⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-02-13 更新
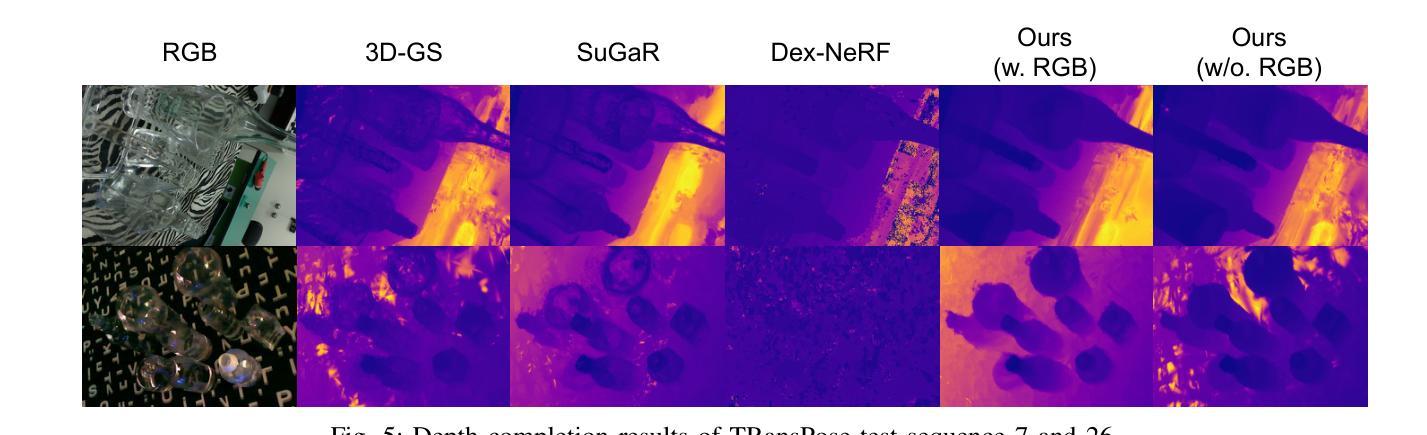
TranSplat: Surface Embedding-guided 3D Gaussian Splatting for Transparent Object Manipulation
Authors:Jeongyun Kim, Jeongho Noh, Dong-Guw Lee, Ayoung Kim
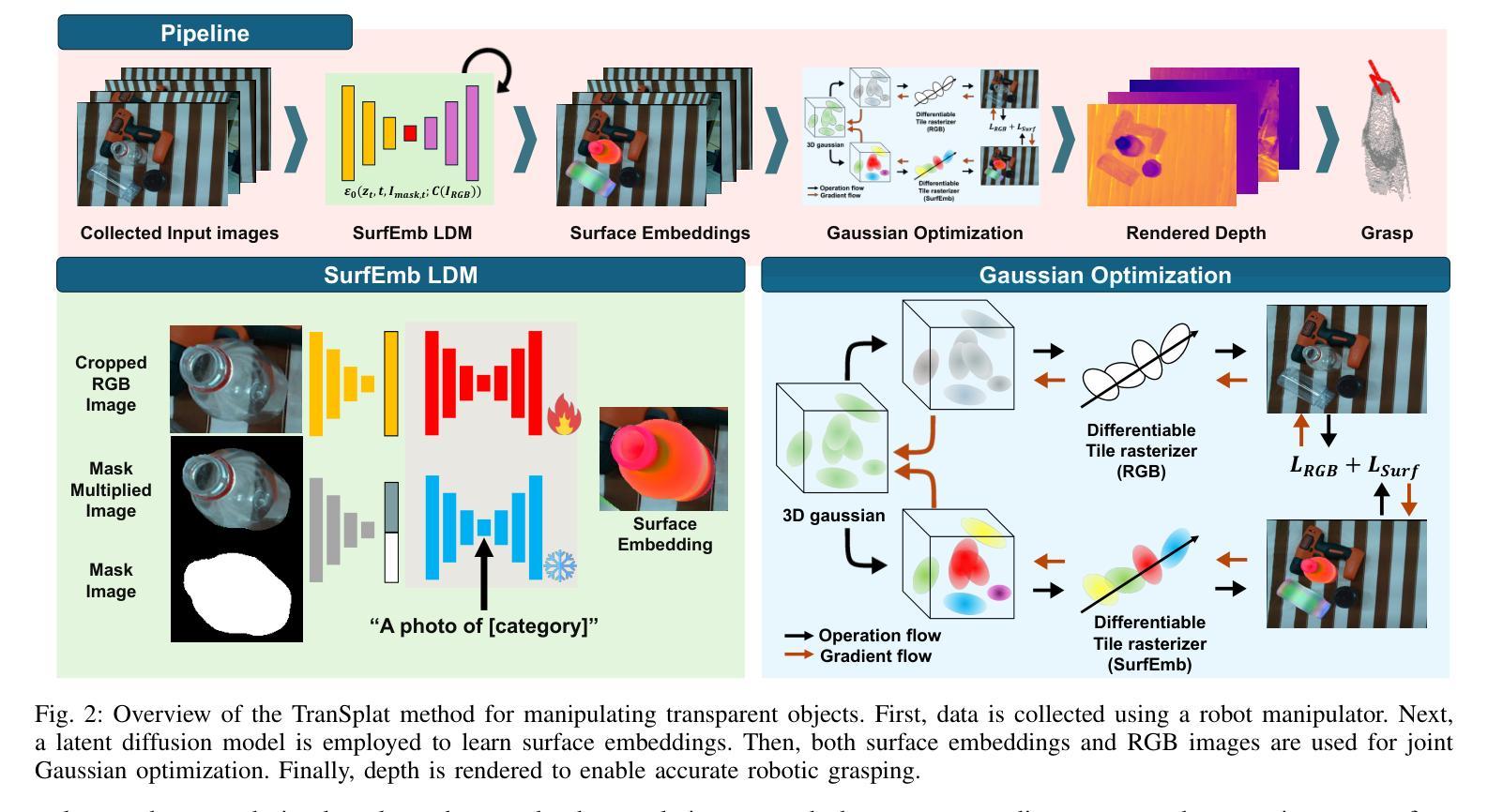
Transparent object manipulation remains a sig- nificant challenge in robotics due to the difficulty of acquiring accurate and dense depth measurements. Conventional depth sensors often fail with transparent objects, resulting in in- complete or erroneous depth data. Existing depth completion methods struggle with interframe consistency and incorrectly model transparent objects as Lambertian surfaces, leading to poor depth reconstruction. To address these challenges, we propose TranSplat, a surface embedding-guided 3D Gaussian Splatting method tailored for transparent objects. TranSplat uses a latent diffusion model to generate surface embeddings that provide consistent and continuous representations, making it robust to changes in viewpoint and lighting. By integrating these surface embeddings with input RGB images, TranSplat effectively captures the complexities of transparent surfaces, enhancing the splatting of 3D Gaussians and improving depth completion. Evaluations on synthetic and real-world transpar- ent object benchmarks, as well as robot grasping tasks, show that TranSplat achieves accurate and dense depth completion, demonstrating its effectiveness in practical applications. We open-source synthetic dataset and model: https://github. com/jeongyun0609/TranSplat
透明物体的操作仍然是机器人技术中的一个重大挑战,因为获取准确且密集的深度测量值很困难。传统的深度传感器通常无法处理透明物体,导致深度数据不完整或错误。现有的深度完成方法在帧间一致性方面表现挣扎,并错误地将透明物体建模为Lambertian表面,导致深度重建效果不佳。为了解决这些挑战,我们提出了针对透明物体的TranSplat方法,这是一种受表面嵌入引导的三维高斯延展法。TranSplat使用潜在扩散模型生成表面嵌入,提供一致且连续的表达,使其对视角和光照变化具有鲁棒性。通过将这些表面嵌入与输入RGB图像集成,TranSplat有效地捕捉了透明表面的复杂性,增强了三维高斯延展,并改进了深度完成。在合成和真实世界的透明物体基准测试以及机器人抓取任务上的评估表明,TranSplat实现了准确且密集的深度完成,证明了其在实际应用中的有效性。我们的开源合成数据集和模型为:https://github. com/jeongyun0609/TranSplat。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 7 pages, 6 figures
Summary
文本指出透明物体的操作在机器人学中仍然是一个重大挑战,主要由于获取准确且密集的深度测量难度较大。传统的深度传感器经常无法处理透明物体,导致深度数据不完整或错误。现有的深度完成方法难以保持帧间一致性,并错误地将透明物体建模为Lambertian表面,导致深度重建效果不佳。为解决这些问题,提出了TranSplat方法,这是一种受表面嵌入引导的三维高斯溅洒法,特别适用于透明物体。该方法使用潜在扩散模型生成表面嵌入,提供一致且连续的表达,对视角和光照变化具有鲁棒性。通过与输入RGB图像集成,TranSplat有效地捕捉了透明表面的复杂性,提高了三维高斯溅洒效果,改善了深度完成。在合成和真实世界的透明物体基准测试以及机器人抓取任务中的评估表明,TranSplat实现了准确且密集的深度完成,证明了其在实际应用中的有效性。
Key Takeaways
- 透明物体的操作是机器人学中的一大挑战,因获取其准确、密集的深度测量难度较高。
- 传统深度传感器在处理透明物体时经常失效。
- 现有深度完成方法在保持帧间一致性和正确建模透明物体方面存在困难。
- TranSplat是一种新的方法,结合表面嵌入和三维高斯溅洒法,特别适用于处理透明物体。
- TranSplat使用潜在扩散模型生成表面嵌入,以提供一致且连续的表达,增强对视角和光照变化的鲁棒性。
- TranSplat能有效捕捉透明表面的复杂性,提高三维高斯溅洒效果,改善深度完成。
点此查看论文截图
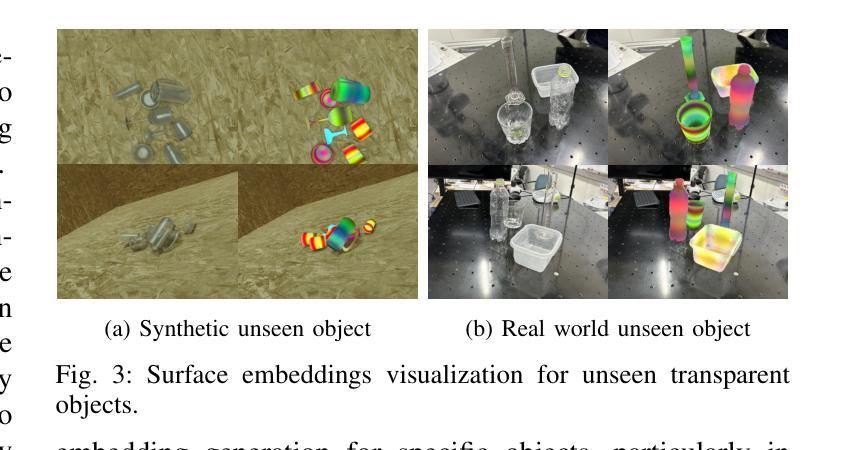
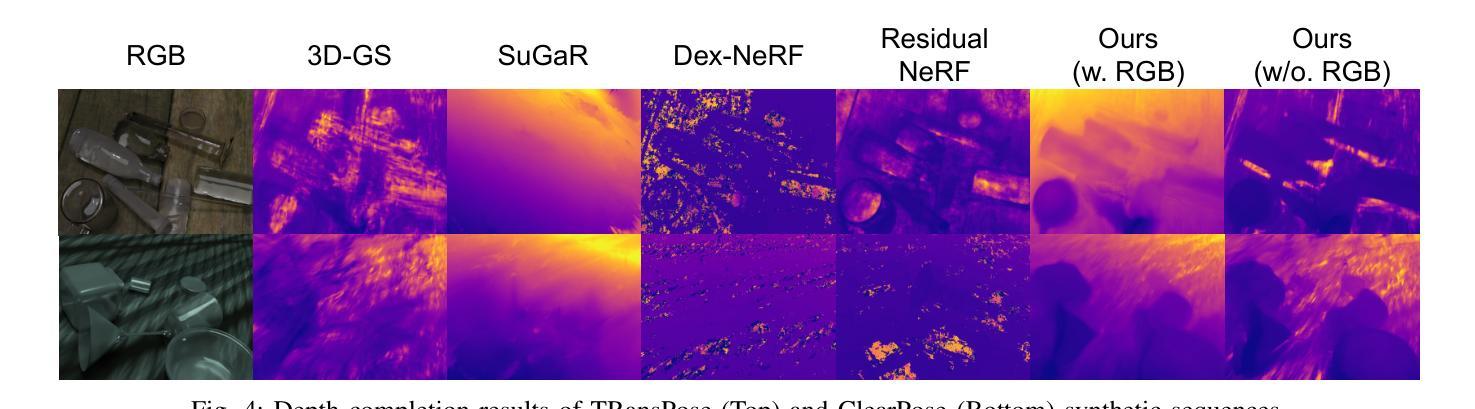
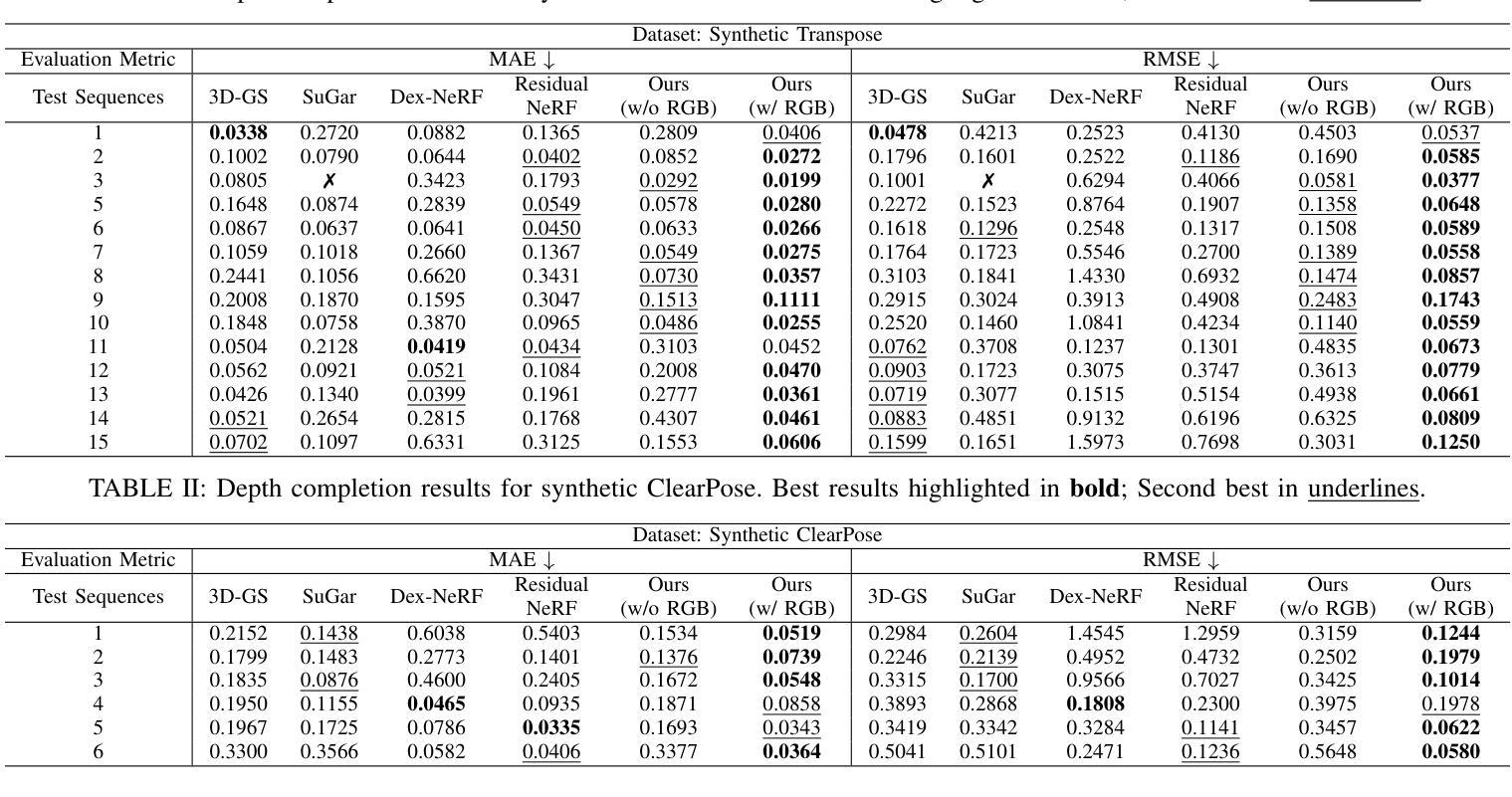

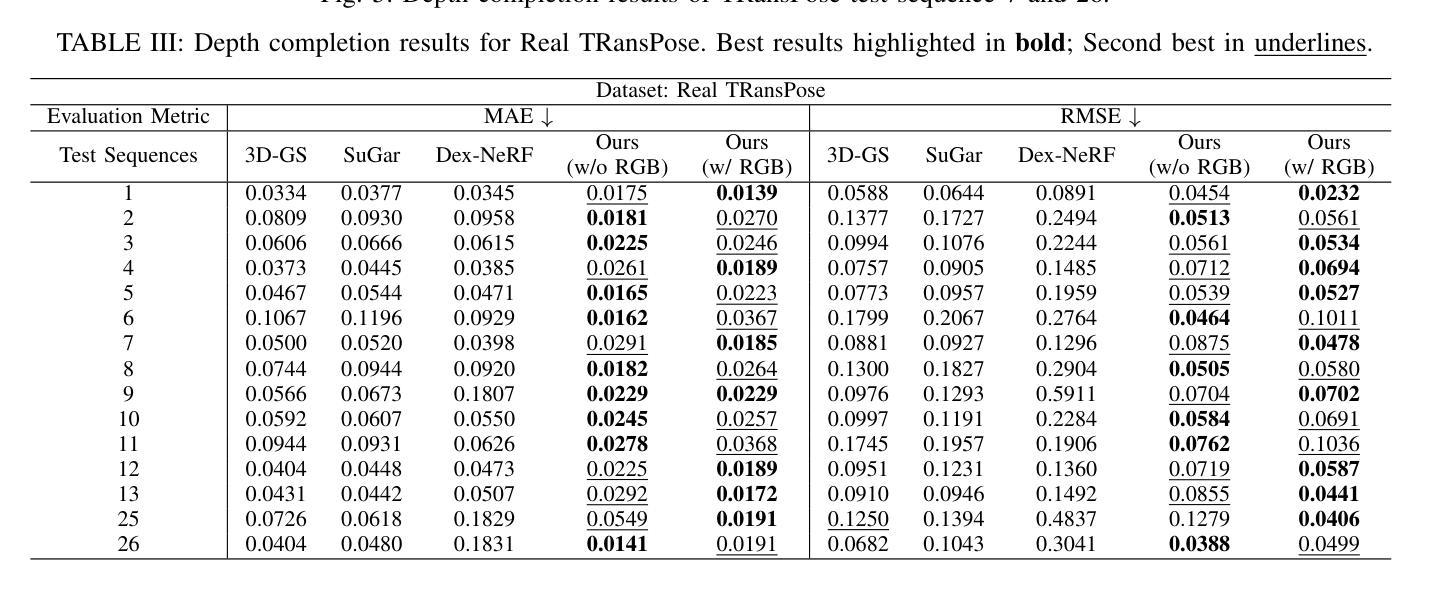
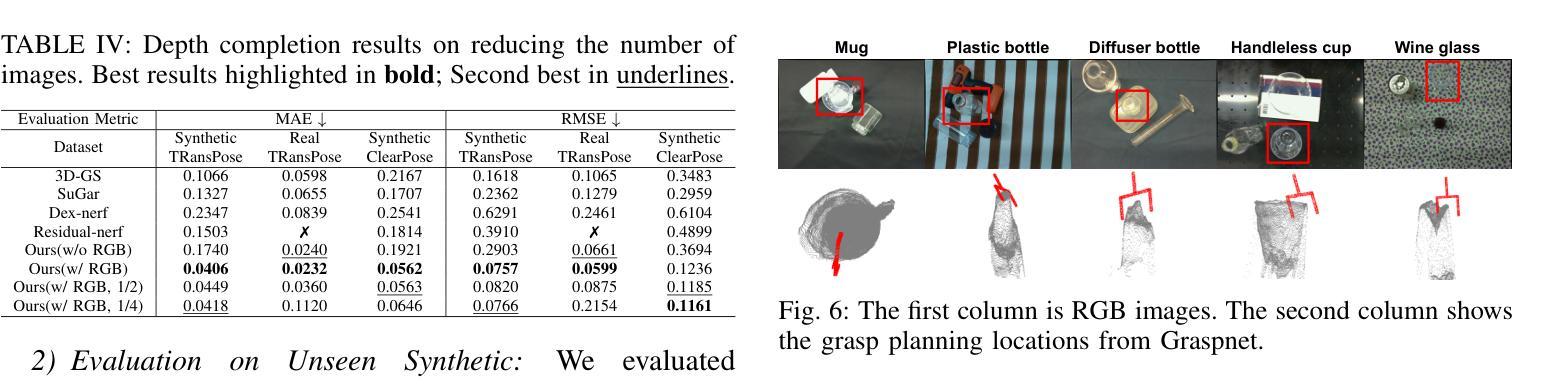
Flow Distillation Sampling: Regularizing 3D Gaussians with Pre-trained Matching Priors
Authors:Lin-Zhuo Chen, Kangjie Liu, Youtian Lin, Siyu Zhu, Zhihao Li, Xun Cao, Yao Yao
3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) has achieved excellent rendering quality with fast training and rendering speed. However, its optimization process lacks explicit geometric constraints, leading to suboptimal geometric reconstruction in regions with sparse or no observational input views. In this work, we try to mitigate the issue by incorporating a pre-trained matching prior to the 3DGS optimization process. We introduce Flow Distillation Sampling (FDS), a technique that leverages pre-trained geometric knowledge to bolster the accuracy of the Gaussian radiance field. Our method employs a strategic sampling technique to target unobserved views adjacent to the input views, utilizing the optical flow calculated from the matching model (Prior Flow) to guide the flow analytically calculated from the 3DGS geometry (Radiance Flow). Comprehensive experiments in depth rendering, mesh reconstruction, and novel view synthesis showcase the significant advantages of FDS over state-of-the-art methods. Additionally, our interpretive experiments and analysis aim to shed light on the effects of FDS on geometric accuracy and rendering quality, potentially providing readers with insights into its performance. Project page: https://nju-3dv.github.io/projects/fds
3D高斯喷溅(3DGS)技术已经实现了高质量的渲染,并具备快速的训练和渲染速度。然而,其优化过程中缺乏明确的几何约束,导致在稀疏或没有观测输入视图的区域几何重建效果不理想。在这项工作中,我们尝试通过引入预训练的匹配先验来减轻这个问题,将其纳入3DGS优化过程。我们提出了流蒸馏采样(FDS)技术,该技术利用预训练的几何知识来提高高斯辐射场的准确性。我们的方法采用了一种战略采样技术,针对输入视图相邻的未观察视图进行定位,利用匹配模型计算的光流(先验流)来指导从3DGS几何分析计算的光流(辐射流)。在深度渲染、网格重建和新颖视图合成方面的综合实验展示了FDS相较于最新技术方法的显著优势。此外,我们的解释性实验和分析旨在阐明FDS对几何精度和渲染质量的影响,可能为读者提供对其性能的认识。项目页面:https://nju-3dv.github.io/projects/fds
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by ICLR 2025
Summary
3DGS技术结合预训练匹配先验以提升渲染质量及几何重建准确性。通过引入Flow Distillation Sampling(FDS)技术,利用预训练几何知识强化高斯辐射场精度。采用策略性采样技术针对输入视图附近的无观测视图进行目标定位,并利用匹配模型计算的光流来指导3DGS几何分析计算的光流。深度渲染、网格重建和新颖视图合成的综合实验展示了FDS相较于最新方法的显著优势。
Key Takeaways
- 3DGS具有优秀的渲染质量和快速的训练和渲染速度。
- 优化过程中缺乏明确的几何约束,导致在稀疏或没有观测输入视图的区域几何重建不佳。
- 为解决此问题,引入预训练匹配先验,增强几何重建的准确性。
- 引入Flow Distillation Sampling (FDS)技术,结合预训练几何知识和高斯辐射场。
- 采用策略性采样技术,针对输入视图附近的无观测视图进行目标定位。
- 利用匹配模型计算的光流指导3DGS几何分析计算的光流,提升辐射场精度。
- 通过深度渲染、网格重建和新颖视图合成的综合实验验证了FDS相较于最新方法的优势。
点此查看论文截图

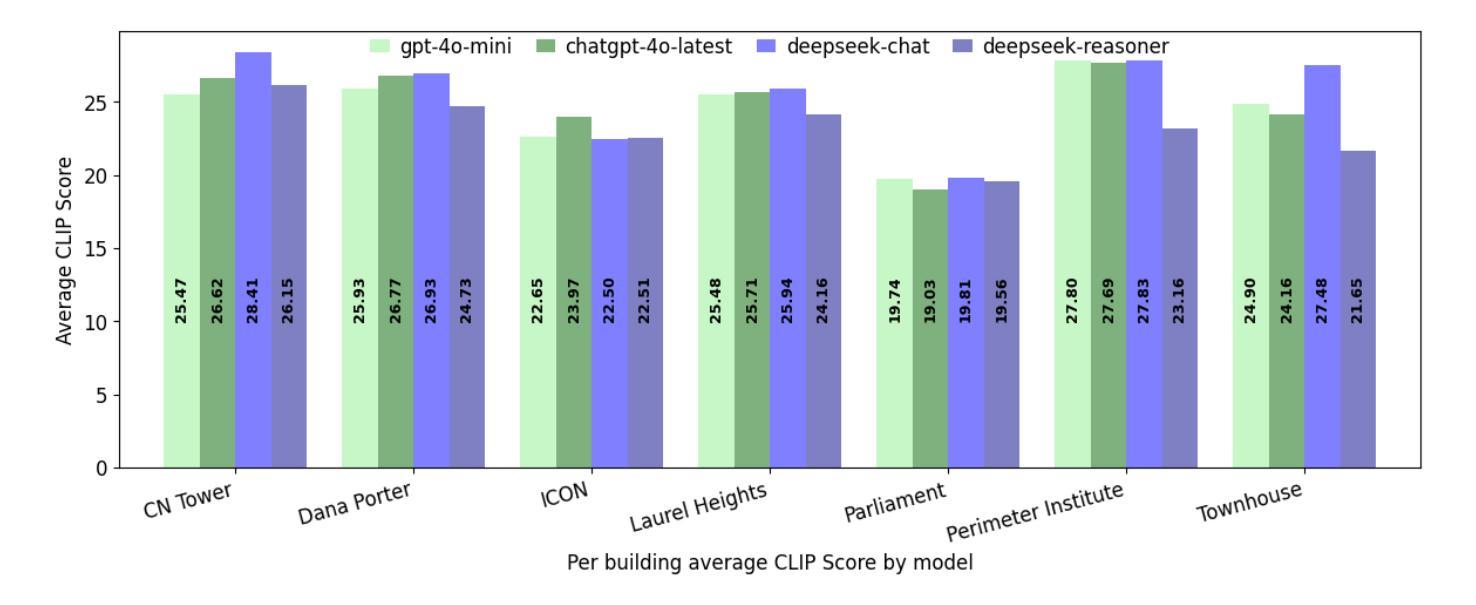
Digital Twin Buildings: 3D Modeling, GIS Integration, and Visual Descriptions Using Gaussian Splatting, ChatGPT/Deepseek, and Google Maps Platform
Authors:Kyle Gao, Dening Lu, Liangzhi Li, Nan Chen, Hongjie He, Linlin Xu, Jonathan Li
Urban digital twins are virtual replicas of cities that use multi-source data and data analytics to optimize urban planning, infrastructure management, and decision-making. Towards this, we propose a framework focused on the single-building scale. By connecting to cloud mapping platforms such as Google Map Platforms APIs, by leveraging state-of-the-art multi-agent Large Language Models data analysis using ChatGPT(4o) and Deepseek-V3/R1, and by using our Gaussian Splatting-based mesh extraction pipeline, our Digital Twin Buildings framework can retrieve a building’s 3D model, visual descriptions, and achieve cloud-based mapping integration with large language model-based data analytics using a building’s address, postal code, or geographic coordinates.
城市数字双胞胎是利用多源数据和数据分析优化城市规划、基础设施管理和决策制定的城市虚拟副本。为此,我们提出了以单栋建筑规模为重点的框架。通过连接到谷歌地图平台API等云地图平台,利用最先进的基于多智能体的语言模型(使用ChatGPT(第4版)和Deepseek-V3/R1进行数据分析),并使用基于高斯渲染技术的网格提取管道,我们的数字双胞胎建筑框架可以检索建筑的3D模型、视觉描述,并通过建筑地址、邮政编码或地理坐标实现基于云的映射集成与基于大型语言模型的数据分析。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF -Fixed minor typo
Summary
城市数字双胞胎是利用多源数据和数据分析优化城市规划、基础设施管理和决策制定的虚拟城市模型。我们提出一个以单栋建筑为尺度的框架,通过连接谷歌地图平台API等云地图平台,利用最新多智能体大型语言模型ChatGPT(第4代)和Deepseek-V3/R1的数据分析,以及高斯平铺网格提取管道技术,数字双胞胎建筑框架能够检索建筑的3D模型、视觉描述,实现基于云的地图集成与大型语言模型的数据分析整合,通过建筑地址、邮政编码或地理坐标来实现。
Key Takeaways
- 城市数字双胞胎是城市的虚拟模型,使用多源数据和数据分析优化城市规划和管理。
- 提出的框架侧重于单栋建筑尺度,可以获取建筑的3D模型和视觉描述。
- 通过连接云地图平台,实现数字双胞胎建筑框架。
- 利用最新多智能体大型语言模型进行数据分析。
- 通过高斯平铺网格提取管道技术实现云地图与大型语言模型的整合。
- 该框架能通过建筑地址、邮政编码或地理坐标进行运作。
点此查看论文截图


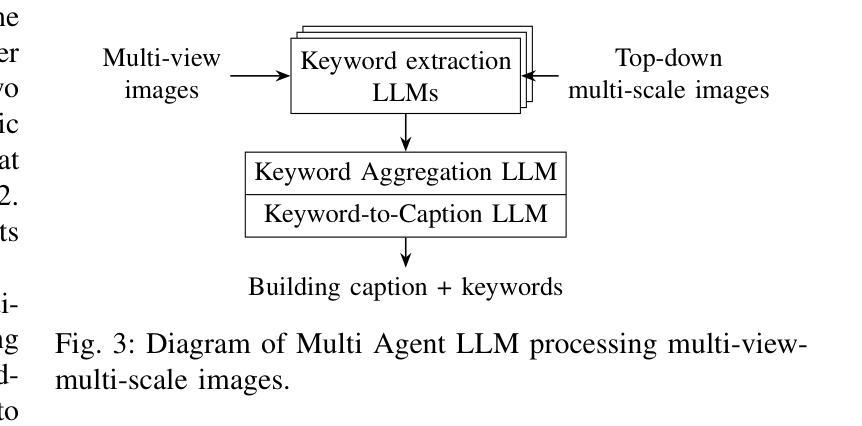
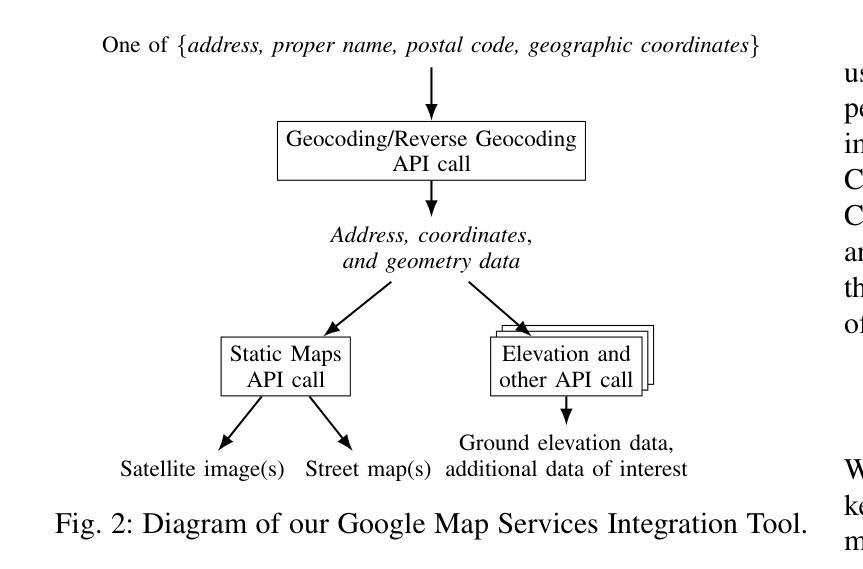
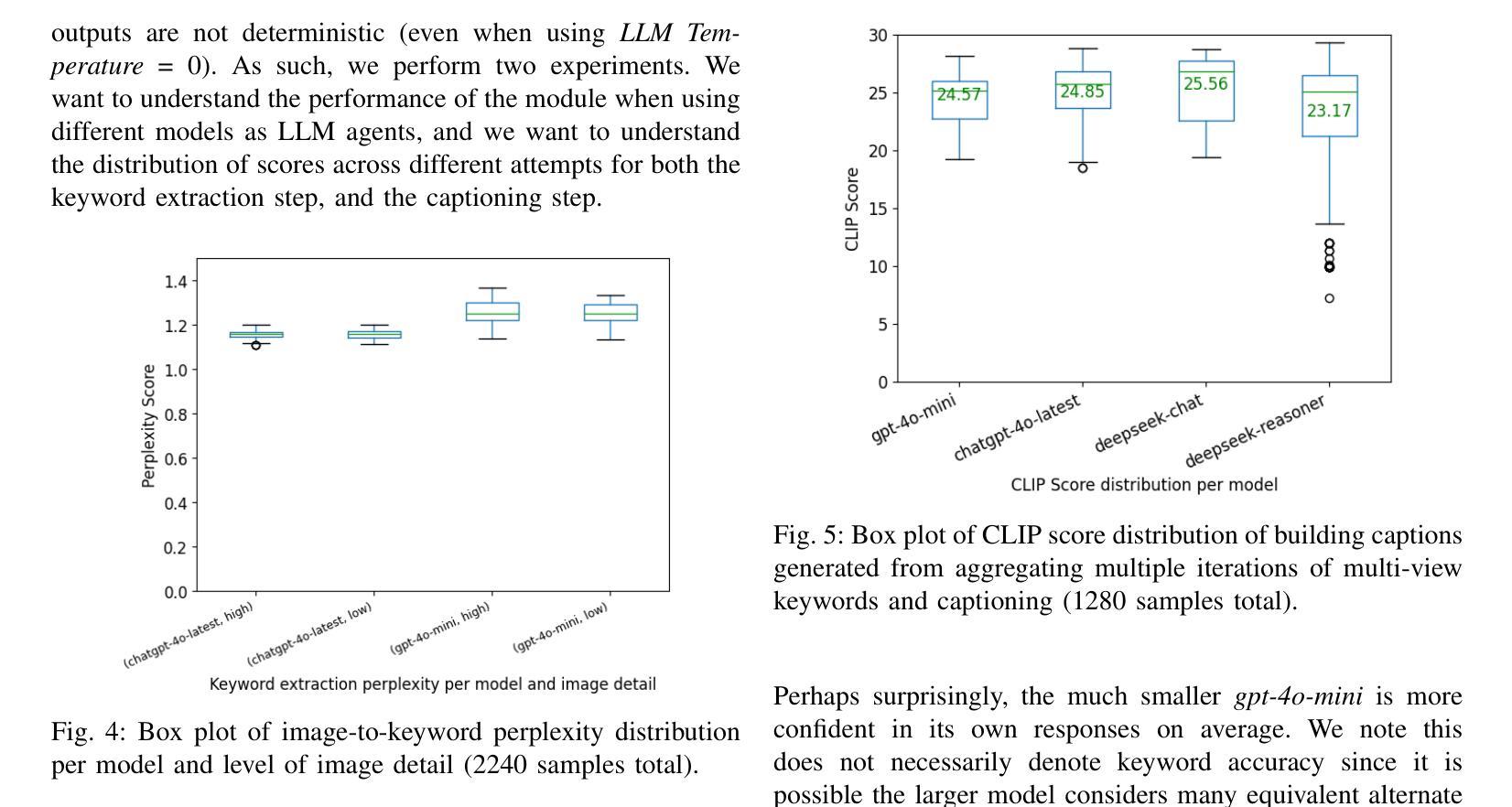
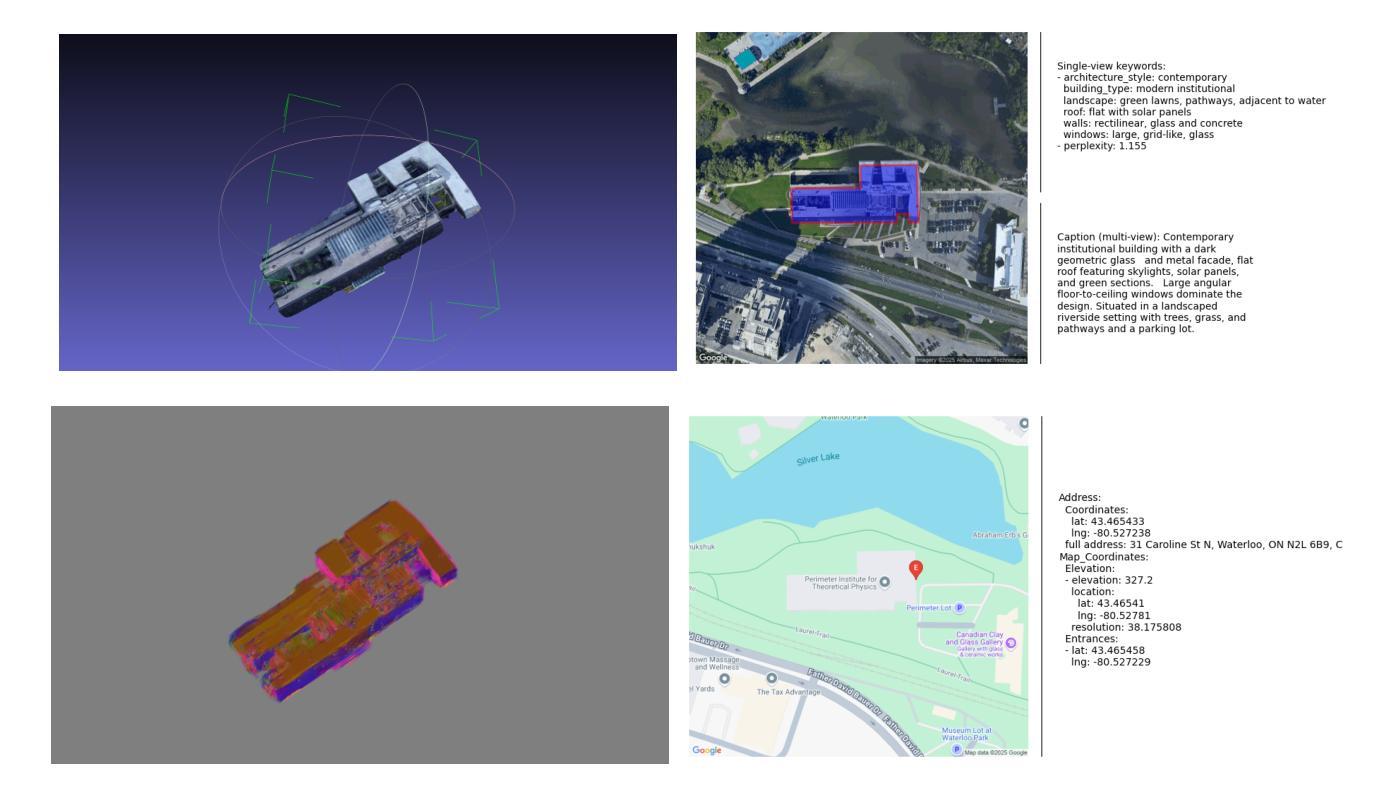
PoI: Pixel of Interest for Novel View Synthesis Assisted Scene Coordinate Regression
Authors:Feifei Li, Qi Song, Chi Zhang, Hui Shuai, Rui Huang
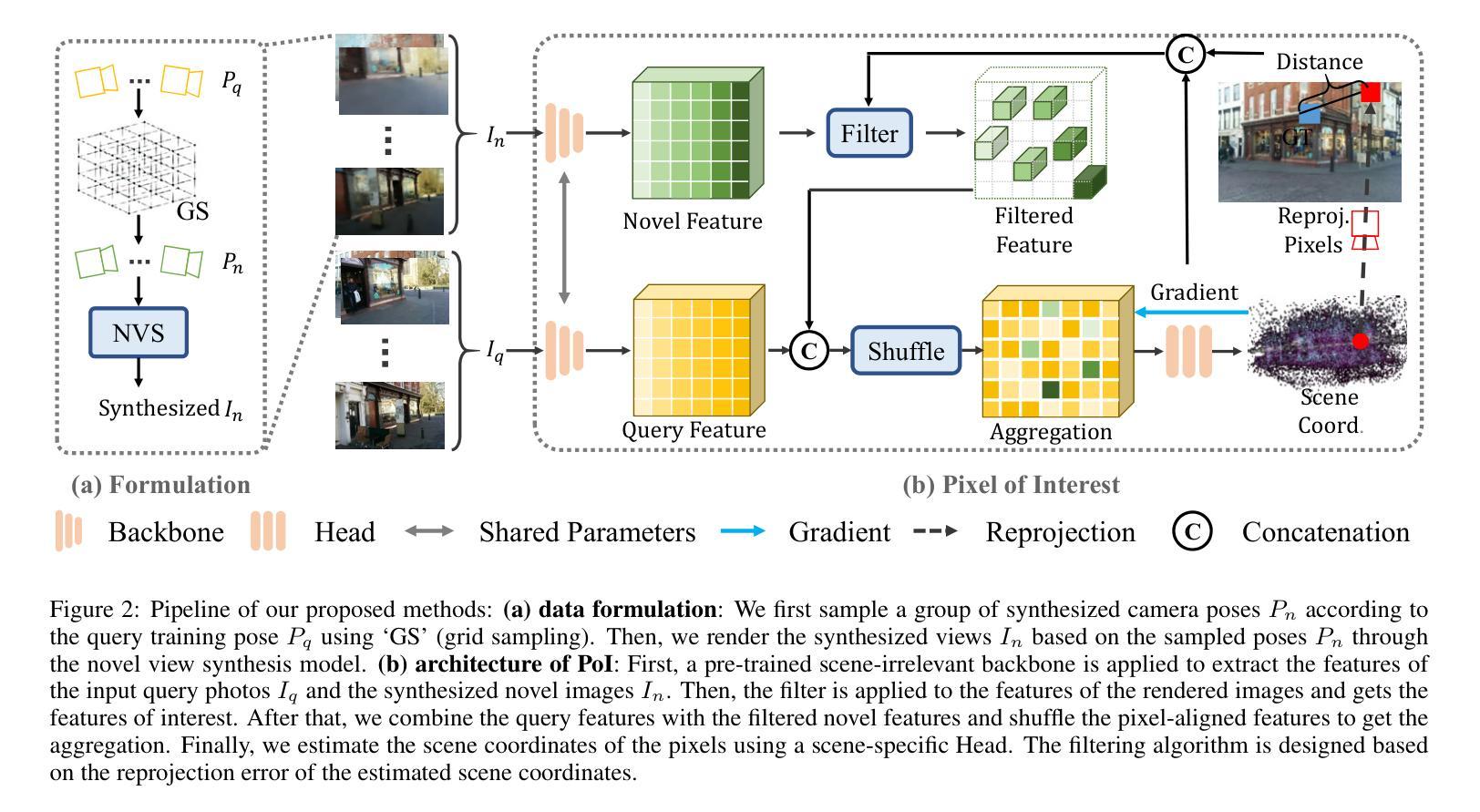
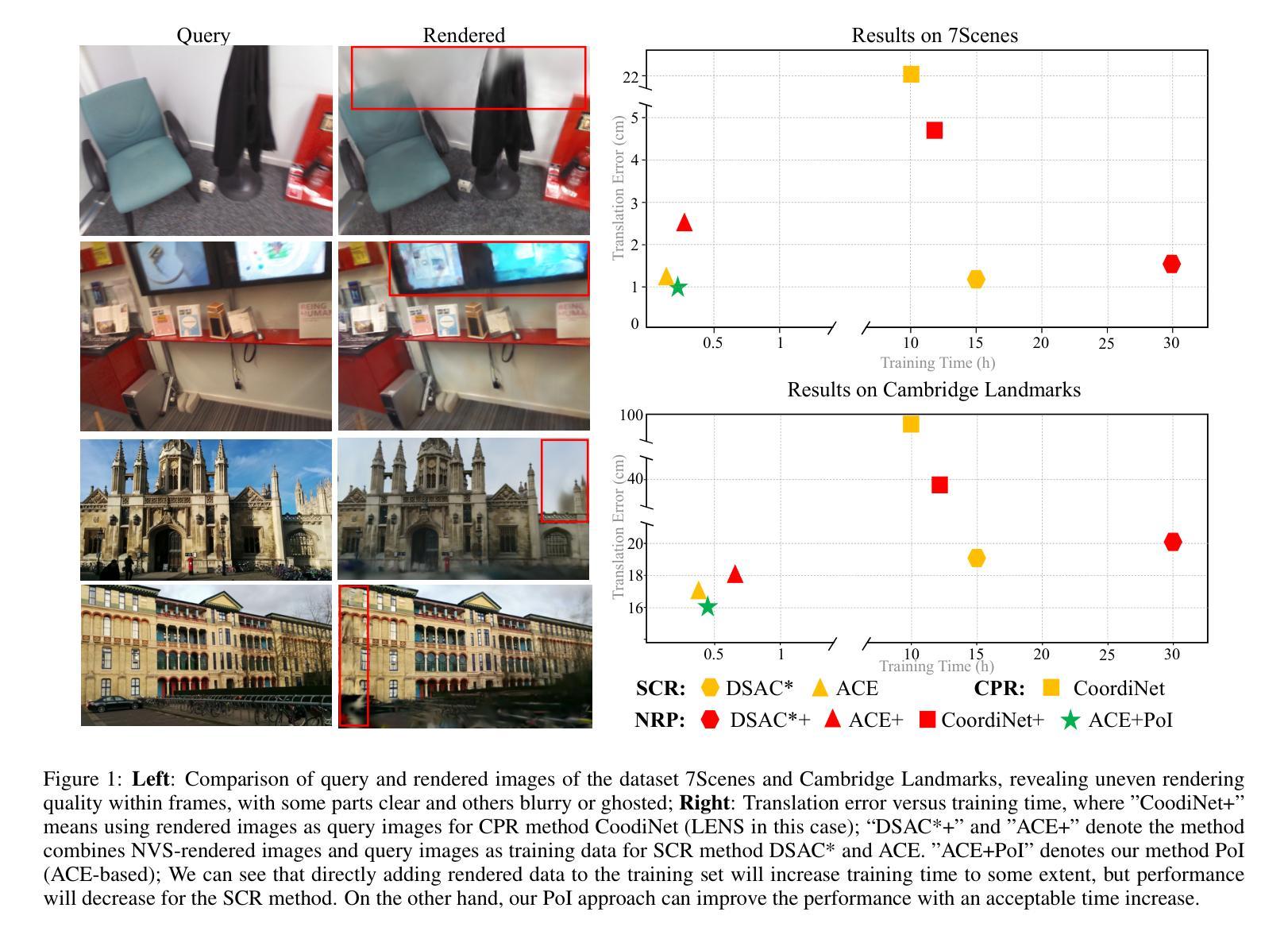
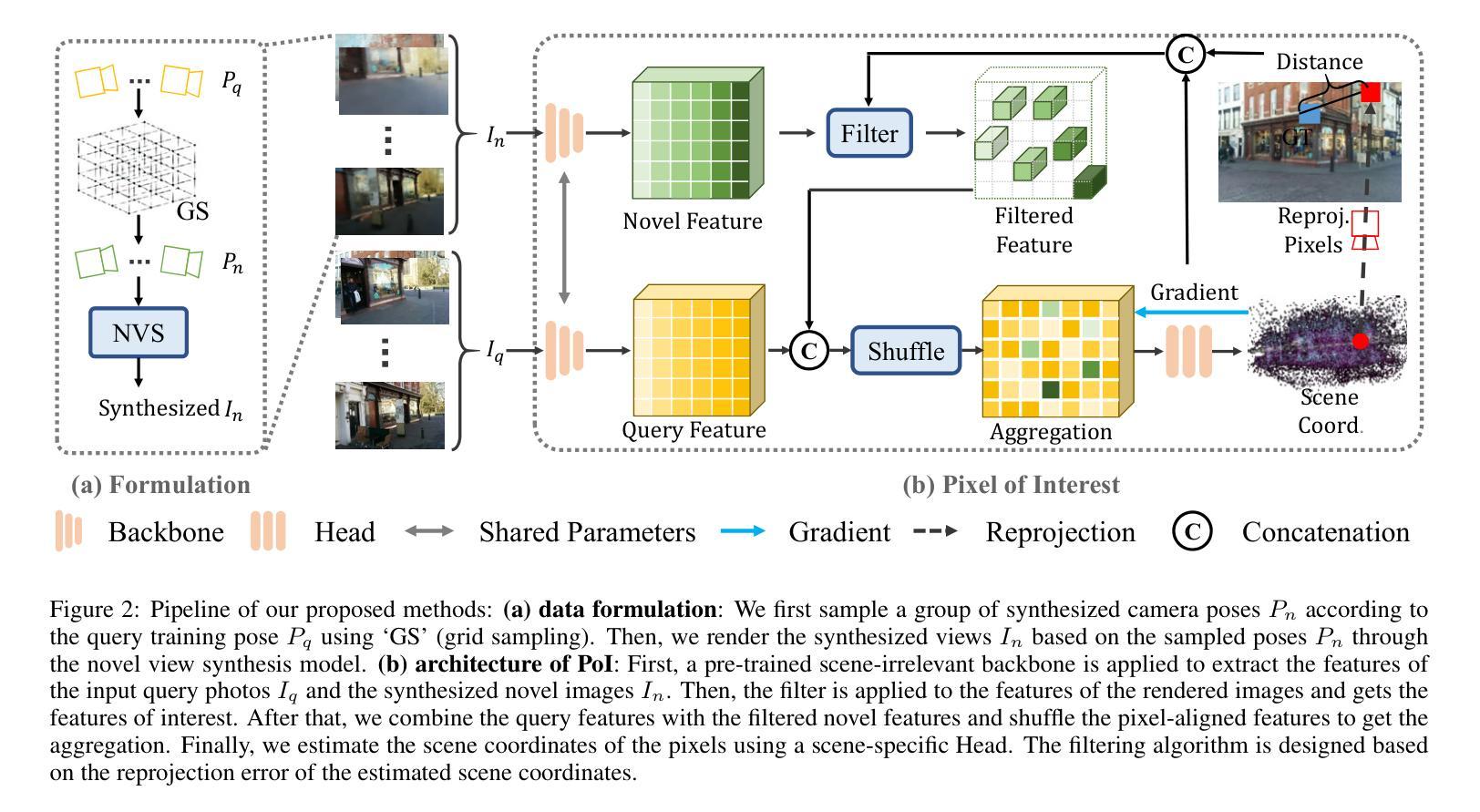
The task of estimating camera poses can be enhanced through novel view synthesis techniques such as NeRF and Gaussian Splatting to increase the diversity and extension of training data. However, these techniques often produce rendered images with issues like blurring and ghosting, which compromise their reliability. These issues become particularly pronounced for Scene Coordinate Regression (SCR) methods, which estimate 3D coordinates at the pixel level. To mitigate the problems associated with unreliable rendered images, we introduce a novel filtering approach, which selectively extracts well-rendered pixels while discarding the inferior ones. This filter simultaneously measures the SCR model’s real-time reprojection loss and gradient during training. Building on this filtering technique, we also develop a new strategy to improve scene coordinate regression using sparse inputs, drawing on successful applications of sparse input techniques in novel view synthesis. Our experimental results validate the effectiveness of our method, demonstrating state-of-the-art performance on indoor and outdoor datasets.
通过NeRF和Gaussian Splatting等新型视图合成技术,可以增强对相机姿态的估计任务,从而提高训练数据的多样性和扩展性。然而,这些技术往往产生的渲染图像存在模糊和重影等问题,从而影响了它们的可靠性。这些问题在场景坐标回归(SCR)方法中尤为突出,这些方法估计像素级别的3D坐标。为了解决与不可靠的渲染图像相关的问题,我们引入了一种新型过滤方法,该方法能够有选择地提取渲染良好的像素,同时丢弃质量较差的像素。该过滤器在训练过程中实时测量SCR模型的再投影损失和梯度。基于这种过滤技术,我们还开发了一种利用稀疏输入改进场景坐标回归的新策略,这借鉴了稀疏输入技术在新型视图合成中的成功应用。我们的实验结果验证了该方法的有效性,在室内和室外数据集上均表现出最先进的性能。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文利用NeRF和Gaussian Splatting等新型视图合成技术提升相机姿态估计任务的性能,以增加训练数据的多样性和扩展性。然而,这些技术生成的渲染图像往往存在模糊和重影等问题,影响了其可靠性。特别是在场景坐标回归(SCR)方法中,这些问题更为突出,因为SCR需要在像素级别估计3D坐标。为了缓解因不可靠的渲染图像带来的问题,本文提出了一种新的滤波方法,该方法能够选择性地提取渲染良好的像素,同时丢弃质量较差的像素。此滤波器会实时测量SCR模型的再投影损失和训练过程中的梯度。基于这种滤波技术,我们还开发了一种利用稀疏输入改进场景坐标回归的新策略,借鉴了稀疏输入在新型视图合成中的成功应用。实验结果验证了该方法的有效性,在室内和室外数据集上均表现出卓越的性能。
Key Takeaways
- 利用NeRF和Gaussian Splatting等新型视图合成技术提升相机姿态估计性能。
- 视图合成技术产生的渲染图像存在模糊和重影问题,影响可靠性。
- 场景坐标回归(SCR)方法在像素级别估计3D坐标,上述问题更为突出。
- 提出新的滤波方法,选择性提取良好渲染的像素,同时丢弃质量较差的像素。
- 滤波器实时测量SCR模型的再投影损失和训练过程中的梯度。
- 结合滤波技术,开发了一种利用稀疏输入改进场景坐标回归的策略。
- 实验结果验证了该方法的有效性,表现出卓越的性能。
点此查看论文截图


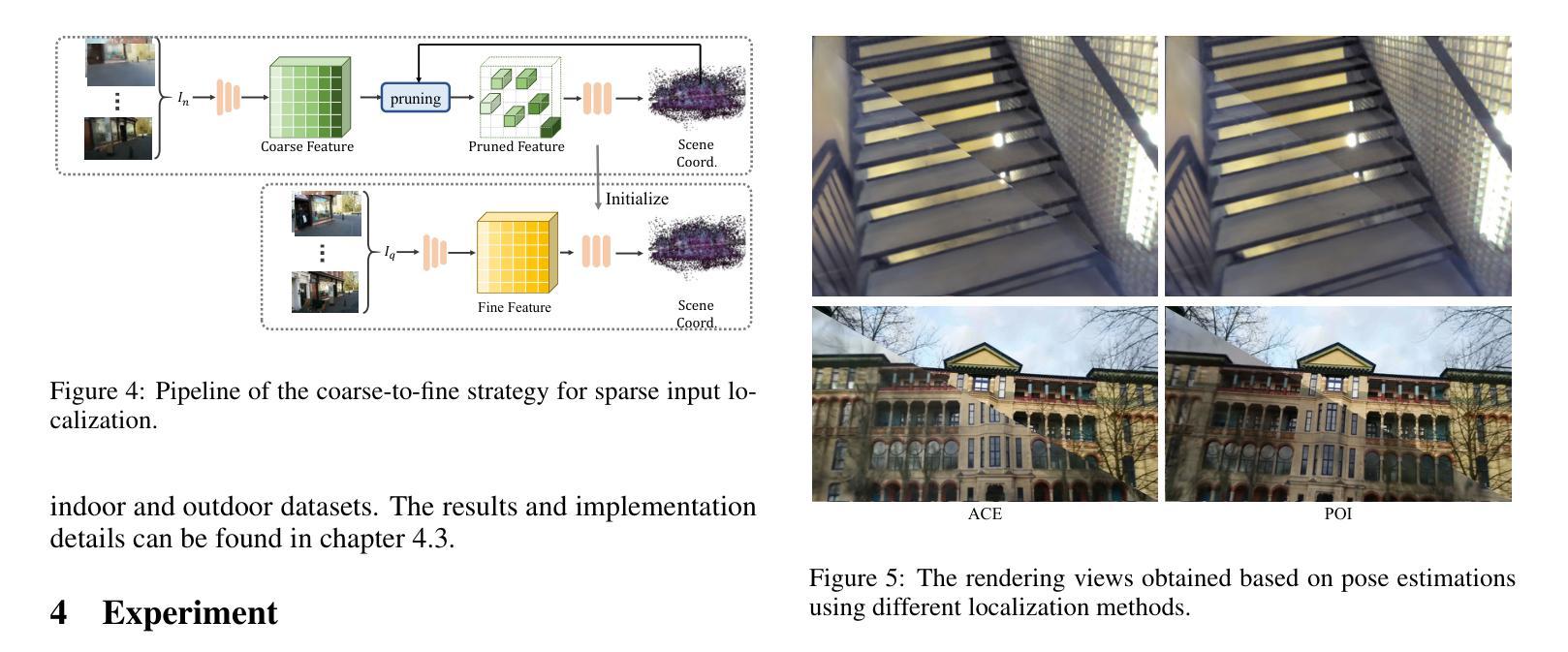
HAC++: Towards 100X Compression of 3D Gaussian Splatting
Authors:Yihang Chen, Qianyi Wu, Weiyao Lin, Mehrtash Harandi, Jianfei Cai
3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) has emerged as a promising framework for novel view synthesis, boasting rapid rendering speed with high fidelity. However, the substantial Gaussians and their associated attributes necessitate effective compression techniques. Nevertheless, the sparse and unorganized nature of the point cloud of Gaussians (or anchors in our paper) presents challenges for compression. To achieve a compact size, we propose HAC++, which leverages the relationships between unorganized anchors and a structured hash grid, utilizing their mutual information for context modeling. Additionally, HAC++ captures intra-anchor contextual relationships to further enhance compression performance. To facilitate entropy coding, we utilize Gaussian distributions to precisely estimate the probability of each quantized attribute, where an adaptive quantization module is proposed to enable high-precision quantization of these attributes for improved fidelity restoration. Moreover, we incorporate an adaptive masking strategy to eliminate invalid Gaussians and anchors. Overall, HAC++ achieves a remarkable size reduction of over 100X compared to vanilla 3DGS when averaged on all datasets, while simultaneously improving fidelity. It also delivers more than 20X size reduction compared to Scaffold-GS. Our code is available at https://github.com/YihangChen-ee/HAC-plus.
3D高斯模糊技术(3DGS)作为一种新型视角合成框架展现出巨大的潜力,它以高速渲染和高保真度受到瞩目。然而,大量的高斯及其相关属性需要大量有效的压缩技术。尽管如此,高斯点云的稀疏性和无组织性(或我们论文中的锚点)给压缩带来了挑战。为了实现紧凑的大小,我们提出了HAC++,它利用无组织锚点之间的关系和结构化哈希网格,利用它们的互信息来进行上下文建模。此外,HAC++捕获了锚点内部的上下文关系,以进一步增强压缩性能。为了促进熵编码,我们利用高斯分布精确估计每个量化属性的概率,并提出了一种自适应量化模块,实现对这些属性的高精度量化,以提高保真度的恢复。此外,我们采用自适应掩码策略来消除无效的高斯和锚点。总的来说,HAC++在所有数据集上平均实现了与基本3DGS相比超过100倍的显著大小缩减,同时提高了保真度。与Scaffold-GS相比,它实现了超过20倍的尺寸缩减。我们的代码可在[https://github.com/YihangChen-ee/HAC-plus找到。]
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project Page: https://yihangchen-ee.github.io/project_hac++/ Code: https://github.com/YihangChen-ee/HAC-plus. This paper is a journal extension of HAC at arXiv:2403.14530 (ECCV 2024)
Summary
本文介绍了基于三维高斯插值(3DGS)技术的视图合成方法,具有快速渲染和高保真度的特点。针对高斯数据量大、结构复杂的问题,提出了基于哈希网格和自适应量化的压缩算法HAC++。通过利用无序锚点间的空间关系以及高斯分布的上下文信息,HAC++实现紧凑的压缩表现,减小数据量。同时,HAC++引入自适应掩码策略,有效去除无效高斯和锚点。相较于传统方法,HAC++在数据集平均上实现了超过100倍的压缩比提升,同时保持较高的保真度。代码已公开于GitHub上。
Key Takeaways
- 3DGS在视图合成领域具有快速渲染和高保真度的优势。
- 高斯数据量大会导致存储和传输挑战,需要有效的压缩技术。
- HAC++利用哈希网格管理无序锚点,通过上下文信息实现紧凑压缩。
- HAC++引入自适应量化模块,提高属性量化的精度,优化保真度恢复。
- HAC++采用自适应掩码策略,去除无效高斯和锚点,进一步提高压缩效率。
- HAC++相较于传统方法实现了显著的压缩比提升,同时保持较高的保真度。
点此查看论文截图

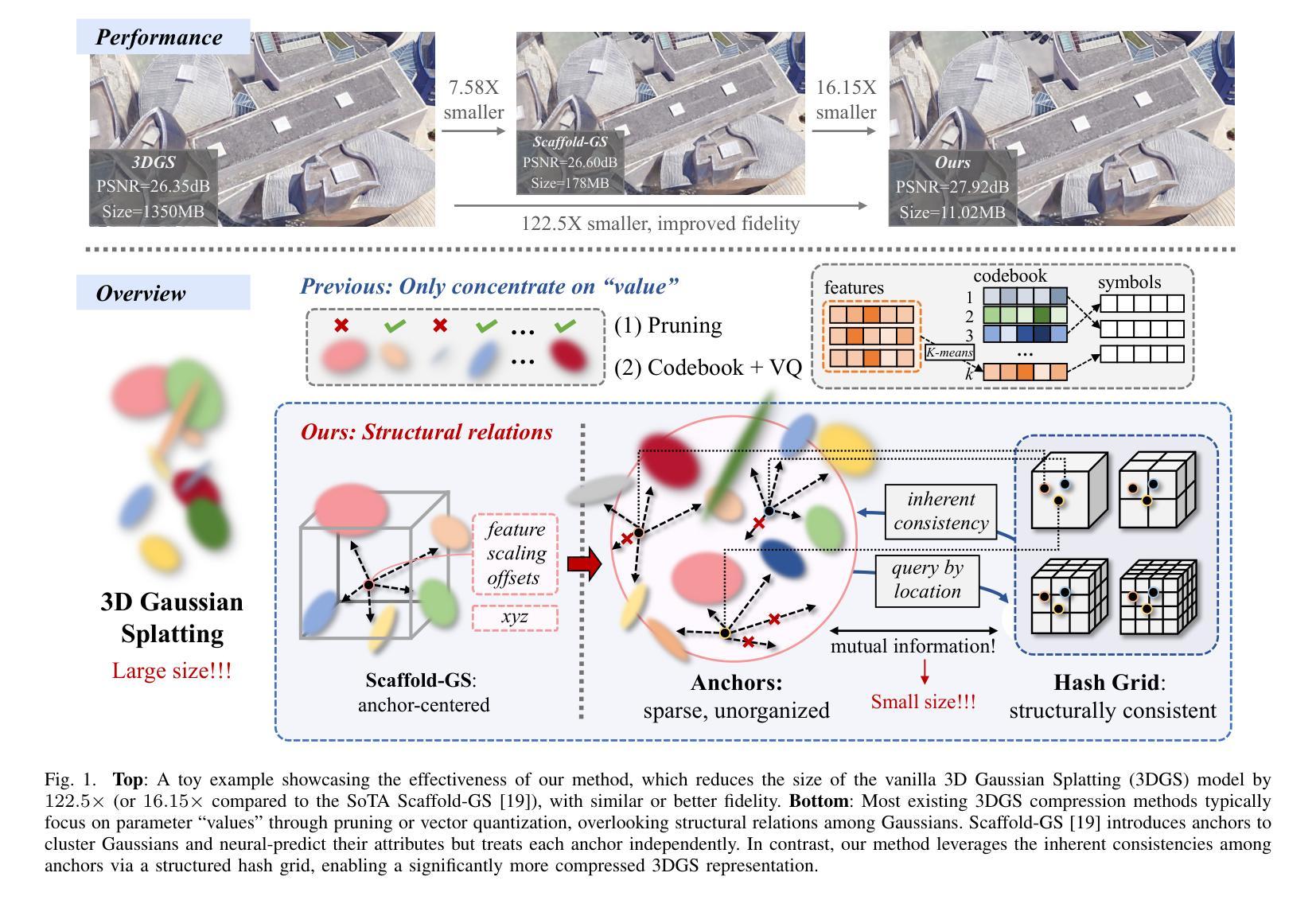
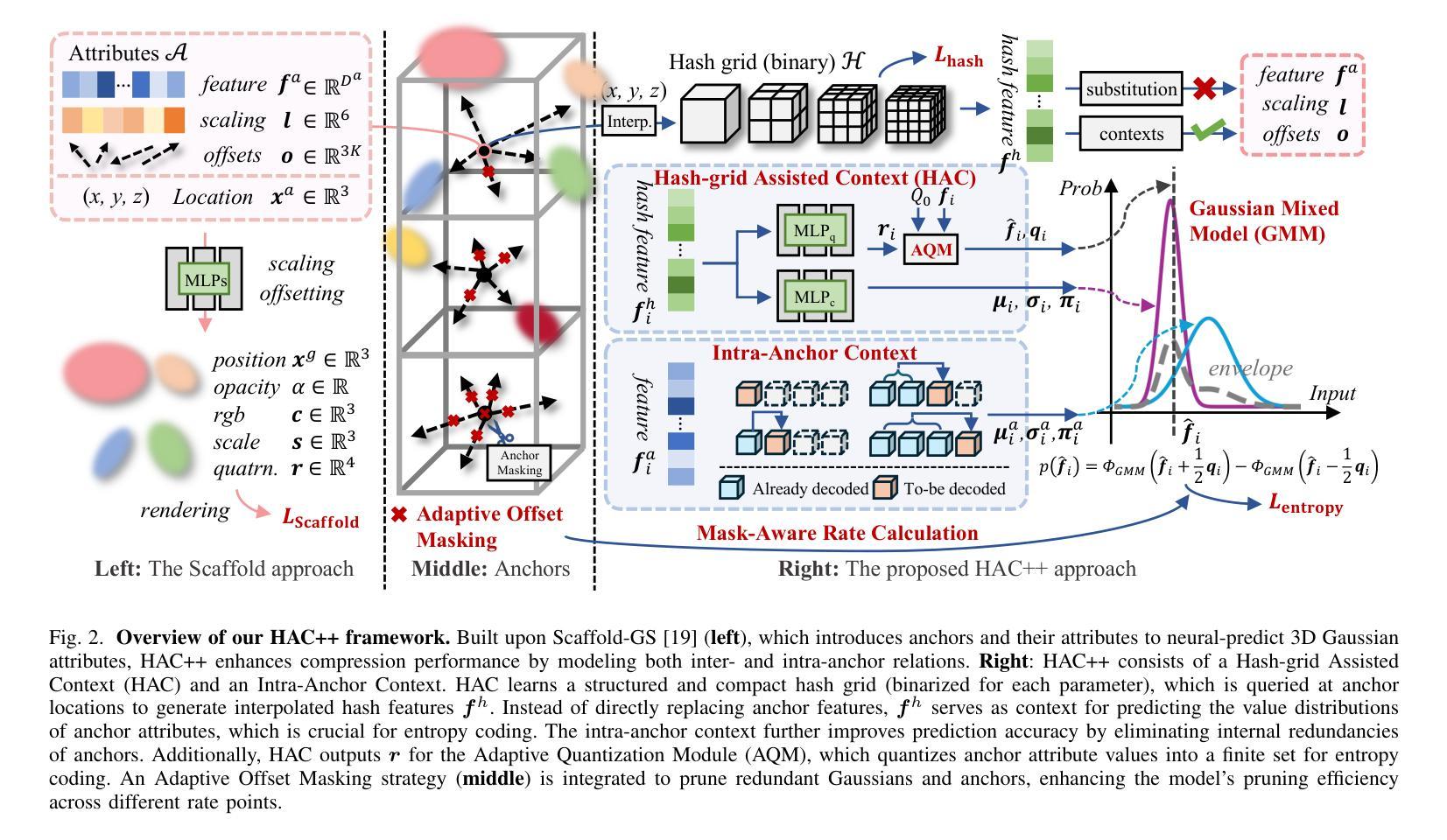
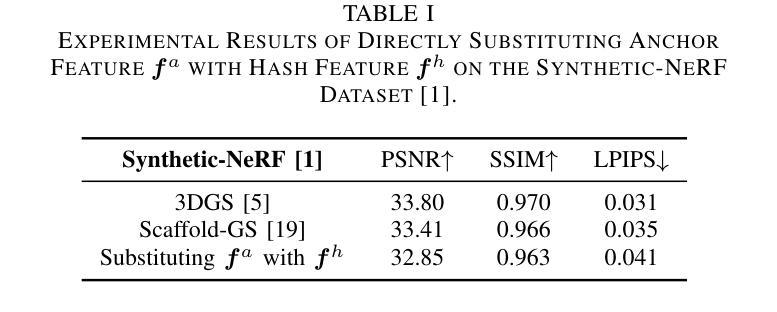
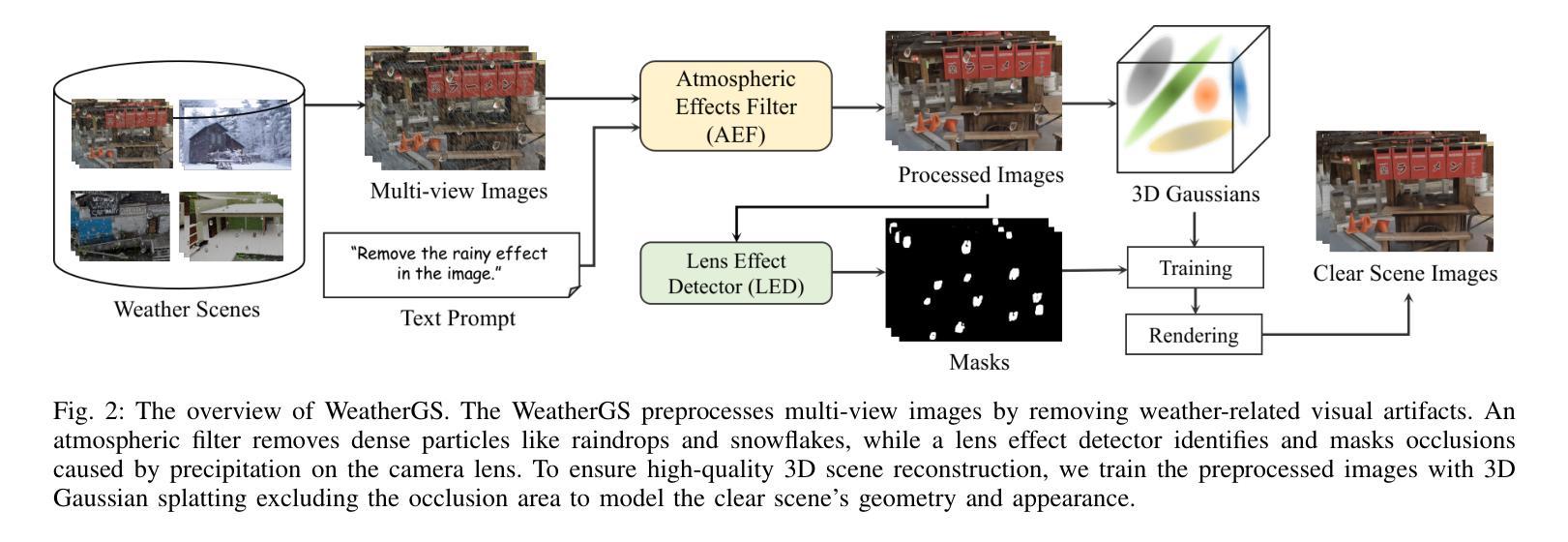
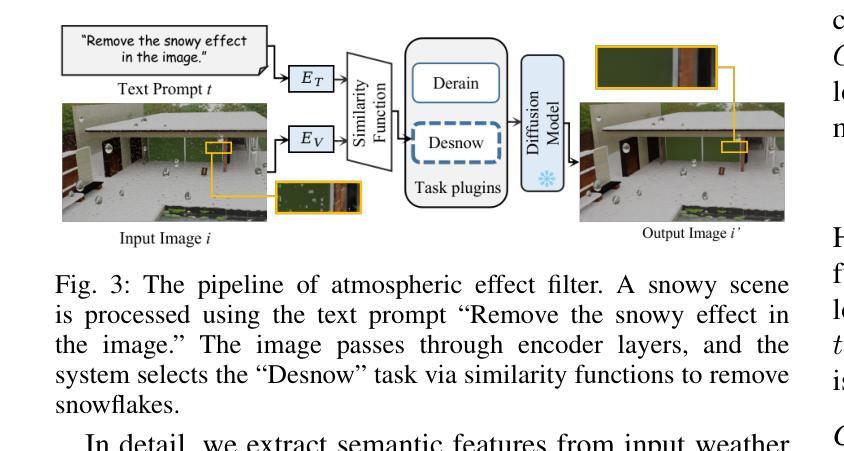
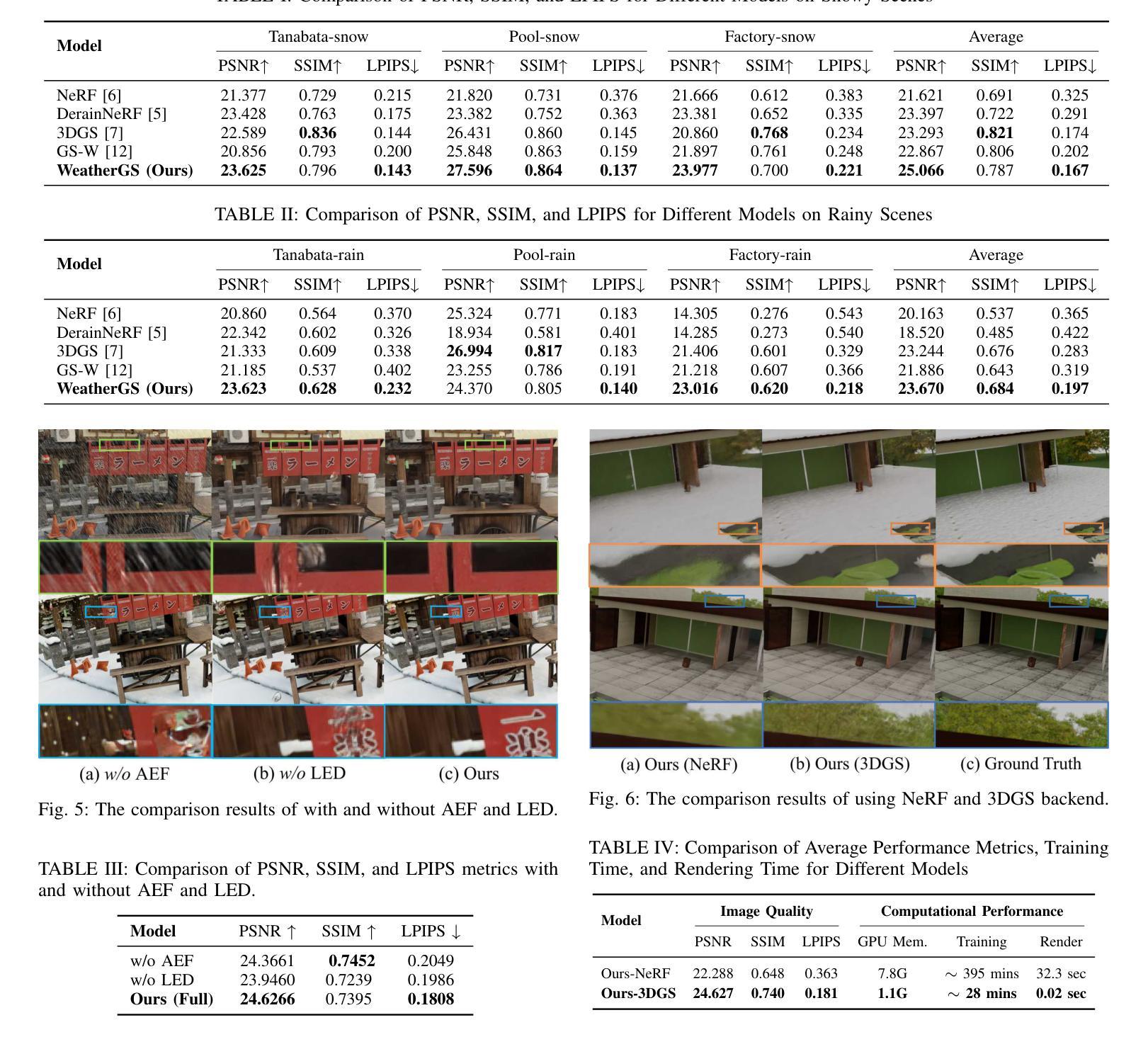
WeatherGS: 3D Scene Reconstruction in Adverse Weather Conditions via Gaussian Splatting
Authors:Chenghao Qian, Yuhu Guo, Wenjing Li, Gustav Markkula
3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) has gained significant attention for 3D scene reconstruction, but still suffers from complex outdoor environments, especially under adverse weather. This is because 3DGS treats the artifacts caused by adverse weather as part of the scene and will directly reconstruct them, largely reducing the clarity of the reconstructed scene. To address this challenge, we propose WeatherGS, a 3DGS-based framework for reconstructing clear scenes from multi-view images under different weather conditions. Specifically, we explicitly categorize the multi-weather artifacts into the dense particles and lens occlusions that have very different characters, in which the former are caused by snowflakes and raindrops in the air, and the latter are raised by the precipitation on the camera lens. In light of this, we propose a dense-to-sparse preprocess strategy, which sequentially removes the dense particles by an Atmospheric Effect Filter (AEF) and then extracts the relatively sparse occlusion masks with a Lens Effect Detector (LED). Finally, we train a set of 3D Gaussians by the processed images and generated masks for excluding occluded areas, and accurately recover the underlying clear scene by Gaussian splatting. We conduct a diverse and challenging benchmark to facilitate the evaluation of 3D reconstruction under complex weather scenarios. Extensive experiments on this benchmark demonstrate that our WeatherGS consistently produces high-quality, clean scenes across various weather scenarios, outperforming existing state-of-the-art methods. See project page:https://jumponthemoon.github.io/weather-gs.
3D高斯点云(3DGS)在3D场景重建方面受到了广泛关注,但仍面临着复杂户外环境的挑战,尤其是在恶劣天气下。这是因为3DGS将恶劣天气引起的伪影视为场景的一部分并将其直接重建,大大降低了重建场景的清晰度。为了应对这一挑战,我们提出了WeatherGS,这是一个基于3DGS的框架,可以从不同天气条件下的多视角图像重建清晰的场景。具体来说,我们明确地将多天气伪影分为密集粒子和镜头遮挡两类,这两类具有非常不同的特性,前者是由空气中的雪花和雨滴引起的,后者是由相机镜头上的沉淀物引起的。鉴于此,我们提出了一种由密集到稀疏的预处理策略,依次通过大气效应滤波器(AEF)去除密集粒子,然后使用镜头效应检测器(LED)提取相对稀疏的遮挡掩膜。最后,我们使用处理过的图像和生成的掩膜训练一组3D高斯模型,排除遮挡区域,并通过高斯点云准确恢复潜在的清晰场景。我们进行了一项多样且具有挑战性的基准测试,以促进在复杂天气场景下3D重建的评估。在该基准测试上的大量实验表明,我们的WeatherGS在各种天气场景下始终产生高质量、清晰的场景,优于现有的最先进的方法。请参见项目页面:https://jumponthemoon.github.io/weather-gs。(翻译至此可能有部分内容损失或无法完全表达原文含义)。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于大气效应过滤器和镜头效应检测器的天气感知三维高斯映射(WeatherGS)框架,能有效解决复杂户外环境下,尤其是恶劣天气条件下的三维场景重建问题。通过预处理策略去除密集粒子,提取稀疏遮挡掩膜,训练高斯模型并排除遮挡区域,最终恢复清晰场景。在复杂天气场景下的三维重建评估基准测试中,WeatherGS表现优异,生成高质量清洁场景。
Key Takeaways
- 3DGS在恶劣天气下的三维场景重建面临挑战。
- WeatherGS框架采用基于密集-稀疏预处理策略来处理不同天气条件的多视角图像。
- 利用大气效应过滤器(AEF)去除密集粒子,再用镜头效应检测器(LED)提取稀疏遮挡掩膜。
- 通过处理过的图像和生成的掩膜训练一组三维高斯模型,排除遮挡区域。
- WeatherGS能准确恢复清晰场景,在各种天气场景下表现稳定,超越现有先进方法。
点此查看论文截图


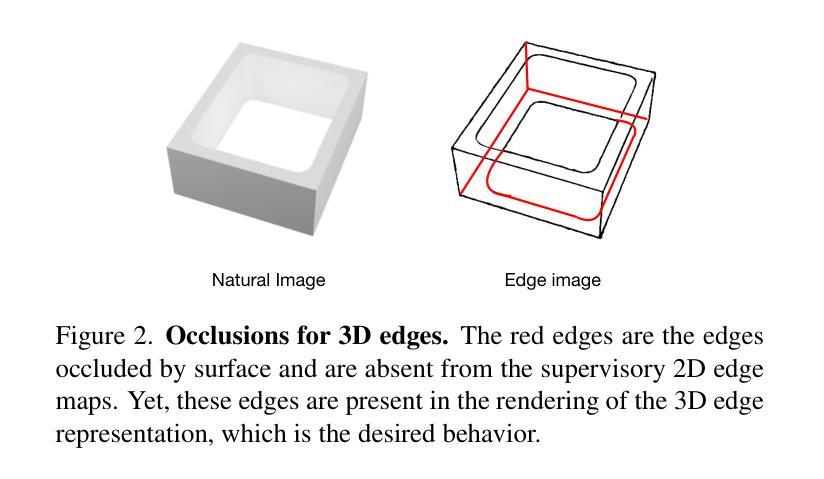
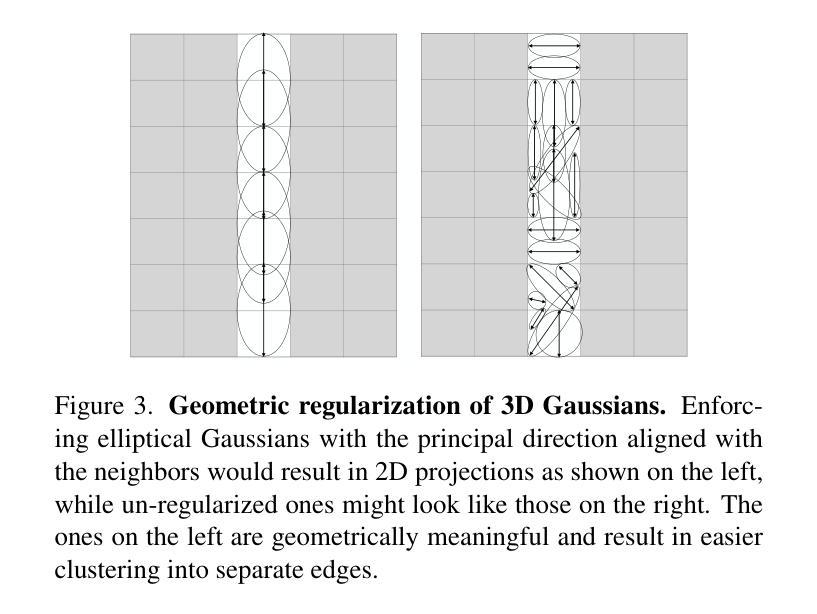
EdgeGaussians – 3D Edge Mapping via Gaussian Splatting
Authors:Kunal Chelani, Assia Benbihi, Torsten Sattler, Fredrik Kahl
With their meaningful geometry and their omnipresence in the 3D world, edges are extremely useful primitives in computer vision. 3D edges comprise of lines and curves, and methods to reconstruct them use either multi-view images or point clouds as input. State-of-the-art image-based methods first learn a 3D edge point cloud then fit 3D edges to it. The edge point cloud is obtained by learning a 3D neural implicit edge field from which the 3D edge points are sampled on a specific level set (0 or 1). However, such methods present two important drawbacks: i) it is not realistic to sample points on exact level sets due to float imprecision and training inaccuracies. Instead, they are sampled within a range of levels so the points do not lie accurately on the 3D edges and require further processing. ii) Such implicit representations are computationally expensive and require long training times. In this paper, we address these two limitations and propose a 3D edge mapping that is simpler, more efficient, and preserves accuracy. Our method learns explicitly the 3D edge points and their edge direction hence bypassing the need for point sampling. It casts a 3D edge point as the center of a 3D Gaussian and the edge direction as the principal axis of the Gaussian. Such a representation has the advantage of being not only geometrically meaningful but also compatible with the efficient training optimization defined in Gaussian Splatting. Results show that the proposed method produces edges as accurate and complete as the state-of-the-art while being an order of magnitude faster. Code is released at https://github.com/kunalchelani/EdgeGaussians.
在三维世界中,边缘因其有意义的几何结构和无处不在的存在,是计算机视觉中非常有用的基本元素。三维边缘由线条和曲线组成,重建它们的方法使用多视图图像或点云作为输入。基于最新图像的方法首先学习一个三维边缘点云,然后将三维边缘拟合到其中。边缘点云是通过从三维神经隐式边缘场学习得到的,其中在该特定水平集(0或1)上从三维边缘点进行采样。然而,这些方法存在两个重要缺点:一)由于浮点精度和训练不准确,在精确的水平集上采样点是不现实的。相反,它们在一定的水平范围内进行采样,因此这些点并不精确地位于三维边缘上,需要进一步处理。二)这种隐式表示计算量大,需要较长的训练时间。在本文中,我们解决了这两个局限性,并提出了一种更简单、更高效且保持准确性的三维边缘映射。我们的方法显式地学习三维边缘点和它们的边缘方向,从而避免了点采样的需要。它将三维边缘点作为三维高斯的中心,将边缘方向作为高斯的主轴。这种表示不仅具有几何意义,而且与高斯Splatting中定义的高效训练优化兼容。结果表明,所提出的方法产生的边缘与最新技术一样准确和完整,但速度更快一个数量级。代码已发布在https://github.com/kunalchelani/EdgeGaussians。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF To appear in the proceedings of WACV 2025
摘要
在计算机视觉领域,边缘作为三维世界中的普遍存在的有意义几何元素,是非常有用的基本元素。本文提出一种新颖的3D边缘映射方法,该方法学习明确的3D边缘点及其边缘方向,从而避免了点采样的需要。该方法将3D边缘点视为3D高斯的中心,将边缘方向视为高斯的主轴。这种表示法不仅具有几何意义,而且与高斯Splatting中定义的高效训练优化兼容。结果证明,该方法产生的边缘既准确又完整,与最新技术相比,速度提高了一个数量级。相关代码已发布在https://github.com/kunalchelani/EdgeGaussians。
关键见解
- 边缘在计算机视觉中是重要的基本元素,用于表示三维世界的几何特征。
- 当前方法通过隐式学习3D边缘点云并拟合到其中存在两大缺点。
- 本文提出一种新颖的显式学习3D边缘点和其方向的方法,绕过点采样的需求。
- 使用高斯表示法来表示3D边缘点及其方向,具有几何意义和计算效率。
- 该方法产生的边缘准确性与最新技术相当,但训练速度显著提高。
- 所提出的方法在GitHub上公开可用,为研究人员提供便利。
点此查看论文截图


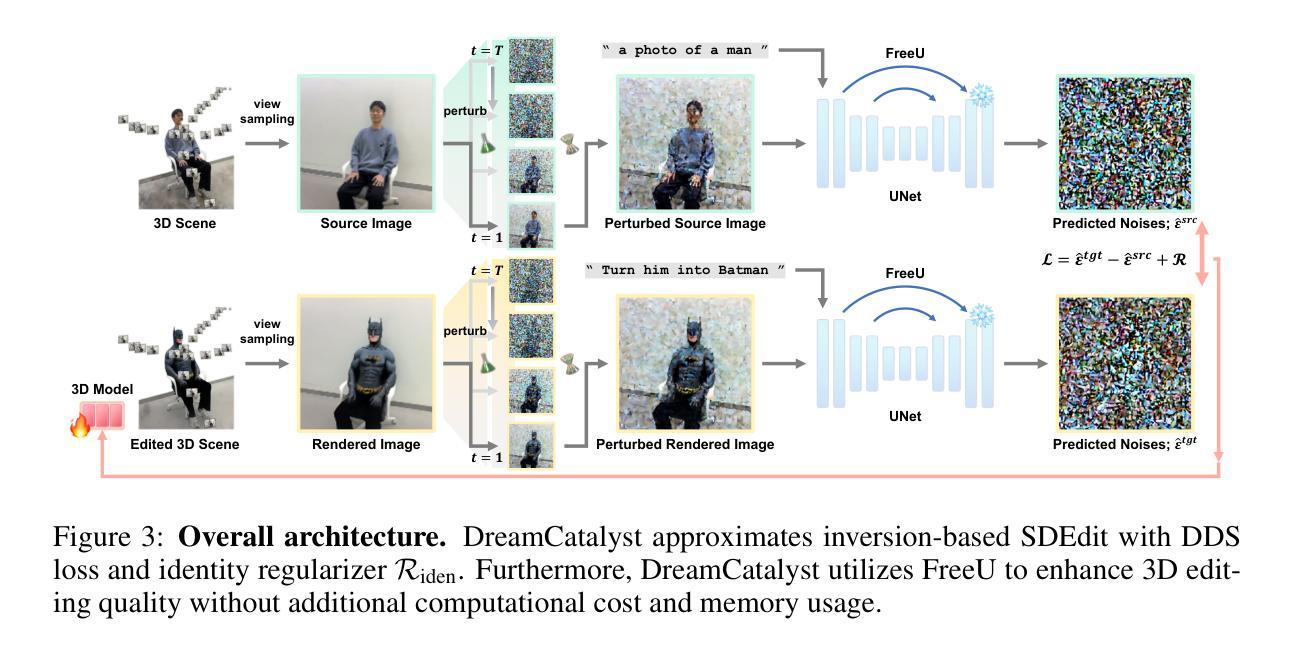
DreamCatalyst: Fast and High-Quality 3D Editing via Controlling Editability and Identity Preservation
Authors:Jiwook Kim, Seonho Lee, Jaeyo Shin, Jiho Choi, Hyunjung Shim
Score distillation sampling (SDS) has emerged as an effective framework in text-driven 3D editing tasks, leveraging diffusion models for 3D-consistent editing. However, existing SDS-based 3D editing methods suffer from long training times and produce low-quality results. We identify that the root cause of this performance degradation is \textit{their conflict with the sampling dynamics of diffusion models}. Addressing this conflict allows us to treat SDS as a diffusion reverse process for 3D editing via sampling from data space. In contrast, existing methods naively distill the score function using diffusion models. From these insights, we propose DreamCatalyst, a novel framework that considers these sampling dynamics in the SDS framework. Specifically, we devise the optimization process of our DreamCatalyst to approximate the diffusion reverse process in editing tasks, thereby aligning with diffusion sampling dynamics. As a result, DreamCatalyst successfully reduces training time and improves editing quality. Our method offers two modes: (1) a fast mode that edits Neural Radiance Fields (NeRF) scenes approximately 23 times faster than current state-of-the-art NeRF editing methods, and (2) a high-quality mode that produces superior results about 8 times faster than these methods. Notably, our high-quality mode outperforms current state-of-the-art NeRF editing methods in terms of both speed and quality. DreamCatalyst also surpasses the state-of-the-art 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) editing methods, establishing itself as an effective and model-agnostic 3D editing solution. See more extensive results on our project page: https://dream-catalyst.github.io.
得分蒸馏采样(SDS)已成为文本驱动的三维编辑任务中的有效框架,利用扩散模型进行三维一致性编辑。然而,现有的基于SDS的三维编辑方法存在训练时间长和结果质量低的问题。我们确定性能下降的根本原因是它们与扩散模型的采样动力存在冲突。解决这种冲突使我们能够将SDS视为通过数据空间采样进行三维编辑的扩散反向过程。相比之下,现有方法只是简单地使用扩散模型对分数函数进行蒸馏。从这些见解出发,我们提出了DreamCatalyst,这是一个在SDS框架中考虑这些采样动力学的全新框架。具体来说,我们设计DreamCatalyst的优化过程以近似编辑任务中的扩散反向过程,从而与扩散采样动力学保持一致。因此,DreamCatalyst成功减少了训练时间并提高了编辑质量。我们的方法提供了两种模式:(1)快速模式,编辑神经辐射场(NeRF)场景的速度比当前最先进的NeRF编辑方法快约23倍;(2)高质量模式,产生优于这些方法的结果,大约快8倍。值得注意的是,我们的高质量模式在速度和品质方面都超越了当前的先进NeRF编辑方法。DreamCatalyst也超越了最先进的3D高斯拼贴(3DGS)编辑方法,成为了一种有效且模型无关的三维编辑解决方案。想了解更多结果,请访问我们的项目页面:https://dream-catalyst.github.io。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICLR 2025
摘要
SDS(分数蒸馏采样)框架在文本驱动的3D编辑任务中展现出强大的效果,特别是利用扩散模型实现3D一致性编辑。然而,现有的SDS-based 3D编辑方法存在训练时间长和结果质量不高的问题。本文指出,这一性能下降的根本原因是SDS与扩散模型的采样动力学存在冲突。解决这一冲突使我们能够将SDS视为通过数据空间采样进行3D编辑的扩散逆过程。相比之下,现有方法只是简单地蒸馏扩散模型中的分数函数。基于此,我们提出了DreamCatalyst框架,该框架考虑了SDS框架中的采样动力学。具体来说,我们设计DreamCatalyst的优化过程以近似编辑任务中的扩散逆过程,从而与扩散采样动力学保持一致。因此,DreamCatalyst成功缩短了训练时间并提高了编辑质量。我们的方法提供了两种模式:(1)快速模式,编辑神经辐射场(NeRF)场景的速度比当前最先进的NeRF编辑方法快约23倍;(2)高质量模式,在速度比这些方法快8倍的同时产生优越的结果。值得注意的是,我们的高质量模式在速度和质量方面都超越了当前的NeRF编辑方法和3D高斯拼贴(3DGS)编辑方法,成为了一种有效且模型无关的3D编辑解决方案。更多详细结果请参见我们的项目页面:https://dream-catalyst.github.io。
要点提炼
- SDS框架在文本驱动的3D编辑中展现出有效性,但存在训练时间长和质量问题。
- 问题的根源在于SDS与扩散模型的采样动力学之间的冲突。
- 提出DreamCatalyst框架,考虑采样动力学,优化SDS框架。
- DreamCatalyst缩短训练时间,提高编辑质量。
- 提供两种模式:快速模式可快速编辑NeRF场景,高质量模式在速度和质量上均超越现有方法。
- DreamCatalyst优于当前的NeRF编辑和3DGS编辑方法,成为有效的3D编辑解决方案。
点此查看论文截图

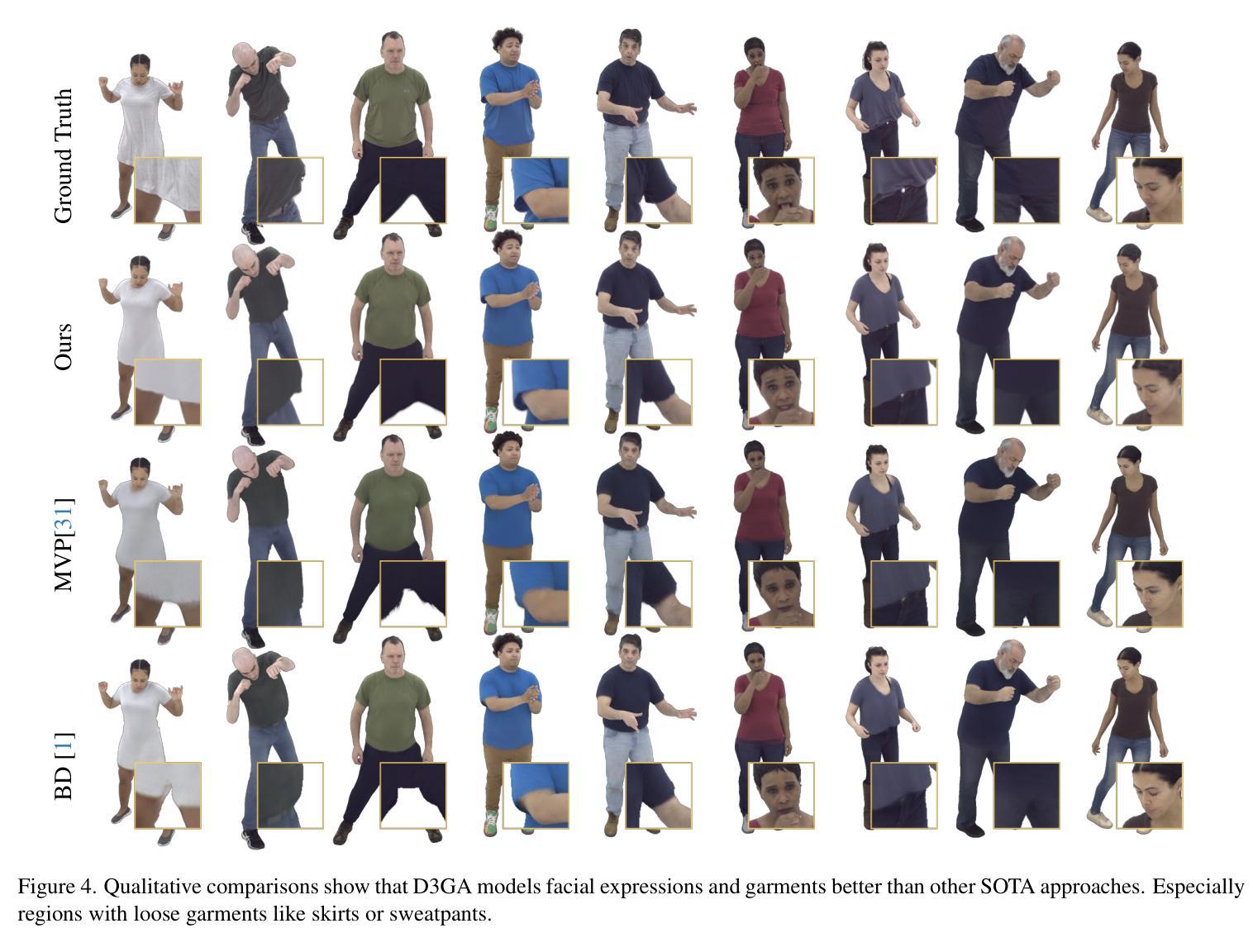
Drivable 3D Gaussian Avatars
Authors:Wojciech Zielonka, Timur Bagautdinov, Shunsuke Saito, Michael Zollhöfer, Justus Thies, Javier Romero
We present Drivable 3D Gaussian Avatars (D3GA), a multi-layered 3D controllable model for human bodies that utilizes 3D Gaussian primitives embedded into tetrahedral cages. The advantage of using cages compared to commonly employed linear blend skinning (LBS) is that primitives like 3D Gaussians are naturally re-oriented and their kernels are stretched via the deformation gradients of the encapsulating tetrahedron. Additional offsets are modeled for the tetrahedron vertices, effectively decoupling the low-dimensional driving poses from the extensive set of primitives to be rendered. This separation is achieved through the localized influence of each tetrahedron on 3D Gaussians, resulting in improved optimization. Using the cage-based deformation model, we introduce a compositional pipeline that decomposes an avatar into layers, such as garments, hands, or faces, improving the modeling of phenomena like garment sliding. These parts can be conditioned on different driving signals, such as keypoints for facial expressions or joint-angle vectors for garments and the body. Our experiments on two multi-view datasets with varied body shapes, clothes, and motions show higher-quality results. They surpass PSNR and SSIM metrics of other SOTA methods using the same data while offering greater flexibility and compactness.
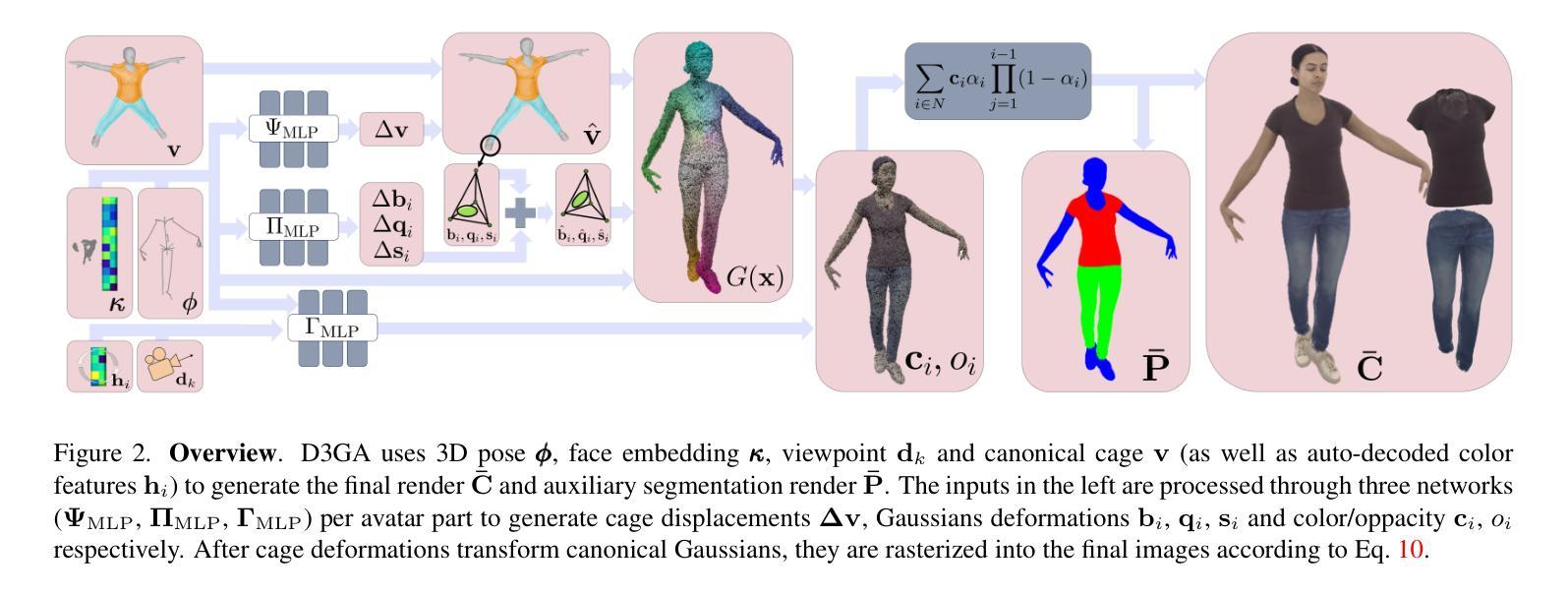
我们推出了可驾驶的3D高斯化身(D3GA),这是一个多层次的可控3D人体模型,它使用嵌入四面体笼的3D高斯基元。与使用普遍采用的线性混合蒙皮(LBS)相比,使用笼的优点在于可以利用封装四面体的变形梯度重新定向基元(如3D高斯),并拉伸其内核。对四面体顶点进行了额外的偏移建模,有效地将低维驱动姿势与要渲染的大量基元解耦。这种分离是通过每个四面体对3D高斯的局部影响来实现的,从而改善了优化效果。使用基于笼的变形模型,我们引入了一种组合管道,将化身分解为多个层次,如服装、手和脸等,这提高了服装滑动等现象的建模效果。这些部分可以根据不同的驱动信号进行调节,如面部表情的关键点或服装和身体关节角度向量。我们在两个具有不同身体形状、服装和运动的多视角数据集上的实验显示,我们的结果具有更高的质量。它们在使用相同数据的PSNR和SSIM指标上超越了其他先进方法,同时提供了更大的灵活性和紧凑性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to 3DV25 Website: https://zielon.github.io/d3ga/
Summary
基于四面体网格框架,利用高斯参数化的混合表示构造了名为可驾驶三维高斯头像(D3GA)的新型三层可控人体模型。此方法利用笼式变形模型改善了物理和机械动态场景的重建效果,使得不同部位具有更强的独立性。此技术优化了分层处理模型并增强了实用性,可实现个性化操作及优质结果。在特定数据集上的实验显示,该模型超越了现有技术水准的PSNR和SSIM指标,实现高画质,拥有出色的灵活性和紧致性。通过集成多元化的驱动器信号组件层系统得到了灵活的支持以更详尽准确地重塑人物特性,有助于提供无缝效果的改进动画建模方法。
Key Takeaways
- 利用四面体网格框架构建新型多层可控人体模型Drivable 3D Gaussian Avatars (D3GA)。通过四面体网格框架实现更精细的模型构建和动态控制。
点此查看论文截图