⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-02-13 更新
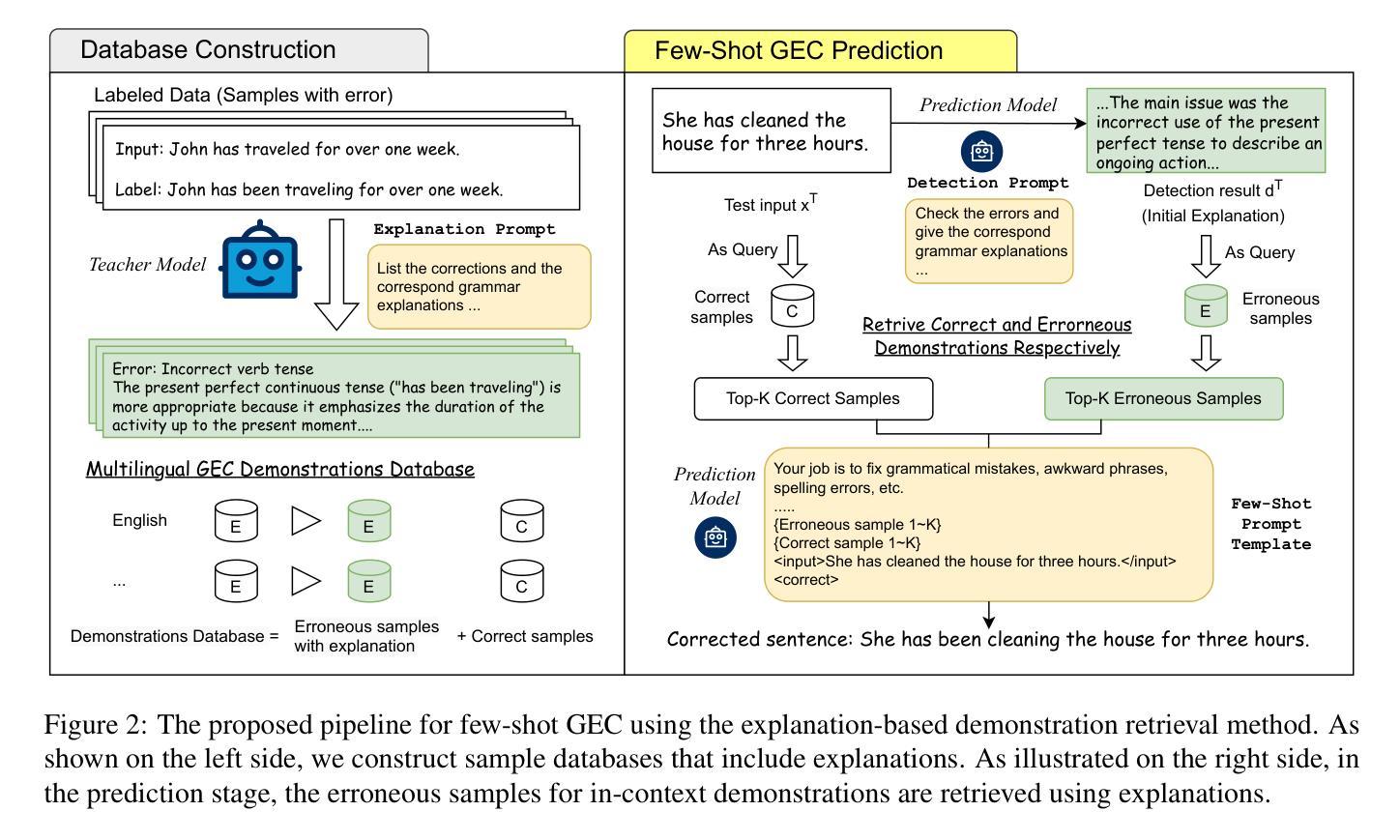
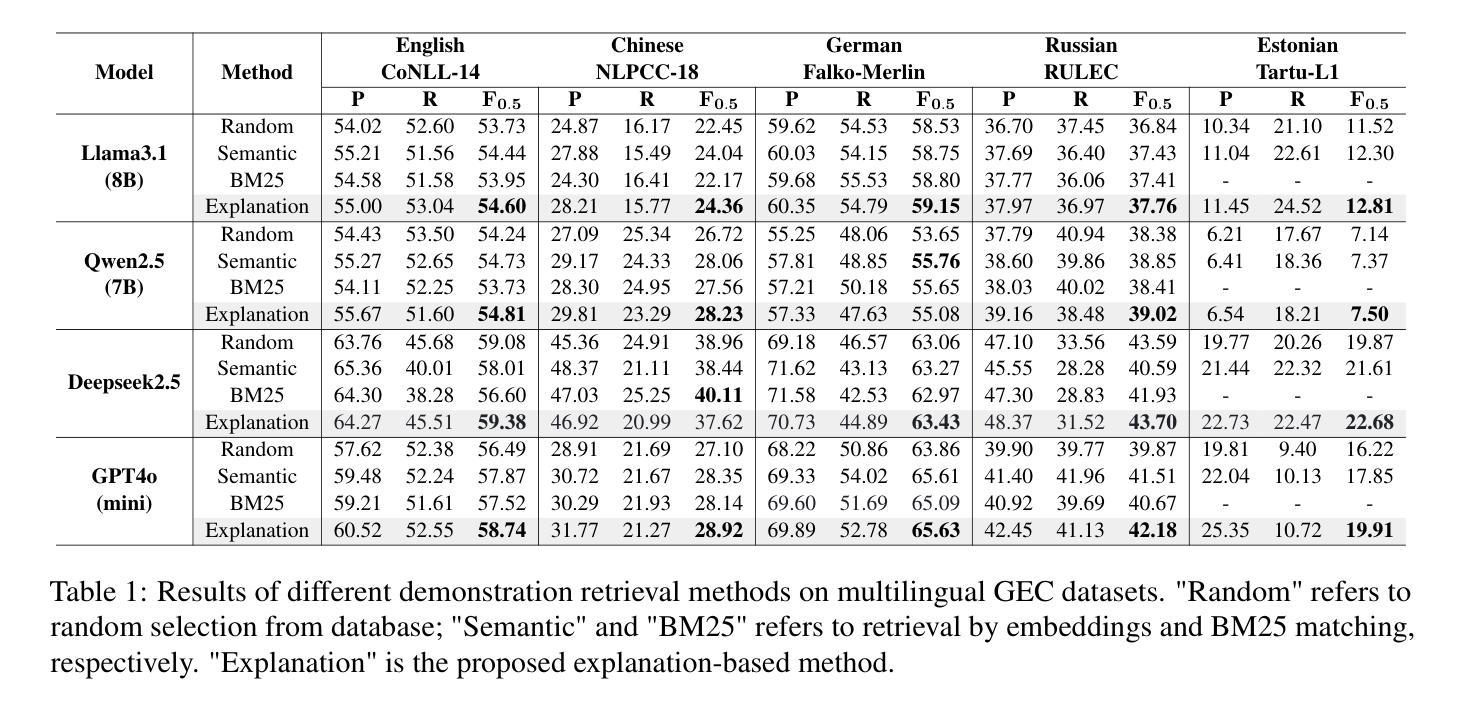
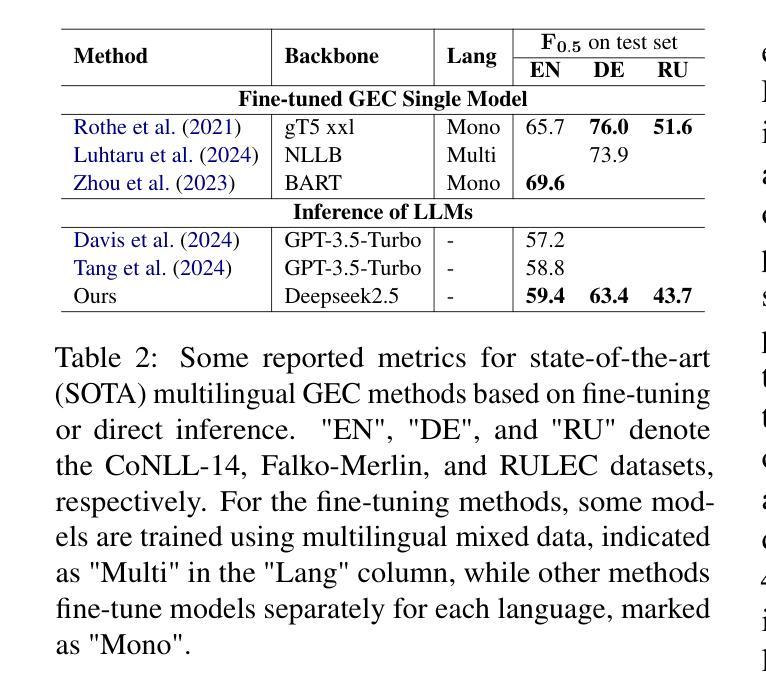
Explanation based In-Context Demonstrations Retrieval for Multilingual Grammatical Error Correction
Authors:Wei Li, Wen Luo, Guangyue Peng, Houfeng Wang
Grammatical error correction (GEC) aims to correct grammatical, spelling, and semantic errors in natural language text. With the growing of large language models (LLMs), direct text generation has gradually become the focus of the GEC methods, and few-shot in-context learning presents a cost-effective solution. However, selecting effective in-context examples remains challenging, as the similarity between input texts does not necessarily correspond to similar grammatical error patterns. In this paper, we propose a novel retrieval method based on natural language grammatical error explanations (GEE) to address this issue. Our method retrieves suitable few-shot demonstrations by matching the GEE of the test input with that of pre-constructed database samples, where explanations for erroneous samples are generated by LLMs. We conducted multilingual GEC few-shot experiments on both major open-source and closed-source LLMs. Experiments across five languages show that our method outperforms existing semantic and BM25-based retrieval techniques, without requiring additional training or language adaptation. This also suggests that matching error patterns is key to selecting examples.
语法错误修正(GEC)旨在修正自然语言文本中的语法、拼写和语义错误。随着大型语言模型(LLM)的增长,直接文本生成逐渐成为GEC方法的重点,而少样本上下文学习提供了一种具有成本效益的解决方案。然而,选择有效的上下文示例仍然具有挑战性,因为输入文本之间的相似性并不一定对应相似的语法错误模式。针对这一问题,我们在本文中提出了一种基于自然语言语法错误解释(GEE)的检索方法。我们的方法通过匹配测试输入的GEE与预先构建的数据库样本的GEE来检索合适的少样本演示,其中错误样本的解释是由LLM生成的。我们在主要的开源和闭源LLM上进行了多语言GEC少样本实验。跨越五种语言的实验表明,我们的方法优于现有的语义和基于BM25的检索技术,无需额外的训练或语言适应。这也表明匹配错误模式是选择示例的关键。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by NAACL 2025 main conference
Summary
自然语言文本中的语法错误修正(GEC)旨在纠正语法、拼写和语义错误。随着大型语言模型(LLM)的发展,直接文本生成逐渐成为GEC方法的重点,而少样本上下文学习则提供了具有成本效益的解决方案。然而,选择有效的上下文实例仍然具有挑战性,因为输入文本之间的相似性并不一定对应相似的语法错误模式。本文提出了一种基于自然语言语法错误解释(GEE)的检索方法来解决这个问题。该方法通过匹配测试输入的GEE与预构建的数据库样本,检索合适的少样本示例,其中错误样本的解释是由LLM生成的。我们在主要开源和闭源的LLM上进行了多语言GEC少样本实验。跨越五种语言的实验表明,该方法优于现有的语义和BM25基础检索技术,无需额外的训练或语言适应。这也表明匹配错误模式是选择示例的关键。
Key Takeaways
- GEC旨在纠正自然语言文本中的语法、拼写和语义错误。
- 随着LLM的发展,直接文本生成成为GEC方法的重点,少样本上下文学习提供成本效益解决方案。
- 选择有效的上下文实例具有挑战性,因为输入文本相似性不一定对应相似的语法错误模式。
- 论文提出了一种基于GEE的检索方法来解决这一问题。
- 该方法通过匹配测试输入的GEE与预构建数据库样本进行检索。
- 实验表明,该方法在多种语言上均优于现有语义和BM25基础检索技术。
点此查看论文截图

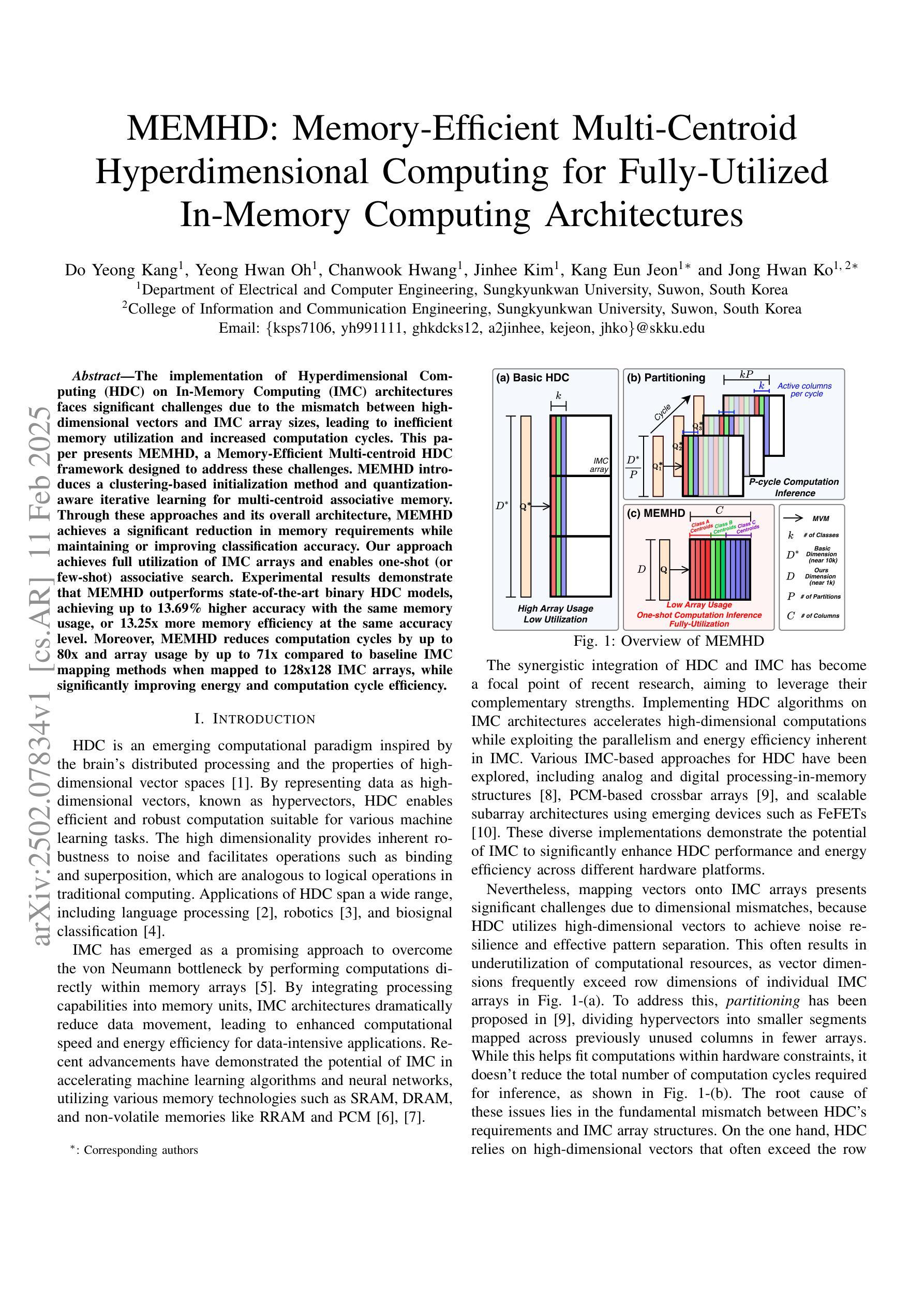
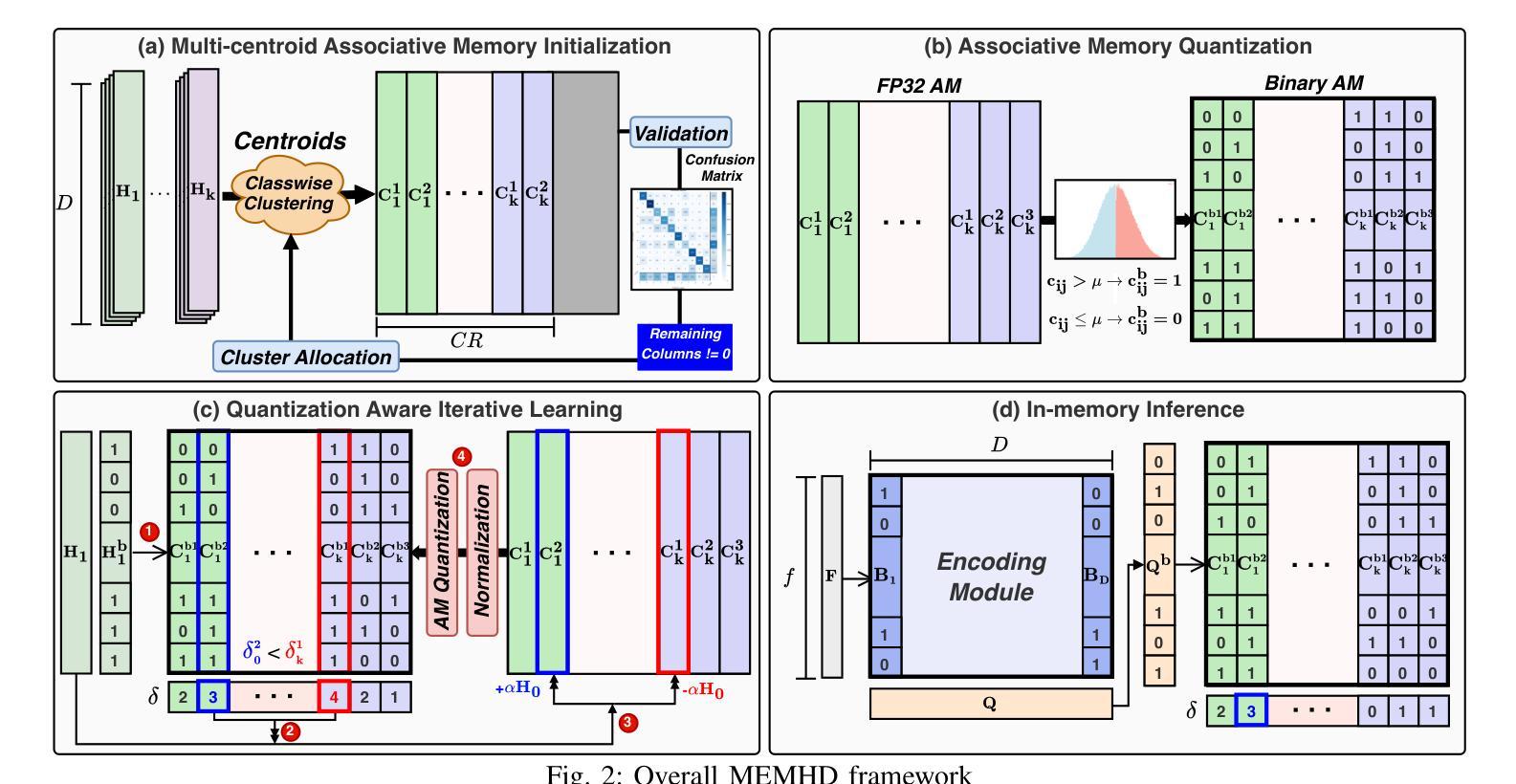
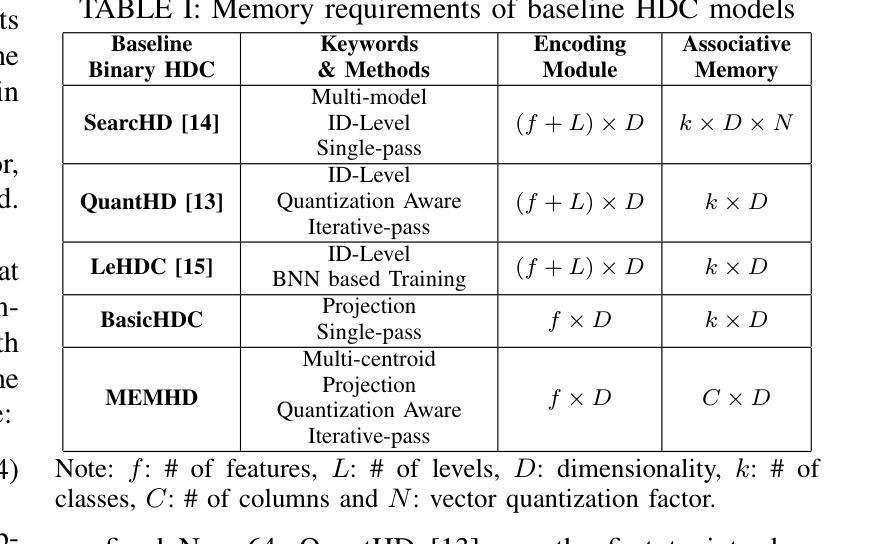
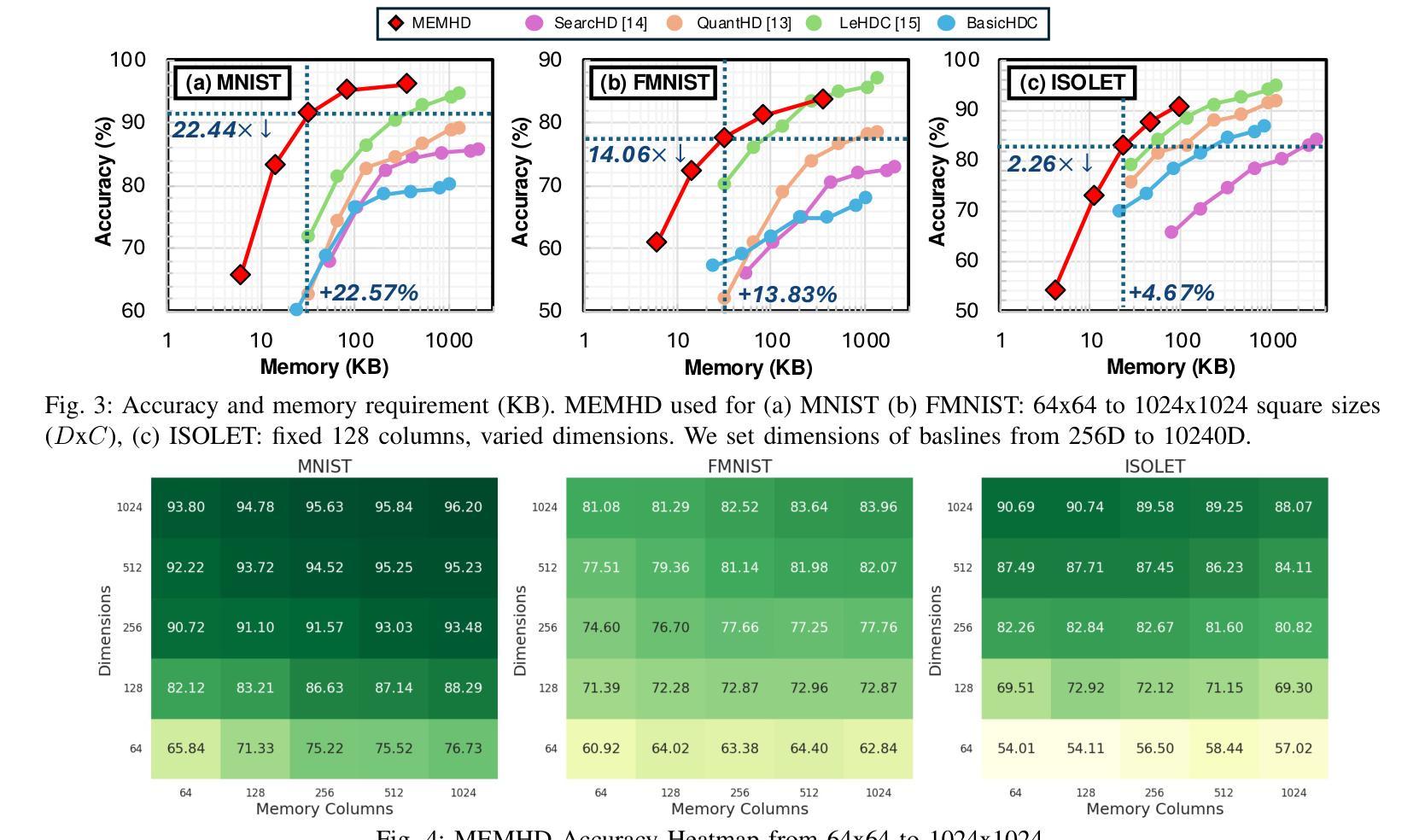
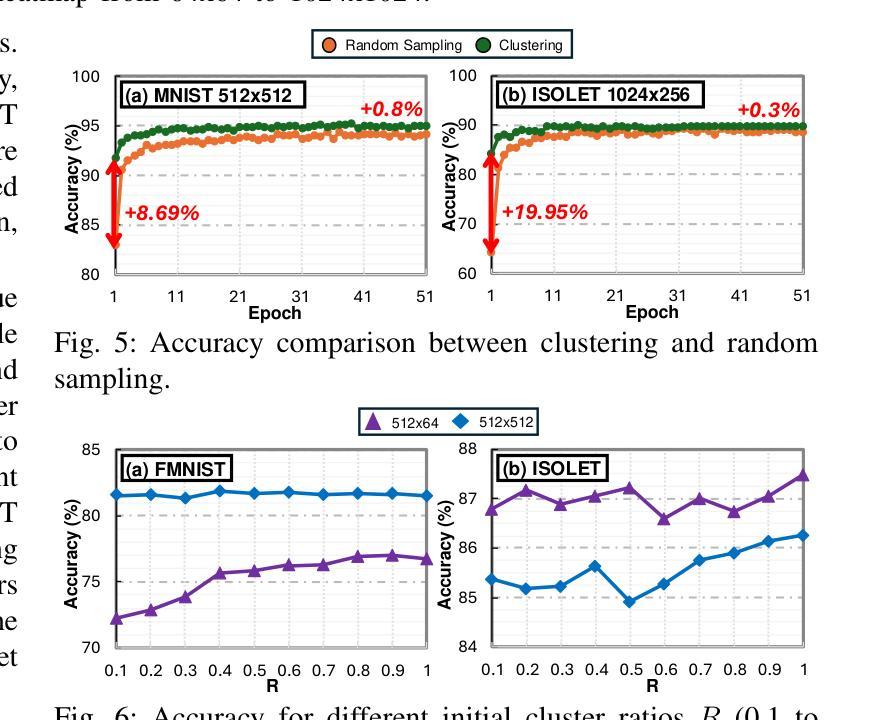
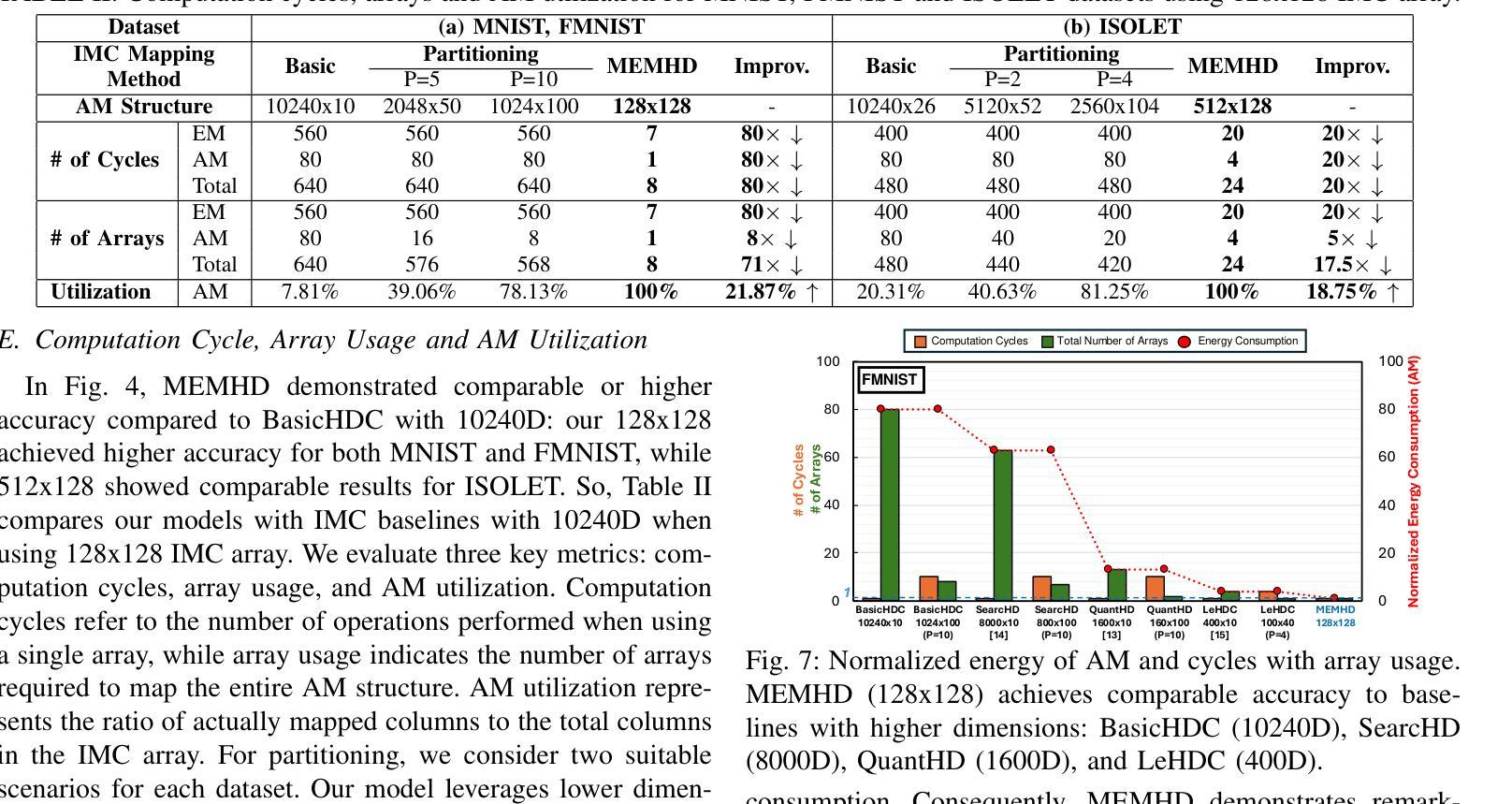
MEMHD: Memory-Efficient Multi-Centroid Hyperdimensional Computing for Fully-Utilized In-Memory Computing Architectures
Authors:Do Yeong Kang, Yeong Hwan Oh, Chanwook Hwang, Jinhee Kim, Kang Eun Jeon, Jong Hwan Ko
The implementation of Hyperdimensional Computing (HDC) on In-Memory Computing (IMC) architectures faces significant challenges due to the mismatch between highdimensional vectors and IMC array sizes, leading to inefficient memory utilization and increased computation cycles. This paper presents MEMHD, a Memory-Efficient Multi-centroid HDC framework designed to address these challenges. MEMHD introduces a clustering-based initialization method and quantization aware iterative learning for multi-centroid associative memory. Through these approaches and its overall architecture, MEMHD achieves a significant reduction in memory requirements while maintaining or improving classification accuracy. Our approach achieves full utilization of IMC arrays and enables one-shot (or few-shot) associative search. Experimental results demonstrate that MEMHD outperforms state-of-the-art binary HDC models, achieving up to 13.69% higher accuracy with the same memory usage, or 13.25x more memory efficiency at the same accuracy level. Moreover, MEMHD reduces computation cycles by up to 80x and array usage by up to 71x compared to baseline IMC mapping methods when mapped to 128x128 IMC arrays, while significantly improving energy and computation cycle efficiency.
将超维计算(HDC)在内存计算(IMC)架构上的实现面临着重大挑战,这是由于高维向量与IMC数组大小之间的不匹配导致的,从而导致了内存利用率低下和计算周期增加。本文针对这些挑战,提出了一种名为MEMHD的高效内存多中心HDC框架。MEMHD引入了一种基于聚类的初始化方法,以及面向多中心关联内存的量化感知迭代学习。通过这些方法及其整体架构,MEMHD在保持或提高分类准确性的同时,显著降低了内存要求。我们的方法实现了IMC阵列的完全利用,并实现了一次(或少数几次)关联搜索。实验结果表明,MEMHD优于最新的二进制HDC模型,在相同内存使用量的情况下,准确率提高了高达13.69%,或在相同准确率水平下,内存使用效率提高了13.25倍。此外,与基准IMC映射方法相比,MEMHD在映射到128x128 IMC阵列时,计算周期减少了高达80倍,阵列使用率减少了高达71倍,同时显著提高了能源和计算周期的效率。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to appear at DATE 2025
Summary
内存高效的多中心超维计算框架MEMHD解决了高维向量与内存计算阵列大小不匹配的问题,提高了内存利用率并减少了计算周期。通过聚类初始化方法和量化感知迭代学习等方法,MEMHD在维持或提高分类准确率的同时显著降低了内存要求。实验结果显示,MEMHD相较于最先进的全二进制超维计算模型表现出更高的性能,并且在相同的内存使用量下准确率提高了高达13.69%,或在相同准确率水平下内存效率提高了高达13.25倍。此外,相较于基线IMC映射方法,MEMHD在计算周期上减少了高达80倍,在阵列使用上减少了高达71倍。
Key Takeaways
- MEMHD是一个针对内存计算架构的超维计算框架,解决了高维向量与内存计算阵列大小不匹配的问题。
- MEMHD引入聚类初始化方法和量化感知迭代学习技术以提高效率和准确性。
- 通过这些技术和整体架构,MEMHD显著降低了内存要求,同时维持或提高了分类准确率。
- 实验结果显示,MEMHD相较于现有技术表现出更高的性能,包括更高的准确率和更高的内存效率。
- MEMHD能够实现一次性或少数几次的关联搜索。
- 与基线IMC映射方法相比,MEMHD在计算周期和阵列使用上实现了显著优化。
点此查看论文截图
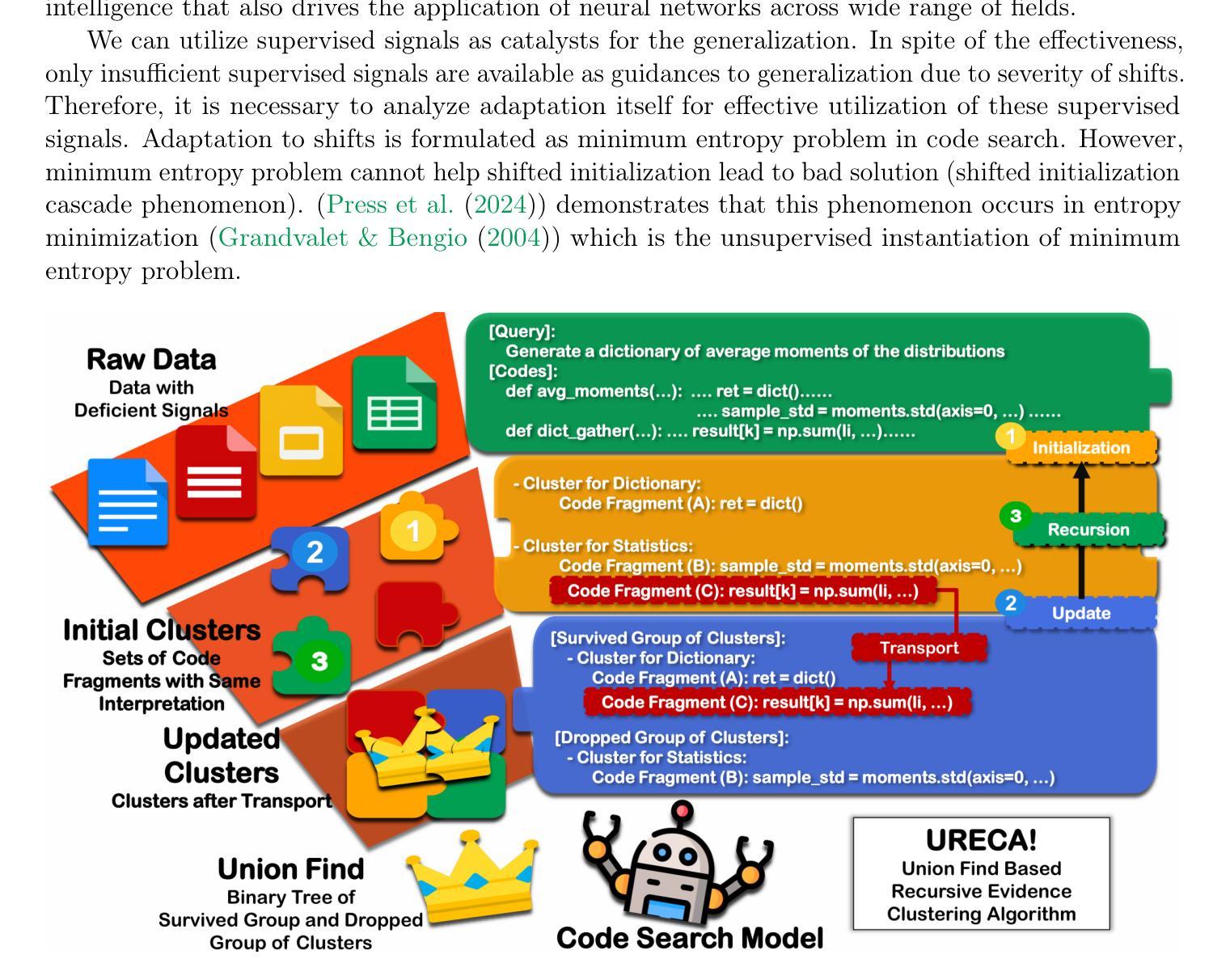
URECA: The Chain of Two Minimum Set Cover Problems exists behind Adaptation to Shifts in Semantic Code Search
Authors:Seok-Ung Choi, Joonghyuk Hahn, Yo-Sub Han
Adaptation is to make model learn the patterns shifted from the training distribution. In general, this adaptation is formulated as the minimum entropy problem. However, the minimum entropy problem has inherent limitation – shifted initialization cascade phenomenon. We extend the relationship between the minimum entropy problem and the minimum set cover problem via Lebesgue integral. This extension reveals that internal mechanism of the minimum entropy problem ignores the relationship between disentangled representations, which leads to shifted initialization cascade. From the analysis, we introduce a new clustering algorithm, Union-find based Recursive Clustering Algorithm~(URECA). URECA is an efficient clustering algorithm for the leverage of the relationships between disentangled representations. The update rule of URECA depends on Thresholdly-Updatable Stationary Assumption to dynamics as a released version of Stationary Assumption. This assumption helps URECA to transport disentangled representations with no errors based on the relationships between disentangled representations. URECA also utilize simulation trick to efficiently cluster disentangled representations. The wide range of evaluations show that URECA achieves consistent performance gains for the few-shot adaptation to diverse types of shifts along with advancement to State-of-The-Art performance in CoSQA in the scenario of query shift.
适应是指使模型学习从训练分布中转移的模式。通常,这种适应被制定为最小熵问题。然而,最小熵问题具有固有的局限性——转移初始化级联现象。我们通过勒贝格积分扩展最小熵问题和最小集覆盖问题之间的关系。这种扩展揭示了最小熵问题的内部机制忽略了解纠缠表示之间的关系,从而导致转移初始化级联。通过分析,我们引入了一种新的聚类算法——基于联合查找的递归聚类算法(URECA)。URECA是一种利用解纠缠表示之间关系的有效聚类算法。URECA的更新规则取决于阈值可更新稳态假设,作为稳态假设的发布版本。这一假设有助于URECA基于解纠缠表示之间的关系无误地传输。URECA还使用仿真技巧有效地聚类解纠缠表示。广泛的评估表明,URECA在少量适应各种类型的变化时实现了性能上的持续增益,并在查询变化的情况下提高了CoSQA的最新性能水平。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
模型适应训练分布变化的问题被一般性地表述为最小熵问题,但存在固有的限制——初始化级联现象。本文通过勒贝格积分扩展了最小熵问题和最小集覆盖问题之间的关系,揭示了最小熵问题内在机制忽视了解纠缠表示之间的关系,导致初始化级联。基于此分析,我们提出了一种新的聚类算法——基于并查集的递归聚类算法(URECA)。URECA是一种高效的聚类算法,能够利用解纠缠表示之间的关系。其更新规则依赖于阈值可更新平稳假设,有助于基于解纠缠表示的关系进行无误传输。URECA还采用模拟技巧以有效地对解纠缠表示进行聚类。广泛评估表明,URECA在多种类型的迁移适应中实现了性能提升,并在查询迁移的场景下达到了CoSQA领域的最新技术水平。
Key Takeaways
- 模型适应训练分布变化的问题可表述为最小熵问题,但存在初始化级联现象。
- 通过勒贝格积分扩展了最小熵问题和最小集覆盖问题之间的关系。
- 最小熵问题忽视了解纠缠表示之间的关系。
- 提出了基于并查集的递归聚类算法(URECA),有效利用解纠缠表示之间的关系。
- URECA的更新规则依赖于阈值可更新平稳假设,实现无误传输。
- URECA采用模拟技巧以有效聚类解纠缠表示。
点此查看论文截图

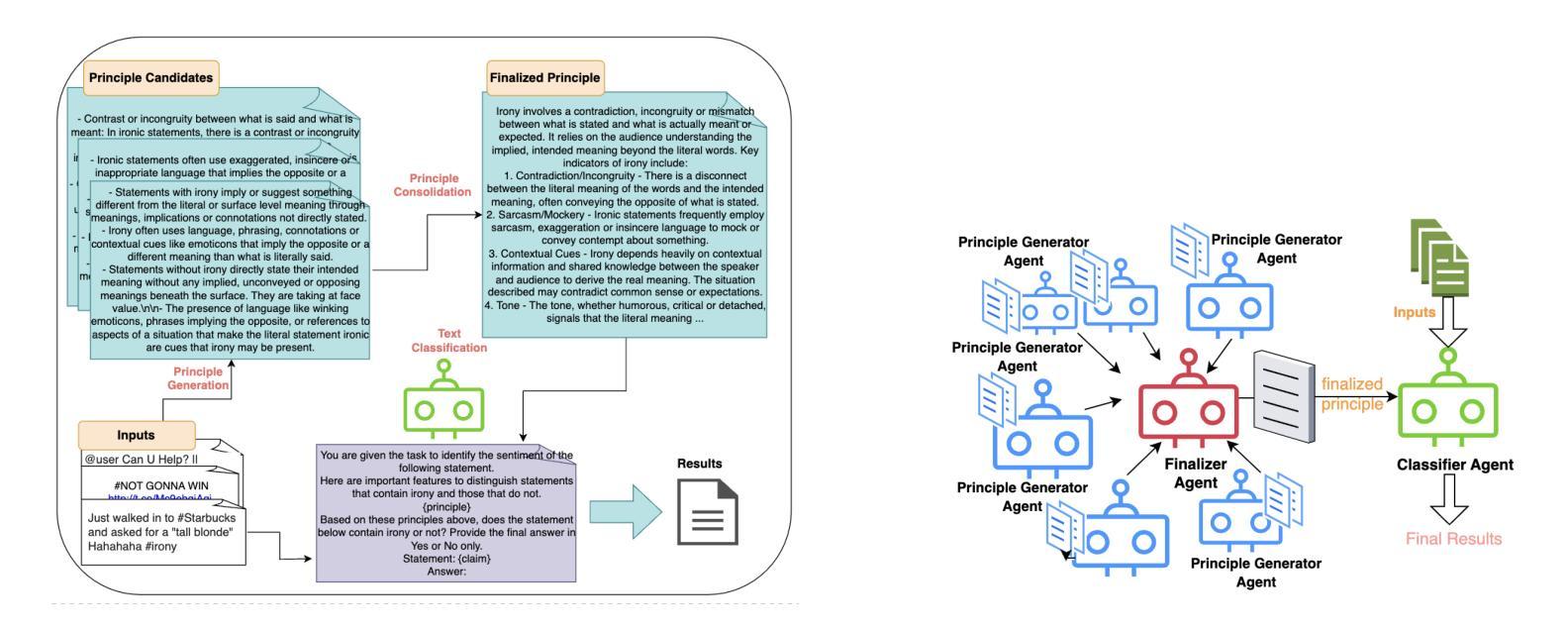
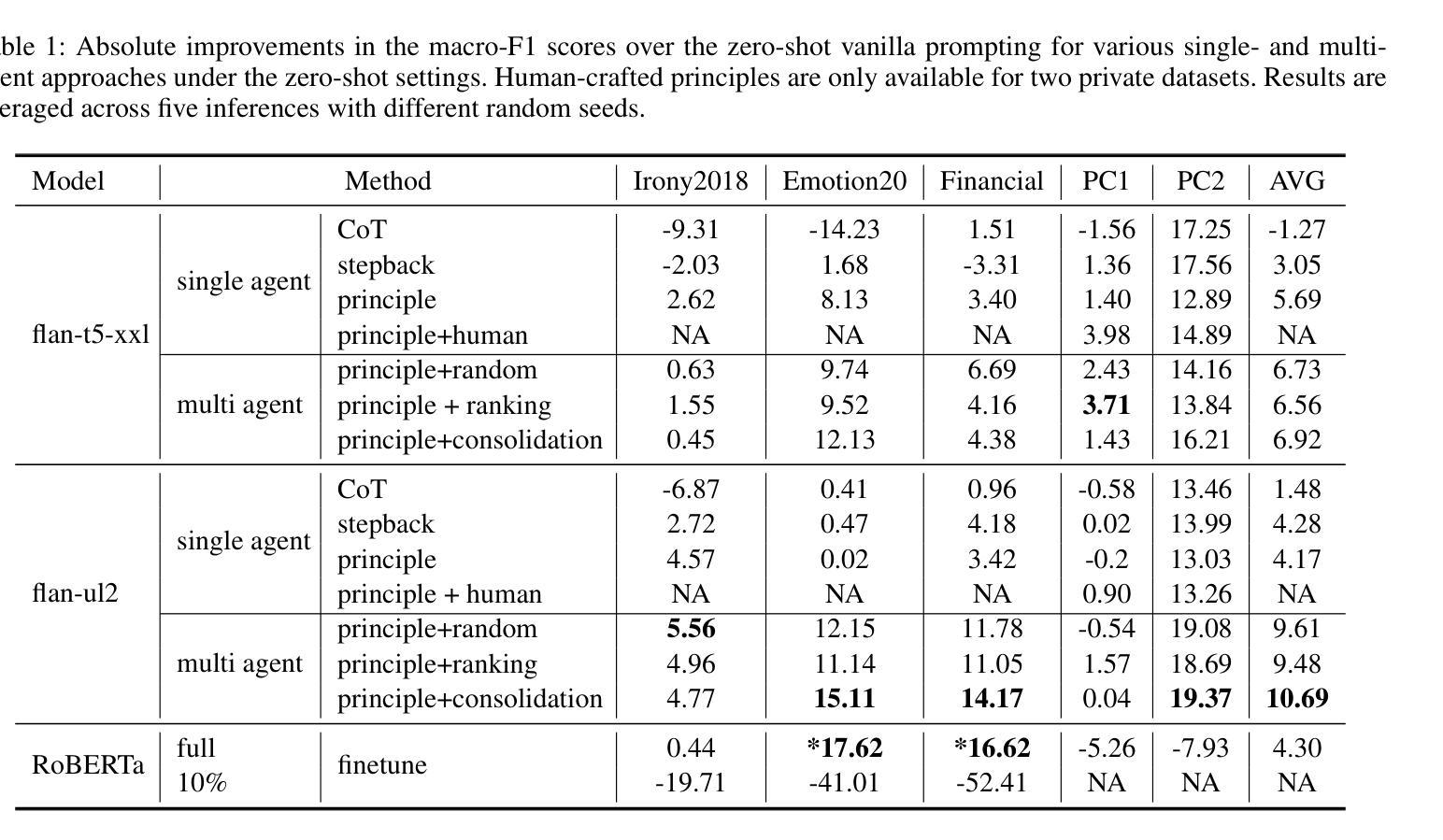
Don’t Just Demo, Teach Me the Principles: A Principle-Based Multi-Agent Prompting Strategy for Text Classification
Authors:Peipei Wei, Dimitris Dimitriadis, Yan Xu, Mingwei Shen
We present PRINCIPLE-BASED PROMPTING, a simple but effective multi-agent prompting strategy for text classification. It first asks multiple LLM agents to independently generate candidate principles based on analysis of demonstration samples with or without labels, consolidates them into final principles via a finalizer agent, and then sends them to a classifier agent to perform downstream classification tasks. Extensive experiments on binary and multi-class classification datasets with different sizes of LLMs show that our approach not only achieves substantial performance gains (1.55% - 19.37%) over zero-shot prompting on macro-F1 score but also outperforms other strong baselines (CoT and stepback prompting). Principles generated by our approach help LLMs perform better on classification tasks than human crafted principles on two private datasets. Our multi-agent PRINCIPLE-BASED PROMPTING approach also shows on-par or better performance compared to demonstration-based few-shot prompting approaches, yet with substantially lower inference costs. Ablation studies show that label information and the multi-agent cooperative LLM framework play an important role in generating high-quality principles to facilitate downstream classification tasks.
我们提出了基于原则的提示(PRINCIPLE-BASED PROMPTING),这是一种简单有效的多智能体提示策略,用于文本分类。它首先要求多个大型语言模型(LLM)智能体基于有或没有标签的演示样本进行独立分析,生成候选原则,并通过终结者智能体将它们整合为最终原则,然后将其发送到分类器智能体执行下游分类任务。在二元和多类分类数据集上的大量实验,以及不同规模的大型语言模型显示,我们的方法不仅在宏观F1分数上实现了显著的性能提升(1.55%-19.3.3%),而且还优于其他强大的基线(如连贯性提示和退步提示)。我们的方法生成的原则有助于大型语言模型在分类任务上比两个私有数据集上的人工原则表现得更好。我们的多智能体基于原则的提示方法还显示出与基于演示的少量提示方法相当或更好的性能,同时大大降低了推理成本。消融研究表明,标签信息和多智能体合作的大型语言模型框架在生成高质量原则以促进下游分类任务中起着重要作用。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF To be published in AAAI 2025 Workshop on Advancing LLM-Based Multi-Agent Collaboration
Summary
基于原则的多智能体提示策略为文本分类提供了一种简单有效的多智能体提示方法。该策略让多个大型语言模型(LLM)智能体独立生成基于样本分析的原则候选,通过整合器智能体合并成最终原则,并发送给分类器智能体执行下游分类任务。实验证明,该方法在二元及多类别分类数据集上表现优异,实现了可观的性能提升,超越了零射提示方法和其它强大的基线方法。该方法生成的原则有助于LLM在分类任务上超越人类制定的原则。此外,基于多智能体的原则提示方法展现出与基于演示的少量样本提示方法相当或更好的性能,同时大大降低了推理成本。消融研究表明,标签信息和多智能体合作框架在生成高质量原则以促进下游分类任务中起到了重要作用。
Key Takeaways
- PRINCIPLE-BASED PROMPTING是一种多智能体提示策略,用于文本分类。
- 该方法通过多个LLM智能体独立生成原则候选,经整合后用于下游分类任务。
- 实验证明,该方法在多种分类数据集上实现了显著性能提升。
- 与零射提示和其它基线方法相比,该方法表现更优。
- 该方法生成的原则有助于LLM在分类任务上超越人类制定的原则。
- 与基于演示的少量样本提示方法相比,该方法的性能相当或更好,同时降低了推理成本。
点此查看论文截图

Few-Shot Multi-Human Neural Rendering Using Geometry Constraints
Authors:Qian li, Victoria Fernàndez Abrevaya, Franck Multon, Adnane Boukhayma
We present a method for recovering the shape and radiance of a scene consisting of multiple people given solely a few images. Multi-human scenes are complex due to additional occlusion and clutter. For single-human settings, existing approaches using implicit neural representations have achieved impressive results that deliver accurate geometry and appearance. However, it remains challenging to extend these methods for estimating multiple humans from sparse views. We propose a neural implicit reconstruction method that addresses the inherent challenges of this task through the following contributions: First, we propose to use geometry constraints by exploiting pre-computed meshes using a human body model (SMPL). Specifically, we regularize the signed distances using the SMPL mesh and leverage bounding boxes for improved rendering. Second, we propose a ray regularization scheme to minimize rendering inconsistencies, and a saturation regularization for robust optimization in variable illumination. Extensive experiments on both real and synthetic datasets demonstrate the benefits of our approach and show state-of-the-art performance against existing neural reconstruction methods.
我们提出了一种仅通过少量图像恢复由多人组成的场景的形状和辐射亮度的方法。多人场景由于额外的遮挡和杂乱而更加复杂。对于单人设置,使用隐式神经表示方法的现有技术已经取得了令人印象深刻的结果,能够准确提供几何结构和外观。然而,从稀疏视角估计多个行人仍然是一个挑战。我们提出了一种隐式神经重建方法,通过以下贡献来解决此任务固有的挑战:首先,我们通过利用人体模型(SMPL)的预先计算网格提出使用几何约束。具体来说,我们用SMPL网格规则化符号距离并利用边界框进行改进渲染。其次,我们提出了一种光线规则化方案,以最小化渲染的不一致性,并提出了用于可变光照的稳健优化的饱和度规则化方法。在真实和合成数据集上的大量实验证明了我们的方法的好处,与现有的神经重建方法相比,表现出了卓越的性能。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种仅通过少量图像恢复多人场景的形状和辐射度的方法。针对多人物场景额外的遮挡和杂乱带来的复杂性,提出一种神经隐式重建方法,通过利用人体模型(SMPL)的预计算网格实现几何约束,通过正则化有符号距离和利用边界框改进渲染。同时,提出一种射线正则化方案来最小化渲染不一致性,以及一种饱和正则化以在可变照明中实现稳健优化。在真实和合成数据集上的广泛实验证明了该方法的好处并显示出与现有神经重建方法相比的卓越性能。
Key Takeaways
- 提出一种针对多人物场景的神经隐式重建方法,解决从稀疏视角估计多个人的挑战。
- 利用人体模型(SMPL)的预计算网格实现几何约束。
- 通过正则化有符号距离和边界框改进渲染。
- 提出射线正则化方案以最小化渲染不一致性。
- 饱和正则化用于在可变照明中实现稳健优化。
- 在真实和合成数据集上的实验证明了该方法的有效性。
点此查看论文截图

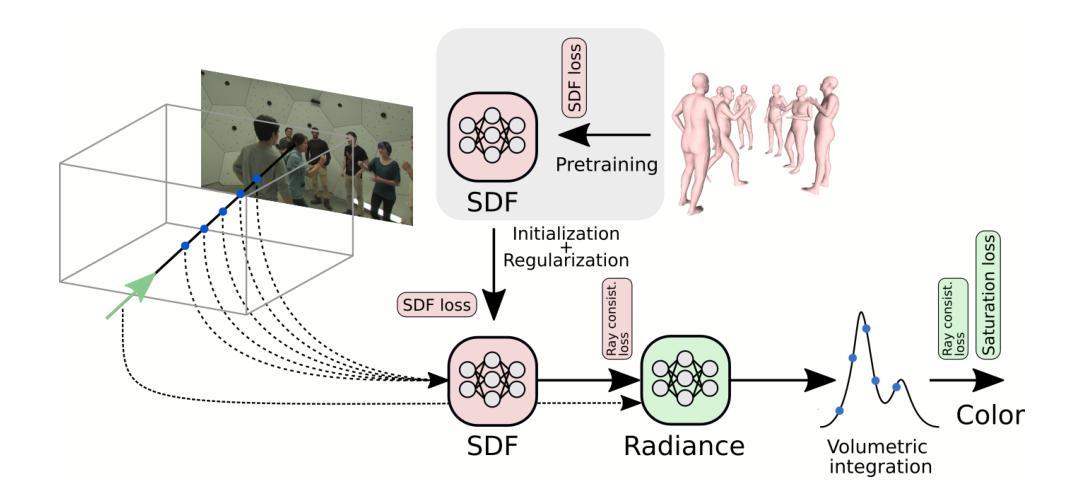

Model Diffusion for Certifiable Few-shot Transfer Learning
Authors:Fady Rezk, Royson Lee, Henry Gouk, Timothy Hospedales, Minyoung Kim
In modern large-scale deep learning, a prevalent and effective workflow for solving low-data problems is adapting powerful pre-trained foundation models (FMs) to new tasks via parameter-efficient fine-tuning (PEFT). However, while empirically effective, the resulting solutions lack generalisation guarantees to certify their accuracy - which may be required for ethical or legal reasons prior to deployment in high-importance applications. In this paper we develop a novel transfer learning approach that is designed to facilitate non-vacuous learning theoretic generalisation guarantees for downstream tasks, even in the low-shot regime. Specifically, we first use upstream tasks to train a distribution over PEFT parameters. We then learn the downstream task by a sample-and-evaluate procedure – sampling plausible PEFTs from the trained diffusion model and selecting the one with the highest likelihood on the downstream data. Crucially, this confines our model hypothesis to a finite set of PEFT samples. In contrast to learning in the typical continuous hypothesis spaces of neural network weights, this facilitates tighter risk certificates. We instantiate our bound and show non-trivial generalization guarantees compared to existing learning approaches which lead to vacuous bounds in the low-shot regime.
在现代大规模深度学习领域,针对低数据问题的一种流行且有效的工作流程是通过参数有效微调(PEFT)将强大的预训练基础模型(FMs)适应到新任务中。然而,尽管在经验上有效,但所得解决方案缺乏泛化保证来证明其准确性,这可能会在部署到高重要性应用之前出于道德或法律原因而要求证明。在本文中,我们开发了一种新型迁移学习方法,旨在促进下游任务的非空洞学习理论泛化保证,即使在低射击情况下也是如此。具体来说,我们首先使用上游任务来训练PEFT参数的分布。然后,我们通过采样和评估程序来学习下游任务——从训练的扩散模型中采样合理的PEFTs,并选择在下游数据上可能性最高的一个。关键的是,这将我们的模型假设限制在PEFT样本的有限集合中。与在神经网络权重的典型连续假设空间中学习不同,这有助于获得更严格的风险证书。我们实例化我们的界限,并显示出与非空洞泛化保证的现有学习方法相比,我们在低射击情况下具有非空洞的泛化保证。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
预训练模型通过参数高效微调(PEFT)适应新任务,是现代大规模深度学习解决低数据问题的有效方法。然而,尽管这种方法在实践中有效,但缺乏泛化保证来验证其在高优先级应用部署前的准确性。本文提出了一种新型迁移学习方法,旨在促进下游任务的非空洞学习理论泛化保证,即使在低资源情况下也是如此。通过上游任务训练一个PEFT参数的分布,然后通过采样和评估程序学习下游任务,从训练的扩散模型中采样可能的PEFTs,并选择在下游数据上可能性最高的一个。通过将模型假设限制在PEFT样本的有限集合中,与传统的神经网络权重连续假设空间学习相比,这有助于获得更严格的风险证书。我们实例化了我们的界限,与现有学习方法相比,在低资源情况下提供了非空洞的泛化保证。
Key Takeaways
- 现代深度学习中的低数据问题可以通过预训练模型的参数高效微调(PEFT)解决。
- 尽管PEFT方法在实践中有效,但在高优先级应用部署前需要泛化保证来验证其准确性。
- 本文提出了一种新型迁移学习方法,旨在促进下游任务的非空洞学习理论泛化保证。
- 方法通过上游任务训练一个关于PEFT参数的分布。
- 通过采样和评估程序学习下游任务,采样可能的PEFTs并从扩散模型中选出最佳的一个。
- 将模型假设限制在PEFT样本的有限集合中,有助于获得更严格的风险证书。
点此查看论文截图

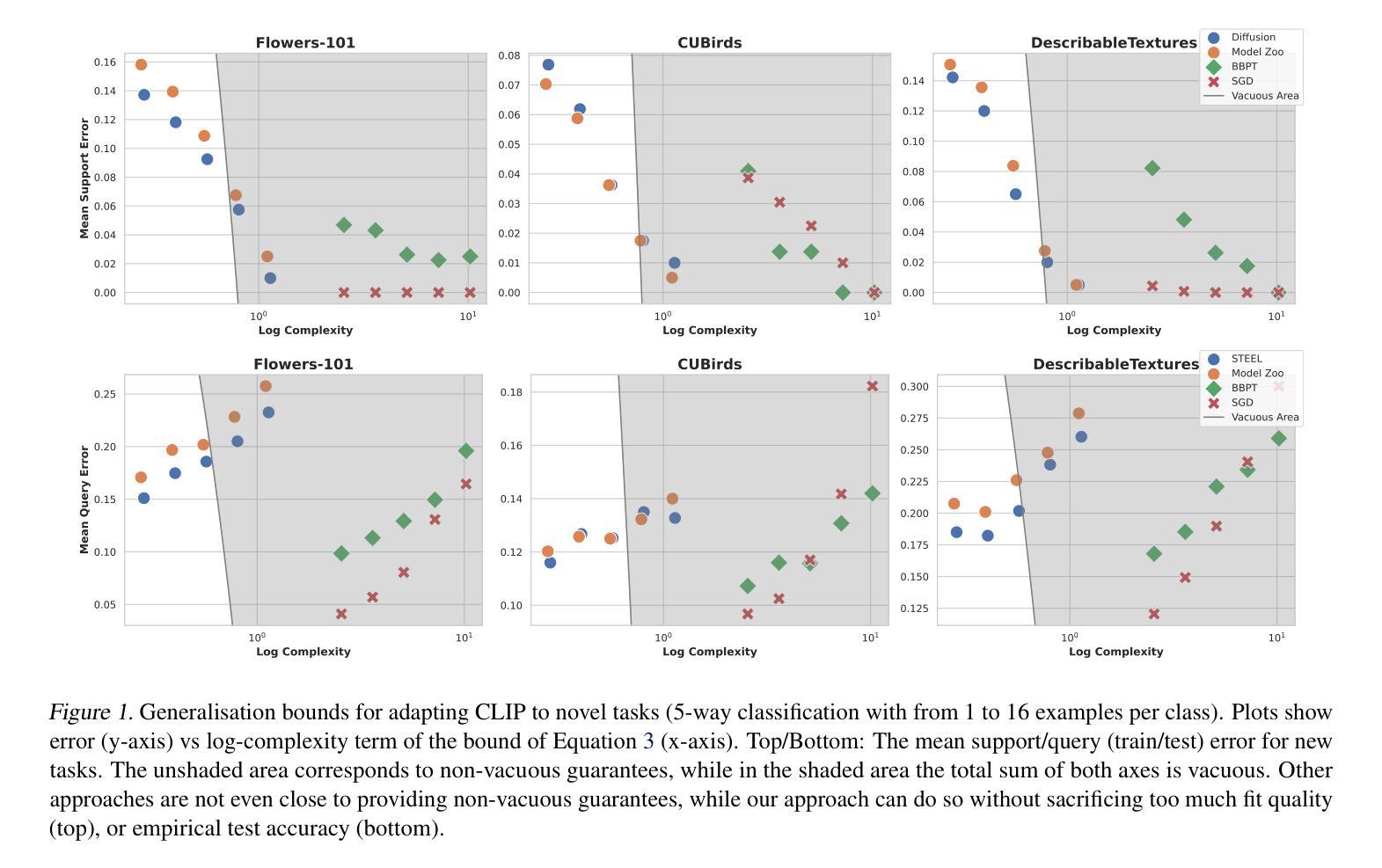
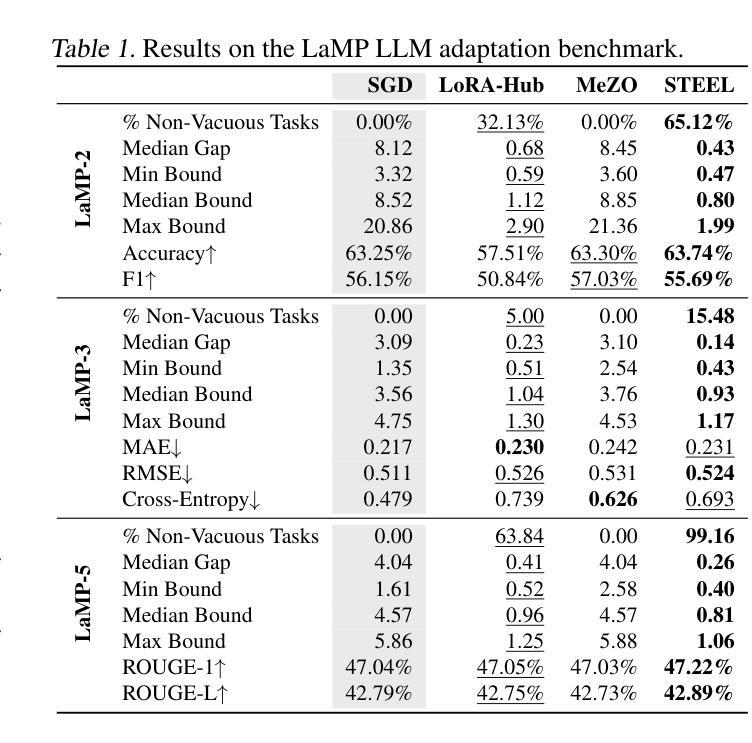
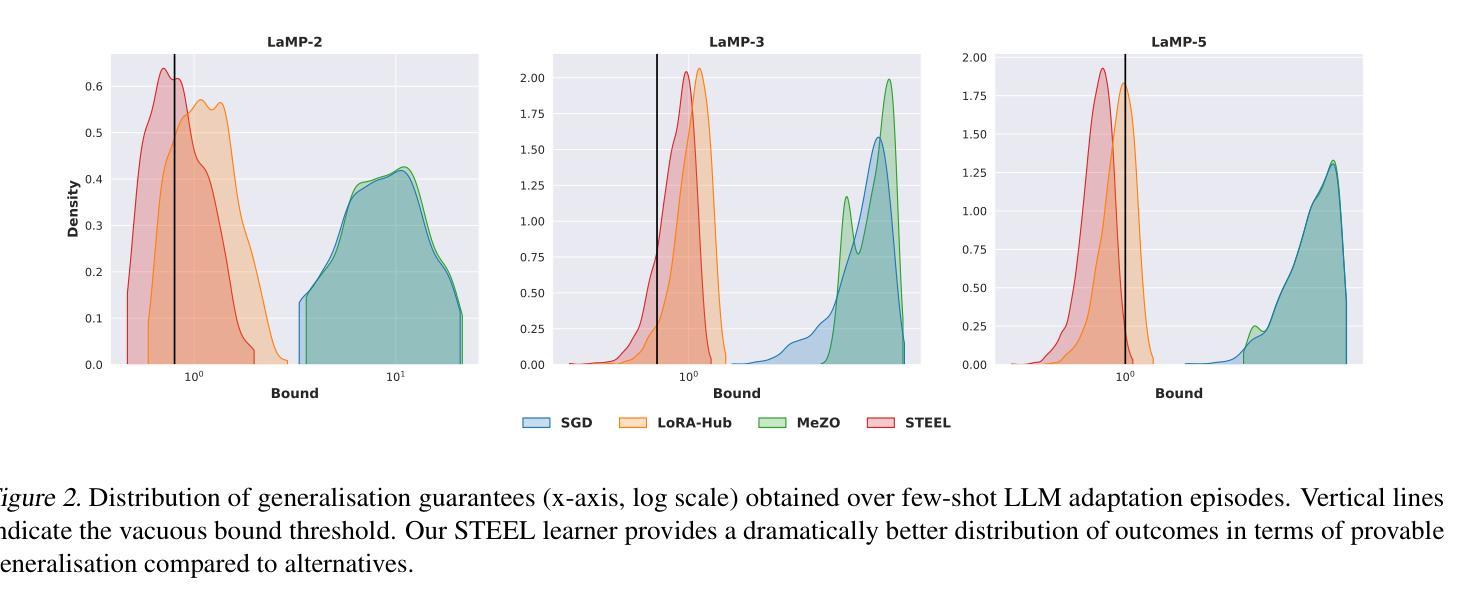
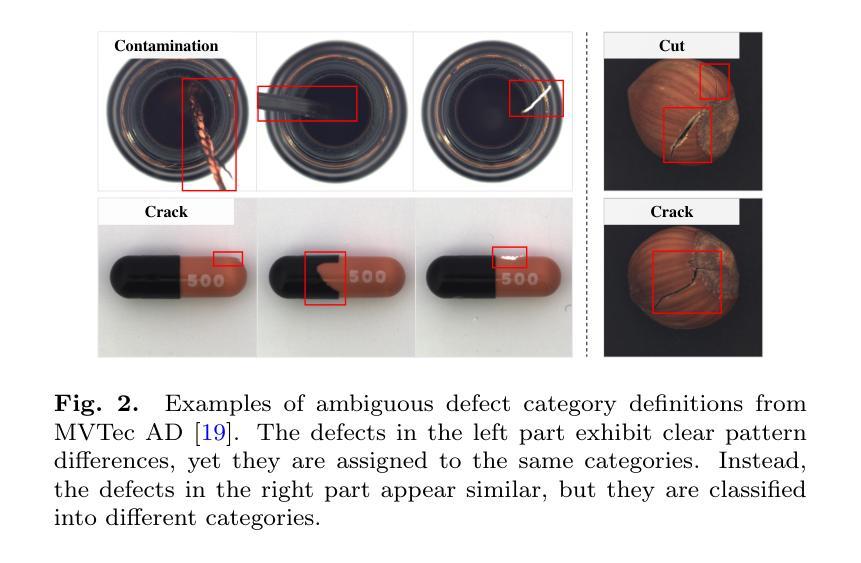
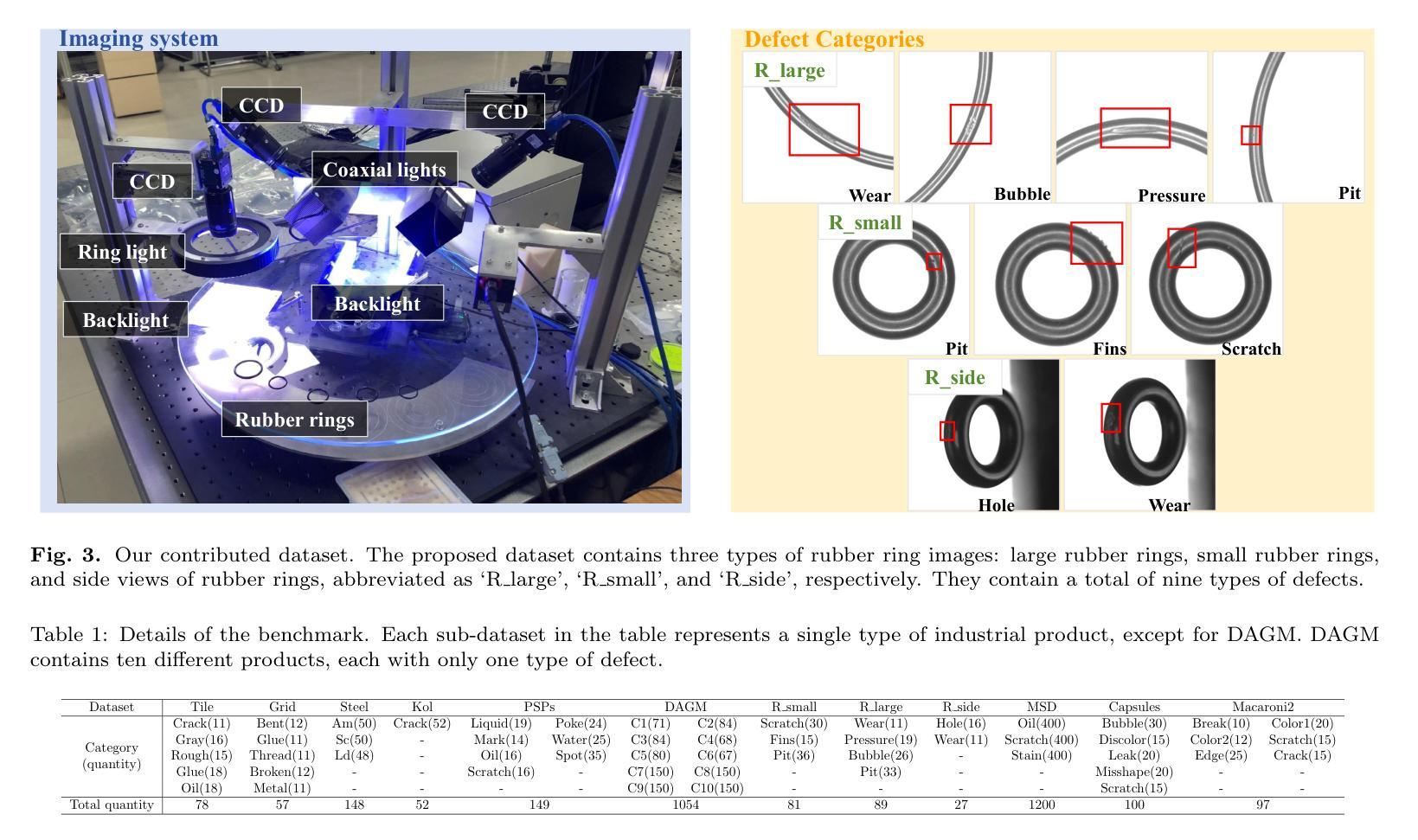
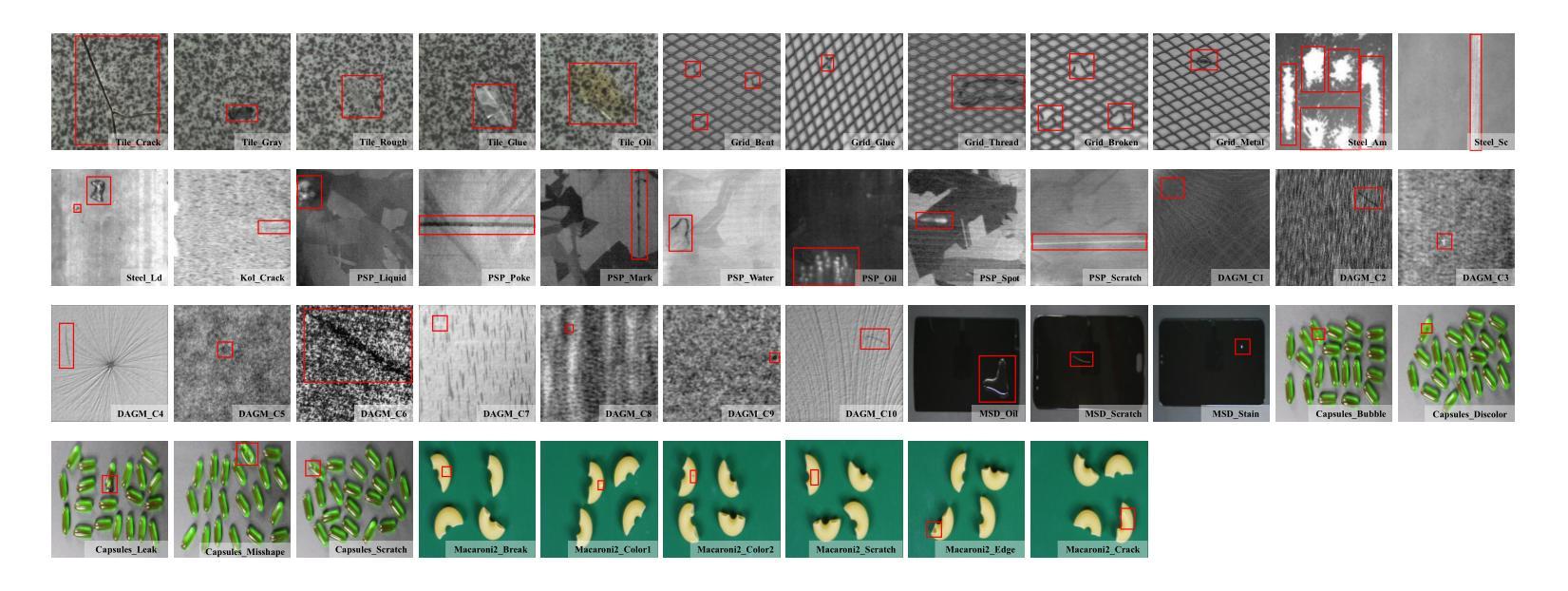
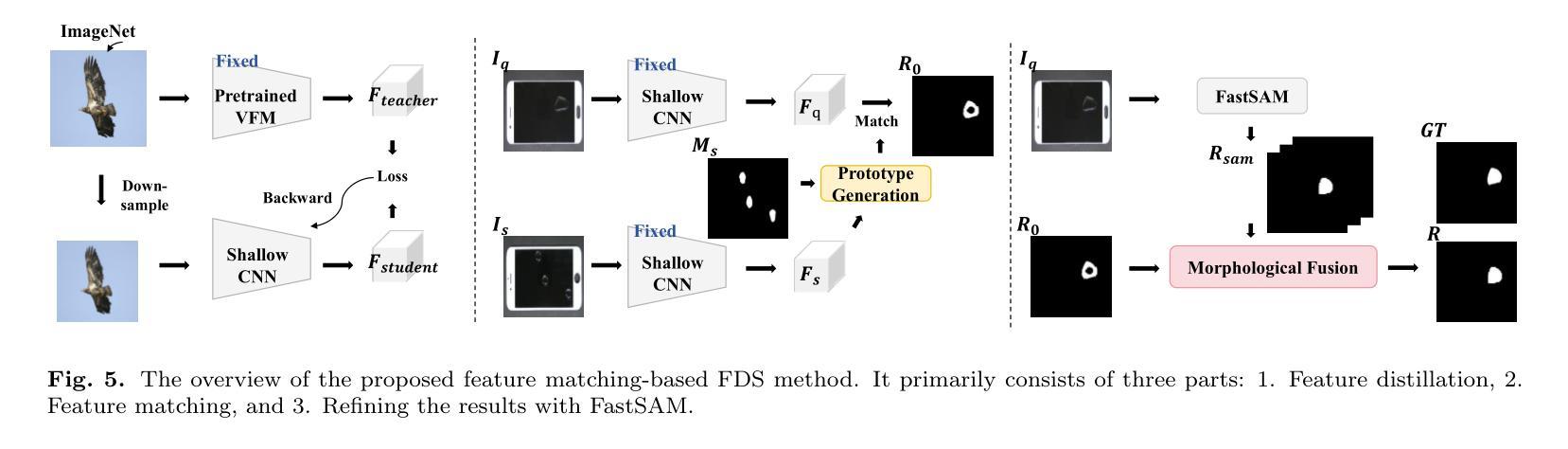
Exploring Few-Shot Defect Segmentation in General Industrial Scenarios with Metric Learning and Vision Foundation Models
Authors:Tongkun Liu, Bing Li, Xiao Jin, Yupeng Shi, Qiuying Li, Xiang Wei
Industrial defect segmentation is critical for manufacturing quality control. Due to the scarcity of training defect samples, few-shot semantic segmentation (FSS) holds significant value in this field. However, existing studies mostly apply FSS to tackle defects on simple textures, without considering more diverse scenarios. This paper aims to address this gap by exploring FSS in broader industrial products with various defect types. To this end, we contribute a new real-world dataset and reorganize some existing datasets to build a more comprehensive few-shot defect segmentation (FDS) benchmark. On this benchmark, we thoroughly investigate metric learning-based FSS methods, including those based on meta-learning and those based on Vision Foundation Models (VFMs). We observe that existing meta-learning-based methods are generally not well-suited for this task, while VFMs hold great potential. We further systematically study the applicability of various VFMs in this task, involving two paradigms: feature matching and the use of Segment Anything (SAM) models. We propose a novel efficient FDS method based on feature matching. Meanwhile, we find that SAM2 is particularly effective for addressing FDS through its video track mode. The contributed dataset and code will be available at: https://github.com/liutongkun/GFDS.
工业缺陷分割对于制造质量控制至关重要。由于训练缺陷样本的稀缺性,小样本语义分割(FSS)在该领域具有重大意义。然而,现有的研究大多将FSS应用于简单纹理上的缺陷检测,并未考虑更多样化的场景。本文旨在通过探索FSS在更广泛的工业产品中的多种缺陷类型来解决这一差距。为此,我们贡献了一个新的真实世界数据集,并重组了一些现有数据集以建立更全面的少数缺陷分割(FDS)基准测试。在这个基准测试上,我们深入研究了基于度量学习的FSS方法,包括基于元学习和基于视觉基础模型(VFMs)的方法。我们发现现有的基于元学习的方法通常不适合这项任务,而VFMs具有巨大潜力。我们进一步系统地研究了各种VFMs在此任务中的应用,涉及特征匹配和使用Segment Anything(SAM)模型的两种范式。我们提出了一种基于特征匹配的高效FDS方法。同时,我们发现SAM2通过其视频跟踪模式在解决FDS问题时特别有效。相关数据集和代码将在https://github.com/liutongkun/GFDS上提供。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文关注工业缺陷分割领域中的小样本语义分割(FSS)问题。针对现有研究主要集中在简单纹理缺陷上,本文旨在探索FSS在更广泛的工业产品中的多样场景应用,并为此贡献新的真实世界数据集和构建全面的少样本缺陷分割(FDS)基准测试集。通过对基于度量学习的FSS方法进行深入研究,发现基于元学习的方法不适用于此任务,而基于视觉基础模型(VFMs)的方法具有潜力。同时系统地研究了各种VFMs在此任务中的应用,并基于特征匹配提出了一种高效的FDS方法。此外,发现SAM模型中的视频跟踪模式对于解决FDS特别有效。
Key Takeaways
- 工业缺陷分割中,小样本语义分割(FSS)具有重要价值,现有研究主要集中在简单纹理缺陷上,本文旨在拓宽其应用范围。
- 贡献了新的真实世界数据集和构建了全面的少样本缺陷分割(FDS)基准测试集。
- 基于度量学习的FSS方法被深入研究,发现基于元学习的方法不适用于此任务。
- 视觉基础模型(VFMs)在此任务中展现出潜力。
- 针对不同VFMs的应用进行了系统研究,包括特征匹配和Segment Anything(SAM)模型。
- 提出了一种基于特征匹配的高效的FDS方法。
点此查看论文截图

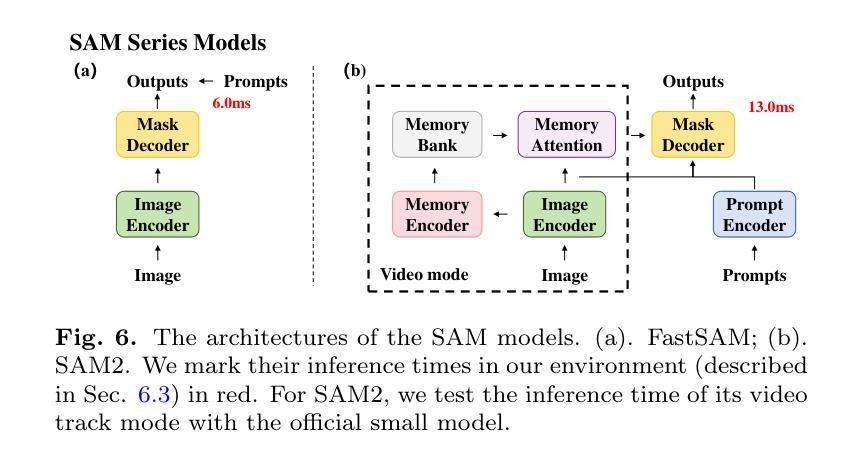
Holistic Semantic Representation for Navigational Trajectory Generation
Authors:Ji Cao, Tongya Zheng, Qinghong Guo, Yu Wang, Junshu Dai, Shunyu Liu, Jie Yang, Jie Song, Mingli Song
Trajectory generation has garnered significant attention from researchers in the field of spatio-temporal analysis, as it can generate substantial synthesized human mobility trajectories that enhance user privacy and alleviate data scarcity. However, existing trajectory generation methods often focus on improving trajectory generation quality from a singular perspective, lacking a comprehensive semantic understanding across various scales. Consequently, we are inspired to develop a HOlistic SEmantic Representation (HOSER) framework for navigational trajectory generation. Given an origin-and-destination (OD) pair and the starting time point of a latent trajectory, we first propose a Road Network Encoder to expand the receptive field of road- and zone-level semantics. Second, we design a Multi-Granularity Trajectory Encoder to integrate the spatio-temporal semantics of the generated trajectory at both the point and trajectory levels. Finally, we employ a Destination-Oriented Navigator to seamlessly integrate destination-oriented guidance. Extensive experiments on three real-world datasets demonstrate that HOSER outperforms state-of-the-art baselines by a significant margin. Moreover, the model’s performance in few-shot learning and zero-shot learning scenarios further verifies the effectiveness of our holistic semantic representation.
轨迹生成已引起时空分析领域研究人员的广泛关注,因为它可以生成大量合成的人类移动轨迹,增强用户隐私并缓解数据稀缺问题。然而,现有的轨迹生成方法往往从单一角度着眼于提高轨迹生成质量,缺乏跨不同尺度的全面语义理解。因此,我们受到启发,开发了一个用于导航轨迹生成的HOlistic SEmantic Representation(HOSER)框架。给定起点和终点(OD)对以及潜在轨迹的起始时间点,我们首先提出一个道路网络编码器,以扩大道路和区域级别的语义感受野。其次,我们设计了一个多粒度轨迹编码器,以整合生成轨迹在点和轨迹两个级别的时空语义。最后,我们采用目的导向的导航器,无缝集成以目的地为中心的导航。在三个真实世界数据集上的大量实验表明,HOSER显著优于最新基线。此外,该模型在少样本学习和零样本学习场景中的表现进一步验证了我们的整体语义表示的有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by AAAI 2025
Summary
本文提出了一种全新的导航轨迹生成框架HOSER(HOlistic SEmantic Representation),该框架结合了道路网络编码器和多粒度轨迹编码器,旨在全面理解不同尺度的语义信息。通过引入目的地导向导航器,生成更符合人类实际驾驶行为的轨迹。在三个真实世界数据集上的实验证明,HOSER相较于其他最先进的方法有着显著优势,并在少样本学习和零样本学习场景中证明了其效能。
Key Takeaways
- HOSER框架结合了道路网络编码器和多粒度轨迹编码器,旨在全面理解不同尺度的语义信息。
- 通过引入道路网络编码器,扩大对道路和区域级别语义的感受野。
- 多粒度轨迹编码器能够整合生成的轨迹在点和轨迹两个层次上的时空语义。
- 目的地导向导航器的引入使得生成的轨迹更符合人类实际驾驶行为。
- 在三个真实世界数据集上的实验证明HOSER相较于其他方法具有显著优势。
- HOSER在少样本学习场景中表现出良好的性能。
点此查看论文截图

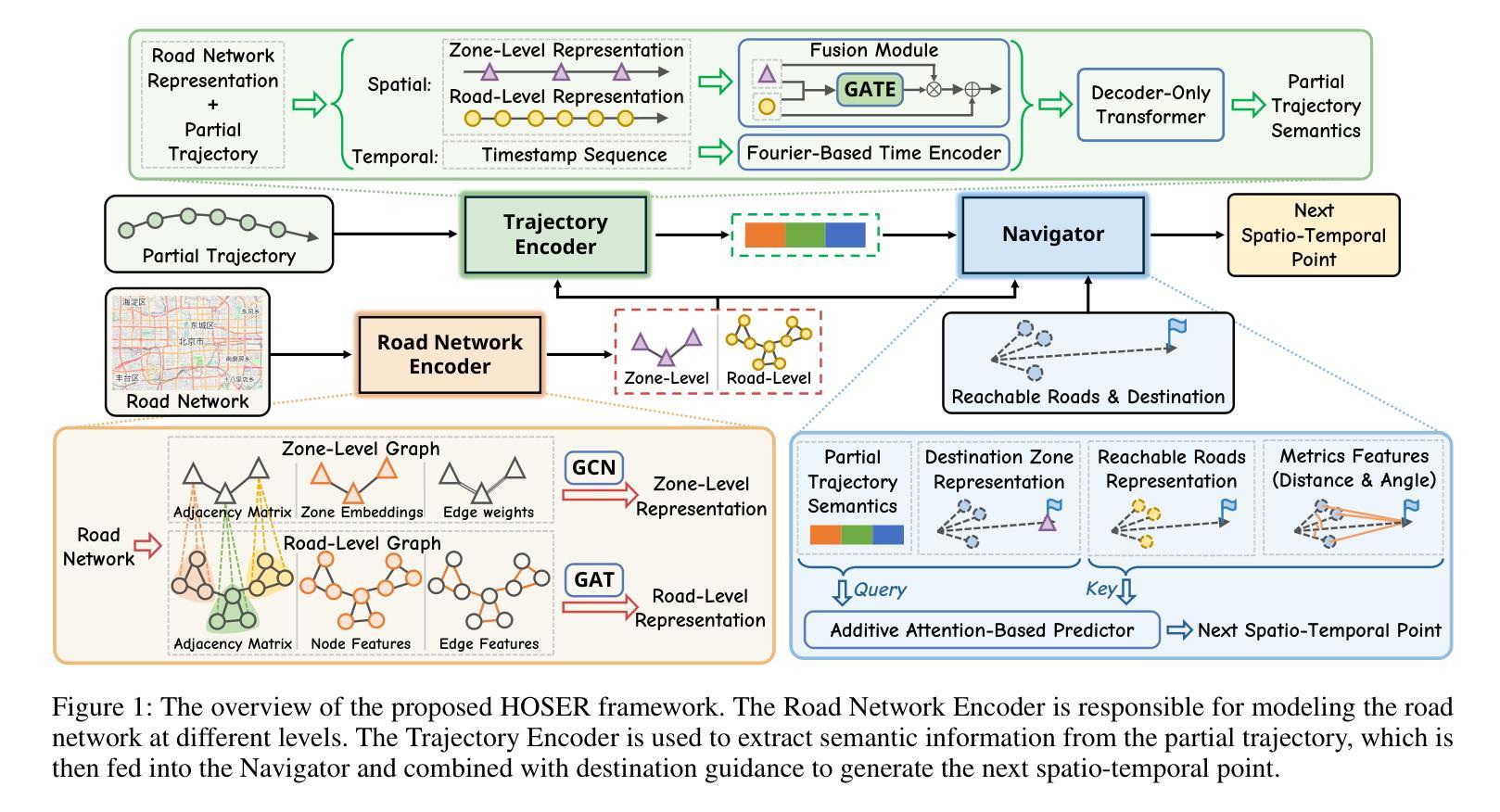
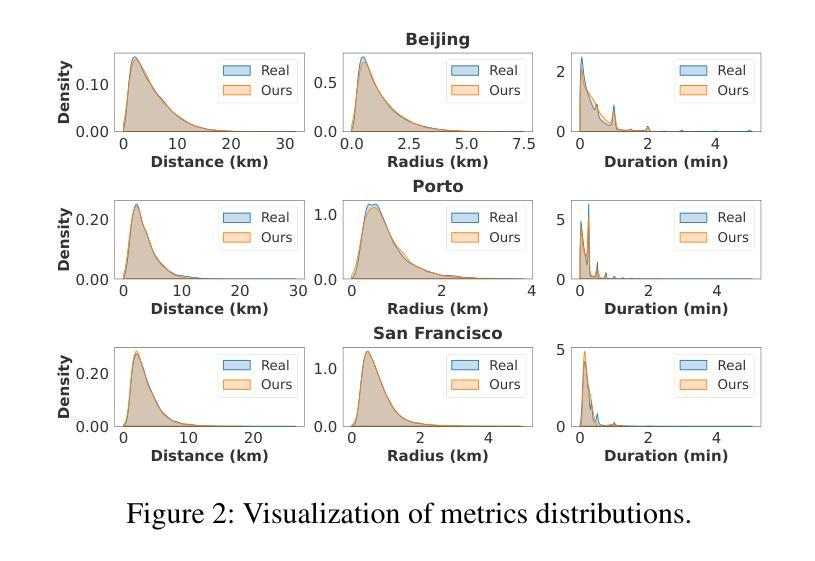
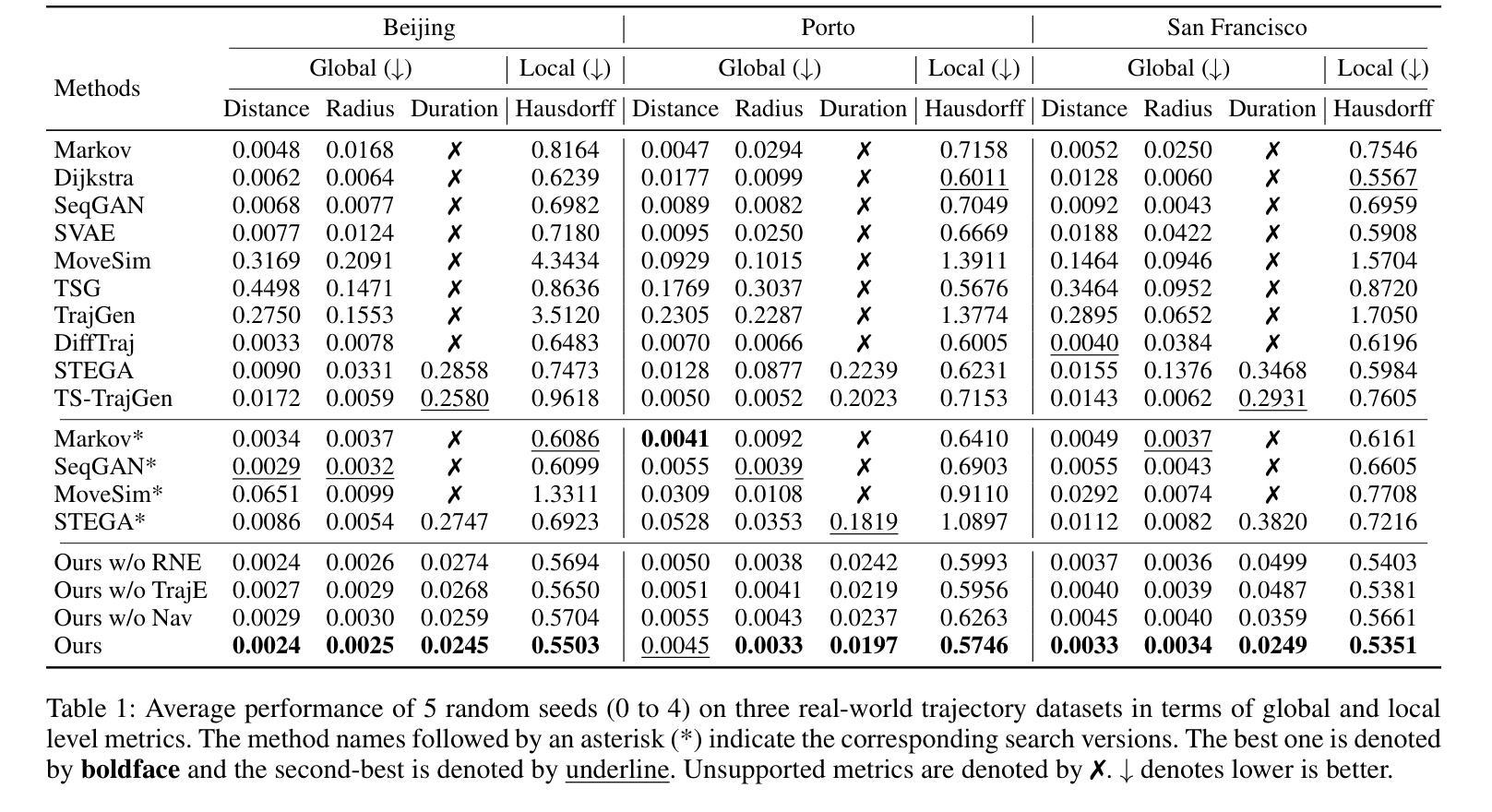
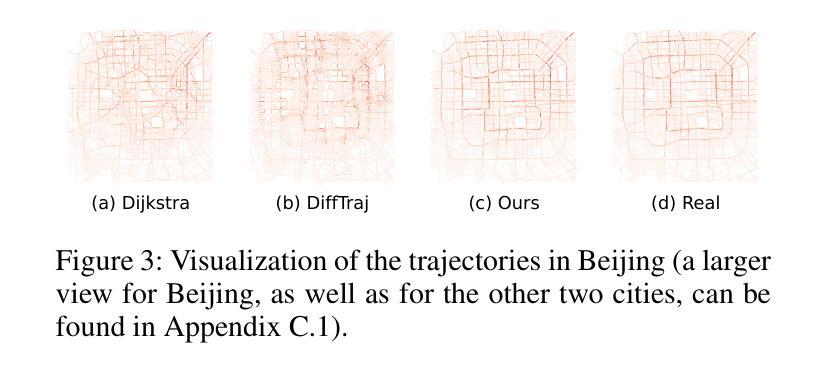
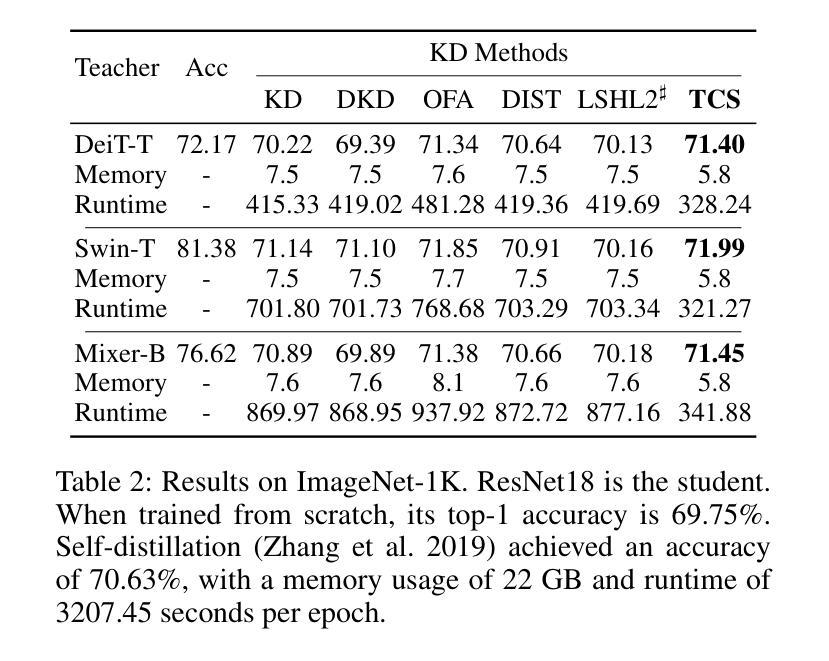
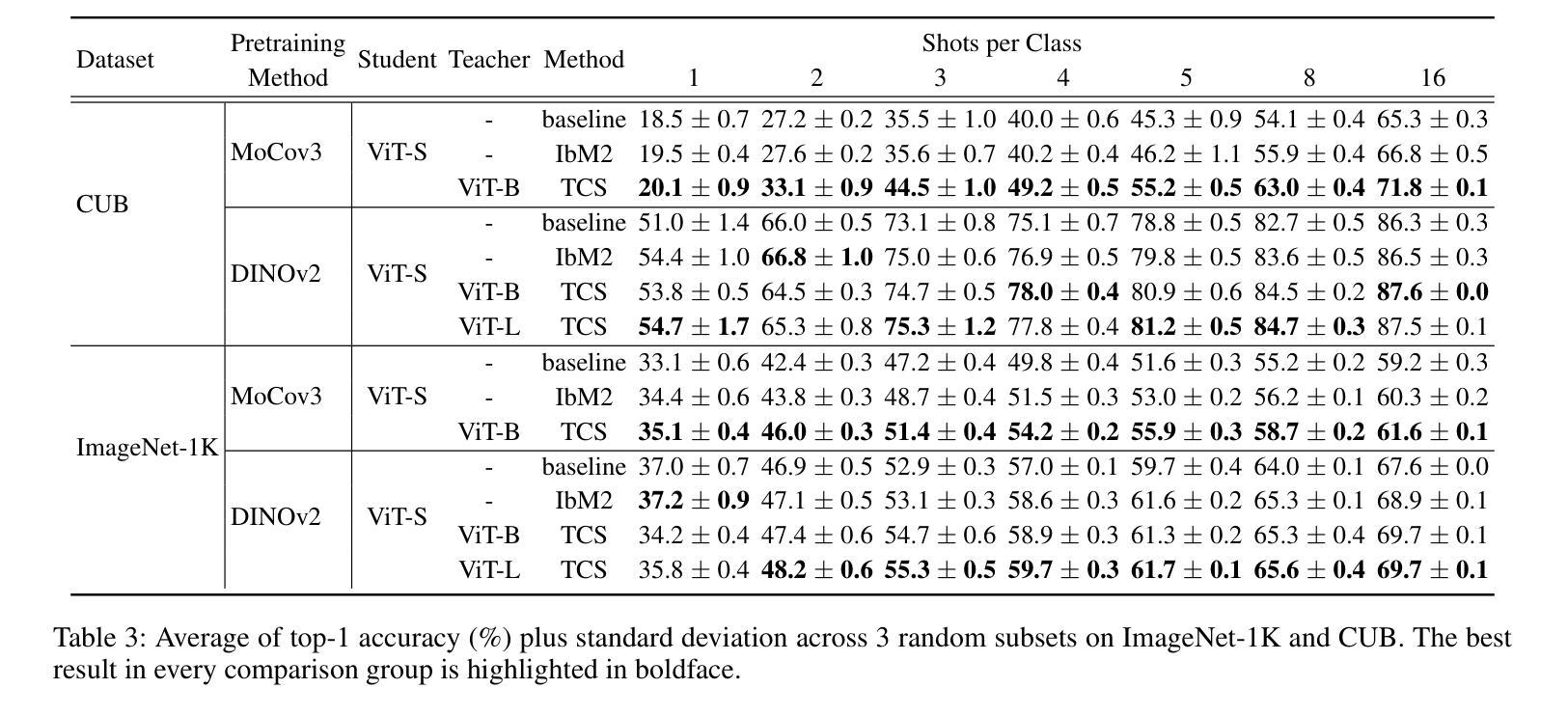
All You Need in Knowledge Distillation Is a Tailored Coordinate System
Authors:Junjie Zhou, Ke Zhu, Jianxin Wu
Knowledge Distillation (KD) is essential in transferring dark knowledge from a large teacher to a small student network, such that the student can be much more efficient than the teacher but with comparable accuracy. Existing KD methods, however, rely on a large teacher trained specifically for the target task, which is both very inflexible and inefficient. In this paper, we argue that a SSL-pretrained model can effectively act as the teacher and its dark knowledge can be captured by the coordinate system or linear subspace where the features lie in. We then need only one forward pass of the teacher, and then tailor the coordinate system (TCS) for the student network. Our TCS method is teacher-free and applies to diverse architectures, works well for KD and practical few-shot learning, and allows cross-architecture distillation with large capacity gap. Experiments show that TCS achieves significantly higher accuracy than state-of-the-art KD methods, while only requiring roughly half of their training time and GPU memory costs.
知识蒸馏(KD)对于将从大型教师网络转移到小型学生网络中的暗知识至关重要,这样学生可以比教师更有效率,但具有相当的准确性。然而,现有的KD方法依赖于专门为目标任务训练的大型教师,这既非常不灵活又效率低下。在本文中,我们认为SSL预训练模型可以有效地作为教师,其暗知识可以通过特征所在的坐标系或线性子空间来捕获。然后我们只需要教师的一次前向传递,然后为学生网络定制坐标系(TCS)。我们的TCS方法无需教师,适用于各种架构,对于KD和实用的少样本学习效果很好,并允许具有大容量差距的跨架构蒸馏。实验表明,TCS方法在准确率上明显优于最新KD方法,同时只需大致减半的训练时间和GPU内存成本。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by AAAI 2025
摘要
本文介绍了知识蒸馏(KD)在将大型教师网络的暗知识转移到小型学生网络中的重要性,使得学生网络可以在效率上比教师网络更高,同时保持相当的准确性。然而,现有的KD方法依赖于针对目标任务专门训练的大型教师网络,这既非常不灵活又效率低下。本文主张使用SSL预训练模型作为教师网络,通过特征所在的坐标系或线性子空间捕获其暗知识。只需教师网络的一次前向传递,然后为学生网络定制坐标系(TCS)。我们的TCS方法无需教师网络,适用于各种架构,对于KD和实际少样本学习效果很好,并允许跨架构蒸馏,具有较大的容量差距。实验表明,TCS实现了比现有KD方法更高的准确性,同时仅需它们大约一半的训练时间和GPU内存成本。
关键见解
- 知识蒸馏(KD)能有效将大型教师网络的暗知识转移至小型学生网络。
- 现有KD方法依赖专门训练的教师网络,缺乏灵活性和效率。
- SSL预训练模型可有效地作为教师网络。
- 通过特征所在的坐标系或线性子空间捕获教师网络的暗知识。
- 只需教师网络一次前向传递,定制坐标系(TCS)为学生网络。
- TCS方法无需教师网络,适用于多种架构。
点此查看论文截图

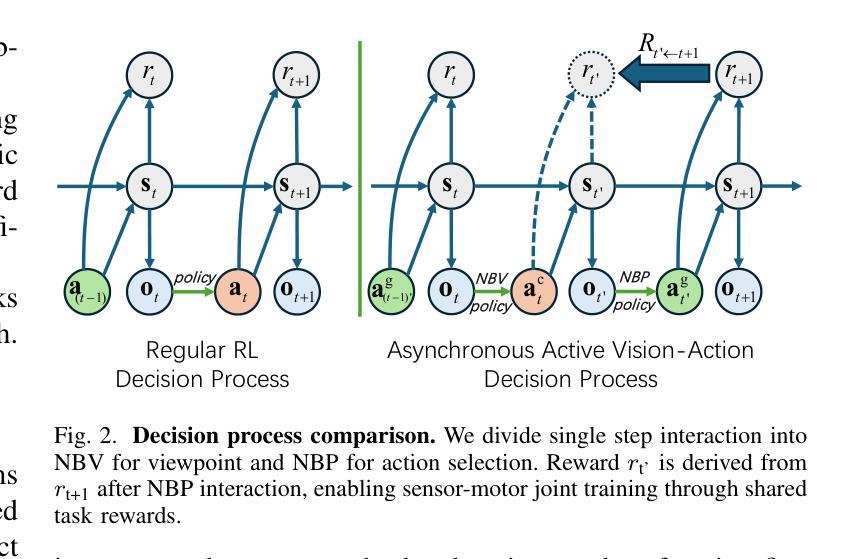
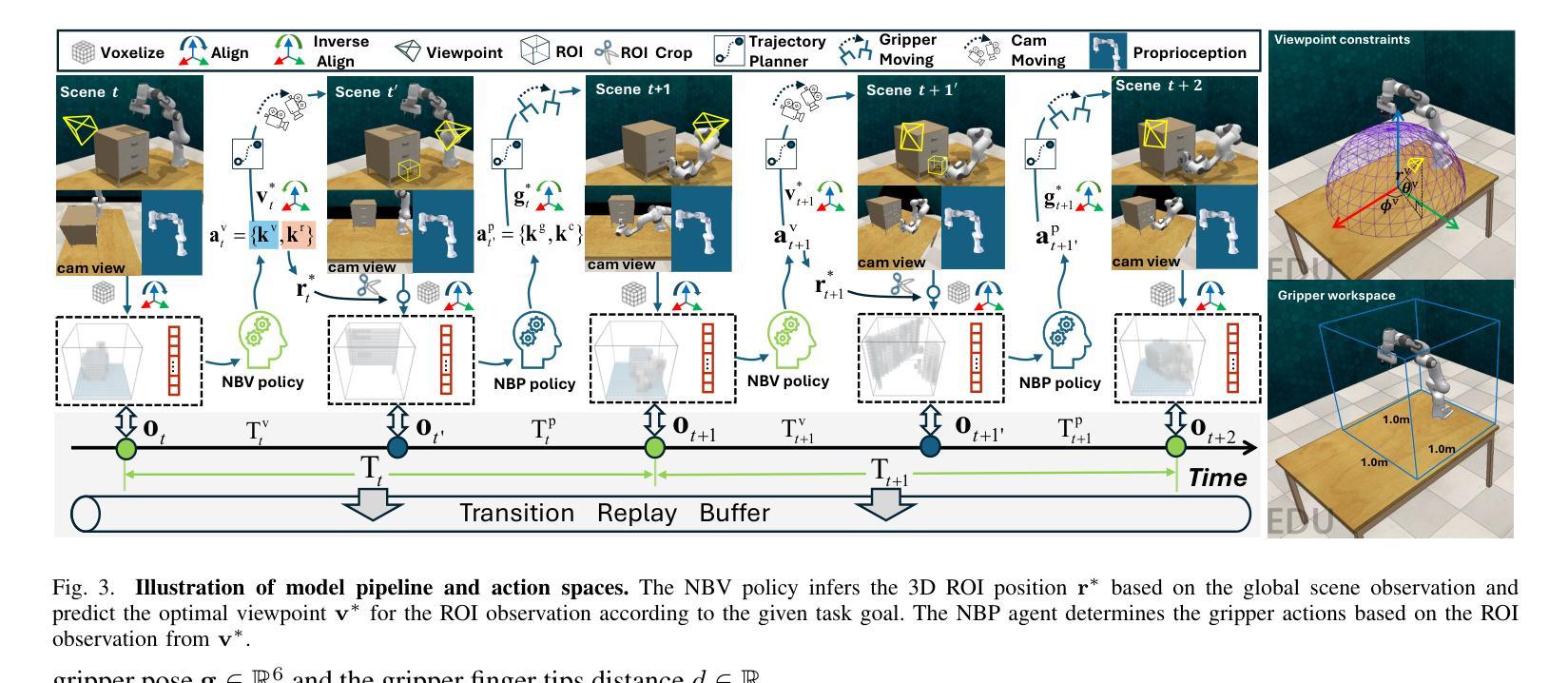
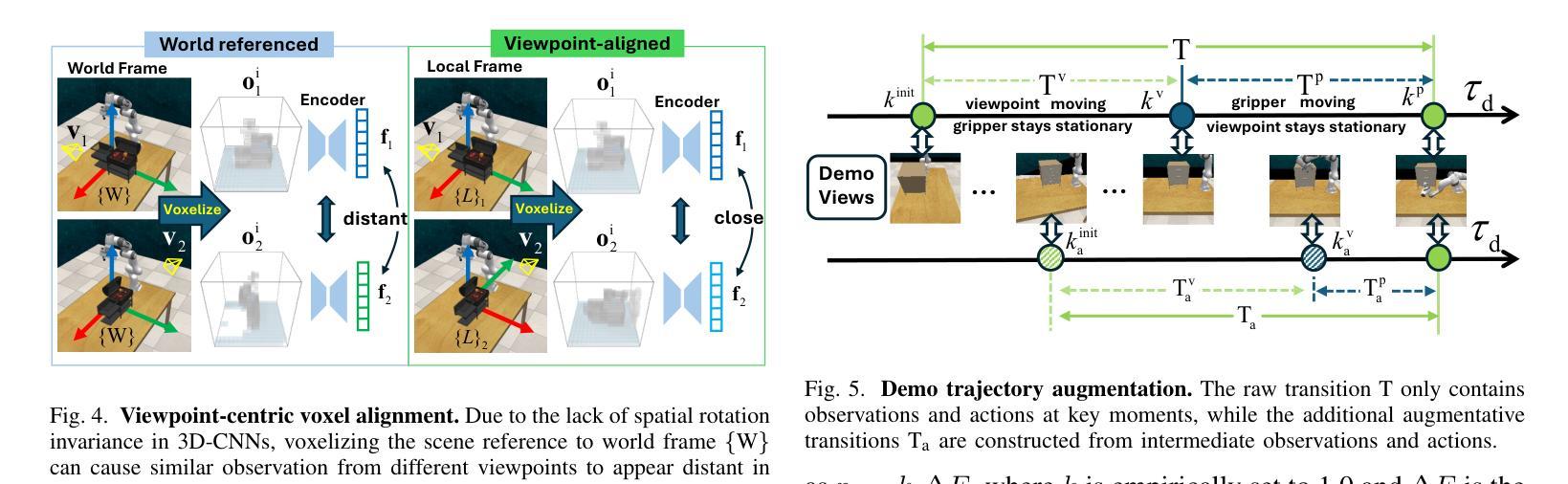
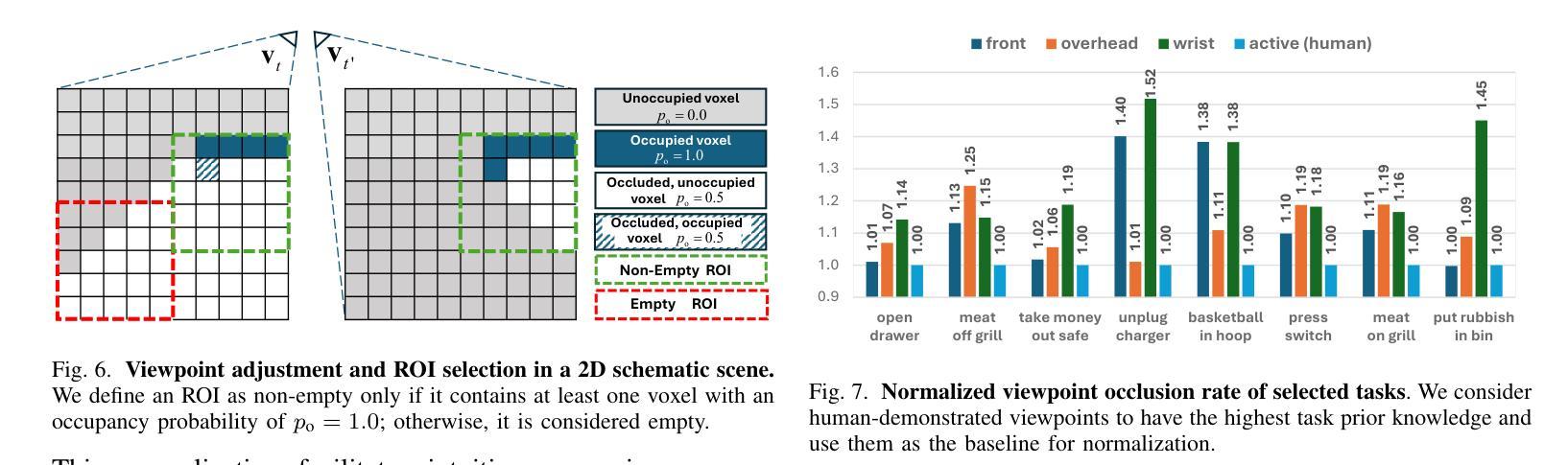
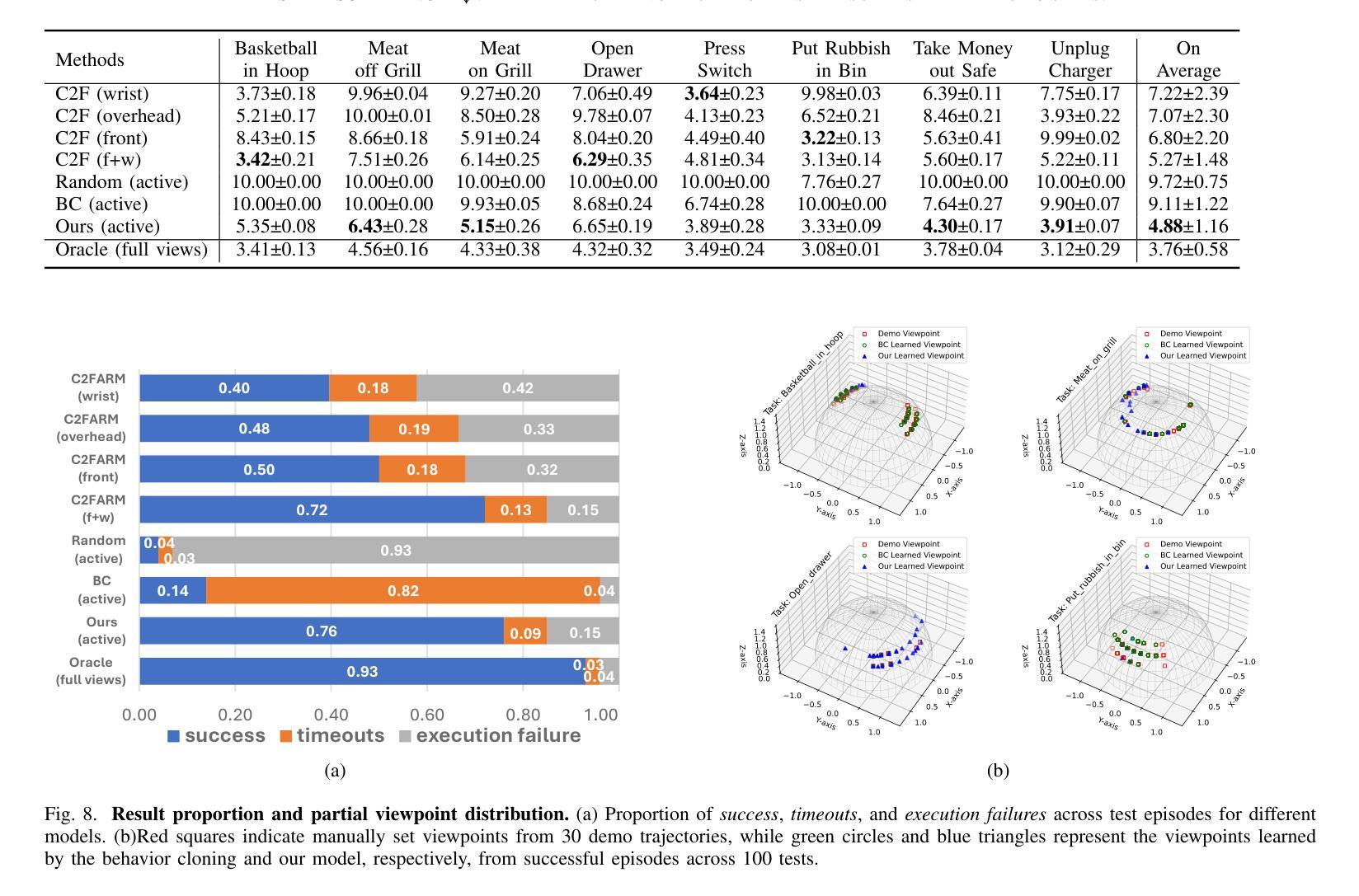
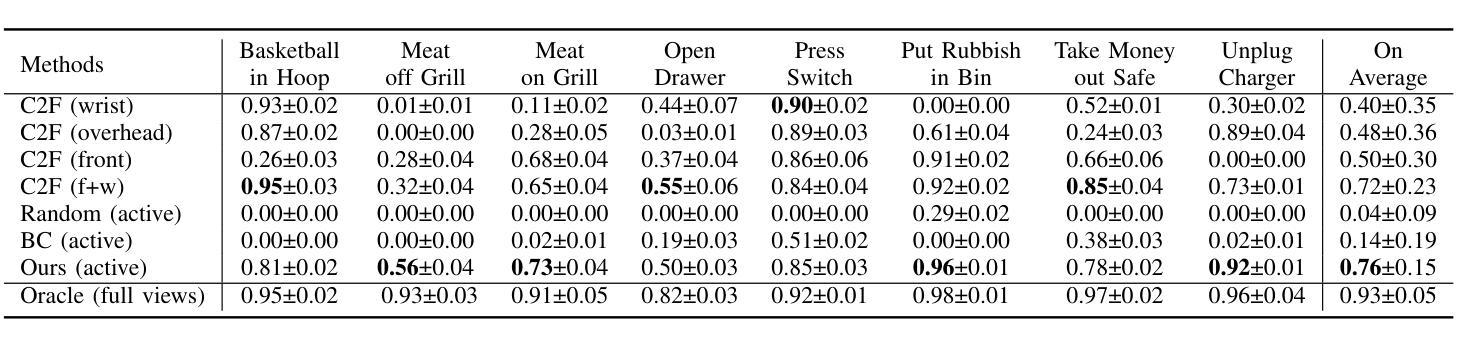
Observe Then Act: Asynchronous Active Vision-Action Model for Robotic Manipulation
Authors:Guokang Wang, Hang Li, Shuyuan Zhang, Di Guo, Yanhong Liu, Huaping Liu
In real-world scenarios, many robotic manipulation tasks are hindered by occlusions and limited fields of view, posing significant challenges for passive observation-based models that rely on fixed or wrist-mounted cameras. In this paper, we investigate the problem of robotic manipulation under limited visual observation and propose a task-driven asynchronous active vision-action model.Our model serially connects a camera Next-Best-View (NBV) policy with a gripper Next-Best Pose (NBP) policy, and trains them in a sensor-motor coordination framework using few-shot reinforcement learning. This approach allows the agent to adjust a third-person camera to actively observe the environment based on the task goal, and subsequently infer the appropriate manipulation actions.We trained and evaluated our model on 8 viewpoint-constrained tasks in RLBench. The results demonstrate that our model consistently outperforms baseline algorithms, showcasing its effectiveness in handling visual constraints in manipulation tasks.
在真实场景中,许多机器人操作任务受到遮挡和视野有限的阻碍,这给依赖固定或手腕式相机的基于被动观察模型带来了巨大的挑战。在本文中,我们研究了在有限视觉观察下的机器人操作问题,并提出了一种任务驱动的异步主动视觉动作模型。我们的模型将相机的下一个最佳视图(NBV)策略与夹具的下一个最佳姿态(NBP)策略串联起来,在一个传感器-电机协调框架中使用少量的强化学习进行训练。这种方法允许智能体根据任务目标主动调整第三人称相机的视角来观察环境,然后推断适当的操作动作。我们在RLBench的8个视点约束任务上训练和评估了我们的模型。结果表明,我们的模型始终优于基线算法,展示了在处理操作任务中的视觉约束方面的有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文研究了在有限视觉观察下的机器人操作问题,并提出了一种任务驱动的异步主动视觉动作模型。该模型通过串联相机最佳视角(NBV)政策和抓手最佳姿态(NBP)政策,在传感器-电机协调框架中使用小样本强化学习进行训练。该方法使机器人能够基于任务目标主动调整第三人称相机观察环境,并据此推断适当的操作动作。在RLBench的8个视角受限任务中,该模型的结果表明其在处理操作任务中的视觉约束方面始终优于基准算法。
Key Takeaways
- 机器人操作任务在实际场景中常常受到遮挡和视野限制的挑战。
- 本文提出了一种任务驱动的异步主动视觉动作模型,解决有限视觉观察下的机器人操作问题。
- 模型通过串联相机最佳视角(NBV)政策和抓手最佳姿态(NBP)政策,以应对视角和操作约束。
- 该模型在传感器-电机协调框架中使用小样本强化学习进行训练。
- 机器人能够基于任务目标主动调整相机观察环境。
- 模型在RLBench的多个视角受限任务中进行了训练和评估,结果优于基准算法。
点此查看论文截图

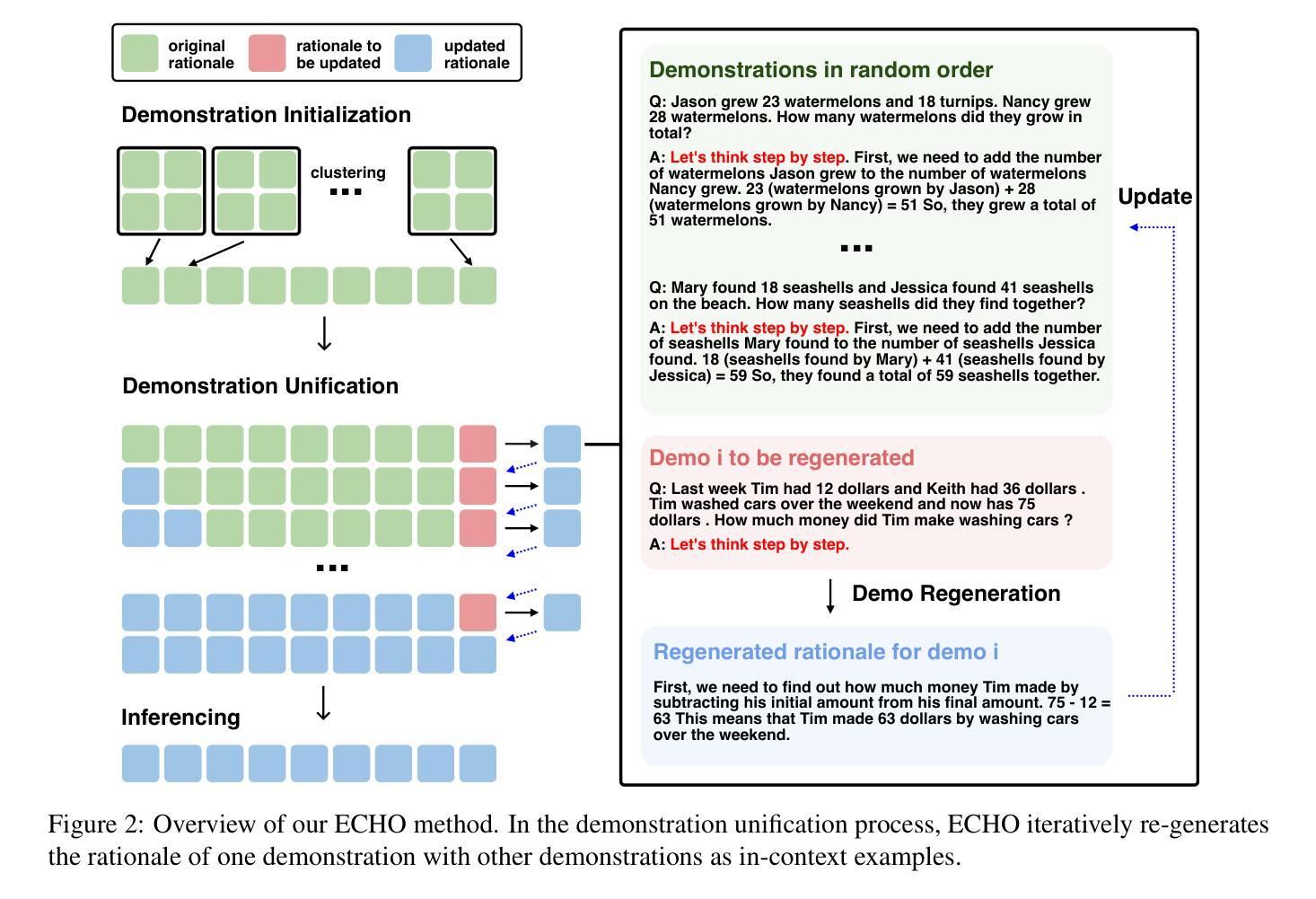
Self-Harmonized Chain of Thought
Authors:Ziqi Jin, Wei Lu
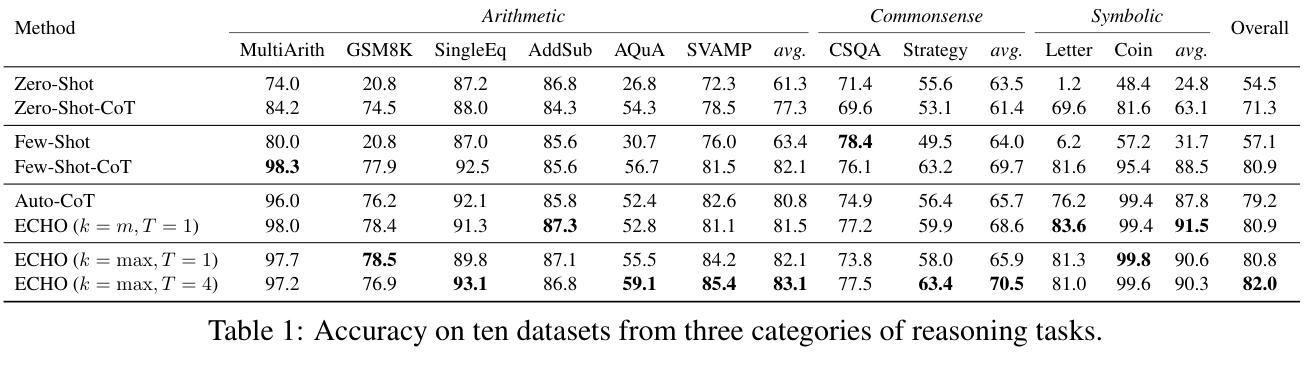
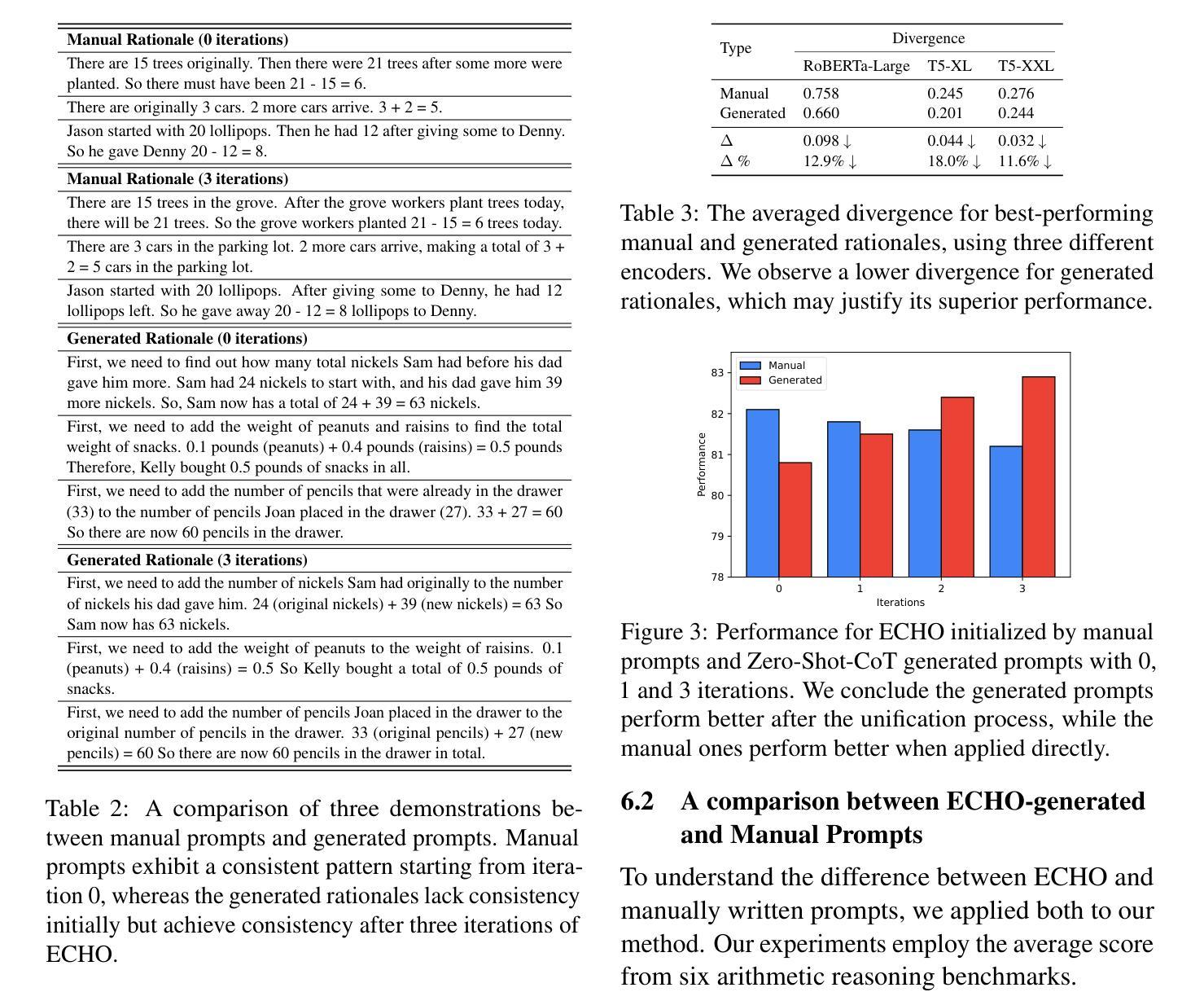
Chain-of-thought (CoT) prompting has demonstrated the capacity of large language models to perform complex reasoning through intermediate steps. While effective, current CoT methods face challenges: Zero-shot-CoT can lead to reasoning errors, and Few-shot-CoT requires labor-intensive manual demonstrations. Auto-CoT attempts to address these issues by automatically generating diverse demonstrations, but this diversity can lead to inconsistent reasoning patterns. We propose ECHO (Self-Harmonized Chain of Thought), a novel method that unifies diverse solution paths into a consistent and effective reasoning pattern. ECHO employs an iterative process to refine and harmonize automatically generated demonstrations, mitigating the limitations of existing approaches. Our comprehensive experiments across arithmetic, commonsense, and symbolic reasoning tasks demonstrate that ECHO outperforms Auto-CoT by an average of 2.8%. These findings suggest that ECHO represents a significant step towards more robust and generalizable automated reasoning in large language models.
思维链(CoT)提示展现了大型语言模型通过中间步骤进行复杂推理的能力。虽然现有CoT方法有效,但面临挑战:零镜头CoT可能导致推理错误,而少镜头CoT需要繁琐的手动演示。Auto-CoT试图通过自动生成多样化的演示来解决这些问题,但这种多样性可能导致推理模式的不一致。我们提出了ECHO(自我协调思维链),这是一种将多样化解决方案路径统一为一致有效推理模式的新方法。ECHO采用迭代过程来优化和协调自动生成的演示,缓解了现有方法的局限性。我们在算术、常识和符号推理任务上的综合实验表明,ECHO的平均性能优于Auto-CoT 2.8%。这些发现表明,ECHO在大型语言模型中实现更稳健和可推广的自动化推理方面迈出了重要一步。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大型语言模型的链式思维(CoT)提示展现出了执行复杂推理的能力,通过中间步骤进行。尽管现有CoT方法有效,但仍面临挑战:零步CoT可能导致推理错误,而少步CoT需要繁琐的手动演示。自动CoT试图通过自动生成多样的演示来解决这些问题,但其多样性可能导致推理模式的不一致。本文提出一种名为ECHO(自我协调的链式思维)的新方法,它将不同的解决方案路径统一为一个一致且有效的推理模式。ECHO采用迭代过程来优化和协调自动生成的演示,缓解了现有方法的局限性。在算术、常识和符号推理任务上的综合实验表明,ECHO的平均性能比自动CoT提高了2.8%。这表明ECHO在朝着大型语言模型中更稳健和更通用的自动化推理迈出了重要一步。
Key Takeaways
- 链式思维(CoT)提示大型语言模型执行复杂推理的中间步骤能力。
- 当前CoT方法面临推理错误和需要繁琐手动演示的问题。
- 自动CoT方法试图通过自动生成多样的演示来解决这些问题,但可能导致推理模式的不一致。
- ECHO(自我协调的链式思维)提出一种将不同解决方案路径统一为一致且有效推理模式的新方法。
- ECHO采用迭代过程优化和协调自动生成的演示。
- 在多个任务上的实验表明,ECHO的性能优于自动CoT。
点此查看论文截图