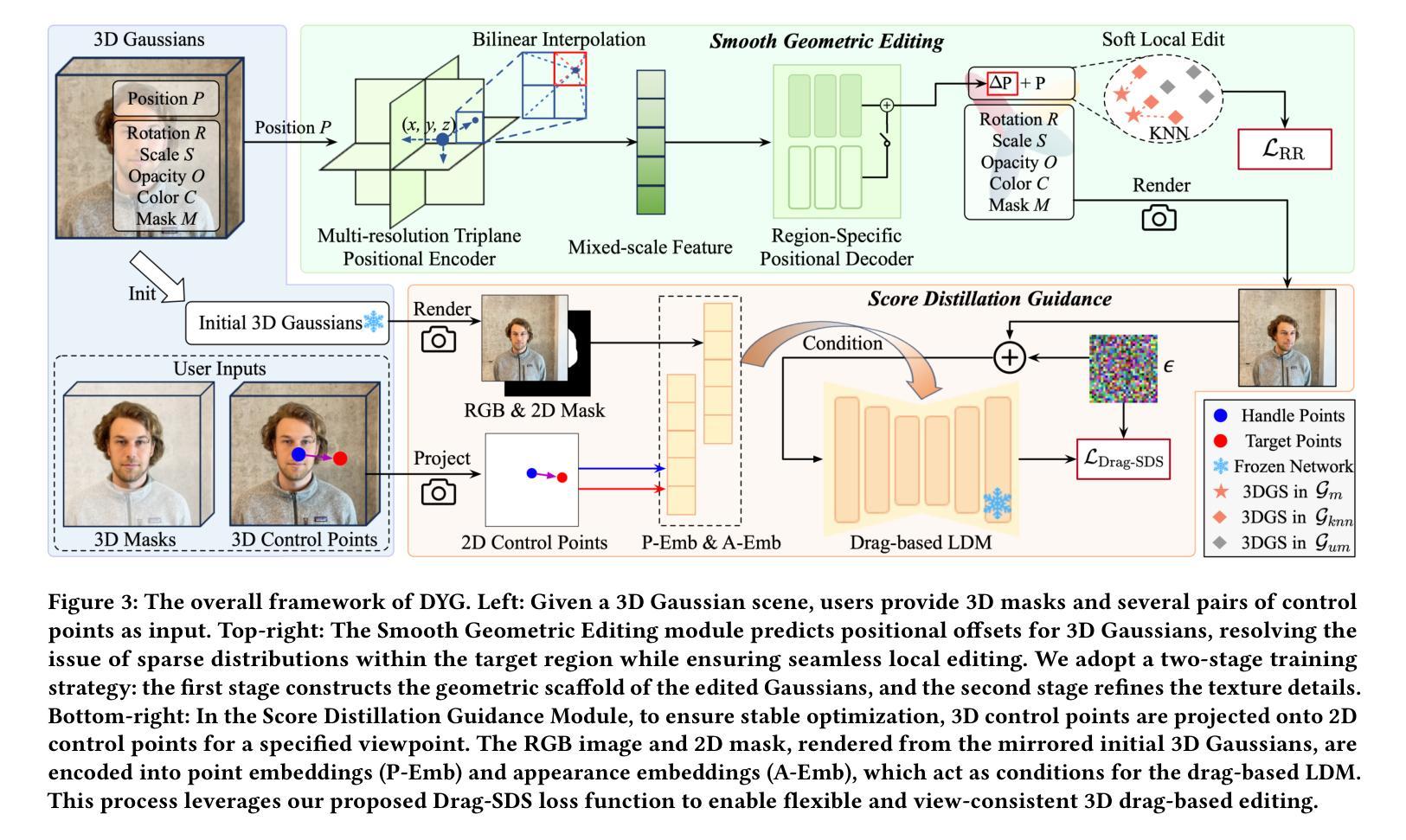
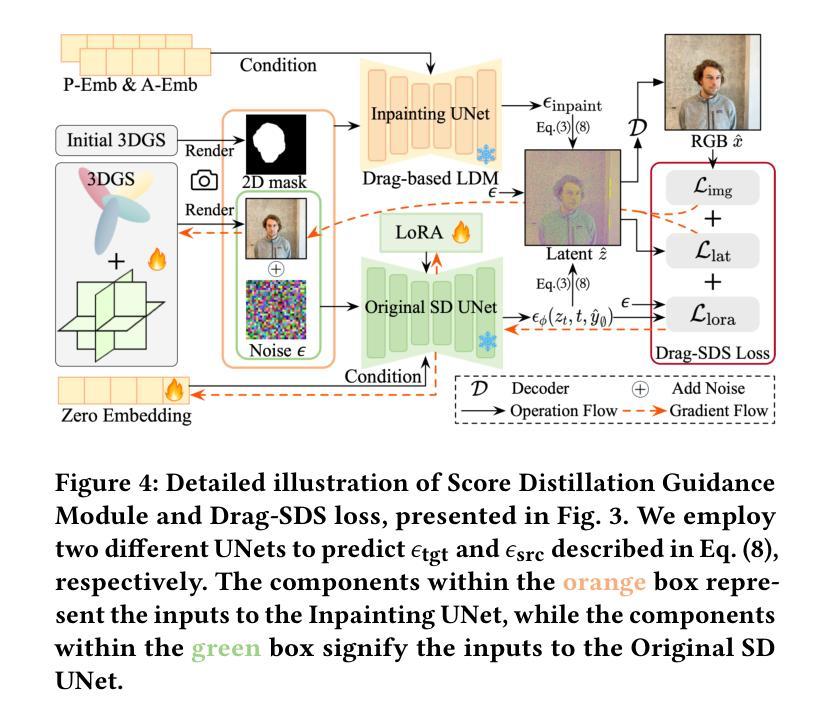
Drag Your Gaussian: Effective Drag-Based Editing with Score Distillation for 3D Gaussian Splatting
Authors:Yansong Qu, Dian Chen, Xinyang Li, Xiaofan Li, Shengchuan Zhang, Liujuan Cao, Rongrong Ji
Recent advancements in 3D scene editing have been propelled by the rapid development of generative models. Existing methods typically utilize generative models to perform text-guided editing on 3D representations, such as 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS). However, these methods are often limited to texture modifications and fail when addressing geometric changes, such as editing a character’s head to turn around. Moreover, such methods lack accurate control over the spatial position of editing results, as language struggles to precisely describe the extent of edits. To overcome these limitations, we introduce DYG, an effective 3D drag-based editing method for 3D Gaussian Splatting. It enables users to conveniently specify the desired editing region and the desired dragging direction through the input of 3D masks and pairs of control points, thereby enabling precise control over the extent of editing. DYG integrates the strengths of the implicit triplane representation to establish the geometric scaffold of the editing results, effectively overcoming suboptimal editing outcomes caused by the sparsity of 3DGS in the desired editing regions. Additionally, we incorporate a drag-based Latent Diffusion Model into our method through the proposed Drag-SDS loss function, enabling flexible, multi-view consistent, and fine-grained editing. Extensive experiments demonstrate that DYG conducts effective drag-based editing guided by control point prompts, surpassing other baselines in terms of editing effect and quality, both qualitatively and quantitatively. Visit our project page at https://quyans.github.io/Drag-Your-Gaussian.
近期三维场景编辑的进展得益于生成模型的快速发展。现有方法通常利用生成模型对三维表示进行文本引导编辑,例如三维高斯平铺(3DGS)。然而,这些方法通常仅限于纹理修改,在几何变化方面表现不佳,例如编辑角色头部以进行旋转。此外,这些方法对编辑结果的空间位置控制不准确,因为语言难以精确描述编辑的程度。为了克服这些限制,我们引入了DYG,这是一种针对三维高斯平铺的有效基于拖拽的三维编辑方法。它使用户可以通过输入三维掩码和控制点对来方便地指定所需的编辑区域和拖拽方向,从而实现对编辑程度的精确控制。DYG结合了隐式三平面表示的优势,建立编辑结果的三维骨架,有效克服了所需编辑区域内3DGS稀疏所导致的次优编辑结果。此外,我们通过提出的Drag-SDS损失函数,将基于拖拽的潜在扩散模型融入我们的方法,实现了灵活、多视角一致、精细的编辑。大量实验表明,DYG通过控制点提示进行有效的基于拖拽的编辑,在编辑效果和品质方面都超越了其他基线方法。请访问我们的项目页面:https://quyans.github.io/Drag-Your-Gaussian了解更多信息。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Visit our project page at https://quyans.github.io/Drag-Your-Gaussian
Summary
本文介绍了基于3D高斯绘制(3DGS)的3D拖拽编辑方法DYG。DYG克服了现有生成模型在3D场景编辑中的局限性,实现了对3D对象几何结构的精准编辑。通过引入3D掩膜和控制点对,DYG为用户提供了便捷的编辑区域和拖拽方向指定方式,同时结合隐式triplane表示和Drag-SDS损失函数,实现了灵活、多视角一致、精细的编辑效果。
Key Takeaways
- 3D场景编辑技术受到生成模型快速发展的推动。
- 现有方法主要利用生成模型进行文本引导的3D表示编辑,但局限于纹理修改,难以进行几何变化。
- DYG方法引入3D掩膜和控制点对,方便用户指定编辑区域和拖拽方向。
- DYG结合隐式triplane表示,建立编辑结果几何骨架,有效克服3DGS在编辑区域的稀疏性问题。
- 引入基于拖拽的潜在扩散模型,通过Drag-SDS损失函数,实现灵活、多视角一致、精细的编辑。
- DYG在编辑效果和品质上超越其他基线方法。
点此查看论文截图


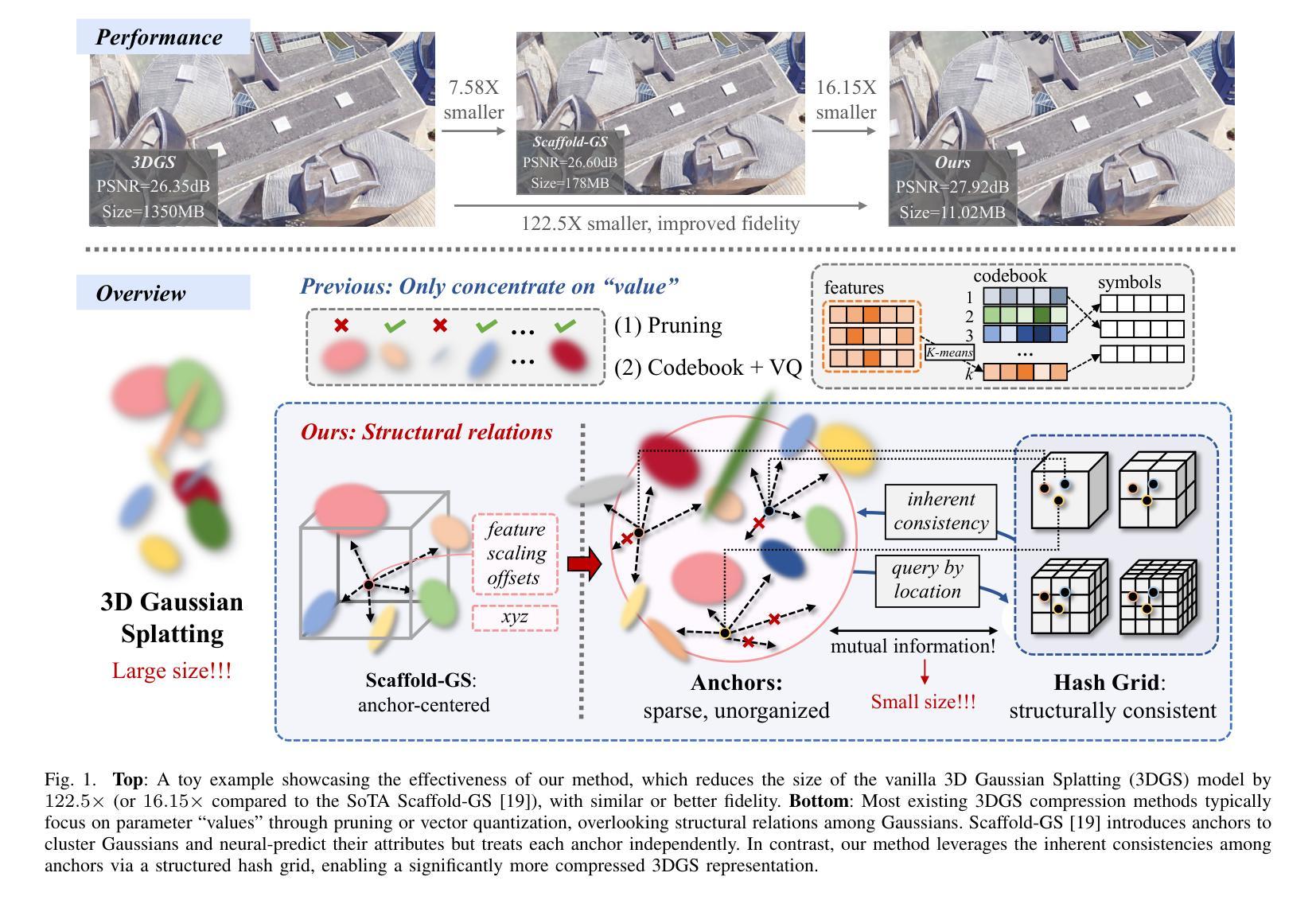
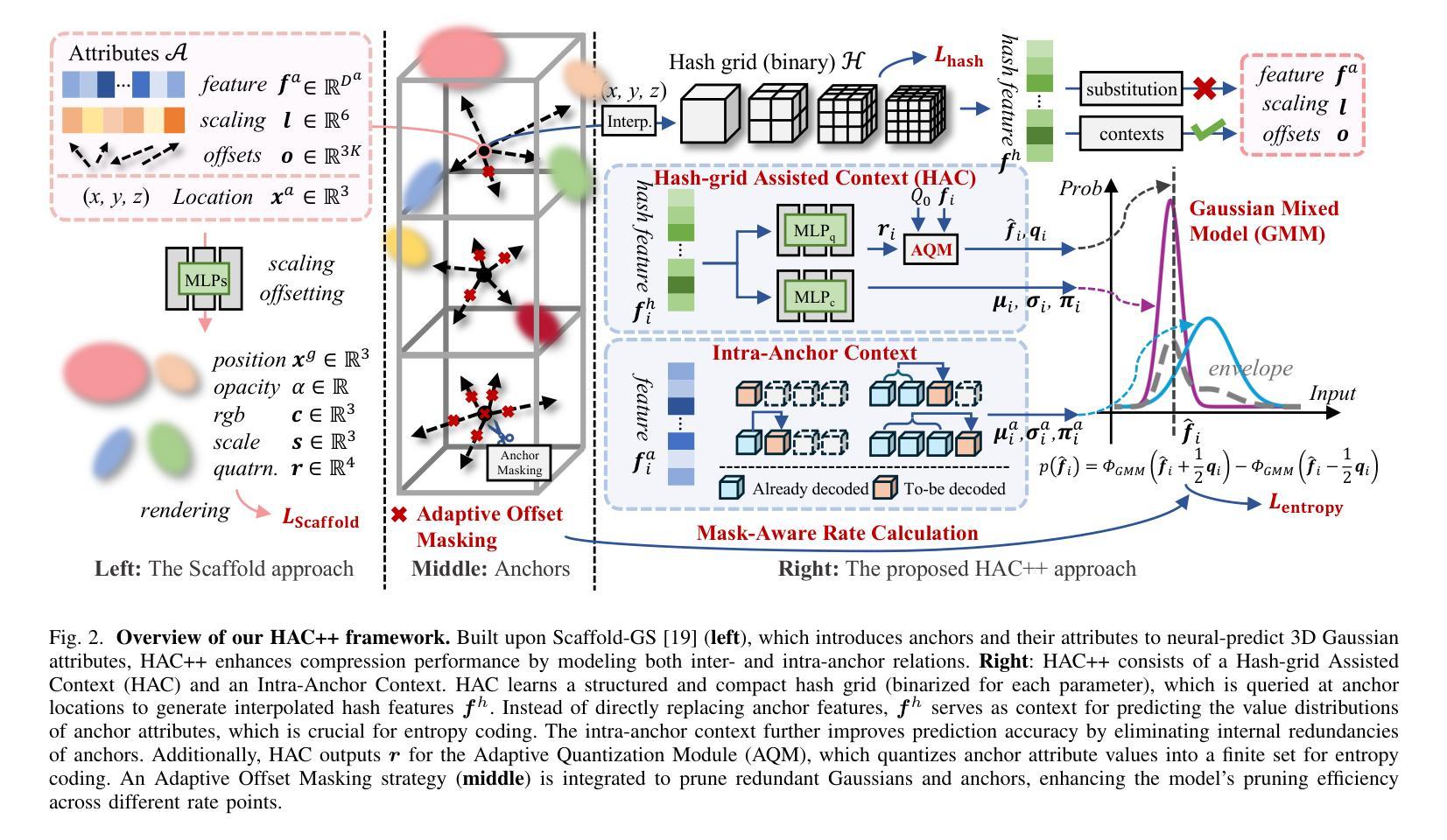
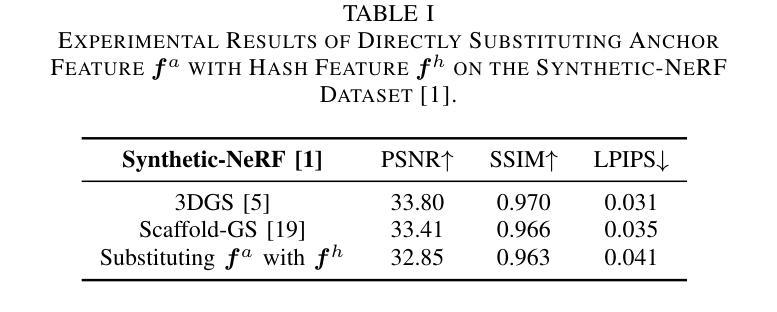
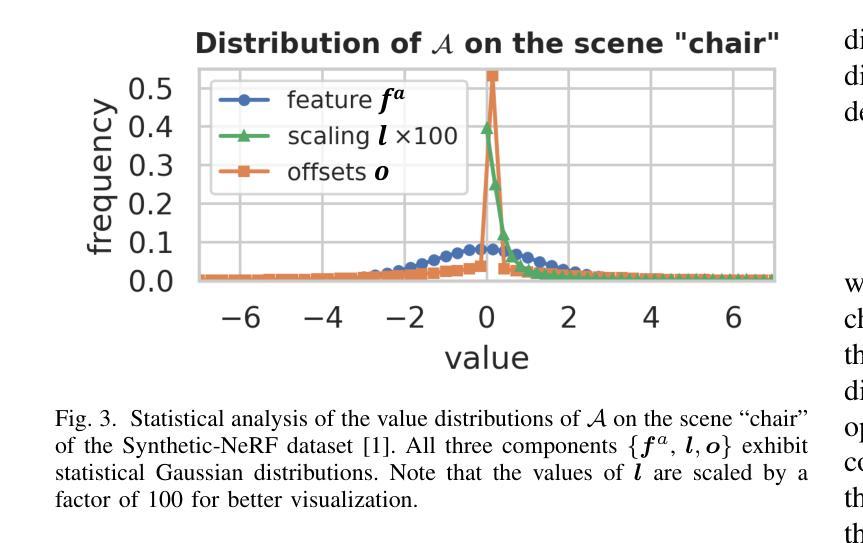
HAC++: Towards 100X Compression of 3D Gaussian Splatting
Authors:Yihang Chen, Qianyi Wu, Weiyao Lin, Mehrtash Harandi, Jianfei Cai
3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) has emerged as a promising framework for novel view synthesis, boasting rapid rendering speed with high fidelity. However, the substantial Gaussians and their associated attributes necessitate effective compression techniques. Nevertheless, the sparse and unorganized nature of the point cloud of Gaussians (or anchors in our paper) presents challenges for compression. To achieve a compact size, we propose HAC++, which leverages the relationships between unorganized anchors and a structured hash grid, utilizing their mutual information for context modeling. Additionally, HAC++ captures intra-anchor contextual relationships to further enhance compression performance. To facilitate entropy coding, we utilize Gaussian distributions to precisely estimate the probability of each quantized attribute, where an adaptive quantization module is proposed to enable high-precision quantization of these attributes for improved fidelity restoration. Moreover, we incorporate an adaptive masking strategy to eliminate invalid Gaussians and anchors. Overall, HAC++ achieves a remarkable size reduction of over 100X compared to vanilla 3DGS when averaged on all datasets, while simultaneously improving fidelity. It also delivers more than 20X size reduction compared to Scaffold-GS. Our code is available at https://github.com/YihangChen-ee/HAC-plus.
3D高斯映射(3DGS)已成为新型视角合成的一种有前途的框架,具有快速渲染和高保真度的特点。然而,大量的高斯及其相关属性需要进行有效的压缩技术处理。尽管如此,高斯点的稀疏性和非组织性(或我们论文中的锚点)给压缩带来了挑战。为了实现紧凑的大小,我们提出了HAC++,它利用非组织锚点之间的关系和一个结构化的哈希网格,利用它们的互信息来进行上下文建模。此外,HAC++捕捉了锚点内的上下文关系,以进一步增强压缩性能。为了促进熵编码,我们利用高斯分布来精确估计每个量化属性的概率,并提出了一种自适应量化模块,实现对这些属性的高精度量化,以提高保真度的恢复。此外,我们采用自适应掩码策略来消除无效的高斯和锚点。总的来说,HAC++在所有数据集上平均相比基础3DGS实现了超过100倍的大小缩减,同时提高了保真度。与Scaffold-GS相比,它实现了超过20倍的大小缩减。我们的代码可在https://github.com/YihangChen-ee/HAC-plus找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project Page: https://yihangchen-ee.github.io/project_hac++/ Code: https://github.com/YihangChen-ee/HAC-plus. This paper is a journal extension of HAC at arXiv:2403.14530 (ECCV 2024)
Summary
本文介绍了基于三维高斯分裂(3DGS)技术的视图合成方法,该方法具有快速渲染和高保真度的特点。针对高斯及其属性的压缩问题,提出了利用点云间关系的HAC++压缩技术,该技术结合了结构化哈希网格与锚点间的互信息关系进行上下文建模,同时优化了量化属性概率估计的熵编码过程。此外,还引入了自适应掩码策略以消除无效的高斯和锚点。相较于传统方法,HAC++实现了超过百倍的数据压缩率提升,同时保证了良好的保真度恢复效果。
Key Takeaways
- 3DGS技术在视图合成领域展现出快速渲染和高保真度的优势。
- 高斯及其属性的压缩是3DGS技术中的关键挑战。
- HAC++技术利用点云间关系进行上下文建模,结合了结构化哈希网格与锚点间的互信息关系。
- HAC++技术优化了量化属性概率估计的熵编码过程。
- 自适应掩码策略用于消除无效的高斯和锚点。
- HAC++相较于传统方法实现了超过百倍的数据压缩率提升。
点此查看论文截图