⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-02-13 更新
Sat-DN: Implicit Surface Reconstruction from Multi-View Satellite Images with Depth and Normal Supervision
Authors:Tianle Liu, Shuangming Zhao, Wanshou Jiang, Bingxuan Guo
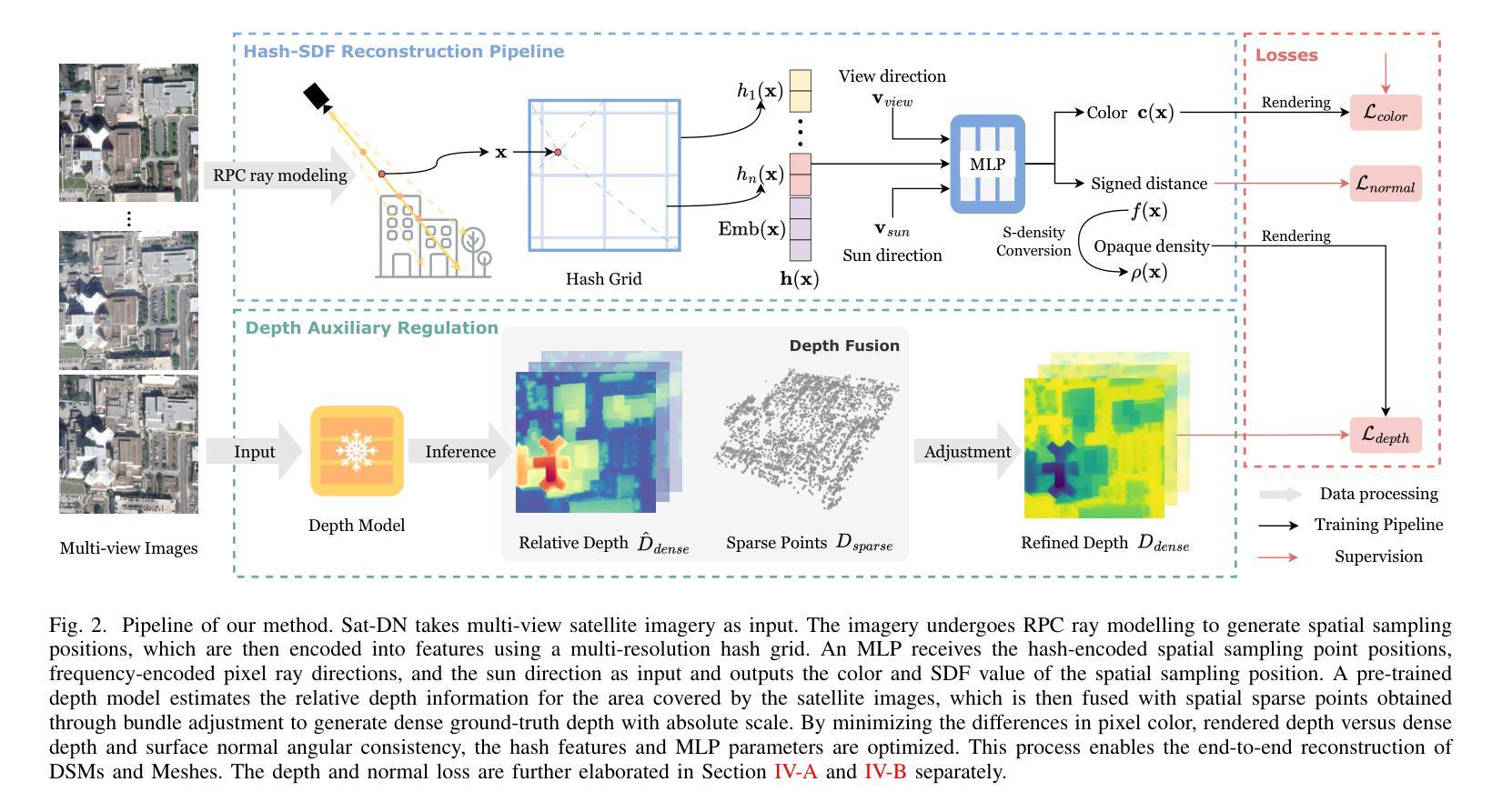
With advancements in satellite imaging technology, acquiring high-resolution multi-view satellite imagery has become increasingly accessible, enabling rapid and location-independent ground model reconstruction. However, traditional stereo matching methods struggle to capture fine details, and while neural radiance fields (NeRFs) achieve high-quality reconstructions, their training time is prohibitively long. Moreover, challenges such as low visibility of building facades, illumination and style differences between pixels, and weakly textured regions in satellite imagery further make it hard to reconstruct reasonable terrain geometry and detailed building facades. To address these issues, we propose Sat-DN, a novel framework leveraging a progressively trained multi-resolution hash grid reconstruction architecture with explicit depth guidance and surface normal consistency constraints to enhance reconstruction quality. The multi-resolution hash grid accelerates training, while the progressive strategy incrementally increases the learning frequency, using coarse low-frequency geometry to guide the reconstruction of fine high-frequency details. The depth and normal constraints ensure a clear building outline and correct planar distribution. Extensive experiments on the DFC2019 dataset demonstrate that Sat-DN outperforms existing methods, achieving state-of-the-art results in both qualitative and quantitative evaluations. The code is available at https://github.com/costune/SatDN.
随着卫星成像技术的进步,获取高分辨率的多视角卫星图像变得越来越容易,这为实现快速和地点独立的地面模型重建提供了可能。然而,传统的立体匹配方法在捕捉细微细节方面遇到了困难,尽管神经辐射场(NeRF)能够实现高质量的重建,但其训练时间却过长。此外,卫星图像中建筑立面的低可见性、像素之间的光照和风格差异以及缺乏纹理的区域等挑战,进一步加大了重建合理的地形几何和详细的建筑立面的难度。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了Sat-DN,这是一个新型框架,利用逐步训练的多分辨率哈希网格重建架构,通过明确的深度指导和表面法线一致性约束来提高重建质量。多分辨率哈希网格加速了训练过程,而逐步策略则逐步提高了学习频率,利用粗略的低频几何来指导精细高频细节的重建。深度和法线约束确保了建筑物的轮廓清晰和平面分布正确。在DFC2019数据集上的大量实验表明,Sat-DN优于现有方法,在定性和定量评估中都达到了最先进的水平。代码可在https://github.com/costune/SatDN获取。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
随着卫星成像技术的进步,获取高分辨率的多视角卫星图像变得越来越容易,促进了地面模型的快速重建。然而,传统立体匹配方法难以捕捉精细细节,而神经辐射场(NeRF)虽然可以实现高质量重建,但训练时间过长。针对这些问题,我们提出了Sat-DN框架,采用渐进式训练的多分辨率哈希网格重建架构,通过明确的深度指导和表面法线一致性约束来提高重建质量。该框架实现了高效训练和高质量重建。
Key Takeaways
- 卫星成像技术进步使得获取高分辨率多视角图像变得容易,促进了地面模型重建。
- 传统立体匹配方法难以捕捉精细细节,需要新的技术来解决。
- 神经辐射场(NeRF)可以实现高质量重建,但训练时间过长,效率较低。
- Sat-DN框架采用多分辨率哈希网格重建架构,可以加速训练过程。
- 渐进式训练策略可以逐步提高学习频率,从粗糙的几何形状开始,逐步添加精细的细节。
- 深度指导和表面法线一致性约束确保了清晰的建筑轮廓和正确的平面分布。
点此查看论文截图

PrismAvatar: Real-time animated 3D neural head avatars on edge devices
Authors:Prashant Raina, Felix Taubner, Mathieu Tuli, Eu Wern Teh, Kevin Ferreira
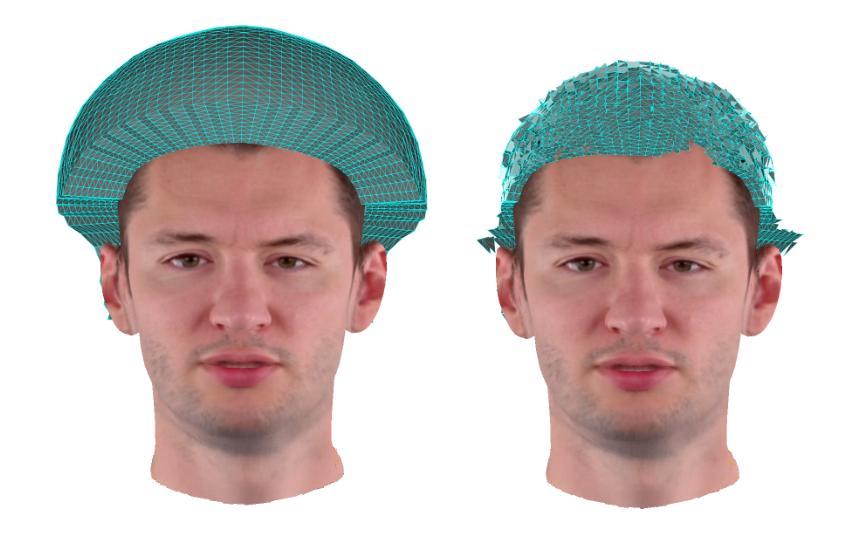
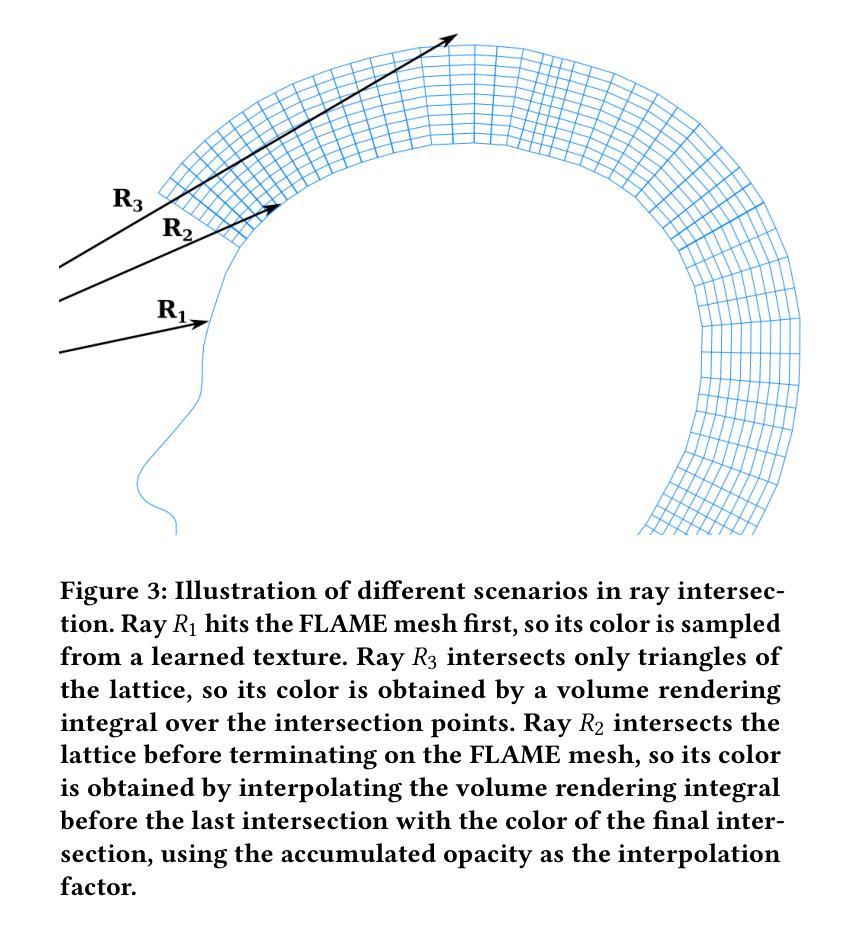
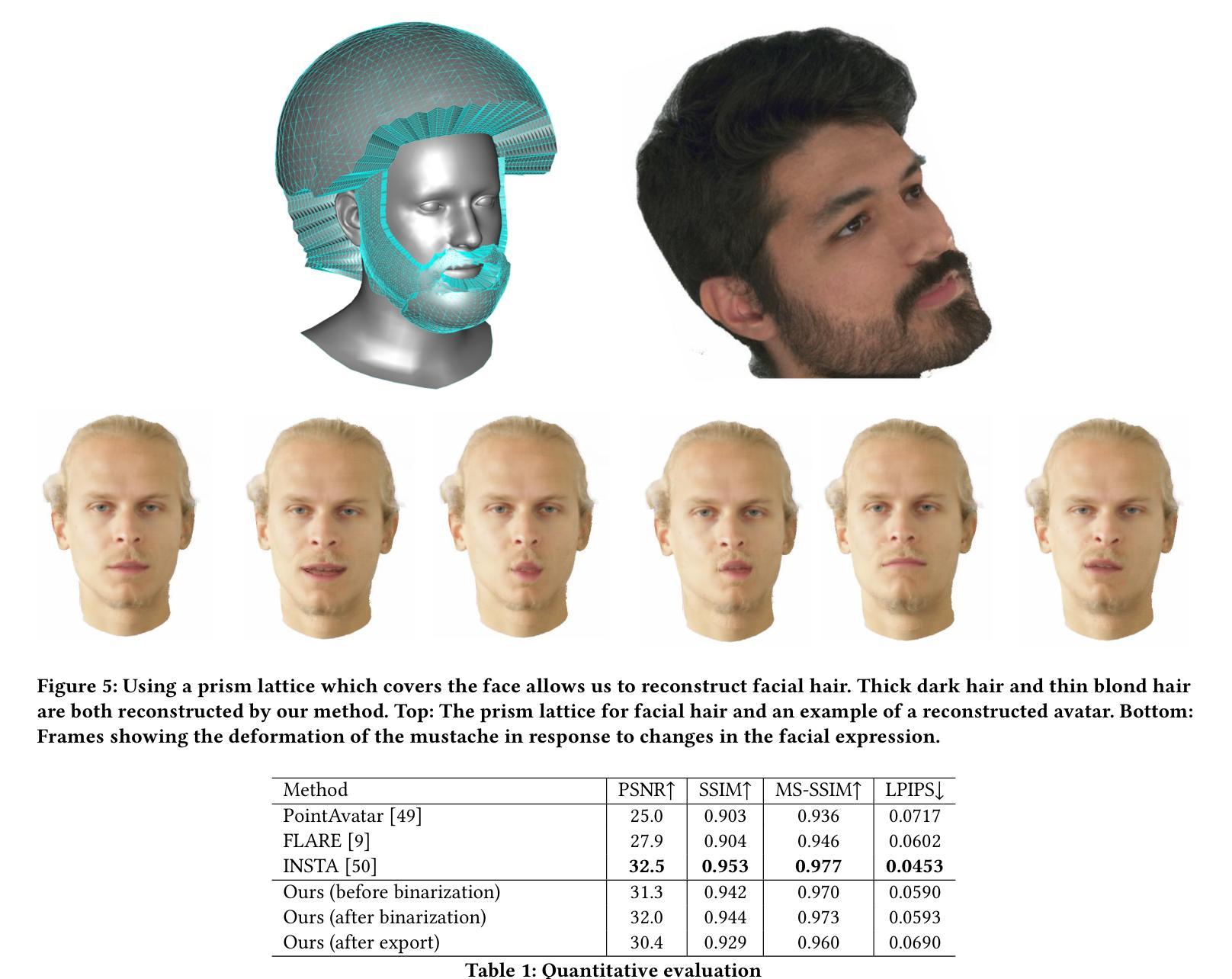
We present PrismAvatar: a 3D head avatar model which is designed specifically to enable real-time animation and rendering on resource-constrained edge devices, while still enjoying the benefits of neural volumetric rendering at training time. By integrating a rigged prism lattice with a 3D morphable head model, we use a hybrid rendering model to simultaneously reconstruct a mesh-based head and a deformable NeRF model for regions not represented by the 3DMM. We then distill the deformable NeRF into a rigged mesh and neural textures, which can be animated and rendered efficiently within the constraints of the traditional triangle rendering pipeline. In addition to running at 60 fps with low memory usage on mobile devices, we find that our trained models have comparable quality to state-of-the-art 3D avatar models on desktop devices.
我们提出 PrismAvatar:一个专为在资源受限的边缘设备上实现实时动画和渲染而设计的3D头部化身模型,同时在训练时仍享受神经体积渲染的优势。通过将刚体棱镜网格与3D形态头部模型相结合,我们使用混合渲染模型同时重建基于网格的头部和可变形的NeRF模型,用于表示3DMM未表示的区域。然后我们将可变形的NeRF蒸馏成刚体网格和神经纹理,可以在传统的三角形渲染管道的约束下进行有效动画和渲染。除了在手机设备上以每秒60帧的速度运行且内存使用率低之外,我们还发现我们的训练模型在桌面设备上的质量与最先进的3D化身模型相当。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 8 pages, 5 figures
Summary
PrismAvatar是一个专为在资源受限的边缘设备上实现实时动画和渲染而设计的3D头像模型。它结合了基于网格的头模型与可变形NeRF模型,能够在训练时享受神经体积渲染的优势。通过将可变形NeRF蒸馏成基于网格的模型和神经纹理,该模型能够在传统三角形渲染管道的约束下实现高效的动画和渲染。此模型在移动设备上以低内存使用实现了每秒60帧的运行速度,并在台式设备上呈现出堪比顶尖3D头像模型的质量。
Key Takeaways
- PrismAvatar专为在资源受限的边缘设备上实现实时动画和渲染而设计。
- 结合基于网格的头模型和可变形NeRF模型,享受神经体积渲染的优势。
- 通过蒸馏技术,将可变形NeRF转换为基于网格的模型和神经纹理。
- 该模型能在传统三角形渲染管道下高效工作。
- 模型在移动设备上有良好的性能表现,以低内存使用实现了每秒60帧的运行速度。
- PrismAvatar的模型质量堪比顶尖3D头像模型。
点此查看论文截图



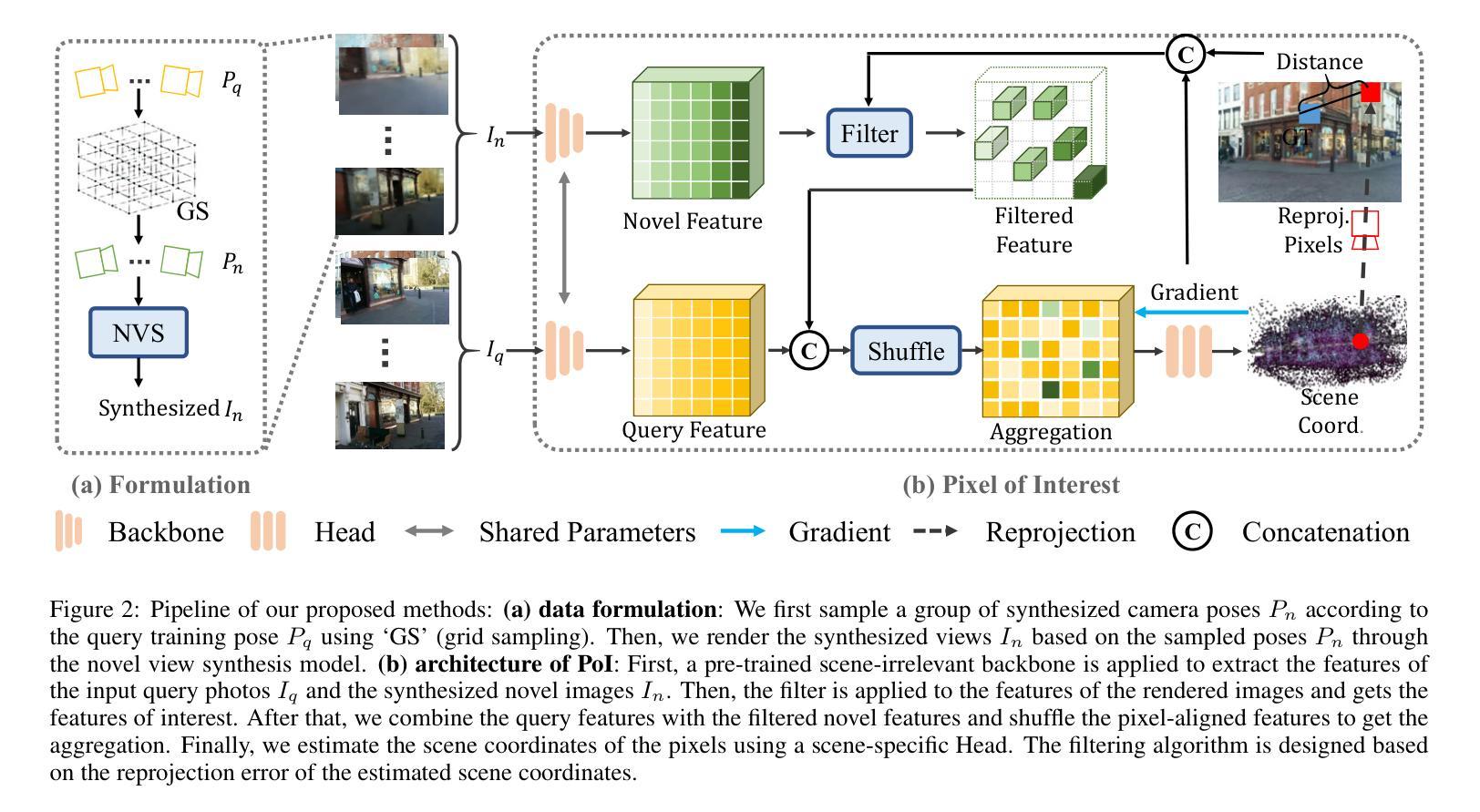
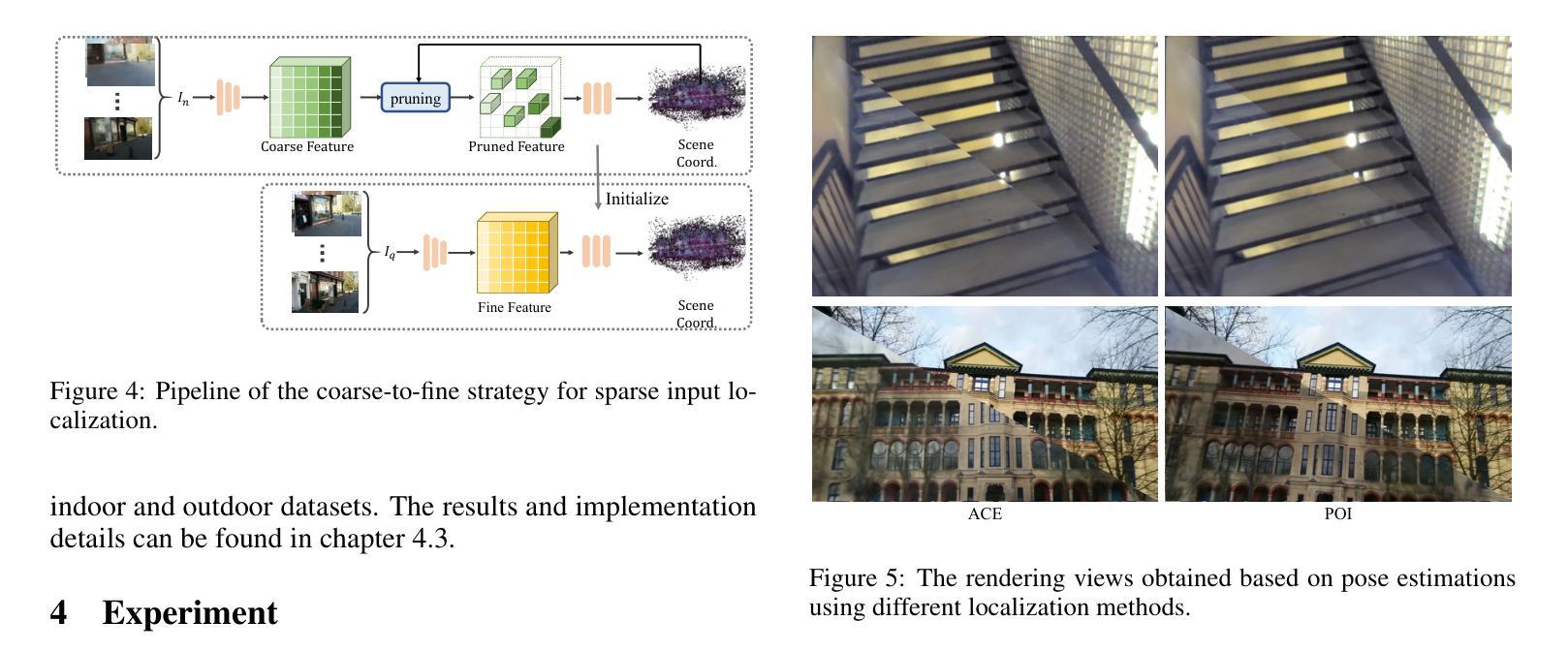
PoI: Pixel of Interest for Novel View Synthesis Assisted Scene Coordinate Regression
Authors:Feifei Li, Qi Song, Chi Zhang, Hui Shuai, Rui Huang
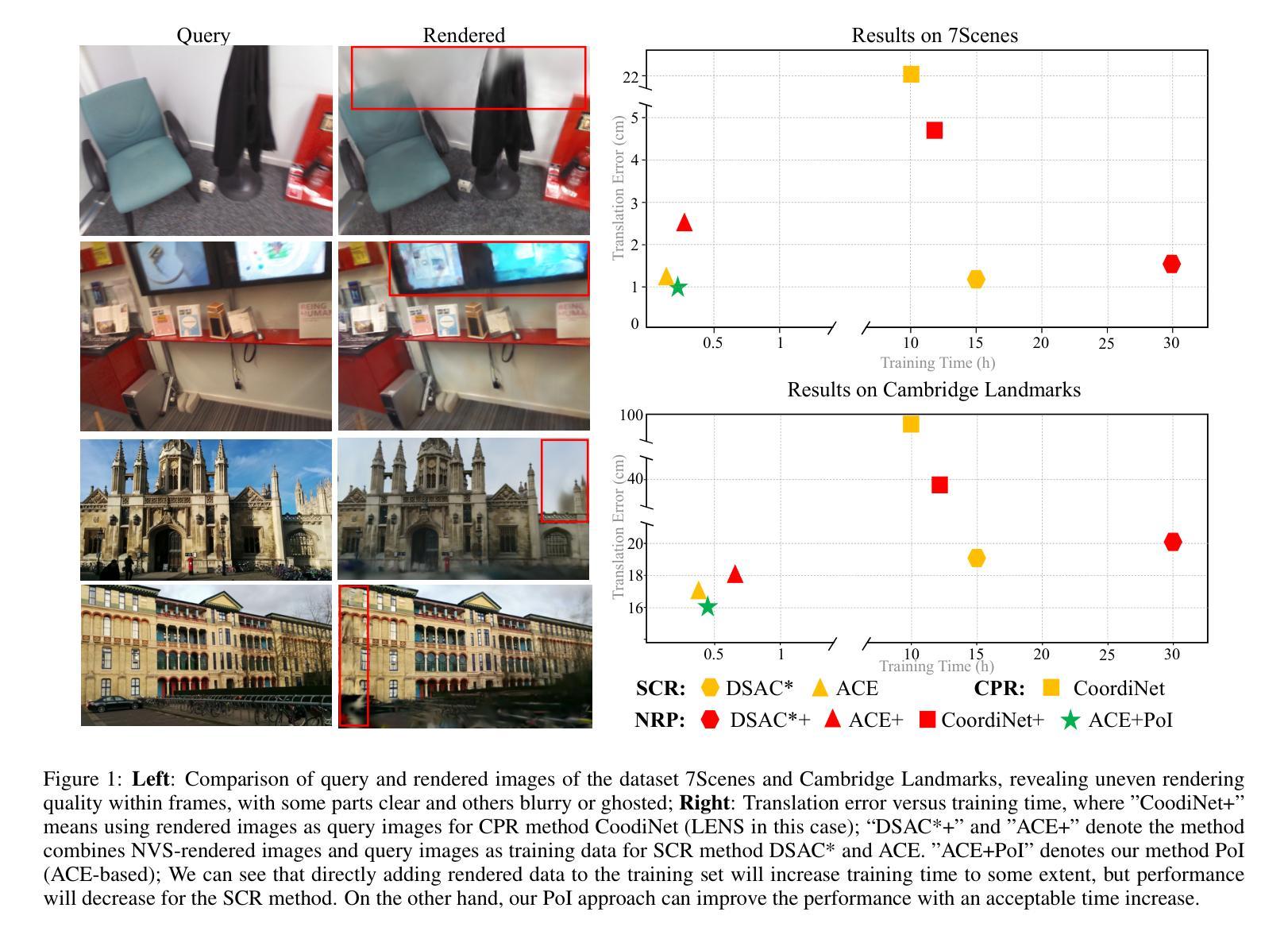
The task of estimating camera poses can be enhanced through novel view synthesis techniques such as NeRF and Gaussian Splatting to increase the diversity and extension of training data. However, these techniques often produce rendered images with issues like blurring and ghosting, which compromise their reliability. These issues become particularly pronounced for Scene Coordinate Regression (SCR) methods, which estimate 3D coordinates at the pixel level. To mitigate the problems associated with unreliable rendered images, we introduce a novel filtering approach, which selectively extracts well-rendered pixels while discarding the inferior ones. This filter simultaneously measures the SCR model’s real-time reprojection loss and gradient during training. Building on this filtering technique, we also develop a new strategy to improve scene coordinate regression using sparse inputs, drawing on successful applications of sparse input techniques in novel view synthesis. Our experimental results validate the effectiveness of our method, demonstrating state-of-the-art performance on indoor and outdoor datasets.
通过NeRF和高斯拼贴板等新型视图合成技术,可以增强对相机姿态的估计任务,从而提高训练数据的多样性和扩展性。然而,这些技术经常产生的渲染图像存在模糊和重影等问题,从而影响其可靠性。这些问题在场景坐标回归(SCR)方法中尤为突出,SCR方法会估计像素级别的3D坐标。为了缓解与不可靠的渲染图像相关的问题,我们引入了一种新型过滤方法,该方法能够有选择地提取渲染良好的像素,同时丢弃质量较差的像素。该过滤器在训练过程中实时测量SCR模型的再投影损失和梯度。基于这种过滤技术,我们还开发了一种利用稀疏输入改进场景坐标回归的新策略,借鉴了稀疏输入技术在新型视图合成中的成功应用。我们的实验结果验证了该方法的有效性,在室内和室外数据集上均表现出卓越的性能。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
本文提出一种结合NeRF和高斯展开等新视图合成技术提高相机姿态估计任务的方法,以增加训练数据的多样性和扩展性。然而,这些技术产生的渲染图像往往存在模糊和重影等问题,影响了其可靠性。特别是在像素级别估计三维坐标的场景坐标回归(SCR)方法中,这些问题更加突出。为缓解不可靠渲染图像带来的问题,本文引入了一种新的滤波方法,可选择性提取渲染良好的像素并丢弃较差的像素。该滤波器同时测量SCR模型的实时重投影损失和训练过程中的梯度。在此基础上,我们还开发了一种利用稀疏输入改进场景坐标回归的新策略,借鉴稀疏输入在新型视图合成中的成功应用。实验结果验证了我们的方法的有效性,在室内和室外数据集上均表现出卓越的性能。
要点
- 新视图合成技术如NeRF和高斯展布能提高相机姿态估计任务的多样性和扩展性。
- 渲染图像常常存在模糊和重影问题,影响了技术的可靠性。
- 引入了一种新的滤波方法,能选择性地提取渲染良好的像素并丢弃质量差的像素。
- 滤波器同时测量场景坐标回归模型的实时重投影损失和训练过程中的梯度。
- 提出了一种利用稀疏输入改进场景坐标回归的新策略。
- 方法在室内外数据集上均表现出卓越性能。
点此查看论文截图


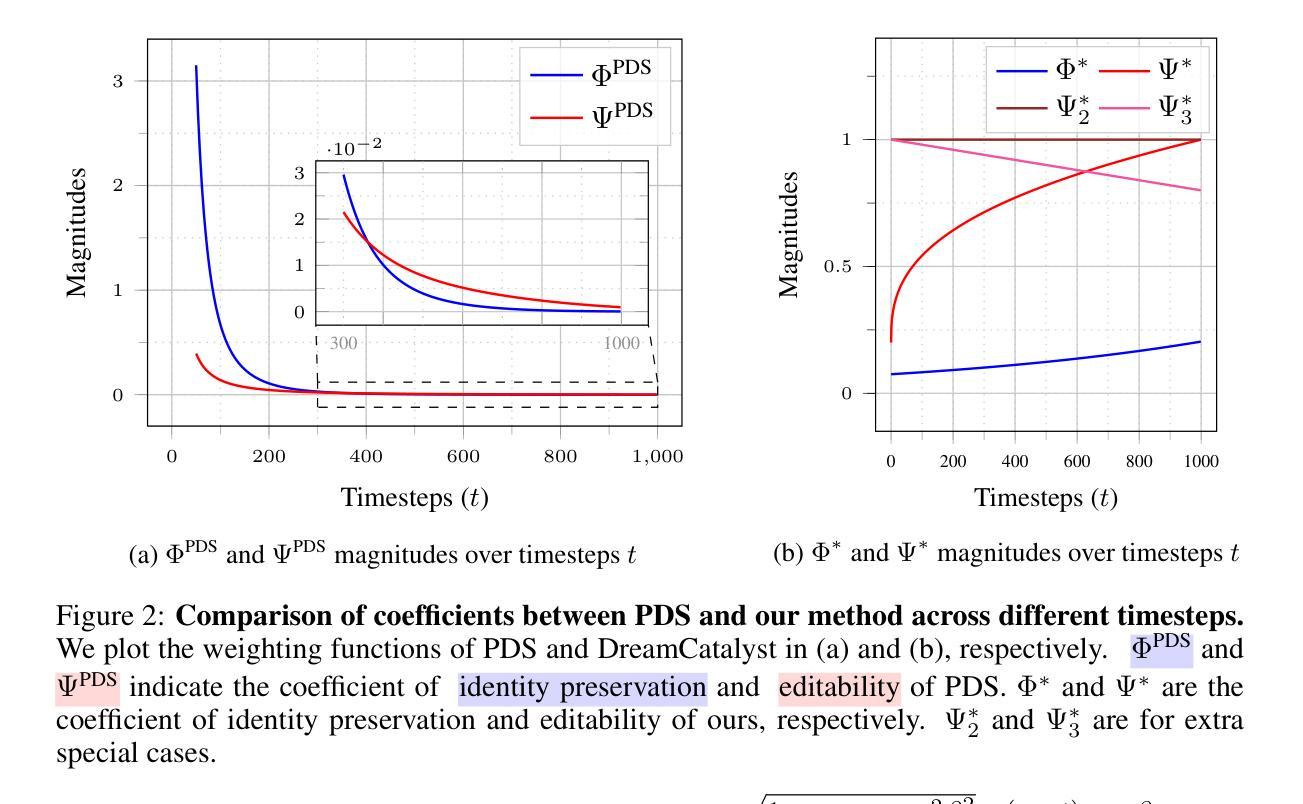
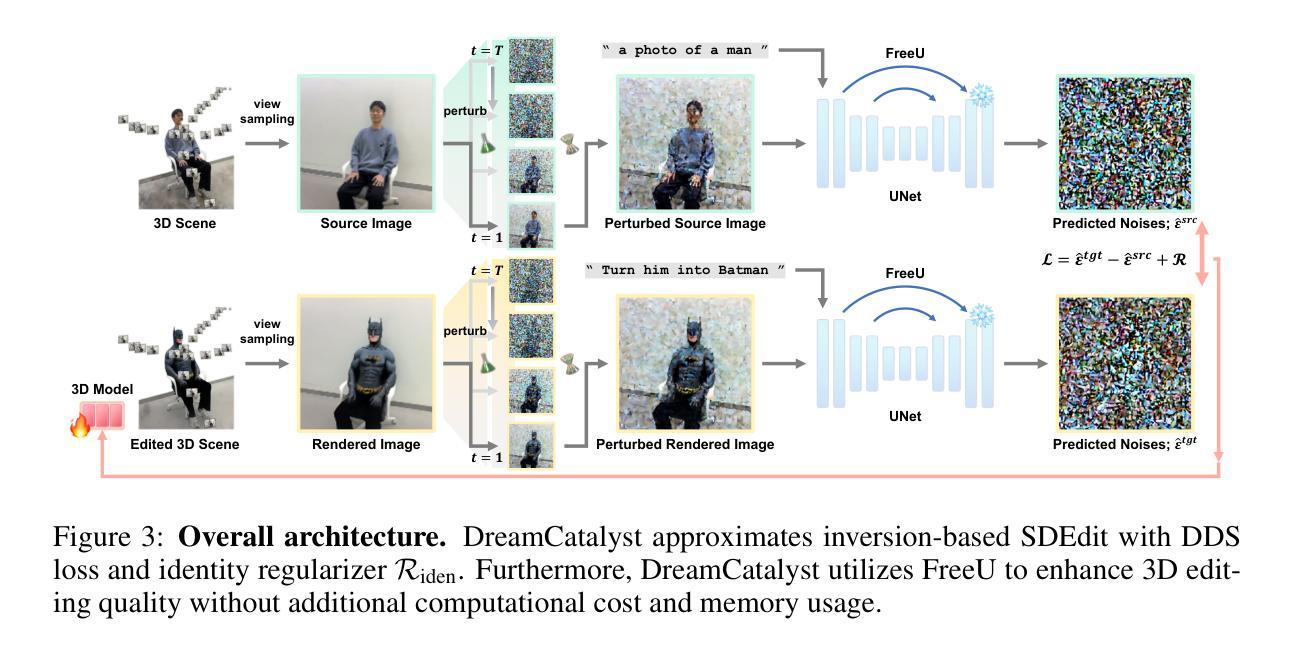
DreamCatalyst: Fast and High-Quality 3D Editing via Controlling Editability and Identity Preservation
Authors:Jiwook Kim, Seonho Lee, Jaeyo Shin, Jiho Choi, Hyunjung Shim
Score distillation sampling (SDS) has emerged as an effective framework in text-driven 3D editing tasks, leveraging diffusion models for 3D-consistent editing. However, existing SDS-based 3D editing methods suffer from long training times and produce low-quality results. We identify that the root cause of this performance degradation is \textit{their conflict with the sampling dynamics of diffusion models}. Addressing this conflict allows us to treat SDS as a diffusion reverse process for 3D editing via sampling from data space. In contrast, existing methods naively distill the score function using diffusion models. From these insights, we propose DreamCatalyst, a novel framework that considers these sampling dynamics in the SDS framework. Specifically, we devise the optimization process of our DreamCatalyst to approximate the diffusion reverse process in editing tasks, thereby aligning with diffusion sampling dynamics. As a result, DreamCatalyst successfully reduces training time and improves editing quality. Our method offers two modes: (1) a fast mode that edits Neural Radiance Fields (NeRF) scenes approximately 23 times faster than current state-of-the-art NeRF editing methods, and (2) a high-quality mode that produces superior results about 8 times faster than these methods. Notably, our high-quality mode outperforms current state-of-the-art NeRF editing methods in terms of both speed and quality. DreamCatalyst also surpasses the state-of-the-art 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) editing methods, establishing itself as an effective and model-agnostic 3D editing solution. See more extensive results on our project page: https://dream-catalyst.github.io.
得分蒸馏采样(SDS)已成为文本驱动的三维编辑任务中的有效框架,它利用扩散模型进行三维一致性编辑。然而,现有的基于SDS的三维编辑方法存在训练时间长和结果质量低的问题。我们确定性能下降的根本原因是它们与扩散模型的采样动力学存在冲突。解决这种冲突使我们能够将SDS视为通过数据空间采样进行三维编辑的扩散反向过程。相比之下,现有方法只是简单地使用扩散模型对分数函数进行蒸馏。基于这些见解,我们提出了DreamCatalyst,这是一个在SDS框架中考虑这些采样动力学的全新框架。具体来说,我们设计DreamCatalyst的优化过程以近似编辑任务中的扩散反向过程,从而与扩散采样动力学保持一致。因此,DreamCatalyst成功减少了训练时间并提高了编辑质量。我们的方法提供了两种模式:(1)快速模式,编辑神经辐射场(NeRF)场景的速度比当前最先进的NeRF编辑方法快约23倍;(2)高质量模式,产生优于这些方法的结果,速度大约快8倍。值得注意的是,我们的高质量模式在速度和质量方面都超越了当前的先进NeRF编辑方法。DreamCatalyst还超越了最先进的3D高斯拼贴(3DGS)编辑方法,成为了一种有效且模型无关的三维编辑解决方案。想了解更多结果,请访问我们的项目页面:https://dream-catalyst.github.io。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICLR 2025
Summary
本文介绍了Score Distillation Sampling(SDS)在文本驱动的3D编辑任务中的有效性,利用扩散模型实现3D一致性编辑。但现有SDS方法存在训练时间长、结果质量低的问题。研究发现,这些问题的根源在于SDS与扩散模型的采样动力学存在冲突。为此,本文提出DreamCatalyst框架,考虑SDS框架中的采样动力学,优化过程模拟扩散反向过程,减少训练时间,提高编辑质量。DreamCatalyst提供快速模式和高质模式两种选项,分别实现了近似于现有技术23倍加速NeRF场景编辑和优于现有技术8倍速度的高质量结果。此外,DreamCatalyst还超越了现有的3D Gaussian Splatting(3DGS)编辑方法,成为有效且通用的3D编辑解决方案。
Key Takeaways
- SDS在文本驱动的3D编辑任务中表现出有效性,但存在训练时间长、结果质量低的问题。
- 问题的根源在于SDS与扩散模型的采样动力学存在冲突。
- DreamCatalyst框架考虑SDS中的采样动力学,优化过程模拟扩散反向过程。
- DreamCatalyst提供快速模式和高质模式两种选项,分别实现快速和高质量的编辑结果。
- DreamCatalyst框架在NeRF编辑任务中表现出超越现有技术的性能。
- DreamCatalyst成为有效且通用的3D编辑解决方案。
点此查看论文截图

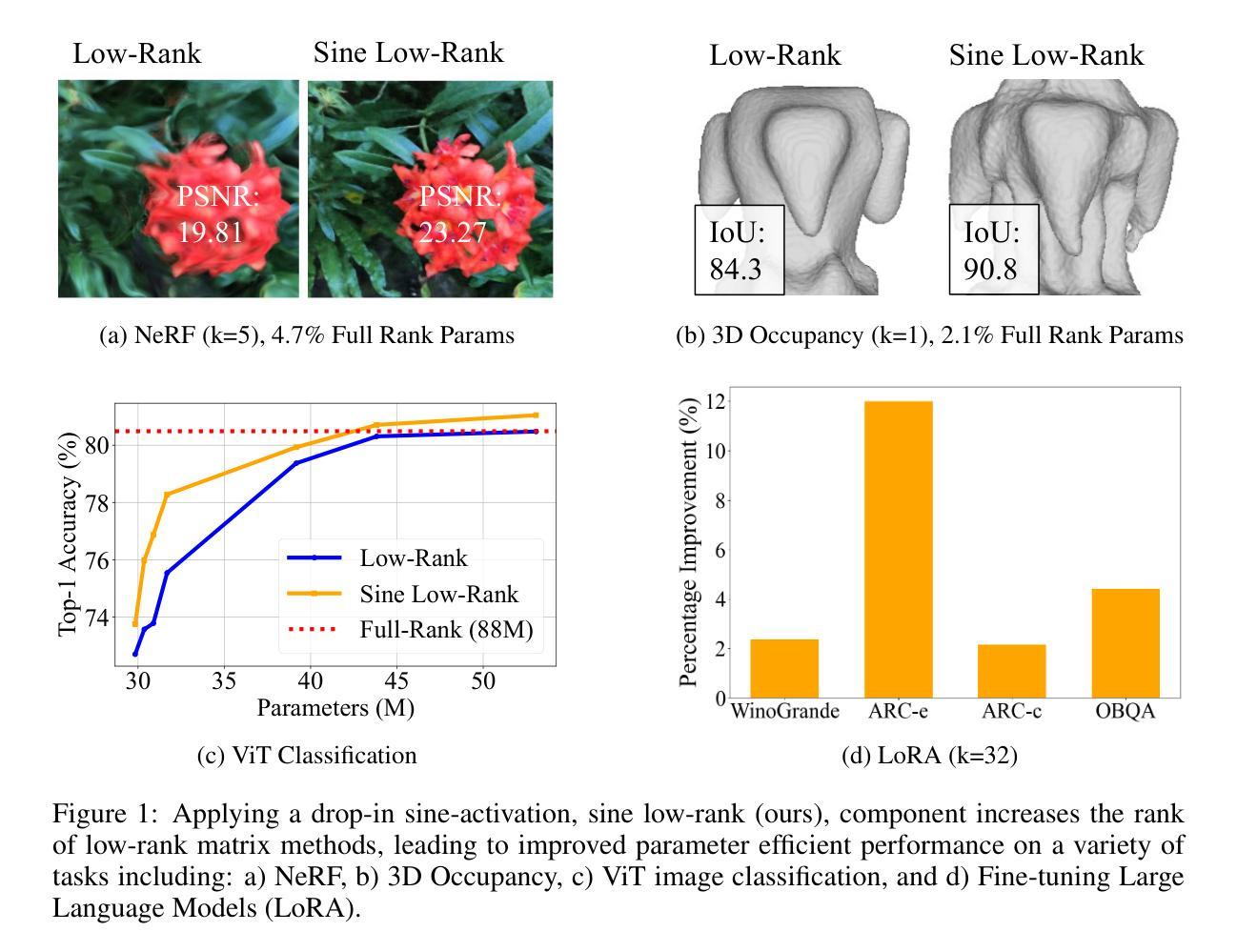
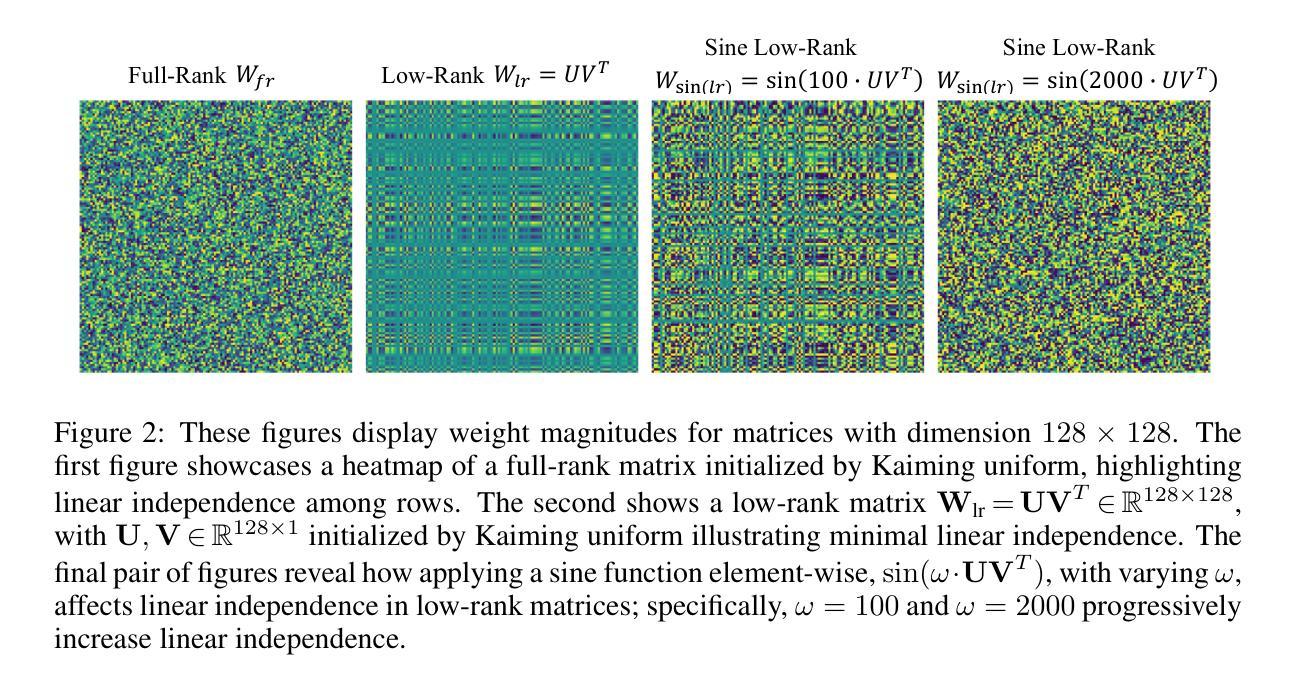
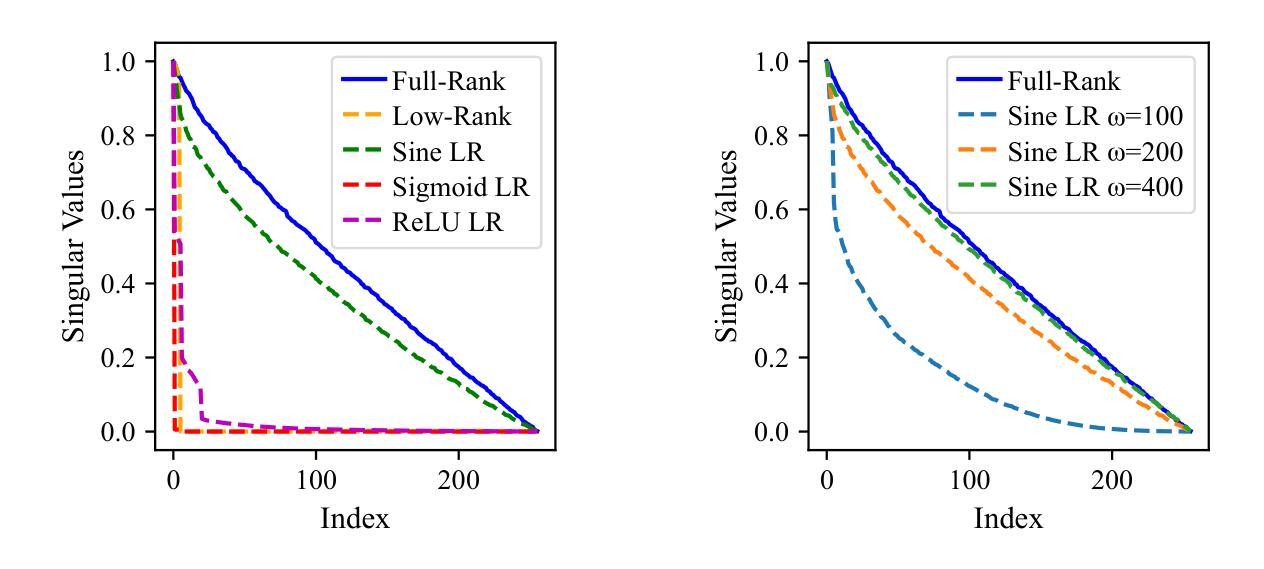
Efficient Learning With Sine-Activated Low-rank Matrices
Authors:Yiping Ji, Hemanth Saratchandran, Cameron Gordon, Zeyu Zhang, Simon Lucey
Low-rank decomposition has emerged as a vital tool for enhancing parameter efficiency in neural network architectures, gaining traction across diverse applications in machine learning. These techniques significantly lower the number of parameters, striking a balance between compactness and performance. However, a common challenge has been the compromise between parameter efficiency and the accuracy of the model, where reduced parameters often lead to diminished accuracy compared to their full-rank counterparts. In this work, we propose a novel theoretical framework that integrates a sinusoidal function within the low-rank decomposition process. This approach not only preserves the benefits of the parameter efficiency characteristic of low-rank methods but also increases the decomposition’s rank, thereby enhancing model performance. Our method proves to be a plug in enhancement for existing low-rank models, as evidenced by its successful application in Vision Transformers (ViT), Large Language Models (LLMs), Neural Radiance Fields (NeRF) and 3D shape modelling.
低秩分解已成为提高神经网络架构参数效率的重要工具,在机器学习的各种应用中受到广泛关注。这些技术显著减少了参数数量,在紧凑性和性能之间取得了平衡。然而,一个常见的挑战是参数效率与模型准确性之间的权衡,减少的参数往往会导致与全秩模型相比准确性降低。在这项工作中,我们提出了一种新的理论框架,该框架将正弦函数整合到低秩分解过程中。这种方法不仅保留了低秩方法参数效率的优点,还提高了分解的秩,从而增强了模型性能。我们的方法被证明是对现有低秩模型的增强插件,其在视觉转换器(ViT)、大型语言模型(LLM)、神经辐射场(NeRF)和3D形状建模中的应用成功证明了这一点。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF The first two authors contributed equally. Paper accepted at ICLR 2025
Summary
神经网络架构中提升参数效率的重要工具是低秩分解,它在机器学习各个领域广泛应用。此方法可大幅降低参数数量,并在紧凑性和性能之间取得平衡。但面临的一个难题是需要在参数效率和模型准确度间做出妥协,减少参数往往会导致性能下降。本研究提出一种新型理论框架,将正弦函数融入低秩分解过程。此方法不仅保留了低秩方法的参数效率优势,还提升了分解的秩,增强了模型性能。此方法可作为现有低秩模型的增强插件,成功应用于视觉转换器(ViT)、大型语言模型(LLMs)、神经辐射场(NeRF)和三维建模等领域。
Key Takeaways
- 低秩分解技术用于增强神经网络架构的参数效率,广泛应用于机器学习各个领域。
- 低秩分解面临参数效率和模型准确度之间的妥协问题。
- 本研究提出一种新型理论框架,融合正弦函数于低秩分解过程中。
- 此方法既保留了低秩方法的参数效率,又提升了模型性能。
- 方法成功应用于视觉转换器(ViT)、大型语言模型(LLMs)、神经辐射场(NeRF)和三维建模等领域。
- 此方法可作为现有低秩模型的增强插件使用。
点此查看论文截图

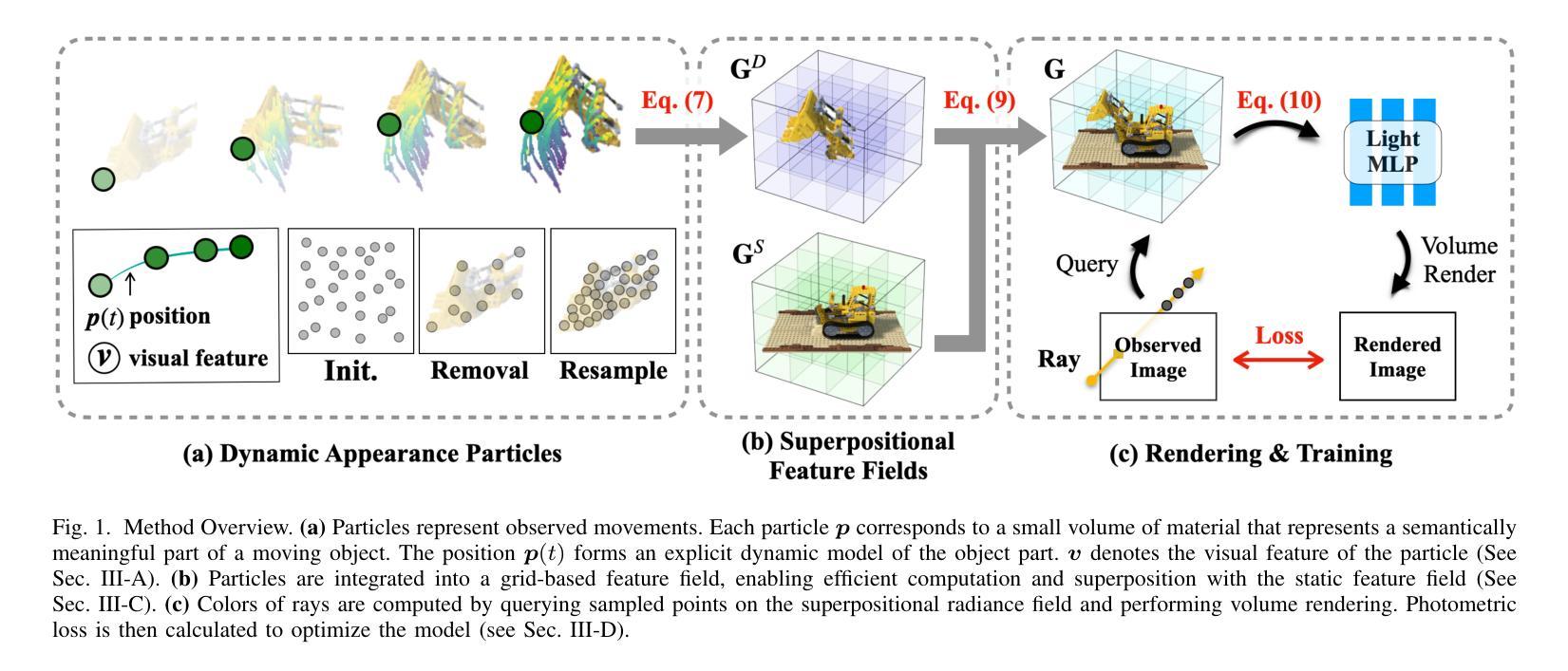
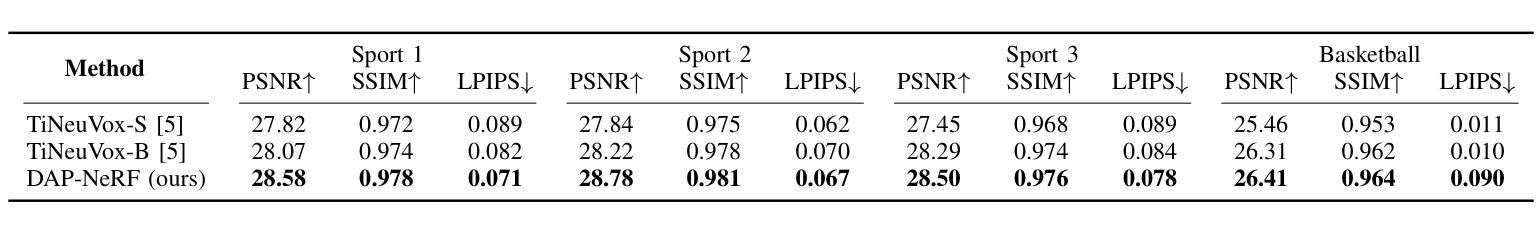
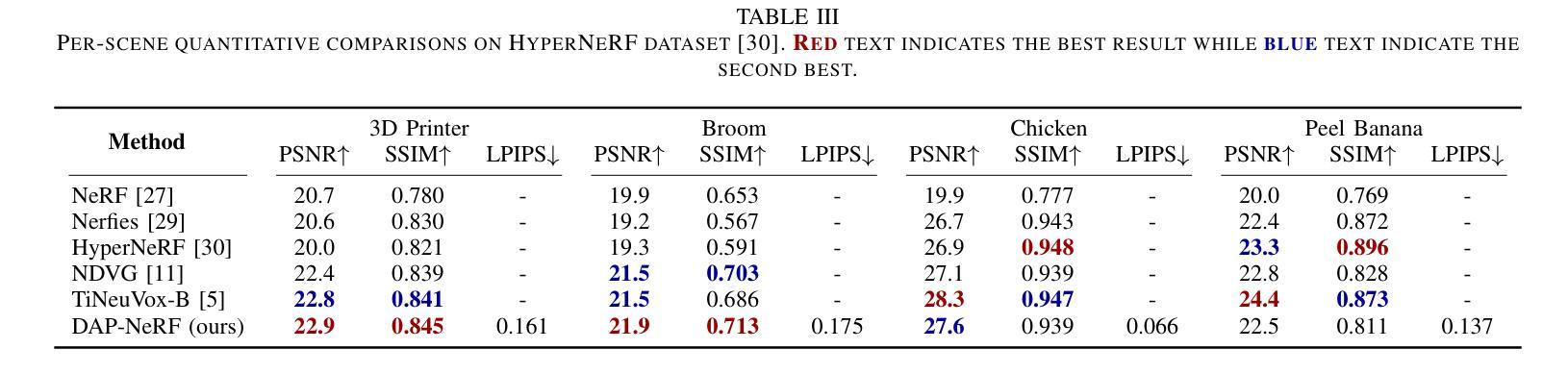
Dynamic Appearance Particle Neural Radiance Field
Authors:Ancheng Lin, Yusheng Xiang, Jun Li, Mukesh Prasad
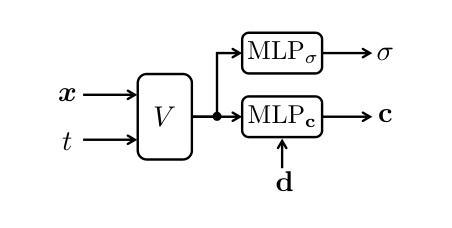
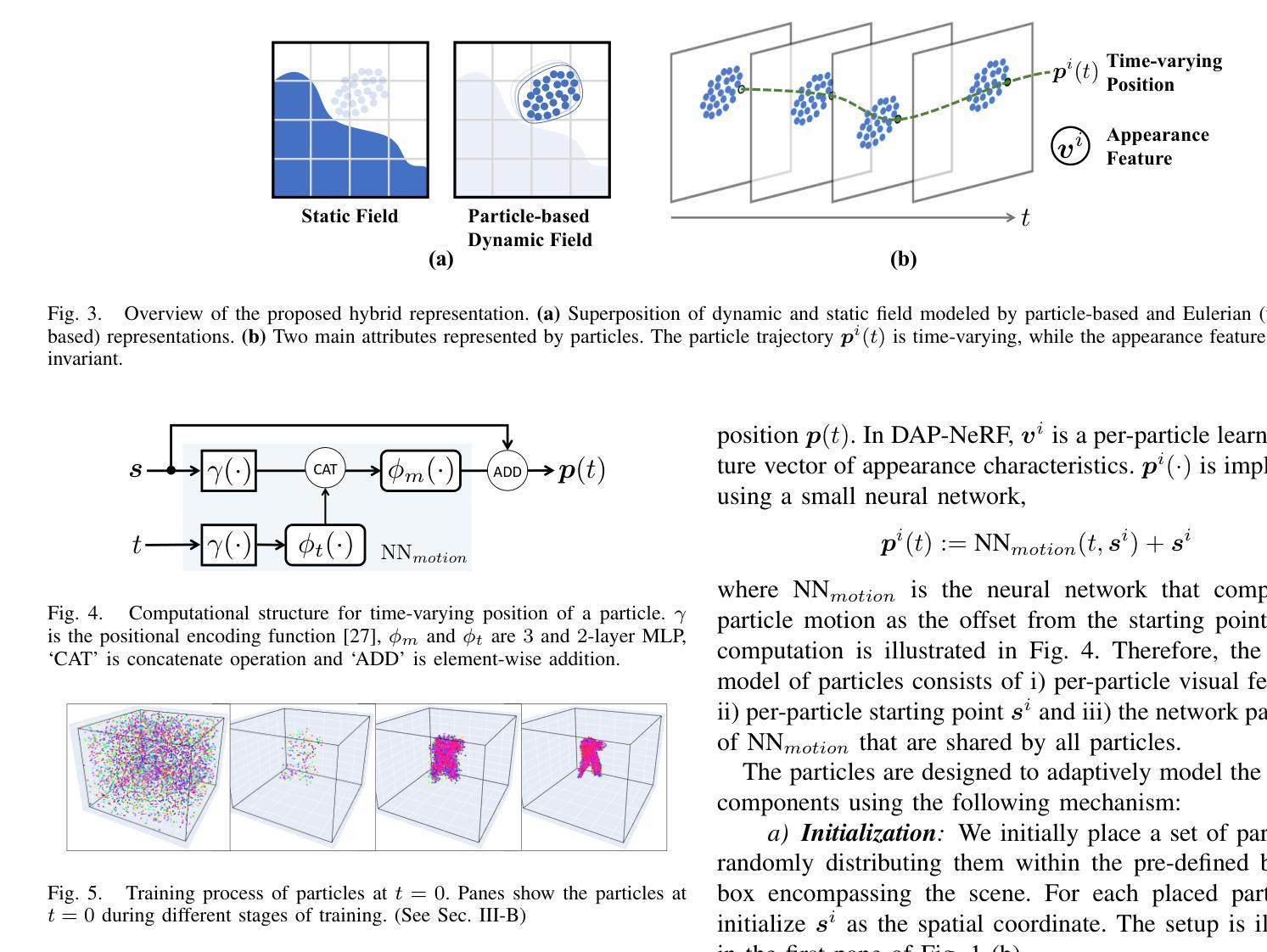
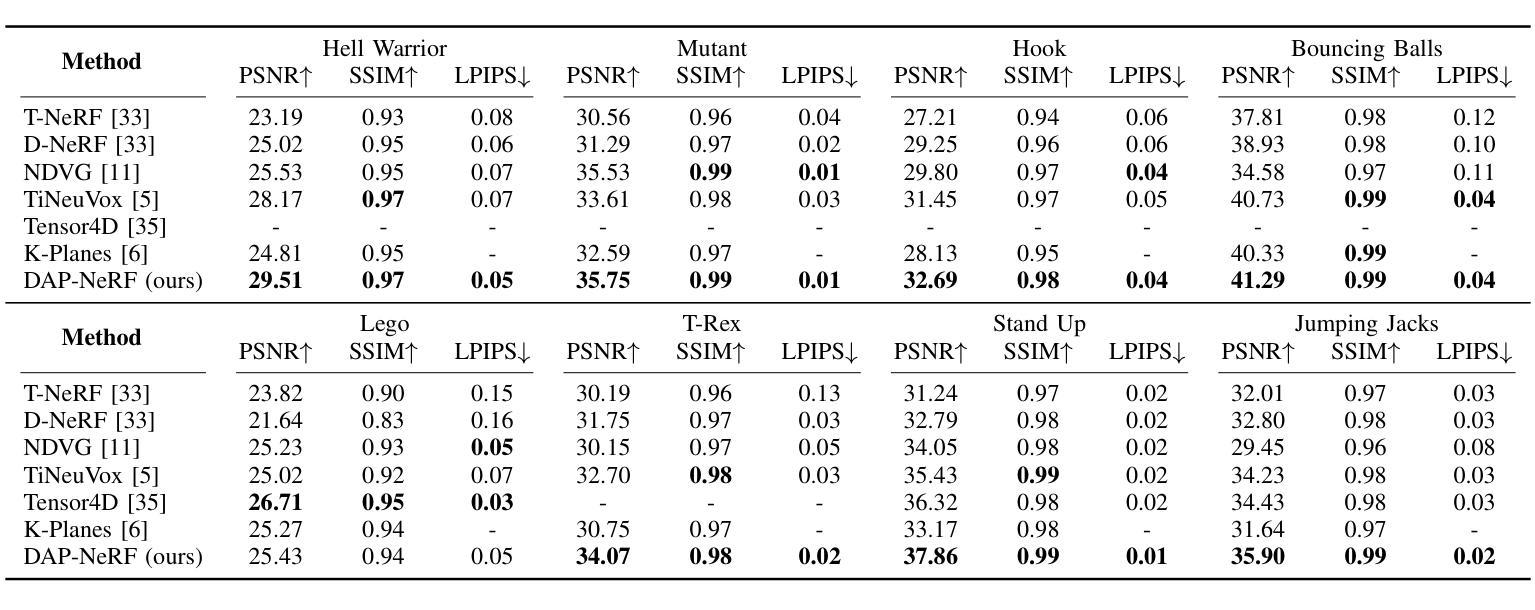
Neural Radiance Fields (NeRFs) have shown great potential in modeling 3D scenes. Dynamic NeRFs extend this model by capturing time-varying elements, typically using deformation fields. The existing dynamic NeRFs employ a similar Eulerian representation for both light radiance and deformation fields. This leads to a close coupling of appearance and motion and lacks a physical interpretation. In this work, we propose Dynamic Appearance Particle Neural Radiance Field (DAP-NeRF), which introduces particle-based representation to model the motions of visual elements in a dynamic 3D scene. DAP-NeRF consists of the superposition of a static field and a dynamic field. The dynamic field is quantized as a collection of appearance particles, which carries the visual information of a small dynamic element in the scene and is equipped with a motion model. All components, including the static field, the visual features and the motion models of particles, are learned from monocular videos without any prior geometric knowledge of the scene. We develop an efficient computational framework for the particle-based model. We also construct a new dataset to evaluate motion modeling. Experimental results show that DAP-NeRF is an effective technique to capture not only the appearance but also the physically meaningful motions in a 3D dynamic scene. Code is available at: https://github.com/Cenbylin/DAP-NeRF.
神经辐射场(NeRF)在建模3D场景方面显示出巨大潜力。动态NeRF通过捕捉随时间变化的元素(通常使用变形场)来扩展此模型。现有的动态NeRF为光辐射和变形场采用相似的欧拉表示法。这导致了外观和运动的紧密耦合,并且缺乏物理解释。在这项工作中,我们提出动态外观粒子神经辐射场(DAP-NeRF),它引入基于粒子的表示法来模拟动态3D场景中视觉元素的运动。DAP-NeRF由静态场和动态场的叠加组成。动态场被量化为一系列外观粒子,这些粒子携带场景中一个小动态元素的可视信息并配备运动模型。所有组件,包括静态场、视觉特征和粒子的运动模型,都是从单目视频中学习的,无需对场景有任何先验的几何知识。我们为基于粒子的模型开发了一个高效的计算框架。我们还构建了一个新的数据集来评估运动建模。实验结果表明,DAP-NeRF是一种有效的技术,不仅能捕捉外观,还能捕捉3D动态场景中的物理意义运动。代码可在:https://github.com/Cenbylin/DAP-NeRF获得。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
NeRF技术在建模动态场景时引入了一种名为DAP-NeRF的动态表现粒子神经辐射场模型。该模型采用基于粒子的表示法模拟场景中视觉元素的运动,包括静态场和动态场。动态场被量化为携带场景中微小动态元素视觉信息的外观粒子集合,并配备了运动模型。所有组件均从单目视频中学习,无需场景的先验几何知识。DAP-NeRF不仅能捕捉场景的外观,还能捕捉物理上有意义的运动。实验结果表明,DAP-NeRF是一种有效的技术。代码地址:https://github.com/Cenbylin/DAP-NeRF。
关键见解
- 动态NeRF扩展了原有的模型,成功捕捉到时间变化的元素。提出了全新的DAP-NeRF模型,用于模拟动态场景中的视觉元素运动。
- DAP-NeRF结合了静态场和动态场,引入基于粒子的表示法,这是一种新颖的方法。
- 动态场被量化为外观粒子集合,每个粒子携带场景中微小动态元素的视觉信息,并配备运动模型。
- 所有组件仅通过单目视频学习,无需依赖场景的先验几何知识。这一点是创新之处并且显示出强大的能力。
- DAP-NeRF提供了一个高效的计算框架来处理基于粒子的模型。
- 为了评估运动建模的效果,建立了一个新的数据集用于实验评估。这表明DAP-NeRF在动态场景中的运动和外观捕捉方面具有良好的表现。
点此查看论文截图