⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-02-13 更新
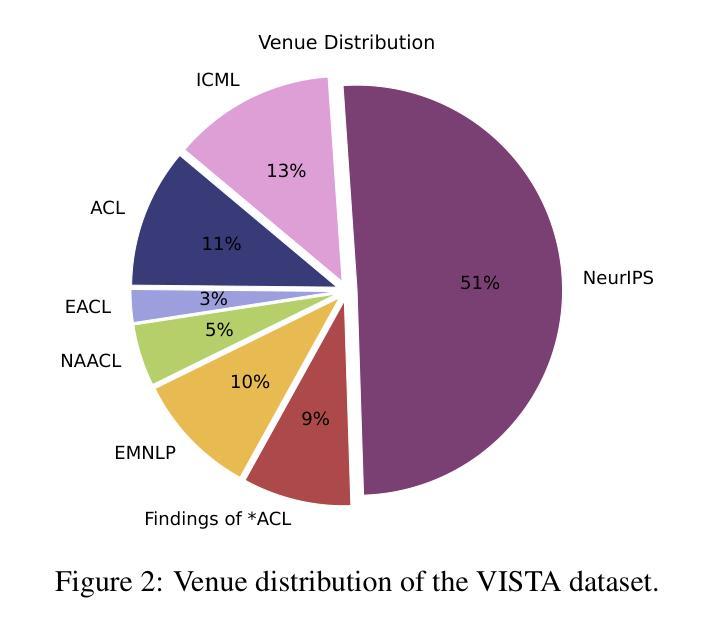
Grammar Control in Dialogue Response Generation for Language Learning Chatbots
Authors:Dominik Glandorf, Peng Cui, Detmar Meurers, Mrinmaya Sachan
Chatbots based on large language models offer cheap conversation practice opportunities for language learners. However, they are hard to control for linguistic forms that correspond to learners’ current needs, such as grammar. We control grammar in chatbot conversation practice by grounding a dialogue response generation model in a pedagogical repository of grammar skills. We also explore how this control helps learners to produce specific grammar. We comprehensively evaluate prompting, fine-tuning, and decoding strategies for grammar-controlled dialogue response generation. Strategically decoding Llama3 outperforms GPT-3.5 when tolerating minor response quality losses. Our simulation predicts grammar-controlled responses to support grammar acquisition adapted to learner proficiency. Existing language learning chatbots and research on second language acquisition benefit from these affordances. Code available on GitHub.
基于大型语言模型的聊天机器人为语言学习者提供了廉价的对话实践机会。然而,它们难以控制与学习者当前需求相对应的语言形式,例如语法。我们通过将对话响应生成模型根植于语法技能的教研存储库中来控制聊天机器人对话练习中的语法。我们还探索了这种控制如何帮助学习者产生特定的语法。我们全面评估了用于语法控制对话响应生成的提示、微调和解码策略。在容忍轻微响应质量损失的情况下,策略解码Llama3的表现优于GPT-3.5。我们的模拟预测了受控语法的响应,以支持适应学习者水平的语法习得。现有的语言学习聊天机器人和第二语言习得研究都从这些优势中获益。代码已在GitHub上提供。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to NAACL 2025
Summary
大型语言模型基础的聊天机器人为语言学习者提供了廉价的对话实践机会,但难以控制符合学习者当前需求的语法等语言形式。研究通过对话响应生成模型与语法技能的教研库结合来控制聊天机器人对话实践中的语法,并探索其对学习者产出特定语法的影响。评估了语法控制对话响应生成的提示、微调和解码策略,发现战略解码Llama3在容忍轻微响应质量损失的情况下优于GPT-3.5。模拟预测语法控制的响应有助于适应学习者水平的语法习得。此研究对现有的语言学习聊天机器人和第二语言习得研究具有益处。GitHub上有相关代码可用。
Key Takeaways
- 聊天机器人基于大型语言模型为语言学习者提供对话实践机会。
- 聊天机器人难以控制语言学习者的语法实践。
- 研究通过将对话响应生成模型与教研库结合来解决这一问题。
- 研究评估了控制语法的对话响应生成的多种策略,发现战略解码Llama3表现较好。
- 语法控制的响应有助于适应学习者水平的语法习得。
- 此研究对现有的语言学习聊天机器人和第二语言习得研究有积极影响。
点此查看论文截图


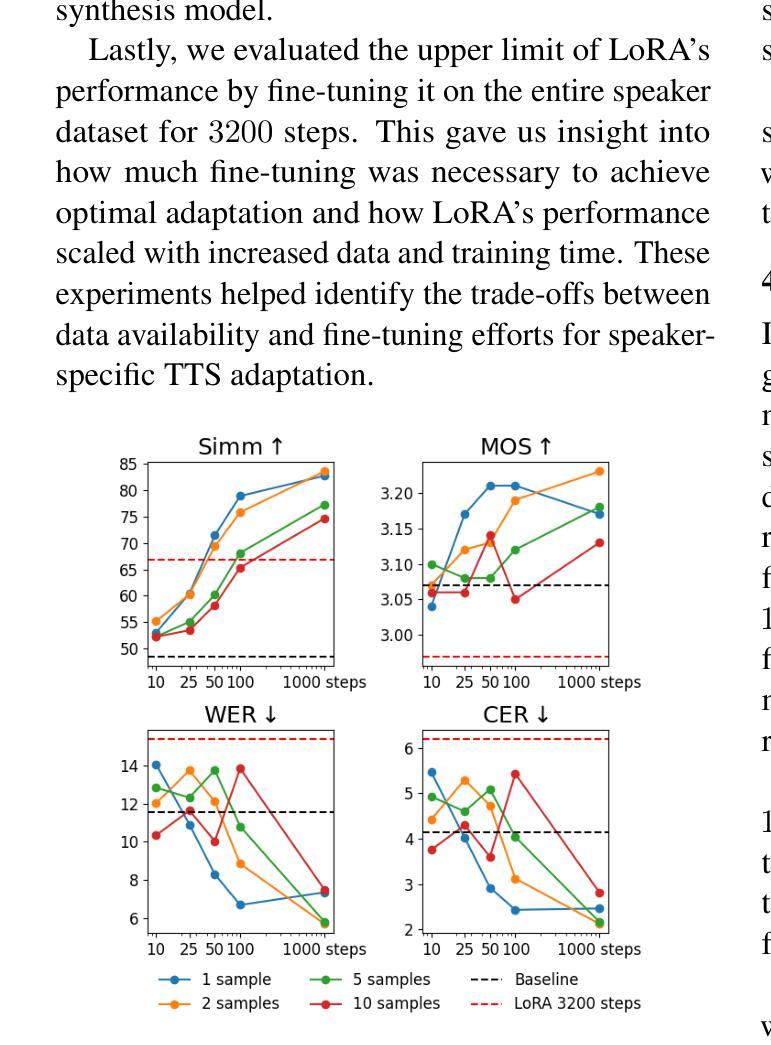
The Evolution of Machine Learning Potentials for Molecules, Reactions and Materials
Authors:Junfan Xia, Yaolong Zhang, Bin Jiang
Recent years have witnessed the fast development of machine learning potentials (MLPs) and their widespread applications in chemistry, physics, and material science. By fitting discrete ab initio data faithfully to continuous and symmetry-preserving mathematical forms, MLPs have enabled accurate and efficient atomistic simulations in a large scale from first principles. In this review, we provide an overview of the evolution of MLPs in the past two decades and focus on the state-of-the-art MLPs proposed in the last a few years for molecules, reactions, and materials. We discuss some representative applications of MLPs and the trend of developing universal potentials across a variety of systems. Finally, we outline a list of open challenges and opportunities in the development and applications of MLPs.
近年来,机器学习势(MLPs)得到了快速发展,并在化学、物理和材料科学等领域得到了广泛应用。通过将离散的第一原理数据忠实拟合到连续且保持对称性的数学形式中,机器学习势能实现了从第一原理进行大规模原子模拟的准确性和高效性。在这篇综述中,我们概述了机器学习势在过去的二十年中的发展,并重点关注了最近几年针对分子、反应和材料提出的最新机器学习势。我们讨论了一些代表性的机器学习势的应用和在不同系统中开发通用势的趋势。最后,我们概述了机器学习中发展潜力与应用的一系列开放挑战和机遇。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 84 pages,8 figures
Summary
机器学习潜能(MLPs)快速发展并在化学、物理学和材料科学领域广泛应用。通过将离散从头数据拟合到连续和保持对称性的数学形式,MLPs可实现大规模的第一性原理原子模拟,既准确又高效。本文回顾了MLPs过去二十年的演变,重点介绍了最近几年针对分子、反应和材料提出的最新MLPs。讨论了代表性应用和跨系统发展通用潜能的趋势,并概述了MLPs发展和应用中的开放挑战和机遇。
Key Takeaways
- 机器学习潜能(MLPs)在化学、物理学和材料科学领域得到广泛应用。
- MLPs能通过拟合离散数据到数学形式,实现大规模的第一性原理原子模拟。
- 文章回顾了MLPs过去二十年的演变,并重点关注了最近几年针对分子、反应和材料的最新MLPs。
- MLPs的代表性应用和跨系统发展通用潜能的趋势被讨论。
- MLPs在发展和应用方面仍面临一些开放挑战和机遇。
- 文章指出,需要进一步研究和解决一些关键问题,以推动MLPs的发展。
点此查看论文截图

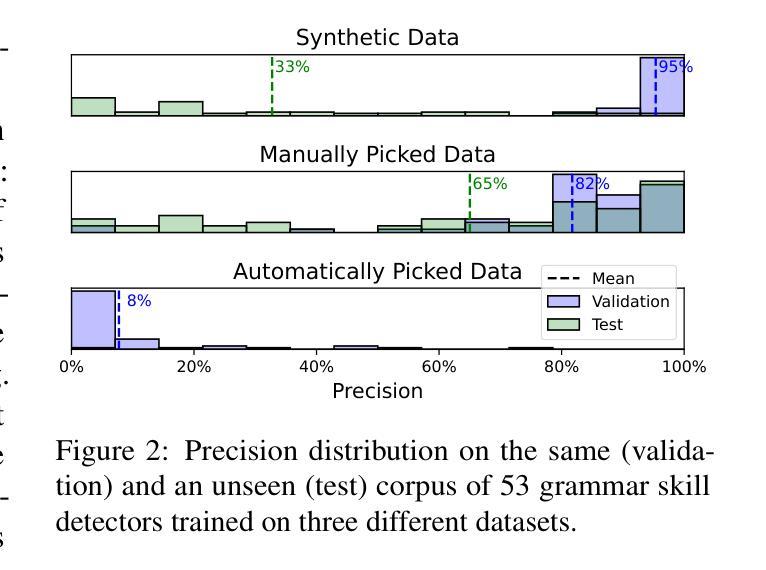
Generation of Drug-Induced Cardiac Reactions towards Virtual Clinical Trials
Authors:Qian Shao, Bang Du, Zepeng Li, Qiyuan Chen, Hongxia Xu, Jimeng Sun, Jian Wu, Jintai Chen
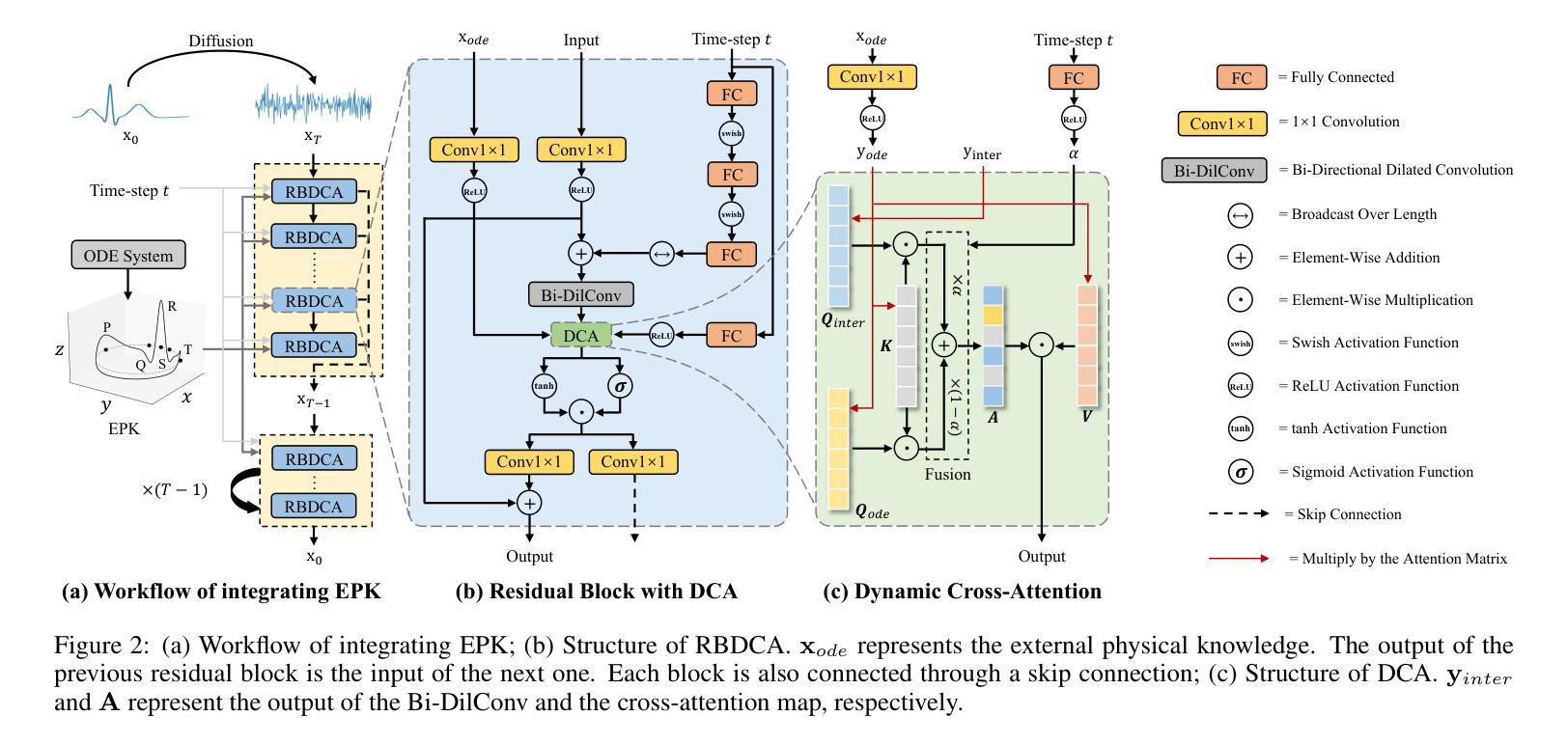
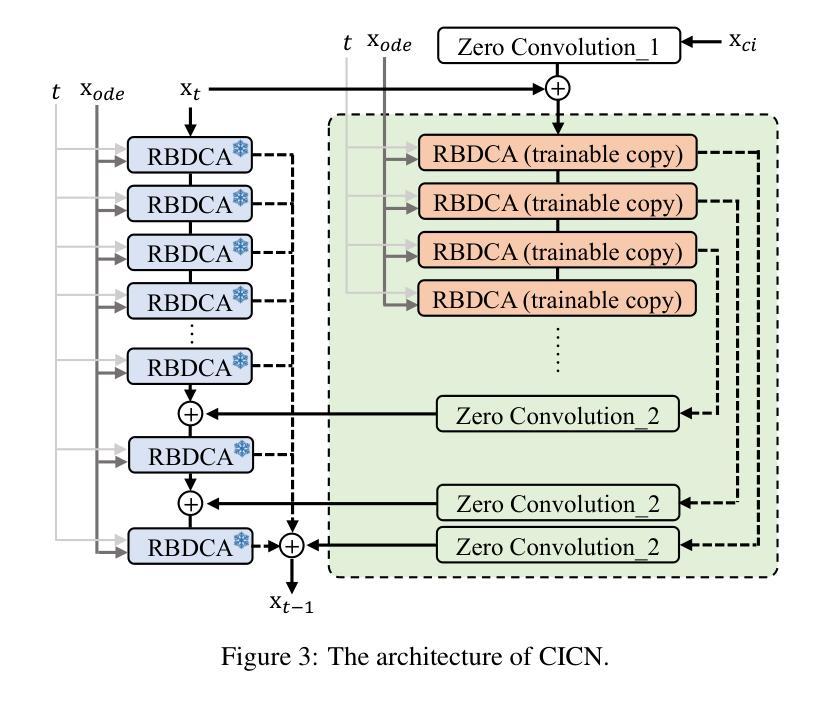
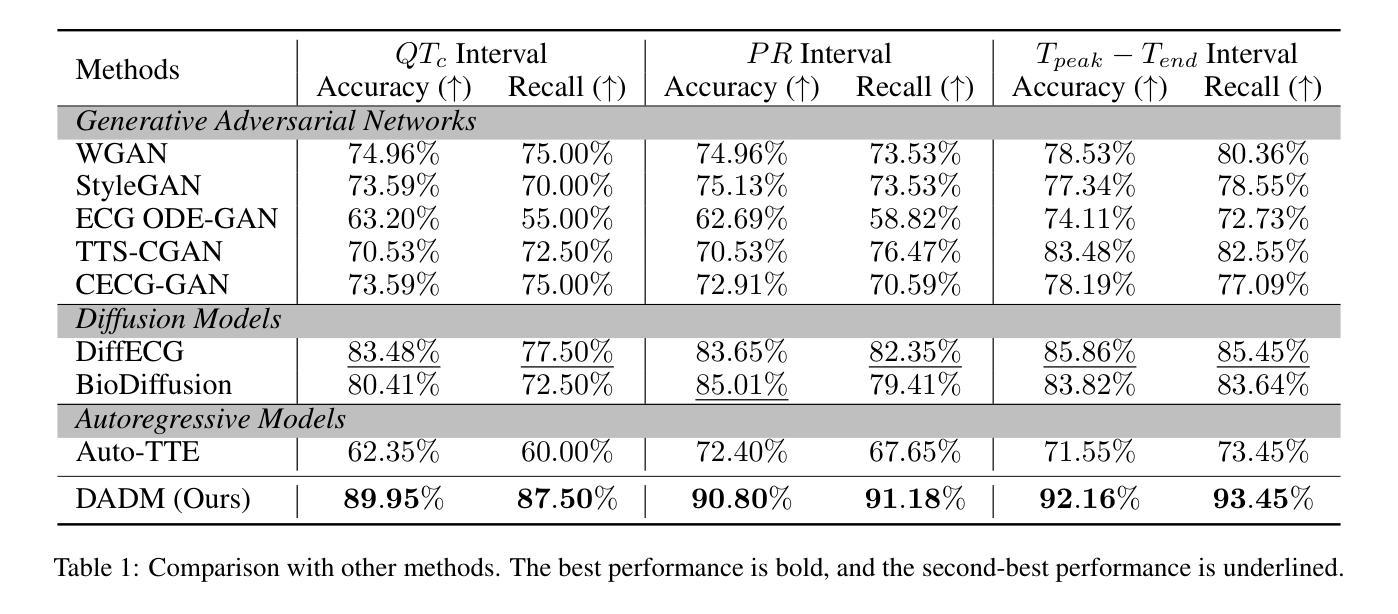
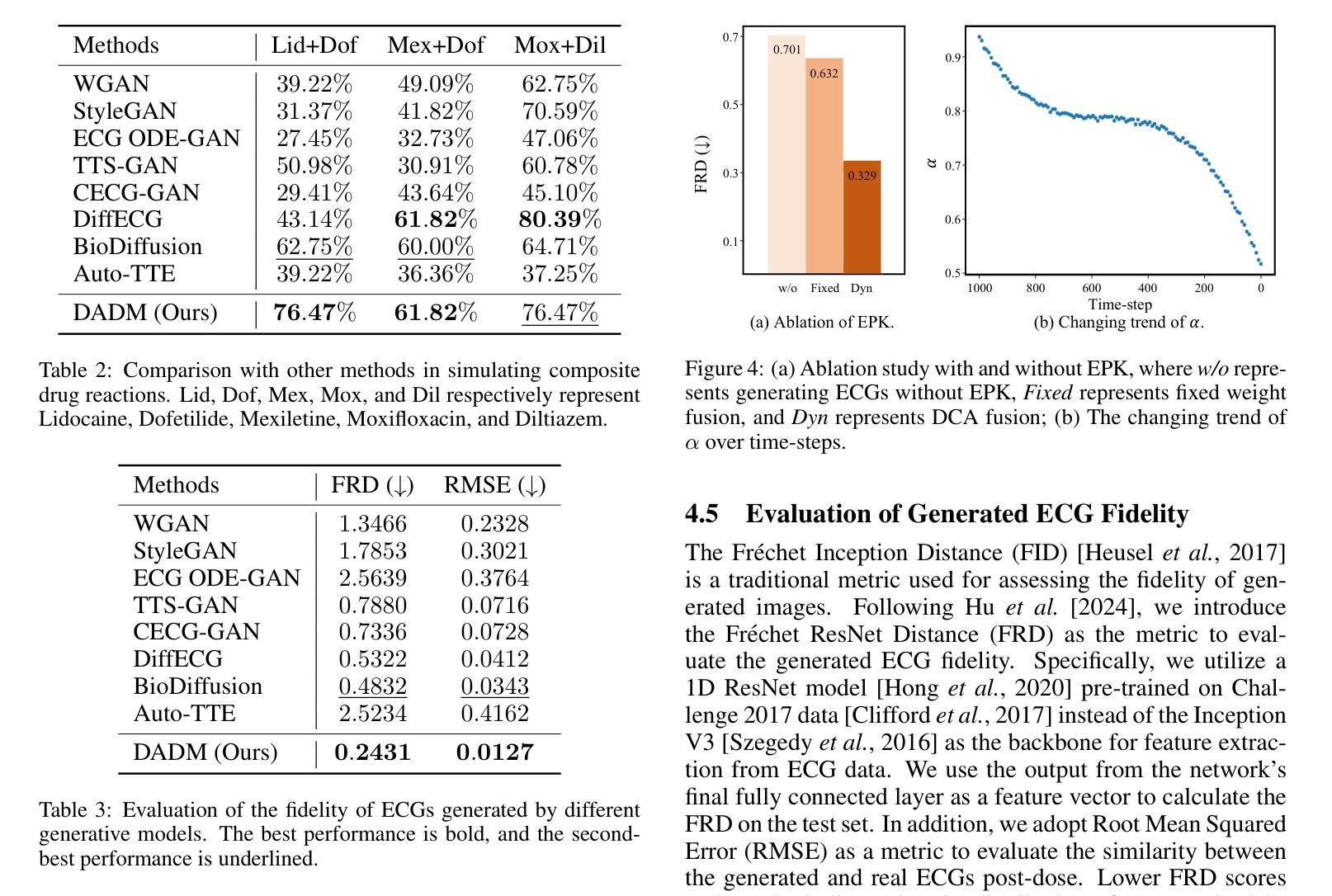
Clinical trials are pivotal in cardiac drug development, yet they often fail due to inadequate efficacy and unexpected safety issues, leading to significant financial losses. Using in-silico trials to replace a part of physical clinical trials, e.g., leveraging advanced generative models to generate drug-influenced electrocardiograms (ECGs), seems an effective method to reduce financial risk and potential harm to trial participants. While existing generative models have demonstrated progress in ECG generation, they fall short in modeling drug reactions due to limited fidelity and inability to capture individualized drug response patterns. In this paper, we propose a Drug-Aware Diffusion Model (DADM), which could simulate individualized drug reactions while ensuring fidelity. To ensure fidelity, we construct a set of ordinary differential equations to provide external physical knowledge (EPK) of the realistic ECG morphology. The EPK is used to adaptively constrain the morphology of the generated ECGs through a dynamic cross-attention (DCA) mechanism. Furthermore, we propose an extension of ControlNet to incorporate demographic and drug data, simulating individual drug reactions. We compare DADM with the other eight state-of-the-art ECG generative models on two real-world databases covering 8 types of drug regimens. The results demonstrate that DADM can more accurately simulate drug-induced changes in ECGs, improving the accuracy by at least 5.79% and recall by 8%.
临床试验在心脏药物开发中至关重要,但由于疗效不足和意外的安全问题,它们常常失败,导致重大经济损失。使用计算机模拟试验(in-silico trials)来替代部分实体临床试验,例如利用先进的生成模型来生成受药物影响的心电图(ECGs),似乎是一种减少财务风险和潜在参与者伤害的有效方法。虽然现有的生成模型在心电图生成方面已经显示出进展,但由于保真度有限以及无法捕捉个体药物反应模式,它们在模拟药物反应方面仍然有所不足。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Under review
Summary
本文介绍了心脏药物开发中临床试验的重要性及其面临的财务与安全性挑战。为了降低风险和潜在伤害,研究提出了利用先进的生成模型进行虚拟临床试验,生成药物影响的心电图(ECG)。针对现有生成模型在模拟药物反应方面的不足,提出了一种药物感知扩散模型(DADM),能模拟个体药物反应并确保真实性。通过构建普通微分方程提供外部物理知识(EPK),并通过动态交叉注意力机制确保ECG形态的适应性约束。同时,对ControlNet进行扩展,以纳入人口学和药物数据,模拟个体药物反应。与其他八个先进的心电图生成模型相比,DADM在模拟药物引起的心电图变化方面表现出更高的准确性。
Key Takeaways
- 临床试验在心脏药物开发中至关重要,但存在财务与安全性风险。
- 使用虚拟临床试验可降低财务风险和潜在伤害。
- 现有生成模型在模拟药物反应方面存在局限性。
- 提出了一种药物感知扩散模型(DADM)来模拟个体药物反应并保证真实性。
- 通过构建普通微分方程提供外部物理知识(EPK)来确保适应性约束心电图形态。
- DADM采用动态交叉注意力机制模拟真实心电图。
点此查看论文截图
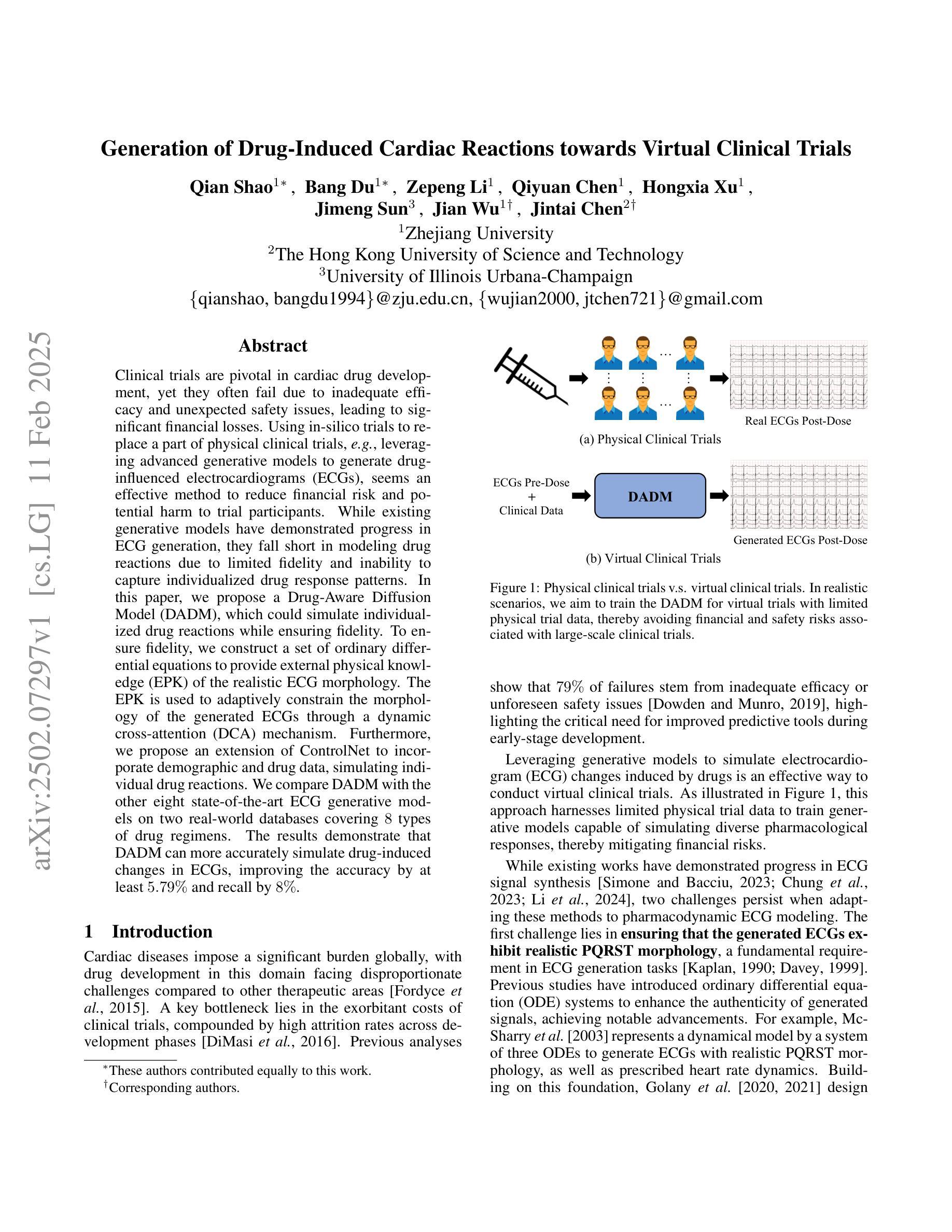
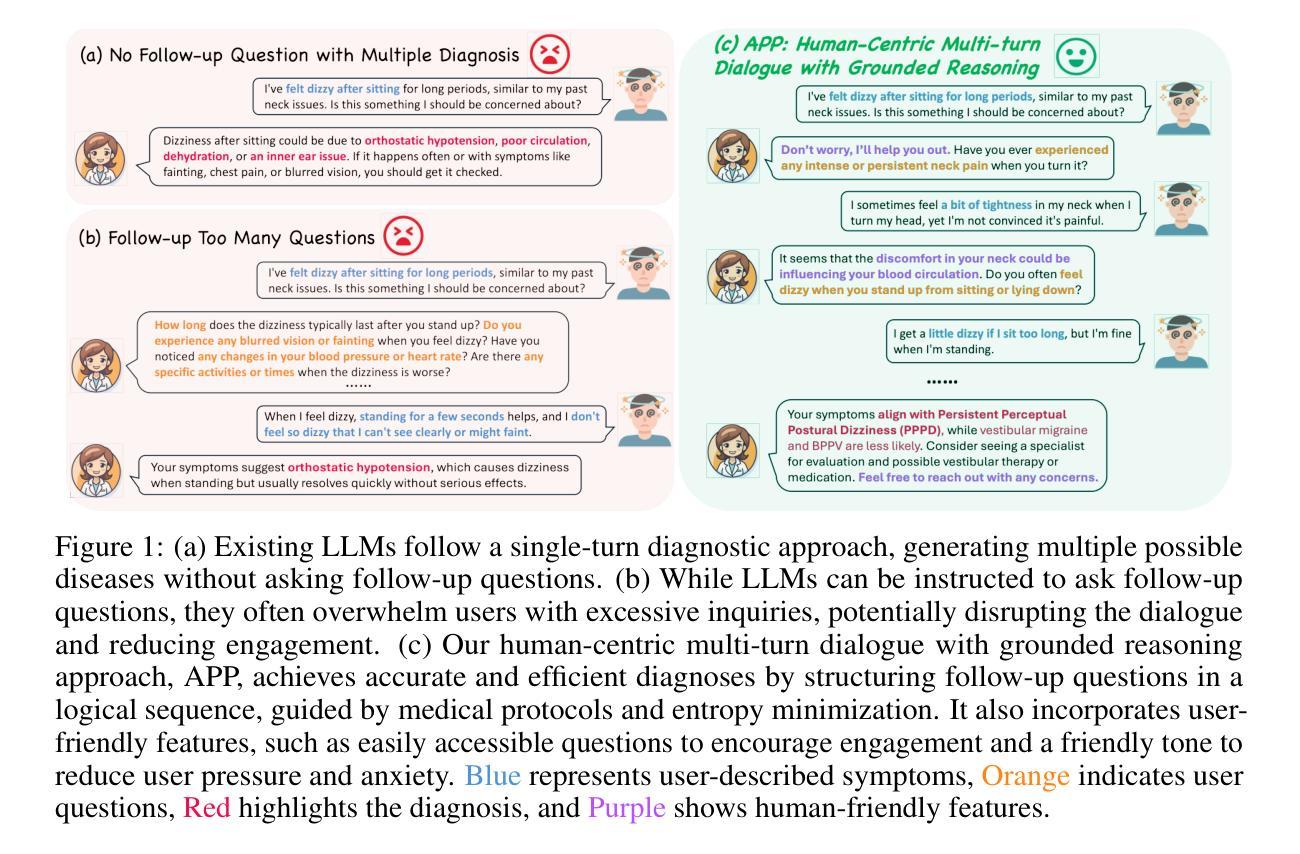
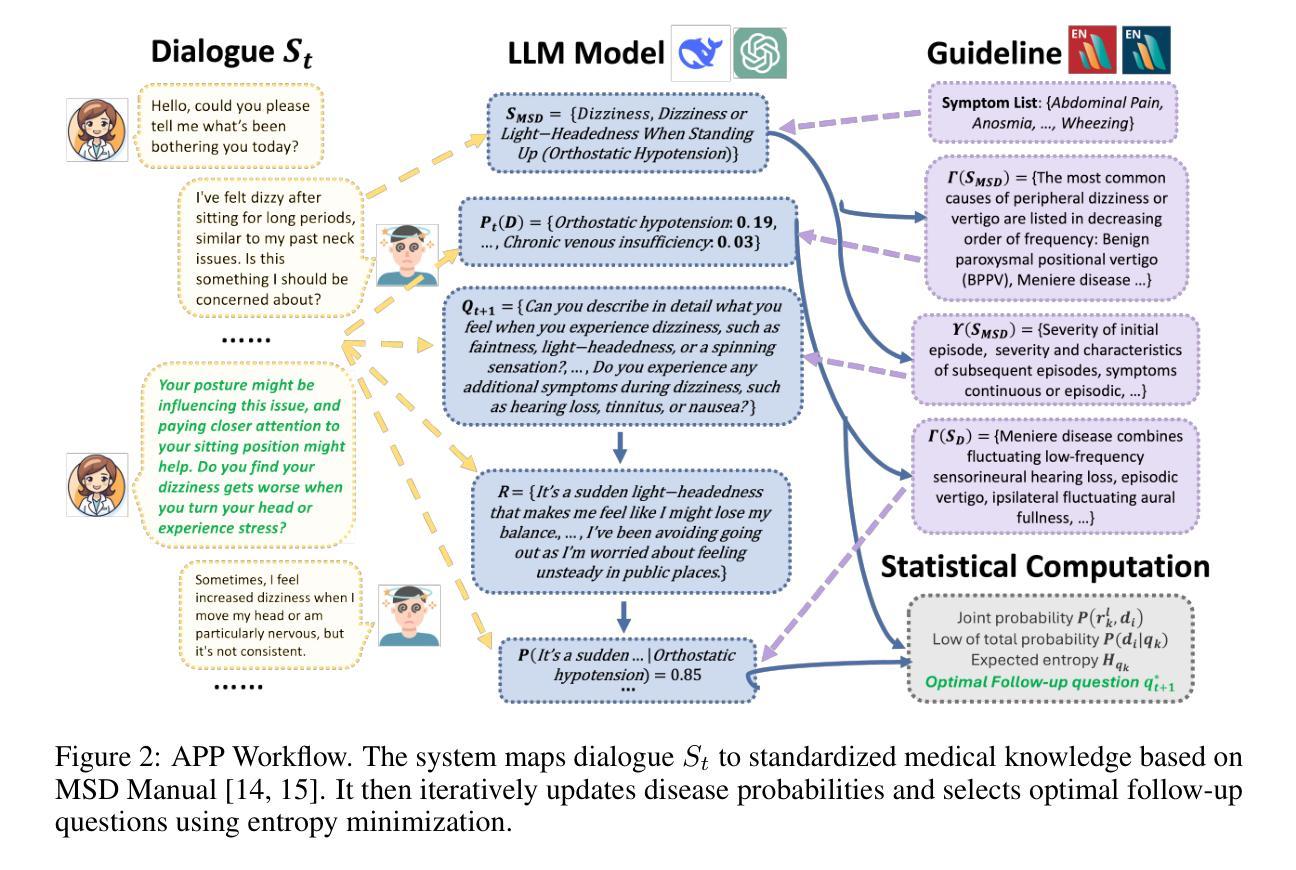
Ask Patients with Patience: Enabling LLMs for Human-Centric Medical Dialogue with Grounded Reasoning
Authors:Jiayuan Zhu, Junde Wu
Accurate and efficient diagnosis in online medical consultations remains a challenge for current large language models. These models often rely on single-turn interactions and lack the ability to refine their predictions through follow-up questions. Additionally, their responses frequently contain complex medical terminology, making them less accessible to non-medical users and creating barriers to effective communication. In this paper, we introduce Ask Patients with Patience (APP), the first multi-turn dialogue that enables LLMs to iteratively refine diagnoses based on grounded reasoning. By integrating medical guidelines and entropy minimization, APP improves both diagnostic accuracy and efficiency. Furthermore, it features human-centric communication that bridges the gap between user comprehension and medical terminology, significantly enhancing user accessibility and engagement. We evaluated APP using a subset of the ReMeDi dataset, comparing it with single-turn and traditional multi-turn LLM baselines. APP achieved higher similarity scores in diagnosis predictions, demonstrating better alignment with ground truth diagnoses. Entropy analysis showed that APP reduces diagnostic uncertainty more rapidly across iterations, increasing confidence in its predictions. APP also excels in user accessibility and empathy, further bridging the gap between complex medical language and user understanding. Code will be released at: https://github.com/SuperMedIntel/AskPatients.
在线医疗咨询中的准确高效诊断仍然是当前大型语言模型的挑战。这些模型通常依赖于单轮互动,缺乏通过后续问题来优化预测的能力。此外,他们的回答经常包含复杂的医学术语,使非医学用户难以接触,从而阻碍了有效沟通。在本文中,我们介绍了“耐心询问患者”(APP),这是第一个多轮对话,能够基于有根据的推理让大型语言模型(LLMs)迭代地完善诊断。通过整合医学指南和熵最小化,APP提高了诊断和效率的准确性。此外,它以人为中心的沟通方式,弥合了用户理解和医学术语之间的差距,大大提高了用户的可接触性和参与度。我们使用ReMeDi数据集的一个子集对APP进行了评估,将其与单轮和传统多轮LLM基线进行了比较。APP在诊断预测方面获得了更高的相似度分数,证明其与真实诊断结果更吻合。熵分析表明,APP在迭代过程中更快地减少了诊断的不确定性,增加了预测的置信度。APP在用户可接触性和同理心方面也表现出色,进一步缩小了复杂医学语言和用户理解之间的差距。代码将在https://github.com/SuperMedIntel/AskPatients发布。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
该文指出在线医疗咨询中准确高效的诊断仍是当前大型语言模型面临的挑战。文章介绍了Ask Patients with Patience(APP)这一多轮对话系统,它能使LLMs基于推理进行迭代诊断,提高诊断的准确性和效率。此外,APP融合了医疗指南和熵最小化技术,实现了人性化的沟通,有效减少了用户理解和医学术语之间的差距。评估结果显示,APP在诊断预测方面的相似度得分更高,并且能更快地减少诊断的不确定性。同时,APP在用户可及性和同理心方面也表现出色,进一步缩短了复杂医学语言和用户理解之间的鸿沟。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型在在线医疗咨询中的诊断和沟通存在挑战。
- Ask Patients with Patience(APP)是一个多轮对话系统,能够基于推理进行迭代诊断。
- APP融合了医疗指南和熵最小化技术,提高了诊断的准确性和效率。
- APP采用人性化的沟通方式,有效减少了用户理解和医学术语之间的差距。
- APP在诊断预测方面的表现优于单轮和多轮LLM基线。
- APP能更快地减少诊断的不确定性。
点此查看论文截图


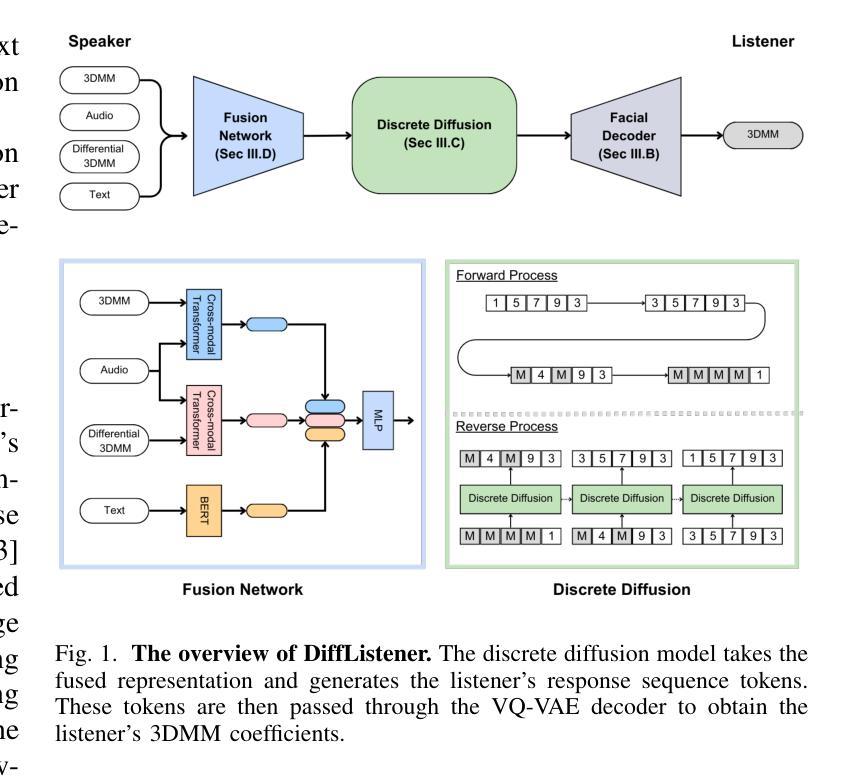
DiffListener: Discrete Diffusion Model for Listener Generation
Authors:Siyeol Jung, Taehwan Kim
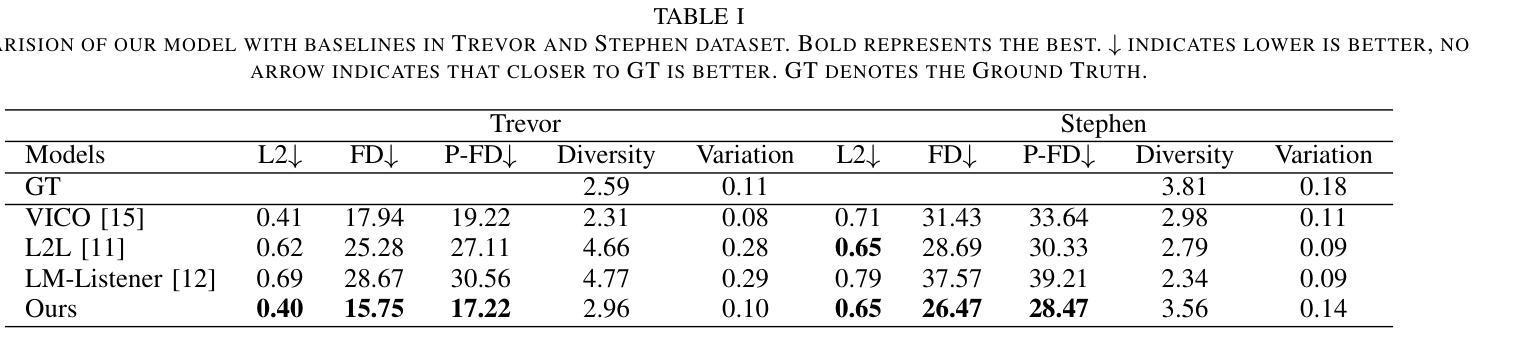
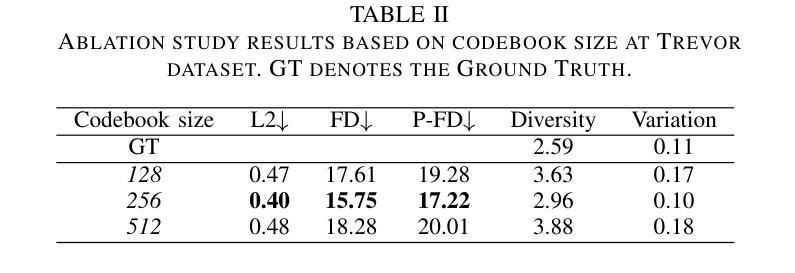
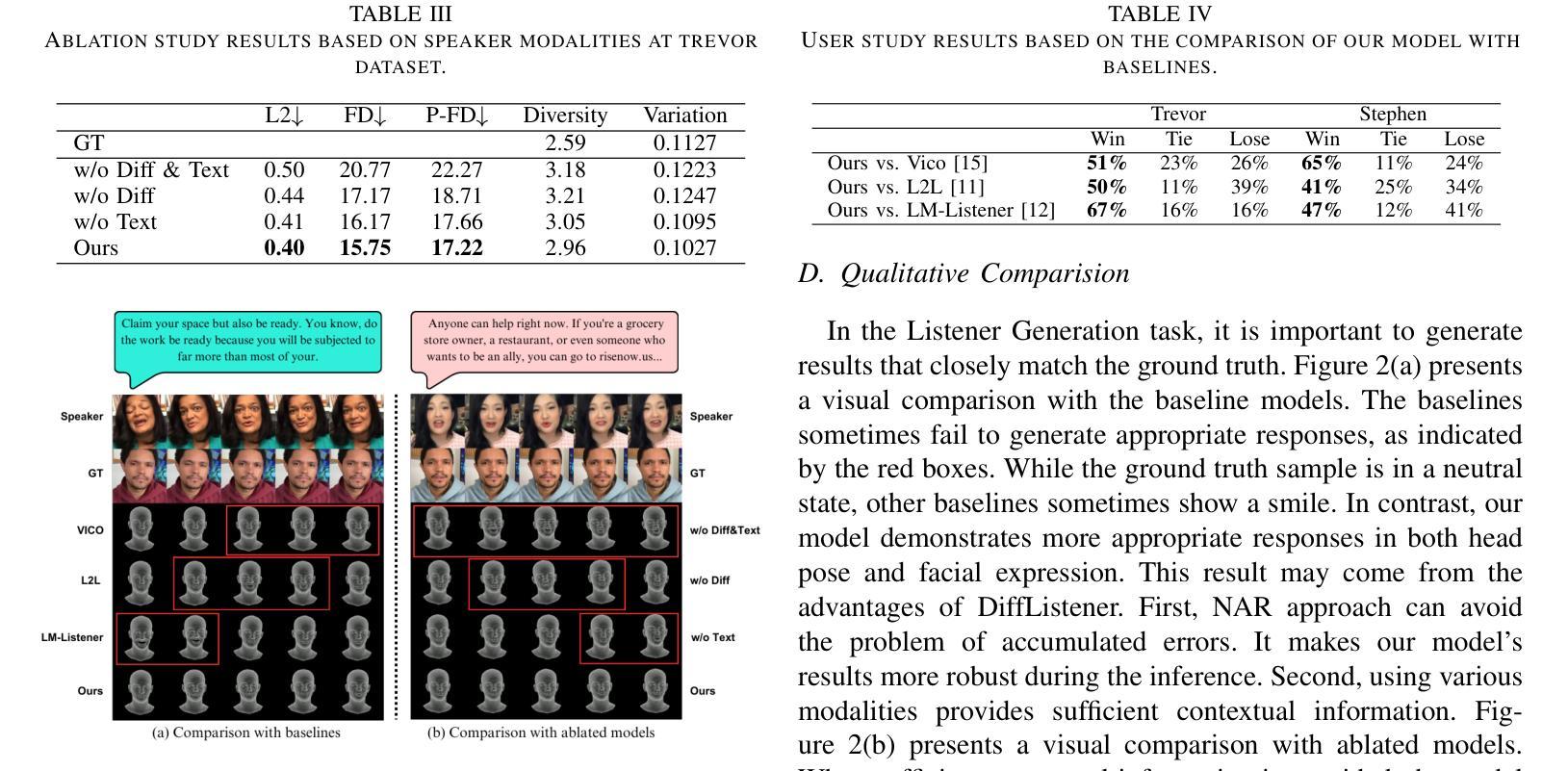
The listener head generation (LHG) task aims to generate natural nonverbal listener responses based on the speaker’s multimodal cues. While prior work either rely on limited modalities (e.g. audio and facial information) or employ autoregressive approaches which have limitations such as accumulating prediction errors. To address these limitations, we propose DiffListener, a discrete diffusion based approach for non-autoregressive listener head generation. Our model takes the speaker’s facial information, audio, and text as inputs, additionally incorporating facial differential information to represent the temporal dynamics of expressions and movements. With this explicit modeling of facial dynamics, DiffListener can generate coherent reaction sequences in a non-autoregressive manner. Through comprehensive experiments, DiffListener demonstrates state-of-the-art performance in both quantitative and qualitative evaluations. The user study shows that DiffListener generates natural context-aware listener reactions that are well synchronized with the speaker. The code and demo videos are available in https://siyeoljung.github.io/DiffListener
监听器头部生成(LHG)任务旨在基于说话者的多模式线索生成自然的非语言听众响应。虽然以前的工作要么依赖于有限的模式(例如音频和面部信息),要么采用存在累积预测误差等局限性的自回归方法。为了解决这些局限性,我们提出了DiffListener,这是一种基于离散扩散的非自回归监听器头部生成方法。我们的模型以说话者的面部信息、音频和文本为输入,另外还融入了面部差异信息,以表达表情和动作的时态动态。通过对面部动态的明确建模,DiffListener能够以非自回归的方式生成连贯的反应序列。通过全面的实验,DiffListener在定量和定性评估中都表现出了卓越的性能。用户研究表明,DiffListener生成的听众反应与自然语境相适应,并与说话者同步。相关代码和演示视频可在https://siyeoljung.github.io/DiffListener查看。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at ICASSP 2025
Summary
基于说话者的多模态线索生成自然的非言语听者响应是Listener Head Generation(LHG)任务的目标。以往的方法依赖于有限的模态或采用有预测误差累积的autoregressive方法。为解决这些问题,我们提出了DiffListener,一种基于离散扩散的非autoregressive听者头生成方法。我们的模型以说话者的面部信息、音频和文本为输入,并额外融入面部差分信息以表达表情和动作的时态动态。通过对面部动态的显式建模,DiffListener能以非autoregressive方式生成连贯的反应序列。通过全面的实验和用户研究,DiffListener在定量和定性评估中都表现出卓越的性能,能生成与说话者同步的自然、符合语境的听者反应。
Key Takeaways
- Listener Head Generation (LHG)任务旨在基于说话者的多模态线索生成自然的非言语听者响应。
- 现有方法存在依赖有限模态或采用有预测误差累积的autoregressive方法的问题。
- DiffListener采用基于离散扩散的非autoregressive方法,能处理多模态信息。
- DiffListener模型融合说话者的面部信息、音频和文本输入,并加入面部差分信息以表达时态动态。
- DiffListener能生成连贯的非言语反应序列,且这些反应与说话者同步。
- 全面的实验证明DiffListener在定量和定性评估中表现卓越。
点此查看论文截图