⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-02-13 更新
Rapid Whole Brain Mesoscale In-vivo MR Imaging using Multi-scale Implicit Neural Representation
Authors:Jun Lyu, Lipeng Ning, William Consagra, Qiang Liu, Richard J. Rushmore, Berkin Bilgic, Yogesh Rathi
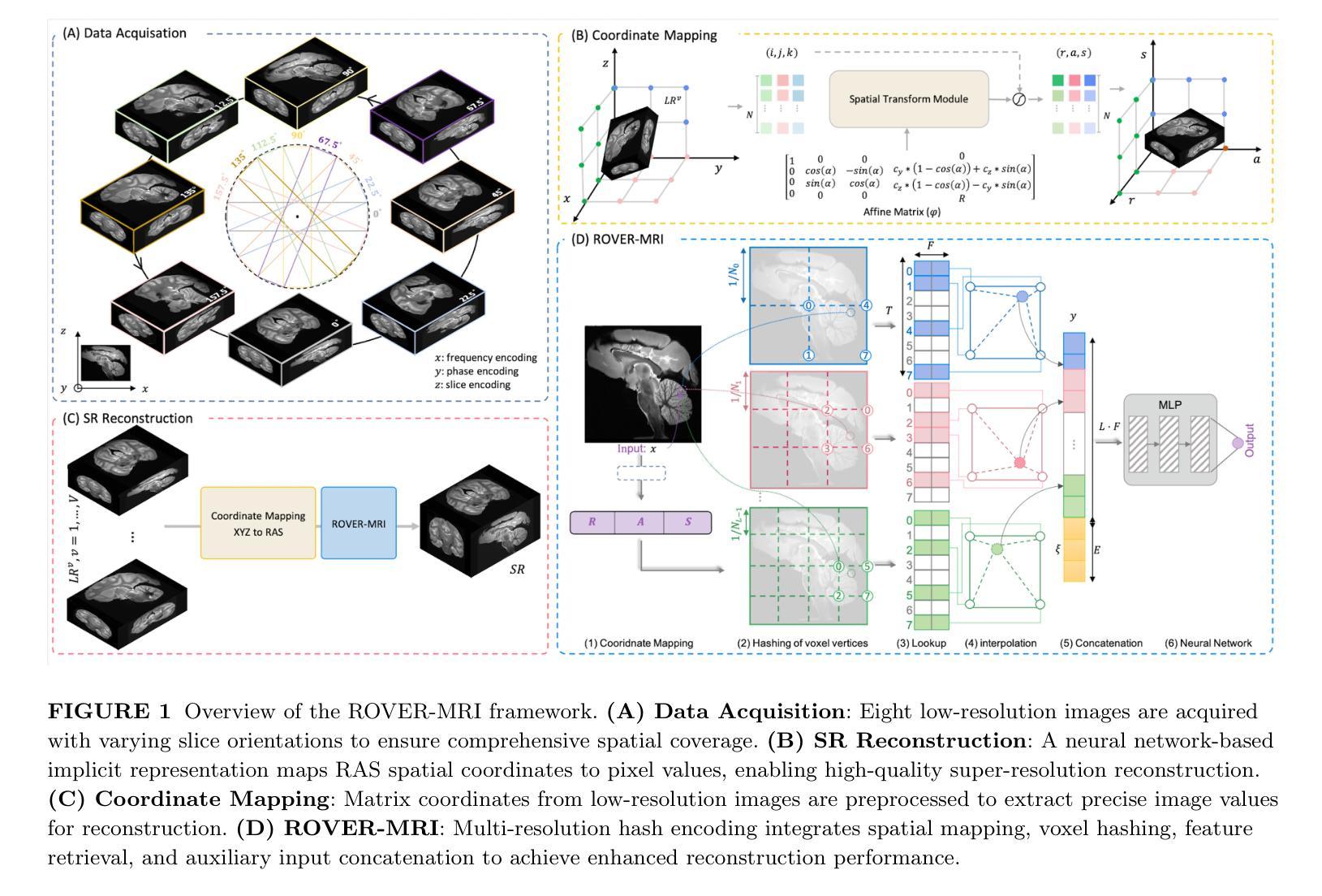
Purpose: To develop and validate a novel image reconstruction technique using implicit neural representations (INR) for multi-view thick-slice acquisitions while reducing the scan time but maintaining high signal-to-noise ratio (SNR). Methods: We propose Rotating-view super-resolution (ROVER)-MRI, an unsupervised neural network-based algorithm designed to reconstruct MRI data from multi-view thick slices, effectively reducing scan time by 2-fold while maintaining fine anatomical details. We compare our method to both bicubic interpolation and the current state-of-the-art regularized least-squares super-resolution reconstruction (LS-SRR) technique. Validation is performed using ground-truth ex-vivo monkey brain data, and we demonstrate superior reconstruction quality across several in-vivo human datasets. Notably, we achieve the reconstruction of a whole human brain in-vivo T2-weighted image with an unprecedented 180{\mu}m isotropic spatial resolution, accomplished in just 17 minutes of scan time on a 7T MRI scanner. Results: ROVER-MRI outperformed LS-SRR method in terms of reconstruction quality with 22.4% lower relative error (RE) and 7.5% lower full-width half maximum (FWHM) indicating better preservation of fine structural details in nearly half the scan time. Conclusion: ROVER-MRI offers an efficient and robust approach for mesoscale MR imaging, enabling rapid, high-resolution whole-brain scans. Its versatility holds great promise for research applications requiring anatomical details and time-efficient imaging.
目的:开发并验证一种新型图像重建技术,利用隐神经表示(INR)进行多视角厚层采集,在缩短扫描时间的同时保持较高的信噪比(SNR)。
方法:我们提出旋转视图超分辨率(ROVER)-MRI,这是一种基于无监督神经网络算法的MRI数据重建方法,可从多视角厚层重建数据,通过有效手段将扫描时间减少一倍,同时保留精细的解剖细节。我们将该方法与双三次插值以及当前最先进的正则化最小二乘超分辨率重建(LS-SRR)技术进行比较。使用真实离体猴子脑部数据进行验证,并在若干体内人体数据集上展示了更高的重建质量。值得注意的是,我们在7T MRI扫描仪上仅用了17分钟的扫描时间,就实现了体内整个人脑T2加权图像的重建,具有前所未有的180μm各向同性空间分辨率。
结果:ROVER-MRI在重建质量方面优于LS-SRR方法,相对误差(RE)降低22.4%,全宽半高(FWHM)降低7.5%,表明在近乎减半的扫描时间内更好地保留了精细结构细节。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本研究开发并验证了一种使用隐神经表示(INR)的新型图像重建技术,用于多视角厚切片采集,可在减少扫描时间的同时保持高信噪比(SNR)。提出的旋转视图超分辨率(ROVER)-MRI算法可有效从多视角厚切片重建MRI数据,将扫描时间减少一倍,同时保持精细的解剖细节。研究使用真实离体猴脑数据验证了该方法,并在多个体内人脑数据集上展示了卓越的重建质量。特别地,该研究在7T MRI扫描仪上仅用了17分钟就重建了一个整个人脑的T2加权图像,具有前所未有的180μm等距空间分辨率。结果表明,ROVER-MRI在重建质量方面优于现有的最小二乘超分辨率重建(LS-SRR)方法,具有更低的相对误差(RE)和全宽半最大值(FWHM),能够在几乎减半的扫描时间内更好地保留精细结构细节。总体而言,ROVER-MRI为快速高效的大规模MR成像提供了可能,在需要解剖细节和时间效率要求的领域具有巨大潜力。
Key Takeaways
- 研究提出了一种基于隐神经表示(INR)的新型图像重建技术——旋转视图超分辨率(ROVER)-MRI。
- ROVER-MRI旨在从多视角厚切片重建MRI数据,可在减少扫描时间的同时保持高质量图像。
- 相较于传统的图像重建方法和现有的最小二乘超分辨率重建(LS-SRR)技术,ROVER-MRI在重建质量上表现更优秀。
- ROVER-MRI成功在多个体内人脑数据集上实现了高质量重建,并且在离体猴脑数据上得到了验证。
- 研究实现了在7T MRI扫描仪上仅17分钟内完成的高分辨率整个人脑T2加权图像的重建。
- ROVER-MRI具有更低的相对误差(RE)和全宽半最大值(FWHM),能更好地保留图像中的精细结构细节。
点此查看论文截图

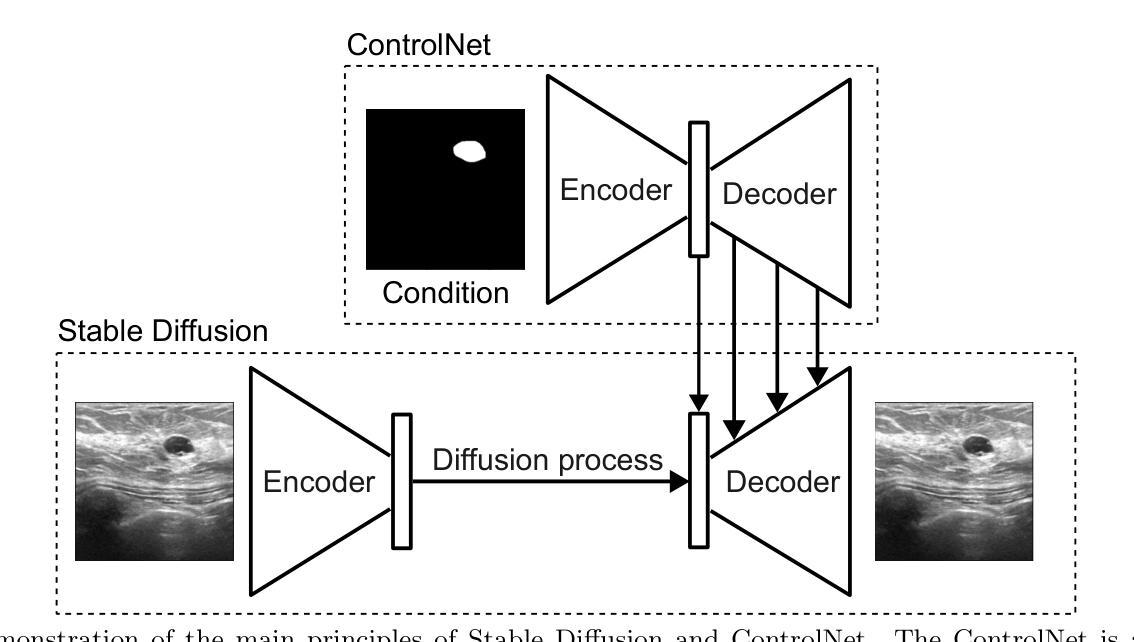
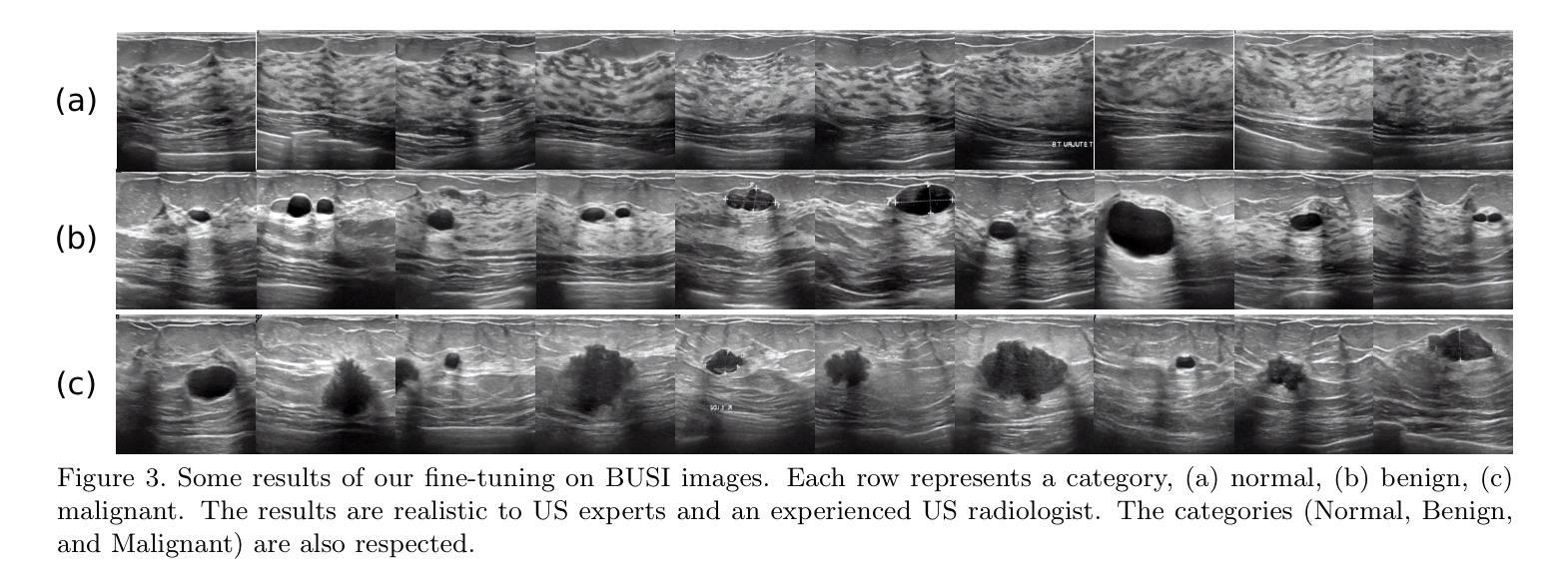
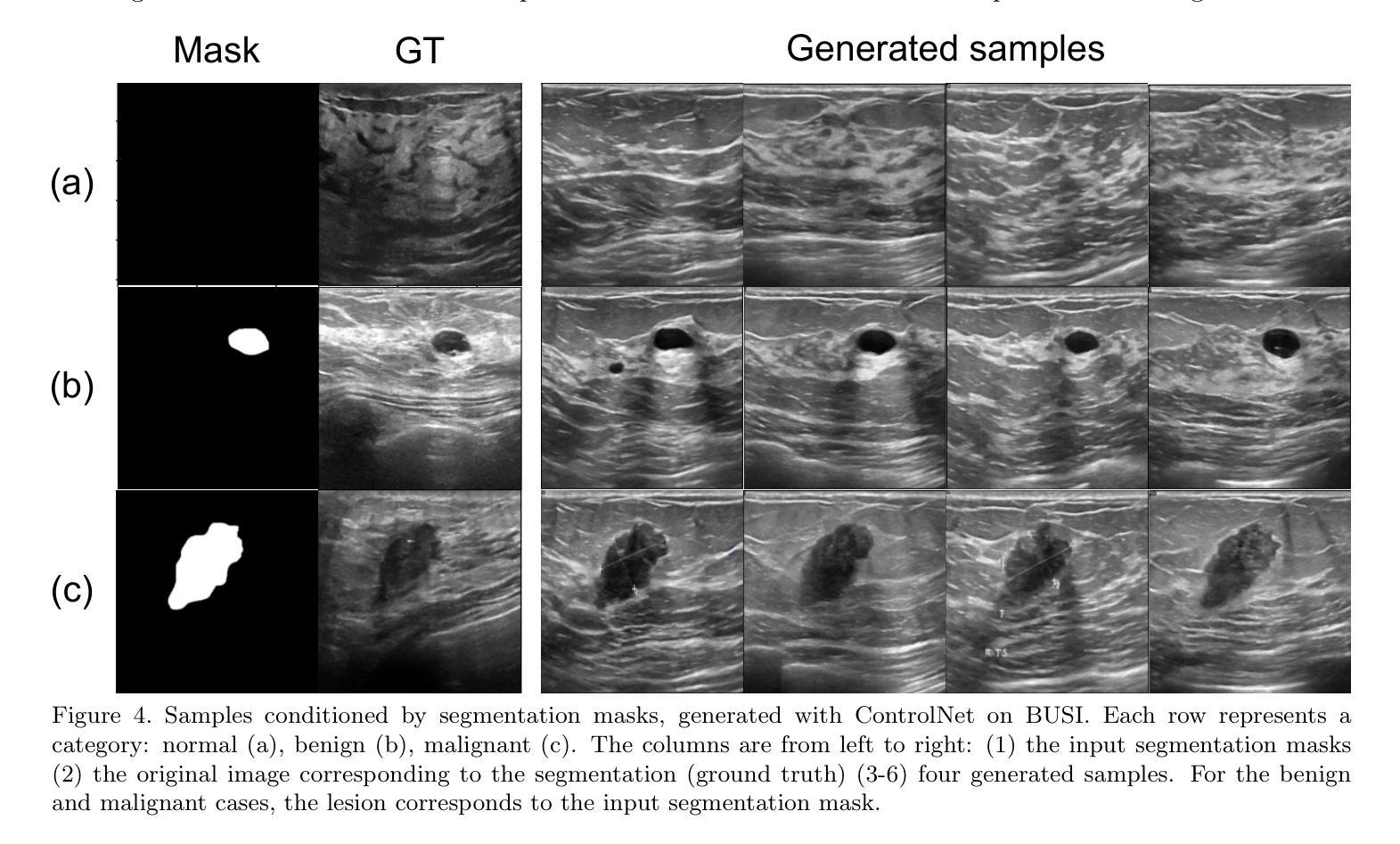
Ultrasound Image Generation using Latent Diffusion Models
Authors:Benoit Freiche, Anthony El-Khoury, Ali Nasiri-Sarvi, Mahdi S. Hosseini, Damien Garcia, Adrian Basarab, Mathieu Boily, Hassan Rivaz
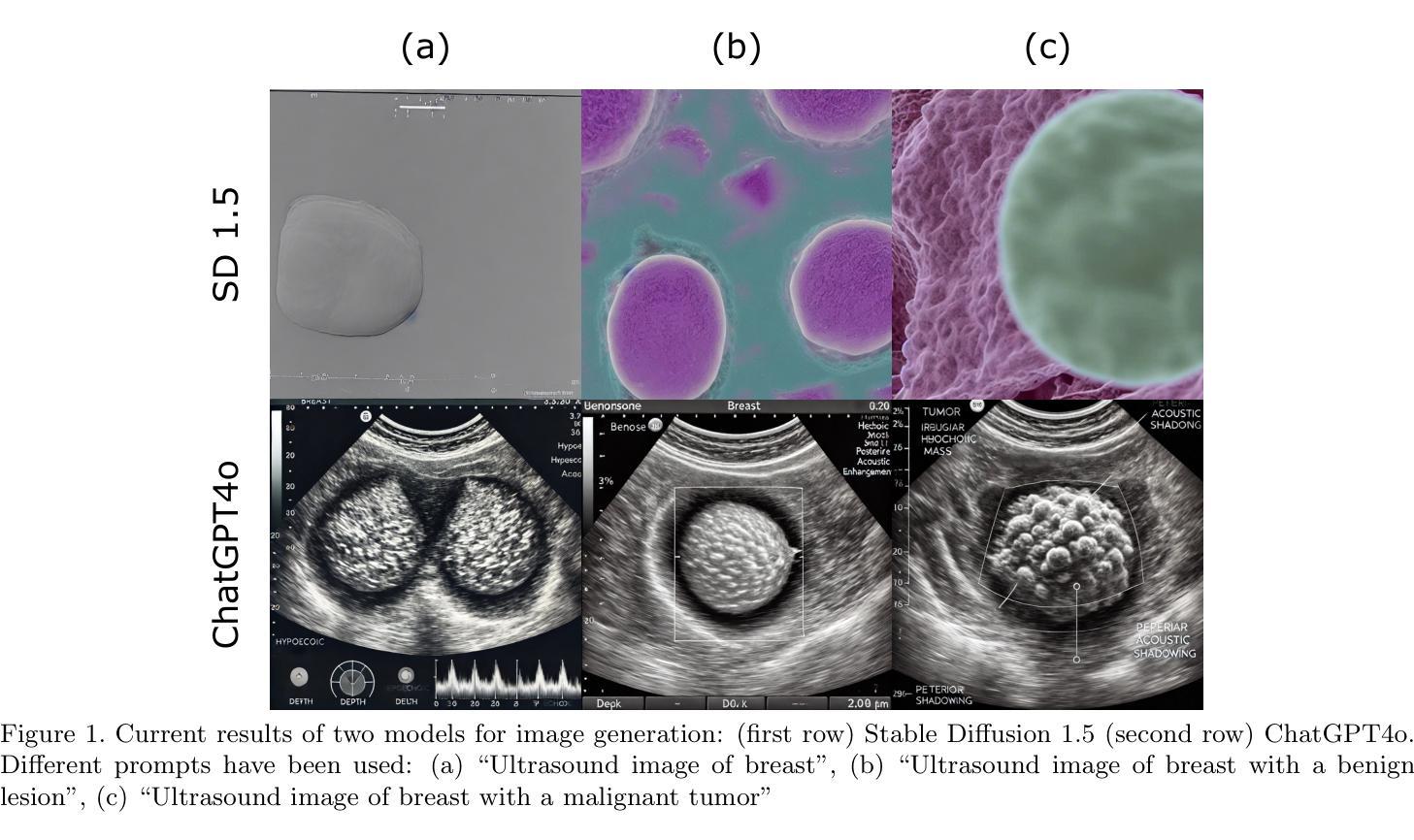
Diffusion models for image generation have been a subject of increasing interest due to their ability to generate diverse, high-quality images. Image generation has immense potential in medical imaging because open-source medical images are difficult to obtain compared to natural images, especially for rare conditions. The generated images can be used later to train classification and segmentation models. In this paper, we propose simulating realistic ultrasound (US) images by successive fine-tuning of large diffusion models on different publicly available databases. To do so, we fine-tuned Stable Diffusion, a state-of-the-art latent diffusion model, on BUSI (Breast US Images) an ultrasound breast image dataset. We successfully generated high-quality US images of the breast using simple prompts that specify the organ and pathology, which appeared realistic to three experienced US scientists and a US radiologist. Additionally, we provided user control by conditioning the model with segmentations through ControlNet. We will release the source code at http://code.sonography.ai/ to allow fast US image generation to the scientific community.
图像生成中的扩散模型因其能够生成多样化、高质量图像而日益受到关注。医学成像领域具有巨大的潜力,因为与自然图像相比,获取开源医学图像更加困难,尤其是对于罕见病症。生成的图像之后可用于训练和分割模型。在本文中,我们通过连续微调大型扩散模型来模拟逼真的超声(US)图像,这些模型在不同可用的公开数据库上具有良好的性能。为此,我们对最新的潜在扩散模型Stable Diffusion进行了微调,以在BUSI(乳腺超声图像)数据集上生成乳腺超声图像。我们成功使用简单的提示(指定器官和病理)生成高质量的乳腺超声图像,这些图像对三位经验丰富的超声科学家和一位超声放射科医生来说看起来非常逼真。此外,我们通过使用ControlNet对模型进行分段控制,提供了用户控制功能。我们将在http://code.sonography.ai/上发布源代码,以允许科学界快速生成超声图像。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 6 pages conference paper for SPIE medical imaging
Summary
本文利用扩散模型生成模拟的超声图像,通过在不同公共数据库上对大型扩散模型进行微调实现。使用稳定扩散模型对乳腺超声图像数据集进行微调,成功生成高质量乳腺超声图像。生成的图像具有真实感,并可通过控制模型与分割相结合实现用户控制。将在[链接地址]发布源代码,供科学界快速生成超声图像。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型用于图像生成正受到越来越多的关注,具有生成多样化、高质量图像的能力。
- 在医学成像领域,图像生成潜力巨大,特别是在获取公开医疗图像困难的情况下,能为罕见病症生成图像。
- 本文提出通过微调大型扩散模型来模拟真实的超声图像,使用了现有的公开数据库。
- 利用稳定扩散模型对乳腺超声图像数据集进行微调,成功生成高质量的乳腺超声图像。
- 生成的图像具有真实感,能够欺骗经验丰富的超声科学家和放射科医生。
- 用户可以通过控制模型与分割的结合来控制模型的生成结果。
- 源码将在指定链接发布,以供科学界使用,促进快速超声图像生成。
点此查看论文截图

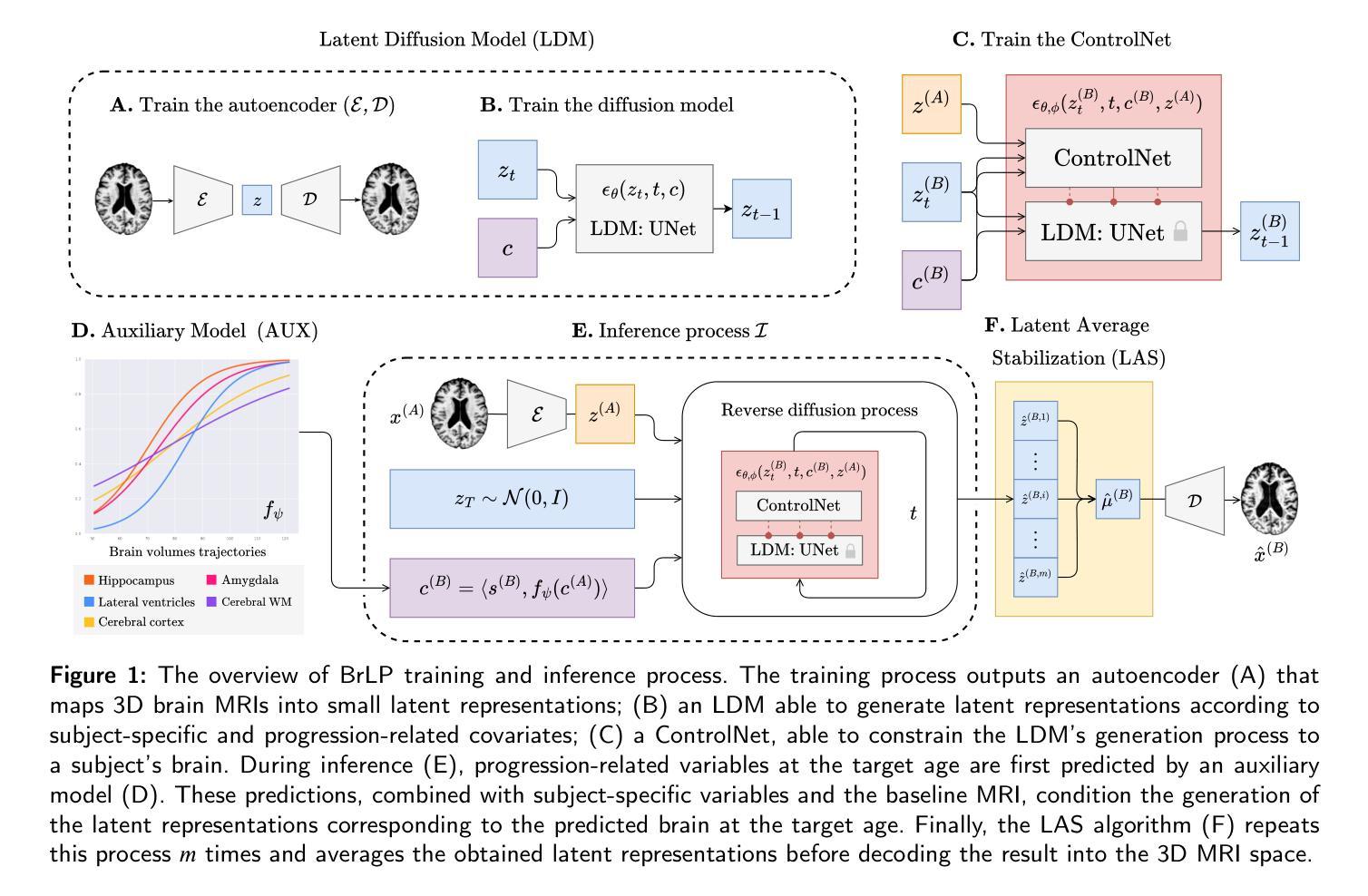
Brain Latent Progression: Individual-based Spatiotemporal Disease Progression on 3D Brain MRIs via Latent Diffusion
Authors:Lemuel Puglisi, Daniel C. Alexander, Daniele Ravì
The growing availability of longitudinal Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) datasets has facilitated Artificial Intelligence (AI)-driven modeling of disease progression, making it possible to predict future medical scans for individual patients. However, despite significant advancements in AI, current methods continue to face challenges including achieving patient-specific individualization, ensuring spatiotemporal consistency, efficiently utilizing longitudinal data, and managing the substantial memory demands of 3D scans. To address these challenges, we propose Brain Latent Progression (BrLP), a novel spatiotemporal model designed to predict individual-level disease progression in 3D brain MRIs. The key contributions in BrLP are fourfold: (i) it operates in a small latent space, mitigating the computational challenges posed by high-dimensional imaging data; (ii) it explicitly integrates subject metadata to enhance the individualization of predictions; (iii) it incorporates prior knowledge of disease dynamics through an auxiliary model, facilitating the integration of longitudinal data; and (iv) it introduces the Latent Average Stabilization (LAS) algorithm, which (a) enforces spatiotemporal consistency in the predicted progression at inference time and (b) allows us to derive a measure of the uncertainty for the prediction. We train and evaluate BrLP on 11,730 T1-weighted (T1w) brain MRIs from 2,805 subjects and validate its generalizability on an external test set comprising 2,257 MRIs from 962 subjects. Our experiments compare BrLP-generated MRI scans with real follow-up MRIs, demonstrating state-of-the-art accuracy compared to existing methods. The code is publicly available at: https://github.com/LemuelPuglisi/BrLP.
随着纵向磁共振成像(MRI)数据集的日益普及,基于人工智能(AI)的疾病进展建模变得更为便利,这使得能够针对个体患者预测未来的医学扫描结果。然而,尽管人工智能取得了重大进展,当前的方法仍然面临挑战,包括实现患者特异性个性化、确保时空一致性、有效利用纵向数据以及管理庞大的三维扫描内存需求。为了应对这些挑战,我们提出了Brain Latent Progression(BrLP)模型,这是一种新型时空预测模型,旨在预测三维脑部MRI的个体疾病进展。BrLP的主要贡献体现在四个方面:(i)它在小潜空间中运行,减轻了高维成像数据带来的计算挑战;(ii)它明确地集成了受试者元数据,以增强预测的个性化;(iii)它通过辅助模型融入疾病动态的先验知识,促进纵向数据的整合;(iv)它引入了Latent Average Stabilization(LAS)算法,该算法(a)在推理时强制预测的进展具有时空一致性,(b)使我们能够得出预测的确定性度量。我们在包含来自2805名受试者的11730张T1加权(T1w)脑MRI上训练和评估BrLP模型,并在包含来自962名受试者的外部测试集上验证其通用性。我们的实验将BrLP生成的MRI扫描与真实的随访MRI进行比较,证明了其相较于现有方法的卓越准确性。代码公开在:https://github.com/LemuelPuglisi/BrLP。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF arXiv admin note: text overlap with arXiv:2405.03328
Summary
提出的Brain Latent Progression(BrLP)模型能预测患者个体化的疾病进展情况。BrLP在四维时空模型中操作,通过降低高维图像数据带来的计算挑战、集成患者元数据以提升预测个性化程度、引入疾病动态先验知识辅助模型并利用Latent Average Stabilization(LAS)算法确保预测时空一致性和不确定性度量,实现了对3D脑MRI中疾病进展的精准预测。经过大规模实验验证,BrLP在公开数据集上的表现优于现有方法。
Key Takeaways
- Brain Latent Progression(BrLP)是一个用于预测3D脑MRI中疾病进展的时空模型。
- BrLP在小型潜在空间内操作,降低高维图像数据的计算挑战。
- BrLP集成了患者的元数据,以增强预测的个性化和准确性。
- BrLP通过引入疾病动态的先验知识,促进纵向数据的整合。
- BrLP引入了Latent Average Stabilization(LAS)算法,确保预测的时空一致性和不确定性度量。
- BrLP在包含大量受试者的大规模数据集上进行训练和评估,表现出优异的性能。
- BrLP的代码已公开可用,为研究人员提供方便的访问途径。
点此查看论文截图

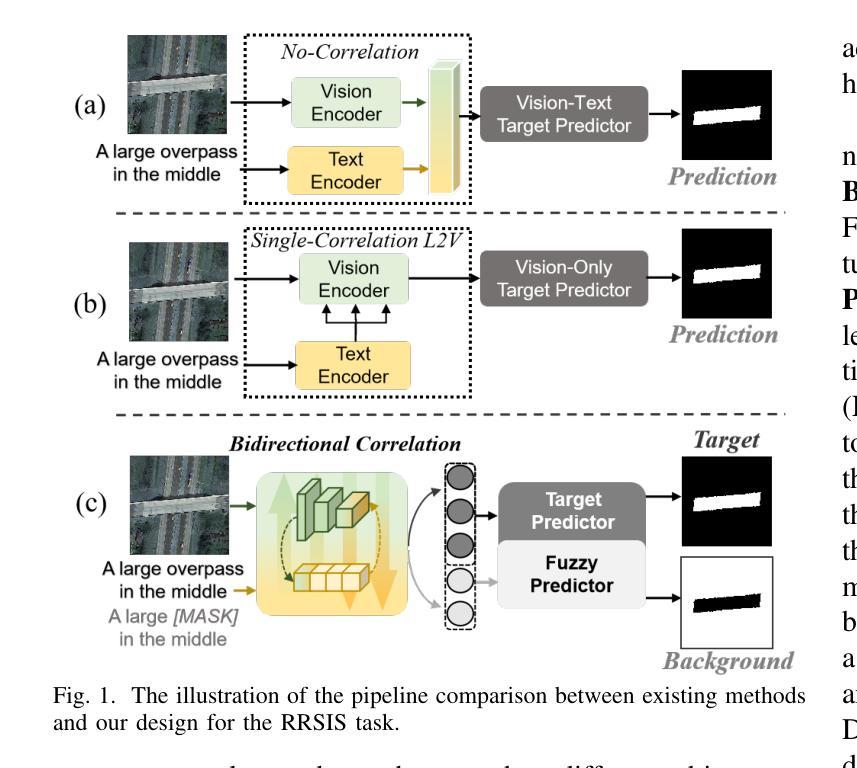
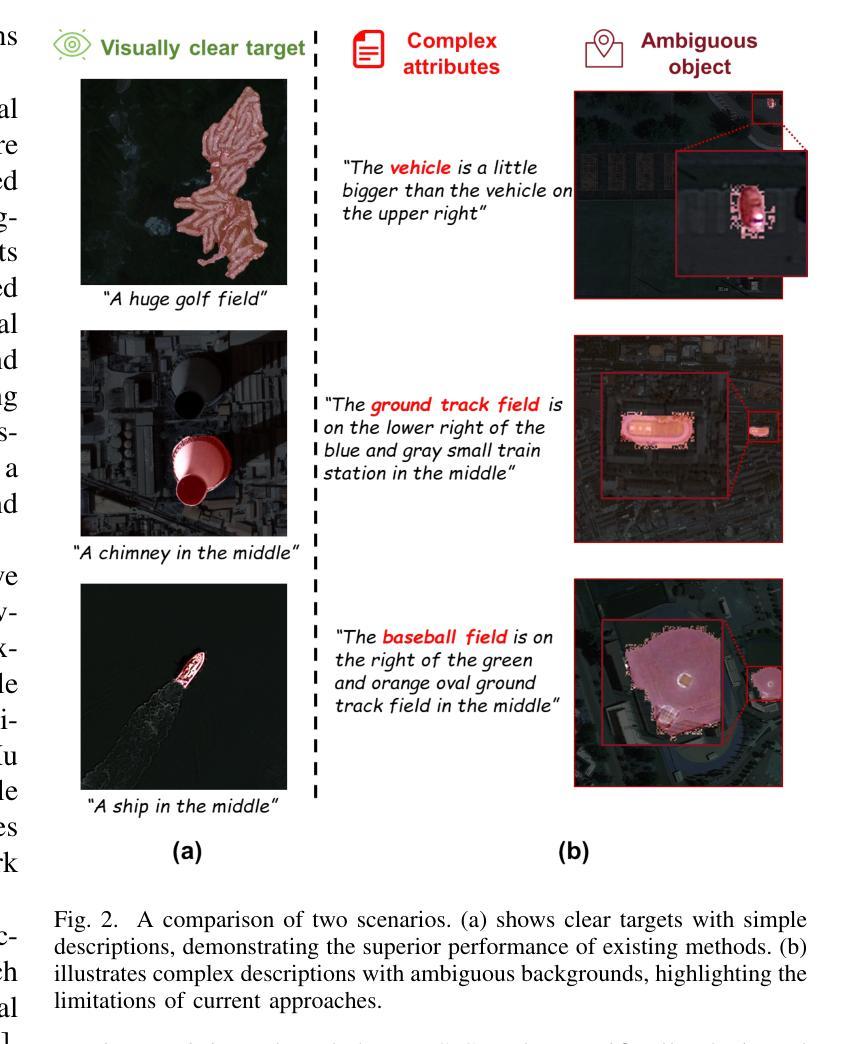
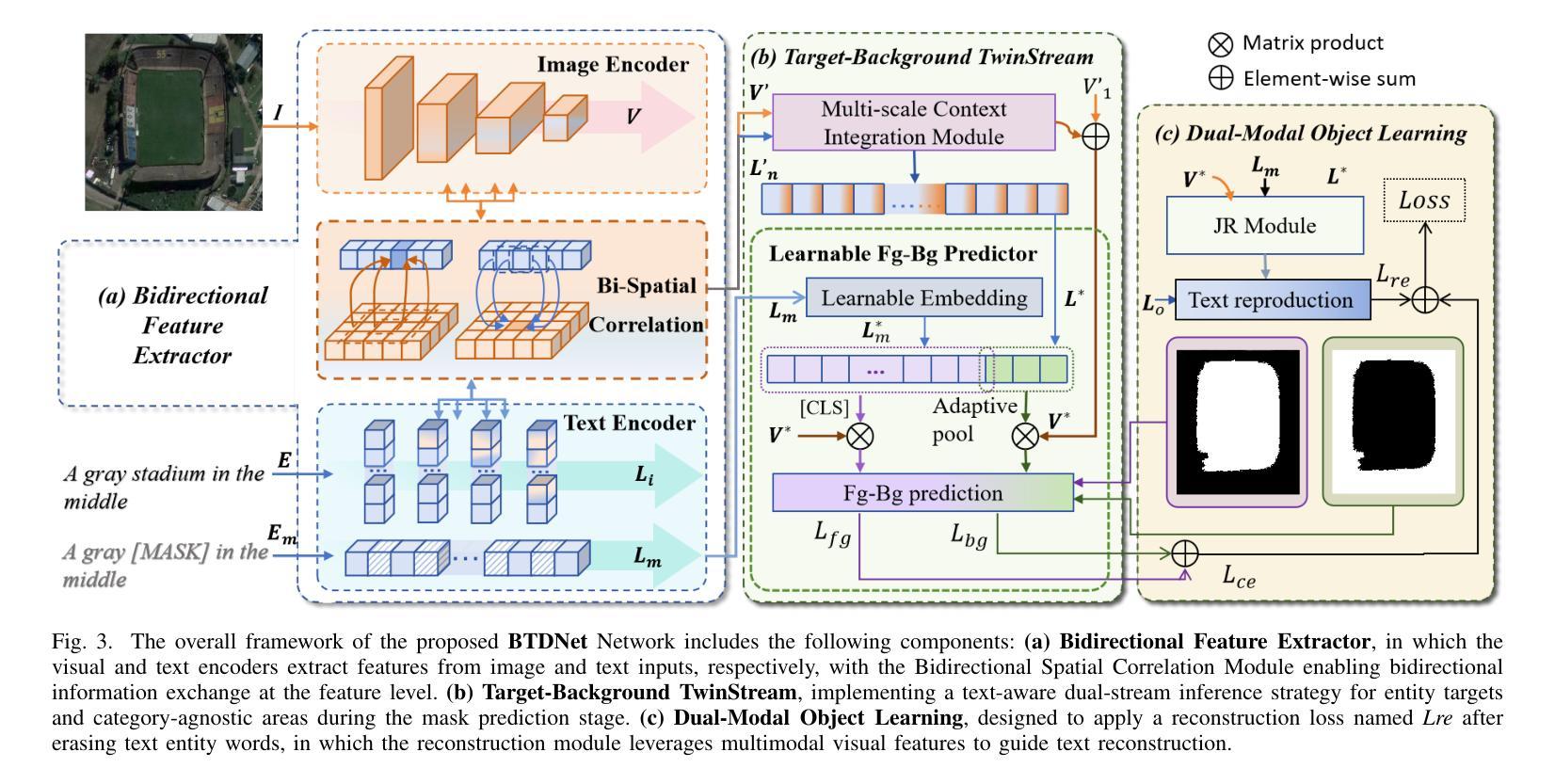
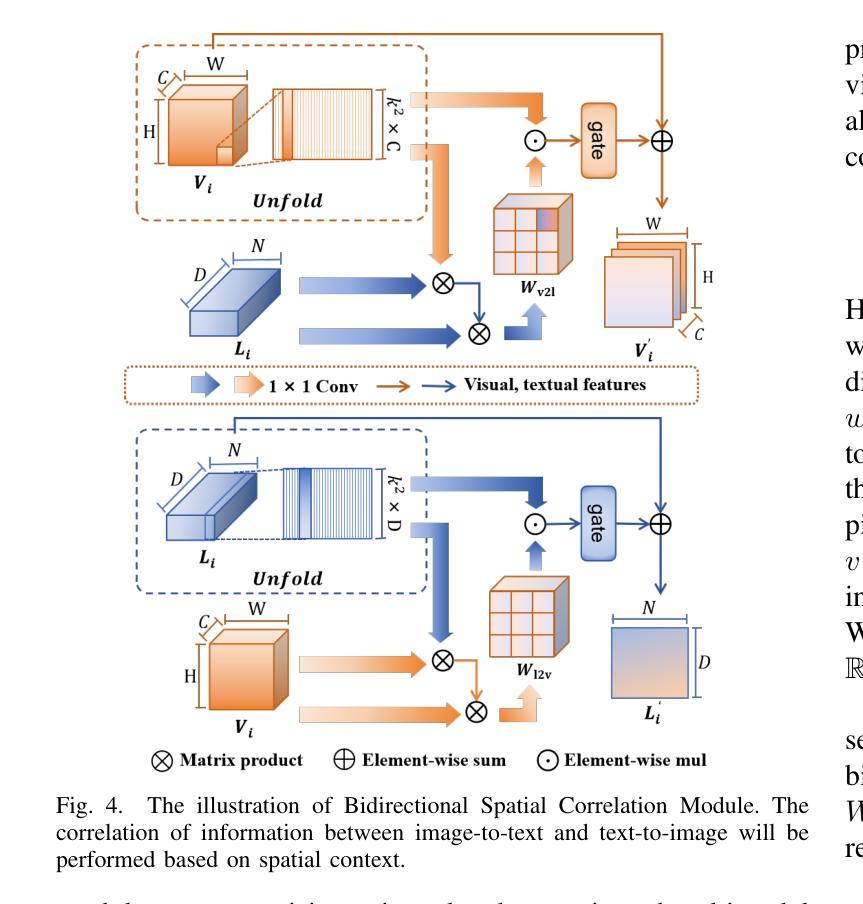
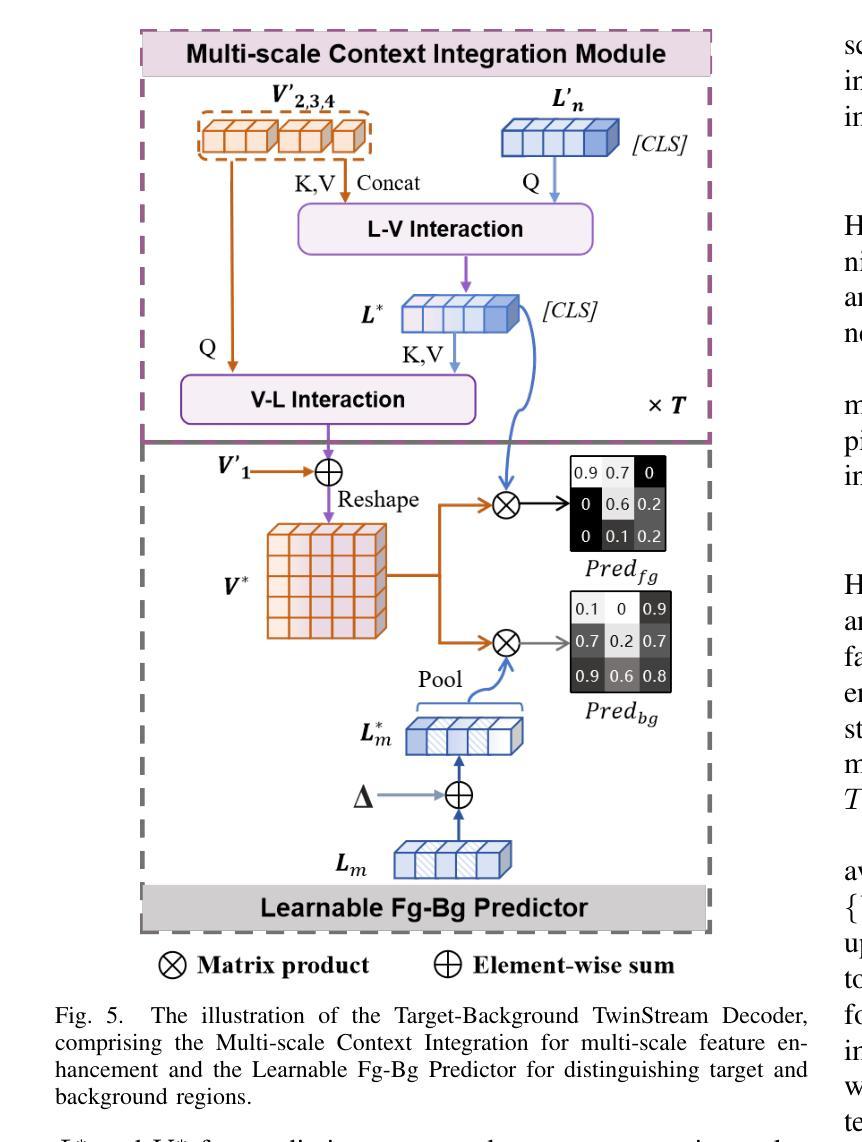
Referring Remote Sensing Image Segmentation via Bidirectional Alignment Guided Joint Prediction
Authors:Tianxiang Zhang, Zhaokun Wen, Bo Kong, Kecheng Liu, Yisi Zhang, Peixian Zhuang, Jiangyun Li
Referring Remote Sensing Image Segmentation (RRSIS) is critical for ecological monitoring, urban planning, and disaster management, requiring precise segmentation of objects in remote sensing imagery guided by textual descriptions. This task is uniquely challenging due to the considerable vision-language gap, the high spatial resolution and broad coverage of remote sensing imagery with diverse categories and small targets, and the presence of clustered, unclear targets with blurred edges. To tackle these issues, we propose \ours, a novel framework designed to bridge the vision-language gap, enhance multi-scale feature interaction, and improve fine-grained object differentiation. Specifically, \ours introduces: (1) the Bidirectional Spatial Correlation (BSC) for improved vision-language feature alignment, (2) the Target-Background TwinStream Decoder (T-BTD) for precise distinction between targets and non-targets, and (3) the Dual-Modal Object Learning Strategy (D-MOLS) for robust multimodal feature reconstruction. Extensive experiments on the benchmark datasets RefSegRS and RRSIS-D demonstrate that \ours achieves state-of-the-art performance. Specifically, \ours improves the overall IoU (oIoU) by 3.76 percentage points (80.57) and 1.44 percentage points (79.23) on the two datasets, respectively. Additionally, it outperforms previous methods in the mean IoU (mIoU) by 5.37 percentage points (67.95) and 1.84 percentage points (66.04), effectively addressing the core challenges of RRSIS with enhanced precision and robustness.
遥感图像分割参照(RRSIS)对于生态监测、城市规划和灾害管理至关重要,它要求根据文本描述精确地分割遥感图像中的对象。由于视语言差距较大,遥感图像的高空间分辨率和广泛覆盖范围,具有多种类别和小目标,以及存在边界模糊、目标不明确的情况,这项任务具有独特的挑战性。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了一个新颖框架\ours,旨在弥合视语言差距,增强多尺度特征交互,并改善精细粒度对象区分。具体来说,\ours引入了:(1)双向空间相关性(BSC)以改进视语言特征对齐;(2)目标背景TwinStream解码器(T-BTD)以精确区分目标和非目标;(3)双模态对象学习策略(D-MOLS)用于稳健的多模态特征重建。在RefSegRS和RRSIS-D基准数据集上的大量实验表明,\ours达到了最先进的性能。具体来说,\ours在两个数据集上的整体IoU(oIoU)分别提高了3.76个百分点(达到80.57)和1.44个百分点(达到79.23)。此外,它在平均IoU(mIoU)上较之前的方法提高了5.37个百分点(达到67.95)和1.84个百分点(达到66.04),有效地解决了RRSIS的核心挑战,提高了精度和稳健性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
所提出的新方法通过引入双向空间相关性(BSC)、目标背景TwinStream解码器(T-BTD)和双模态对象学习策略(D-MOLS),成功解决了遥感图像分割中的视觉语言差距、多尺度特征交互以及精细对象区分等问题,在RefSegRS和RRSIS-D等基准数据集上实现了卓越的性能。
Key Takeaways
- 新提出的框架解决了远程遥感图像分割(RRSIS)中的视觉语言差距问题。
- 通过引入双向空间相关性(BSC),改进了视觉语言特征的匹配。
- 目标背景TwinStream解码器(T-BTD)的设计,能够精确区分目标和非目标。
- 双模态对象学习策略(D-MOLS)增强了多模态特征的重建能力。
- 在RefSegRS和RRSIS-D数据集上的实验表明,新框架实现了最先进的性能。
- 新框架提高了整体IoU(oIoU)指标,相比之前的方法有明显优势。
点此查看论文截图

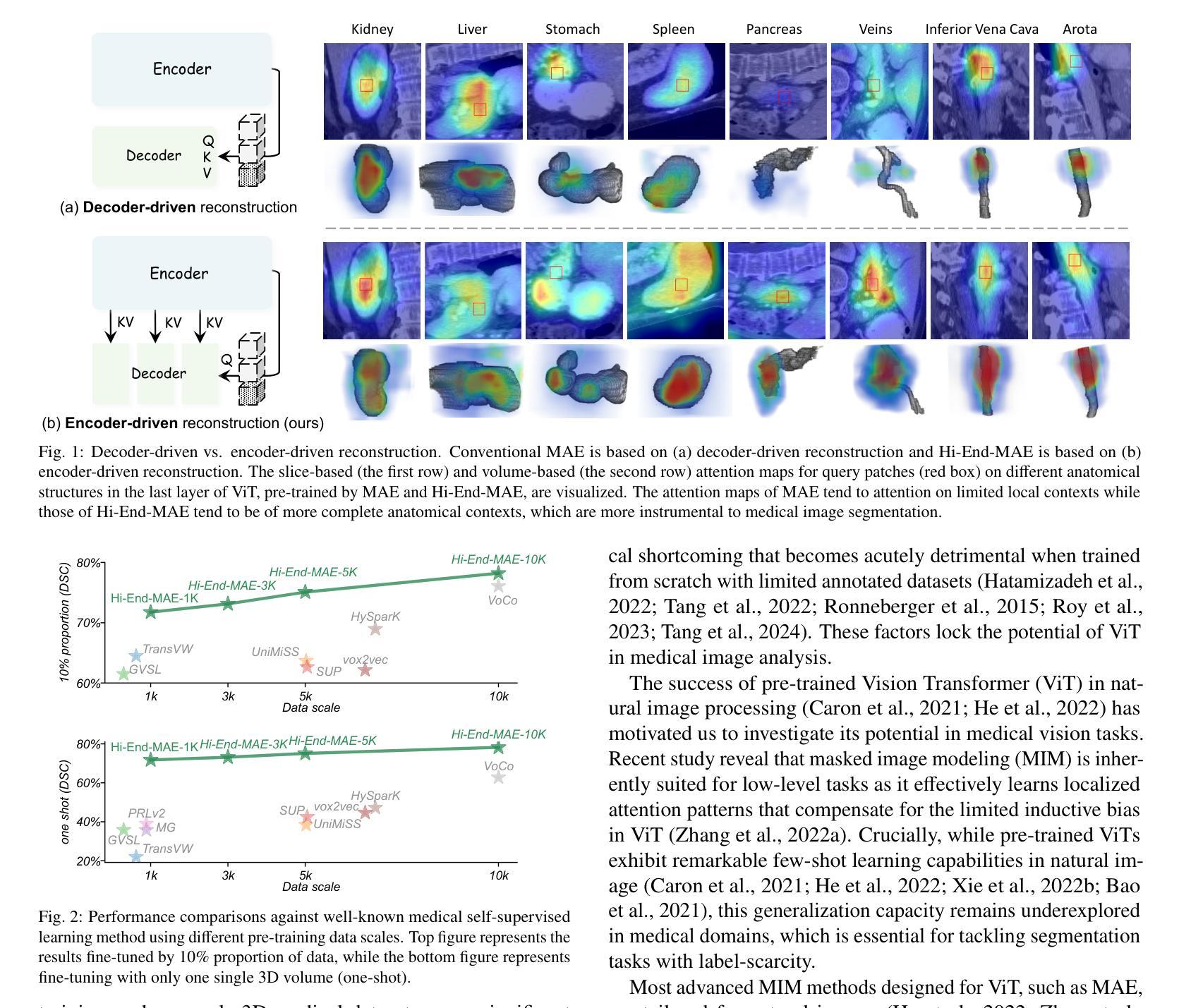
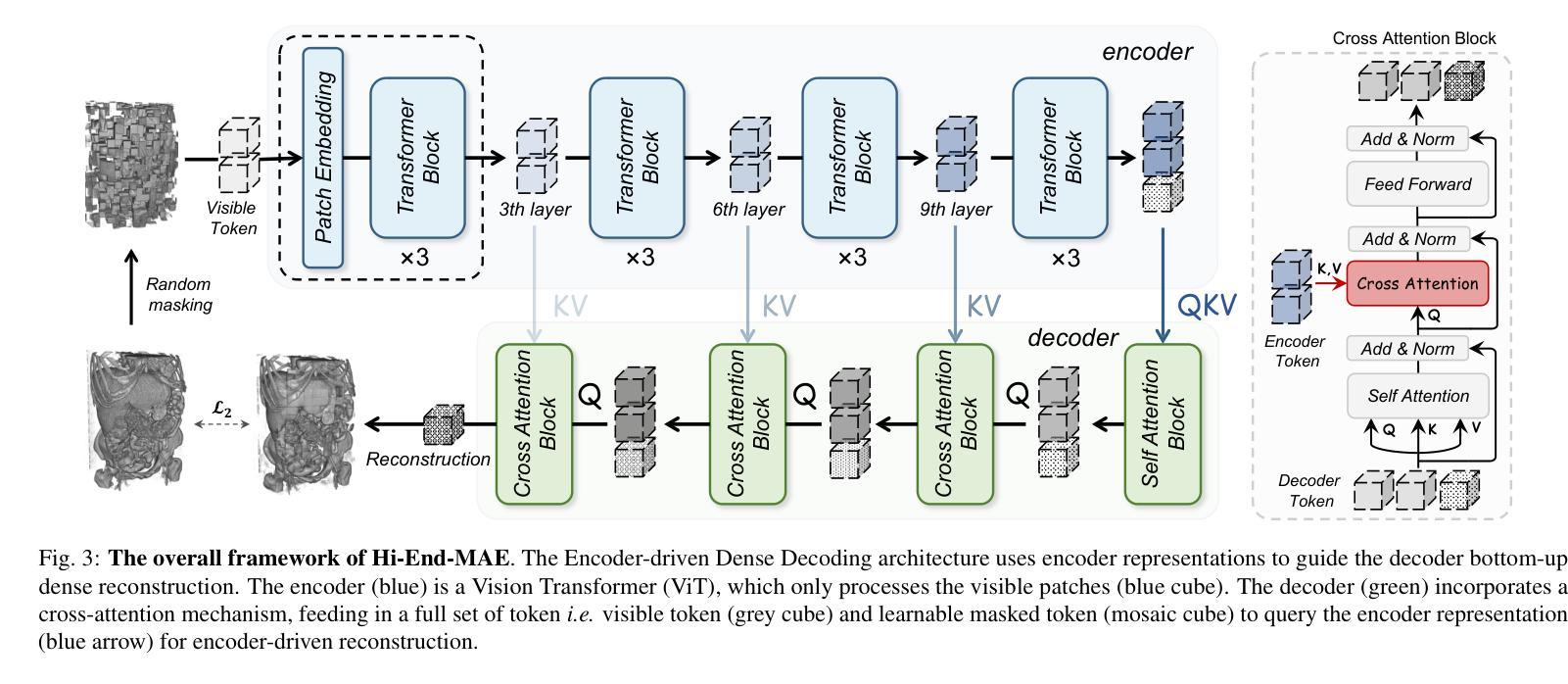
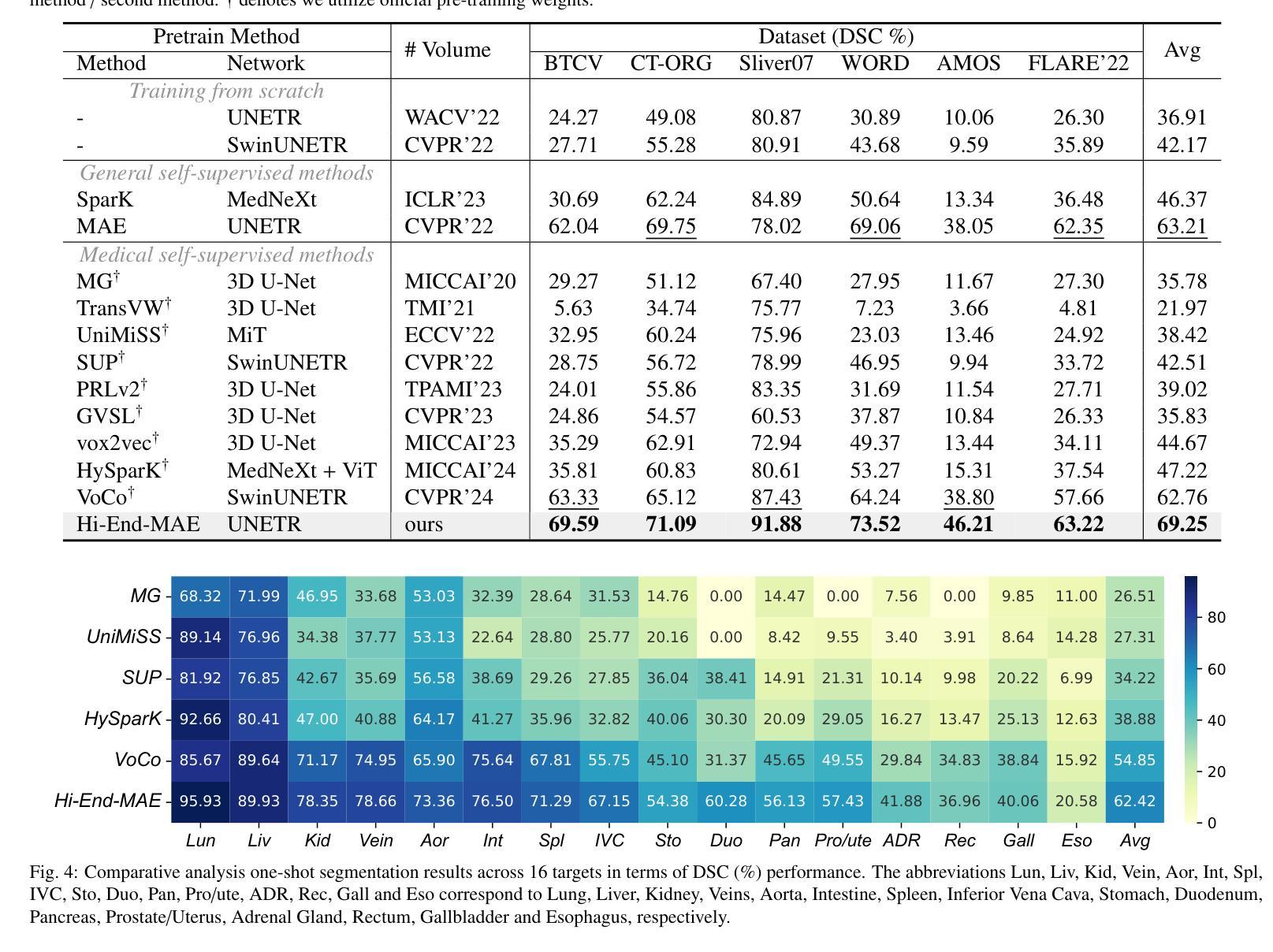
Hi-End-MAE: Hierarchical encoder-driven masked autoencoders are stronger vision learners for medical image segmentation
Authors:Fenghe Tang, Qingsong Yao, Wenxin Ma, Chenxu Wu, Zihang Jiang, S. Kevin Zhou
Medical image segmentation remains a formidable challenge due to the label scarcity. Pre-training Vision Transformer (ViT) through masked image modeling (MIM) on large-scale unlabeled medical datasets presents a promising solution, providing both computational efficiency and model generalization for various downstream tasks. However, current ViT-based MIM pre-training frameworks predominantly emphasize local aggregation representations in output layers and fail to exploit the rich representations across different ViT layers that better capture fine-grained semantic information needed for more precise medical downstream tasks. To fill the above gap, we hereby present Hierarchical Encoder-driven MAE (Hi-End-MAE), a simple yet effective ViT-based pre-training solution, which centers on two key innovations: (1) Encoder-driven reconstruction, which encourages the encoder to learn more informative features to guide the reconstruction of masked patches; and (2) Hierarchical dense decoding, which implements a hierarchical decoding structure to capture rich representations across different layers. We pre-train Hi-End-MAE on a large-scale dataset of 10K CT scans and evaluated its performance across seven public medical image segmentation benchmarks. Extensive experiments demonstrate that Hi-End-MAE achieves superior transfer learning capabilities across various downstream tasks, revealing the potential of ViT in medical imaging applications. The code is available at: https://github.com/FengheTan9/Hi-End-MAE
医学图像分割仍然是一个巨大的挑战,主要是由于缺乏标签。通过大规模无标签医学数据集对视觉转换器(ViT)进行掩模图像建模(MIM)的预训练,呈现出一种很有前景的解决方案,为各种下游任务提供了计算效率和模型泛化能力。然而,当前的基于ViT的MIM预训练框架主要侧重于输出层的局部聚合表示,并未能充分利用不同ViT层中的丰富表示,这些层能更好地捕捉用于更精确医学下游任务的细粒度语义信息。为了填补上述空白,我们在此提出分层编码器驱动的MAE(Hi-End-MAE),这是一种简单有效的基于ViT的预训练解决方案,其核心包含两项重要创新:(1)编码器驱动重建,这鼓励编码器学习更多信息特征以指导掩码块的重建;(2)分层密集解码,这实现了一种分层解码结构,以捕获不同层的丰富表示。我们在包含10K次CT扫描的大规模数据集上预训练Hi-End-MAE,并在七个公共医学图像分割基准上评估其性能。大量实验表明,Hi-End-MAE在各种下游任务上实现了卓越的迁移学习能力,揭示了ViT在医学成像应用中的潜力。代码可用在:https://github.com/FengheTan9/Hi-End-MAE
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 19 pages, Code: https://github.com/FengheTan9/Hi-End-MAE
Summary
医学图像分割因标签稀缺而面临挑战。通过大规模无标签医学数据集对视觉转换器(ViT)进行掩模图像建模(MIM)的预训练展现出一种解决方案的潜力,能提高计算效率和模型在各种下游任务中的泛化能力。然而,现有的基于ViT的MIM预训练框架主要侧重于输出层的局部聚合表示,未能充分利用不同ViT层中的丰富表示,这些表示能更好地捕捉用于更精确医学下游任务的细粒度语义信息。为填补上述空白,我们提出层次编码器驱动的MAE(Hi-End-MAE),这是一种简单有效的基于ViT的预训练解决方案,其核心创新点在于:一是编码器驱动的重构,鼓励编码器学习更多信息特征以指导掩码补丁的重构;二是层次密集解码,实现层次解码结构以捕获不同层次的丰富表示。我们在包含一万次CT扫描的大规模数据集上预训练Hi-End-MAE,并在七个公开医学图像分割基准上评估其性能。实验表明,Hi-End-MAE在各种下游任务中具有出色的迁移学习能力,展现了ViT在医学成像应用中的潜力。
Key Takeaways
- 医学图像分割面临标签稀缺的挑战。
- 预训练视觉转换器(ViT)通过掩模图像建模(MIM)在大型无标签医学数据集上是一种有前景的解决方案。
- 当前基于ViT的MIM预训练框架主要关注输出层的局部聚合表示。
- Hi-End-MAE通过编码器驱动的重构和层次密集解码来解决上述问题。
- 编码器驱动的重构鼓励编码器学习更多信息特征以指导掩码补丁的重构。
- 层次密集解码旨在捕获不同层次的丰富表示。
点此查看论文截图

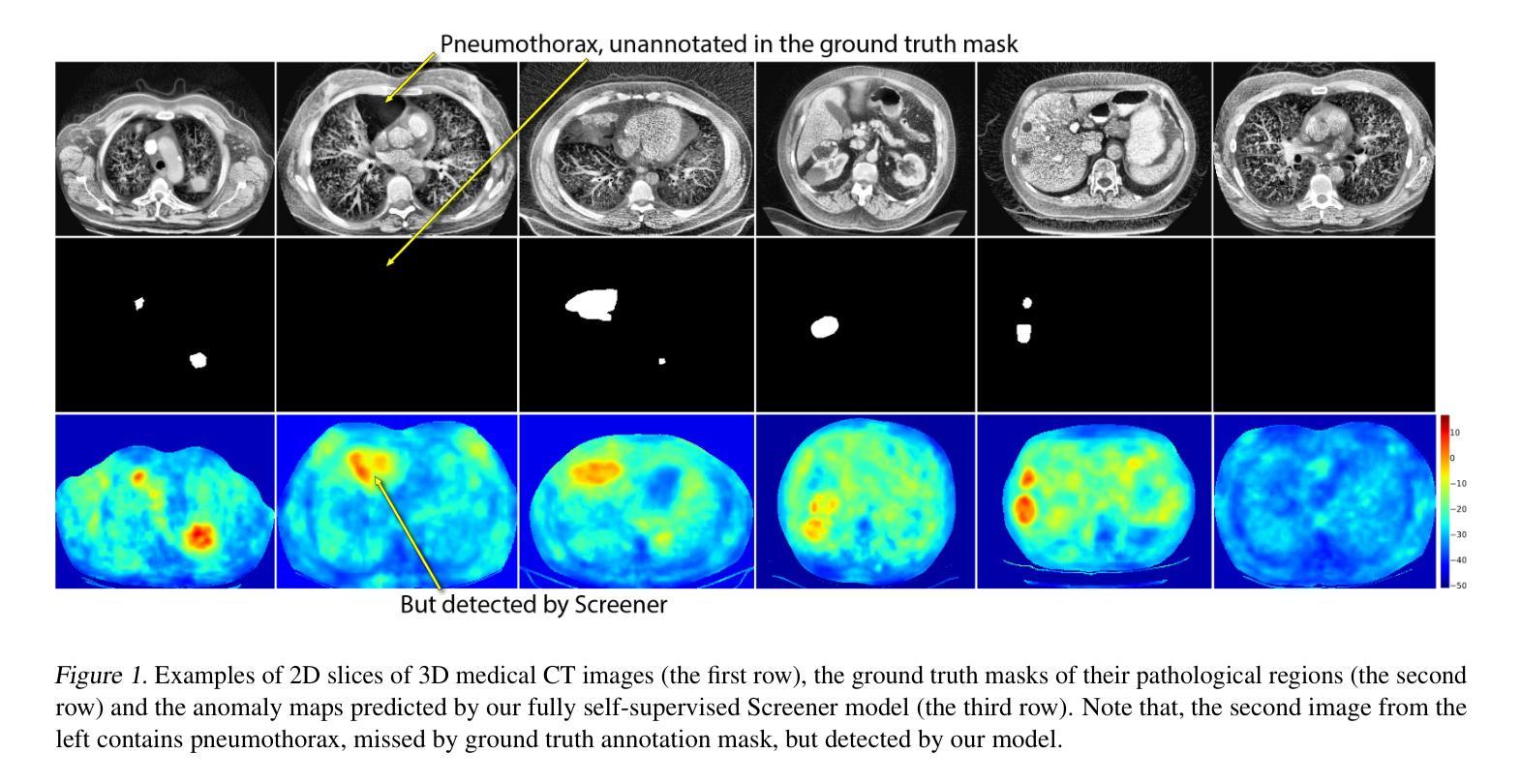
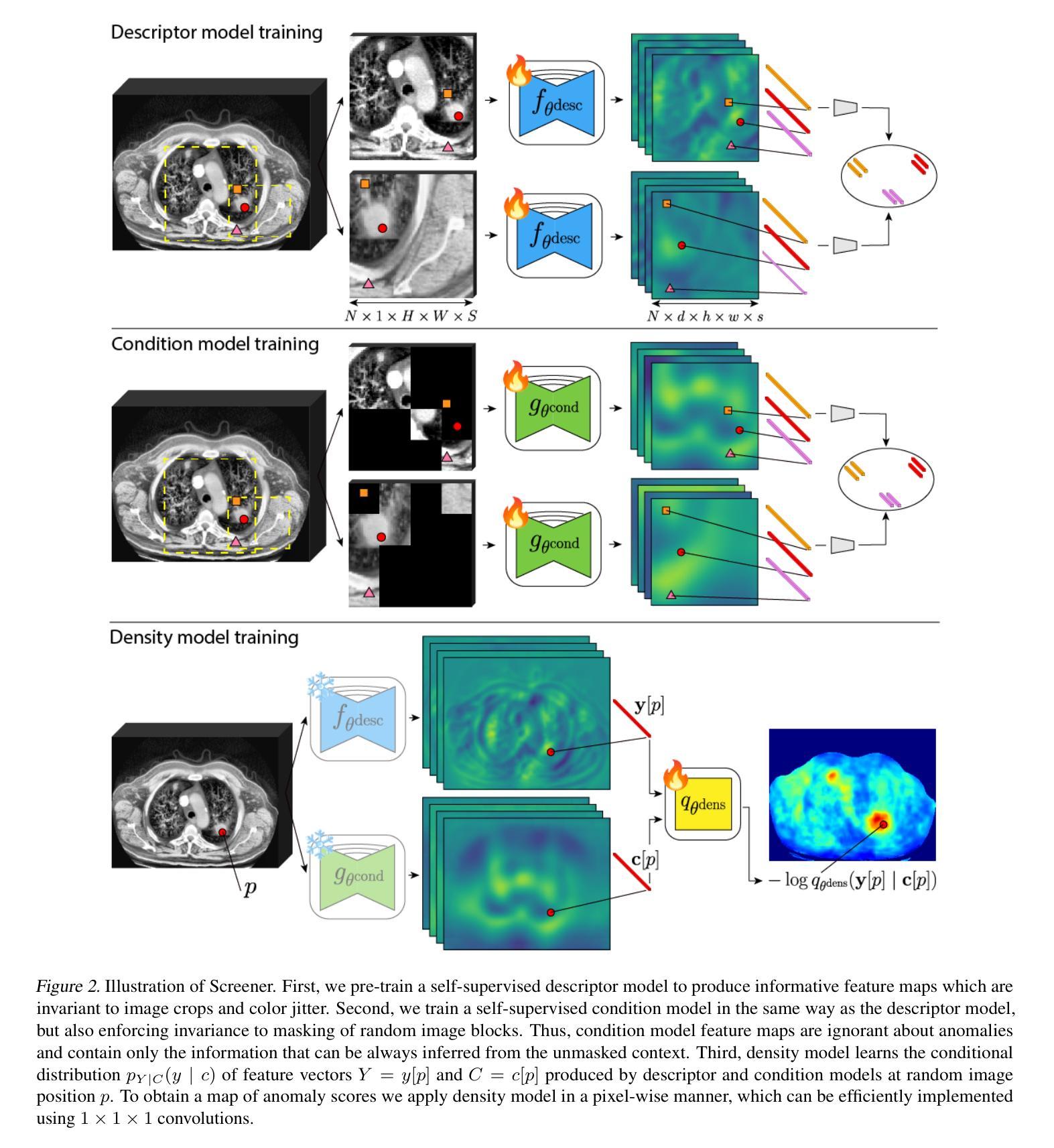
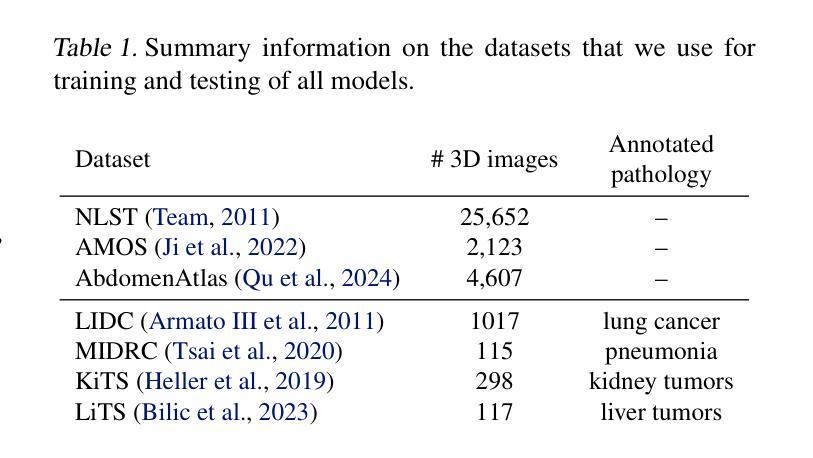
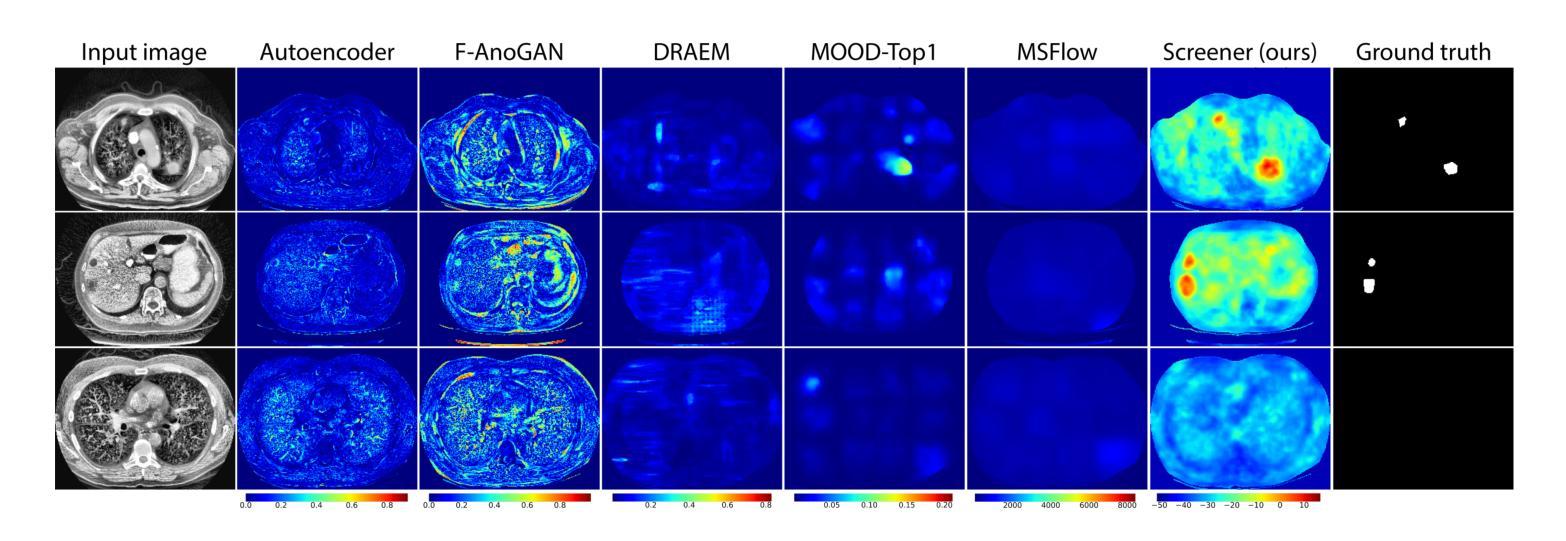
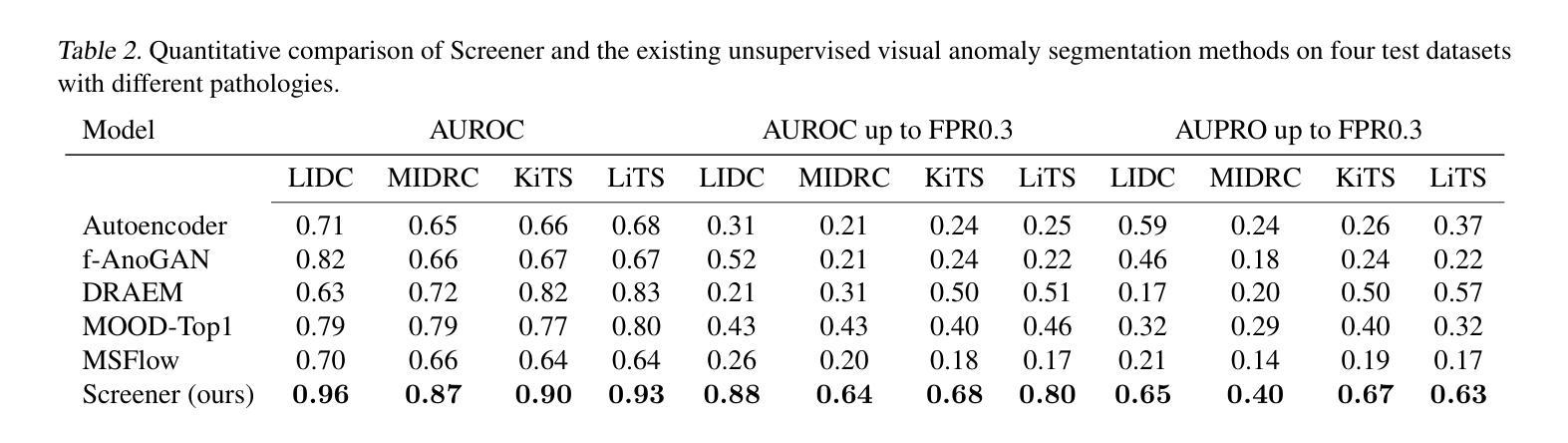
Screener: Self-supervised Pathology Segmentation Model for 3D Medical Images
Authors:Mikhail Goncharov, Eugenia Soboleva, Mariia Donskova, Ivan Oseledets, Marina Munkhoeva, Maxim Panov
Accurate segmentation of all pathological findings in 3D medical images remains a significant challenge, as supervised models are limited to detecting only the few pathology classes annotated in existing datasets. To address this, we frame pathology segmentation as an unsupervised visual anomaly segmentation (UVAS) problem, leveraging the inherent rarity of pathological patterns compared to healthy ones. We enhance the existing density-based UVAS framework with two key innovations: (1) dense self-supervised learning (SSL) for feature extraction, eliminating the need for supervised pre-training, and (2) learned, masking-invariant dense features as conditioning variables, replacing hand-crafted positional encodings. Trained on over 30,000 unlabeled 3D CT volumes, our model, Screener, outperforms existing UVAS methods on four large-scale test datasets comprising 1,820 scans with diverse pathologies. Code and pre-trained models will be made publicly available.
在3D医学图像中对所有病理表现进行精确分割仍然是一个巨大的挑战,因为监督模型仅限于检测现有数据集中已标注的少数病理类别。为了解决这一问题,我们将病理分割作为一个无监督的视觉异常分割(UVAS)问题来解决,利用病理模式与健康模式相比固有的稀有性。我们对现有的基于密度的UVAS框架进行了两项关键创新:一是密集的自监督学习(SSL)用于特征提取,无需监督预训练;二是学习得到的、对遮挡具有不变性的密集特征作为条件变量,取代了手工位置编码。在超过3万个无标签的3D CT体积上进行训练后,我们的模型——筛选器在由多个包含各种病理表现的扫描组成的大规模测试数据集上的表现优于现有的UVAS方法,共涵盖1820个扫描图像。模型和预训练模型将公开提供。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
本文提出一种针对三维医学图像中所有病理特征的分割问题,通过构建基于密度分析的无监督视觉异常分割框架,实现了对多种病理特征的准确分割。本文创新性地引入两项技术:一是通过密集自监督学习提取特征,避免了需要标注数据进行预训练的问题;二是利用训练出的、具有遮挡不变性的密集特征作为条件变量,取代了手工设计的位置编码方式。该模型在超过三万份无标签的三维CT图像数据上进行训练,在包含千余张含有不同病理的扫描数据的测试集上表现出了优异的性能。此外,作者将公开模型和代码供公众使用。
关键见解
- 提出将病理分割问题视为无监督视觉异常分割(UVAS)问题,利用病理模式与健康模式之间的固有差异进行识别。
- 创新性地引入密集自监督学习进行特征提取,简化了对标注数据的依赖。
- 利用训练出的、具有遮挡不变性的密集特征作为条件变量替代传统手工设计的位置编码。
- 模型在大量无标签的三维CT图像数据上进行训练,证明了其对不同病理特征的有效识别能力。
- 模型在包含多种病理的大规模测试数据集上表现优异,证明了其广泛的应用潜力。
- 模型和代码将公开供公众使用,为相关研究提供便利。
- 此方法提供了一个全新的视角来解决医学图像分割中的挑战性问题,具有广泛的应用前景和重要的实用价值。
点此查看论文截图

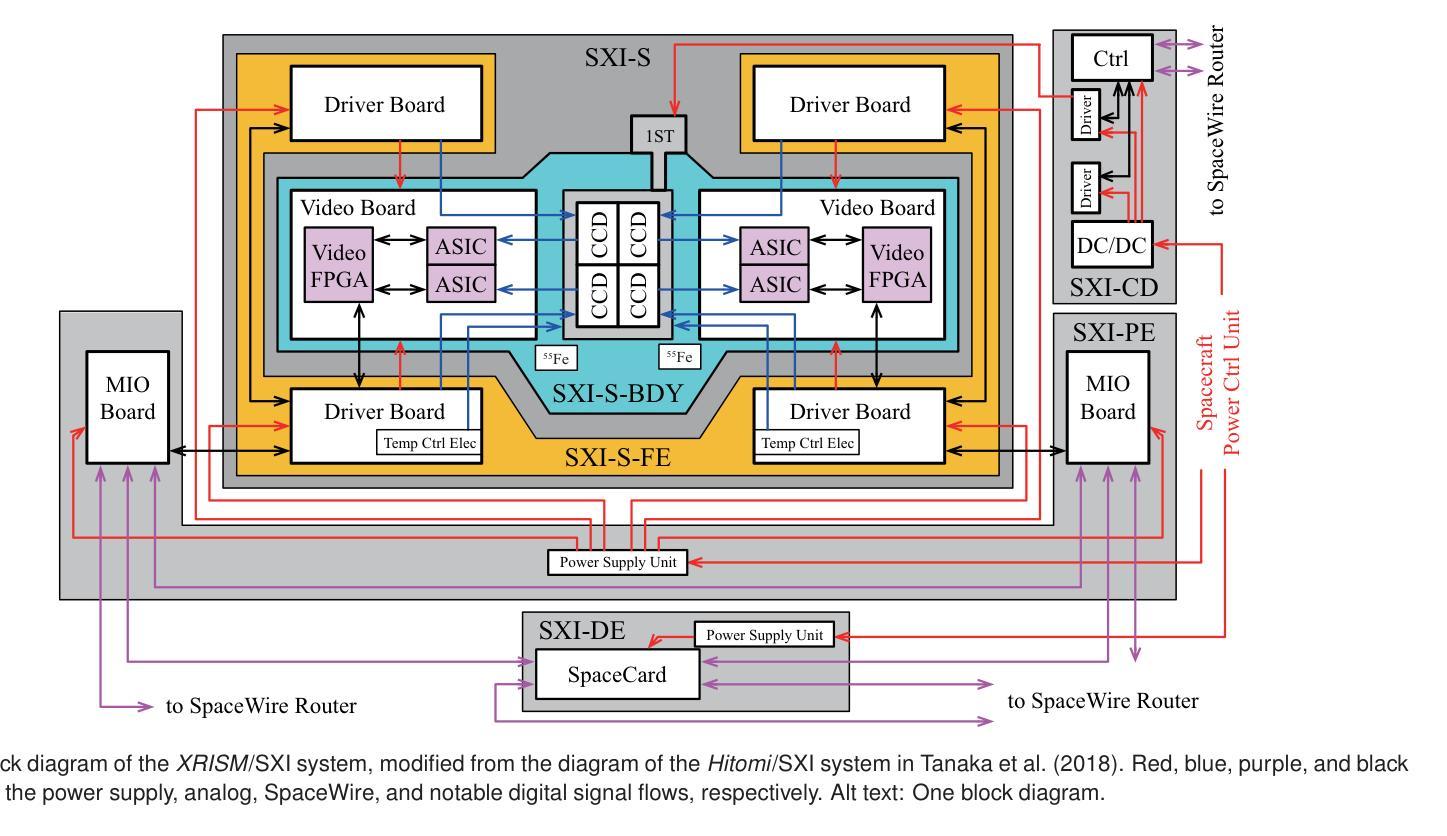
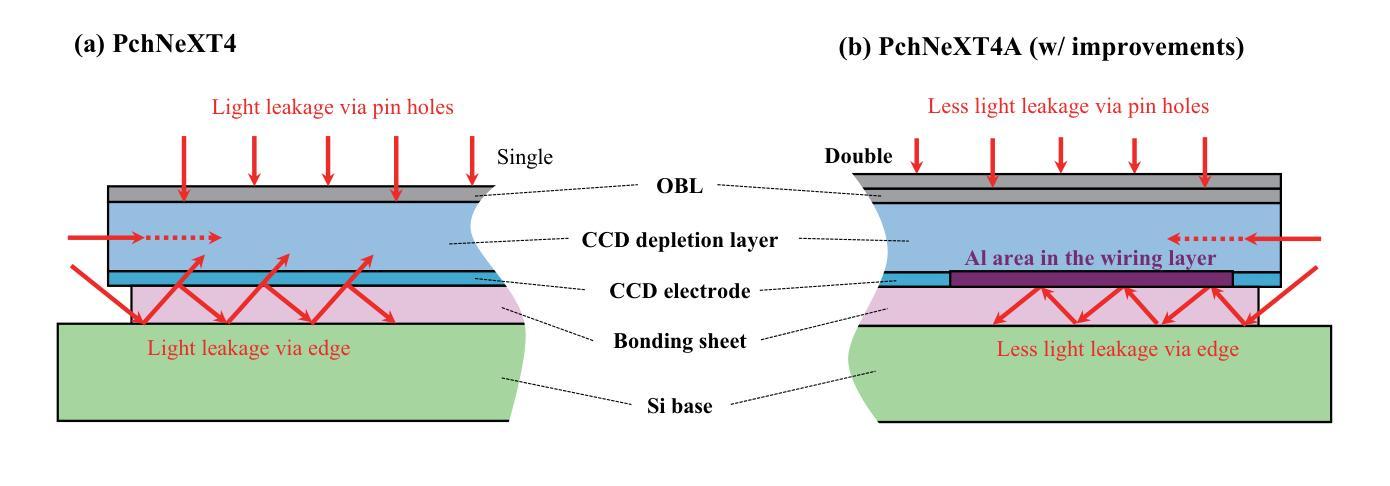
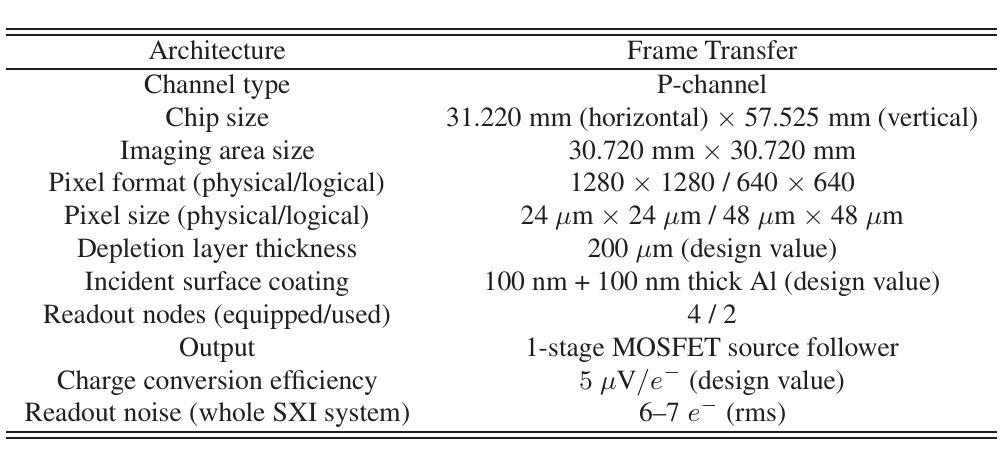
Soft X-ray Imager of the Xtend system onboard XRISM
Authors:Hirofumi Noda, Koji Mori, Hiroshi Tomida, Hiroshi Nakajima, Takaaki Tanaka, Hiroshi Murakami, Hiroyuki Uchida, Hiromasa Suzuki, Shogo Benjamin Kobayashi, Tomokage Yoneyama, Kouichi Hagino, Kumiko Nobukawa, Hideki Uchiyama, Masayoshi Nobukawa, Hironori Matsumoto, Takeshi Go Tsuru, Makoto Yamauchi, Isamu Hatsukade, Hirokazu Odaka, Takayoshi Kohmura, Kazutaka Yamaoka, Tessei Yoshida, Yoshiaki Kanemaru, Junko Hiraga, Tadayasu Dotani, Masanobu Ozaki, Hiroshi Tsunemi, Jin Sato, Toshiyuki Takaki, Yuta Terada, Keitaro Miyazaki, Kohei Kusunoki, Yoshinori Otsuka, Haruhiko Yokosu, Wakana Yonemaru, Kazuhiro Ichikawa, Hanako Nakano, Reo Takemoto, Tsukasa Matsushima, Reika Urase, Jun Kurashima, Kotomi Fuchi, Kaito Hayakawa, Masahiro Fukuda, Takamitsu Kamei, Yoh Asahina, Shun Inoue, Amano Yuki, Yuma Aoki, Yamato Ito, Tomoya Kamatani, Kouta Takayama, Takashi Sako, Marina Yoshimoto, Kohei Shima, Mayu Higuchi, Kaito Ninoyu, Daiki Aoki, Shun Tsunomachi, Kiyoshi Hayashida
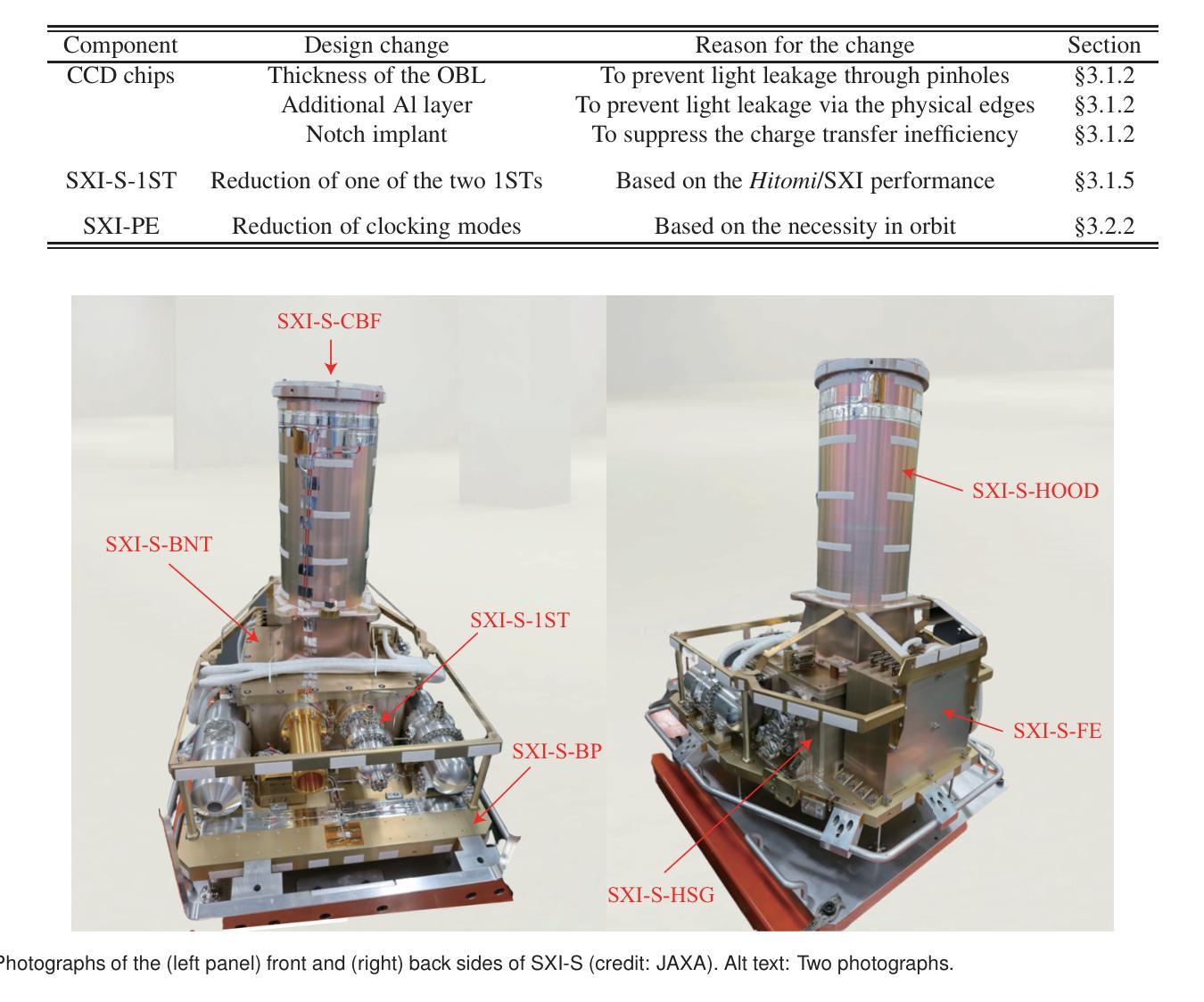
The Soft X-ray Imager (SXI) is the X-ray charge-coupled device (CCD) camera for the soft X-ray imaging telescope Xtend installed on the X-ray Imaging and Spectroscopy Mission (XRISM), which was adopted as a recovery mission for the Hitomi X-ray satellite and was successfully launched on 2023 September 7 (JST). In order to maximize the science output of XRISM, we set the requirements for Xtend and find that the CCD set employed in the Hitomi/SXI or similar, i.e., a $2 \times 2$ array of back-illuminated CCDs with a $200~\mu$m-thick depletion layer, would be practically best among available choices, when used in combination with the X-ray mirror assembly. We design the XRISM/SXI, based on the Hitomi/SXI, to have a wide field of view of $38’ \times 38’$ in the $0.4-13$ keV energy range. We incorporated several significant improvements from the Hitomi/SXI into the CCD chip design to enhance the optical-light blocking capability and to increase the cosmic-ray tolerance, reducing the degradation of charge-transfer efficiency in orbit. By the time of the launch of XRISM, the imaging and spectroscopic capabilities of the SXI has been extensively studied in on-ground experiments with the full flight-model configuration or equivalent setups and confirmed to meet the requirements. The optical blocking capability, the cooling and temperature control performance, and the transmissivity and quantum efficiency to incident X-rays of the CCDs are also all confirmed to meet the requirements. Thus, we successfully complete the pre-flight development of the SXI for XRISM.
软X射线成像仪(SXI)是安装在X射线成像和光谱任务(XRISM)上的软X射线成像望远镜Xtend的X射线电荷耦合器件(CCD)相机。XRISM是被Hitomi X射线卫星的复苏任务所采纳的,并于2023年9月7日(日本标准时间)成功发射。为了最大化XRISM的科学产出,我们对Xtend提出了要求,并发现与X射线镜面组合装配时,采用Hitomi/SXI或类似的CCD集,即采用背照式CCD的$2\times 2$阵列,其中含一个厚为$200\mu m$的耗尽层,在现有选择中,这种配置实际上最为理想。我们基于Hitomi/SXI设计XRISM/SXI,在$0.4-13$keV能量范围内具有广阔的视野,即$38’\times 38’$。我们对CCD芯片设计进行了重大改进,增强了光学光屏蔽能力和宇宙射线容忍度,减少了轨道上的电荷传输效率下降。截至XRISM发射时,SXI的成像和光谱能力已经通过地面实验进行了广泛的研究,实验采用全飞行模型配置或等效设置,并确认满足要求。此外,我们还确认了CCD的光学屏蔽能力、冷却与温度控制性能以及对入射X射线的透射率和量子效率均符合要求。因此,我们成功完成了为XRISM准备的SXI的飞行前开发。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 14 pages, 11 figures, 3 tables, Accepted for publication in PASJ XRISM special issue
Summary
成功研发软X射线成像仪(SXI),搭载于X射线成像与光谱任务(XRISM)的望远镜Xtend上,应用于Hitomi X射线卫星的后续任务。采用由Hitomi/SXI实践验证的背照式CCD阵列,结合X射线镜组件,设计具有宽广视野和高效能表现的XRISM/SXI。经过地面实验验证,其成像和光谱能力符合任务要求。预飞行开发成功完成。
Key Takeaways
- SXI是搭载于XRISM任务中的软X射线成像望远镜Xtend的X射线电荷耦合器件(CCD)相机。
- SXI的设计基于Hitomi/SXI,采用背照式CCD阵列,具有$2 \times 2$的CCD集阵和200微米的耗尽层厚度。
- XRISM/SXI具有宽广的视野范围,能在$0.4-13$ keV能量范围内进行成像。
- 对Hitomi/SXI的CCD芯片设计进行了重大改进,提高了光学光屏蔽能力和宇宙射线耐受性,减少了轨道上电荷转移效率的下降。
- 地面实验验证了SXI的成像和光谱能力、光学屏蔽能力、冷却与温度控制性能以及CCDs对入射X射线的透射性和量子效率等符合任务要求。
- 成功完成了SXI的预飞行开发。
点此查看论文截图


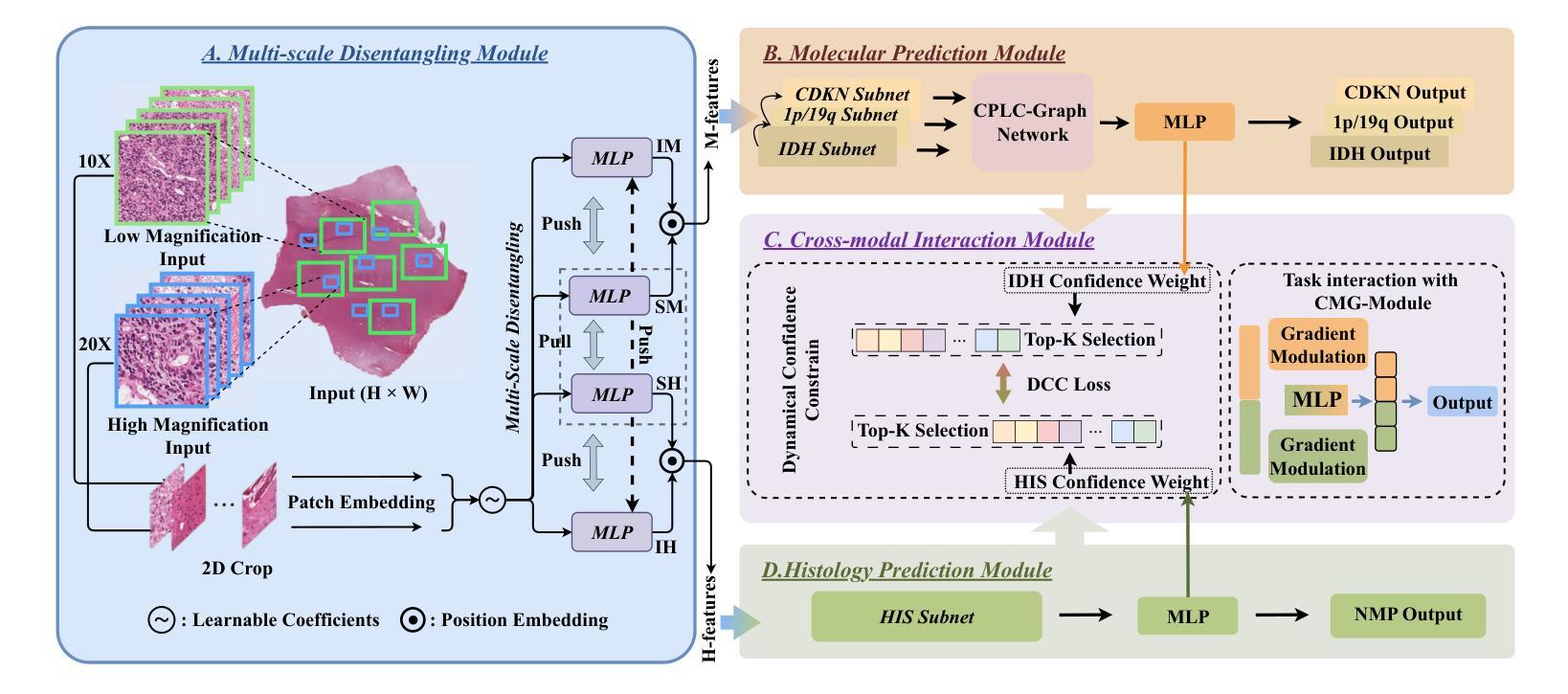
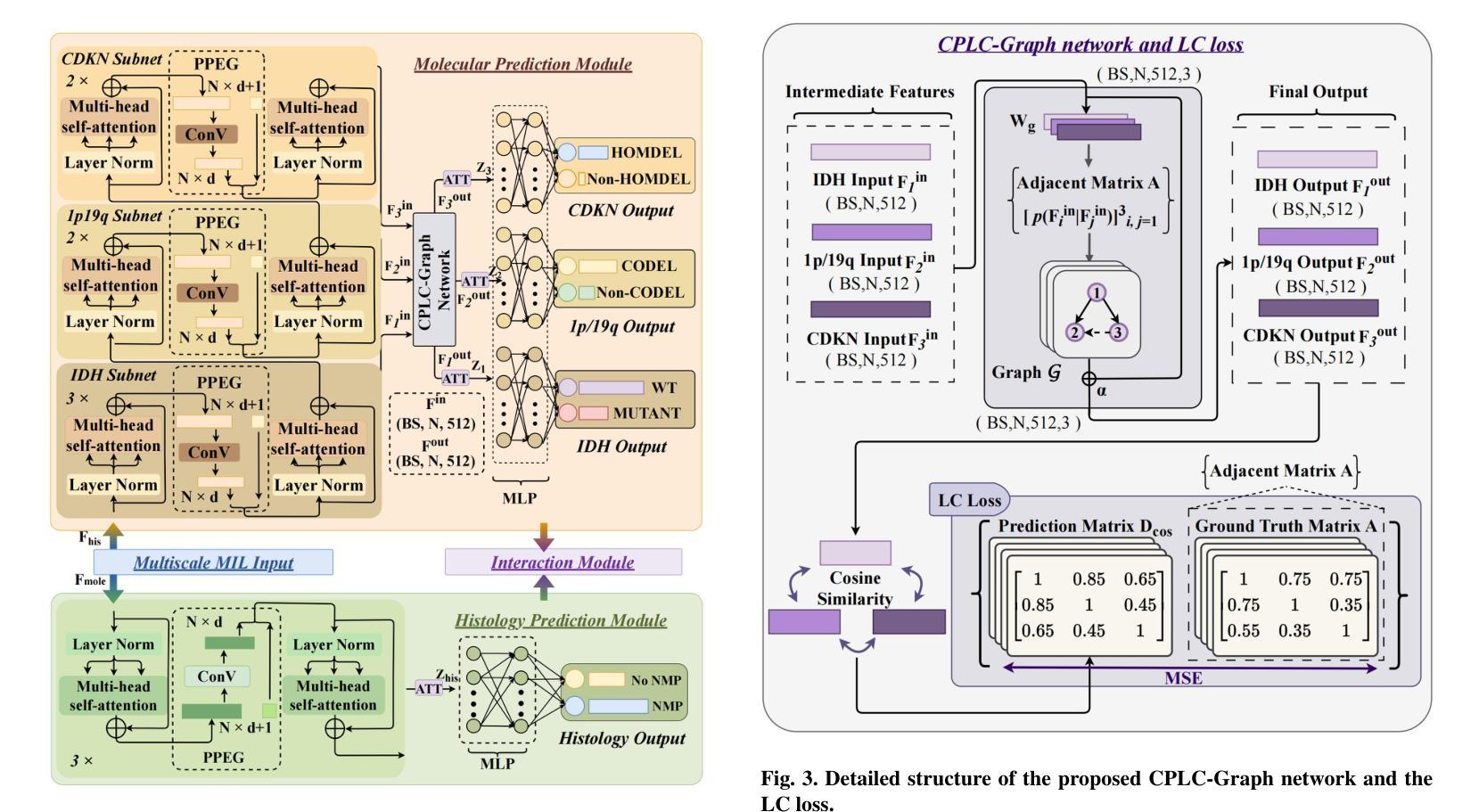
Joint Modelling Histology and Molecular Markers for Cancer Classification
Authors:Xiaofei Wang, Hanyu Liu, Yupei Zhang, Boyang Zhao, Hao Duan, Wanming Hu, Yonggao Mou, Stephen Price, Chao Li
Cancers are characterized by remarkable heterogeneity and diverse prognosis. Accurate cancer classification is essential for patient stratification and clinical decision-making. Although digital pathology has been advancing cancer diagnosis and prognosis, the paradigm in cancer pathology has shifted from purely relying on histology features to incorporating molecular markers. There is an urgent need for digital pathology methods to meet the needs of the new paradigm. We introduce a novel digital pathology approach to jointly predict molecular markers and histology features and model their interactions for cancer classification. Firstly, to mitigate the challenge of cross-magnification information propagation, we propose a multi-scale disentangling module, enabling the extraction of multi-scale features from high-magnification (cellular-level) to low-magnification (tissue-level) whole slide images. Further, based on the multi-scale features, we propose an attention-based hierarchical multi-task multi-instance learning framework to simultaneously predict histology and molecular markers. Moreover, we propose a co-occurrence probability-based label correlation graph network to model the co-occurrence of molecular markers. Lastly, we design a cross-modal interaction module with the dynamic confidence constrain loss and a cross-modal gradient modulation strategy, to model the interactions of histology and molecular markers. Our experiments demonstrate that our method outperforms other state-of-the-art methods in classifying glioma, histology features and molecular markers. Our method promises to promote precise oncology with the potential to advance biomedical research and clinical applications. The code is available at https://github.com/LHY1007/M3C2
癌症具有显著的异质性和多样的预后。准确的癌症分类对于患者分层和临床决策至关重要。尽管数字病理学已经推动了癌症的诊断和预后,但癌症病理学的范式已经从单纯依赖组织特征转变为结合分子标志物。因此,迫切需要数字病理学方法满足新范式的需求。我们介绍了一种新型数字病理学方法,可联合预测分子标志物和组织学特征,并建模它们之间的相互作用以进行癌症分类。首先,为了减轻跨放大倍数信息传播的挑战,我们提出了一种多尺度分解模块,能够从高倍(细胞水平)到低倍(组织水平)的全幻灯片图像中提取多尺度特征。其次,基于多尺度特征,我们提出了一个基于注意力的分层多任务多实例学习框架,可以同时预测组织学和分子标志物。此外,我们提出了基于共发生概率的标签关联图网络,以模拟分子标志物的共发生。最后,我们设计了一个跨模态交互模块,采用动态置信约束损失和跨模态梯度调制策略,以模拟组织学和分子标志物的相互作用。实验表明,我们的方法在分类胶质瘤、组织学特征和分子标志物方面优于其他最先进的方法。我们的方法有望推动精准肿瘤学的发展,具有推动生物医学研究和临床应用的潜力。代码可在https://github.com/LHY1007/M3C2上找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF accepted by Medical Image Analysis
Summary
在癌症诊断和治疗中,数字病理学方法已经变得越来越重要。本文介绍了一种新型数字病理学方法,通过联合预测分子标记和组织学特征,以及模拟两者间的交互作用来进行癌症分类。该方法采用多尺度分离模块解决跨尺度信息传播的挑战,并利用基于注意力机制的分层多任务多实例学习框架同时预测组织学和分子标记。实验证明该方法在胶质细胞瘤的分类上表现优于其他最先进的方法。
Key Takeaways
- 癌症具有显著异质性和多样的预后,准确的癌症分类对于患者分层和临床决策至关重要。
- 数字病理学已经逐渐从单纯依赖组织学特征转变为结合分子标记,以更好地适应癌症病理学的变化。
- 介绍了一种新型数字病理学方法,联合预测分子标记和组织学特征,并模拟其交互作用进行分类。
- 该方法通过使用多尺度分离模块处理跨尺度信息传播的挑战。
- 利用基于注意力机制的分层多任务多实例学习框架进行预测。
- 通过建立基于共现概率的标签关联图网络来模拟分子标记的共现。
点此查看论文截图

Markarian 501 reincarnates with vigor as a temporary EHBL during VHE flaring in July 2014
Authors:Sarira Sahu A. U. Puga Oliveros, D. I. Páez-Sánchez, G. Sánchez-Colón, 2 Subhash Rajpoot, M. E. Iglesias Martínez, José Guerra Carmenate, P. Fernández de Córdoba, Gaetano Lambiase
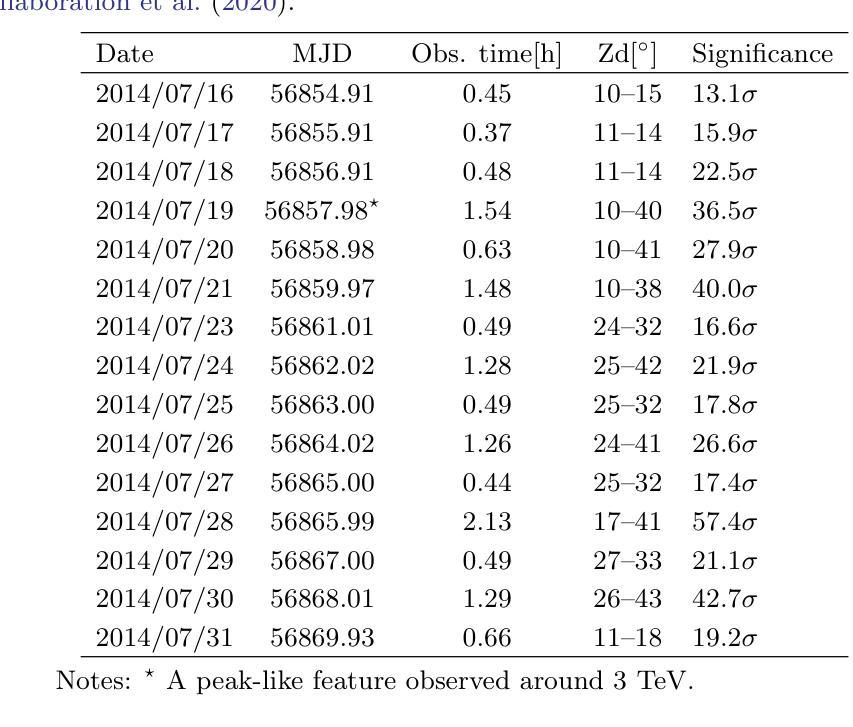
Markarian 501, a well known high energy BL Lac object, has exhibited several epochs of very high energy (VHE) gamma-ray flaring events when its synchrotron peak frequency shifted above $10^{17}$ Hz, a signature of extreme behavior. From July 16 to July 31, 2014 such flaring events were observed for 15 days by various telescopes. On July 19 (MJD 56857.98), the X-ray outburst from the source was at its highest and on the same day an intriguing narrow peak-like feature around 3 TeV was observed by MAGIC telescopes, a feature inconsistent with standard interpretations. Using the well known two-zone photohadronic model, we study these VHE gamma-ray spectra on a day-by-day basis and offer explanation. Our two-zone photohadronic scenario shows that, on MJD 56857.98, the peak-like feature appears at a cutoff energy of $E^c_{\gamma}$ = 3.18 TeV. Below this energy the observed VHE spectrum increases slowly and above $E^c_{\gamma}$ it falls faster, thus resulting in a mild peak-like feature.
马克里安501是一颗著名的高能BL Lac天体,当它的同步辐射峰值频率移到$10^{17}$赫兹以上时,它表现出了多个非常高能(VHE)的伽马射线耀斑事件时段,这是极端行为的一个标志。从2014年7月16日至7月31日,这样的耀斑事件被各种望远镜持续观察了15天。在7月19日(MJD 56857.98),该源的X射线爆发达到最高,同一天,MAGIC望远镜观察到了一个有趣的在3TeV附近的窄峰状特征,这一特征与标准解释不符。我们使用众所周知的双区光子强子模型,逐日研究这些非常高能伽马射线光谱,并给出解释。我们的双区光子强子场景显示,在MJD 56857.98,峰值特征出现在截止能量$E^c_{\gamma}$= 3.18 TeV。在此能量以下,观察到的VHE光谱增长缓慢,而在$E^c_{\gamma}$以上则下降得更快,从而产生了一个温和的峰值特征。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 14 pages, 8 figures, 1 table
Summary
马克瑞安501号天体在观测期间展现了极高能伽马射线耀斑活动,特别是其同步加速器峰值频率高于$10^{17}$ Hz时,这暗示其极端行为状态。基于新的模型——双区光子中子模型进行研究分析后揭示了在特定的日期(MJD 56857.98),观察到高能伽马射线谱的峰值特征,并解释了其成因。这一特征表现为在截止能量$E^c_{\gamma}$ = 3.18 TeV处出现一个峰值,该峰值以下观测到的VHE谱增长缓慢,而以上则迅速下降,形成轻微峰值特征。
Key Takeaways
- Markarian 501在高能伽马射线耀斑活动期间表现出极端行为状态,特别是在同步加速器峰值频率高于特定值的情况下。
- 在特定日期(MJD 56857.98),观察到高能伽马射线谱的峰值特征。
- 使用双区光子中子模型进行解释,揭示出峰值特征在截止能量处形成。
- 在截止能量以下,观测到的VHE谱增长缓慢;而超过该能量时,则迅速下降。这种特征表现为轻微峰值形态。
点此查看论文截图

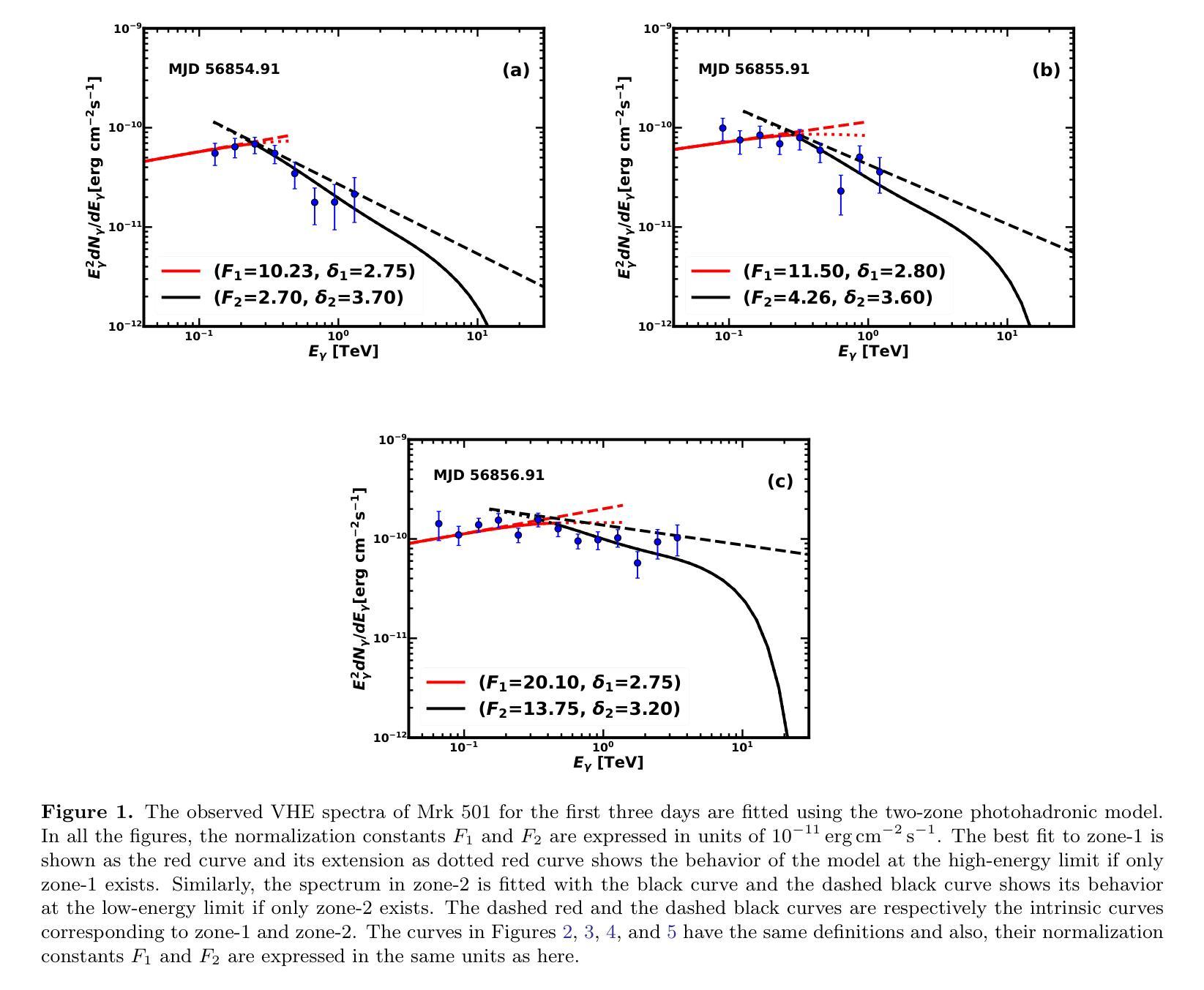
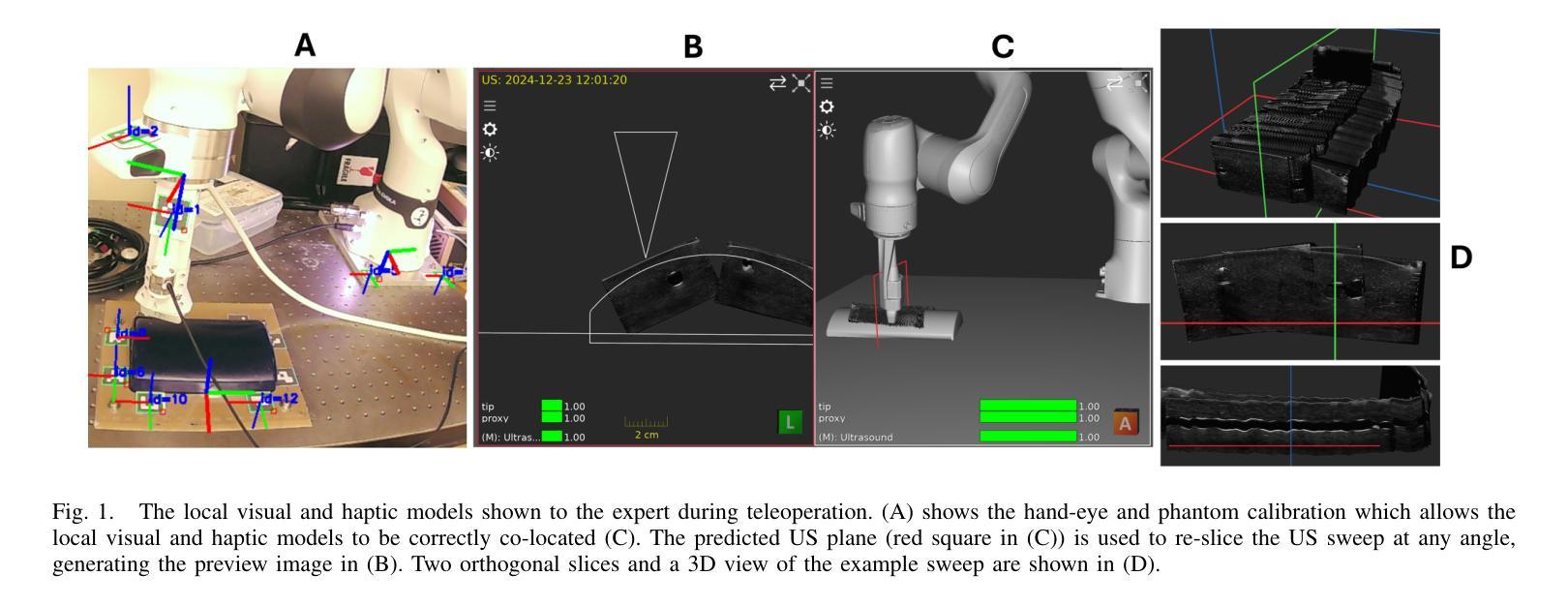
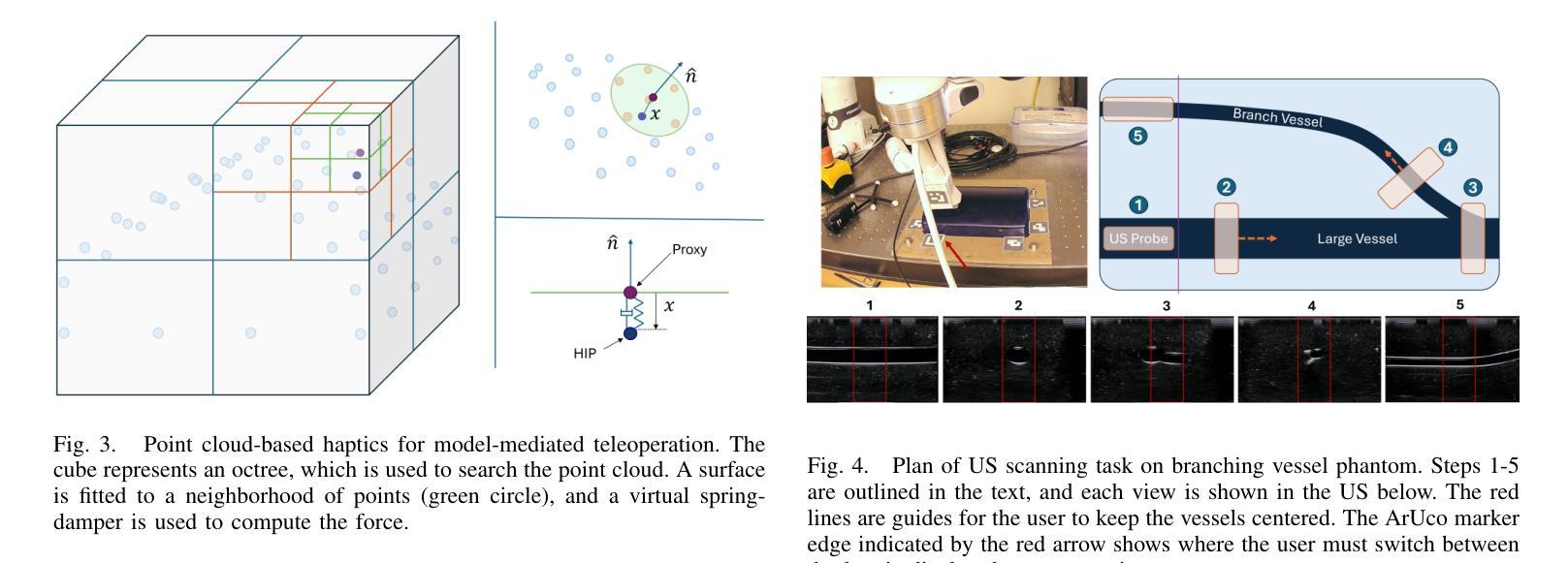
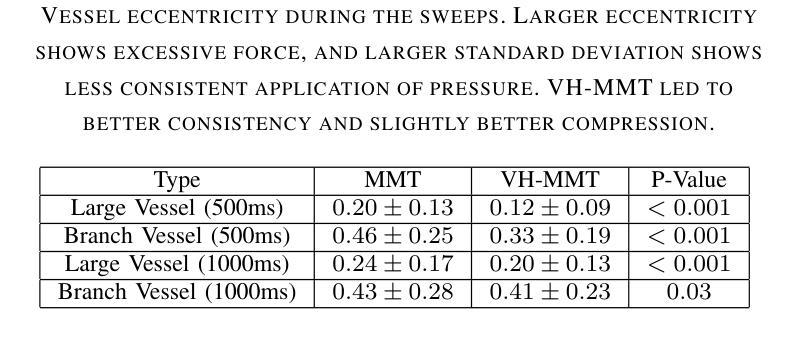
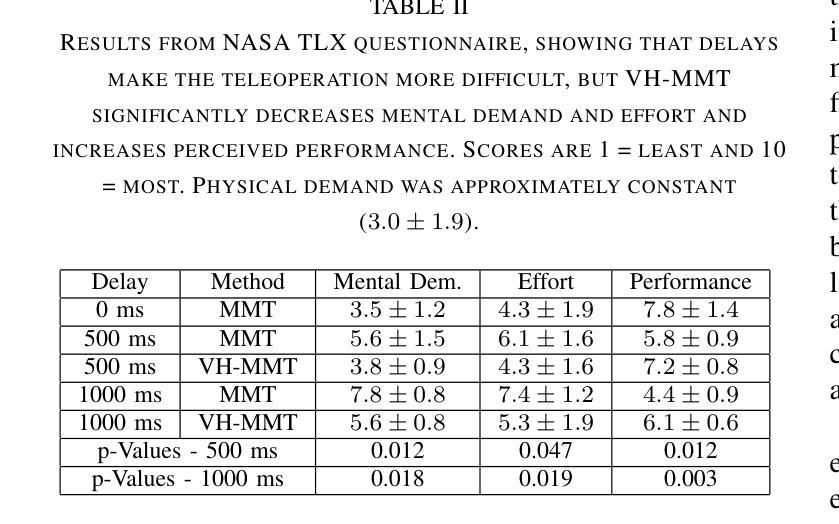
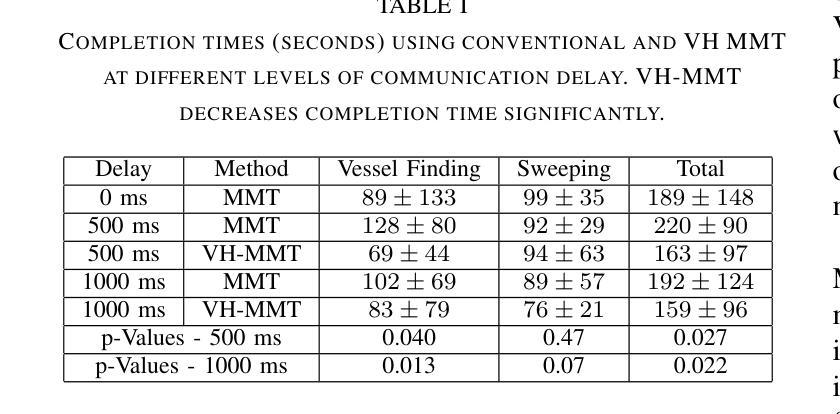
Visual-Haptic Model Mediated Teleoperation for Remote Ultrasound
Authors:David Black, Maria Tirindelli, Septimiu Salcudean, Wolfgang Wein, Marco Esposito
Tele-ultrasound has the potential greatly to improve health equity for countless remote communities. However, practical scenarios involve potentially large time delays which cause current implementations of telerobotic ultrasound (US) to fail. Using a local model of the remote environment to provide haptics to the expert operator can decrease teleoperation instability, but the delayed visual feedback remains problematic. This paper introduces a robotic tele-US system in which the local model is not only haptic, but also visual, by re-slicing and rendering a pre-acquired US sweep in real time to provide the operator a preview of what the delayed image will resemble. A prototype system is presented and tested with 15 volunteer operators. It is found that visual-haptic model-mediated teleoperation (MMT) compensates completely for time delays up to 1000 ms round trip in terms of operator effort and completion time while conventional MMT does not. Visual-haptic MMT also significantly outperforms MMT for longer time delays in terms of motion accuracy and force control. This proof-of-concept study suggests that visual-haptic MMT may facilitate remote robotic tele-US.
远程超声具有为无数偏远地区社区提升健康公平的巨大潜力。然而,实际应用场景中涉及的时间延迟可能导致当前远程机器人超声(US)实施失败。使用远程环境的本地模型为专业操作人员提供触觉可以减小远程操作的稳定性问题,但延迟的视觉反馈仍然是个难题。本文介绍了一种机器人远程超声系统,该系统不仅通过触觉提供本地模型,还通过视觉提供模型,通过实时重新切片和渲染预先获取的超声扫描来为操作人员提供延迟图像预览。该系统的一个原型被展示给并测试了15名志愿者操作人员。研究发现,视觉触觉模型介导的远程操作(MMT)在操作者努力和完成时间方面可以完全补偿高达1000毫秒的往返时间延迟,而传统的MMT则不能。视觉触觉MMT在运动准确性和力量控制方面也显著优于更长时间延迟下的MMT。这项概念验证研究结果表明,视觉触觉MMT可能有助于远程机器人超声操作。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Supplementary video: https://youtu.be/fDLBah7bPeo . This work has been submitted to the IEEE for possible publication
Summary
远程医疗超声(Tele-ultrasound)对改善偏远地区的医疗公平具有巨大潜力。然而,实际应用中存在时间延迟问题,导致当前远程遥控超声机器人(Telerobotic ultrasound,简称US)的实施失败。本文引入了一种机器人远程超声系统,该系统不仅提供触觉反馈,还通过实时重新切片和渲染预先获取的超声扫描提供视觉反馈,为操作者提供了一个延迟图像的预览。实验表明,视觉触觉模型介导的遥控操作(Visual-haptic Model-Mediated Teleoperation,简称MMT)能够在时间延迟达1000毫秒往返的情况下完全补偿操作者的努力和完成时间,而传统的MMT则无法实现。此外,视觉触觉MMT在运动准确性和力量控制方面也显著优于传统MMT。这为远程遥控超声机器人的应用提供了新的可能性。
Key Takeaways
- 远程医疗超声有望改善偏远地区的医疗公平问题。
- 时间延迟是遥控超声机器人实际应用中的主要挑战之一。
- 通过视觉触觉模型介导的遥控操作(MMT)可以有效补偿时间延迟的影响。
- MMT能在时间延迟达1000毫秒往返的情况下改善操作者的努力和完成时间。
- 在运动准确性和力量控制方面,视觉触觉MMT显著优于传统MMT。
- 本文提出的新型遥控超声机器人系统结合了触觉和视觉反馈,通过实时重新切片和渲染预先获取的超声扫描来提供延迟图像的预览。
点此查看论文截图

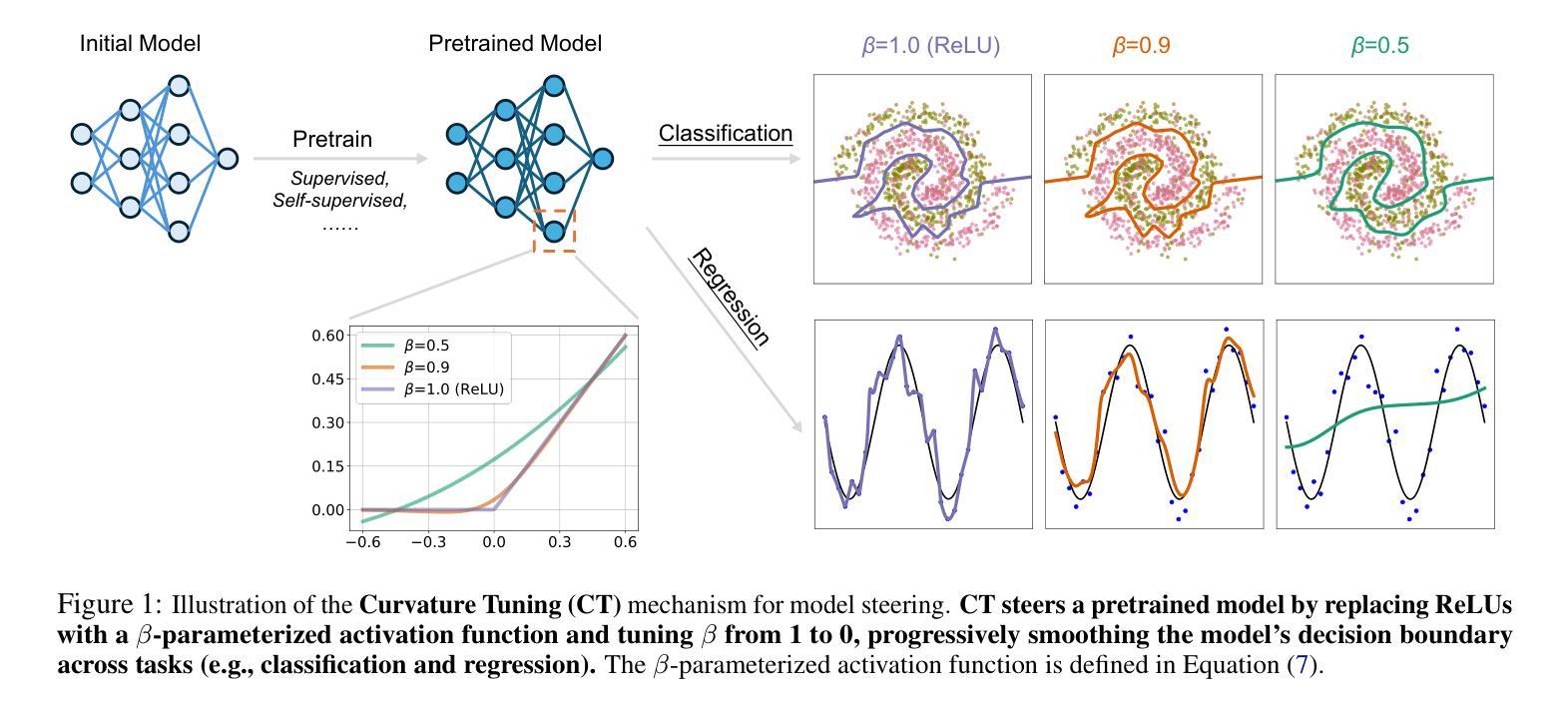
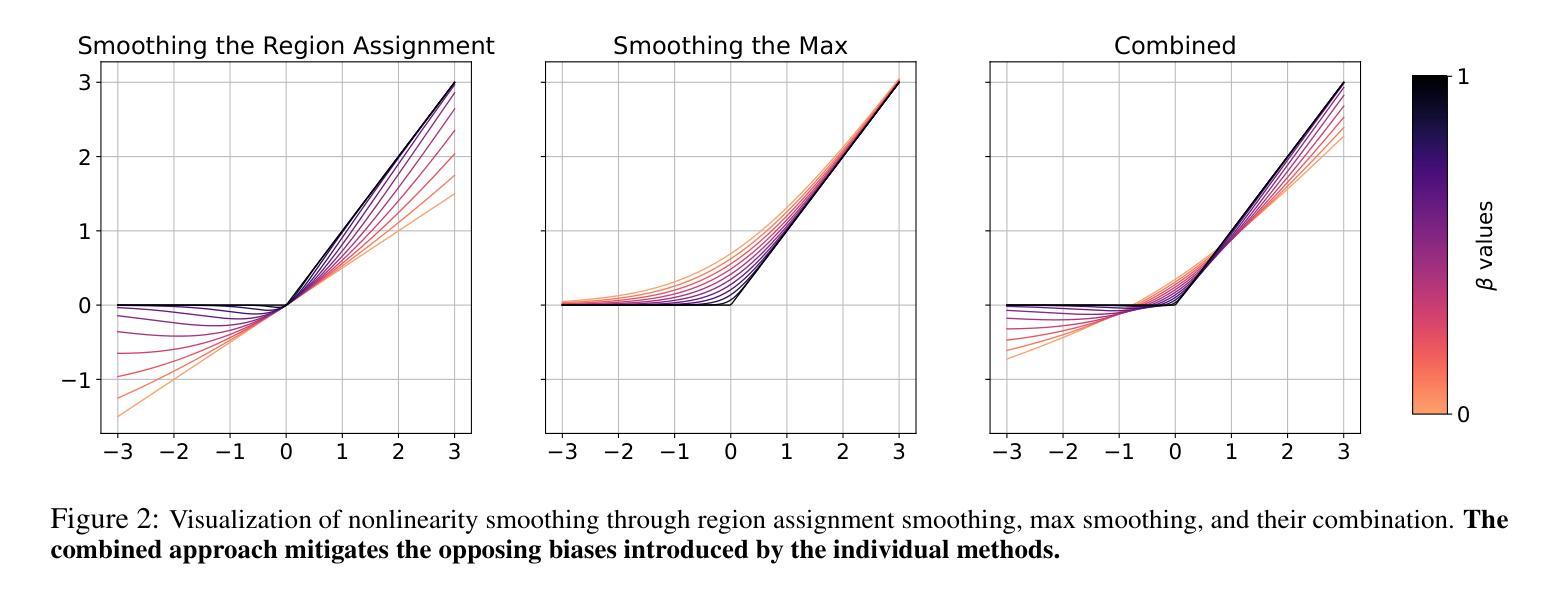
Curvature Tuning: Provable Training-free Model Steering From a Single Parameter
Authors:Leyang Hu, Randall Balestriero
The scaling of model size and data size has reshaped the paradigm of AI. As a result, the common protocol to leverage the latest models is to steer them towards a specific downstream task of interest through {\em fine-tuning}. Despite its importance, the main methods for fine-tuning remain limited to full or low-rank adapters–containing countless hyper-parameters and lacking interpretability. In this paper, we take a step back and demonstrate how novel and explainable post-training steering solutions can be derived theoretically from {\em spline operators}, a rich mathematical framing of Deep Networks that was recently developed. Our method–coined \textbf{Curvature Tuning (CT)}–has a single parameter that provably modulates the curvature of the model’s decision boundary henceforth allowing training-free steering. This makes CT both more efficient and interpretable than conventional fine-tuning methods. We empirically validate its effectiveness in improving generalization and robustness of pretrained models. For example, CT improves out-of-distribution transfer performances of ResNet-18/50 by 2.57%/1.74% across seventeen downstream datasets, and improves RobustBench robust accuracy by 11.76%/348.44%. Additionally, we apply CT to ReLU-based Swin-T/S, improving their generalization on nine downstream datasets by 2.43%/3.33%. Our code is available at \href{https://github.com/Leon-Leyang/curvature-tuning}{https://github.com/Leon-Leyang/curvature-tuning}.
模型规模和数据规模的扩展已经重塑了人工智能的范式。因此,利用最新模型的通用协议是通过微调将它们导向特定的下游任务。尽管微调很重要,但主要方法仍然局限于全参数或低秩适配器——包含无数超参数且缺乏可解释性。在本文中,我们退一步,展示了如何从深度网络的丰富数学框架“样条算子”中理论上推导出新颖且可解释的后训练微调解决方案。我们的方法——被称为“曲率调整(CT)”,有一个参数可以调整模型决策边界的曲率,从而实现无训练微调。这使得CT比传统微调方法更高效且更具可解释性。我们通过实验验证了其在提高预训练模型的通用性和鲁棒性方面的有效性。例如,CT在十七个下游数据集上提高了ResNet-18/50的跨分布迁移性能,分别提高了2.57%/1.74%,并在RobustBench上的鲁棒精度提高了11.76%/348.44%。此外,我们将CT应用于ReLU基础的Swin-T/S,在九个下游数据集上提高了它们的通用性,分别提高了2.43%/3.33%。我们的代码可在https://github.com/Leon-Leyang/curvature-tuning链接中访问。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
模型规模和数据规模的扩展重塑了人工智能范式,其中的关键手段之一是对模型进行微调。现有的微调方法多依赖大量参数并且缺乏可解释性。本研究提出了基于曲线操作的理论方法——弯曲度微调(Curvature Tuning, CT)。CT通过一个参数即可调控模型决策边界的曲率,从而实现训练分离调整策略,显著提升了预训练模型的泛化和鲁棒性。本研究的结果证明CT较传统微调方法更具效能和可解释性。该成果已在GitHub上公开代码。
Key Takeaways
- 模型规模和数据规模的扩展重塑了人工智能的范式。
- 现有微调方法多采用大量参数的调整策略,但缺乏解释性。
- 研究者提出新的训练后微调方法——弯曲度微调(CT),利用曲线操作理论来实现模型调整。
- CT通过一个参数调整模型决策边界的曲率,实现了训练分离的调整策略。
点此查看论文截图

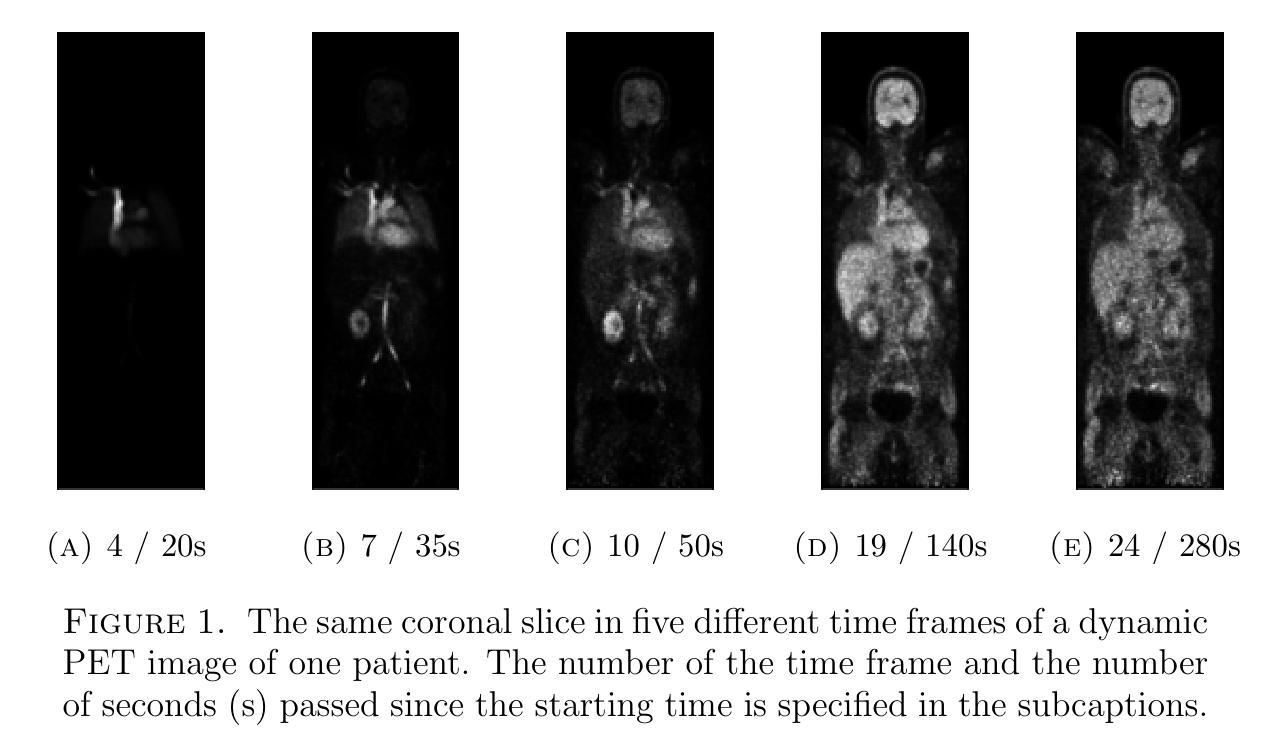
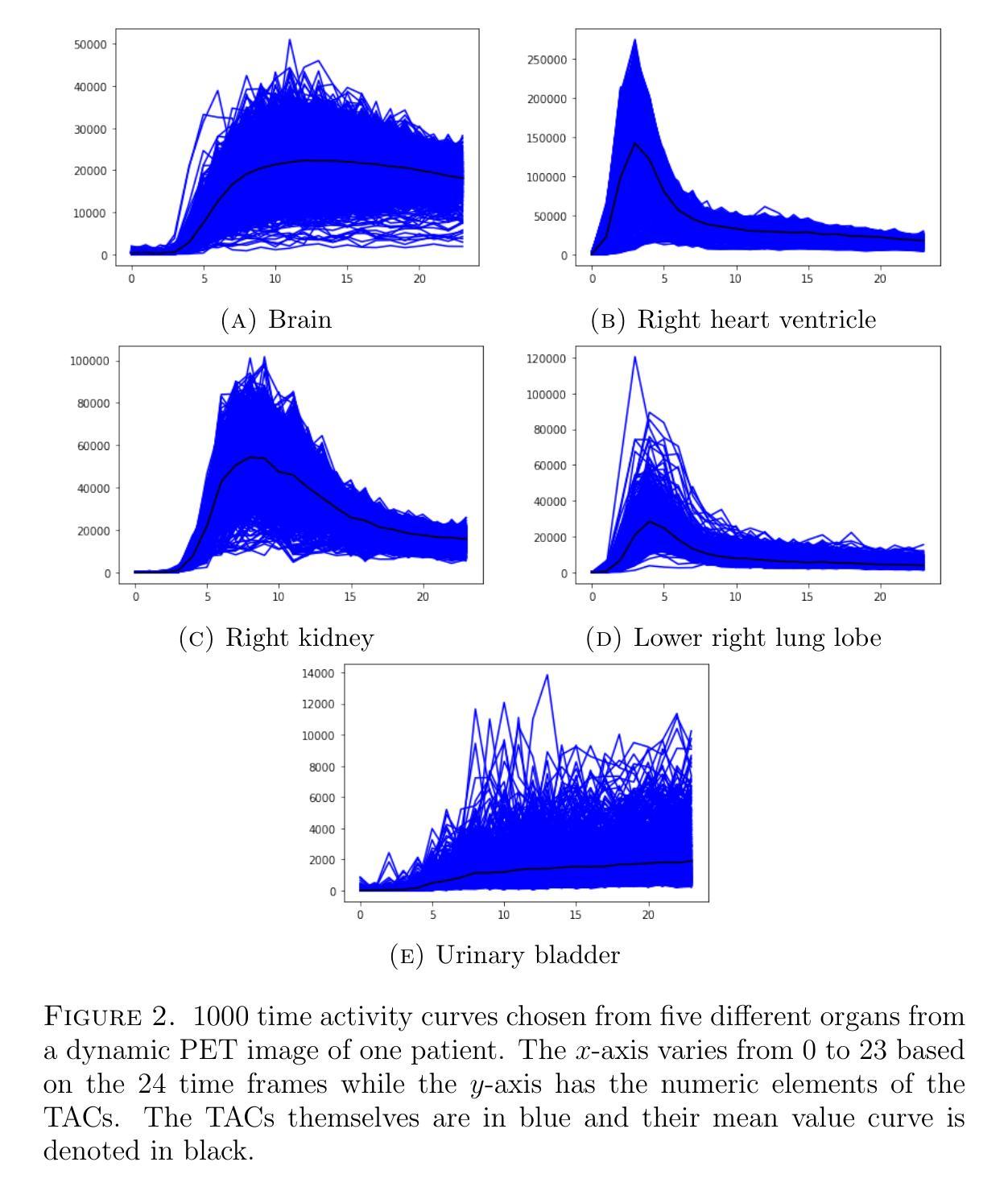
Quantitative evaluation of unsupervised clustering algorithms for dynamic total-body PET image analysis
Authors:Oona Rainio, Maria K. Jaakkola, Riku Klén
Background. Recently, dynamic total-body positron emission tomography (PET) imaging has become possible due to new scanner devices. While clustering algorithms have been proposed for PET analysis already earlier, there is still little research systematically evaluating these algorithms for processing of dynamic total-body PET images. Materials and methods. Here, we compare the performance of 15 unsupervised clustering methods, including K-means either by itself or after principal component analysis (PCA) or independent component analysis (ICA), Gaussian mixture model (GMM), fuzzy c-means (FCM), agglomerative clustering, spectral clustering, and several newer clustering algorithms, for classifying time activity curves (TACs) in dynamic PET images. We use dynamic total-body $^{15}$O-water PET images collected from 30 patients with suspected or confirmed coronary artery disease. To evaluate the clustering algorithms in a quantitative way, we use them to classify 5000 TACs from each image based on whether the curve is taken from brain, right heart ventricle, right kidney, lower right lung lobe, or urinary bladder. Results. According to our results, the best methods are GMM, FCM, and ICA combined with mini batch K-means, which classified the TACs with a median accuracies of 89%, 83%, and 81%, respectively, in a processing time of half a second or less on average for each image. Conclusion. GMM, FCM, and ICA with mini batch K-means show promise for dynamic total-body PET analysis.
背景。最近,由于新的扫描设备,动态全身正电子发射断层扫描(PET)成像已经变得可能。虽然聚类算法在较早的时候就已经被提出用于PET分析,但对于处理动态全身PET图像,仍少有研究系统地评估这些算法。材料和方法。在这里,我们对15种无监督聚类方法进行了比较,包括K-means(单独或与主成分分析(PCA)或独立成分分析(ICA)结合使用)、高斯混合模型(GMM)、模糊c-均值(FCM)、凝聚聚类、谱聚类和几种新的聚类算法,用于对动态PET图像中的时间活动曲线(TACs)进行分类。我们使用从疑似或确诊冠状动脉疾病的30例患者收集的动态全身$^{15}$O-水PET图像。为了定量评估聚类算法,我们使用它们根据曲线是否来自大脑、右心室、右肾、右下肺叶或膀胱来分类每个图像的5000条TACs。结果。根据我们的结果,最佳方法是GMM、FCM和与mini batch K-means结合的ICA,它们分类TACs的中值准确度分别为89%、83%和81%,每张图像的平均处理时间不超过半秒。结论。对于动态全身PET分析,GMM、FCM以及与mini batch K-means结合的ICA显示出良好的前景。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 12 pages, 2 figures
Summary
动态全身正电子发射断层扫描(PET)成像技术的最新发展对聚类算法提出了新的挑战与机遇。本文对比了15种无监督聚类算法在处理动态全身PET图像中的表现。研究发现,高斯混合模型(GMM)、模糊C-均值(FCM)和独立成分分析(ICA)结合小批量K-均值的方法表现最佳,对时间活动曲线(TACs)的分类准确率中位数分别为89%、83%和81%,且处理时间平均每秒不到半秒。
Key Takeaways
- 动态全身PET成像技术对聚类算法提出了新的挑战。
- 对比了多种无监督聚类算法在处理动态PET图像中的性能。
- 高斯混合模型(GMM)、模糊C-均值(FCM)和独立成分分析(ICA)结合小批量K-均值的方法在分类TACs方面表现最佳。
- 这些最佳方法的分类准确率中位数超过80%,处理时间迅速。
点此查看论文截图

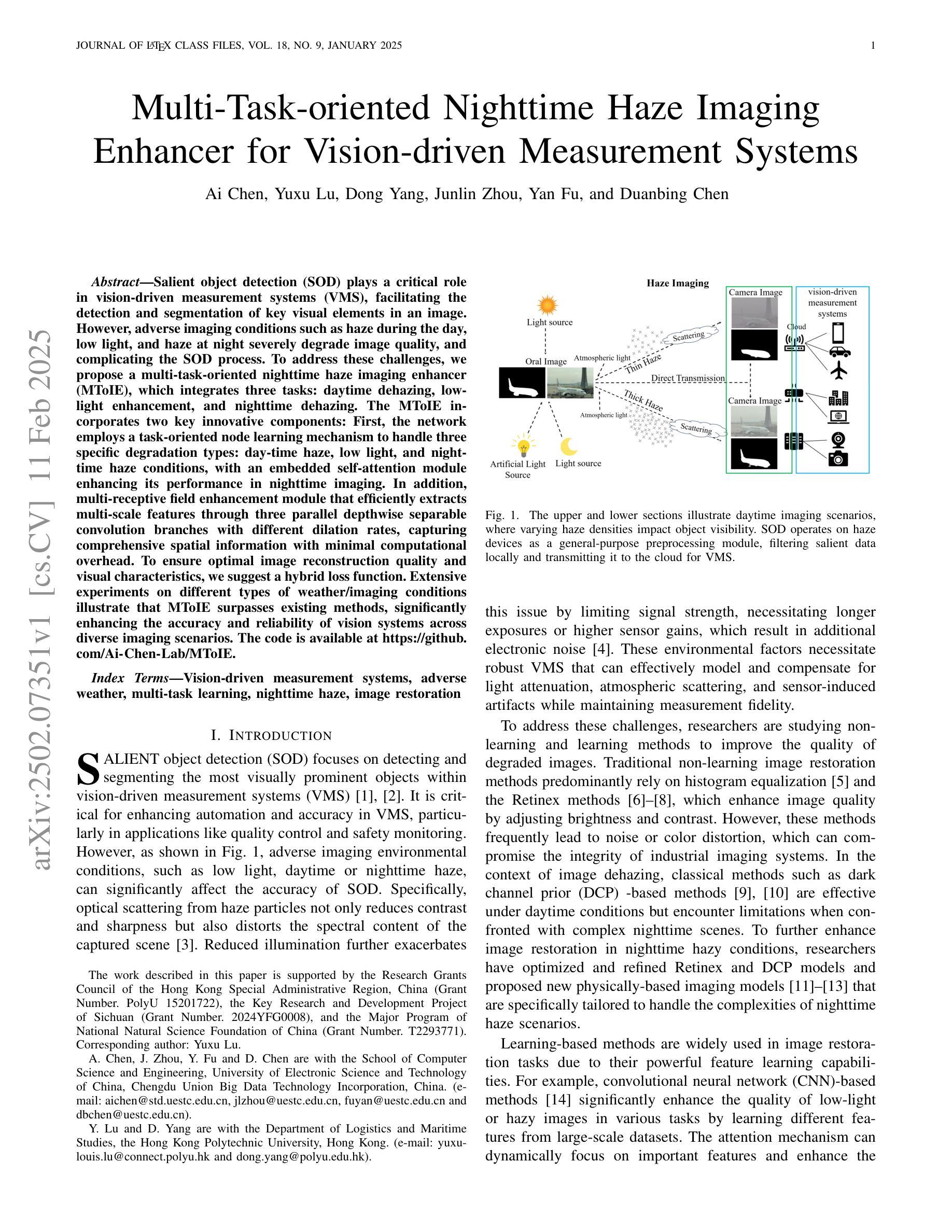
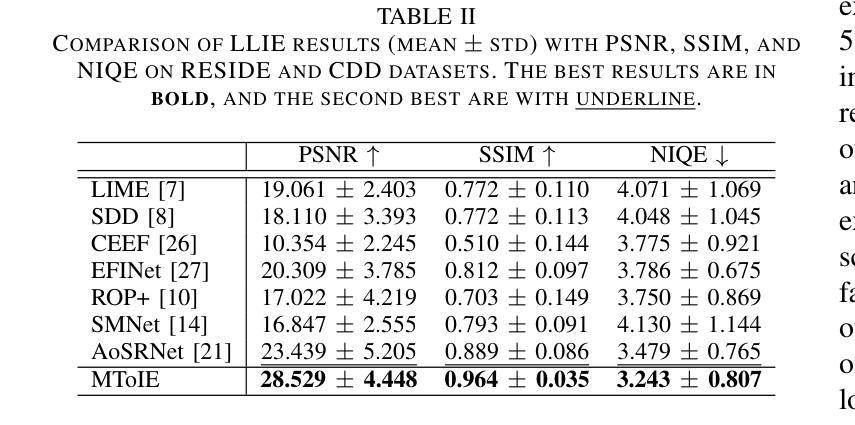
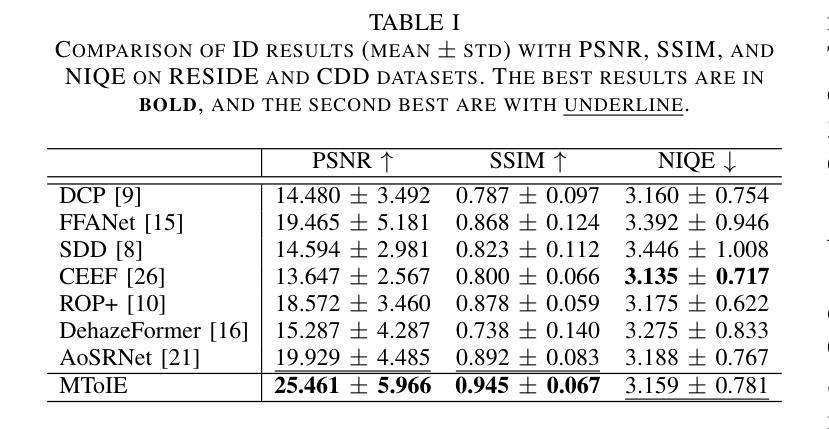
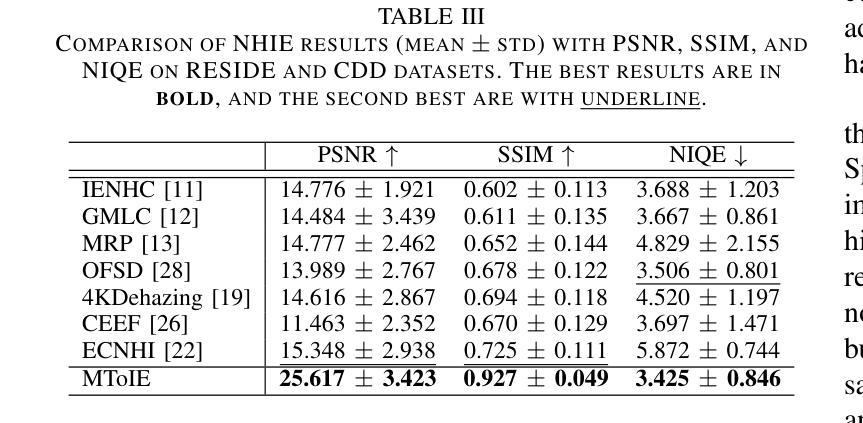
Multi-Task-oriented Nighttime Haze Imaging Enhancer for Vision-driven Measurement Systems
Authors:Ai Chen, Yuxu Lu, Dong Yang, Junlin Zhou, Yan Fu, Duanbing Chen
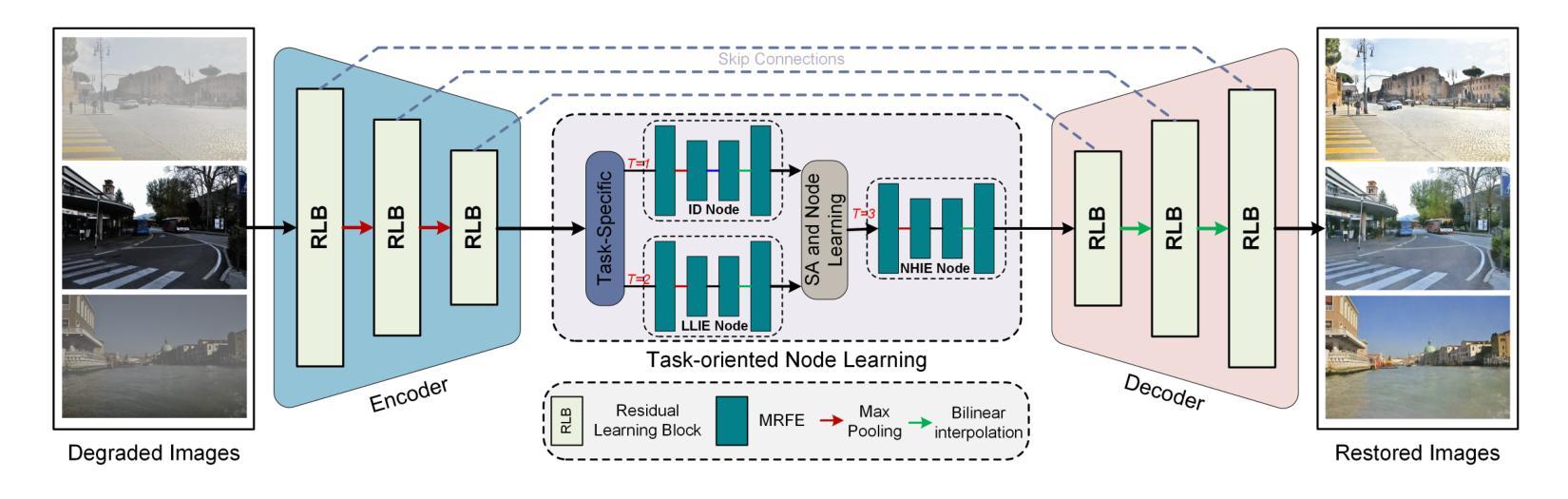
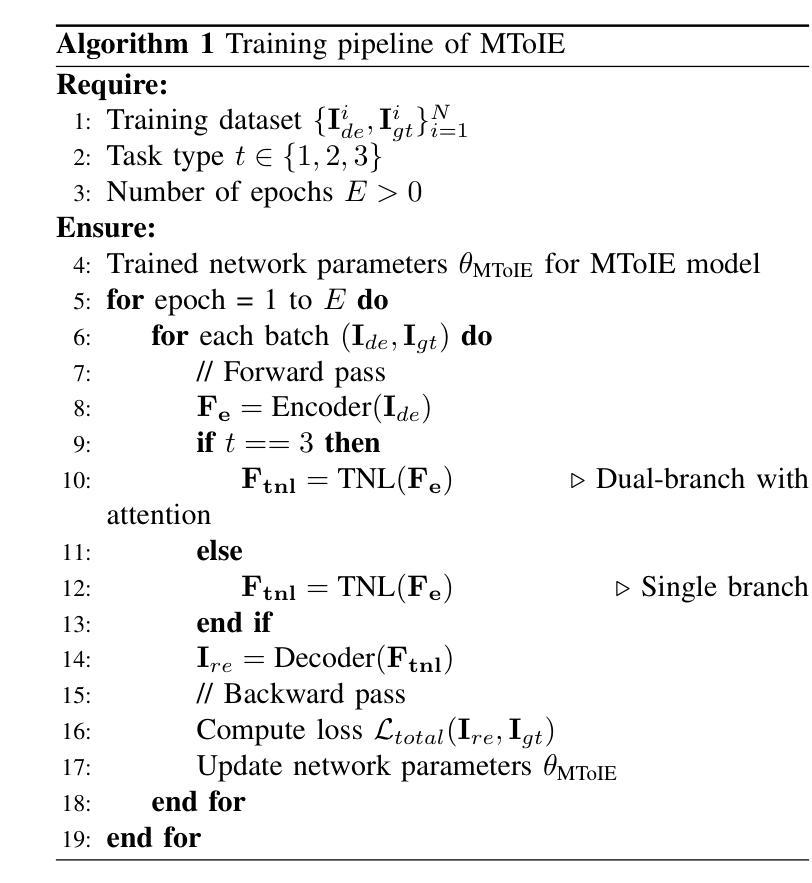
Salient object detection (SOD) plays a critical role in vision-driven measurement systems (VMS), facilitating the detection and segmentation of key visual elements in an image. However, adverse imaging conditions such as haze during the day, low light, and haze at night severely degrade image quality, and complicating the SOD process. To address these challenges, we propose a multi-task-oriented nighttime haze imaging enhancer (MToIE), which integrates three tasks: daytime dehazing, low-light enhancement, and nighttime dehazing. The MToIE incorporates two key innovative components: First, the network employs a task-oriented node learning mechanism to handle three specific degradation types: day-time haze, low light, and night-time haze conditions, with an embedded self-attention module enhancing its performance in nighttime imaging. In addition, multi-receptive field enhancement module that efficiently extracts multi-scale features through three parallel depthwise separable convolution branches with different dilation rates, capturing comprehensive spatial information with minimal computational overhead. To ensure optimal image reconstruction quality and visual characteristics, we suggest a hybrid loss function. Extensive experiments on different types of weather/imaging conditions illustrate that MToIE surpasses existing methods, significantly enhancing the accuracy and reliability of vision systems across diverse imaging scenarios. The code is available at https://github.com/Ai-Chen-Lab/MToIE.
显著性目标检测(SOD)在视觉驱动测量系统(VMS)中发挥着关键作用,可以促进图像中关键视觉元素的检测和分割。然而,不利的成像条件,如白天的雾霾、低光照和夜间雾霾,严重降低了图像质量,并使得SOD过程复杂化。为了应对这些挑战,我们提出了一种多任务导向的夜间雾霾成像增强器(MToIE),它结合了三项任务:白天去雾、低光增强和夜间去雾。MToIE包含两个关键的创新组件:首先,网络采用任务导向的节点学习机制来处理三种特定的退化类型:白天的雾霾、低光和夜间雾霾条件,其中嵌入的自注意模块增强了其在夜间成像的性能。此外,多感受野增强模块通过三个并行深度可分离卷积分支高效地提取多尺度特征,这些分支具有不同的膨胀率,以最小的计算开销捕获全面的空间信息。为了确保最佳的图像重建质量和视觉特性,我们提出了一种混合损失函数。在不同天气/成像条件下的大量实验表明,MToIE超越了现有方法,显著提高了不同成像场景中视觉系统的准确性和可靠性。代码可在https://github.com/Ai-Chen-Lab/MToIE上找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出了一种多任务导向的夜间雾霾成像增强器(MToIE),集成了日间去雾、低光增强和夜间去雾三个任务。该增强器采用任务导向节点学习机制和带有自注意力模块的网络,提高了在夜间成像中的性能。同时,引入了一种高效的多尺度特征提取模块,通过三个具有不同膨胀率的并行深度可分离卷积分支捕获全面的空间信息。此外,为了确保图像重建质量和视觉特性达到最佳,建议使用混合损失函数。在多种天气和成像条件下的广泛实验表明,MToIE超越了现有方法,显著提高了视觉系统在不同成像场景中的准确性和可靠性。
Key Takeaways
- MToIE针对三种不同的成像条件(日间雾霾、低光和夜间雾霾)进行任务导向的设计。
- 采用任务导向节点学习机制和自注意力模块提高夜间成像性能。
- 多尺度特征提取模块通过并行深度可分离卷积分支有效捕获全面的空间信息。
- 混合损失函数确保图像重建质量和视觉特性的优化。
- MToIE在多种天气和成像条件下的表现超越了现有方法。
- MToIE显著提高视觉系统在不同成像场景中的准确性和可靠性。
点此查看论文截图

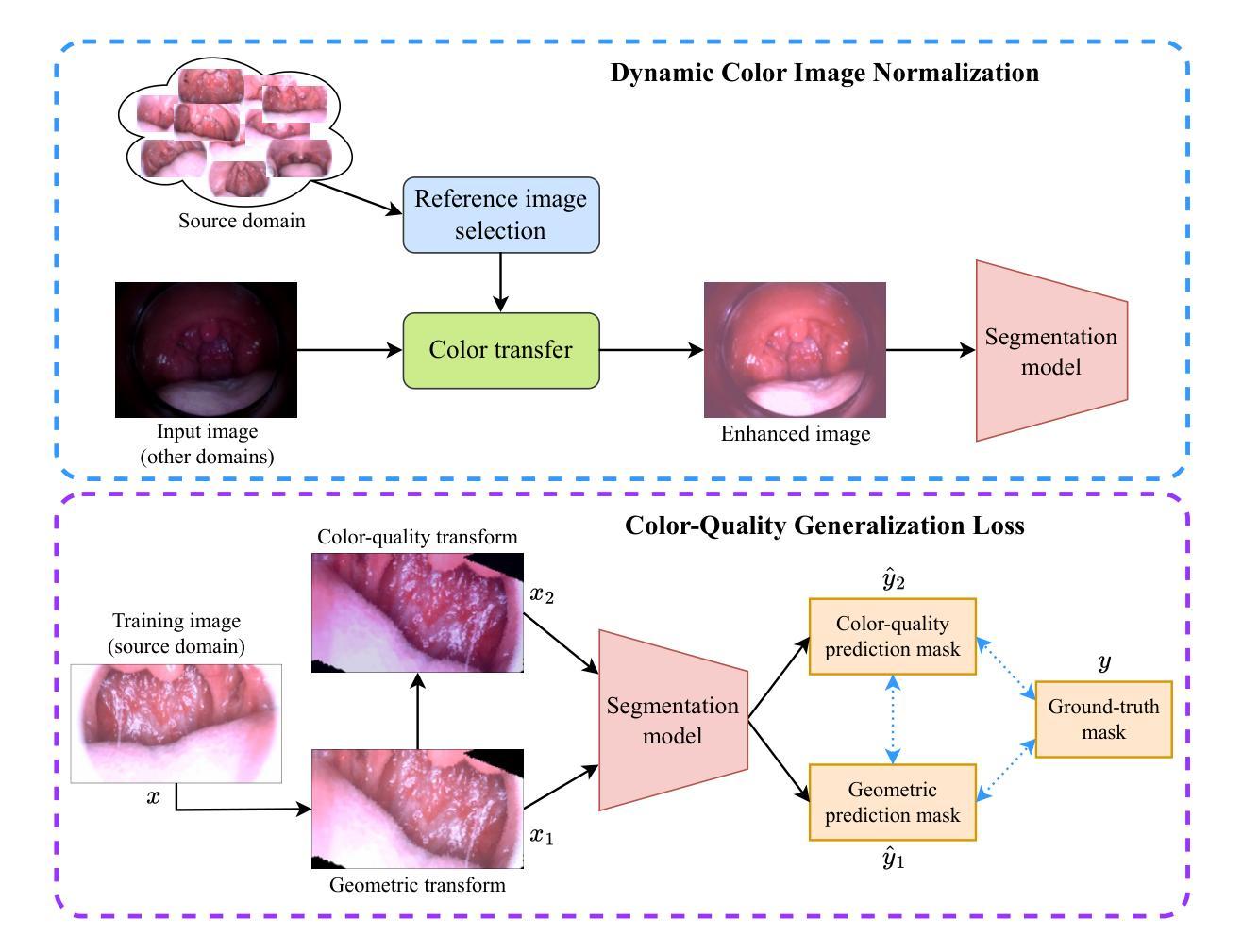
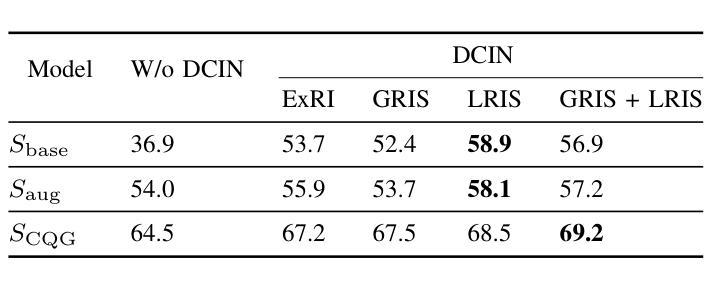
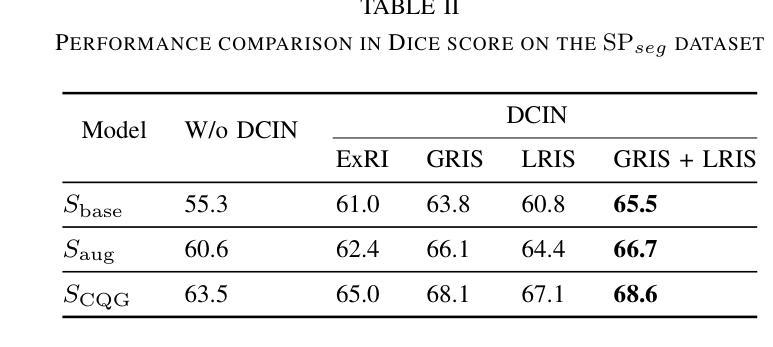
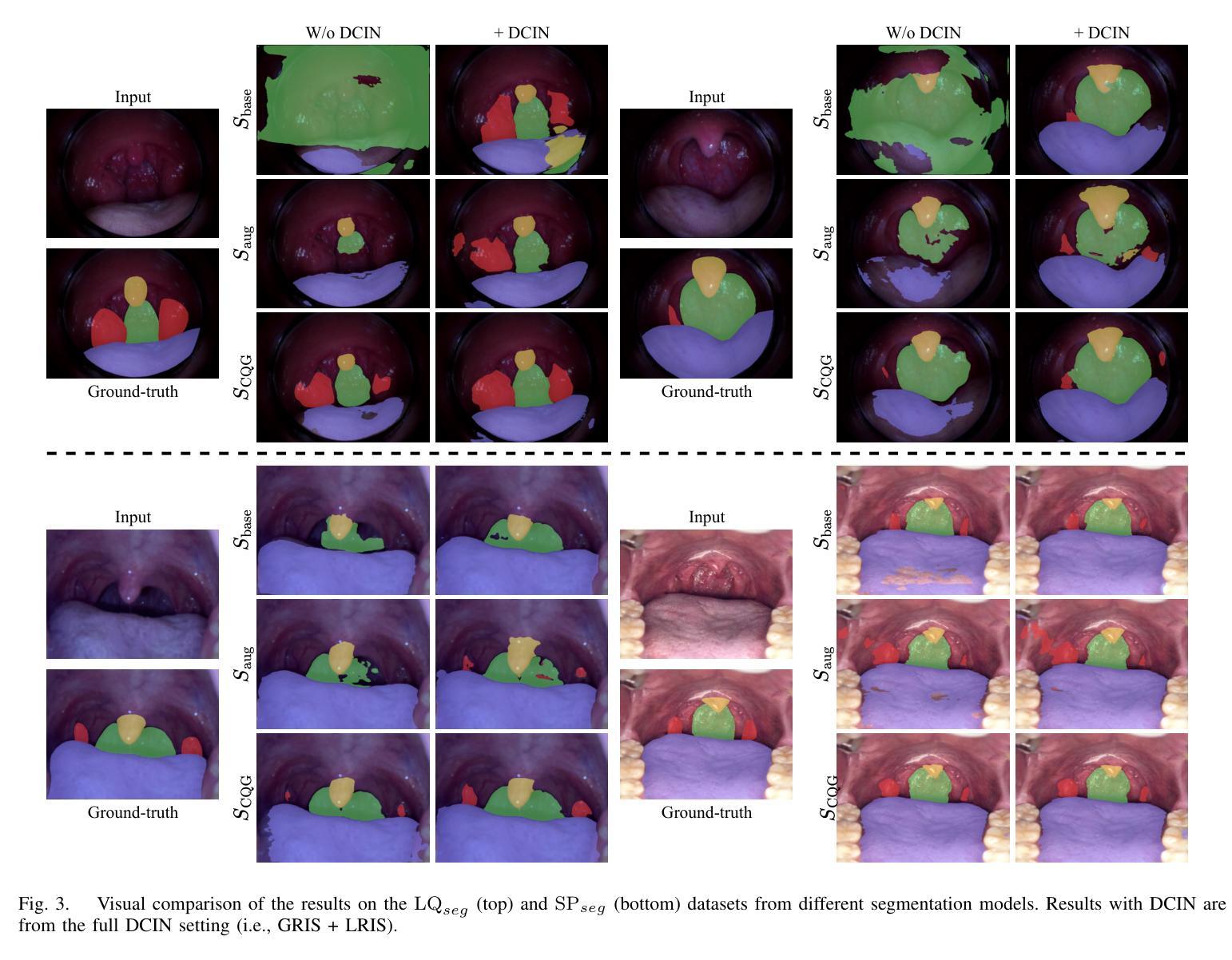
Color-Quality Invariance for Robust Medical Image Segmentation
Authors:Ravi Shah, Atsushi Fukuda, Quan Huu Cap
Single-source domain generalization (SDG) in medical image segmentation remains a significant challenge, particularly for images with varying color distributions and qualities. Previous approaches often struggle when models trained on high-quality images fail to generalize to low-quality test images due to these color and quality shifts. In this work, we propose two novel techniques to enhance generalization: dynamic color image normalization (DCIN) module and color-quality generalization (CQG) loss. The DCIN dynamically normalizes the color of test images using two reference image selection strategies. Specifically, the DCIN utilizes a global reference image selection (GRIS), which finds a universal reference image, and a local reference image selection (LRIS), which selects a semantically similar reference image per test sample. Additionally, CQG loss enforces invariance to color and quality variations by ensuring consistent segmentation predictions across transformed image pairs. Experimental results show that our proposals significantly improve segmentation performance over the baseline on two target domain datasets, despite being trained solely on a single source domain. Notably, our model achieved up to a 32.3-point increase in Dice score compared to the baseline, consistently producing robust and usable results even under substantial domain shifts. Our work contributes to the development of more robust medical image segmentation models that generalize across unseen domains. The implementation code is available at https://github.com/RaviShah1/DCIN-CQG.
医学图像分割中的单源域泛化(SDG)仍然是一个重大挑战,特别是对于颜色分布和质量各异的图像。以前的方法常常在训练于高质量图像上的模型无法泛化到低质量测试图像时遇到困扰,这是由于颜色和质量的偏移导致的。在这项工作中,我们提出了两种增强泛化的新技术:动态彩色图像归一化(DCIN)模块和颜色质量泛化(CQG)损失。DCIN通过两种参考图像选择策略动态地归一化测试图像的颜色。具体来说,DCIN利用全局参考图像选择(GRIS),找到通用参考图像;局部参考图像选择(LRIS)则为每个测试样本选择语义上相似的参考图像。此外,CQG损失通过确保变换图像对之间的分割预测一致,来强制执行颜色和质量变化的不变性。实验结果表明,尽管只在一个源域上进行训练,但我们的方法在两个目标域数据集上的分割性能都有了显著提高。值得注意的是,我们的模型在迪克分数上最高提高了32.3分,即使在很大的域偏移下也始终产生稳健和可用的结果。我们的工作为开发更稳健的医学图像分割模型做出了贡献,这些模型可以在未见过的领域进行泛化。实现代码可在https://github.com/RaviShah1/DCIN-CQG找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出两种技术来解决医学图像分割中的单源域泛化问题,即动态色彩图像归一化模块(DCIN)和色彩质量泛化(CQG)损失。DCIN通过两种参考图像选择策略动态归一化测试图像的颜色,而CQG损失通过确保对变换图像对的分割预测的一致性来强制执行颜色和质量的变异不变性。实验结果表明,与基线相比,该方法在目标域数据集上的分割性能显著提高,并且在单一源域训练的情况下也能实现良好的泛化效果。
Key Takeaways
- 医学图像分割中的单源域泛化(SDG)是一个挑战,特别是在颜色分布和质量变化大的图像中。
- 提出的DCIN模块通过两种参考图像选择策略动态归一化测试图像颜色。
- CQG损失通过确保对变换图像对分割预测的一致性,实现对颜色和质量的变异不变性。
- 实验结果显示,与基线相比,该方法在目标域数据集上的分割性能显著提高,Dice得分提高达32.3个点。
- 该模型在显著域偏移下仍能产生稳健和可用的结果。
- 该工作的贡献在于开发出更稳健的医学图像分割模型,能够在未见过的领域进行泛化。
点此查看论文截图

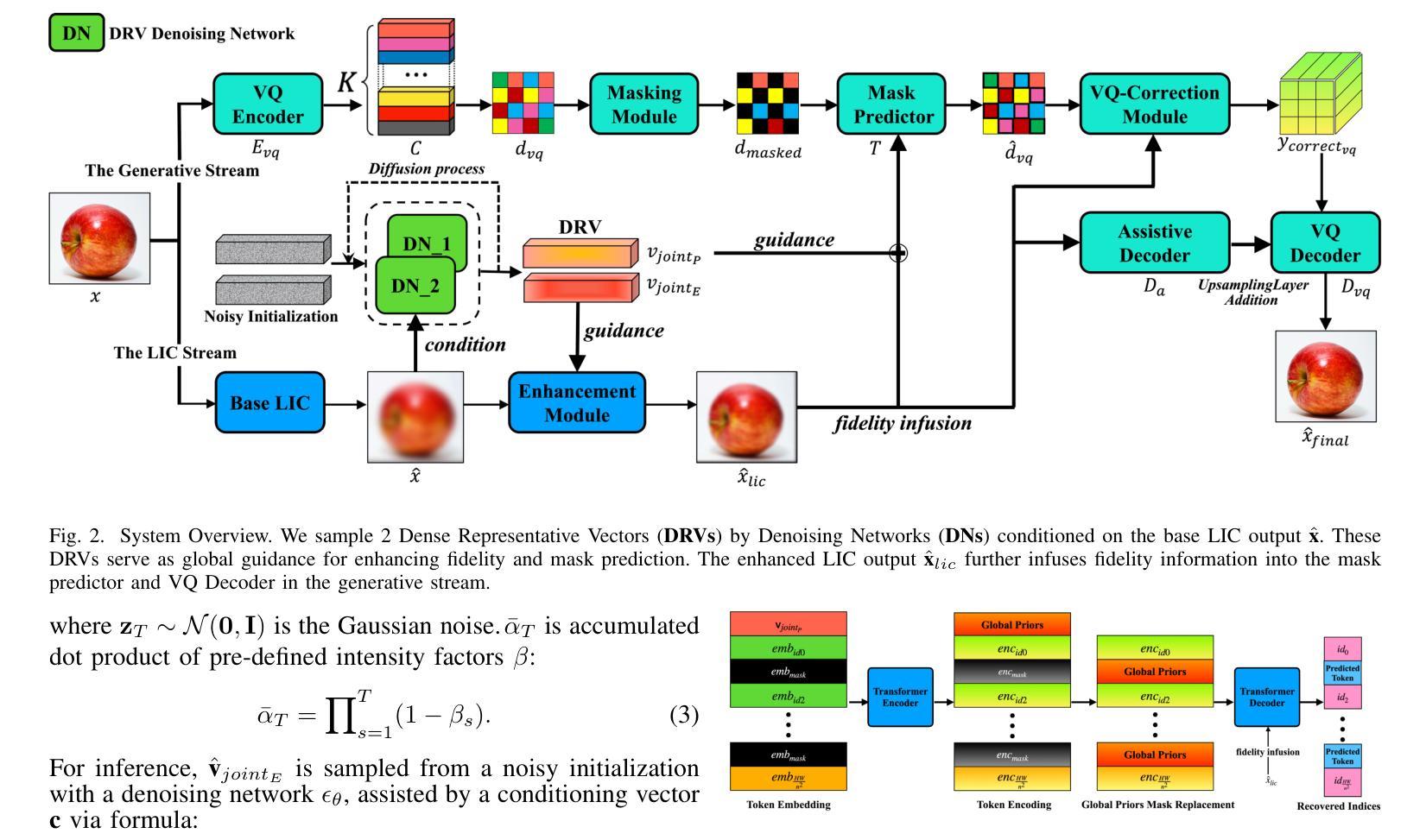
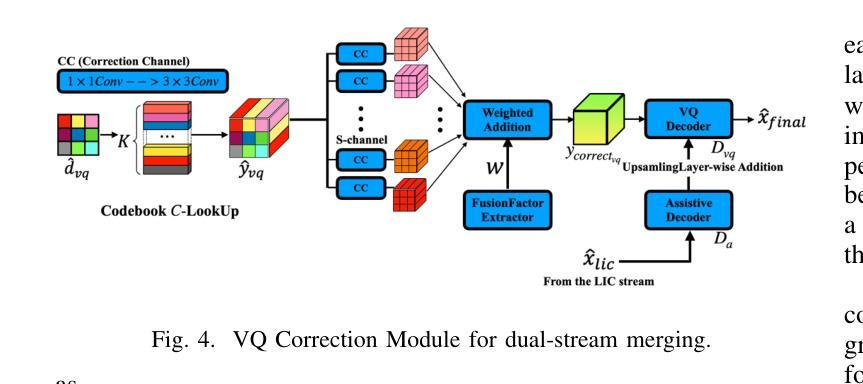
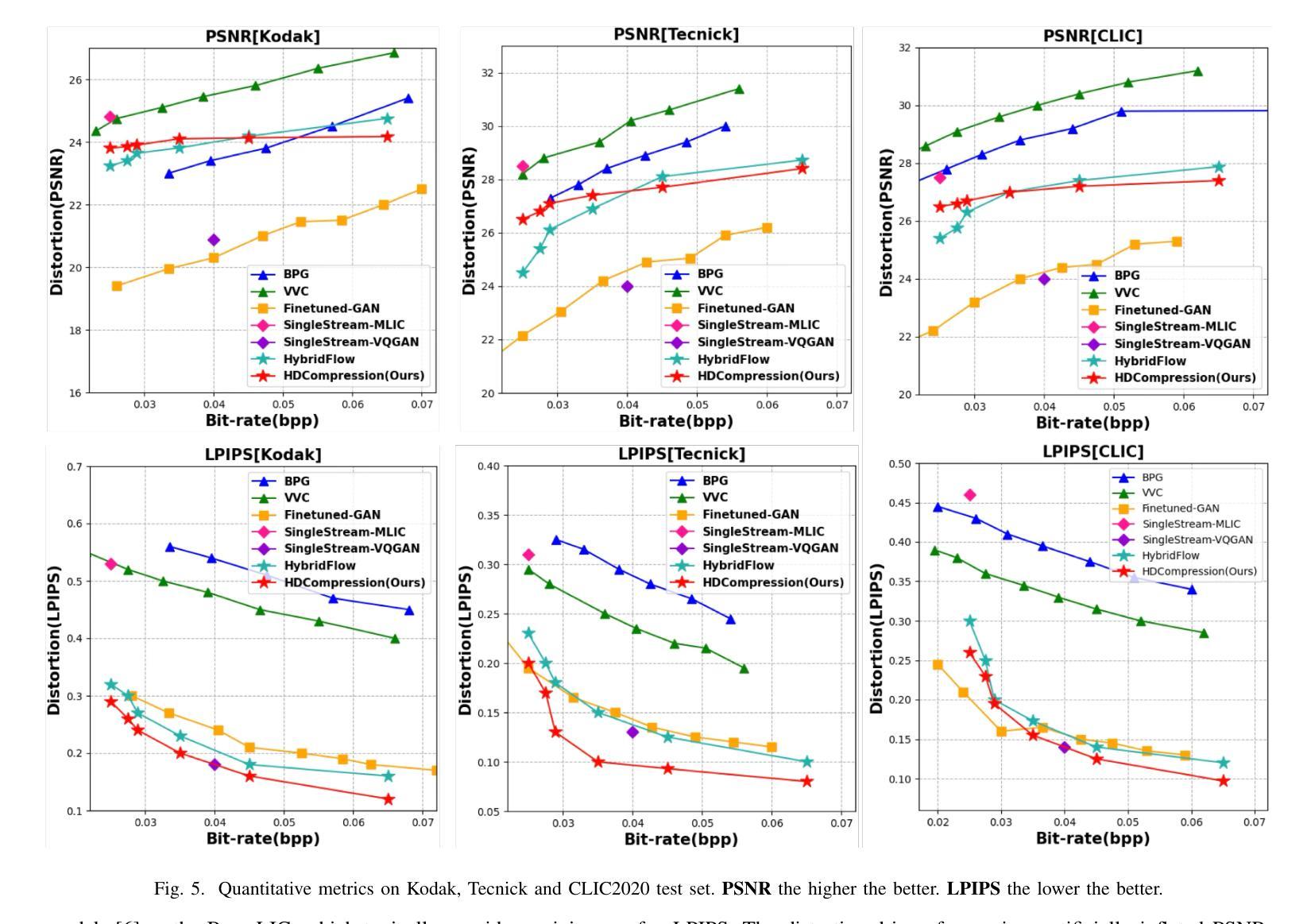
HDCompression: Hybrid-Diffusion Image Compression for Ultra-Low Bitrates
Authors:Lei Lu, Yize Li, Yanzhi Wang, Wei Wang, Wei Jiang
Image compression under ultra-low bitrates remains challenging for both conventional learned image compression (LIC) and generative vector-quantized (VQ) modeling. Conventional LIC suffers from severe artifacts due to heavy quantization, while generative VQ modeling gives poor fidelity due to the mismatch between learned generative priors and specific inputs. In this work, we propose Hybrid-Diffusion Image Compression (HDCompression), a dual-stream framework that utilizes both generative VQ-modeling and diffusion models, as well as conventional LIC, to achieve both high fidelity and high perceptual quality. Different from previous hybrid methods that directly use pre-trained LIC models to generate low-quality fidelity-preserving information from heavily quantized latent, we use diffusion models to extract high-quality complimentary fidelity information from the ground-truth input, which can enhance the system performance in several aspects: improving indices map prediction, enhancing the fidelity-preserving output of the LIC stream, and refining conditioned image reconstruction with VQ-latent correction. In addition, our diffusion model is based on a dense representative vector (DRV), which is lightweight with very simple sampling schedulers. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our HDCompression outperforms the previous conventional LIC, generative VQ-modeling, and hybrid frameworks in both quantitative metrics and qualitative visualization, providing balanced robust compression performance at ultra-low bitrates.
在超低比特率下,图像压缩对于传统的图像压缩(LIC)和生成向量量化(VQ)建模仍然具有挑战性。传统LIC由于重量化而容易出现严重伪影,而生成VQ建模由于学习到的生成先验与特定输入之间的不匹配而导致保真度较低。在这项工作中,我们提出了混合扩散图像压缩(HDCompression),这是一种双流框架,结合了生成VQ建模和扩散模型以及传统LIC,以实现高保真和高感知质量。不同于之前直接使用预训练的LIC模型从重度量化的潜在信息中产生低质量保真度保持信息的混合方法,我们使用扩散模型从原始真实输入中提取高质量补充保真信息,这可以在多方面提升系统性能:改善索引映射预测,提高LIC流的保真度保持输出,并通过VQ潜在校正进行条件图像重建。此外,我们的扩散模型基于密集表示向量(DRV),具有轻量级和非常简单的采样调度器。大量实验表明,我们的HDCompression在定量指标和定性可视化方面均优于之前的传统LIC、生成VQ建模和混合框架,在超低比特率下提供了平衡的稳健压缩性能。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Under Review
Summary
本工作提出一种名为Hybrid-Diffusion Image Compression(HDCompression)的混合扩散图像压缩技术,该技术结合了生成式VQ建模、传统图像压缩和扩散模型,旨在实现高保真度和高感知质量。不同于以往直接使用预训练的传统图像压缩模型生成低质量保真度信息的方法,我们的扩散模型从原始真实输入中提取高质量互补保真信息,从而提高了系统性能。此外,我们的扩散模型基于轻量级的密集代表向量(DRV),采样调度器非常简单。实验证明,在超低比特率下,HDCompression在定量指标和定性可视化方面都优于传统的图像压缩和生成式VQ建模方法。
Key Takeaways
- HDCompression结合了生成式VQ建模、传统图像压缩和扩散模型,旨在解决超低比特率下的图像压缩挑战。
- 传统的图像压缩方法面临严重的量化失真问题,而生成式VQ建模则由于生成先验与特定输入的不匹配而导致保真度低。
- HDCompression使用扩散模型从原始真实输入中提取高质量互补保真信息,提高系统性能。
- HDCompression通过改进索引映射预测、增强传统图像压缩流的保真度保持输出以及细化基于VQ潜在校正的条件图像重建来增强系统性能。
- 与其他混合方法不同,HDCompression使用基于轻量级密集代表向量(DRV)的扩散模型,具有非常简单的采样调度器。
- 实验证明,HDCompression在定量指标和定性可视化方面优于传统的图像压缩和生成式VQ建模方法。
点此查看论文截图


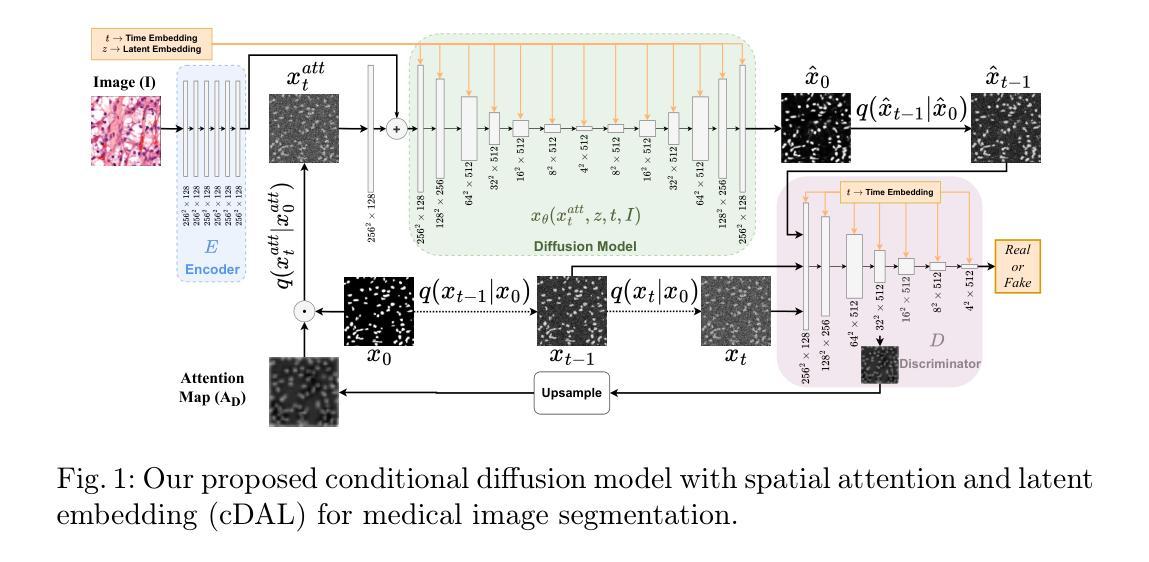
Conditional diffusion model with spatial attention and latent embedding for medical image segmentation
Authors:Behzad Hejrati, Soumyanil Banerjee, Carri Glide-Hurst, Ming Dong
Diffusion models have been used extensively for high quality image and video generation tasks. In this paper, we propose a novel conditional diffusion model with spatial attention and latent embedding (cDAL) for medical image segmentation. In cDAL, a convolutional neural network (CNN) based discriminator is used at every time-step of the diffusion process to distinguish between the generated labels and the real ones. A spatial attention map is computed based on the features learned by the discriminator to help cDAL generate more accurate segmentation of discriminative regions in an input image. Additionally, we incorporated a random latent embedding into each layer of our model to significantly reduce the number of training and sampling time-steps, thereby making it much faster than other diffusion models for image segmentation. We applied cDAL on 3 publicly available medical image segmentation datasets (MoNuSeg, Chest X-ray and Hippocampus) and observed significant qualitative and quantitative improvements with higher Dice scores and mIoU over the state-of-the-art algorithms. The source code is publicly available at https://github.com/Hejrati/cDAL/.
扩散模型已被广泛应用于高质量图像和视频生成任务。在本文中,我们提出了一种具有空间注意力和潜在嵌入(cDAL)的新型条件扩散模型,用于医学图像分割。在cDAL中,扩散过程的每一步都使用基于卷积神经网络(CNN)的鉴别器来区分生成的标签和真实的标签。基于鉴别器学习的特征计算空间注意力图,帮助cDAL生成输入图像中判别区域的更准确分割。此外,我们将随机潜在嵌入融入模型中的每一层,以大大减少训练和采样步骤的数量,从而使它比其他用于图像分割的扩散模型更快。我们在三个公开的医学图像分割数据集(MoNuSeg、Chest X-ray和Hippocampus)上应用了cDAL,与最先进的算法相比,在定性和定量方面都取得了显著的改进,Dice得分和mIoU更高。源代码可在https://github.com/Hejrati/cDAL/公开获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 11 pages, 2 figures, 3 tables, Accepted in MICCAI 2024
Summary
扩散模型在医学图像分割中展现出显著优势。本文提出了一种具有空间注意力和潜在嵌入的新条件扩散模型(cDAL)。利用基于卷积神经网络(CNN)的鉴别器提高图像生成质量,通过空间注意力图更精确地分割输入图像中的判别区域。此外,模型中嵌入随机潜在向量以加快训练和采样过程,显著优于其他图像分割扩散模型。应用于三个公开医学图像分割数据集上的结果表明,cDAL实现了更高的狄克系数和平均交并比,优于现有算法。源代码已公开。
Key Takeaways
- 本文提出了一种新型条件扩散模型cDAL,用于医学图像分割。
- cDAL模型利用CNN鉴别器在扩散过程的每个时间步长中区分生成的标签和真实标签,以提高图像生成质量。
- 空间注意力图有助于cDAL更精确地分割输入图像中的判别区域。
- cDAL模型通过嵌入随机潜在向量,显著减少了训练和采样的时间步长,从而提高了速度。
- cDAL在三个公开的医学图像分割数据集上的表现优于现有算法,具有更高的狄克系数和平均交并比。
- cDAL模型的源代码已经公开,便于其他研究者使用和改进。
点此查看论文截图

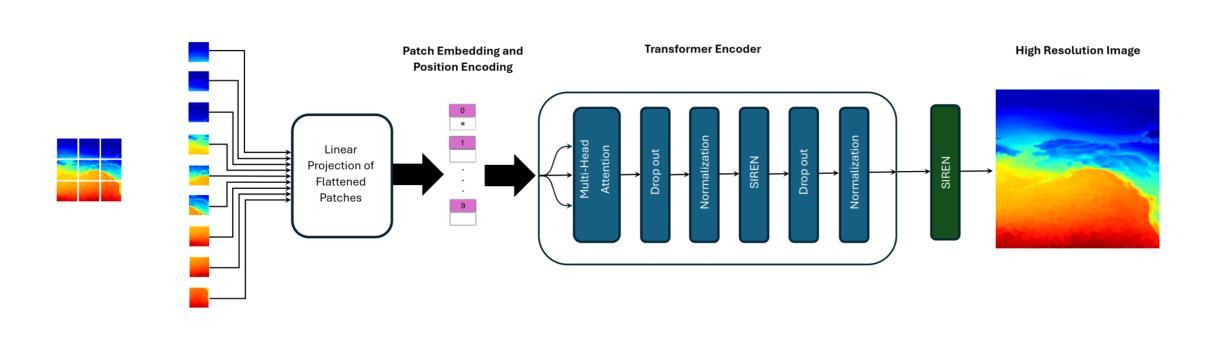
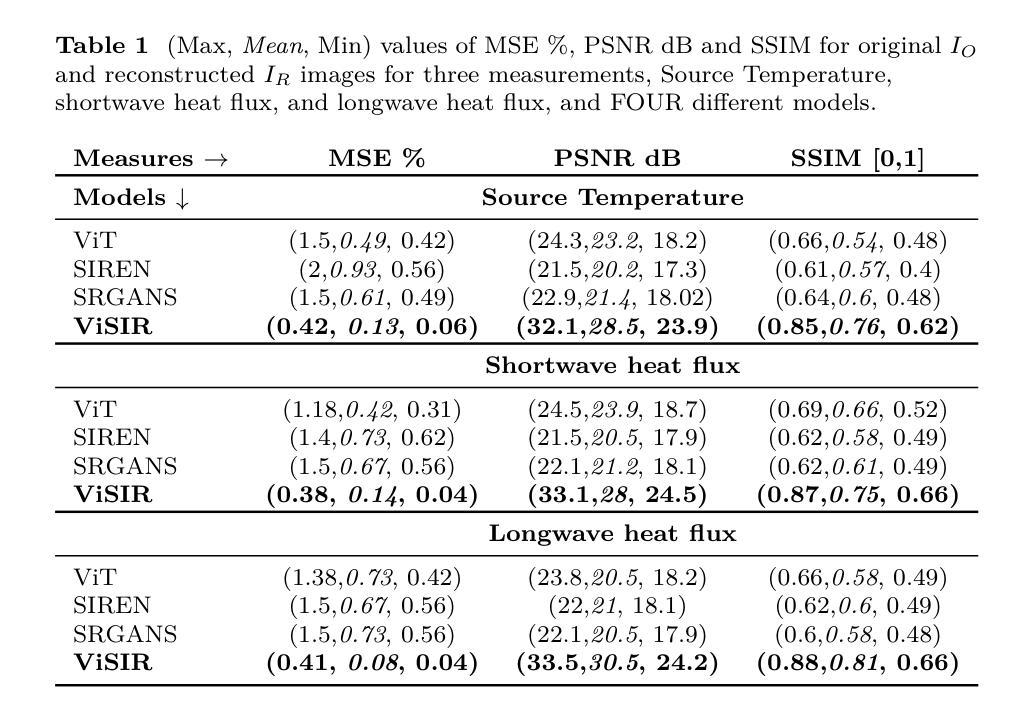
ViSIR: Vision Transformer Single Image Reconstruction Method for Earth System Models
Authors:Ehsan Zeraatkar, Salah Faroughi, Jelena Tešić
Purpose: Earth system models (ESMs) integrate the interactions of the atmosphere, ocean, land, ice, and biosphere to estimate the state of regional and global climate under a wide variety of conditions. The ESMs are highly complex, and thus, deep neural network architectures are used to model the complexity and store the down-sampled data. In this paper, we propose the Vision Transformer Sinusoidal Representation Networks (ViSIR) to improve the single image SR (SR) reconstruction task for the ESM data. Methods: ViSIR combines the SR capability of Vision Transformers (ViT) with the high-frequency detail preservation of the Sinusoidal Representation Network (SIREN) to address the spectral bias observed in SR tasks. Results: The ViSIR outperforms ViT by 4.1 dB, SIREN by 7.5 dB, and SR-Generative Adversarial (SR-GANs) by 7.1dB PSNR on average for three different measurements. Conclusion: The proposed ViSIR is evaluated and compared with state-of-the-art methods. The results show that the proposed algorithm is outperforming other methods in terms of Mean Square Error(MSE), Peak-Signal-to-Noise-Ratio(PSNR), and Structural Similarity Index Measure(SSIM).
目的:地球系统模型(ESM)整合了大气、海洋、陆地、冰层和生物圈的相互作用,以在多种条件下估计区域和全球气候的状态。由于ESM高度复杂,因此使用深度神经网络架构来对其复杂性进行建模并存储降采样数据。在本文中,我们提出了Vision Transformer Sinusoidal Representation Networks(ViSIR),旨在改进ESM数据的单图像超分辨率(SR)重建任务。
方法:ViSIR结合了Vision Transformer(ViT)的SR能力和Sinusoidal Representation Network(SIREN)的高频细节保留能力,以解决SR任务中观察到的频谱偏见。
结果:ViSIR在三种不同测量上平均比ViT高出4.1 dB,比SIREN高出7.5 dB,比SR-生成对抗网络(SR-GANs)高出7.1 dB的峰值信噪比(PSNR)。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种新的基于Vision Transformer和Sinusoidal Representation Network结合的模型——Vision Transformer Sinusoidal Representation Networks(ViSIR),旨在改善地球系统模型中超分辨率重建(SR)任务的效果。该模型结合了ViT的超分辨率能力和SIREN的高频细节保留特性,解决了SR任务中的光谱偏差问题。实验结果显示,ViSIR相较于其他模型在PSNR等指标上有所提升。
Key Takeaways
- ESMs利用深度神经网络进行复杂模拟并处理降采样数据。
- Vision Transformer Sinusoidal Representation Networks (ViSIR)结合ViT和SIREN的优点,旨在改进ESM数据的超分辨率重建(SR)。
- ViSIR解决了SR任务中的光谱偏差问题。
- ViSIR在PSNR、MSE和SSIM等指标上的性能优于其他模型。
- ViSIR相较于ViT、SIREN和SR-GANs平均提高了4.1dB、7.5dB和7.1dB的PSNR。
- ViSIR模型在改善SR任务方面的效果显著,具有实际应用潜力。
点此查看论文截图

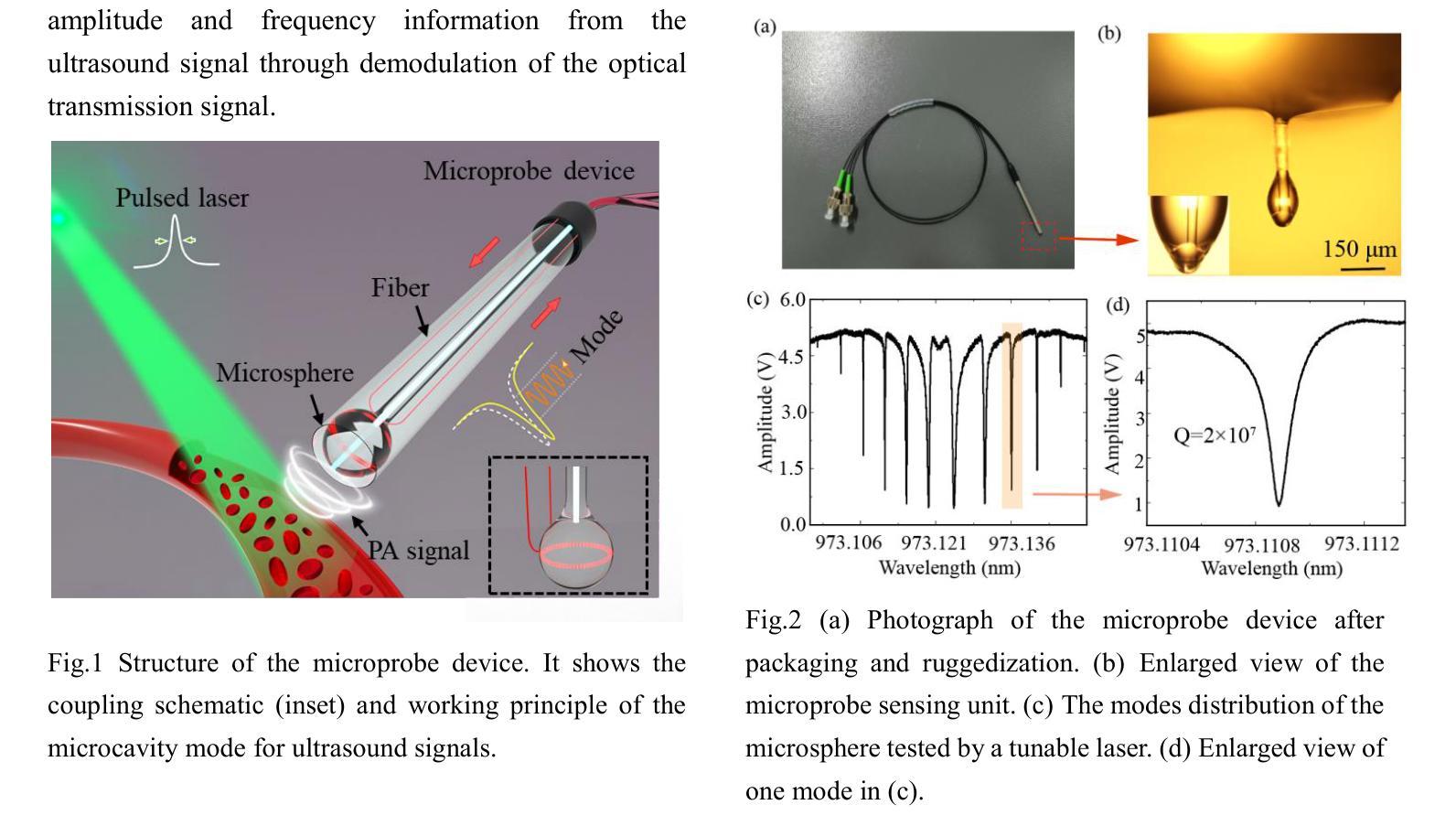
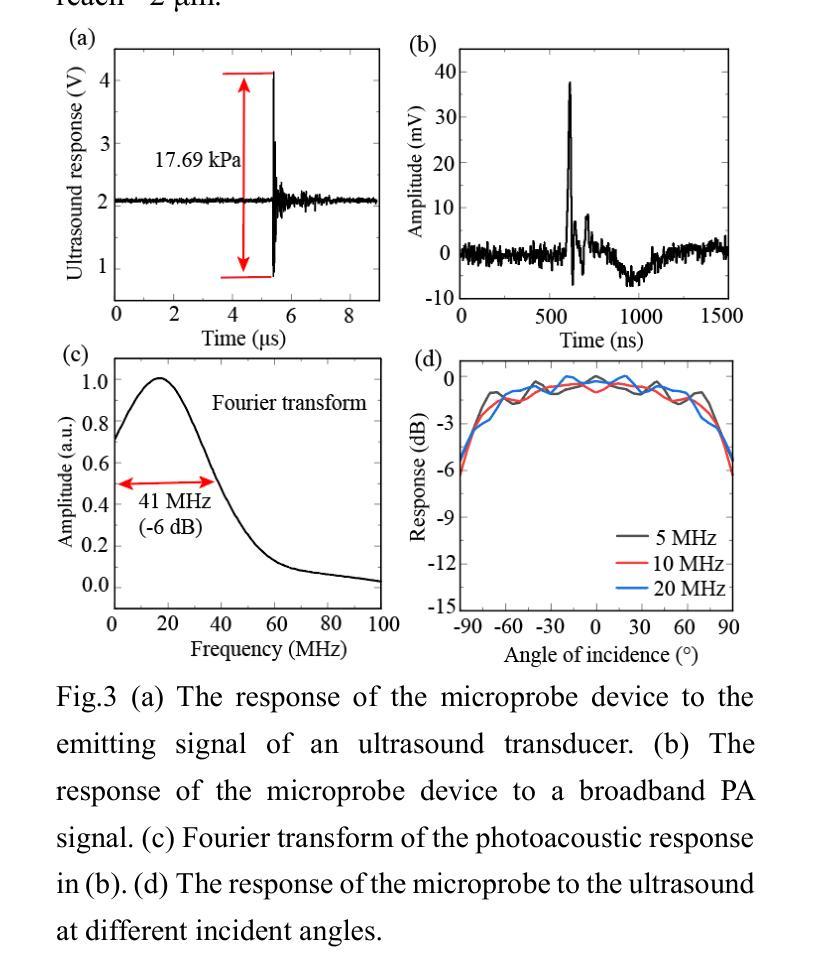
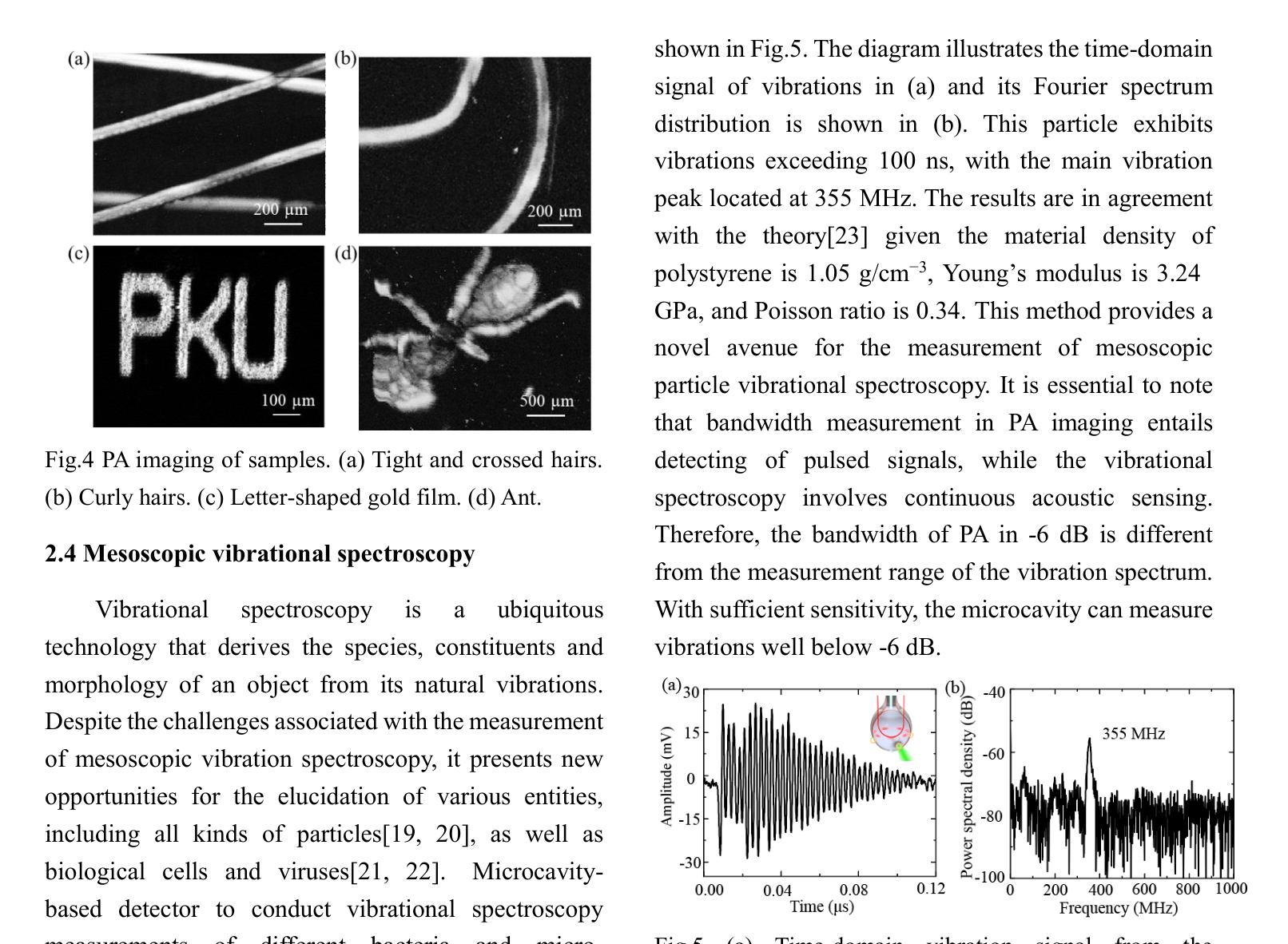
WGM microprobe device for high-sensitivity and broadband ultrasound detection
Authors:Jialve Sun, Shengnan Huangfu, Tinglan Chen, Zijing Cai, Bowen Ruan, Fangxing Zhang
Whispering-gallery-mode (WGM) microcavities have emerged as a promising alternative to traditional ultrasound probes, offering high sensitivity and wide bandwidth. In our research, we propose a novel silica WGM microprobe device, with impressive Q factors up to 10^7.The side-coupled approach and special encapsulation design make the device small, robust, and capable of utilizing in both gaseous and liquid environments.We have successfully conducted photoacoustic (PA) imaging on various samples using this device which demonstrates a high sensitivity of 5.4 mPa/sqrt(Hz) and a board bandwidth of 41 MHz at -6 dB for ultrasound. What’s more, it’s capable of capturing the vibration spectrum of microparticles up to a few hundred megahertz. Our compact and lightweight device exhibits significant application potential in PA endoscopic detection, near-field ultrasound sensing and other aspects.
微腔中的嗡嗡模式(WGM)已成为传统超声探针的一种很有前途的替代品,具有灵敏度高和带宽大的特点。在我们的研究中,我们提出了一种新型二氧化硅WGM微型探针装置,其Q因子高达10^7。侧面耦合的方法和特殊的封装设计使该设备体积小、稳定性高,既能在气态环境中使用也能在液态环境中使用。我们已经成功使用该设备对各种样品进行光声成像,其灵敏度高达5.4 mPa/sqrt(Hz),在超声-6 dB下的带宽为41 MHz。此外,它能捕捉到高达数百兆赫兹的微粒子振动光谱。我们的紧凑轻便的设备在光声内窥检测、近场超声传感和其他方面表现出巨大的应用潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
微腔中的轻声模式(WGM)微腔提供了一种对传统超声探针颇具潜力的替代方案,具有灵敏度高和带宽宽的特点。研究中提出了一种新型二氧化硅WGM微探针器件,具有高达10^7的Q值。其侧耦合方式和特殊封装设计使器件小巧、稳健,既可用于气体环境也可用于液体环境。利用该器件成功进行了光声成像实验,展示了高灵敏度和宽频带特性,并能够捕捉到高达数百兆赫兹的微颗粒振动谱。此紧凑轻便的器件在光声内窥检测、近场超声传感等方面具有显著的应用潜力。
Key Takeaways
- WGM微腔作为传统超声探针的替代方案,具有高灵敏度和宽频带特性。
- 新型二氧化硅WGM微探针器件具有高达10^7的Q值。
- 侧耦合和特殊封装设计使器件适应于各种环境,包括气体和液体。
- 成功进行光声成像实验,展示了高灵敏度(5.4 mPa/sqrt(Hz))和宽频带(-6 dB下41 MHz)。
- 器件能够捕捉到高达数百兆赫兹的微颗粒振动谱。
- 器件紧凑轻便,具有显著的应用潜力。
点此查看论文截图

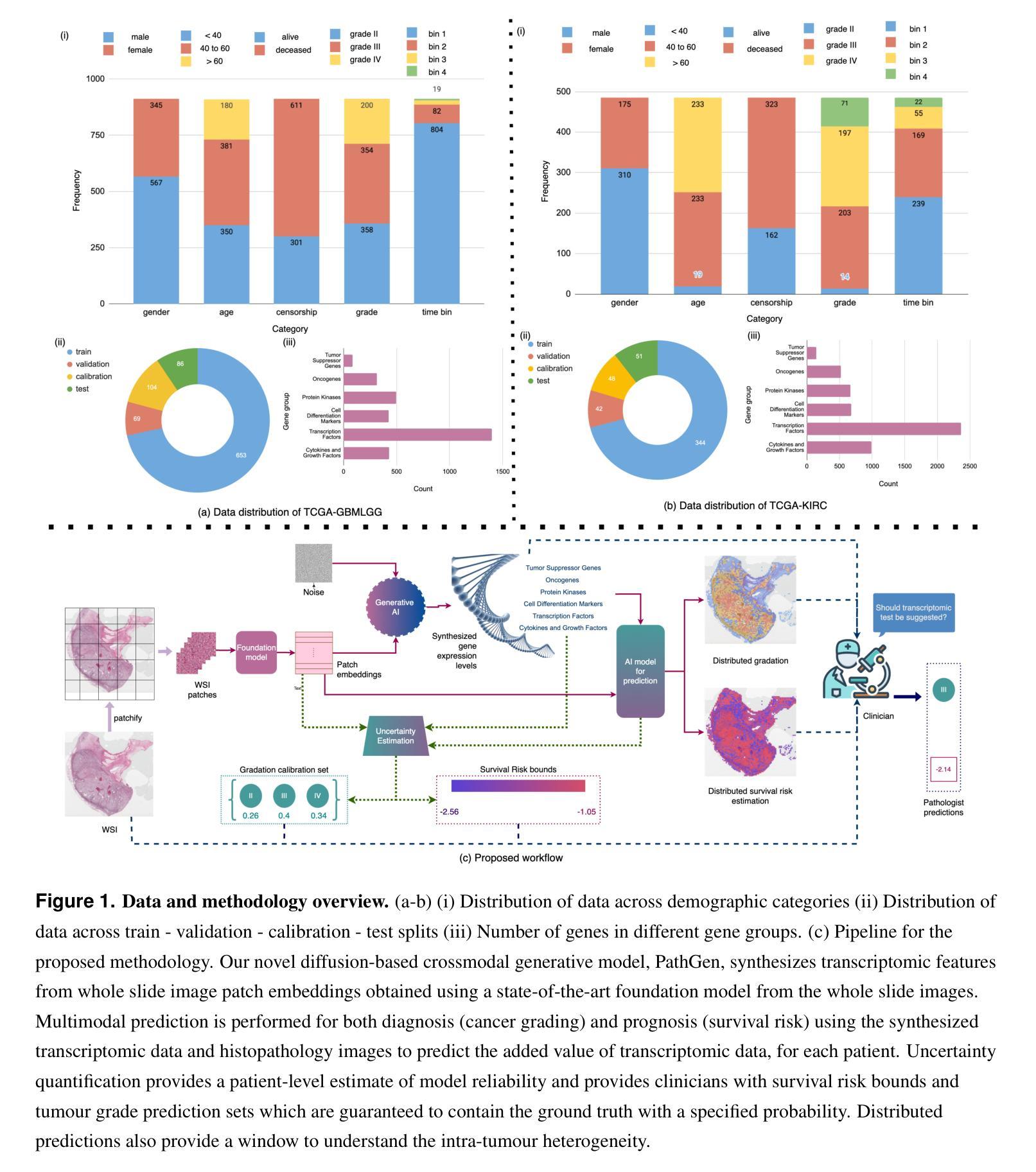
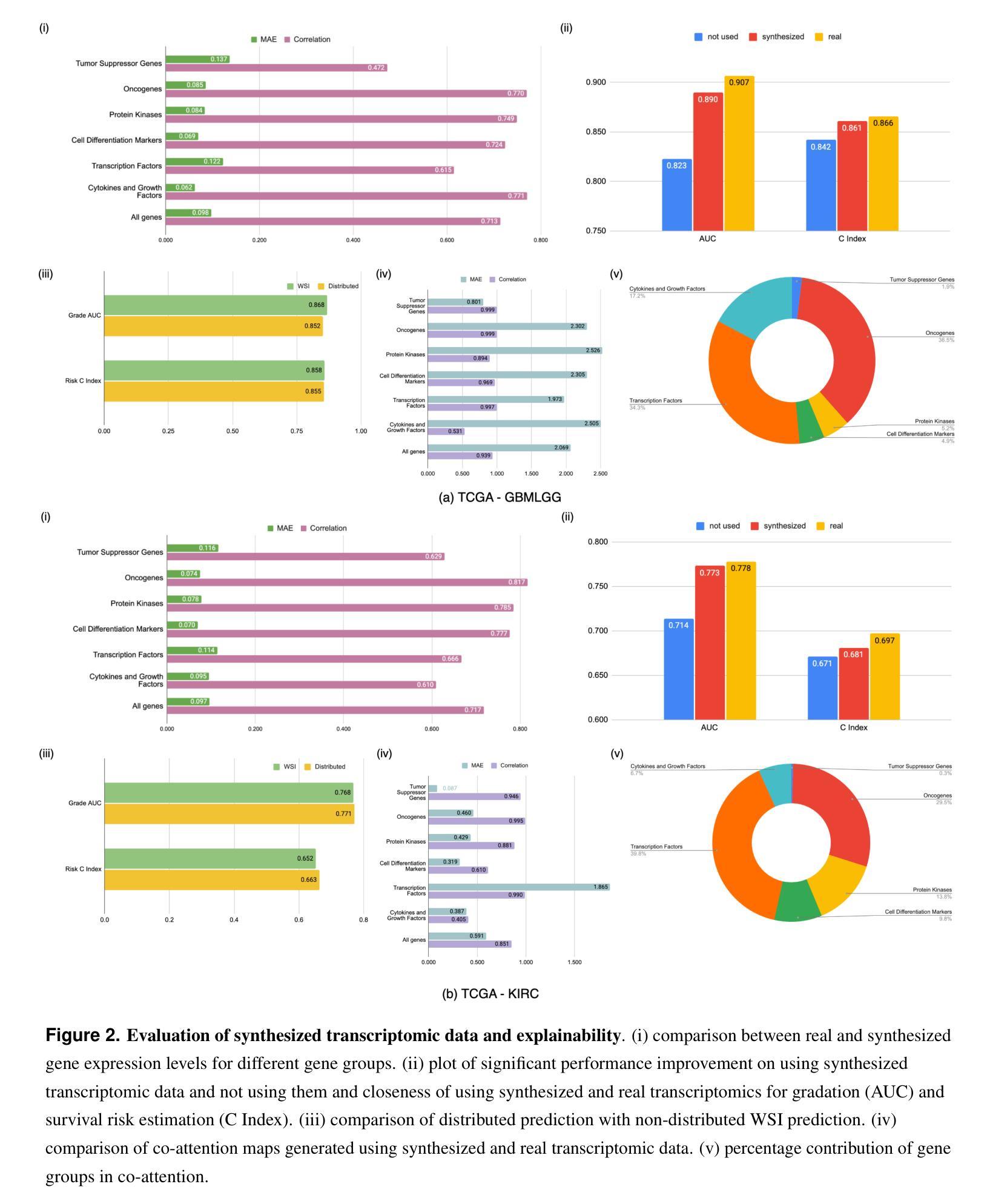
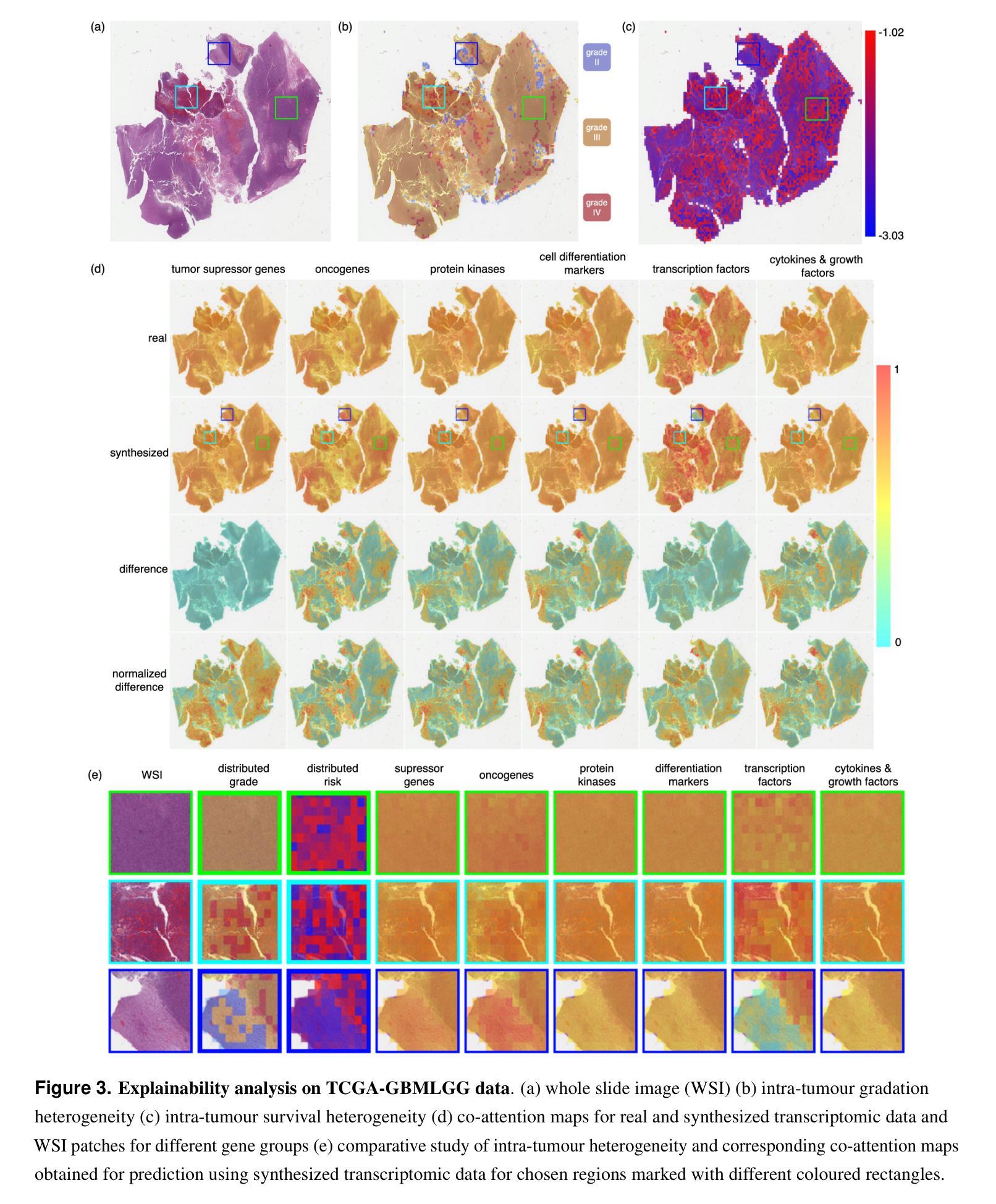
Generating crossmodal gene expression from cancer histopathology improves multimodal AI predictions
Authors:Samiran Dey, Christopher R. S. Banerji, Partha Basuchowdhuri, Sanjoy K. Saha, Deepak Parashar, Tapabrata Chakraborti
Emerging research has highlighted that artificial intelligence based multimodal fusion of digital pathology and transcriptomic features can improve cancer diagnosis (grading/subtyping) and prognosis (survival risk) prediction. However, such direct fusion for joint decision is impractical in real clinical settings, where histopathology is still the gold standard for diagnosis and transcriptomic tests are rarely requested, at least in the public healthcare system. With our novel diffusion based crossmodal generative AI model PathGen, we show that genomic expressions synthesized from digital histopathology jointly predicts cancer grading and patient survival risk with high accuracy (state-of-the-art performance), certainty (through conformal coverage guarantee) and interpretability (through distributed attention maps). PathGen code is available for open use by the research community through GitHub at https://github.com/Samiran-Dey/PathGen.
新兴研究突出表明,基于人工智能的数字病理和转录组特征的多模式融合可以提高癌症诊断(分级/亚型)和预后(生存风险)预测的准确性。然而,在实际临床环境中,这种直接融合进行联合决策并不切实际。特别是在公共医疗体系中,组织病理学仍是诊断的金标准,转录组测试很少被要求。通过我们新颖的基于扩散的跨模态生成人工智能模型PathGen,我们展示了由数字病理学合成的基因表达能够联合预测癌症分级和患者生存风险,具有很高的准确性(达到最新性能)、确定性(通过合形覆盖保证)和可解释性(通过分布式注意力图)。PathGen代码可通过GitHub供研究界开放使用,网址为:https://github.com/Samiran-Dey/PathGen。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文探讨了人工智能在数字病理与转录组特征融合方面的新兴研究,指出这种融合能提高癌症诊断(分级/亚型)和预后(生存风险)预测的准确性。然而,在实际临床环境中直接融合进行联合决策并不现实。通过使用新型的基于扩散的跨模态生成人工智能模型PathGen,我们展示了从数字病理合成的基因组表达联合预测癌症分级和患者生存风险的高准确性、确定性和可解释性。PathGen代码已开源,供研究社区通过GitHub使用。
Key Takeaways
- 人工智能在数字病理和转录组特征的融合方面能提高癌症诊断和预后预测的准确性。
- 直接融合进行联合决策在实际临床环境中并不现实,因为病理组织学仍是诊断的金标准,转录组测试在公共医疗系统中很少被要求。
- 新型扩散基于跨模态生成人工智能模型PathGen能够合成基因组表达,联合预测癌症分级和患者生存风险。
- PathGen具有高准确性、达到最新性能水平,提供确定性(通过覆盖保证)和可解释性(通过分布式注意力图)。
- PathGen代码已开源,供研究社区使用。
- 该模型的应用有助于推动人工智能在医学图像分析领域的进一步发展。
点此查看论文截图
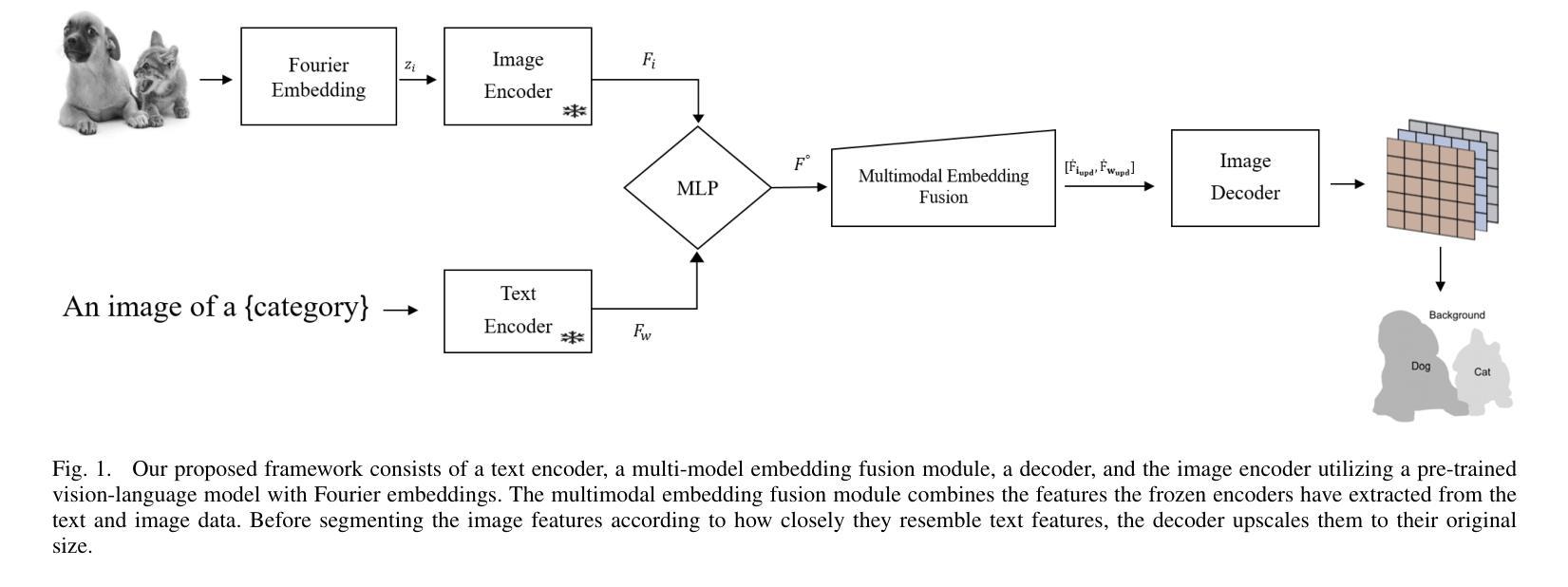
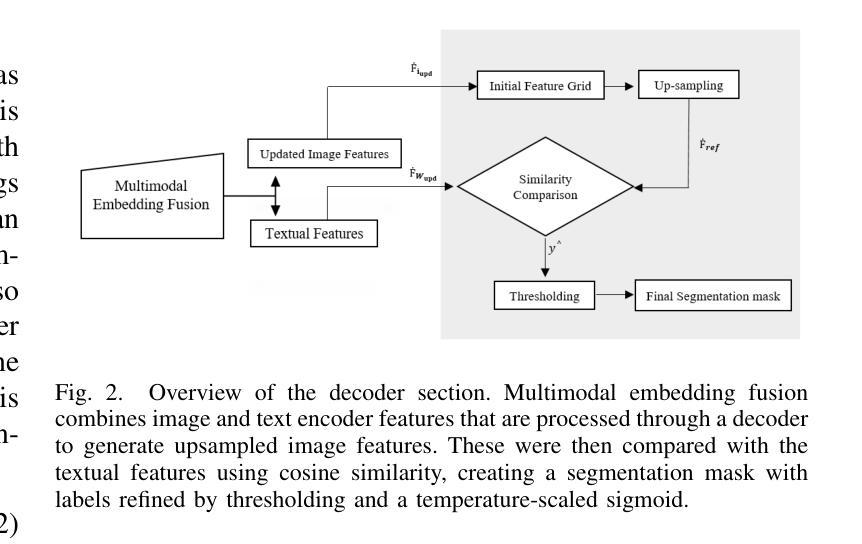
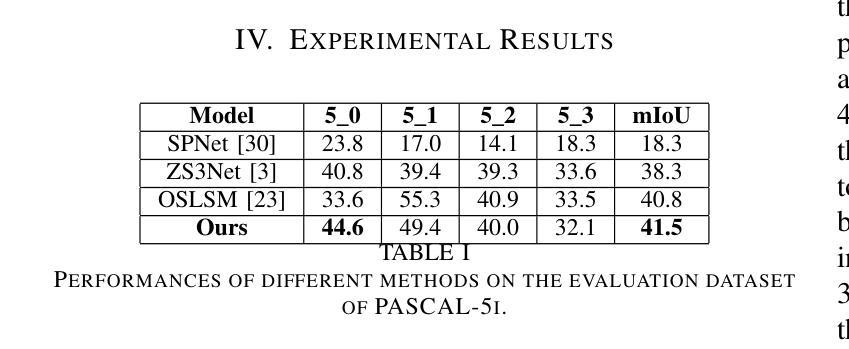
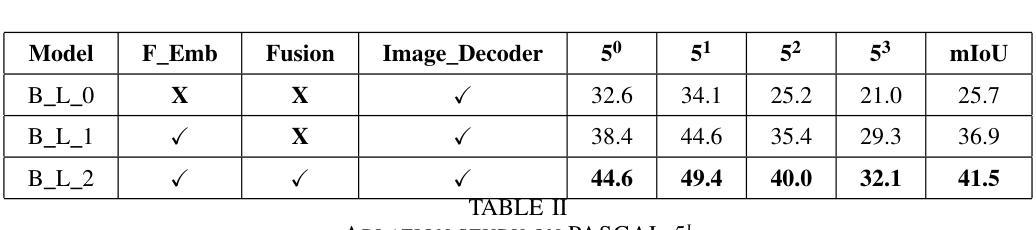
Beyond-Labels: Advancing Open-Vocabulary Segmentation With Vision-Language Models
Authors:Muhammad Atta ur Rahman
Self-supervised learning can resolve numerous image or linguistic processing problems when effectively trained. This study investigated simple yet efficient methods for adapting previously learned foundation models for open-vocabulary semantic segmentation tasks. Our research proposed “Beyond-Labels,” a lightweight transformer-based fusion module that uses a handful of image segmentation data to fuse frozen image representations with language concepts. This strategy allows the model to successfully actualize enormous knowledge from pretrained models without requiring extensive retraining, making the model data-efficient and scalable. Furthermore, we efficiently captured positional information in images using Fourier embeddings, thus improving the generalization across various image sizes, addressing one of the key limitations of previous methods. Extensive ablation tests were performed to investigate the important components of our proposed method; when tested against the common benchmark PASCAL-5i, it demonstrated superior performance despite being trained on frozen image and language characteristics.
自监督学习在得到有效的训练后,可以解决许多图像或语言处理方面的问题。本研究探讨了适应先前学习的基础模型用于开放词汇语义分割任务的简单而高效的方法。我们的研究提出了“超越标签”的概念,这是一个轻量级的基于transformer的融合模块,它使用少量的图像分割数据来融合冻结的图像表示和语言概念。这一策略使得模型能够成功地从预训练模型中实现大量知识,而无需进行大规模的重训,从而提高了模型的数据效率和可扩展性。此外,我们利用傅里叶嵌入有效地捕获了图像中的位置信息,从而提高了模型在不同图像大小上的泛化能力,解决了之前方法的关键限制之一。我们进行了广泛的消融实验,以研究我们提出方法的重要组件;在针对常用基准PASCAL-5i进行的测试中,即使在冻结的图像和语言特征上进行的训练,也表现出了卓越的性能。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本研究探讨了简单而高效的方法,用于将先前学习的基本模型适应于开放词汇语义分割任务。研究提出了“超越标签”的轻量级转换器融合模块,该模块使用少量的图像分割数据将冻结的图像表示与语言概念相融合。此方法使模型能够在不需要大量重新训练的情况下成功实现预训练模型中的巨大知识,使模型具有数据高效性和可扩展性。此外,通过傅立叶嵌入有效地捕获了图像中的位置信息,从而提高了不同图像大小的泛化能力,解决了以前方法的关键局限性之一。广泛的消融测试验证了所提出方法的重要成分;在针对常用基准PASCAL-5i的测试中,尽管是在冻结的图像和语言特征上训练的,但其性能仍表现出卓越。
Key Takeaways
- 本研究使用自监督学习来解决图像或语言处理中的许多问题。
- 提出了一种名为“超越标签”的融合模块,该模块可以适应开放词汇语义分割任务。
- 通过将冻结的图像表示与语言概念相融合,实现了预训练模型中的知识转移。
- 使用傅立叶嵌入捕获图像中的位置信息,提高了模型的泛化能力。
- 所提出的方法在数据效率和可扩展性方面表现出优势。
- 通过广泛的消融测试验证了方法的关键成分。
点此查看论文截图