⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-02-13 更新
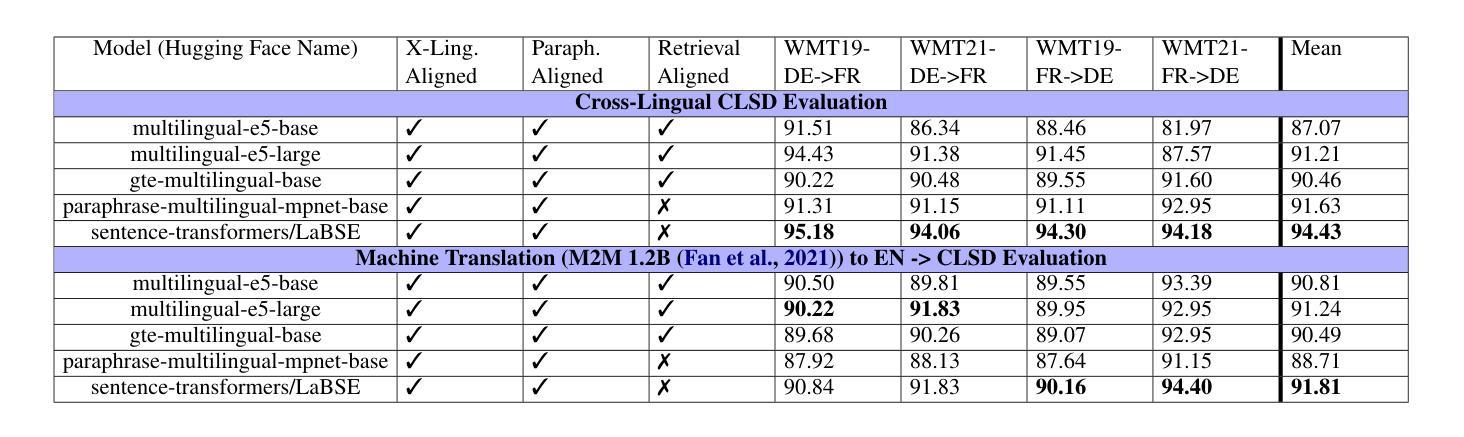
Examining Multilingual Embedding Models Cross-Lingually Through LLM-Generated Adversarial Examples
Authors:Andrianos Michail, Simon Clematide, Rico Sennrich
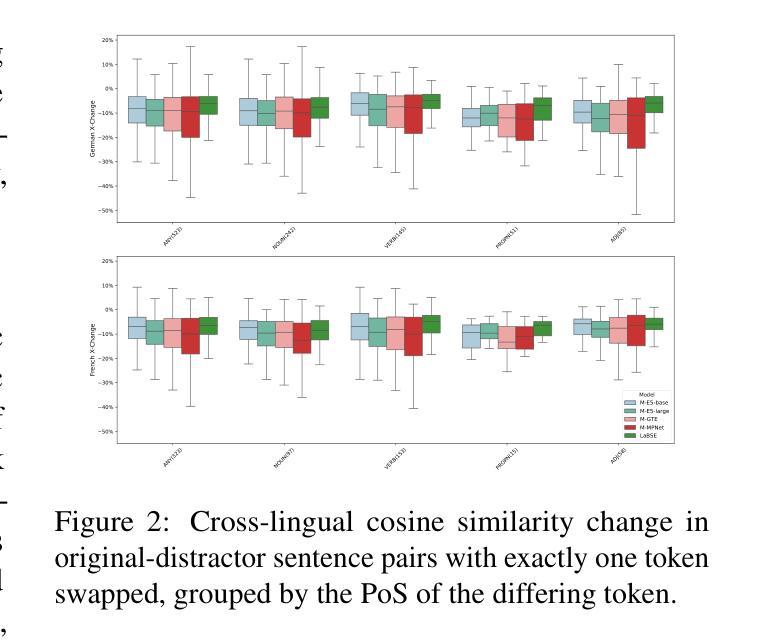
The evaluation of cross-lingual semantic search capabilities of models is often limited to existing datasets from tasks such as information retrieval and semantic textual similarity. To allow for domain-specific evaluation, we introduce Cross Lingual Semantic Discrimination (CLSD), a novel cross-lingual semantic search task that requires only a set of parallel sentence pairs of the language pair of interest within the target domain. This task focuses on the ability of a model to cross-lingually rank the true parallel sentence higher than hard negatives generated by a large language model. We create four instances of our introduced CLSD task for the language pair German-French within the domain of news. Within this case study, we find that models that are also fine-tuned for retrieval tasks (e.g., multilingual E5) benefit from using English as the pivot language, while bitext mining models such as LaBSE perform best directly cross-lingually. We also show a fine-grained similarity analysis enabled by our distractor generation strategy, indicating that different embedding models are sensitive to different types of perturbations.
对模型的跨语言语义搜索能力的评估通常仅限于信息检索和语义文本相似性之类的现有数据集。为了进行特定领域的评估,我们引入了跨语言语义辨别(CLSD),这是一种新的跨语言语义搜索任务,它只需要目标领域内感兴趣语言对的并行句子对集合。此任务侧重于模型将真正的并行句子排名高于由大型语言模型生成硬负样本的跨语言能力。我们为新闻领域的德法语言对创建了四个CLSD任务的实例。在此案例研究中,我们发现进行检索任务微调(例如多语言E5)的模型受益于使用英语作为中心语言,而直接进行跨语言处理的双文本挖掘模型(如LaBSE)表现最佳。我们还通过干扰项生成策略展示了精细的相似性分析,这表明不同的嵌入模型对不同类型的扰动有不同的敏感性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了跨语言语义搜索能力模型评估的新挑战。为应对领域特定的评估需求,提出了跨语言语义判别(CLSD)这一新任务。CLSD任务只需针对目标领域内的语言对设置平行句子对即可。研究发现,针对检索任务进行微调(如多语种E5)的模型使用英语作为中介语言受益较大,而直接进行跨语言处理的模型(如LaBSE)表现最佳。此外,本文通过干扰项生成策略展示了精细的相似性分析,表明不同的嵌入模型对不同类型的扰动有不同的敏感性。
Key Takeaways
- 跨语言语义搜索能力模型的评估受限于现有数据集和信息检索等任务。
- 提出了一种新的跨语言语义判别(CLSD)任务,只需设置平行句子对即可进行领域特定评估。
- 在新闻领域的德语-法语语言对实例中,发现针对检索任务进行微调(如多语种E5)的模型在使用英语作为中介语言时表现出优势。
- 直接进行跨语言处理的模型(如LaBSE)表现最佳。
- CLSD任务能够展示精细的相似性分析,这有助于理解不同嵌入模型的敏感性。
- 不同嵌入模型对不同类型的扰动反应不同,这为改进模型提供了方向。
点此查看论文截图


QA-Expand: Multi-Question Answer Generation for Enhanced Query Expansion in Information Retrieval
Authors:Wonduk Seo, Seunghyun Lee
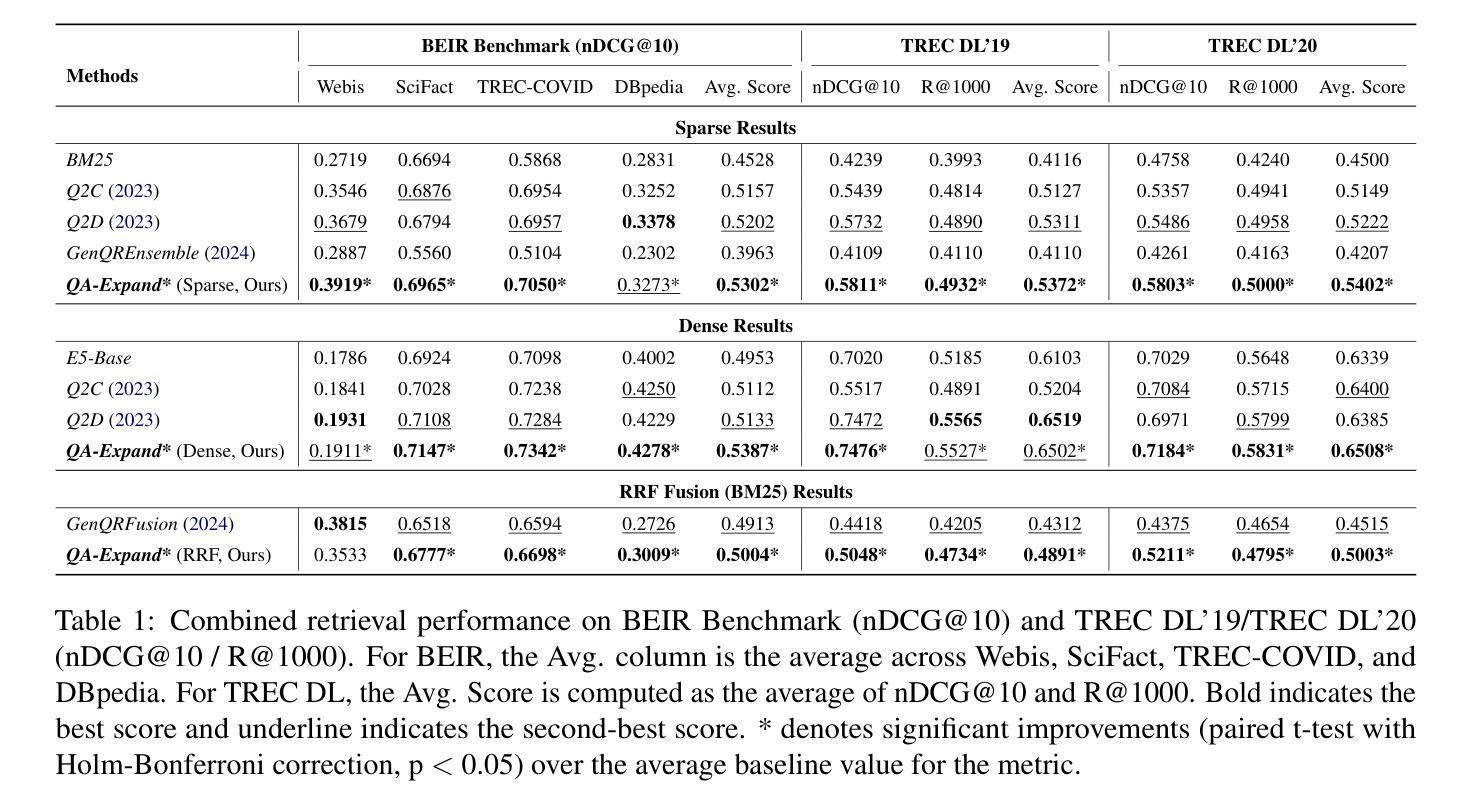
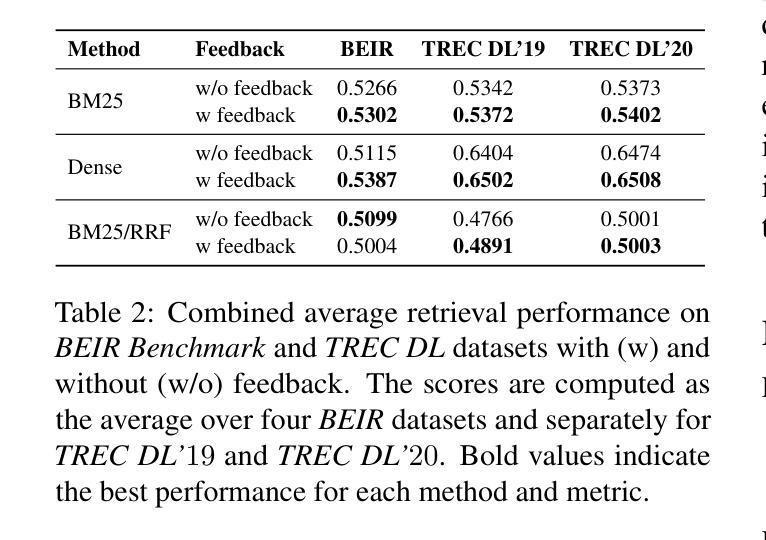
Query expansion is widely used in Information Retrieval (IR) to improve search outcomes by enriching queries with additional contextual information. Although recent Large Language Model (LLM) based methods generate pseudo-relevant content and expanded terms via multiple prompts, they often yield repetitive, narrow expansions that lack the diverse context needed to retrieve all relevant information. In this paper, we introduce QA-Expand, a novel and effective framework for query expansion. It first generates multiple relevant questions from the initial query and subsequently produces corresponding pseudo-answers as surrogate documents. A feedback model further rewrites and filters these answers to ensure only the most informative augmentations are incorporated. Extensive experiments on benchmarks such as BEIR and TREC demonstrate that QA-Expand enhances retrieval performance by up to 13% over state-of-the-art methods, offering a robust solution for modern retrieval challenges.
查询扩展在信息检索(IR)中得到了广泛应用,通过添加额外的上下文信息来丰富查询,从而改进搜索结果。尽管最近基于大型语言模型(LLM)的方法通过多个提示生成伪相关内容并扩展术语,但它们通常会产生重复性高、范围狭窄的扩展内容,缺乏检索所有相关信息所需的各种上下文。在本文中,我们介绍了QA-Expand,这是一个用于查询扩展的新型有效框架。它首先根据初始查询生成多个相关问题,然后生成相应的伪答案作为替代文档。反馈模型进一步重写和过滤这些答案,以确保只合并最具有信息性的增强内容。在BEIR和TREC等基准测试上的大量实验表明,与最新技术相比,QA-Expand的检索性能提高了高达13%,为现代检索挑战提供了稳健的解决方案。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 8 pages
Summary
基于信息检索中的查询扩展技术,本文提出了一种新的查询扩展框架QA-Expand。该框架通过生成多个相关问题和对应的伪答案作为替代文档来扩展查询,并利用反馈模型重写和过滤答案,确保只融入最具有信息性的扩展内容。实验结果表明,QA-Expand在BEIR和TREC等基准测试上的检索性能提高了高达13%,为解决现代检索挑战提供了稳健的解决方案。
Key Takeaways
- 查询扩展在信息检索中用于通过增加上下文信息提高搜索效果。
- 最新大型语言模型(LLM)方法虽然能生成伪相关内容和扩展词项,但常常产生重复性高、范围狭窄的扩展,缺乏多样化的上下文信息。
- QA-Expand框架通过生成多个相关问题及其伪答案进行查询扩展。
- 反馈模型用于重写和过滤答案,确保仅融入最具有信息性的内容。
- 在基准测试如BEIR和TREC上的实验表明,QA-Expand提高了检索性能。
- QA-Expand性能优于现有技术,提高幅度高达13%。
点此查看论文截图

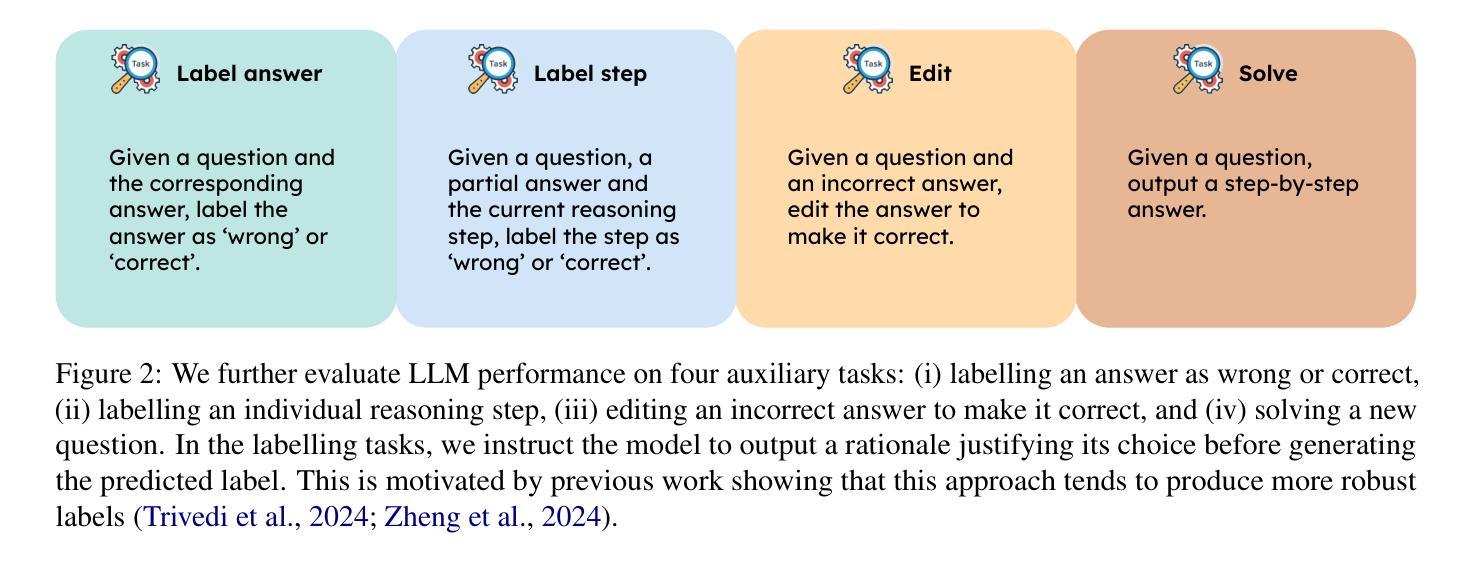
LLMs can implicitly learn from mistakes in-context
Authors:Lisa Alazraki, Maximilian Mozes, Jon Ander Campos, Yi Chern Tan, Marek Rei, Max Bartolo
Learning from mistakes is a fundamental feature of human intelligence. Previous work has shown that Large Language Models (LLMs) can also learn from incorrect answers when provided with a comprehensive rationale detailing why an answer is wrong or how to correct it. In this work, we examine whether LLMs can learn from mistakes in mathematical reasoning tasks when these explanations are not provided. We investigate if LLMs are able to implicitly infer such rationales simply from observing both incorrect and correct answers. Surprisingly, we find that LLMs perform better, on average, when rationales are eliminated from the context and incorrect answers are simply shown alongside correct ones. This approach also substantially outperforms chain-of-thought prompting in our evaluations. We show that these results are consistent across LLMs of different sizes and varying reasoning abilities. Further, we carry out an in-depth analysis, and show that prompting with both wrong and correct answers leads to greater performance and better generalisation than introducing additional, more diverse question-answer pairs into the context. Finally, we show that new rationales generated by models that have only observed incorrect and correct answers are scored equally as highly by humans as those produced with the aid of exemplar rationales. Our results demonstrate that LLMs are indeed capable of in-context implicit learning.
从错误中学习是人类智能的基本特征。之前的研究表明,大型语言模型(LLM)能够在提供全面理由的情况下,详细说明答案为何错误或如何改正,从而从错误的答案中学习。在这项工作中,我们研究的是在没有提供这些解释的情况下,LLM是否能在数学推理任务中从错误中学习。我们调查LLM是否仅通过观察正确的和错误的答案就能隐式推断出这些理由。令人惊讶的是,我们发现,在上下文中消除理由,而只是简单地展示正确的和错误的答案时,LLM的平均表现更好。这种方法也在我们的评估中大大优于思考链提示法。我们证明了这些结果在不同规模和不同推理能力的LLM之间是一致的。此外,我们进行了深入的分析,并证明用正确和错误的答案提示比把更多多样的问题和答案对引入上下文能产生更好的性能和更好的泛化能力。最后,我们证明了只通过观察正确和错误的答案而生成的新理由,与人类辅助示例理由产生的评分相同。我们的结果表明,LLM确实具备上下文隐式学习能力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:
本文探讨了大型语言模型(LLMs)在数学推理任务中能否从错误中学习,而无需提供解释。研究发现,当从上下文中消除解释,仅展示正确和错误的答案时,LLMs的表现更佳。这种方法在评估中显著优于思维链提示。进一步的分析表明,同时呈现正确和错误的答案提示可以提高性能并增强模型的泛化能力,而引入更多的问题答案对则效果不大。最后,仅通过观察正确和错误的答案而生成的模型新解释被人类评价为与有示例解释的同样出色,证明了LLMs确实具备上下文隐式学习能力。
Key Takeaways:
- LLMs可以从错误中学习,尤其在数学推理任务中。
- 当仅展示正确和错误的答案时,LLMs的表现更佳,且这种方法优于思维链提示。
- 同时呈现正确和错误的答案可以提高LLMs的性能和泛化能力。
- 引入更多的问题答案对并不一定能提高LLMs的学习效果。
- LLMs能够通过观察正确和错误的答案生成新的解释,这些解释被人类评价为与有示例解释的同样出色。
- LLMs具备上下文隐式学习能力。
点此查看论文截图

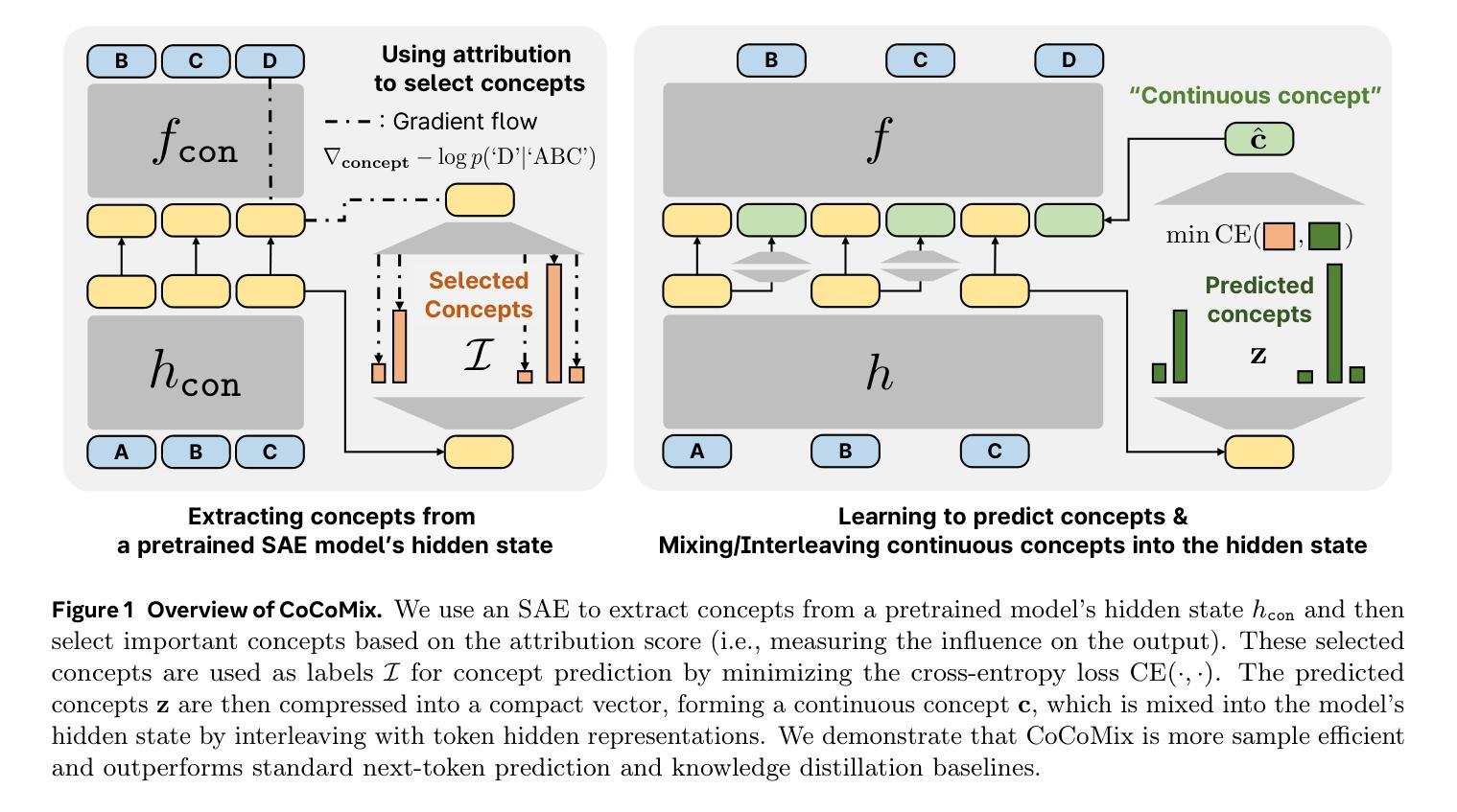
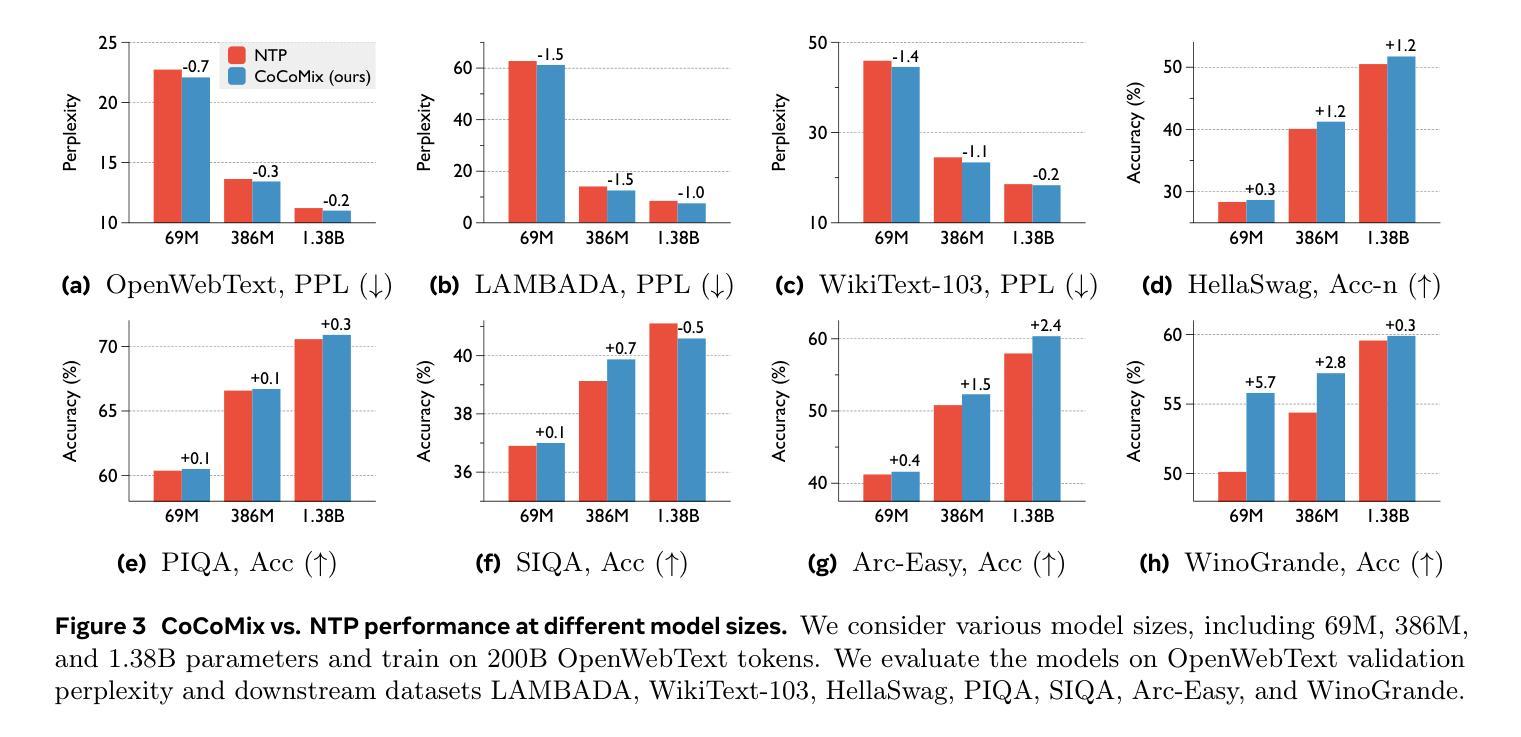
LLM Pretraining with Continuous Concepts
Authors:Jihoon Tack, Jack Lanchantin, Jane Yu, Andrew Cohen, Ilia Kulikov, Janice Lan, Shibo Hao, Yuandong Tian, Jason Weston, Xian Li
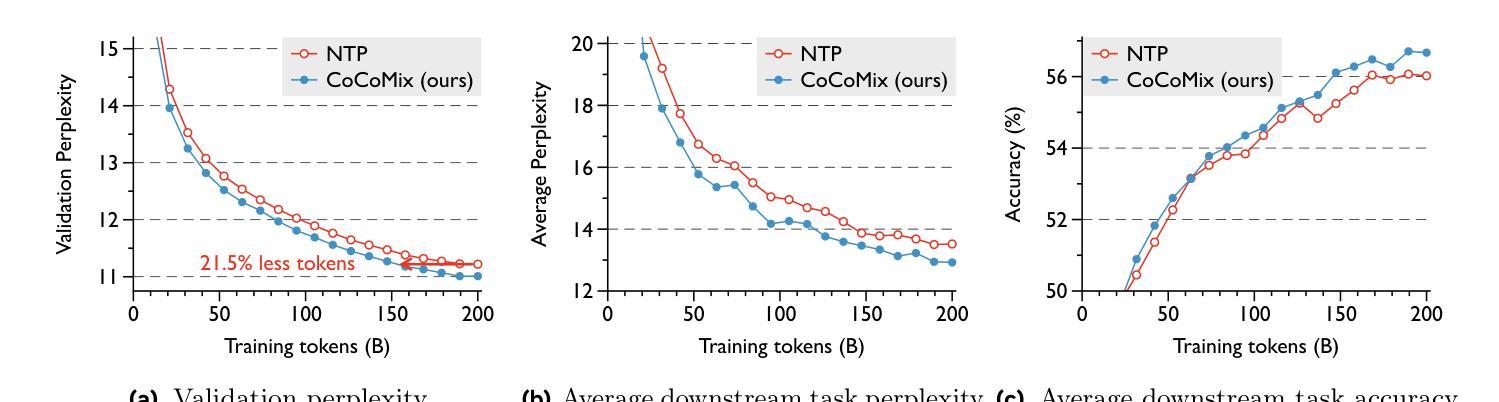
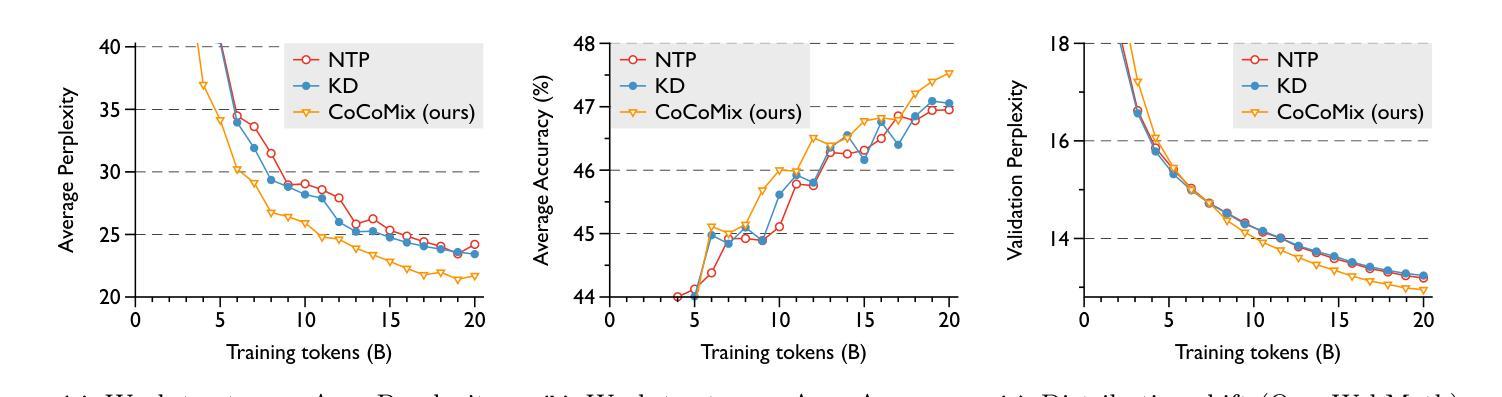
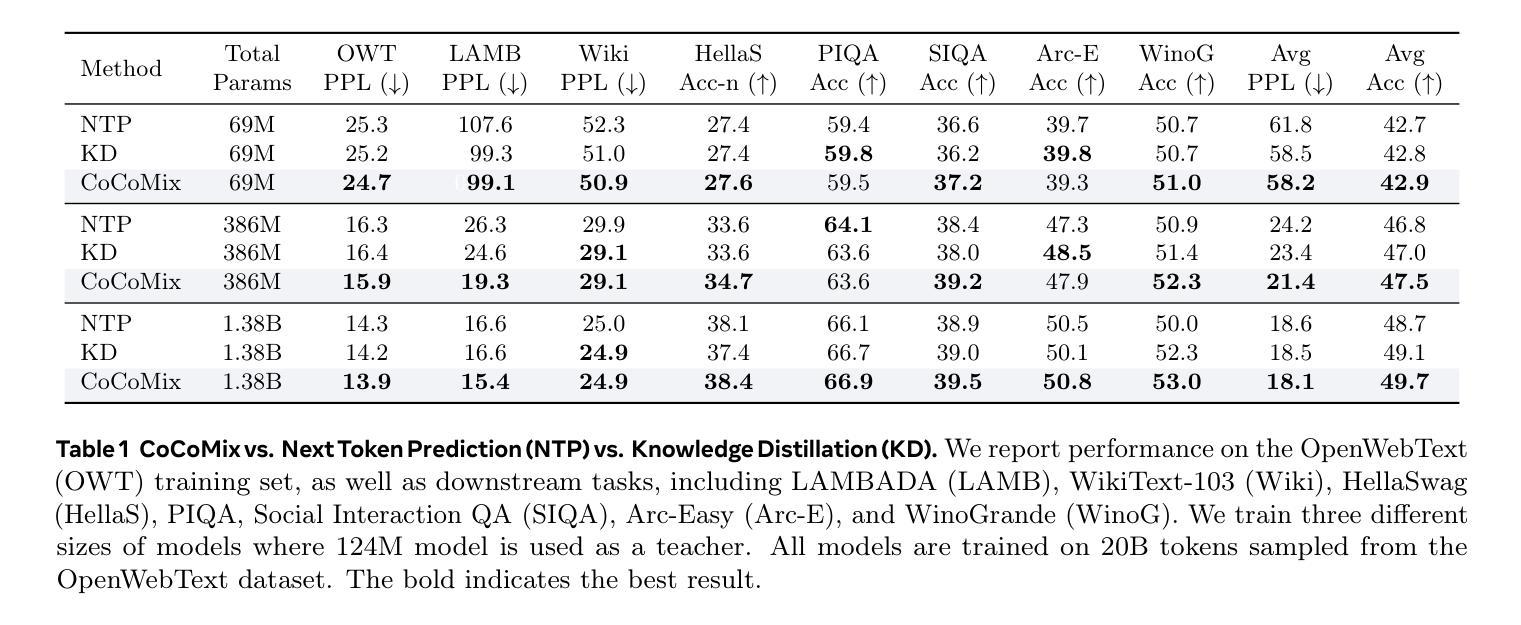
Next token prediction has been the standard training objective used in large language model pretraining. Representations are learned as a result of optimizing for token-level perplexity. We propose Continuous Concept Mixing (CoCoMix), a novel pretraining framework that combines discrete next token prediction with continuous concepts. Specifically, CoCoMix predicts continuous concepts learned from a pretrained sparse autoencoder and mixes them into the model’s hidden state by interleaving with token hidden representations. Through experiments on multiple benchmarks, including language modeling and downstream reasoning tasks, we show that CoCoMix is more sample efficient and consistently outperforms standard next token prediction, knowledge distillation and inserting pause tokens. We find that combining both concept learning and interleaving in an end-to-end framework is critical to performance gains. Furthermore, CoCoMix enhances interpretability and steerability by allowing direct inspection and modification of the predicted concept, offering a transparent way to guide the model’s internal reasoning process.
下一个词预测作为大型语言模型预训练的标准训练目标已经被广泛应用。表示是通过优化令牌级别的困惑度来学习的。我们提出了连续概念混合(CoCoMix),这是一种新型的预训练框架,结合了离散下一个词预测和连续概念。具体来说,CoCoMix预测从预训练的稀疏自动编码器中学得的连续概念,并通过与令牌隐藏表示交替的方式将它们混合到模型的隐藏状态。通过包括语言建模和下游推理任务等多个基准实验,我们证明了CoCoMix的样本效率更高,并且始终优于标准下一个词预测、知识蒸馏和插入暂停令牌。我们发现在一个端到端的框架中结合概念学习和交替方式对于性能提升至关重要。此外,CoCoMix通过允许直接检查和修改预测的概念,提供了一种透明的方式来引导模型的内部推理过程,从而增强了可解释性和可控制性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出了一个新的预训练框架——连续概念混合(CoCoMix),结合了离散下一个令牌预测和连续概念预测。CoCoMix利用预训练的稀疏自动编码器学习连续概念,并通过交错方式与令牌隐藏表示混合到模型的隐藏状态中。实验表明,CoCoMix在多个基准测试中表现出更高的样本效率和性能,优于标准下一个令牌预测、知识蒸馏和插入暂停令牌等方法。结合概念学习和交错在端到端框架中对性能提升至关重要。此外,CoCoMix通过允许直接检查和修改预测的概念,提供了透明的指导模型内部推理过程的方式,增强了模型的解释性和可操控性。
Key Takeaways
- CoCoMix是一个结合离散下一个令牌预测和连续概念预测的新型预训练框架。
- CoCoMix利用预训练的稀疏自动编码器学习连续概念。
- 实验证明CoCoMix在多个基准测试中样本效率更高,性能更好。
- 结合概念学习和交错在端到端框架中对性能提升有关键作用。
- CoCoMix增强了模型的解释性和可操控性,允许直接检查和修改预测的概念。
- CoCoMix通过预测连续概念并混合到模型的隐藏状态中,提高了模型的性能。
点此查看论文截图

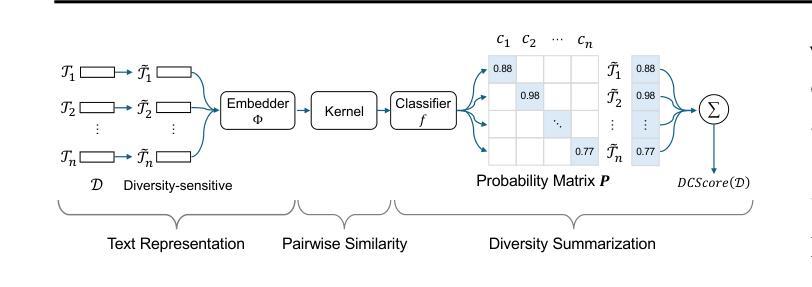
Measuring Diversity in Synthetic Datasets
Authors:Yuchang Zhu, Huizhe Zhang, Bingzhe Wu, Jintang Li, Zibin Zheng, Peilin Zhao, Liang Chen, Yatao Bian
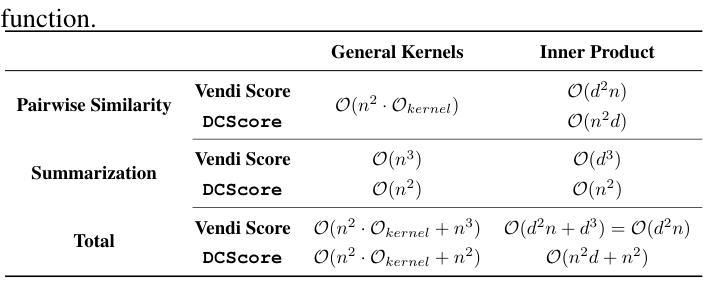
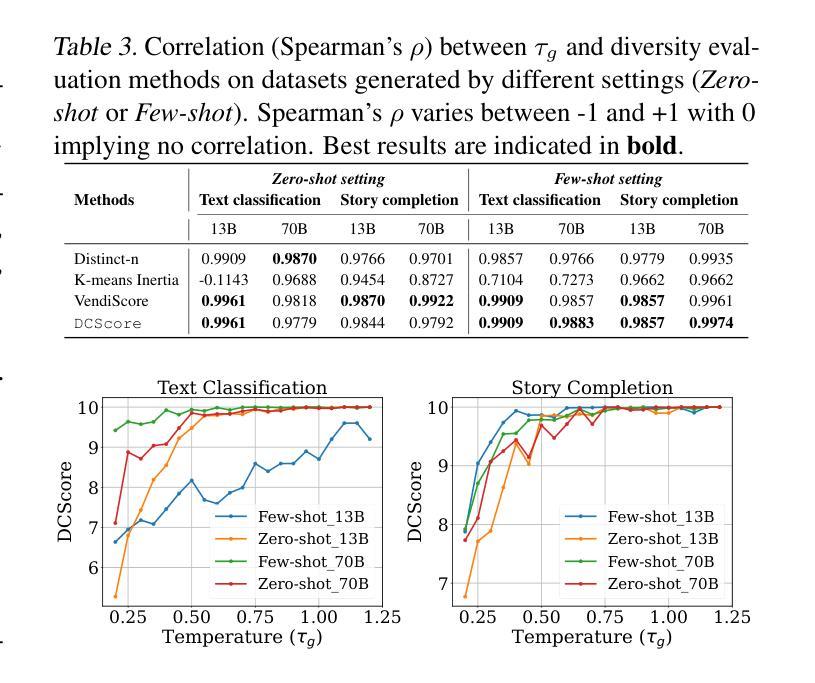
Large language models (LLMs) are widely adopted to generate synthetic datasets for various natural language processing (NLP) tasks, such as text classification and summarization. However, accurately measuring the diversity of these synthetic datasets-an aspect crucial for robust model performance-remains a significant challenge. In this paper, we introduce DCScore, a novel method for measuring synthetic dataset diversity from a classification perspective. Specifically, DCScore formulates diversity evaluation as a sample classification task, leveraging mutual relationships among samples. We further provide theoretical verification of the diversity-related axioms satisfied by DCScore, highlighting its role as a principled diversity evaluation method. Experimental results on synthetic datasets reveal that DCScore enjoys a stronger correlation with multiple diversity pseudo-truths of evaluated datasets, underscoring its effectiveness. Moreover, both empirical and theoretical evidence demonstrate that DCScore substantially reduces computational costs compared to existing approaches. Code is available at: https://github.com/BlueWhaleLab/DCScore.
大型语言模型(LLM)被广泛用于生成各种自然语言处理(NLP)任务(如文本分类和摘要)的合成数据集。然而,准确测量这些合成数据集的多样性——对模型稳健性能至关重要的一个方面——仍然是一个巨大的挑战。在本文中,我们介绍了DCScore,这是一种从分类角度衡量合成数据集多样性的新方法。具体来说,DCScore将多样性评估制定为样本分类任务,利用样本之间的相互作用关系。我们还提供了DCScore满足的多样性公理的理论验证,强调了其作为有原则的多样性评估方法的作用。在合成数据集上的实验结果表明,DCScore与评估数据集的多个多样性伪真相具有更强的相关性,这突出了其有效性。此外,实证和理论证据都表明,DCScore与现有方法相比大大减少了计算成本。代码可从以下网址获取:https://github.com/BlueWhaleLab/DCScore。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大型语言模型(LLM)生成的合成数据集广泛应用于自然语言处理(NLP)任务,如文本分类和摘要。然而,准确测量这些合成数据集的多样性对于模型的稳健性能至关重要,仍是一个巨大挑战。本文介绍了一种新的测量合成数据集多样性的方法DCScore,从分类的角度进行评估。DCScore将多样性评估制定为样本分类任务,利用样本间的相互关联。实验结果表明,DCScore与评估数据集的多个多样性伪真实值具有更强的相关性,凸显了其有效性。同时,DCScore在理论和实践证据方面都显著降低了计算成本。
Key Takeaways
- LLMs被广泛用于生成合成数据集,用于NLP任务如文本分类和摘要。
- 合成数据集的多样性测量是一个关键挑战,对模型性能有重要影响。
- DCScore是一种新的测量合成数据集多样性的方法,将多样性评估转化为样本分类任务。
- DCScore利用样本间的相互关系来评估多样性。
- 实验证明DCScore与多个多样性伪真实值的相关性更强,表明其有效性。
- DCScore在理论和实践两个方面都显著降低了计算成本。
点此查看论文截图

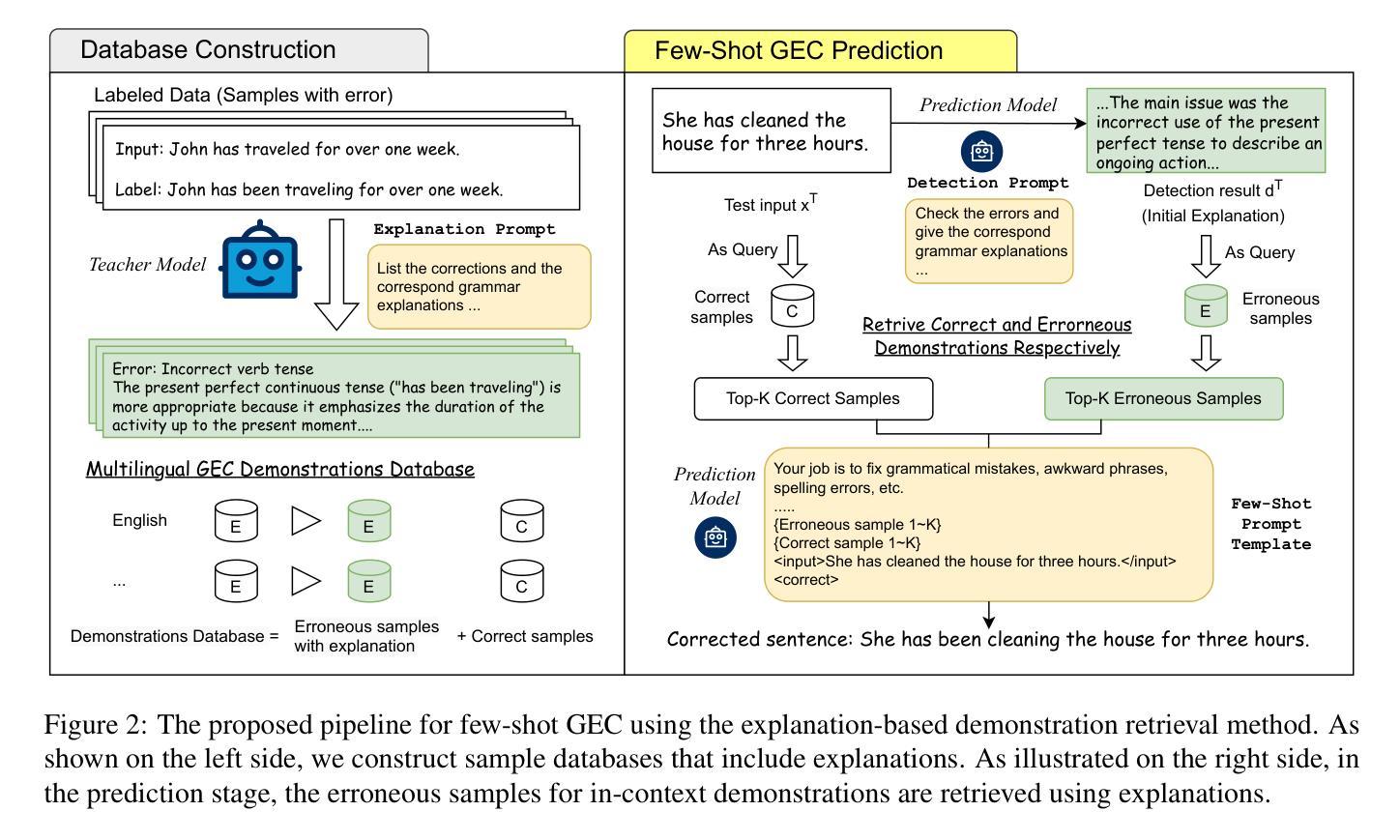
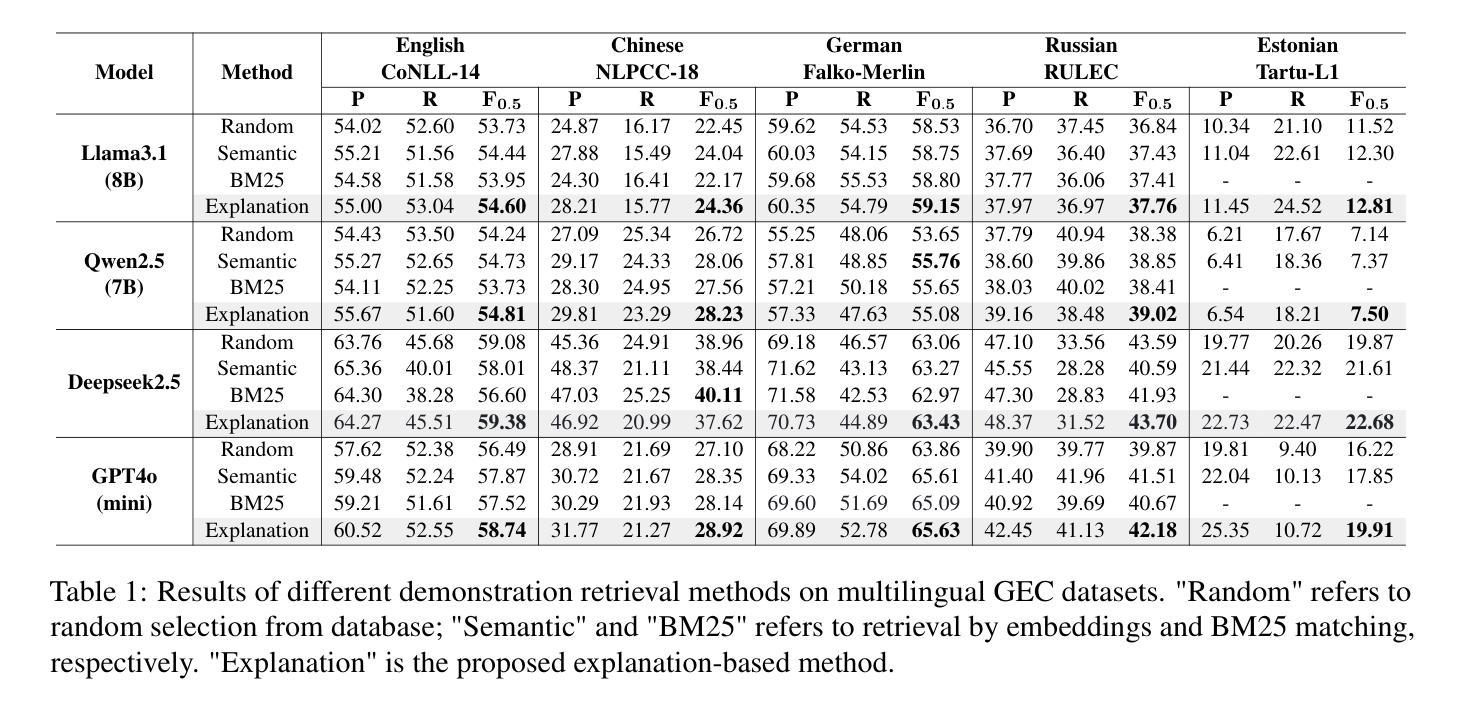
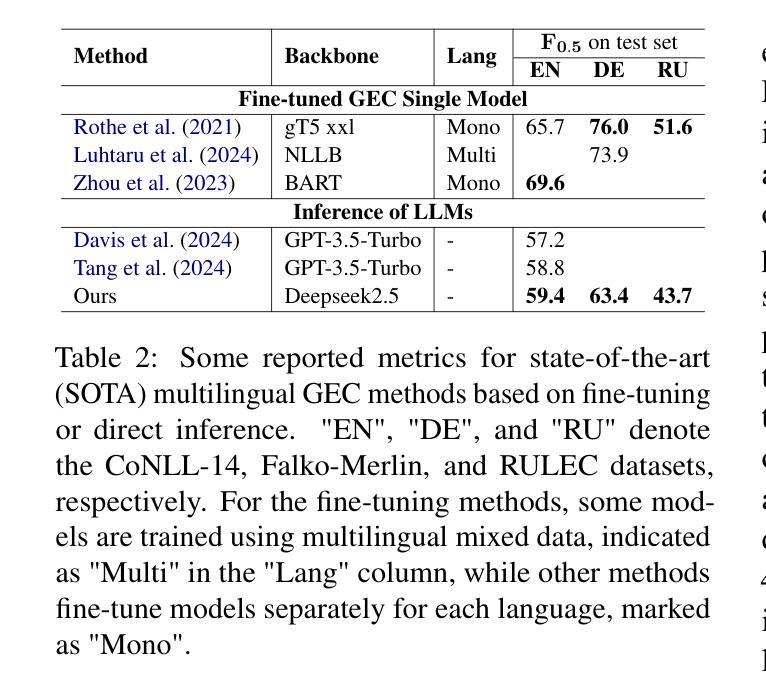
Explanation based In-Context Demonstrations Retrieval for Multilingual Grammatical Error Correction
Authors:Wei Li, Wen Luo, Guangyue Peng, Houfeng Wang
Grammatical error correction (GEC) aims to correct grammatical, spelling, and semantic errors in natural language text. With the growing of large language models (LLMs), direct text generation has gradually become the focus of the GEC methods, and few-shot in-context learning presents a cost-effective solution. However, selecting effective in-context examples remains challenging, as the similarity between input texts does not necessarily correspond to similar grammatical error patterns. In this paper, we propose a novel retrieval method based on natural language grammatical error explanations (GEE) to address this issue. Our method retrieves suitable few-shot demonstrations by matching the GEE of the test input with that of pre-constructed database samples, where explanations for erroneous samples are generated by LLMs. We conducted multilingual GEC few-shot experiments on both major open-source and closed-source LLMs. Experiments across five languages show that our method outperforms existing semantic and BM25-based retrieval techniques, without requiring additional training or language adaptation. This also suggests that matching error patterns is key to selecting examples.
语法错误修正(GEC)旨在修正自然语言文本中的语法、拼写和语义错误。随着大型语言模型(LLM)的增长,直接文本生成逐渐成为GEC方法的焦点,而少量上下文学习提供了一种具有成本效益的解决方案。然而,选择有效的上下文示例仍然具有挑战性,因为输入文本之间的相似性并不一定对应相似的语法错误模式。在本文中,我们提出了一种基于自然语言语法错误解释(GEE)的新型检索方法来解决这个问题。我们的方法通过匹配测试输入的GEE与预先构建的数据库样本的GEE来检索合适的少量示例,其中错误样本的解释是由LLM生成的。我们在主要的开源和闭源LLM上进行了多语言GEC少量实验。跨越五种语言的实验表明,我们的方法优于现有的语义和基于BM25的检索技术,且无需额外的训练或语言适应。这也表明匹配错误模式是选择示例的关键。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by NAACL 2025 main conference
Summary
文本主要介绍了基于自然语言语法错误解释(GEE)的检索方法在语法错误修正(GEC)中的应用。该方法通过匹配测试输入的GEE与预构建的数据库样本,检索出合适的少量示例。实验表明,该方法在多语言GEC中的表现优于现有的语义和BM25基于检索技术的检索方法,且无需额外的训练或语言适应。这表明匹配错误模式是选择示例的关键。
Key Takeaways
- 语法错误修正(GEC)旨在纠正自然语言文本中的语法、拼写和语义错误。
- 随着大型语言模型(LLM)的发展,直接文本生成逐渐成为GEC方法的重点。
- 少样本上下文学习为GEC提供了一个具有成本效益的解决方案。
- 选择有效的上下文示例仍然具有挑战性,因为输入文本之间的相似性并不一定对应相似的语法错误模式。
- 提出了一种基于自然语言语法错误解释(GEE)的检索方法来解决这个问题。
- 该方法通过匹配测试输入的GEE与预构建的数据库样本,检索出合适的少量示例,以进行GEC。
点此查看论文截图

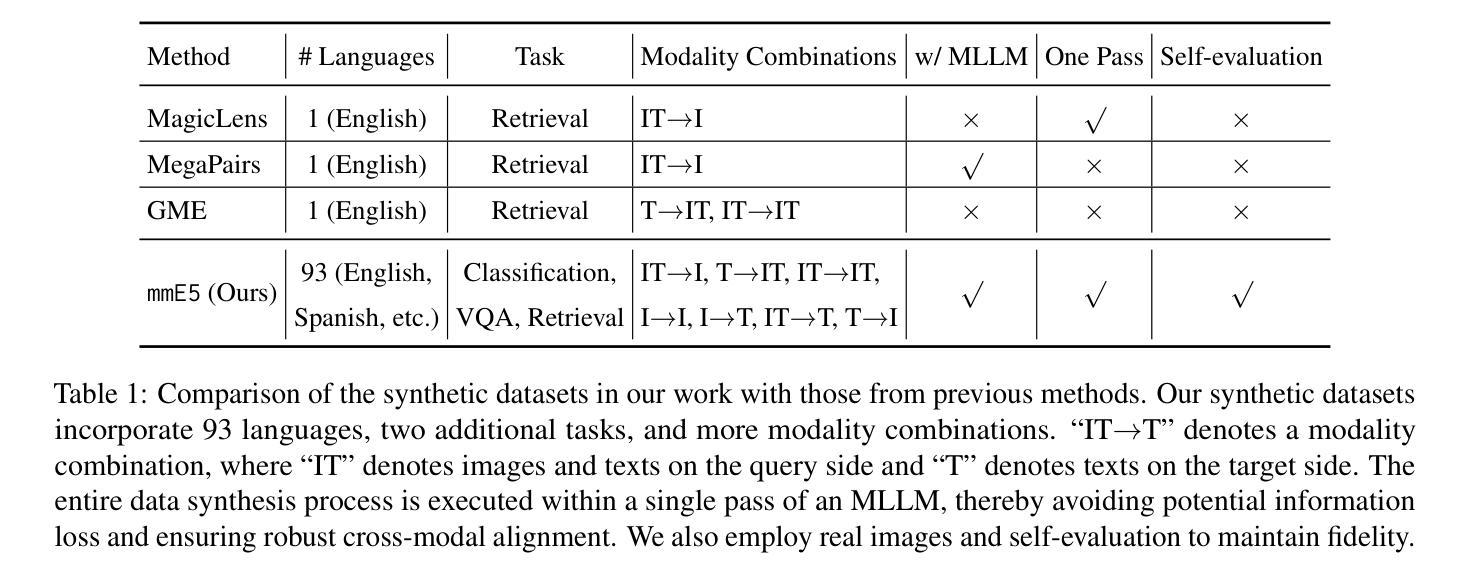
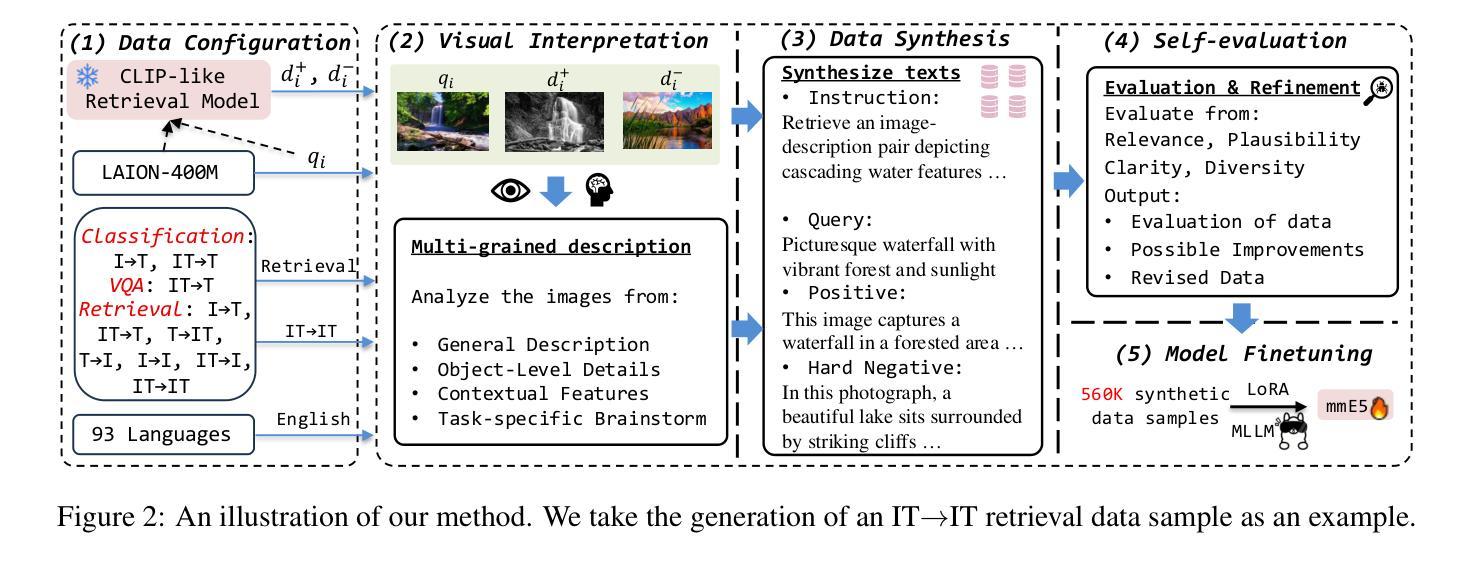
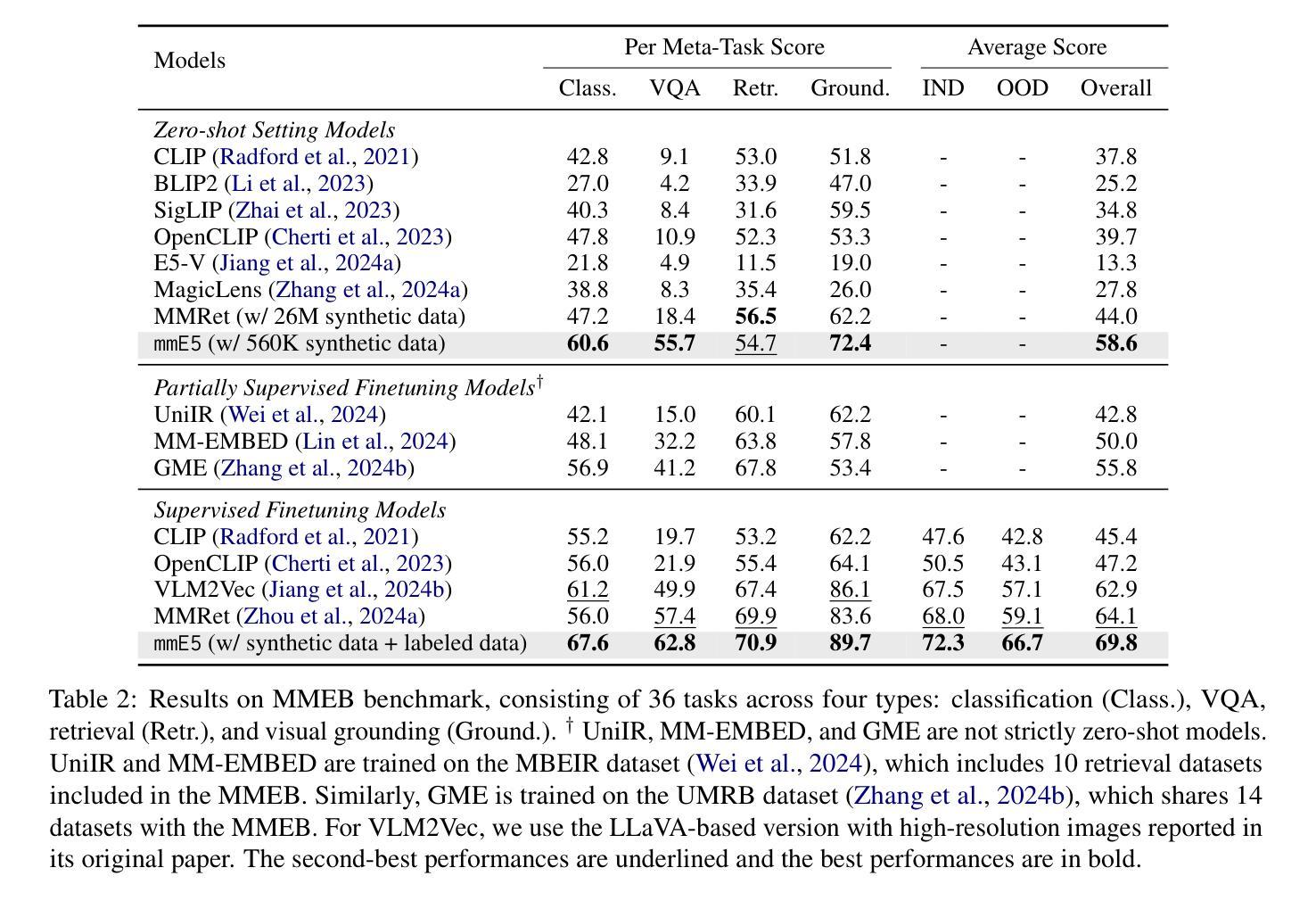
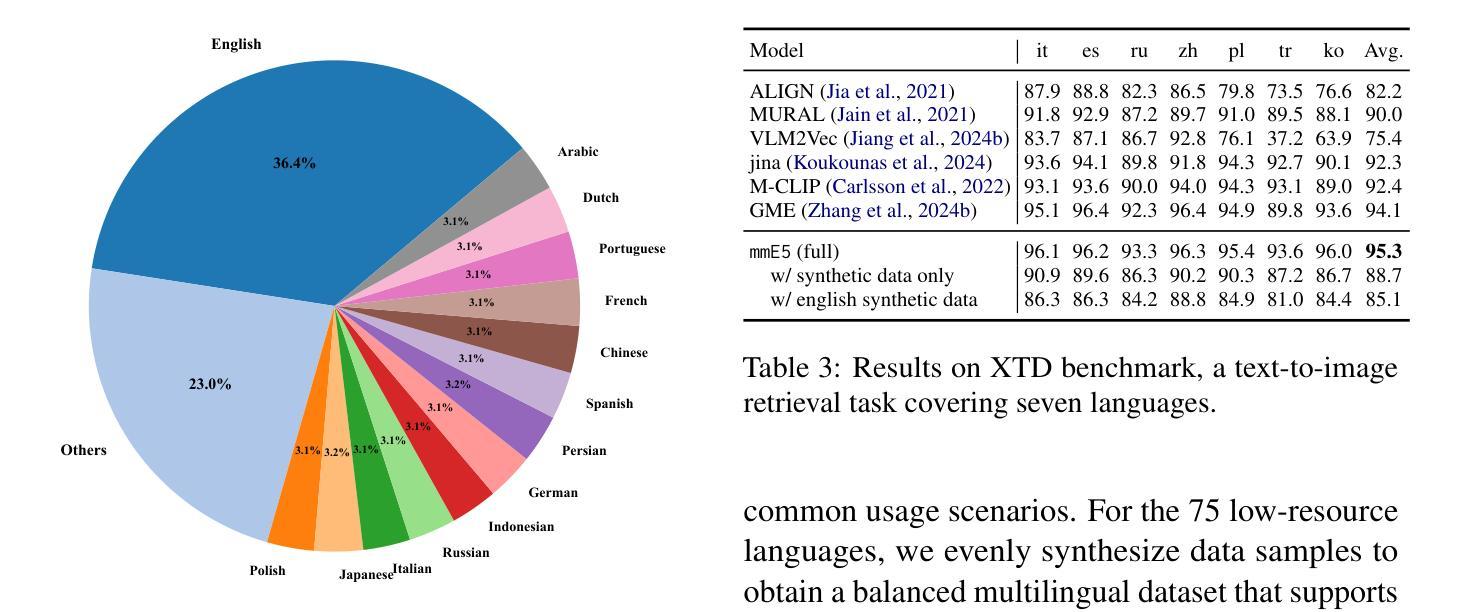
mmE5: Improving Multimodal Multilingual Embeddings via High-quality Synthetic Data
Authors:Haonan Chen, Liang Wang, Nan Yang, Yutao Zhu, Ziliang Zhao, Furu Wei, Zhicheng Dou
Multimodal embedding models have gained significant attention for their ability to map data from different modalities, such as text and images, into a unified representation space. However, the limited labeled multimodal data often hinders embedding performance. Recent approaches have leveraged data synthesis to address this problem, yet the quality of synthetic data remains a critical bottleneck. In this work, we identify three criteria for high-quality synthetic multimodal data. First, broad scope ensures that the generated data covers diverse tasks and modalities, making it applicable to various downstream scenarios. Second, robust cross-modal alignment makes different modalities semantically consistent. Third, high fidelity ensures that the synthetic data maintains realistic details to enhance its reliability. Guided by these principles, we synthesize datasets that: (1) cover a wide range of tasks, modality combinations, and languages, (2) are generated via a deep thinking process within a single pass of a multimodal large language model, and (3) incorporate real-world images with accurate and relevant texts, ensuring fidelity through self-evaluation and refinement. Leveraging these high-quality synthetic and labeled datasets, we train a multimodal multilingual E5 model mmE5. Extensive experiments demonstrate that mmE5 achieves state-of-the-art performance on the MMEB Benchmark and superior multilingual performance on the XTD benchmark. Our codes, datasets and models are released in https://github.com/haon-chen/mmE5.
多模态嵌入模型因其能够将文本和图像等不同模态的数据映射到统一表示空间的能力而受到广泛关注。然而,有限的标记多模态数据通常会影响嵌入性能。最近的方法利用数据合成来解决这个问题,但合成数据的质量仍然是关键瓶颈。在我们的研究中,我们确定了高质量合成多模态数据的三个标准。首先,广泛覆盖要求生成的数据涵盖各种任务和模态,使其适用于各种下游场景。其次,稳健的跨模态对齐使得不同模态在语义上保持一致。第三,高保真度确保合成数据保持现实世界的细节,以提高其可靠性。遵循这些原则,我们合成的数据集包括:(1)涵盖广泛的任务、模态组合和语言;(2)通过单通道多模态大型语言模型的深度思考过程生成;(3)结合现实世界的图像和准确相关的文本,通过自我评估和精炼确保保真度。利用这些高质量合成和标记的数据集,我们训练了一个多模态多语言E5模型mmE5。大量实验表明,mmE5在MMEB基准测试上达到了最先进的性能,并在XTD基准测试上表现出卓越的多语言能力。我们的代码、数据集和模型已在https://github.com/haon-chen/mmE5上发布。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文关注多模态嵌入模型在数据映射方面的能力,特别是在处理不同模态数据(如文本和图像)时面临的挑战。针对有限标记多模态数据的问题,研究通过数据合成来解决,同时强调高质量合成数据的重要性。提出三个标准:范围广泛、跨模态对齐和高质量保真。基于这些标准,研究团队合成了一系列数据集并训练了mmE5模型。该模型在MMEB和XTD基准测试中表现出卓越性能。相关代码和数据集已发布在[链接地址]。
Key Takeaways
- 多模态嵌入模型能够将不同模态的数据映射到统一表示空间。
- 有限的标记多模态数据限制了嵌入模型的性能。
- 数据合成是解决此问题的一种策略,但合成数据的质量是关键瓶颈。
- 高质量合成数据的三个标准是:范围广泛、跨模态对齐和高质量保真。
- 研究团队基于这些标准合成了一系列数据集,并训练了mmE5模型。
- mmE5在MMEB和XTD基准测试中表现出卓越性能。
点此查看论文截图

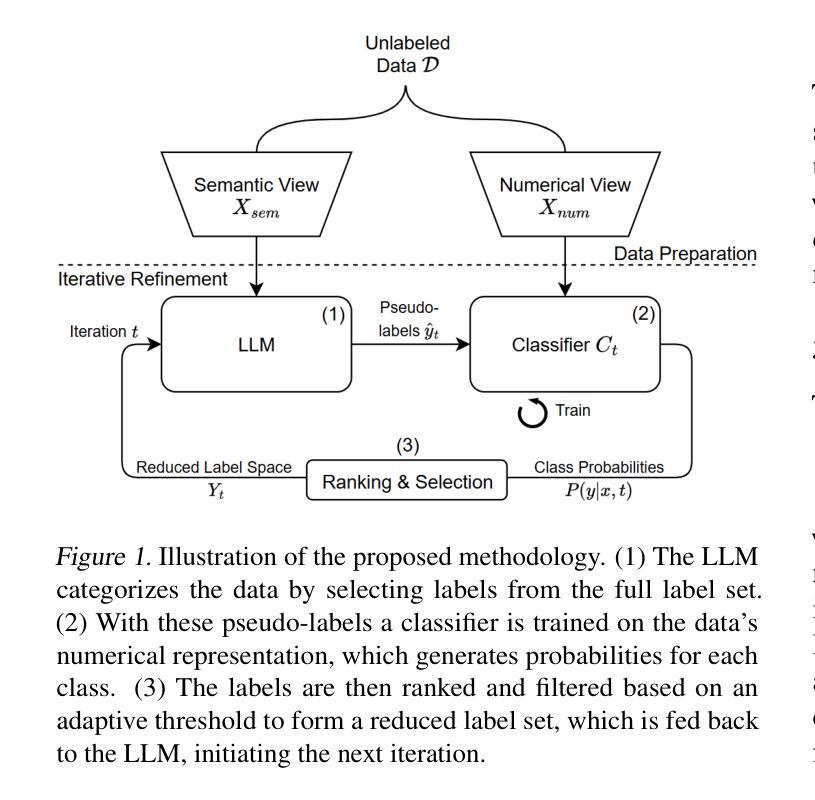
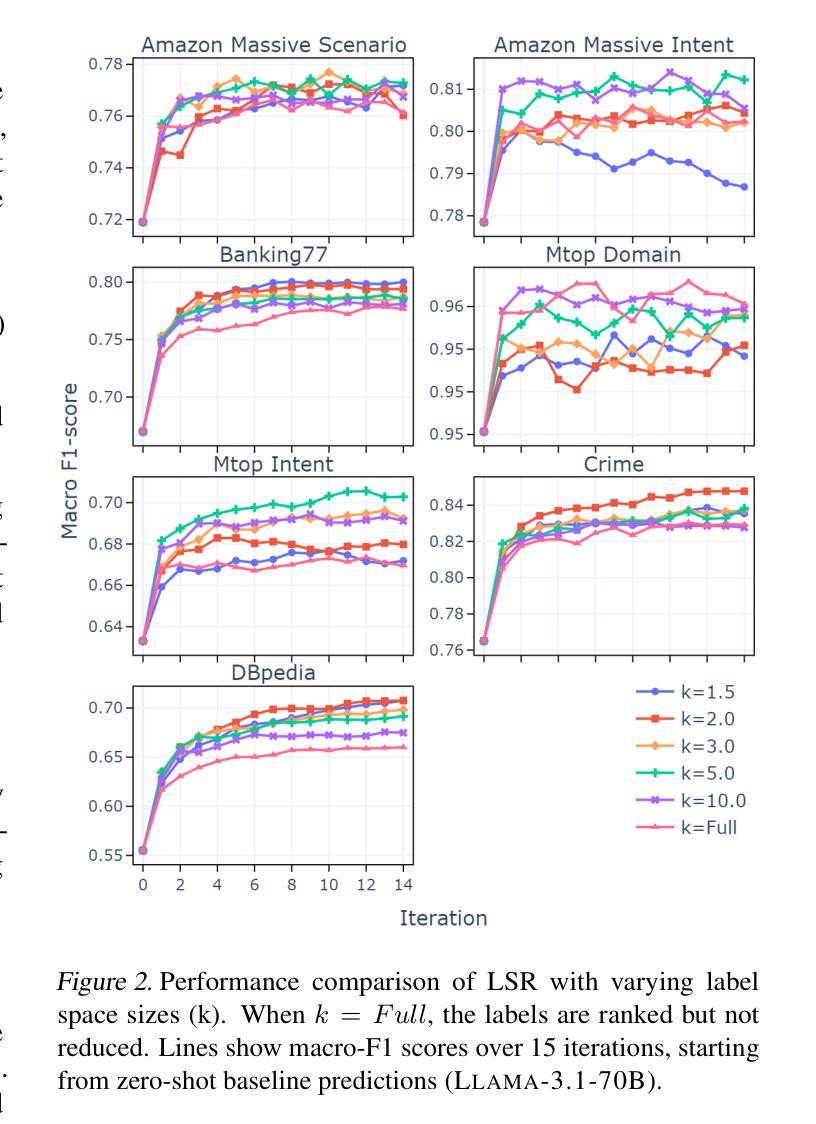
From Haystack to Needle: Label Space Reduction for Zero-shot Classification
Authors:Nathan Vandemoortele, Bram Steenwinckel, Femke Ongenae, Sofie Van Hoecke
We present Label Space Reduction (LSR), a novel method for improving zero-shot classification performance of Large Language Models (LLMs). LSR iteratively refines the classification label space by systematically ranking and reducing candidate classes, enabling the model to concentrate on the most relevant options. By leveraging unlabeled data with the statistical learning capabilities of data-driven models, LSR dynamically optimizes the label space representation at test time. Our experiments across seven benchmarks demonstrate that LSR improves macro-F1 scores by an average of 7.0% (up to 14.2%) with Llama-3.1-70B and 3.3% (up to 11.1%) with Claude-3.5-Sonnet compared to standard zero-shot classification baselines. To reduce the computational overhead of LSR, which requires an additional LLM call at each iteration, we propose distilling the model into a probabilistic classifier, allowing for efficient inference.
我们提出了一种名为标签空间缩减(LSR)的新方法,用于提升大型语言模型(LLM)的零样本分类性能。LSR通过系统地排序和缩减候选类别,对分类标签空间进行迭代优化,使模型能够专注于最相关的选项。该方法利用无标签数据以及数据驱动模型的统计学习能力,在测试时动态优化标签空间表示。我们在七个基准测试上的实验表明,与标准的零样本分类基线相比,LSR使用Llama-3.1-70B将宏F1分数平均提高了7.0%(最高达14.2%),使用Claude-3.5-Sonnet提高了3.3%(最高达11.1%)。为了减少LSR的计算开销(需要在每次迭代时进行额外的LLM调用),我们提出将模型蒸馏成概率分类器,以实现高效推理。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Under review at ICML 2025
摘要
本文提出了Label Space Reduction(LSR)这一新方法,旨在提高大型语言模型(LLM)的零样本分类性能。LSR通过系统地对候选类别进行排名和减少,迭代地优化分类标签空间,使模型能够专注于最相关的选项。该方法利用无标签数据的统计学习能力,在测试时动态优化标签空间表示。实验表明,在七个基准测试中,LSR与标准零样本分类基线相比,使用Llama-3.1-70B时的宏观F1分数平均提高了7.0%(最高达14.2%),使用Claude-3.5-Sonnet时提高了3.3%(最高达11.1%)。为了降低LSR的计算开销(每次迭代需要额外的LLM调用),我们提出了将其蒸馏成概率分类器的方法,以实现高效推理。
关键见解
- LSR是一种提高大型语言模型零样本分类性能的新方法。
- LSR通过迭代地优化分类标签空间,提高了模型的关注度和性能。
- LSR利用无标签数据的统计学习能力,在测试时动态调整标签空间。
- 实验表明,LSR在多个基准测试中显著提高了宏观F1分数。
- 与标准零样本分类基线相比,LSR在Llama-3.1-70B上的性能平均提高了7.0%,在Claude-3.5-Sonnet上提高了3.3%。
- LSR方法虽然有效,但需要额外的计算开销。
- 为了提高推理效率,提出了将模型蒸馏成概率分类器的解决方案。
点此查看论文截图

Tractable Transformers for Flexible Conditional Generation
Authors:Anji Liu, Xuejie Liu, Dayuan Zhao, Mathias Niepert, Yitao Liang, Guy Van den Broeck
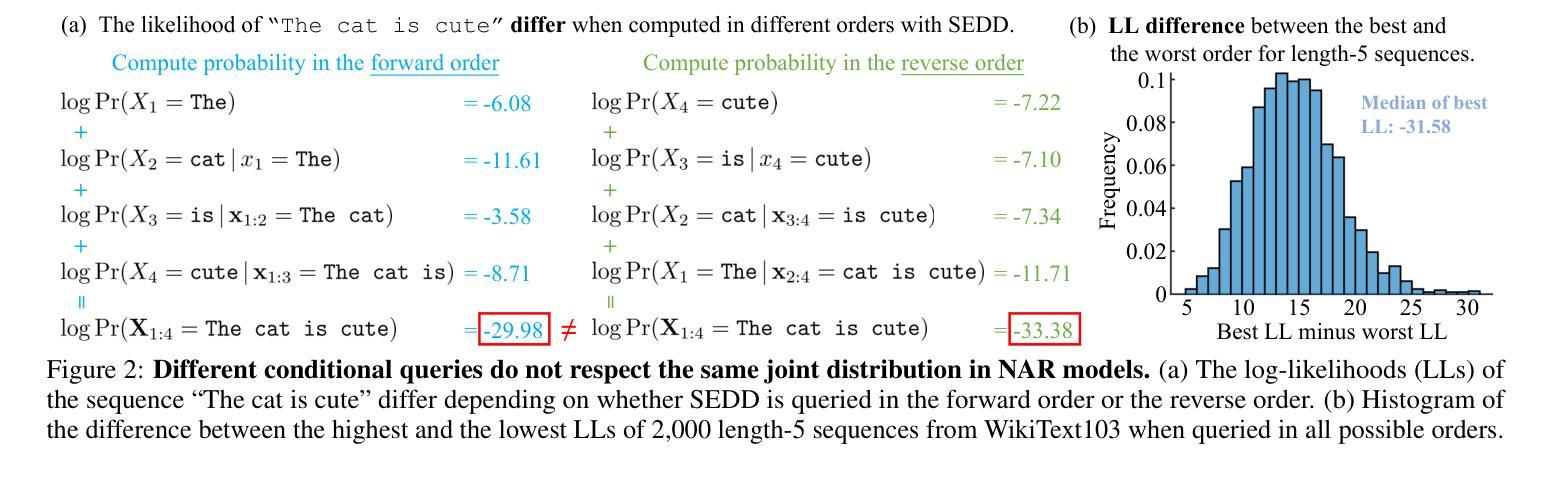
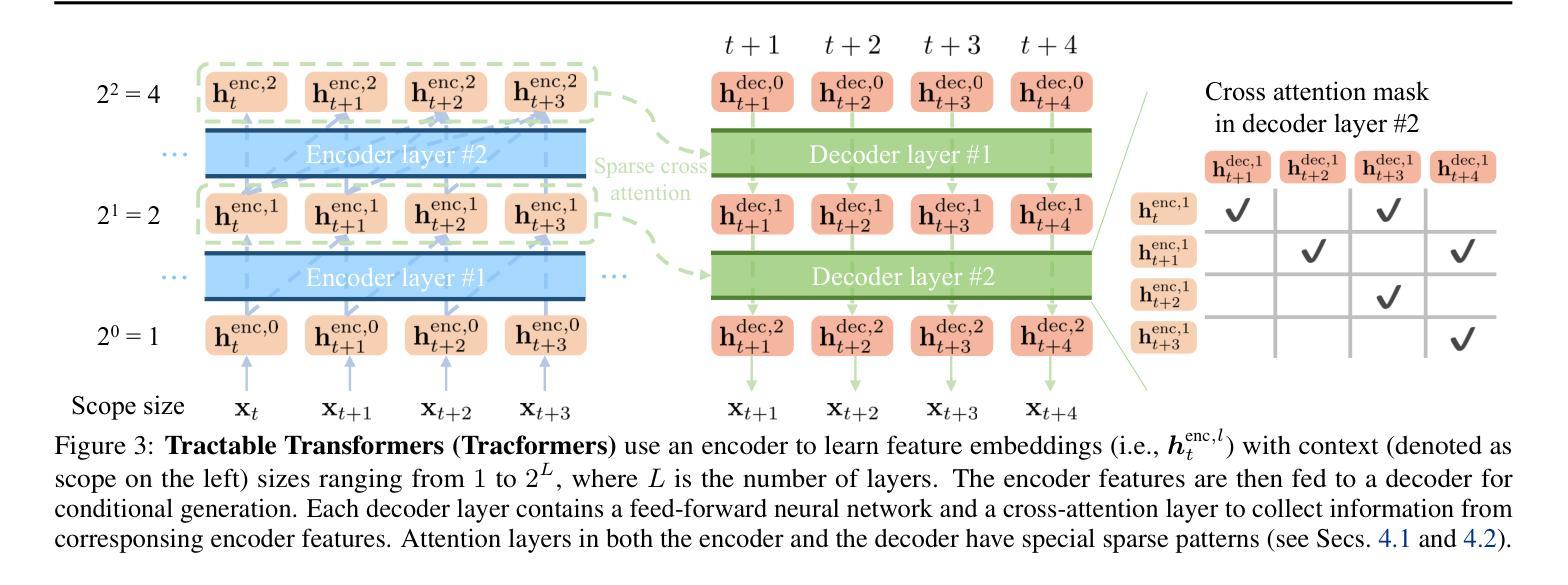
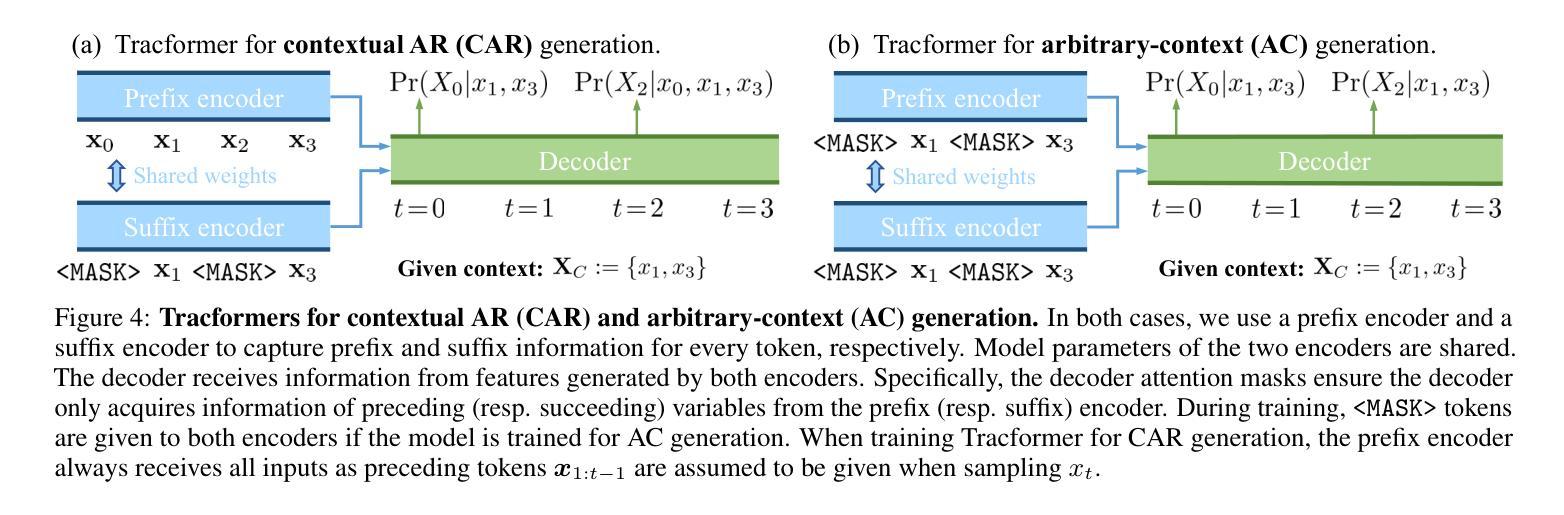
Non-autoregressive (NAR) generative models are valuable because they can handle diverse conditional generation tasks in a more principled way than their autoregressive (AR) counterparts, which are constrained by sequential dependency requirements. Recent advancements in NAR models, such as diffusion language models, have demonstrated superior performance in unconditional generation compared to AR models (e.g., GPTs) of similar sizes. However, such improvements do not always lead to improved conditional generation performance. We show that a key reason for this gap is the difficulty in generalizing to conditional probability queries unseen during training. As a result, strong unconditional generation performance does not guarantee high-quality conditional generation. This paper proposes Tractable Transformers (Tracformer), a Transformer-based generative model that is more robust to different conditional generation tasks. Unlike existing models that rely solely on global contextual features derived from full inputs, Tracformers incorporate a sparse Transformer encoder to capture both local and global contextual information. This information is routed through a decoder for conditional generation. Empirical results demonstrate that Tracformers achieve state-of-the-art conditional generation performance on text modeling compared to recent diffusion and AR model baselines.
非自回归(NAR)生成模型具有价值,因为它们能够以比自回归(AR)模型更原则化的方式处理多种条件生成任务。自回归模型受到序列依赖性的约束。近期NAR模型的进步,如扩散语言模型,在无条件生成方面表现出了与类似规模的AR模型(如GPT)相比的卓越性能。然而,这些改进并不总是导致条件生成性能的提高。我们表明,这一差距的关键原因是难以推广到训练期间未见过的条件概率查询。因此,强大的无条件生成性能并不保证高质量的条件生成。本文提出了“可处理变换器(Tracformer)”,这是一种基于Transformer的生成模型,对于不同的条件生成任务更具鲁棒性。与现有仅依赖全局上下文特征的模型不同,Tracformers结合稀疏Transformer编码器来捕获局部和全局上下文信息。这些信息通过解码器进行条件生成。经验结果表明,在文本建模方面,Tracformers实现了与最新扩散和AR模型基线相比的最先进条件生成性能。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
近期非自回归(NAR)生成模型在处理条件生成任务时展现出优势,尤其是通过扩散语言模型等新技术。尽管在无条件生成方面性能优越,但在条件生成上不一定优于自回归(AR)模型。研究发现,这源于对新条件下概率查询的泛化难度。本文提出Tractable Transformers(Tracformer),结合局部与全局上下文信息,在条件生成上表现卓越。
Key Takeaways
- 非自回归生成模型能更灵活地处理多样化的条件生成任务。
- 扩散语言模型等非自回归模型在无条件生成方面表现优于类似规模的自回归模型。
- 仅依赖全局上下文特征的现有模型在条件生成任务上可能存在局限性。
- 条件生成性能的提升需要模型对新条件下概率查询的泛化能力。
- Tractable Transformers结合了局部和全局上下文信息,提高了条件生成的效果。
- Tractable Transformers在文本建模上实现了对近期扩散模型和自回归模型基准测试的条件生成性能的最佳表现。
点此查看论文截图

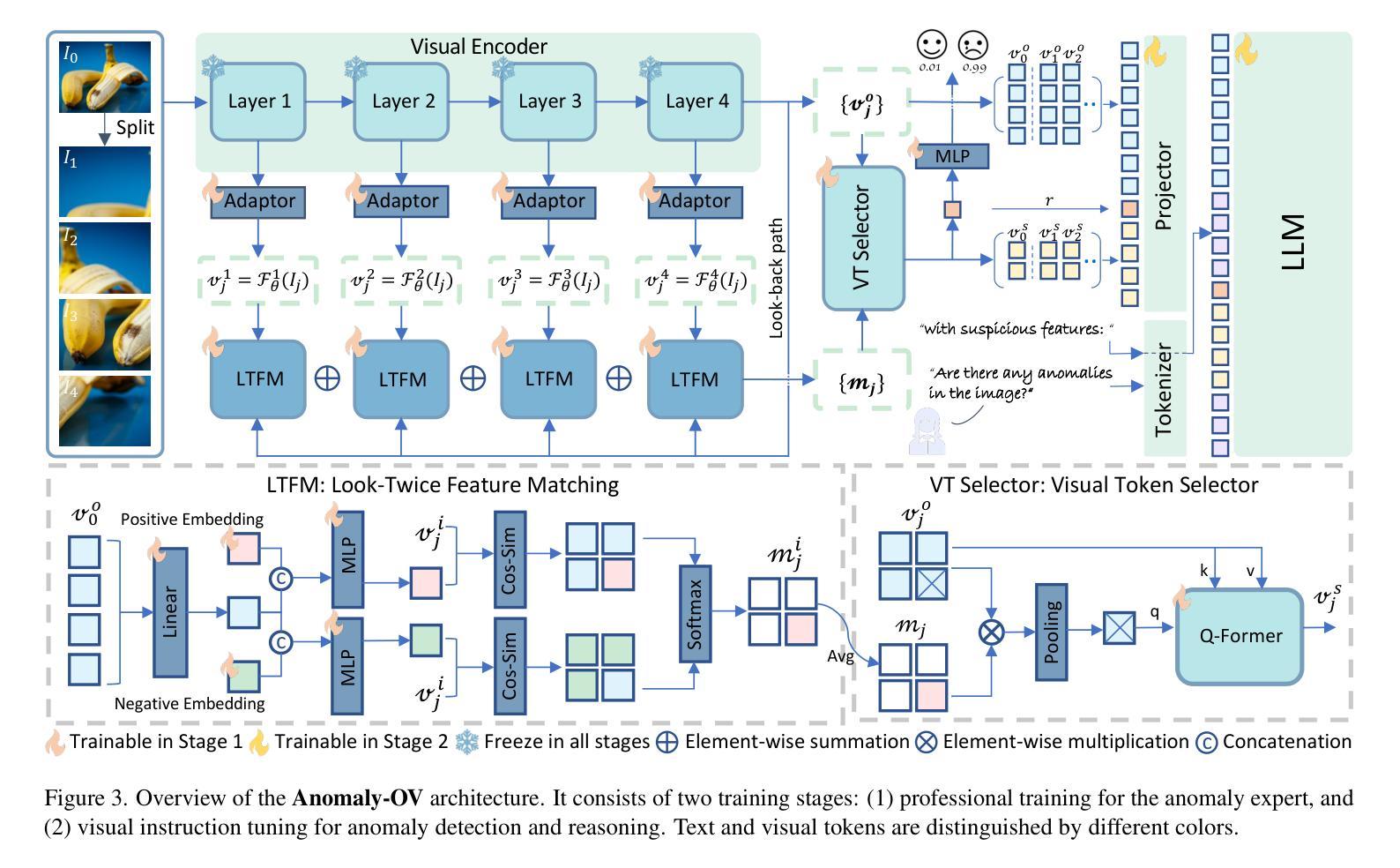
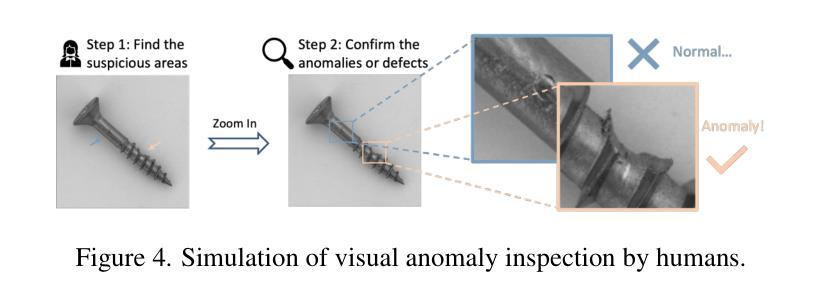
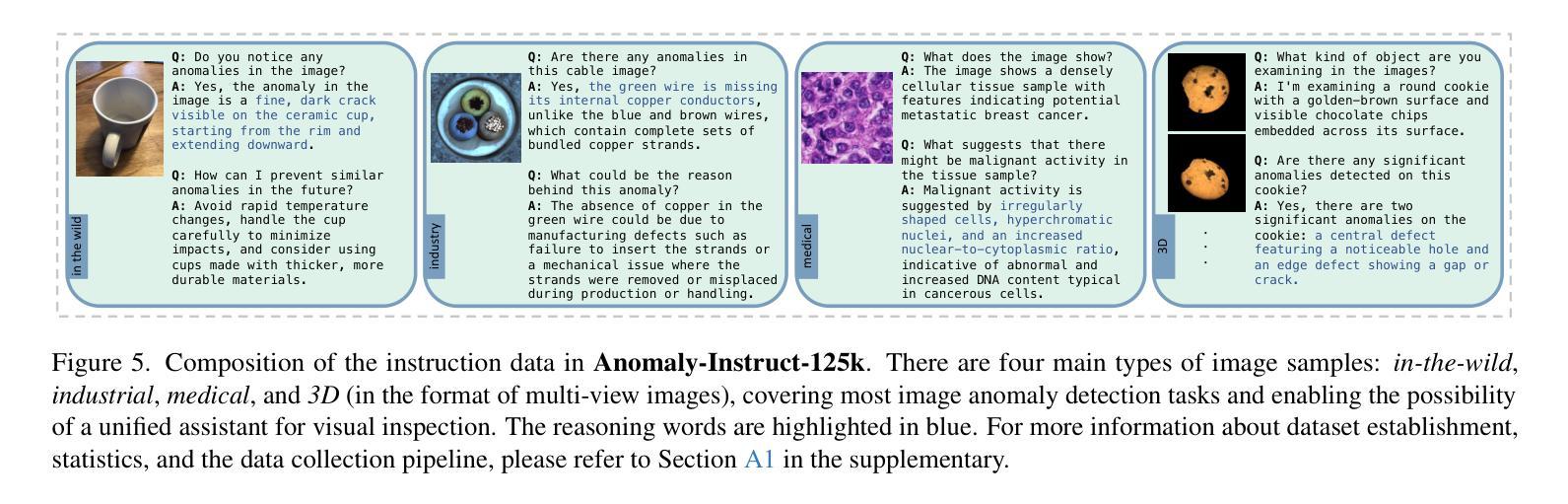
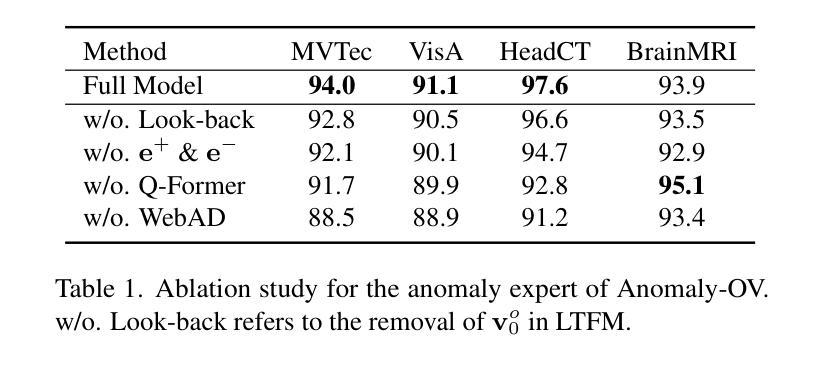
Towards Zero-Shot Anomaly Detection and Reasoning with Multimodal Large Language Models
Authors:Jiacong Xu, Shao-Yuan Lo, Bardia Safaei, Vishal M. Patel, Isht Dwivedi
Zero-Shot Anomaly Detection (ZSAD) is an emerging AD paradigm. Unlike the traditional unsupervised AD setting that requires a large number of normal samples to train a model, ZSAD is more practical for handling data-restricted real-world scenarios. Recently, Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) have shown revolutionary reasoning capabilities in various vision tasks. However, the reasoning of image abnormalities remains underexplored due to the lack of corresponding datasets and benchmarks. To facilitate research in AD & reasoning, we establish the first visual instruction tuning dataset, Anomaly-Instruct-125k, and the evaluation benchmark, VisA-D&R. Through investigation with our benchmark, we reveal that current MLLMs like GPT-4o cannot accurately detect and describe fine-grained anomalous details in images. To address this, we propose Anomaly-OneVision (Anomaly-OV), the first specialist visual assistant for ZSAD and reasoning. Inspired by human behavior in visual inspection, Anomaly-OV leverages a Look-Twice Feature Matching (LTFM) mechanism to adaptively select and emphasize abnormal visual tokens. Extensive experiments demonstrate that Anomaly-OV achieves significant improvements over advanced generalist models in both detection and reasoning. Extensions to medical and 3D AD are provided for future study. The link to our project page: https://xujiacong.github.io/Anomaly-OV/
零样本异常检测(ZSAD)是一种新兴的异常检测范式。与传统的需要大批量正常样本来训练模型的监督型异常检测不同,ZSAD在应对数据受限的实际情况时更具实用性。近期,多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)在各种视觉任务中展现出革命性的推理能力。然而,由于缺乏相应的数据集和基准测试,图像异常的推理仍然被忽视。为了促进异常检测和推理的研究,我们建立了首个视觉指令调整数据集Anomaly-Instruct-125k和评估基准VisA-D&R。通过我们的基准调查,我们发现当前的MLLMs如GPT-4o无法准确检测和描述图像中的精细异常细节。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了Anomaly-OneVision(Anomaly-OV),这是专为ZSAD和推理设计的首个专业视觉助理。Anomaly-OV受到人类视觉检查行为的启发,利用二次特征匹配(LTFM)机制自适应选择和强调异常的视觉标记。大量实验表明,在检测和推理方面,Anomaly-OV较先进的通用模型有显著改进。还为医学和3D异常检测提供了扩展研究的方向。我们的项目页面链接:https://xujiacong.github.io/Anomaly-OV/
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 19 pages, 10 figures
Summary
基于零样本异常检测(ZSAD)的新兴发展趋势,当前面临缺乏训练数据和实际应用场景的挑战。本文通过建立首个视觉指令调整数据集Anomaly-Instruct-125k和评估基准VisA-D&R,推动了对多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)在异常检测和推理领域的研究。研究表明,现有的MLLMs无法准确检测和描述图像中的细微异常细节。为解决这一问题,本文提出了首个针对ZSAD和推理的专家视觉助手Anomaly-OneVision(Anomaly-OV)。它采用类似人类视觉检查的Look-Twice Feature Matching(LTFM)机制,自适应选择和强调异常的视觉标记。实验证明,Anomaly-OV在检测和推理方面都取得了显著的改进。此外,还为未来的医学和三维异常检测提供了扩展研究。
Key Takeaways
- 零样本异常检测(ZSAD)是处理数据限制现实场景的更实用方法,与传统无监督异常检测设置相比,无需大量正常样本进行模型训练。
- 建立了首个视觉指令调整数据集Anomaly-Instruct-125k和评估基准VisA-D&R,推动了对多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)在异常检测和推理方面的应用。
- 当前MLLMs在图像异常检测方面存在局限性,无法准确识别和描述细微的异常细节。
- Anomaly-OneVision(Anomaly-OV)作为一种专家视觉助手,通过采用Look-Twice Feature Matching(LTFM)机制解决了上述问题。
- Anomaly-OV在异常检测和推理方面实现了显著改进,通过自适应选择和强调异常的视觉标记来提高性能。
- Anomaly-OV的扩展研究包括医学和三维异常检测的潜在应用。
点此查看论文截图



Exoplanet Transit Candidate Identification in TESS Full-Frame Images via a Transformer-Based Algorithm
Authors:Helem Salinas, Rafael Brahm, Greg Olmschenk, Richard K. Barry, Karim Pichara, Stela Ishitani Silva, Vladimir Araujo
The Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite (TESS) is surveying a large fraction of the sky, generating a vast database of photometric time series data that requires thorough analysis to identify exoplanetary transit signals. Automated learning approaches have been successfully applied to identify transit signals. However, most existing methods focus on the classification and validation of candidates, while few efforts have explored new techniques for the search of candidates. To search for new exoplanet transit candidates, we propose an approach to identify exoplanet transit signals without the need for phase folding or assuming periodicity in the transit signals, such as those observed in multi-transit light curves. To achieve this, we implement a new neural network inspired by Transformers to directly process Full Frame Image (FFI) light curves to detect exoplanet transits. Transformers, originally developed for natural language processing, have recently demonstrated significant success in capturing long-range dependencies compared to previous approaches focused on sequential data. This ability allows us to employ multi-head self-attention to identify exoplanet transit signals directly from the complete light curves, combined with background and centroid time series, without requiring prior transit parameters. The network is trained to learn characteristics of the transit signal, like the dip shape, which helps distinguish planetary transits from other variability sources. Our model successfully identified 214 new planetary system candidates, including 122 multi-transit light curves, 88 single-transit and 4 multi-planet systems from TESS sectors 1-26 with a radius > 0.27 $R_{\mathrm{Jupiter}}$, demonstrating its ability to detect transits regardless of their periodicity.
凌日系外行星探测卫星(TESS)正在对天空进行大规模勘测,生成了大量光度时间序列数据,需要深入分析以识别系外行星凌日信号。自动化学习方法已成功应用于识别凌日信号。然而,大多数现有方法都集中在候选对象的分类和验证上,而很少有人探索寻找候选对象的新技术。为了寻找新的系外行星凌日候选对象,我们提出了一种无需相位折叠或假设凌日信号周期性的方法来识别系外行星凌日信号,例如多凌日光度曲线中所观察到的信号。为了实现这一点,我们受到Transformer启发的神经网络直接处理全帧图像(FFI)光度曲线来检测系外行星凌日现象。Transformer最初是为自然语言处理而开发的,最近的研究表明,与以前专注于顺序数据的方法相比,它在捕获长期依赖关系方面取得了显著的成功。这种能力使我们能够利用多头自注意力机制直接从完整的光度曲线中识别出系外行星凌日信号,并结合背景和质心时间序列,无需预先设定的凌日参数。网络经过训练,学习凌日信号的特征,如凹陷形状,这有助于区分行星凌日和其他变源。我们的模型成功识别了214个新的行星系统候选对象,包括122个多凌日光度曲线、88个单凌日和4个多行星系统,这些系统来自TESS的1-26个区域,其半径大于0.27个木星半径,证明了其检测凌日的能力,无论其周期性如何。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本研究使用受Transformer启发的神经网络直接处理全帧图像(FFI)光变曲线,无需相位折叠或假设周期性,即可检测行星过境信号。该方法成功识别了TESS扇区1-26中的214个新行星系统候选者,证明了其检测周期性不论的过境能力。
Key Takeaways
- TESS正在开展大规模天空调查,产生大量光度时间序列数据,需要深入分析以识别行星过境信号。
- 目前大多数方法集中在候选者的分类和验证上,很少有探索新方法寻找候选者。
- 研究提出了一种新的神经网络方法,直接处理全帧图像(FFI)光变曲线来检测行星过境信号,无需相位折叠或假设周期性。
- 该方法使用Transformer原理,能够捕捉长时间依赖性,成功识别出新的行星系统候选者。
- 该网络被训练学习过境信号的特征,如下降形状,有助于区分行星过境和其他变化源。
- 研究从TESS扇区1-26中成功识别了214个新的行星系统候选者,包括多过春光变曲线、单过光变和多重行星系统。
点此查看论文截图


Optimizing Knowledge Distillation in Transformers: Enabling Multi-Head Attention without Alignment Barriers
Authors:Zhaodong Bing, Linze Li, Jiajun Liang
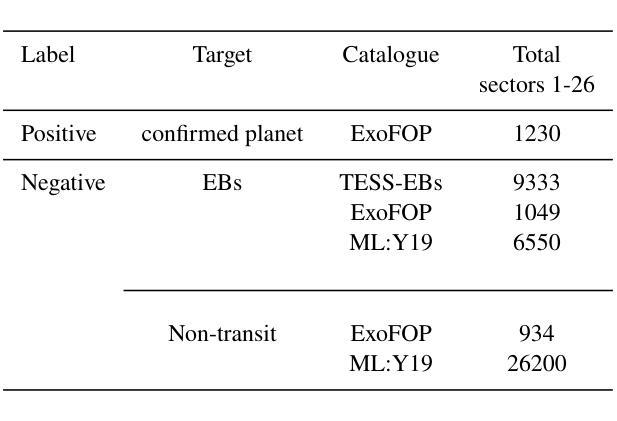
Knowledge distillation (KD) in transformers often faces challenges due to misalignment in the number of attention heads between teacher and student models. Existing methods either require identical head counts or introduce projectors to bridge dimensional gaps, limiting flexibility and efficiency. We propose Squeezing-Heads Distillation (SHD), a novel approach that enables seamless knowledge transfer between models with varying head counts by compressing multi-head attention maps via efficient linear approximation. Unlike prior work, SHD eliminates alignment barriers without additional parameters or architectural modifications. Our method dynamically approximates the combined effect of multiple teacher heads into fewer student heads, preserving fine-grained attention patterns while reducing redundancy. Experiments across language (LLaMA, GPT) and vision (DiT, MDT) generative and vision (DeiT) discriminative tasks demonstrate SHD’s effectiveness: it outperforms logit-based and feature-alignment KD baselines, achieving state-of-the-art results in image classification, image generation language fine-tuning, and language pre-training. The key innovations of flexible head compression, projector-free design, and linear-time complexity make SHD a versatile and scalable solution for distilling modern transformers. This work bridges a critical gap in KD, enabling efficient deployment of compact models without compromising performance.
知识蒸馏(KD)在转换器(transformer)中常因教师和学生在注意力头数量上的不匹配而面临挑战。现有方法要么要求头数相同,要么引入投影器来弥补维度差距,从而限制了灵活性和效率。我们提出了挤压头蒸馏法(SHD),这是一种新型方法,通过有效的线性近似压缩多头注意力图,实现在不同头数的模型之间进行无缝知识转移。不同于以前的工作,SHD消除了对齐障碍,无需额外的参数或架构修改。我们的方法动态地将多个教师头的综合效应近似为少数学生头,既保留了精细的注意力模式又减少了冗余。在语言生成(LLaMA、GPT)和视觉生成(DiT、MDT)以及视觉判别(DeiT)任务上的实验表明SHD的有效性:它超越了基于对数概率和教师头特征的基准知识蒸馏方法,在图像分类、图像生成语言微调以及语言预训练方面取得了最先进的成果。头压缩灵活性、无投影器设计以及线性时间复杂度等关键创新使SHD成为一种适用于现代转换器蒸馏的通用和可扩展解决方案。这项工作解决了KD中的一个关键空白,能够实现紧凑模型的高效部署,而不损害性能。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出了一个新的知识蒸馏(KD)方法——挤压头蒸馏(SHD),该方法能够在注意力头数量不同的模型间实现无缝知识迁移。通过高效线性近似压缩多头注意力图,SHD能够消除对齐障碍,无需额外的参数或架构修改。实验表明,SHD在跨语言生成和视觉判别任务上表现出卓越性能,实现了图像分类、图像生成语言微调以及语言预训练的最先进结果。
Key Takeaways
- SHD解决了知识蒸馏中由于教师模型和学生模型注意力头数量不匹配带来的挑战。
- 通过压缩多头注意力图,SHD实现了不同模型间的无缝知识迁移。
- SHD采用高效线性近似,无需额外的参数或架构修改。
- SHD在跨语言生成和视觉判别任务上表现出卓越性能。
- SHD在图像分类、图像生成语言微调以及语言预训练领域实现了最先进结果。
- SHD具有灵活的头压缩能力,使其成为知识蒸馏中通用且可伸缩的解决方案。
点此查看论文截图


On Iterative Evaluation and Enhancement of Code Quality Using GPT-4o
Authors:Rundong Liu, Andre Frade, Amal Vaidya, Maxime Labonne, Marcus Kaiser, Bismayan Chakrabarti, Jonathan Budd, Sean Moran
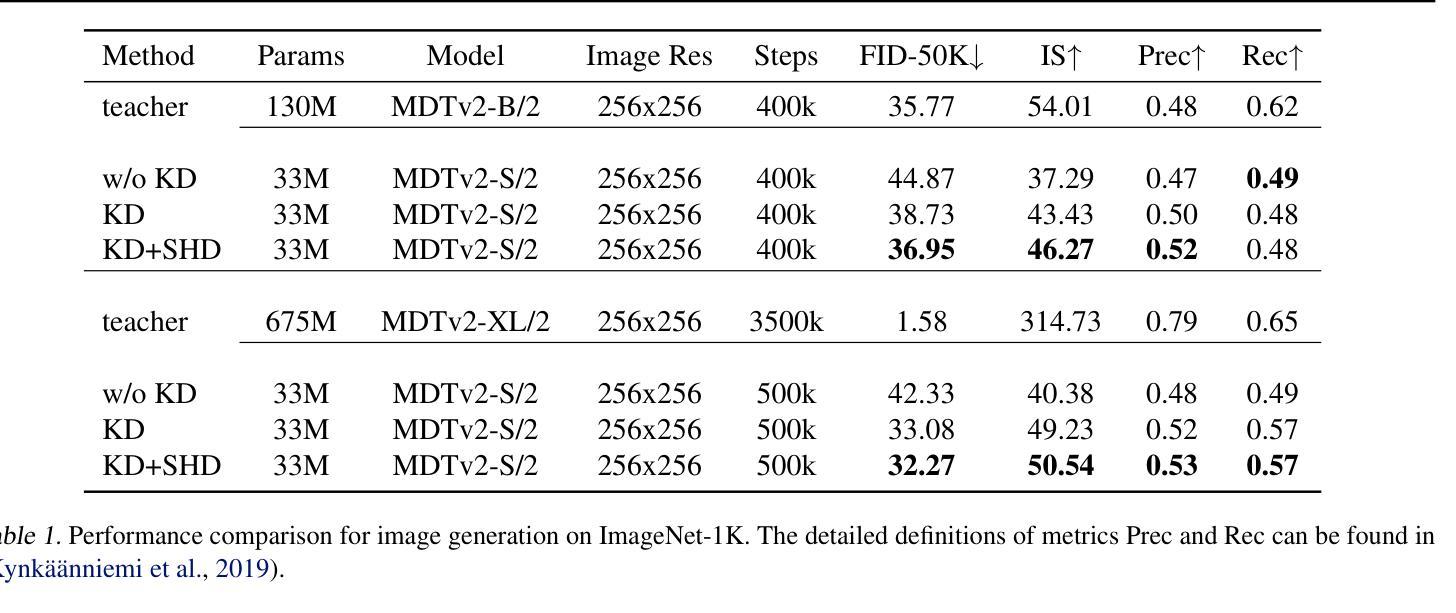
This paper introduces CodeQUEST, a novel framework leveraging Large Language Models (LLMs) to iteratively evaluate and enhance code quality across multiple dimensions, including readability, maintainability, efficiency, and security. The framework is divided into two main components: an Evaluator that assesses code quality across ten dimensions, providing both quantitative scores and qualitative summaries, and an Optimizer that iteratively improves the code based on the Evaluator’s feedback. Our study demonstrates that CodeQUEST can effectively and robustly evaluate code quality, with its assessments aligning closely with established code quality metrics. Through a series of experiments using a curated dataset of Python and JavaScript examples, CodeQUEST demonstrated significant improvements in code quality, achieving a mean relative percentage improvement of 52.6%. The framework’s evaluations were validated against a set of proxy metrics comprising of Pylint Score, Radon Maintainability Index, and Bandit output logs, showing a meaningful correlation. This highlights the potential of LLMs in automating code quality evaluation and improvement processes, presenting a significant advancement toward enhancing software development practices. The code implementation of the framework is available at: https://github.com/jpmorganchase/CodeQuest.
本文介绍了CodeQUEST,这是一个新型框架,利用大型语言模型(LLM)来多维度评估和提升代码质量,包括可读性、可维护性、效率和安全性。该框架分为两个主要组成部分:评估器,用于在十个维度上评估代码质量,提供定量评分和定性摘要;优化器,则基于评估器的反馈来迭代改进代码。我们的研究表明,CodeQUEST能够有效且稳定地评估代码质量,其评估结果与既定的代码质量指标高度吻合。通过一系列使用精选的Python和JavaScript示例数据集进行的实验,CodeQUEST在代码质量方面取得了显著的提升,平均相对百分比提升了52.6%。该框架的评估结果经过一组代理指标的验证,包括Pylint评分、Radon可维护性指数和Bandit输出日志,显示出有意义的相关性。这突显了大型语言模型在自动化代码质量评估和改进过程中的潜力,为改进软件开发实践带来了重大进展。该框架的代码实现可在https://github.com/jpmorganchase/CodeQuest获得。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
代码质量评估与提升框架CodeQUEST介绍。该框架利用大型语言模型(LLM)从可读性、可维护性、效率和安全性等多个维度评估代码质量,并提供反馈进行优化。实验表明,CodeQUEST能有效提升代码质量,平均相对提升率达52.6%。该框架的潜力在于能自动化代码质量评估和提升过程,有助于改进软件开发实践。
Key Takeaways
- CodeQUEST是一个利用大型语言模型(LLM)评估和提升代码质量的框架。
- 框架包含两个主要组件:Evaluator用于多维度评估代码质量,Optimizer则基于反馈优化代码。
- CodeQUEST能有效评估代码质量,与现有代码质量指标高度一致。
- 实验表明,CodeQUEST能显著提升代码质量,平均相对提升率达52.6%。
- 框架通过自动化代码质量评估和提升过程,有助于改进软件开发实践。
- CodeQUEST已经实现了代码实施框架,并可通过特定链接获取。
点此查看论文截图

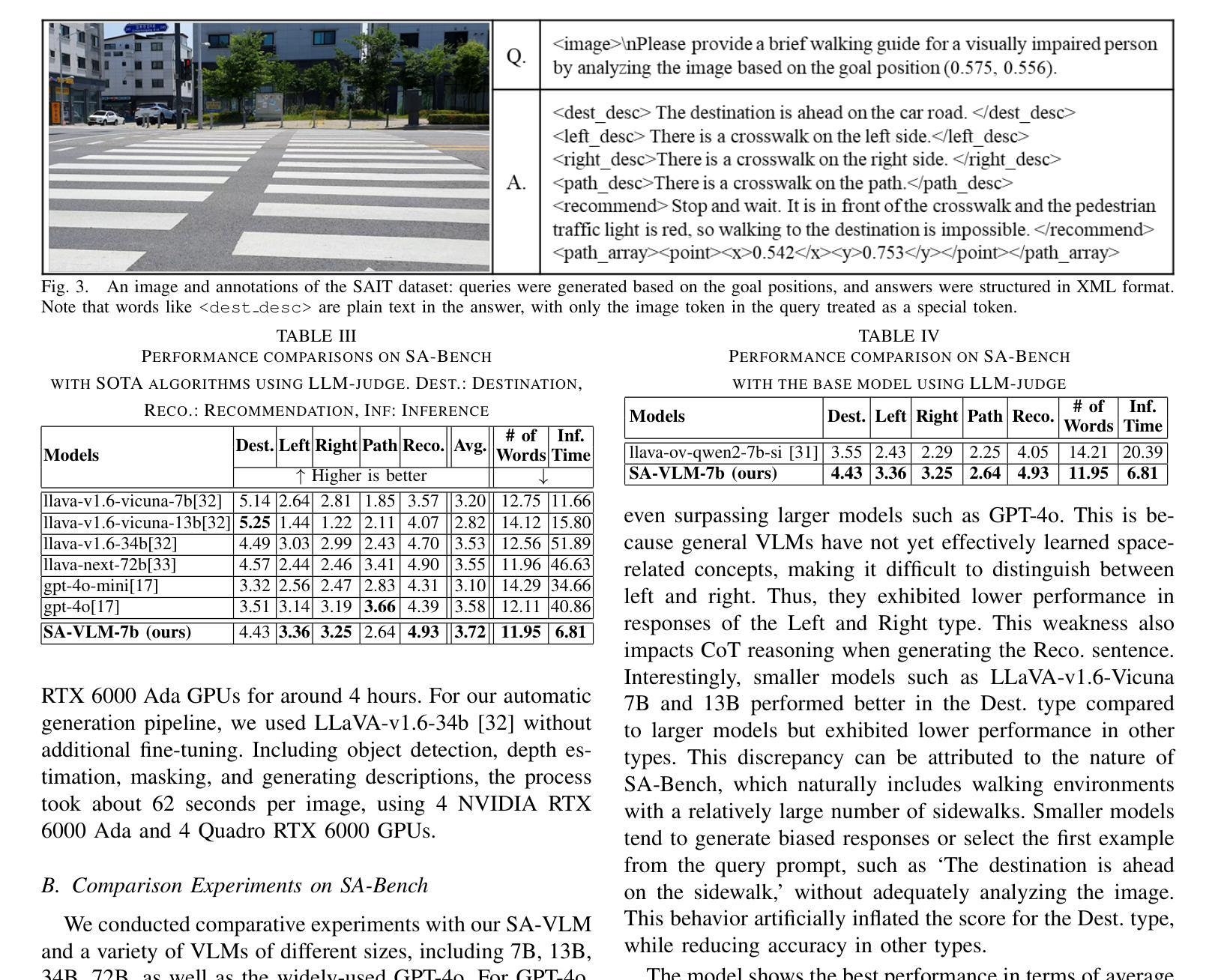
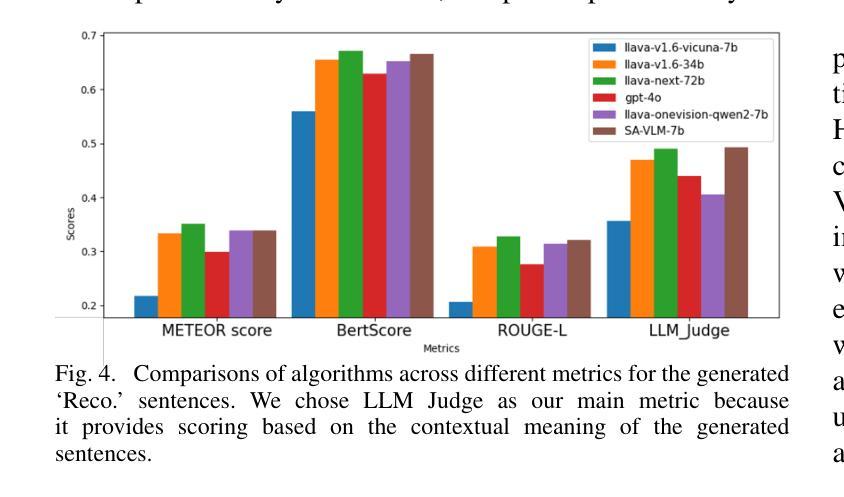
Space-Aware Instruction Tuning: Dataset and Benchmark for Guide Dog Robots Assisting the Visually Impaired
Authors:ByungOk Han, Woo-han Yun, Beom-Su Seo, Jaehong Kim
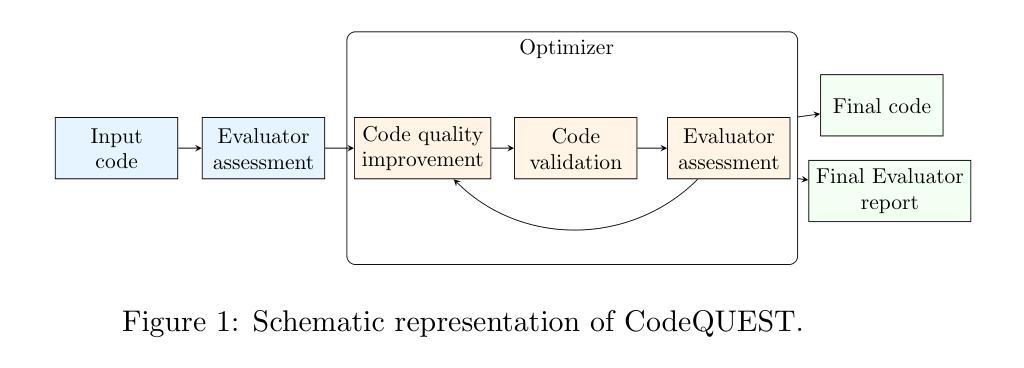
Guide dog robots offer promising solutions to enhance mobility and safety for visually impaired individuals, addressing the limitations of traditional guide dogs, particularly in perceptual intelligence and communication. With the emergence of Vision-Language Models (VLMs), robots are now capable of generating natural language descriptions of their surroundings, aiding in safer decision-making. However, existing VLMs often struggle to accurately interpret and convey spatial relationships, which is crucial for navigation in complex environments such as street crossings. We introduce the Space-Aware Instruction Tuning (SAIT) dataset and the Space-Aware Benchmark (SA-Bench) to address the limitations of current VLMs in understanding physical environments. Our automated data generation pipeline focuses on the virtual path to the destination in 3D space and the surroundings, enhancing environmental comprehension and enabling VLMs to provide more accurate guidance to visually impaired individuals. We also propose an evaluation protocol to assess VLM effectiveness in delivering walking guidance. Comparative experiments demonstrate that our space-aware instruction-tuned model outperforms state-of-the-art algorithms. We have fully open-sourced the SAIT dataset and SA-Bench, along with the related code, at https://github.com/byungokhan/Space-awareVLM
导航犬机器人对增强视障人士的机动性和安全性提供了有前景的解决方案,解决了传统导航犬在感知智能和沟通方面的局限。随着视觉语言模型(VLMs)的出现,机器人现在能够生成周围环境的自然语言描述,有助于做出更安全的决策。然而,现有的VLMs在解读和传达空间关系方面常常遇到困难,这在复杂环境(如十字路口)的导航中至关重要。为了解决当前VLMs在理解物理环境方面的局限性,我们推出了空间感知指令调优(SAIT)数据集和空间感知基准测试(SA-Bench)。我们的自动化数据生成管道专注于以目的地为中心的虚拟路径和空间周围环境,增强对环境的理解,使VLMs能够为视障人士提供更准确的导航。我们还提出了一个评估协议,以评估VLM在提供步行指导方面的有效性。对比实验表明,我们的空间感知指令调优模型优于最新算法。我们已在https://github.com/byungokhan/Space-awareVLM上完全开源了SAIT数据集和SA-Bench以及相关代码。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICRA 2025
Summary
该指南犬机器人提供了增强视力障碍者行动能力和安全性的解决方案,解决了传统指南犬在感知智能和沟通方面的局限。借助视觉语言模型(VLMs)的兴起,机器人可以生成周围环境中的自然语言描述,辅助做出更安全的决策。然而,现有的VLMs在解读和传达空间关系方面存在困难,这对在街道交叉口等复杂环境中的导航至关重要。为解决当前VLMs在理解物理环境方面的局限性,我们推出了空间感知指令调优(SAIT)数据集和空间感知基准测试(SA-Bench)。我们的自动化数据生成管道侧重于虚拟目标路径的三维空间及周围环境,提升环境理解能力,使VLMs能为视力障碍者提供更准确的指导。我们还提出了一个评估协议来评估VLM在提供步行指导方面的有效性。对比实验表明,我们的空间感知指令调优模型优于目前最先进的算法。我们已在https://github.com/byungokhan/Space-awareVLM上完全开源了SAIT数据集和SA-Bench及相关代码。
Key Takeaways
- 指南犬机器人通过视觉语言模型(VLMs)提高视力障碍者的行动能力。
- 现有VLMs在解读和传达空间关系方面存在挑战,影响导航准确性。
- 为解决这一问题,推出了空间感知指令调优(SAIT)数据集和空间感知基准测试(SA-Bench)。
- 自动化数据生成管道集中于虚拟路径及其三维空间环境,强化环境理解。
- 开放源码的SAIT数据集和SA-Bench旨在促进VLM在导航领域的研究进展。
- 提出的评估协议可有效评估VLM在提供步行指导方面的性能。
点此查看论文截图


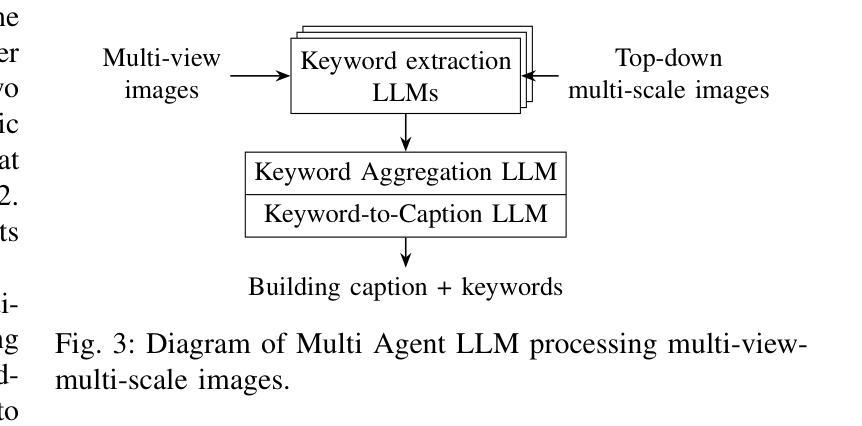
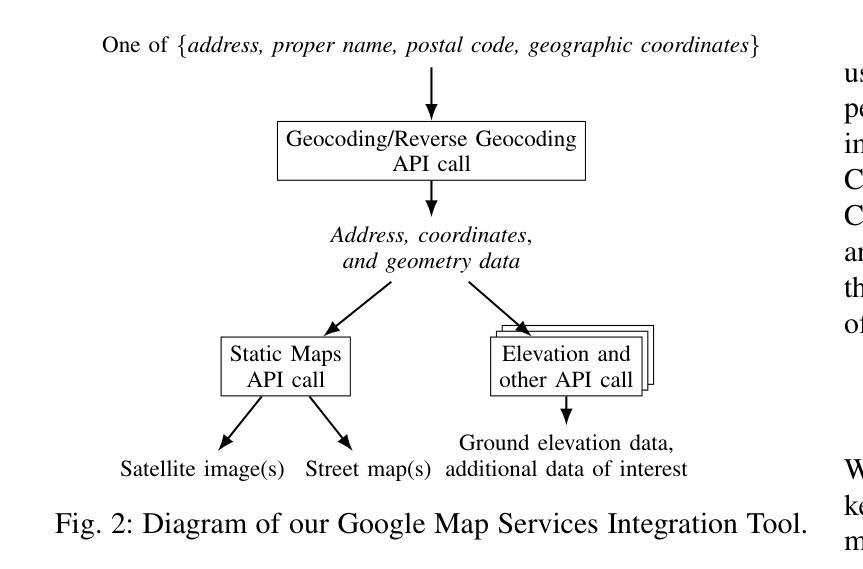
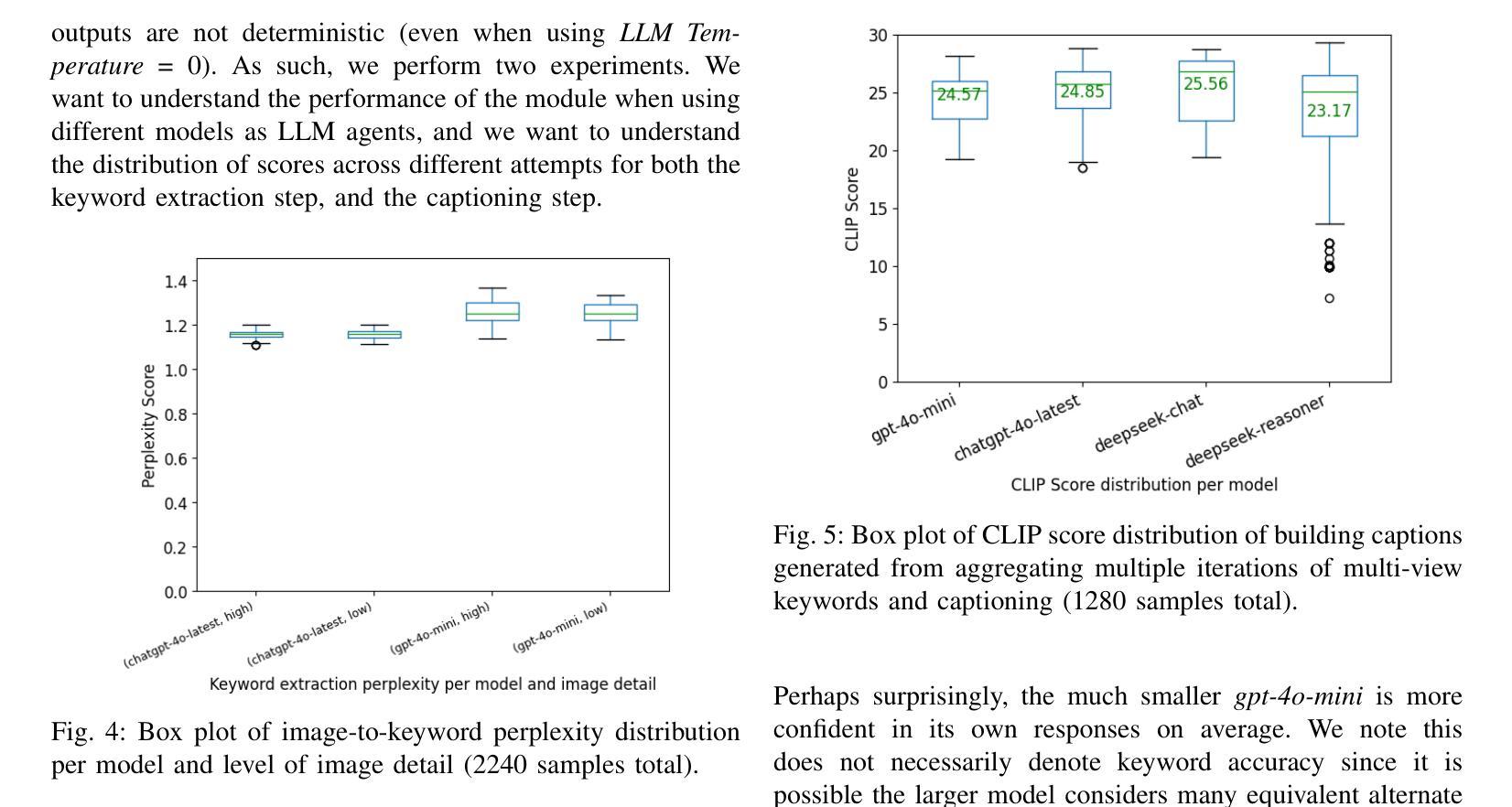
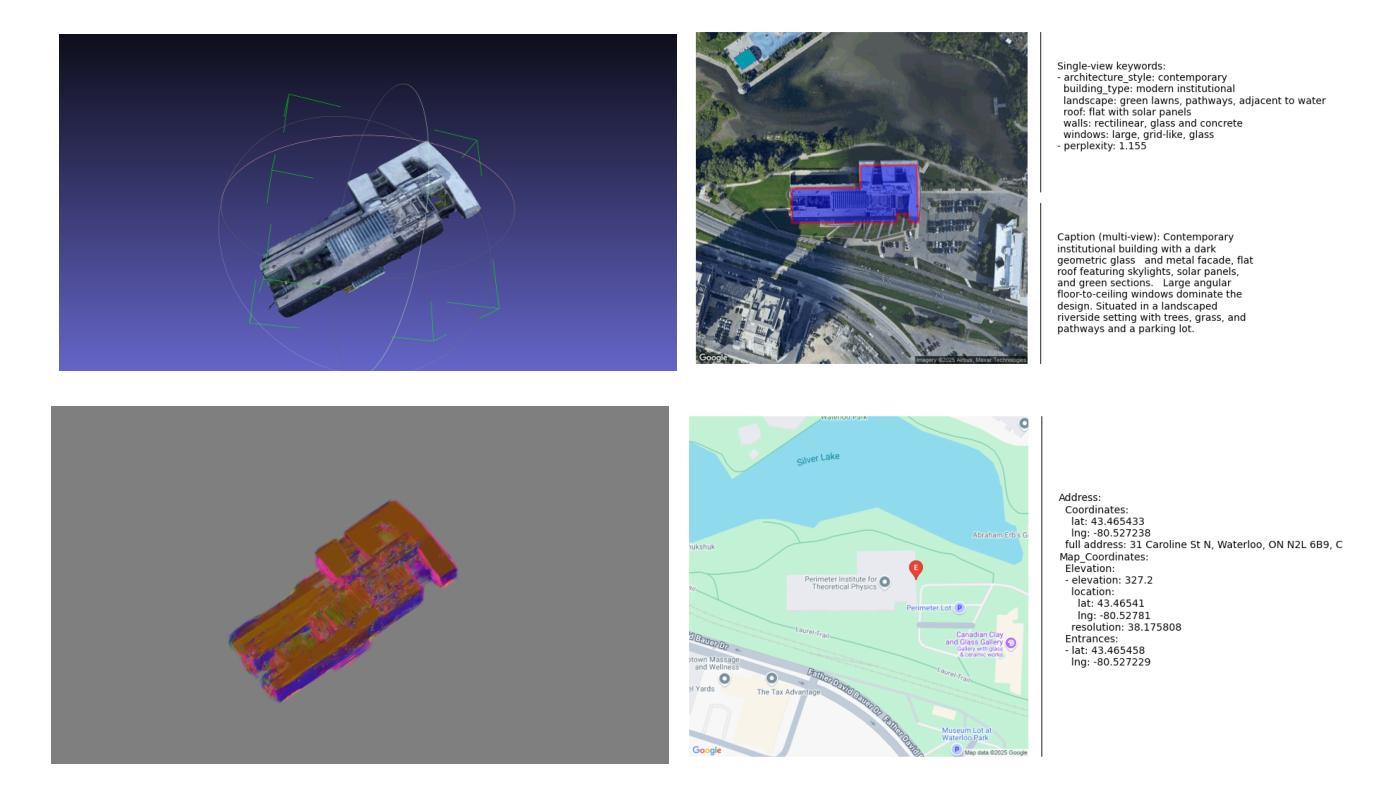
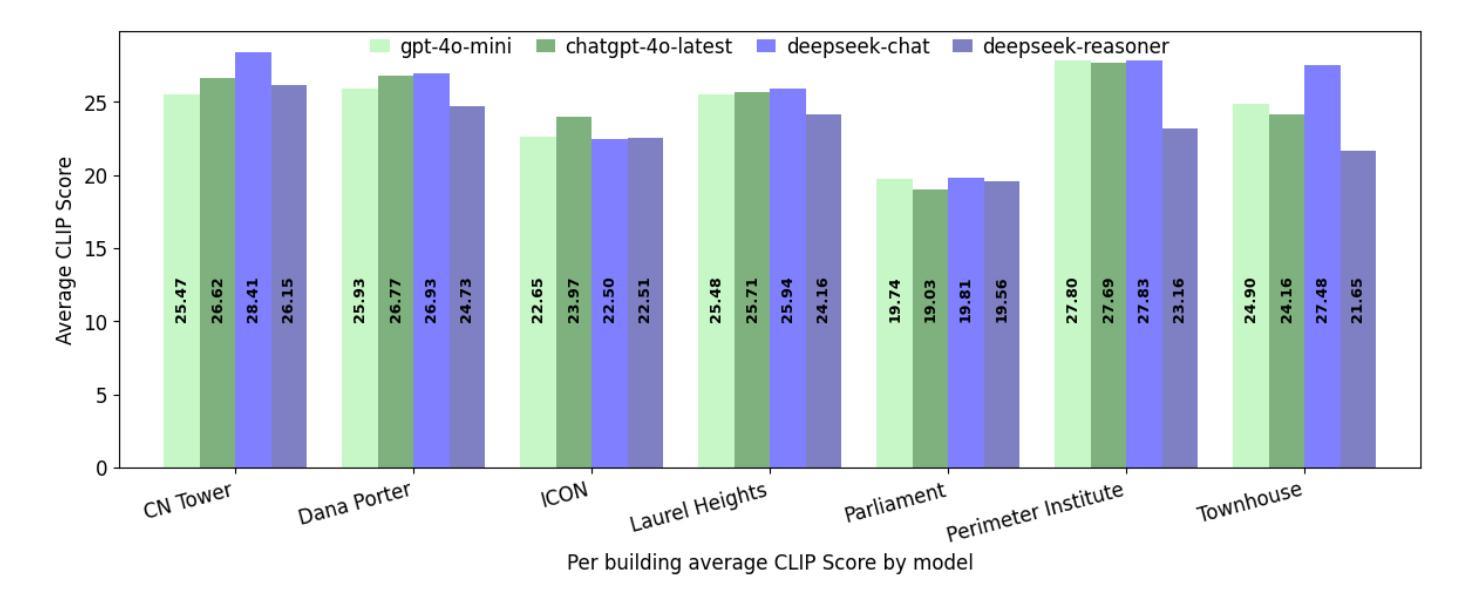
Digital Twin Buildings: 3D Modeling, GIS Integration, and Visual Descriptions Using Gaussian Splatting, ChatGPT/Deepseek, and Google Maps Platform
Authors:Kyle Gao, Dening Lu, Liangzhi Li, Nan Chen, Hongjie He, Linlin Xu, Jonathan Li
Urban digital twins are virtual replicas of cities that use multi-source data and data analytics to optimize urban planning, infrastructure management, and decision-making. Towards this, we propose a framework focused on the single-building scale. By connecting to cloud mapping platforms such as Google Map Platforms APIs, by leveraging state-of-the-art multi-agent Large Language Models data analysis using ChatGPT(4o) and Deepseek-V3/R1, and by using our Gaussian Splatting-based mesh extraction pipeline, our Digital Twin Buildings framework can retrieve a building’s 3D model, visual descriptions, and achieve cloud-based mapping integration with large language model-based data analytics using a building’s address, postal code, or geographic coordinates.
城市数字双胞胎是利用多源数据和数据分析优化城市规划、基础设施管理和决策制定的城市虚拟副本。为此,我们提出了一个以单栋建筑规模为重点的框架。通过连接到谷歌地图平台API等云地图平台,利用最新的多智能体大型语言模型,使用ChatGPT(4o)和Deepseek-V3/R1进行数据分析,以及利用我们的基于高斯喷涂技术的网格提取管道,我们的数字双胞胎建筑框架可以检索建筑的3D模型和视觉描述,并实现基于云的映射集成,通过大型语言模型数据分析与建筑地址、邮政编码或地理坐标相结合。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF -Fixed minor typo
Summary
城市数字双胞胎是城市的虚拟副本,利用多源数据和数据分析优化城市规划、基础设施管理和决策制定。我们提出一个专注于单体建筑尺度的框架,通过连接云计算地图平台、利用最新的多智能体大数据模型和算法,实现数字双胞胎建筑的云映射集成,能检索建筑物的三维模型、视觉描述等。
Key Takeaways
- 城市数字双胞胎是城市的虚拟副本,使用多源数据和数据分析优化城市规划和管理。
- 提出的框架专注于单体建筑尺度。
- 通过连接云计算地图平台获取建筑物的三维模型和视觉描述。
- 利用最新的多智能体大数据模型和算法,如ChatGPT和Deepseek-V3/R1,进行数据分析。
- 数字双胞胎建筑框架可以通过建筑地址、邮政编码或地理坐标实现云映射集成。
- 该框架有助于优化决策制定,提升城市规划、基础设施管理的效率和准确性。
点此查看论文截图


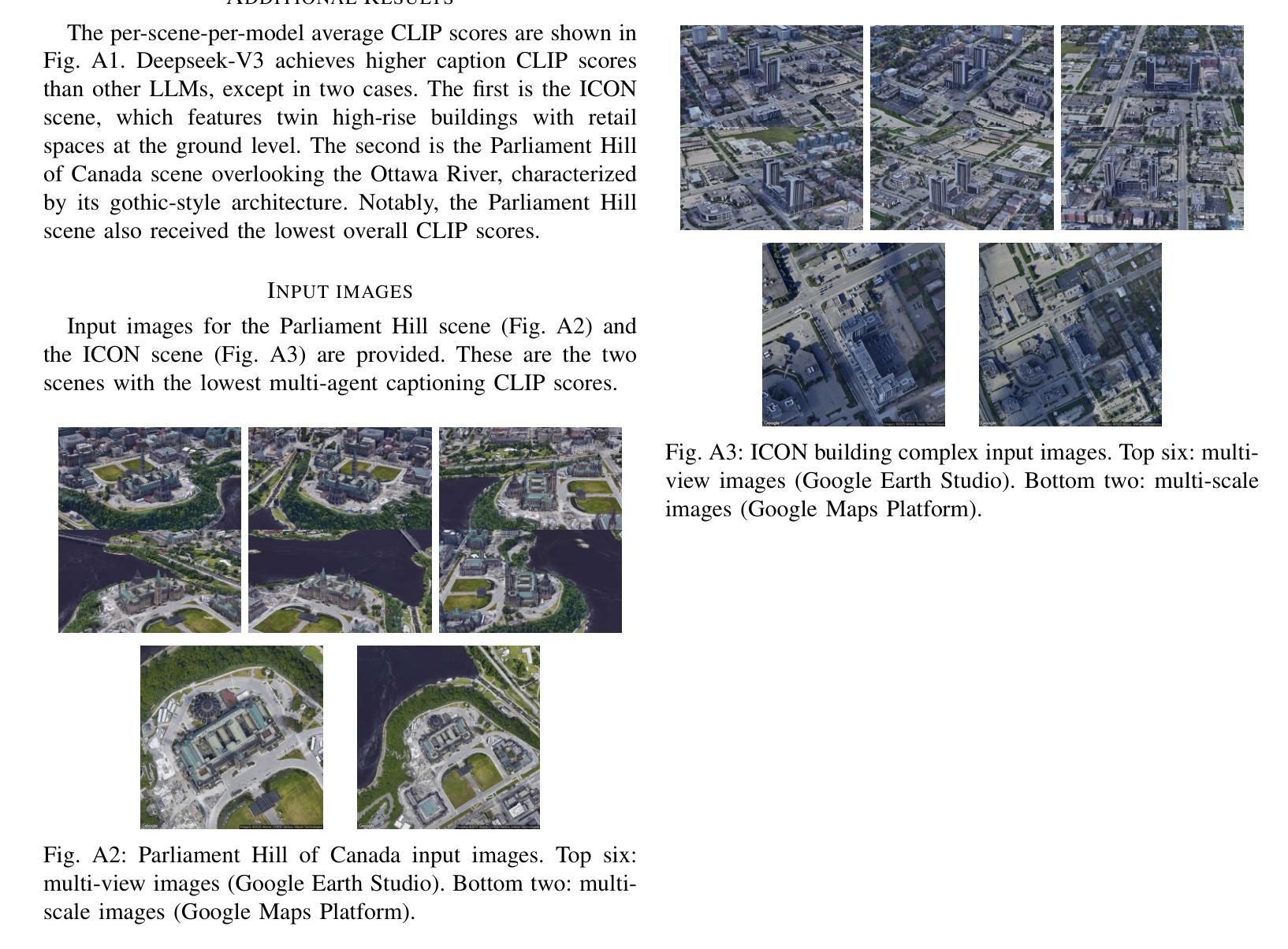
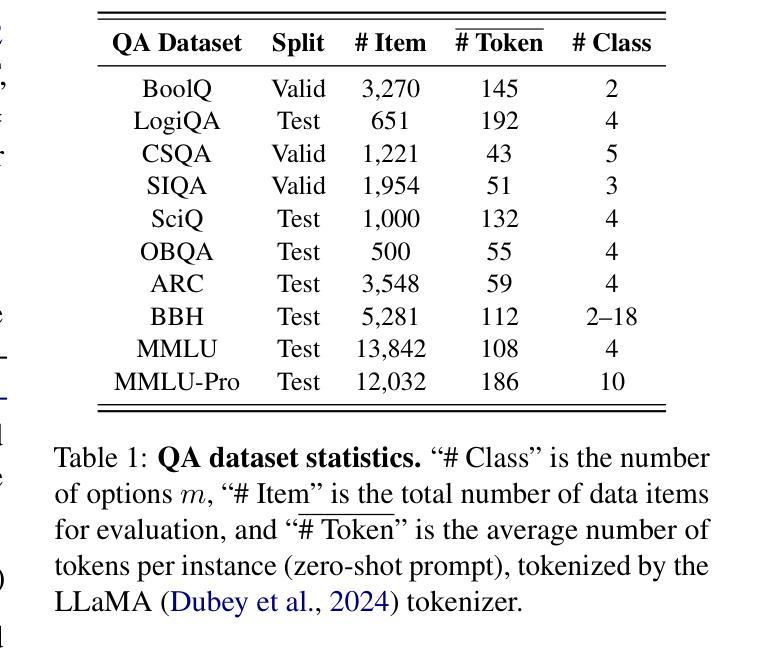
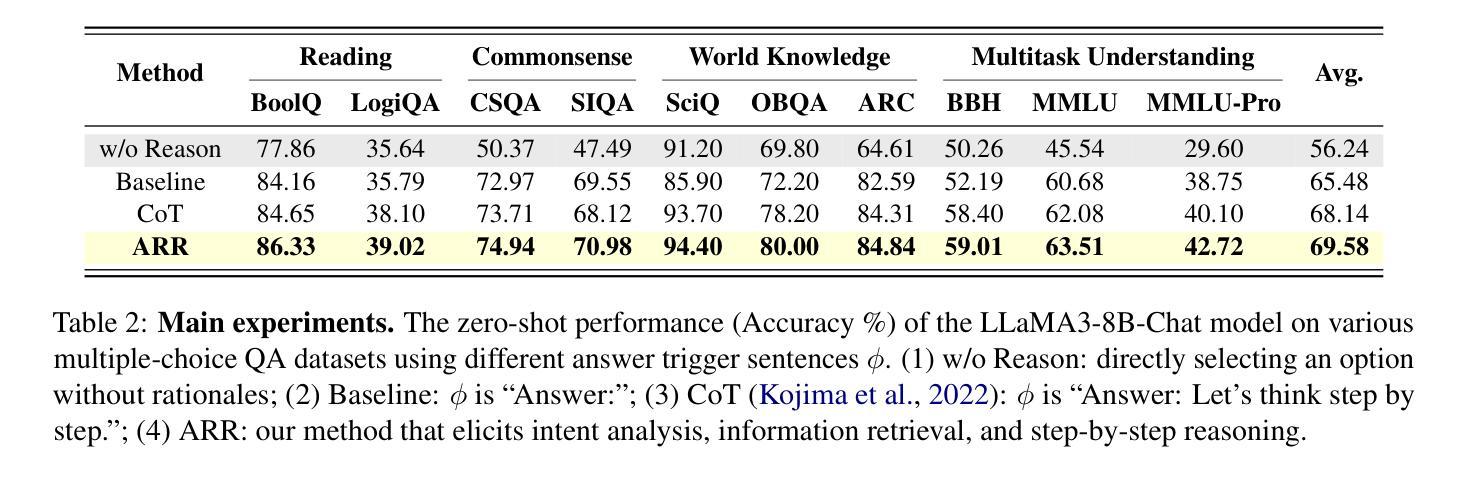
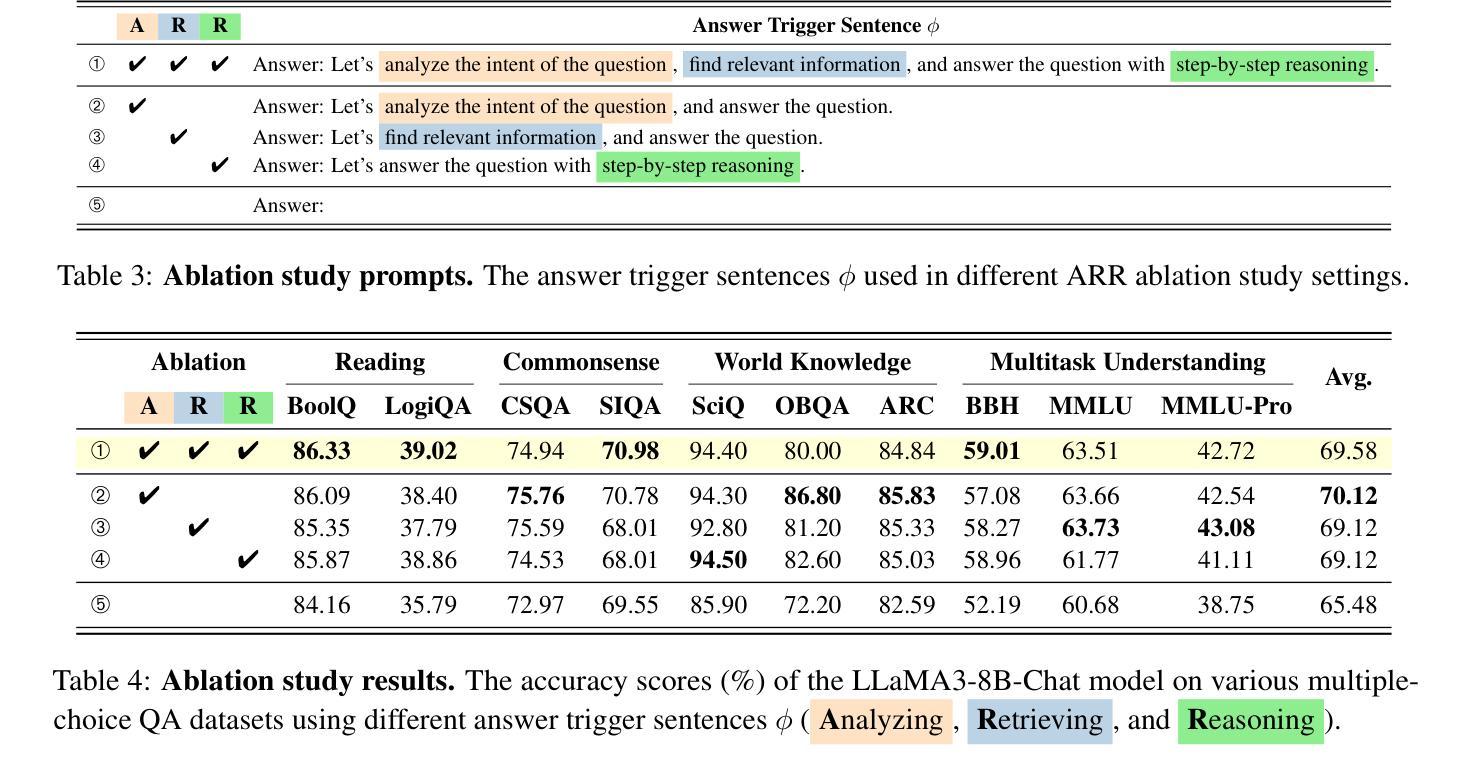
ARR: Question Answering with Large Language Models via Analyzing, Retrieving, and Reasoning
Authors:Yuwei Yin, Giuseppe Carenini
Large language models (LLMs) achieve remarkable performance on challenging benchmarks that are often structured as multiple-choice question-answering (QA) tasks. Zero-shot Chain-of-Thought (CoT) prompting enhances reasoning in LLMs but provides only vague and generic guidance (“think step by step”). This paper introduces ARR, an intuitive and effective zero-shot prompting method that explicitly incorporates three key steps in QA solving: analyzing the intent of the question, retrieving relevant information, and reasoning step by step. Comprehensive experiments across diverse and challenging QA tasks demonstrate that ARR consistently improves the Baseline (without ARR prompting) and outperforms CoT. Ablation and case studies further validate the positive contributions of each component: analyzing, retrieving, and reasoning. Notably, intent analysis plays a vital role in ARR. Additionally, extensive evaluations across various model sizes, LLM series, and generation settings solidify the effectiveness, robustness, and generalizability of ARR.
大型语言模型(LLM)在具有挑战性的基准测试中表现出卓越的性能,这些测试通常被构建为多选问答(QA)任务。零样本思维链(CoT)提示增强了LLM中的推理能力,但只提供了模糊和通用的指导(“逐步思考”)。本文介绍了一种直观有效的零样本提示方法ARR,该方法显式地结合了问答解决中的三个关键步骤:分析问题的意图、检索相关信息和逐步推理。在多样化和具有挑战性的问答任务上的综合实验表明,ARR始终改进了基线(无ARR提示)并优于CoT。消融研究和案例研究进一步验证了每个组件的正面贡献:分析、检索和推理。值得注意的是,意图分析在ARR中起着至关重要的作用。此外,在不同模型大小、LLM系列和生成设置上的广泛评估巩固了ARR的有效性、稳定性和通用性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 20 pages. Code: https://github.com/YuweiYin/ARR
Summary
大型语言模型(LLM)在作为多选问答任务的结构化挑战基准测试中表现出卓越性能。零样本思维链(CoT)提示增强了LLM的推理能力,但仅提供模糊和通用的指导。本文介绍了一种直观有效的零样本提示方法ARR,该方法明确结合了问答解决的三个关键步骤:分析问题的意图、检索相关信息和逐步推理。在多样化和具有挑战性的问答任务上的综合实验表明,ARR在基线(无ARR提示)的基础上持续提高了性能,并优于CoT。此外,通过消除研究和案例研究进一步验证了分析、检索和推理每个组件的积极作用。意图分析在ARR中扮演了至关重要的角色。同时,跨不同模型大小、LLM系列和生成设置的广泛评估巩固了ARR的有效性、稳健性和通用性。
Key Takeaways
- LLM在多选问答任务的挑战基准测试中表现优秀。
- 零样本思维链(CoT)提示增强了LLM的推理能力,但指导较为模糊。
- ARR是一种新的零样本提示方法,明确结合了QA解决的三个关键步骤:分析、检索和推理。
- ARR在多种问答任务上表现出比CoT更好的性能。
- 消融和案例研究验证了ARR中分析、检索和推理每个组件的有效性。
- 意图分析在ARR中起关键作用。
点此查看论文截图


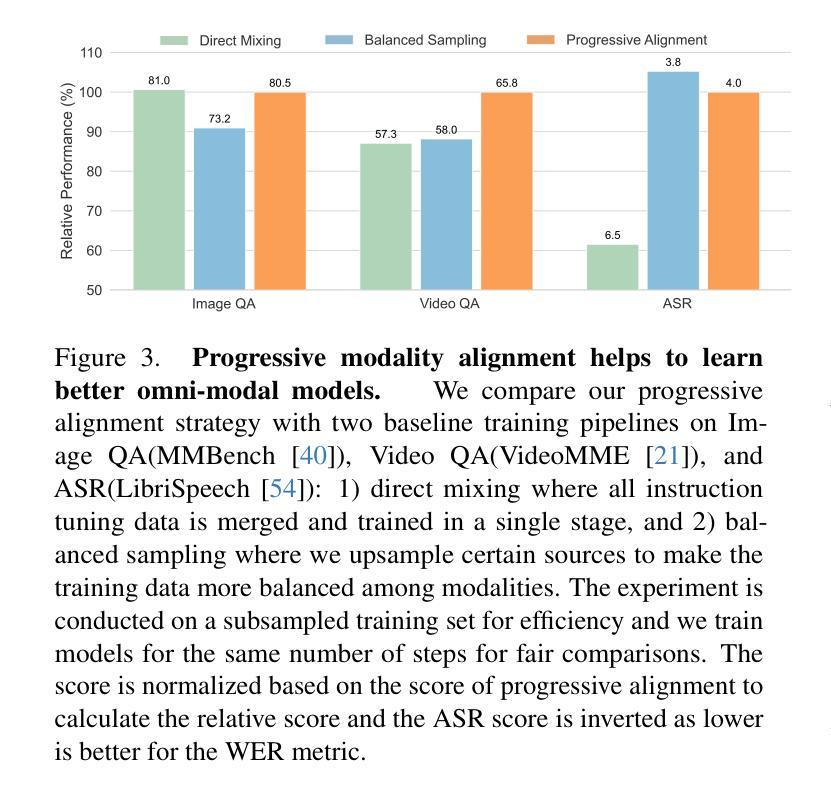
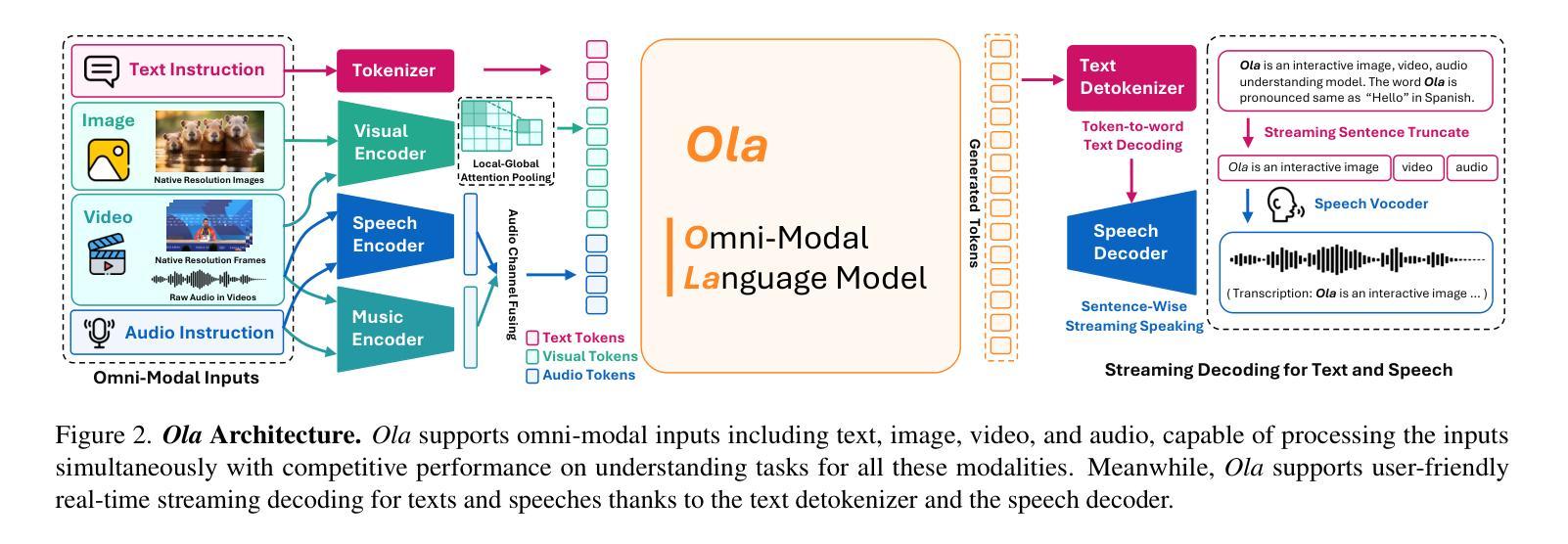
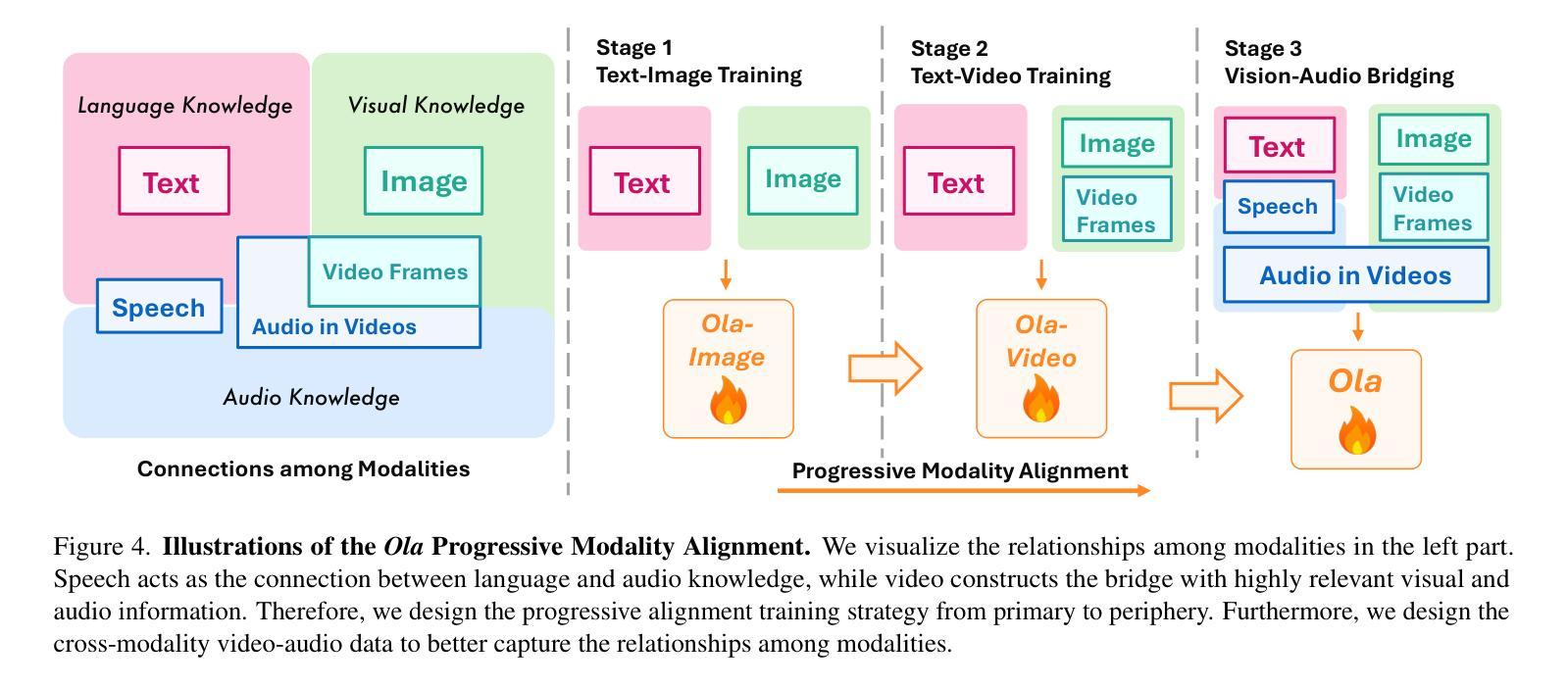
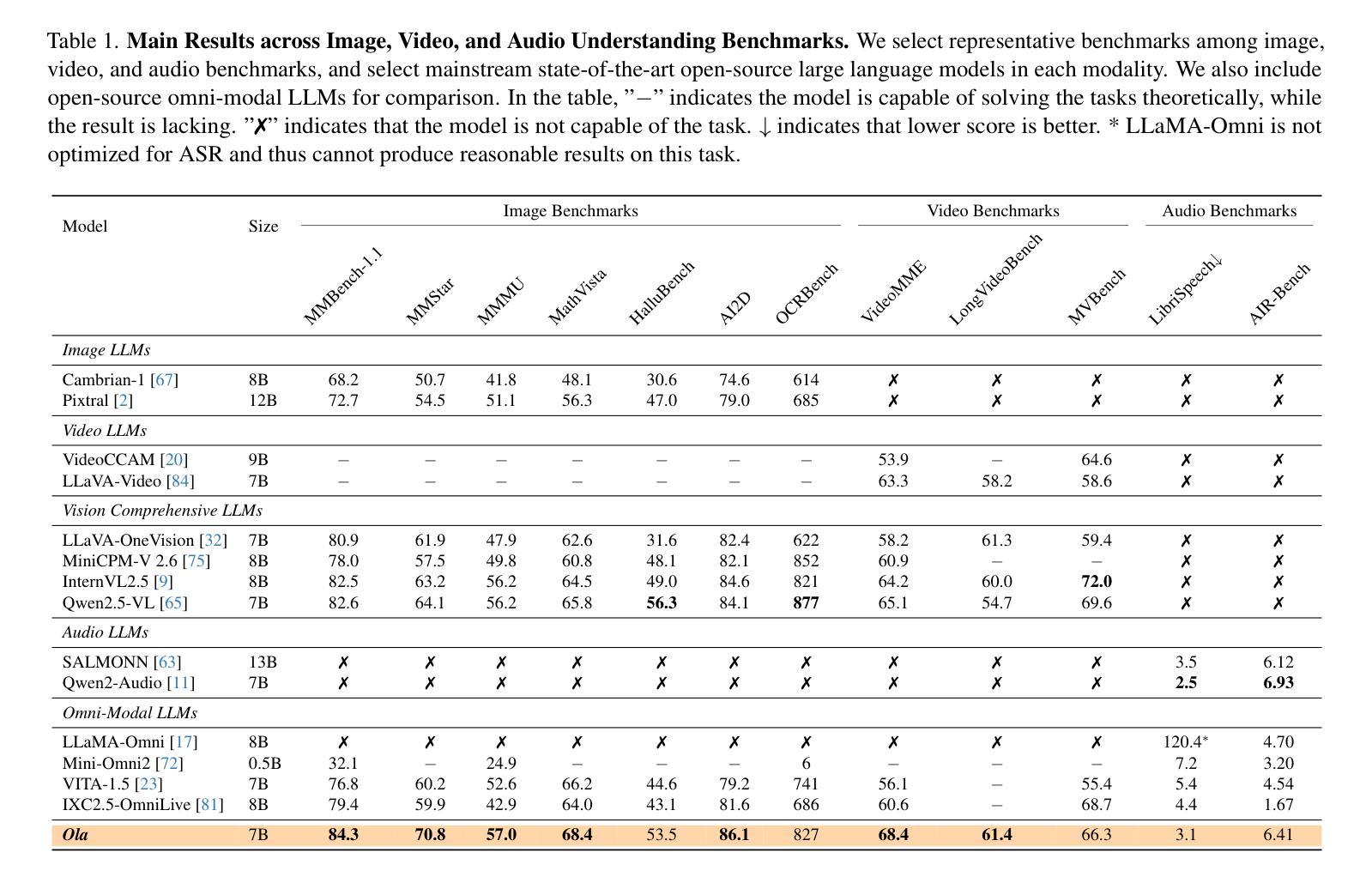
Ola: Pushing the Frontiers of Omni-Modal Language Model with Progressive Modality Alignment
Authors:Zuyan Liu, Yuhao Dong, Jiahui Wang, Ziwei Liu, Winston Hu, Jiwen Lu, Yongming Rao
Recent advances in large language models, particularly following GPT-4o, have sparked increasing interest in developing omni-modal models capable of understanding more modalities. While some open-source alternatives have emerged, there is still a notable lag behind specialized single-modality models in performance. In this paper, we present Ola, an Omni-modal language model that achieves competitive performance across image, video, and audio understanding compared to specialized counterparts. The core design of Ola lies in its progressive modality alignment strategy that extends the supporting modality of the language model progressively. Our training pipeline begins with the most distinct modalities: image and text, then gradually expands the skill sets of the model using speech data that connects language and audio knowledge, and video data that connects all modalities. The progressive learning pipeline also enables us to maintain a relatively small size of the cross-modal alignment data, making developing omni-modal from existing vision-language models easy and less costly. Moreover, to unlock an advanced interactive experience like GPT-4o, we further design a sentence-wise decoding solution for streaming speech generation. Extensive experiments demonstrate that Ola surpasses existing open omni-modal LLMs across all modalities while achieving highly competitive performance compared to state-of-the-art specialized models of similar sizes. We aim to make Ola a fully open omni-modal understanding solution to advance future research in this emerging field. Model weights, code, and data are open-sourced at https://github.com/Ola-Omni/Ola.
最近大型语言模型的进步,尤其是GPT-4o之后,引发了人们对开发能够理解更多模态的通模模型的浓厚兴趣。虽然已经出现了一些开源的替代品,但在性能上仍然明显落后于专业的单模态模型。在本文中,我们介绍了Ola,这是一款通模态语言模型,在图像、视频和音频理解方面与专业化模型相比具有竞争力。Ola的核心设计在于其渐进的模态对齐策略,该策略逐步扩展语言模型的支持模态。我们的训练管道始于最独特的模态:图像和文本,然后使用连接语言和音频知识的语音数据以及连接所有模态的视频数据,逐步扩大模型的技能集。这种渐进的学习管道还使我们能够保持相对较小的跨模态对齐数据集规模,从而更容易、更经济地从现有的视觉语言模型开发通模态模型。此外,为了解锁类似GPT-4o的高级交互体验,我们还设计了一种基于句子的解码解决方案,用于流式语音生成。大量实验表明,Ola在所有模态上超越了现有的开源通模态大型语言模型,同时在类似规模的专业模型中取得了高度竞争的性能。我们的目标是使Ola成为完全开放的通模态解决方案,以推动这一新兴领域未来的研究。模型权重、代码和数据已在https://github.com/Ola-Omni/Ola上开源。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
近期大型语言模型的进步,尤其是GPT-4o之后,引发了多模态模型的兴趣,它们能理解更多模态。本文介绍了一款名为Ola的通用多模态语言模型,在图像、视频和音频理解方面表现出竞争力。Ola的核心设计在于其渐进式模态对齐策略,逐步扩展语言模型的支持模态。其训练流程从最具特色的模态开始,即图像和文本,然后逐步使用连接语言和音频知识的语音数据以及连接所有模态的视频数据来扩展模型技能集。这种渐进式学习流程也让我们得以维持较小的跨模态对齐数据量,使从现有视觉语言模型发展出Omni-modal变得更加容易且成本更低。此外,为了解锁类似GPT-4o的高级交互体验,我们进一步设计了流式语音生成的句子级解码解决方案。实验表明,Ola在所有模态上都超越了现有的开源Omni-modal大型语言模型,并在类似规模的最新专业模型上取得了具有竞争力的表现。我们的目标是让Ola成为完全开源的多模态理解解决方案,以推动这一新兴领域的研究发展。模型权重、代码和数据已在GitHub上开源。
Key Takeaways
- Ola是一款多模态语言模型,具备在图像、视频和音频理解方面的竞争力。
- Ola采用渐进式模态对齐策略进行训练,逐步扩展语言模型的模态支持能力。
- Ola的训练流程从图像和文本开始,然后逐步引入语音和视频数据来扩展模型技能集。
- 渐进式学习流程使得跨模态对齐的数据量相对较小,降低了开发成本。
- Ola设计了句子级解码解决方案,以支持流式语音生成等高级交互体验。
- Ola在多个实验上超越了现有的开源Omni-modal大型语言模型。
点此查看论文截图

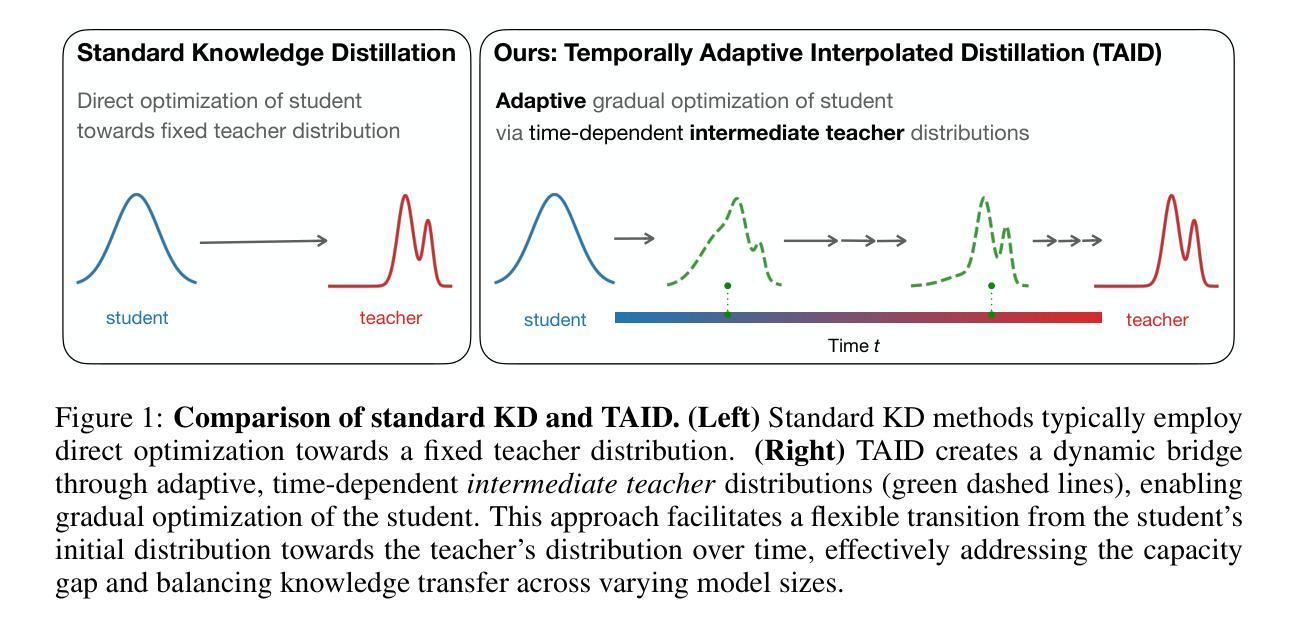
TAID: Temporally Adaptive Interpolated Distillation for Efficient Knowledge Transfer in Language Models
Authors:Makoto Shing, Kou Misaki, Han Bao, Sho Yokoi, Takuya Akiba
Causal language models have demonstrated remarkable capabilities, but their size poses significant challenges for deployment in resource-constrained environments. Knowledge distillation, a widely-used technique for transferring knowledge from a large teacher model to a small student model, presents a promising approach for model compression. A significant remaining issue lies in the major differences between teacher and student models, namely the substantial capacity gap, mode averaging, and mode collapse, which pose barriers during distillation. To address these issues, we introduce $\textit{Temporally Adaptive Interpolated Distillation (TAID)}$, a novel knowledge distillation approach that dynamically interpolates student and teacher distributions through an adaptive intermediate distribution, gradually shifting from the student’s initial distribution towards the teacher’s distribution. We provide a theoretical analysis demonstrating TAID’s ability to prevent mode collapse and empirically show its effectiveness in addressing the capacity gap while balancing mode averaging and mode collapse. Our comprehensive experiments demonstrate TAID’s superior performance across various model sizes and architectures in both instruction tuning and pre-training scenarios. Furthermore, we showcase TAID’s practical impact by developing two state-of-the-art compact foundation models: $\texttt{TAID-LLM-1.5B}$ for language tasks and $\texttt{TAID-VLM-2B}$ for vision-language tasks. These results demonstrate TAID’s effectiveness in creating high-performing and efficient models, advancing the development of more accessible AI technologies.
因果语言模型展现出了显著的能力,但它们的规模给在资源受限环境中部署带来了重大挑战。知识蒸馏是一种广泛使用的技术,可以从大型教师模型转移到小型学生模型,这为模型压缩提供了一种有前景的方法。然而,仍然存在一个主要问题,即教师模型和学生模型之间的差异,包括显著的能力差距、模式平均和模式崩溃,这些在蒸馏过程中构成了障碍。为了解决这些问题,我们引入了时序自适应插值蒸馏(TAID),这是一种新型的知识蒸馏方法,通过自适应中间分布动态插值学生和教师的分布,从学生最初的分布逐渐转向教师的分布。我们进行了理论分析,证明了TAID在防止模式崩溃方面的能力,并实证证明了它在解决能力差距、平衡模式平均和模式崩溃方面的有效性。我们的综合实验表明,TAID在各种型号和架构的模型中,无论是在指令微调还是预训练场景中,都表现出卓越的性能。此外,我们通过开发两个最先进的紧凑基础模型:用于语言任务的TAID-LLM-1.5B和用于视觉语言任务的TAID-VLM-2B,展示了TAID的实际影响。这些结果证明了TAID在创建高性能和高效模型方面的有效性,推动了更可访问的人工智能技术的发展。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF To appear at the 13th International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR 2025) as a Spotlight presentation
Summary
本文介绍了因果语言模型在资源受限环境中的部署挑战,以及知识蒸馏技术在此方面的应用。为解决知识蒸馏中教师模型与学生模型间存在的容量差距、模式平均和模式崩溃等问题,提出了一种新型知识蒸馏方法——Temporally Adaptive Interpolated Distillation (TAID)。该方法通过自适应中间分布动态插值学生模型和教师模型的分布,逐步从学生模型的初始分布向教师模型的分布转变。理论分析证明了TAID在防止模式崩溃方面的能力,并通过实验验证了其在解决容量差距、平衡模式平均和模式崩溃方面的有效性。此外,通过开发两个先进的紧凑基础模型TAID-LLM-1.5B和TAID-VLM-2B,展示了TAID的实际影响力。
Key Takeaways
- 因果语言模型在资源受限环境中的部署面临挑战。
- 知识蒸馏是解决这一挑战的一种有前景的方法。
- 教师模型和学生模型之间存在显著的差异,如容量差距、模式平均和模式崩溃。
- 新型知识蒸馏方法——Temporally Adaptive Interpolated Distillation (TAID) 被提出以解决这些问题。
- TAID通过自适应中间分布动态插值学生模型和教师模型的分布。
- 理论和实验证明了TAID在解决容量差距和平衡模式平均与模式崩溃方面的有效性。
点此查看论文截图


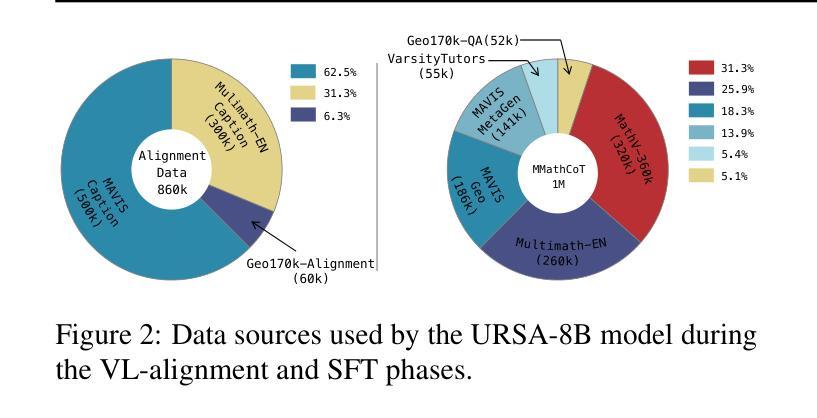
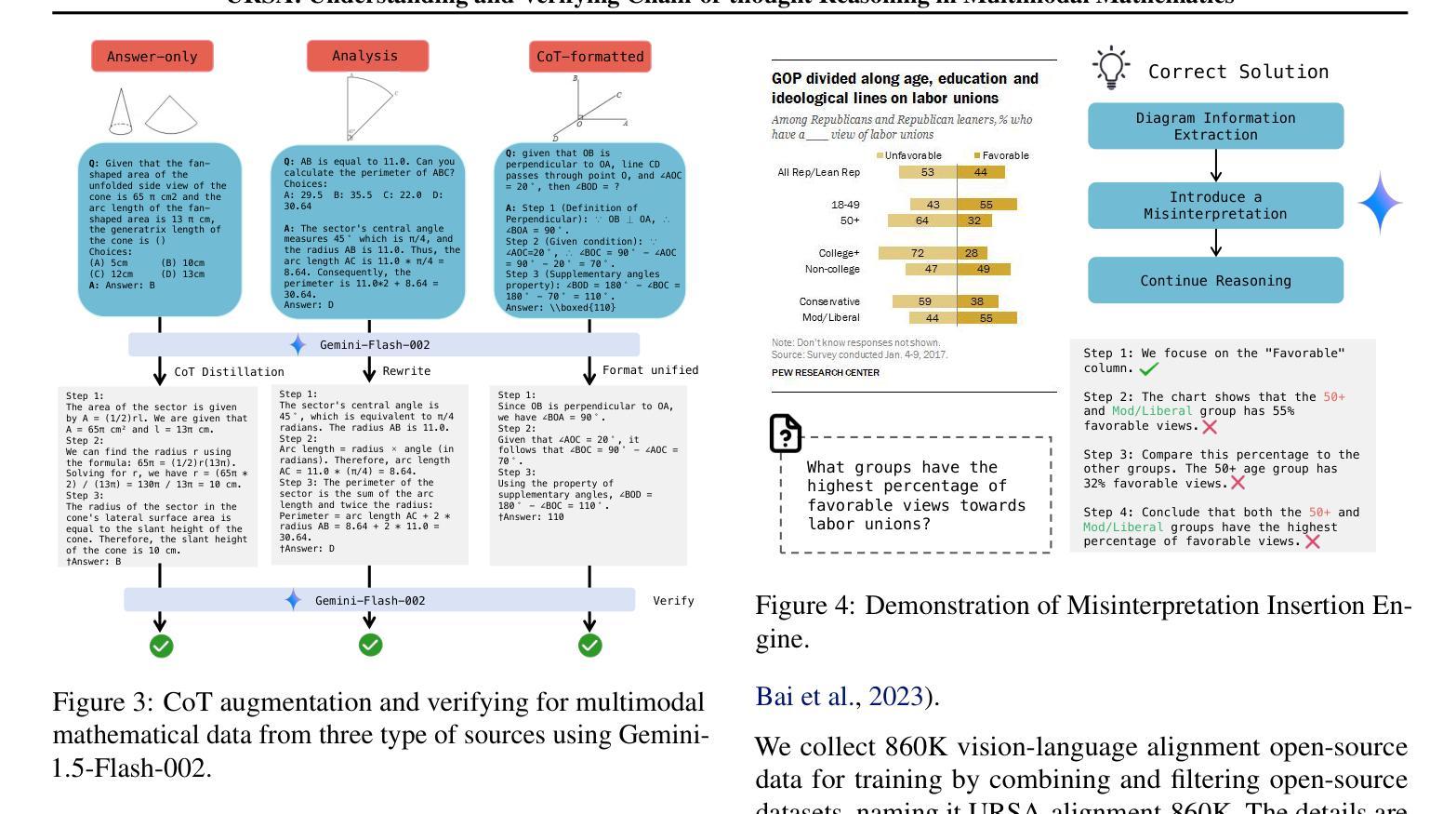
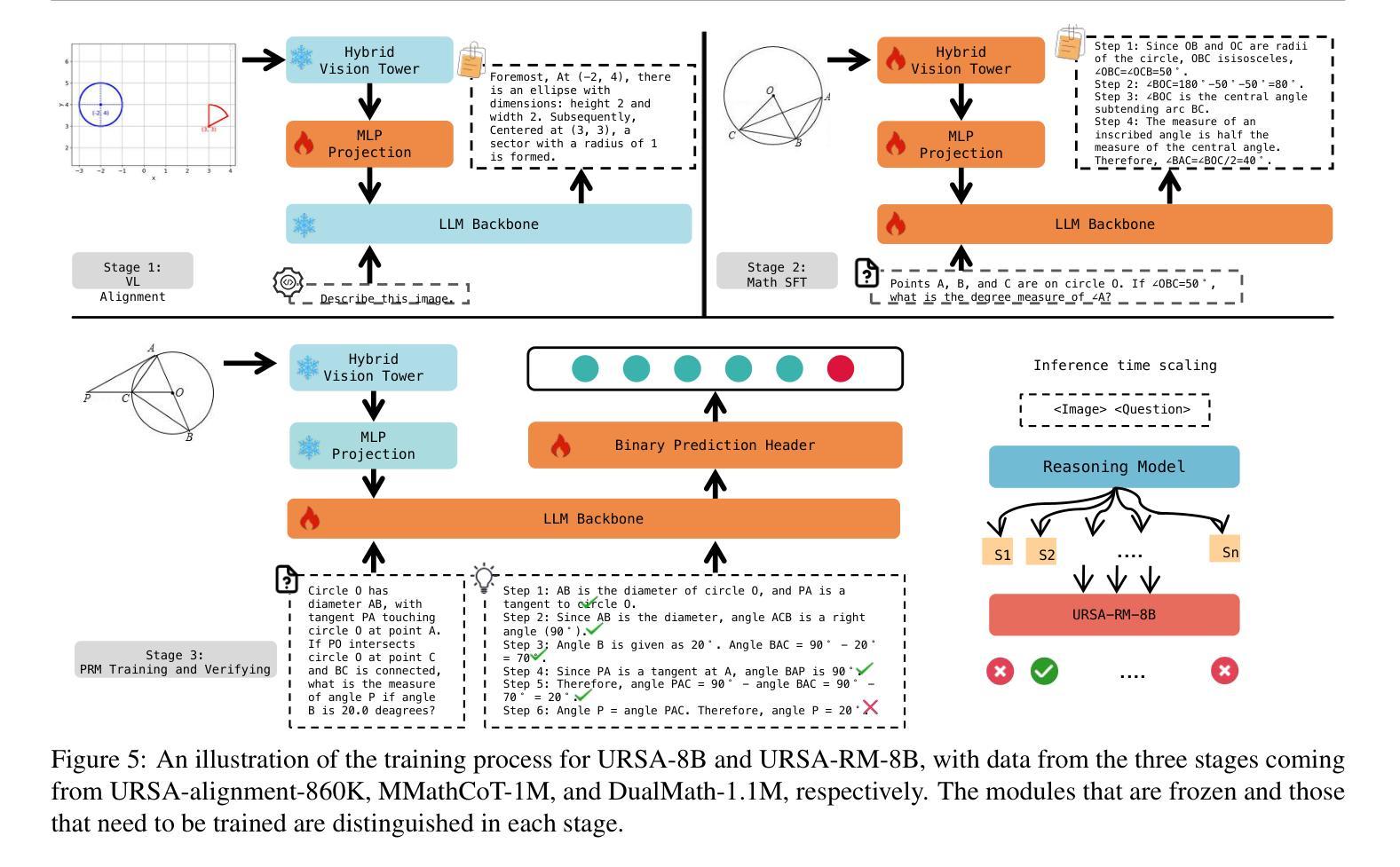
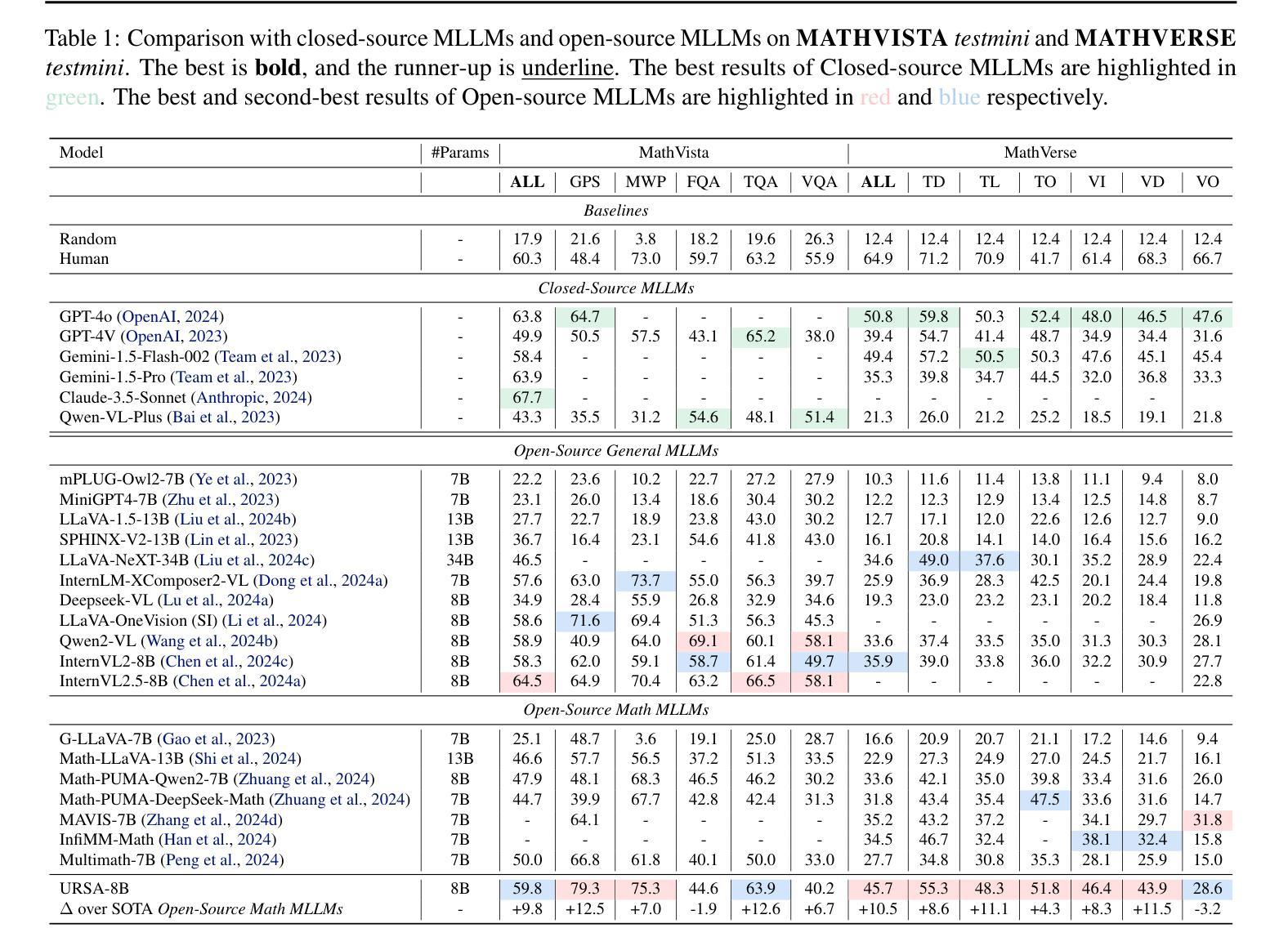
URSA: Understanding and Verifying Chain-of-thought Reasoning in Multimodal Mathematics
Authors:Ruilin Luo, Zhuofan Zheng, Yifan Wang, Yiyao Yu, Xinzhe Ni, Zicheng Lin, Jin Zeng, Yujiu Yang
Chain-of-Thought (CoT) reasoning is widely used to enhance the mathematical reasoning capabilities of large language models (LLMs). The introduction of process supervision for CoT trajectories has sparked discussions on improving test-time scaling, thereby unlocking the System 2-style thinking capabilities of these models. However, in multimodal mathematical reasoning, the scarcity of high-quality CoT training data has hindered existing models from achieving both deliberate reasoning and fine-grained verification. In this work, we propose a novel framework that introduces System 2-style thinking to multimodal mathematical reasoning. We introduce a three-module CoT data synthesis process that integrates CoT distillation, trajectory-format rewriting, and format unification. This process generates MMathCoT-1M, a high-quality CoT reasoning instruction fine-tuning dataset. Furthermore, we implement a dual-view trajectory labeling automation that targets both visual grounding fidelity and deductive chain validity, resulting in the DualMath-1.1M dataset. The URSA-8B model, trained on MMathCoT-1M, achieves new state-of-the-art (SOTA) performance among similarly sized multimodal LLMs on six popular reasoning benchmarks. Training URSA-8B further on the DualMath-1.1M dataset yields URSA-RM-8B, a verifier that enhances URSA-8B’s test-time performance and surpasses strong closed-source multimodal MLLMs like GPT-4o. The model weights, training data, and code have been open-sourced: https://github.com/URSA-MATH/URSA-MATH.
链式思维(CoT)推理被广泛应用于增强大型语言模型(LLM)的数学推理能力。引入过程监督以优化CoT轨迹的讨论,从而解锁这些模型的System 2式思维能力。然而,在多模态数学推理中,高质量CoT训练数据的稀缺阻碍了现有模型实现深思熟虑的推理和精细的验证。在这项工作中,我们提出了一种引入System 2式思维到多模态数学推理的新型框架。我们引入了包含CoT蒸馏、轨迹格式重写和格式统一的三个模块CoT数据合成过程,生成了高质量的MMathCoT-1M CoT推理指令微调数据集。此外,我们实现了旨在实现视觉定位保真性和演绎链有效性的双视图轨迹标记自动化,创建了DualMath-1.1M数据集。在六个流行的推理基准测试上,训练在MMathCoT-1M上的URSA-8B模型取得了最新最先进的性能。进一步在DualMath-1.1M数据集上训练URSA-8B,产生了增强测试时性能和超越强大封闭源多模态LLLMs(如GPT-4o)的验证器URSA-RM-8B。模型权重、训练数据和代码均已开源:https://github.com/URSA-MATH/URSA-MATH。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Fix typos and add results. 27 pages, 11 tables, 17 figures. Models, training data and code have been open-sourced. Project url: https://ursa-math.github.io
Summary
本文介绍了如何将System 2风格的思考引入多模态数学推理中,通过提出一个包含三个模块的认知链数据合成过程(CoT蒸馏、轨迹格式重写和格式统一),生成了MMathCoT-1M高质量CoT推理指令微调数据集。此外,还实现了针对视觉定位准确性和演绎链有效性的双视图轨迹标签自动化,创建了DualMath-1.1M数据集。在六个流行的推理基准测试上,经过MMathCoT-1M数据训练的URSA-8B模型取得了最新状态的最优性能。进一步在DualMath-1.1M数据集上训练得到的URSA-RM-8B验证器提升了URSA-8B的测试性能,超越了强大的封闭源多模态大型语言模型,如GPT-4o。模型权重、训练数据和代码均已开源。
Key Takeaways
- System 2风格的思考被引入多模态数学推理中,以提高模型的推理能力。
- 提出一个包含CoT蒸馏、轨迹格式重写和格式统一的三模块CoT数据合成过程,用于生成高质量的CoT推理指令微调数据集MMathCoT-1M。
- 通过双视图轨迹标签自动化,创建了DualMath-1.1M数据集,该数据集旨在提高视觉定位准确性和演绎链有效性。
- URSA-8B模型在多个推理基准测试上表现出最新状态的最优性能。
- URSA-RM-8B验证器在URSA-8B的基础上进一步提升测试性能,超越了某些先进的大型语言模型。
- 模型权重、训练数据和代码已开源,便于公众访问和使用。
点此查看论文截图


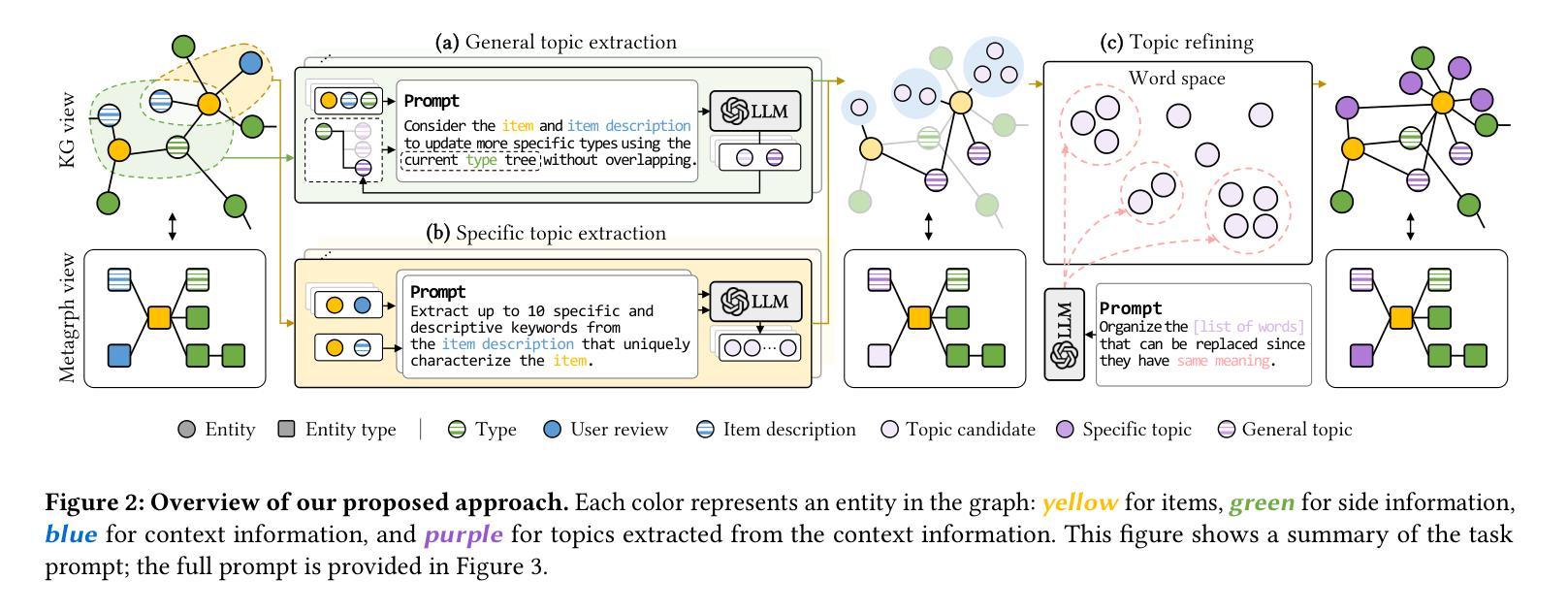
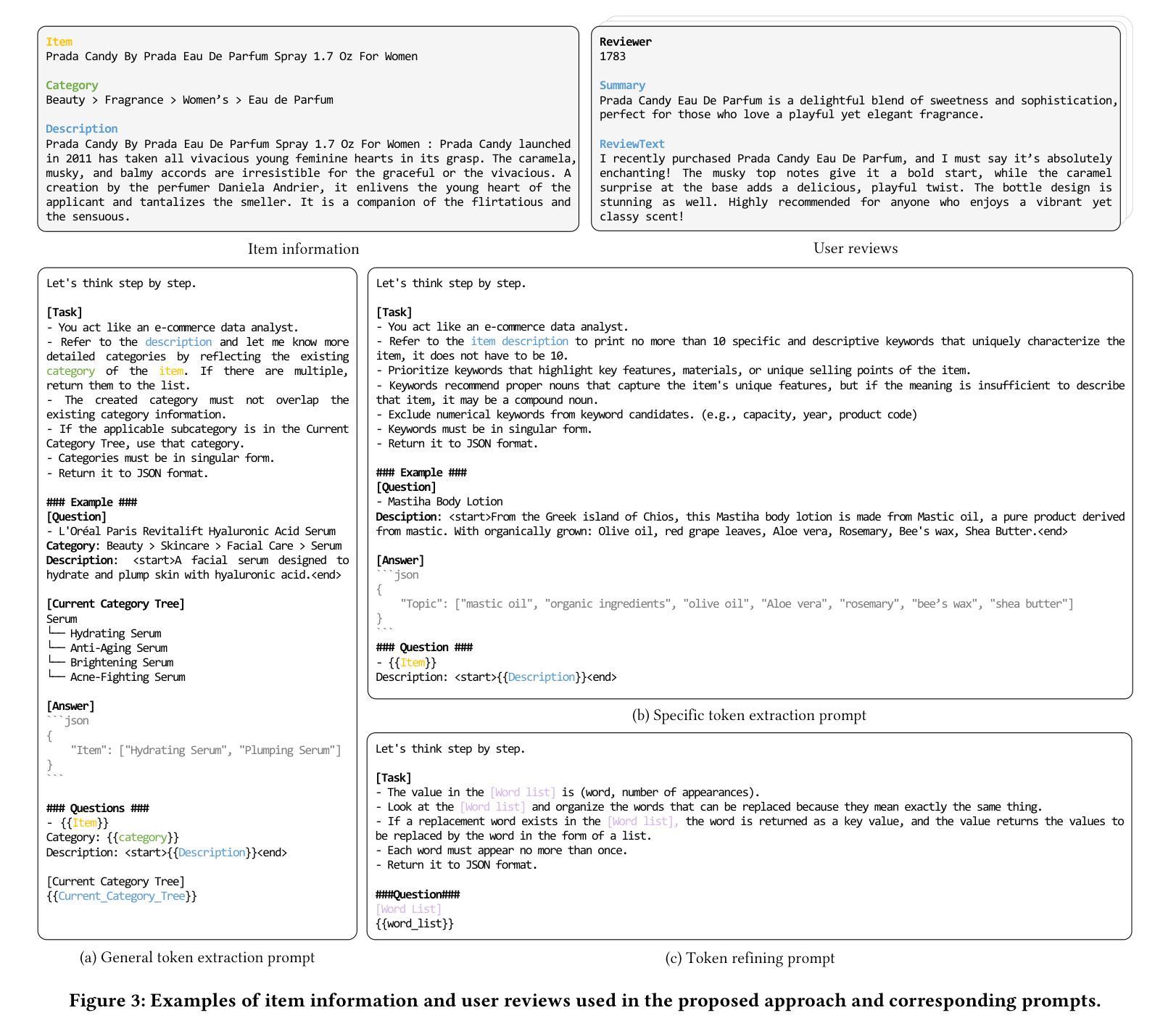
Topic-Aware Knowledge Graph with Large Language Models for Interoperability in Recommender Systems
Authors:Minhye Jeon, Seokho Ahn, Young-Duk Seo
The use of knowledge graphs in recommender systems has become one of the common approaches to addressing data sparsity and cold start problems. Recent advances in large language models (LLMs) offer new possibilities for processing side and context information within knowledge graphs. However, consistent integration across various systems remains challenging due to the need for domain expert intervention and differences in system characteristics. To address these issues, we propose a consistent approach that extracts both general and specific topics from both side and context information using LLMs. First, general topics are iteratively extracted and updated from side information. Then, specific topics are extracted using context information. Finally, to address synonymous topics generated during the specific topic extraction process, a refining algorithm processes and resolves these issues effectively. This approach allows general topics to capture broad knowledge across diverse item characteristics, while specific topics emphasize detailed attributes, providing a more comprehensive understanding of the semantic features of items and the preferences of users. Experimental results demonstrate significant improvements in recommendation performance across diverse knowledge graphs.
推荐系统中使用知识图谱已成为解决数据稀疏和冷启动问题的常见方法之一。大型语言模型(LLM)的最新进展为处理知识图谱中的侧面和上下文信息提供了新的可能性。然而,由于需要领域专家干预和系统特性差异,跨各种系统的集成仍然具有挑战性。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了一种一致的方法,该方法使用LLM从侧面和上下文信息中提取一般和特定主题。首先,从侧信息中迭代提取和更新一般主题。然后,使用上下文信息提取特定主题。最后,为了解决特定主题提取过程中产生的同义主题问题,采用精炼算法对其进行有效处理。这种方法允许一般主题捕捉跨不同项目特征的广泛知识,而特定主题强调详细属性,从而更全面地理解项目的语义特征以及用户的偏好。实验结果表明,在多种知识图谱中推荐性能得到了显著提高。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by The 40th ACM/SIGAPP Symposium On Applied Computing(SAC) 2025
Summary
知识图谱在推荐系统中应用广泛,以解决数据稀疏和冷启动问题。大型语言模型(LLM)的最新进展为处理知识图谱中的侧信息和上下文信息提供了新的可能性。本文提出一种方法,通过LLM从侧信息和上下文信息中提取一般和特定主题,解决跨系统整合中的挑战。实验结果表明,该方法在多种知识图谱中显著提高推荐性能。
Key Takeaways
- 知识图谱在推荐系统中用于解决数据稀疏和冷启动问题。
- 大型语言模型(LLM)在处理知识图谱中的侧信息和上下文信息方面表现出新可能性。
- 本文方法通过LLM从侧信息和上下文信息中提取一般和特定主题,以应对跨系统整合的挑战。
- 一般主题能捕捉跨不同项目特征的广泛知识,而特定主题强调详细属性,更全面地理解项目的语义特征和用户偏好。
- 该方法通过迭代提取和更新一般主题,以及使用上下文信息提取特定主题来实施。
- 为解决特定主题提取过程中产生的同义词主题,采用精炼算法进行处理,有效提高效果。
点此查看论文截图