⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-02-13 更新
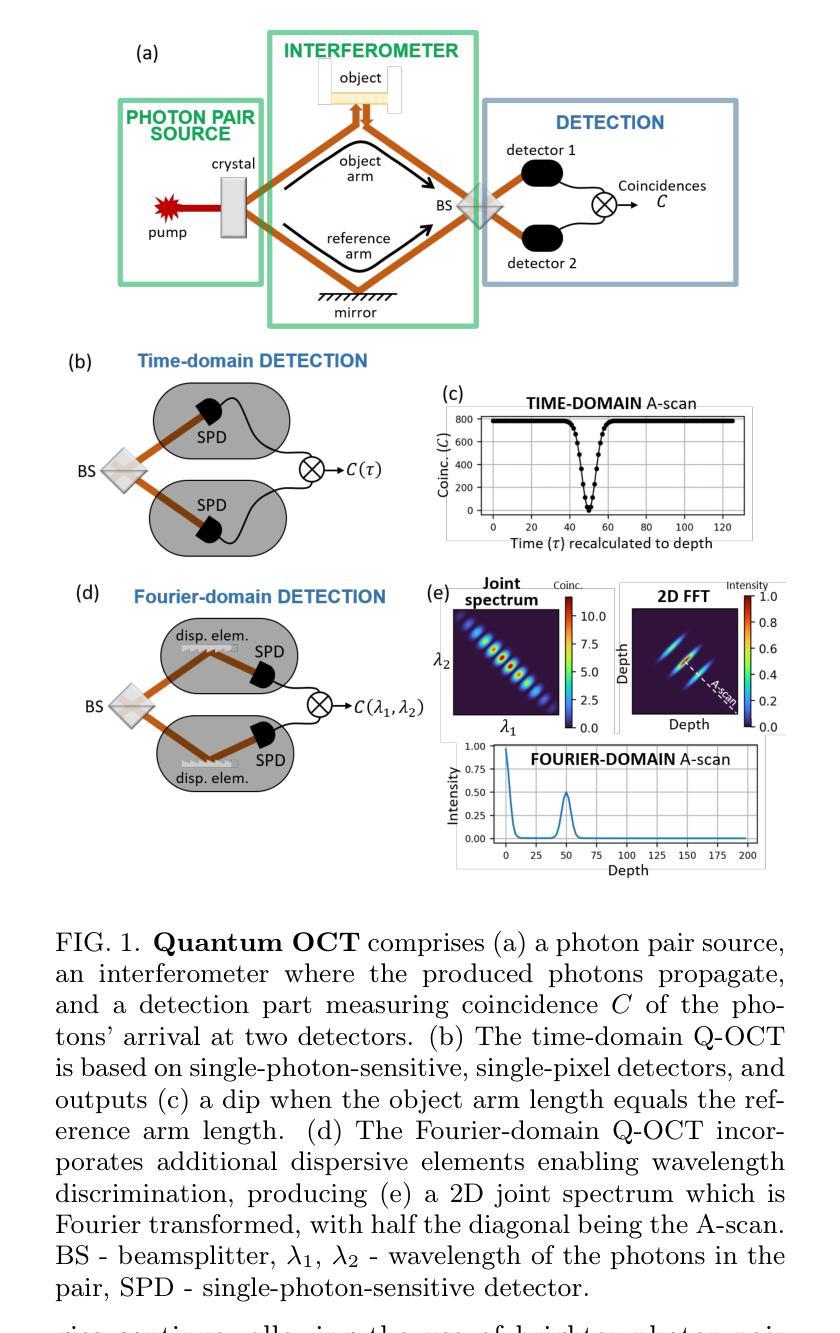
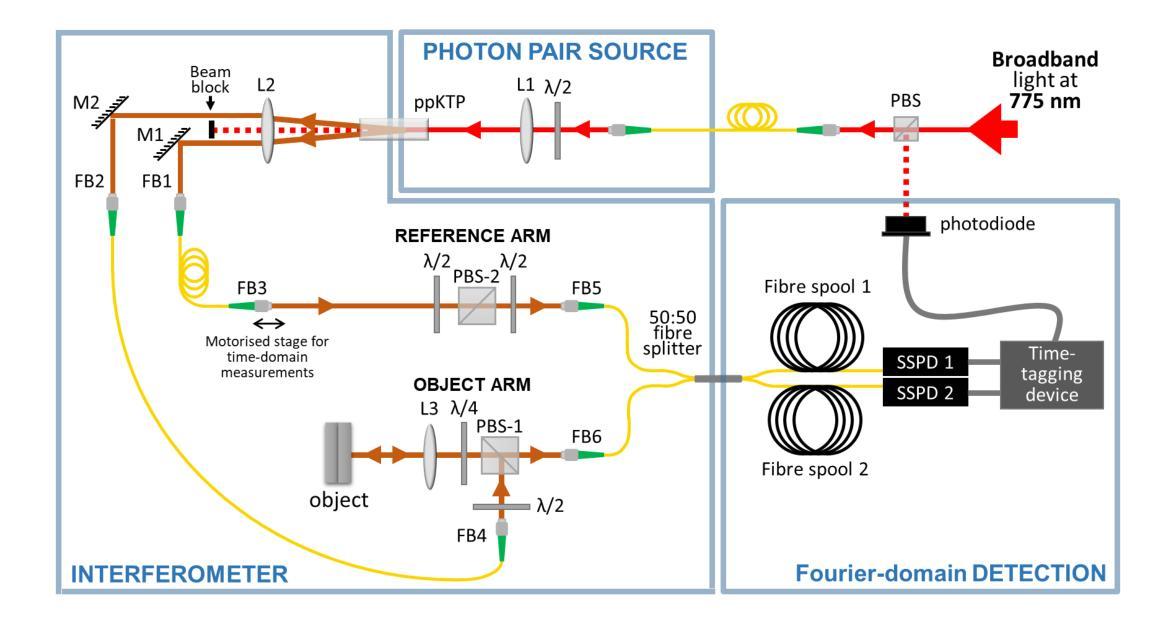
Demonstration of Fourier-domain Quantum Optical Coherence Tomography for a fast tomographic quantum imaging
Authors:Sylwia M. Kolenderska, Crislane Vieira de Brito, Piotr Kolenderski
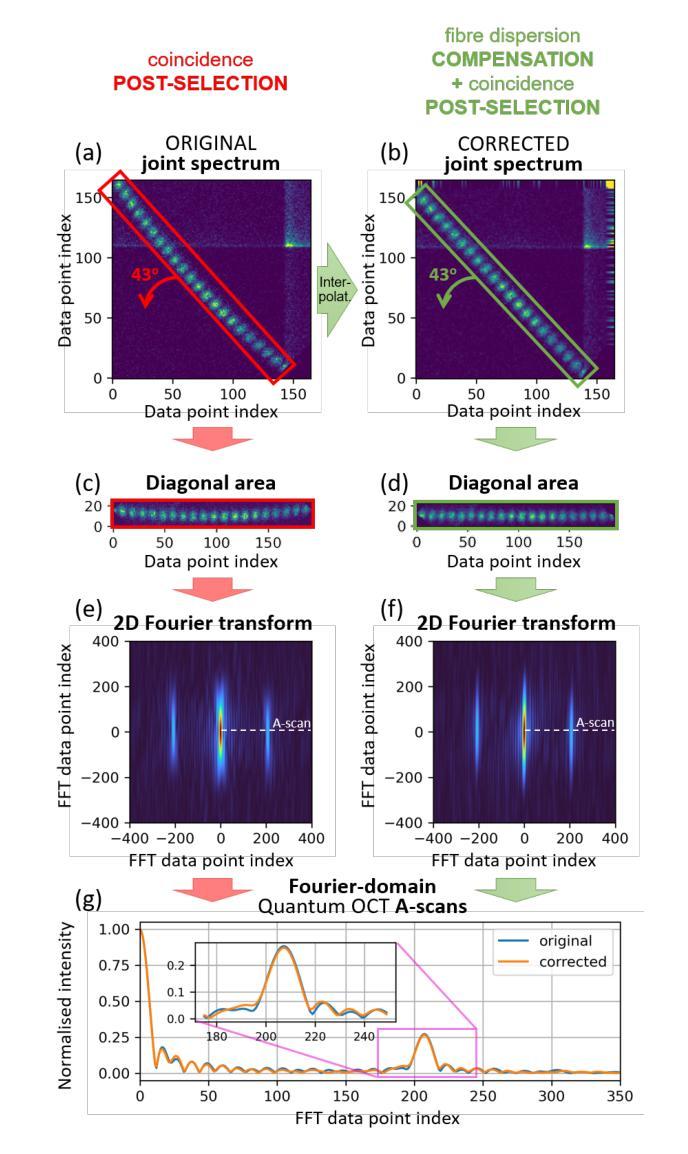
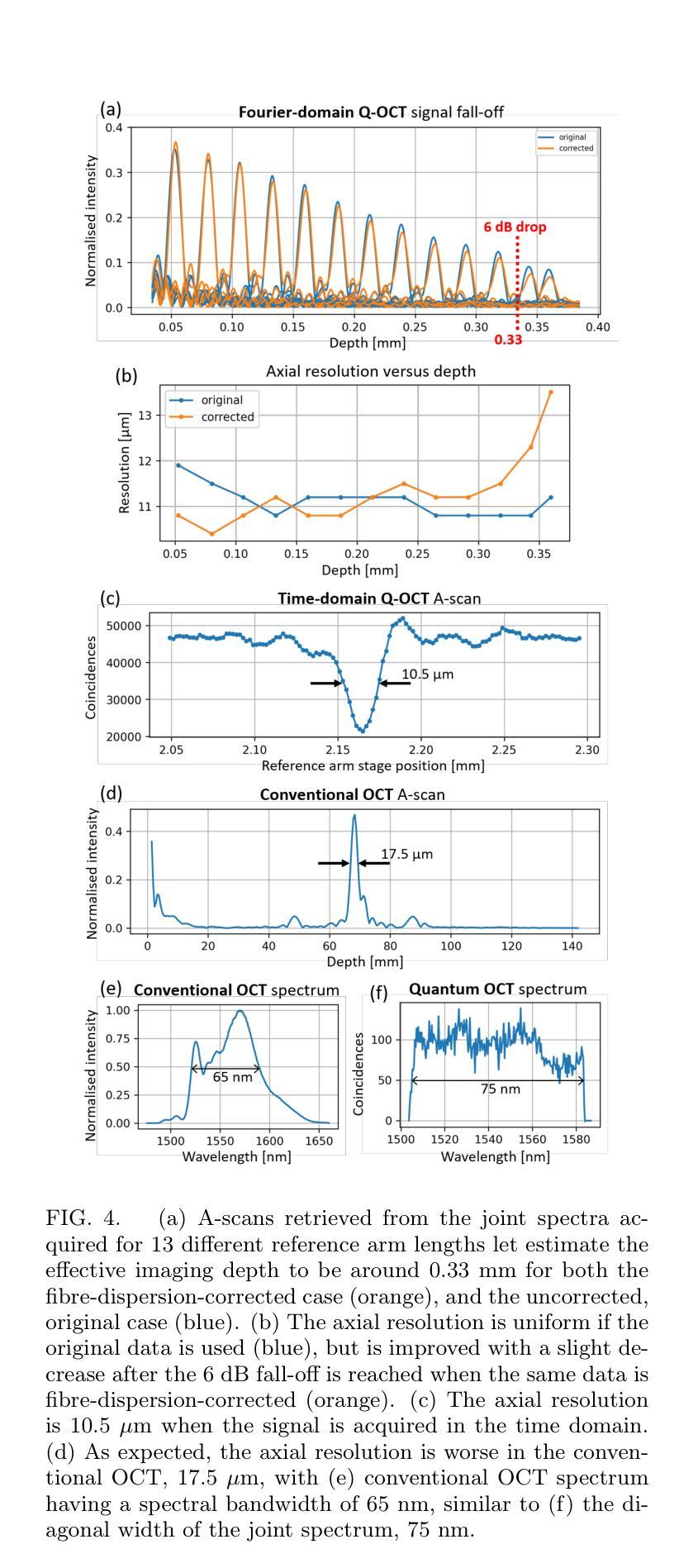
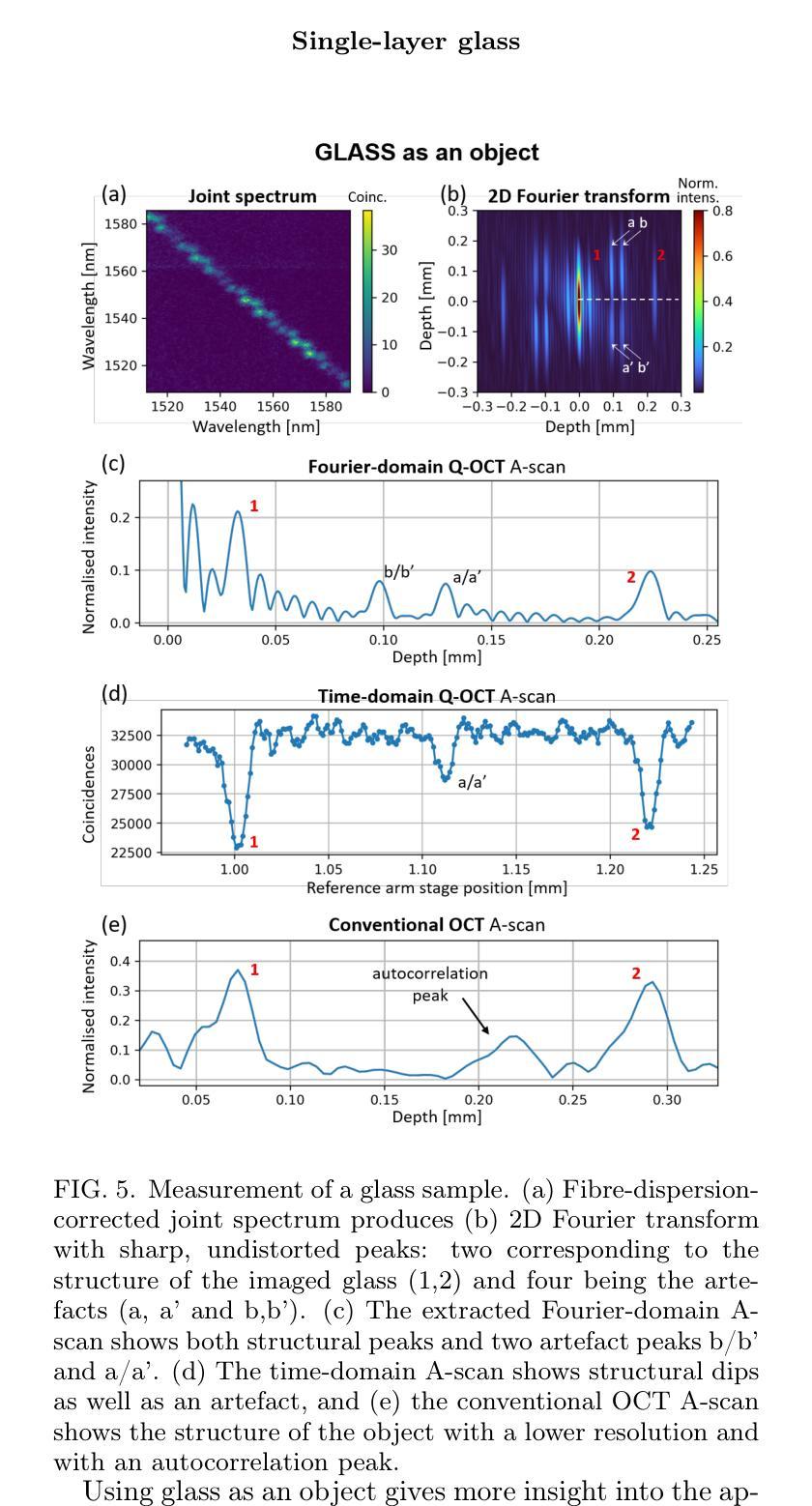
Using spectrally correlated photon pairs instead of classical laser light and coincidence detection instead of light intensity detection, Quantum Optical Coherence Tomography (Q-OCT) outperforms classical OCT in several experimental terms. It provides twice better axial resolution with the same spectral bandwidth and it is immune to even-order chromatic dispersion, including Group Velocity Dispersion responsible for the bulk of axial resolution degradation in the OCT images. Q-OCT has been performed in the time domain configuration, where one line of the two-dimensional image is acquired by axially translating the mirror in the interferometer’s reference arm and measuring the coincidence rate of photons arriving at two single-photon-sensitive detectors. Although successful at producing resolution-doubled and dispersion-cancelled images, it is still relatively slow and cannot compete with its classical counterpart. Here, we experimentally demonstrate Q-OCT in a novel Fourier-domain configuration, theoretically proposed in 2020, where the reference mirror is fixed and the joint spectra are acquired. We show that such a configuration allows for faster image acquisition than its time-domain configuration, providing a step forward towards a practical and competitive solution in the OCT arena. The limitations of the novel approach are discussed, contrasted with the limitations of both the time-domain approach and the traditional OCT.
利用光谱相关光子对代替经典激光光,以及符合检测代替光强度检测,量子光学相干断层扫描(Q-OCT)在多个实验方面优于经典OCT。它在相同的光谱带宽下提供了两倍的轴向分辨率,并且不受偶次色散的影响,包括引起OCT图像中大部分轴向分辨率退化的群速度色散。Q-OCT已经在时域配置中进行,其中二维图像的一行是通过在干涉仪的参考臂中轴向平移镜子并测量到达两个单光子敏感检测器的光子符合率来获得的。尽管成功产生了分辨率加倍且消散的图像,但它仍然相对较慢,无法与其经典同类竞争。在这里,我们在实验上展示了在傅立叶域配置中的Q-OCT,该配置在理论上于2020年提出,其中参考镜是固定的并且联合光谱被采集。我们表明这样的配置允许比其时域配置更快的图像采集速度,这为在OCT领域中实现实用且竞争的解决方案向前迈出了一步。对新型方法的局限性进行了讨论,并将其与时域方法和传统OCT的局限性进行了对比。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 11 pages, 7 figures, 1 table
Summary:量子光学相干层析成像(Q-OCT)采用光谱相关光子对替代经典激光光,采用符合检测替代光强度检测,在多个实验条件下表现优于传统OCT。它在相同的谱带宽下提供两倍的轴向分辨率,并对包括群速度色散在内的偶阶色散具有免疫性,这是OCT图像中大部分轴向分辨率退化的原因。尽管成功实现了分辨率加倍和色散抵消的图像,但Q-OCT仍然相对较慢,无法与其经典对应物竞争。在此,我们在实验上证明了Q-OCT的一种新型傅立叶域配置,该配置的理论提出于2020年,其中参考镜是固定的,且获得联合光谱。我们表明,这种配置允许比其时域配置更快的图像采集,朝着实用和竞争的OCT解决方案迈出了一步。
Key Takeaways:
- Q-OCT利用光谱相关光子对和符合检测,相比传统OCT在实验上表现出优势。
- Q-OCT在相同的谱带宽下提供两倍的轴向分辨率,并对偶阶色散具有免疫性。
- Q-OCT的时域配置虽然能生成分辨率加倍和色散抵消的图像,但速度较慢。
- 新型傅立叶域配置的Q-OCT允许更快的图像采集,朝实用和竞争的OCT解决方案迈进。
- 新配置的Q-OCT仍存在局限性,需与其时域配置和传统OCT的局限性进行对比。
- Q-OCT的发展对于提高光学成像技术的性能和实用性具有重要意义。
点此查看论文截图

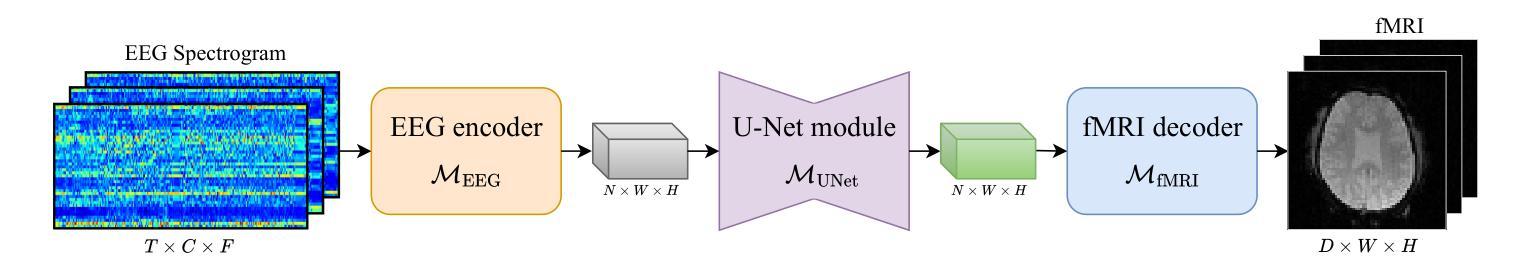
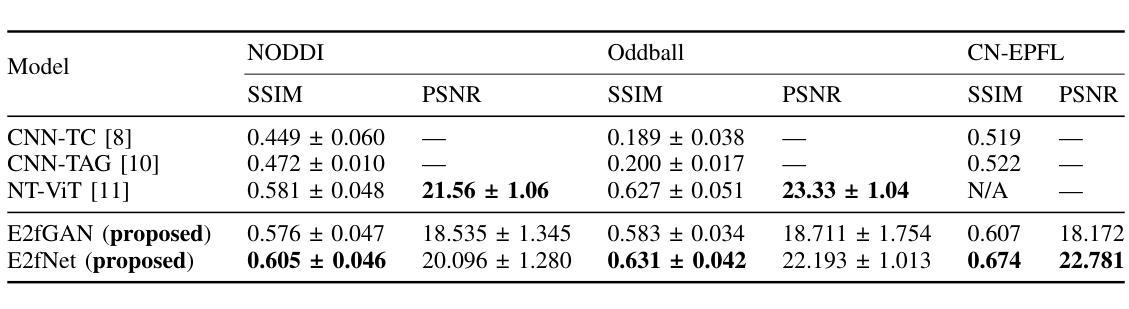
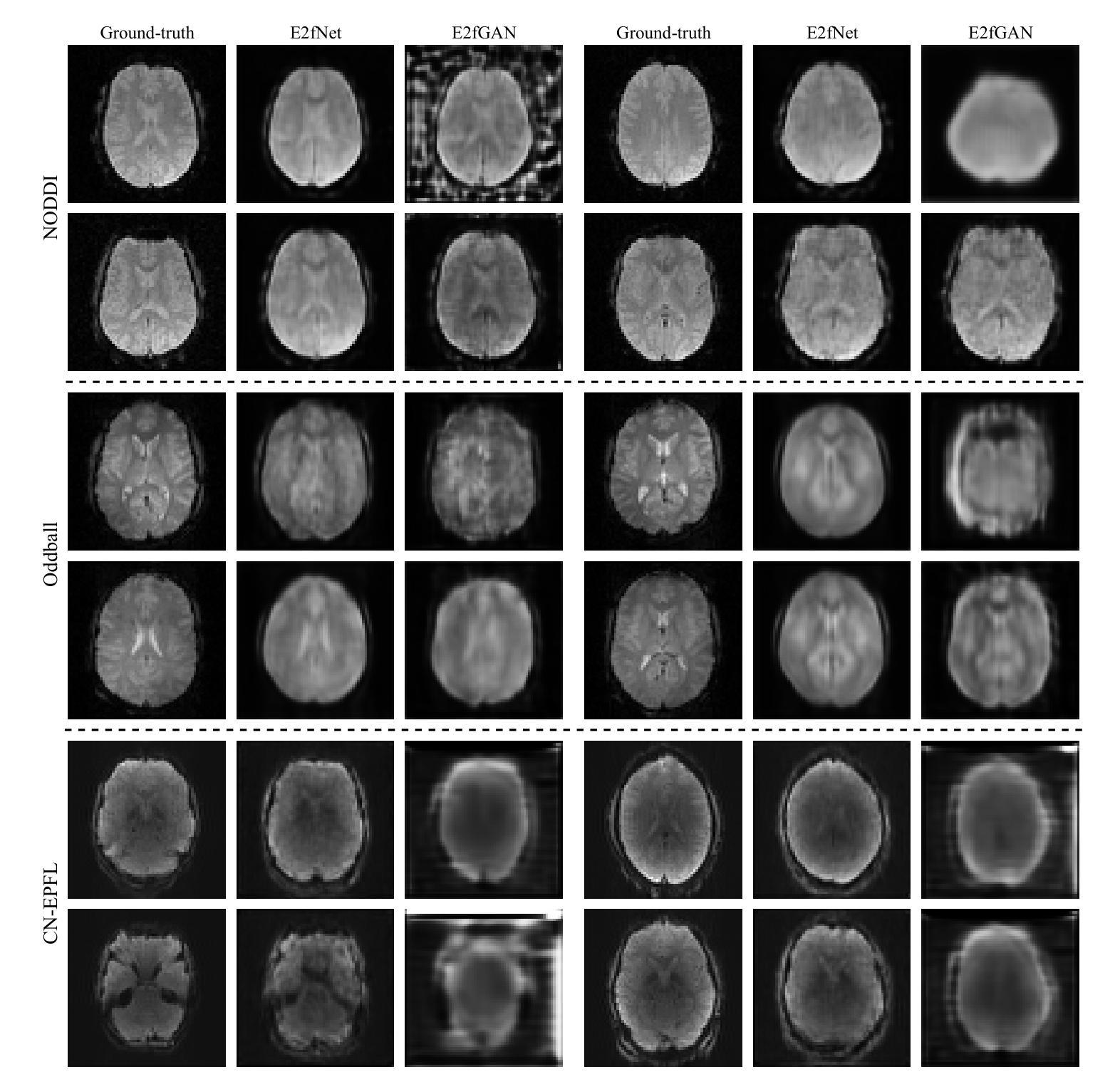
From Brainwaves to Brain Scans: A Robust Neural Network for EEG-to-fMRI Synthesis
Authors:Kristofer Grover Roos, Quan Huu Cap, Atsushi Fukuda
While functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) offers rich spatial resolution, it is limited by high operational costs and significant infrastructural demands. In contrast, electroencephalography (EEG) provides millisecond-level precision in capturing electrical activity but lacks the spatial resolution necessary for precise neural localization. To bridge these gaps, we introduce E2fNet, a simple yet effective deep learning model for synthesizing fMRI images from low-cost EEG data. E2fNet is specifically designed to capture and translate meaningful features from EEG across electrode channels into accurate fMRI representations. Extensive evaluations across three datasets demonstrate that E2fNet consistently outperforms existing methods, achieving state-of-the-art results in terms of the structural similarity index measure (SSIM). Our findings suggest that E2fNet is a promising, cost-effective solution for enhancing neuroimaging capabilities. The code is available at https://github.com/kgr20/E2fNet.
虽然功能磁共振成像(fMRI)提供了丰富的空间分辨率,但由于其高昂的操作成本和巨大的基础设施需求而受到限制。相比之下,脑电图(EEG)在捕捉电活动方面具有毫秒级的精确度,但在精确神经定位方面缺乏必要的空间分辨率。为了弥补这些差距,我们引入了E2fNet,这是一个简单而有效的深度学习模型,可以从低成本EEG数据中合成fMRI图像。E2fNet专门设计用于捕获电极通道中的EEG有意义特征,并将其转化为准确的fMRI表示。在三个数据集上的广泛评估表明,E2fNet始终优于现有方法,在结构相似性指数度量(SSIM)方面达到最新结果。我们的研究结果表明,E2fNet是一个有前景的、性价比高的解决方案,可增强神经成像能力。代码可在 https://github.com/kgr20/E2fNet 找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:
利用深度学习模型E2fNet将EEG数据转化为fMRI图像,实现低成本、高效的神经常规成像。E2fNet能够捕捉EEG数据中的有意义特征,并转化为准确的fMRI表示,通过跨电极通道的合成提高结构相似性指数(SSIM)。
Key Takeaways:
- E2fNet是一种用于从低成本EEG数据中合成fMRI图像的深度学习模型。
- E2fNet旨在捕捉EEG数据中的有意义特征,并转化为fMRI表示。
- E2fNet通过跨电极通道的合成,实现了从EEG到fMRI的转化。
- E2fNet在三个数据集上的表现均优于现有方法,达到最先进的结构相似性指数(SSIM)。
- E2fNet的引入为神经成像提供了一种成本效益高、实用的解决方案。
- E2fNet的代码已公开发布,便于其他研究者使用和改进。
点此查看论文截图

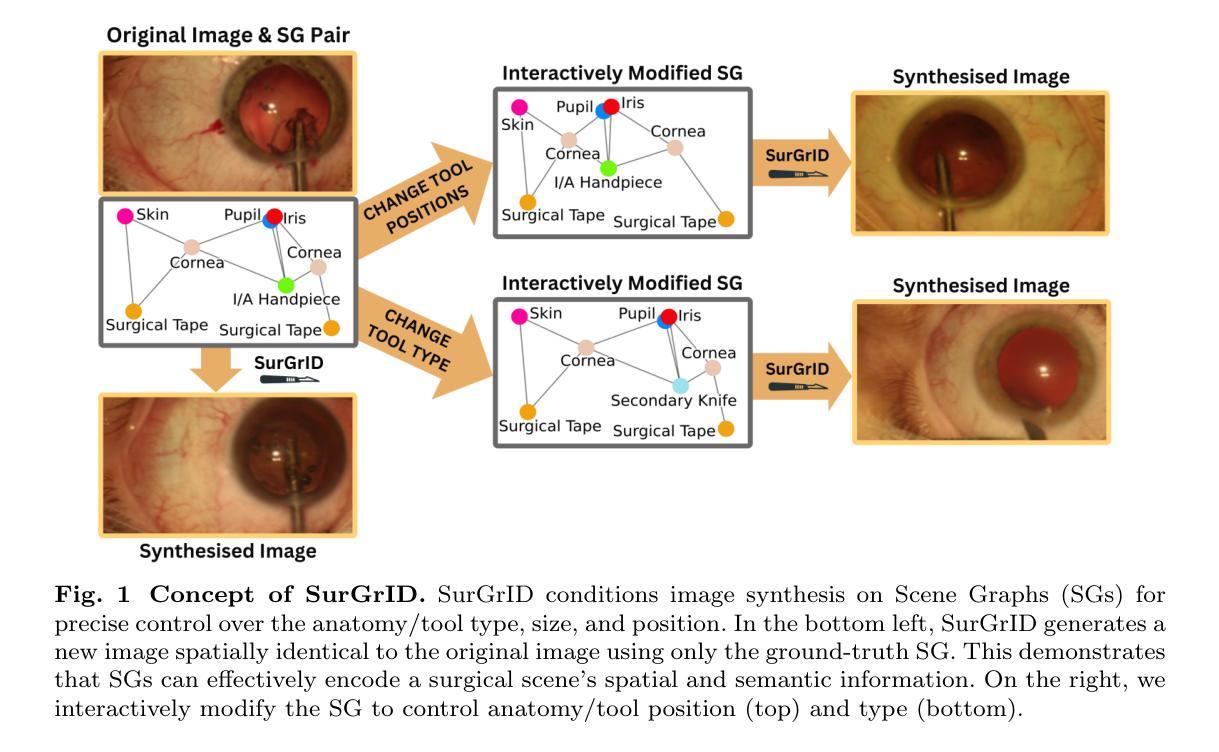
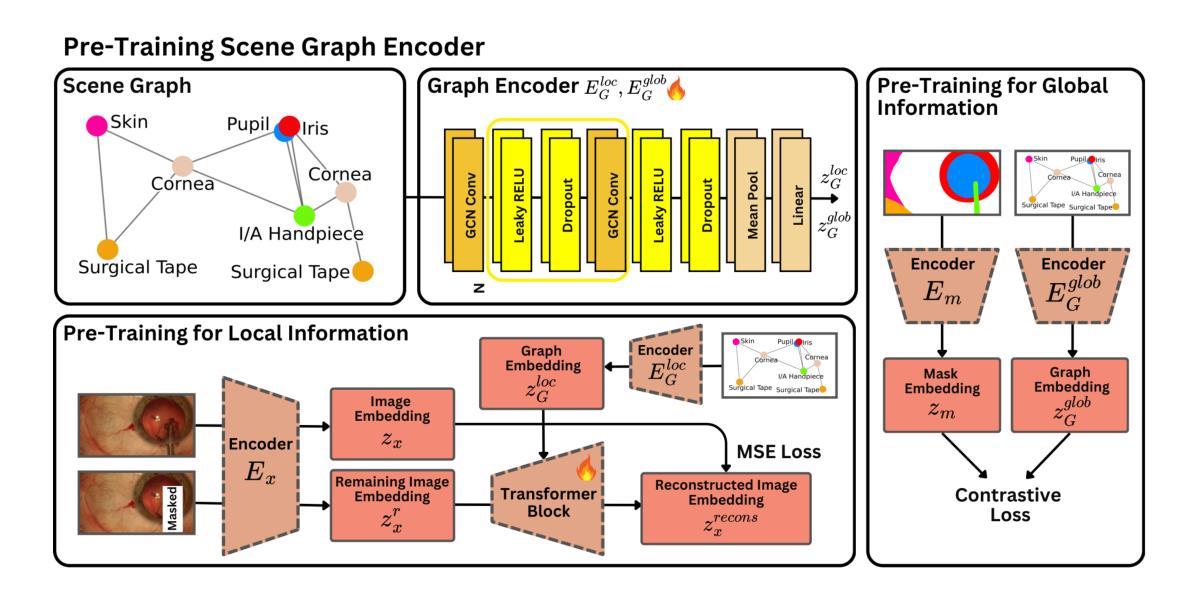
SurGrID: Controllable Surgical Simulation via Scene Graph to Image Diffusion
Authors:Yannik Frisch, Ssharvien Kumar Sivakumar, Çağhan Köksal, Elsa Böhm, Felix Wagner, Adrian Gericke, Ghazal Ghazaei, Anirban Mukhopadhyay
Surgical simulation offers a promising addition to conventional surgical training. However, available simulation tools lack photorealism and rely on hardcoded behaviour. Denoising Diffusion Models are a promising alternative for high-fidelity image synthesis, but existing state-of-the-art conditioning methods fall short in providing precise control or interactivity over the generated scenes. We introduce SurGrID, a Scene Graph to Image Diffusion Model, allowing for controllable surgical scene synthesis by leveraging Scene Graphs. These graphs encode a surgical scene’s components’ spatial and semantic information, which are then translated into an intermediate representation using our novel pre-training step that explicitly captures local and global information. Our proposed method improves the fidelity of generated images and their coherence with the graph input over the state-of-the-art. Further, we demonstrate the simulation’s realism and controllability in a user assessment study involving clinical experts. Scene Graphs can be effectively used for precise and interactive conditioning of Denoising Diffusion Models for simulating surgical scenes, enabling high fidelity and interactive control over the generated content.
手术模拟为传统手术训练提供了有前途的补充。然而,现有的模拟工具缺乏逼真的视觉效果,并依赖于硬编码的行为。去噪扩散模型是高保真图像合成的有前途的替代方案,但现有的最先进的条件设定方法在提供对生成场景的精确控制或交互方面存在不足。我们引入了SurGrID,一种场景图到图像扩散模型,通过利用场景图,实现可控手术场景合成。这些图编码了手术场景组件的空间和语义信息,然后利用我们新颖的预训练步骤将这些信息翻译为一种中间表示形式,该步骤能够显式捕获局部和全局信息。相比现有技术,我们提出的方法提高了生成图像的真实性和与图的输入的一致性。此外,我们还通过涉及临床专家的用户评估研究证明了模拟的真实性和可控性。场景图可有效地用于对去噪扩散模型进行精确和交互式的条件设定,以模拟手术场景,实现对生成内容的高保真和交互式控制。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
手术模拟为传统手术训练提供了有前景的补充。现有的模拟工具缺乏逼真度并依赖硬编码行为。我们引入SurGrID,一个场景图到图像扩散模型,通过利用场景图,实现可控手术场景合成。该方法提高了生成图像的逼真度和与图形输入的连贯性,并在涉及临床专家的用户评估研究中证明了模拟的真实性和可控性。
Key Takeaways
- 手术模拟是传统手术训练的有前景的补充。
- 当前模拟工具存在逼真度不足和依赖硬编码行为的问题。
- Denoising Diffusion Models可用于高保真图像合成,但在精确控制和交互性方面存在不足。
- SurGrID是一个场景图到图像扩散模型,利用场景图实现可控手术场景合成。
- 该方法提高了生成图像的逼真度和与图形输入的连贯性。
- 用户评估研究证明了模拟的真实性和可控性。
点此查看论文截图

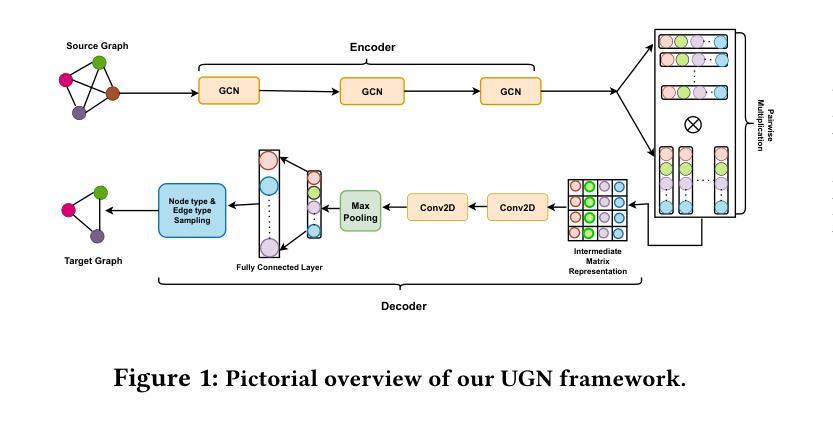
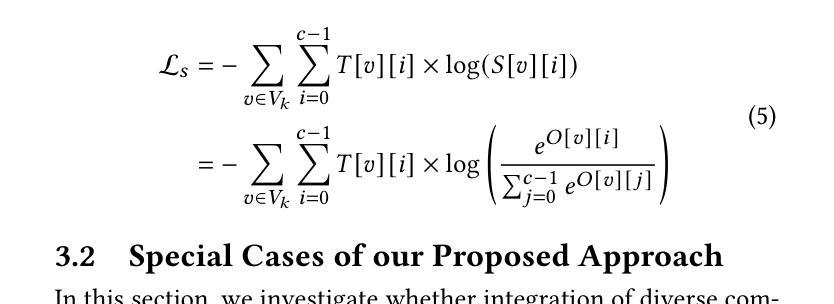
Unified Graph Networks (UGN): A Deep Neural Framework for Solving Graph Problems
Authors:Rudrajit Dawn, Madhusudan Ghosh, Partha Basuchowdhuri, Sudip Kumar Naskar
Deep neural networks have enabled researchers to create powerful generalized frameworks, such as transformers, that can be used to solve well-studied problems in various application domains, such as text and image. However, such generalized frameworks are not available for solving graph problems. Graph structures are ubiquitous in many applications around us and many graph problems have been widely studied over years. In recent times, there has been a surge in deep neural network based approaches to solve graph problems, with growing availability of graph structured datasets across diverse domains. Nevertheless, existing methods are mostly tailored to solve a specific task and lack the capability to create a generalized model leading to solutions for different downstream tasks. In this work, we propose a novel, resource-efficient framework named \emph{U}nified \emph{G}raph \emph{N}etwork (UGN) by leveraging the feature extraction capability of graph convolutional neural networks (GCN) and 2-dimensional convolutional neural networks (Conv2D). UGN unifies various graph learning tasks, such as link prediction, node classification, community detection, graph-to-graph translation, knowledge graph completion, and more, within a cohesive framework, while exercising minimal task-specific extensions (e.g., formation of supernodes for coarsening massive networks to increase scalability, use of \textit{mean target connectivity matrix} (MTCM) representation for achieving scalability in graph translation task, etc.) to enhance the generalization capability of graph learning and analysis. We test the novel UGN framework for six uncorrelated graph problems, using twelve different datasets. Experimental results show that UGN outperforms the state-of-the-art baselines by a significant margin on ten datasets, while producing comparable results on the remaining dataset.
深度神经网络使研究人员能够创建强大的通用框架,如变压器等,这些框架可用于解决文本和图像等领域的公认问题。然而,尚不存在用于解决图形问题的此类通用框架。图形结构在我们周围的许多应用中无处不在,许多图形问题多年来得到了广泛的研究。最近有基于深度神经网络的解决图形问题的新方法涌现,以及不同领域图形结构数据集的日益可用。然而,现有方法大多针对特定任务而定制,缺乏创建通用模型以用于解决不同下游任务的能力。在此工作中,我们提出了一个名为统一图网络(UGN)的新型资源高效框架,它通过利用图卷积神经网络(GCN)和二维卷积神经网络(Conv2D)的特征提取能力。UGN在一个连贯的框架内统一了各种图形学习任务,如链接预测、节点分类、社区检测、图到图的翻译、知识图谱补全等,同时进行了最小的特定任务扩展(例如,通过形成超节点来粗化大规模网络以提高可扩展性,使用平均目标连接矩阵(MTCM)表示来实现图翻译任务的扩展性等),以增强图形学习和分析的一般化能力。我们在六个不相关的图形问题上测试了新型UGN框架,使用了十二种不同的数据集。实验结果表明,UGN在十个数据集上的性能远超最新基准线,并在其余数据集上取得了相当的结果。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
深度学习神经网络已广泛应用于文本和图像等领域的问题解决,但对于图结构问题仍缺乏通用框架。近期基于深度神经网络的方法不断涌现,但多数针对特定任务。本研究提出了一种名为UGN的统一图网络框架,结合图卷积神经网络和二维卷积神经网络的特点,实现了多种图学习任务的统一。实验结果显示,UGN在多个数据集上的性能优于现有方法。
Key Takeaways
- 目前深度学习在图结构问题上缺乏通用框架。
- 基于深度神经网络的图问题解决方法日益增多,但大多针对特定任务。
- UGN框架结合了图卷积神经网络和二维卷积神经网络的特点。
- UGN框架能够统一多种图学习任务,如链接预测、节点分类、社区检测、图对图翻译和知识图谱补全等。
- UGN通过形成超节点等方法增强了大规模网络的扩展性。
- UGN使用平均目标连接矩阵表示法,实现了图翻译任务的扩展性。
点此查看论文截图

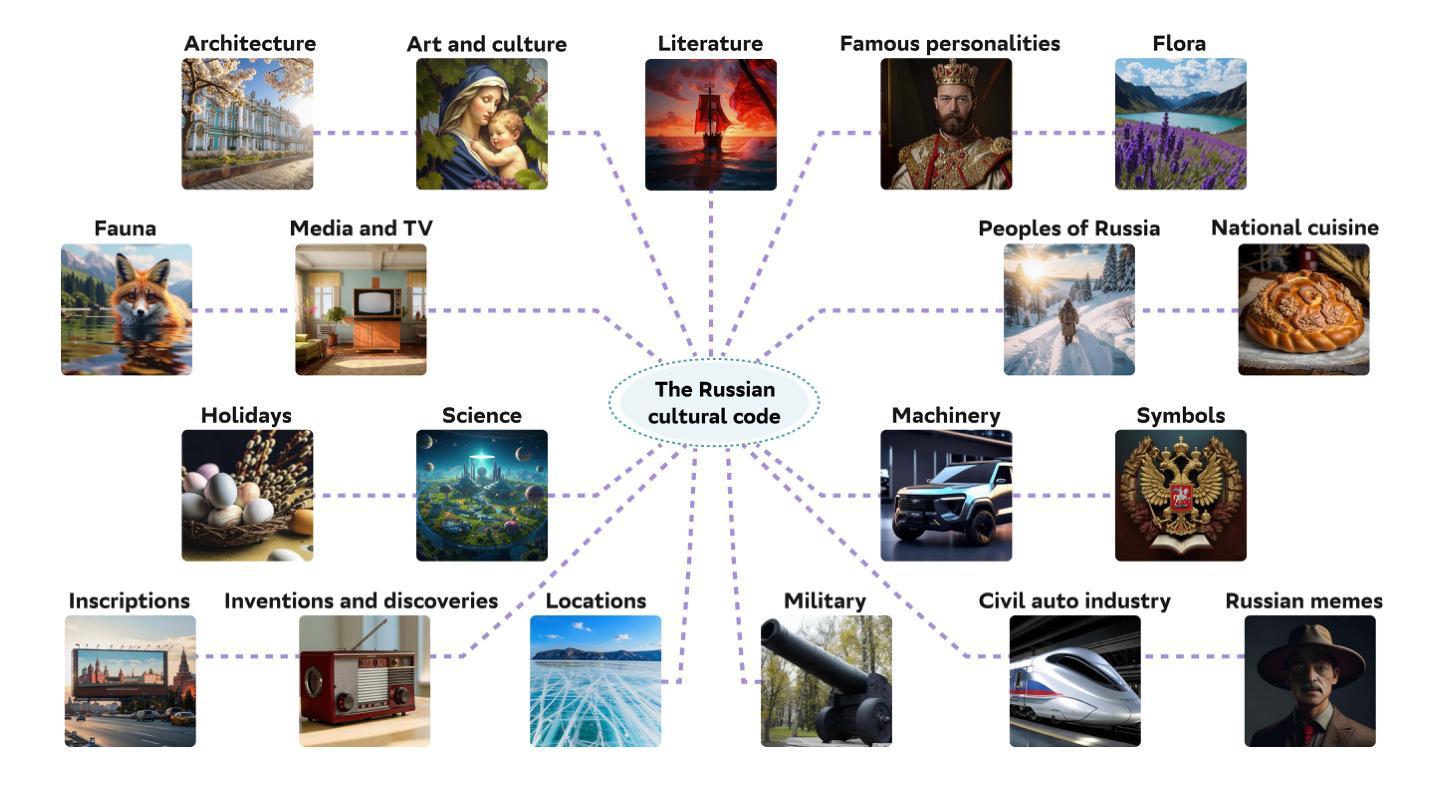
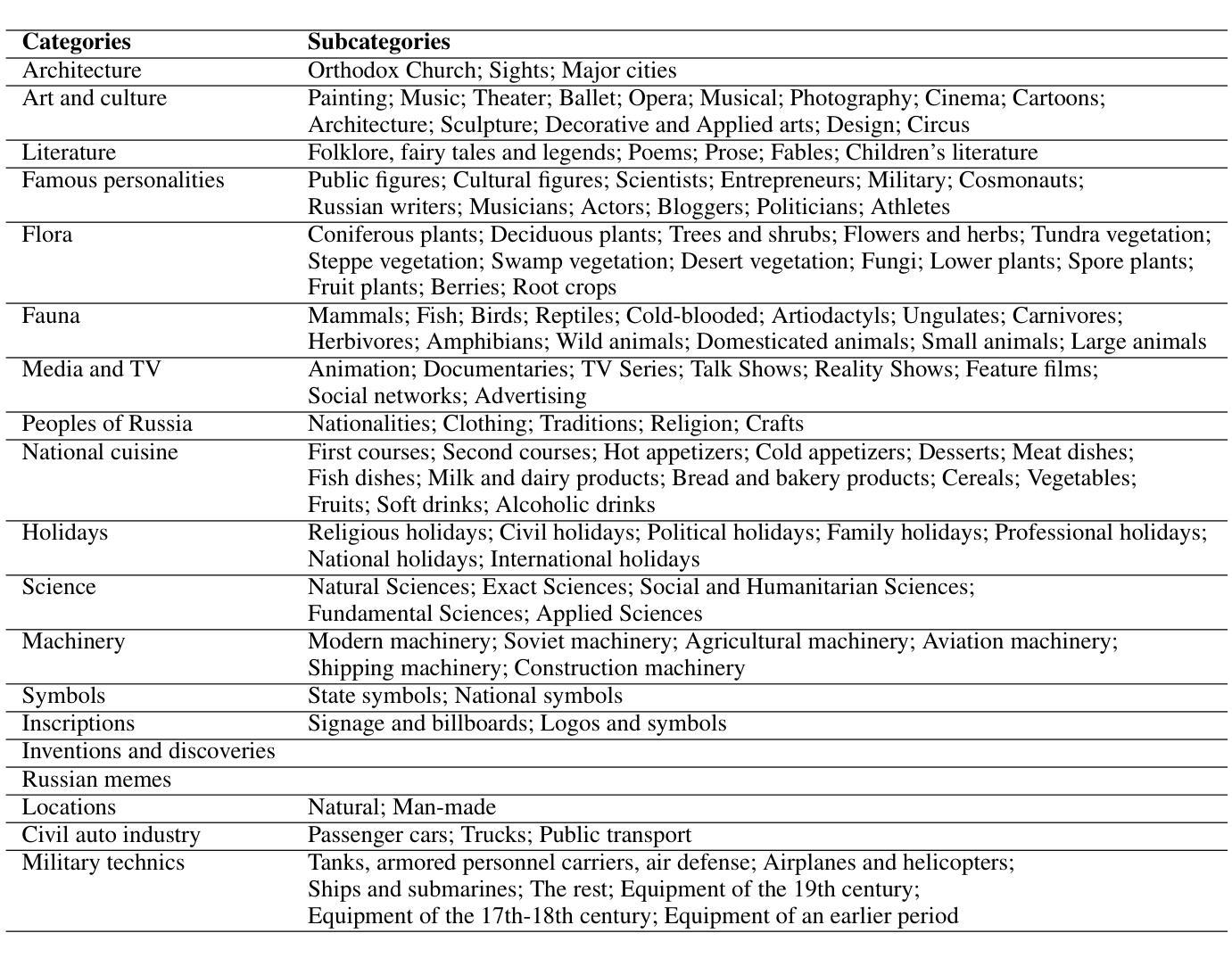
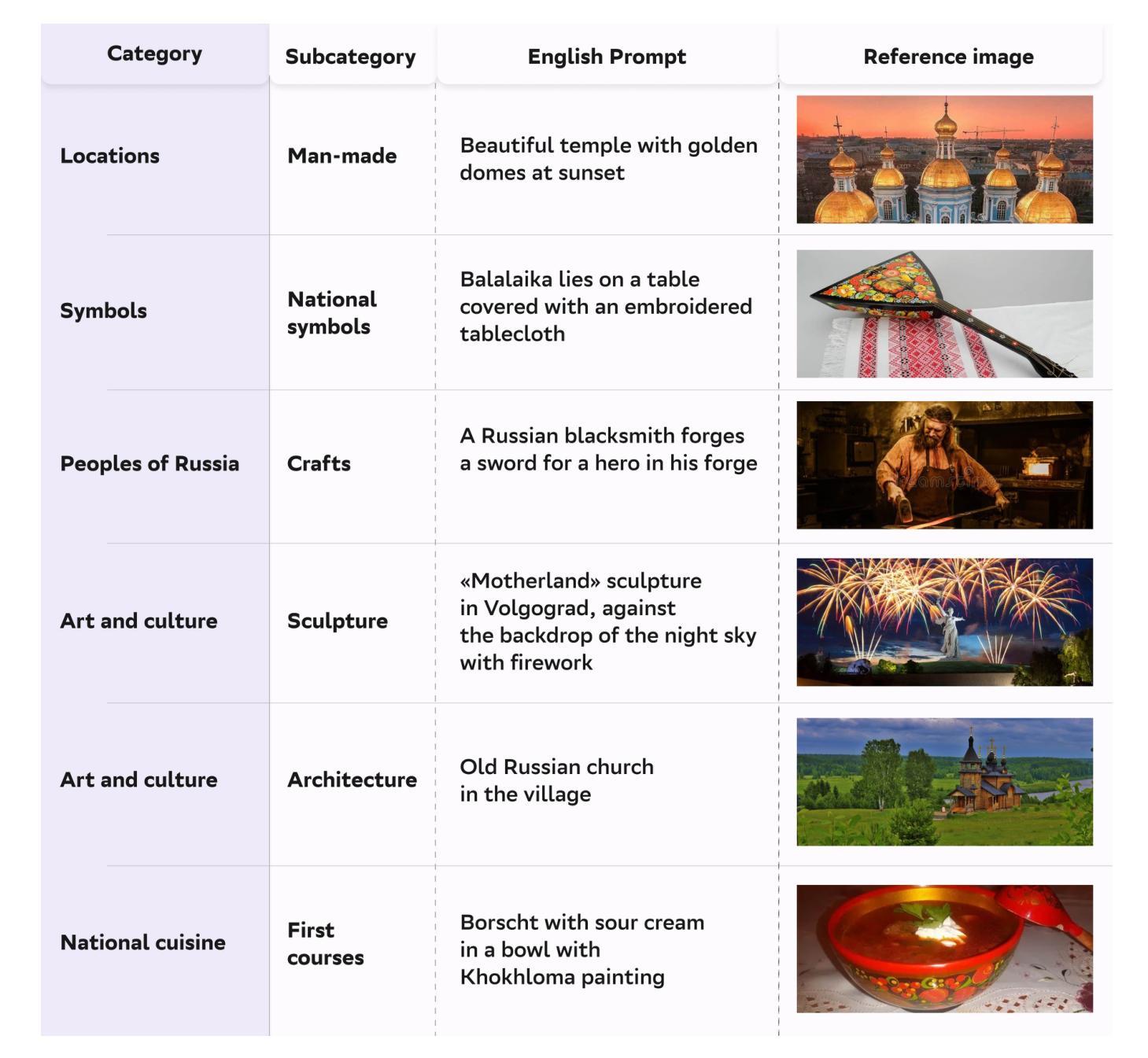
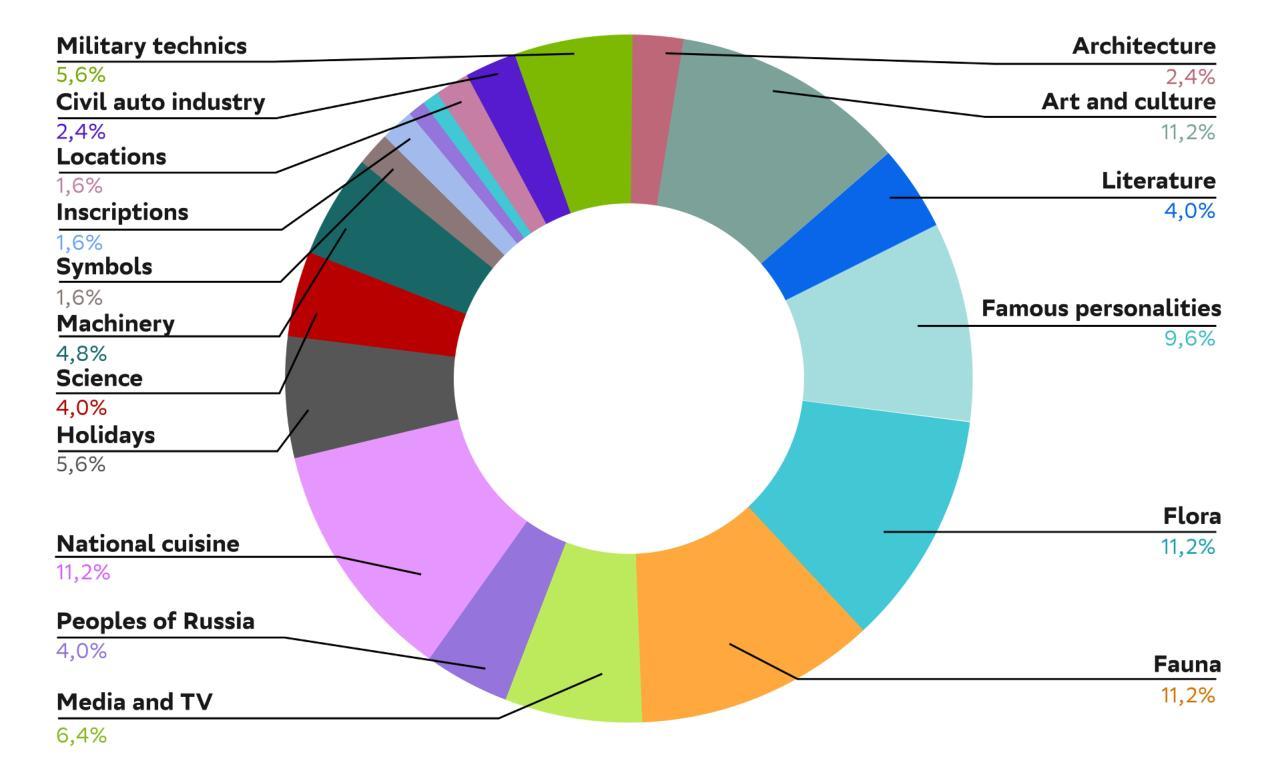
RusCode: Russian Cultural Code Benchmark for Text-to-Image Generation
Authors:Viacheslav Vasilev, Julia Agafonova, Nikolai Gerasimenko, Alexander Kapitanov, Polina Mikhailova, Evelina Mironova, Denis Dimitrov
Text-to-image generation models have gained popularity among users around the world. However, many of these models exhibit a strong bias toward English-speaking cultures, ignoring or misrepresenting the unique characteristics of other language groups, countries, and nationalities. The lack of cultural awareness can reduce the generation quality and lead to undesirable consequences such as unintentional insult, and the spread of prejudice. In contrast to the field of natural language processing, cultural awareness in computer vision has not been explored as extensively. In this paper, we strive to reduce this gap. We propose a RusCode benchmark for evaluating the quality of text-to-image generation containing elements of the Russian cultural code. To do this, we form a list of 19 categories that best represent the features of Russian visual culture. Our final dataset consists of 1250 text prompts in Russian and their translations into English. The prompts cover a wide range of topics, including complex concepts from art, popular culture, folk traditions, famous people’s names, natural objects, scientific achievements, etc. We present the results of a human evaluation of the side-by-side comparison of Russian visual concepts representations using popular generative models.
文本到图像生成模型在全球范围内受到用户的欢迎。然而,许多这些模型对英文文化表现出强烈的偏见,忽略或错误代表其他语言群体、国家和民族的独特特征。缺乏文化意识可能会降低生成质量,并导致一些不希望的后果,如无意冒犯和偏见的传播。与自然语言处理领域不同,计算机视觉中的文化意识尚未得到广泛探索。在本文中,我们努力缩小这一差距。我们提出了一种用于评估文本到图像生成质量的RusCode基准测试,其中包含俄罗斯文化代码的元素。为此,我们形成了最能代表俄罗斯视觉文化特征的19个类别列表。我们的最终数据集包含1250个俄语文本提示及其英文翻译。提示涵盖广泛的主题,包括艺术、流行文化、民间传统、名人姓名、自然物体、科学成就等中的复杂概念。我们展示了使用流行生成模型对俄罗斯视觉概念表示进行并排比较的人类评估结果。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted for NAACL 2025 Findings, GitHub: https://github.com/ai-forever/RusCode
Summary
文本转图像生成模型受到全球用户的欢迎,但多数模型存在对英语文化偏好的问题,忽视或误代表其他语言群体、国家和民族的特征。缺乏文化意识会降低生成质量,并可能导致不良后果,如无意冒犯和传播偏见。本文旨在缩小这一差距,提出一个用于评估文本转图像生成质量的RusCode基准测试,包含俄罗斯文化代码的元素。通过形成最能代表俄罗斯视觉文化特征的19个类别,构建最终数据集,包含1250个俄语文本提示及其英文翻译。本文还介绍了使用流行生成模型进行俄罗斯视觉概念表示的人类评估结果。
Key Takeaways
- 文本转图像生成模型在全球范围内受欢迎,但存在对英语文化的偏好问题。
- 缺乏文化意识可能导致生成质量下降,甚至引发无意冒犯和传播偏见等后果。
- 本文旨在提高文化意识,提出一个评估文本转图像生成质量的基准测试——RusCode。
- RusCode包含代表俄罗斯文化代码的元素,形成19个代表俄罗斯视觉文化特征的类别。
- 最终数据集包含1250个俄语文本提示及其英文翻译,涵盖艺术、流行文化、民间传统、名人姓名、自然物体、科学成就等话题。
- 通过人类评估,对比了使用流行生成模型的俄罗斯视觉概念表示。
点此查看论文截图

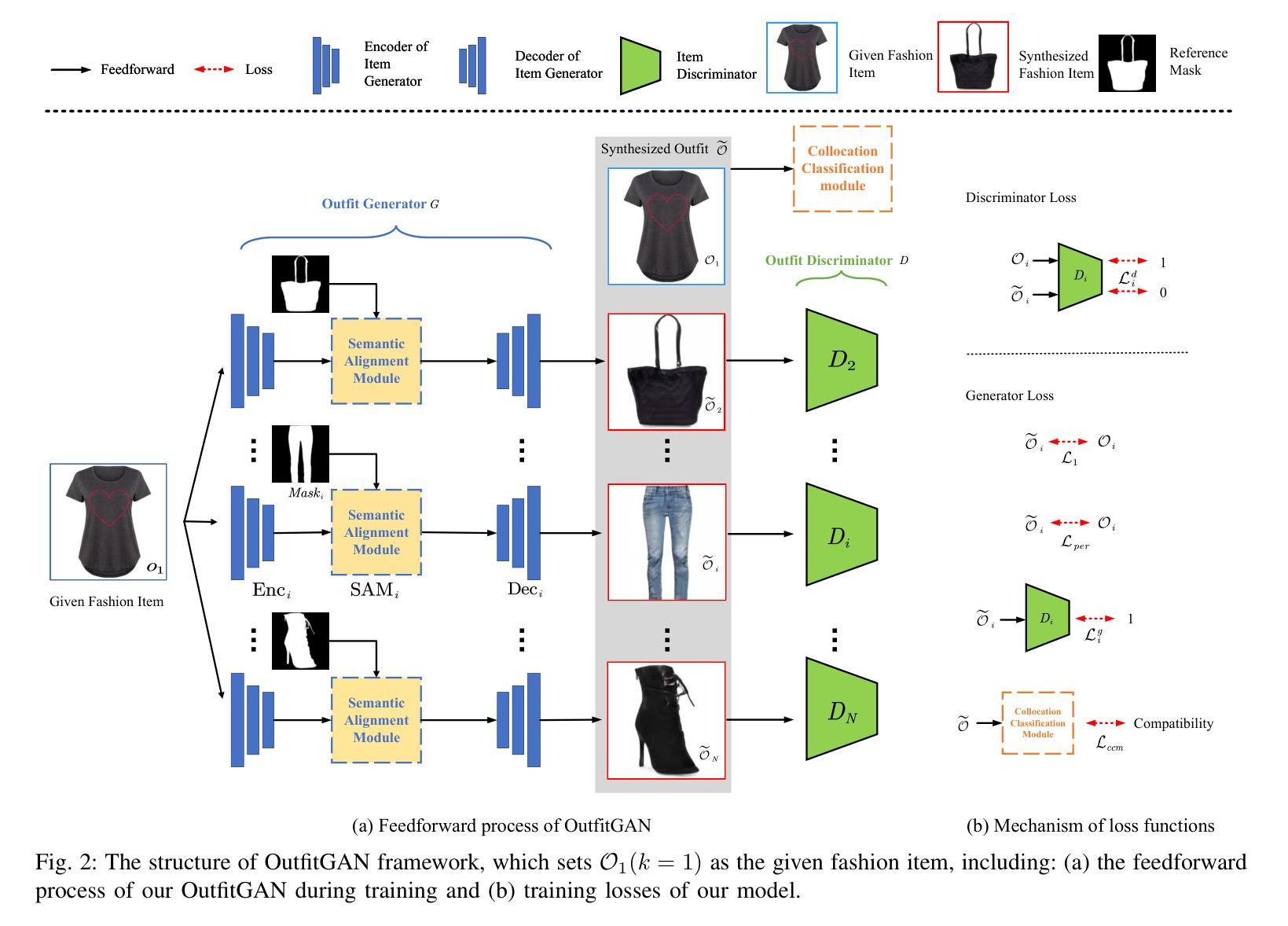
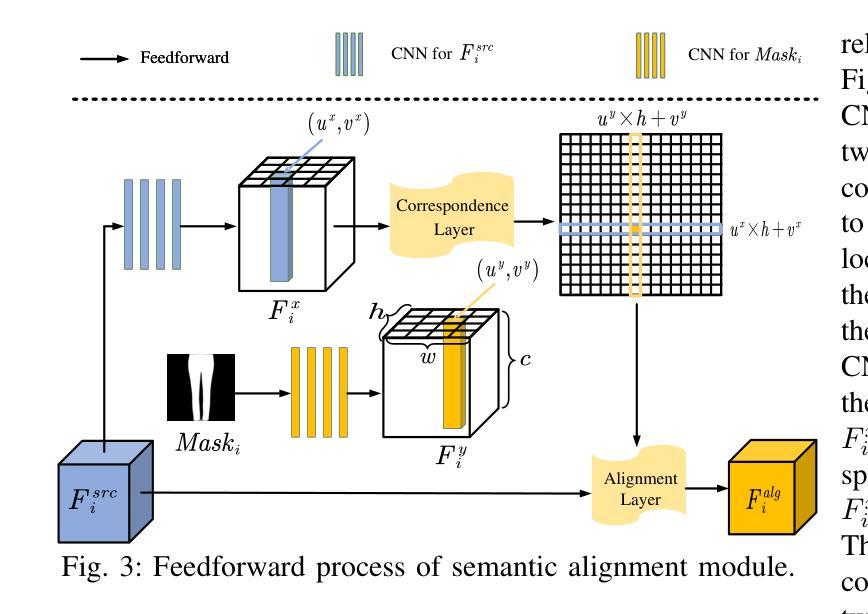
Learning to Synthesize Compatible Fashion Items Using Semantic Alignment and Collocation Classification: An Outfit Generation Framework
Authors:Dongliang Zhou, Haijun Zhang, Kai Yang, Linlin Liu, Han Yan, Xiaofei Xu, Zhao Zhang, Shuicheng Yan
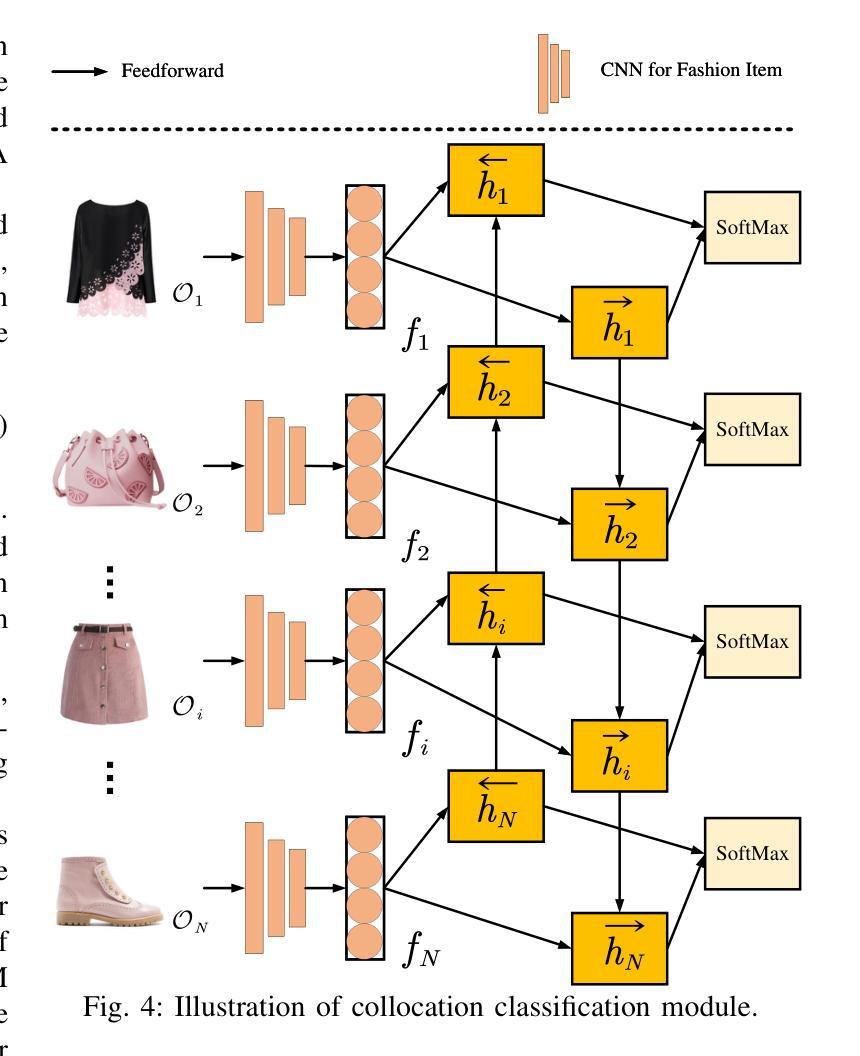
The field of fashion compatibility learning has attracted great attention from both the academic and industrial communities in recent years. Many studies have been carried out for fashion compatibility prediction, collocated outfit recommendation, artificial intelligence (AI)-enabled compatible fashion design, and related topics. In particular, AI-enabled compatible fashion design can be used to synthesize compatible fashion items or outfits in order to improve the design experience for designers or the efficacy of recommendations for customers. However, previous generative models for collocated fashion synthesis have generally focused on the image-to-image translation between fashion items of upper and lower clothing. In this paper, we propose a novel outfit generation framework, i.e., OutfitGAN, with the aim of synthesizing a set of complementary items to compose an entire outfit, given one extant fashion item and reference masks of target synthesized items. OutfitGAN includes a semantic alignment module, which is responsible for characterizing the mapping correspondence between the existing fashion items and the synthesized ones, to improve the quality of the synthesized images, and a collocation classification module, which is used to improve the compatibility of a synthesized outfit. In order to evaluate the performance of our proposed models, we built a large-scale dataset consisting of 20,000 fashion outfits. Extensive experimental results on this dataset show that our OutfitGAN can synthesize photo-realistic outfits and outperform state-of-the-art methods in terms of similarity, authenticity and compatibility measurements.
近年来,时尚搭配学习领域引起了学术界和工业界的广泛关注。关于时尚搭配预测、搭配服饰推荐、人工智能(AI)支持的兼容时尚设计以及相关主题,已经进行了许多研究。特别是,AI支持的兼容时尚设计可用于合成兼容的时尚单品或搭配,以提高设计师的设计体验或提高客户推荐的效率。然而,之前用于合成搭配的生成模型一般主要关注上下衣之间图像到图像的翻译。在本文中,我们提出了一种新的服饰生成框架,即OutfitGAN,它的目标是在给定一个现有的时尚单品和目标合成单品的参考掩模的情况下,合成一系列互补单品以组成一套完整的搭配。OutfitGAN包括一个语义对齐模块,负责表征现有时尚单品和合成单品之间的映射对应关系,以提高合成图像的质量,以及一个搭配分类模块,用于提高合成搭配的兼容性。为了评估我们提出的模型性能,我们构建了一个包含2万套时尚搭配的大规模数据集。在该数据集上的大量实验结果表明,我们的OutfitGAN能够合成逼真的搭配,并在相似性、真实性和兼容性测量方面优于现有最新方法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF This paper was accepted by IEEE TNNLS
Summary:
本文提出了一个新颖的服饰生成框架OutfitGAN,旨在通过合成一系列互补的服饰单品来组成一套完整的服饰。该框架包括语义对齐模块和搭配分类模块,旨在提高合成图像的质量和服饰的兼容性。实验结果表明,OutfitGAN能够合成逼真的服饰并在相似性、真实性和兼容性方面超越现有方法。
Key Takeaways:
- 时尚兼容性学习领域近年来受到学术界和工业界的广泛关注。
- AI技术可用于进行时尚兼容性预测、搭配推荐和兼容时尚设计。
- 现有生成模型主要关注上下装之间的图像到图像翻译。
- 本文提出了一个新颖的服饰生成框架OutfitGAN,能够合成一系列互补的服饰单品来组成一套完整的服饰。
- OutfitGAN包括语义对齐模块,负责表征现有服饰单品与合成单品之间的映射对应关系,以提高合成图像的质量。
- OutfitGAN还包括一个搭配分类模块,旨在提高合成服饰的兼容性。
点此查看论文截图

UniDB: A Unified Diffusion Bridge Framework via Stochastic Optimal Control
Authors:Kaizhen Zhu, Mokai Pan, Yuexin Ma, Yanwei Fu, Jingyi Yu, Jingya Wang, Ye Shi
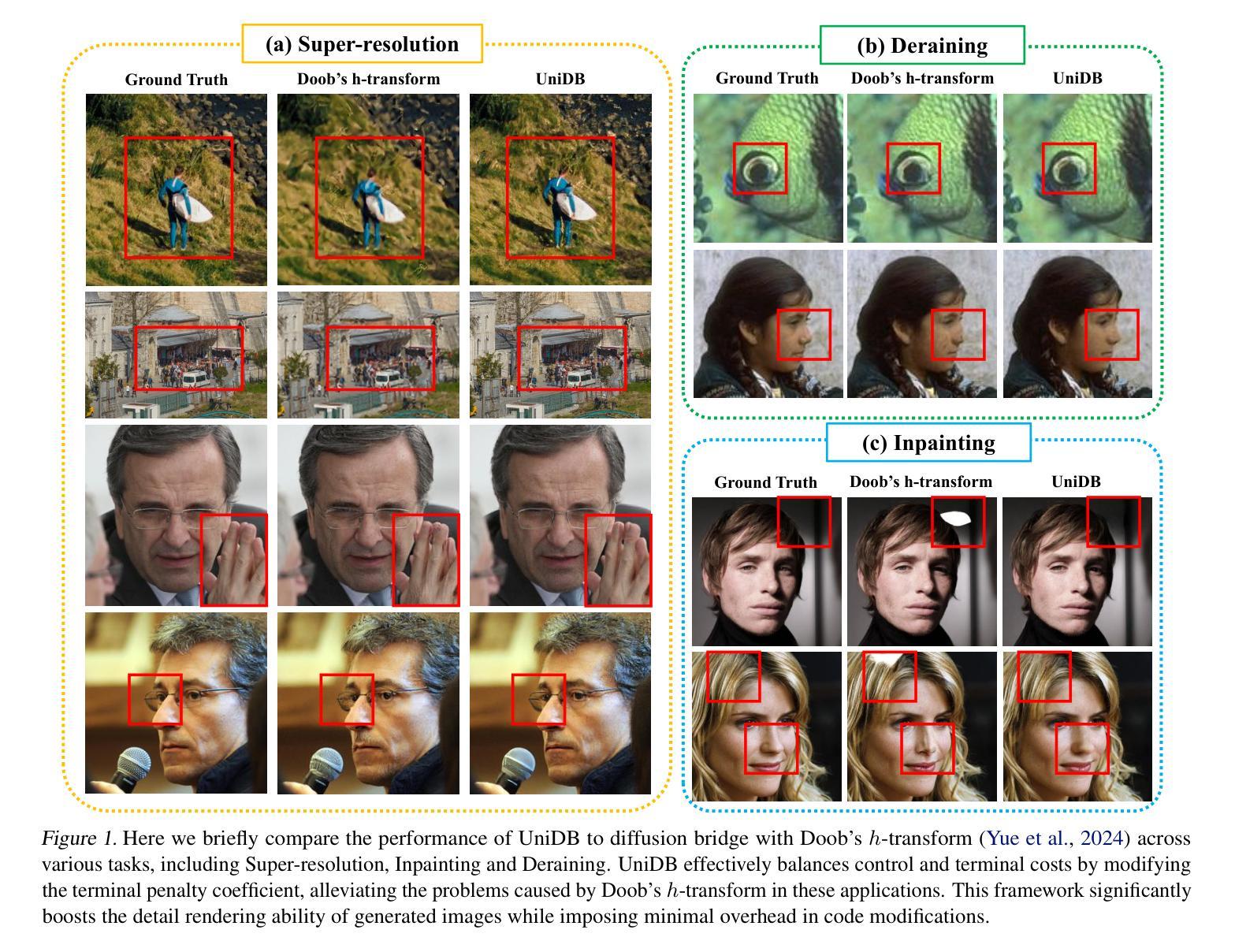
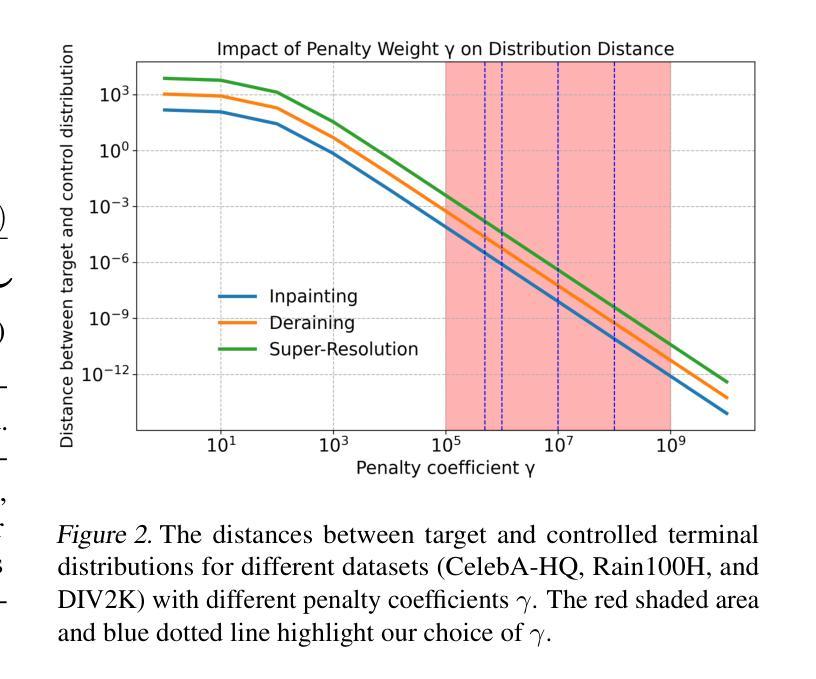
Recent advances in diffusion bridge models leverage Doob’s $h$-transform to establish fixed endpoints between distributions, demonstrating promising results in image translation and restoration tasks. However, these approaches frequently produce blurred or excessively smoothed image details and lack a comprehensive theoretical foundation to explain these shortcomings. To address these limitations, we propose UniDB, a unified framework for diffusion bridges based on Stochastic Optimal Control (SOC). UniDB formulates the problem through an SOC-based optimization and derives a closed-form solution for the optimal controller, thereby unifying and generalizing existing diffusion bridge models. We demonstrate that existing diffusion bridges employing Doob’s $h$-transform constitute a special case of our framework, emerging when the terminal penalty coefficient in the SOC cost function tends to infinity. By incorporating a tunable terminal penalty coefficient, UniDB achieves an optimal balance between control costs and terminal penalties, substantially improving detail preservation and output quality. Notably, UniDB seamlessly integrates with existing diffusion bridge models, requiring only minimal code modifications. Extensive experiments across diverse image restoration tasks validate the superiority and adaptability of the proposed framework. Our code is available at https://github.com/UniDB-SOC/UniDB/.
近期扩散桥模型的新进展利用Doob的$h$-变换在分布之间建立固定端点,在图像翻译和恢复任务中展现出有前景的结果。然而,这些方法经常产生模糊或过度平滑的图像细节,并且缺乏全面的理论基础来解释这些不足。为了解决这些局限性,我们提出了基于随机最优控制(SOC)的扩散桥统一框架UniDB。UniDB通过基于SOC的优化来制定问题,并推导出最优控制器的封闭形式解决方案,从而统一并推广现有的扩散桥模型。我们证明,采用Doob的$h$-变换的现有扩散桥构成了我们框架的一种特殊情况,出现在SOC成本函数的终端惩罚系数趋于无穷大时。通过引入可调终端惩罚系数,UniDB实现了控制成本与终端惩罚之间的最佳平衡,大大提高了细节保留和输出质量。值得注意的是,UniDB可以无缝地融入现有的扩散桥模型,只需进行最小的代码修改。在不同图像恢复任务上的广泛实验验证了所提出框架的优越性和适应性。我们的代码位于https://github.com/UniDB-SOC/UniDB/。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于随机最优控制(SOC)的UniDB统一框架,通过解决扩散桥梁模型中的短板,有效改进了图像翻译和恢复任务。该框架解决了现有扩散桥梁模型产生的模糊或过度平滑图像细节的问题,并通过引入可调终端惩罚系数,实现了控制成本与终端惩罚之间的最优平衡,提高了细节保留和输出质量。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散桥梁模型利用Doob的$h$-变换在分布之间建立固定端点,在图像翻译和恢复任务中展现出有前景的结果。
- 现有方法常产生模糊或过度平滑的图像细节,且缺乏全面理论来解释这些短板。
- UniDB基于随机最优控制(SOC)提出统一框架,解决扩散桥梁问题并导出最优控制器的封闭形式解决方案。
- UniDB将现有使用Doob的$h$-变换的扩散桥梁视为框架的特殊情形,当SOC成本函数中的终端惩罚系数趋于无穷时。
- 通过引入可调终端惩罚系数,UniDB在控制成本与终端惩罚之间达到最优平衡,改善细节保留和输出质量。
- UniDB与现有扩散桥梁模型无缝集成,只需最小代码修改。
点此查看论文截图

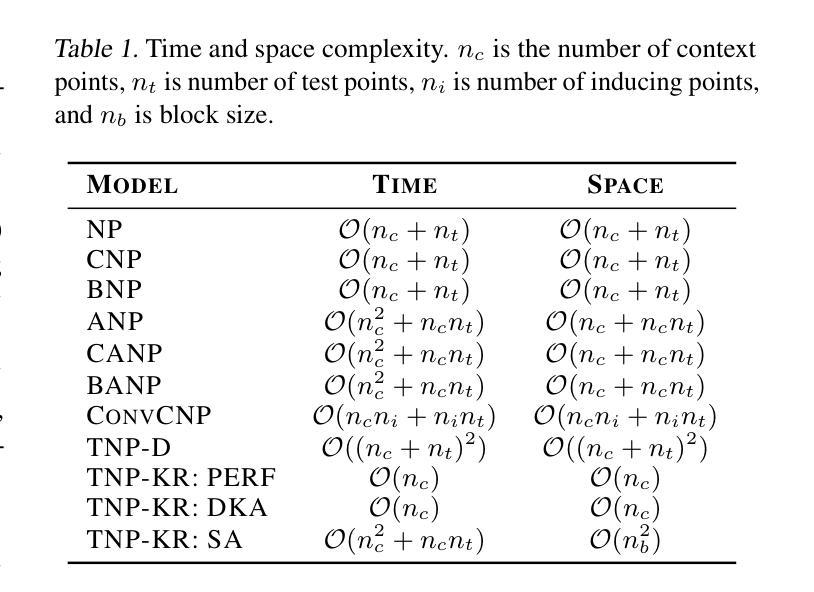
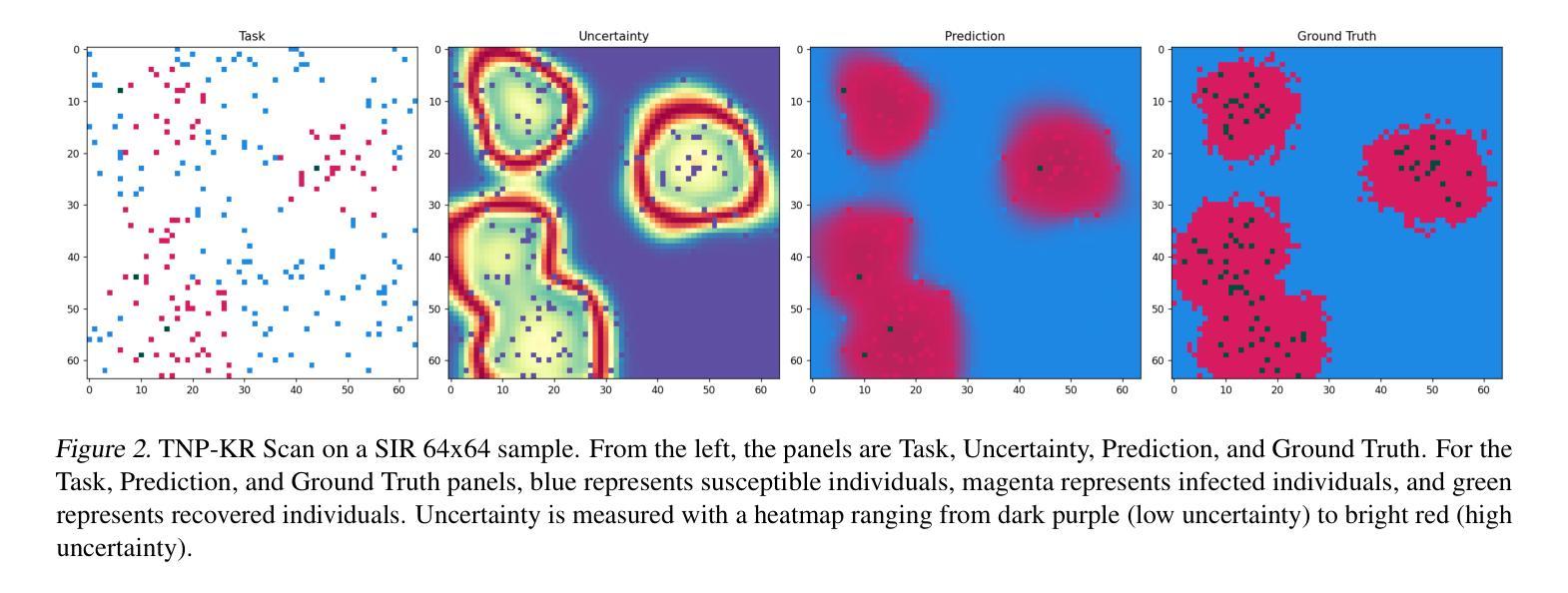
Transformer Neural Processes - Kernel Regression
Authors:Daniel Jenson, Jhonathan Navott, Mengyan Zhang, Makkunda Sharma, Elizaveta Semenova, Seth Flaxman
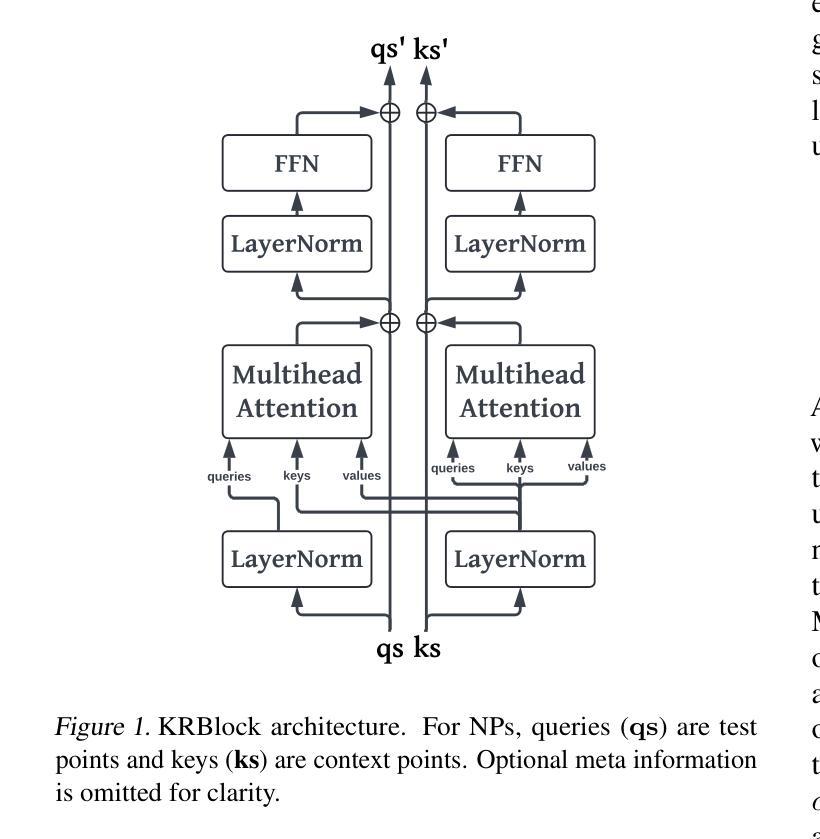
Neural Processes (NPs) are a rapidly evolving class of models designed to directly model the posterior predictive distribution of stochastic processes. Originally developed as a scalable alternative to Gaussian Processes (GPs), which are limited by $O(n^3)$ runtime complexity, the most accurate modern NPs can often rival GPs but still suffer from an $O(n^2)$ bottleneck due to their attention mechanism. We introduce the Transformer Neural Process - Kernel Regression (TNP-KR), a scalable NP featuring: (1) a Kernel Regression Block (KRBlock), a simple, extensible, and parameter efficient transformer block with complexity $O(n_c^2 + n_c n_t)$, where $n_c$ and $n_t$ are the number of context and test points, respectively; (2) a kernel-based attention bias; and (3) two novel attention mechanisms: scan attention (SA), a memory-efficient scan-based attention that when paired with a kernel-based bias can make TNP-KR translation invariant, and deep kernel attention (DKA), a Performer-style attention that implicitly incoporates a distance bias and further reduces complexity to $O(n_c)$. These enhancements enable both TNP-KR variants to perform inference with 100K context points on over 1M test points in under a minute on a single 24GB GPU. On benchmarks spanning meta regression, Bayesian optimization, image completion, and epidemiology, TNP-KR with DKA outperforms its Performer counterpart on nearly every benchmark, while TNP-KR with SA achieves state-of-the-art results.
神经过程(NPs)是一类快速演变的模型,旨在直接对随机过程的后验预测分布进行建模。最初作为高斯过程(GPs)的可扩展替代方案而开发,高斯过程受到$O(n^3)$运行时间复杂度的限制,而现代最准确的神经过程往往可以与高斯过程相竞争,但由于其注意力机制,仍然受到$O(n^2)$瓶颈的限制。我们介绍了Transformer神经过程-核回归(TNP-KR),这是一种可扩展的NP,具有以下特点:(1)核回归块(KRBlock),这是一种简单、可扩展、参数高效的变压器块,复杂度为$O(n_c^2 + n_c n_t)$,其中$n_c$和$n_t$分别是上下文点和测试点的数量;(2)基于核的注意力偏差;(3)两种新型注意力机制:扫描注意力(SA),这是一种基于扫描的、内存高效的注意力,与基于核的偏差相结合,可以使TNP-KR具有平移不变性;深度核注意力(DKA),这是一种隐式包含距离偏差的Performer风格的注意力,进一步将复杂度降低到$O(n_c)$。这些增强功能使TNP-KR的两个变体能够在单个24GB GPU上在一分钟内对超过一百万测试点进行一万个上下文点的推理。在涵盖元回归、贝叶斯优化、图像补全和流行病学等多个基准测试中,带有DKA的TNP-KR在几乎每个基准测试中都超过了其Performer对手,而带有SA的TNP-KR则实现了最新结果。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
神经网络过程(NPs)是一类直接模拟随机过程后验预测分布的模型。作为一种可扩展的替代高斯过程(GPs)的模型,神经网络过程最初克服了GPs的O(n^3)运行时间复杂度限制。我们引入Transformer神经网络过程-核回归(TNP-KR),这是一种可扩展的NP,具有以下特点:简单的核回归块(KRBlock);基于核的注意力偏差;两种新型注意力机制:扫描注意力(SA)和深度核注意力(DKA)。这些改进使得TNP-KR能够在单个24GB GPU上在一分钟内完成对超过一百万测试点的一万点进行推断。在涵盖元回归、贝叶斯优化、图像补全和流行病学等领域的基准测试中,TNP-KR优于其表演者竞品,实现了卓越的结果。
Key Takeaways
- 神经网络过程(NPs)直接模拟随机过程的后验预测分布。
- TNP-KR作为一种可扩展的NP模型,旨在解决高斯过程(GPs)的运算瓶颈。
- TNP-KR引入了Kernel Regression Block(KRBlock),具有简单、可扩展和参数高效的特性。
- TNP-KR采用了基于核的注意力偏差和两种新型注意力机制:扫描注意力(SA)和深度核注意力(DKA)。
- TNP-KR能够处理大量的上下文点和测试点,实现高效推断。
- TNP-KR在多个领域,包括元回归、贝叶斯优化、图像补全和流行病学等基准测试中表现优异。
点此查看论文截图

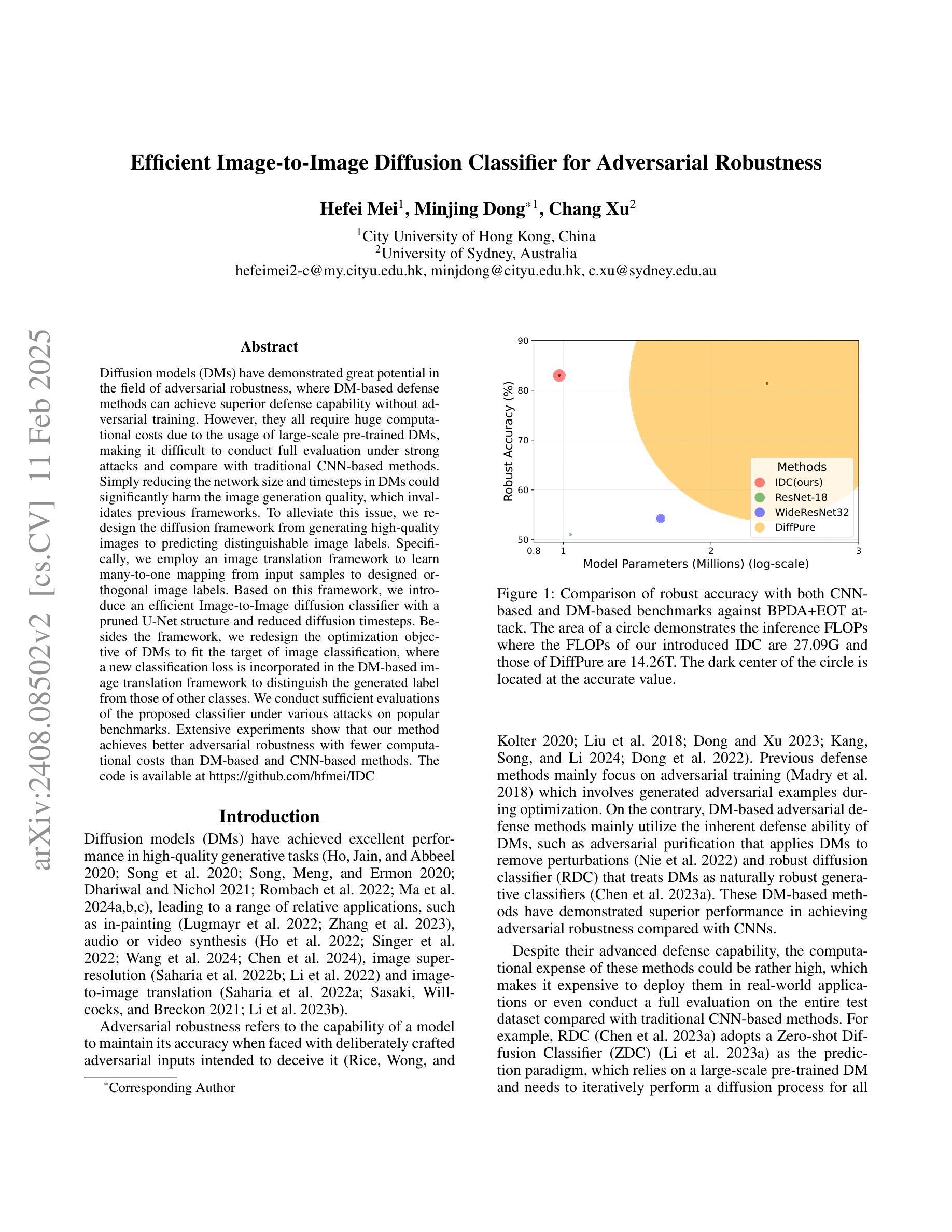
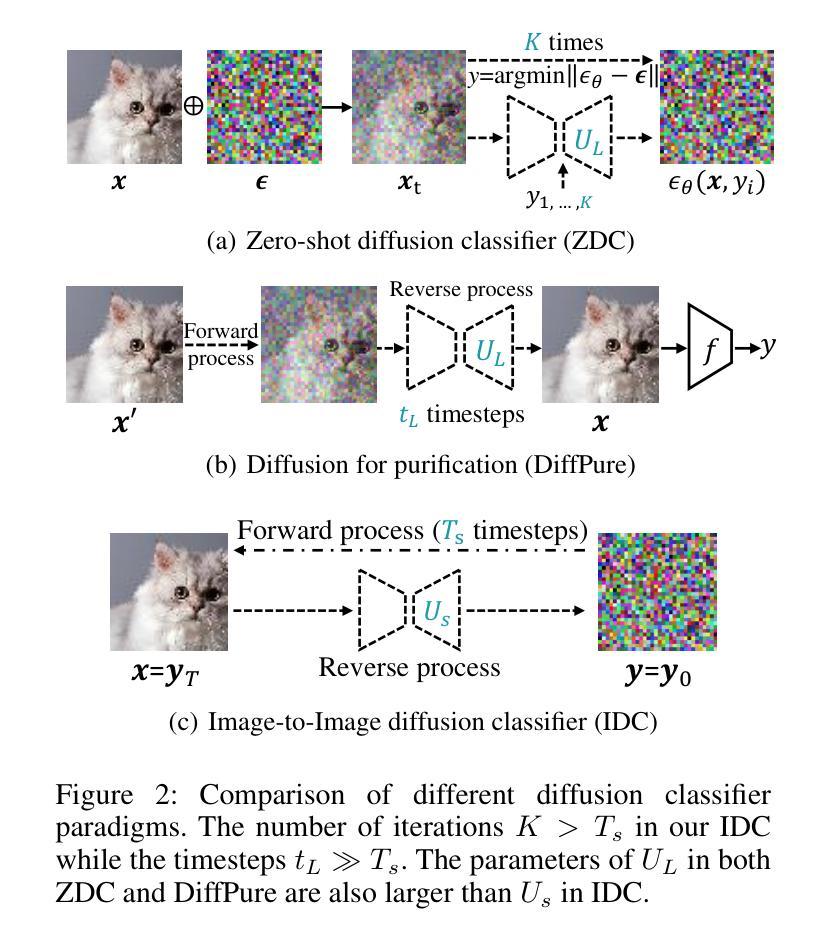
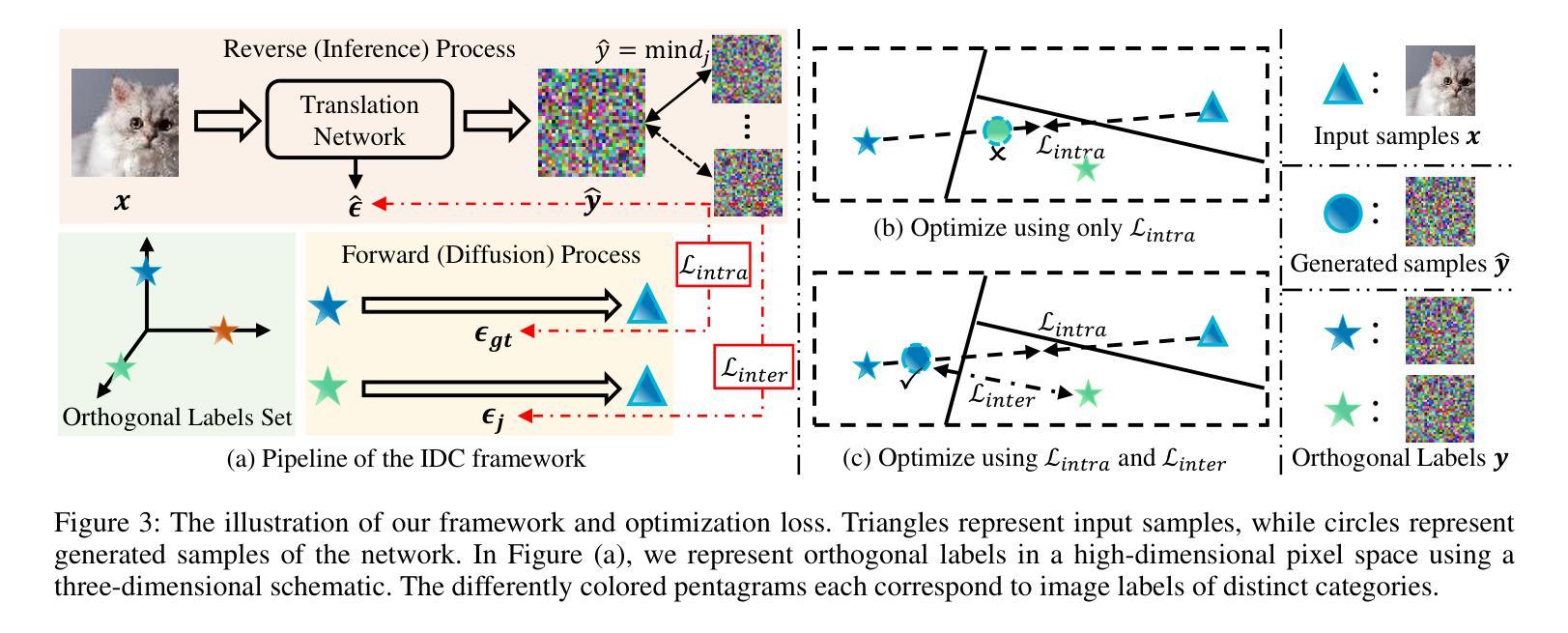
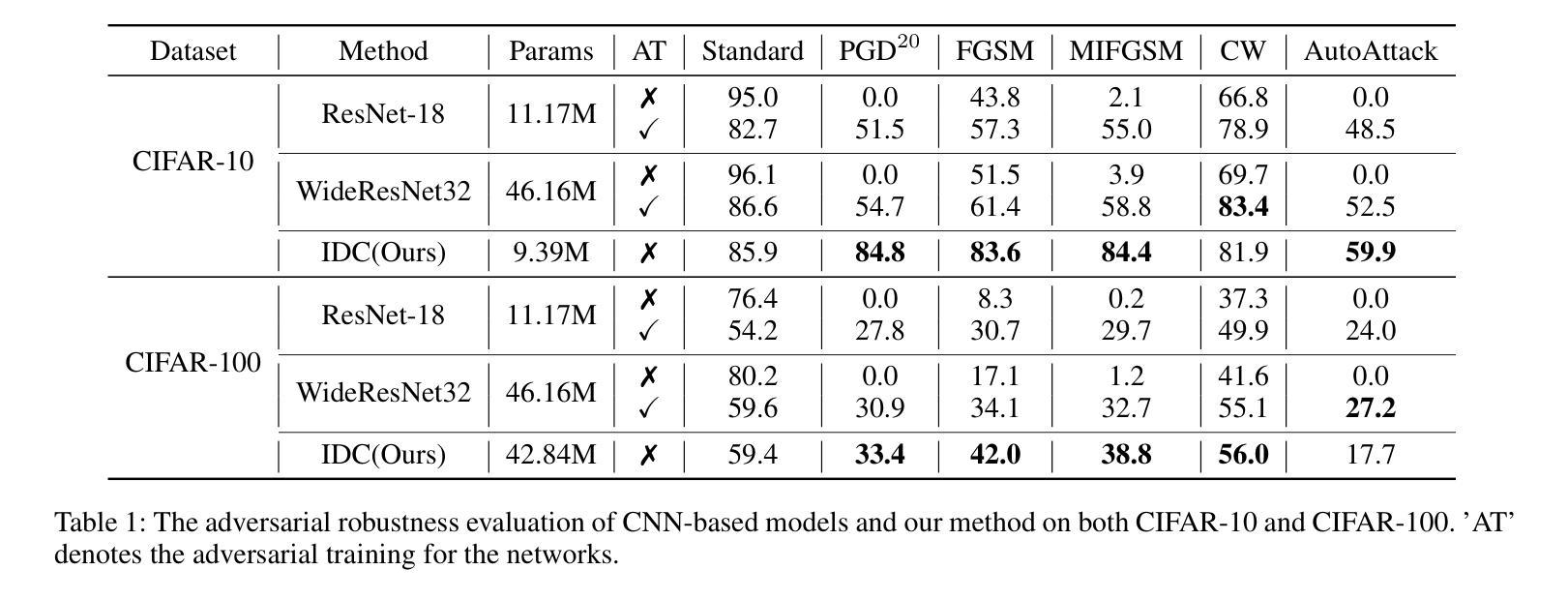
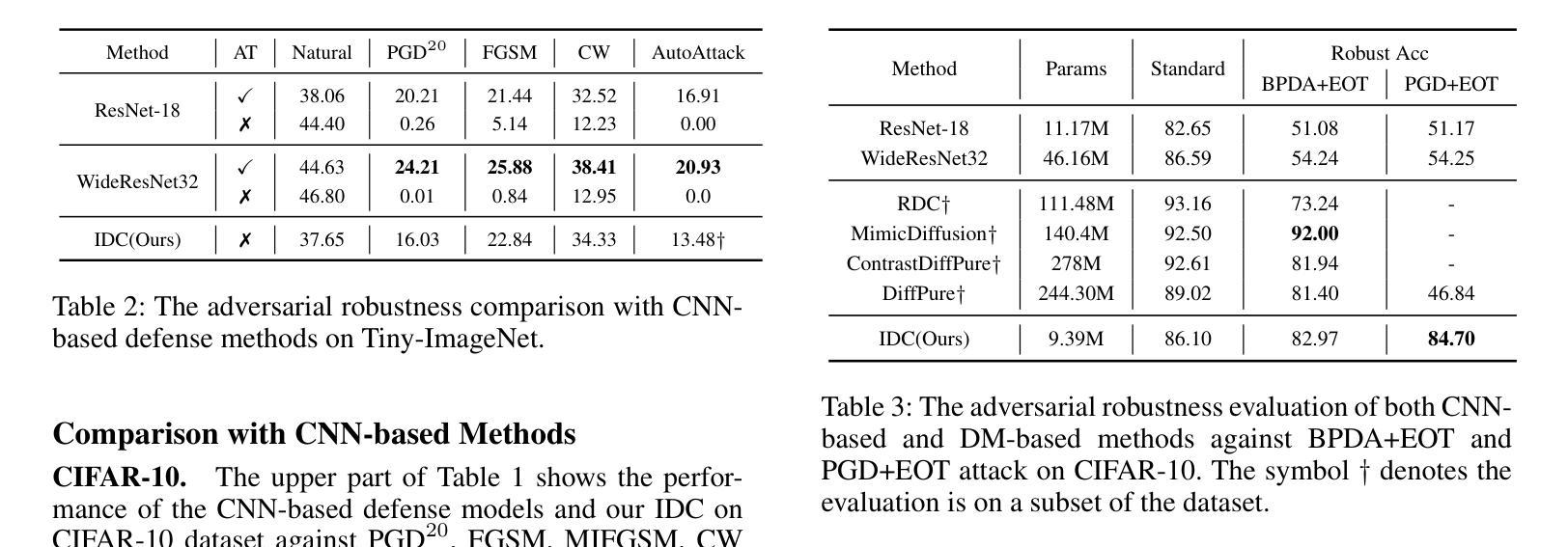
Efficient Image-to-Image Diffusion Classifier for Adversarial Robustness
Authors:Hefei Mei, Minjing Dong, Chang Xu
Diffusion models (DMs) have demonstrated great potential in the field of adversarial robustness, where DM-based defense methods can achieve superior defense capability without adversarial training. However, they all require huge computational costs due to the usage of large-scale pre-trained DMs, making it difficult to conduct full evaluation under strong attacks and compare with traditional CNN-based methods. Simply reducing the network size and timesteps in DMs could significantly harm the image generation quality, which invalidates previous frameworks. To alleviate this issue, we redesign the diffusion framework from generating high-quality images to predicting distinguishable image labels. Specifically, we employ an image translation framework to learn many-to-one mapping from input samples to designed orthogonal image labels. Based on this framework, we introduce an efficient Image-to-Image diffusion classifier with a pruned U-Net structure and reduced diffusion timesteps. Besides the framework, we redesign the optimization objective of DMs to fit the target of image classification, where a new classification loss is incorporated in the DM-based image translation framework to distinguish the generated label from those of other classes. We conduct sufficient evaluations of the proposed classifier under various attacks on popular benchmarks. Extensive experiments show that our method achieves better adversarial robustness with fewer computational costs than DM-based and CNN-based methods. The code is available at https://github.com/hfmei/IDC
扩散模型(DMs)在对抗稳健性领域表现出了巨大的潜力,该领域中的DMs防御方法可以在无需对抗训练的情况下实现出色的防御能力。然而,由于使用了大规模的预训练DMs,所有这些方法都需要巨大的计算成本,使得在强攻击下进行全面评估和与传统基于CNN的方法进行比较变得困难。简单缩小DMs的网络规模和减少时间步长可能会极大地损害图像生成质量,从而使现有框架失效。为了缓解这一问题,我们重新设计了扩散框架,从生成高质量图像转向预测可区分的图像标签。具体来说,我们采用图像翻译框架来学习从输入样本到设计的正交图像标签的多对一映射。基于这一框架,我们引入了一种高效的图像到图像的扩散分类器,它具有修剪的U-Net结构和减少的扩散时间步长。除了框架之外,我们还重新设计了DMs的优化目标以适应图像分类的目标,在基于DM的图像翻译框架中融入新的分类损失来区分生成的标签与其他类别的标签。我们在流行的基准测试上对提出的分类器进行了各种攻击下的充分评估。大量实验表明,我们的方法在计算成本更低的情况下实现了比基于DM和基于CNN的方法更好的对抗稳健性。代码可在https://github.com/hfmei/IDC找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了扩散模型(DMs)在对抗鲁棒性领域的应用。针对DMs计算成本高的问题,提出了一种新的图像分类扩散模型。该方法采用图像翻译框架,通过许多一对一的映射方式生成设计正交图像标签。优化后的模型具有更高的对抗鲁棒性和更低的计算成本。相关代码已发布在GitHub上。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型在对抗鲁棒性领域具有巨大潜力,无需对抗训练即可实现出色的防御能力。
- 现有的扩散模型计算成本高,难以在强攻击下进行全面评估并与传统的CNN方法进行比较。
- 提出了一种新的图像分类扩散模型,通过图像翻译框架实现输入样本到设计正交图像标签的映射。
- 引入了具有修剪U-Net结构和减少扩散时步的高效图像到图像的扩散分类器。
- 对DM的优化目标进行了重新设计,以适应图像分类的目标,将新的分类损失纳入DM基于图像翻译框架中,以区分生成的标签与其他类别的标签。
- 在流行的基准测试上进行了充分的评估,实验结果表明该方法在对抗鲁棒性方面表现更好,计算成本更低,优于DM和CNN方法。
点此查看论文截图