⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-02-11 更新
Long-VITA: Scaling Large Multi-modal Models to 1 Million Tokens with Leading Short-Context Accuray
Authors:Yunhang Shen, Chaoyou Fu, Shaoqi Dong, Xiong Wang, Peixian Chen, Mengdan Zhang, Haoyu Cao, Ke Li, Xiawu Zheng, Yan Zhang, Yiyi Zhou, Rongrong Ji, Xing Sun
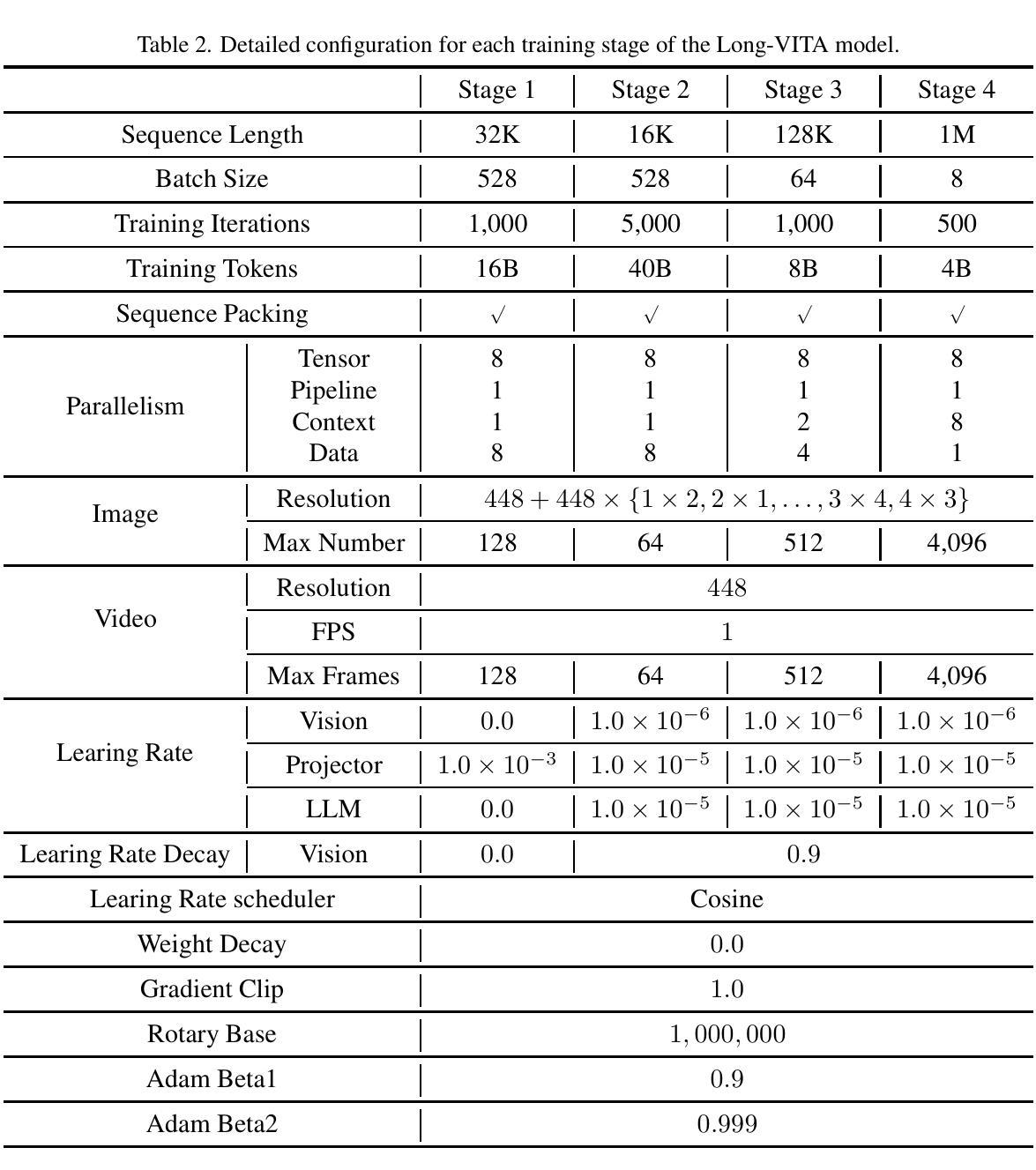
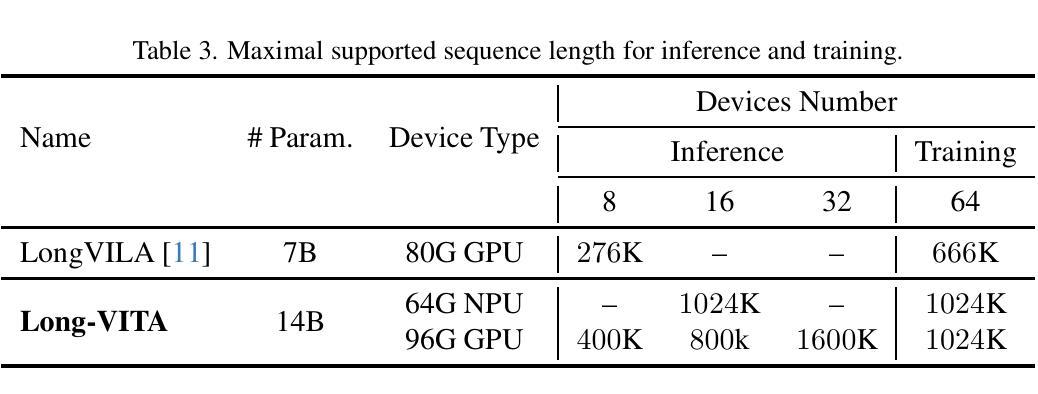
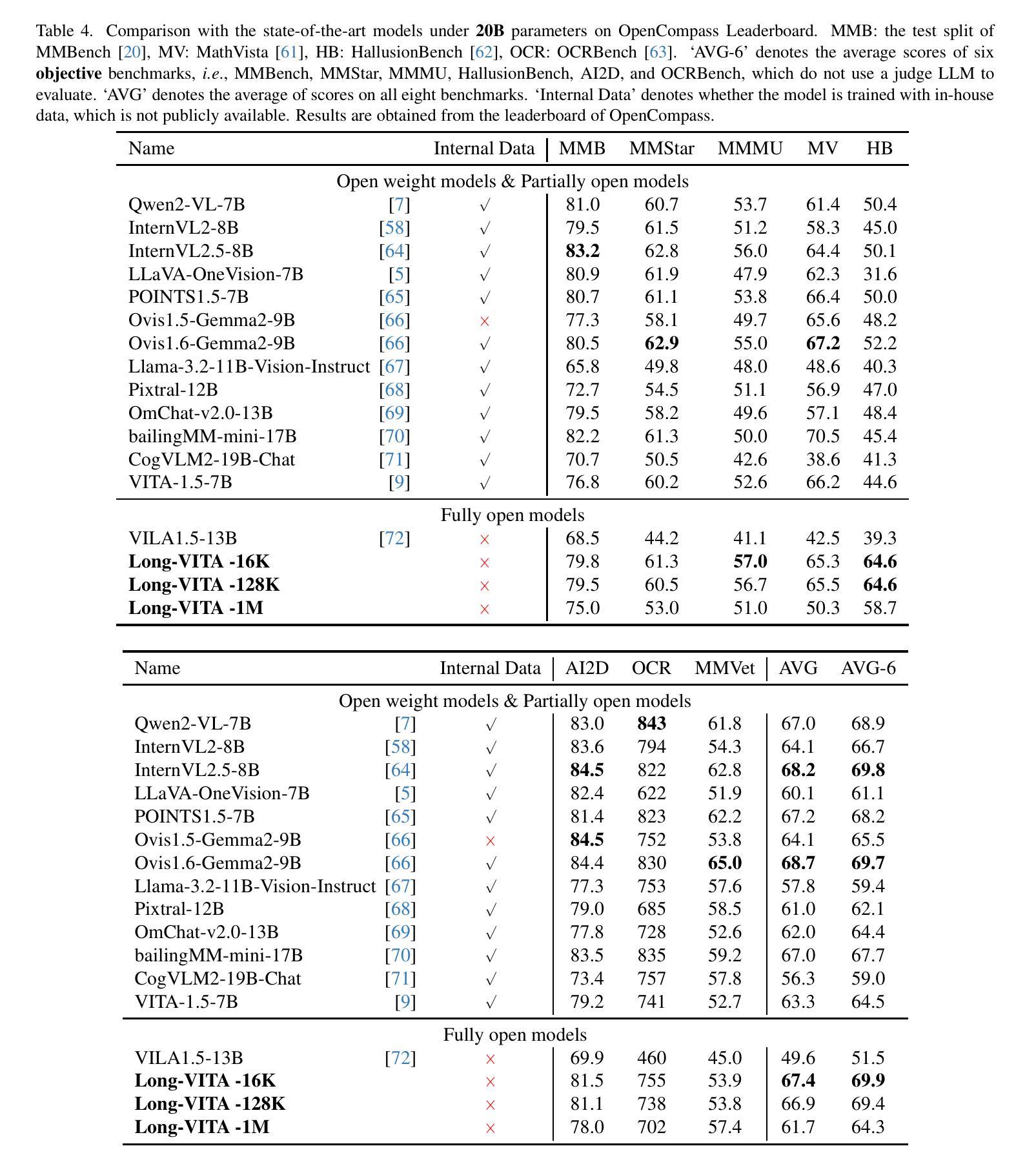
Establishing the long-context capability of large vision-language models is crucial for video understanding, high-resolution image understanding, multi-modal agents and reasoning. We introduce Long-VITA, a simple yet effective large multi-modal model for long-context visual-language understanding tasks. It is adept at concurrently processing and analyzing modalities of image, video, and text over 4K frames or 1M tokens while delivering advanced performances on short-context multi-modal tasks. We propose an effective multi-modal training schema that starts with large language models and proceeds through vision-language alignment, general knowledge learning, and two sequential stages of long-sequence fine-tuning. We further implement context-parallelism distributed inference and logits-masked language modeling head to scale Long-VITA to infinitely long inputs of images and texts during model inference. Regarding training data, Long-VITA is built on a mix of $17$M samples from public datasets only and demonstrates the state-of-the-art performance on various multi-modal benchmarks, compared against recent cutting-edge models with internal data. Long-VITA is fully reproducible and supports both NPU and GPU platforms for training and testing. We hope Long-VITA can serve as a competitive baseline and offer valuable insights for the open-source community in advancing long-context multi-modal understanding.
建立大型视觉语言模型的长上下文能力是视频理解、高分辨率图像理解、多模态代理和推理的关键。我们介绍了Long-VITA,这是一个简单有效的大型多模态模型,用于长上下文视觉语言理解任务。它擅长同时处理和分析图像、视频和文本的模态,可在4K帧或1M令牌上进行操作,同时在短上下文多模态任务上实现先进性能。我们提出了一种有效的多模态训练方案,该方案以大型语言模型开始,通过视觉语言对齐、一般知识学习以及两个连续的长序列微调阶段进行。我们进一步实现了上下文并行分布式推理和logits-masked语言建模头,以在模型推理期间将Long-VITA扩展到无限长的图像和文本输入。关于训练数据,Long-VITA仅建立在公共数据集的1700万个样本的混合上,与最近使用内部数据的尖端模型相比,在各种多模态基准测试上展示了最先进的性能。Long-VITA可完全复制,支持NPU和GPU平台进行训练和测试。我们希望Long-VITA可以作为有竞争力的基准,为开源社区在推进长上下文多模态理解方面提供有价值的见解。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF https://github.com/VITA-MLLM/Long-VITA
Summary
大型视觉语言模型建立长期上下文能力是视频理解、高分辨率图像理解、多模态代理和推理的关键。本文介绍了一种简单有效的长期上下文视觉语言理解任务的大型多模态模型Long-VITA,它能够同时处理和分析图像、视频和文本的模态,并在短上下文多模态任务上表现出卓越性能。本文提出了一种有效的多模态训练模式,通过大型语言模型开始,进行视觉语言对齐、一般知识学习以及两个连续的长序列微调阶段。通过实施上下文并行分布式推理和logits掩码语言建模头,将Long-VITA扩展到无限长的图像和文本输入。该模型在多种多模态基准测试上达到了最新水平,与其他使用内部数据的先进模型相比具有卓越性能。Long-VITA完全可复现,支持NPU和GPU平台进行训练和测试,旨在为开源社区提供有价值的见解,推动长期上下文多模态理解的进步。
Key Takeaways
- Long-VITA是一种用于长期上下文视觉语言理解任务的大型多模态模型。
- Long-VITA能够同时处理和分析图像、视频和文本的模态。
- Long-VITA在短上下文多模态任务上表现出卓越性能。
- 提出了一种有效的多模态训练模式,包括视觉语言对齐、一般知识学习和长序列微调阶段。
- 通过上下文并行分布式推理和logits掩码语言建模头,Long-VITA可扩展到无限长的图像和文本输入。
- Long-VITA在多种多模态基准测试上达到了最新水平。
点此查看论文截图

DuoGuard: A Two-Player RL-Driven Framework for Multilingual LLM Guardrails
Authors:Yihe Deng, Yu Yang, Junkai Zhang, Wei Wang, Bo Li
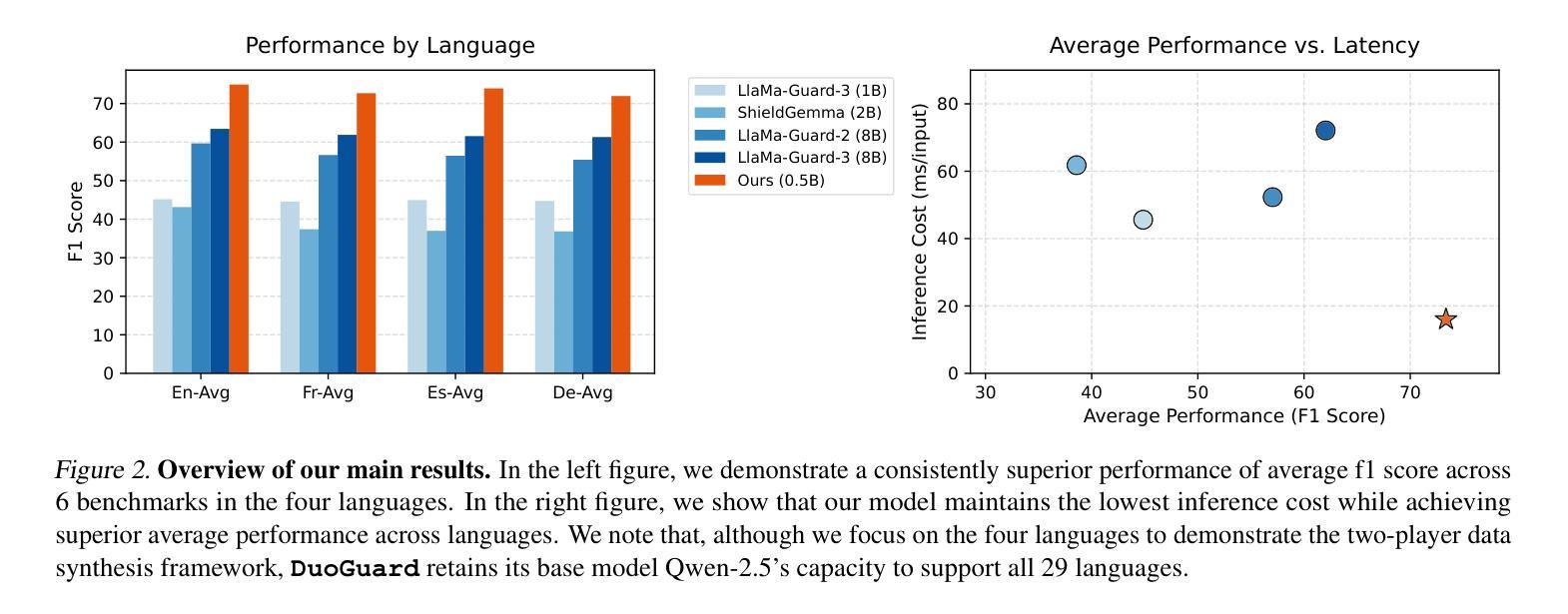
The rapid advancement of large language models (LLMs) has increased the need for guardrail models to ensure responsible use, particularly in detecting unsafe and illegal content. While substantial safety data exist in English, multilingual guardrail modeling remains underexplored due to the scarcity of open-source safety data in other languages. To address this gap, we propose a novel two-player Reinforcement Learning (RL) framework, where a generator and a guardrail model co-evolve adversarially to produce high-quality synthetic data for multilingual guardrail training. We theoretically formalize this interaction as a two-player game, proving convergence to a Nash equilibrium. Empirical evaluations show that our model \ours outperforms state-of-the-art models, achieving nearly 10% improvement over LlamaGuard3 (8B) on English benchmarks while being 4.5x faster at inference with a significantly smaller model (0.5B). We achieve substantial advancements in multilingual safety tasks, particularly in addressing the imbalance for lower-resource languages in a collected real dataset. Ablation studies emphasize the critical role of synthetic data generation in bridging the imbalance in open-source data between English and other languages. These findings establish a scalable and efficient approach to synthetic data generation, paving the way for improved multilingual guardrail models to enhance LLM safety. Code, model, and data will be open-sourced at https://github.com/yihedeng9/DuoGuard.
大型语言模型(LLM)的快速发展增加了对护栏模型的需求,以确保其使用责任,特别是在检测不安全和非法内容方面。虽然英语中有大量的安全数据,但由于其他语言中开源安全数据的稀缺,多语言护栏建模仍然被较少探索。为了弥补这一空白,我们提出了一种新型的双人强化学习(RL)框架,其中生成器和护栏模型对抗性地共同进化,以产生高质量合成数据,用于多语言护栏训练。我们从理论上将这种互动形式化为一个双人游戏,并证明了其收敛到纳什均衡点。经验评估表明,我们的模型“ours”优于当前最先进的模型,在英语基准测试中相对于LlamaGuard3(8B)有近10%的提升,同时在推理过程中模型更小(0.5B)且速度更快(4.5倍)。我们在多语言安全任务方面取得了重大进展,特别是在解决收集的真实数据集中对低资源语言的不平衡问题方面表现尤为突出。消融研究强调了合成数据生成在弥合英语和其他语言之间开源数据不平衡中的关键作用。这些发现建立了一种可扩展和高效的合成数据生成方法,为改进多语言护栏模型以提高LLM安全性铺平了道路。代码、模型和数据将在https://github.com/yihedeng9/DuoGuard上开源。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 24 pages, 9 figures, 5 tables
Summary
大型语言模型(LLM)的快速发展增加了对防护模型的需求,以确保其负责任的使用,特别是在检测不安全和非法内容方面。针对多语言防护建模的缺乏,本文提出了一种新型的两玩家强化学习(RL)框架,生成器和防护模型对抗性共同进化以产生高质量合成数据用于多语言防护训练。本文理论形式化这种互动为两玩家游戏,并证明收敛到纳什均衡。经验评估表明,我们的模型在英语基准测试中较当前顶尖模型提升了近10%,同时推理速度更快、模型更小。我们在多语言安全任务上取得了重大进展,特别是在解决收集的真实数据集中对低资源语言的不平衡问题方面。这些发现建立了一种可扩展和高效合成数据生成方法,为改进多语言防护模型以提高LLM安全性铺平了道路。相关代码、模型和资料已公开于https://github.com/yihedeng9/DuoGuard。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLM)需要防护模型以确保其负责任的使用,特别是在检测有害和非法内容方面。
- 针对多语言防护建模的缺乏,提出了新型的两玩家强化学习(RL)框架。
- 生成器和防护模型通过对抗性共同进化产生高质量合成数据用于多语言防护训练。
- 本文理论形式化该框架为一种两玩家游戏,证明其收敛至纳什均衡。
- 经验评估显示所提模型性能优异,包括提高准确性、推理速度和模型规模方面。
- 该方法在多语言安全任务上表现突出,解决了低资源语言的不平衡问题。
点此查看论文截图


Refining Integration-by-Parts Reduction of Feynman Integrals with Machine Learning
Authors:Matt von Hippel, Matthias Wilhelm
Integration-by-parts reductions of Feynman integrals pose a frequent bottle-neck in state-of-the-art calculations in theoretical particle and gravitational-wave physics, and rely on heuristic approaches for selecting integration-by-parts identities, whose quality heavily influences the performance. In this paper, we investigate the use of machine-learning techniques to find improved heuristics. We use funsearch, a genetic programming variant based on code generation by a Large Language Model, in order to explore possible approaches, then use strongly typed genetic programming to zero in on useful solutions. Both approaches manage to re-discover the state-of-the-art heuristics recently incorporated into integration-by-parts solvers, and in one example find a small advance on this state of the art.
在理论粒子物理和引力波物理的最新计算中,分部积分法的Feynman积分构成了一个瓶颈问题,并依赖于启发式方法来选择分部积分法身份,其质量对性能有着重大影响。在本文中,我们研究了使用机器学习技术来找到改进启发式方法的应用。我们使用了funsearch,这是一种基于大型语言模型进行代码生成的新型遗传程序设计变体,来探索可能的方法,然后使用强类型遗传程序设计来寻找可行的解决方案。这两种方法都能够重新发现最近融入分部积分求解器的最新启发式技术,并在一个例子中取得了轻微的进展。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 28 pages, 9 figures
Summary
集成-分部积分法(integration-by-parts)在理论粒子和引力波物理学的先进计算中经常遇到瓶颈,依赖于启发式方法来选择积分恒等式,其质量严重影响性能。本文研究使用机器学习技术来改进启发式方法,采用基于大型语言模型的代码生成的遗传编程变体funsearch进行探索,然后使用强类型遗传编程来集中寻找有用的解决方案。两种方法都能够重新发现目前集成-分部积分求解器中使用的最新启发式技术,并在一个例子中取得了微小的进展。
Key Takeaways
- 集成-分部积分法是理论粒子和引力波物理学中先进计算的一个瓶颈。
- 启发式方法的选择对集成-分部积分法的性能有重要影响。
- 机器学习技术被用于改进启发式方法以提高集成-分部积分法的效率。
- funsearch是一种基于大型语言模型的遗传编程变体,用于探索可能的解决方案。
- 强类型遗传编程被用于集中寻找有用的解决方案。
- 两种方法都能够重新发现当前启发式技术的前沿。
点此查看论文截图

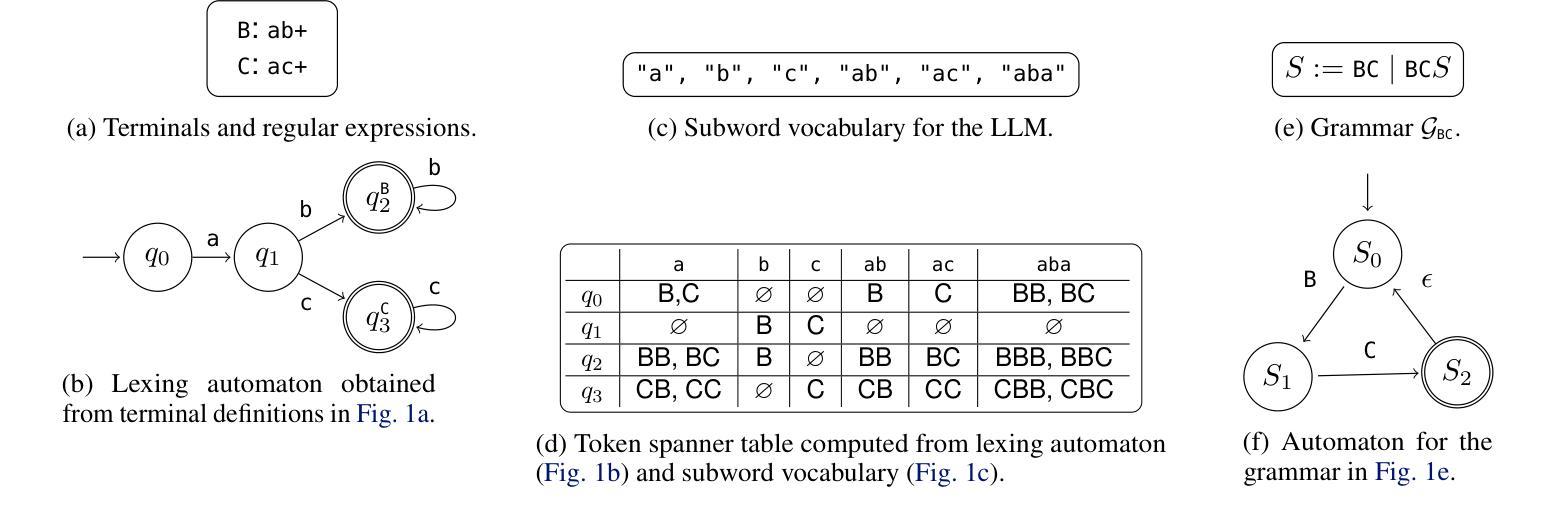
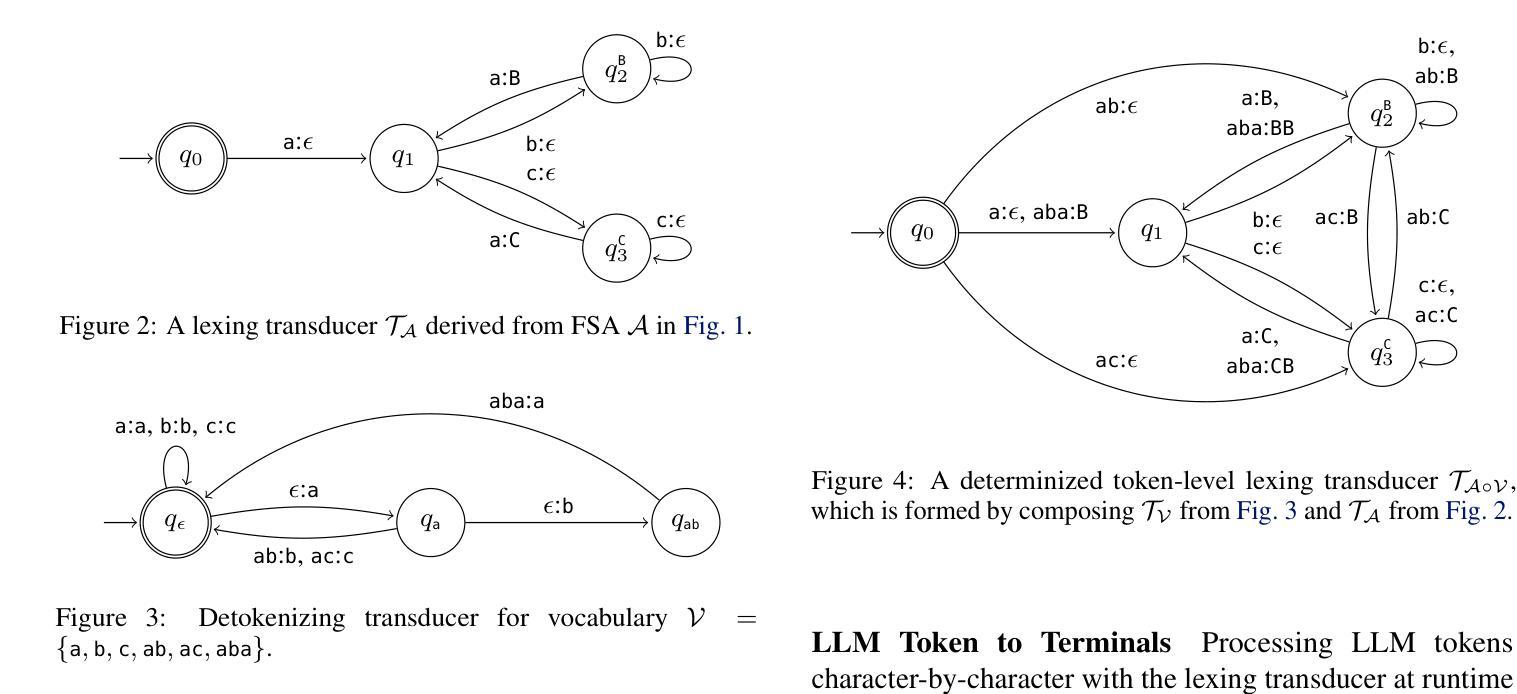
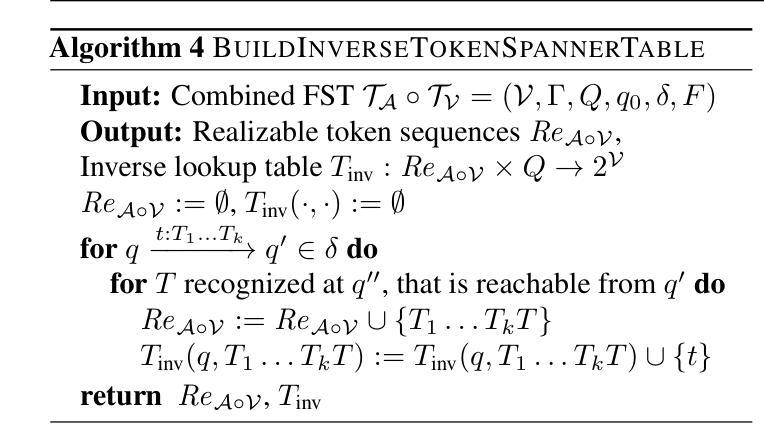
Flexible and Efficient Grammar-Constrained Decoding
Authors:Kanghee Park, Timothy Zhou, Loris D’Antoni
Large Language Models (LLMs) are often asked to generate structured outputs that obey precise syntactic rules, such as code snippets or formatted data. Grammar-constrained decoding (GCD) can guarantee that LLM outputs matches such rules by masking out tokens that will provably lead to outputs that do not belong to a specified context-free grammar (CFG). To guarantee soundness, GCD algorithms have to compute how a given LLM subword tokenizer can align with the tokens used by a given context-free grammar and compute token masks based on this information. Doing so efficiently is challenging and existing GCD algorithms require tens of minutes to preprocess common grammars. We present a new GCD algorithm together with an implementation that offers 17.71x faster offline preprocessing than existing approaches while preserving state-of-the-art efficiency in online mask computation.
大型语言模型(LLM)通常被要求生成遵循精确句法规则的结构化输出,例如代码片段或格式化数据。语法约束解码(GCD)可以通过屏蔽那些明显会导致输出不符合特定上下文无关语法(CFG)的令牌,来保证LLM输出符合这些规则。为了保证正确性,GCD算法必须计算给定的LLM子词标记器如何与特定的上下文无关语法所使用的令牌对齐,并基于这些信息计算令牌掩码。高效地完成这一过程具有挑战性,现有的GCD算法需要数分钟预处理常见的语法。我们提出了一种新的GCD算法及其实现,与传统的做法相比,该算法线下预处理速度提高了17.71倍,同时在线掩码计算效率达到了最新水平。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大型语言模型(LLM)在生成需遵循精确句法规则的结构化输出(如代码片段或格式化数据)时面临挑战。本文提出了一种新的语法约束解码(GCD)算法,该算法可以高效地保证LLM输出与指定上下文无关语法(CFG)匹配。相较于现有方法,新算法的离线预处理速度提高了17.71倍,同时保持在线掩码计算的最新效率。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLM)需要生成遵循精确句法规则的结构化输出。
- 语法约束解码(GCD)可保证LLM输出与上下文无关语法(CFG)匹配。
- 现有GCD算法在预处理常见语法时效率较低,需要数十分钟。
- 新GCD算法提高了离线预处理速度,相较于现有方法提高了17.71倍。
- 新算法在在线掩码计算方面保持最新效率。
- GCD算法通过掩码输出确定会导致不符合指定语法的标记,从而保证健全性。
点此查看论文截图


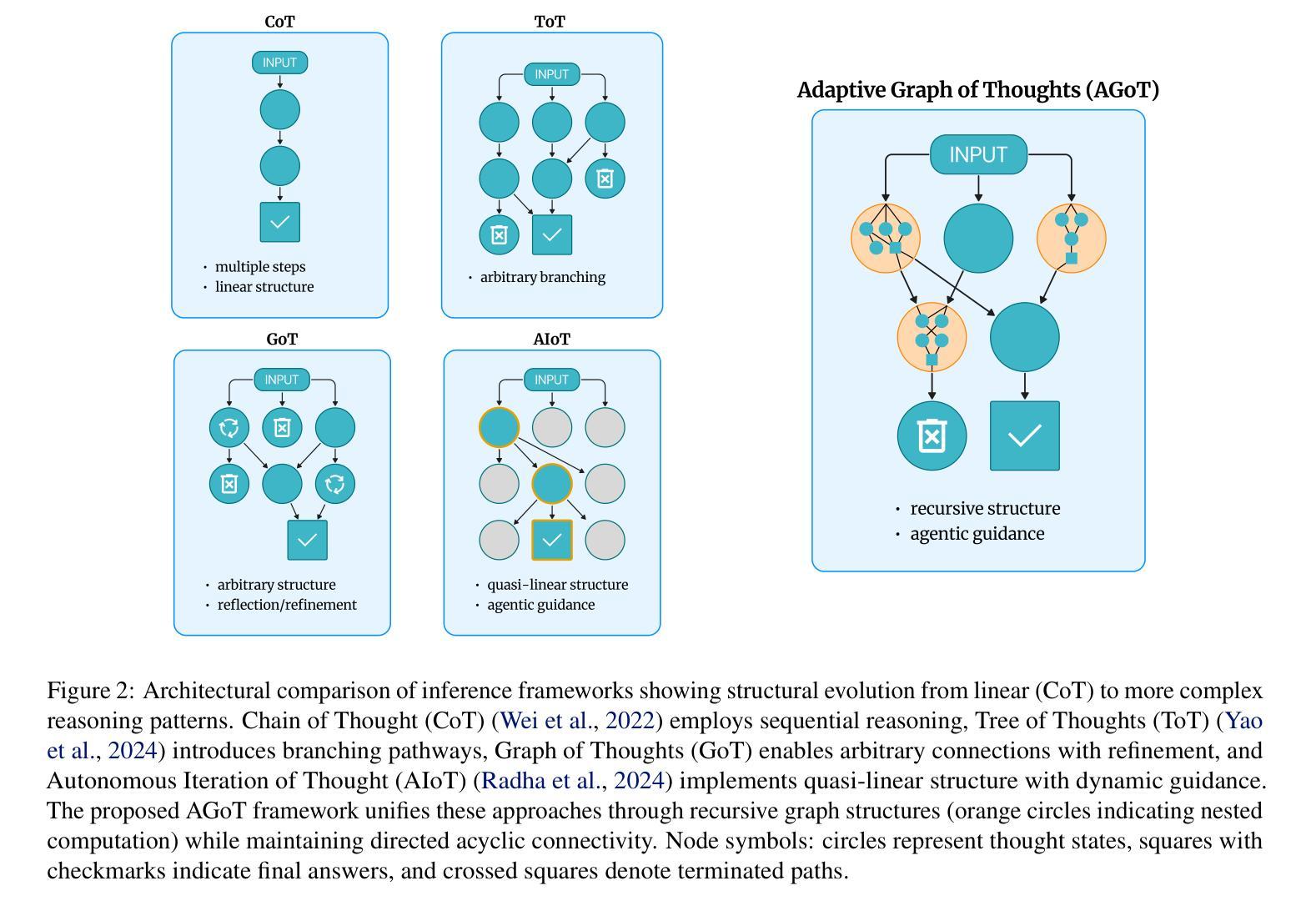
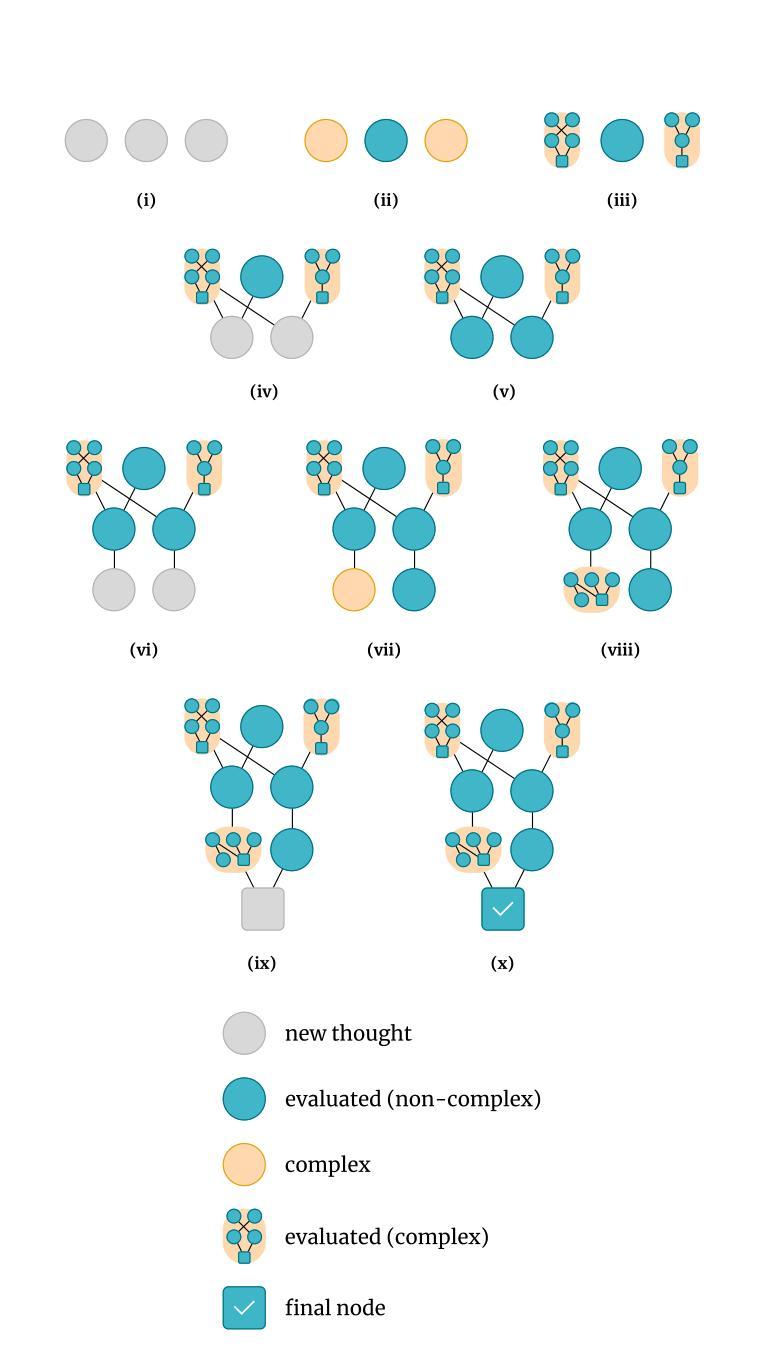
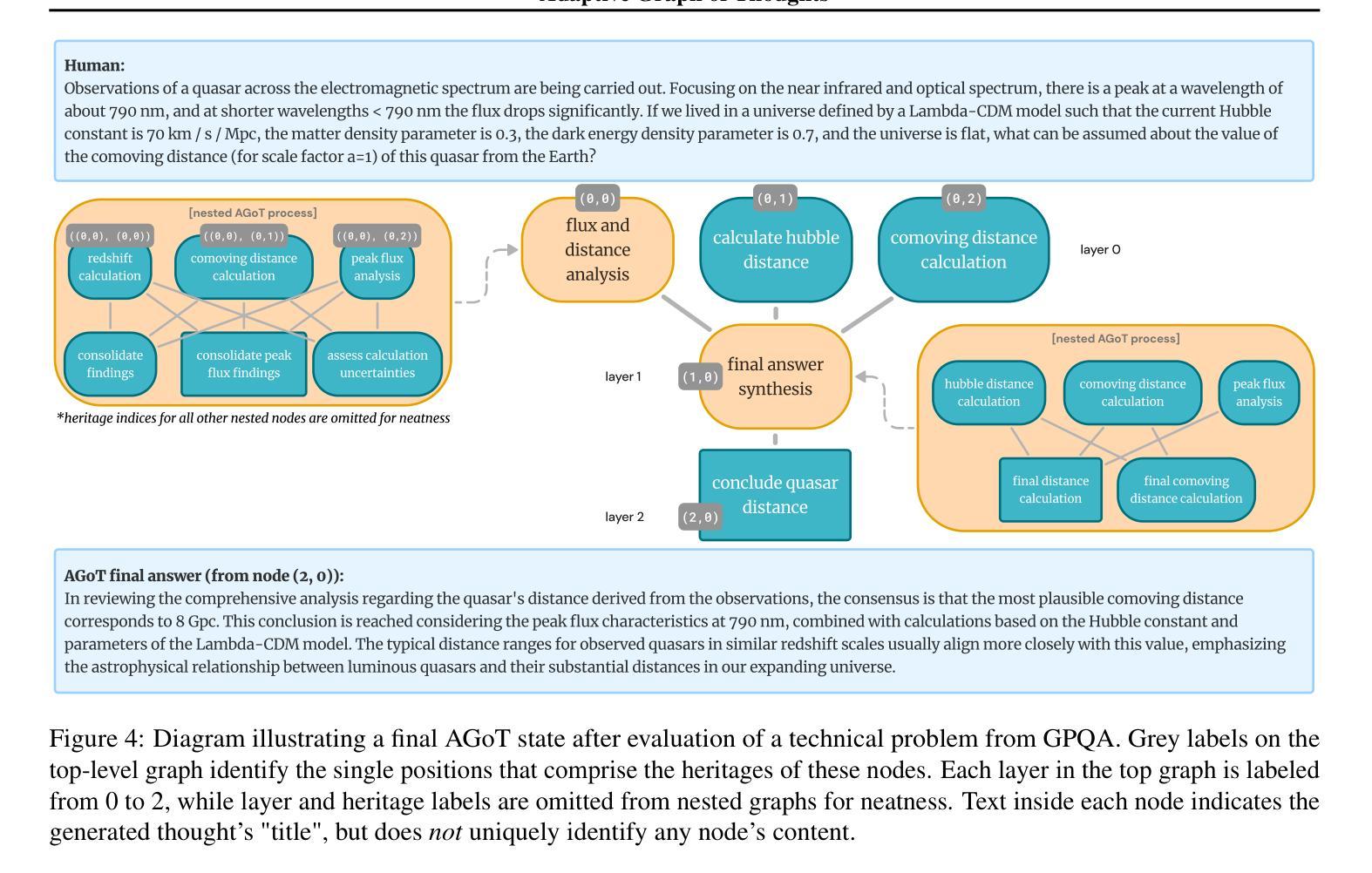
Adaptive Graph of Thoughts: Test-Time Adaptive Reasoning Unifying Chain, Tree, and Graph Structures
Authors:Tushar Pandey, Ara Ghukasyan, Oktay Goktas, Santosh Kumar Radha
Large Language Models (LLMs) have demonstrated impressive reasoning capabilities, yet their performance is highly dependent on the prompting strategy and model scale. While reinforcement learning and fine-tuning have been deployed to boost reasoning, these approaches incur substantial computational and data overhead. In this work, we introduce Adaptive Graph of Thoughts (AGoT), a dynamic, graph-based inference framework that enhances LLM reasoning solely at test time. Rather than relying on fixed-step methods like Chain of Thought (CoT) or Tree of Thoughts (ToT), AGoT recursively decomposes complex queries into structured subproblems, forming an dynamic directed acyclic graph (DAG) of interdependent reasoning steps. By selectively expanding only those subproblems that require further analysis, AGoT unifies the strengths of chain, tree, and graph paradigms into a cohesive framework that allocates computation where it is most needed. We validate our approach on diverse benchmarks spanning multi-hop retrieval, scientific reasoning, and mathematical problem-solving, achieving up to 46.2% improvement on scientific reasoning tasks (GPQA) - comparable to gains achieved through computationally intensive reinforcement learning approaches and outperforming state-of-the-art iterative approaches. These results suggest that dynamic decomposition and structured recursion offer a scalable, cost-effective alternative to post-training modifications, paving the way for more robust, general-purpose reasoning in LLMs.
大型语言模型(LLM)已经展现出令人印象深刻的推理能力,但其性能高度依赖于提示策略和模型规模。虽然强化学习和微调已被用于提升推理能力,但这些方法产生了大量的计算和数据开销。在这项工作中,我们引入了自适应思维图(AGoT),这是一种基于动态图的推理框架,能够在测试时增强LLM的推理能力。与依赖固定步骤的方法(如思维链(CoT)或思维树(ToT))不同,AGoT递归地将复杂查询分解为结构化的子问题,形成一个动态的、有向的无环图(DAG),包含相互依赖的推理步骤。通过有选择地扩展那些需要进一步分析的子问题,AGoT将链、树和图范式的优点结合在一个协调一致的框架中,在需要的地方分配计算资源。我们在跨越多跳检索、科学推理和数学问题解决等多种基准测试上验证了我们的方法,在科学推理任务(GPQA)上实现了高达46.2%的改进,这一成绩与强化学习方法的增益相当,并超越了最先进的迭代方法。这些结果表明,动态分解和结构递归是一种可扩展、经济高效的替代方法,为训练后的的大型语言模型改进了推理能力,为更稳健、通用的推理能力铺平了道路。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大型语言模型(LLM)具备强大的推理能力,但其性能高度依赖于提示策略和模型规模。当前方法如强化学习和微调虽然能提高推理能力,但计算和数据成本较高。本研究提出一种动态的图推理框架——自适应思维图(AGoT),在测试时增强LLM的推理能力。AGoT通过递归分解复杂查询到结构化子问题,形成动态的有向无环图(DAG),根据需求选择性扩展子问题。该框架融合了链式思维、树状思维和图思维的优势,在计算需求处分配资源。在跨越多跳检索、科学推理和数学问题解决等多种基准测试上验证了该方法的有效性,实现了在科学推理任务(GPQA)上高达46.2%的改进——与强化学习方法的计算密集型增益相当,并优于最先进的迭代方法。这些结果表明,动态分解和结构化递归是一种可扩展且经济实惠的替代方案,为LLM中更稳健、通用的推理铺平了道路。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLM)的推理能力受提示策略和模型规模的影响。
- 当前提高LLM推理能力的方法如强化学习和微调计算成本高。
- 自适应思维图(AGoT)是一种新型动态的图推理框架,能在测试时增强LLM的推理能力。
- AGoT通过递归分解复杂查询到结构化子问题,形成动态的有向无环图(DAG)。
- AGoT能融合多种思维框架(如链式思维、树状思维和图思维)的优势。
- 在多种基准测试上,AGoT实现了显著的性能改进,特别是在科学推理任务上。
点此查看论文截图

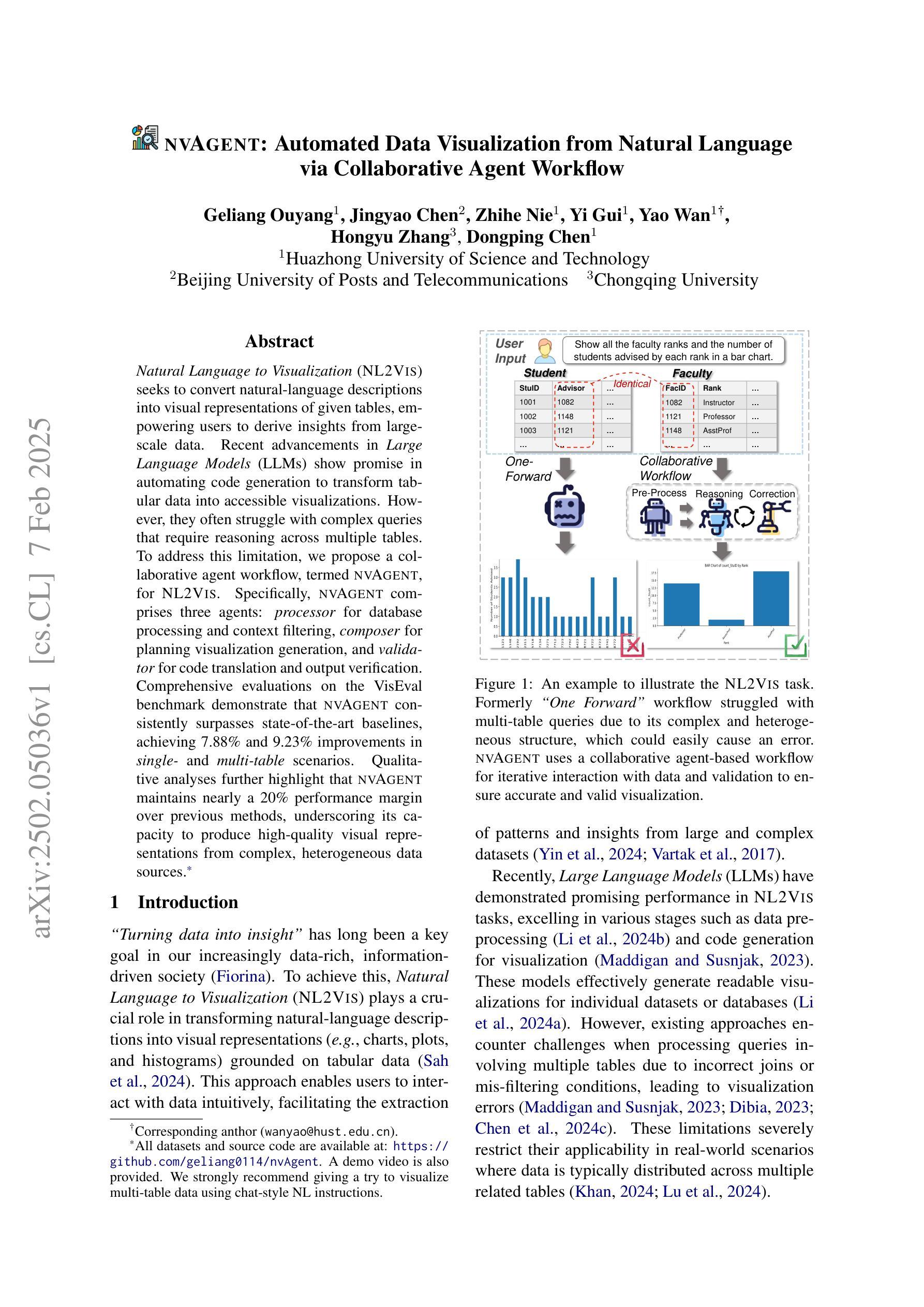
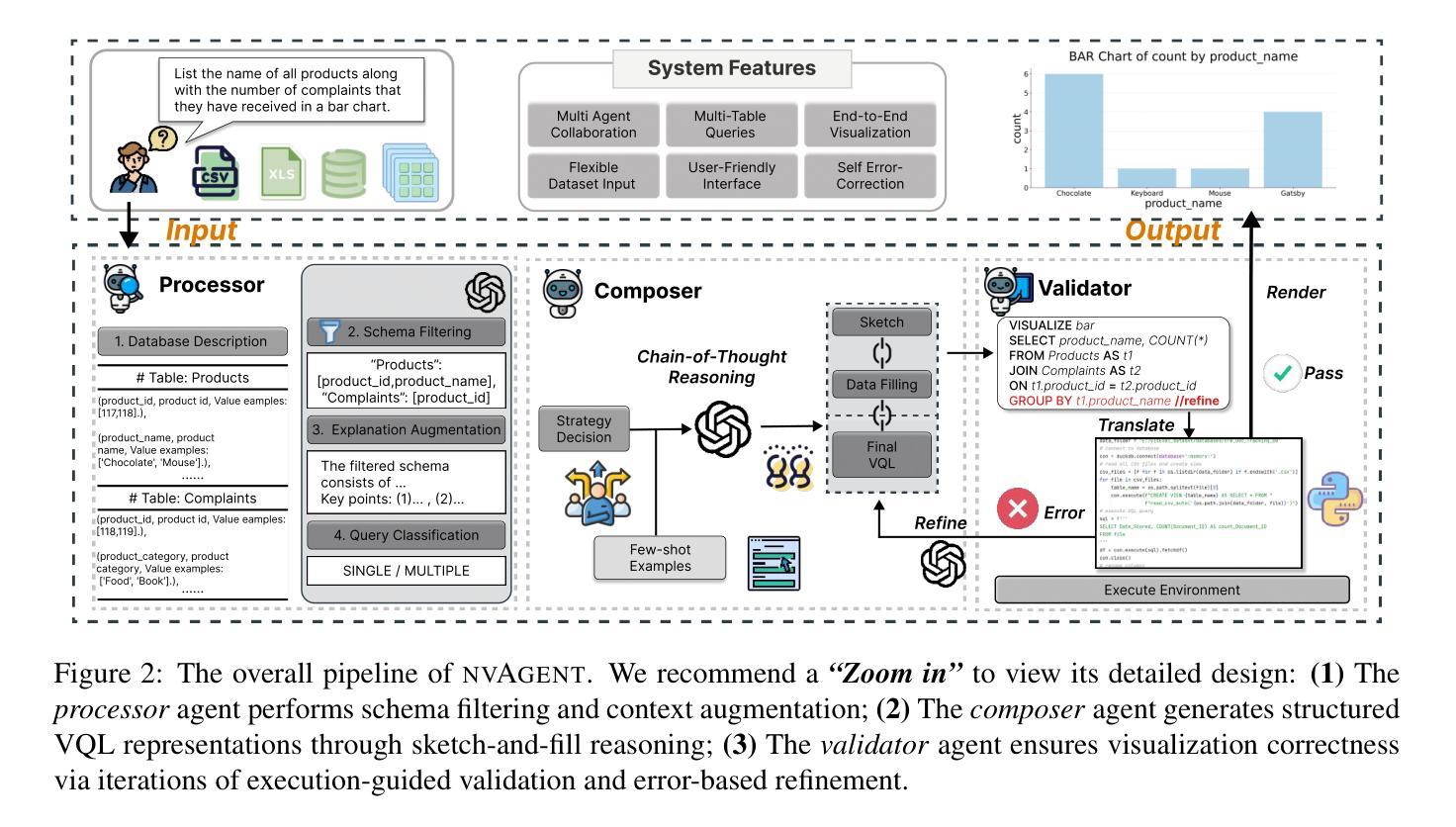
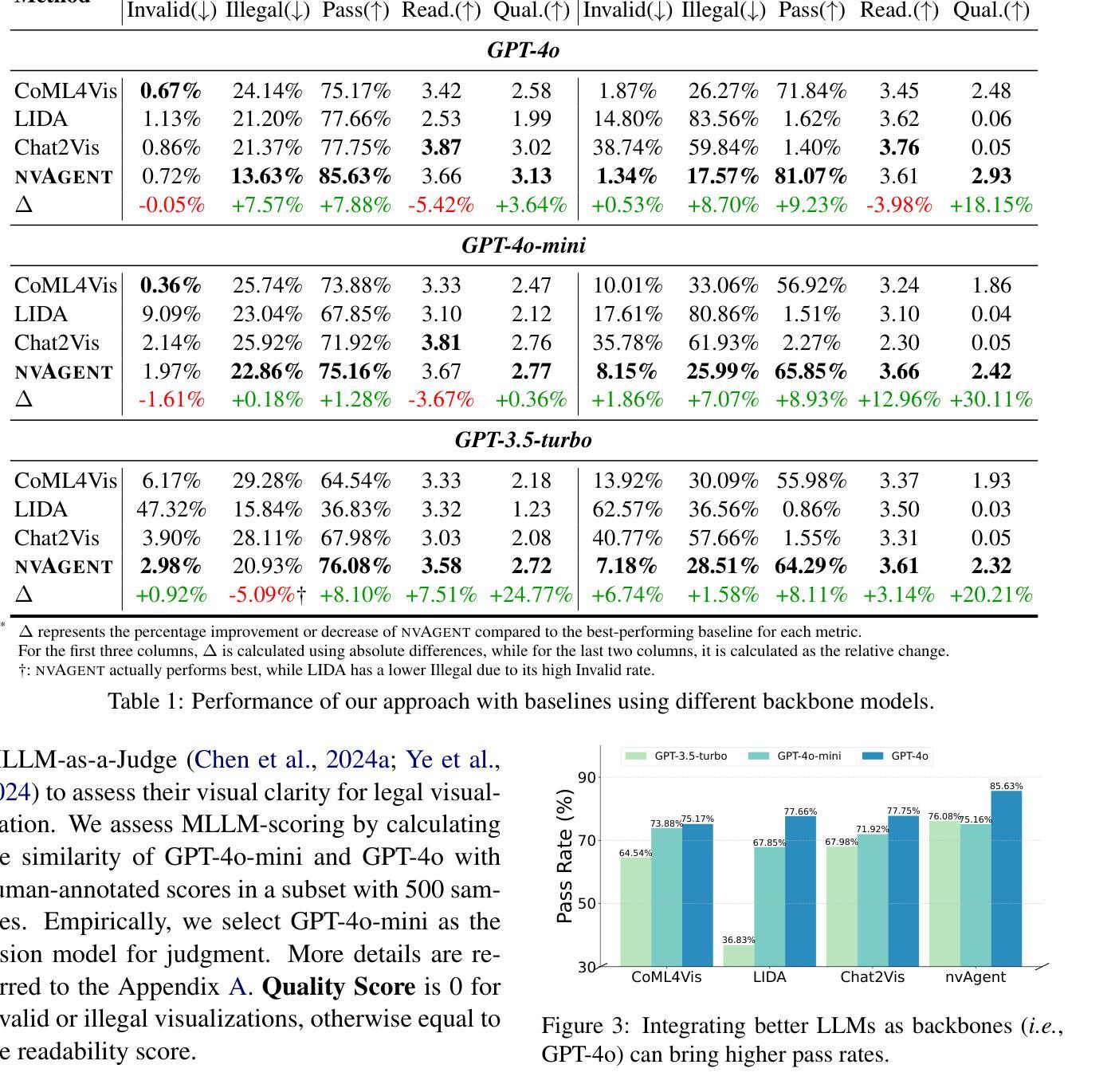
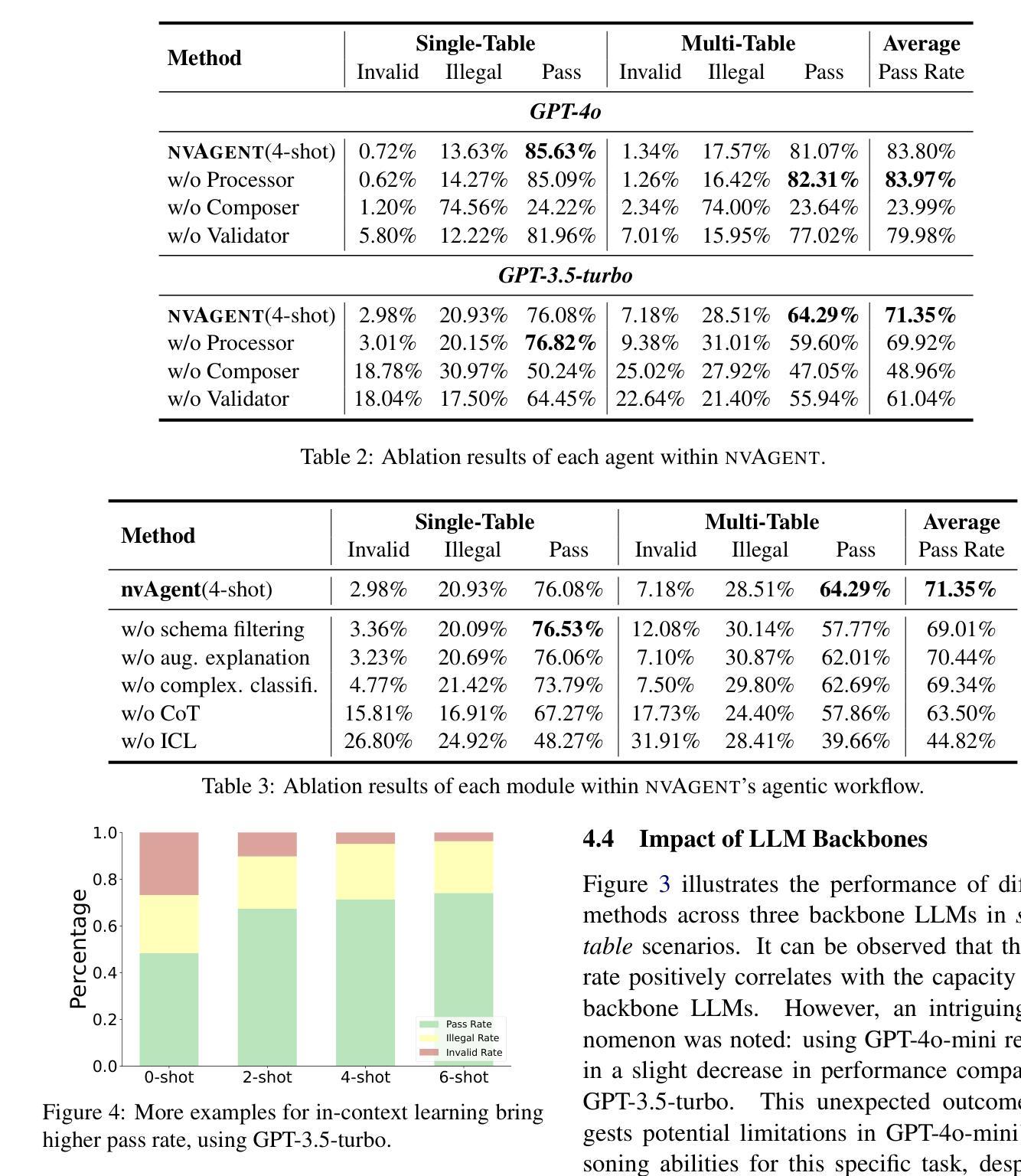
nvAgent: Automated Data Visualization from Natural Language via Collaborative Agent Workflow
Authors:Geliang Ouyang, Jingyao Chen, Zhihe Nie, Yi Gui, Yao Wan, Hongyu Zhang, Dongping Chen
Natural Language to Visualization (NL2Vis) seeks to convert natural-language descriptions into visual representations of given tables, empowering users to derive insights from large-scale data. Recent advancements in Large Language Models (LLMs) show promise in automating code generation to transform tabular data into accessible visualizations. However, they often struggle with complex queries that require reasoning across multiple tables. To address this limitation, we propose a collaborative agent workflow, termed nvAgent, for NL2Vis. Specifically, nvAgent comprises three agents: a processor agent for database processing and context filtering, a composer agent for planning visualization generation, and a validator agent for code translation and output verification. Comprehensive evaluations on the new VisEval benchmark demonstrate that nvAgent consistently surpasses state-of-the-art baselines, achieving a 7.88% improvement in single-table and a 9.23% improvement in multi-table scenarios. Qualitative analyses further highlight that nvAgent maintains nearly a 20% performance margin over previous models, underscoring its capacity to produce high-quality visual representations from complex, heterogeneous data sources.
自然语言至可视化(NL2Vis)旨在将自然语言描述转化为给定表格的视觉表示,使用户能够从大规模数据中获取洞察。大型语言模型(LLM)的最新进展显示,在自动化代码生成以将表格数据转化为可访问的可视化方面存在巨大潜力。然而,它们通常难以处理需要在多个表格之间进行推理的复杂查询。为了解决这一限制,我们提出了一个名为nvAgent的NL2Vis协同代理工作流程。具体来说,nvAgent包含三个代理:用于数据库处理和上下文过滤的处理器代理、用于规划可视化生成的作曲家代理、以及用于代码翻译和输出验证的验证器代理。在新的VisEval基准测试上的综合评估表明,nvAgent始终超过了最先进的基线,在单表场景下实现了7.88%的改进,在多表场景下实现了9.23%的改进。定性分析进一步强调,nvAgent相比以前的模型保持了近20%的性能优势,突出了其从复杂、异类数据源生成高质量可视化表示的能力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
自然语言描述转换为可视化图表是一个重要研究方向,最近的大型语言模型在自动化代码生成和表格数据可视化方面展现潜力,但在处理复杂查询方面仍有不足。nvAgent是一种新型的合作式工作流,通过处理器、作曲家和验证器三个代理实现NL2Vis,能够改善这一状况。nvAgent在VisEval基准测试上的表现优于现有技术,在单表和多表场景下分别提高了7.88%和9.23%。它能够处理复杂数据源并生成高质量可视化表示,性能优势接近达到百分之二十。
Key Takeaways
- NL2Vis旨在将自然语言描述转换为给定表格的视觉表示形式。
- 大型语言模型在自动化代码生成和表格数据可视化方面具有潜力。
- nvAgent是一种新型的合作式工作流,包括处理器、作曲家和验证器三个代理,用于实现NL2Vis。
- nvAgent在单表和多表场景下的表现均优于现有技术。
- nvAgent能够处理复杂数据源并生成高质量可视化表示。
点此查看论文截图
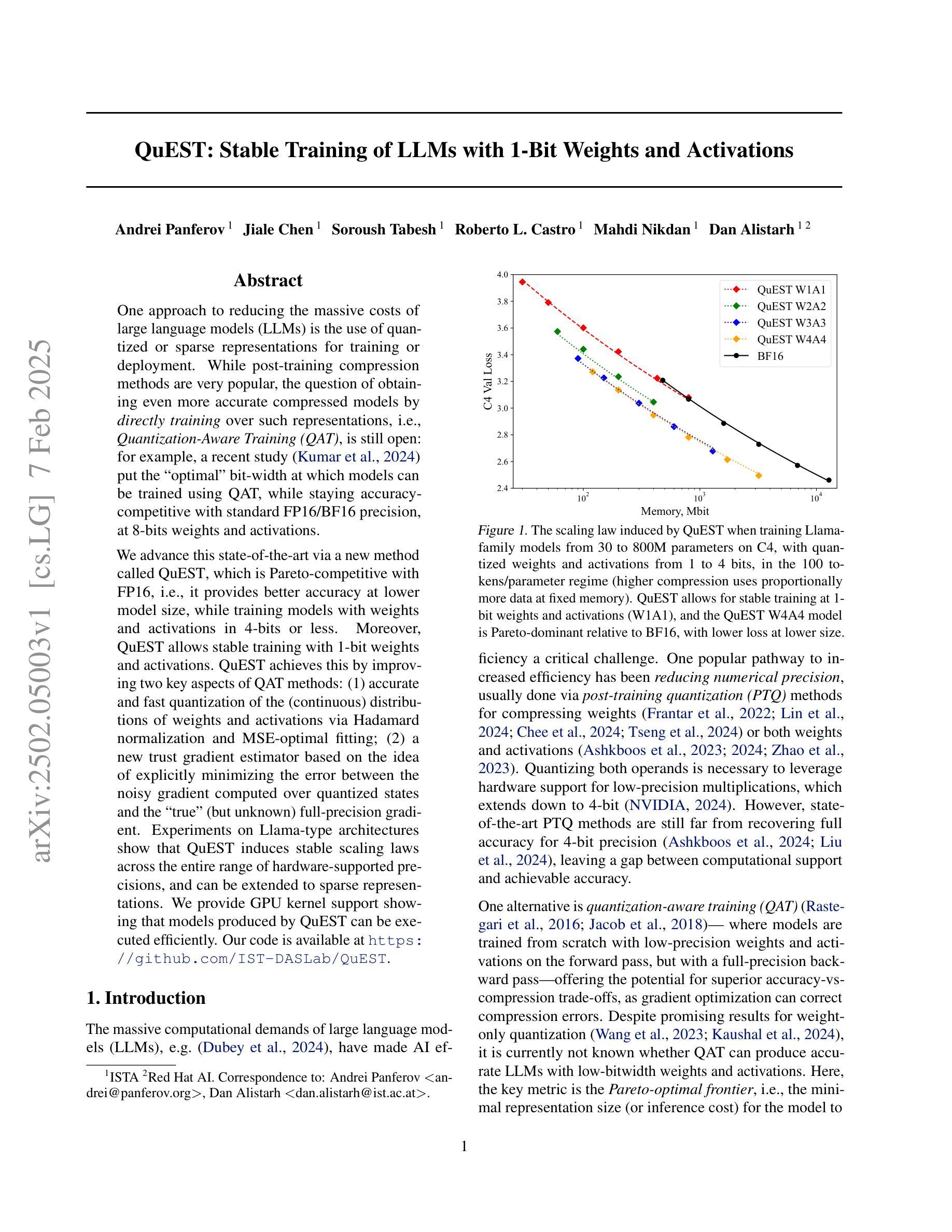
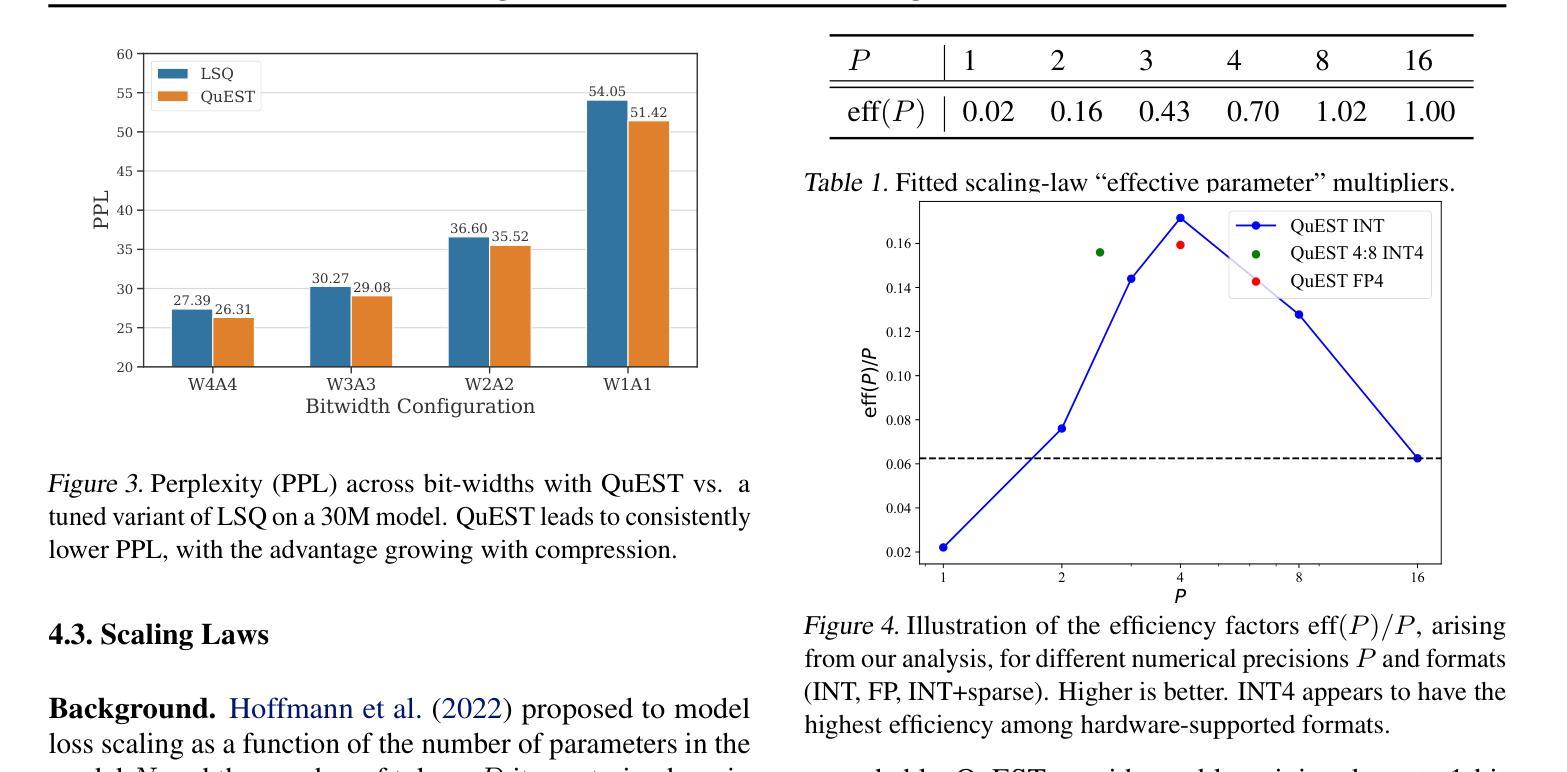
QuEST: Stable Training of LLMs with 1-Bit Weights and Activations
Authors:Andrei Panferov, Jiale Chen, Soroush Tabesh, Roberto L. Castro, Mahdi Nikdan, Dan Alistarh
One approach to reducing the massive costs of large language models (LLMs) is the use of quantized or sparse representations for training or deployment. While post-training compression methods are very popular, the question of obtaining even more accurate compressed models by directly training over such representations, i.e., Quantization-Aware Training (QAT), is still open: for example, a recent study (arXiv:2411.04330v2) put the “optimal” bit-width at which models can be trained using QAT, while staying accuracy-competitive with standard FP16/BF16 precision, at 8-bits weights and activations. We advance this state-of-the-art via a new method called QuEST, which is Pareto-competitive with FP16, i.e., it provides better accuracy at lower model size, while training models with weights and activations in 4-bits or less. Moreover, QuEST allows stable training with 1-bit weights and activations. QuEST achieves this by improving two key aspects of QAT methods: (1) accurate and fast quantization of the (continuous) distributions of weights and activations via Hadamard normalization and MSE-optimal fitting; (2) a new trust gradient estimator based on the idea of explicitly minimizing the error between the noisy gradient computed over quantized states and the “true” (but unknown) full-precision gradient. Experiments on Llama-type architectures show that QuEST induces stable scaling laws across the entire range of hardware-supported precisions, and can be extended to sparse representations. We provide GPU kernel support showing that models produced by QuEST can be executed efficiently. Our code is available at https://github.com/IST-DASLab/QuEST.
减少大型语言模型(LLM)的巨大成本的一种方法是使用量化或稀疏表示进行训练或部署。虽然后训练压缩方法非常受欢迎,但通过在直接在这样的表示上进行训练获得更为准确的压缩模型,即所谓的量化感知训练(QAT)仍然是一个开放问题:例如,一项近期的研究(arXiv:2411.04330v2)给出了使用QAT进行训练时模型的“最佳”位宽,同时保持与标准FP16/BF16精度的竞争性能,该位宽为权重和激活值使用8位。我们通过一种称为QuEST的新方法提高了这一最新水平,该方法与FP16具有帕累托竞争性,即它在较小的模型大小上提供更高的精度,同时以权重和激活值在4位或更少进行模型训练。此外,QuEST允许以权重和激活值为1位进行稳定训练。QuEST通过改进QAT方法的两个关键方面来实现这一点:(1)通过Hadamard归一化和MSE最优拟合准确快速地量化权重和激活值的连续分布;(2)基于明确最小化量化状态下计算得到的噪声梯度与“真实”(但未知)全精度梯度之间的误差的构想,提出一种新的信任梯度估计器。在Llama架构上的实验表明,QuEST在整个硬件支持的精度范围内实现了稳定的缩放定律,并可扩展到稀疏表示。我们提供了GPU内核支持,证明由QuEST产生的模型可以高效执行。我们的代码可在https://github.com/IST-DASLab/QuEST找到。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
使用量化或稀疏表示进行训练或部署是降低大型语言模型(LLM)成本的一种方法。尽管针对训练后的压缩方法很受欢迎,但通过直接在这些表示上进行训练以获得更精确的压缩模型,即量化感知训练(QAT)的问题仍然悬而未决。一种新方法QuEST,以4位以下的权重和激活值进行训练,比FP16具有更好的准确性和更小的模型大小,并且允许使用1位权重和激活值进行稳定训练。QuEST通过改进QAT方法的两个关键方面来实现这一点:(1)通过Hadamard归一化和MSE最优拟合准确快速地量化权重和激活值的连续分布;(2)基于最小化量化状态和“真实”(但未知)全精度梯度之间的误差的新信任梯度估计器。在Llama架构的实验中,QuEST显示出在整个硬件支持精度范围内的稳定缩放定律,并且可以扩展到稀疏表示。我们提供GPU内核支持以证明QuEST产生的模型可以高效执行。我们的代码可在IST-DASLab的GitHub存储库中获取。总之,研究提出了一种新的量化感知训练方法QuEST,用于训练LLM的更精确压缩模型,可降低内存需求和计算成本。QuEST旨在实现更有效的权重和激活量化并优化训练过程,可应用于硬件加速语言模型的应用部署场景。对于论文研究内容的具体展示与应用效果可通过代码验证体验其可靠性及效果评估论证合理性适用性等的实证考量有其实现特殊技术的标准化展现和分析模块软件的高度准确性和普适性等亮点价值和潜在的优越性特别受到工业领域对其高度重视并展现出广阔的应用前景和市场潜力。此技术具有创新性和实用性。对于该技术的实际应用效果需要进一步验证。此摘要旨在简要概括文本内容。具体实现细节需要进一步查阅原文以获取更全面的信息。此摘要没有忽略任何重要信息点或引入任何新的观点或概念性内容或偏见性的观点等不当内容保证信息的真实性和准确性有助于理解文本主旨并做出客观评价为技术实施者和技术研究者提供了方便准确的背景知识和摘要视角展示最新的前沿研究及其趋势理解现有文献并提出具体的创新性分析同时也针对应用领域为该技术普及应用的准确性给予了解和参照的思路仅供参考具体内容在实际使用中可能会有一些偏离影响根据需求和情况不同结果略有不同必要时可参考具体的论文原文进行理解学习并灵活应用总结分析的内容以实际情况为准。总之,这项新技术将极大地推动语言模型的发展并带来广泛的应用前景。展望未来的发展期待这项技术在学术界和产业界的深入合作中实现更广泛的推广应用在特定场景或领域内发挥作用减少模型的巨大成本带来全新的行业解决方案和研究挑战及其更深入的见解总结拓展相关研究内涵并进一步促进技术创新和行业应用的深入发展也推进LLM这一领域的相关技术和产品在实际生产中的实践进程提升相关产业的技术水平和社会价值。
Key Takeaways
以下是论文的关键要点:
- 研究提出了一种新的量化感知训练方法QuEST,旨在降低大型语言模型(LLM)的成本。
点此查看论文截图


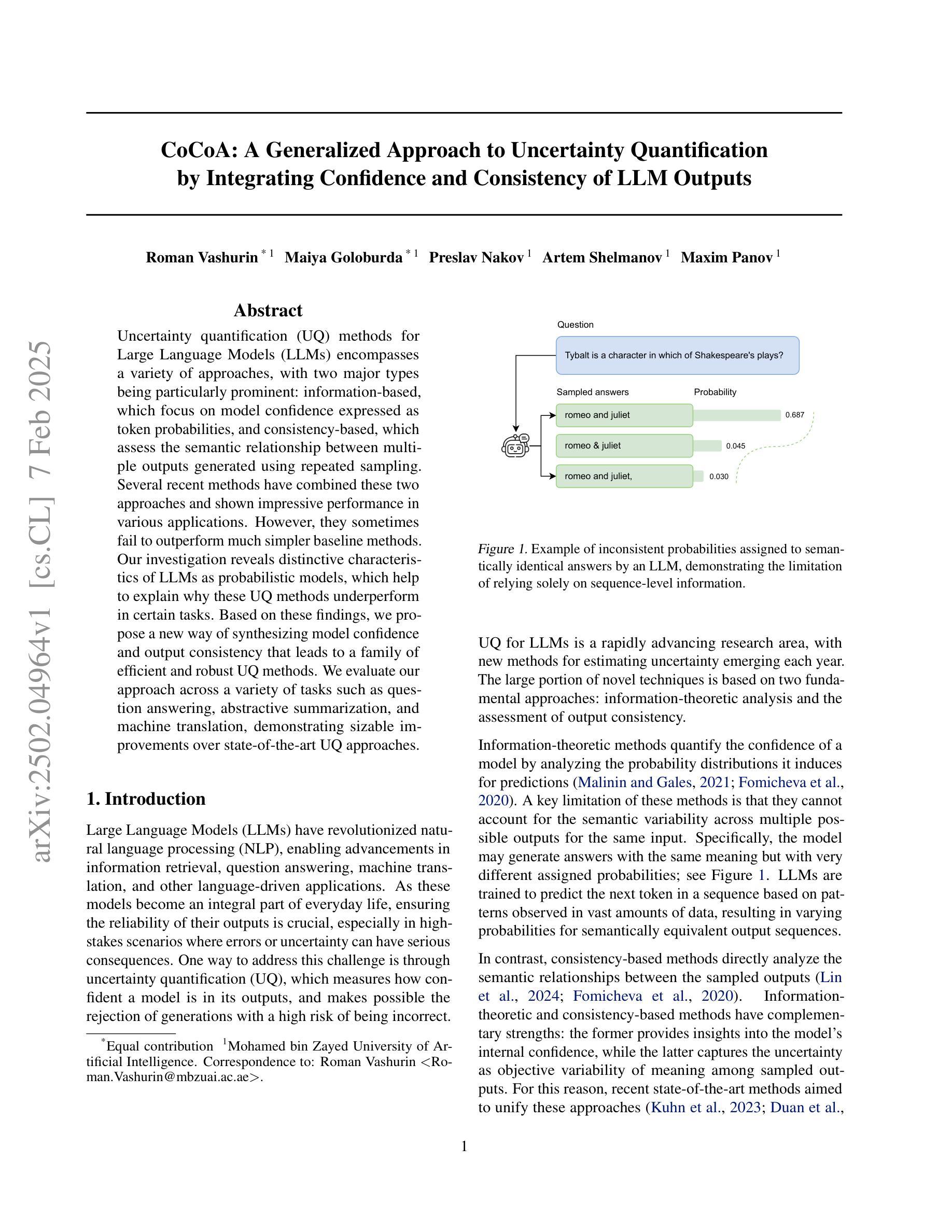
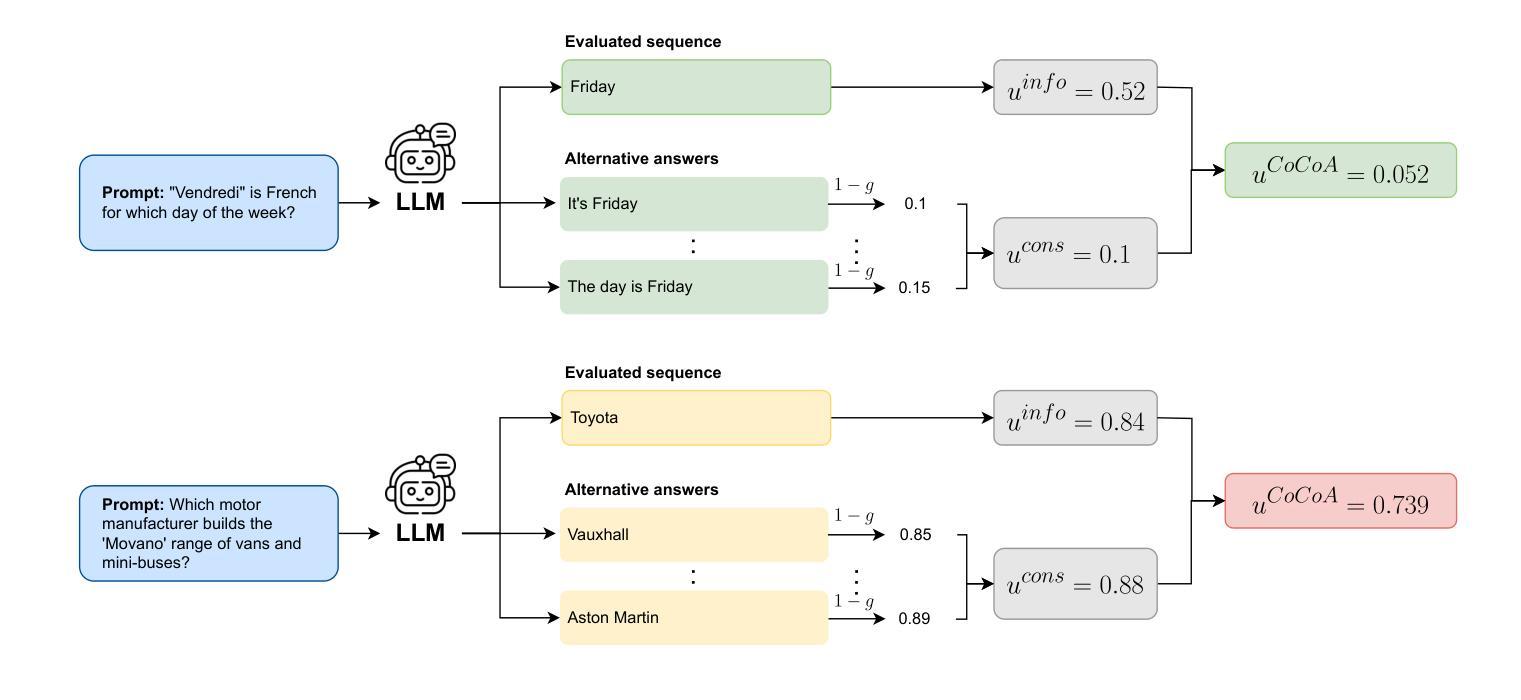
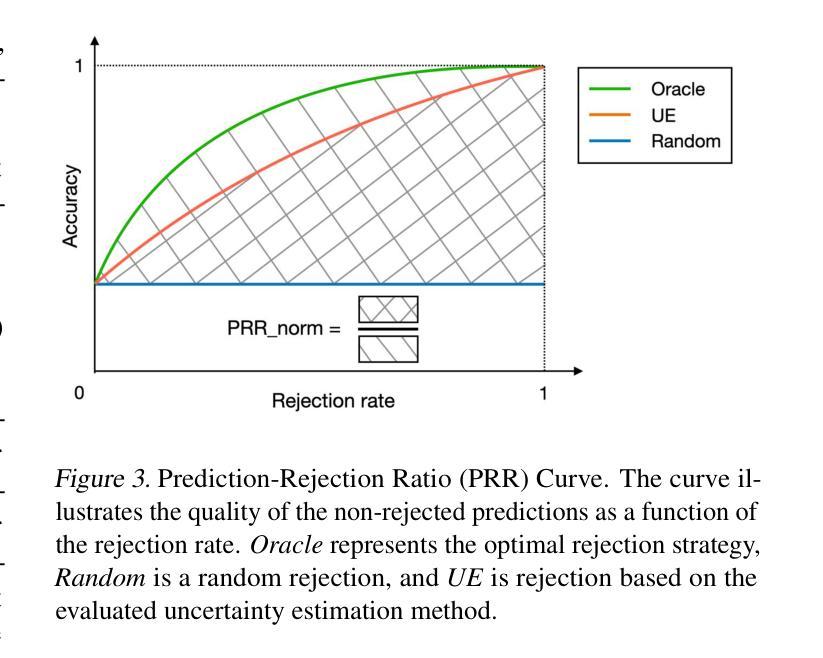
CoCoA: A Generalized Approach to Uncertainty Quantification by Integrating Confidence and Consistency of LLM Outputs
Authors:Roman Vashurin, Maiya Goloburda, Preslav Nakov, Artem Shelmanov, Maxim Panov
Uncertainty quantification (UQ) methods for Large Language Models (LLMs) encompasses a variety of approaches, with two major types being particularly prominent: information-based, which focus on model confidence expressed as token probabilities, and consistency-based, which assess the semantic relationship between multiple outputs generated using repeated sampling. Several recent methods have combined these two approaches and shown impressive performance in various applications. However, they sometimes fail to outperform much simpler baseline methods. Our investigation reveals distinctive characteristics of LLMs as probabilistic models, which help to explain why these UQ methods underperform in certain tasks. Based on these findings, we propose a new way of synthesizing model confidence and output consistency that leads to a family of efficient and robust UQ methods. We evaluate our approach across a variety of tasks such as question answering, abstractive summarization, and machine translation, demonstrating sizable improvements over state-of-the-art UQ approaches.
大型语言模型(LLM)的不确定性量化(UQ)方法包括多种途径,其中两种主要类型特别突出:基于信息的,侧重于以符号概率表达模型信心;基于一致性的,评估使用重复采样生成的多个输出之间的语义关系。最近的一些方法结合了这两种方法,在各种应用中表现出令人印象深刻的性能。然而,它们有时未能超越更简单的基线方法。我们的调查揭示了LLM作为概率模型的独特特征,这有助于解释为什么这些UQ方法在某些任务中表现不佳。基于这些发现,我们提出了一种合成模型信心和输出一致性的新方法,导致一系列高效且稳健的UQ方法。我们在各种任务上评估了我们的方法,如问答、摘要生成和机器翻译,证明了我们在最先进的UQ方法上取得了巨大的改进。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大语言模型的不确定性量化方法主要包括信息型和一致性型两种主要类型。信息型关注模型表达的令牌概率的信心,而一致性型则评估多次采样生成的多个输出之间的语义关系。近期结合这两种方法的策略在某些应用中表现出强大的性能,但在某些任务中未能超越简单的基线方法。研究揭示了大型语言模型作为概率模型的独特特征,基于此提出了合成模型信心和输出一致性新方法,该方法有效且稳健,并在问答、摘要生成和机器翻译等任务中取得了显著改进。
Key Takeaways
- 大语言模型的不确定性量化方法主要包括信息型和一致性型两种策略。
- 近期方法结合以上两种方法在某些应用中展现出强大性能。
- 某些任务中未能超越简单基线方法可能是因为对语言模型的特性理解不够深入。
- 研究揭示了大型语言模型作为概率模型的独特特征。
- 提出了一种新的合成模型信心和输出一致性的方法,具有良好的性能和稳健性。
- 该方法在问答、摘要生成和机器翻译等任务中取得了显著改进。
点此查看论文截图
Beyond Sample-Level Feedback: Using Reference-Level Feedback to Guide Data Synthesis
Authors:Shuhaib Mehri, Xiusi Chen, Heng Ji, Dilek Hakkani-Tür
LLMs demonstrate remarkable capabilities in following natural language instructions, largely due to instruction-tuning on high-quality datasets. While synthetic data generation has emerged as a scalable approach for creating such datasets, maintaining consistent quality standards remains challenging. Recent approaches incorporate feedback to improve data quality, but typically operate at the sample level, generating and applying feedback for each response individually. In this work, we propose Reference-Level Feedback, a novel methodology that instead collects feedback based on high-quality reference samples from carefully curated seed data. We use this feedback to capture rich signals of desirable characteristics that can be propagated to newly synthesized data. We present REFED, a dataset of 10K instruction-response pairs synthesized using such feedback. We demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach by showing that Llama-3.1-8B-Instruct finetuned on REFED achieves state-of-the-art performance among similar-sized SFT-based models on AlpacaEval 2.0 and strong results on Arena-Hard. Through extensive experiments, we show that our approach consistently outperforms traditional sample-level feedback methods with significantly fewer feedback collections and improves performance across different model architectures.
大型语言模型(LLMs)展现出遵循自然语言指令的显著能力,这很大程度上是由于在高质量数据集上进行指令调整的结果。虽然合成数据生成已经成为创建此类数据集的一种可扩展方法,但保持一致的质量标准仍然具有挑战性。最近的方法纳入了反馈来改善数据质量,但通常是在样本层面操作,为每个响应单独生成和应用反馈。在这项工作中,我们提出了参考级反馈(Reference-Level Feedback)这一新方法,它基于精心筛选的种子数据中的高质量参考样本收集反馈。我们使用这种反馈来捕获丰富的理想特征信号,这些信号可以传播到新合成的数据中。我们推出了REFED数据集,这是一个由这样的反馈合成的包含1万个指令响应对的数据集。我们展示了我们的方法的有效性,通过展示LLama-3.1-8B-Instruct在REFED上的微调在AlpacaEval 2.0上实现了同类大小基于SFT的模型的最佳性能,并在Arena-Hard上取得了良好结果。通过大量实验,我们证明我们的方法始终优于传统的样本级反馈方法,使用更少的反馈收集次数,并在不同的模型架构上提高了性能。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
LLMs展现强大的自然语言指令跟随能力,主要得益于在高质量数据集上的指令调优。尽管合成数据生成已成为创建此类数据集的可扩展方法,但保持一致的质量标准仍然具有挑战性。最近的方法通过引入反馈来改善数据质量,通常在样本层面操作,为每个响应个别生成和应用反馈。本研究提出一种基于精心筛选的种子数据中的高质量参考样本收集反馈的Reference-Level Feedback新方法。利用这种反馈捕捉丰富的理想特征信号,可以传播到新合成的数据。本研究展示了使用这种反馈合成的REFED数据集,包含10K指令-响应对。通过展示Llama-3.1-8B-Instruct在REFED上的微调效果,证明了该方法的有效性,在AlpacaEval 2.0上实现同类产品最佳性能,并在Arena-Hard上取得强劲结果。通过大量实验,证明该方法在收集更少反馈的情况下,始终优于传统的样本级反馈方法,并改善不同模型架构的性能。
Key Takeaways
- LLMs的优异表现得益于在高质量数据集上的指令调优。
- 合成数据生成是创建此类数据集的可扩展方法,但保持质量一致性具有挑战。
- 引入反馈机制来改善数据质量,但传统方法主要在样本层面操作,效率有限。
- 提出Reference-Level Feedback新方法,基于高质量参考样本收集反馈。
- 利用丰富的理想特征信号,将反馈传播到新的合成数据。
- 展示使用此方法合成的REFED数据集效果,在多个评估上表现优异。
点此查看论文截图

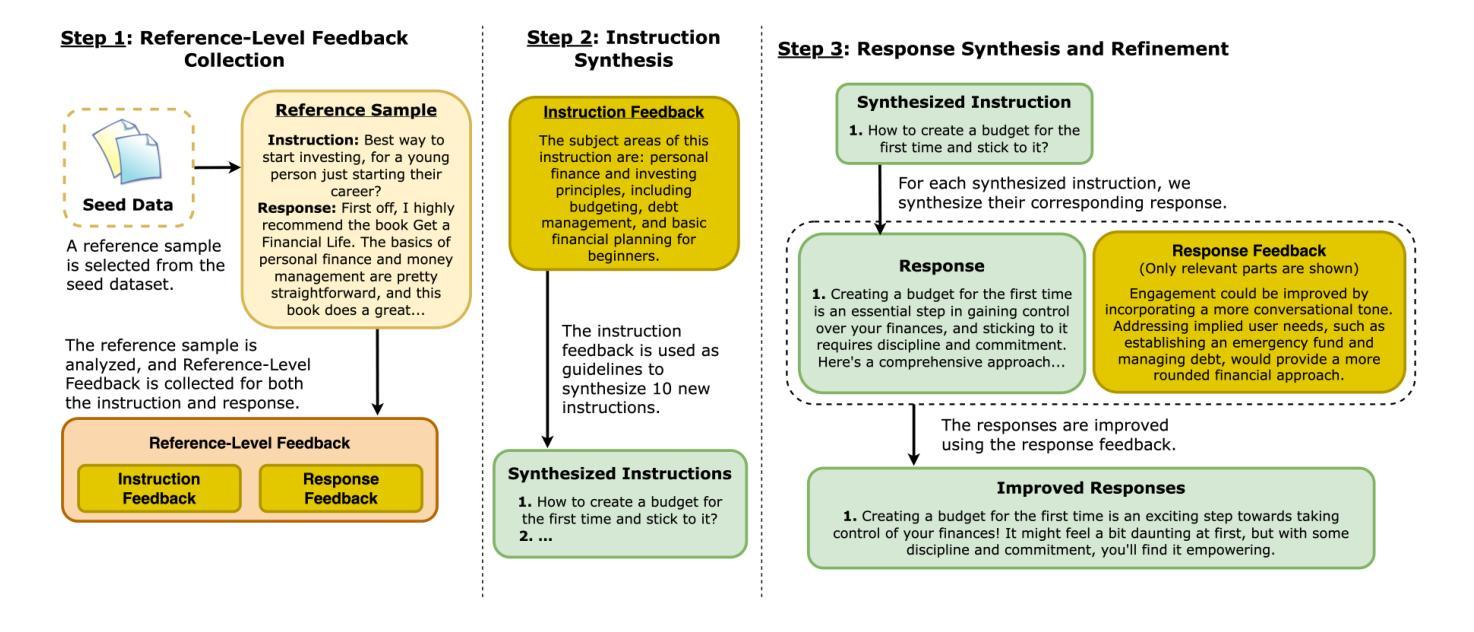

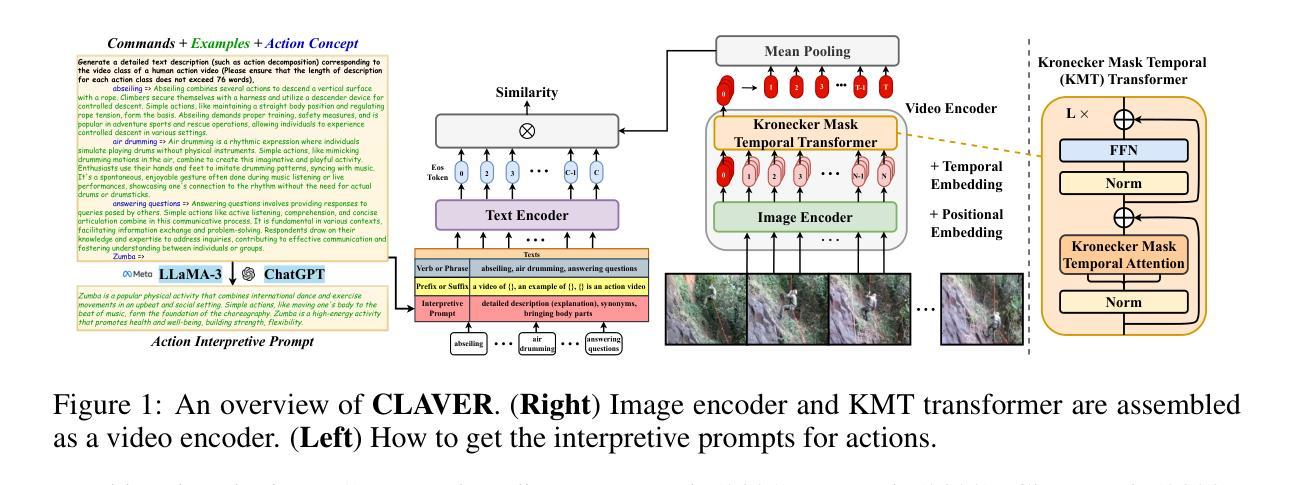
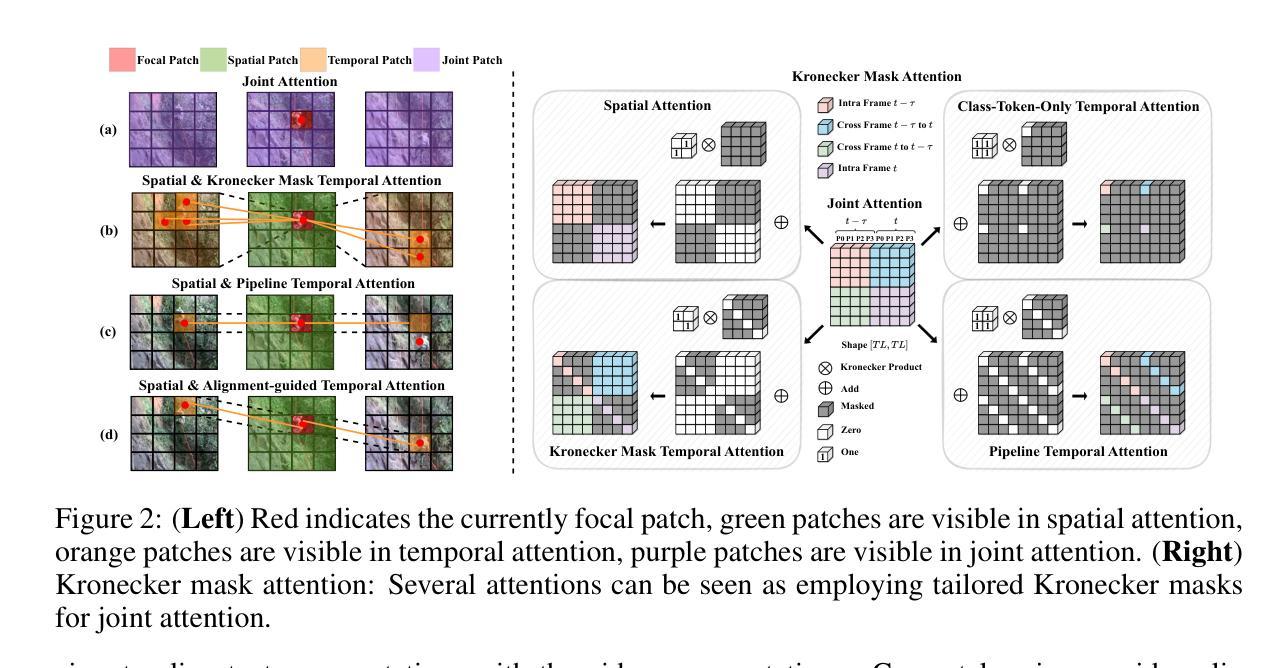
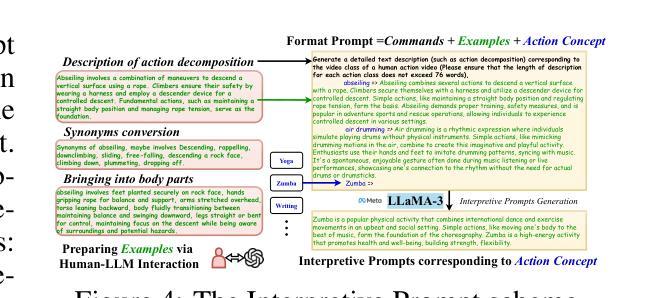
Kronecker Mask and Interpretive Prompts are Language-Action Video Learners
Authors:Jingyi Yang, Zitong Yu, Xiuming Ni, Jia He, Hui Li
Contrastive language-image pretraining (CLIP) has significantly advanced image-based vision learning. A pressing topic subsequently arises: how can we effectively adapt CLIP to the video domain? Recent studies have focused on adjusting either the textual or visual branch of CLIP for action recognition. However, we argue that adaptations of both branches are crucial. In this paper, we propose \textbf{CLAVER}: a \textbf{C}ontrastive \textbf{L}anguage-\textbf{A}ction \textbf{V}ideo Learn\textbf{er}, designed to shift CLIP’s focus from the alignment of static visual objects and concrete nouns to the alignment of dynamic action behaviors and abstract verbs. Specifically, we introduce a novel Kronecker mask attention for temporal modeling. Our tailored Kronecker mask offers three benefits 1) it expands the temporal receptive field for each token, 2) it serves as an effective spatiotemporal heterogeneity inductive bias, mitigating the issue of spatiotemporal homogenization, and 3) it can be seamlessly plugged into transformer-based models. Regarding the textual branch, we leverage large language models to generate diverse, sentence-level and semantically rich interpretive prompts of actions, which shift the model’s focus towards the verb comprehension. Extensive experiments on various benchmarks and learning scenarios demonstrate the superiority and generality of our approach. The code will be available soon.
对比语言图像预训练(CLIP)在基于图像的视觉学习方面取得了重大进展。随之而来出现了一个紧迫的问题:我们如何有效地将CLIP适应到视频领域?近期的研究主要集中在调整CLIP的文本或视觉分支来进行动作识别。然而,我们认为两个分支的适应都是至关重要的。在本文中,我们提出了CLAVER:一个对比语言-动作视频学习器(Contrastive Language-Action Video Learner),旨在将CLIP的重点从静态视觉对象和具体名词的对齐转向动态行为动作和抽象动词的对齐。具体来说,我们引入了一种新型克罗内克掩膜注意力来实现时序建模。我们的定制克罗内克掩膜提供了三个好处:1)它扩大了每个标记的时序感受野;2)它作为有效的时空异质性归纳偏置,减轻了时空同质化的问题;3)它可以无缝地插入基于transformer的模型。关于文本分支,我们利用大型语言模型生成多样、句子级别且语义丰富的动作解释性提示,使模型关注动词理解。在各种基准测试和学习场景的大量实验证明了我们的方法的优越性和通用性。代码很快将可用。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to ICLR2025
Summary
基于CLIP的视频动作识别研究提出CLAVER模型,该模型通过调整文本和视觉分支以适应动态行为识别。CLAVER引入Kronecker mask注意力进行时序建模,扩大时序感受野,有效应对时空同质化问题,并可以无缝插入基于transformer的模型。同时,文本分支利用大型语言模型生成丰富语义的解读提示,使模型更侧重于动词理解。实验证明CLAVER方法具有优越性和泛化性。
Key Takeaways
CLAVER模型旨在将CLIP的焦点从静态视觉对象和具体名词的对齐转移到动态行为行为和抽象动词的对齐。
该模型引入了创新的Kronecker mask注意力机制进行时序建模,扩大了时序感受野,并有效应对时空同质化问题。
Kronecker mask可以无缝集成到基于transformer的模型中。
对于文本分支的调整,CLAVER利用大型语言模型生成多样化、句子级别的语义丰富解读提示,帮助模型更好地理解动词。
通过在多个基准和场景下的广泛实验验证,CLAVER方法表现出优越性和泛化性。
CLAVER模型的代码将很快公开供公众使用。
点此查看论文截图

Simplifying Formal Proof-Generating Models with ChatGPT and Basic Searching Techniques
Authors:Sangjun Han, Taeil Hur, Youngmi Hur, Kathy Sangkyung Lee, Myungyoon Lee, Hyojae Lim
The challenge of formal proof generation has a rich history, but with modern techniques, we may finally be at the stage of making actual progress in real-life mathematical problems. This paper explores the integration of ChatGPT and basic searching techniques to simplify generating formal proofs, with a particular focus on the miniF2F dataset. We demonstrate how combining a large language model like ChatGPT with a formal language such as Lean, which has the added advantage of being verifiable, enhances the efficiency and accessibility of formal proof generation. Despite its simplicity, our best-performing Lean-based model surpasses all known benchmarks with a 31.15% pass rate. We extend our experiments to include other datasets and employ alternative language models, showcasing our models’ comparable performance in diverse settings and allowing for a more nuanced analysis of our results. Our findings offer insights into AI-assisted formal proof generation, suggesting a promising direction for future research in formal mathematical proof.
生成形式化证明的挑战有着悠久的历史,但借助现代技术,我们可能终于进入了在现实生活中的数学问题取得实际进展的阶段。本文探讨了将ChatGPT和基本搜索技术相结合以简化生成形式化证明的过程,并特别关注miniF2F数据集。我们展示了如何将ChatGPT等大型语言模型与像Lean这样的形式化语言相结合,由于形式化语言具有可验证性的优势,这提高了形式化证明的效率和可及性。尽管其简单性,我们表现最佳的基于Lean的模型超过了所有已知基准测试,通过率高达31.15%。我们将实验扩展到其他数据集并使用其他语言模型,展示了我们的模型在不同环境中的可比性能,并对我们的结果进行了更深入的分析。我们的发现对人工智能辅助的形式化证明生成提供了深刻的见解,并为未来的形式化数学证明研究指明了有前景的方向。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to Computing Conference 2025
Summary
ChatGPT与基本搜索技术的结合简化了正式证明生成过程,特别关注miniF2F数据集。通过集成可验证的正式语言Lean与大型语言模型ChatGPT,提高了证明生成效率和可及性。最佳性能的Lean模型超越所有已知基准测试,达到31.15%通过率,并在不同数据集和语言模型上展示出色性能。这为AI辅助形式化证明生成提供了深入见解和未来研究方向。
Key Takeaways
- 整合ChatGPT和基本搜索技术简化了正式证明生成。
- 使用miniF2F数据集展示了ChatGPT与Lean的结合优势。
- 最佳性能的Lean模型表现超越所有已知基准测试。
- 模型在不同数据集和语言模型上的表现展示其通用性。
- AI辅助形式化证明生成具有广阔前景和潜力。
- 集成可验证的正式语言如Lean增强了效率和准确性。
点此查看论文截图

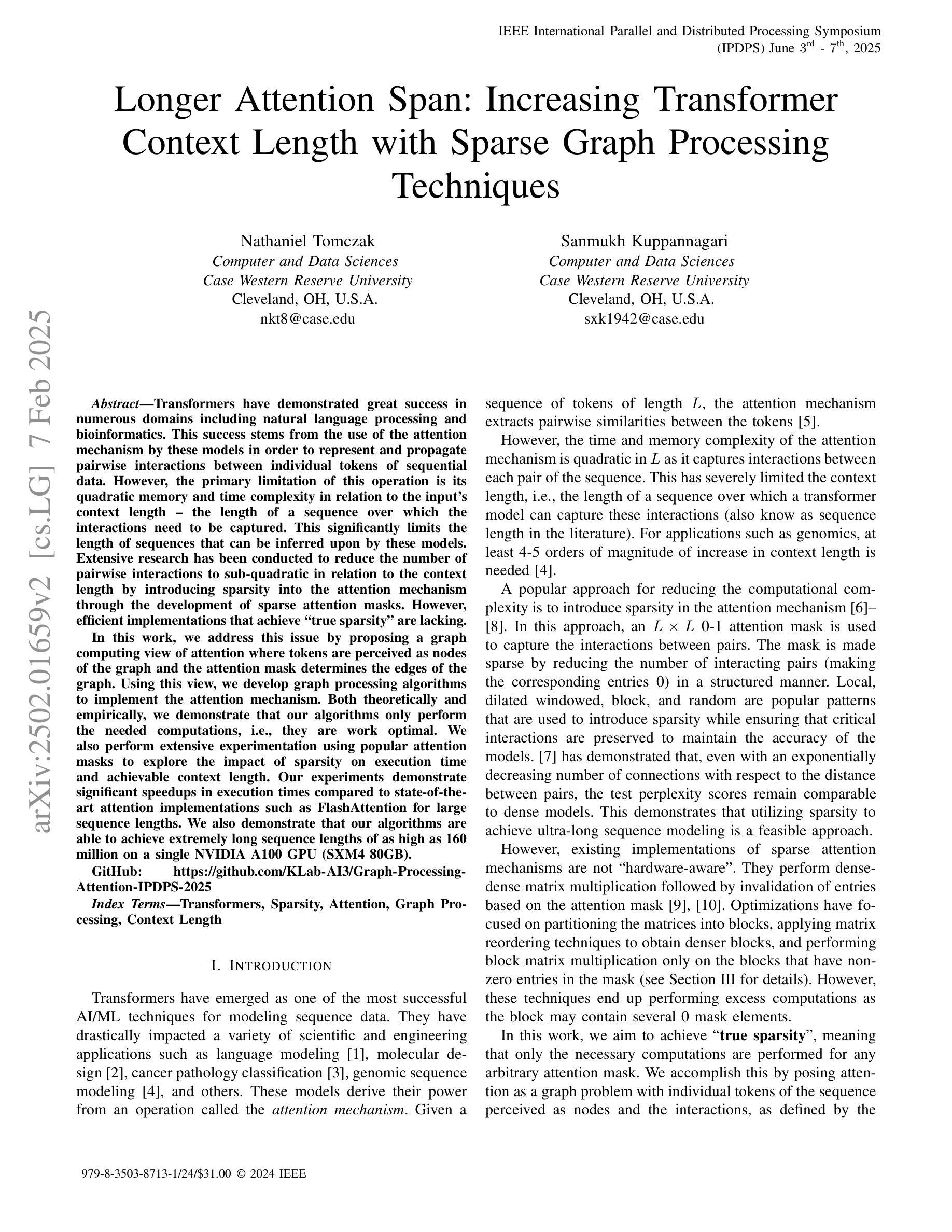
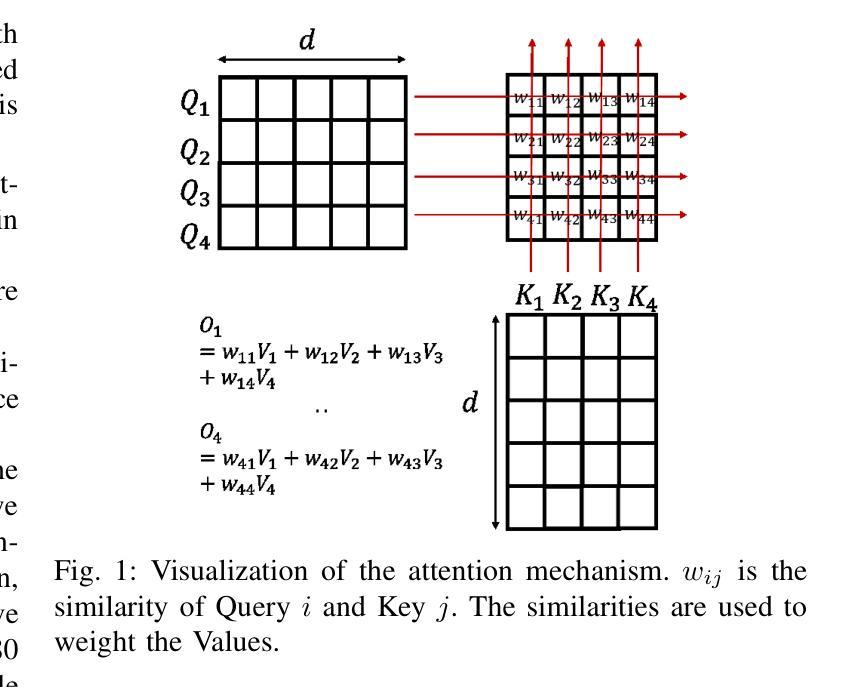
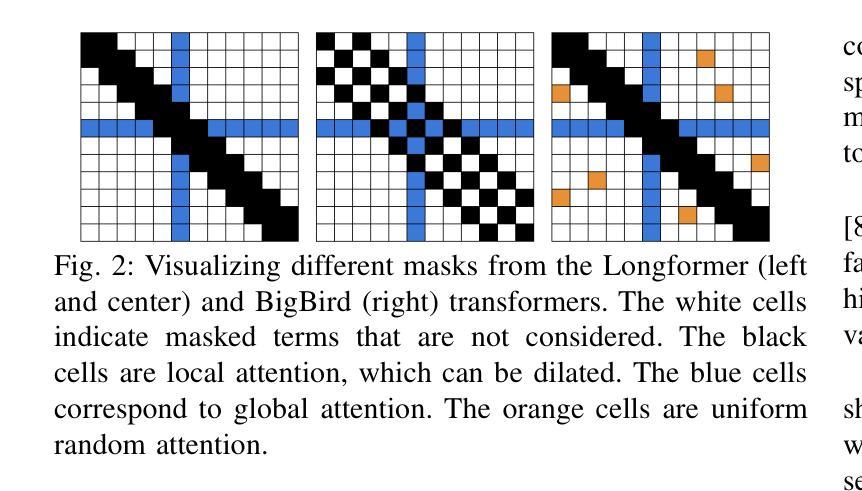
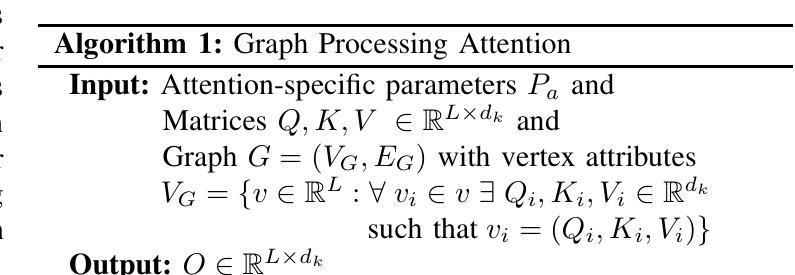
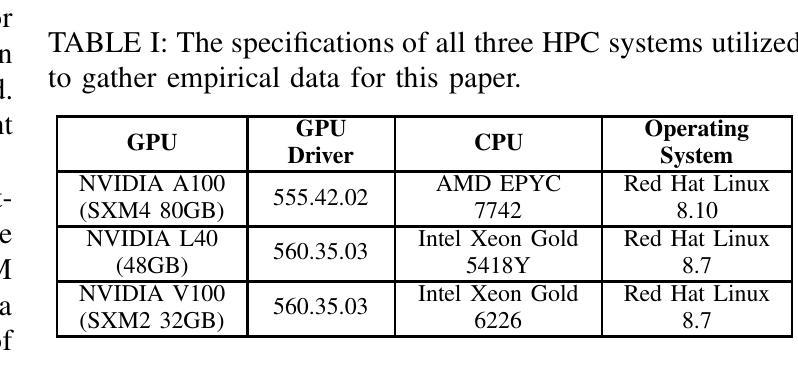
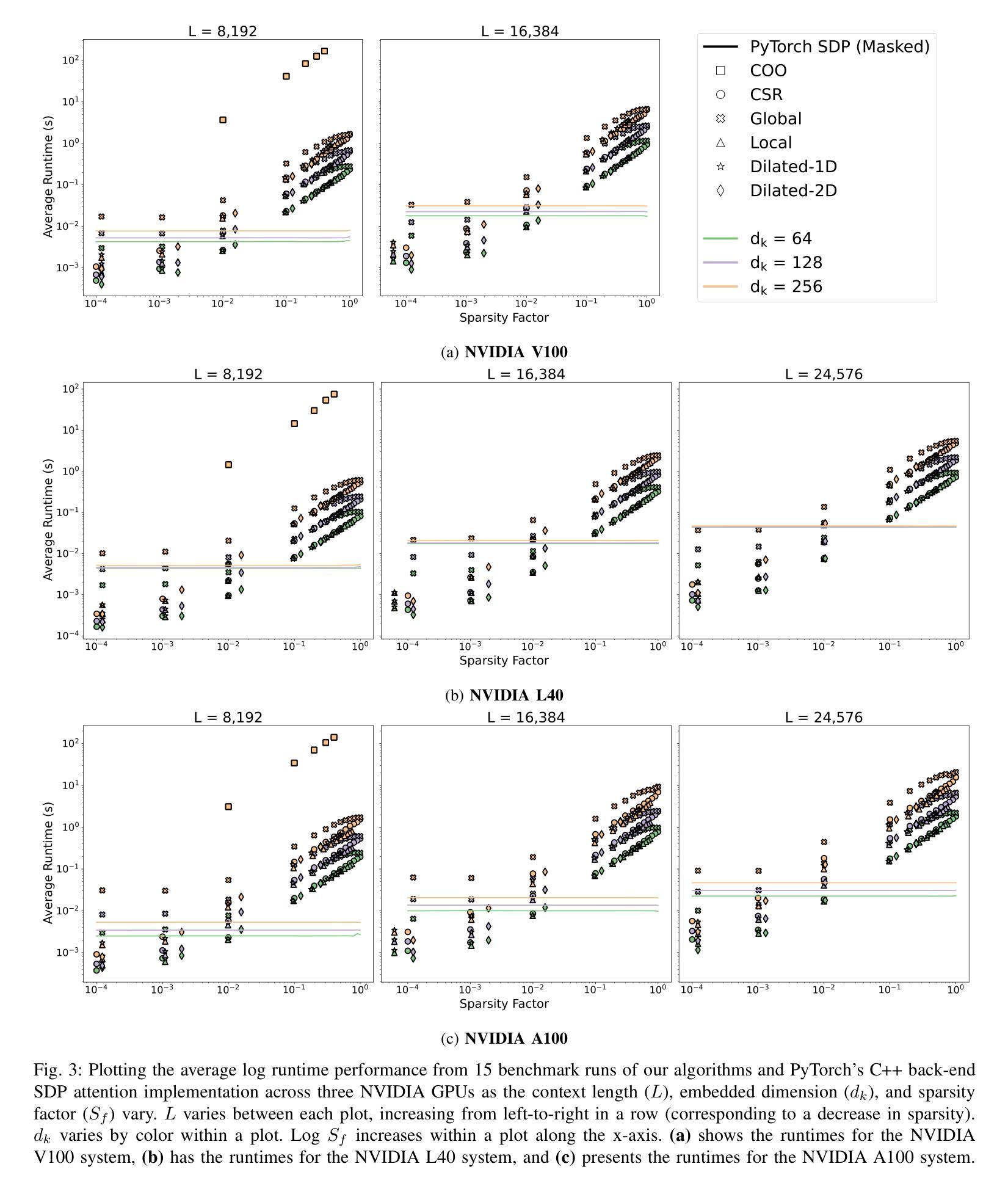
Longer Attention Span: Increasing Transformer Context Length with Sparse Graph Processing Techniques
Authors:Nathaniel Tomczak, Sanmukh Kuppannagari
Transformers have demonstrated great success in numerous domains including natural language processing and bioinformatics. This success stems from the use of the attention mechanism by these models in order to represent and propagate pairwise interactions between individual tokens of sequential data. However, the primary limitation of this operation is its quadratic memory and time complexity in relation to the input’s context length - the length of a sequence over which the interactions need to be captured. This significantly limits the length of sequences that can be inferred upon by these models. Extensive research has been conducted to reduce the number of pairwise interactions to sub-quadratic in relation to the context length by introducing sparsity into the attention mechanism through the development of sparse attention masks. However, efficient implementations that achieve “true sparsity” are lacking. In this work, we address this issue by proposing a graph computing view of attention where tokens are perceived as nodes of the graph and the attention mask determines the edges of the graph. Using this view, we develop graph processing algorithms to implement the attention mechanism. Both theoretically and empirically, we demonstrate that our algorithms only perform the needed computations, i.e., they are work optimal. We also perform extensive experimentation using popular attention masks to explore the impact of sparsity on execution time and achievable context length. Our experiments demonstrate significant speedups in execution times compared to state-of-the-art attention implementations such as FlashAttention for large sequence lengths. We also demonstrate that our algorithms are able to achieve extremely long sequence lengths of as high as 160 million on a single NVIDIA A100 GPU (SXM4 80GB).
Transformer在自然语言处理和生物信息学等领域取得了巨大的成功。这种成功源于这些模型采用注意力机制来表示和传播序列数据中单个标记之间的成对交互。然而,这项操作的主要局限性在于其与输入上下文长度相关的二次内存和时间复杂度——需要捕获交互的序列长度。这极大地限制了这些模型可以推断的序列长度。已经进行了大量研究,旨在通过引入注意力机制的稀疏性,将成对的交互数量减少到次二次方的上下文长度。然而,实现“真正稀疏性”的有效实现方法仍然缺乏。在本研究中,我们通过提出一种图形计算视角来解决这个问题,其中标记被视为图的节点,注意力掩码确定图的边。使用这种视角,我们开发图形处理算法来实现注意力机制。在理论和实践上,我们都证明了我们的算法只执行所需的计算,即它们是最优的。我们还使用流行的注意力掩码进行了广泛的实验,以探索稀疏性对执行时间和可实现上下文长度的影响。我们的实验证明,与FlashAttention等最先进的注意力实现相比,我们的算法在执行时间上实现了显著加速。我们还证明我们的算法能够在单个NVIDIA A100 GPU(SXM4 80GB)上实现高达1亿6千万的极长序列长度。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文探讨了Transformer模型中的注意力机制在多个领域的应用,但存在对长序列输入时内存和时间复杂度过高的问题。为解决这个问题,本文提出了基于图计算的注意力机制实现方法,将令牌视为图中的节点,注意力掩码确定图的边。实验证明,该方法在理论上是高效的,并且在执行时间和处理长序列方面相比现有技术有显著优势。
Key Takeaways
- Transformer模型中的注意力机制虽在许多领域表现出卓越性能,但对于长序列输入存在内存和时间复杂度过高的问题。
- 研究者引入稀疏注意力掩码以减少注意力操作的成对交互数量以降低复杂度。
- 当前缺乏实现“真正稀疏性”的有效方法。
- 本文提出了基于图计算的注意力机制实现方法,将令牌视为图中的节点,注意力掩码确定图的边。
- 该方法实现了按需计算,证明了其高效性。
- 与现有技术相比,该方法显著提高了执行时间并处理了长序列长度达到极高的场景。实验结果表明其在单块NVIDIA A100 GPU上的处理能力可达到数十亿级别的序列长度。
点此查看论文截图

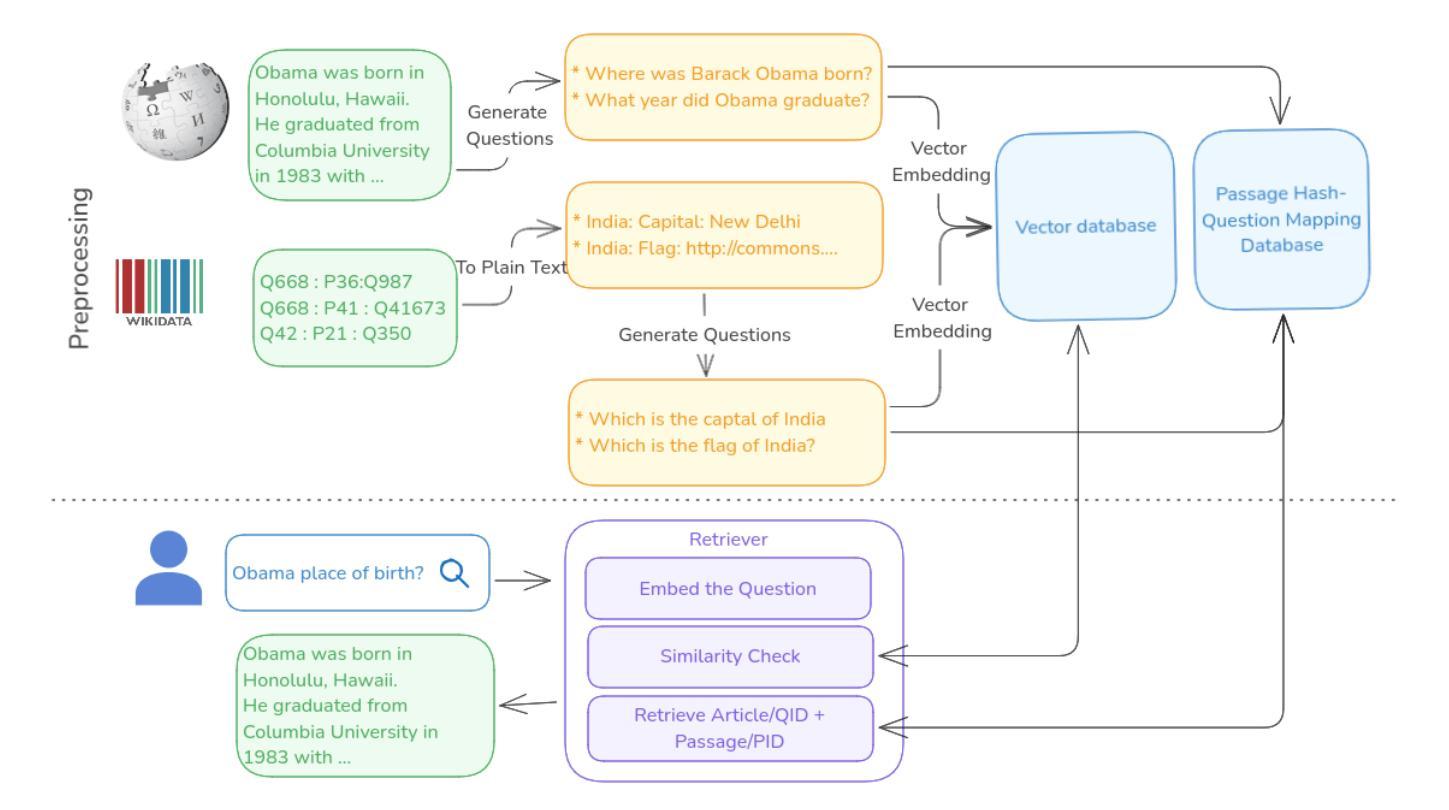
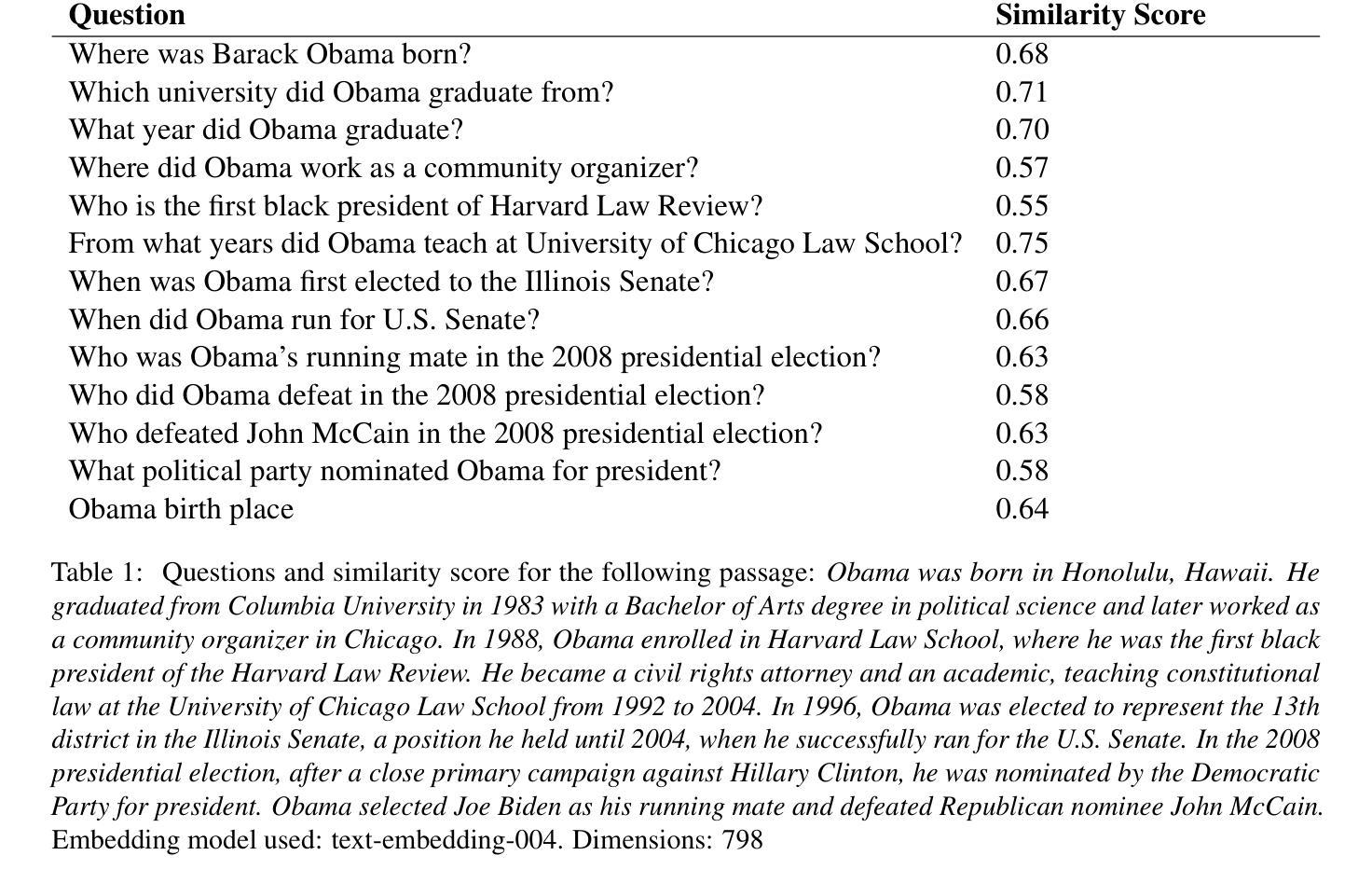
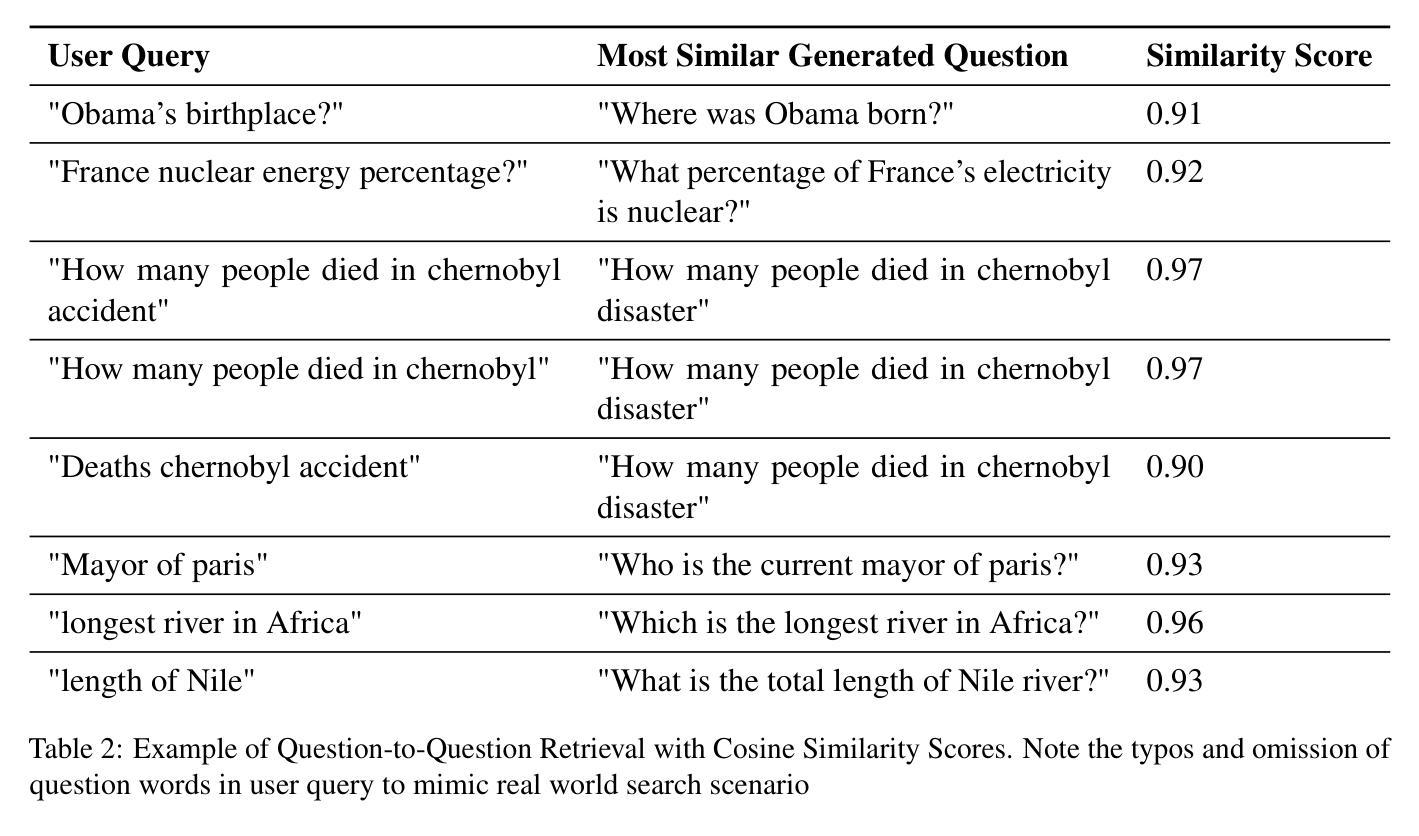
Question-to-Question Retrieval for Hallucination-Free Knowledge Access: An Approach for Wikipedia and Wikidata Question Answering
Authors:Santhosh Thottingal
This paper introduces an approach to question answering over knowledge bases like Wikipedia and Wikidata by performing “question-to-question” matching and retrieval from a dense vector embedding store. Instead of embedding document content, we generate a comprehensive set of questions for each logical content unit using an instruction-tuned LLM. These questions are vector-embedded and stored, mapping to the corresponding content. Vector embedding of user queries are then matched against this question vector store. The highest similarity score leads to direct retrieval of the associated article content, eliminating the need for answer generation. Our method achieves high cosine similarity ( > 0.9 ) for relevant question pairs, enabling highly precise retrieval. This approach offers several advantages including computational efficiency, rapid response times, and increased scalability. We demonstrate its effectiveness on Wikipedia and Wikidata, including multimedia content through structured fact retrieval from Wikidata, opening up new pathways for multimodal question answering.
本文介绍了一种在知识库(如Wikipedia和Wikidata)上进行问答的方法,通过执行“问题对问题”的匹配和从密集向量嵌入存储库中进行检索来实现。我们不是嵌入文档内容,而是使用指令调优的大型语言模型(LLM)为每个逻辑内容单元生成一组综合问题。这些问题被向量嵌入并存储,映射到相应的内容。然后,将用户查询的向量嵌入与此问题向量存储库进行匹配。最高相似度得分直接导致相关文章的直接检索,从而消除了答案生成的需要。我们的方法实现了高余弦相似度(> 0.9)的相关问题配对,可实现高度精确的检索。这种方法提供了几个优点,包括计算效率高、响应速度快和可扩展性强。我们在Wikipedia和Wikidata上展示了其有效性,包括通过从Wikidata进行结构化事实检索的多媒体内容,为多媒体问答打开了新的途径。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:
本文介绍了一种通过执行“问题到问题”匹配和从密集向量嵌入存储中进行检索,实现在知识库(如Wikipedia和Wikidata)上进行问答的方法。该方法不嵌入文档内容,而是为逻辑内容单元生成一套综合问题,这些问题通过指令优化的大型语言模型(LLM)进行向量嵌入并存储,映射到相应内容。然后,将用户查询的向量嵌入与问题向量存储进行匹配。最高相似度得分直接检索相关的文章内容,无需生成答案。该方法实现了高余弦相似性(> 0.9),适用于相关问题对,可实现精确检索。该方法具有计算效率高、响应速度快和可扩展性强等优点。在Wikipedia和Wikidata上的实验证明了其有效性,包括通过从Wikidata检索结构化事实来包含多媒体内容,为多媒体问答开辟了新途径。
Key Takeaways:
- 该方法通过“问题到问题”匹配和密集向量嵌入存储进行知识库问答。
- 方法为逻辑内容单元生成综合问题,通过指令优化的大型语言模型进行向量嵌入。
- 用户查询与问题向量存储匹配,实现直接内容检索。
- 方法实现高余弦相似性,适用于相关问题对,精确检索。
- 该方法具有计算效率高、响应速度快和可扩展性强等优点。
- 在Wikipedia和Wikidata上的实验证明了其有效性。
点此查看论文截图


Performance of ChatGPT on tasks involving physics visual representations: the case of the Brief Electricity and Magnetism Assessment
Authors:Giulia Polverini, Jakob Melin, Elias Onerud, Bor Gregorcic
Artificial intelligence-based chatbots are increasingly influencing physics education due to their ability to interpret and respond to textual and visual inputs. This study evaluates the performance of two large multimodal model-based chatbots, ChatGPT-4 and ChatGPT-4o on the Brief Electricity and Magnetism Assessment (BEMA), a conceptual physics inventory rich in visual representations such as vector fields, circuit diagrams, and graphs. Quantitative analysis shows that ChatGPT-4o outperforms both ChatGPT-4 and a large sample of university students, and demonstrates improvements in ChatGPT-4o’s vision interpretation ability over its predecessor ChatGPT-4. However, qualitative analysis of ChatGPT-4o’s responses reveals persistent challenges. We identified three types of difficulties in the chatbot’s responses to tasks on BEMA: (1) difficulties with visual interpretation, (2) difficulties in providing correct physics laws or rules, and (3) difficulties with spatial coordination and application of physics representations. Spatial reasoning tasks, particularly those requiring the use of the right-hand rule, proved especially problematic. These findings highlight that the most broadly used large multimodal model-based chatbot, ChatGPT-4o, still exhibits significant difficulties in engaging with physics tasks involving visual representations. While the chatbot shows potential for educational applications, including personalized tutoring and accessibility support for students who are blind or have low vision, its limitations necessitate caution. On the other hand, our findings can also be leveraged to design assessments that are difficult for chatbots to solve.
基于人工智能的聊天机器人因其解释和响应文本和视觉输入的能力,正越来越多地影响物理教育。本研究评估了两个大型多模式模型基础聊天机器人ChatGPT-4和ChatGPT-4o在“简短的电与磁评估(BEMA)”上的表现。BEMA是一个概念丰富的物理题库,包含矢量场、电路图和图表等视觉表示形式。定量分析表明,ChatGPT-4o在ChatGPT-4和大量大学生样本中的表现更为出色,并展示了其相较于前身ChatGPT-4在视觉解释能力方面的改进。然而,对ChatGPT-4o的回应进行定性分析揭示了持续存在的挑战。我们确定了聊天机器人在BEMA任务回应中的三种困难类型:(1)视觉解释困难,(2)提供正确物理定律或规则困难,(3)空间协调和物理表示应用困难。空间推理任务,尤其是那些需要使用右手定则的任务,证明尤其困难。这些发现表明,最广泛使用的大型多模式模型基础聊天机器人ChatGPT-4o在涉及视觉表达的物理任务中仍存在显著困难。虽然聊天机器人在教育应用方面显示出潜力,包括个性化辅导和失明或视力受损学生的辅助支持,但其局限性需要谨慎对待。另一方面,我们的发现也可以用来设计聊天机器人难以解决的评估题目。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文研究了人工智能聊天机器人对物理教育的影响,特别是它们对视觉输入的解读和响应能力。通过对比两个大型多模态模型聊天机器人ChatGPT-4和ChatGPT-4o在概念物理测试中的表现,发现ChatGPT-4o在视觉解读能力上有所改进,但其解答仍存在挑战。针对视觉解读、物理定律或规则提供正确性以及空间协调和物理表示应用等方面存在困难。虽然该聊天机器人在教育应用方面显示出潜力,但其局限性仍需谨慎对待。
Key Takeaways
- 人工智能聊天机器人对物理教育产生影响,特别是在解读和响应视觉输入方面。
- ChatGPT-4o在视觉解读能力上相较于ChatGPT-4有所提升。
- ChatGPT-4o在回答物理任务时仍面临困难,尤其在涉及视觉解读、物理定律或规则的正确提供以及空间协调等方面。
- 空间推理任务,特别是需要使用右手规则的任务,对聊天机器人来说特别具有挑战性。
- 虽然ChatGPT-4o在个性化辅导和视力障碍学生支持方面具有教育应用潜力,但其局限性需要谨慎对待。
- 研究结果可用于设计针对聊天机器人的评估难题。
点此查看论文截图

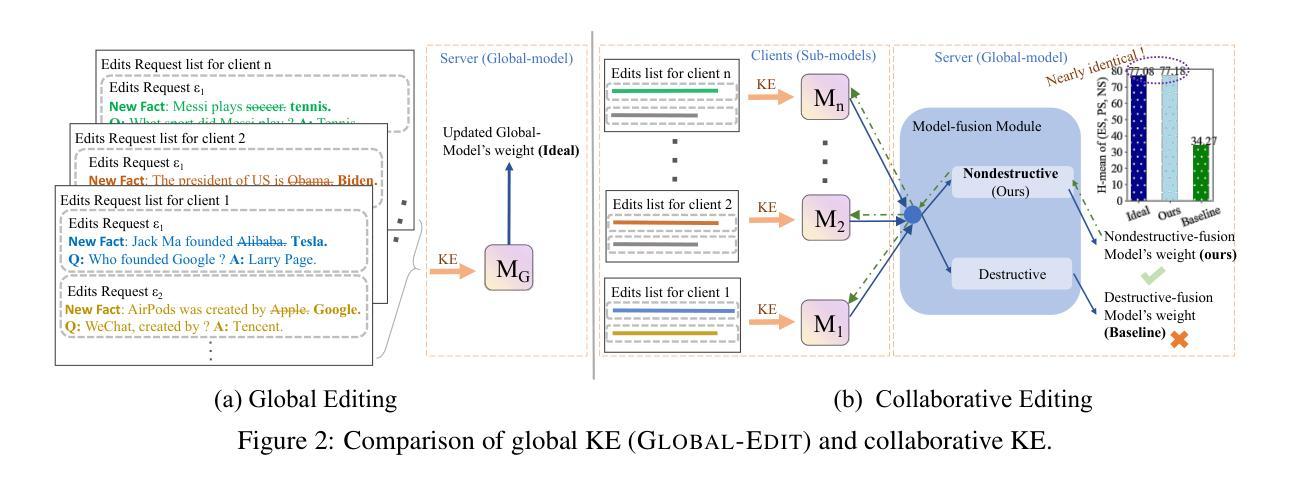
CollabEdit: Towards Non-destructive Collaborative Knowledge Editing
Authors:Jiamu Zheng, Jinghuai Zhang, Tianyu Du, Xuhong Zhang, Jianwei Yin, Tao Lin
Collaborative learning of large language models (LLMs) has emerged as a new paradigm for utilizing private data from different parties to guarantee efficiency and privacy. Meanwhile, Knowledge Editing (KE) for LLMs has also garnered increased attention due to its ability to manipulate the behaviors of LLMs explicitly, yet leaves the collaborative KE case (in which knowledge edits of multiple parties are aggregated in a privacy-preserving and continual manner) unexamined. To this end, this manuscript dives into the first investigation of collaborative KE, in which we start by carefully identifying the unique three challenges therein, including knowledge overlap, knowledge conflict, and knowledge forgetting. We then propose a non-destructive collaborative KE framework, COLLABEDIT, which employs a novel model merging mechanism to mimic the global KE behavior while preventing the severe performance drop. Extensive experiments on two canonical datasets demonstrate the superiority of COLLABEDIT compared to other destructive baselines, and results shed light on addressing three collaborative KE challenges and future applications. Our code is available at https://github.com/LINs-lab/CollabEdit.
大规模语言模型(LLM)的协作学习已经成为利用不同方的私有数据的新范式,以保证效率和隐私。与此同时,由于能够明确操控LLM的行为,LLM的知识编辑(KE)也引起了越来越多的关注,然而协作KE的情况(即多方知识编辑以隐私保护和持续的方式进行聚合)尚未被研究。为此,本文深入研究了协作KE,首先仔细确定了其中的三个独特挑战,包括知识重叠、知识冲突和知识遗忘。然后,我们提出了非破坏性的协作KE框架COLLABEDIT,该框架采用新型模型合并机制来模拟全局KE行为,同时防止性能严重下降。在两个典型数据集上的广泛实验证明了COLLABEDIT与其他破坏性基准线的优越性,实验结果为解决三个协作KE挑战和未来应用提供了启示。我们的代码位于https://github.com/LINs-lab/CollabEdit。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 20 pages, 11 figures. Published as a conference paper at ICLR 2025. Code at https://github.com/LINs-lab/CollabEdit
Summary
大规模语言模型(LLM)的协作学习已成为利用各方私有数据的新范式,保证了效率和隐私。知识编辑(KE)技术对于LLM的操控能力备受关注,但在协作KE的情况下(即多方知识编辑在保护隐私和持续性的方式进行聚合)尚未被研究。本文首次探究协作KE,首先明确了其中的三大独特挑战,包括知识重叠、知识冲突和知识遗忘。随后,提出了一种非破坏性的协作KE框架COLLABEDIT,采用新型模型合并机制来模拟全局KE行为,同时防止性能严重下降。在典型数据集上的广泛实验表明,COLLABEDIT与其他破坏性基线相比具有优越性,为解决三项协作KE挑战和未来应用提供了启示。
Key Takeaways
- 协作学习成为利用LLM的新范式,旨在保证效率和隐私。
- 知识编辑(KE)技术能够明确操控LLM的行为。
- 协作知识编辑(CKE)尚未得到充分研究,特别是在隐私保护和持续性方面。
- CKE面临三大挑战:知识重叠、知识冲突和知识遗忘。
- COLLABEDIT框架被提出用于解决CKE的挑战,采用新型模型合并机制。
- 实验表明COLLABEDIT框架在典型数据集上表现优越。
点此查看论文截图

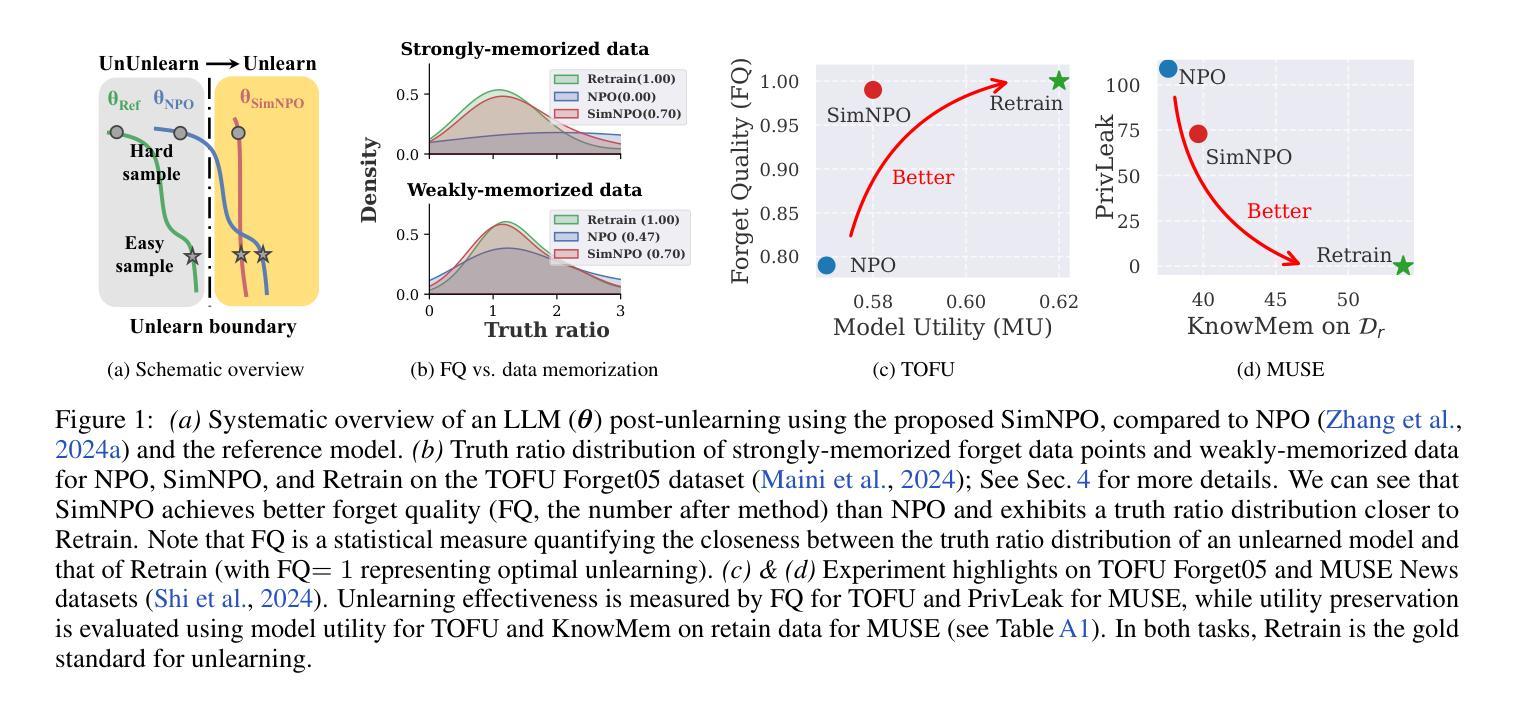
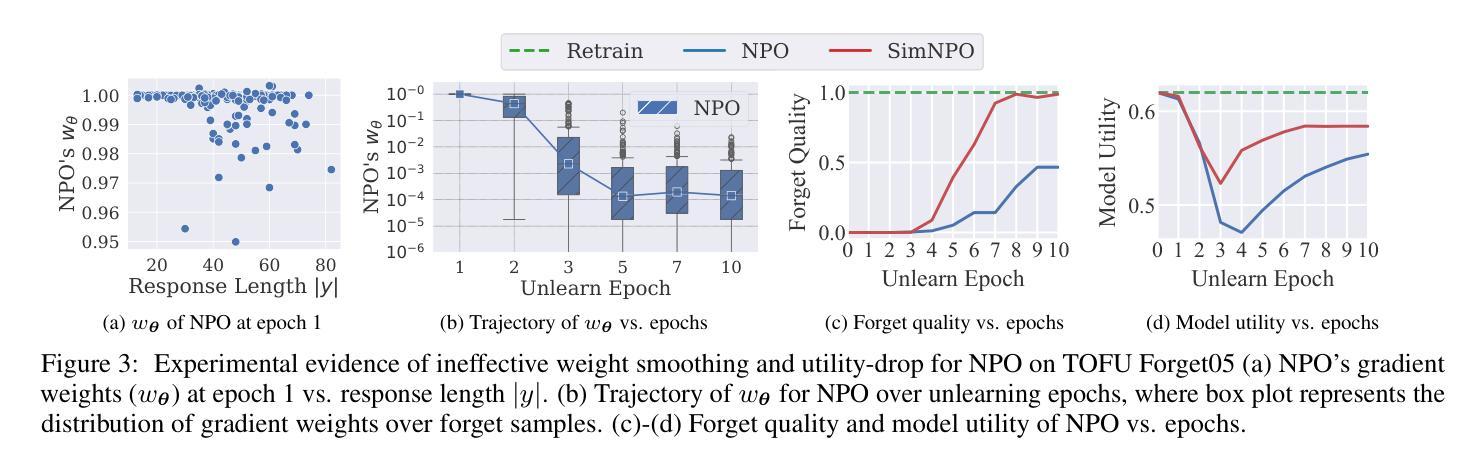
Simplicity Prevails: Rethinking Negative Preference Optimization for LLM Unlearning
Authors:Chongyu Fan, Jiancheng Liu, Licong Lin, Jinghan Jia, Ruiqi Zhang, Song Mei, Sijia Liu
This work studies the problem of large language model (LLM) unlearning, aiming to remove unwanted data influences (e.g., copyrighted or harmful content) while preserving model utility. Despite the increasing demand for unlearning, a technically-grounded optimization framework is lacking. Gradient ascent (GA)-type methods, though widely used, are suboptimal as they reverse the learning process without controlling optimization divergence (i.e., deviation from the pre-trained state), leading to risks of over-forgetting and potential model collapse. Negative preference optimization (NPO) has been proposed to address this issue and is considered one of the state-of-the-art LLM unlearning approaches. In this work, we revisit NPO and identify another critical issue: reference model bias. This bias arises from using the reference model (i.e., the model prior to unlearning) to evaluate the unlearning success, which can compromise NPO’s effectiveness. Specifically, it leads to (a) uneven allocation of optimization power across forget data with varying difficulty levels and (b) ineffective gradient weight smoothing during the early stages of unlearning optimization. To overcome these challenges, we propose a simple yet effective unlearning optimization framework, called SimNPO, showing that `simplicity’ in removing the reliance on a reference model (through the lens of simple preference optimization) benefits unlearning. We provide deeper insights into SimNPO’s advantages through an analysis based on mixtures of Markov chains. Extensive experiments further validate SimNPO’s efficacy on benchmarks like TOFU and MUSE, as well as its robustness against relearning attacks. Codes are available at https://github.com/OPTML-Group/Unlearn-Simple.
本文研究大型语言模型(LLM)的去学习问题,旨在消除不必要的数据影响(例如版权或有害内容),同时保持模型的实用性。尽管对去学习的需求不断增长,但缺乏技术基础的优化框架。梯度上升(GA)类方法虽然应用广泛,但并不理想,因为它们逆转学习过程,同时不控制优化发散(即偏离预训练状态),导致过度遗忘和潜在模型崩溃的风险。负偏好优化(NPO)已被提出来解决这个问题,并被认为是最新的LLM去学习方法之一。在这项工作中,我们重新审视NPO并确定了另一个关键问题:参考模型偏见。这种偏见来自于使用参考模型(即去学习之前的模型)来评估去学习的成功程度,这可能会危及NPO的有效性。具体来说,它会导致(a)在具有不同难度级别的遗忘数据上分配不均匀的优化能力;(b)在去学习的早期阶段,梯度权重平滑无效。为了克服这些挑战,我们提出了一个简单有效的去学习优化框架,称为SimNPO,表明在去除对参考模型的依赖(通过简单偏好优化的视角)方面,“简洁性”有益于去学习。我们通过基于马尔可夫链混合的分析提供了对SimNPO优势的深入了解。广泛的实验进一步验证了SimNPO在TOFU和MUSE等基准测试上的有效性,以及其对抗重新学习攻击的稳健性。代码可在https://github.com/OPTML-Group/Unlearn-Simple获取。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文探讨大型语言模型(LLM)的遗忘学习问题,旨在移除不必要的数据影响(如版权或有害内容),同时保留模型的实用性。针对遗忘学习缺乏技术性的优化框架,文章提出了一个新的优化框架SimNPO,它简化了对参考模型的依赖,通过简单的偏好优化实现遗忘学习,并通过混合马尔可夫链的分析深入探讨了SimNPO的优势。实验结果表明,SimNPO在TOFU和MUSE等基准测试上具有良好的效果,并且对于重新学习攻击具有鲁棒性。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLM)的遗忘学习是移除不必要数据影响同时保留模型实用性的研究问题。
- 现有遗忘学习方法如基于梯度上升的方法存在优化发散的问题,可能导致过度遗忘和模型崩溃。
- 负偏好优化(NPO)被认为是目前先进的LLM遗忘学习方法之一,但存在参考模型偏见问题。
- 参考模型偏见源于使用未遗忘前的模型来评估遗忘成功的程度,可能影响NPO的有效性。
- 本文提出的SimNPO框架通过简化偏好优化,去除对参考模型的依赖,解决了参考模型偏见问题。
- SimNPO框架在TOFU和MUSE等基准测试上表现出良好的效能,且对重新学习攻击具有鲁棒性。
点此查看论文截图