⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-02-13 更新
Amnesia as a Catalyst for Enhancing Black Box Pixel Attacks in Image Classification and Object Detection
Authors:Dongsu Song, Daehwa Ko, Jay Hoon Jung
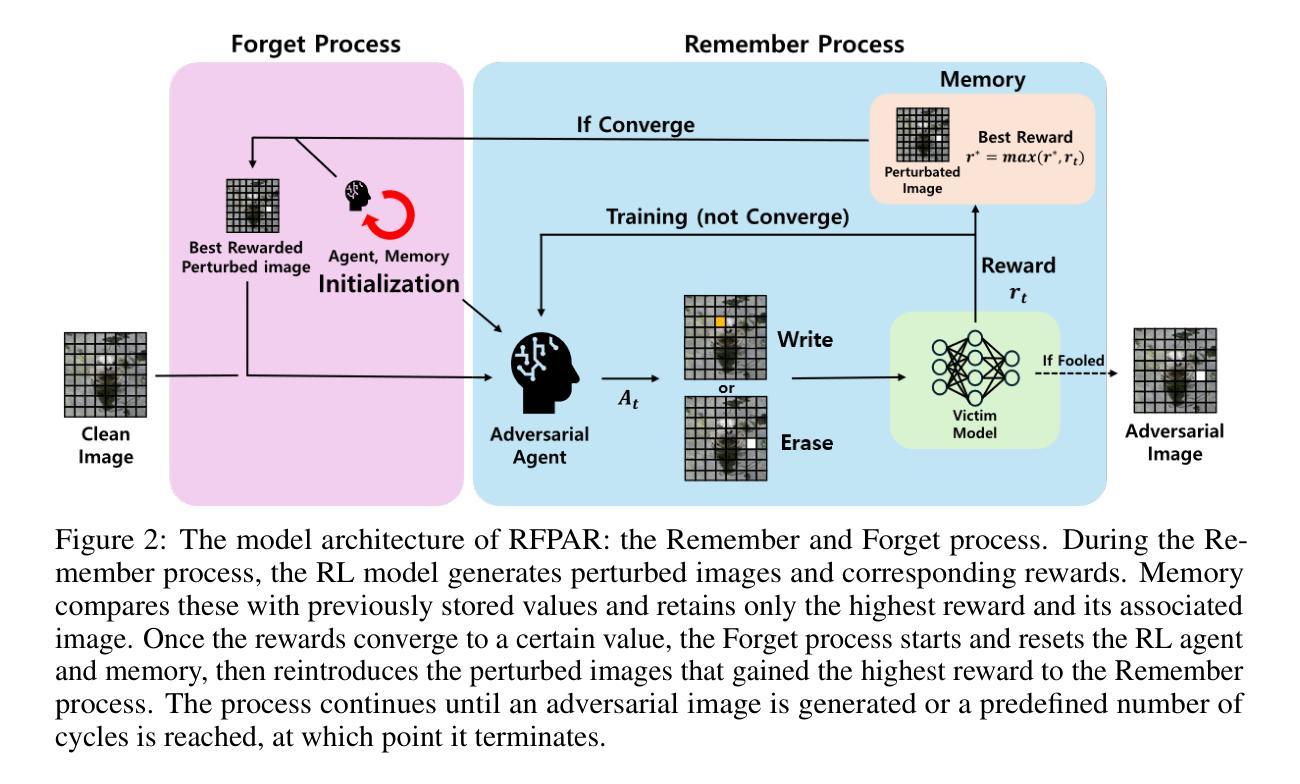
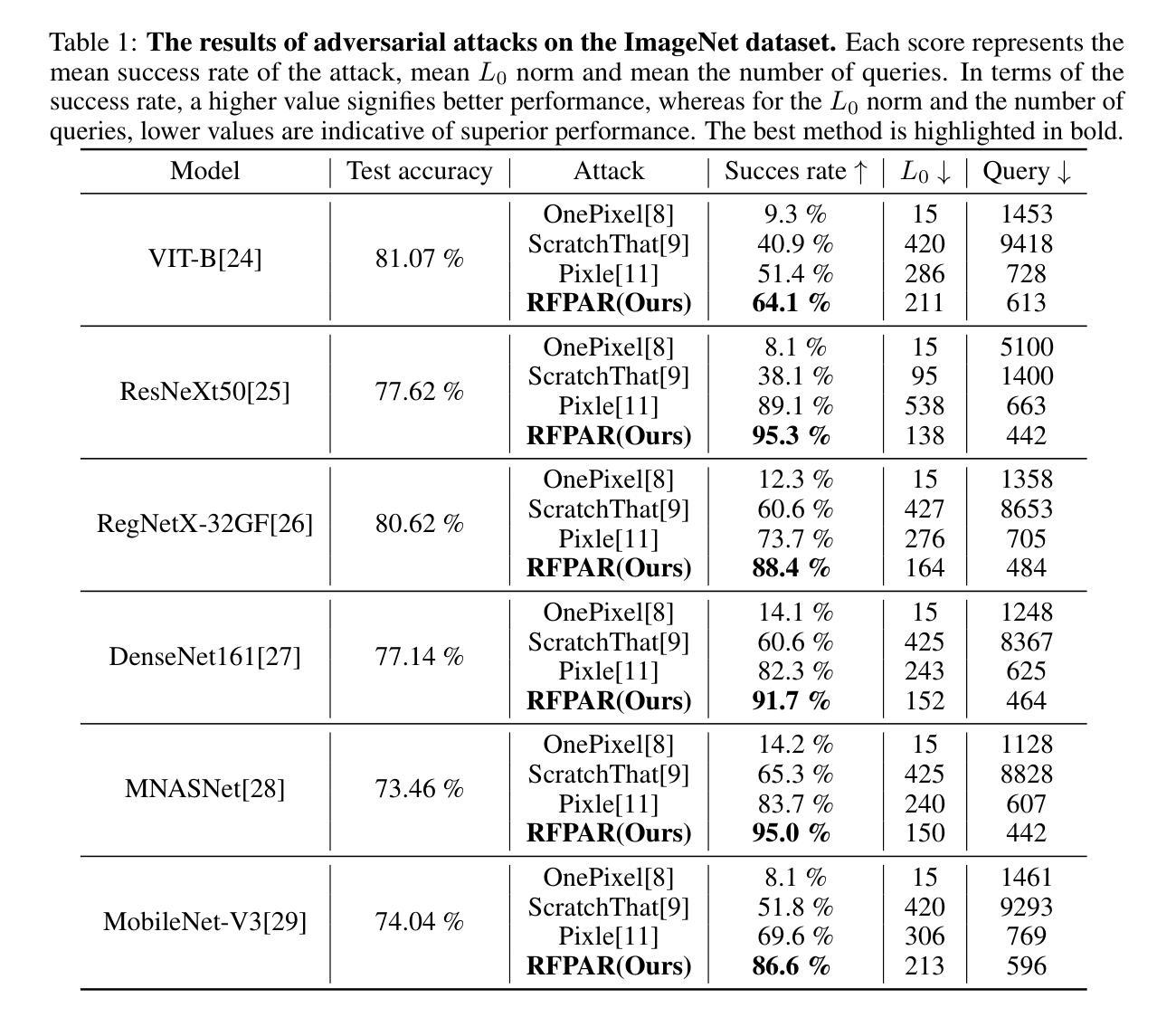
It is well known that query-based attacks tend to have relatively higher success rates in adversarial black-box attacks. While research on black-box attacks is actively being conducted, relatively few studies have focused on pixel attacks that target only a limited number of pixels. In image classification, query-based pixel attacks often rely on patches, which heavily depend on randomness and neglect the fact that scattered pixels are more suitable for adversarial attacks. Moreover, to the best of our knowledge, query-based pixel attacks have not been explored in the field of object detection. To address these issues, we propose a novel pixel-based black-box attack called Remember and Forget Pixel Attack using Reinforcement Learning(RFPAR), consisting of two main components: the Remember and Forget processes. RFPAR mitigates randomness and avoids patch dependency by leveraging rewards generated through a one-step RL algorithm to perturb pixels. RFPAR effectively creates perturbed images that minimize the confidence scores while adhering to limited pixel constraints. Furthermore, we advance our proposed attack beyond image classification to object detection, where RFPAR reduces the confidence scores of detected objects to avoid detection. Experiments on the ImageNet-1K dataset for classification show that RFPAR outperformed state-of-the-art query-based pixel attacks. For object detection, using the MSCOCO dataset with YOLOv8 and DDQ, RFPAR demonstrates comparable mAP reduction to state-of-the-art query-based attack while requiring fewer query. Further experiments on the Argoverse dataset using YOLOv8 confirm that RFPAR effectively removed objects on a larger scale dataset. Our code is available at https://github.com/KAU-QuantumAILab/RFPAR.
已知基于查询的攻击在敌对黑箱攻击中具有相对较高的成功率。尽管关于黑箱攻击的研究正在积极进行,但针对仅针对有限像素目标的像素攻击的研究相对较少。在图像分类中,基于查询的像素攻击通常依赖于补丁,这很大程度上依赖于随机性,并忽略了分散的像素更适合于对抗性攻击的事实。而且,据我们所知,基于查询的像素攻击在目标检测领域尚未得到探索。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了一种使用强化学习(RL)的基于像素的黑箱攻击方法,称为“记住和遗忘像素攻击”(RFPAR),它包含两个主要过程:记住和遗忘。RFPAR通过利用一步RL算法生成的奖励来扰动像素,从而减轻了随机性并避免了补丁依赖。RFPAR有效地创建了扰动图像,这些图像在遵循有限像素约束的同时最小化了置信度分数。此外,我们将提出的攻击推进到了目标检测领域,RFPAR通过降低检测对象的置信度分数来避免检测。在ImageNet-1K数据集上的分类实验表明,RFPAR优于最先进的基于查询的像素攻击。对于目标检测,使用MSCOCO数据集与YOLOv8和DDQ的RFPAR实现了与最先进的基于查询的攻击相当的mAP减少,同时需要较少的查询次数。使用YOLOv8进行的Argoverse数据集上的进一步实验证实,RFPAR在大规模数据集上有效地移除了对象。我们的代码可在https://github.com/KAU-QuantumAILab/RFPAR找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted as a poster at NeurIPS 2024
Summary
该文本提出了一种名为RFPAR的基于像素的黑盒攻击方法,用于图像分类和对象检测。RFPAR使用强化学习来记住并忘记像素攻击,通过生成奖励来减少随机性并避免补丁依赖。它在ImageNet-1K数据集上的分类表现优于其他基于查询的像素攻击,并在MSCOCO数据集上使用YOLOv8和DDQ的对象检测中表现出良好的性能。代码已公开在GitHub上。
Key Takeaways
- RFPAR是一种基于像素的黑盒攻击方法,旨在解决针对图像分类和对象检测的查询基于像素攻击的问题。
- RFPAR使用强化学习来记住和忘记像素攻击,通过生成奖励来减少随机性和避免补丁依赖。
- RFPAR可以在有限的像素约束内创建扰动图像,降低置信度分数。
- 在ImageNet-1K数据集上的分类实验表明,RFPAR的性能优于其他先进的查询基于像素的攻击。
- 在使用YOLOv8和DDQ的MSCOCO数据集上的对象检测实验中,RFPAR表现出与最先进的查询攻击相当的mAP减少,但需要较少的查询。
- Argoverse数据集上的实验进一步证明了RFPAR在大规模数据集上移除对象的有效性。
点此查看论文截图


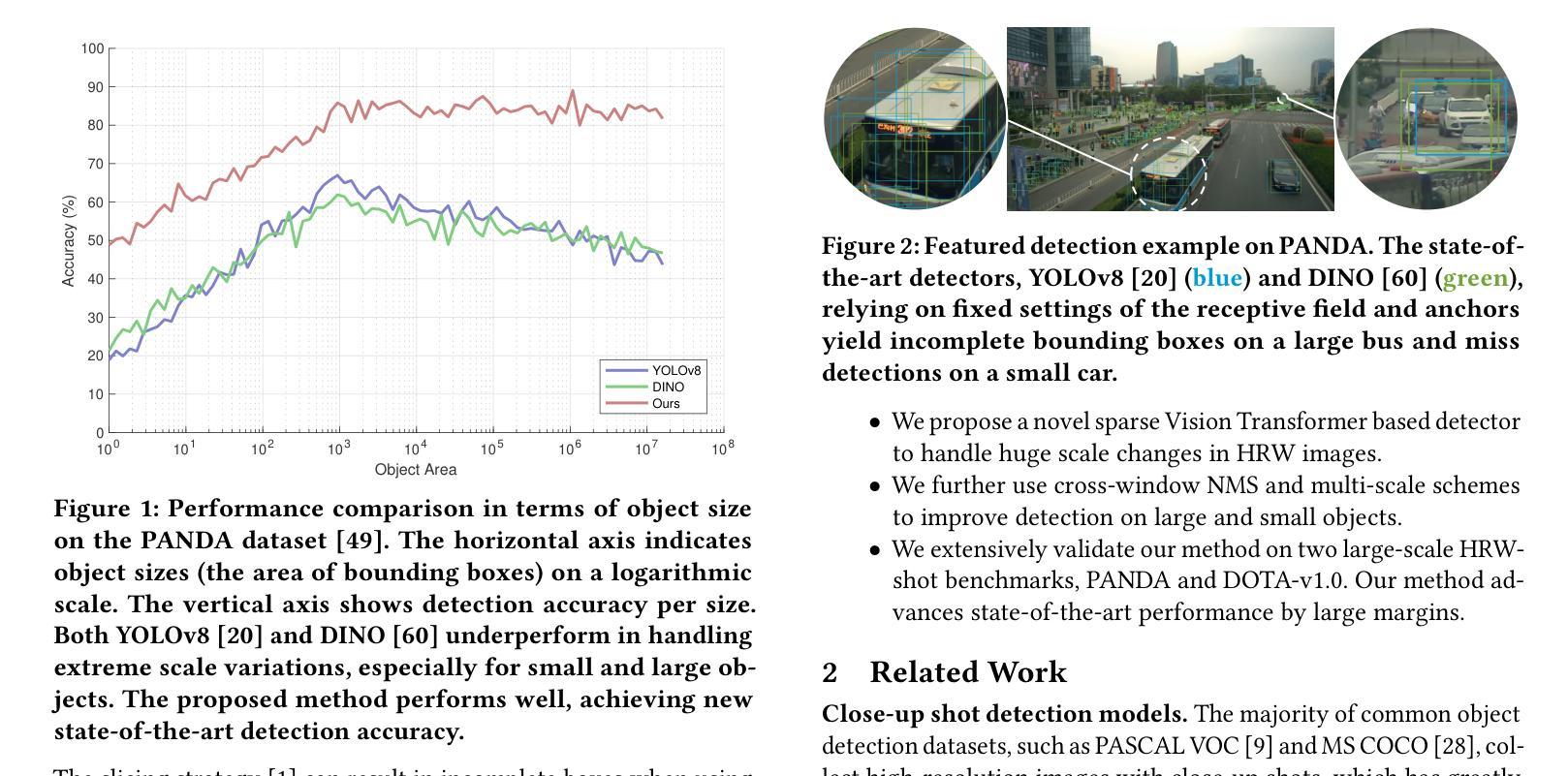
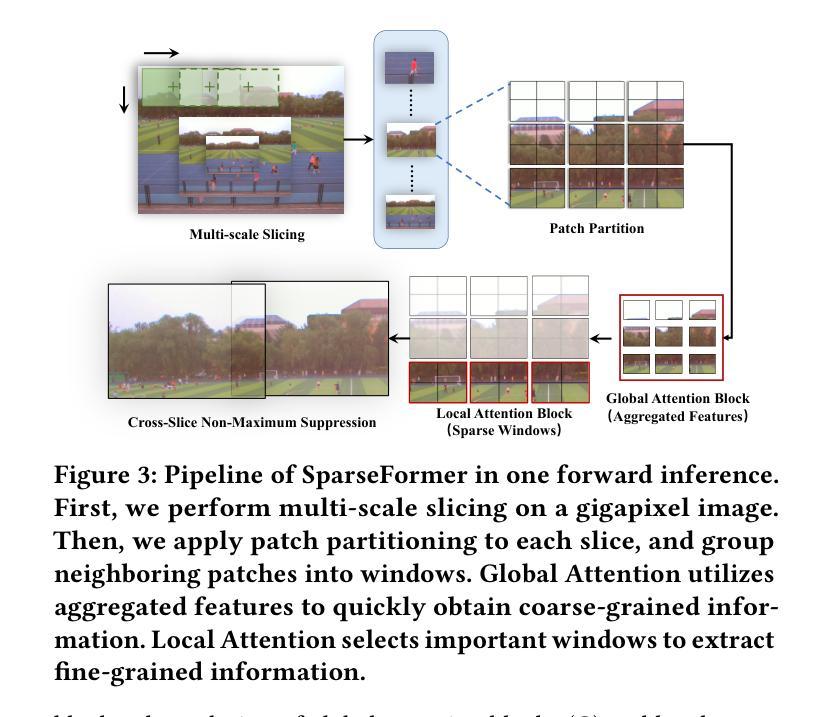
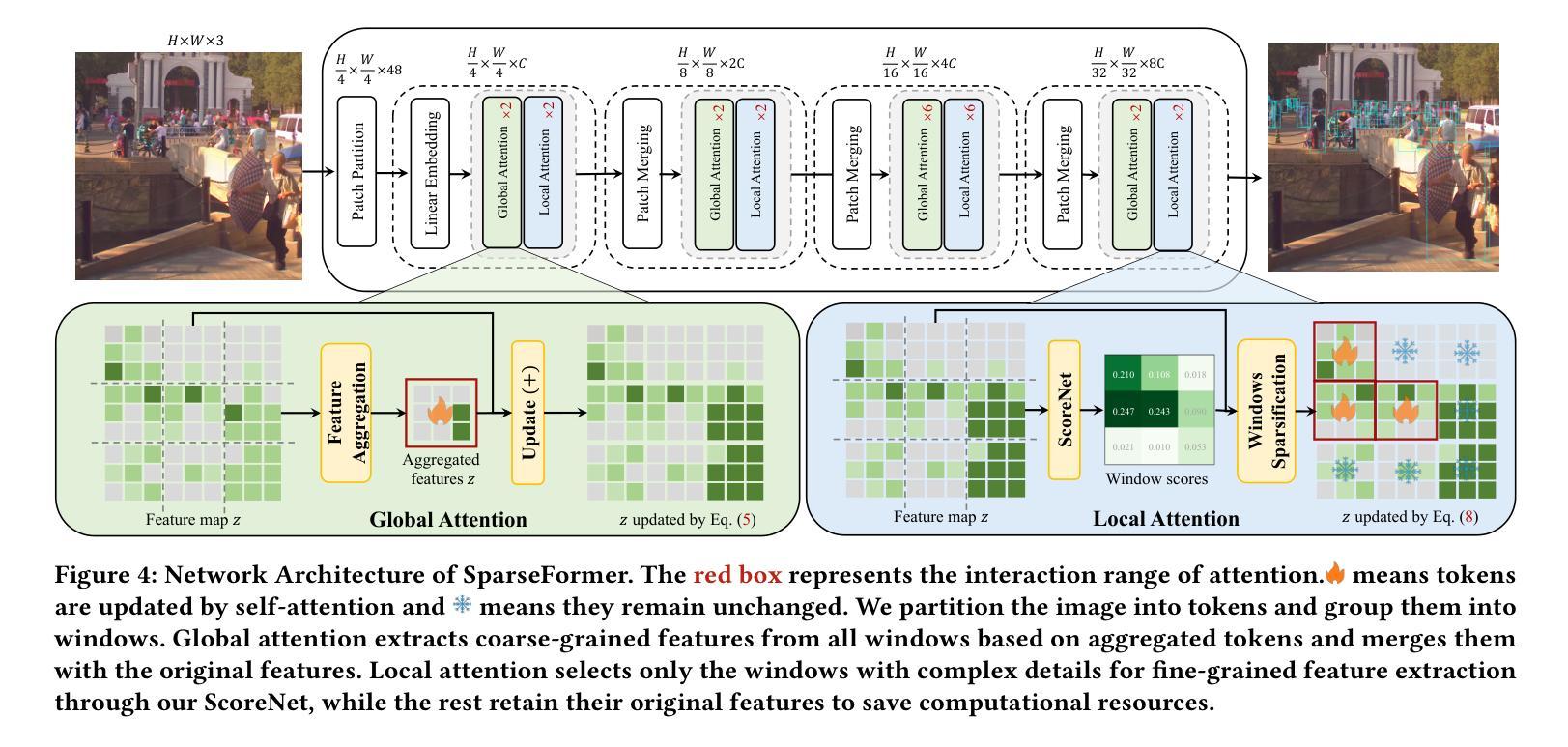
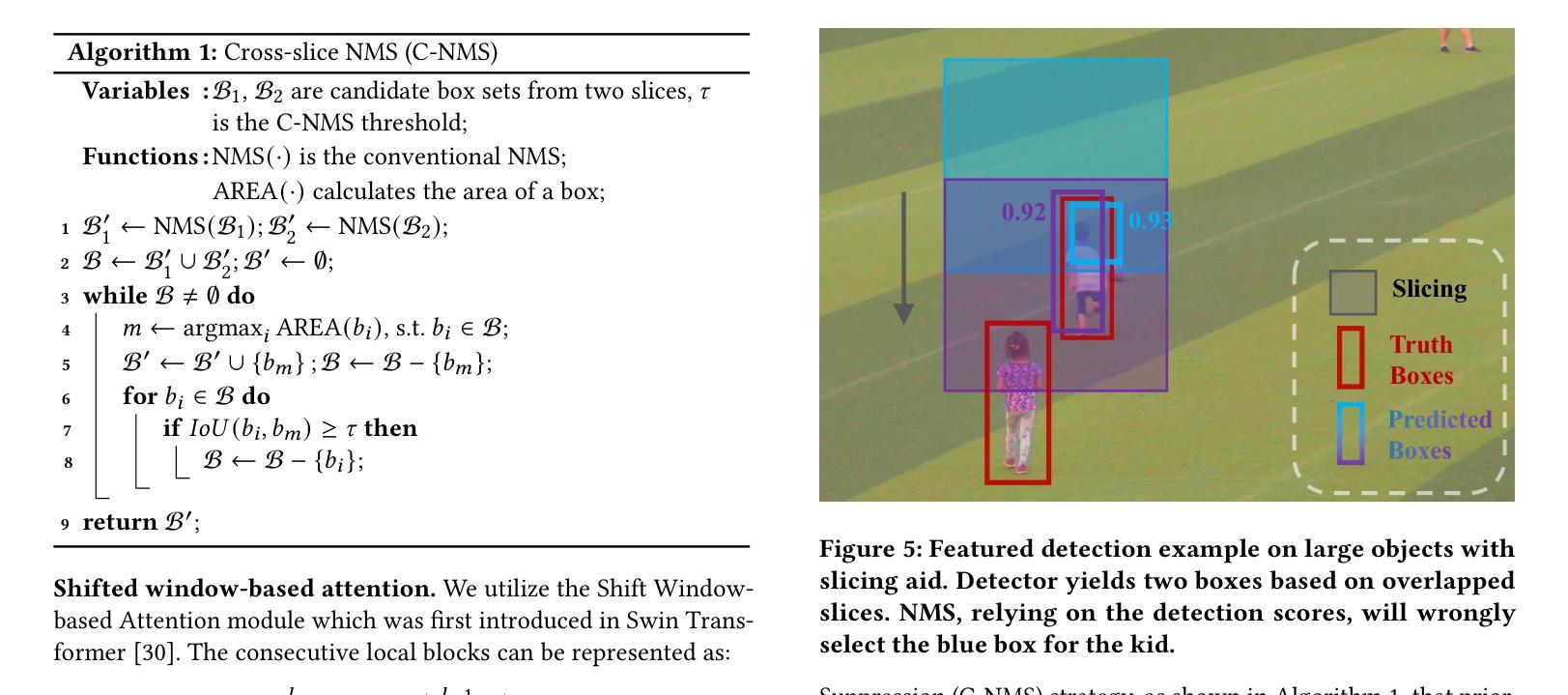
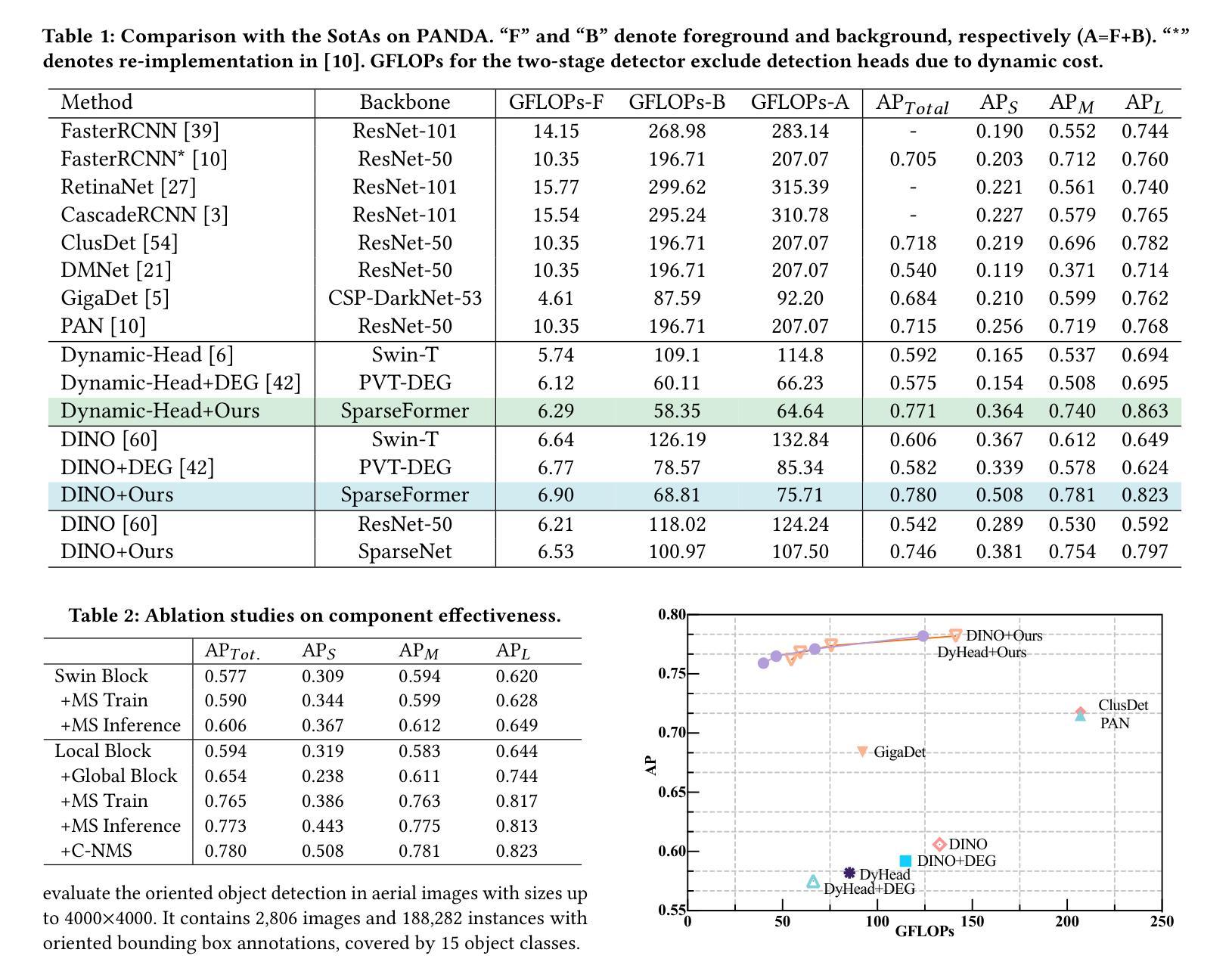
SparseFormer: Detecting Objects in HRW Shots via Sparse Vision Transformer
Authors:Wenxi Li, Yuchen Guo, Jilai Zheng, Haozhe Lin, Chao Ma, Lu Fang, Xiaokang Yang
Recent years have seen an increase in the use of gigapixel-level image and video capture systems and benchmarks with high-resolution wide (HRW) shots. However, unlike close-up shots in the MS COCO dataset, the higher resolution and wider field of view raise unique challenges, such as extreme sparsity and huge scale changes, causing existing close-up detectors inaccuracy and inefficiency. In this paper, we present a novel model-agnostic sparse vision transformer, dubbed SparseFormer, to bridge the gap of object detection between close-up and HRW shots. The proposed SparseFormer selectively uses attentive tokens to scrutinize the sparsely distributed windows that may contain objects. In this way, it can jointly explore global and local attention by fusing coarse- and fine-grained features to handle huge scale changes. SparseFormer also benefits from a novel Cross-slice non-maximum suppression (C-NMS) algorithm to precisely localize objects from noisy windows and a simple yet effective multi-scale strategy to improve accuracy. Extensive experiments on two HRW benchmarks, PANDA and DOTA-v1.0, demonstrate that the proposed SparseFormer significantly improves detection accuracy (up to 5.8%) and speed (up to 3x) over the state-of-the-art approaches.
近年来,使用千兆像素级别的图像和视频捕获系统以及高分辨率宽视角(HRW)镜头基准测试的情况日益增多。然而,与MS COCO数据集中的特写镜头不同,更高的分辨率和更宽的视野带来了独特的挑战,例如极端稀疏和巨大尺度变化,导致现有特写检测器的不准确和效率低下。在本文中,我们提出了一种新型模型无关的稀疏视觉变压器,称为SparseFormer,以弥补特写镜头和高分辨率宽视角镜头之间物体检测的差距。提出的SparseFormer有选择地使用注意力标记来仔细审查可能包含物体的稀疏分布窗口。通过这种方式,它可以通过融合粗粒度和细粒度特征来共同探索全局和局部注意力,以处理巨大的尺度变化。SparseFormer还受益于一种新的跨切片非最大抑制(C-NMS)算法,可从嘈杂的窗口中精确定位物体,以及一种简单有效的多尺度策略,以提高准确性。在PANDA和DOTA-v1.0两个高分辨率宽视角基准测试的大量实验表明,与传统的先进方法相比,所提出的SparseFormer在检测精度上提高了高达5.8%,速度提高了高达三倍。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF This paper is accepted to ACM MM 2024
Summary:针对高分辨率宽视角图像和视频捕获系统中存在的极端稀疏性和巨大尺度变化等挑战,本文提出了一种新型模型无关的稀疏视觉转换器SparseFormer,用于在近距离拍摄和高分辨率宽视角拍摄之间建立目标检测桥梁。SparseFormer能够结合全局和局部注意力,处理大规模变化问题。同时采用跨切片非最大抑制算法和多尺度策略,提高了目标定位和检测精度。在PANDA和DOTA-v1.0两个高分辨率宽视角数据集上的实验表明,SparseFormer在检测精度和速度上均优于现有技术。
Key Takeaways:
- SparseFormer针对高分辨率宽视角图像的目标检测提出了新颖的解决方案。
- SparseFormer利用选择性注意力令牌处理稀疏分布窗口中的目标,联合探索全局和局部注意力。
- SparseFormer利用粗粒度和细粒度特征的融合来处理大规模变化问题。
- SparseFormer采用跨切片非最大抑制算法和多尺度策略提高目标定位精度和检测性能。
- SparseFormer在PANDA和DOTA-v1.0数据集上的实验结果表明其显著提高了检测精度和速度。
- SparseFormer对现有的目标检测器进行了改进,使其在高分辨率宽视角图像上更准确、更高效。
点此查看论文截图

Globality Strikes Back: Rethinking the Global Knowledge of CLIP in Training-Free Open-Vocabulary Semantic Segmentation
Authors:Jingyun Wang, Cilin Yan, Guoliang Kang
Recent works modify CLIP to perform open-vocabulary semantic segmentation in a training-free manner (TF-OVSS). In CLIP, patch-wise image representations mainly encode the homogeneous image-level properties and thus are not discriminative enough, hindering its application to the dense prediction task. Previous works make image features more distinct across patches, through making each patch mainly attend to itself or the neighboring patches within a narrow local window. However, with their modifications, the ability of CLIP to aggregate global context information, which is known to be useful for distinguishing confusing categories, is largely weakened. In this paper, we propose a new method named GCLIP, which mines the beneficial global knowledge of CLIP to facilitate the TF-OVSS task. Firstly, we aim to equip the last-block attention with image-level properties while not introducing homogeneous attention patterns across patches. In GCLIP, we merge the attention from the global token emerging blocks with the Query-Query attention to realize this goal. Secondly, we aim to make the Value embeddings of the last-block attention module more distinct and semantically correlated. To realize this, we design a novel channel suppression strategy. As the representation of each patch is finally determined by the attention weights and the Value embeddings, our method can generate more discriminative patch-level image features while absorbing global context information. Extensive experiments on five standard benchmarks demonstrate that our method consistently outperforms previous state-of-the-arts.
近期的研究对CLIP进行了修改,以无训练的方式执行开放词汇语义分割(TF-OVSS)。在CLIP中,图像分块的表示主要编码了图像级别的同质属性,因此区分度不足,阻碍了其在密集预测任务中的应用。早期的研究使图像特征在不同的分块之间更加不同,方法是通过使每个分块主要关注自身或狭窄局部窗口内的相邻分块。然而,这些修改在很大程度上削弱了CLIP聚合全局上下文信息的能力,这是区分混淆类别所必需的。在本文中,我们提出了一种名为GCLIP的新方法,它挖掘CLIP的有益全局知识以促进TF-OVSS任务。首先,我们的目标是使最后一层注意力具备图像级别的属性,同时不在分块之间引入同质注意力模式。在GCLIP中,我们将来自全局令牌生成块的注意力与Query-Query注意力合并来实现这一目标。其次,我们旨在使最后一层注意力模块的Value嵌入更加不同且语义相关。为此,我们设计了一种新型通道抑制策略。由于每个分块的表示最终由注意力权重和Value嵌入决定,因此我们的方法可以在吸收全局上下文信息的同时生成更具区分性的分块级图像特征。在五个标准基准测试上的广泛实验表明,我们的方法始终优于先前的技术水平。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Under review
Summary
基于CLIP模型,该文提出了一种新的方法GCLIP,旨在解决图像语义分割中面临的问题。通过挖掘CLIP的全局知识来提升开放词汇表下的无训练语义分割(TF-OVSS)性能。GCLIP通过合并全局令牌突出块的注意力与Query-Query注意力,使最后一个注意力块的注意力具有图像级别属性同时不引入同质化的注意力模式。此外,还设计了一种新的通道抑制策略使最后一个注意力块的Value嵌入更加独特和语义相关。实验证明,该方法在五个标准数据集上均优于先前的方法。
Key Takeaways
- 文章基于CLIP模型进行改进,提出GCLIP方法,旨在解决图像语义分割中的难题。
- GCLIP通过合并全局知识与Query-Query注意力来提升性能,使最后一个注意力块具有图像级别属性。
- 设计了新的通道抑制策略,使Value嵌入更加独特和语义相关。
- GCLIP在五个标准数据集上的表现均优于先前的方法。
- 原方法主要关注局部窗口内的特征,而GCLIP则注重全局上下文信息的利用。
- GCLIP能够生成更具区分性的补丁级图像特征。
点此查看论文截图



Enhancing Ground-to-Aerial Image Matching for Visual Misinformation Detection Using Semantic Segmentation
Authors:Emanuele Mule, Matteo Pannacci, Ali Ghasemi Goudarzi, Francesco Pro, Lorenzo Papa, Luca Maiano, Irene Amerini
The recent advancements in generative AI techniques, which have significantly increased the online dissemination of altered images and videos, have raised serious concerns about the credibility of digital media available on the Internet and distributed through information channels and social networks. This issue particularly affects domains that rely heavily on trustworthy data, such as journalism, forensic analysis, and Earth observation. To address these concerns, the ability to geolocate a non-geo-tagged ground-view image without external information, such as GPS coordinates, has become increasingly critical. This study tackles the challenge of linking a ground-view image, potentially exhibiting varying fields of view (FoV), to its corresponding satellite image without the aid of GPS data. To achieve this, we propose a novel four-stream Siamese-like architecture, the Quadruple Semantic Align Net (SAN-QUAD), which extends previous state-of-the-art (SOTA) approaches by leveraging semantic segmentation applied to both ground and satellite imagery. Experimental results on a subset of the CVUSA dataset demonstrate significant improvements of up to 9.8% over prior methods across various FoV settings.
最近生成式人工智能技术的进展大大增加了网络上的篡改图像和视频的传播,引发了人们对互联网上可通过信息渠道和社交网络获得的数字媒体可信度的严重关注。这一问题尤其影响到那些严重依赖于可信数据的领域,如新闻业、法医学分析和地球观测。为了应对这些担忧,在不依赖外部信息(如GPS坐标)的情况下对未带地理标签的地面视图图像进行地理定位的能力变得至关重要。本研究解决了在没有GPS数据辅助的情况下,将可能展现不同视野范围的地面视图图像与其对应的卫星图像相关联的挑战。为了实现这一点,我们提出了一种新型的四流Siamese风格架构——Quadruple Semantic Align Net(SAN-QUAD),它通过应用于地面和卫星图像的语义分割来扩展之前最先进的(SOTA)方法。在CVUSA数据集的一个子集上的实验结果表明,在各种视野设置下,相较于之前的方法,最多可提高9.8%。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 9 pages, 4 figures
Summary
近期生成式AI技术的进展导致网络上传播大量修改后的图像和视频,引发对互联网上数字媒体可信度严重关切的问题,影响了依赖于可信数据的领域,如新闻业、司法分析和地球观测等。为解决这个问题,一种新技术推出能够不需依赖GPS信息给非地理标签地面视图图像进行地理定位。该研究提出了一种新型的四流Siamese架构——Quadruple Semantic Align Net (SAN-QUAD),它通过语义分割应用在地面和卫星图像上,在CVUSA数据集子集上的实验结果表明,在各种视野设置下,与之前的方法相比,其改进幅度高达9.8%。
Key Takeaways
- 生成式AI技术的进展导致数字媒体的可信度问题。
- 对非地理标签地面视图图像进行地理定位的需求日益迫切。
- 提出了一种新型的四流Siamese架构——Quadruple Semantic Align Net (SAN-QUAD)。
- SAN-QUAD利用语义分割应用在地面和卫星图像上。
- 在CVUSA数据集子集上的实验结果表明,SAN-QUAD相较于之前的方法有显著提升。
- 不同视野设置下,SAN-QUAD的改进幅度高达9.8%。
点此查看论文截图


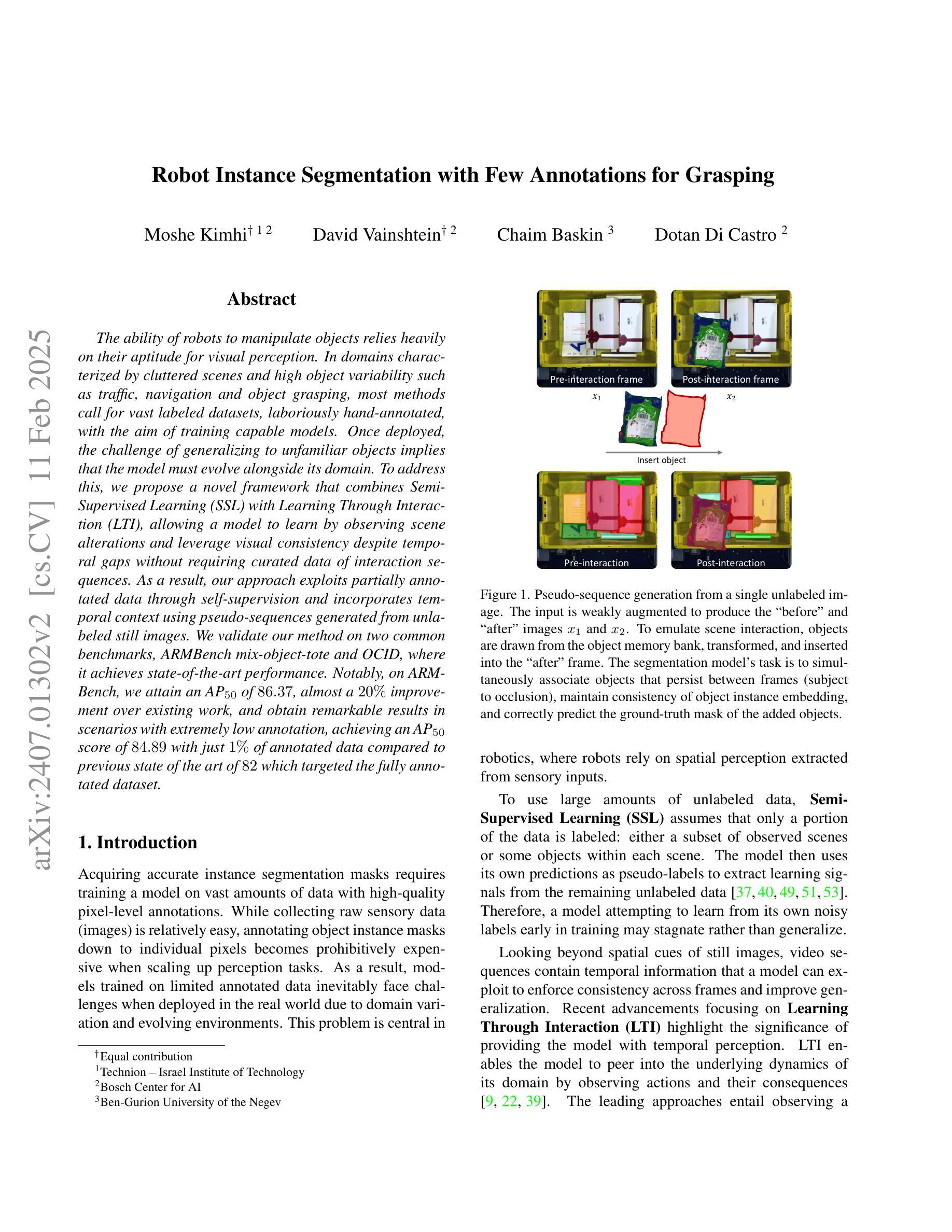
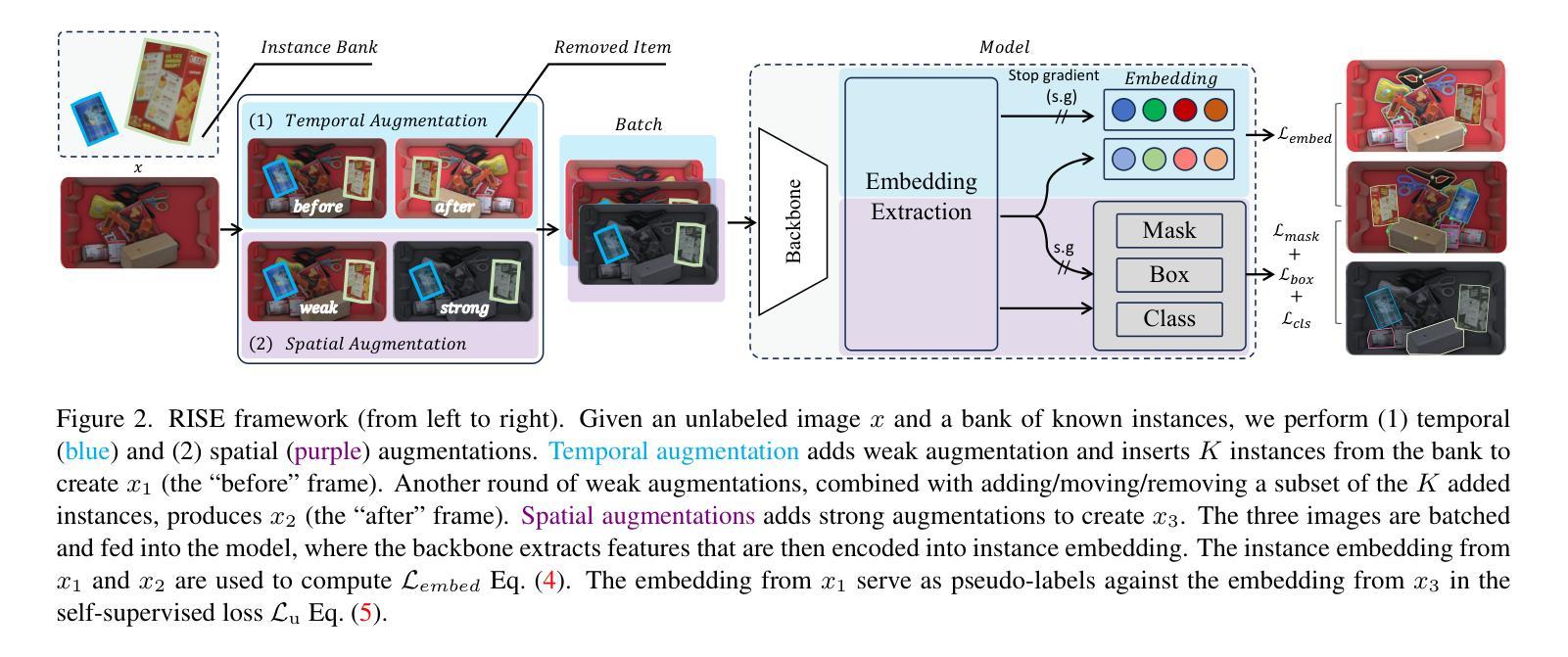
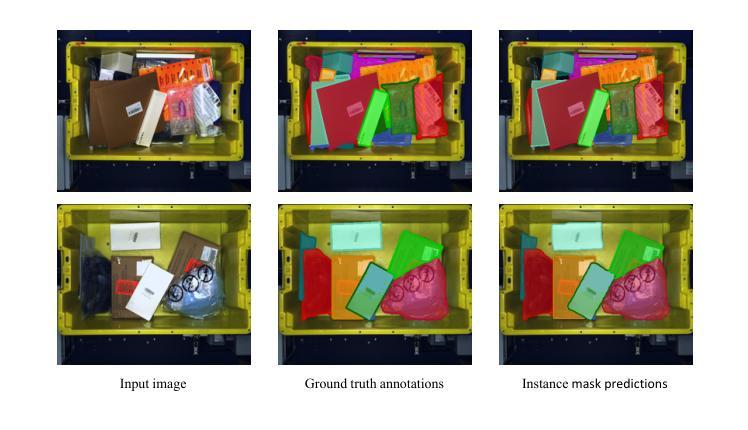
Robot Instance Segmentation with Few Annotations for Grasping
Authors:Moshe Kimhi, David Vainshtein, Chaim Baskin, Dotan Di Castro
The ability of robots to manipulate objects relies heavily on their aptitude for visual perception. In domains characterized by cluttered scenes and high object variability, most methods call for vast labeled datasets, laboriously hand-annotated, with the aim of training capable models. Once deployed, the challenge of generalizing to unfamiliar objects implies that the model must evolve alongside its domain. To address this, we propose a novel framework that combines Semi-Supervised Learning (SSL) with Learning Through Interaction (LTI), allowing a model to learn by observing scene alterations and leverage visual consistency despite temporal gaps without requiring curated data of interaction sequences. As a result, our approach exploits partially annotated data through self-supervision and incorporates temporal context using pseudo-sequences generated from unlabeled still images. We validate our method on two common benchmarks, ARMBench mix-object-tote and OCID, where it achieves state-of-the-art performance. Notably, on ARMBench, we attain an $\text{AP}{50}$ of $86.37$, almost a $20%$ improvement over existing work, and obtain remarkable results in scenarios with extremely low annotation, achieving an $\text{AP}{50}$ score of $84.89$ with just $1 %$ of annotated data compared to $72$ presented in ARMBench on the fully annotated counterpart.
机器人操作物体的能力在很大程度上取决于它们的视觉感知能力。在场景混乱、物体变化性高的领域中,大多数方法都需要大量经手工标注的数据集,旨在训练具备能力的模型。一旦部署,如何推广到陌生物体的挑战意味着模型必须与其领域共同进化。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了一种新的框架,结合了半监督学习(SSL)和通过交互学习(LTI),使模型能够观察场景变化并借助视觉一致性,即使存在时间间隔,也不需要交互序列的定制数据。因此,我们的方法通过自我监督利用部分注释的数据,并使用从无标签静态图像生成的伪序列来融入时间上下文。我们在两个常用基准测试(ARMBench混合对象托架和OCID)上验证了我们的方法,实现了最先进的性能。值得注意的是,在ARMBench上,我们的$\text{AP}{50}$达到86.3fi,较现有工作几乎提高了20%,并且在极低的注释场景中取得了显著的结果,在仅有1%的注释数据的情况下,$\text{AP}{50}$得分达到84.89,而ARMBench在全注释的对应物上的得分为72。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
机器人操控物体的能力依赖于其视觉感知能力。针对杂乱场景和高对象可变性的领域,大多数方法需要大量手工标注的数据集进行模型训练。为解决模型对新物体的泛化挑战,我们提出结合半监督学习和通过交互学习的新框架。模型可通过观察场景变化和利用视觉一致性,在无需交互序列的定制数据情况下进行自我监督学习。我们的方法在ARMBench和OCID两个常用基准测试中实现了最先进的性能,特别是在ARMBench上,我们达到了86.37的AP50得分,较现有工作有近20%的提升。在标注数据极低的情况下,仅使用1%的标注数据便取得了84.89的AP50得分。
Key Takeaways
- 机器人的物体操控能力依赖于其视觉感知能力。
- 在杂乱场景和高对象可变性的领域,机器人需要大规模标注数据集进行模型训练。
- 模型的泛化能力对于处理新物体至关重要。
- 提出结合半监督学习和通过交互学习的新框架,使模型能够通过观察场景变化和利用视觉一致性进行自我监督学习。
- 新框架在ARMBench和OCID基准测试中实现了最先进的性能。
- 在ARMBench测试中,新框架的AP50得分较现有工作有近20%的提升。
点此查看论文截图
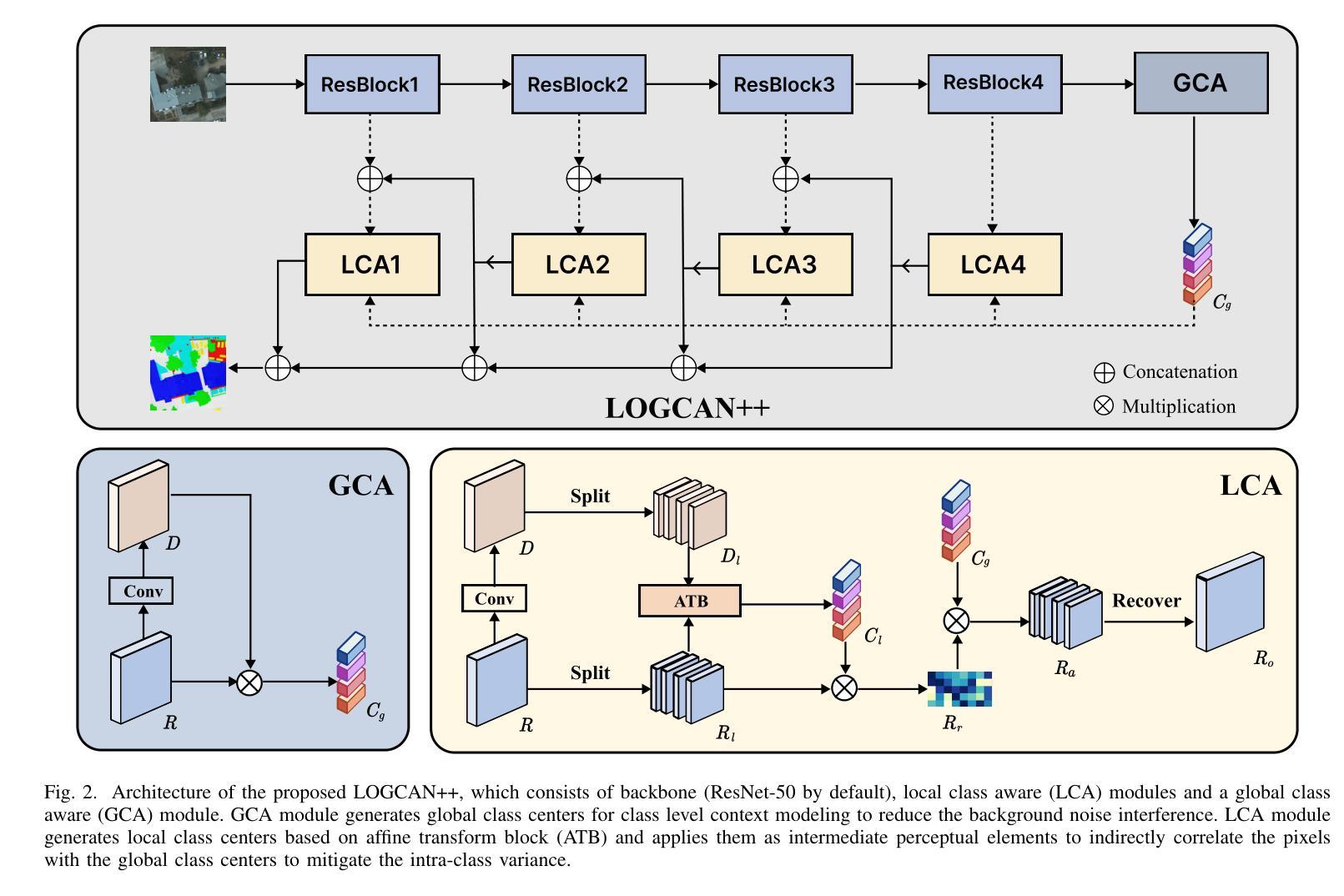
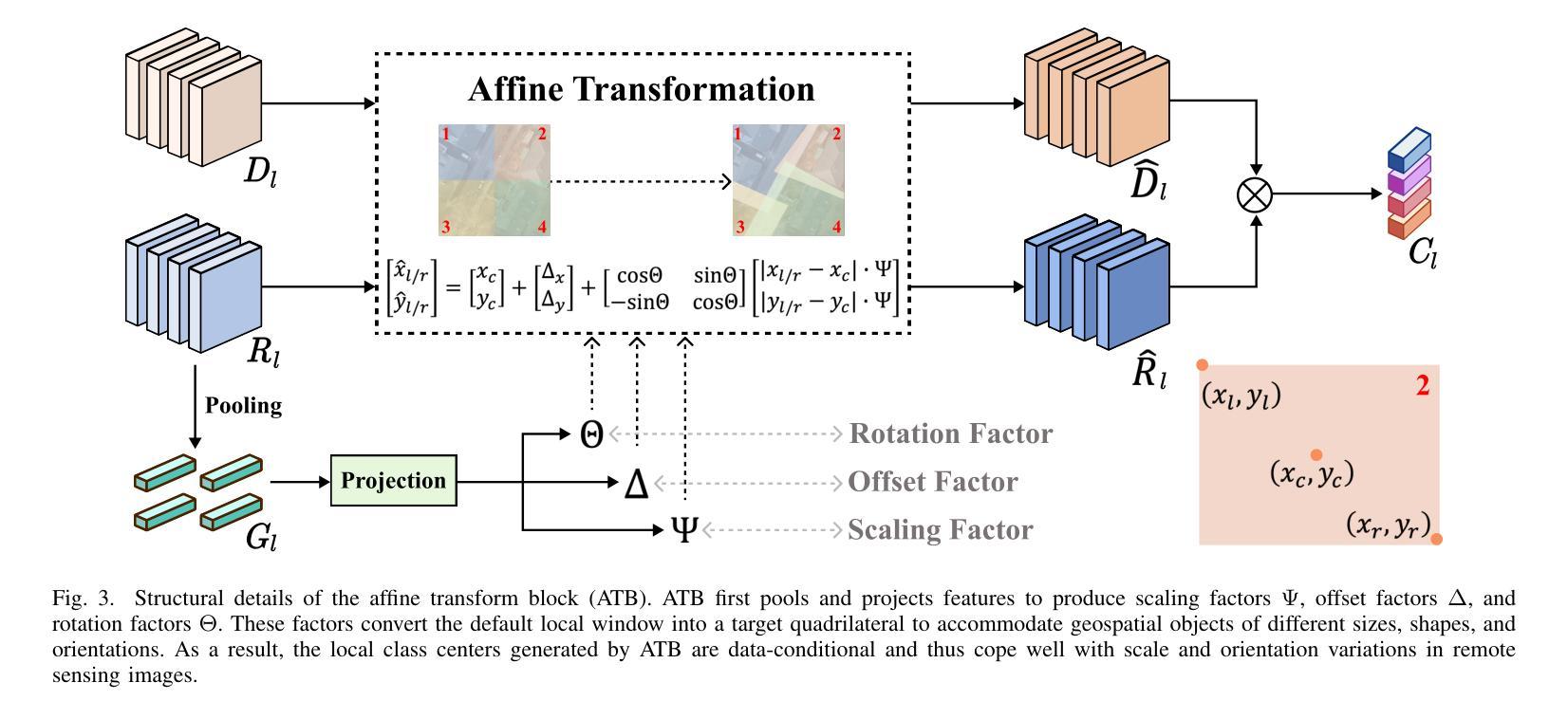
LOGCAN++: Adaptive Local-global class-aware network for semantic segmentation of remote sensing imagery
Authors:Xiaowen Ma, Rongrong Lian, Zhenkai Wu, Hongbo Guo, Mengting Ma, Sensen Wu, Zhenhong Du, Siyang Song, Wei Zhang
Remote sensing images usually characterized by complex backgrounds, scale and orientation variations, and large intra-class variance. General semantic segmentation methods usually fail to fully investigate the above issues, and thus their performances on remote sensing image segmentation are limited. In this paper, we propose our LOGCAN++, a semantic segmentation model customized for remote sensing images, which is made up of a Global Class Awareness (GCA) module and several Local Class Awareness (LCA) modules. The GCA module captures global representations for class-level context modeling to reduce the interference of background noise. The LCA module generates local class representations as intermediate perceptual elements to indirectly associate pixels with the global class representations, targeting at dealing with the large intra-class variance problem. In particular, we introduce affine transformations in the LCA module for adaptive extraction of local class representations to effectively tolerate scale and orientation variations in remotely sensed images. Extensive experiments on three benchmark datasets show that our LOGCAN++ outperforms current mainstream general and remote sensing semantic segmentation methods and achieves a better trade-off between speed and accuracy. Code is available at https://github.com/xwmaxwma/rssegmentation.
遥感图像通常具有复杂的背景、尺度和方向变化以及较大的类内差异。一般的语义分割方法通常无法完全解决上述问题,因此在遥感图像分割方面的性能受到限制。在本文中,我们提出了针对遥感图像的定制语义分割模型LOGCAN++,它由全局类别意识(GCA)模块和多个局部类别意识(LCA)模块组成。GCA模块捕获全局表示来进行类别上下文建模,以减少背景噪声的干扰。LCA模块生成局部类别表示作为中间感知元素,间接地将像素与全局类别表示关联起来,旨在处理较大的类内差异问题。特别是,我们在LCA模块中引入了仿射变换,以自适应提取局部类别表示,从而有效地容忍遥感图像中的尺度和方向变化。在三个基准数据集上的大量实验表明,我们的LOGCAN++在速度和准确性之间取得了更好的权衡,优于当前主流的一般和遥感语义分割方法。代码可在https://github.com/xwmaxwma/rssegmentation找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by TGRS2025
Summary
针对遥感图像复杂背景、尺度与方向变化以及大类内差异等问题,本文提出了LOGCAN++模型,该模型包含全局类感知模块和多个局部类感知模块。全局类感知模块用于捕捉全局类上下文表示,减少背景噪声的干扰;局部类感知模块生成局部类表示,间接关联像素与全局类表示,以处理大类内差异问题。在三个基准数据集上的实验表明,LOGCAN++在速度和准确性之间取得了更好的平衡,优于主流的一般和遥感语义分割方法。
Key Takeaways
- 遥感图像通常具有复杂背景、尺度与方向变化和较大的类内差异。
- 一般语义分割方法在遥感图像分割上性能受限。
- LOGCAN++是一个针对遥感图像的语义分割模型。
- LOGCAN++包含全局类感知模块(GCA),用于捕捉全局类上下文表示。
- LOGCAN++包含局部类感知模块(LCA),处理局部类表示和像素关联。
- LCA模块引入仿射变换,以自适应提取局部类表示,有效应对遥感图像的尺度和方向变化。
点此查看论文截图


UEMM-Air: A Synthetic Multi-modal Dataset for Unmanned Aerial Vehicle Object Detection
Authors:Liang Yao, Fan Liu, Shengxiang Xu, Chuanyi Zhang, Xing Ma, Jianyu Jiang, Zequan Wang, Shimin Di, Jun Zhou
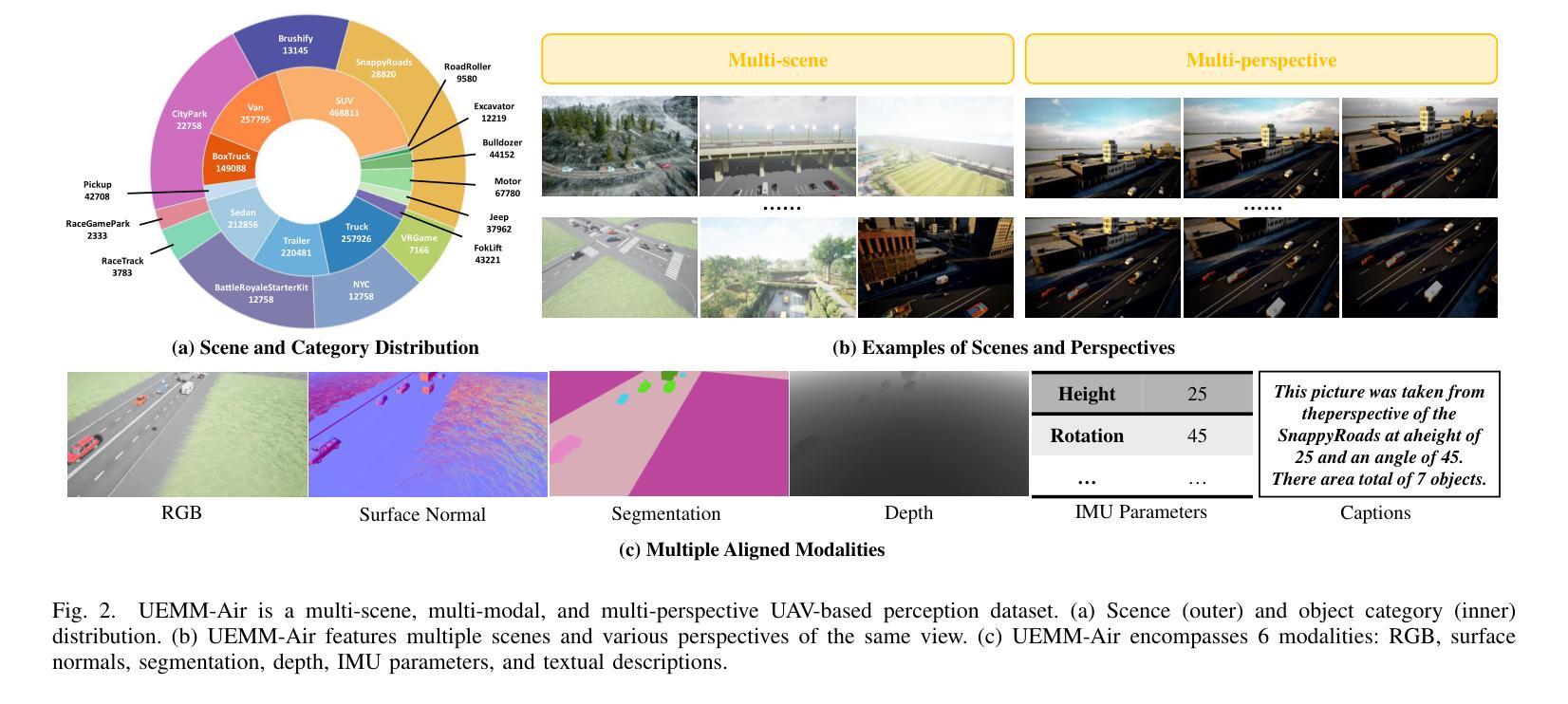
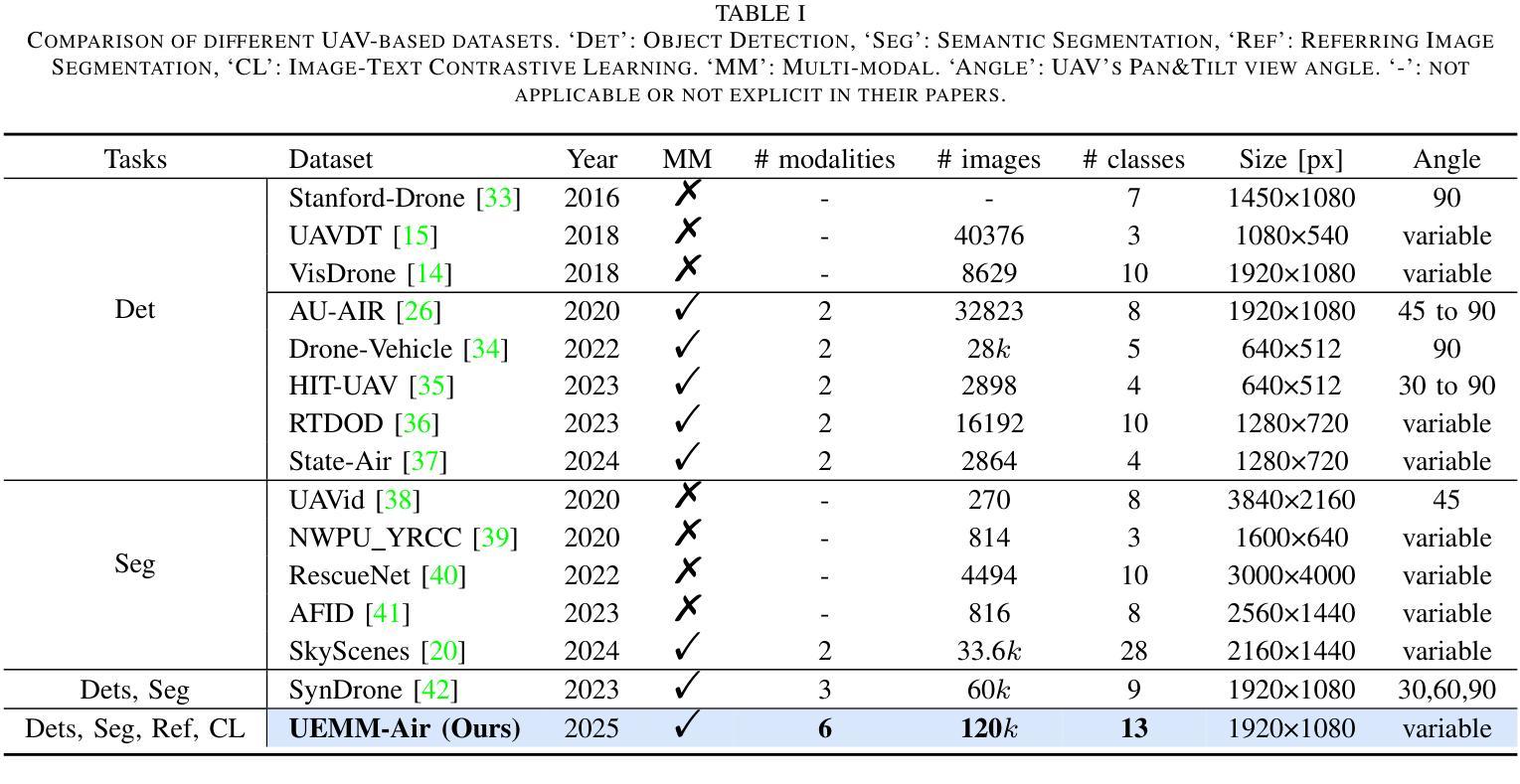
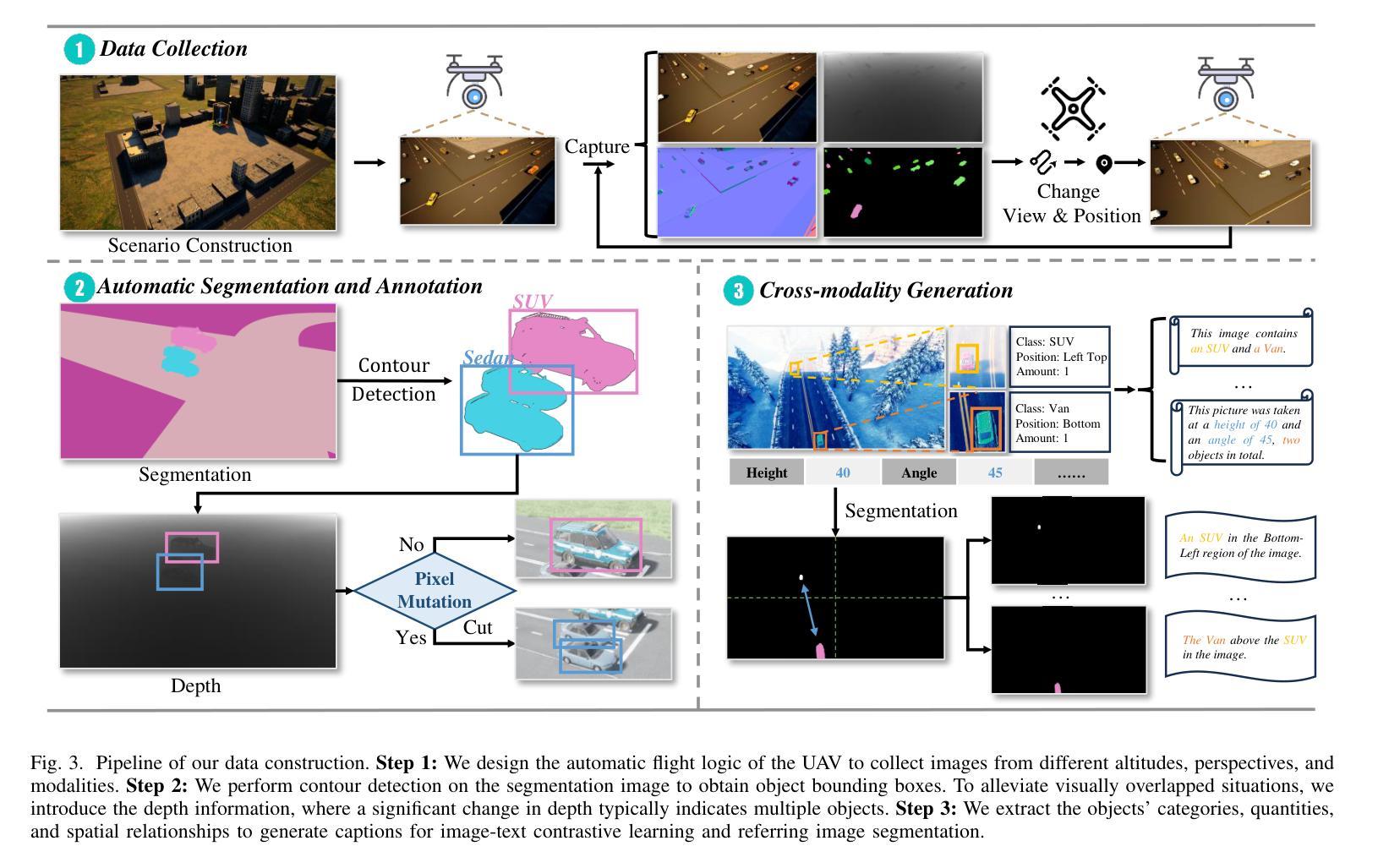
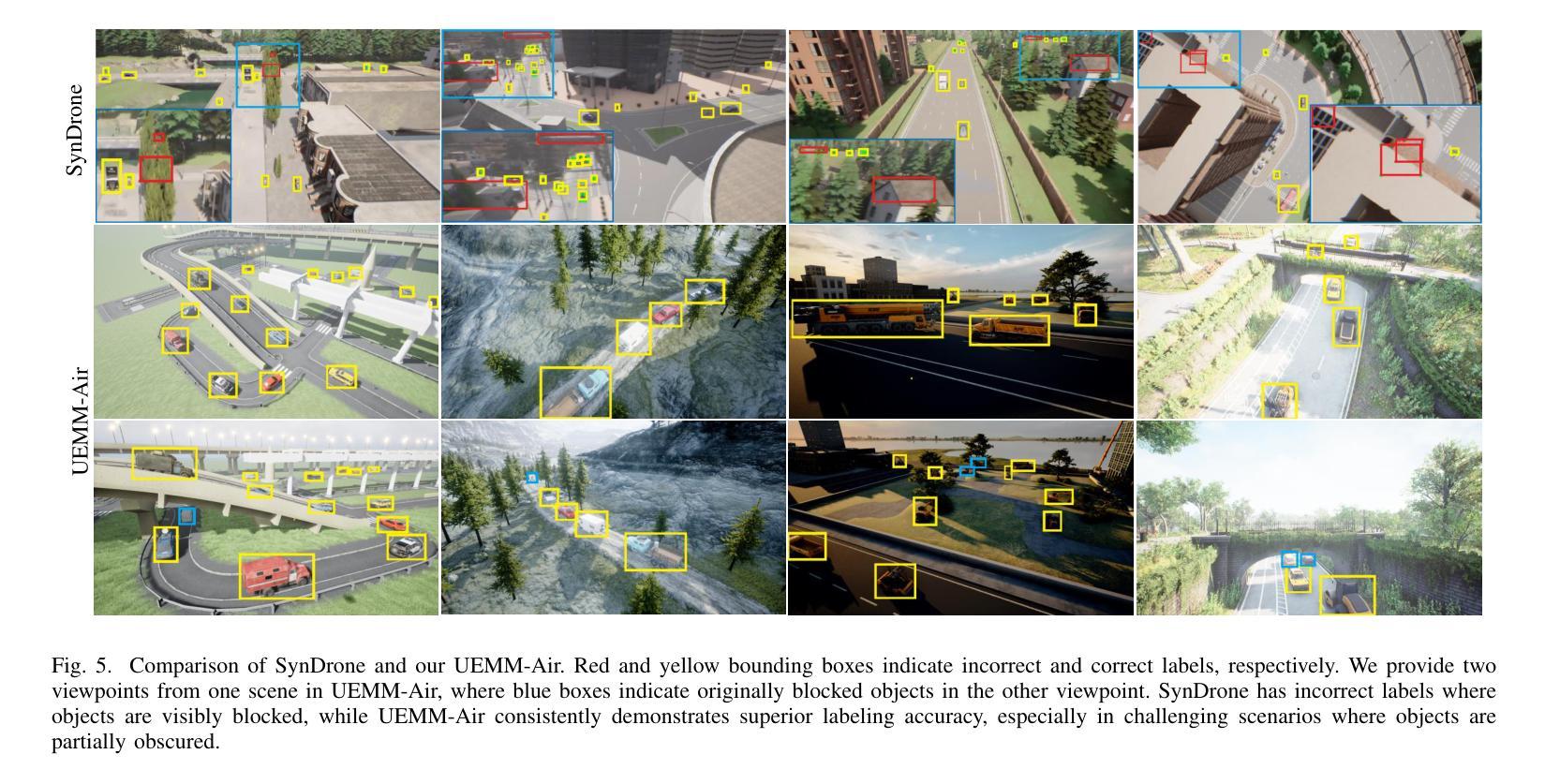
The development of multi-modal learning for Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs) typically relies on a large amount of pixel-aligned multi-modal image data. However, existing datasets face challenges such as limited modalities, high construction costs, and imprecise annotations. To this end, we propose a synthetic multi-modal UAV-based multi-task dataset, UEMM-Air. Specifically, we simulate various UAV flight scenarios and object types using the Unreal Engine (UE). Then we design the UAV’s flight logic to automatically collect data from different scenarios, perspectives, and altitudes. Furthermore, we propose a novel heuristic automatic annotation algorithm to generate accurate object detection labels. Finally, we utilize labels to generate text descriptions of images to make our UEMM-Air support more cross-modality tasks. In total, our UEMM-Air consists of 120k pairs of images with 6 modalities and precise annotations. Moreover, we conduct numerous experiments and establish new benchmark results on our dataset. We also found that models pre-trained on UEMM-Air exhibit better performance on downstream tasks compared to other similar datasets. The dataset is publicly available (https://github.com/1e12Leon/UEMM-Air) to support the research of multi-modal tasks on UAVs.
无人机多模态学习的开发通常依赖于大量的像素对齐多模态图像数据。然而,现有数据集面临模态有限、建设成本高和标注不精确等挑战。为此,我们提出了基于合成多模态的无人机多任务数据集UEMM-Air。具体来说,我们使用Unreal Engine(UE)模拟各种无人机飞行场景和对象类型。然后,我们设计无人机的飞行逻辑,以从不同场景、角度和高度自动收集数据。此外,我们提出了一种新的启发式自动标注算法,以生成精确的目标检测标签。最后,我们利用这些标签生成图像文本描述,使我们的UEMM-Air支持更多跨模态任务。总共,我们的UEMM-Air包含12万对图像,具有6种模态和精确标注。此外,我们在自己的数据集上进行了大量实验,并建立了新的基准测试结果。我们还发现,在UEMM-Air上预训练的模型在下游任务上的性能优于其他类似数据集。该数据集公开可用(https://github.com/1e12Leon/UEMM-Air),以支持无人机多模态任务的研究。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
针对无人机多模态学习发展面临的挑战,如数据量不足、模态有限、构建成本高和标注不精确等问题,我们提出了一个基于合成多模态的无人机多任务数据集UEMM-Air。通过模拟多种无人机飞行场景和物体类型,自动收集数据并设计启发式自动标注算法生成精确的目标检测标签。UEMM-Air包含12万对图像数据,共6种模态和精确标注。实验表明,预训练于UEMM-Air的模型在下游任务上表现优异,该数据集已公开供研究使用。
Key Takeaways
- UEMM-Air是一个基于合成多模态的无人机多任务数据集。
- 通过Unreal Engine模拟多种无人机飞行场景和物体类型。
- 设计了自动收集数据的无人机飞行逻辑,涵盖不同场景、视角和高度。
- 提出启发式自动标注算法生成精确的目标检测标签。
- UEMM-Air包含12万对图像数据,共6种模态和精确标注。
- 在UEMM-Air上预训练的模型在下游任务上表现优异。
点此查看论文截图