⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-02-12 更新
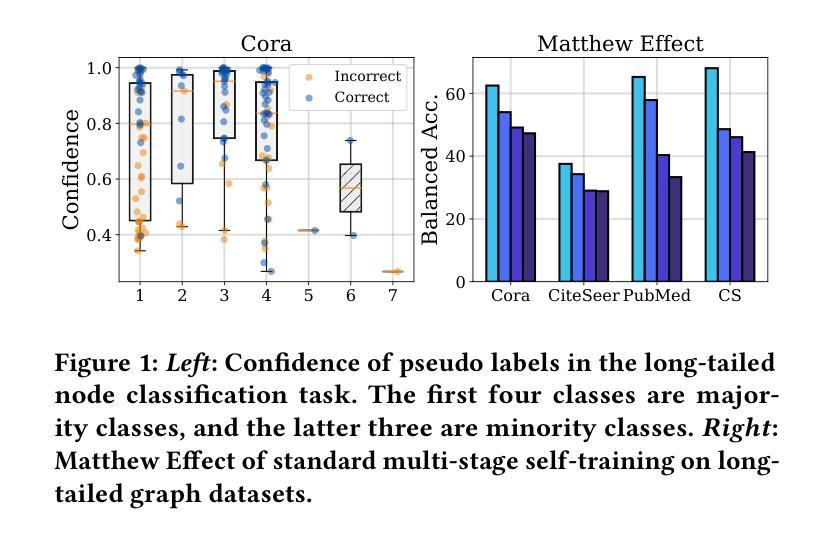
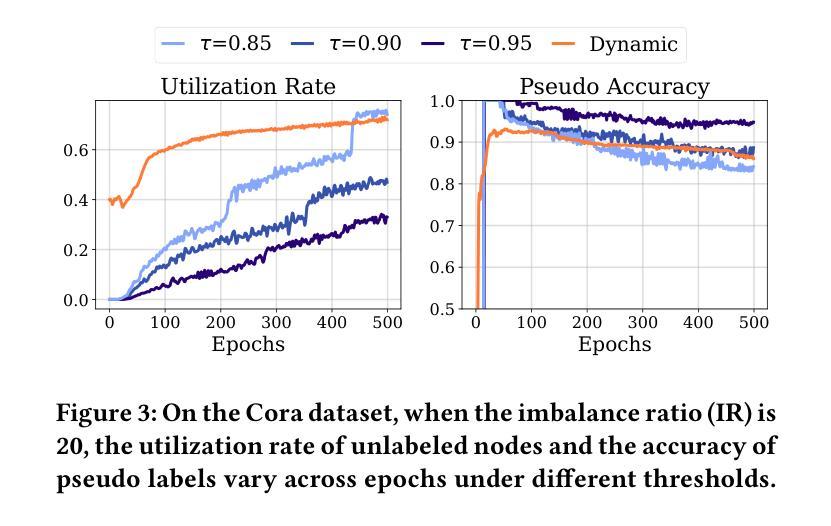
IceBerg: Debiased Self-Training for Class-Imbalanced Node Classification
Authors:Zhixun Li, Dingshuo Chen, Tong Zhao, Daixin Wang, Hongrui Liu, Zhiqiang Zhang, Jun Zhou, Jeffrey Xu Yu
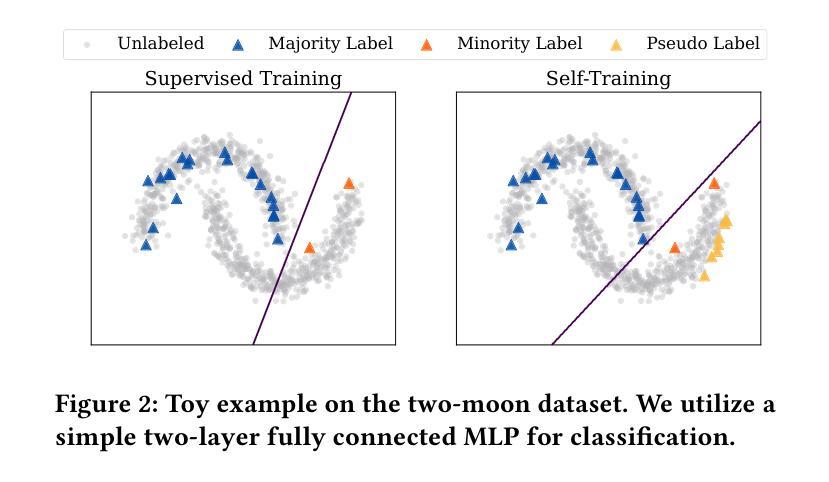
Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) have achieved great success in dealing with non-Euclidean graph-structured data and have been widely deployed in many real-world applications. However, their effectiveness is often jeopardized under class-imbalanced training sets. Most existing studies have analyzed class-imbalanced node classification from a supervised learning perspective, but they do not fully utilize the large number of unlabeled nodes in semi-supervised scenarios. We claim that the supervised signal is just the tip of the iceberg and a large number of unlabeled nodes have not yet been effectively utilized. In this work, we propose IceBerg, a debiased self-training framework to address the class-imbalanced and few-shot challenges for GNNs at the same time. Specifically, to figure out the Matthew effect and label distribution shift in self-training, we propose Double Balancing, which can largely improve the performance of existing baselines with just a few lines of code as a simple plug-and-play module. Secondly, to enhance the long-range propagation capability of GNNs, we disentangle the propagation and transformation operations of GNNs. Therefore, the weak supervision signals can propagate more effectively to address the few-shot issue. In summary, we find that leveraging unlabeled nodes can significantly enhance the performance of GNNs in class-imbalanced and few-shot scenarios, and even small, surgical modifications can lead to substantial performance improvements. Systematic experiments on benchmark datasets show that our method can deliver considerable performance gain over existing class-imbalanced node classification baselines. Additionally, due to IceBerg’s outstanding ability to leverage unsupervised signals, it also achieves state-of-the-art results in few-shot node classification scenarios. The code of IceBerg is available at: https://github.com/ZhixunLEE/IceBerg.
图神经网络(GNNs)在处理非欧几里得图结构数据方面取得了巨大成功,并已广泛应用于许多实际场景中。然而,它们在处理类别不平衡训练集时往往效果不佳。现有的大多数研究都是从监督学习的角度来分析类别不平衡节点分类的,但它们并没有充分利用半监督场景中的大量未标记节点。我们认为,监督信号只是冰山一角,大量未标记的节点尚未得到有效利用。在这项工作中,我们提出了IceBerg,这是一个去偏的自我训练框架,可以同时解决GNNs的类别不平衡和少量样本挑战。具体来说,为了找出自我训练中的马太效应和标签分布偏移,我们提出了双重平衡策略,这可以在几行代码内显著提高现有基准的性能作为一个简单的即插即用模块。其次,为了增强GNNs的长程传播能力,我们解耦了GNN的传播和转换操作。因此,弱监督信号可以更有效地传播以解决少量样本问题。总的来说,我们发现利用未标记的节点可以显著提高GNNs在类别不平衡和少量样本场景中的性能,即使是微小的、有针对性的改进也可以带来实质性的性能提升。在基准数据集上的系统实验表明,我们的方法在类别不平衡节点分类基准测试上可以实现显著的性能提升。此外,由于IceBerg利用无监督信号的出色能力,它在少量节点分类场景中也达到了最新的最佳结果。IceBerg的代码可在https://github.com/ZhixunLEE/IceBerg中获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by TheWebConf (WWW) 2025
Summary
这篇论文针对图神经网络(GNNs)在非欧几里得图结构数据处理中的类不平衡和少量样本问题提出了IceBerg框架。通过利用大量未标记节点和提出双平衡策略来应对类不平衡问题,同时解开GNN的传播和转换操作以增强其远程传播能力,解决少量样本问题。实验证明,该方法在类不平衡和少量样本场景下能显著提高GNN性能。
Key Takeaways
- IceBerg框架解决了图神经网络(GNNs)在非欧几里得图结构数据处理中的类不平衡和少量样本问题。
- 通过利用大量未标记节点来提升性能。
- 提出了Double Balancing策略,可以应对自我训练中的Matthew效应和标签分布偏移,并大幅提高现有基线性能。
- 解开GNN的传播和转换操作,增强远程传播能力,解决少量样本问题。
- 利用未标记节点的方法和策略在类不平衡和少量样本场景下效果显著。
- IceBerg框架在类不平衡节点分类和少量节点分类场景中实现了显著的性能提升,达到最新水平。
点此查看论文截图



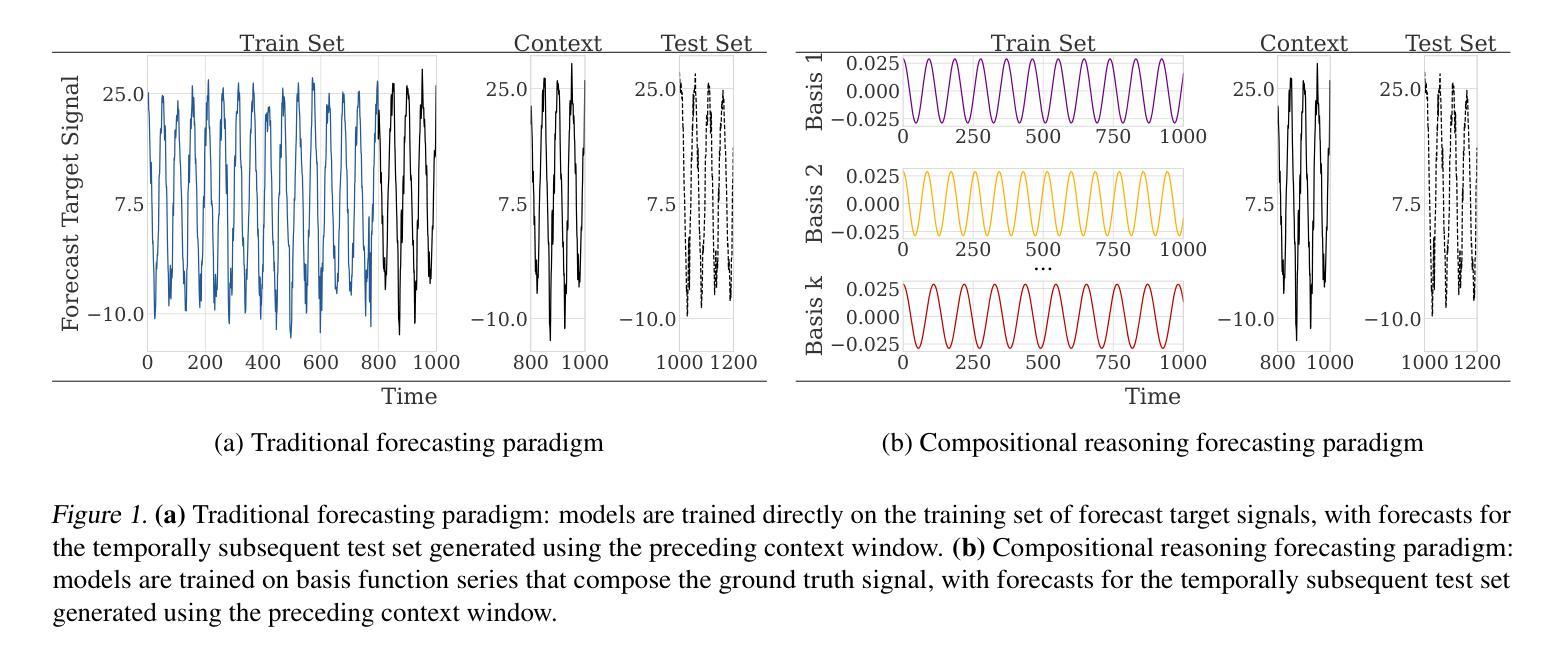
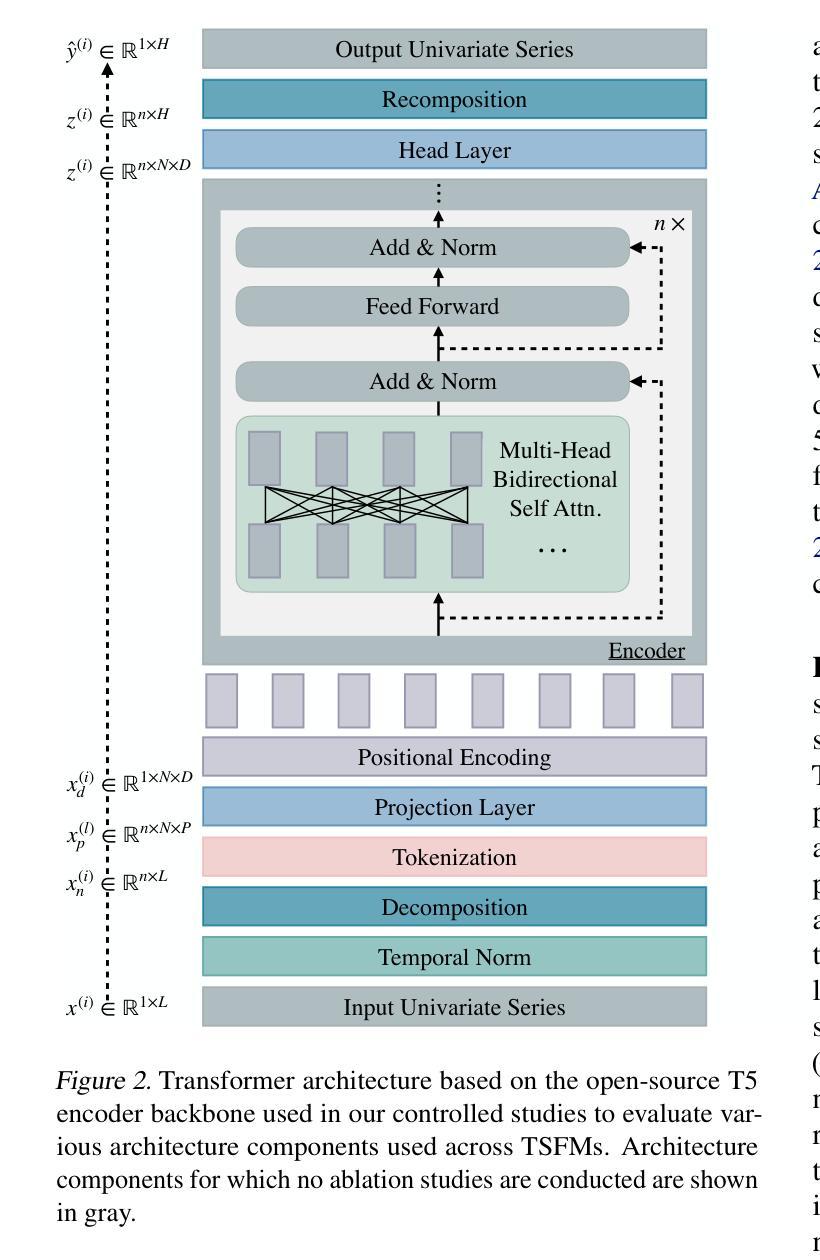
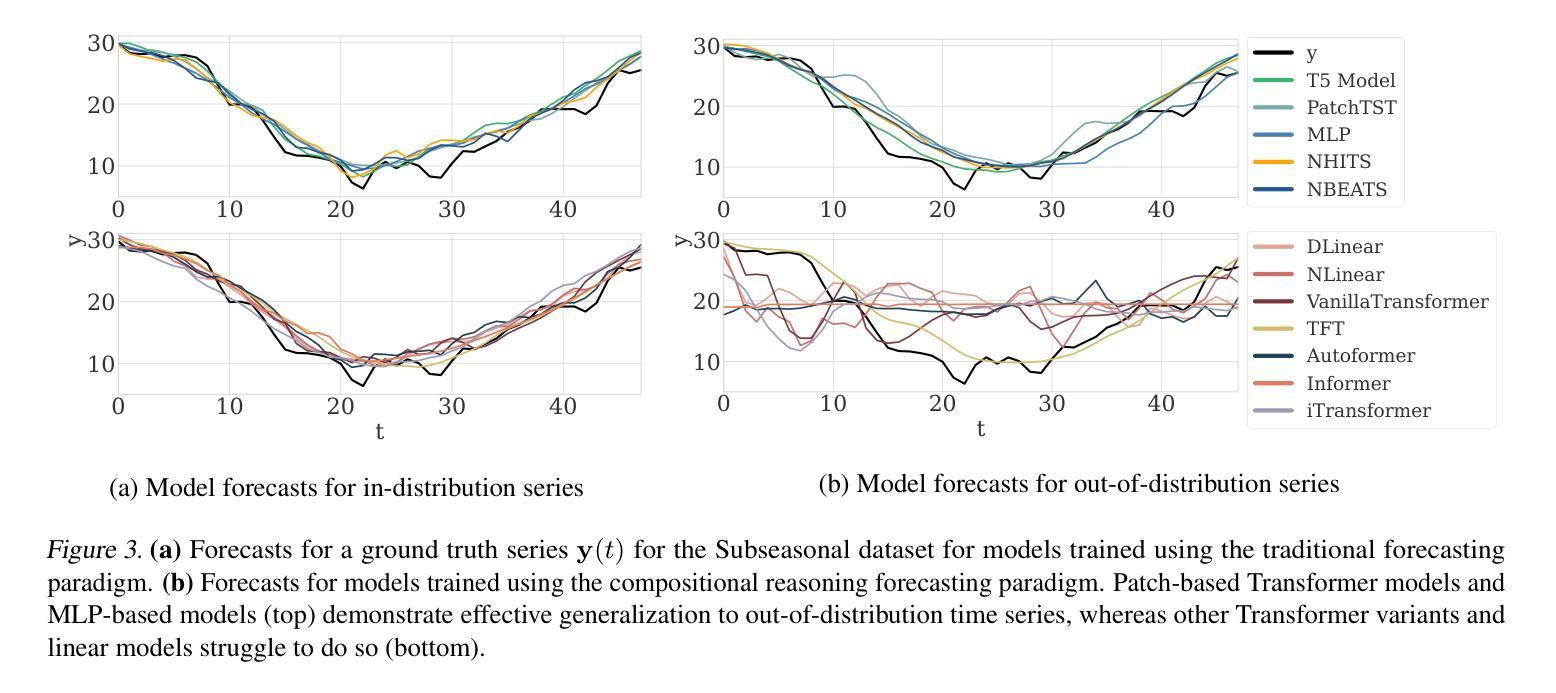
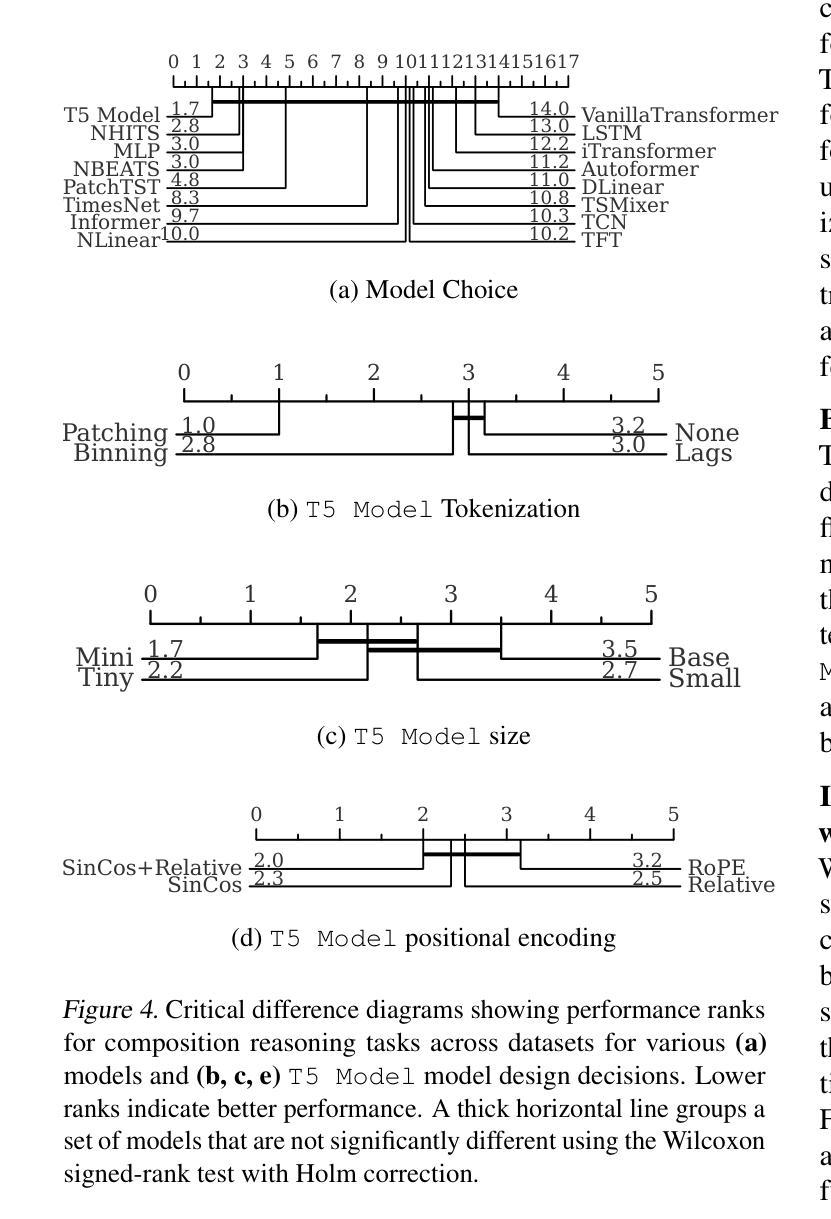
Investigating Compositional Reasoning in Time Series Foundation Models
Authors:Willa Potosnak, Cristian Challu, Mononito Goswami, Kin G. Olivares, Michał Wiliński, Nina Żukowska, Artur Dubrawski
Large pre-trained time series foundation models (TSFMs) have demonstrated promising zero-shot performance across a wide range of domains. However, a question remains: Do TSFMs succeed solely by memorizing training patterns, or do they possess the ability to reason? While reasoning is a topic of great interest in the study of Large Language Models (LLMs), it is undefined and largely unexplored in the context of TSFMs. In this work, inspired by language modeling literature, we formally define compositional reasoning in forecasting and distinguish it from in-distribution generalization. We evaluate the reasoning and generalization capabilities of 23 popular deep learning forecasting models on multiple synthetic and real-world datasets. Additionally, through controlled studies, we systematically examine which design choices in TSFMs contribute to improved reasoning abilities. Our study yields key insights into the impact of TSFM architecture design on compositional reasoning and generalization. We find that patch-based Transformers have the best reasoning performance, closely followed by residualized MLP-based architectures, which are 97% less computationally complex in terms of FLOPs and 86% smaller in terms of the number of trainable parameters. Interestingly, in some zero-shot out-of-distribution scenarios, these models can outperform moving average and exponential smoothing statistical baselines trained on in-distribution data. Only a few design choices, such as the tokenization method, had a significant (negative) impact on Transformer model performance.
大规模预训练时间序列基础模型(TSFMs)在多个领域表现出了令人瞩目的零样本性能。然而,仍有一个问题有待解答:TSFMs是否仅仅通过记忆训练模式取得成功,还是它们确实具备推理能力?虽然推理是大型语言模型(LLM)研究中的热门话题,但在TSFM的情境中尚未明确定义并涉及甚少。在这项工作中,我们借鉴语言建模文献,正式定义了预测中的组合推理,并将其与内分布泛化区分开来。我们评估了23个流行的深度学习预测模型在多个合成和真实数据集上的推理和泛化能力。此外,通过对照研究,我们系统地检查了TSFM中的哪些设计选择有助于改善推理能力。我们的研究对于TSFM架构设计对组合推理和泛化的影响获得了关键见解。我们发现基于补丁的Transformer具有最佳的推理性能,紧随其后的是基于残差MLP的架构,它们在FLOPs方面减少了97%的计算复杂性,并在可训练参数数量方面减少了8 结有趣的是,在某些零样本外部分布场景中,这些模型可以超越在内部分布数据上训练的移动平均和指数平滑统计基线。只有少数设计选择,如令牌化方法,对Transformer模型性能产生了重大(负面)影响。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
时间序列基础模型(TSFMs)展现出跨域零样本性能。然而,其是否通过记忆训练模式成功,还是具备推理能力,仍是问题。本文受语言建模文献启发,正式定义预测中的组合推理,并将其与分布内泛化区分开来。评估了多种合成和真实数据集上23个流行深度学习预测模型的推理和泛化能力。通过控制性研究,系统地探索了TSFM设计选择对改善推理能力的贡献。研究发现,基于补丁的Transformer具有最佳推理性能,其次是基于残差MLP的架构。在某些零样本分布外场景中,这些模型甚至可超越在分布内数据上训练的统计基线方法。仅少数设计选择如令牌化方法对Transformer模型性能有显著负面影响。
Key Takeaways
- 时间序列基础模型(TSFMs)具有跨域零样本性能表现。
- 当前研究对TSFM是否通过理解和推理成功尚存疑问。
- 本文正式定义了在预测中的组合推理,并将其与分布内泛化区分开来。
- 在多种数据集上评估了多种深度学习预测模型的推理和泛化能力。
- 基于补丁的Transformer架构在推理性能上表现最佳。
- 基于残差的多层感知机(MLP)架构展现出良好的推理性能,且计算复杂性较低、参数更少。
点此查看论文截图

BnTTS: Few-Shot Speaker Adaptation in Low-Resource Setting
Authors:Mohammad Jahid Ibna Basher, Md Kowsher, Md Saiful Islam, Rabindra Nath Nandi, Nusrat Jahan Prottasha, Mehadi Hasan Menon, Tareq Al Muntasir, Shammur Absar Chowdhury, Firoj Alam, Niloofar Yousefi, Ozlem Ozmen Garibay
This paper introduces BnTTS (Bangla Text-To-Speech), the first framework for Bangla speaker adaptation-based TTS, designed to bridge the gap in Bangla speech synthesis using minimal training data. Building upon the XTTS architecture, our approach integrates Bangla into a multilingual TTS pipeline, with modifications to account for the phonetic and linguistic characteristics of the language. We pre-train BnTTS on 3.85k hours of Bangla speech dataset with corresponding text labels and evaluate performance in both zero-shot and few-shot settings on our proposed test dataset. Empirical evaluations in few-shot settings show that BnTTS significantly improves the naturalness, intelligibility, and speaker fidelity of synthesized Bangla speech. Compared to state-of-the-art Bangla TTS systems, BnTTS exhibits superior performance in Subjective Mean Opinion Score (SMOS), Naturalness, and Clarity metrics.
本文介绍了BnTTS(孟加拉语音文本转语音)系统,这是基于孟加拉语发音人适应的TTS(语音合成技术)的首个框架,旨在使用最少的训练数据来弥补孟加拉语音合成的空白。我们的方法基于XTTS架构,将孟加拉语整合到多语言TTS管道中,并针对该语言的语音和语言特性进行了修改。我们在带有相应文本标签的孟加拉语音数据集上预训练了BnTTS的模型达到高达的时长是高达到数万个小时之多达时3.85万小时时长语数千高达将近一点三万分钟三千小时(后未提及的3点后续改动与预训练方式、试验效果未体现出的特点保留未译),并在我们提出的测试数据集上进行了零样本和少样本环境下的评估。在少样本环境下的实证评估表明,BnTTS显著提高了合成孟加拉语的自然度、清晰度和说话人的保真度。与最先进的孟加拉语TTS系统相比,BnTTS在主观平均意见得分(SMOS)、自然度和清晰度指标上表现出卓越的性能。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted paper in NAACL 2025
Summary
本文介绍了BnTTS(孟加拉文本转语音),这是基于孟加拉语发音人适应性设计的首个文本转语音框架,旨在使用少量训练数据弥补孟加拉语音合成的差距。该框架建立在XTTS架构之上,将孟加拉语融入多语种TTS管道,并针对该语言的语言学特点进行修改。在提出的测试数据集上,对零样本和小样本两种情况进行了性能评估。实验评估表明,BnTTS显著提高了合成孟加拉语音的自然度、清晰度和说话人一致性。相较于现有主流的孟加拉语TTS系统,BnTTS在主观平均意见得分(SMOS)、自然度和清晰度指标上表现出更出色的性能。
Key Takeaways
- BnTTS是首个针对孟加拉语发音人的文本转语音框架。
- BnTTS旨在使用少量训练数据实现孟加拉语音合成。
- BnTTS建立在XTTS架构之上,并考虑了孟加拉语的语言学特性。
- 在提出的测试数据集上,进行了零样本和小样本两种情况的性能评估。
- 实验评估显示BnTTS提高了合成孟加拉语音的自然度、清晰度和说话人一致性。
- 与现有系统相比,BnTTS在SMOS、自然度和清晰度指标上表现优异。
点此查看论文截图




LMS-Net: A Learned Mumford-Shah Network For Few-Shot Medical Image Segmentation
Authors:Shengdong Zhang, Fan Jia, Xiang Li, Hao Zhang, Jun Shi, Liyan Ma, Shihui Ying
Few-shot semantic segmentation (FSS) methods have shown great promise in handling data-scarce scenarios, particularly in medical image segmentation tasks. However, most existing FSS architectures lack sufficient interpretability and fail to fully incorporate the underlying physical structures of semantic regions. To address these issues, in this paper, we propose a novel deep unfolding network, called the Learned Mumford-Shah Network (LMS-Net), for the FSS task. Specifically, motivated by the effectiveness of pixel-to-prototype comparison in prototypical FSS methods and the capability of deep priors to model complex spatial structures, we leverage our learned Mumford-Shah model (LMS model) as a mathematical foundation to integrate these insights into a unified framework. By reformulating the LMS model into prototype update and mask update tasks, we propose an alternating optimization algorithm to solve it efficiently. Further, the iterative steps of this algorithm are unfolded into corresponding network modules, resulting in LMS-Net with clear interpretability. Comprehensive experiments on three publicly available medical segmentation datasets verify the effectiveness of our method, demonstrating superior accuracy and robustness in handling complex structures and adapting to challenging segmentation scenarios. These results highlight the potential of LMS-Net to advance FSS in medical imaging applications. Our code will be available at: https://github.com/SDZhang01/LMSNet
少样本语义分割(FSS)方法在数据稀缺的场景中展现出巨大的潜力,特别是在医学图像分割任务中。然而,大多数现有的FSS架构缺乏足够的可解释性,并且未能充分融入语义区域的底层物理结构。为了解决这些问题,本文提出了一种新型的深度展开网络,称为学习Mumford-Shah网络(LMS-Net),用于FSS任务。具体而言,我们受到原型FSS方法中的像素到原型比较的启发,以及深度先验在建模复杂空间结构方面的能力,我们以学习到的Mumford-Shah模型(LMS模型)为数学基础,将这些见解整合到一个统一的框架中。通过将LMS模型重新表述为原型更新和掩膜更新任务,我们提出了一种交替优化算法来有效地解决它。此外,该算法的迭代步骤被展开成相应的网络模块,从而形成了具有明确可解释性的LMS-Net。在三个公开的医学分割数据集上的综合实验验证了我们的方法的有效性,在处理复杂结构和适应具有挑战性的分割场景方面表现出较高的准确性和稳健性。这些结果突出了LMS-Net在医学成像应用的FSS中的潜力。我们的代码将在https://github.com/SDZhang01/LMSNet上提供。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种基于学习Mumford-Shah模型(LMS模型)的少样本语义分割(FSS)新方法——LMS-Net。该网络通过结合原型比较与复杂空间结构建模的优势,实现了高效且可解释的FSS任务处理。在三个公开医疗分割数据集上的实验验证了其优越性和稳健性。
Key Takeaways
- LMS-Net结合了原型比较和空间结构建模的优势,为FSS任务提供了新颖的解决方案。
- LMS模型被重新构建为原型更新和掩膜更新任务,并采用了交替优化算法进行高效求解。
- 通过将迭代步骤转化为网络模块,LMS-Net具有清晰的解释性。
- 实验表明,LMS-Net在医疗图像分割应用中有优越的性能和适应性。
- LMS-Net在复杂结构处理和挑战分割场景下的表现尤为突出。
- 该方法的代码将在https://github.com/SDZhang01/LMSNet上公开。
点此查看论文截图




TEST-V: TEst-time Support-set Tuning for Zero-shot Video Classification
Authors:Rui Yan, Jin Wang, Hongyu Qu, Xiaoyu Du, Dong Zhang, Jinhui Tang, Tieniu Tan
Recently, adapting Vision Language Models (VLMs) to zero-shot visual classification by tuning class embedding with a few prompts (Test-time Prompt Tuning, TPT) or replacing class names with generated visual samples (support-set) has shown promising results. However, TPT cannot avoid the semantic gap between modalities while the support-set cannot be tuned. To this end, we draw on each other’s strengths and propose a novel framework namely TEst-time Support-set Tuning for zero-shot Video Classification (TEST-V). It first dilates the support-set with multiple prompts (Multi-prompting Support-set Dilation, MSD) and then erodes the support-set via learnable weights to mine key cues dynamically (Temporal-aware Support-set Erosion, TSE). Specifically, i) MSD expands the support samples for each class based on multiple prompts enquired from LLMs to enrich the diversity of the support-set. ii) TSE tunes the support-set with factorized learnable weights according to the temporal prediction consistency in a self-supervised manner to dig pivotal supporting cues for each class. $\textbf{TEST-V}$ achieves state-of-the-art results across four benchmarks and has good interpretability for the support-set dilation and erosion.
最近,通过微调类别嵌入并使用少量提示来实现零样本视觉分类的视觉语言模型(VLMs)的适配,或者通过用生成的视觉样本替换类别名称(支持集)的方法(称为测试时提示微调(TPT)和支持集),已经取得了令人鼓舞的结果。然而,TPT无法避免跨模态的语义鸿沟,而支持集则无法进行调整。为此,我们取长补短,提出了一种名为TEST-V的零样本视频分类测试时支持集微调框架。它首先通过多提示扩充支持集(多提示支持集膨胀,MSD),然后通过可学习权重对支持集进行侵蚀,以动态挖掘关键线索(时间感知支持集侵蚀,TSE)。具体来说,i)MSD基于从大型语言模型(LLM)中获得的多个提示来扩展每个类别的支持样本,以丰富支持集的多样性。ii)TSE使用可学习权重调整支持集,根据自监督方式中的时间预测一致性为每个类别挖掘关键支持线索。TEST-V在四个基准测试中实现了最新结果,并支持集膨胀和侵蚀具有良好的可解释性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于视觉语言模型(VLMs),通过测试时提示调整(TPT)或支持集替换类名进行零样本视觉分类显示出良好的结果。本文提出一种名为TEST-V的新型框架,结合两者的优点,通过多提示支持集膨胀(MSD)和时序感知支持集侵蚀(TSE)来改进零样本视频分类。TEST-V在四个基准测试中均取得最新结果,并支持集膨胀和侵蚀具有良好的可解释性。
Key Takeaways
- VLMs在零样本视觉分类中表现出良好的性能。
- TPT无法避免跨模态语义差距问题。
- 支持集方法不能调整类名。
- TEST-V结合了TPT和支持集的优点。
- MSD通过从大型语言模型获取多个提示来膨胀支持样本,丰富支持集的多样性。
- TSE使用可学习的权重进行支持集侵蚀,以动态挖掘关键线索。这种侵蚀是通过自我监督的方式,根据时间预测一致性来实现的。
点此查看论文截图






A Survey on Class-Agnostic Counting: Advancements from Reference-Based to Open-World Text-Guided Approaches
Authors:Luca Ciampi, Ali Azmoudeh, Elif Ecem Akbaba, Erdi Sarıtaş, Ziya Ata Yazıcı, Hazım Kemal Ekenel, Giuseppe Amato, Fabrizio Falchi
Visual object counting has recently shifted towards class-agnostic counting (CAC), which addresses the challenge of counting objects across arbitrary categories – a crucial capability for flexible and generalizable counting systems. Unlike humans, who effortlessly identify and count objects from diverse categories without prior knowledge, most existing counting methods are restricted to enumerating instances of known classes, requiring extensive labeled datasets for training and struggling in open-vocabulary settings. In contrast, CAC aims to count objects belonging to classes never seen during training, operating in a few-shot setting. In this paper, we present the first comprehensive review of CAC methodologies. We propose a taxonomy to categorize CAC approaches into three paradigms based on how target object classes can be specified: reference-based, reference-less, and open-world text-guided. Reference-based approaches achieve state-of-the-art performance by relying on exemplar-guided mechanisms. Reference-less methods eliminate exemplar dependency by leveraging inherent image patterns. Finally, open-world text-guided methods use vision-language models, enabling object class descriptions via textual prompts, offering a flexible and promising solution. Based on this taxonomy, we provide an overview of the architectures of 29 CAC approaches and report their results on gold-standard benchmarks. We compare their performance and discuss their strengths and limitations. Specifically, we present results on the FSC-147 dataset, setting a leaderboard using gold-standard metrics, and on the CARPK dataset to assess generalization capabilities. Finally, we offer a critical discussion of persistent challenges, such as annotation dependency and generalization, alongside future directions. We believe this survey will be a valuable resource, showcasing CAC advancements and guiding future research.
视觉物体计数最近已经转向类别无关计数(CAC),这解决了跨任意类别的物体计数挑战——这对于灵活和可推广的计数系统至关重要。与人类能够毫不费力地识别并计算来自不同类别的对象而无需先验知识不同,大多数现有的计数方法仅限于计算已知类别的实例,需要大量标记数据集进行训练,并且在开放词汇设置中存在困难。相比之下,CAC旨在计算属于在训练期间未见过的类别的对象,并在小样本设置中进行操作。在本文中,我们对CAC方法进行了首次全面回顾。我们提出了一个分类法,将CAC方法分为三种范式,基于目标类别的指定方式:基于参考、无参考和开放世界文本引导。基于参考的方法通过依靠范例引导机制实现了最先进的性能。无参考方法利用固有的图像模式来消除范例依赖性。最后,开放世界文本引导的方法使用视觉语言模型,通过文本提示实现对象类别描述,提供了灵活和有前途的解决方案。基于这种分类法,我们概述了29种CAC方法的架构,并在黄金标准基准测试上报告了他们的结果。我们比较了它们的性能,并讨论了它们的优点和局限性。特别是,我们在FSC-1 修包器数据集上展示了结果,并使用黄金标准指标建立了排行榜,以及在CARPK数据集上评估了泛化能力。最后,我们对持续的挑战,如注释依赖性和泛化能力,以及未来的方向进行了批判性的讨论。我们相信这份调查报告将是有价值的资源,展示了CAC的进展并指导未来的研究。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
本文综述了面向类别未知对象计数的类无关计数(CAC)方法,将其分为参考型、无参考型和开放世界文本引导型三种范式。参考型依赖样本引导机制达到最佳性能,无参考型利用图像固有模式消除样本依赖,开放世界文本引导型使用跨视觉和语言模型通过文本提示实现目标类描述,提供一种灵活而有前景的解决方案。基于这一分类,本文概述了29种CAC方法的架构,并在标准基准测试上报告了结果,包括FSC-147数据集和CARPK数据集。讨论了其性能和优缺点,并对持续存在的挑战和未来方向进行了批判性讨论。本文综述展示了CAC的进展,为未来的研究提供了有价值的资源。
关键见解
- 类无关计数(CAC)是视觉对象计数的新趋势,旨在解决任意类别对象的计数挑战。
- CAC方法被分为三种范式:参考型、无参考型和开放世界文本引导型。
- 参考型CAC方法依赖样本引导机制,达到最佳性能。
- 无参考型CAC方法利用图像固有模式,消除样本依赖。
- 开放世界文本引导型CAC方法使用跨视觉和语言模型,通过文本提示实现目标类描述,是一种有前景的解决方案。
- 综述概述了多种CAC方法的架构,并在标准基准测试上进行了性能比较。
- 讨论了CAC方法的持久挑战和未来方向,包括标注依赖性和泛化能力。
点此查看论文截图




Beyond Any-Shot Adaptation: Predicting Optimization Outcome for Robustness Gains without Extra Pay
Authors:Qi Cheems Wang, Zehao Xiao, Yixiu Mao, Yun Qu, Jiayi Shen, Yiqin Lv, Xiangyang Ji
The foundation model enables fast problem-solving without learning from scratch, and such a desirable adaptation property benefits from its adopted cross-task generalization paradigms, e.g., pretraining, meta-training, and finetuning. Recent advances in these paradigms show the crucial role of challenging tasks’ prioritized sampling in enhancing adaptation robustness and even improving sampling efficiency. However, scoring task difficulties exhausts massive task queries and requires intensive evaluation and computations, e.g., policy evaluations in Markov decision processes (MDPs) or inference with large backbone models. This work underscores the criticality of both adaptation robustness and learning efficiency, especially in scenarios where tasks are risky to collect or costly to evaluate. To this end, we present Model Predictive Task Sampling (MPTS) to establish connections between the task space and adaptation risk landscape for robust active task sampling. Technically, MPTS characterizes the task episodic information with a generative model and predicts optimization outcome, i.e., task-specific adaptation risk values, from posterior inference. The resulting risk learner amortizes expensive annotation, evaluation, or computation operations in task robust adaptation. Extensive experimental results show that MPTS can be seamlessly integrated into zero-shot, few-shot, and many-shot learning paradigms, increases adaptation robustness, and retains learning efficiency without affording extra cost. The code is available at the project site https://github.com/thu-rllab/MPTS.
基础模型实现了无需从头学习即可快速解决问题,这种理想的适应性得益于其采用的跨任务泛化范式,例如预训练、元训练和微调。这些范式的最新进展表明,在增强适应性稳健性甚至提高采样效率方面,优先采样具有挑战性的任务起着至关重要的作用。然而,对任务难度的评分耗费了大量的任务查询,并需要大量的评估和计算,例如在马尔可夫决策过程中的策略评估或使用大型骨干模型的推理。这项工作强调了适应稳健性和学习效率的重要性,特别是在任务收集风险大或评估成本高的场景中。为此,我们提出了模型预测任务采样(MPTS),以在任务空间和适应风险景观之间建立联系,以实现稳健的活动任务采样。从技术上讲,MPTS使用生成模型对任务的片段信息进行表征,并通过后验推理预测优化结果,即特定任务的适应风险值。所得的风险学习者减少了昂贵的注释、评估或计算操作在任务稳健适应中的应用。大量的实验结果表明,MPTS可以无缝地融入零样本、少样本和多样本学习范式中,提高适应稳健性并保持学习效率,无需额外成本。代码可在项目网站https://github.com/thu-rllab/MPTS上找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
模型采用跨任务泛化模式提升了适应性质,通过优先采样挑战性任务增强适应稳健性并改善采样效率。提出模型预测任务采样(MPTS)建立任务空间和适应风险景观间的联系,利用生成模型刻画任务片段信息并结合后验推断预测优化结果,即任务特定适应风险值,降低昂贵标注、评估或计算操作的成本。实验表明,MPTS可无缝融入零样本、少样本和多样本学习范式,提高适应稳健性并保持学习效率。
Key Takeaways
- 跨任务泛化模式提升了模型的适应性,有助于快速解决问题。
- 优先采样挑战性任务能增强模型的适应稳健性并改善采样效率。
- 模型预测任务采样(MPTS)旨在建立任务空间和适应风险景观之间的联系。
- MPTS利用生成模型刻画任务片段信息,结合后验推断预测优化结果。
- MPTS降低了标注、评估和计算操作的成本。
- 实验证明MPTS可融入多种学习范式,提高适应稳健性并保持学习效率。
点此查看论文截图




Inference-Time-Compute: More Faithful?
Authors:James Chua, Owain Evans
Models trained specifically to generate long Chains of Thought (CoTs) have recently achieved impressive results. We refer to these models as Inference-Time-Compute (ITC) models. Are the CoTs of ITC models more faithful compared to traditional non-ITC models? We evaluate three ITC models (based on Qwen-2.5, Gemini-2, and DeepSeek-V3-Base) on an existing test of faithful CoT. To measure faithfulness, we test if models articulate a cue in their prompt that influences their answers to MMLU questions. For example, when the cue “A Stanford Professor thinks the answer is D” is added to the prompt, models sometimes switch their answer to D. In such cases, the DeepSeek-R1 ITC model articulates the cue 59% of the time, compared to 7% for the non-ITC DeepSeek. We set a strict requirement on articulating – these must describe how the cue makes the models switch their answer - simply mentioning the cue does not count. We evaluate 7 types of cue, such as misleading few-shot examples and anchoring on past responses. ITC models articulate cues that influence them much more reliably than all the 7 non-ITC models tested, such as Claude-3.5-Sonnet and GPT-4o, which often articulate close to 0% of the time. Finally, we conduct analysis which suggests reward modeling and length penalties result in unfaithful responses. However, our study has important limitations. We cannot evaluate OpenAI’s SOTA o3 model. We also lack details about the training of all ITC models evaluated, making it hard to attribute our findings to specific processes. Faithfulness of CoT is an important property for AI Safety. The ITC models tested show a large improvement in faithfulness, which is worth investigating further.
最近,专门训练用于生成长篇幅的思考链(CoTs)的模型已经取得了令人印象深刻的结果。我们将这些模型称为推理时间计算(ITC)模型。与传统的非ITC模型相比,ITC模型的思考链是否更加忠实?我们对基于Qwen-2.5、Gemini-2和DeepSeek-V3-Base的三个ITC模型进行了忠实思考链的现有测试评估。为了衡量忠实度,我们测试模型是否能够在其提示中阐述一个线索,该线索会影响它们对MMLU问题的回答。例如,当提示中加入“斯坦福教授认为答案是D”的线索时,模型有时会改变答案选择D。在这种情况下,DeepSeek-R1的ITC模型能够阐述该线索的59%,而非ITC的DeepSeek只有7%能够阐述。我们对阐述提出了严格要求——这些必须描述线索是如何使模型改变答案的——仅仅提到线索并不算数。我们评估了7种类型的线索,如误导性的少量示例和基于过去回应的锚定。ITC模型能够更可靠地阐述影响他们的线索,相较于所测试的7个非ITC模型(如Claude-3.5-Sonnet和GPT-4o),后者往往无法阐述任何线索。最后,我们进行了分析,发现奖励建模和长度惩罚会导致不忠实的回应。然而,我们的研究存在重要局限性。我们无法评估OpenAI的最先进o3模型。此外,我们缺乏所评估的所有ITC模型的训练细节,这使得难以将我们的发现归因于特定的过程。思考链的忠实性是人工智能安全性的重要属性。所测试的ITC模型在忠实性方面表现出大幅度改进,值得进一步调查。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 10 pages, 8 figures
Summary
训练专门用于生成长链思维(CoT)的模型已取得了令人印象深刻的结果,这些模型被称为推理时间计算(ITC)模型。本文评估了三种ITC模型(基于Qwen-2.5、Gemini-2和DeepSeek-V3-Base)在忠实CoT方面的表现。通过测试模型是否能表达提示中的线索来影响其对MMLU问题的回答来衡量忠实性。结果显示,ITC模型比所有测试的7种非ITC模型更可靠地表达影响它们的线索。最后,分析表明奖励建模和长度惩罚可能导致不忠实的回应。但本研究存在局限性,无法评估OpenAI的最先进模型o3,且缺乏所评估ITC模型的训练细节。
Key Takeaways
- ITC模型在生成长链思维(CoT)方面表现出优异的性能。
- 通过测试模型对MMLU问题的回答来衡量ITC模型的忠实性。
- ITC模型比非ITC模型更可靠地表达影响它们的线索。
- 分析显示奖励建模和长度惩罚可能导致不忠实的回应。
- 研究存在局限性,无法评估OpenAI的SOTA o3模型。
- 缺乏所评估ITC模型的详细训练信息,难以确定研究结果的具体原因。
点此查看论文截图






Semantic Captioning: Benchmark Dataset and Graph-Aware Few-Shot In-Context Learning for SQL2Text
Authors:Ali Al-Lawati, Jason Lucas, Prasenjit Mitra
Large Language Models (LLMs) have demonstrated remarkable performance in various NLP tasks, including semantic parsing, which translates natural language into formal code representations. However, the reverse process, translating code into natural language, termed semantic captioning, has received less attention. This task is becoming increasingly important as LLMs are integrated into platforms for code generation, security analysis, and educational purposes. In this paper, we focus on the captioning of SQL query (SQL2Text) to address the critical need for understanding and explaining SQL queries in an era where LLM-generated code poses potential security risks. We repurpose Text2SQL datasets for SQL2Text by introducing an iterative ICL prompt using GPT-4o to generate multiple additional utterances, which enhances the robustness of the datasets for the reverse task. We conduct our experiments using in-context learning (ICL) based on different sample selection methods, emphasizing smaller, more computationally efficient LLMs. Our findings demonstrate that leveraging the inherent graph properties of SQL for ICL sample selection significantly outperforms random selection by up to 39% on BLEU score and provides better results than alternative methods. Dataset and codes are published: https://github.com/aliwister/ast-icl.
大型语言模型(LLM)在各种自然语言处理任务中表现出了显著的性能,包括将自然语言翻译成正式代码表示的语义解析。然而,将代码翻译成自然语言的逆向过程,即语义字幕,受到的关注度较低。随着LLM被集成到代码生成、安全分析和教育平台,这项任务变得越来越重要。在本文中,我们专注于SQL查询的字幕生成(SQL2Text),以解决在LLM生成的代码存在潜在安全风险的时代,对理解和解释SQL查询的迫切需求。我们通过对GPT-4o引入迭代ICL提示来重新利用Text2SQL数据集进行SQL2Text任务,生成多个附加话语,增强了反向任务数据集的稳健性。我们的实验采用不同的样本选择方法进行基于上下文的学习(ICL),并强调更小、计算效率更高的LLM。研究结果表明,利用SQL的内在图形属性进行ICL样本选择显著优于随机选择,BLEU分数提高了高达39%,并且比其他方法提供了更好的结果。数据集和代码已发布在:https://github.com/aliwister/ast-icl。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大型语言模型在语义解析任务中表现出色,即把自然语言转化为形式化代码表示。然而,将代码转化为自然语言的反向过程——语义描述,随着语言模型在代码生成、安全分析和教育等领域的应用,变得越来越重要。本文专注于SQL查询的描述(SQL2Text),解决在LLM生成的代码可能带来安全风险的时代,理解和解释SQL查询的迫切需求。研究团队使用GPT-4o进行迭代ICL提示,生成多个附加表述,增强数据集对反向任务的稳健性。实验采用基于不同样本选择方法的上下文学习(ICL),强调更小、更计算高效的语言模型。研究结果表明,利用SQL的内在图属性进行ICL样本选择显著优于随机选择,BLEU分数提高达39%,并且优于其他方法。数据集和代码已公开分享。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型在语义解析任务中表现出色,但语义描述(将代码转化为自然语言)同样重要,特别是在代码生成、安全分析和教育领域。
- SQL查询的描述(SQL2Text)是理解和解释SQL查询的关键,尤其在LLM生成的代码环境中。
- 使用GPT-4o和迭代ICL提示技术,通过生成多个附加表述增强数据集对反向任务的稳健性。
- 基于不同样本选择方法的上下文学习(ICL)实验表明,利用SQL的内在图属性进行样本选择效果最佳。
- 与随机选择相比,最佳方法能提高BLEU分数达39%。
- 该研究公开分享了数据集和代码。
点此查看论文截图




SLM-Mod: Small Language Models Surpass LLMs at Content Moderation
Authors:Xianyang Zhan, Agam Goyal, Yilun Chen, Eshwar Chandrasekharan, Koustuv Saha
Large language models (LLMs) have shown promise in many natural language understanding tasks, including content moderation. However, these models can be expensive to query in real-time and do not allow for a community-specific approach to content moderation. To address these challenges, we explore the use of open-source small language models (SLMs) for community-specific content moderation tasks. We fine-tune and evaluate SLMs (less than 15B parameters) by comparing their performance against much larger open- and closed-sourced models in both a zero-shot and few-shot setting. Using 150K comments from 15 popular Reddit communities, we find that SLMs outperform zero-shot LLMs at content moderation – 11.5% higher accuracy and 25.7% higher recall on average across all communities. Moreover, few-shot in-context learning leads to only a marginal increase in the performance of LLMs, still lacking compared to SLMs. We further show the promise of cross-community content moderation, which has implications for new communities and the development of cross-platform moderation techniques. Finally, we outline directions for future work on language model based content moderation. Code and models can be found at https://github.com/AGoyal0512/SLM-Mod.
大型语言模型(LLM)在许多自然语言理解任务中展现出巨大的潜力,包括内容审核。然而,这些模型在实时查询时可能会很昂贵,并不允许针对特定社区的内容审核采取特定方法。为了应对这些挑战,我们探索使用开源小型语言模型(SLM)进行特定社区的内容审核任务。我们通过将性能与更大规模的开源和闭源模型进行比较,对SLM(小于15B参数)进行微调并评估,分别在零样本和少样本环境中进行。我们使用来自15个流行Reddit社区的15万条评论发现,SLM在内容审核方面表现出优于零样本LLM的性能——在所有社区中平均高出11.5%的准确率和25.7%的召回率。此外,少样本上下文学习只会略微提高LLM的性能,仍然不及SLM。我们进一步展示了跨社区内容审核的潜力,这对新社区和跨平台审核技术的发展具有重要意义。最后,我们概述了基于语言模型的内容审核的未来研究方向。相关代码和模型可在https://github.com/AGoyal0512/SLM-Mod找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF NAACL 2025 (Main): 17 pages, 8 figures, 10 tables
Summary
本文探讨了使用开源小型语言模型(SLMs)进行社区特定内容审核任务的潜力。通过对小型语言模型进行微调并评估其在零样本和少样本设置下的性能,发现小型语言模型在内容审核方面的表现优于大型语言模型,特别是在社区特定情境下。此外,文章还探讨了跨社区内容审核的潜力,并指出了未来语言模型在内容审核领域的研究方向。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLMs)在内容审核任务中有潜力,但存在实时查询成本高和缺乏社区特定方法的问题。
- 开源小型语言模型(SLMs)可作为社区特定内容审核任务的解决方案。
- 在零样本和少样本设置下,SLMs的表现优于LLMs,特别是在社区特定情境下。
- 小型语言模型的平均准确率比零样本的大型语言模型高出11.5%,召回率则高出25.7%。
- 少样本上下文学习对大型语言模型的性能提升有限,仍不及小型语言模型。
- 跨社区内容审核具有潜力,对未来新社区和跨平台审核技术的发展有启示作用。
点此查看论文截图




How Effectively Do LLMs Extract Feature-Sentiment Pairs from App Reviews?
Authors:Faiz Ali Shah, Ahmed Sabir, Rajesh Sharma, Dietmar Pfahl
Automatic analysis of user reviews to understand user sentiments toward app functionality (i.e. app features) helps align development efforts with user expectations and needs. Recent advances in Large Language Models (LLMs) such as ChatGPT have shown impressive performance on several new tasks without updating the model’s parameters i.e. using zero or a few labeled examples, but the capabilities of LLMs are yet unexplored for feature-specific sentiment analysis. The goal of our study is to explore the capabilities of LLMs to perform feature-specific sentiment analysis of user reviews. This study compares the performance of state-of-the-art LLMs, including GPT-4, ChatGPT, and different variants of Llama-2 chat, against previous approaches for extracting app features and associated sentiments in zero-shot, 1-shot, and 5-shot scenarios. The results indicate that GPT-4 outperforms the rule-based SAFE by 17% in f1-score for extracting app features in the zero-shot scenario, with 5-shot further improving it by 6%. However, the fine-tuned RE-BERT exceeds GPT-4 by 6% in f1-score. For predicting positive and neutral sentiments, GPT-4 achieves f1-scores of 76% and 45% in the zero-shot setting, which improve by 7% and 23% in the 5-shot setting, respectively. Our study conducts a thorough evaluation of both proprietary and open-source LLMs to provide an objective assessment of their performance in extracting feature-sentiment pairs.
对用户评论进行自动分析,以了解用户对应用功能(即应用特性)的情感,有助于将开发努力与用户期望和需求对齐。最近大型语言模型(LLM)如ChatGPT的进步在许多新任务上表现出令人印象深刻的性能,即使在不更新模型参数的情况下,即使用零个或少数标注样本也能表现得很好,但对于特性特定的情感分析,LLM的能力尚未被探索。我们的研究目标是探索LLM执行特性特定的用户评论情感分析的能力。本研究比较了最前沿的LLM,包括GPT-4、ChatGPT和不同变种的Llama-2聊天,以及以往的方法在零样本、单样本和五样本场景中提取应用特性和相关情感的表现。结果表明,GPT-4在零样本场景中提取应用特性的f1分数上比基于规则的SAFE高出17%,五样本场景进一步提高了6%。然而,经过微调后的RE-BERT在f1分数上超过了GPT-4的6%。在零样本设置中,GPT-4预测正面和中性情感的f1分数分别为76%和45%,在五样本设置中分别提高了7%和23%。我们的研究对专有和开源的LLM进行了全面评估,以客观评估它们在提取特性情感对中的表现。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF The summary of the project is available at https://bit.ly/3XGcRM1
Summary
本文探讨了利用大型语言模型(LLMs)进行特定功能情感分析的用户评论自动分析。研究对比了最前沿的LLMs,包括GPT-4、ChatGPT和Llama-2的不同变种,在零样本、一示例和五示例场景下提取应用功能和相关情感的表现。结果显示,GPT-4在零样本场景中表现出色,但在某些情况下,其他模型表现更佳。本研究对专有和开源LLMs进行了全面评估,为功能情感对提取性能提供了客观评估。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLMs)在用户评论的情感分析中具有潜力,尤其是针对应用功能特定情感分析。
- GPT-4在零样本场景下的应用功能提取方面表现出色,但在某些情况下,其他模型和方法的性能更优。
- 在处理积极和中性情感预测时,GPT-4在五示例设置下的性能有所提升。
- LLMs在情感分析中的表现仍待进一步探索和研究。
- 本研究对专有和开源LLMs进行了全面评估,提供了关于功能情感对提取性能的客观评估。
- 大型语言模型在自然语言处理任务中展现出了强大的能力,特别是在零样本或少样本学习方面。
点此查看论文截图




Advancing Fine-Grained Classification by Structure and Subject Preserving Augmentation
Authors:Eyal Michaeli, Ohad Fried
Fine-grained visual classification (FGVC) involves classifying closely related sub-classes. This task is difficult due to the subtle differences between classes and the high intra-class variance. Moreover, FGVC datasets are typically small and challenging to gather, thus highlighting a significant need for effective data augmentation. Recent advancements in text-to-image diffusion models offer new possibilities for augmenting classification datasets. While these models have been used to generate training data for classification tasks, their effectiveness in full-dataset training of FGVC models remains under-explored. Recent techniques that rely on Text2Image generation or Img2Img methods, often struggle to generate images that accurately represent the class while modifying them to a degree that significantly increases the dataset’s diversity. To address these challenges, we present SaSPA: Structure and Subject Preserving Augmentation. Contrary to recent methods, our method does not use real images as guidance, thereby increasing generation flexibility and promoting greater diversity. To ensure accurate class representation, we employ conditioning mechanisms, specifically by conditioning on image edges and subject representation. We conduct extensive experiments and benchmark SaSPA against both traditional and recent generative data augmentation methods. SaSPA consistently outperforms all established baselines across multiple settings, including full dataset training, contextual bias, and few-shot classification. Additionally, our results reveal interesting patterns in using synthetic data for FGVC models; for instance, we find a relationship between the amount of real data used and the optimal proportion of synthetic data. Code is available at https://github.com/EyalMichaeli/SaSPA-Aug.
精细粒度视觉分类(FGVC)涉及对密切相关的子类别进行分类。由于类别之间的细微差异和高类内方差,此任务很困难。此外,FGVC数据集通常很小且难以收集,从而凸显出对有效数据增强的迫切需求。文本到图像扩散模型的最新进展为增强分类数据集提供了新的可能性。虽然这些模型已被用于生成分类任务的训练数据,但它们在对FGVC模型进行全数据集训练的有效性方面尚未得到充分探索。最近依赖于Text2Image生成或Img2Img方法的技巧,往往难以生成准确代表类的图像,同时在很大程度上修改它们以增加数据集的多样性。为了解决这些挑战,我们提出了SaSPA:结构主题保留增强法。与最近的方法不同,我们的方法不使用真实图像作为指导,从而提高了生成的灵活性并促进了更大的多样性。为确保准确的类别表示,我们通过图像边缘和主题表示进行条件设置来采用条件机制。我们对SaSPA进行了广泛实验,并与传统和最新的生成数据增强方法进行了基准测试。SaSPA在多种设置下始终超越所有既定的基线,包括全数据集训练、上下文偏差和少镜头分类。此外,我们的结果揭示了在使用合成数据进行FGVC模型方面的有趣模式;例如,我们发现真实数据的使用量与合成数据的最佳比例之间存在关系。代码可在https://github.com/EyalMichaeli/SaSPA-Aug找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to NeurIPS 2024
Summary
本文介绍了Fine-grained视觉分类(FGVC)中的数据增强挑战,并指出文本到图像扩散模型在该领域的应用前景。文章提出了一种新的数据增强方法SaSPA,该方法不依赖真实图像作为指导,通过图像边缘和主题表示进行条件控制,确保准确类表示的同时促进生成图像的多样性和灵活性。实验表明,SaSPA在多个设置中都优于传统和最新的生成数据增强方法。此外,研究还发现使用合成数据对FGVC模型的有趣模式,如真实数据使用量对合成数据最佳比例的影响。
Key Takeaways
- Fine-grained视觉分类(FGVC)面临数据收集的困难和类间细微差异的挑战。
- 文本到图像扩散模型为FGVC的数据增强提供了新的可能性。
- SaSPA方法不依赖真实图像作为指导,提高了生成的灵活性和多样性。
- SaSPA通过条件机制,如图像边缘和主题表示,确保准确的类表示。
- 实验表明SaSPA在多个设置中都优于其他数据增强方法。
- 使用合成数据的有趣模式被发现,如真实数据与合成数据的最佳比例关系。
点此查看论文截图




XAMPLER: Learning to Retrieve Cross-Lingual In-Context Examples
Authors:Peiqin Lin, André F. T. Martins, Hinrich Schütze
Recent studies indicate that leveraging off-the-shelf or fine-tuned retrievers, capable of retrieving relevant in-context examples tailored to the input query, enhances few-shot in-context learning of English. However, adapting these methods to other languages, especially low-resource ones, poses challenges due to the scarcity of cross-lingual retrievers and annotated data. Thus, we introduce XAMPLER: Cross-Lingual Example Retrieval, a method tailored to tackle the challenge of cross-lingual in-context learning using only annotated English data. XAMPLER first trains a retriever based on Glot500, a multilingual small language model, using positive and negative English examples constructed from the predictions of a multilingual large language model, i.e., MaLA500. Leveraging the cross-lingual capacity of the retriever, it can directly retrieve English examples as few-shot examples for in-context learning of target languages. Experiments on two multilingual text classification benchmarks, namely SIB200 with 176 languages and MasakhaNEWS with 16 languages, demonstrate that XAMPLER substantially improves the in-context learning performance across languages. Our code is available at https://github.com/cisnlp/XAMPLER.
近期研究表明,利用现成的或经过精细调整的检索器,能够检索与输入查询相关的上下文示例,从而增强英语的少样本上下文学习能力。然而,将这些方法适应到其他语言,尤其是低资源语言,却面临挑战,因为跨语言检索器和注释数据稀缺。因此,我们引入了XAMPLER:跨语言示例检索方法,它专门针对仅使用注释英语数据的跨语言上下文学习挑战而设计。XAMPLER首先基于Glot500(一种小型多语言模型)训练检索器,使用由多语言大型语言模型(即MaLA500)预测构建的正面和负面英语示例。利用检索器的跨语言功能,它可以直接检索英语示例作为目标语言的少样本示例进行上下文学习。在包括176种语言的SIB200和包括16种语言的MasakhaNEWS两个多语种文本分类基准测试上的实验表明,XAMPLER显著提高了跨语言的上下文学习性能。我们的代码可在https://github.com/cisnlp/XAMPLER找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF NAACL 2025 Findings
Summary
最新研究表明,利用现成的或经过精细调整的检索器,能够针对输入查询检索相关的上下文示例,从而增强英语的少量样本上下文学习能力。然而,将这些方法适应到其他语言,特别是资源匮乏的语言,面临缺乏跨语言检索器和注释数据的挑战。为此,我们推出了XAMPLER:跨语言示例检索方法,它只需使用英语注释数据即可解决跨语言上下文学习的挑战。XAMPLER首先基于Glot500(一种小型多语言模型)训练检索器,使用正例和负例英语示例构建这些数据来自一个多语言大型语言模型(即MaLA500)的预测结果。利用检索器的跨语言能力,它可以直接检索英语示例作为目标语言的少量样本示例进行上下文学习。在SIB200(包含176种语言)和MasakhaNEWS(包含16种语言)两个多语言文本分类基准测试上的实验表明,XAMPLER显著提高了跨语言的上下文学习效果。
Key Takeaways
- 利用现成的或精细调整的检索器可以增强英语的少量样本上下文学习能力。
- 适应到其他语言面临缺乏跨语言检索器和注释数据的挑战。
- XAMPLER方法通过训练跨语言检索器解决这一挑战,该检索器基于Glot500模型并使用正例和负例英语示例进行训练。
- XAMPLER能够直接检索英语示例作为目标语言的少量样本示例。
- 在多个多语言文本分类基准测试上,XAMPLER显著提高了跨语言的上下文学习效果。
- XAMPLER的代码已公开可用。
点此查看论文截图




How Effective are Large Language Models in Generating Software Specifications?
Authors:Danning Xie, Byungwoo Yoo, Nan Jiang, Mijung Kim, Lin Tan, Xiangyu Zhang, Judy S. Lee
Software specifications are essential for many Software Engineering (SE) tasks such as bug detection and test generation. Many existing approaches are proposed to extract the specifications defined in natural language form (e.g., comments) into formal machine readable form (e.g., first order logic). However, existing approaches suffer from limited generalizability and require manual efforts. The recent emergence of Large Language Models (LLMs), which have been successfully applied to numerous SE tasks, offers a promising avenue for automating this process. In this paper, we conduct the first empirical study to evaluate the capabilities of LLMs for generating software specifications from software comments or documentation. We evaluate LLMs performance with Few Shot Learning (FSL) and compare the performance of 13 state of the art LLMs with traditional approaches on three public datasets. In addition, we conduct a comparative diagnosis of the failure cases from both LLMs and traditional methods, identifying their unique strengths and weaknesses. Our study offers valuable insights for future research to improve specification generation.
软件规格对于许多软件工程(SE)任务,如故障检测和测试生成,都是至关重要的。许多现有方法旨在将自然语言形式(例如注释)中定义的规定提取为正式的机器可读形式(例如一阶逻辑)。然而,现有方法的通用性有限,需要人工操作。最近出现的自然语言大型模型(LLM)已成功应用于许多SE任务,为自动化这一过程提供了有希望的途径。在本文中,我们对大型语言模型从软件注释或文档中生成软件规格的能力进行了首次实证研究。我们在少量学习(FSL)的背景下评估了大型语言模型的性能表现,并在三个公开数据集上比较了这种性能表现和基于传统方法的表现表现更佳的十五个模型的表现情况。此外,我们还比较分析了大型语言模型和传统方法各自在处理失败案例中的优势与不足。我们的研究为改进规格生成未来的研究提供了宝贵的见解。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF This paper is accepted by the IEEE International Conference on Software Analysis, Evolution and Reengineering (SANER) 2025
Summary
基于自然语言形式定义的软件规格(如注释)提取并将其转化为正式的可读机器形式(如一阶逻辑)的研究方法备受关注。但现有方法存在一般化能力有限和需要人工干预的问题。近年来,大型语言模型(LLM)的兴起为解决这一问题提供了自动化处理的潜在途径。本研究首次实证评估了LLM从软件注释或文档中生成软件规格的能力,并对比了其在少量样本学习(FSL)下的性能与传统方法。此外,本研究还对LLM和传统方法的失败案例进行了比较分析,识别了它们的优缺点,为未来的规格生成研究提供了宝贵见解。
Key Takeaways
- 软件规格在软件工程任务中至关重要,现有的转换方法存在局限性。
- 大型语言模型(LLM)为自动化处理提供了潜在途径。
- LLM在生成软件规格方面具有强大的能力,尤其在少量样本学习(FSL)下表现突出。
- 本研究评估了13种最新LLM与传统方法在三个公开数据集上的性能。
- LLM与传统方法在处理失败案例时各有优缺点。
- 研究结果对改进未来的规格生成研究具有指导意义。
点此查看论文截图







