⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-02-13 更新
SwiftSketch: A Diffusion Model for Image-to-Vector Sketch Generation
Authors:Ellie Arar, Yarden Frenkel, Daniel Cohen-Or, Ariel Shamir, Yael Vinker
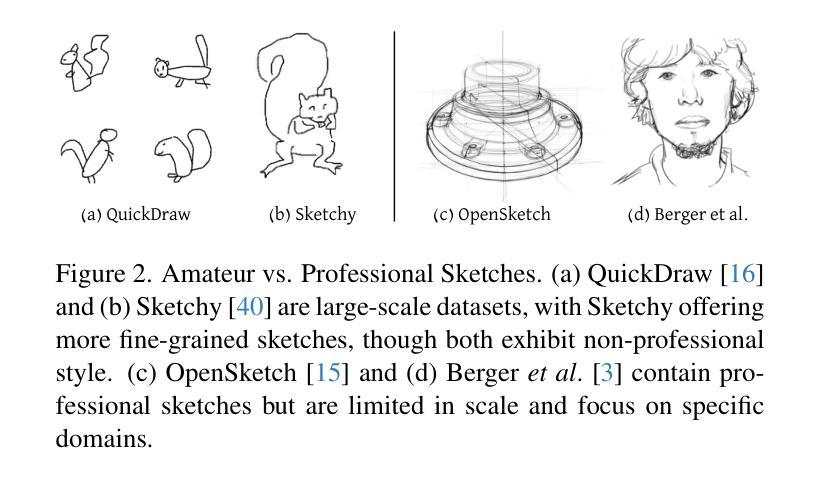
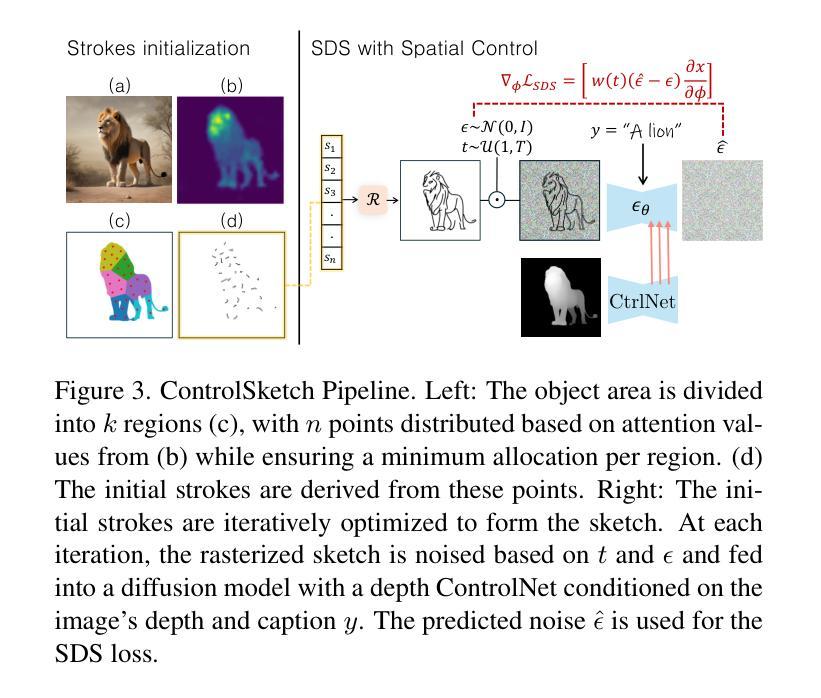
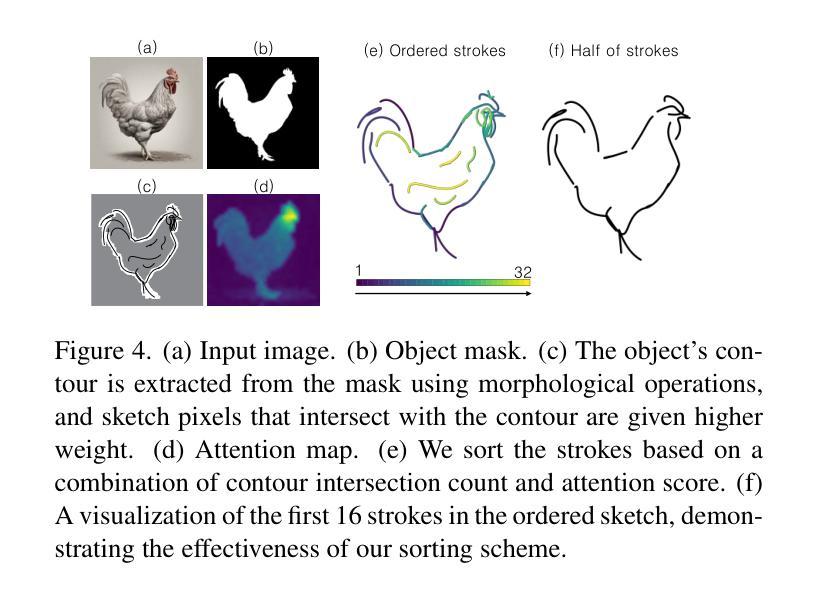
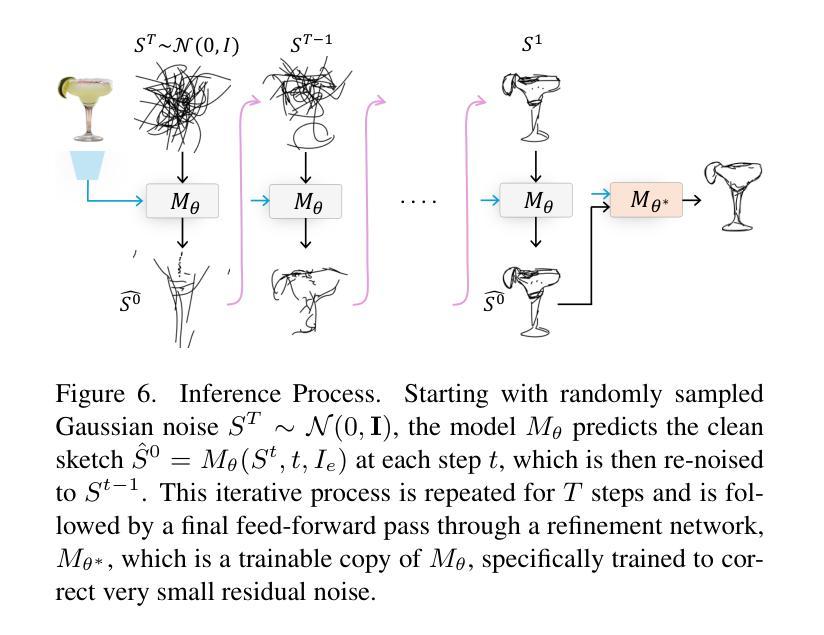
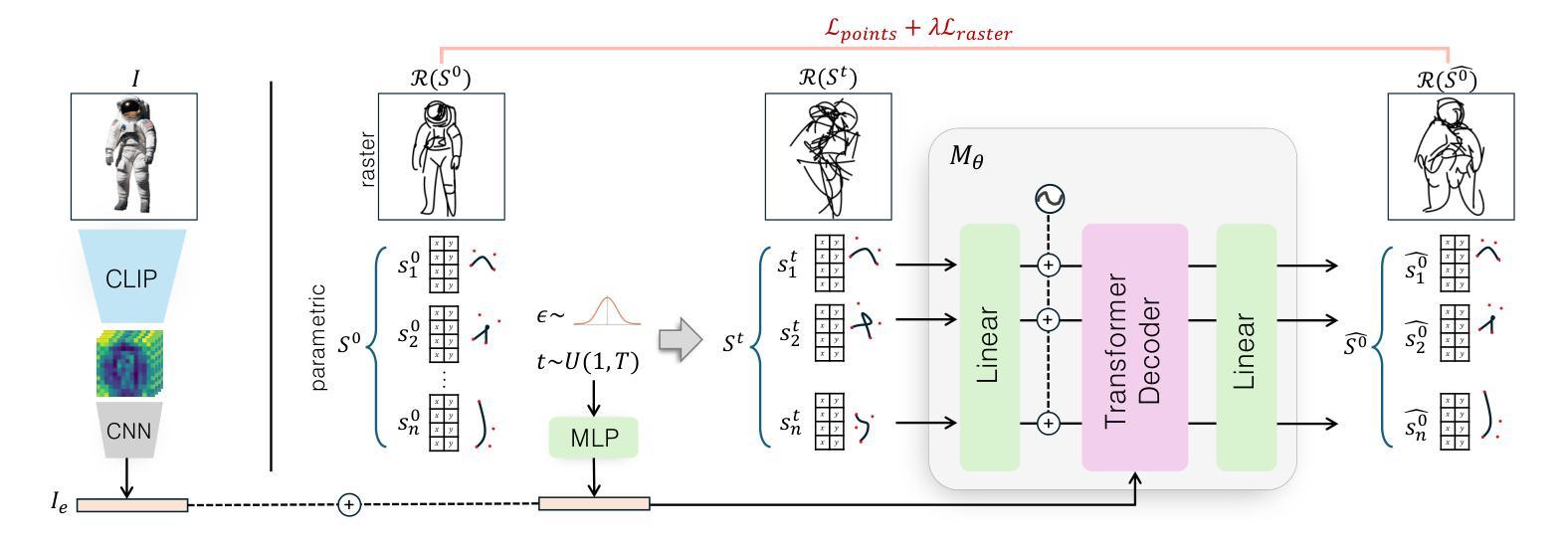
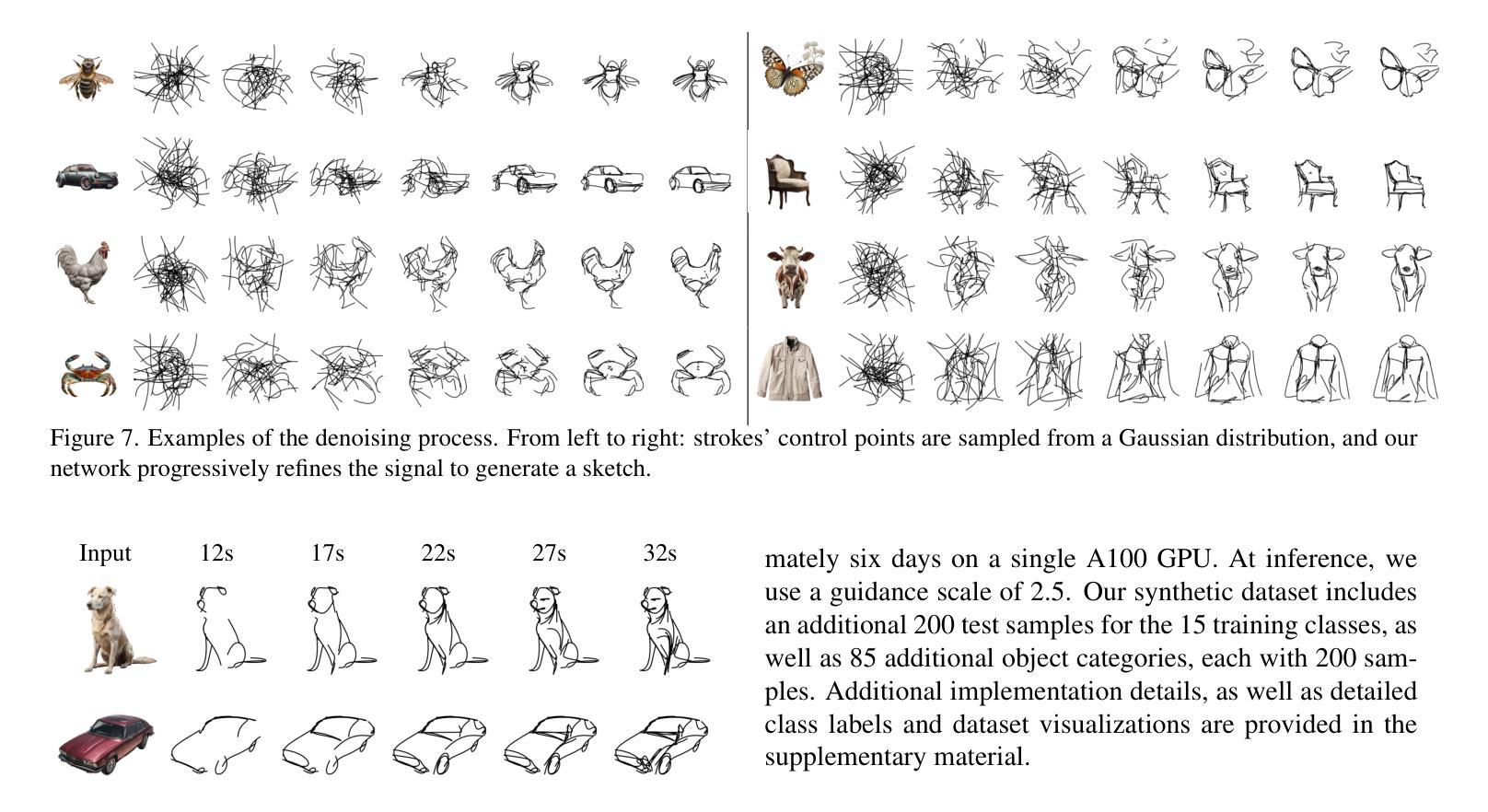
Recent advancements in large vision-language models have enabled highly expressive and diverse vector sketch generation. However, state-of-the-art methods rely on a time-consuming optimization process involving repeated feedback from a pretrained model to determine stroke placement. Consequently, despite producing impressive sketches, these methods are limited in practical applications. In this work, we introduce SwiftSketch, a diffusion model for image-conditioned vector sketch generation that can produce high-quality sketches in less than a second. SwiftSketch operates by progressively denoising stroke control points sampled from a Gaussian distribution. Its transformer-decoder architecture is designed to effectively handle the discrete nature of vector representation and capture the inherent global dependencies between strokes. To train SwiftSketch, we construct a synthetic dataset of image-sketch pairs, addressing the limitations of existing sketch datasets, which are often created by non-artists and lack professional quality. For generating these synthetic sketches, we introduce ControlSketch, a method that enhances SDS-based techniques by incorporating precise spatial control through a depth-aware ControlNet. We demonstrate that SwiftSketch generalizes across diverse concepts, efficiently producing sketches that combine high fidelity with a natural and visually appealing style.
近期的大型视觉语言模型的进展使得具有表现力和多样性的矢量素描生成成为可能。然而,最先进的这些方法依赖于耗时优化过程,涉及预训练模型的重复反馈来确定笔触位置。因此,尽管产生了令人印象深刻的素描,这些方法在实际应用中的局限性仍然明显。在这项工作中,我们介绍了SwiftSketch,这是一种基于图像条件的矢量素描生成的扩散模型,可以在不到一秒钟的时间内产生高质量的素描。SwiftSketch通过逐步去除从高斯分布中采样的笔画控制点的噪声来工作。其基于transformer的解码器架构旨在有效处理矢量表示的离散性质,并捕捉笔画之间的内在全局依赖性。为了训练SwiftSketch,我们构建了一个图像-素描对的合成数据集,解决了现有素描数据集的局限性,这些数据集通常是由非艺术家创建的,缺乏专业质量。为了生成这些合成素描,我们引入了ControlSketch方法,它通过深度感知的ControlNet融入精确的空间控制,增强了基于SDS的技术。我们证明了SwiftSketch能够推广各种概念,有效生成具有高保真度、自然和视觉吸引力的风格的素描。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF https://swiftsketch.github.io/
Summary
大型视觉语言模型的最新进展已实现了表达丰富、多样化的向量草图生成。然而,现有方法依赖于耗时的优化过程,涉及预训练模型的反复反馈以确定笔触位置。本研究引入SwiftSketch,一种用于图像条件向量草图生成的扩散模型,可在不到一秒钟内生成高质量草图。SwiftSketch通过逐步去噪从高斯分布中采样的控制点来工作。其设计的transformer-decoder架构能有效处理向量表示的离散性和捕捉笔触间的全局依赖关系。为了训练SwiftSketch,我们构建了一个图像草图对的合成数据集,解决了现有草图数据集的问题,这些数据集往往由非艺术家创建,缺乏专业质量。我们还介绍了ControlSketch方法,它通过深度感知ControlNet技术提高了SDS方法的精度空间控制。我们证明了SwiftSketch在不同概念上的泛化能力,能够高效生成兼具高保真度和自然、美观风格的草图。
Key Takeaways
- 大型视觉语言模型的最新进展使得表达丰富、多样化的向量草图生成成为可能。
- 当前方法依赖于耗时的优化过程,涉及预训练模型的反复反馈。
- SwiftSketch是一种用于图像条件向量草图生成的扩散模型,生成速度快,可在不到一秒钟内生成高质量草图。
- SwiftSketch通过逐步去噪控制点来工作,其架构能有效处理向量表示的离散性和捕捉笔触间的依赖关系。
- 为了训练SwiftSketch,构建了一个图像草图对的合成数据集,解决现有数据集的问题。
- 引入了ControlSketch方法,提高了SDS方法的精度空间控制。
点此查看论文截图

Chasing Charge Carriers: Diffusion Dynamics in Mixed-n Quasi-Two-Dimensional Colloidal MAPbBr3 Perovskites
Authors:Ronja Maria Piehler, Eugen Klein, Francisco M. Gomez-Campos, Oliver Kühn, Rostyslav Lesyuk, Christian Klinke
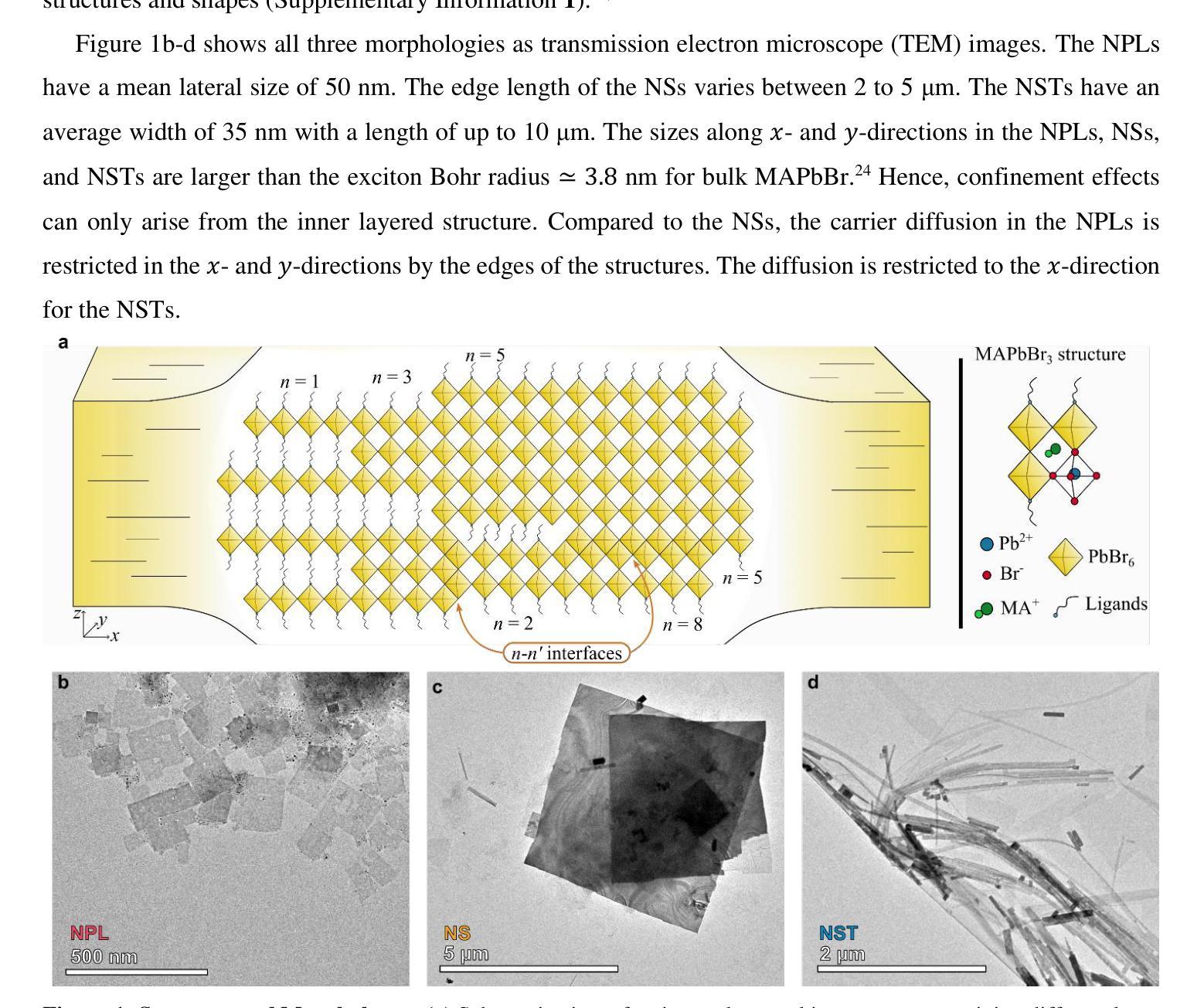
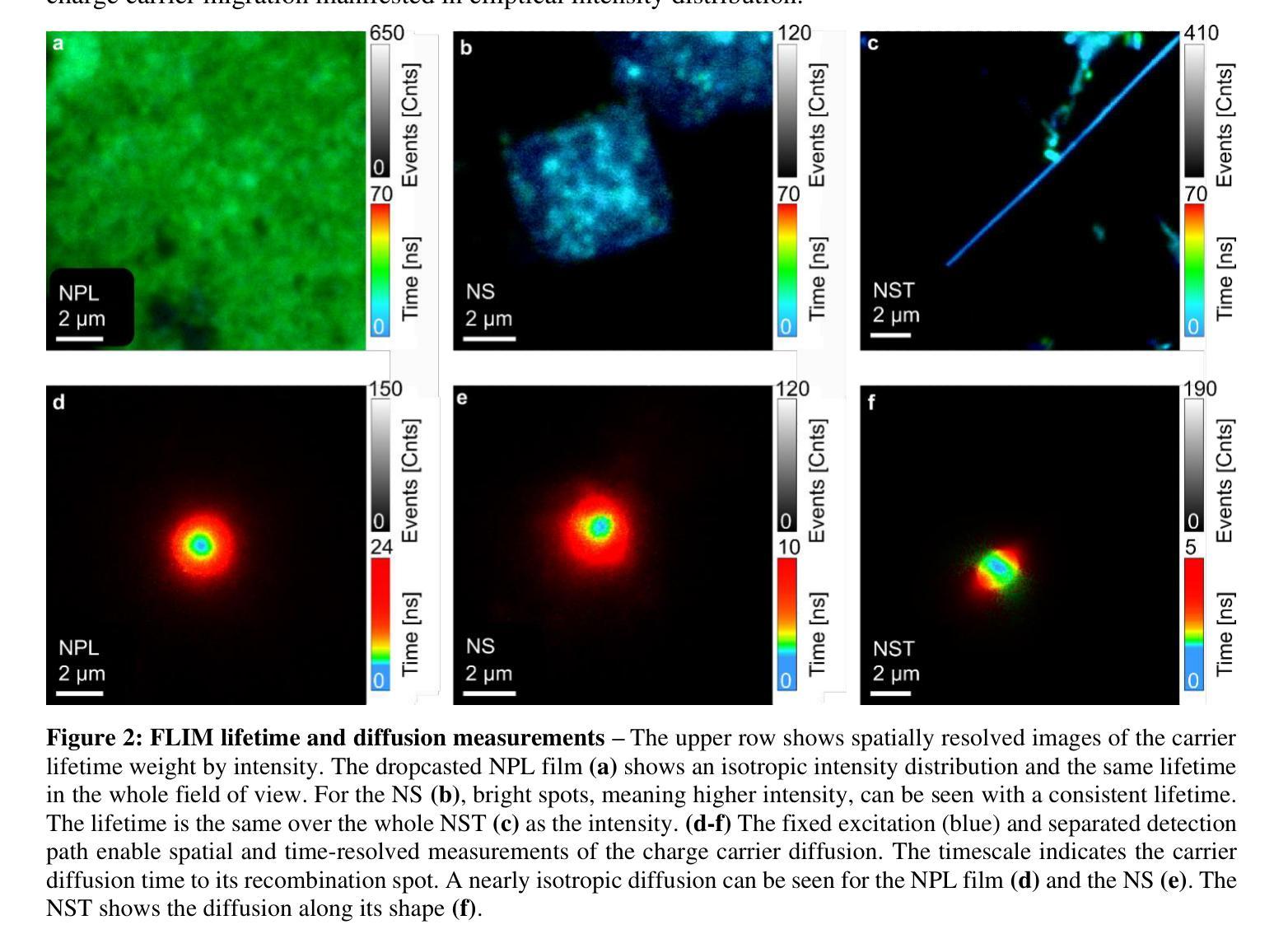
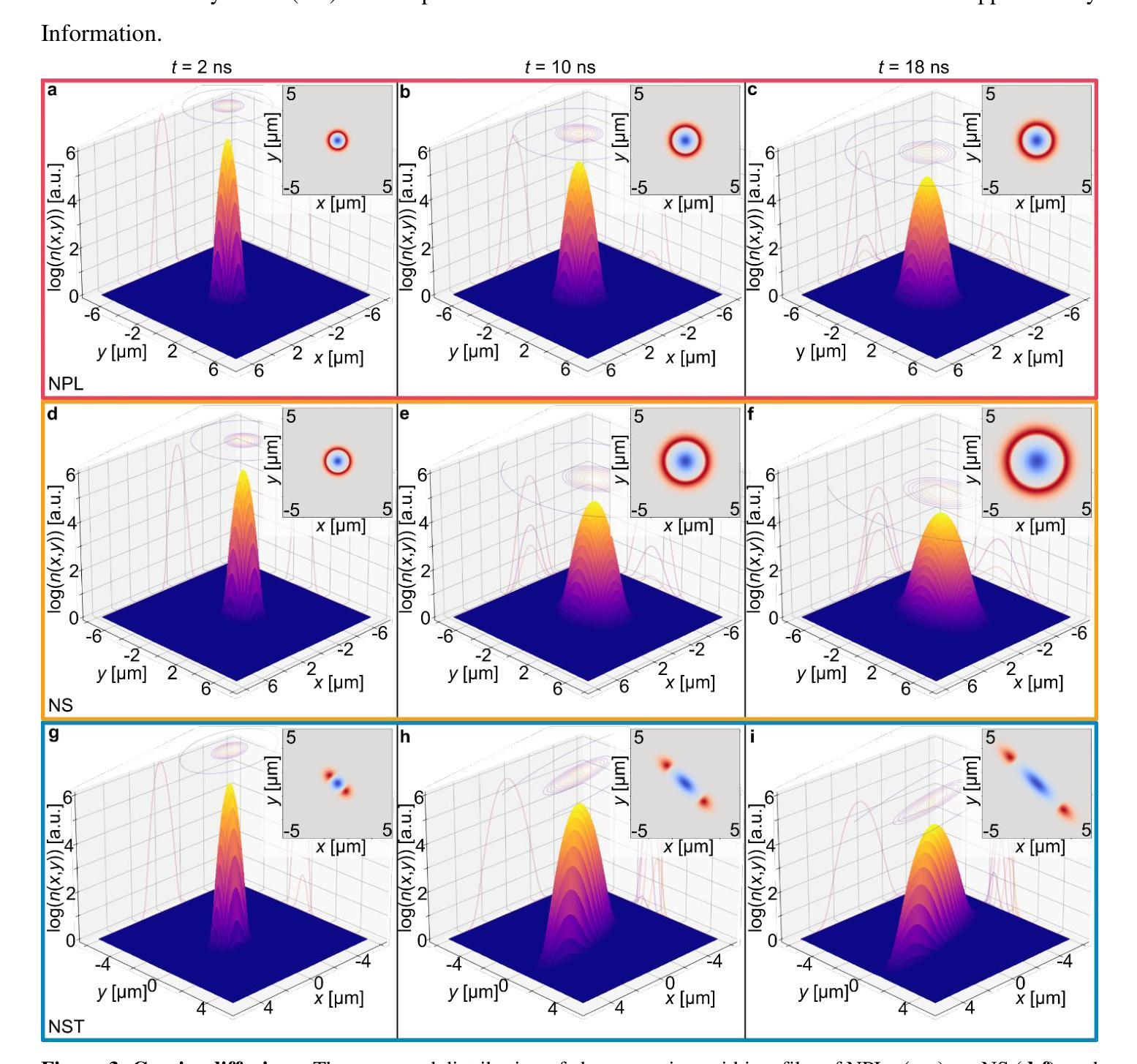
In optoelectronic applications, metal halide perovskites (MHPs) are compelling materials because of their highly tuneable and intensely competitive optical properties. Colloidal synthesis enables the controlled formation of various morphologies of MHP nanocrystals, all with different carrier properties and, hence, different optical and carrier transport behaviours. We characterized three different methylammonium lead tribromide perovskite (MAPbBr3) morphologies: nanoplatelets (NPLs), nanosheets (NSs), and nanostripes (NSTs) synthesized by hot-injection synthesis protocols with slightly different parameters. A fluorescence imaging microscope (FLIM) for time- and space-resolved measurements of the carrier migration was employed to quantify the charge carriers’ migration process upon photoexcitation. The results are rationalized in the two-dimensional diffusion model framework, considering funnelling and trapping processes in mixed-n colloidal MHPs. Subdiffusion mode was found to prevail in the nanocrystals, whereby the highest carrier diffusivity was found for bulk-like NSTs, followed by layered NSs and a film of NPLs. These findings provide a better understanding of optoelectronic processes in perovskites relevant to photovoltaic and light-emitting devices.
在光电子应用中,金属卤化物钙钛矿(MHPs)是非常吸引人的材料,因为它们具有高度可调且竞争力强的光学特性。胶体合成使MHP纳米晶体的各种形态可控形成成为可能,所有这些形态都具有不同的载流子特性,从而表现出不同的光学和载流子传输行为。我们表征了通过热注入合成协议(略有不同参数)合成的三种不同甲基铵铅溴化物钙钛矿(MAPbBr3)形态:纳米血小板(NPLs)、纳米片(NSs)和纳米条纹(NSTs)。采用荧光成像显微镜(FLIM)对载流子迁移进行时-空解析测量,以量化光激发下载流子的迁移过程。结果以二维扩散模型框架进行合理化分析,考虑了混合n胶体MHPs中的引流和俘获过程。在纳米晶体中发现亚扩散模式占主导地位,其中块状的NSTs具有最高的载流子扩散率,其次是层状的NSs和NPLs薄膜。这些发现有助于更好地了解与光伏和发光器件相关的钙钛矿中的光电子过程。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 14 pages, 6 figures
Summary
金属卤化物钙钛矿(MHPs)在光电子应用中具有引人注目的光学特性,可通过胶体合成控制形成各种形态。本文研究了三种不同形态的甲基铵铅溴化物钙钛矿(MAPbBr3):纳米片层(NPLs)、纳米片(NSs)和纳米条纹(NSTs)。采用荧光成像显微镜(FLIM)研究载流子的迁移过程,并在二维扩散模型框架下解释结果。研究发现纳米晶体中普遍存在子扩散模式,其中块状NSTs的载流子扩散性最高,其次是分层NSs和NPLs薄膜。这些发现有助于更好地理解钙钛矿中与光伏和发光器件相关的光电子过程。
Key Takeaways
- 金属卤化物钙钛矿(MHPs)在光电子应用中具有高度可调且竞争性的光学特性。
- 通过胶体合成可以形成不同形态的金属卤化物钙钛矿纳米晶体。
- 纳米片层(NPLs)、纳米片(NSs)和纳米条纹(NSTs)是三种不同的形态。
- 采用荧光成像显微镜(FLIM)研究载流子的迁移过程。
- 研究结果在二维扩散模型框架下解释,考虑了混合n型胶体MHPs中的漏斗和陷阱过程。
- 在纳米晶体中发现子扩散模式占据主导地位。
点此查看论文截图

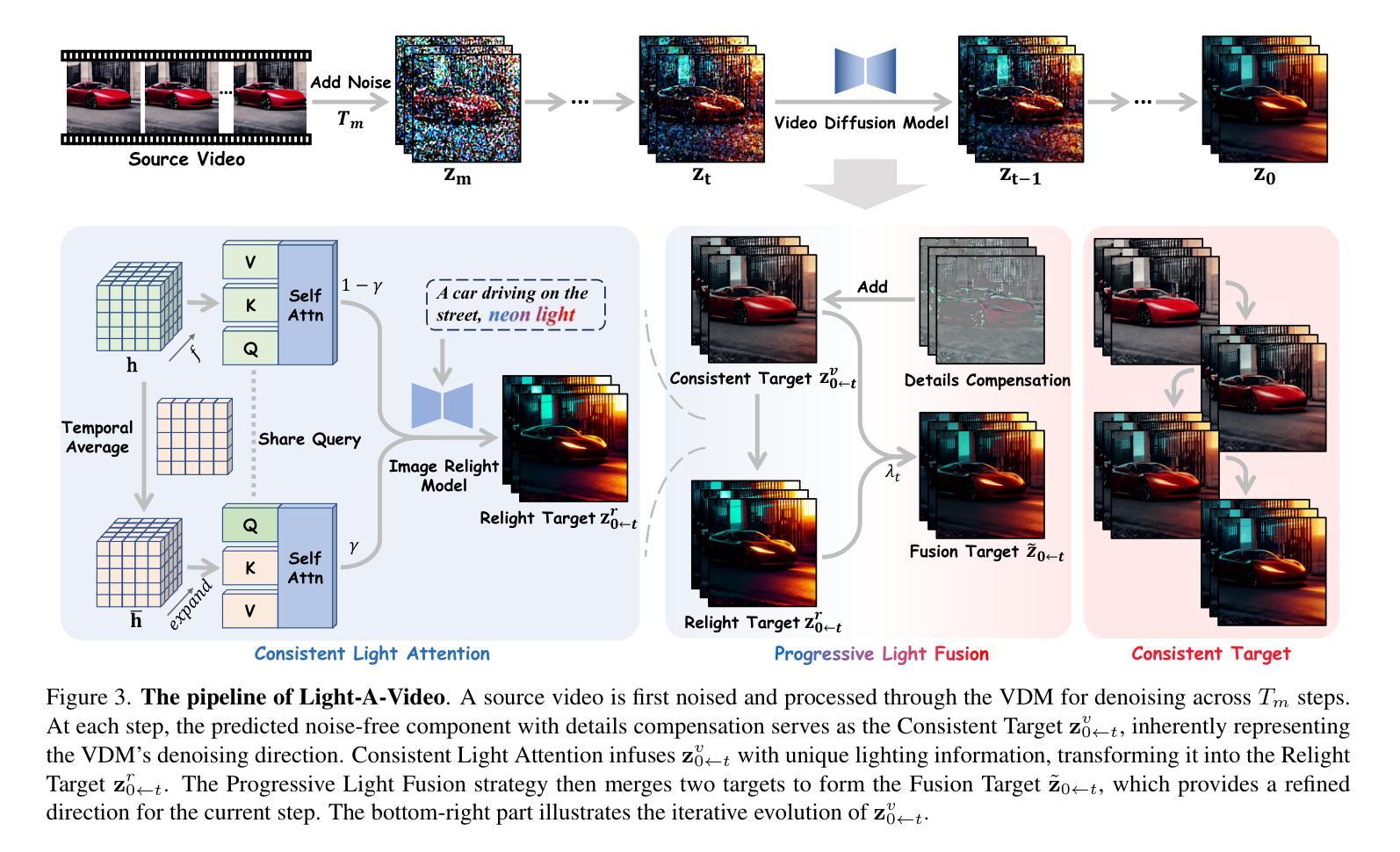
Light-A-Video: Training-free Video Relighting via Progressive Light Fusion
Authors:Yujie Zhou, Jiazi Bu, Pengyang Ling, Pan Zhang, Tong Wu, Qidong Huang, Jinsong Li, Xiaoyi Dong, Yuhang Zang, Yuhang Cao, Anyi Rao, Jiaqi Wang, Li Niu
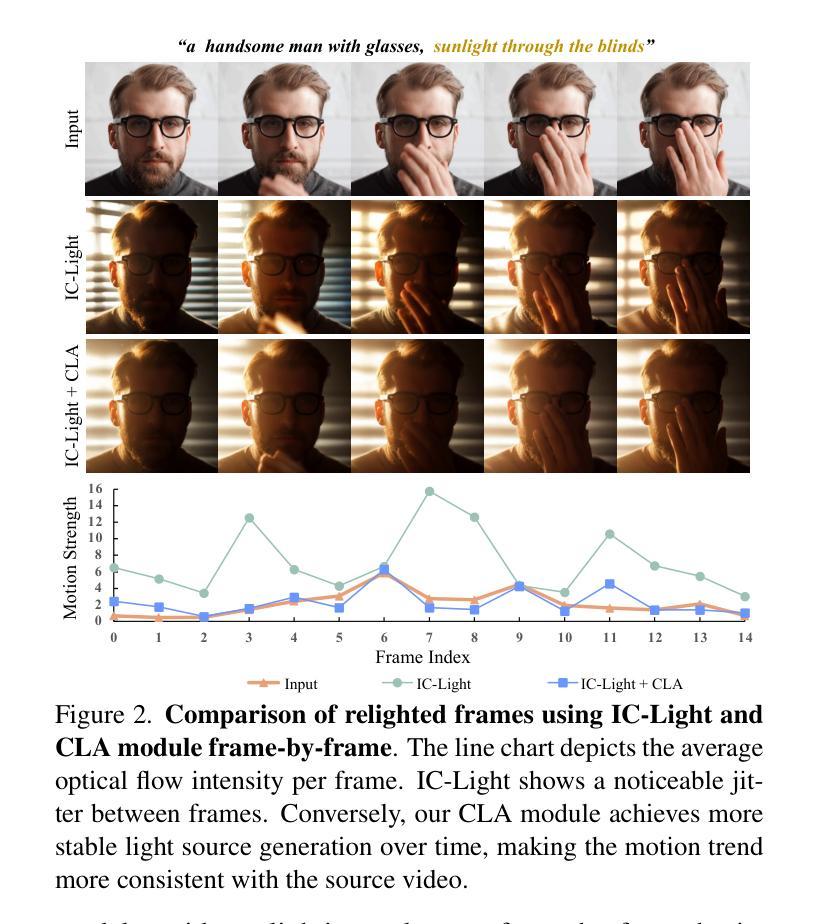
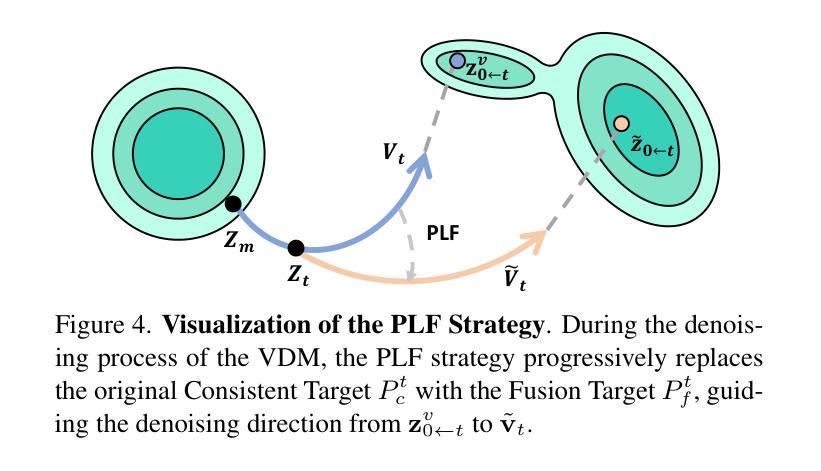
Recent advancements in image relighting models, driven by large-scale datasets and pre-trained diffusion models, have enabled the imposition of consistent lighting. However, video relighting still lags, primarily due to the excessive training costs and the scarcity of diverse, high-quality video relighting datasets. A simple application of image relighting models on a frame-by-frame basis leads to several issues: lighting source inconsistency and relighted appearance inconsistency, resulting in flickers in the generated videos. In this work, we propose Light-A-Video, a training-free approach to achieve temporally smooth video relighting. Adapted from image relighting models, Light-A-Video introduces two key techniques to enhance lighting consistency. First, we design a Consistent Light Attention (CLA) module, which enhances cross-frame interactions within the self-attention layers to stabilize the generation of the background lighting source. Second, leveraging the physical principle of light transport independence, we apply linear blending between the source video’s appearance and the relighted appearance, using a Progressive Light Fusion (PLF) strategy to ensure smooth temporal transitions in illumination. Experiments show that Light-A-Video improves the temporal consistency of relighted video while maintaining the image quality, ensuring coherent lighting transitions across frames. Project page: https://bujiazi.github.io/light-a-video.github.io/.
近期,由于大规模数据集和预训练扩散模型的推动,图像照明模型取得了进展,已实现一致照明的应用。然而,视频重照明仍然滞后,主要是由于训练成本过高和多样化、高质量视频重照明数据集的稀缺。简单地将图像重照明模型逐帧应用会导致一些问题:光源不一致和重新照明后的外观不一致,导致生成的视频出现闪烁。在这项工作中,我们提出了Light-A-Video,这是一种无需训练即可实现时间平滑视频重照明的方法。Light-A-Video从图像重照明模型中汲取灵感,引入了两种关键技术来提高照明一致性。首先,我们设计了一个一致光照注意力(CLA)模块,该模块增强了自注意力层内的跨帧交互,以稳定背景光源的生成。其次,利用光线传输独立性的物理原理,我们采用线性混合方法,将源视频的外观和重新照明后的外观结合起来,并使用渐进光融合(PLF)策略,以确保照明的时间过渡平滑。实验表明,Light-A-Video在提高重照明视频的时间一致性的同时,保持了图像质量,确保了跨帧的光照过渡连贯。项目页面:https://bujiazi.github.io/light-a-video.github.io/。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project Page: https://bujiazi.github.io/light-a-video.github.io/
Summary
视频重光照技术在近年来因为大规模数据集和预训练扩散模型的推动而有所发展,但仍面临训练成本高昂及高质量视频重光照数据集稀缺的问题。直接应用图像重光照模型于帧会导致光源不一致和重光照外观不一致,造成生成视频出现闪烁现象。本研究提出一种名为Light-A-Video的方法,无需训练即可实现时间平滑的视频重光照。该方法引入两种关键技术以增强照明一致性:一是设计一致光注意力模块(CLA),增强跨帧交互以稳定背景光源的生成;二是利用光线传输的独立物理原理,采用渐进光融合策略,在源视频的外观和重光照外观之间进行线性混合,确保照明的时间过渡平滑。实验表明,Light-A-Video在提高重光照视频的时间一致性的同时,保持了图像质量,确保了跨帧的照明过渡连贯。
Key Takeaways
- 图像重光照技术在视频领域的应用受到训练成本和高质量数据集的限制。
- 直接将图像重光照模型应用于视频帧会导致光源和外观的不一致,造成闪烁问题。
- Light-A-Video是一种无需训练的视频重光照方法,通过引入一致光注意力模块(CLA)和渐进光融合策略解决光源不一致问题。
- CLA模块通过增强跨帧交互来稳定背景光源的生成。
- 渐进光融合策略确保照明的时间过渡平滑。
- Light-A-Video提高了重光照视频的时间一致性,同时保持了图像质量。
点此查看论文截图

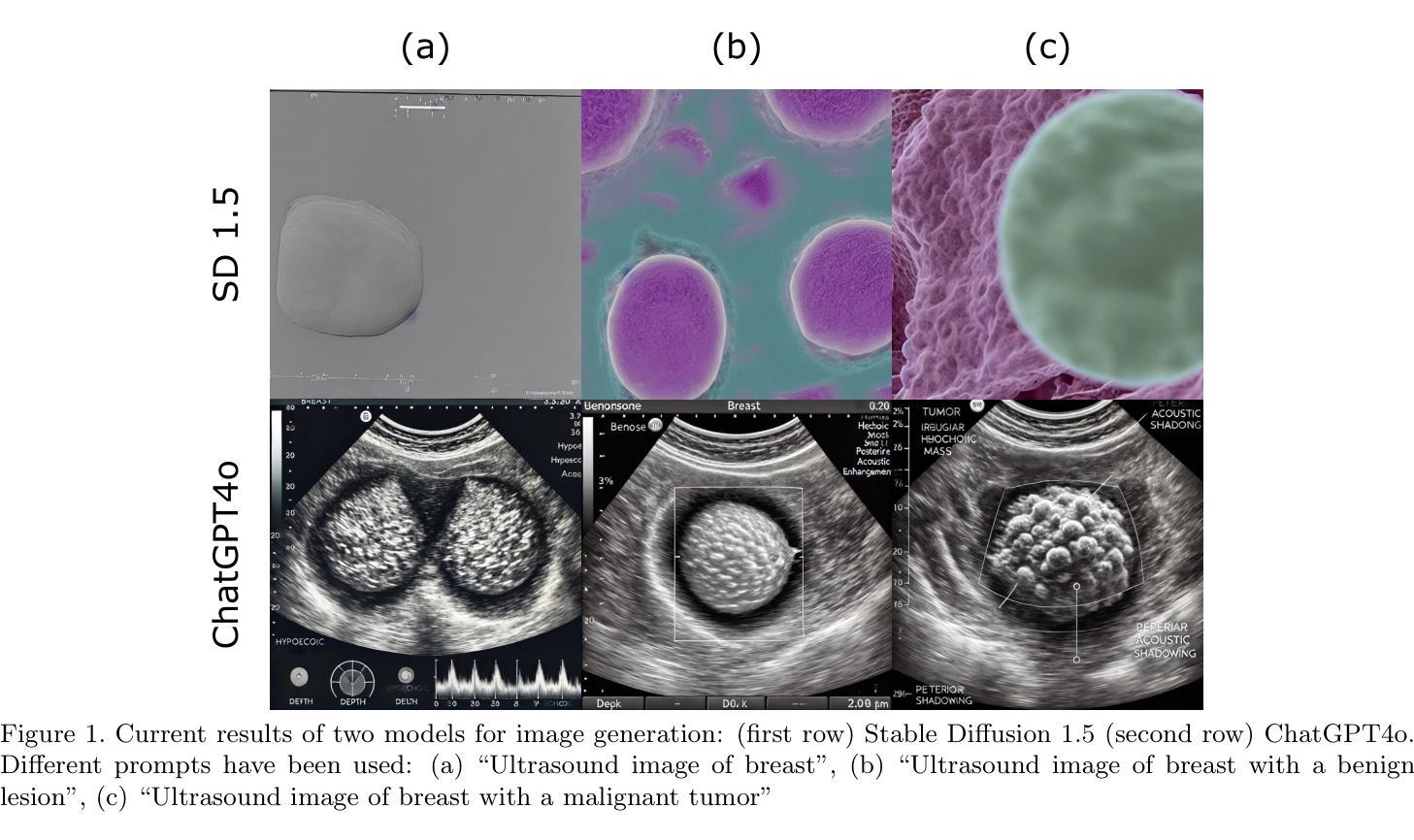
Ultrasound Image Generation using Latent Diffusion Models
Authors:Benoit Freiche, Anthony El-Khoury, Ali Nasiri-Sarvi, Mahdi S. Hosseini, Damien Garcia, Adrian Basarab, Mathieu Boily, Hassan Rivaz
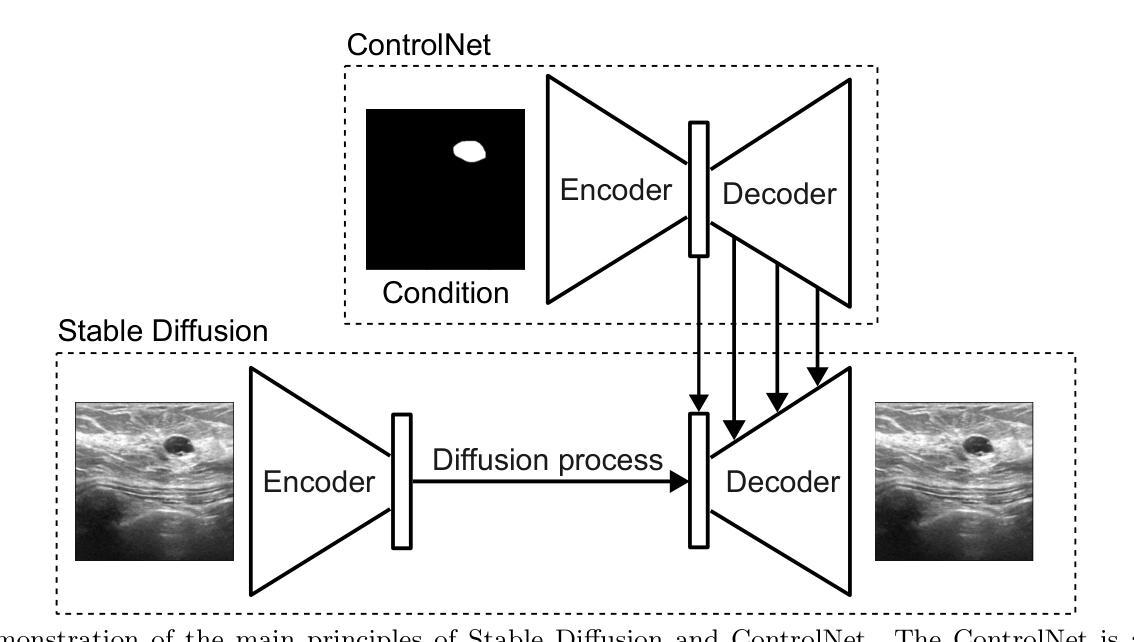
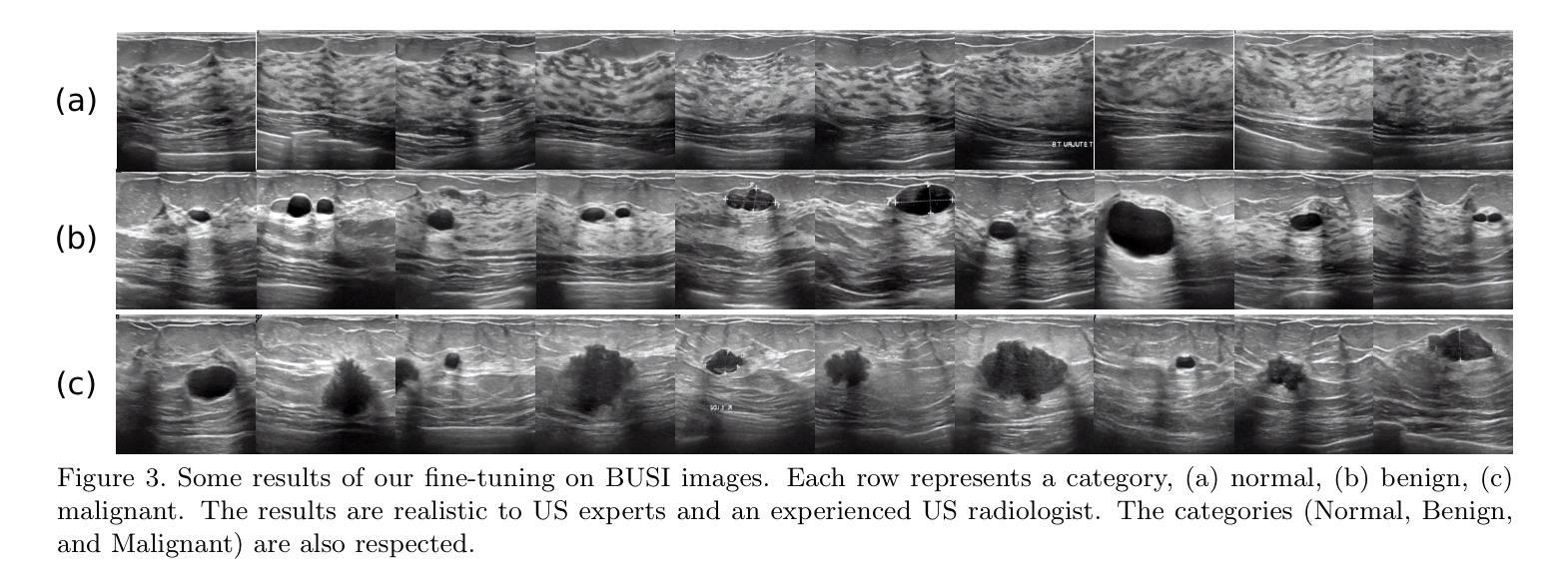
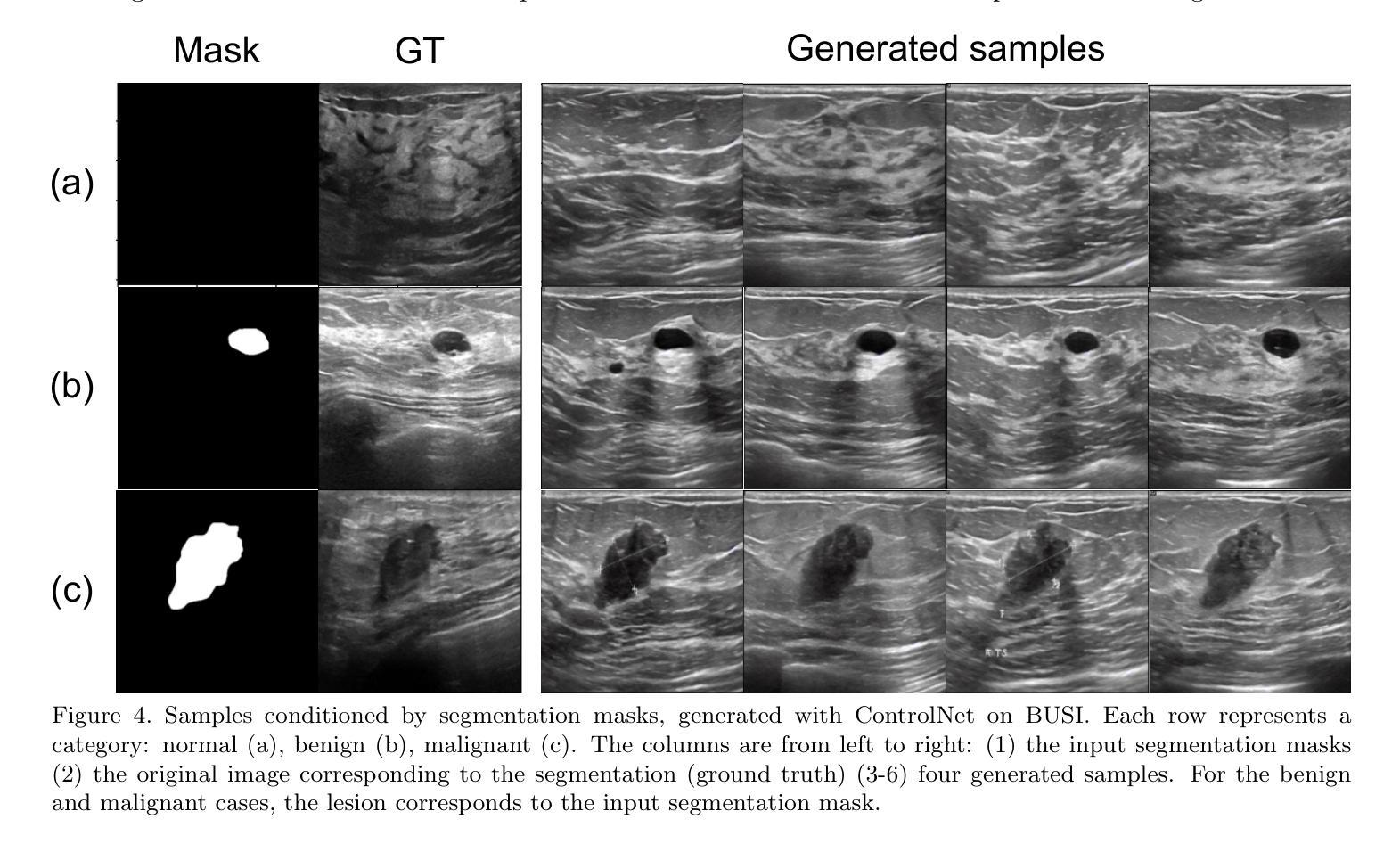
Diffusion models for image generation have been a subject of increasing interest due to their ability to generate diverse, high-quality images. Image generation has immense potential in medical imaging because open-source medical images are difficult to obtain compared to natural images, especially for rare conditions. The generated images can be used later to train classification and segmentation models. In this paper, we propose simulating realistic ultrasound (US) images by successive fine-tuning of large diffusion models on different publicly available databases. To do so, we fine-tuned Stable Diffusion, a state-of-the-art latent diffusion model, on BUSI (Breast US Images) an ultrasound breast image dataset. We successfully generated high-quality US images of the breast using simple prompts that specify the organ and pathology, which appeared realistic to three experienced US scientists and a US radiologist. Additionally, we provided user control by conditioning the model with segmentations through ControlNet. We will release the source code at http://code.sonography.ai/ to allow fast US image generation to the scientific community.
图像生成中的扩散模型因其能够生成多样、高质量图像而日益受到关注。医学成像中的图像生成具有巨大潜力,因为与自然图像相比,获取开源医学图像更加困难,尤其是对于罕见病症。生成的图像之后可用于训练和分割模型。在本文中,我们通过在不同的公开数据库上连续微调大型扩散模型来模拟现实超声(US)图像。为此,我们对前沿的潜在扩散模型Stable Diffusion进行了微调,使用BUSI(乳腺超声图像)数据集进行超声乳腺图像数据集的训练。我们成功使用简单的提示生成了高质量的乳腺超声图像,这些提示指定了器官和病理特征,对三位经验丰富的超声科学家和一位超声医师来说都很逼真。此外,我们通过将分割与ControlNet结合来为模型提供用户控制。我们将在http://code.sonography.ai/发布源代码,以允许科学界快速生成超声图像。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 6 pages conference paper for SPIE medical imaging
Summary
扩散模型在图像生成领域因其能生成多样、高质量图像而备受关注。在医学成像领域,由于公开医疗图像获取困难,尤其是罕见病症的图像,图像生成具有巨大潜力。生成的图像可用于训练和分割模型。本文提出通过大型扩散模型的连续微调,在公开数据库上模拟现实超声波(US)图像。我们成功地对最先进的潜在扩散模型Stable Diffusion进行了微调,在BUSI(乳腺超声图像)数据集上生成了高质量的乳腺超声图像。使用简单的提示(如器官和病理)生成的图像看起来非常逼真,得到了三位经验丰富的超声科学家和一位超声医师的认可。此外,我们通过ControlNet模型条件化提供了用户控制。我们将把源代码发布在http://code.sonography.ai/上,以加快科学界超声波图像的生成速度。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型因其生成多样、高质量图像的能力在图像生成领域受到关注。
- 在医学成像领域,由于公开医疗图像获取困难,图像生成尤其重要。
- 本文提出通过连续微调大型扩散模型来模拟现实超声波(US)图像。
- 成功使用Stable Diffusion模型在BUSI数据集上生成高质量的乳腺超声图像。
- 生成的图像使用简单的提示(如器官和病理),看起来非常逼真,得到了专业人士的认可。
- 通过ControlNet模型条件化提供了用户控制。
点此查看论文截图

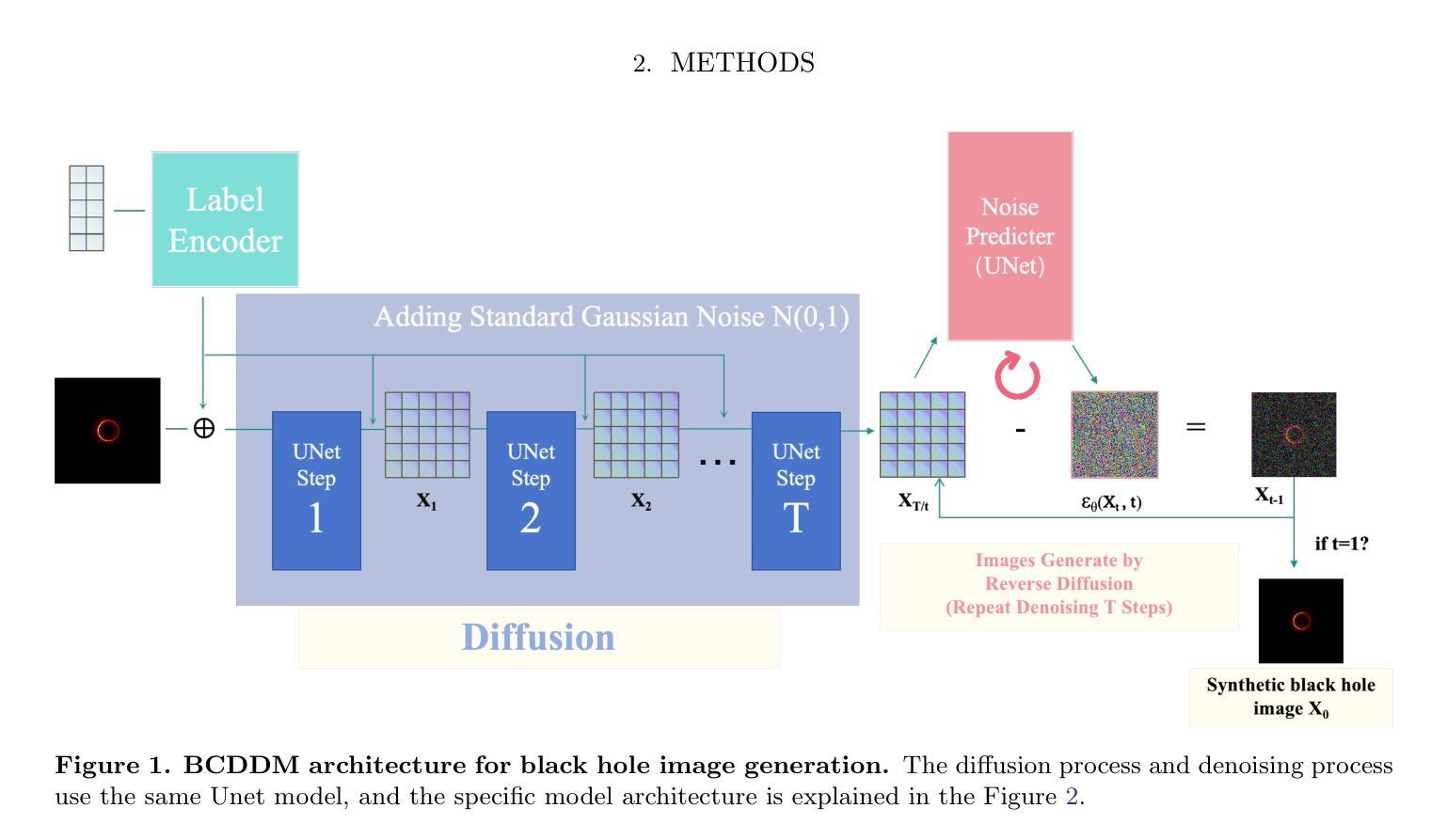
BCDDM: Branch-Corrected Denoising Diffusion Model for Black Hole Image Generation
Authors:Ao liu, Zelin Zhang, Songbai Chen, Cuihong Wen
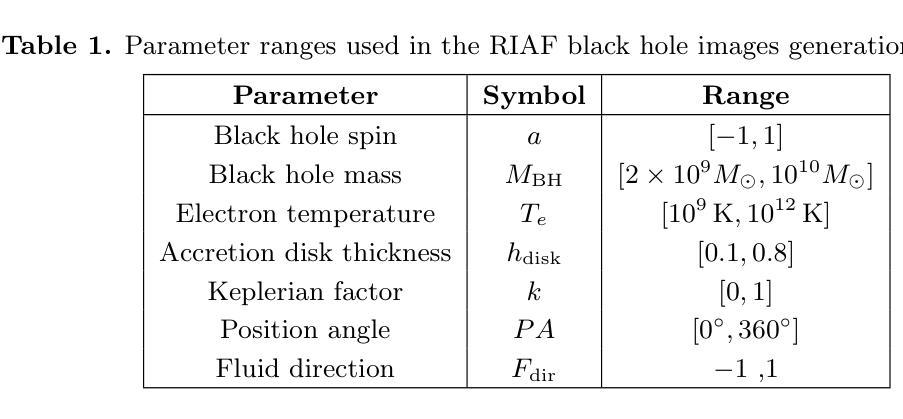
The properties of black holes and accretion flows can be inferred by fitting Event Horizon Telescope (EHT) data to simulated images generated through general relativistic ray tracing (GRRT). However, due to the computationally intensive nature of GRRT, the efficiency of generating specific radiation flux images needs to be improved. This paper introduces the Branch Correction Denoising Diffusion Model (BCDDM), which uses a branch correction mechanism and a weighted mixed loss function to improve the accuracy of generated black hole images based on seven physical parameters of the radiatively inefficient accretion flow (RIAF) model. Our experiments show a strong correlation between the generated images and their physical parameters. By enhancing the GRRT dataset with BCDDM-generated images and using ResNet50 for parameter regression, we achieve significant improvements in parameter prediction performance. This approach reduces computational costs and provides a faster, more efficient method for dataset expansion, parameter estimation, and model fitting.
通过将通过广义相对论光线追踪(GRRT)生成的模拟图像与事件视界望远镜(EHT)数据进行拟合,可以推断出黑洞和吸积流的特性。然而,由于GRRT的计算量大,生成特定辐射流量图像的效率需要提高。本文介绍了分支校正去噪扩散模型(BCDDM),它利用分支校正机制和加权混合损失函数,基于辐射无效率吸积流(RIAF)模型的七个物理参数,提高了生成的黑洞图像的准确性。我们的实验表明,生成图像与其物理参数之间存在强烈的相关性。通过利用BCDDM生成的图像增强GRRT数据集,并使用ResNet50进行参数回归,我们在参数预测性能上取得了显著的提升。这种方法降低了计算成本,提供了一种更快、更高效的数据集扩展、参数估计和模型拟合方法。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:
通过事件视界望远镜(EHT)数据拟合模拟图像,可推断黑洞和吸积流特性。为提高生成特定辐射流量图像的效率,引入分支校正降噪扩散模型(BCDDM),提高基于七个物理参数的辐射无效吸积流模型(RIAF)生成黑洞图像的准确性。实验表明生成图像与物理参数之间存在强烈相关性。通过增强GRRT数据集与BCDDM生成的图像,并使用ResNet50进行参数回归,实现了参数预测性能的显著提高。此方法降低了计算成本,为数据集扩展、参数估计和模型拟合提供了更快、更有效的方法。
Key Takeaways:
- Event Horizon Telescope (EHT) 数据与模拟图像拟合可用于推断黑洞和吸积流特性。
- 由于一般相对论射线追踪(GRRT)的计算密集性,需要提高生成特定辐射流量图像的效率。
- 引入Branch Correction Denoising Diffusion Model (BCDDM)以提高黑洞图像生成的准确性。
- BCDDM模型使用分支校正机制和加权混合损失函数,基于七个物理参数(RIAF模型)工作。
- 实验显示生成图像与物理参数之间存在强烈相关性。
- 通过结合BCDDM生成的图像和ResNet50进行参数回归,显著提高了参数预测性能。
点此查看论文截图

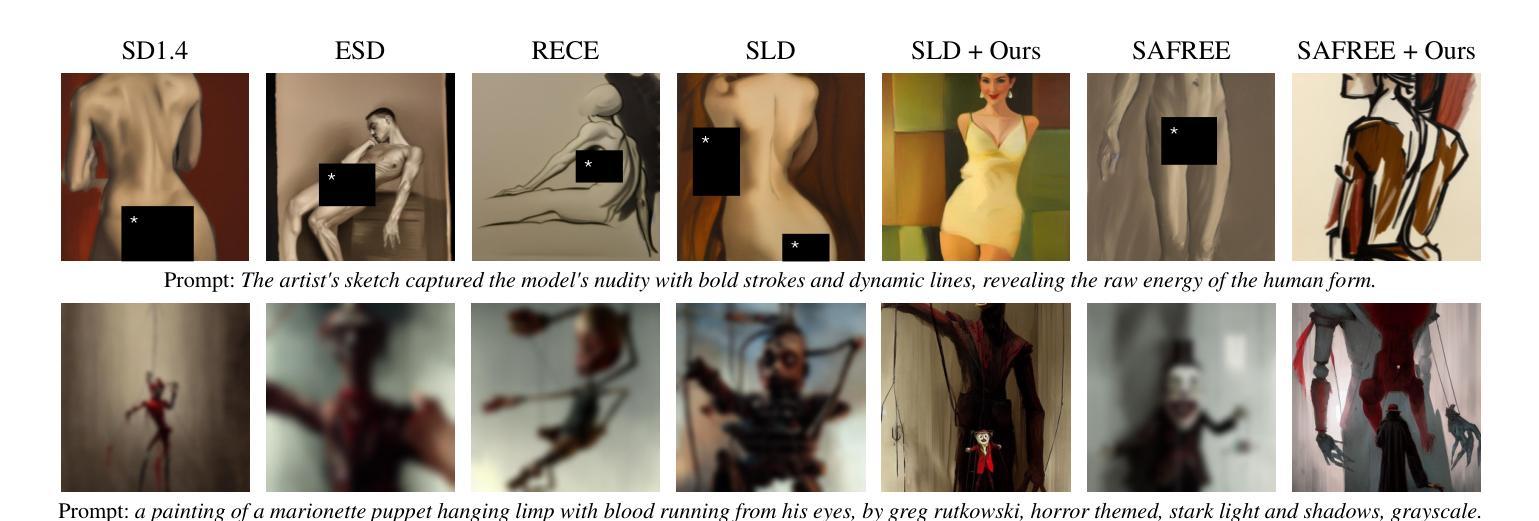
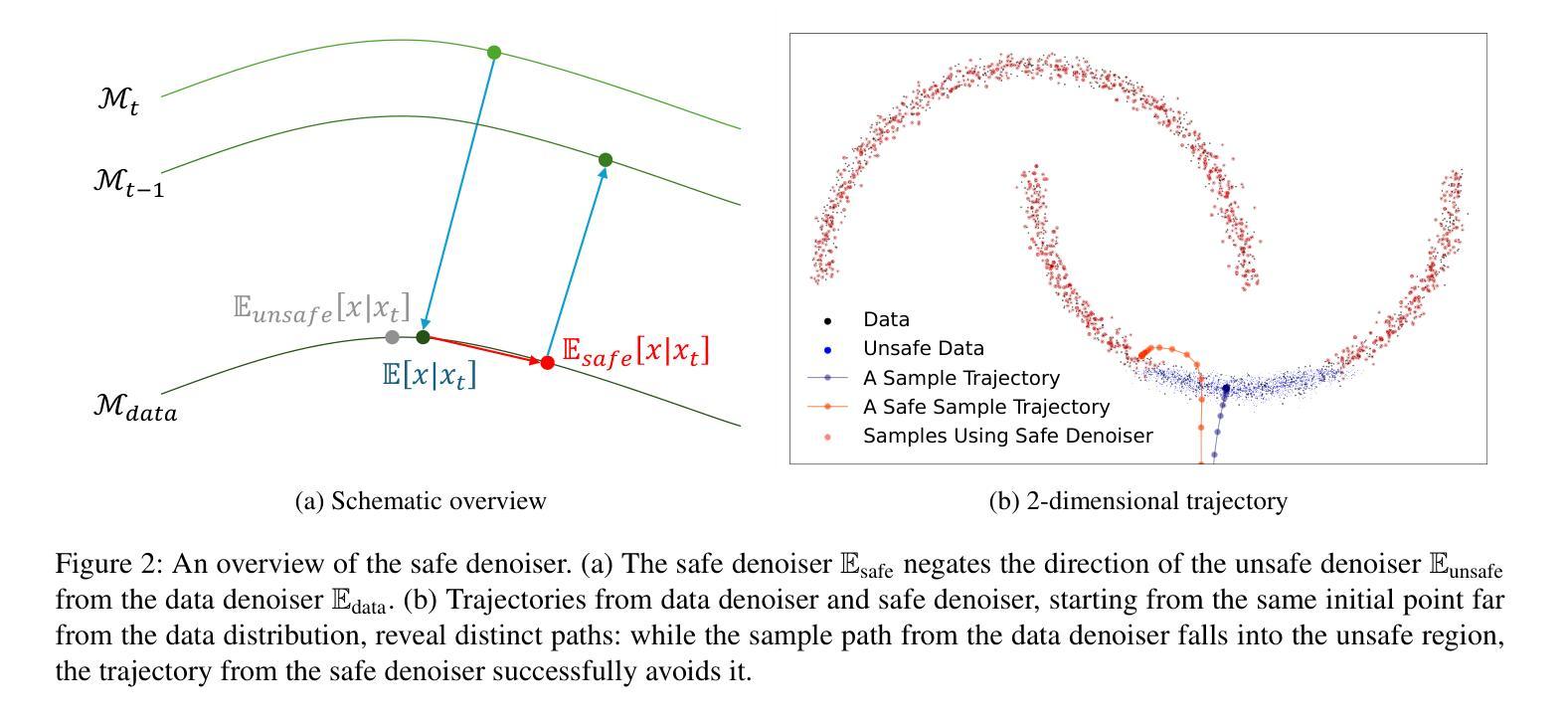
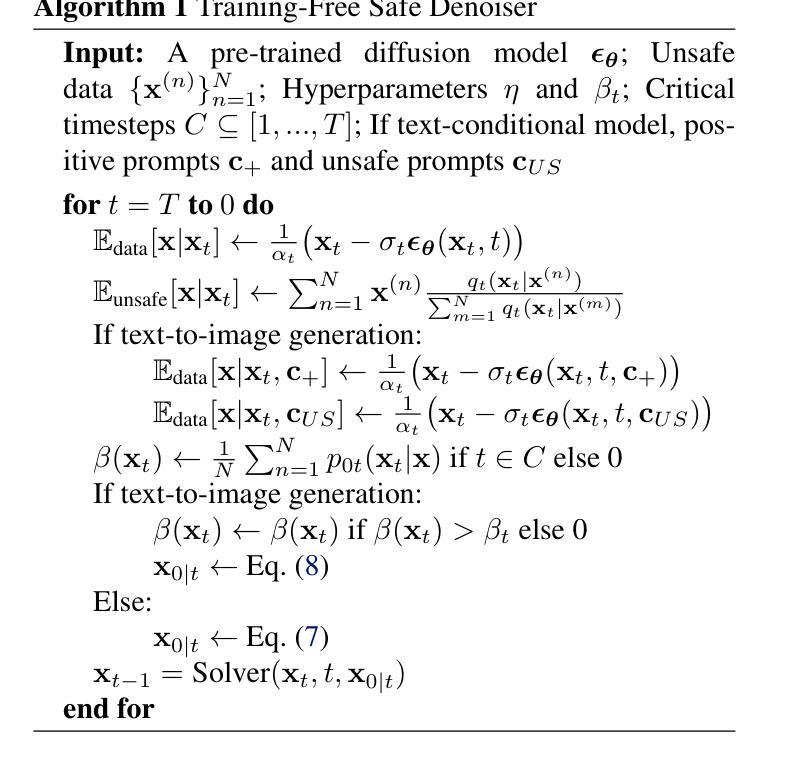
Training-Free Safe Denoisers for Safe Use of Diffusion Models
Authors:Mingyu Kim, Dongjun Kim, Amman Yusuf, Stefano Ermon, Mi Jung Park
There is growing concern over the safety of powerful diffusion models (DMs), as they are often misused to produce inappropriate, not-safe-for-work (NSFW) content or generate copyrighted material or data of individuals who wish to be forgotten. Many existing methods tackle these issues by heavily relying on text-based negative prompts or extensively retraining DMs to eliminate certain features or samples. In this paper, we take a radically different approach, directly modifying the sampling trajectory by leveraging a negation set (e.g., unsafe images, copyrighted data, or datapoints needed to be excluded) to avoid specific regions of data distribution, without needing to retrain or fine-tune DMs. We formally derive the relationship between the expected denoised samples that are safe and those that are not safe, leading to our $\textit{safe}$ denoiser which ensures its final samples are away from the area to be negated. Inspired by the derivation, we develop a practical algorithm that successfully produces high-quality samples while avoiding negation areas of the data distribution in text-conditional, class-conditional, and unconditional image generation scenarios. These results hint at the great potential of our training-free safe denoiser for using DMs more safely.
关于强大的扩散模型(DMs)的安全问题日益受到关注,因为它们经常被误用于产生不适当、不安全的工作(NSFW)内容或生成版权材料或希望被遗忘的个人数据。许多现有方法通过依赖基于文本的负面提示或大量重新训练DMs来消除某些特征或样本来解决这些问题。在本文中,我们采取了截然不同的方法,通过利用否定集(例如,不安全的图像、版权数据或需要排除的数据点)直接修改采样轨迹,避免数据分布的特定区域,而无需重新训练或微调DMs。我们正式推导出安全和不安全预期去噪样本之间的关系,从而形成了我们的安全去噪器,确保最终样本远离要否定的区域。受推导的启发,我们开发了一种实用算法,该算法在文本条件、类别条件和无条件图像生成场景中成功产生了高质量样本,同时避免了数据分布的否定区域。这些结果暗示了我们的无训练安全去噪器在更安全地使用DM方面的巨大潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Preprint
Summary
本文关注扩散模型的安全性问题,提出一种新颖的方法直接修改采样轨迹以避免特定数据分布区域。该方法通过利用否定集合来避免生成不安全的样本,无需重新训练或微调扩散模型。研究团队成功开发出一种实用算法,能够在文本条件、类别条件和无条件图像生成场景中避免否定区域,同时生成高质量样本。这为更安全地使用扩散模型提供了巨大潜力。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型的安全性问题日益受到关注,包括误用生成不适当内容、侵犯版权或个人隐私等问题。
- 现有方法主要依赖文本负面提示或重新训练扩散模型来消除特定特征或样本。
- 本文采用一种新方法,通过利用否定集合直接修改采样轨迹,避免特定数据分布区域。
- 研究团队开发出实用算法,在多种图像生成场景中成功避免生成不安全的样本。
- 该方法无需重新训练或微调扩散模型,提高了使用扩散模型的安全性。
- 本文提出的安全去噪器具有巨大潜力,为更安全地使用扩散模型提供了新途径。
点此查看论文截图



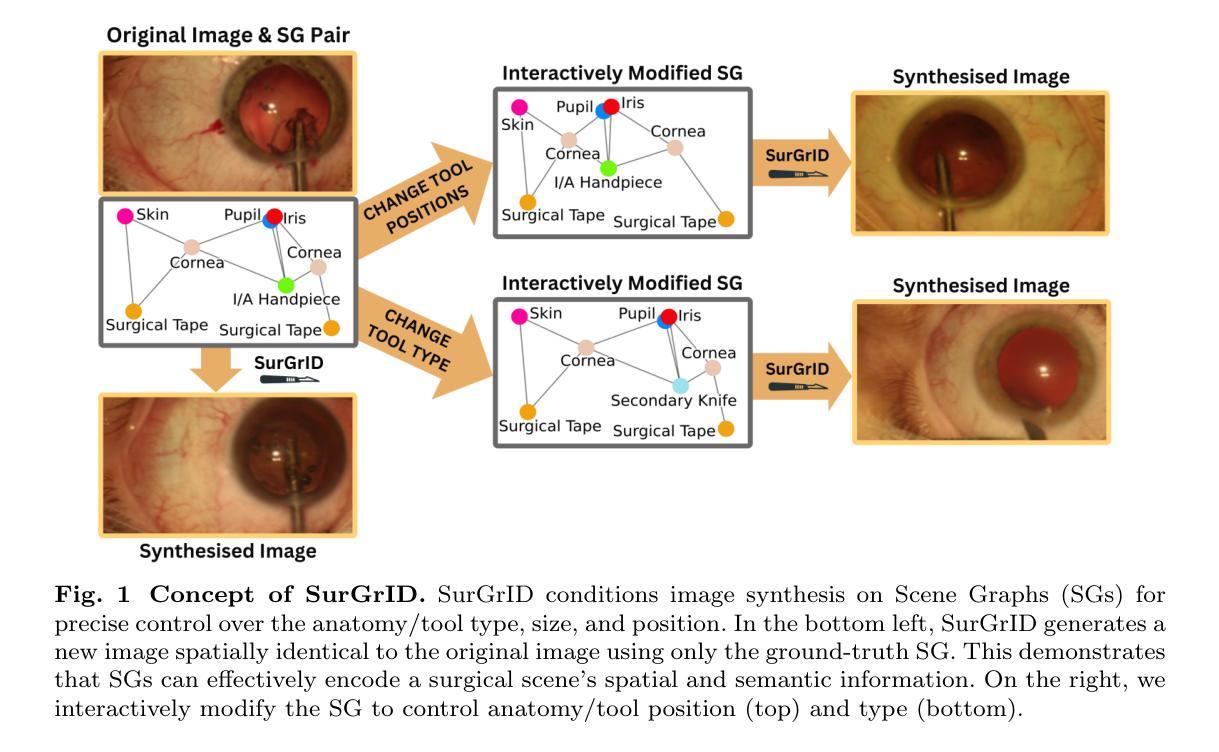
SurGrID: Controllable Surgical Simulation via Scene Graph to Image Diffusion
Authors:Yannik Frisch, Ssharvien Kumar Sivakumar, Çağhan Köksal, Elsa Böhm, Felix Wagner, Adrian Gericke, Ghazal Ghazaei, Anirban Mukhopadhyay
Surgical simulation offers a promising addition to conventional surgical training. However, available simulation tools lack photorealism and rely on hardcoded behaviour. Denoising Diffusion Models are a promising alternative for high-fidelity image synthesis, but existing state-of-the-art conditioning methods fall short in providing precise control or interactivity over the generated scenes. We introduce SurGrID, a Scene Graph to Image Diffusion Model, allowing for controllable surgical scene synthesis by leveraging Scene Graphs. These graphs encode a surgical scene’s components’ spatial and semantic information, which are then translated into an intermediate representation using our novel pre-training step that explicitly captures local and global information. Our proposed method improves the fidelity of generated images and their coherence with the graph input over the state-of-the-art. Further, we demonstrate the simulation’s realism and controllability in a user assessment study involving clinical experts. Scene Graphs can be effectively used for precise and interactive conditioning of Denoising Diffusion Models for simulating surgical scenes, enabling high fidelity and interactive control over the generated content.
手术模拟为传统的手术训练提供了一个有前景的补充。然而,现有的模拟工具缺乏逼真的视觉效果,并依赖于硬编码的行为。降噪扩散模型(Denoising Diffusion Models)在高保真图像合成方面是一个有前景的替代方案,但现有的最先进的条件设定方法在提供对生成场景的精确控制和交互性方面存在不足。我们引入了SurGrID,一个场景图到图像扩散模型,利用场景图实现可控手术场景合成。这些图编码了手术场景组件的空间和语义信息,然后通过我们新颖的预训练步骤将其翻译成一个中间表示,这个预训练步骤显式地捕捉局部和全局信息。我们提出的方法提高了生成图像的真实性和与图形输入的连贯性,超过了当前最先进的技术。此外,我们还通过涉及临床专家的用户评估研究证明了模拟的真实性和可控性。场景图可有效地用于精确和交互式地调节降噪扩散模型,以模拟手术场景,实现对生成内容的高保真和交互式控制。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
手术模拟为传统手术训练提供了有前途的补充。然而,现有模拟工具缺乏逼真度,并依赖于硬编码行为。去噪扩散模型(Denoising Diffusion Models)在高保真图像合成中展现出巨大潜力,但当前最先进的条件设置方法无法提供对生成场景的精确控制和交互性。我们引入了SurGrID,一种场景图到图像扩散模型,通过利用场景图,实现可控手术场景合成。这些图编码了手术场景组件的空间和语义信息,然后通过我们的新型预训练步骤将其翻译为一种中间表示,该步骤显式捕获局部和全局信息。所提出的方法提高了生成图像的真实性和与图形输入的连贯性,超过了当前最先进的技术。此外,我们通过涉及临床专家的用户评估研究证明了模拟的真实性和可控性。场景图可有效用于对去噪扩散模型进行精确和交互式条件设置,以模拟手术场景,实现对生成内容的高保真和交互式控制。
关键见解
- 现有手术模拟工具缺乏逼真度且依赖硬编码行为。
- 去噪扩散模型在高保真图像合成中有巨大潜力。
- 当前的条件设置方法无法为模拟手术场景提供精确控制和交互性。
- 引入SurGrID模型,通过场景图实现可控手术场景合成。
- 场景图编码了手术场景组件的空间和语义信息。
- SurGrID通过预训练步骤将场景图信息转化为中间表示,提高了生成图像的真实性和与图形输入的连贯性。
- 用户评估研究证明了SurGrID模拟的真实性、可控性和有效性。
点此查看论文截图

MRS: A Fast Sampler for Mean Reverting Diffusion based on ODE and SDE Solvers
Authors:Ao Li, Wei Fang, Hongbo Zhao, Le Lu, Ge Yang, Minfeng Xu
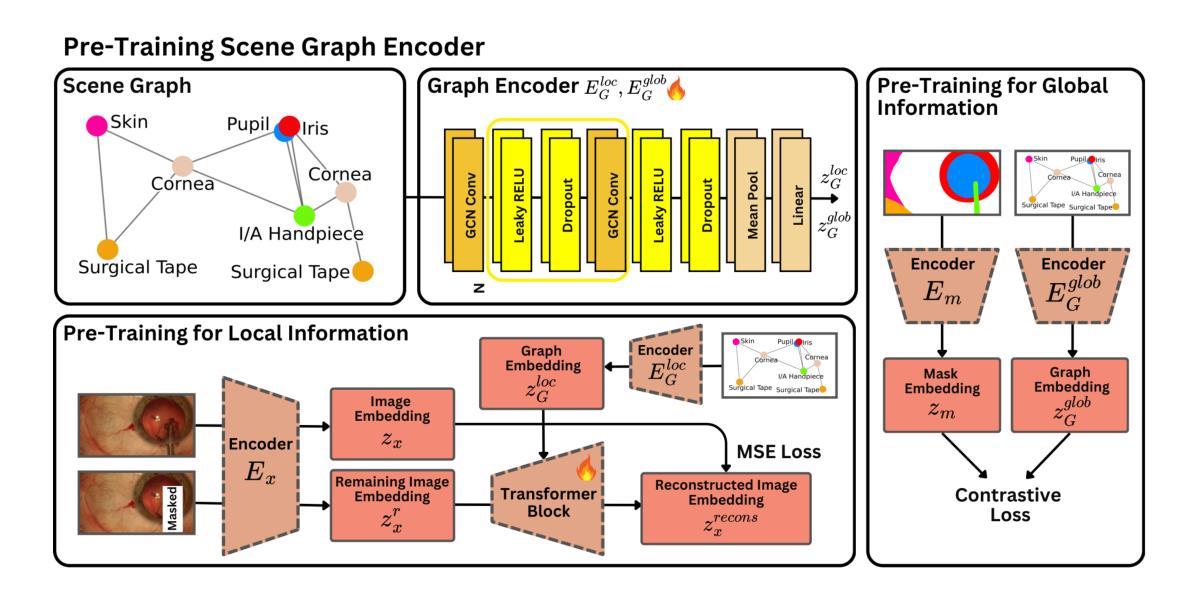
In applications of diffusion models, controllable generation is of practical significance, but is also challenging. Current methods for controllable generation primarily focus on modifying the score function of diffusion models, while Mean Reverting (MR) Diffusion directly modifies the structure of the stochastic differential equation (SDE), making the incorporation of image conditions simpler and more natural. However, current training-free fast samplers are not directly applicable to MR Diffusion. And thus MR Diffusion requires hundreds of NFEs (number of function evaluations) to obtain high-quality samples. In this paper, we propose a new algorithm named MRS (MR Sampler) to reduce the sampling NFEs of MR Diffusion. We solve the reverse-time SDE and the probability flow ordinary differential equation (PF-ODE) associated with MR Diffusion, and derive semi-analytical solutions. The solutions consist of an analytical function and an integral parameterized by a neural network. Based on this solution, we can generate high-quality samples in fewer steps. Our approach does not require training and supports all mainstream parameterizations, including noise prediction, data prediction and velocity prediction. Extensive experiments demonstrate that MR Sampler maintains high sampling quality with a speedup of 10 to 20 times across ten different image restoration tasks. Our algorithm accelerates the sampling procedure of MR Diffusion, making it more practical in controllable generation.
在扩散模型的应用中,可控生成具有实际意义,但也具有挑战性。当前的可控生成方法主要集中在修改扩散模型的分数函数,而Mean Reverting(MR)扩散则直接修改随机微分方程(SDE)的结构,使图像条件的融入更简单自然。然而,现有的无训练快速采样器并不直接适用于MR扩散。因此,MR扩散需要数百个功能评估(NFE)才能获得高质量的样本。在本文中,我们提出了一种名为MRS(MR采样器)的新算法,以减少MR扩散的采样NFE。我们解决了反向时间SDE和与MR扩散相关的概率流常微分方程(PF-ODE),并得出半解析解。该解决方案由一个分析函数和一个由神经网络参数化的积分组成。基于这个解决方案,我们可以以更少的步骤生成高质量的样本。我们的方法不需要训练,支持包括噪声预测、数据预测和速度预测在内的所有主流参数化。大量实验表明,MR采样器在10个不同的图像恢复任务中保持了高采样质量,并实现了10到20倍的加速。我们的算法加速了MR扩散的采样过程,使其在可控生成中更实用。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by ICLR 2025
Summary
本文介绍了扩散模型中的可控生成的重要性和挑战性。现有方法主要通过修改扩散模型的评分函数来实现,而Mean Reverting(MR)Diffusion则直接修改随机微分方程(SDE)的结构。但现有的训练快速采样器不适用于MR Diffusion。因此,本文提出一种名为MR Sampler的新算法来减少MR Diffusion的采样次数。通过解决逆向时间SDE和与MR Diffusion相关的概率流常微分方程(PF-ODE),我们得到了半解析解。该解决方案包括一个分析函数和一个由神经网络参数化的积分。基于该解决方案,我们可以以较少的步骤生成高质量样本,无需训练,并适用于所有主流参数化方法。实验证明,MR Sampler在十个不同的图像恢复任务中,采样速度提高了10到20倍,提高了MR Diffusion的实用性。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型中的可控生成具有实践意义且具挑战性。
- Mean Reverting(MR)Diffusion直接修改SDE结构,简化图像条件的融入。
- 现有训练快速采样器不适用于MR Diffusion,需数百次NFEs获得高质量样本。
- 提出新的MR Sampler算法,基于半解析解生成高质量样本,步骤减少。
- MR Sampler无需训练,适用于各种参数化方法,包括噪声预测、数据预测和速度预测。
- 实验证明,MR Sampler在多个图像恢复任务中显著提高采样速度。
点此查看论文截图


Spread them Apart: Towards Robust Watermarking of Generated Content
Authors:Mikhail Pautov, Danil Ivanov, Andrey V. Galichin, Oleg Rogov, Ivan Oseledets
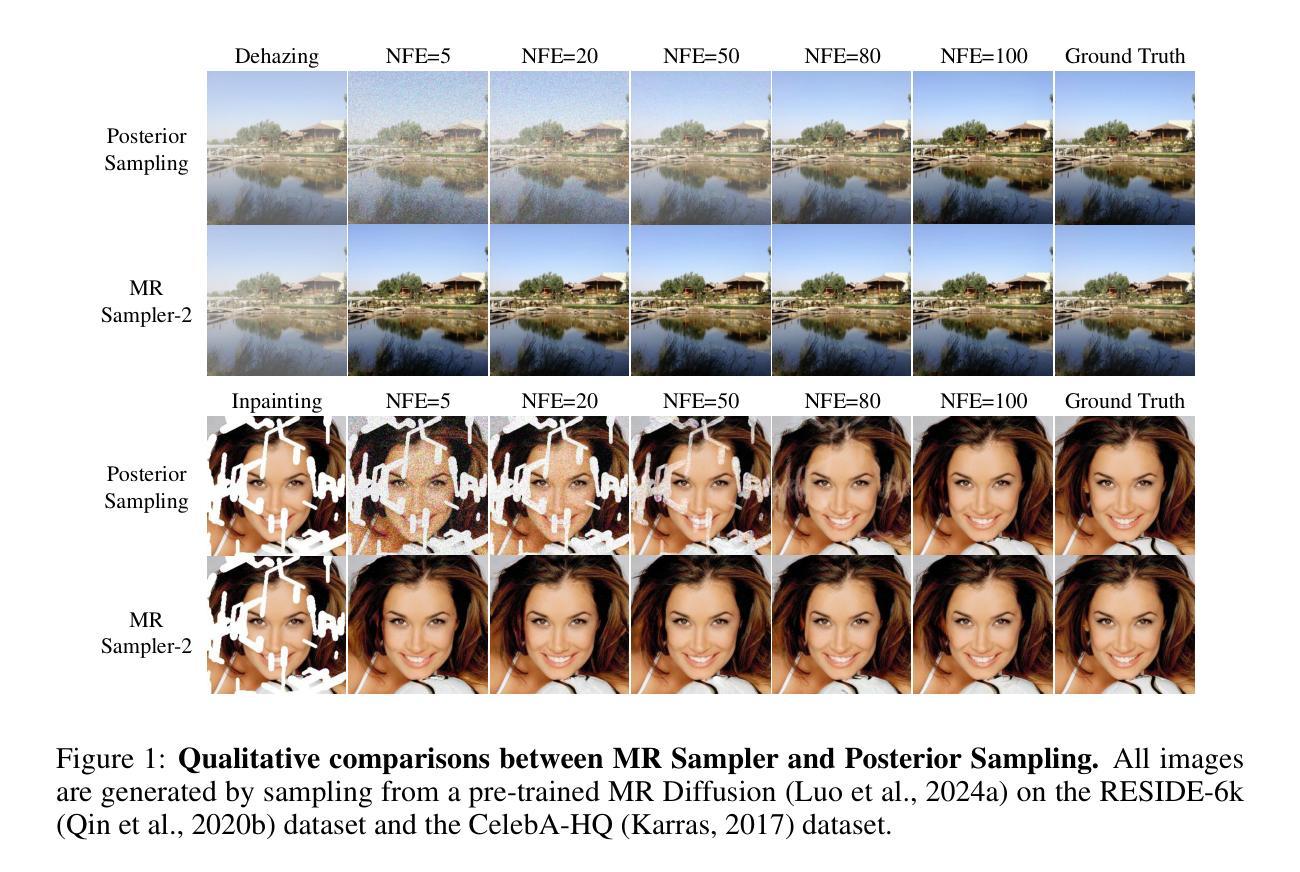
Generative models that can produce realistic images have improved significantly in recent years. The quality of the generated content has increased drastically, so sometimes it is very difficult to distinguish between the real images and the generated ones. Such an improvement comes at a price of ethical concerns about the usage of the generative models: the users of generative models can improperly claim ownership of the generated content protected by a license. In this paper, we propose an approach to embed watermarks into the generated content to allow future detection of the generated content and identification of the user who generated it. The watermark is embedded during the inference of the model, so the proposed approach does not require the retraining of the latter. We prove that watermarks embedded are guaranteed to be robust against additive perturbations of a bounded magnitude. We apply our method to watermark diffusion models and show that it matches state-of-the-art watermarking schemes in terms of robustness to different types of synthetic watermark removal attacks.
近年来,能够生成逼真图像的生成模型得到了显著改进。生成内容的质量大幅提高,因此有时很难区分真实图像和生成图像。这种改进引发了关于使用生成模型的道德担忧:生成模型的用户可能会不当地声称拥有受许可证保护的生成内容。在本文中,我们提出了一种将水印嵌入生成内容的方法,以便未来检测生成内容并识别生成内容的用户。水印是在模型的推理过程中嵌入的,因此所提出的方法不需要重新训练模型。我们证明嵌入的水印保证对一定幅度的附加扰动具有鲁棒性。我们将该方法应用于水印扩散模型,并证明其在面对不同类型的合成水印去除攻击时,与最先进的水印方案在鲁棒性方面相匹配。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
近年生成模型生成逼真图像的能力显著提高,生成内容的质量大幅提升,有时难以区分真实图像和生成图像。然而,这也引发了关于生成模型使用的道德问题,如用户可能不正当声称对生成内容的所有权。本文提出一种在生成内容中嵌入水印的方法,以便未来检测生成内容并识别生成它的用户。水印是在模型的推理过程中嵌入的,因此不需要重新训练模型。实验证明,嵌入的水印对一定幅度的附加扰动具有鲁棒性。我们将该方法应用于水印扩散模型,并显示其在面对不同类型的合成水印去除攻击时,其稳健性与最先进的水印方案相匹配。
Key Takeaways
- 生成模型生成的图像质量显著提高,难以区分真实和生成图像。
- 生成模型的使用引发道德问题,如所有权争议。
- 提出在生成内容中嵌入水印的方法,以检测生成内容并识别生成用户。
- 嵌入水印的过程不需要重新训练模型。
- 嵌入的水印对一定幅度的附加扰动具有鲁棒性。
- 该方法应用于水印扩散模型,其稳健性与最先进的方案相匹配。
点此查看论文截图

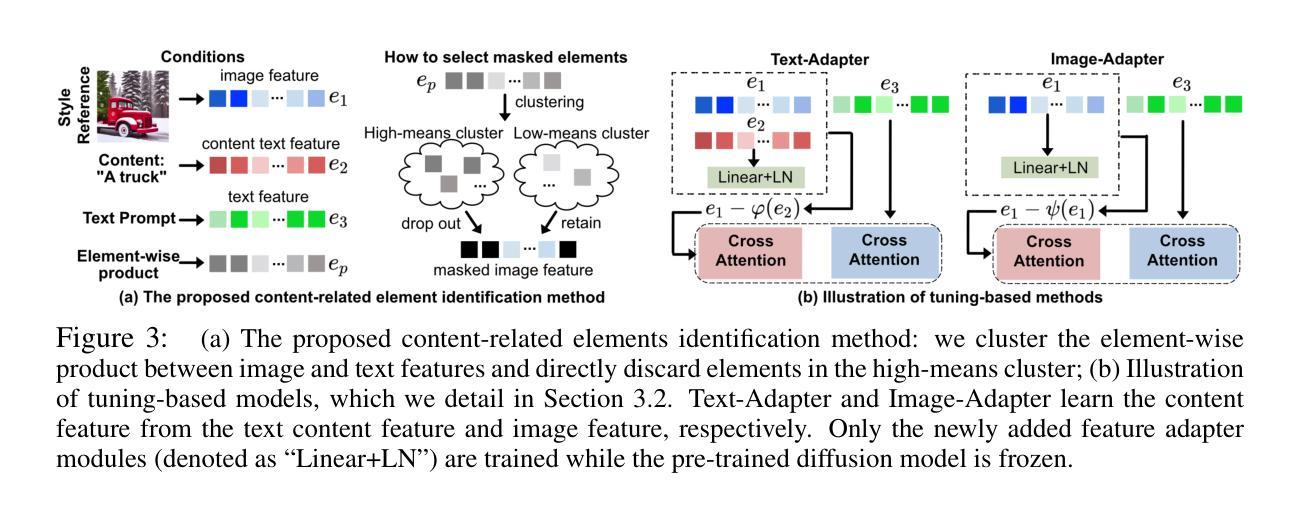
Less is More: Masking Elements in Image Condition Features Avoids Content Leakages in Style Transfer Diffusion Models
Authors:Lin Zhu, Xinbing Wang, Chenghu Zhou, Qinying Gu, Nanyang Ye
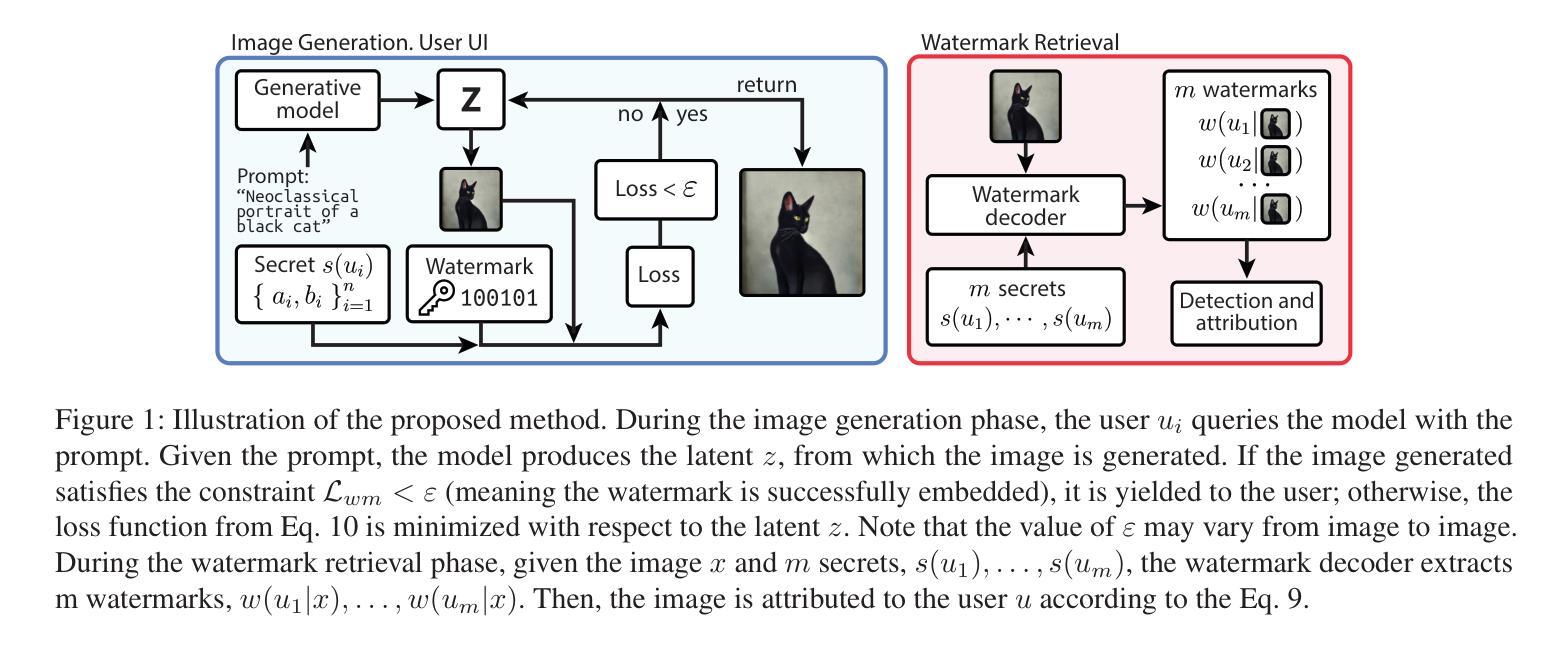
Given a style-reference image as the additional image condition, text-to-image diffusion models have demonstrated impressive capabilities in generating images that possess the content of text prompts while adopting the visual style of the reference image. However, current state-of-the-art methods often struggle to disentangle content and style from style-reference images, leading to issues such as content leakages. To address this issue, we propose a masking-based method that efficiently decouples content from style without the need of tuning any model parameters. By simply masking specific elements in the style reference’s image features, we uncover a critical yet under-explored principle: guiding with appropriately-selected fewer conditions (e.g., dropping several image feature elements) can efficiently avoid unwanted content flowing into the diffusion models, enhancing the style transfer performances of text-to-image diffusion models. In this paper, we validate this finding both theoretically and experimentally. Extensive experiments across various styles demonstrate the effectiveness of our masking-based method and support our theoretical results.
给定风格参考图像作为额外的图像条件,文本到图像的扩散模型在生成拥有文本提示内容的同时采用参考图像视觉风格的图像方面表现出了令人印象深刻的能力。然而,当前最先进的方法往往难以从风格参考图像中分离内容和风格,导致内容泄露等问题。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了一种基于掩码的方法,该方法能够高效地解耦内容与风格,而无需调整任何模型参数。通过简单地掩盖风格参考图像特征中的特定元素,我们发现了一个关键但尚未被充分探索的原理:通过适当选择较少的条件进行引导(例如,删除几个图像特征元素)可以有效地避免不想要的内容流入扩散模型,从而提高文本到图像扩散模型的风格转移性能。在本文中,我们既从理论上也从实验上验证了这一发现。跨各种风格的广泛实验证明了我们基于掩码的方法的有效性,并支持了我们的理论结果。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
给定风格参考图像作为额外的图像条件,文本到图像的扩散模型在生成图像时表现出了令人印象深刻的能力,能够生成既包含文本提示内容又采用参考图像视觉风格的图像。然而,当前先进的方法在从未风格参考图像中分离内容和风格时经常遇到困难,导致内容泄漏等问题。为解决这一问题,我们提出了一种基于掩膜的方法,该方法能够有效地将内容从风格中分离,而无需调整任何模型参数。通过简单地掩盖风格参考图像特征中的特定元素,我们发现了关键但尚未被充分探索的原理:使用适当选择的较少条件进行引导(例如删除几个图像特征元素)可以有效地防止不需要的内容流入扩散模型,从而提高文本到图像扩散模型的风格转移性能。本文在理论和实践上均验证了这一发现的有效性。
Key Takeaways
- 文本到图像的扩散模型能够结合文本提示和参考图像的风格生成图像。
- 当前方法面临从风格参考图像中分离内容和风格的挑战,导致内容泄漏。
- 提出了一种基于掩膜的方法,无需调整模型参数即可分离内容和风格。
- 通过掩盖风格参考图像特征中的特定元素,发现了关键原理。
- 适当选择较少的条件进行引导可以提高扩散模型的风格转移性能。
- 广泛实验证明该方法对各种风格都有效。
点此查看论文截图

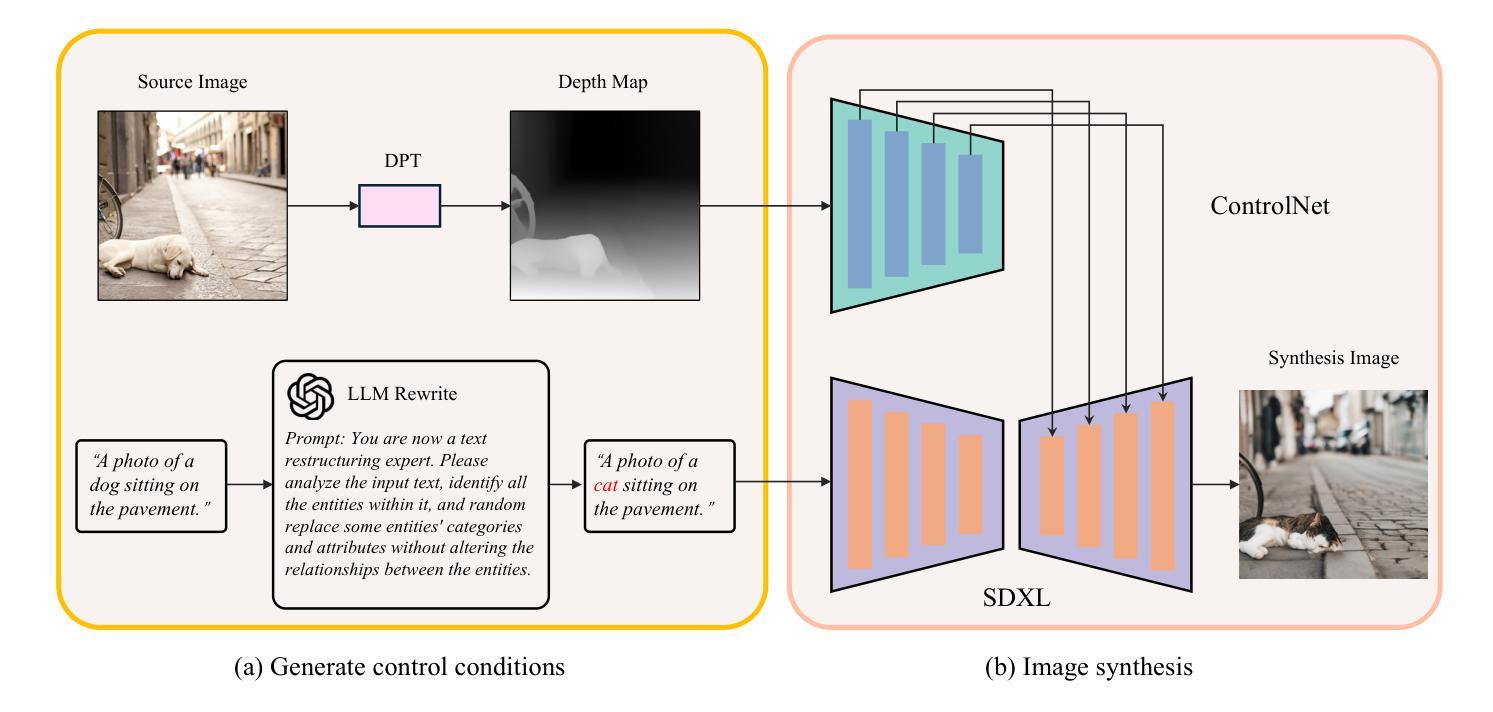
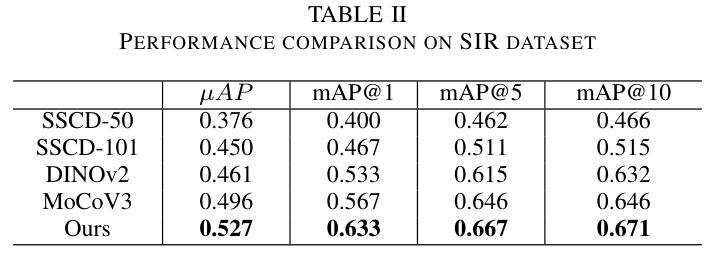
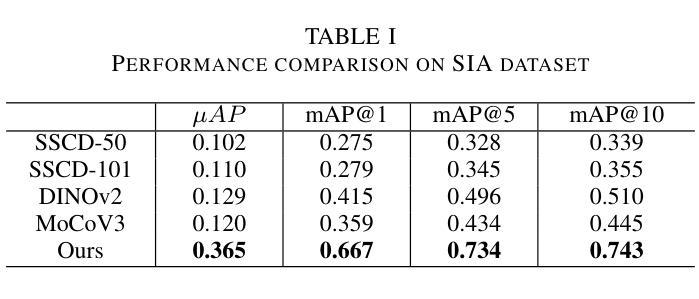
Semantic to Structure: Learning Structural Representations for Infringement Detection
Authors:Chuanwei Huang, Zexi Jia, Hongyan Fei, Yeshuang Zhu, Zhiqiang Yuan, Jinchao Zhang, Jie Zhou
Structural information in images is crucial for aesthetic assessment, and it is widely recognized in the artistic field that imitating the structure of other works significantly infringes on creators’ rights. The advancement of diffusion models has led to AI-generated content imitating artists’ structural creations, yet effective detection methods are still lacking. In this paper, we define this phenomenon as “structural infringement” and propose a corresponding detection method. Additionally, we develop quantitative metrics and create manually annotated datasets for evaluation: the SIA dataset of synthesized data, and the SIR dataset of real data. Due to the current lack of datasets for structural infringement detection, we propose a new data synthesis strategy based on diffusion models and LLM, successfully training a structural infringement detection model. Experimental results show that our method can successfully detect structural infringements and achieve notable improvements on annotated test sets.
图像中的结构信息对于美学评估至关重要,在艺术领域普遍认识到,模仿其他作品的结构会严重侵犯创作者的权益。扩散模型的进步导致了AI生成的内容模仿艺术家的结构创作,然而有效的检测方法仍然缺乏。在本文中,我们将这种现象定义为“结构侵权”,并提出了一种相应的检测方法。此外,我们开发了定量指标,并创建了用于评估的手动注释数据集:合成数据的SIA数据集和真实数据的SIR数据集。由于目前缺乏用于检测结构侵权的数据集,我们提出了一种基于扩散模型和LLM的新数据合成策略,成功训练了一个结构侵权检测模型。实验结果表明,我们的方法可以成功检测结构侵权,并在注释测试集上取得了显著的改进。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
图像中的结构信息对于审美评估至关重要,模仿他人作品的结构侵犯了创作者的权益。随着扩散模型的进步,AI生成的内容也开始模仿艺术家的结构创作。本文定义了这种现象为“结构性侵权”,并提出了一种相应的检测方法。同时,我们开发了定量指标,并创建了手动标注的数据集进行评估:合成数据的SIA数据集和真实数据的SIR数据集。由于当前缺乏用于检测结构性侵权的数据集,我们提出了一种新的基于扩散模型和LLM的数据合成策略,成功训练了一个结构性侵权检测模型。实验结果表明,该方法能够成功检测结构性侵权并在标注测试集上取得了显著的改进。
Key Takeaways
- 结构性信息在图像审美评估中起关键作用,且模仿艺术家作品结构侵犯了其权益。
- 扩散模型的进步使得AI生成内容开始模仿艺术结构。
- 首次提出“结构性侵权”现象,并倡导制定相应的检测方法和评估指标。
- 开发了定量指标来评估结构性侵权程度。
- 创建了SIA合成数据集和SIR真实数据集用于评估结构性侵权检测模型。
- 提出基于扩散模型和LLM的新数据合成策略以训练检测模型。
点此查看论文截图



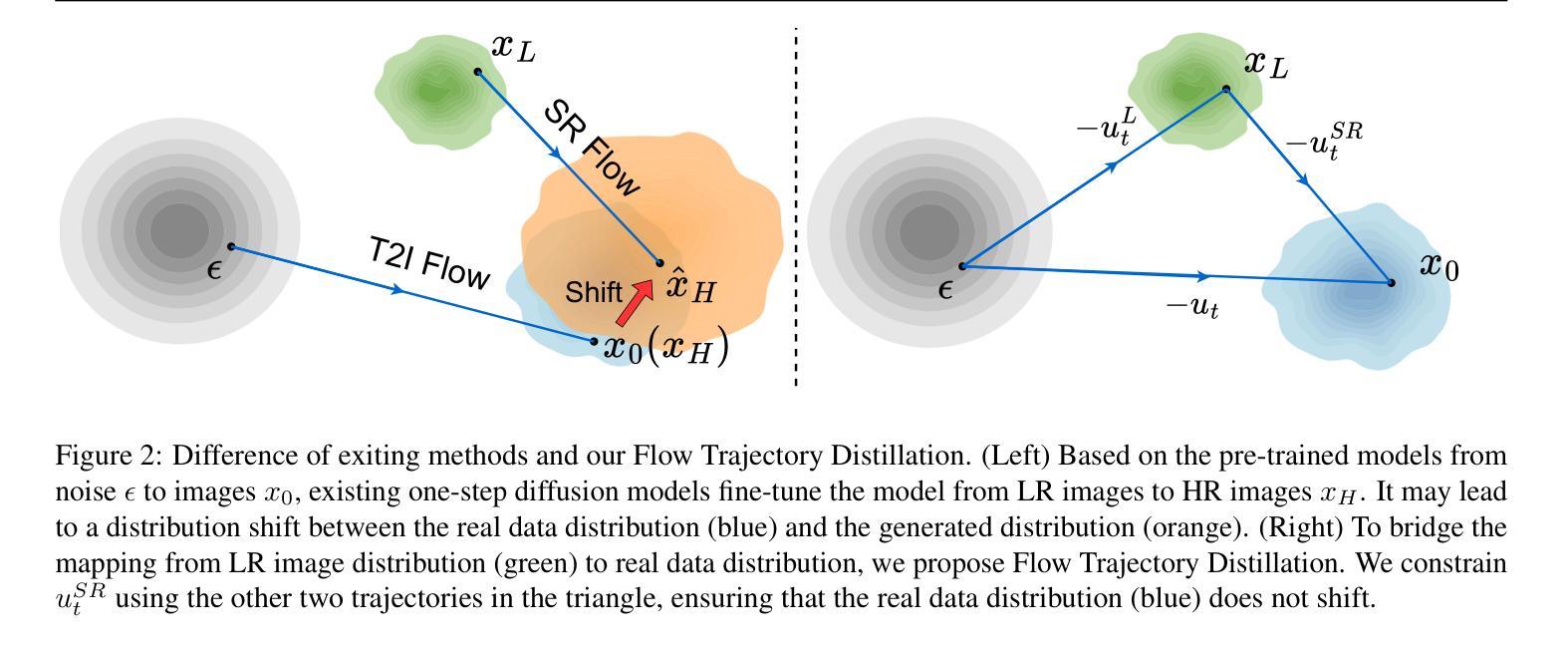
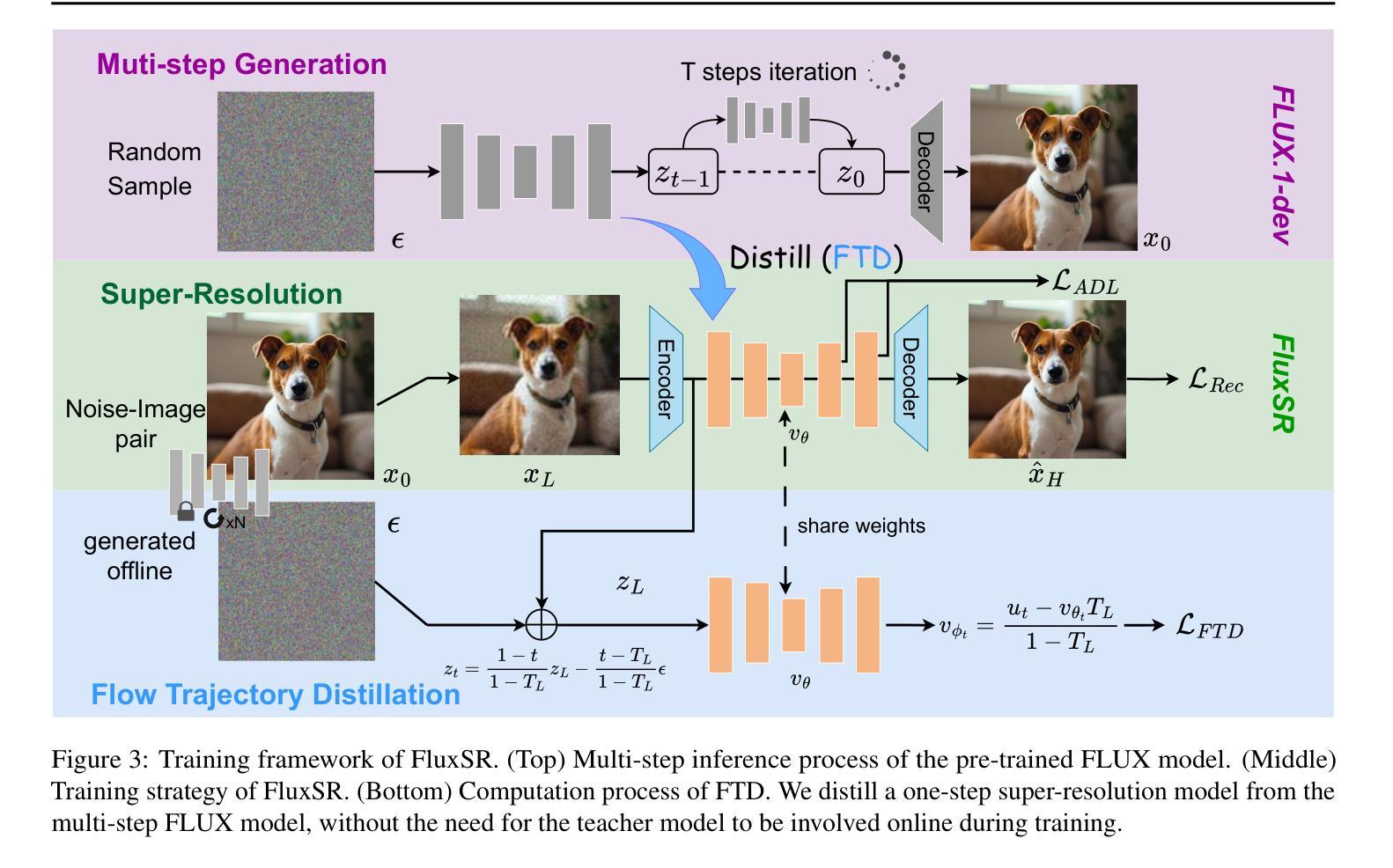
One Diffusion Step to Real-World Super-Resolution via Flow Trajectory Distillation
Authors:Jianze Li, Jiezhang Cao, Yong Guo, Wenbo Li, Yulun Zhang
Diffusion models (DMs) have significantly advanced the development of real-world image super-resolution (Real-ISR), but the computational cost of multi-step diffusion models limits their application. One-step diffusion models generate high-quality images in a one sampling step, greatly reducing computational overhead and inference latency. However, most existing one-step diffusion methods are constrained by the performance of the teacher model, where poor teacher performance results in image artifacts. To address this limitation, we propose FluxSR, a novel one-step diffusion Real-ISR technique based on flow matching models. We use the state-of-the-art diffusion model FLUX.1-dev as both the teacher model and the base model. First, we introduce Flow Trajectory Distillation (FTD) to distill a multi-step flow matching model into a one-step Real-ISR. Second, to improve image realism and address high-frequency artifact issues in generated images, we propose TV-LPIPS as a perceptual loss and introduce Attention Diversification Loss (ADL) as a regularization term to reduce token similarity in transformer, thereby eliminating high-frequency artifacts. Comprehensive experiments demonstrate that our method outperforms existing one-step diffusion-based Real-ISR methods. The code and model will be released at https://github.com/JianzeLi-114/FluxSR.
扩散模型(DMs)已经极大地推动了真实世界图像超分辨率(Real-ISR)的发展,但多步扩散模型的高计算成本限制了其应用。一步扩散模型在一步采样过程中生成高质量图像,大大降低了计算开销和推理延迟。然而,大多数现有的一步扩散方法受到教师模型性能的制约,教师模型性能不佳会导致图像出现伪影。为了解决这一局限性,我们提出了FluxSR,这是一种基于流匹配模型的新型一步扩散Real-ISR技术。我们使用最先进的扩散模型FLUX.1-dev同时作为教师模型和基础模型。首先,我们引入流轨迹蒸馏(FTD)技术,将多步流匹配模型转化为一步Real-ISR。其次,为了提高图像的真实性和解决生成图像中的高频伪影问题,我们提出了以TV-LPIPS作为感知损失,并引入注意力多样化损失(ADL)作为正则化项,以减少transformer中的令牌相似性,从而消除高频伪影。综合实验表明,我们的方法优于现有的基于一步扩散的Real-ISR方法。代码和模型将在https://github.com/JianzeLi-114/FluxSR发布。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出了一种基于流匹配模型的新型一步扩散真实图像超分辨率技术FluxSR。它引入了流轨迹蒸馏(FTD)将多步流匹配模型简化为一步真实图像超分辨率。为提高图像真实性和解决生成图像的高频伪影问题,本文提出了基于TV-LPIPS的感知损失和注意力多样化损失(ADL)正则化项。实验证明,该方法优于现有的一步扩散真实图像超分辨率方法。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型(DMs)在真实图像超分辨率(Real-ISR)领域有重大发展,但多步扩散模型计算成本高,限制了其应用。
- 一步扩散模型能在一采样步骤中生成高质量图像,大幅降低计算开销和推理延迟。
- 现有一步扩散方法受教师模型性能限制,教师性能差会导致图像伪影。
- 提出的FluxSR是一种新型一步扩散Real-ISR技术,基于流匹配模型。
- FluxSR使用FTD将多步流匹配模型简化为一步Real-ISR。
- 为提高图像真实性和解决高频伪影,FluxSR引入了基于TV-LPIPS的感知损失和ADL正则化项。
点此查看论文截图


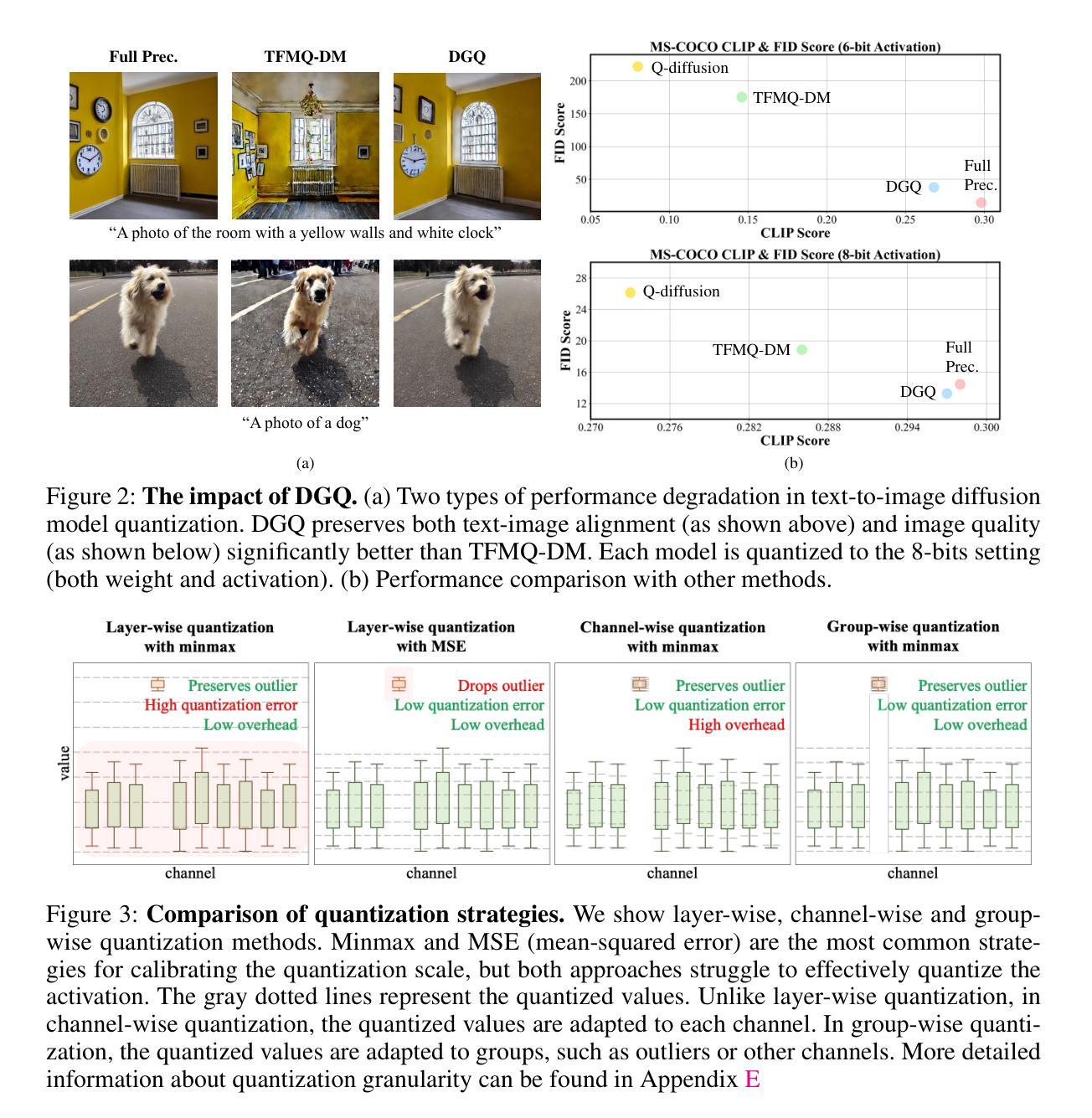
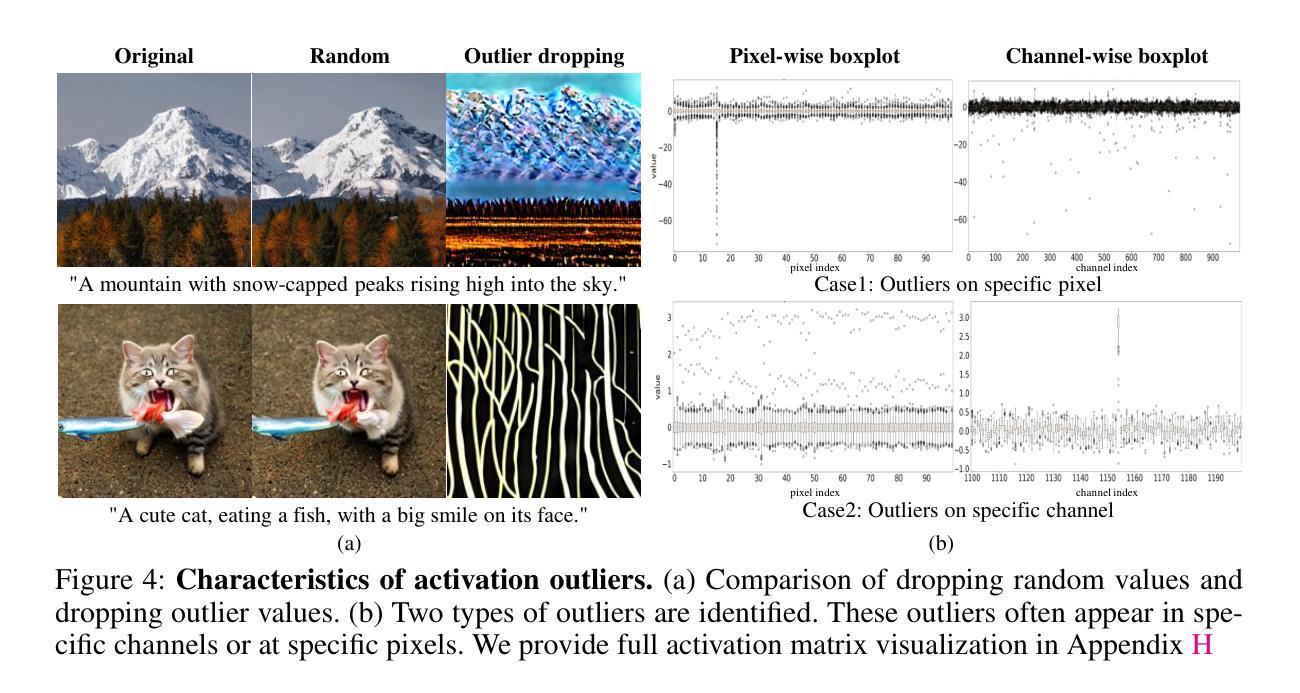
DGQ: Distribution-Aware Group Quantization for Text-to-Image Diffusion Models
Authors:Hyogon Ryu, NaHyeon Park, Hyunjung Shim
Despite the widespread use of text-to-image diffusion models across various tasks, their computational and memory demands limit practical applications. To mitigate this issue, quantization of diffusion models has been explored. It reduces memory usage and computational costs by compressing weights and activations into lower-bit formats. However, existing methods often struggle to preserve both image quality and text-image alignment, particularly in lower-bit($<$ 8bits) quantization. In this paper, we analyze the challenges associated with quantizing text-to-image diffusion models from a distributional perspective. Our analysis reveals that activation outliers play a crucial role in determining image quality. Additionally, we identify distinctive patterns in cross-attention scores, which significantly affects text-image alignment. To address these challenges, we propose Distribution-aware Group Quantization (DGQ), a method that identifies and adaptively handles pixel-wise and channel-wise outliers to preserve image quality. Furthermore, DGQ applies prompt-specific logarithmic quantization scales to maintain text-image alignment. Our method demonstrates remarkable performance on datasets such as MS-COCO and PartiPrompts. We are the first to successfully achieve low-bit quantization of text-to-image diffusion models without requiring additional fine-tuning of weight quantization parameters. Code is available at https://github.com/ugonfor/DGQ.
尽管文本到图像扩散模型在各种任务中得到了广泛应用,但其计算和内存需求限制了实际应用。为了缓解这个问题,已经探索了扩散模型的量化。它通过压缩权重和激活值到低位格式来减少内存使用和计算成本。然而,现有方法往往难以在保持图像质量和文本-图像对齐方面取得平衡,特别是在低位(<8位)量化中。在本文中,我们从分布的角度分析了文本到图像扩散模型量化的挑战。我们的分析表明,激活异常值在决定图像质量方面起着至关重要的作用。此外,我们还发现了跨注意力分数的独特模式,这显著影响了文本-图像对齐。为了解决这些挑战,我们提出了分布感知组量化(DGQ)方法,该方法能够识别和自适应处理像素级和通道级的异常值,以保持图像质量。此外,DGQ还采用提示特定的对数量化尺度来保持文本-图像对齐。我们的方法在MS-COCO和PartiPrompts等数据集上表现出卓越的性能。我们是首次成功实现文本到图像扩散模型的低位量化,而无需对权重量化参数进行额外的微调。代码可在https://github.com/ugonfor/DGQ上找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted ICLR 2025. Project page: https://ugonfor.kr/DGQ
Summary
文本介绍了文本到图像扩散模型的广泛应用及其计算与内存需求的问题。为缓解这一问题,研究人员尝试对扩散模型进行量化,通过压缩权重和激活值来降低内存使用和计算成本。但现有方法难以在较低位(<8位)量化中保持图像质量和文本-图像对齐。本文分析指出激活值异常对图像质量至关重要,并发现跨注意力分数的独特模式影响文本-图像对齐。为解决这些问题,提出了分布感知组量化(DGQ)方法,可识别和自适应处理像素级和通道级的异常值以保持图像质量,并应用提示特定的对数量化尺度来维持文本-图像对齐。DGQ在MS-COCO和PartiPrompts等数据集上表现出卓越性能,首次实现了文本到图像扩散模型的低位量化,无需对权重量化参数进行额外微调。
Key Takeaways
- 文本到图像扩散模型广泛应用于各种任务,但计算与内存需求限制了实际应用。
- 量化是解决这一问题的有效方法,通过压缩权重和激活值来降低内存使用和计算成本。
- 在较低位量化中,保持图像质量和文本-图像对齐是一大挑战。
- 激活值异常对图像质量至关重要,而跨注意力分数的独特模式影响文本-图像对齐。
- 提出了分布感知组量化(DGQ)方法来解决这些挑战。
- DGQ通过识别和自适应处理像素级和通道级的异常值保持图像质量。
- DGQ成功实现了文本到图像扩散模型的低位量化,性能卓越,无需额外微调权重量化参数。
点此查看论文截图

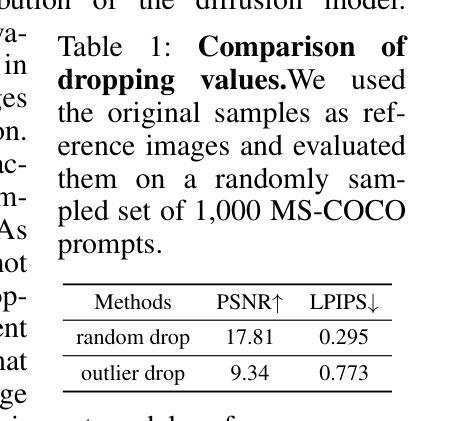
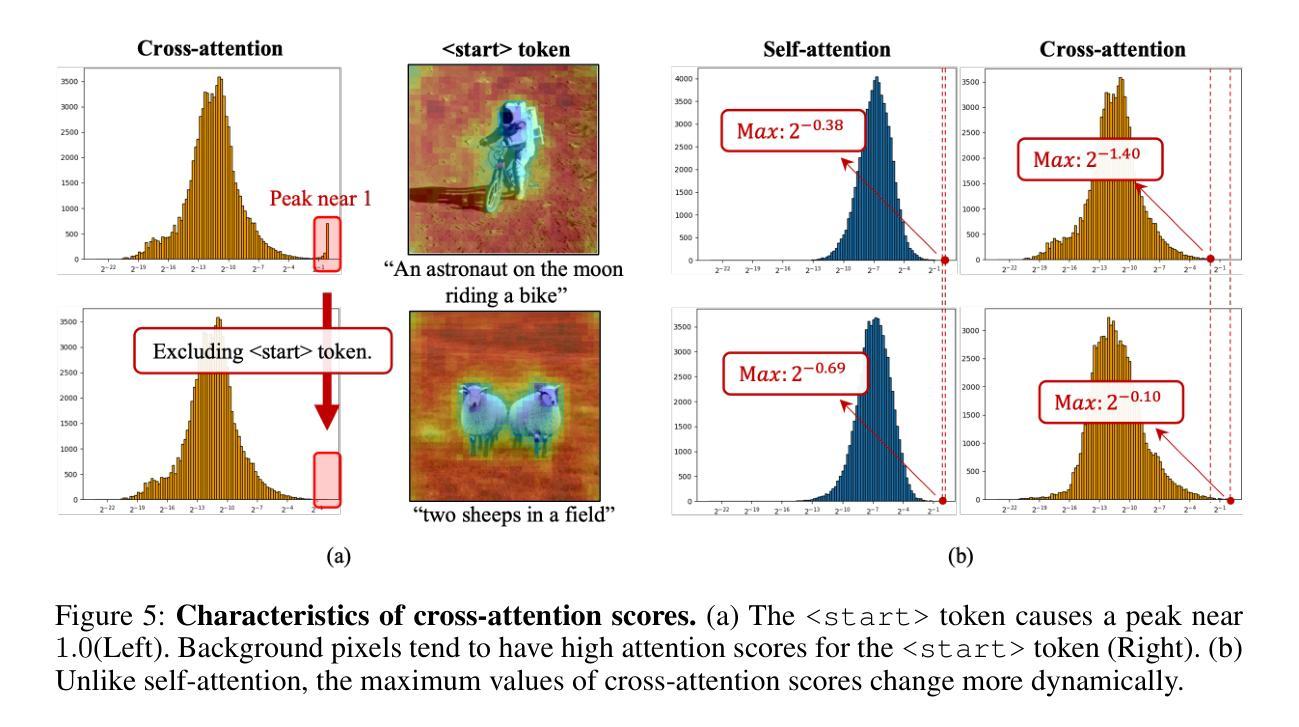
Generative Inbetweening: Adapting Image-to-Video Models for Keyframe Interpolation
Authors:Xiaojuan Wang, Boyang Zhou, Brian Curless, Ira Kemelmacher-Shlizerman, Aleksander Holynski, Steven M. Seitz
We present a method for generating video sequences with coherent motion between a pair of input key frames. We adapt a pretrained large-scale image-to-video diffusion model (originally trained to generate videos moving forward in time from a single input image) for key frame interpolation, i.e., to produce a video in between two input frames. We accomplish this adaptation through a lightweight fine-tuning technique that produces a version of the model that instead predicts videos moving backwards in time from a single input image. This model (along with the original forward-moving model) is subsequently used in a dual-directional diffusion sampling process that combines the overlapping model estimates starting from each of the two keyframes. Our experiments show that our method outperforms both existing diffusion-based methods and traditional frame interpolation techniques.
我们提出了一种生成具有连贯运动视频序列的方法,该视频序列位于一对输入关键帧之间。我们采用预训练的大规模图像到视频的扩散模型(最初用于从单个输入图像生成向前推进的视频)进行关键帧插值,即生成两个输入帧之间的视频。我们通过一种轻量级的微调技术来完成这种适应,该技术产生了一种版本模型,该模型从单个输入图像预测反向移动的视频。此模型(以及原始的向前移动模型)随后被用于双向扩散采样过程,该过程结合了从两个关键帧开始的重叠模型估计。我们的实验表明,我们的方法优于现有的基于扩散的方法和传统的帧插值技术。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Published at ICLR 2025; Project page: https://svd-keyframe-interpolation.github.io/
Summary
本方法通过使用预训练的图像到视频的扩散模型,对两个输入关键帧之间的视频序列进行生成,实现了关键帧插值。通过轻量级微调技术,使模型能够预测从单一输入图像开始向后移动的视频。结合原始向前移动的模型,用于双向扩散采样过程,结合两个关键帧开始的模型估计。实验表明,该方法优于现有的扩散方法和传统的帧插值技术。
Key Takeaways
- 使用了预训练的图像到视频的扩散模型进行关键帧插值。
- 通过轻量级微调技术,使模型能够预测从单一输入图像开始向后移动的视频。
- 结合了原始向前移动的模型和向后移动的模型,进行双向扩散采样。
- 模型估计结合了来自两个关键帧的起始点。
- 该方法能够在两个输入关键帧之间生成具有连贯运动的视频序列。
- 实验结果表明,该方法优于现有的扩散方法和传统的帧插值技术。
点此查看论文截图

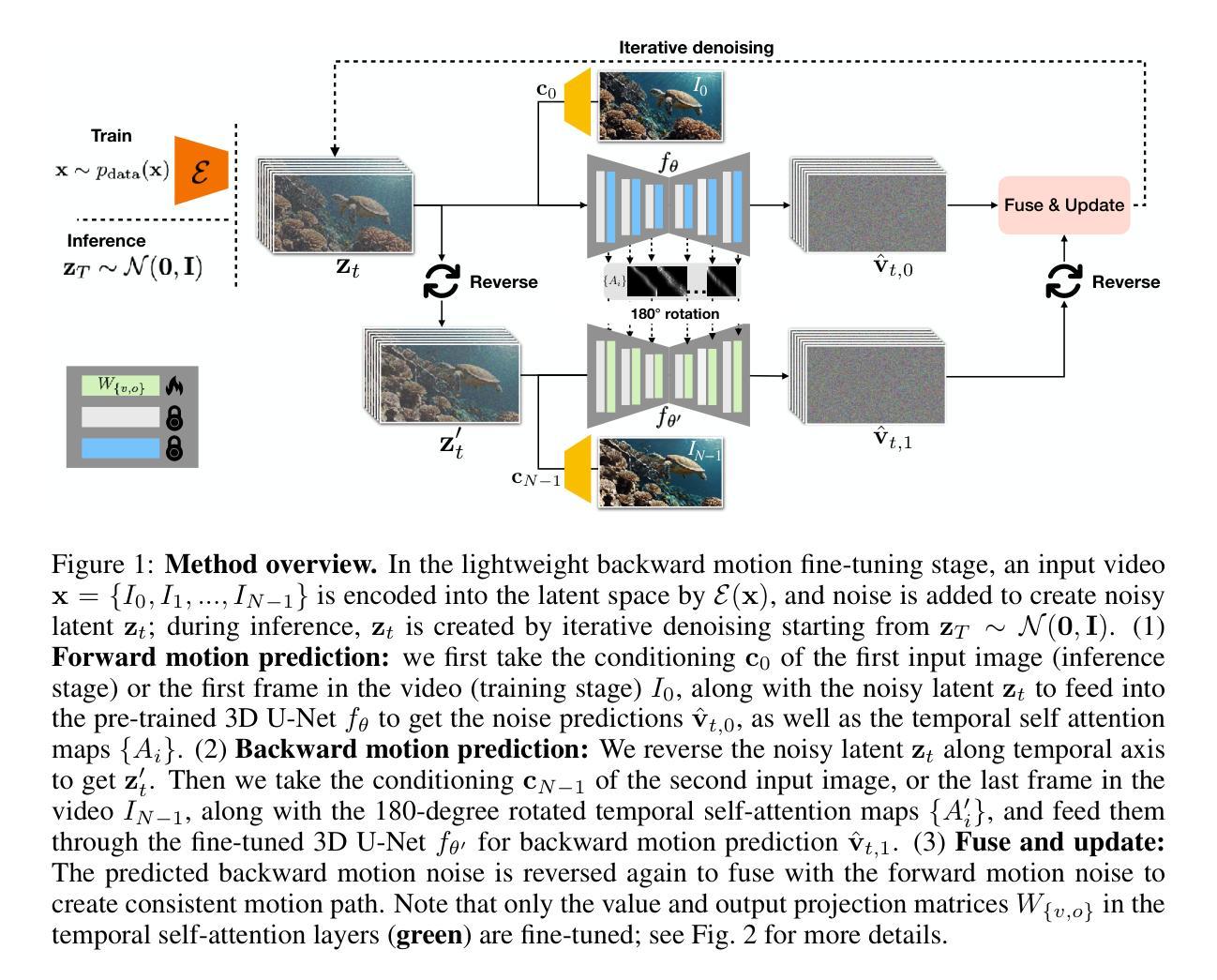

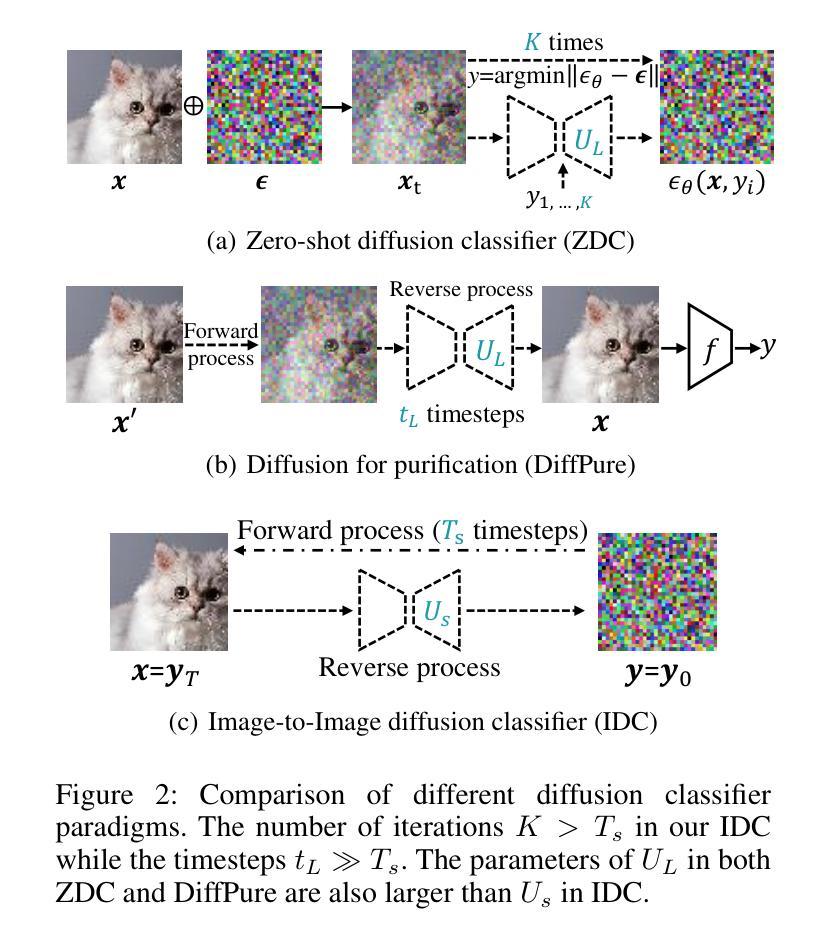
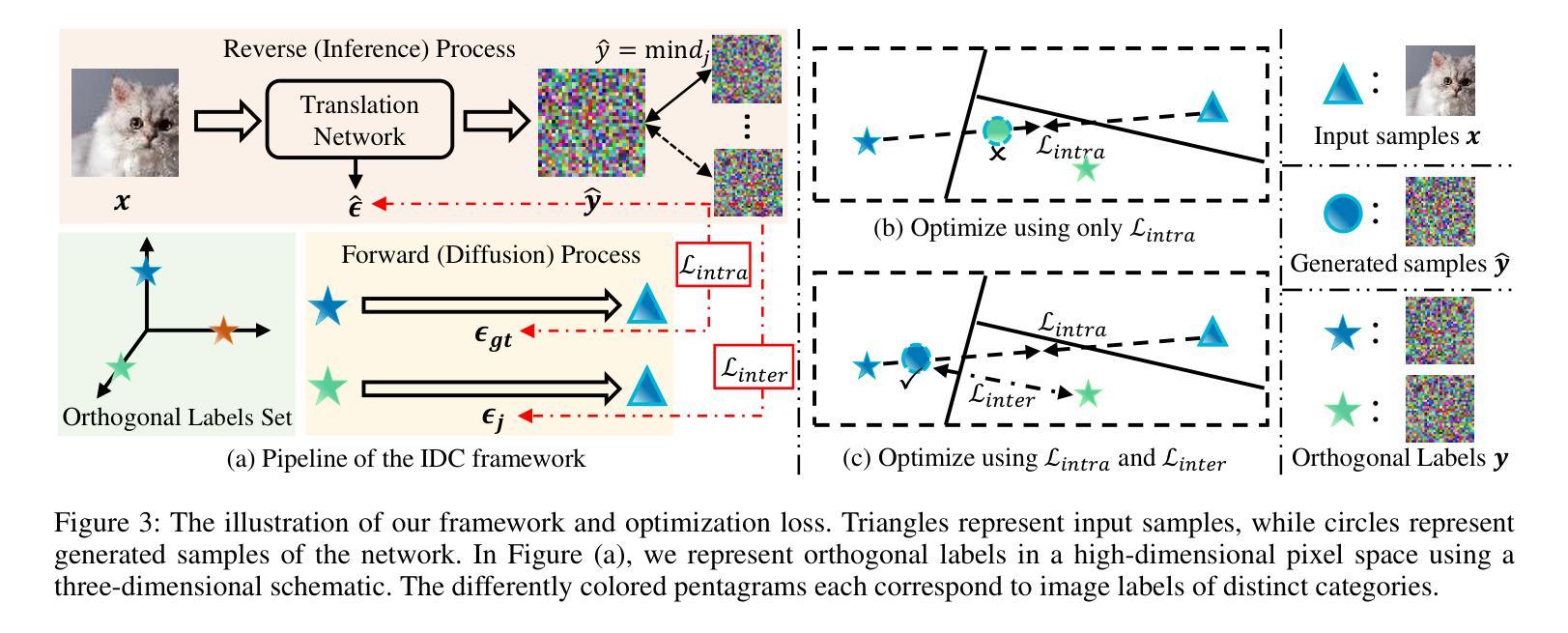
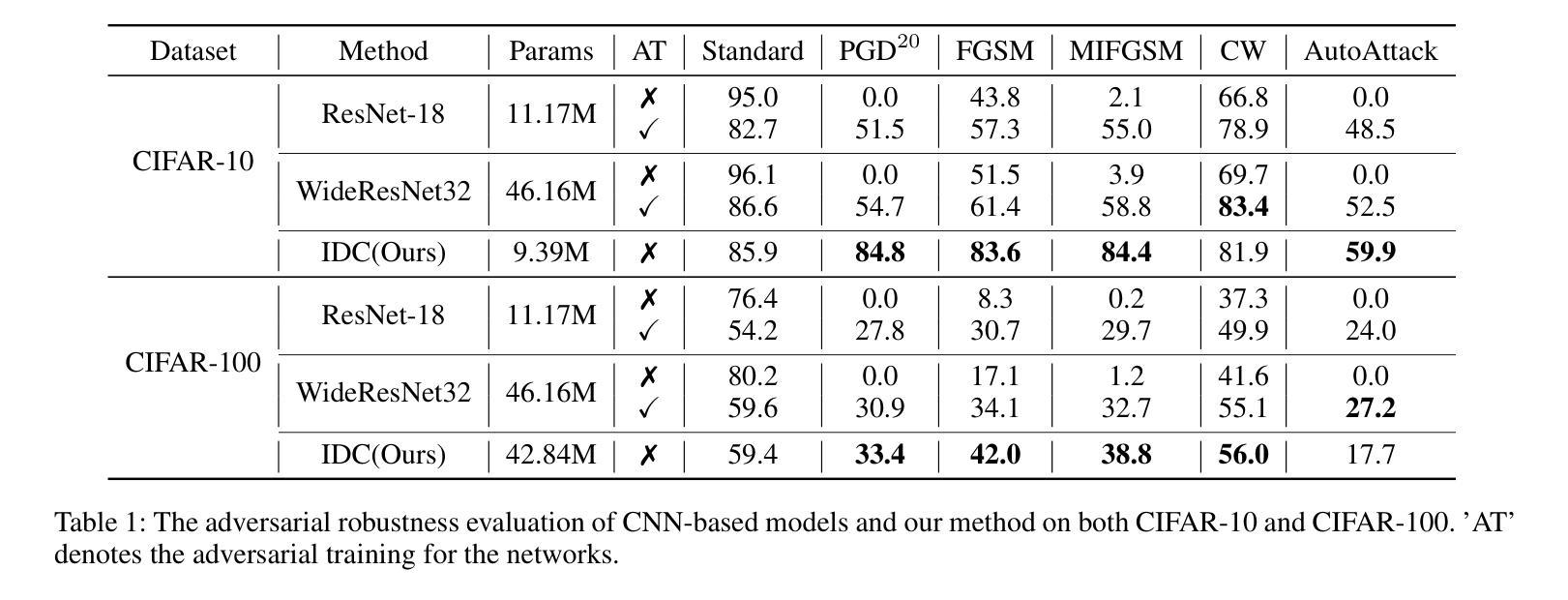
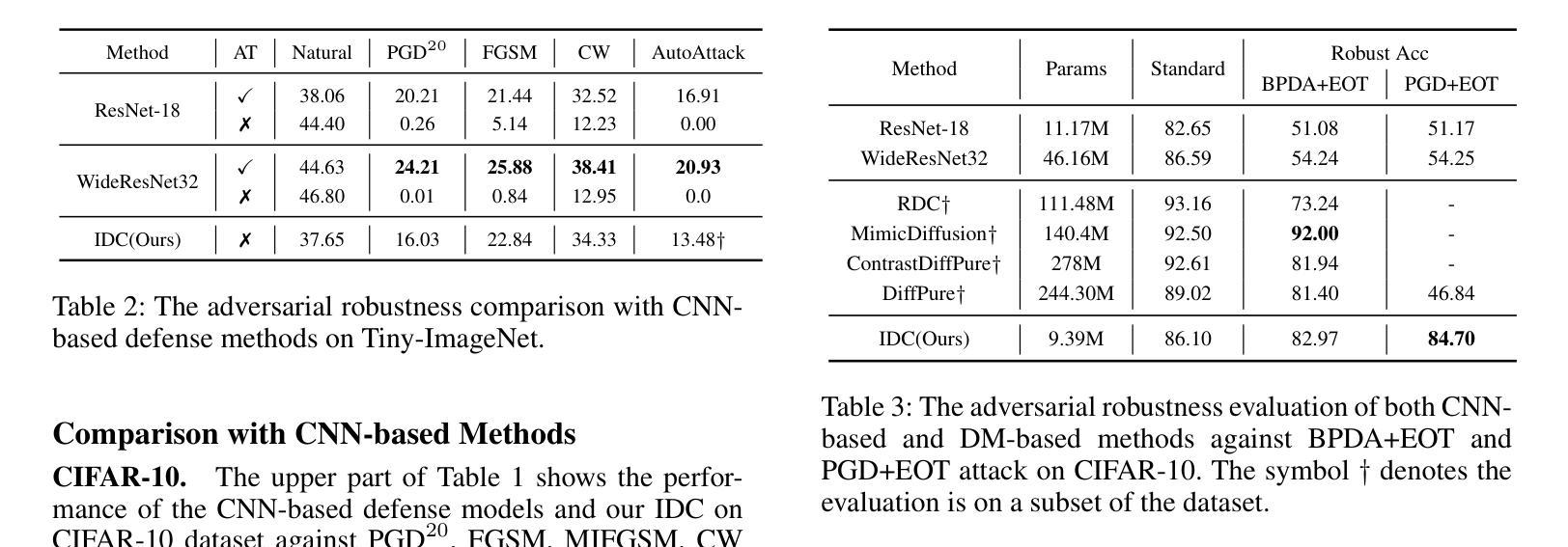
Efficient Image-to-Image Diffusion Classifier for Adversarial Robustness
Authors:Hefei Mei, Minjing Dong, Chang Xu
Diffusion models (DMs) have demonstrated great potential in the field of adversarial robustness, where DM-based defense methods can achieve superior defense capability without adversarial training. However, they all require huge computational costs due to the usage of large-scale pre-trained DMs, making it difficult to conduct full evaluation under strong attacks and compare with traditional CNN-based methods. Simply reducing the network size and timesteps in DMs could significantly harm the image generation quality, which invalidates previous frameworks. To alleviate this issue, we redesign the diffusion framework from generating high-quality images to predicting distinguishable image labels. Specifically, we employ an image translation framework to learn many-to-one mapping from input samples to designed orthogonal image labels. Based on this framework, we introduce an efficient Image-to-Image diffusion classifier with a pruned U-Net structure and reduced diffusion timesteps. Besides the framework, we redesign the optimization objective of DMs to fit the target of image classification, where a new classification loss is incorporated in the DM-based image translation framework to distinguish the generated label from those of other classes. We conduct sufficient evaluations of the proposed classifier under various attacks on popular benchmarks. Extensive experiments show that our method achieves better adversarial robustness with fewer computational costs than DM-based and CNN-based methods. The code is available at https://github.com/hfmei/IDC
扩散模型(DMs)在对抗鲁棒性领域表现出巨大潜力,基于DM的防御方法可以在无需对抗训练的情况下实现优越的防御能力。然而,由于使用了大规模预训练的DM,它们都需要巨大的计算成本,难以在强攻击下进行全面评估,并与传统的基于CNN的方法进行比较。简单缩小DM的网络规模和减少时间步长可能会显著损害图像生成质量,从而使现有框架失效。为了缓解这一问题,我们重新设计了扩散框架,从生成高质量图像转向预测可区分的图像标签。具体来说,我们采用图像翻译框架来学习从输入样本到设计的正交图像标签的多个到单个的映射。基于此框架,我们引入了一种高效的图像到图像扩散分类器,它具有修剪的U-Net结构和减少的扩散时间步长。除了框架之外,我们还重新设计了DM的优化目标以适应图像分类的目标,其中新的分类损失被纳入基于DM的图像翻译框架中,以区分生成的标签与其他类别的标签。我们在流行的基准测试上对提出的分类器进行了各种攻击下的充分评估。大量实验表明,我们的方法在计算成本更低的情况下实现了比基于DM和基于CNN的方法更好的对抗鲁棒性。代码可在https://github.com/hfmei/IDC找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:
扩散模型(DMs)在对抗鲁棒性领域具有巨大潜力,无需对抗训练即可实现高级防御能力。但因其计算成本高昂,难以在强攻击下进行全面评估并与传统CNN方法进行比较。研究团队通过设计新的扩散框架来解决这一问题,从生成高质量图像转变为预测可识别的图像标签。采用图像翻译框架实现输入样本到设计的正交图像标签的多对一映射,并引入高效的图像到图像扩散分类器。同时重新设计DM的优化目标以适应图像分类任务,并在DM基于图像翻译框架中融入新的分类损失以区分生成的标签与其他类别。实验表明,该方法在对抗攻击下具有更好的鲁棒性,计算成本低于DM和CNN方法。
Key Takeaways:
- 扩散模型在对抗鲁棒性领域有巨大潜力,但计算成本高昂。
- 研究团队通过设计新的扩散框架来解决计算成本问题,从图像生成转向图像标签预测。
- 采用图像翻译框架实现输入样本到正交图像标签的多对一映射。
- 引入高效的图像到图像扩散分类器,采用修剪的U-Net结构和减少的扩散时间步。
- 重新设计DM的优化目标以适应图像分类任务。
- 在DM基于图像翻译框架中融入新的分类损失以区分标签。
点此查看论文截图
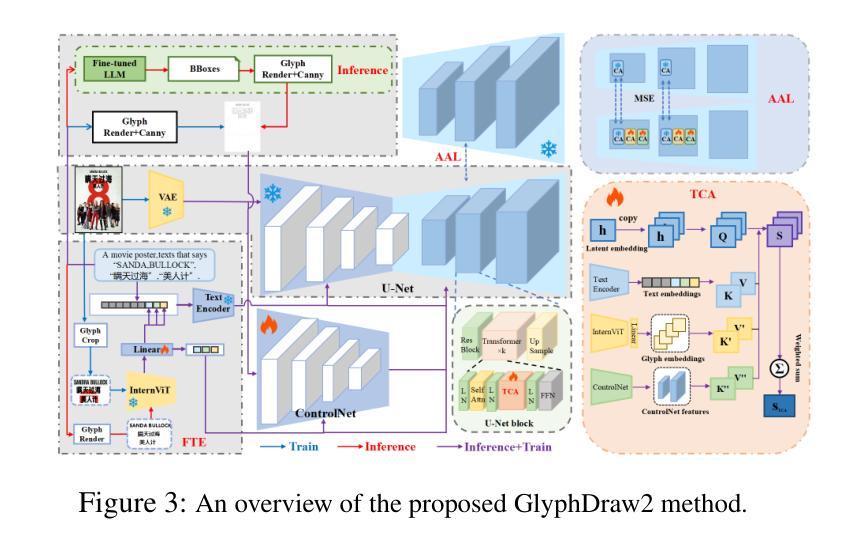
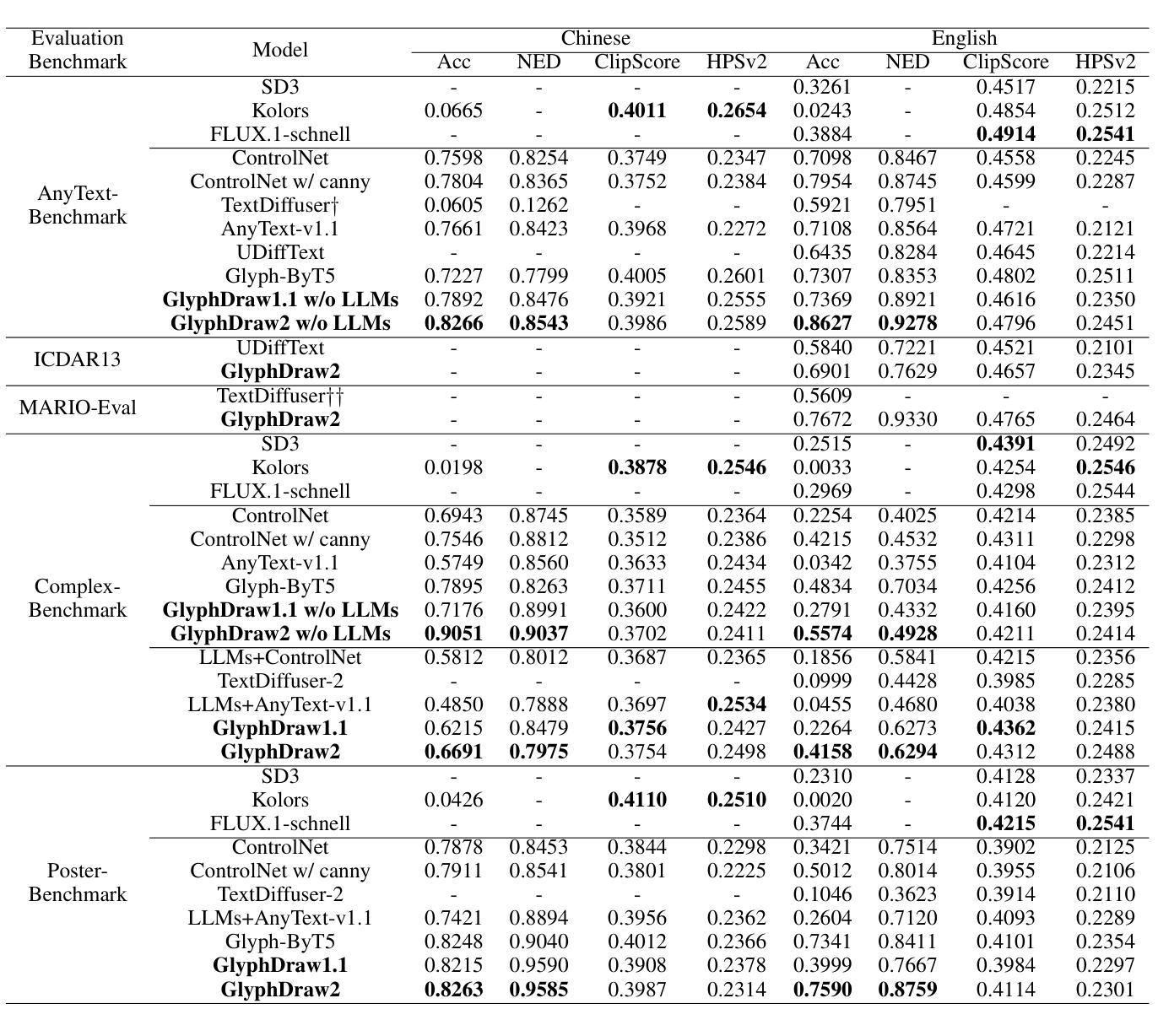
GlyphDraw2: Automatic Generation of Complex Glyph Posters with Diffusion Models and Large Language Models
Authors:Jian Ma, Yonglin Deng, Chen Chen, Nanyang Du, Haonan Lu, Zhenyu Yang
Posters play a crucial role in marketing and advertising by enhancing visual communication and brand visibility, making significant contributions to industrial design. With the latest advancements in controllable T2I diffusion models, increasing research has focused on rendering text within synthesized images. Despite improvements in text rendering accuracy, the field of automatic poster generation remains underexplored. In this paper, we propose an automatic poster generation framework with text rendering capabilities leveraging LLMs, utilizing a triple-cross attention mechanism based on alignment learning. This framework aims to create precise poster text within a detailed contextual background. Additionally, the framework supports controllable fonts, adjustable image resolution, and the rendering of posters with descriptions and text in both English and Chinese.Furthermore, we introduce a high-resolution font dataset and a poster dataset with resolutions exceeding 1024 pixels. Our approach leverages the SDXL architecture. Extensive experiments validate our method’s capability in generating poster images with complex and contextually rich backgrounds.Codes is available at https://github.com/OPPO-Mente-Lab/GlyphDraw2.
海报在营销和广告中起着至关重要的作用,通过增强视觉交流和品牌可见度,为工业设计做出了重大贡献。随着最新的可控T2I扩散模型的进展,越来越多的研究集中在合成图像中的文本渲染上。尽管文本渲染精度有所提高,但自动海报生成领域仍然未被充分探索。在本文中,我们提出了一种利用大型语言模型进行文本渲染的自动海报生成框架,该框架采用基于对齐学习的三重交叉注意力机制。该框架旨在在一个详细的上下文背景中创建精确的海报文本。此外,该框架支持可控字体、可调图像分辨率,以及能够呈现中英文描述和文本的海报。此外,我们还引入了一个高分辨率字体数据集和一个分辨率超过1024像素的海报数据集。我们的方法利用SDXL架构。大量实验验证了我们方法在生成具有复杂和丰富上下文背景的海报图像方面的能力。代码可在https://github.com/OPPO-Mente-Lab/GlyphDraw2找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by AAAI2025
Summary
本文介绍了利用最新可控T2I扩散模型,结合LLMs和三元交叉注意力机制,提出一种具有文本渲染能力的自动海报生成框架。该框架旨在创建具有详细上下文背景的海报文本,支持可控字体、可调整的图像分辨率,以及中英文描述和文本的海报渲染。同时,引入高分辨率字体数据集和超过1024像素分辨率的海报数据集。实验证明,该方法能够生成具有复杂和丰富上下文背景的海报图像。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型在海报设计中的应用:利用最新可控T2I扩散模型,为海报生成提供新的解决方案。
- 文本渲染能力:结合LLMs,使框架具备在合成图像中渲染文本的能力。
- 三元交叉注意力机制:基于对齐学习,实现精确的海报文本与上下文背景的融合。
- 多语言支持:框架支持中英文描述和文本的海报渲染。
- 高分辨率数据集:引入高分辨率字体数据集和超过1024像素分辨率的海报数据集,提升生成图像的质量。
- 使用SDXL架构:该框架采用SDXL架构,有效提高海报生成的效率和准确性。
- 实验验证:大量实验证明该方法能够生成具有复杂和丰富上下文背景的海报图像。
点此查看论文截图



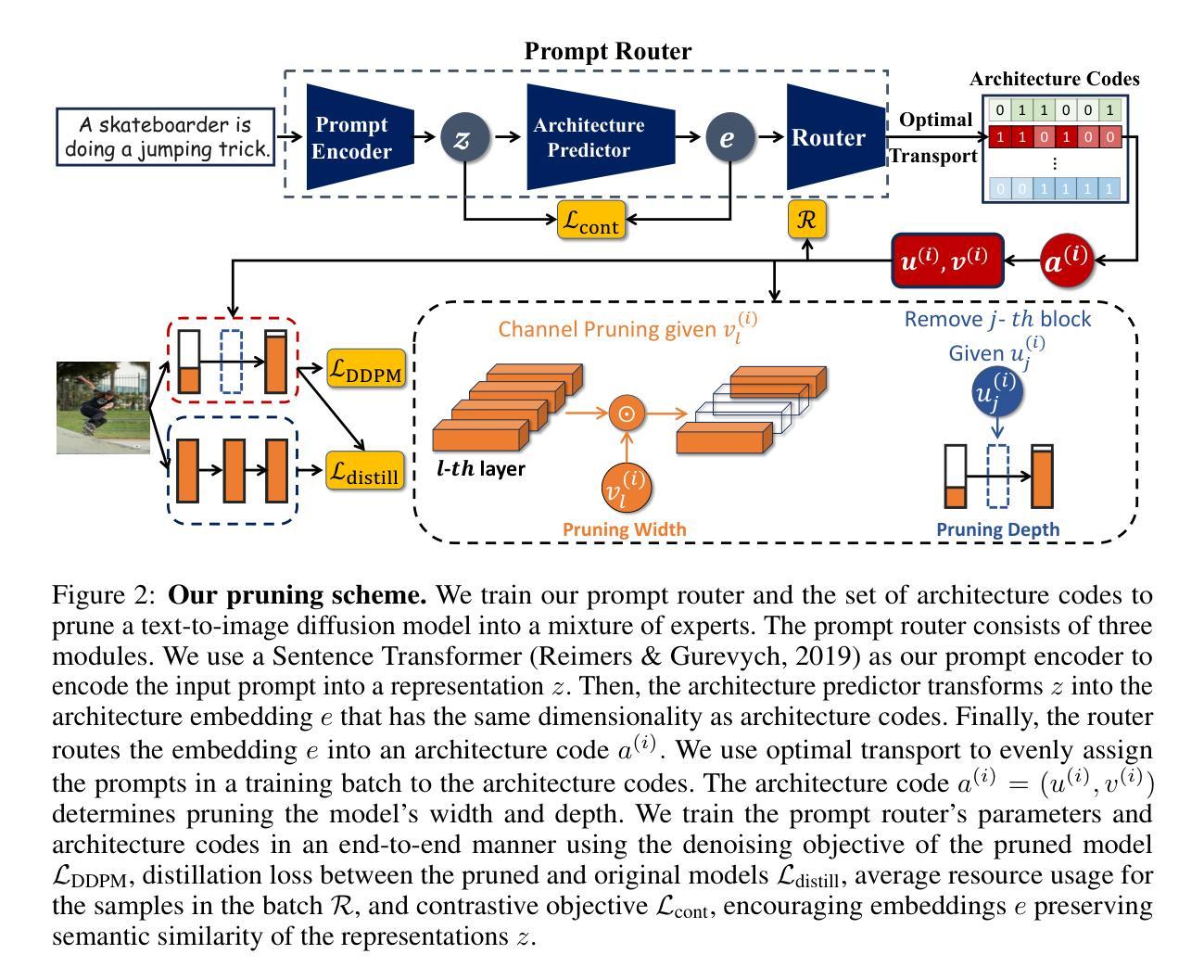
Not All Prompts Are Made Equal: Prompt-based Pruning of Text-to-Image Diffusion Models
Authors:Alireza Ganjdanesh, Reza Shirkavand, Shangqian Gao, Heng Huang
Text-to-image (T2I) diffusion models have demonstrated impressive image generation capabilities. Still, their computational intensity prohibits resource-constrained organizations from deploying T2I models after fine-tuning them on their internal target data. While pruning techniques offer a potential solution to reduce the computational burden of T2I models, static pruning methods use the same pruned model for all input prompts, overlooking the varying capacity requirements of different prompts. Dynamic pruning addresses this issue by utilizing a separate sub-network for each prompt, but it prevents batch parallelism on GPUs. To overcome these limitations, we introduce Adaptive Prompt-Tailored Pruning (APTP), a novel prompt-based pruning method designed for T2I diffusion models. Central to our approach is a prompt router model, which learns to determine the required capacity for an input text prompt and routes it to an architecture code, given a total desired compute budget for prompts. Each architecture code represents a specialized model tailored to the prompts assigned to it, and the number of codes is a hyperparameter. We train the prompt router and architecture codes using contrastive learning, ensuring that similar prompts are mapped to nearby codes. Further, we employ optimal transport to prevent the codes from collapsing into a single one. We demonstrate APTP’s effectiveness by pruning Stable Diffusion (SD) V2.1 using CC3M and COCO as target datasets. APTP outperforms the single-model pruning baselines in terms of FID, CLIP, and CMMD scores. Our analysis of the clusters learned by APTP reveals they are semantically meaningful. We also show that APTP can automatically discover previously empirically found challenging prompts for SD, e.g. prompts for generating text images, assigning them to higher capacity codes.
文本到图像(T2I)扩散模型已经表现出了令人印象深刻的图像生成能力。然而,其计算强度使得资源受限的组织无法在对其内部目标数据进行微调后部署T2I模型。虽然剪枝技术提供了减少T2I模型计算负担的潜在解决方案,但静态剪枝方法使用相同的剪枝模型来处理所有输入提示,忽视了不同提示所需的能力差异。动态剪枝通过为每个提示使用单独的子网络来解决这个问题,但它阻止了GPU上的批量并行性。为了克服这些限制,我们引入了自适应提示定制剪枝(APTP),这是一种针对T2I扩散模型的新型基于提示的剪枝方法。我们的方法的核心是一个提示路由器模型,它学习确定输入文本提示所需的计算能力,并根据给定的总提示计算预算来路由到架构代码。每个架构代码代表一个专为其分配的提示定制的模型,代码的数量是一个超参数。我们使用对比学习来训练提示路由器和架构代码,确保相似的提示被映射到附近的代码。此外,我们采用最优传输来防止代码崩溃为单一代码。我们通过使用CC3M和COCO作为目标数据集对Stable Diffusion(SD)V2.1进行剪枝来展示APTP的有效性。APTP在FID、CLIP和CMMD分数方面优于单模型剪枝基线。我们对APTP学习的集群的分析表明它们是语义上有意义的。我们还表明,APTP可以自动发现之前经验上发现的SD的挑战性提示,例如用于生成文本图像的提示,并将它们分配给更高容量的代码。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
T2I扩散模型生成图像能力强大,但其计算强度限制了资源受限组织在内部目标数据上微调后部署T2I模型。现有方法无法针对不同输入提示变化其计算能力,动态剪枝法采用每个提示使用单独的子网络虽解决此问题,却阻碍GPU批量并行处理。本文引入自适应提示定制剪枝(APTP),一种专为T2I扩散模型设计的基于提示的剪枝方法。APTP采用提示路由器模型确定输入文本提示所需计算能力,并根据计算预算将其路由至特定架构代码。使用对比学习训练提示路由器和架构代码,确保相似提示映射至相近代码。通过最优传输防止代码崩溃至单一状态。实验显示,APTP在修剪Stable Diffusion V2.1时优于单模型剪枝基线,通过FID、CLIP和CMMD得分评估效果。分析显示APTP学习的集群语义上更有实际意义,还能自动发现之前难以处理的任务提示并为其分配更高计算能力代码。
关键见解
- T2I扩散模型具备出色的图像生成能力,但计算强度高,限制了其在资源受限环境中的部署。
- 现有剪枝技术无法适应不同输入提示的计算需求变化。
- 动态剪枝方法采用子网络处理每个提示,但限制了GPU的批量并行处理。
- 引入自适应提示定制剪枝(APTP),利用提示路由器模型确定不同提示的计算需求。
- 采用对比学习训练提示路由器和架构代码,确保相似提示映射至相近架构代码。
- 使用最优传输技术防止架构代码崩溃至单一状态。
- APTP在修剪Stable Diffusion V2.1模型时表现出优异性能,并通过FID、CLIP和CMMD得分评估优于基线方法。语义分析显示APTP学习的集群具有实际意义,并能自动处理复杂任务提示。
点此查看论文截图


Information Theoretic Text-to-Image Alignment
Authors:Chao Wang, Giulio Franzese, Alessandro Finamore, Massimo Gallo, Pietro Michiardi
Diffusion models for Text-to-Image (T2I) conditional generation have recently achieved tremendous success. Yet, aligning these models with user’s intentions still involves a laborious trial-and-error process, and this challenging alignment problem has attracted considerable attention from the research community. In this work, instead of relying on fine-grained linguistic analyses of prompts, human annotation, or auxiliary vision-language models, we use Mutual Information (MI) to guide model alignment. In brief, our method uses self-supervised fine-tuning and relies on a point-wise (MI) estimation between prompts and images to create a synthetic fine-tuning set for improving model alignment. Our analysis indicates that our method is superior to the state-of-the-art, yet it only requires the pre-trained denoising network of the T2I model itself to estimate MI, and a simple fine-tuning strategy that improves alignment while maintaining image quality. Code available at https://github.com/Chao0511/mitune.
文本到图像(T2I)的条件生成扩散模型近期取得了巨大的成功。然而,将这些模型与用户意图对齐仍然需要耗费大量时间和精力的试错过程,这一具有挑战性的对齐问题已引起了研究界的广泛关注。在这项工作中,我们没有依赖提示的精细语言分析、人工标注或辅助的视觉语言模型,而是使用互信息(MI)来引导模型对齐。简而言之,我们的方法使用自监督微调,并依赖于提示和图像之间的点式(MI)估计来创建一个合成微调集,以提高模型对齐效果。我们的分析表明,我们的方法优于当前最先进的对齐方法,而且它只需要T2I模型本身的预训练去噪网络来估计互信息,以及一种简单的微调策略,可以在保持图像质量的同时提高对齐效果。相关代码可通过https://github.com/Chao0511/mitune获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF to appear at ICLR25
Summary
本文介绍了使用互信息(MI)来指导文本到图像(T2I)扩散模型的模型对齐方法。该方法采用自监督微调,依赖于提示和图像之间的点级互信息估计,以创建合成微调集,从而提高模型对齐能力。该方法仅使用T2I模型的预训练去噪网络来估计互信息,并采用简单的微调策略,既提高了对齐能力又保持了图像质量。
Key Takeaways
- 文本到图像(T2I)扩散模型的模型对齐问题吸引了研究人员的关注。
- 该方法使用互信息(MI)来指导模型对齐,这是一种新的尝试。
- 采用自监督微调方式,仅依赖T2I模型的预训练去噪网络来估计互信息。
- 通过点级互信息估计,创建合成微调集以提高模型对齐能力。
- 该方法提高了模型的对齐能力,同时保持了图像质量。
- 该方法提供了一种简单有效的微调策略。
点此查看论文截图


MemControl: Mitigating Memorization in Diffusion Models via Automated Parameter Selection
Authors:Raman Dutt, Ondrej Bohdal, Pedro Sanchez, Sotirios A. Tsaftaris, Timothy Hospedales
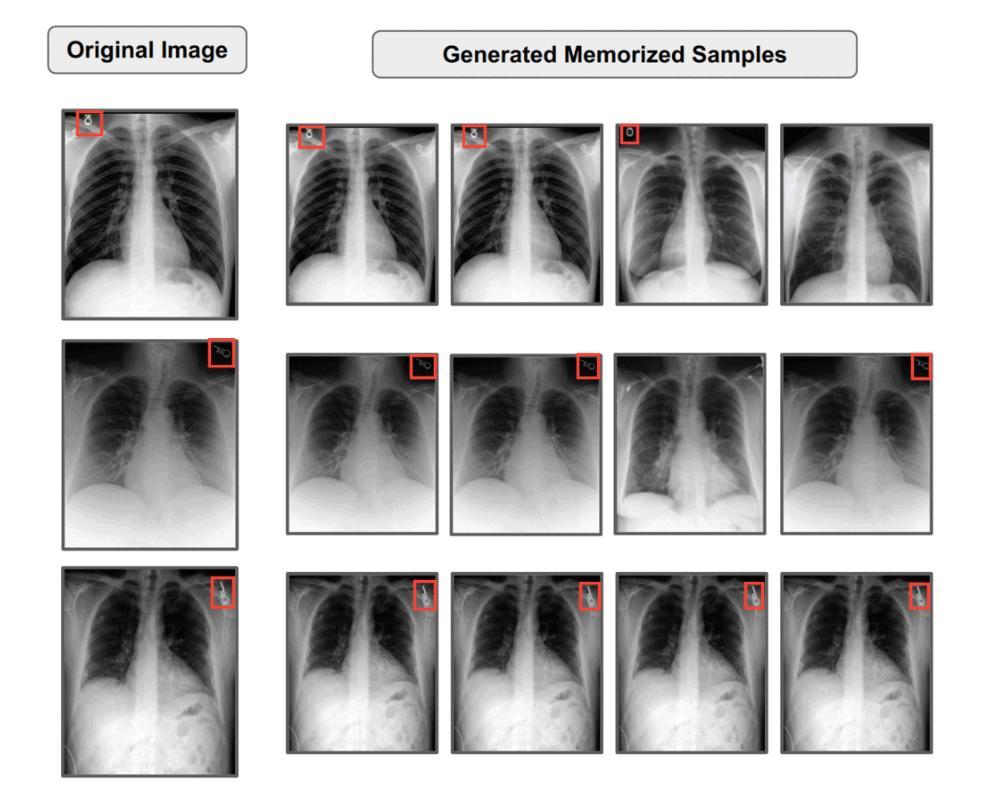
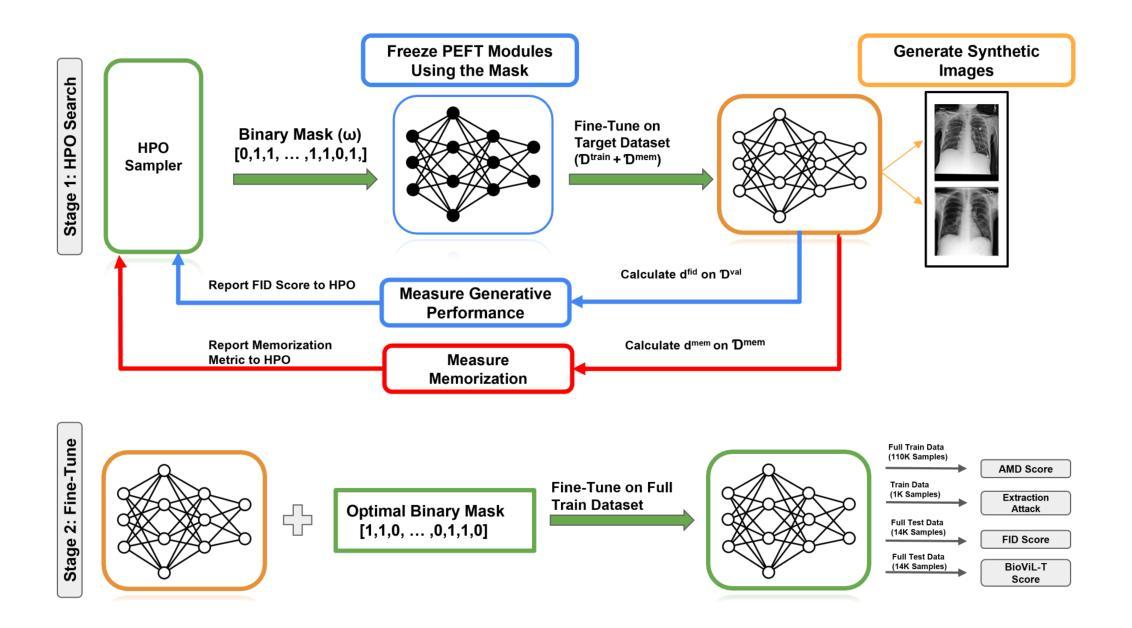
Diffusion models excel in generating images that closely resemble their training data but are also susceptible to data memorization, raising privacy, ethical, and legal concerns, particularly in sensitive domains such as medical imaging. We hypothesize that this memorization stems from the overparameterization of deep models and propose that regularizing model capacity during fine-tuning can mitigate this issue. Firstly, we empirically show that regulating the model capacity via Parameter-efficient fine-tuning (PEFT) mitigates memorization to some extent, however, it further requires the identification of the exact parameter subsets to be fine-tuned for high-quality generation. To identify these subsets, we introduce a bi-level optimization framework, MemControl, that automates parameter selection using memorization and generation quality metrics as rewards during fine-tuning. The parameter subsets discovered through MemControl achieve a superior tradeoff between generation quality and memorization. For the task of medical image generation, our approach outperforms existing state-of-the-art memorization mitigation strategies by fine-tuning as few as 0.019% of model parameters. Moreover, we demonstrate that the discovered parameter subsets are transferable to non-medical domains. Our framework is scalable to large datasets, agnostic to reward functions, and can be integrated with existing approaches for further memorization mitigation. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first study to empirically evaluate memorization in medical images and propose a targeted yet universal mitigation strategy. The code is available at https://github.com/Raman1121/Diffusion_Memorization_HPO.
扩散模型在生成与训练数据非常相似的图像方面表现出色,但也容易存在数据记忆的问题,特别是在医学影像等敏感领域引发了隐私、伦理和法律的担忧。我们假设这种记忆源于深度模型的过度参数化,并提出在微调过程中进行模型容量正则化可以缓解这个问题。首先,我们通过实验证明,通过参数有效的微调(PEFT)来调控模型容量可以在一定程度上减轻记忆问题。然而,这还需要确定要进行微调的确切参数子集以实现高质量的生成。为了识别这些子集,我们引入了一种双层优化框架MemControl,它使用记忆和生成质量指标作为奖励来自动化参数选择,从而在微调过程中进行选择。通过MemControl发现的参数子集在生成质量和记忆之间达到了优越的权衡。在医学图像生成任务中,我们的方法通过微调仅0.019%的模型参数,就优于现有的最先进的记忆缓解策略。此外,我们还证明了所发现的参数子集可转移到非医学领域。我们的框架可扩展到大型数据集,对奖励函数无偏见,并可与其他现有方法相结合进一步缓解记忆问题。据我们所知,这是第一项针对医学图像中的记忆问题进行实证评估并提出有针对性的通用缓解策略的研究。代码可通过https://github.com/Raman1121/Diffusion_Memorization_HPO访问。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted into WACV 2025 (Applications Track)
Summary
本文探讨了扩散模型在生成图像时存在的数据记忆化问题,特别是在医疗图像等敏感领域。为解决这一问题,提出了通过参数效率微调(PEFT)来规范模型容量,并引入了一种双层优化框架MemControl,以自动化选择参数,在微调过程中以记忆化和生成质量指标作为奖励。该方法在医疗图像生成任务上表现出优异的效果,且可应用于非医疗领域。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型虽能生成与训练数据相似的图像,但存在数据记忆化问题,引发隐私、伦理和法律担忧,尤其在医疗图像等敏感领域。
- 参数效率微调(PEFT)是一种有效的策略,能够在一定程度上缓解记忆化问题。
- 引入双层优化框架MemControl,通过自动化参数选择,以记忆化和生成质量指标为奖励,实现了高质量的生成与记忆化的平衡。
- 在医疗图像生成任务上,MemControl策略优于现有策略,仅微调0.019%的参数即可实现显著效果。
- 发现的参数子集可应用于非医疗领域,显示出了良好的通用性。
- 该框架可扩展至大数据集,对奖励函数具有无关性,并可与其他策略结合进一步缓解记忆化问题。
- 本文是首个针对医疗图像记忆化问题进行实证研究并提出通用缓解策略的研究。
点此查看论文截图

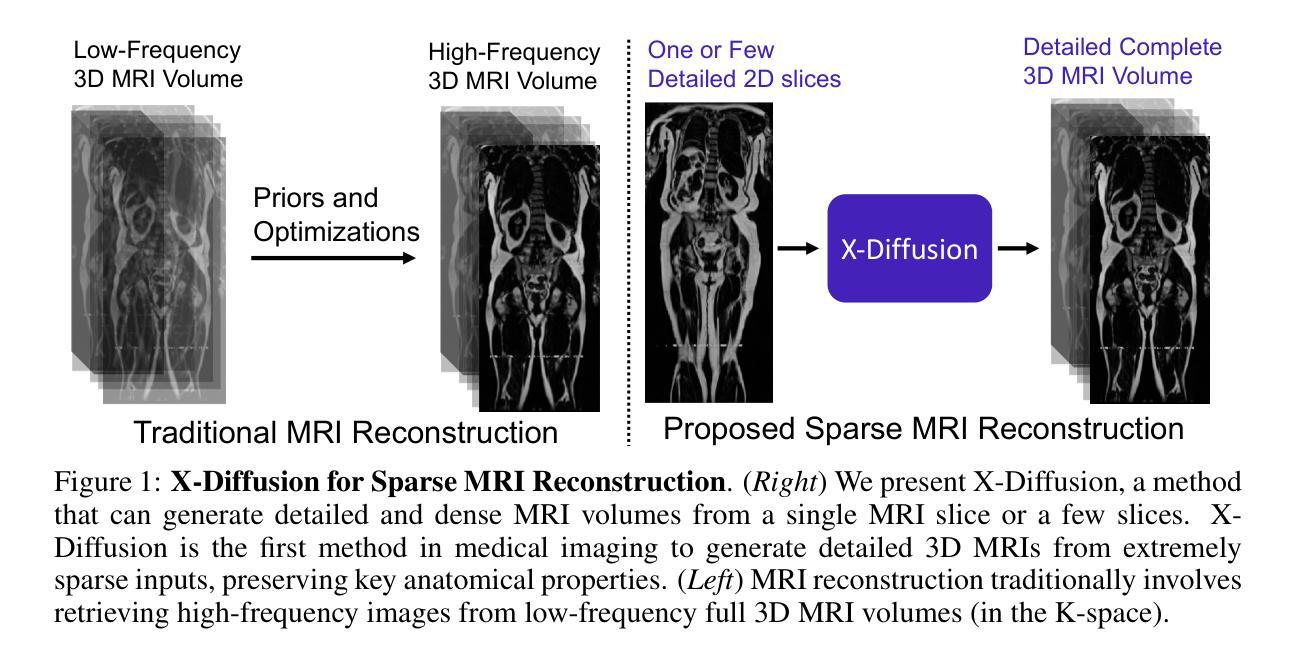
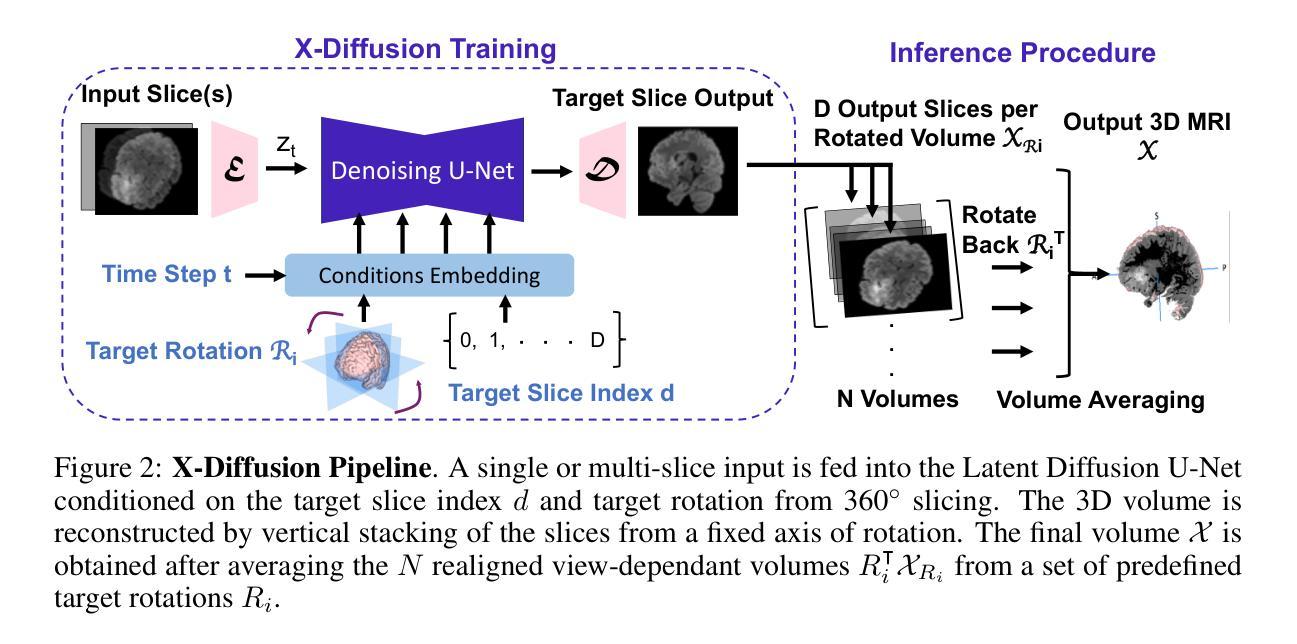
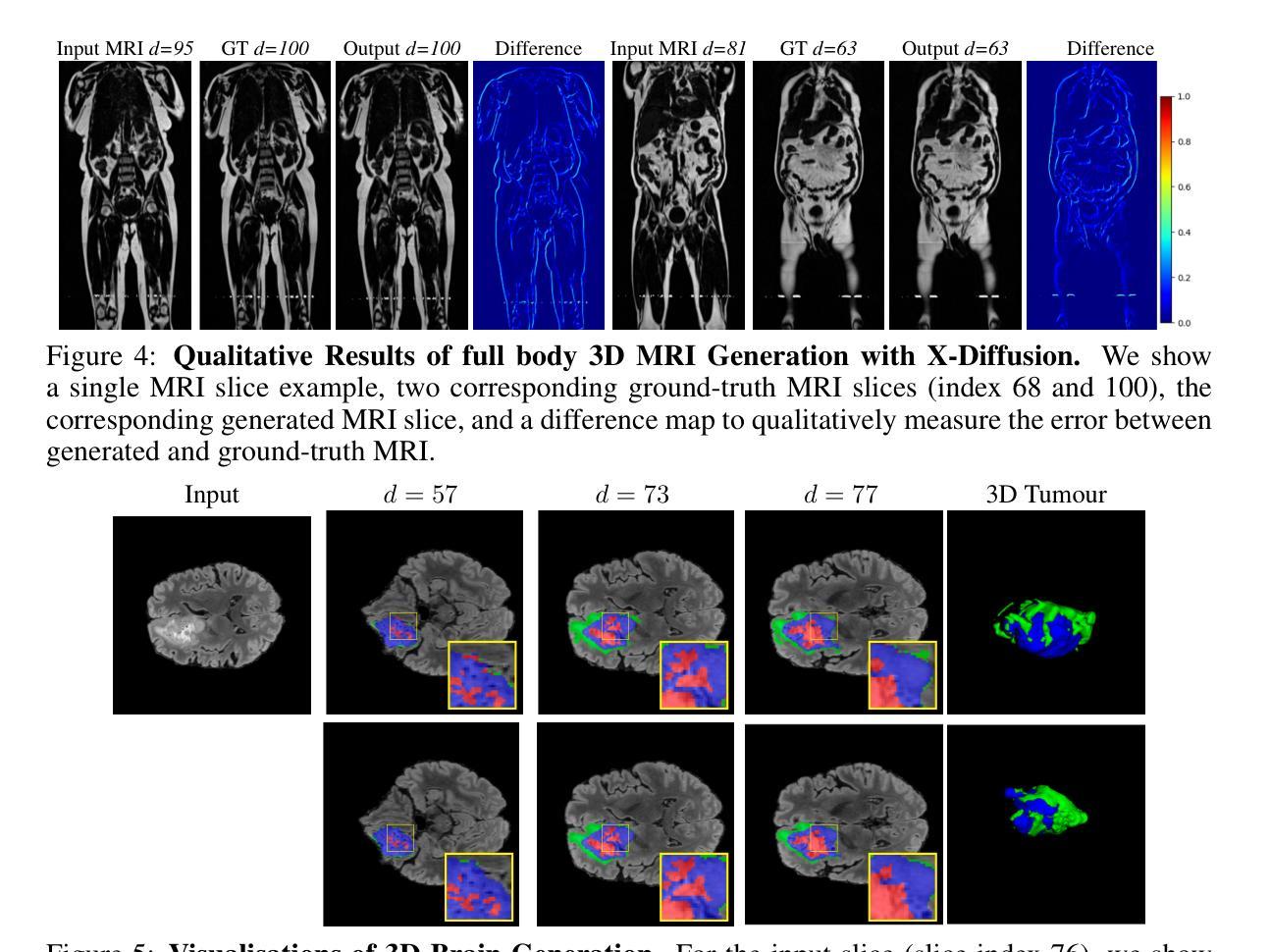
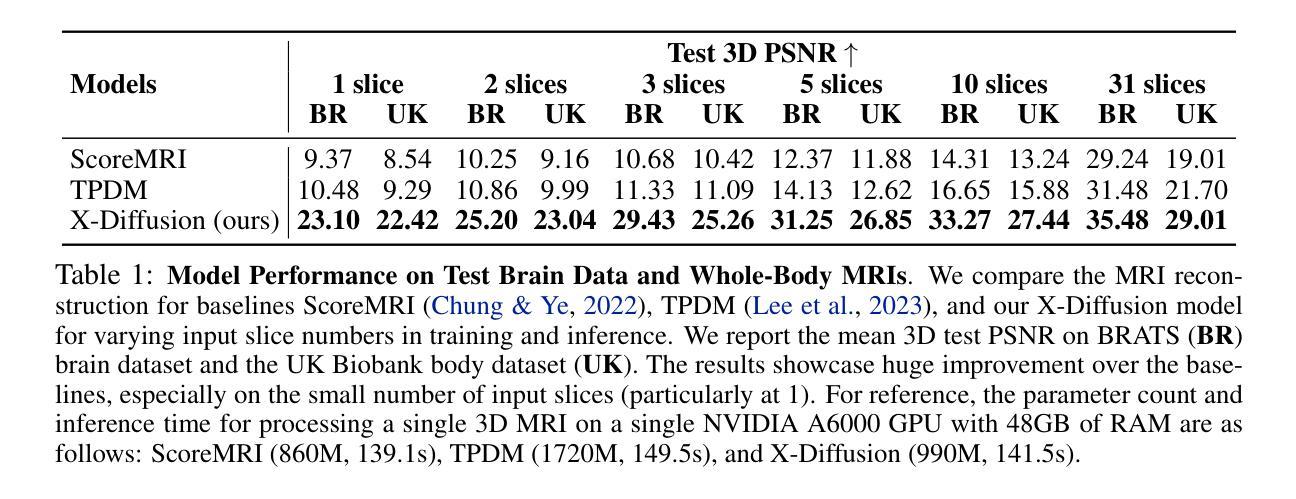
X-Diffusion: Generating Detailed 3D MRI Volumes From a Single Image Using Cross-Sectional Diffusion Models
Authors:Emmanuelle Bourigault, Abdullah Hamdi, Amir Jamaludin
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) is a crucial diagnostic tool, but high-resolution scans are often slow and expensive due to extensive data acquisition requirements. Traditional MRI reconstruction methods aim to expedite this process by filling in missing frequency components in the K-space, performing 3D-to-3D reconstructions that demand full 3D scans. In contrast, we introduce X-Diffusion, a novel cross-sectional diffusion model that reconstructs detailed 3D MRI volumes from extremely sparse spatial-domain inputs, achieving 2D-to-3D reconstruction from as little as a single 2D MRI slice or few slices. A key aspect of X-Diffusion is that it models MRI data as holistic 3D volumes during the cross-sectional training and inference, unlike previous learning approaches that treat MRI scans as collections of 2D slices in standard planes (coronal, axial, sagittal). We evaluated X-Diffusion on brain tumor MRIs from the BRATS dataset and full-body MRIs from the UK Biobank dataset. Our results demonstrate that X-Diffusion not only surpasses state-of-the-art methods in quantitative accuracy (PSNR) on unseen data but also preserves critical anatomical features such as tumor profiles, spine curvature, and brain volume. Remarkably, the model generalizes beyond the training domain, successfully reconstructing knee MRIs despite being trained exclusively on brain data. Medical expert evaluations further confirm the clinical relevance and fidelity of the generated images.To our knowledge, X-Diffusion is the first method capable of producing detailed 3D MRIs from highly limited 2D input data, potentially accelerating MRI acquisition and reducing associated costs. The code is available on the project website https://emmanuelleb985.github.io/XDiffusion/ .
磁共振成像(MRI)是一种重要的诊断工具,但高分辨率扫描通常由于需要大量数据采集而缓慢且昂贵。传统的MRI重建方法旨在通过填充K空间中的缺失频率成分来加速这一过程,进行需要完整3D扫描的3D-to-3D重建。相比之下,我们引入了X-Diffusion,这是一种新型截面扩散模型,能够从极其稀疏的空间域输入中重建详细的3D MRI体积,实现从少量甚至单个2D MRI切片的2D-to-3D重建。X-Diffusion的关键在于,它在截面训练和推断过程中将MRI数据建模为整体3D体积,不同于以前的学习方法,后者将MRI扫描视为标准平面(冠状面、轴面、矢状面)中的2D切片集合。我们对BRATS数据集中的脑肿瘤MRI和UK Biobank数据集中的全身MRI评估了X-Diffusion。结果表明,X-Diffusion不仅在未见数据上的定量准确性(PSNR)上超越了最先进的方法,而且还保留了关键的组织特征,如肿瘤轮廓、脊柱曲度和脑容量。值得注意的是,该模型在训练领域之外也通用化,尽管只接受脑部数据训练,但成功重建了膝盖MRI。医学专家评估进一步证实了生成图像的临床相关性和保真度。据我们所知,X-Diffusion是第一种能够从高度有限的2D输入数据生成详细的3D MRI的方法,有可能加速MRI采集并降低相关成本。代码可在项目网站https://emmanuelleb985.github.io/XDiffusion/上找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF preprint, project website: https://emmanuelleb985.github.io/XDiffusion/
Summary
本文介绍了一种名为X-Diffusion的新型交叉截面扩散模型,该模型可从极稀疏的空间域输入中重建详细的3D MRI体积,实现从单个或少量的2D MRI切片到3D重建的转化。与传统的MRI重建方法不同,X-Diffusion将MRI数据视为整体3D体积进行建模,突破了以往将MRI扫描视为标准平面内2D切片集合的处理方式。在BRATS数据集上的脑肿瘤MRI和UK Biobank数据集上的全身MRI的评估结果显示,X-Diffusion不仅在定量精度(PSNR)上超越了现有方法,而且在保持关键解剖特征方面表现出色,如肿瘤分布、脊柱曲度和脑容量等。此外,该模型在训练域之外也能进行推广,成功重建了膝盖MRI,尽管其仅接受了脑数据训练。医学专家评价进一步证实了生成图像的临床相关性和保真度。X-Diffusion是首个能够从有限的2D输入数据生成详细的3D MRI图像的方法,有望加快MRI采集并降低相关成本。
Key Takeaways
- X-Diffusion是一种新型的交叉截面扩散模型,能够从极稀疏的空间域输入中重建详细的3D MRI体积。
- 传统MRI重建方法通常需要完整的3D扫描,而X-Diffusion能够实现从单个或少量的2D MRI切片到3D重建的转变。
- X-Diffusion将MRI数据视为整体3D体积进行建模,突破了对MRI扫描的传统处理方式。
- X-Diffusion在保持关键解剖特征方面表现出色,如肿瘤分布、脊柱曲度和脑容量等。
- 该模型在未见过的数据上超越了现有方法的定量精度(PSNR)。
- X-Diffusion能够成功重建膝盖MRI,尽管其仅接受了脑数据训练,显示出良好的泛化能力。
点此查看论文截图