⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-02-13 更新
Supervised contrastive learning for cell stage classification of animal embryos
Authors:Yasmine Hachani, Patrick Bouthemy, Elisa Fromont, Sylvie Ruffini, Ludivine Laffont, Alline de Paula Reis
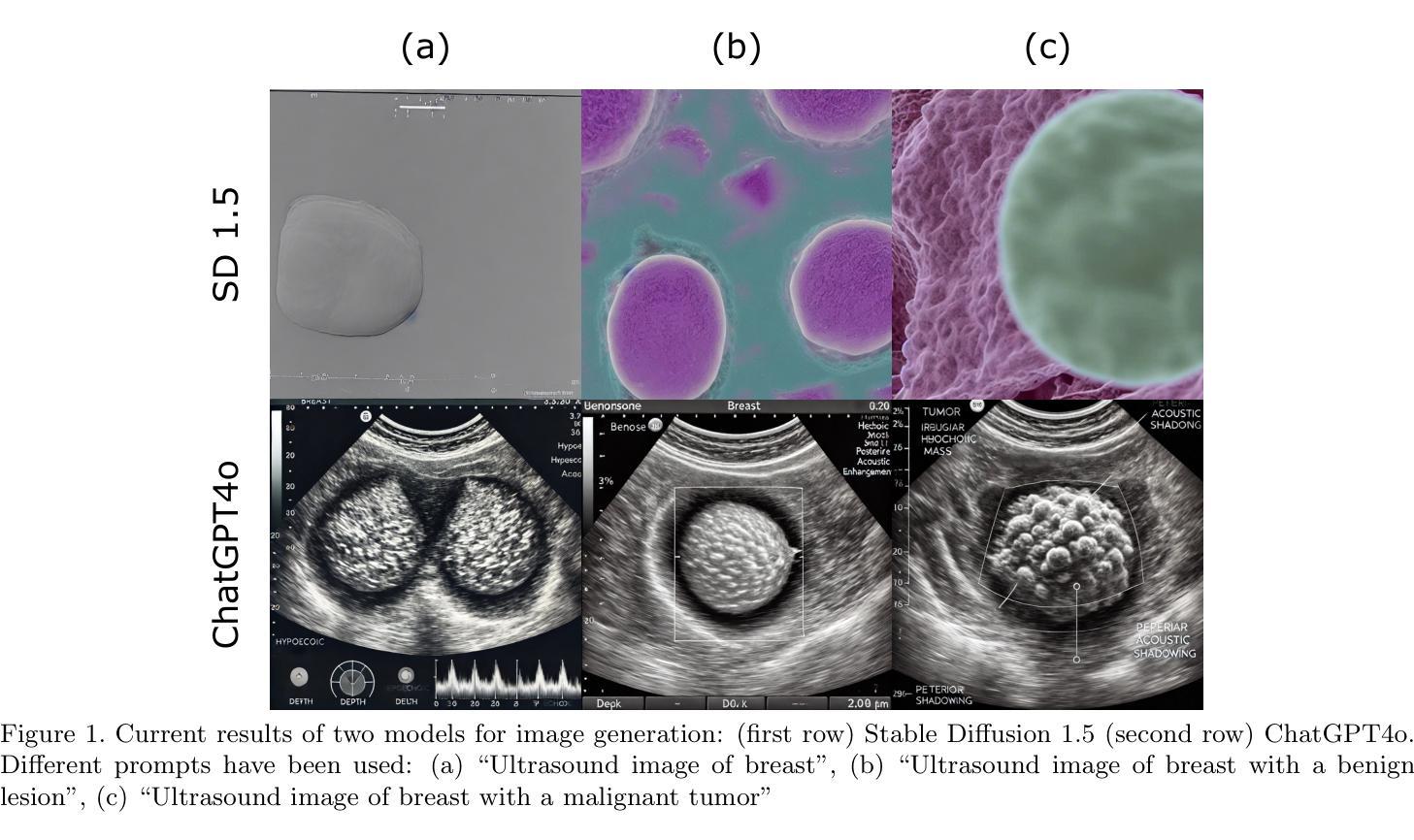
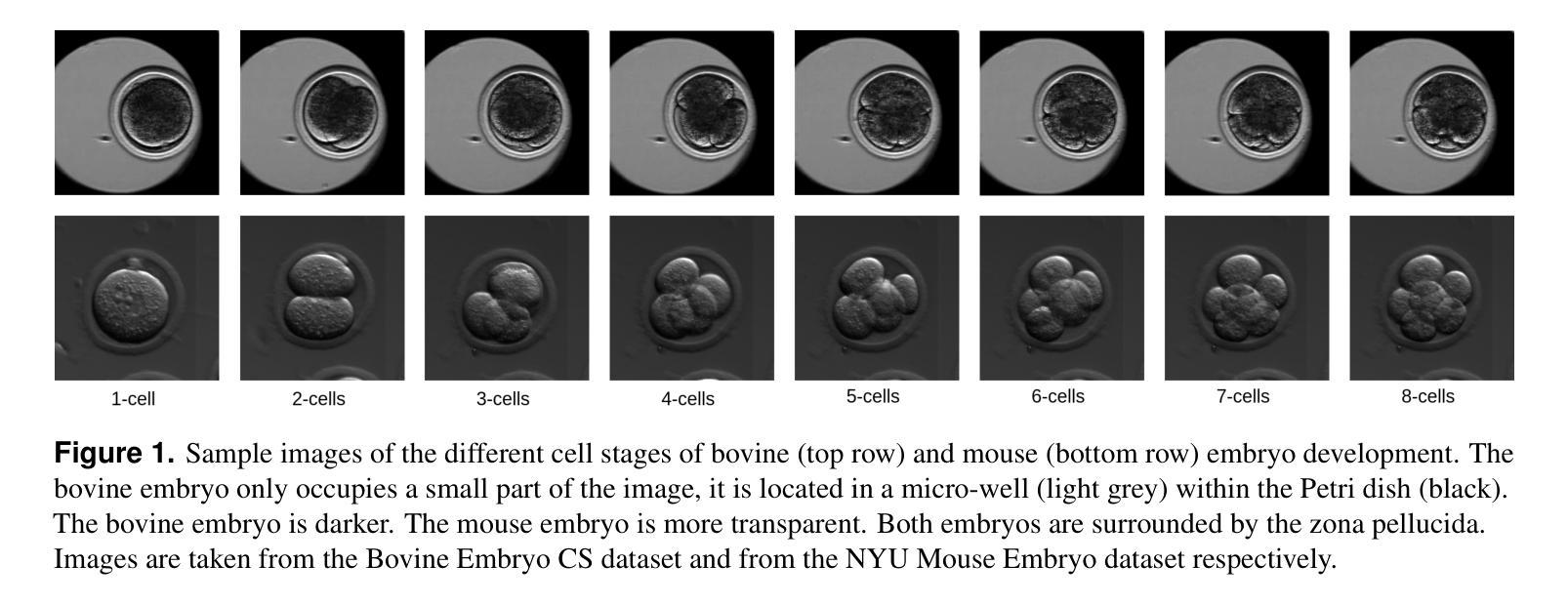
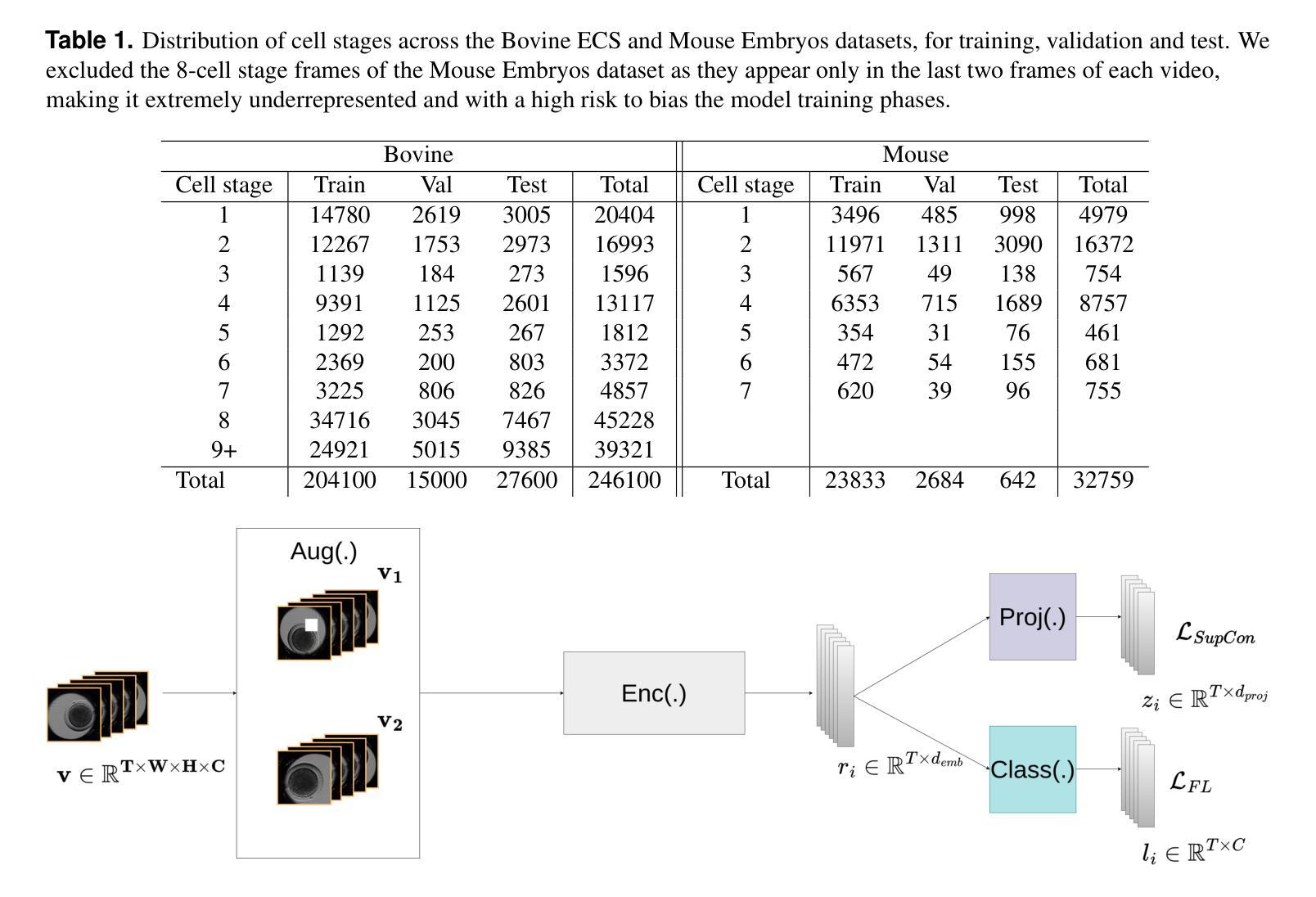
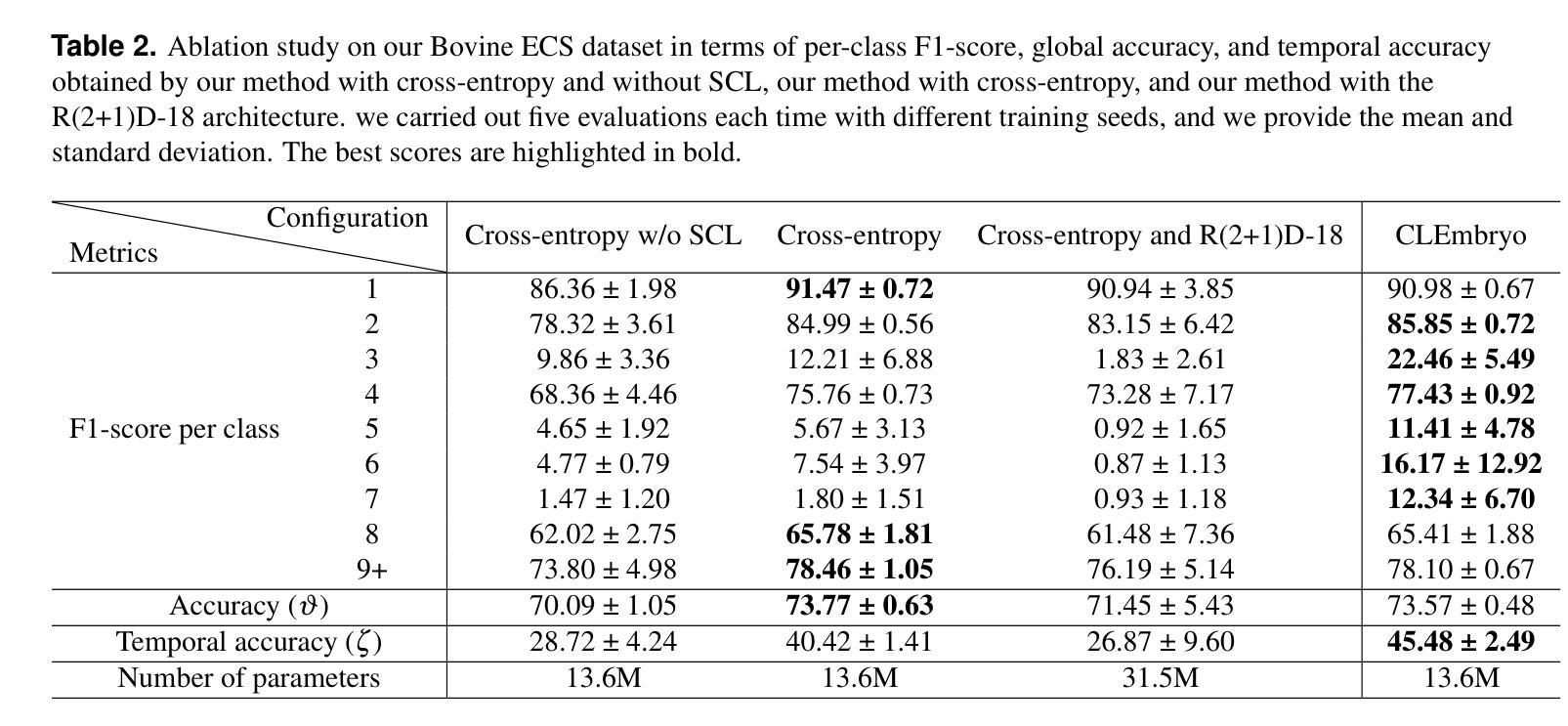
Video microscopy, when combined with machine learning, offers a promising approach for studying the early development of in vitro produced (IVP) embryos. However, manually annotating developmental events, and more specifically cell divisions, is time-consuming for a biologist and cannot scale up for practical applications. We aim to automatically classify the cell stages of embryos from 2D time-lapse microscopy videos with a deep learning approach. We focus on the analysis of bovine embryonic development using video microscopy, as we are primarily interested in the application of cattle breeding, and we have created a Bovine Embryos Cell Stages (ECS) dataset. The challenges are three-fold: (1) low-quality images and bovine dark cells that make the identification of cell stages difficult, (2) class ambiguity at the boundaries of developmental stages, and (3) imbalanced data distribution. To address these challenges, we introduce CLEmbryo, a novel method that leverages supervised contrastive learning combined with focal loss for training, and the lightweight 3D neural network CSN-50 as an encoder. We also show that our method generalizes well. CLEmbryo outperforms state-of-the-art methods on both our Bovine ECS dataset and the publicly available NYU Mouse Embryos dataset.
视频显微镜结合机器学习为研究体外生产(IVP)胚胎的早期发育提供了一种前景广阔的方法。然而,生物学家手动注释发育事件,尤其是细胞分裂,既耗时又无法规模化应用于实际应用。我们的目标是使用深度学习的方法自动对胚胎细胞阶段进行分类,分析来自二维延时显微镜视频的资料。我们专注于使用视频显微镜分析牛胚胎的发育,因为我们主要对牛育种的应用感兴趣,并且我们已经创建了牛胚胎细胞阶段(ECS)数据集。面临的挑战主要有三个:(1)图像质量低下和牛暗细胞使得细胞阶段的识别变得困难;(2)发育阶段边界的类别模糊性;(3)数据分布不平衡。为了应对这些挑战,我们引入了CLEmbryo这一新方法,它利用有监督对比学习结合焦点损失进行训练,并使用轻量级三维神经网络CSN-50作为编码器。我们还展示了我们的方法具有良好的泛化性。无论是在我们的牛ECS数据集还是在公开可用的NYU小鼠胚胎数据集上,CLEmbryo都优于最新方法。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
结合视频显微镜与机器学习,为体外培养胚胎的早期发育研究提供有前途的方法。手动标注发育事件(特别是细胞分裂)耗时耗力,无法规模化应用。本研究旨在通过深度学习自动分类胚胎细胞阶段。研究焦点是牛胚胎发育的视频显微镜分析,并创建了牛胚胎细胞阶段(ECS)数据集。面临图像质量低、细胞暗化识别难、发育阶段边界类别模糊和数据分布不均等挑战。本研究提出CLEmbryo新方法,采用有监督对比学习结合焦点损失进行训练,并使用轻量级3D神经网络CSN-50作为编码器。结果表明,该方法在牛ECS数据集和公开可用的纽约大学小鼠胚胎数据集上的表现均优于现有方法。
Key Takeaways
- 结合视频显微镜与机器学习,对体外培养胚胎的早期发育进行研究,自动分类胚胎细胞阶段成为研究重点。
- 研究中面临图像质量低、细胞暗化识别难、发育阶段边界类别模糊和数据分布不均等挑战。
- 引入CLEmbryo新方法,结合有监督对比学习与焦点损失进行训练,并使用轻量级3D神经网络CSN-50作为编码器。
- 方法在牛胚胎细胞阶段(ECS)数据集和纽约大学小鼠胚胎数据集上的表现均优于现有技术。
点此查看论文截图

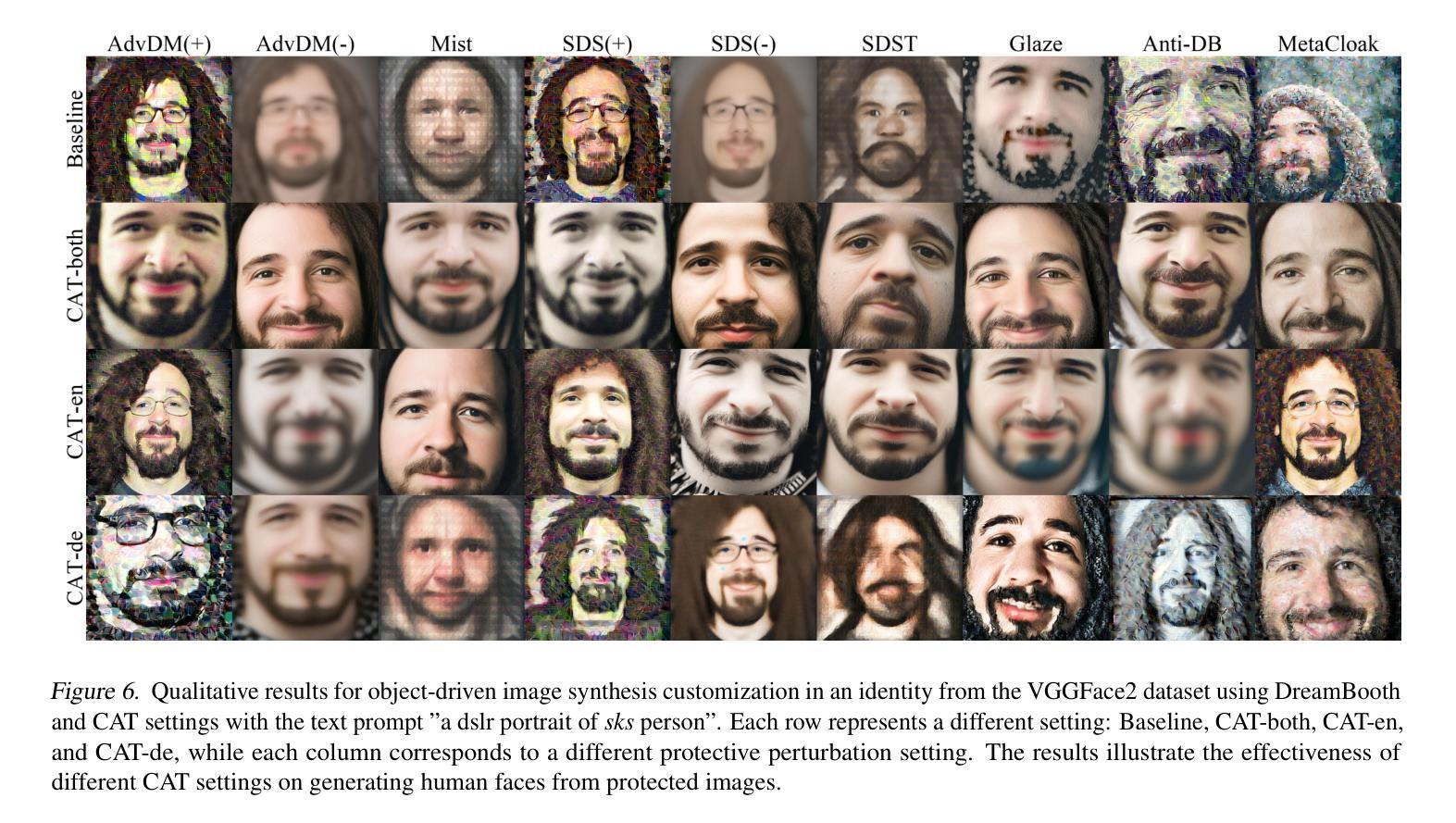
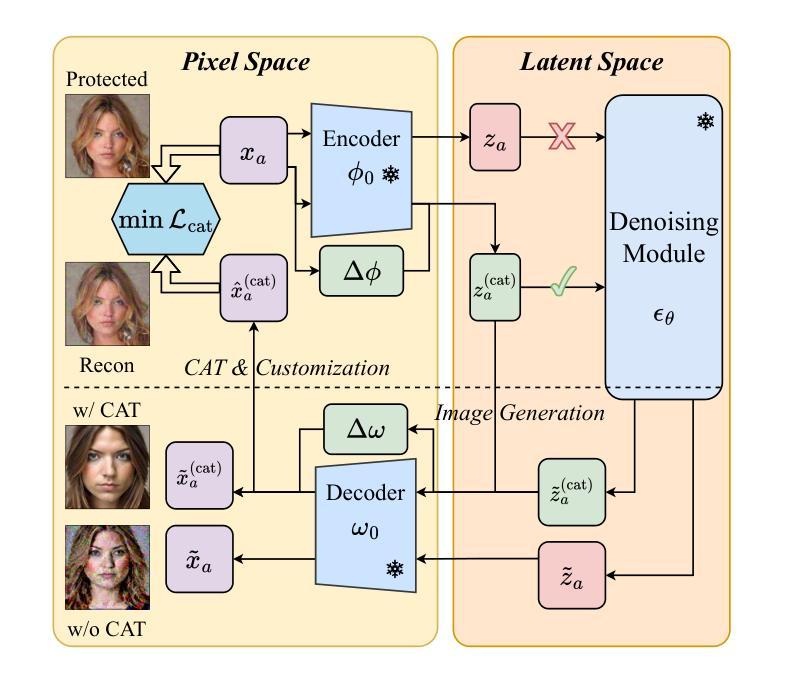
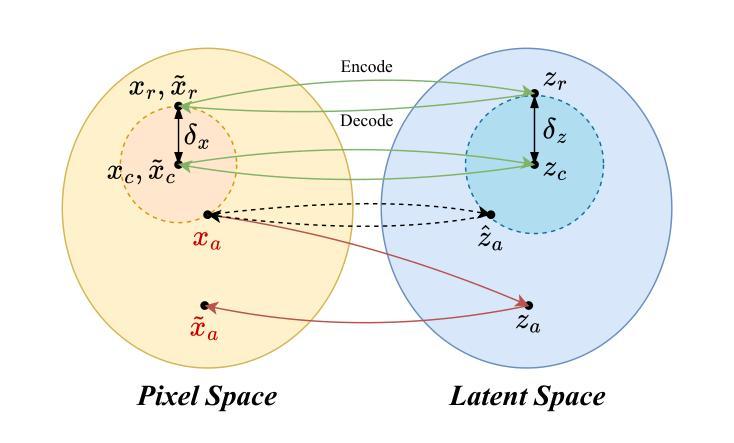
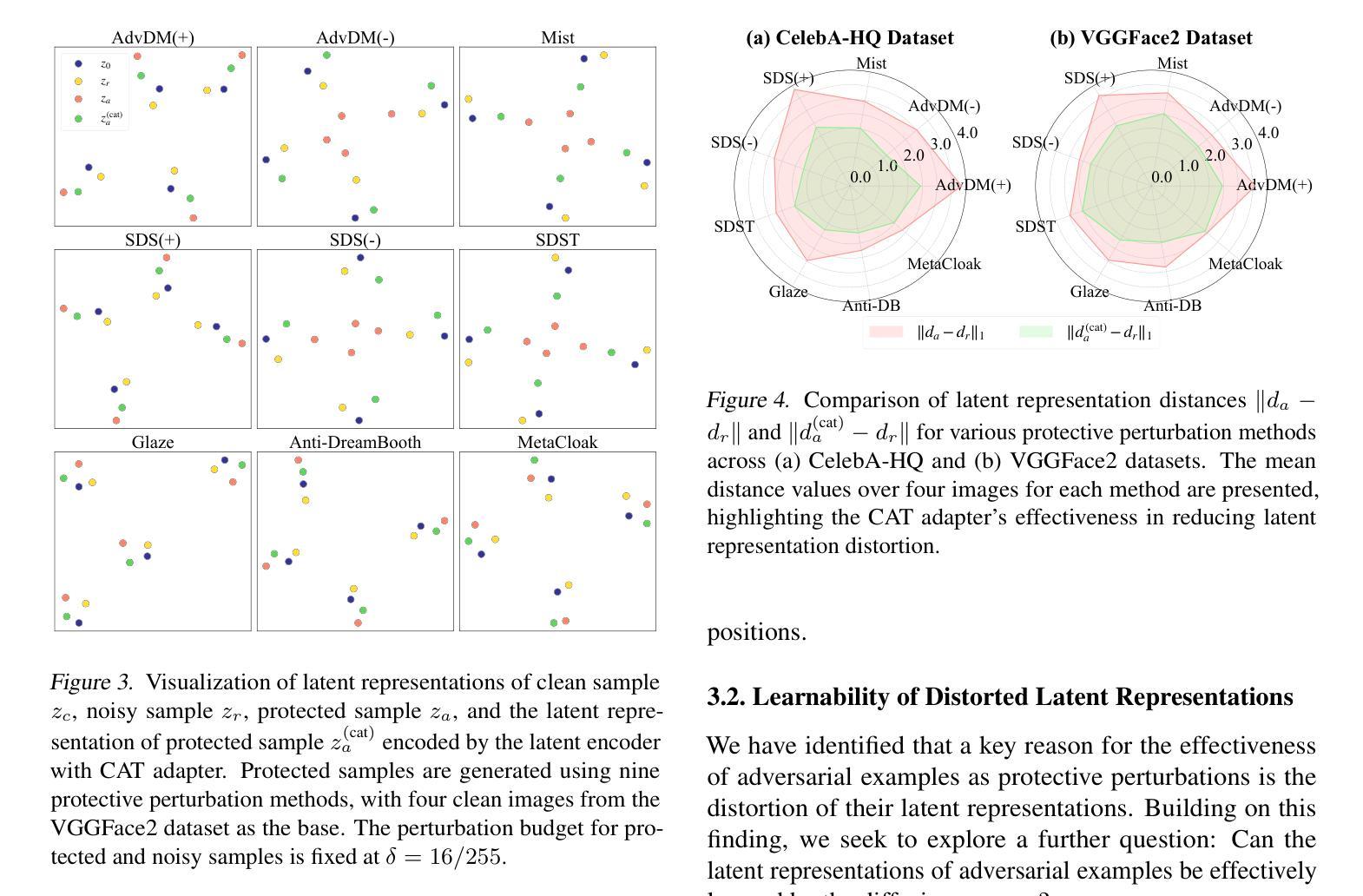
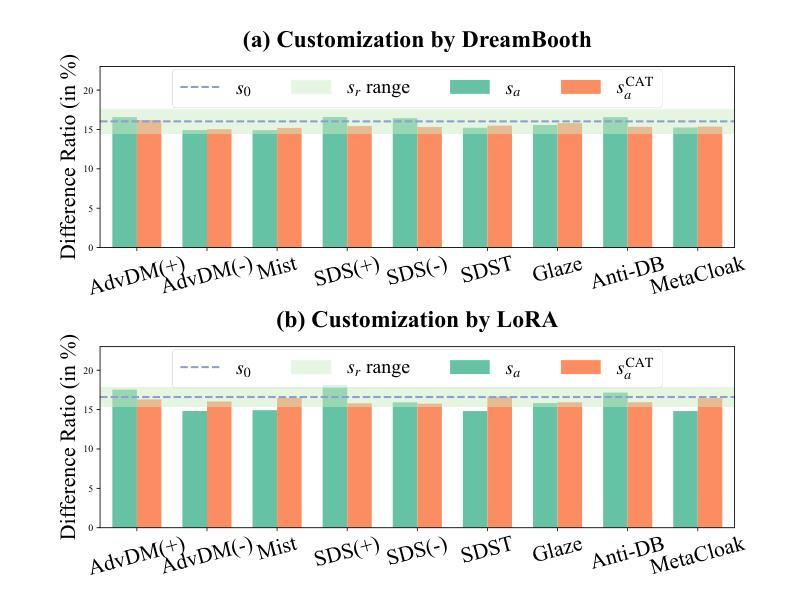
CAT: Contrastive Adversarial Training for Evaluating the Robustness of Protective Perturbations in Latent Diffusion Models
Authors:Sen Peng, Mingyue Wang, Jianfei He, Jijia Yang, Xiaohua Jia
Latent diffusion models have recently demonstrated superior capabilities in many downstream image synthesis tasks. However, customization of latent diffusion models using unauthorized data can severely compromise the privacy and intellectual property rights of data owners. Adversarial examples as protective perturbations have been developed to defend against unauthorized data usage by introducing imperceptible noise to customization samples, preventing diffusion models from effectively learning them. In this paper, we first reveal that the primary reason adversarial examples are effective as protective perturbations in latent diffusion models is the distortion of their latent representations, as demonstrated through qualitative and quantitative experiments. We then propose the Contrastive Adversarial Training (CAT) utilizing adapters as an adaptive attack against these protection methods, highlighting their lack of robustness. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our CAT method significantly reduces the effectiveness of protective perturbations in customization configurations, urging the community to reconsider and enhance the robustness of existing protective perturbation methods. Code is available at \hyperlink{here}{https://github.com/senp98/CAT}.
潜在扩散模型已在许多下游图像合成任务中展现出卓越的能力。然而,使用未经授权的数据对潜在扩散模型进行定制会严重损害数据所有者的隐私和知识产权。对抗性样本作为保护扰动得到了开发,通过向定制样本中添加几乎不可察觉的噪声来防止扩散模型有效地学习,从而防止未经授权的数据使用。在本文中,我们首先揭示了对抗样本作为潜在扩散模型中的保护扰动的首要原因是其潜在表示的失真,这已通过定性和定量实验得到证明。然后,我们提出利用适配器作为对抗性训练的对比(CAT),以有针对性的攻击这些保护方法,突出其缺乏稳健性。大量实验表明,我们的CAT方法显著降低了保护扰动在定制配置中的有效性,敦促社区重新考虑并增强现有保护扰动方法的稳健性。代码可在https://github.com/senp98/CAT处获取。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
文本介绍了潜在扩散模型在图像合成任务中的优势,但同时也存在使用未经授权数据的风险。为了保护数据隐私和知识产权,研究人员提出了对抗性示例作为保护扰动,通过引入不可察觉的噪声来防止扩散模型有效地学习。本文通过实验揭示了对抗性示例作为潜在扩散模型中的保护扰动的有效性原因,并提出了对比对抗训练(CAT)方法,利用适配器作为对这些保护方法的自适应攻击,凸显其缺乏稳健性。实验证明,CAT方法显著降低了保护扰动在定制配置中的有效性。
Key Takeaways
- 潜在扩散模型在图像合成任务中表现出卓越的能力,但使用未经授权数据存在风险。
- 对抗性示例被用作保护扰动,通过引入不可察觉的噪声防止扩散模型学习。
- 对抗性示例之所以有效,是因为它们能够扭曲潜在扩散模型的潜在表示。
- 提出了对比对抗训练(CAT)方法,利用适配器作为自适应攻击,针对保护扰动方法。
- 实验表明,CAT方法显著降低了保护扰动在定制配置中的有效性。
- 现有保护扰动方法的稳健性需要重新考虑和增强。
点此查看论文截图