⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-02-12 更新
Visual Agentic AI for Spatial Reasoning with a Dynamic API
Authors:Damiano Marsili, Rohun Agrawal, Yisong Yue, Georgia Gkioxari
Visual reasoning – the ability to interpret the visual world – is crucial for embodied agents that operate within three-dimensional scenes. Progress in AI has led to vision and language models capable of answering questions from images. However, their performance declines when tasked with 3D spatial reasoning. To tackle the complexity of such reasoning problems, we introduce an agentic program synthesis approach where LLM agents collaboratively generate a Pythonic API with new functions to solve common subproblems. Our method overcomes limitations of prior approaches that rely on a static, human-defined API, allowing it to handle a wider range of queries. To assess AI capabilities for 3D understanding, we introduce a new benchmark of queries involving multiple steps of grounding and inference. We show that our method outperforms prior zero-shot models for visual reasoning in 3D and empirically validate the effectiveness of our agentic framework for 3D spatial reasoning tasks. Project website: https://glab-caltech.github.io/vadar/
视觉推理——解释视觉世界的能力——对于在三维场景中操作的实体代理至关重要。人工智能的进步导致了能够回答图像问题的视觉和语言模型的出现。然而,当面对3D空间推理任务时,它们的性能会下降。为了解决这类推理问题的复杂性,我们引入了一种代理程序综合方法,其中大型语言模型(LLM)代理协同生成Pythonic API,并添加新函数以解决常见子问题。我们的方法克服了以前依赖于静态人为定义的API的方法的局限性,使其能够处理更广泛的查询。为了评估AI对三维场景的理解能力,我们引入了一种新的查询基准测试,涉及多个步骤的接地和推理。我们证明了我们的方法在三维视觉推理方面优于之前的零样本模型,并通过实证验证了我们的代理框架在三维空间推理任务中的有效性。项目网站:https://glab-caltech.github.io/vadar/
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project website: https://glab-caltech.github.io/vadar/
Summary
视觉推理——解释视觉世界的能力对于在三维场景中操作的实体代理至关重要。随着人工智能的进步,出现了能够回答图像问题的视觉和语言模型。然而,当面对三维空间推理任务时,它们的性能会下降。为解决此类复杂推理问题,我们采用了一种代理程序综合方法,其中LLM代理协同生成Pythonic API的新功能来解决常见子问题。我们的方法克服了以前依赖于静态、人为定义的API的方法的局限性,能够处理更广泛的查询。为了评估AI对三维理解的能力,我们引入了一个新的查询基准测试,涉及多步定位和推理。我们展示了我们的方法在三维视觉推理方面优于先前的零样本模型,并通过实验验证了我们的代理框架在三维空间推理任务上的有效性。
Key Takeaways
- 视觉推理对于在三维场景中操作的实体代理至关重要。
- AI的进步已经推动了视觉和语言模型的发展,能够回答图像相关的问题。
- 面对三维空间推理任务时,现有模型的性能会下降。
- 提出了一种代理程序综合方法,LLM代理能够协同工作,生成新的Pythonic API功能来解决常见的子问题。
- 与以前的方法相比,该方法能够处理更广泛的查询,因为它不依赖于静态、人为定义的API。
- 为了评估AI在三维理解方面的能力,引入了一个新的查询基准测试,涵盖多步定位和推理。
点此查看论文截图

AgilePilot: DRL-Based Drone Agent for Real-Time Motion Planning in Dynamic Environments by Leveraging Object Detection
Authors:Roohan Ahmed Khan, Valerii Serpiva, Demetros Aschalew, Aleksey Fedoseev, Dzmitry Tsetserukou
Autonomous drone navigation in dynamic environments remains a critical challenge, especially when dealing with unpredictable scenarios including fast-moving objects with rapidly changing goal positions. While traditional planners and classical optimisation methods have been extensively used to address this dynamic problem, they often face real-time, unpredictable changes that ultimately leads to sub-optimal performance in terms of adaptiveness and real-time decision making. In this work, we propose a novel motion planner, AgilePilot, based on Deep Reinforcement Learning (DRL) that is trained in dynamic conditions, coupled with real-time Computer Vision (CV) for object detections during flight. The training-to-deployment framework bridges the Sim2Real gap, leveraging sophisticated reward structures that promotes both safety and agility depending upon environment conditions. The system can rapidly adapt to changing environments, while achieving a maximum speed of 3.0 m/s in real-world scenarios. In comparison, our approach outperforms classical algorithms such as Artificial Potential Field (APF) based motion planner by 3 times, both in performance and tracking accuracy of dynamic targets by using velocity predictions while exhibiting 90% success rate in 75 conducted experiments. This work highlights the effectiveness of DRL in tackling real-time dynamic navigation challenges, offering intelligent safety and agility.
动态环境下自主无人机的导航仍然是一个关键挑战,特别是在处理快速移动的物体和快速变化的目标位置等不可预测的场景时。虽然传统规划器和经典优化方法已被广泛用于解决这一动态问题,但它们经常面临实时、不可预测的变更,这最终导致在适应性和实时决策方面的性能表现不佳。在这项工作中,我们提出了一种新型的基于深度强化学习(DRL)的运动规划器AgilePilot,它在动态条件下进行训练,并结合实时计算机视觉(CV)进行飞行过程中的目标检测。从训练到部署的框架,它缩小了模拟到现实的差距,利用复杂的奖励结构,根据环境条件促进安全性和机动性的平衡。该系统能够迅速适应变化的环境,同时在真实场景中实现最高时速3.0米/秒。相比之下,我们的方法通过使用速度预测,在性能和动态目标的跟踪精度方面,是基于人工势能场(APF)的运动规划器的三倍之多,并且在进行的75次实验中成功率达到了90%。这项工作突出了深度强化学习在处理实时动态导航挑战方面的有效性,提供了智能的安全性和机动性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Manuscript has been submitted to 2025 INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON UNMANNED AIRCRAFT SYSTEMS (ICUAS)
Summary
该文章介绍了基于深度强化学习(DRL)的无人机动态导航技术。传统规划方法难以适应动态环境中的变化,导致实时决策效果差。该研究提出一种新型运动规划器AgilePilot,结合实时计算机视觉进行目标检测,能在动态环境中快速适应并做出决策。通过复杂的奖励结构促进安全性和灵活性,缩小仿真与现实差距。系统能在真实场景中达到最高时速3米每秒,超越传统算法三倍,且成功率为实验数的百分之九十。这一研究展示了DRL解决实时动态导航挑战的有效性。
Key Takeaways
- 该研究提出一种基于深度强化学习的新型无人机运动规划器AgilePilot,旨在解决动态环境中的自主导航挑战。
- AgilePilot结合实时计算机视觉技术用于目标检测,以提高无人机的决策效率。
- 通过复杂的奖励结构促进安全性和灵活性的平衡,缩小仿真与真实环境之间的差距。
- 该系统能够在真实场景中实现高达每秒3米的速度运行,表现出出色的性能。
- 与传统算法相比,如人工势能场(APF)算法,AgilePilot在性能和跟踪动态目标方面表现更优越。
- 在进行的实验中,AgilePilot达到了百分之九十的成功率。
点此查看论文截图


Hephaestus: Improving Fundamental Agent Capabilities of Large Language Models through Continual Pre-Training
Authors:Yuchen Zhuang, Jingfeng Yang, Haoming Jiang, Xin Liu, Kewei Cheng, Sanket Lokegaonkar, Yifan Gao, Qing Ping, Tianyi Liu, Binxuan Huang, Zheng Li, Zhengyang Wang, Pei Chen, Ruijie Wang, Rongzhi Zhang, Nasser Zalmout, Priyanka Nigam, Bing Yin, Chao Zhang
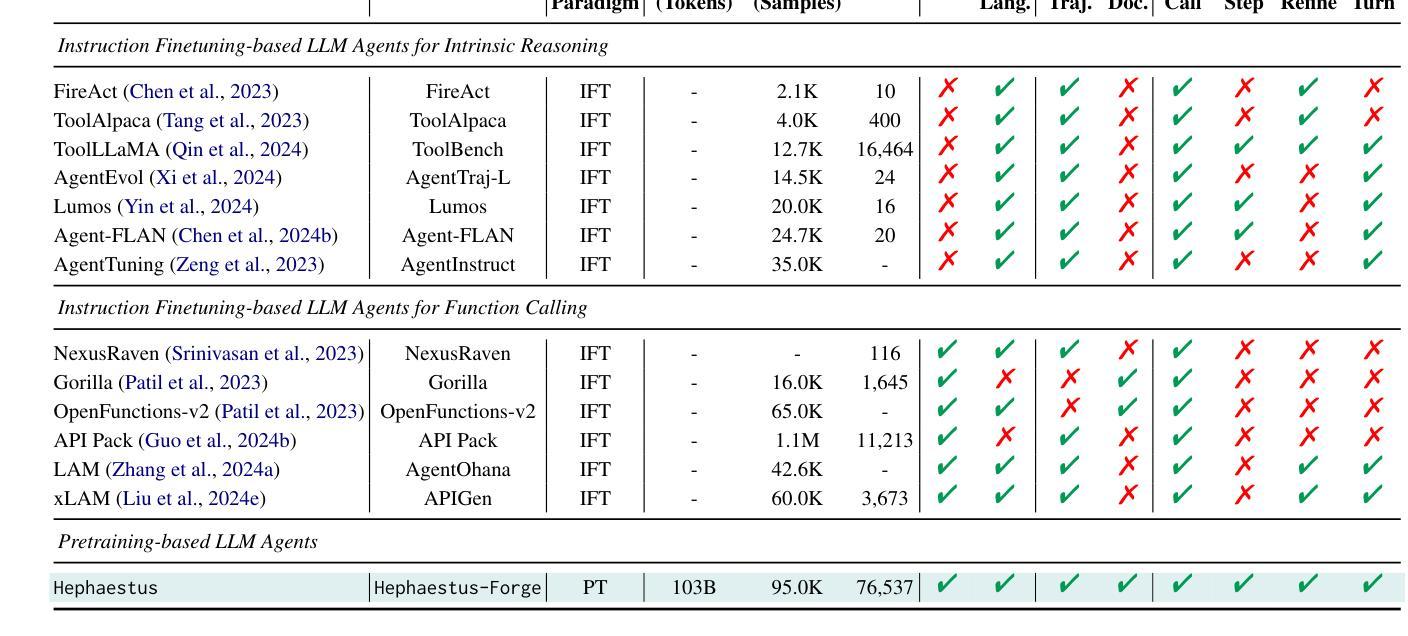
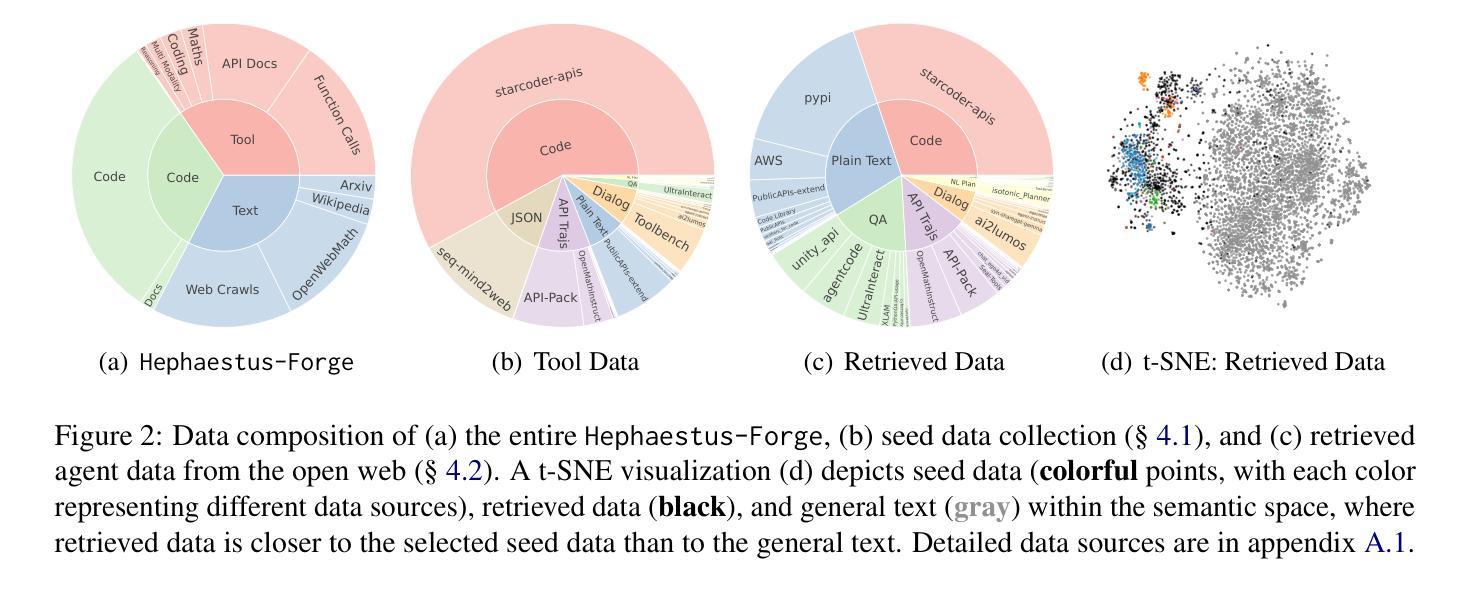
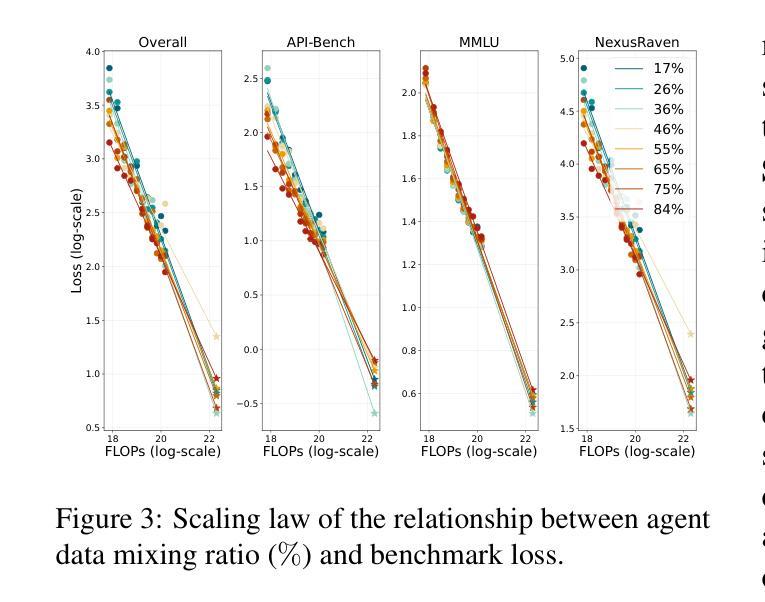
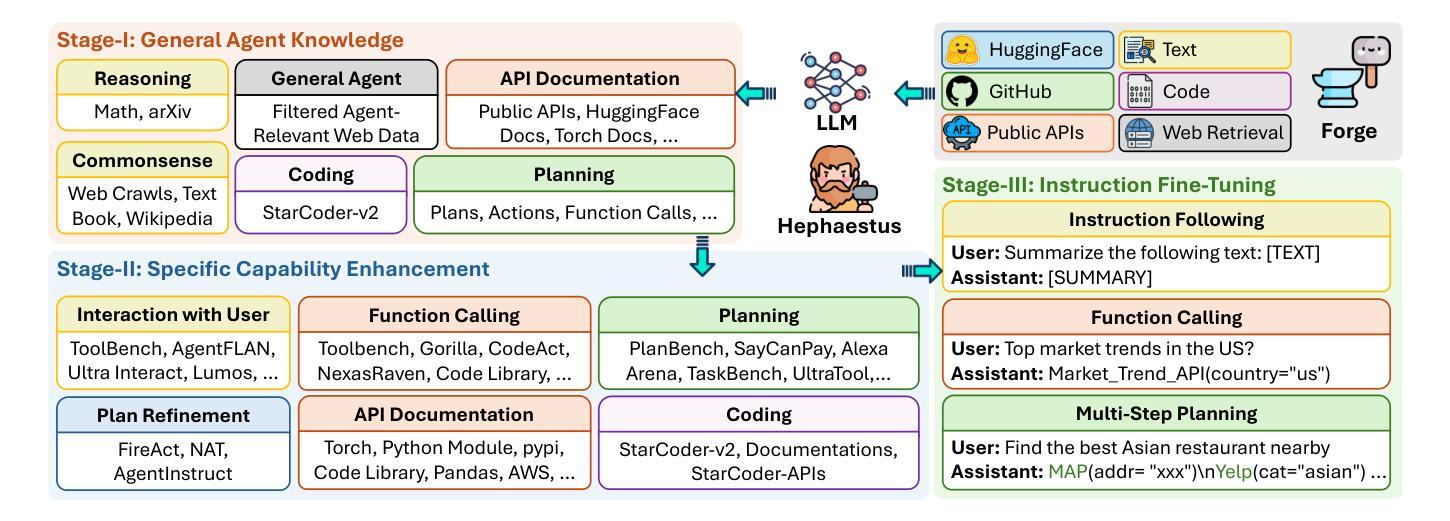
Due to the scarcity of agent-oriented pre-training data, LLM-based autonomous agents typically rely on complex prompting or extensive fine-tuning, which often fails to introduce new capabilities while preserving strong generalizability. We introduce Hephaestus-Forge, the first large-scale pre-training corpus designed to enhance the fundamental capabilities of LLM agents in API function calling, intrinsic reasoning and planning, and adapting to environmental feedback. Hephaestus-Forge comprises 103B agent-specific data encompassing 76,537 APIs, including both tool documentation to introduce knowledge of API functions and function calling trajectories to strengthen intrinsic reasoning. To explore effective training protocols, we investigate scaling laws to identify the optimal recipe in data mixing ratios. By continual pre-training on Hephaestus-Forge, Hephaestus outperforms small- to medium-scale open-source LLMs and rivals commercial LLMs on three agent benchmarks, demonstrating the effectiveness of our pre-training corpus in enhancing fundamental agentic capabilities and generalization of LLMs to new tasks or environments.
由于面向代理的预训练数据的稀缺,基于LLM的自主代理通常依赖于复杂的提示或大量的微调,这往往难以在保持强大的泛化能力的同时引入新的能力。我们推出了赫淮斯托斯锻造(Hephaestus-Forge),这是第一个大规模预训练语料库,旨在增强LLM代理在API函数调用、内在推理和规划以及适应环境反馈方面的基本能力。赫淮斯托斯锻造包含了103B的代理特定数据,涵盖76,537个API,其中包括工具文档以介绍API函数的知识和函数调用轨迹以加强内在推理。为了探索有效的训练协议,我们研究了扩展定律,以确定数据混合比例中的最佳配方。通过不断在赫淮斯托斯锻造上进行预训练,赫淮斯托斯在三个代理基准测试上的表现超越了中小规模的开源LLM,并与商业LLM相匹敌,这证明了我们的预训练语料库在增强LLM的基本代理能力和泛化新任务或环境方面的有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to NAACL 2025 main conference
总结
面向自主代理人的预训练数据稀缺,基于大型语言模型(LLM)的自主代理人通常依赖复杂的提示或大量的微调,这往往难以在引入新能力的同时保持强大的泛化能力。为此,我们推出了Hephaestus-Forge,这是首个为增强LLM代理人在API函数调用、内在推理和规划以及适应环境反馈方面的基本能力而设计的大型预训练语料库。Hephaestus-Forge包含103B的代理特定数据,涵盖76,537个API,既包括工具文档以介绍API函数知识,也包括函数调用轨迹以加强内在推理。为了探索有效的训练协议,我们研究了规模定律以确定数据混合比例的最佳配方。通过不断在Hephaestus-Forge上进行预训练,Hephaestus在三个代理基准测试上的表现超越了中小规模的开源LLM,并与商业LLM相抗衡,证明了我们的预训练语料库在提高LLM的基本代理能力和泛化新任务或环境方面的有效性。
关键见解
- 面向自主代理人的预训练数据稀缺,导致LLM代理人面临挑战。
- Hephaestus-Forge是首个针对LLM代理人的大型预训练语料库,旨在增强API函数调用、内在推理和规划等能力。
- Hephaestus-Forge包含丰富的数据资源,涵盖API知识及函数调用轨迹,以强化内在推理。
- 通过研究规模定律,确定了最佳的数据混合比例。
- 通过在Hephaestus-Forge上持续预训练,Hephaestus在多个基准测试中表现出色。
- Hephaestus超越了中小规模的开源LLM,并与商业LLM相抗衡。
- 预训练语料库对提高LLM的基本代理能力和泛化新任务或环境具有重要意义。
点此查看论文截图

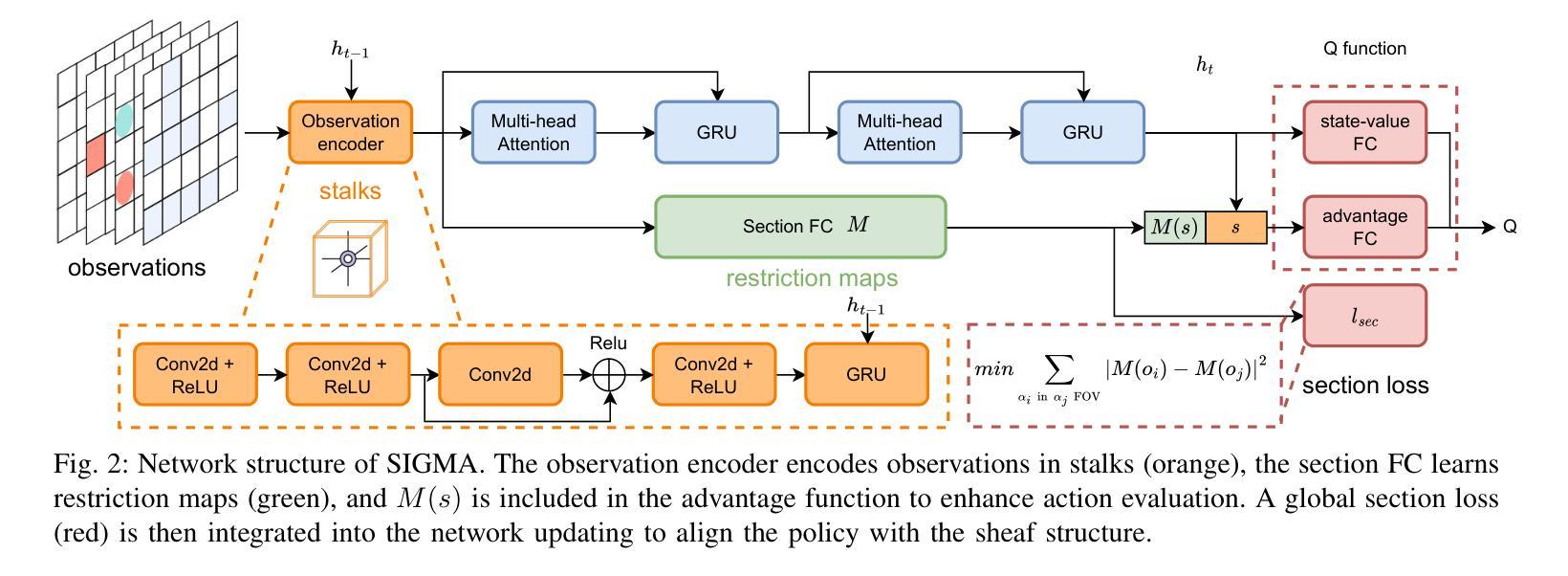
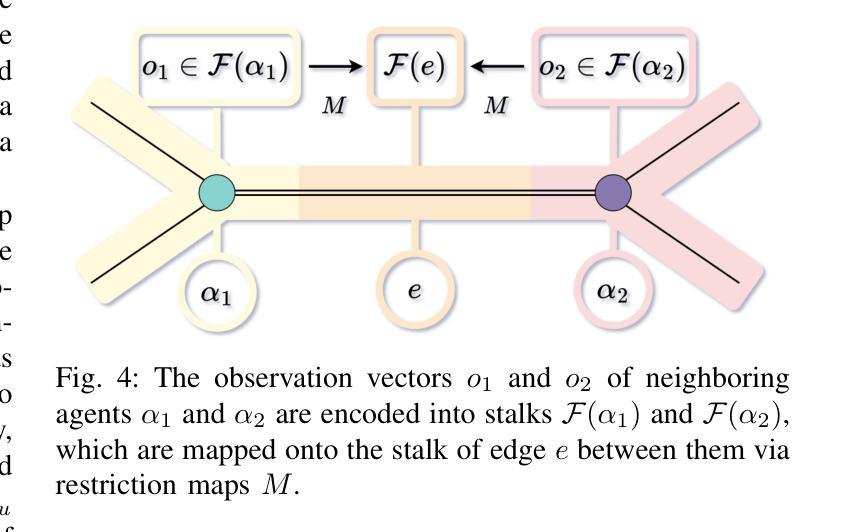
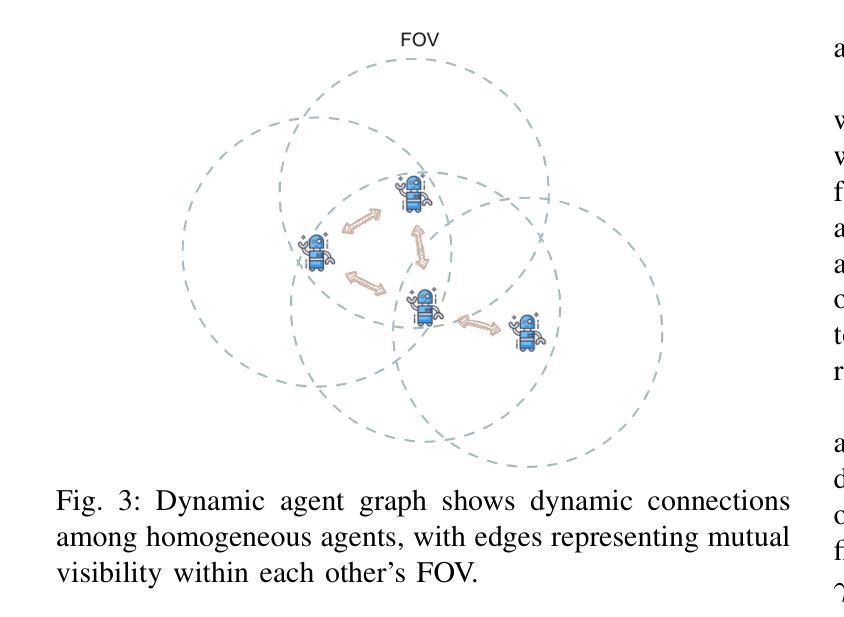
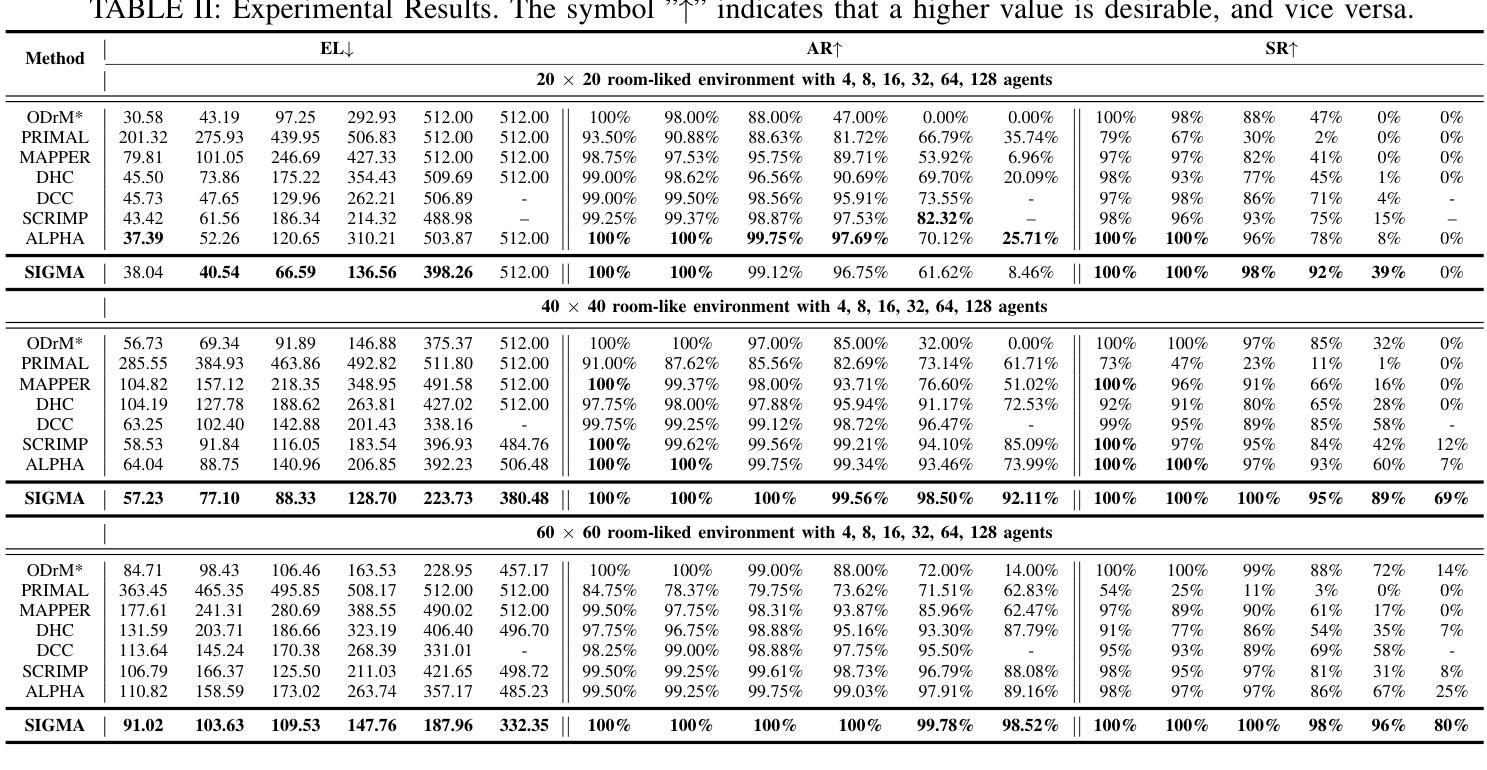
SIGMA: Sheaf-Informed Geometric Multi-Agent Pathfinding
Authors:Shuhao Liao, Weihang Xia, Yuhong Cao, Weiheng Dai, Chengyang He, Wenjun Wu, Guillaume Sartoretti
The Multi-Agent Path Finding (MAPF) problem aims to determine the shortest and collision-free paths for multiple agents in a known, potentially obstacle-ridden environment. It is the core challenge for robotic deployments in large-scale logistics and transportation. Decentralized learning-based approaches have shown great potential for addressing the MAPF problems, offering more reactive and scalable solutions. However, existing learning-based MAPF methods usually rely on agents making decisions based on a limited field of view (FOV), resulting in short-sighted policies and inefficient cooperation in complex scenarios. There, a critical challenge is to achieve consensus on potential movements between agents based on limited observations and communications. To tackle this challenge, we introduce a new framework that applies sheaf theory to decentralized deep reinforcement learning, enabling agents to learn geometric cross-dependencies between each other through local consensus and utilize them for tightly cooperative decision-making. In particular, sheaf theory provides a mathematical proof of conditions for achieving global consensus through local observation. Inspired by this, we incorporate a neural network to approximately model the consensus in latent space based on sheaf theory and train it through self-supervised learning. During the task, in addition to normal features for MAPF as in previous works, each agent distributedly reasons about a learned consensus feature, leading to efficient cooperation on pathfinding and collision avoidance. As a result, our proposed method demonstrates significant improvements over state-of-the-art learning-based MAPF planners, especially in relatively large and complex scenarios, demonstrating its superiority over baselines in various simulations and real-world robot experiments.
多智能体路径寻找(MAPF)问题旨在确定在已知且可能充满障碍的环境中,多个智能体的无碰撞最短路径。它是大规模物流和运输中机器人部署的核心挑战。去中心化的基于学习的方法在解决MAPF问题上显示出巨大潜力,提供了更灵活和可扩展的解决方案。然而,现有的基于学习的MAPF方法通常依赖于智能体基于有限的视野(FOV)做出决策,导致短视策略和复杂场景中的合作效率低下。因此,一个关键挑战是在有限的观察和通信基础上实现智能体之间潜在运动的共识。为了应对这一挑战,我们引入了一个新框架,该框架将层叠理论应用于去中心化深度强化学习,使智能体能够通过局部共识学习彼此之间的几何交叉依赖性,并利用它们进行紧密合作决策。特别是,层叠理论提供了通过局部观察实现全局共识的条件数学证明。受此启发,我们结合神经网络,基于层叠理论在潜在空间中近似建模共识,并通过自我监督学习对其进行训练。在任务中,除了MAPF的正常特征外,每个智能体还分布式地考虑学习到的共识特征,从而在路径查找和避免碰撞方面实现高效合作。因此,我们提出的方法在相对较大和复杂的场景中,相较于最新的基于学习的MAPF规划器显示出显著改进,在各种模拟和真实机器人实验中超过基线标准的优越性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted for presentation at the 2025 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA)
Summary
针对多智能体路径规划问题(MAPF),引入了一种基于流形理论的新框架来解决分散式深度强化学习中的局部共识问题,使智能体能够通过局部观察学习几何交叉依赖关系并紧密合作进行决策。此框架提供了通过局部观察实现全局共识的数学证明条件。通过神经网络对基于流形理论的共识进行建模,并通过自我监督学习进行训练。智能体在任务中同时考虑传统MAPF特征和学习的共识特征,有效提升了路径规划和避免碰撞的效率。在模拟和真实机器人实验中,新方法均显示出显著优势。
Key Takeaways
- MAPF问题的核心挑战在于确定多个智能体在已知环境中无碰撞的最短路径,特别是在大规模物流和运输领域。
- 分散式学习方法是解决MAPF问题的潜力所在,但现有方法通常基于有限视野(FOV)进行决策,导致政策短视和复杂场景下合作低效。
- 流形理论应用于分散式深度强化学习的新框架,使得智能体能通过局部共识学习几何交叉依赖关系。
- 流形理论提供了通过局部观察实现全局共识的数学证明条件。
- 通过神经网络建模基于流形理论的共识,并采用自我监督学习方式进行训练。
- 智能体在任务中同时考虑传统MAPF特征和学习的共识特征,显著提升了路径规划和碰撞避免的效率。
点此查看论文截图


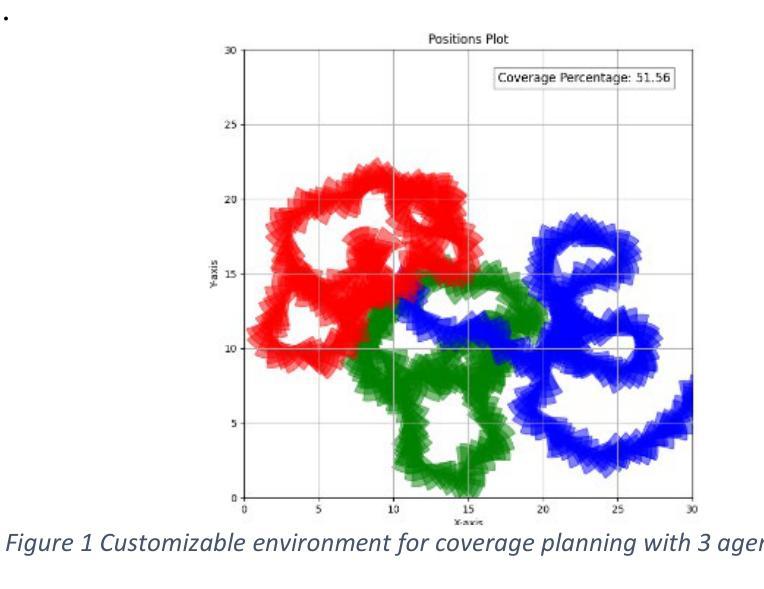
Towards Bio-inspired Heuristically Accelerated Reinforcement Learning for Adaptive Underwater Multi-Agents Behaviour
Authors:Antoine Vivien, Thomas Chaffre, Matthew Stephenson, Eva Artusi, Paulo Santos, Benoit Clement, Karl Sammut
This paper describes the problem of coordination of an autonomous Multi-Agent System which aims to solve the coverage planning problem in a complex environment. The considered applications are the detection and identification of objects of interest while covering an area. These tasks, which are highly relevant for space applications, are also of interest among various domains including the underwater context, which is the focus of this study. In this context, coverage planning is traditionally modelled as a Markov Decision Process where a coordinated MAS, a swarm of heterogeneous autonomous underwater vehicles, is required to survey an area and search for objects. This MDP is associated with several challenges: environment uncertainties, communication constraints, and an ensemble of hazards, including time-varying and unpredictable changes in the underwater environment. MARL algorithms can solve highly non-linear problems using deep neural networks and display great scalability against an increased number of agents. Nevertheless, most of the current results in the underwater domain are limited to simulation due to the high learning time of MARL algorithms. For this reason, a novel strategy is introduced to accelerate this convergence rate by incorporating biologically inspired heuristics to guide the policy during training. The PSO method, which is inspired by the behaviour of a group of animals, is selected as a heuristic. It allows the policy to explore the highest quality regions of the action and state spaces, from the beginning of the training, optimizing the exploration/exploitation trade-off. The resulting agent requires fewer interactions to reach optimal performance. The method is applied to the MSAC algorithm and evaluated for a 2D covering area mission in a continuous control environment.
本文描述了一个旨在解决复杂环境中覆盖规划问题的自主多智能体系统(Multi-Agent System,简称MAS)的协调问题。所考虑的应用是覆盖区域时的目标检测和识别。这些任务对于空间应用高度相关,也在各种领域(包括本研究重点关注的水下环境)中引起了兴趣。在这种情况下,覆盖规划传统上被建模为马尔可夫决策过程(Markov Decision Process,简称MDP),需要协调的MAS(由多种自主水下车辆组成的群体)来调查区域并搜索目标。这个MDP面临几个挑战:环境不确定性、通信约束以及一系列危险,包括水下环境中随时间变化且不可预测的变化。多智能体强化学习(Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning,简称MARL)算法可以解决高度非线性问题,利用深度神经网络表现出很好的可扩展性,对抗大量智能体。然而,由于MARL算法的学习时间较长,目前在水下领域的大部分结果仅限于模拟。因此,引入了一种新策略来通过融入生物启发式算法加速收敛速率以引导训练期间的策略。粒子群优化(Particle Swarm Optimization,简称PSO)方法受到动物群体行为的启发,被选择为一种启发式方法。它允许策略从训练开始就探索行为和状态空间中质量最高的区域,优化探索与开发的权衡。最终智能体达到最优性能所需的交互次数减少。该方法应用于MSAC算法,并在连续控制环境中针对二维覆盖区域任务进行了评估。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF i-SAIRAS 2024 Conference
Summary
本文探讨了在复杂环境下,自主多智能体系统(MAS)的协调问题,旨在解决覆盖规划问题。文章重点介绍了水下环境中的覆盖规划,将其传统地建模为马尔可夫决策过程(MDP)。由于环境不确定性和通信约束等挑战,多智能体强化学习(MARL)算法结合深度神经网络解决了高度非线性问题。为提高收敛速率,文章提出一种新型策略,结合生物启发式方法来引导训练过程中的策略。最后通过实验验证,应用粒子群优化(PSO)方法的MSAC算法在连续控制环境下的二维覆盖区域任务表现出色。
Key Takeaways
- 该研究解决自主多智能体系统(MAS)在复杂环境中的覆盖规划问题。
- 水下环境是该研究的重点应用领域,涉及高度相关的任务,如检测和识别感兴趣的对象。
- 将覆盖规划建模为马尔可夫决策过程(MDP),面临环境不确定性、通信约束和多种危险等挑战。
- 使用多智能体强化学习(MARL)算法解决高度非线性问题,并结合深度神经网络进行训练。
- 为提高收敛速率,结合生物启发式方法引导训练策略。
- 采用粒子群优化(PSO)方法作为启发式方法,优化探索与开发之间的平衡。
点此查看论文截图

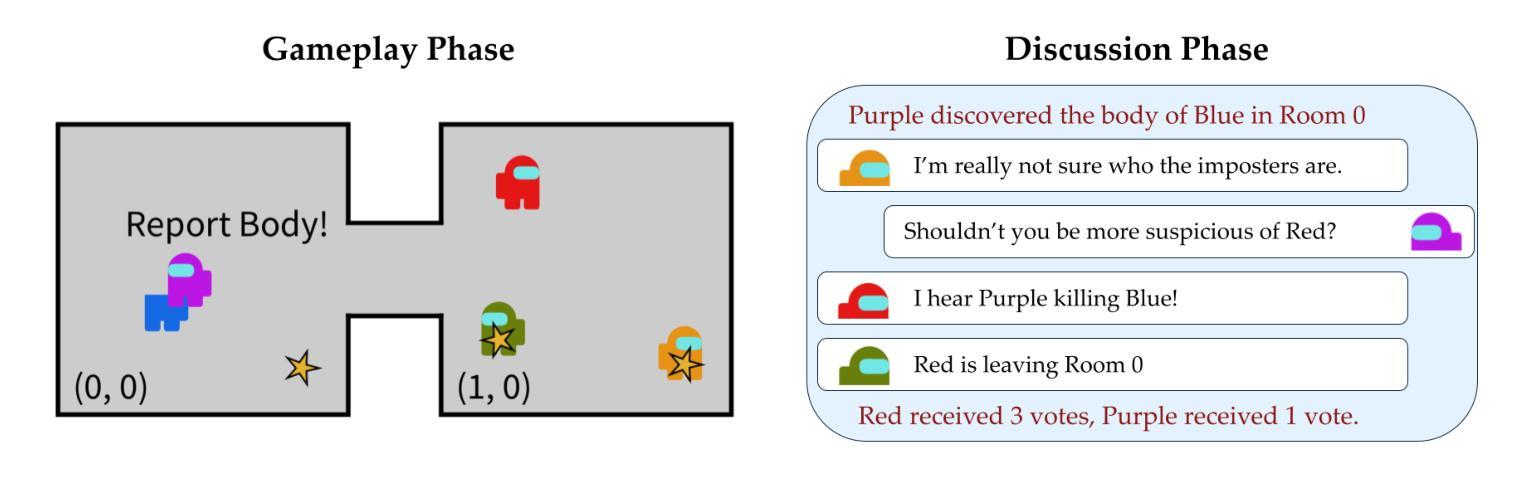
Training Language Models for Social Deduction with Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning
Authors:Bidipta Sarkar, Warren Xia, C. Karen Liu, Dorsa Sadigh
Communicating in natural language is a powerful tool in multi-agent settings, as it enables independent agents to share information in partially observable settings and allows zero-shot coordination with humans. However, most prior works are limited as they either rely on training with large amounts of human demonstrations or lack the ability to generate natural and useful communication strategies. In this work, we train language models to have productive discussions about their environment in natural language without any human demonstrations. We decompose the communication problem into listening and speaking. Our key idea is to leverage the agent’s goal to predict useful information about the world as a dense reward signal that guides communication. Specifically, we improve a model’s listening skills by training them to predict information about the environment based on discussions, and we simultaneously improve a model’s speaking skills with multi-agent reinforcement learning by rewarding messages based on their influence on other agents. To investigate the role and necessity of communication in complex social settings, we study an embodied social deduction game based on Among Us, where the key question to answer is the identity of an adversarial imposter. We analyze emergent behaviors due to our technique, such as accusing suspects and providing evidence, and find that it enables strong discussions, doubling the win rates compared to standard RL. We release our code and models at https://socialdeductionllm.github.io/
在自然语言交流在多智能体环境中的沟通是一项强大的工具,因为它能够在部分可观察的环境中使独立智能体共享信息,并与人类实现零射击协同工作。然而,大多数先前的工作都有局限性,因为它们要么依赖于大量的人类演示进行训练,要么缺乏生成自然和有用的沟通策略的能力。在这项工作中,我们训练语言模型以自然语言进行有关其环境的有见地的讨论,而无需任何人类演示。我们将沟通问题分解为听和说。我们的关键想法是利用智能体的目标来预测有关世界的有用信息,并将其作为密集奖励信号来指导沟通。具体来说,我们通过训练模型根据讨论来预测有关环境的信息来提高其听力技能,同时,我们通过基于信息对其他智能体的影响来奖励信息来提高模型的说话技能,采用多智能体强化学习的方式。为了研究沟通在复杂社会环境中的作用和必要性,我们研究了基于《Among Us》的具身社会推理游戏,其中的关键问题是确定对抗性的骗子身份。我们分析了由于我们的技术而产生的突发行为,例如指责嫌疑人和提供证据,并发现它能够促进激烈的讨论,与标准强化学习相比,将胜率提高了一倍。我们在https://socialdeductionllm.github.io/发布我们的代码和模型。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 14 pages, 5 figures, 24th International Conference on Autonomous Agents and Multiagent Systems (AAMAS 2025)
Summary
自然语言交流在多智能体环境中是强大的工具,可实现独立智能体在部分可观察环境下的信息共享以及与人类的零拍摄协调。但先前的研究多依赖于大量的人类演示数据或缺乏生成自然、有效的沟通策略的能力。本研究训练语言模型以自然语言形式讨论其环境,无需任何人类演示。通过分解沟通问题为听与说两部分,利用智能体的目标预测世界的有用信息作为丰富的奖励信号来指导沟通。本研究通过社交推理游戏探究沟通在复杂社交环境中的角色和必要性,技术促进紧急行为的出现,如指控嫌疑人和提供证据等,分析发现该技术能引发激烈讨论,相较于标准强化学习,胜率翻倍。代码和模型已发布在https://socialdeductionllm.github.io/。
Key Takeaways
- 自然语言交流在多智能体环境中非常重要,可以实现信息共享和与人类协调。
- 先前研究依赖大量人类演示数据或缺乏生成自然沟通策略的能力。
- 本研究训练语言模型以讨论环境,无需人类演示。
- 通过分解沟通问题为听与说两部分,利用智能体的目标作为奖励信号来指导沟通。
- 在社交推理游戏中探究沟通角色和必要性。
- 技术促进紧急行为出现,如指控和提供证据。
点此查看论文截图

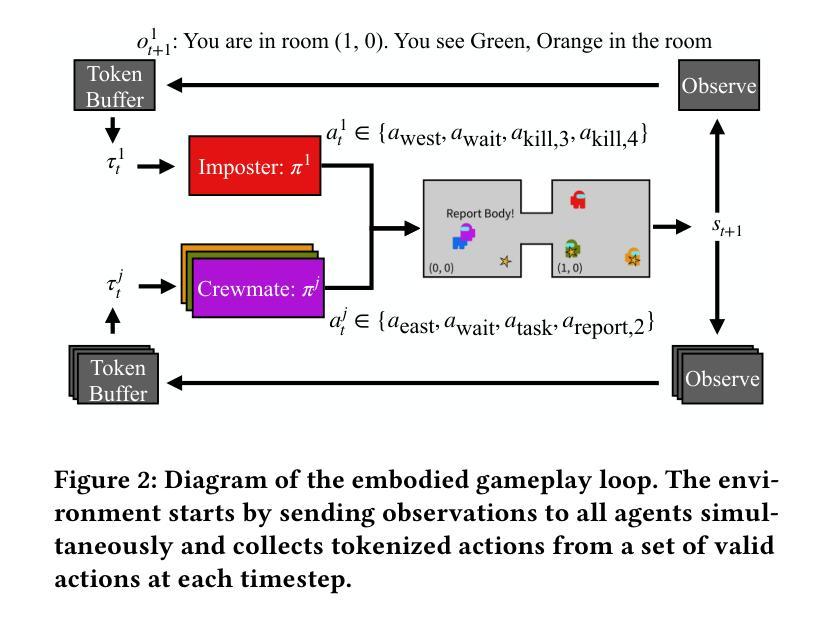
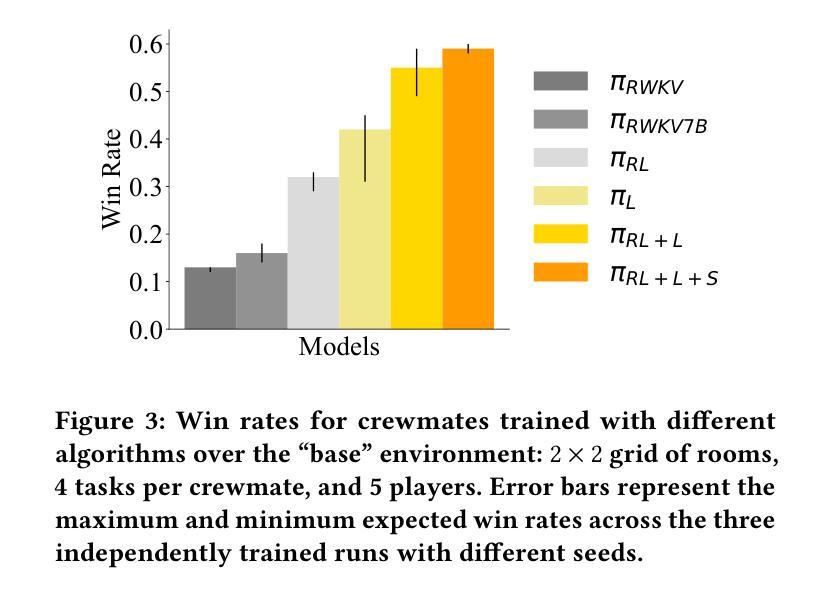
Preventing Rogue Agents Improves Multi-Agent Collaboration
Authors:Ohav Barbi, Ori Yoran, Mor Geva
Multi-agent systems, where specialized agents collaborate to solve a shared task hold great potential, from increased modularity to simulating complex environments. However, they also have a major caveat – a single agent can cause the entire system to fail. Consider a simple game where the knowledge to solve the task is distributed between agents, which share information in a communication channel. At each round, any of the agents can terminate the game and make the final prediction, even if they are uncertain about the outcome of their action. Detection of such rogue agents $\textit{before they act}$ may prevent the system’s failure. In this work, we propose to $\textit{monitor}$ agents during action prediction and $\textit{intervene}$ when a future error is likely to occur. To test our approach, we introduce WhoDunitEnv, a multi-agent collaboration environment that allows modular control over task complexity and communication structure. Experiments on two variants of WhoDunitEnv and the GovSim environment for resource sustainability show that our approach leads to substantial performance gains up to 17.4% and 20%, respectively. Moreover, a thorough analysis shows that our monitors successfully identify critical points of agent confusion and our interventions effectively stop agent errors from propagating.
多智能体系统具有巨大的潜力,其中专职智能体协作完成共同任务,从增加的模块化到模拟复杂环境。然而,它们也存在一个主要的缺陷,即单个智能体可能导致整个系统失败。考虑一个简单的游戏,其中解决问题的知识在智能体之间进行分布,它们在通信通道中共享信息。在每一轮中,任何智能体都可以终止游戏并进行最终预测,即使他们对行动的结果不确定。在行动预测期间监测此类流氓智能体,并在可能发生未来错误时干预,可以防止系统失败。在这项工作中,我们提出在行动预测期间进行智能体监控,并在可能发生未来错误时进行干预。为了测试我们的方法,我们引入了WhoDunitEnv多智能体协作环境,它允许对任务复杂性和通信结构进行模块化控制。在WhoDunitEnv的两个变体和GovSim环境进行的资源可持续性实验表明,我们的方法实现了高达17.4%和20%的显著性能提升。此外,深入的分析表明,我们的监控器成功地识别出了智能体混淆的关键点,我们的干预措施有效地阻止了智能体错误的传播。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
多智能体系统通过专业智能体协作完成共同任务,具有模块化模拟复杂环境等优点,但单个智能体的失误可能导致整个系统失效。文章提出了监控智能体进行行动预测的方法,并在可能发生未来错误时干预。实验表明,该方法显著提高性能,并在识别智能体混淆的关键点和阻止智能体错误传播方面表现出色。
Key Takeaways
- 多智能体系统具有模块化与模拟复杂环境的潜力,但单一智能体的失败可能导致整个系统失效。
- 监控智能体在行动预测中的表现可预防系统失败。
- 介绍了WhoDunitEnv多智能体协作环境,允许对任务复杂性和通信结构进行模块化控制。
- 实验证明监控方法可有效提高性能,并在识别智能体混淆的关键点和阻止错误传播方面有效。
- 监控方法通过识别未来可能出现的错误来干预智能体的行为。
- 该方法在资源可持续性的GovSim环境中也表现出良好的性能提升。
点此查看论文截图

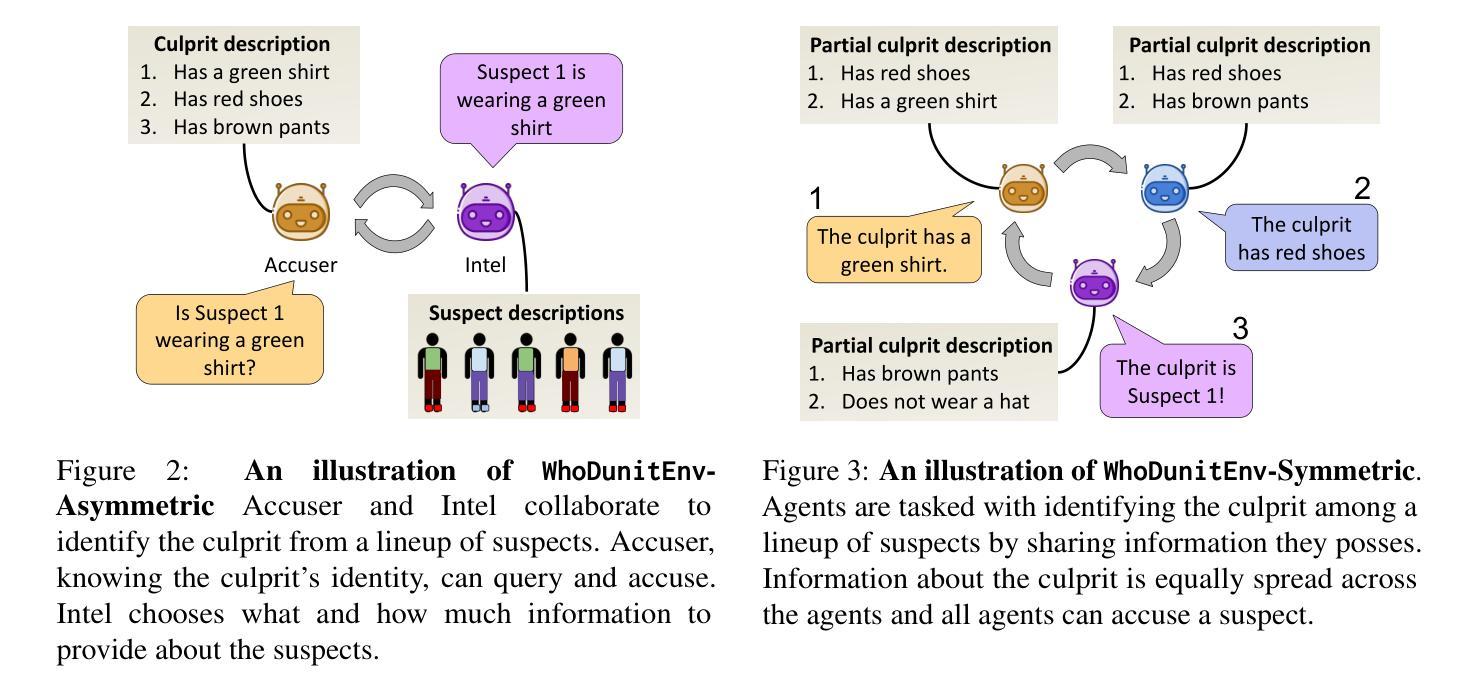
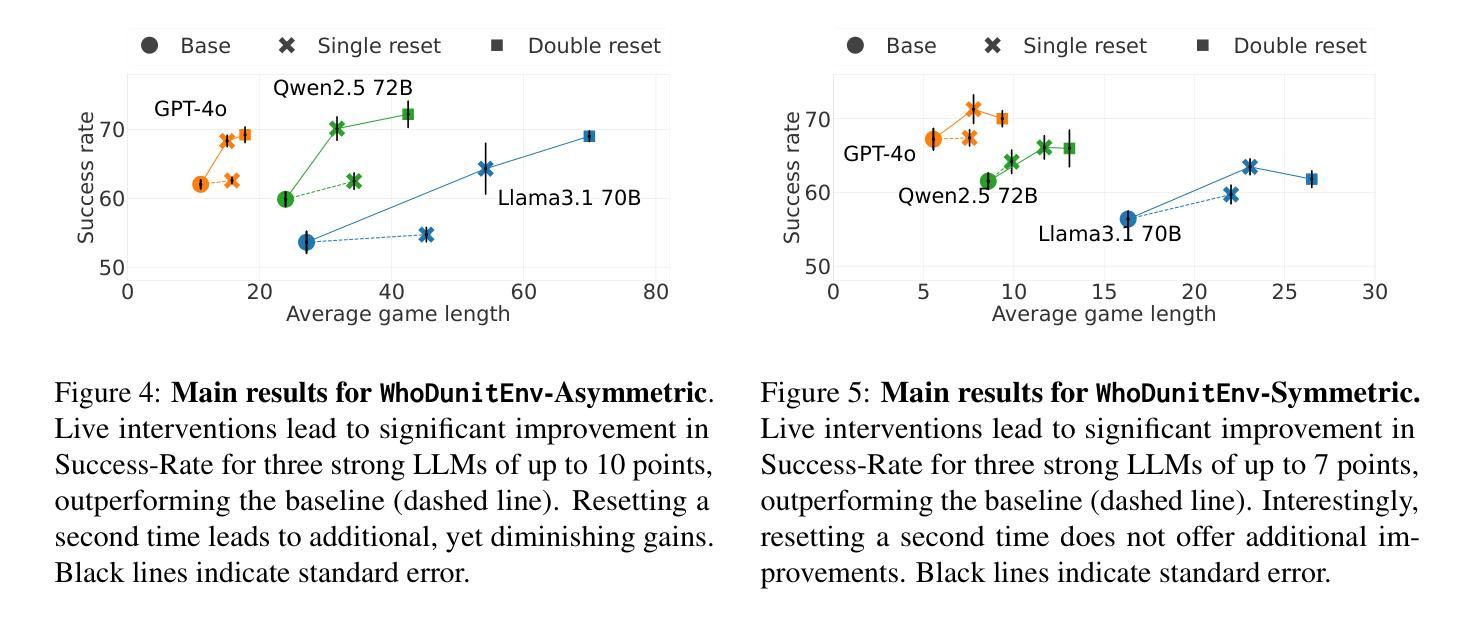
HamRaz: A Culture-Based Persian Conversation Dataset for Person-Centered Therapy Using LLM Agents
Authors:Mohammad Amin Abbasi, Farnaz Sadat Mirnezami, Hassan Naderi
This paper presents HamRaz, a novel Persian-language mental health dataset designed for Person-Centered Therapy (PCT) using Large Language Models (LLMs). Despite the growing application of LLMs in AI-driven psychological counseling, existing datasets predominantly focus on Western and East Asian contexts, overlooking cultural and linguistic nuances essential for effective Persian-language therapy. To address this gap, HamRaz combines script-based dialogues with adaptive LLM role-playing, ensuring coherent and dynamic therapy interactions. We also introduce HamRazEval, a dual evaluation framework that measures conversational quality and therapeutic effectiveness using General Dialogue Metrics and the Barrett-Lennard Relationship Inventory (BLRI). Experimental results show HamRaz outperforms conventional Script Mode and Two-Agent Mode, producing more empathetic, context-aware, and realistic therapy sessions. By releasing HamRaz, we contribute a culturally adapted, LLM-driven resource to advance AI-powered psychotherapy research in diverse communities.
本文介绍了HamRaz,这是一个为以人为中心的治疗(PCT)而设计的新型波斯语心理健康数据集,使用大型语言模型(LLM)。尽管大型语言模型在AI驱动的心理咨询中的应用日益广泛,但现有数据集主要集中在西方和东亚背景上,忽视了有效波斯语治疗所需的文化和语言细微差别。为了解决这一差距,HamRaz结合了基于脚本的对话和自适应LLM角色扮演,确保连贯且动态的治疗互动。我们还介绍了HamRazEval,这是一个双重评估框架,使用通用对话指标和巴雷特-伦纳德关系量表(BLRI)来衡量对话质量和治疗的有效性。实验结果表明,HamRaz在常规脚本模式和双代理模式方面表现更优越,产生更富有同情心、注重上下文和现实的治疗会话。通过发布HamRaz,我们为不同社区的AI驱动的心理治疗研究提供了文化适应的大型语言模型资源。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
HamRaz是一款基于波斯语的心理健康数据集,旨在利用大型语言模型(LLM)进行以病人为中心的治疗(PCT)。针对现有数据集主要关注西方和东亚情境而忽视波斯语治疗的文化和语言细微差别的问题,HamRaz结合了脚本对话和自适应LLM角色扮演技术,确保连贯和动态的疗法互动。此外,引入HamRazEval双评估框架,使用通用对话指标和巴雷特-伦纳德关系量表来评估对话质量和治疗效果。实验结果表明,HamRaz优于传统的脚本模式和双代理模式,能够产生更具同情心、更具上下文意识和更真实的治疗会话。
Key Takeaways
- HamRaz是一个针对波斯语的心理健康数据集,用于以病人为中心的治疗(PCT)。
- HamRaz结合了脚本对话和自适应的大型语言模型(LLM)角色扮演技术。
- HamRaz设计考虑了文化和语言的细微差别,适用于波斯语疗法。
- HamRazEval是一个评估框架,用于衡量对话质量和治疗效果。
- HamRaz优于传统的治疗模式,能产生更真实的、富有同情心的治疗会话。
- HamRaz的发布为多元文化背景的AI心理疗法研究提供了资源。
点此查看论文截图

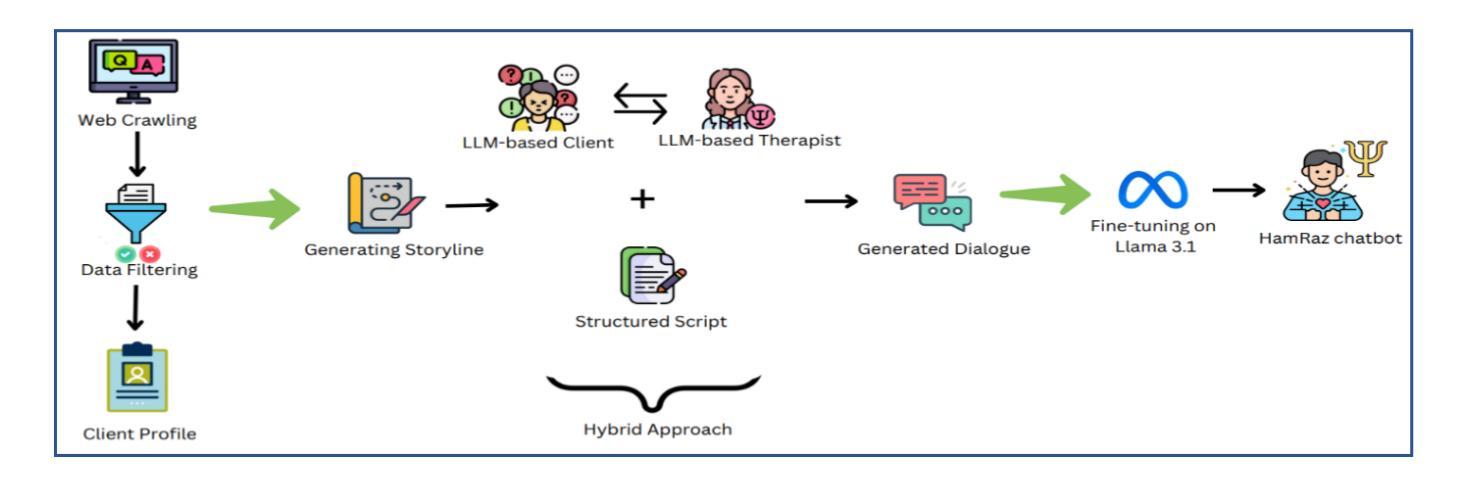
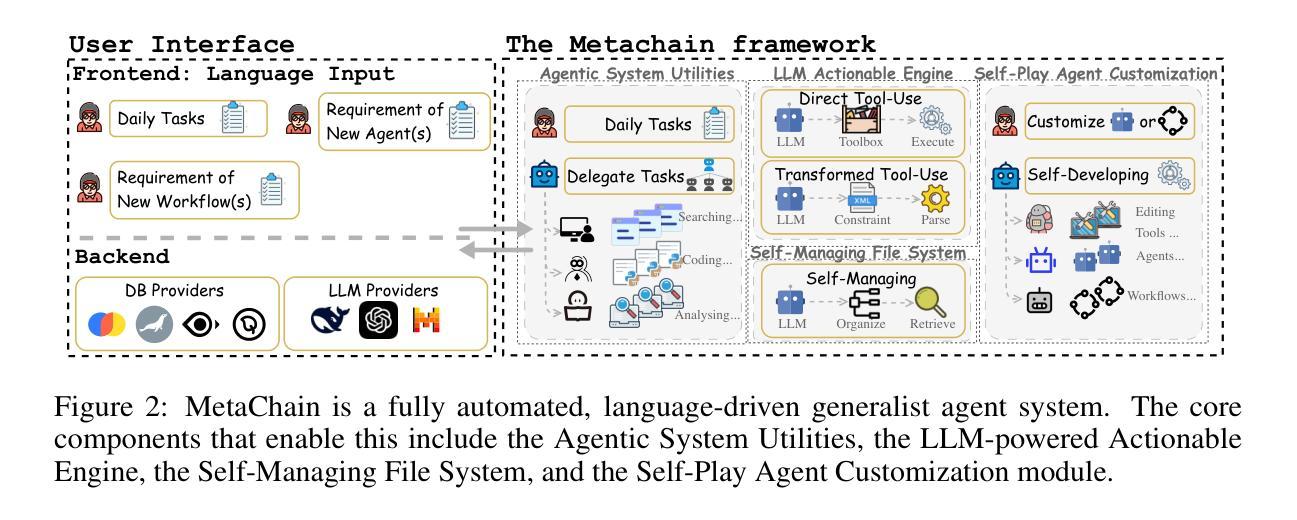
MetaChain: A Fully-Automated and Zero-Code Framework for LLM Agents
Authors:Jiabin Tang, Tianyu Fan, Chao Huang
Large Language Model (LLM) Agents have demonstrated remarkable capabilities in task automation and intelligent decision-making, driving the widespread adoption of agent development frameworks such as LangChain and AutoGen. However, these frameworks predominantly serve developers with extensive technical expertise - a significant limitation considering that only 0.03 % of the global population possesses the necessary programming skills. This stark accessibility gap raises a fundamental question: Can we enable everyone, regardless of technical background, to build their own LLM agents using natural language alone? To address this challenge, we introduce MetaChain-a Fully-Automated and highly Self-Developing framework that enables users to create and deploy LLM agents through Natural Language Alone. Operating as an autonomous Agent Operating System, MetaChain comprises four key components: i) Agentic System Utilities, ii) LLM-powered Actionable Engine, iii) Self-Managing File System, and iv) Self-Play Agent Customization module. This lightweight yet powerful system enables efficient and dynamic creation and modification of tools, agents, and workflows without coding requirements or manual intervention. Beyond its code-free agent development capabilities, MetaChain also serves as a versatile multi-agent system for General AI Assistants. Comprehensive evaluations on the GAIA benchmark demonstrate MetaChain’s effectiveness in generalist multi-agent tasks, surpassing existing state-of-the-art methods. Furthermore, MetaChain’s Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG)-related capabilities have shown consistently superior performance compared to many alternative LLM-based solutions.
大型语言模型(LLM)代理在任务自动化和智能决策方面展现出卓越的能力,推动了诸如LangChain和AutoGen等代理开发框架的广泛采用。然而,这些框架主要服务于具有丰富技术专长的开发者——考虑到全球只有0.03%的人口具备必要的编程技能,这是一个重要的限制。这一严峻的可达性差距提出了一个根本性的问题:我们是否可以通过自然语言本身,让每个人无论其技术背景如何,都能构建自己的LLM代理?为了应对这一挑战,我们引入了MetaChain——一个全自动且高度自我发展的框架,它使用户能够通过自然语言创建和部署LLM代理。作为自主代理操作系统,MetaChain包含四个关键组件:i)代理系统实用程序,ii)LLM驱动的可行引擎,iii)自我管理文件系统,以及iv)自我玩耍代理自定义模块。这个轻便而强大的系统能够高效、动态地创建和修改工具、代理和工作流程,无需编码要求或人工干预。除了无需编码的代理开发能力外,MetaChain还作为通用人工智能助理的多代理系统。在GAIA基准上的综合评估表明,MetaChain在通用多代理任务中的有效性超过了现有的最先进方法。此外,MetaChain的检索增强生成(RAG)相关功能在许多其他LLM解决方案中表现出了一致的优势性能。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Code: https://github.com/HKUDS/MetaChain
Summary:
大型语言模型(LLM)驱动了诸如LangChain和AutoGen等智能代理开发框架的广泛应用,但主要服务于技术专家。针对全球只有0.03%的人具备编程技能的问题,我们提出MetaChain框架,这是一个全自动化且高度自我发展的系统,通过自然语言即可创建和部署LLM代理。MetaChain包含四个关键组件,并能有效、动态地创建和修改工具、代理和工作流程,无需编码和人工干预。它同时也是一个通用的人工智能助理的多代理系统。
Key Takeaways:
- LLM代理具备自动化任务和智能决策的能力。
- 当前框架主要服务于技术专家,存在普及性限制。
- MetaChain框架旨在通过自然语言让非技术背景的用户也能创建和部署LLM代理。
- MetaChain是一个全自动化和高度自我发展的系统,包含四个关键组件。
- MetaChain能有效、动态地创建和修改工具、代理和工作流程,无需编码和人工干预。
- MetaChain是一个通用的人工智能助理的多代理系统。
点此查看论文截图

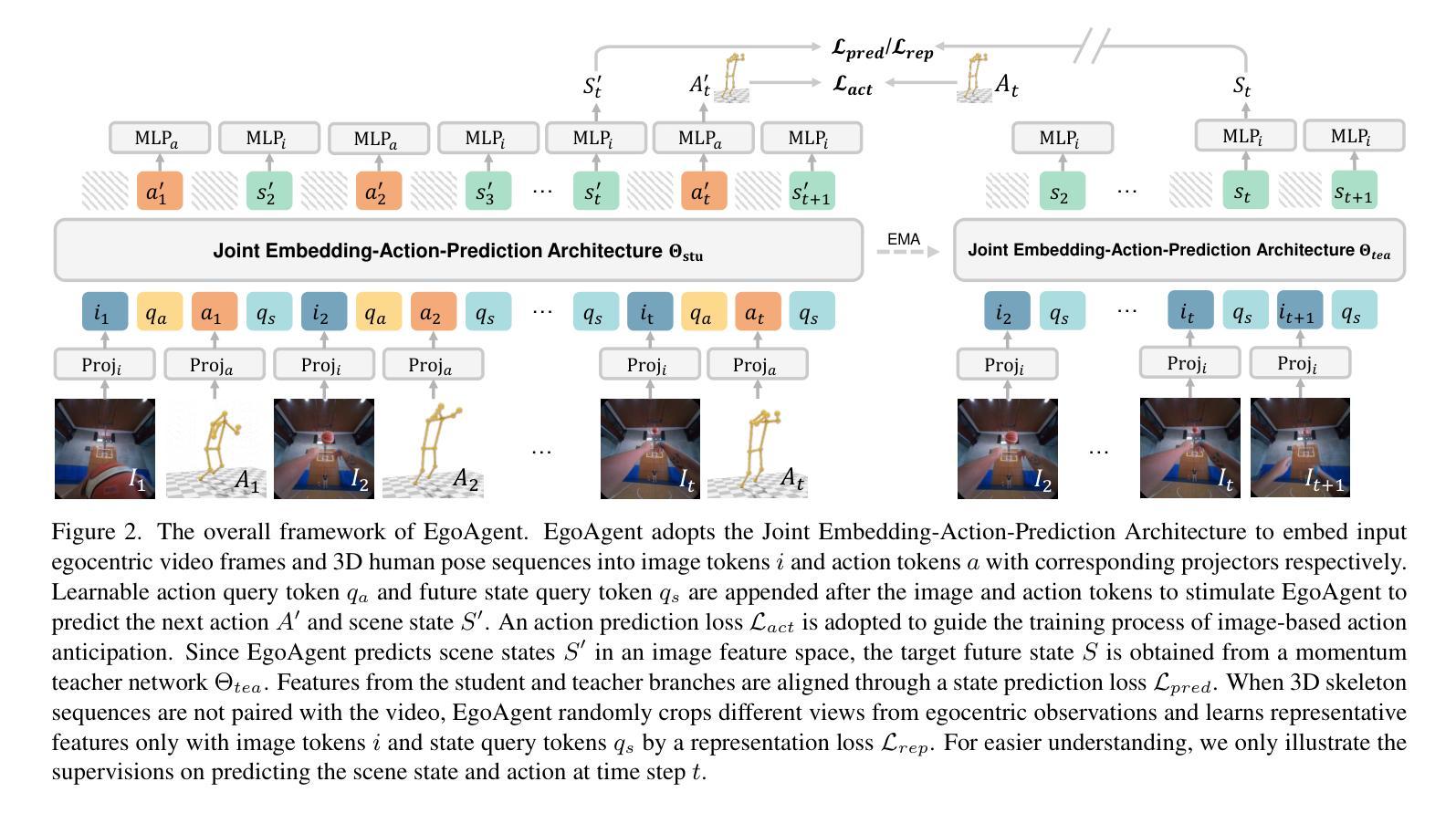
Acquisition through My Eyes and Steps: A Joint Predictive Agent Model in Egocentric Worlds
Authors:Lu Chen, Yizhou Wang, Shixiang Tang, Qianhong Ma, Tong He, Wanli Ouyang, Xiaowei Zhou, Hujun Bao, Sida Peng
This paper addresses the task of learning an agent model behaving like humans, which can jointly perceive, predict, and act in egocentric worlds. Previous methods usually train separate models for these three abilities, leading to information silos among them, which prevents these abilities from learning from each other and collaborating effectively. In this paper, we propose a joint predictive agent model, named EgoAgent, that simultaneously learns to represent the world, predict future states, and take reasonable actions with a single transformer. EgoAgent unifies the representational spaces of the three abilities by mapping them all into a sequence of continuous tokens. Learnable query tokens are appended to obtain current states, future states, and next actions. With joint supervision, our agent model establishes the internal relationship among these three abilities and effectively mimics the human inference and learning processes. Comprehensive evaluations of EgoAgent covering image classification, egocentric future state prediction, and 3D human motion prediction tasks demonstrate the superiority of our method. The code and trained model will be released for reproducibility.
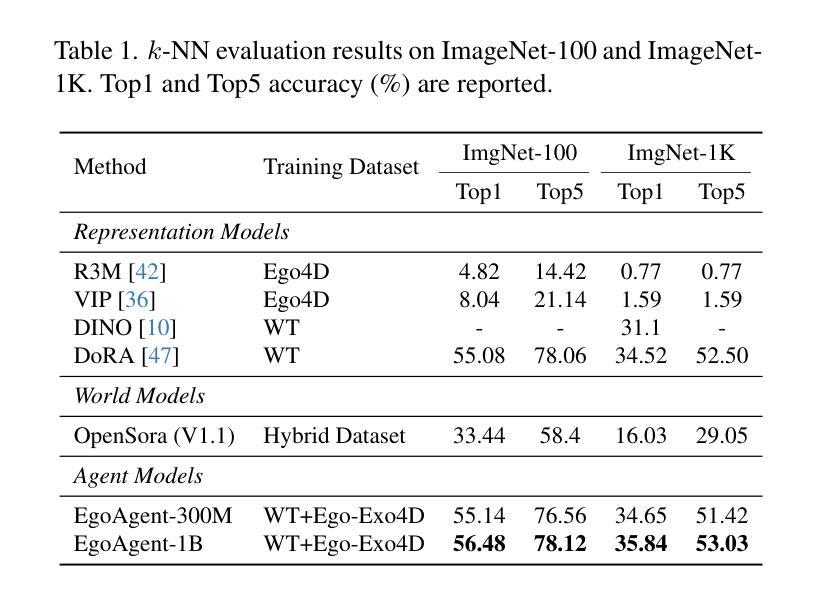
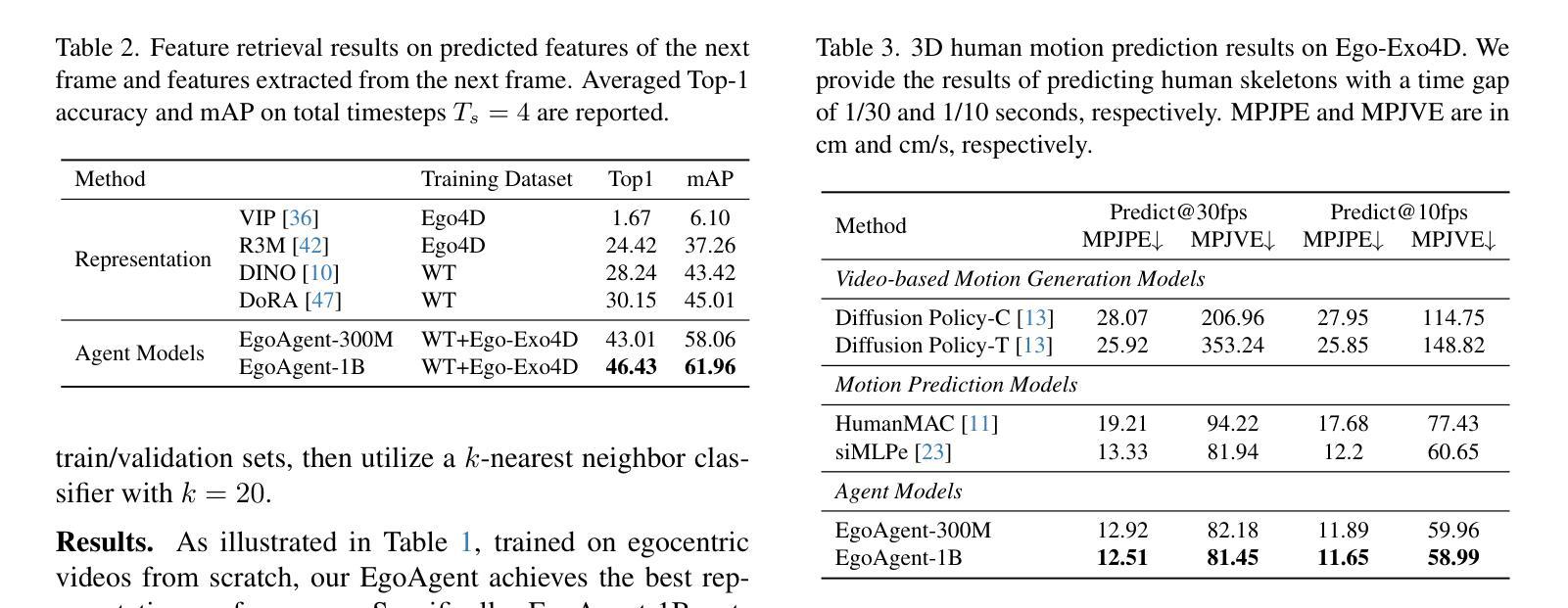
本文旨在解决学习一种像人类一样行为的代理模型的任务,该模型可以在以自我为中心的世界中共同感知、预测和行动。以前的方法通常针对这三种能力分别训练模型,导致它们之间存在信息孤岛,这阻碍了这些能力相互学习和有效协作。在本文中,我们提出了一种联合预测代理模型,名为EgoAgent。EgoAgent使用单个变压器同时学习表示世界、预测未来状态和采取合理行动。EgoAgent通过将所有三种能力映射到一系列连续令牌序列来统一它们的表示空间。通过添加可学习的查询令牌来获得当前状态、未来状态和下一个动作。通过联合监督,我们的代理模型建立了这三种能力之间的内部关系,并有效地模仿了人类的推理和学习过程。对EgoAgent在图像分类、以自我为中心的未来状态预测和3D人类运动预测任务上的综合评估证明了我们的方法优越性。我们将发布代码和训练模型以供复制。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:
本文提出一种名为EgoAgent的联合预测代理模型,该模型能够在以自我为中心的世界中联合感知、预测和行动,表现出类似人类的行为。通过采用单一变压器进行学习,EgoAgent将世界的表示、未来状态的预测和合理行动的采取融为一体,通过映射为一系列连续的令牌序列,统一了三种能力的表示空间。实验评估表明,EgoAgent在图像分类、以自我为中心的未来状态预测和3D人类运动预测任务上表现优越。
Key Takeaways:
- 代理模型EgoAgent能够联合感知、预测和行动在以自我为中心的世界中,模拟人类行为。
- EgoAgent采用单一变压器进行学习,将世界的表示、未来状态的预测和行动的采取整合在一起。
- 通过将不同能力映射为连续的令牌序列,EgoAgent统一了三种能力的表示空间。
- 学习查询令牌用于获取当前状态、未来状态和下一步行动。
- EgoAgent通过联合监督建立这三种能力之间的内部关系,并有效模仿人类推理和学习过程。
- 实验评估显示,EgoAgent在多种任务上表现优越,包括图像分类、以自我为中心的未来状态预测和3D人类运动预测。
点此查看论文截图

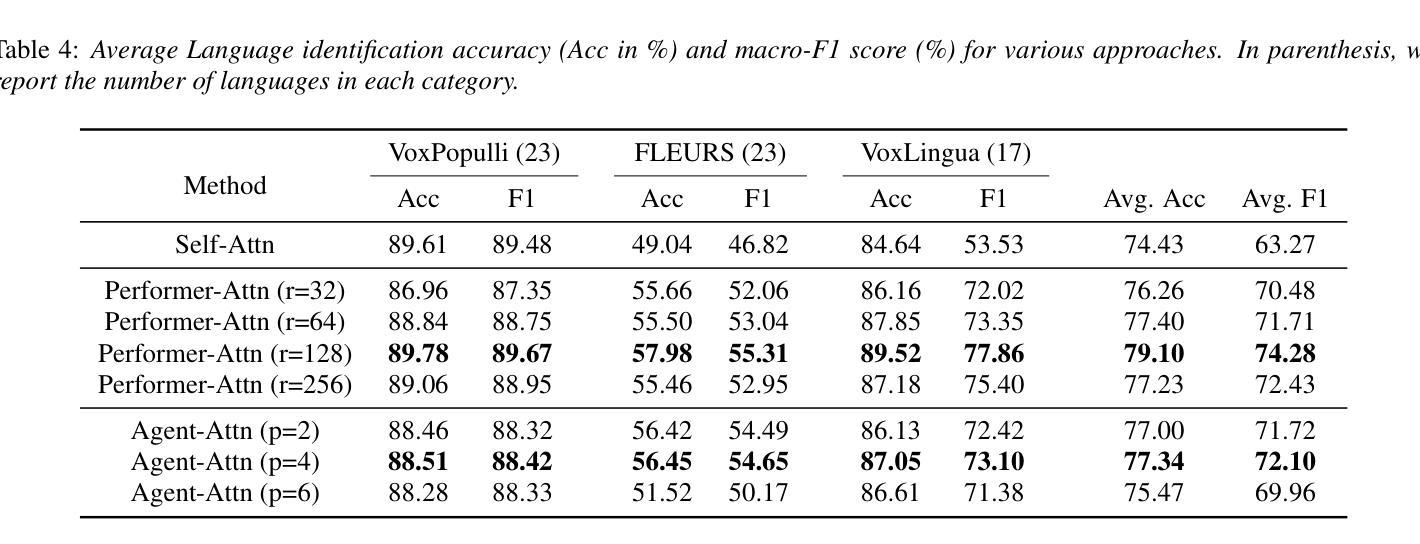
On the use of Performer and Agent Attention for Spoken Language Identification
Authors:Jitendra Kumar dhiman, Jainag Ambati
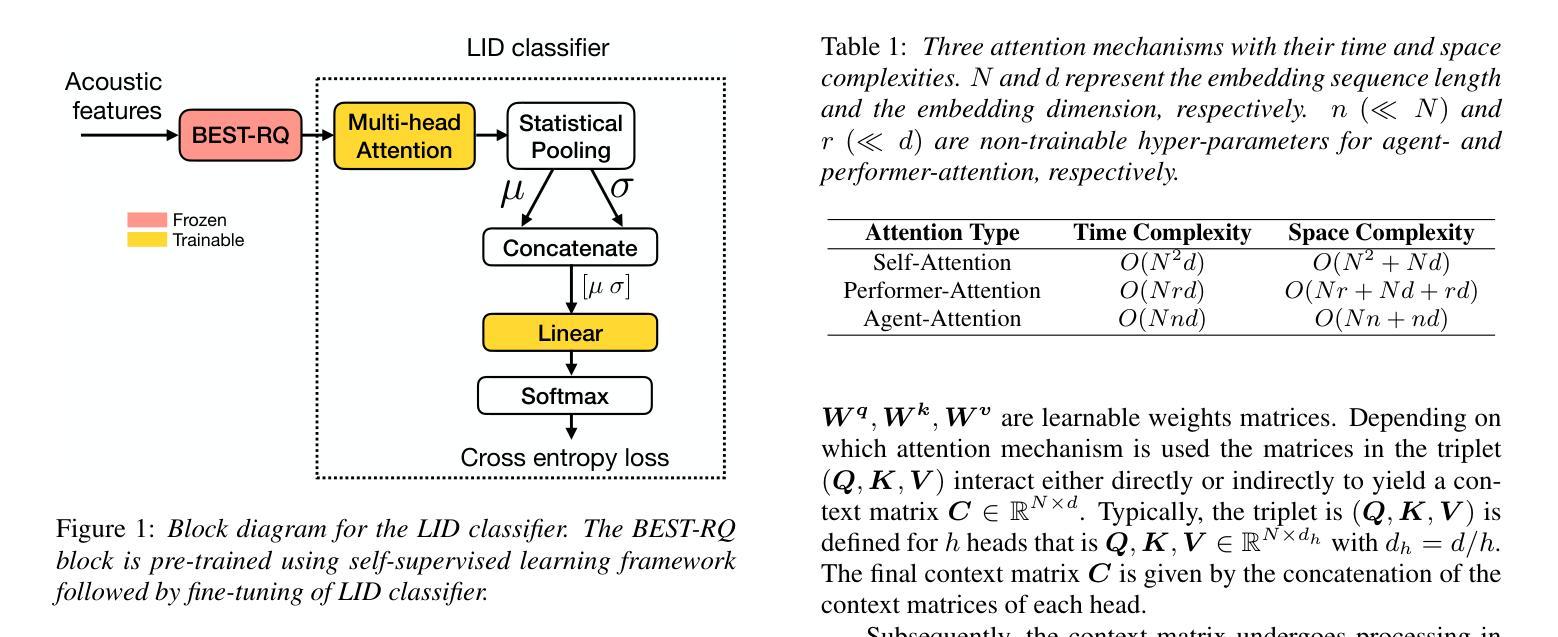
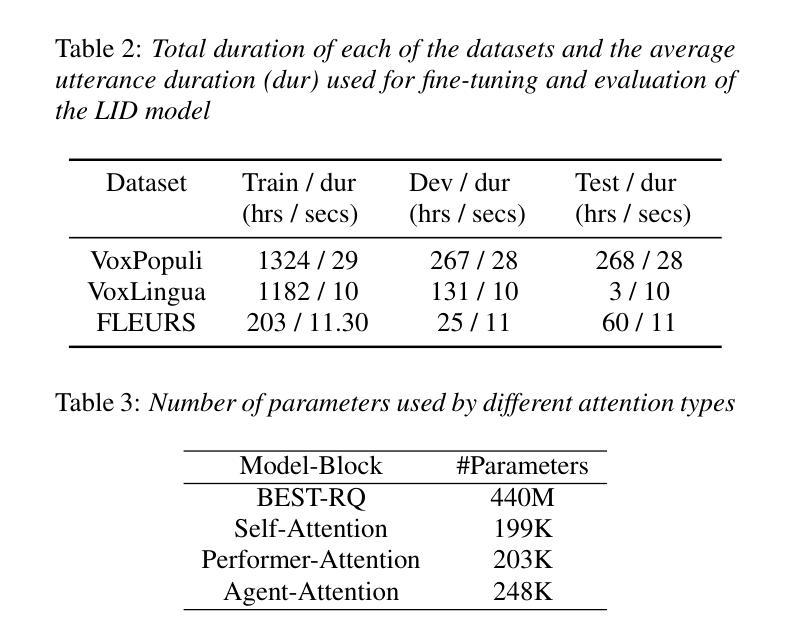
One of the methods for language Identification (LID) involves deriving speech representation from pre-trained models using self-supervised learning, followed by fine-tuning the model for the LID task. State-of-the-art approaches for LID use an attention-based statistical pooling layer to facilitate the aggregation of contextual information across time frames of the embedding vectors extracted from the pre-trained model. In this paper, we delve into exploring recently proposed attention mechanisms, namely performer and agent-attention, in conjunction with the statistical pooling layer. The LID experiments are performed on three datasets: VoxPopuli, FLEURS, and VoxLingua. We compare their performance against vanilla self-attention. Our findings suggest that performer-attention outperforms self-attention and agent-attention exhibits comparable or occasionally superior performance to self-attention, while also being computationally less expensive.
语言识别(LID)的方法之一涉及使用自监督学习从预训练模型中推导语音表示,随后对模型进行微调以进行LID任务。LID的最先进方法使用基于注意力的统计池层,以促进从预训练模型中提取的嵌入向量的时间帧上上下文信息的聚合。在本文中,我们深入探讨了最近提出的注意力机制,即表演者和agent-attention,以及与统计池层的结合。LID实验是在三个数据集上进行的:VoxPopuli、FLEURS和VoxLingua。我们将它们的性能与基本的自注意力进行了比较。我们的研究发现,表演者注意力优于自注意力,agent-attention表现出与自注意力相当或偶尔更优的性能,同时在计算上更加经济。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 5 pages, 1 figure
Summary
利用预训练模型通过自监督学习进行语言表征的推导,随后对模型进行微调以进行语言识别(LID)。当前高级LID方法使用基于注意力的统计池化层来促进从预训练模型中提取的嵌入向量时间帧的上下文信息的聚合。本文深入探讨了最近提出的注意力机制,即Performer和Agent-Attention,以及与统计池化层的结合。在VoxPopuli、FLEURS和VoxLingua三个数据集上进行了LID实验。结果表明,Performer-Attention表现优于自注意力,而Agent-Attention与自注意力表现相当,有时更胜一筹,同时计算成本更低。
Key Takeaways
- LID的一种方法是使用预训练模型通过自监督学习进行语言表征推导。
- 当前高级LID方法使用基于注意力的统计池化层来促进上下文信息的聚合。
- 本文探讨了Performer和Agent-Attention这两种新提出的注意力机制。
- LID实验在VoxPopuli、FLEURS和VoxLingua三个数据集上进行。
- Performer-Attention表现优于自注意力。
- Agent-Attention与自注意力相当或有时表现更好,同时计算成本更低。
点此查看论文截图

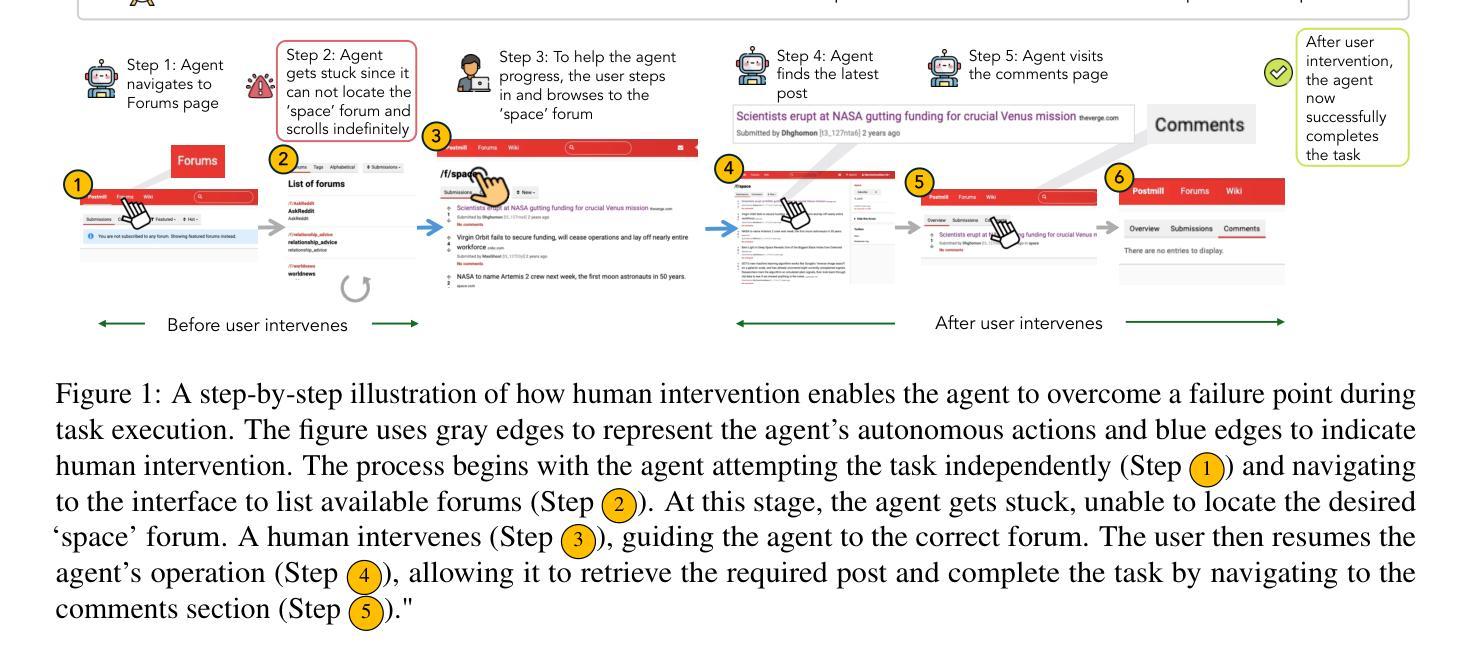
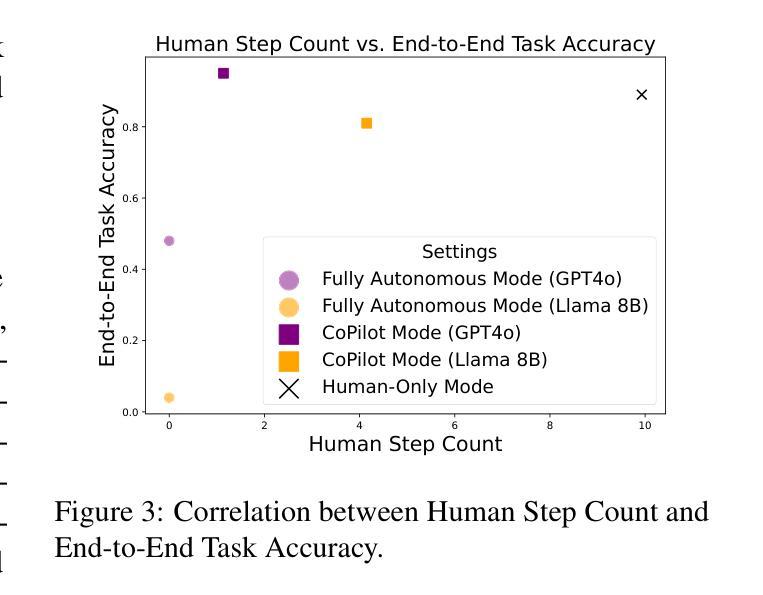
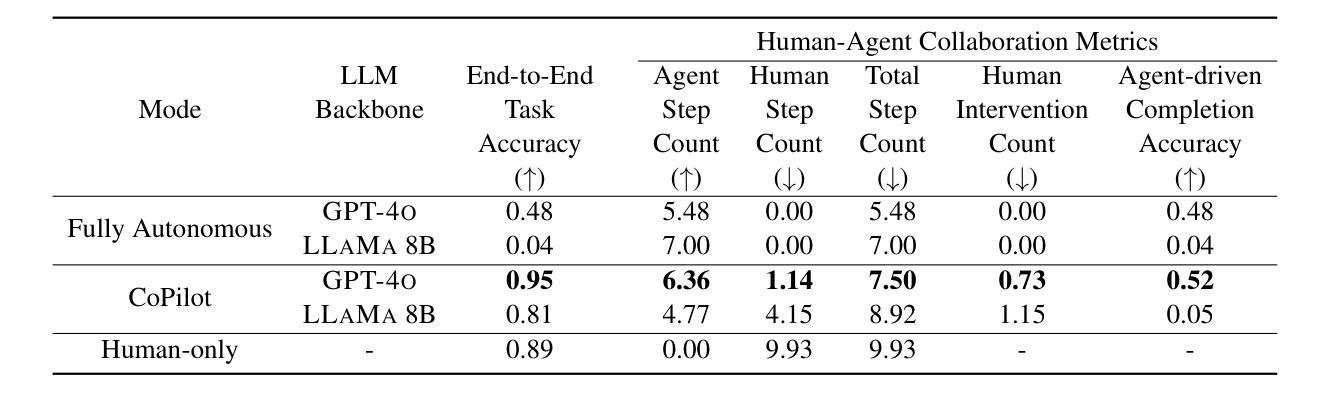
CowPilot: A Framework for Autonomous and Human-Agent Collaborative Web Navigation
Authors:Faria Huq, Zora Zhiruo Wang, Frank F. Xu, Tianyue Ou, Shuyan Zhou, Jeffrey P. Bigham, Graham Neubig
While much work on web agents emphasizes the promise of autonomously performing tasks on behalf of users, in reality, agents often fall short on complex tasks in real-world contexts and modeling user preference. This presents an opportunity for humans to collaborate with the agent and leverage the agent’s capabilities effectively. We propose CowPilot, a framework supporting autonomous as well as human-agent collaborative web navigation, and evaluation across task success and task efficiency. CowPilot reduces the number of steps humans need to perform by allowing agents to propose next steps, while users are able to pause, reject, or take alternative actions. During execution, users can interleave their actions with the agent by overriding suggestions or resuming agent control when needed. We conducted case studies on five common websites and found that the human-agent collaborative mode achieves the highest success rate of 95% while requiring humans to perform only 15.2% of the total steps. Even with human interventions during task execution, the agent successfully drives up to half of task success on its own. CowPilot can serve as a useful tool for data collection and agent evaluation across websites, which we believe will enable research in how users and agents can work together. Video demonstrations are available at https://oaishi.github.io/cowpilot.html
关于网络代理的研究虽然强调了其自主执行用户任务的潜力,但在现实中,代理在处理复杂任务和模拟用户偏好方面往往表现不足。这为人类与代理协作并有效利用代理的能力提供了机会。我们提出了CowPilot框架,它支持自主和网络用户与代理的协作导航,并通过对任务成功和效率的评价进行评估。CowPilot通过允许代理提出下一步的建议,减少了人类执行任务的步骤数量,同时用户能够暂停、拒绝或采取替代行动。在执行过程中,用户可以通过覆盖建议或在需要时恢复代理控制来交替执行他们的行动与代理的行动。我们在五个常见网站上进行了案例研究,发现人机协作模式取得了最高的成功率,达到95%,而人类仅需要执行总步骤的15.2%。即使在任务执行过程中有人类干预,代理也能独立完成高达一半的任务。CowPilot可以作为跨网站的数据收集和代理评估的有用工具,我们相信这将有助于研究用户和代理如何协同工作。视频演示可在https://oaishi.github.io/cowpilot.html观看。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Preprint
Summary
本文探讨了web代理在复杂任务和模拟用户偏好方面的不足,并提出了一个名为CowPilot的框架,支持自主和人类代理协同的网页浏览。通过案例研究,发现人类代理协同模式在任务成功率上表现最佳,达到95%,同时人类只需执行总步骤的15.2%。CowPilot还可作为跨网站的数据收集和分析工具,促进对人机协同工作的研究。视频演示请参见链接。
Key Takeaways
- Web代理在复杂任务和模拟用户偏好方面存在不足,需要人类协作以提高效率。
- CowPilot框架支持自主和人类代理协同的网页浏览,提升任务执行效率。
- 人类代理协同模式在任务成功率上表现最佳,达到95%。
- 在人类干预的情况下,代理仍能独立完成一半以上的任务。
- CowPilot框架可用于数据收集和分析,促进人机协同工作的研究。
- 用户可以在执行过程中随时接管或恢复代理控制,实现灵活的人机交互。
点此查看论文截图



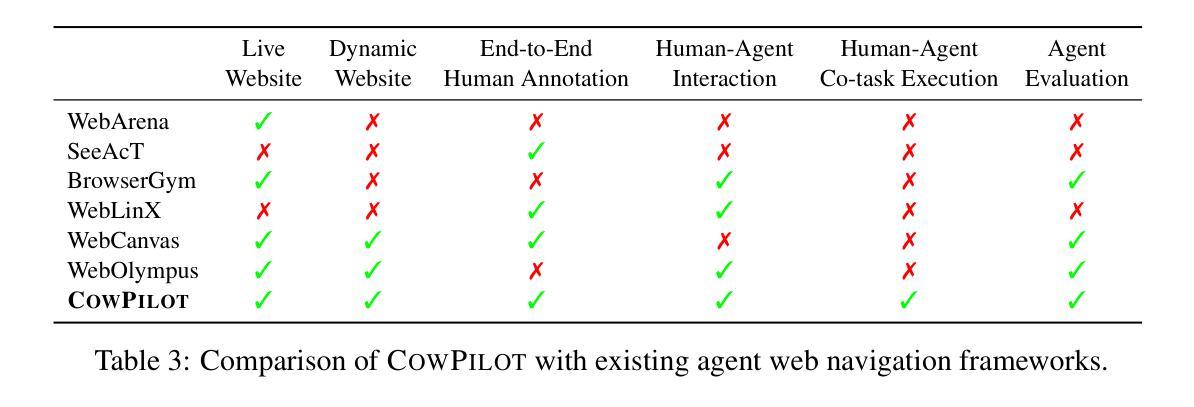
AgentMove: A Large Language Model based Agentic Framework for Zero-shot Next Location Prediction
Authors:Jie Feng, Yuwei Du, Jie Zhao, Yong Li
Next location prediction plays a crucial role in various real-world applications. Recently, due to the limitation of existing deep learning methods, attempts have been made to apply large language models (LLMs) to zero-shot next location prediction task. However, they directly generate the final output using LLMs without systematic design, which limits the potential of LLMs to uncover complex mobility patterns and underestimates their extensive reserve of global geospatial knowledge. In this paper, we introduce AgentMove, a systematic agentic prediction framework to achieve generalized next location prediction. In AgentMove, we first decompose the mobility prediction task and design specific modules to complete them, including spatial-temporal memory for individual mobility pattern mining, world knowledge generator for modeling the effects of urban structure and collective knowledge extractor for capturing the shared patterns among population. Finally, we combine the results of three modules and conduct a reasoning step to generate the final predictions. Extensive experiments utilizing mobility data from two distinct sources reveal that AgentMove surpasses the leading baseline by 3.33% to 8.57% across 8 out of 12 metrics and it shows robust predictions with various LLMs as base and also less geographical bias across cities. Our codes are available via https://github.com/tsinghua-fib-lab/AgentMove.
下一个位置预测在各种实际应用中发挥着至关重要的作用。最近,由于现有深度学习方法的局限性,人们试图将大型语言模型(LLMs)应用于零样本下一个位置预测任务。然而,它们直接使用LLMs生成最终输出,而没有进行系统性的设计,这限制了LLMs揭示复杂移动模式的能力,并低估了它们丰富的全球地理空间知识储备。在本文中,我们介绍了AgentMove,这是一个系统性的智能预测框架,以实现通用的下一个位置预测。在AgentMove中,我们首先对移动性预测任务进行分解,并设计特定的模块来完成它们,包括用于个人移动模式挖掘的空间时间记忆、用于建模城市结构影响的全球知识生成器以及用于捕捉人群共享模式的集体知识提取器。最后,我们结合三个模块的结果进行推理,生成最终的预测。利用来自两个不同来源的出行数据进行的广泛实验表明,AgentMove在12个指标中的8个指标上超越了领先的基线模型3.33%至8.57%,它表现出对各种LLMs基础的稳健预测,并且在不同城市之间的地理偏见也较小。我们的代码可通过https://github.com/tsinghua-fib-lab/AgentMove获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by NAACL 2025 as main conference paper, https://github.com/tsinghua-fib-lab/AgentMove
Summary
基于深度学习方法的局限性,现有研究尝试将大型语言模型(LLMs)应用于零起点位置预测任务。然而,由于缺乏系统性设计,直接生成最终输出限制了LLMs挖掘复杂移动模式的能力,并低估了其丰富的全球地理空间知识。本文提出AgentMove,一个系统性的代理预测框架,实现通用位置预测。AgentMove通过分解移动预测任务并设计特定模块来完成,包括个体移动模式挖掘的时空记忆、建模城市结构影响的世界知识生成器以及捕捉人口间共享模式的集体知识提取器。最后,结合三个模块的结果进行推理生成最终预测。实验表明,AgentMove在8个指标中的预测效果超过领先基线模型3.33%~8.57%,表现出稳健的预测性能且在不同LLMs基础上具有较强的鲁棒性,同时减少了城市间的地理偏见。相关代码可通过链接访问。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLMs)被尝试应用于零起点位置预测任务。
- 直接使用LLMs生成最终输出存在局限性,无法挖掘复杂移动模式并低估其全球地理空间知识。
- AgentMove是一个系统性的预测框架,包括时空记忆、世界知识生成器和集体知识提取器三个模块。
- AgentMove通过分解移动预测任务并使用特定模块完成,以提高预测性能。
- AgentMove在多个指标上超越领先基线模型,表现出稳健的预测性能。
- AgentMove具有鲁棒性,能够在不同的LLMs基础上进行预测。
点此查看论文截图



Visual Agents as Fast and Slow Thinkers
Authors:Guangyan Sun, Mingyu Jin, Zhenting Wang, Cheng-Long Wang, Siqi Ma, Qifan Wang, Tong Geng, Ying Nian Wu, Yongfeng Zhang, Dongfang Liu
Achieving human-level intelligence requires refining cognitive distinctions between System 1 and System 2 thinking. While contemporary AI, driven by large language models, demonstrates human-like traits, it falls short of genuine cognition. Transitioning from structured benchmarks to real-world scenarios presents challenges for visual agents, often leading to inaccurate and overly confident responses. To address the challenge, we introduce FaST, which incorporates the Fast and Slow Thinking mechanism into visual agents. FaST employs a switch adapter to dynamically select between System 1/2 modes, tailoring the problem-solving approach to different task complexity. It tackles uncertain and unseen objects by adjusting model confidence and integrating new contextual data. With this novel design, we advocate a flexible system, hierarchical reasoning capabilities, and a transparent decision-making pipeline, all of which contribute to its ability to emulate human-like cognitive processes in visual intelligence. Empirical results demonstrate that FaST outperforms various well-known baselines, achieving 80.8% accuracy over VQA^{v2} for visual question answering and 48.7% GIoU score over ReasonSeg for reasoning segmentation, demonstrate FaST’s superior performance. Extensive testing validates the efficacy and robustness of FaST’s core components, showcasing its potential to advance the development of cognitive visual agents in AI systems. The code is available at ttps://github.com/GuangyanS/Sys2-LLaVA.
实现人类水平的智能需要精进系统1和系统2思维之间的认知区分。虽然当代人工智能,由大型语言模型驱动,展现出人类特征,但仍未达到真正的认知水平。从结构化基准测试过渡到现实世界场景,对视觉智能体来说是一个挑战,常常导致不准确且过于自信的回应。为了应对这一挑战,我们引入了FaST,它将快速和慢速思考机制融入视觉智能体。FaST采用开关适配器来动态选择系统1/2模式,根据任务复杂度定制问题解决方式。它通过调整模型信心并整合新的上下文数据来应对不确定和未见过的物体。凭借这一新颖设计,我们提倡一个灵活的系统、分层推理能力和透明的决策制定流程,所有这些都有助于其在视觉智能中模拟人类认知过程。实证结果表明,FaST在各种知名基准测试中表现出色,在视觉问答的VQA^{v2}上达到80.8%的准确率,在推理分割的ReasonSeg上达到48.7%的GIoU分数,证明了FaST的优越性。大量测试验证了FaST核心组件的有效性和稳健性,展示了其在推动人工智能系统中认知视觉智能体发展的潜力。代码可在https://github.com/GuangyanS/Sys2-LLaVA获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR 2025)
Summary
实现人类水平的智能需要优化系统1和系统2思维之间的认知区分。当代的大型语言模型驱动的AI表现出人类特质,但尚未达到真正的认知水平。从结构化基准测试过渡到现实世界场景,视觉代理面临挑战,导致反应不准确且过于自信。为解决此问题,我们引入了FaST,它将快速和慢速思考机制融入视觉代理中。FaST通过开关适配器动态选择系统1/2模式,针对任务复杂性调整解决方法。它处理不确定和未见物体通过调整模型信心并集成新的情境数据。凭借新颖的设计,我们提倡灵活的系统、分层推理能力和透明的决策制定流程,所有这些都有助于模拟人类认知过程在视觉智能中的表现。经验结果表明,FaST在各种知名基准测试中表现优异,在视觉问答和推理分割任务中分别达到了80.8%的准确率和48.7%的GIoU分数。广泛的测试验证了FaST核心组件的有效性和稳健性,展示了其在推动AI系统中认知视觉代理发展的潜力。
Key Takeaways
- 实现人类水平智能需优化系统1和系统2思维的认知区分。
- 当代AI虽具人类特质,但仍未达到真正的认知水平。
- 视觉代理在现实世界场景下面临挑战,需提高准确性和应对不确定性。
- FaST通过结合快速和慢速思考机制解决这些问题。
- FaST通过开关适配器动态调整系统1和系统2的模式以适应任务复杂性。
- FaST在处理不确定和未见物体时,能调整模型信心并集成新情境数据。
点此查看论文截图




Learning to Steer Markovian Agents under Model Uncertainty
Authors:Jiawei Huang, Vinzenz Thoma, Zebang Shen, Heinrich H. Nax, Niao He
Designing incentives for an adapting population is a ubiquitous problem in a wide array of economic applications and beyond. In this work, we study how to design additional rewards to steer multi-agent systems towards desired policies \emph{without} prior knowledge of the agents’ underlying learning dynamics. Motivated by the limitation of existing works, we consider a new and general category of learning dynamics called \emph{Markovian agents}. We introduce a model-based non-episodic Reinforcement Learning (RL) formulation for our steering problem. Importantly, we focus on learning a \emph{history-dependent} steering strategy to handle the inherent model uncertainty about the agents’ learning dynamics. We introduce a novel objective function to encode the desiderata of achieving a good steering outcome with reasonable cost. Theoretically, we identify conditions for the existence of steering strategies to guide agents to the desired policies. Complementing our theoretical contributions, we provide empirical algorithms to approximately solve our objective, which effectively tackles the challenge in learning history-dependent strategies. We demonstrate the efficacy of our algorithms through empirical evaluations.
针对适应人群设计激励机制是众多经济应用以及其他领域中的普遍问题。在这项工作中,我们研究如何设计附加奖励来引导多智能体系统实现期望的策略,而无需事先了解智能体的基本学习动态。受现有工作的局限性的启发,我们考虑了一种新的通用学习动态类别,称为“马尔可夫智能体”。我们对引导问题采用了基于模型的非片段性强化学习(RL)公式。重要的是,我们专注于学习一种依赖于历史的引导策略,以应对关于智能体学习动态固有的模型不确定性。我们引入了一个新的目标函数,以编码在合理成本下实现良好引导结果的愿望。从理论上讲,我们确定了存在引导策略的条件,以指导智能体达到期望的策略。除了理论贡献之外,我们还提供了经验算法来近似解决我们的目标,这有效地解决了学习历史依赖策略的挑战。我们通过经验评估证明了算法的有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 35 Pages; ICLR 2025
Summary
本文研究了如何设计额外奖励来引导多智能体系统朝向期望的策略,且无需事先了解智能体的学习动态。文章提出了一种基于模型的非片段式强化学习(RL)公式来解决引导问题,并关注学习一个依赖历史的引导策略来处理对智能体学习动态的固有模型不确定性。引入了一个新颖的目标函数,以编码在合理成本下实现良好引导结果的要求。理论上,文章确定了存在引导策略的条件,以指导智能体达到期望的策略。同时,提供了实证算法来近似解决目标问题,并通过实证评估验证了算法的有效性。
Key Takeaways
- 本文研究如何设计奖励以引导多智能体系统达到期望策略,且无需预先了解智能体的学习动态。
- 提出了一种基于模型的非片段式强化学习公式来解决该问题。
- 关注学习依赖历史的引导策略,处理对智能体学习动态的模型不确定性。
- 引入新颖目标函数,以编码在合理成本下实现良好引导结果的要求。
- 确定了存在引导策略的理论条件。
- 提供了实证算法来解决目标问题。
点此查看论文截图


How Far Are We on the Decision-Making of LLMs? Evaluating LLMs’ Gaming Ability in Multi-Agent Environments
Authors:Jen-tse Huang, Eric John Li, Man Ho Lam, Tian Liang, Wenxuan Wang, Youliang Yuan, Wenxiang Jiao, Xing Wang, Zhaopeng Tu, Michael R. Lyu
Decision-making is a complex process requiring diverse abilities, making it an excellent framework for evaluating Large Language Models (LLMs). Researchers have examined LLMs’ decision-making through the lens of Game Theory. However, existing evaluation mainly focus on two-player scenarios where an LLM competes against another. Additionally, previous benchmarks suffer from test set leakage due to their static design. We introduce GAMA($\gamma$)-Bench, a new framework for evaluating LLMs’ Gaming Ability in Multi-Agent environments. It includes eight classical game theory scenarios and a dynamic scoring scheme specially designed to quantitatively assess LLMs’ performance. $\gamma$-Bench allows flexible game settings and adapts the scoring system to different game parameters, enabling comprehensive evaluation of robustness, generalizability, and strategies for improvement. Our results indicate that GPT-3.5 demonstrates strong robustness but limited generalizability, which can be enhanced using methods like Chain-of-Thought. We also evaluate 13 LLMs from 6 model families, including GPT-3.5, GPT-4, Gemini, LLaMA-3.1, Mixtral, and Qwen-2. Gemini-1.5-Pro outperforms others, scoring of $69.8$ out of $100$, followed by LLaMA-3.1-70B ($65.9$) and Mixtral-8x22B ($62.4$). Our code and experimental results are publicly available at https://github.com/CUHK-ARISE/GAMABench.
决策是一个需要多种能力的复杂过程,因此它是评估大型语言模型(LLM)的理想框架。研究者已经通过博弈论的角度研究了LLM的决策制定。然而,现有的评估主要集中在两人场景中,即LLM与其他LLM之间的竞争。此外,以前的基准测试由于其静态设计而遭受测试集泄露的问题。我们引入了GAMA($\gamma$)-Bench,这是一个新的评估LLM在多智能体环境中的游戏能力的框架。它包括八个经典的游戏理论场景和一种动态评分方案,专门用于定量评估LLM的性能。$\gamma$-Bench允许灵活的游戏设置,并适应不同的游戏参数来调整评分系统,能够全面评估LLM的稳健性、泛化能力和改进策略。我们的结果表明,GPT-3.5表现出很强的稳健性,但泛化能力有限,可以通过如“思维链”等方法进行增强。我们还评估了来自六个模型家族的13个LLM,包括GPT-3.5、GPT-4、双子座、LLaMA-3.1、Mixtral和Qwen-2。其中,双子座-1.5-Pro表现最佳,得分为69.8(满分100),其次是LLaMA-3.1-70B(得分65.9)和Mixtral-8x22B(得分62.4)。我们的代码和实验结果已公开发布在https://github.com/CUHK-ARISE/GAMABench上。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to ICLR 2025; 11 pages of main text; 26 pages of appendices; Included models: GPT-3.5-{0613, 1106, 0125}, GPT-4-0125, GPT-4o-0806, Gemini-{1.0, 1.5)-Pro, LLaMA-3.1-{7, 70, 405}B, Mixtral-8x{7, 22}B, Qwen-2-72B
Summary
决策制定是一个需要多种能力的复杂过程,因此成为评估大型语言模型(LLM)的理想框架。研究者通过博弈论的角度研究LLM的决策制定。然而,现有评估主要集中在两玩家情境下LLM的竞争表现。此外,先前的基准测试因静态设计而面临测试集泄露问题。为此,我们推出了GAMA($\gamma$)-Bench新框架,用于评估LLM在多智能体环境中的游戏能力。它包括八个经典博弈论场景和专门设计的动态评分方案,以定量评估LLM的表现。$\gamma$-Bench可以灵活设置游戏环境并适应不同的游戏参数评分系统,全面评估LLM的稳健性、通用性和改进策略。我们的结果显示GPT-3.5表现出强大的稳健性但有限的通用性,可以通过链式思维等方法加以改进。我们还评估了来自六个模型家族的13个LLM,包括GPT-3.5、GPT-4、双子座、LLaMA-3.1、Mixtral和Qwen-2等。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLM)的决策制定能力通过博弈论角度进行了研究。
- 现有评估框架主要集中在两玩家情境,且存在测试集泄露问题。
- 推出了新的评估框架GAMA($\gamma$)-Bench,用于评估LLM在多智能体环境中的游戏能力。
- GAMA($\gamma$)-Bench包含八个经典博弈论场景和动态评分方案。
- GAMA($\gamma$)-Bench能灵活设置游戏环境,评估LLM的稳健性、通用性和改进策略。
- GPT-3.5展现出强大的稳健性,但通用性有限,可通过特定方法如Chain-of-Thought进行改进。
点此查看论文截图