⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-02-13 更新
Causal Analysis of ASR Errors for Children: Quantifying the Impact of Physiological, Cognitive, and Extrinsic Factors
Authors:Vishwanath Pratap Singh, Md. Sahidullah, Tomi Kinnunen
The increasing use of children’s automatic speech recognition (ASR) systems has spurred research efforts to improve the accuracy of models designed for children’s speech in recent years. The current approach utilizes either open-source speech foundation models (SFMs) directly or fine-tuning them with children’s speech data. These SFMs, whether open-source or fine-tuned for children, often exhibit higher word error rates (WERs) compared to adult speech. However, there is a lack of systemic analysis of the cause of this degraded performance of SFMs. Understanding and addressing the reasons behind this performance disparity is crucial for improving the accuracy of SFMs for children’s speech. Our study addresses this gap by investigating the causes of accuracy degradation and the primary contributors to WER in children’s speech. In the first part of the study, we conduct a comprehensive benchmarking study on two self-supervised SFMs (Wav2Vec2.0 and Hubert) and two weakly supervised SFMs (Whisper and MMS) across various age groups on two children speech corpora, establishing the raw data for the causal inference analysis in the second part. In the second part of the study, we analyze the impact of physiological factors (age, gender), cognitive factors (pronunciation ability), and external factors (vocabulary difficulty, background noise, and word count) on SFM accuracy in children’s speech using causal inference. The results indicate that physiology (age) and particular external factor (number of words in audio) have the highest impact on accuracy, followed by background noise and pronunciation ability. Fine-tuning SFMs on children’s speech reduces sensitivity to physiological and cognitive factors, while sensitivity to the number of words in audio persists. Keywords: Children’s ASR, Speech Foundational Models, Causal Inference, Physiology, Cognition, Pronunciation
近年来,儿童自动语音识别(ASR)系统的使用越来越频繁,这刺激了努力提高针对儿童语音设计的模型的准确性。目前的方法直接使用开源语音基础模型(SFMs)或对儿童语音数据进行微调。这些SFMs,无论是开源的还是针对儿童进行微调,与成人语音相比,往往表现出更高的词错误率(WERs)。然而,缺乏对SFM性能下降的系统性分析。理解和解决这种性能差异的原因对于提高儿童语音的SFM准确性至关重要。我们的研究通过调查准确性的下降原因和儿童语音中WER的主要贡献者来弥补这一空白。在研究的第一部分中,我们对两种自监督的SFMs(Wav2Vec 2.0和Hubert)和两种弱监督的SFMs(Whisper和MMS)进行了全面的基准测试研究,并在两个儿童语音语料库中针对不同年龄组进行了评估,为第二部分中的因果推理分析提供了原始数据。在研究的第二部分中,我们利用因果推理分析了生理因素(年龄、性别)、认知因素(发音能力)和外部因素(词汇难度、背景噪音和单词数量)对儿童语音中SFM精度的影响。结果表明,生理(年龄)和特定外部因素(音频中的单词数)对精度的影响最大,其次是背景噪音和发音能力。对儿童语音数据进行微调SFMs可以减少对生理和认知因素的敏感性,但对音频中的单词数量的敏感性仍然存在。关键词:儿童ASR、语音基础模型、因果推理、生理学、认知、发音。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Submitted to Computer Speech & Language
Summary
近年来,随着儿童自动语音识别(ASR)系统的广泛应用,针对儿童语音设计的模型准确性提升成为了研究热点。当前的研究方法包括直接使用开源语音基础模型(SFMs)或对其进行儿童语音数据的微调。然而,这些模型在识别儿童语音时相较于成人语音存在较高的词错误率(WERs)。本研究旨在填补这一空白,探究模型准确性下降的原因以及对儿童语音WER的主要贡献因素。研究分为两部分:首先,对两款自监督的SFMs和两款弱监督的SFMs在不同年龄组进行基准测试;其次,利用因果推理分析生理因素(年龄、性别)、认知因素(发音能力)和外部因素(词汇难度、背景噪音和单词数量)对模型准确性的影响。结果显示,生理因素(年龄)和特定外部因素(音频中的单词数量)对准确性的影响最大,其次是背景噪音和发音能力。对SFMs进行儿童语音微调能减少生理和认知因素的影响,但对音频中单词数量的敏感性仍然存在。
Key Takeaways
- 儿童自动语音识别(ASR)系统的应用促使了对提高儿童语音模型准确性的研究。
- 当前使用的语音基础模型(SFMs)在识别儿童语音时存在较高的词错误率(WERs)。
- 研究分为基准测试与因果分析两部分,旨在找出模型准确性下降的原因。
- 生理因素(年龄)和对音频中单词数量的特定外部因素对模型准确性的影响最大。
- 背景噪音和发音能力也对模型准确性产生影响。
- 对SFMs进行儿童语音微调能减少生理和认知因素的影响。
点此查看论文截图

LoRP-TTS: Low-Rank Personalized Text-To-Speech
Authors:Łukasz Bondaruk, Jakub Kubiak
Speech synthesis models convert written text into natural-sounding audio. While earlier models were limited to a single speaker, recent advancements have led to the development of zero-shot systems that generate realistic speech from a wide range of speakers using their voices as additional prompts. However, they still struggle with imitating non-studio-quality samples that differ significantly from the training datasets. In this work, we demonstrate that utilizing Low-Rank Adaptation (LoRA) allows us to successfully use even single recordings of spontaneous speech in noisy environments as prompts. This approach enhances speaker similarity by up to $30pp$ while preserving content and naturalness. It represents a significant step toward creating truly diverse speech corpora, that is crucial in all speech-related tasks.
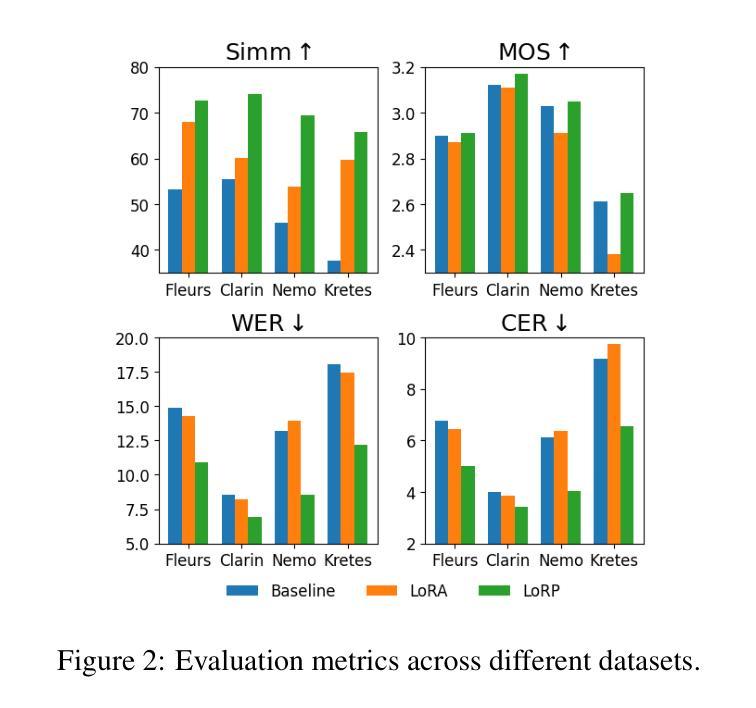
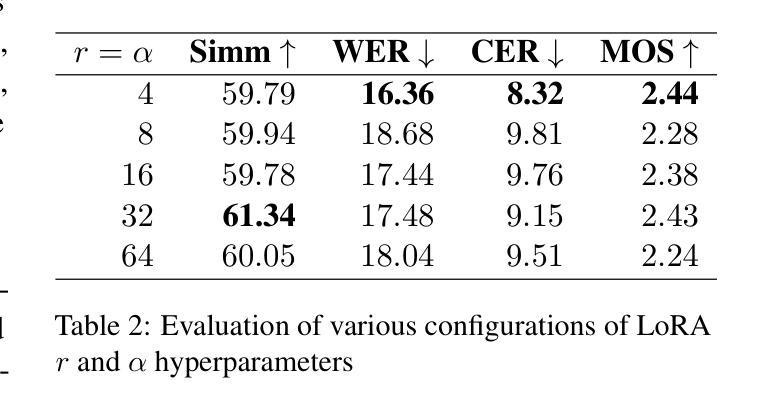
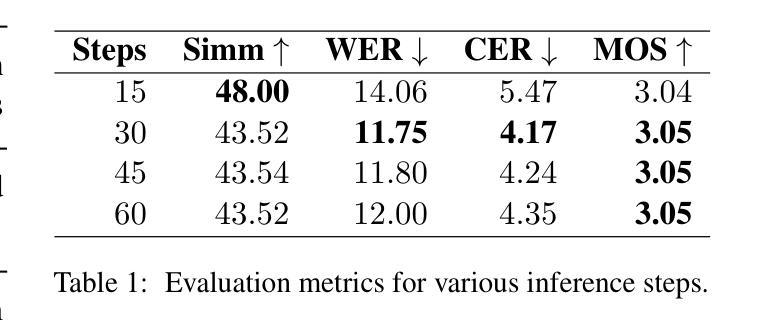
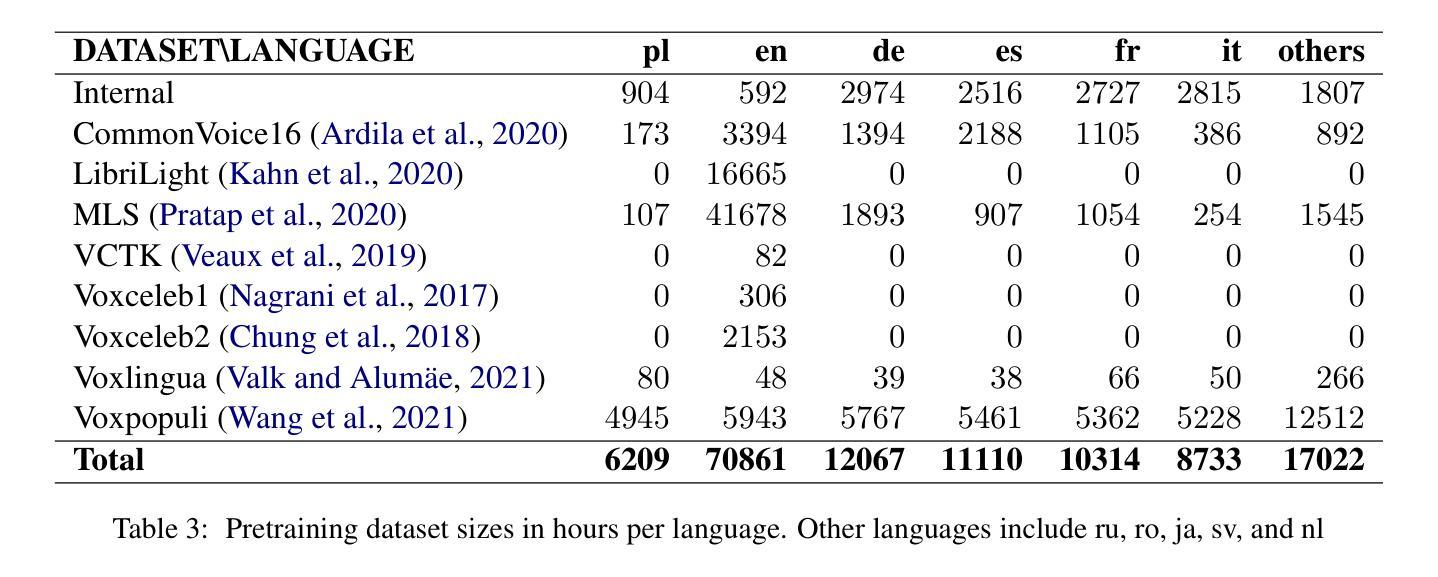
语音合成模型将书面文字转换为自然音频。虽然早期模型仅限于单一发言人,但最近的进步已经开发出零样本系统,这些系统可以使用各种发言人的声音作为额外提示来生成逼真的语音。然而,它们仍然难以模仿与训练数据集差异很大的非工作室质量样本。在这项工作中,我们证明利用低秩适应(LoRA)技术,即使在使用单一的环境嘈杂语音样本作为提示时,也能成功应用。这种方法在提高说话人相似度方面提高了高达30个百分点,同时保持了内容和自然度。这朝着创建真正多样化的语音语料库迈出了重要的一步,这在所有与语音相关的任务中都至关重要。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
本研究探讨语音合成模型的最新发展。早期模型仅支持单一发言人,但现在的零样本系统可以利用不同发言人的声音进行生成。尽管如此,它们仍然难以模仿非专业录音样本。本研究展示低秩适应(LoRA)技术如何成功使用单一的自然环境录音作为提示,增强发言人相似性达30pp,同时保持内容和自然性。这标志着在创建真正多样化的语音语料库方面取得了重要进展,这对所有语音任务都至关重要。
关键见解
- 语音合成模型可将文字转换为自然的声音。
- 早期模型受限于单一发言人,但现代系统通过使用不同发言人的声音进行生成,实现了零样本。
- 当前模型在模仿非专业录音样本方面存在挑战。
- 低秩适应(LoRA)技术允许使用单一的自然环境录音作为提示。
- LoRA技术增强了发言人相似性达30pp。
- LoRA技术在保持内容和自然性的同时,增强了语音合成的质量。
点此查看论文截图

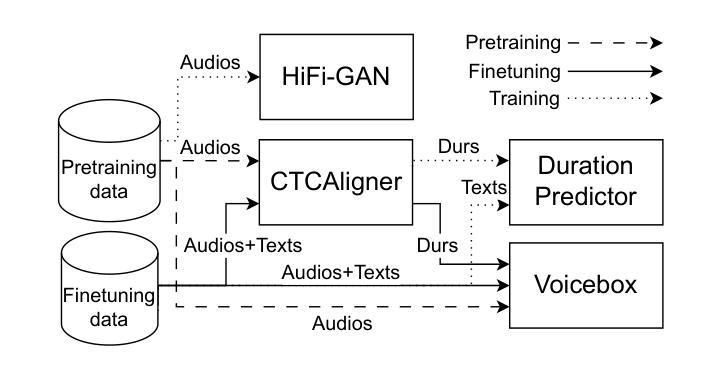
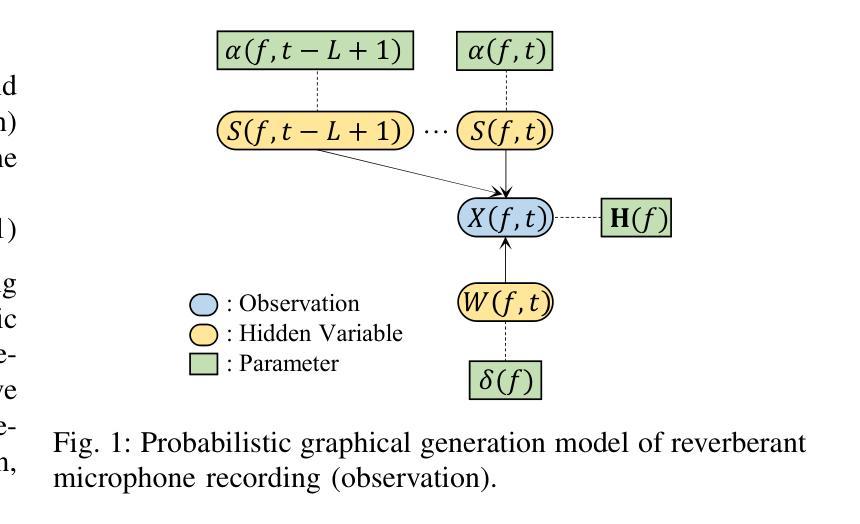
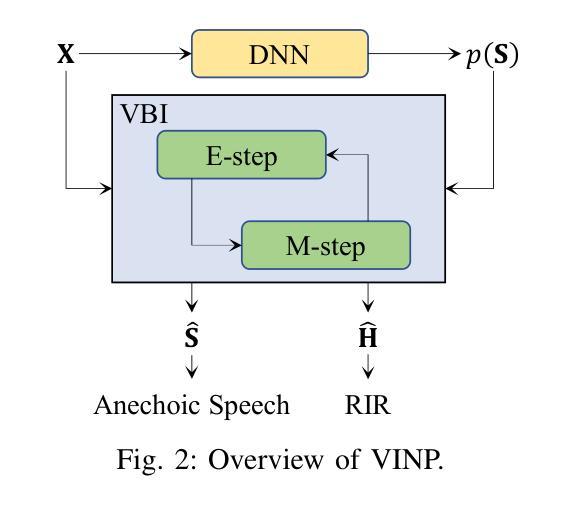
VINP: Variational Bayesian Inference with Neural Speech Prior for Joint ASR-Effective Speech Dereverberation and Blind RIR Identification
Authors:Pengyu Wang, Ying Fang, Xiaofei Li
Reverberant speech, denoting the speech signal degraded by the process of reverberation, contains crucial knowledge of both anechoic source speech and room impulse response (RIR). This work proposes a variational Bayesian inference (VBI) framework with neural speech prior (VINP) for joint speech dereverberation and blind RIR identification. In VINP, a probabilistic signal model is constructed in the time-frequency (T-F) domain based on convolution transfer function (CTF) approximation. For the first time, we propose using an arbitrary discriminative dereverberation deep neural network (DNN) to predict the prior distribution of anechoic speech within a probabilistic model. By integrating both reverberant speech and the anechoic speech prior, VINP yields the maximum a posteriori (MAP) and maximum likelihood (ML) estimations of the anechoic speech spectrum and CTF filter, respectively. After simple transformations, the waveforms of anechoic speech and RIR are estimated. Moreover, VINP is effective for automatic speech recognition (ASR) systems, which sets it apart from most deep learning (DL)-based single-channel dereverberation approaches. Experiments on single-channel speech dereverberation demonstrate that VINP reaches an advanced level in most metrics related to human perception and displays unquestionable state-of-the-art (SOTA) performance in ASR-related metrics. For blind RIR identification, experiments indicate that VINP attains the SOTA level in blind estimation of reverberation time at 60 dB (RT60) and direct-to-reverberation ratio (DRR). Codes and audio samples are available online.
带有混响的语音信号包含了关于无混响源语音和房间冲击响应(RIR)的关键知识。这项工作提出了一种基于神经语音先验(VINP)的变贝叶斯推断(VBI)框架,用于联合语音去混响和盲RIR识别。在VINP中,基于卷积传递函数(CTF)近似值在时频(T-F)域中构建概率信号模型。我们首次提出使用任意判别去混响深度神经网络(DNN)在概率模型中预测无混响语音的先验分布。通过整合带混响语音和无混响语音先验,VINP获得无混响语音谱和CTF滤波器的最大后验(MAP)和最大似然(ML)估计。经过简单变换后,可以估算出无混响语音和RIR的波形。此外,VINP对于自动语音识别(ASR)系统也有效,这与大多数基于深度学习的单通道去混响方法形成了鲜明对比。在单通道语音去混响方面的实验表明,VINP在人类感知相关的大多数指标上达到了先进水平,并在与ASR相关的指标中表现出无可争议的最先进技术水平。对于盲RIR识别,实验表明VINP在60分贝(RT60)的混响时间盲估计和直接-混响比(DRR)方面达到了最先进水平。代码和音频样本可在网上获得。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Submitted to IEEE/ACM Trans. on TASLP
摘要
该文本介绍了基于神经语音先验的变分贝叶斯推理框架,用于联合语音去混响和盲房间脉冲响应识别。该框架在时频域构建了基于卷积传递函数近似的概率信号模型。首次提出使用任意判别去混响深度神经网络预测概率模型中的无混响语音先验分布。通过结合混响语音和无混响语音先验,该框架获得了无混响语音谱和卷积传递函数滤波器的最大后验和最大似然估计。此外,该框架对提高自动语音识别系统的性能有效,区别于大多数基于深度学习的单通道去混响方法。实验表明,该框架在与人类感知相关的大多数指标上达到先进水平,并且在语音识别相关指标上表现出最佳性能。对于盲房间脉冲响应识别,实验显示该框架在60分贝的混响时间和直接混响比率方面达到了最佳水平。
关键见解
- 文本介绍了基于神经语音先验的变分贝叶斯推理框架,旨在联合处理语音去混响和盲房间脉冲响应识别。
- 构建了概率信号模型,该模型在时频域基于卷积传递函数近似。
- 首次提出使用深度神经网络预测无混响语音的先验分布。
- 该框架能获得无混响语音谱和卷积传递函数的最大后验和最大似然估计。
- 框架对自动语音识别系统的性能提升有效。
- 实验表明,该框架在人类感知和语音识别相关指标上达到最佳性能。
- 对于盲房间脉冲响应识别,该框架在混响时间的估计上达到最佳水平。
点此查看论文截图

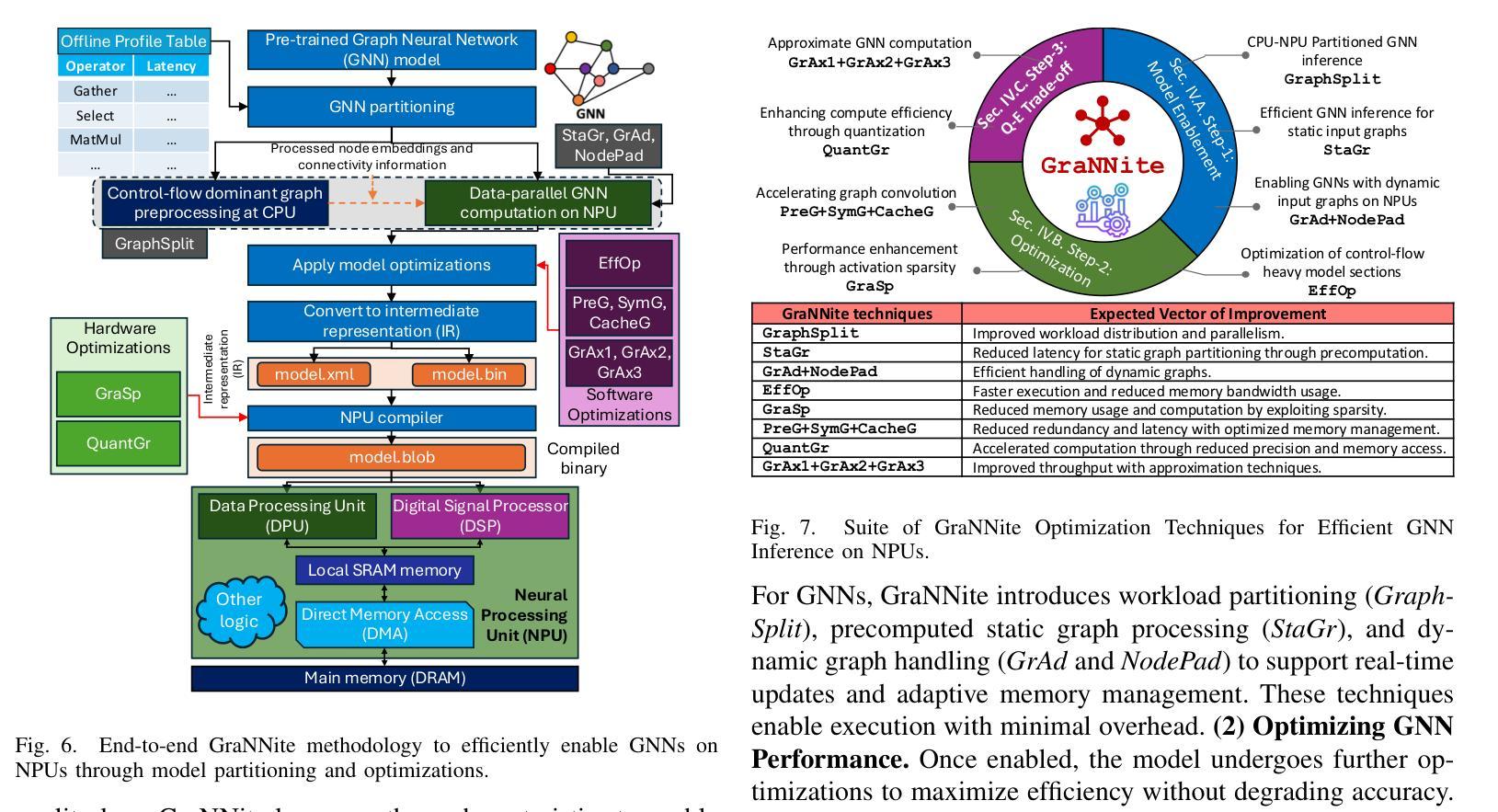
GraNNite: Enabling High-Performance Execution of Graph Neural Networks on Resource-Constrained Neural Processing Units
Authors:Arghadip Das, Shamik Kundu, Arnab Raha, Soumendu Ghosh, Deepak Mathaikutty, Vijay Raghunathan
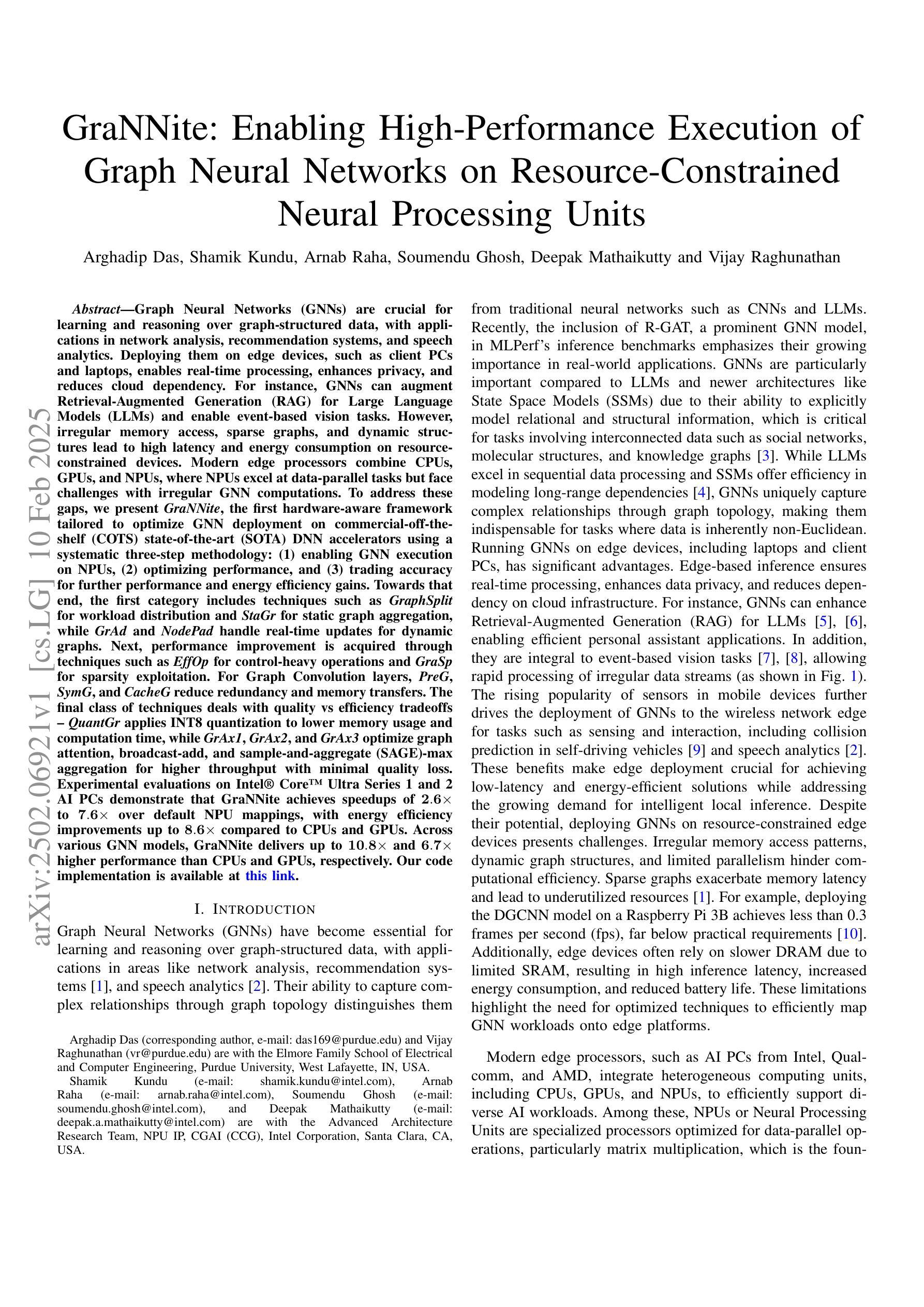
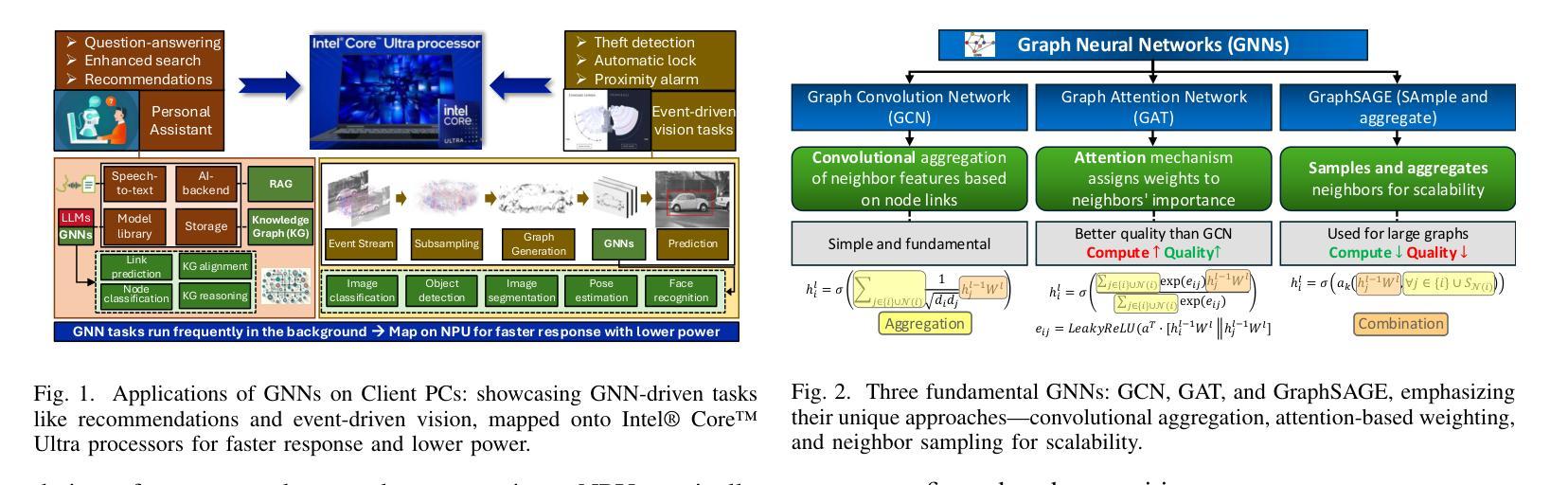
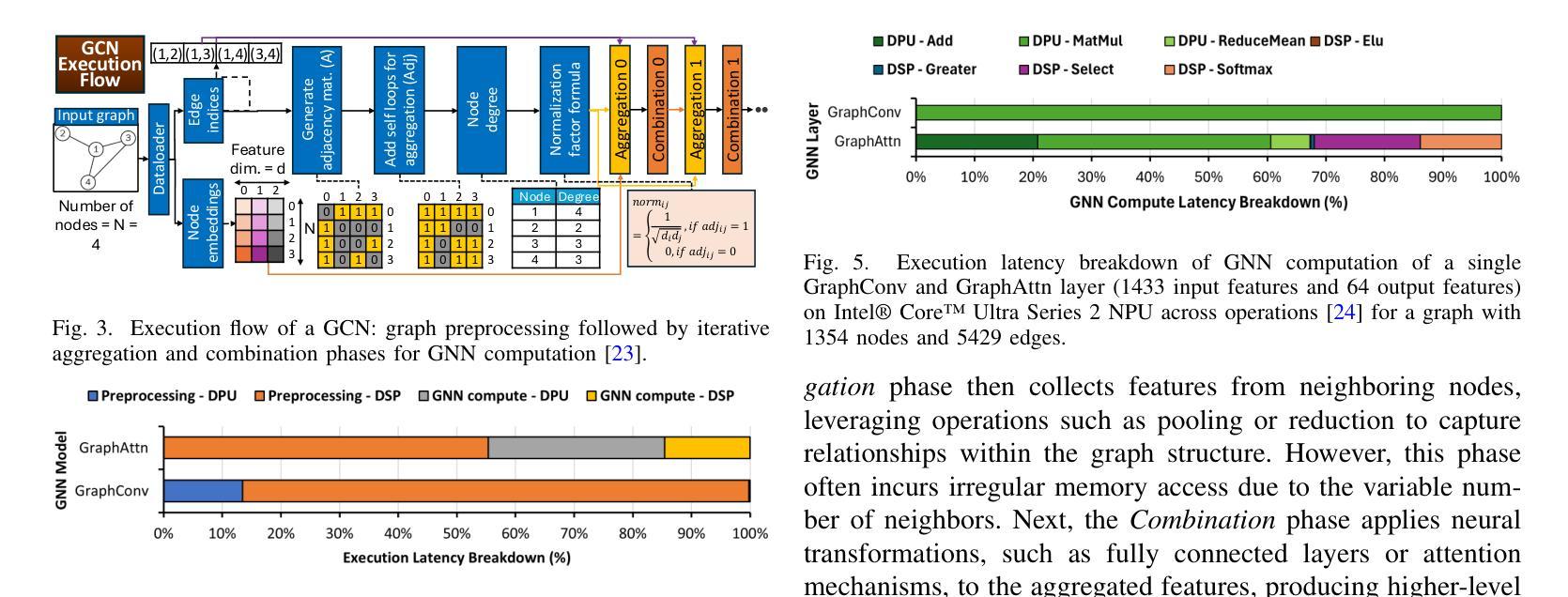
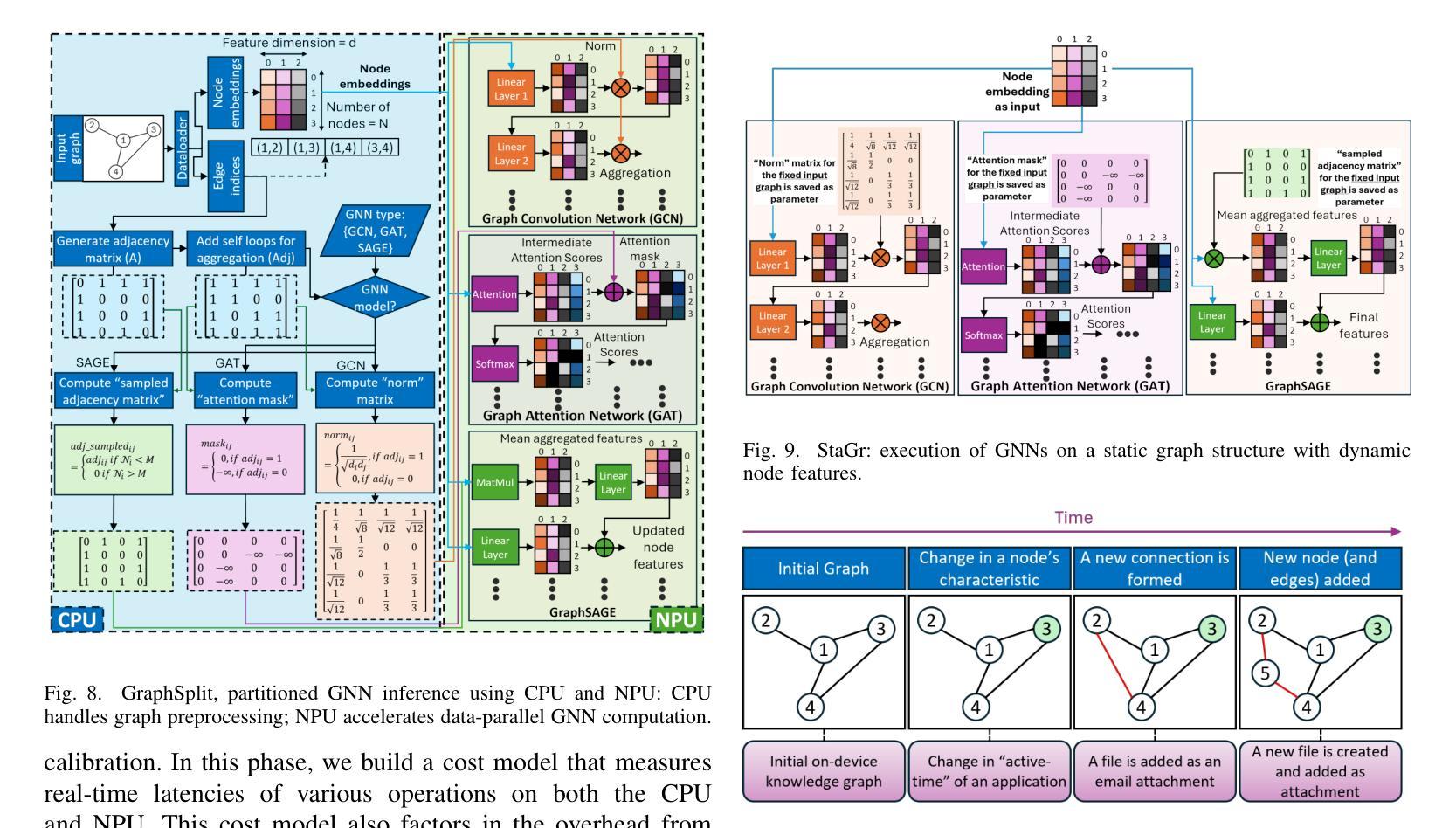
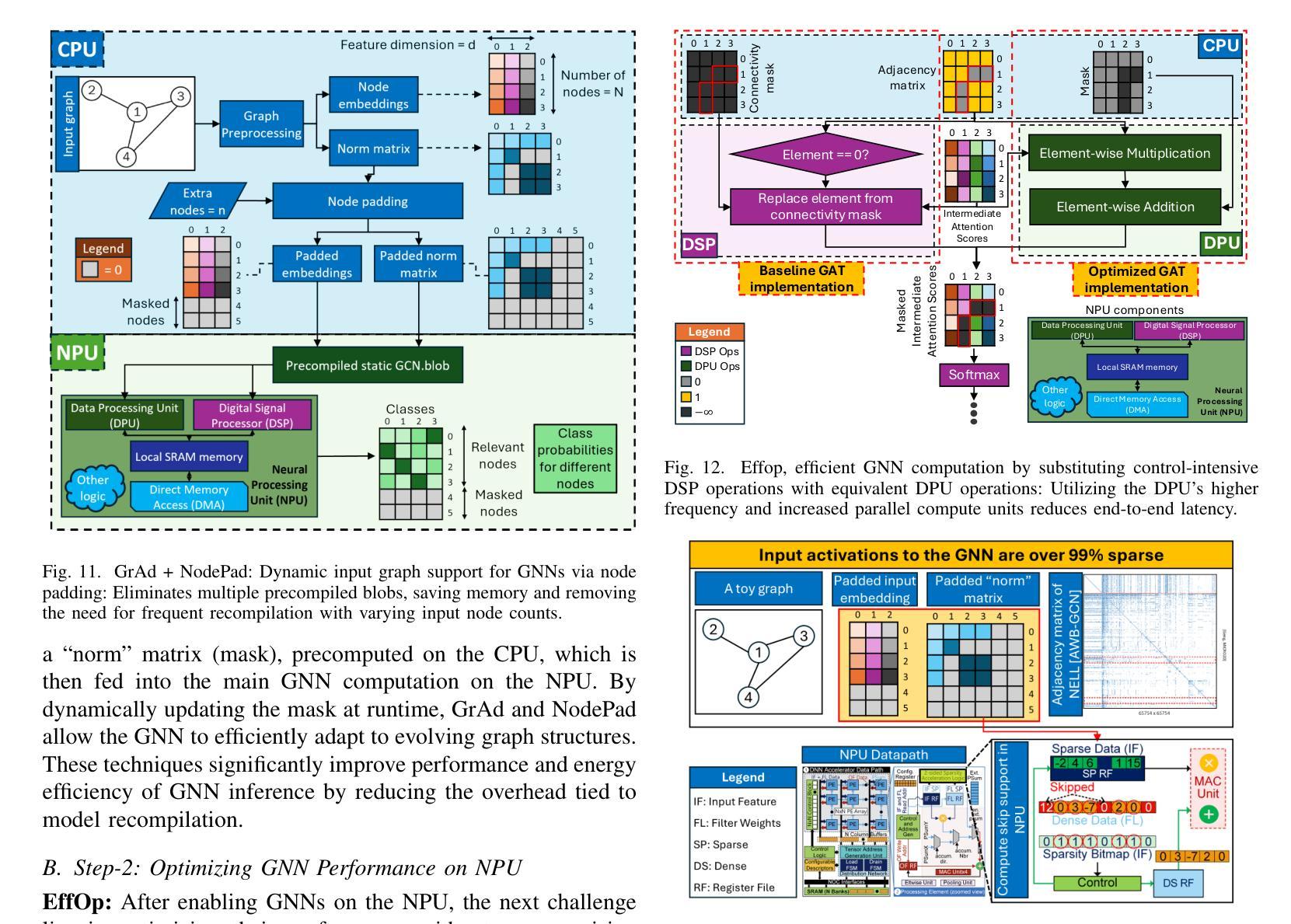
Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) are vital for learning from graph-structured data, enabling applications in network analysis, recommendation systems, and speech analytics. Deploying them on edge devices like client PCs and laptops enhances real-time processing, privacy, and cloud independence. GNNs aid Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) for Large Language Models (LLMs) and enable event-based vision tasks. However, irregular memory access, sparsity, and dynamic structures cause high latency and energy overhead on resource-constrained devices. While modern edge processors integrate CPUs, GPUs, and NPUs, NPUs designed for data-parallel tasks struggle with irregular GNN computations. We introduce GraNNite, the first hardware-aware framework optimizing GNN execution on commercial-off-the-shelf (COTS) SOTA DNN accelerators via a structured three-step methodology: (1) enabling NPU execution, (2) optimizing performance, and (3) trading accuracy for efficiency gains. Step 1 employs GraphSplit for workload distribution and StaGr for static aggregation, while GrAd and NodePad handle dynamic graphs. Step 2 boosts performance using EffOp for control-heavy tasks and GraSp for sparsity exploitation. Graph Convolution optimizations PreG, SymG, and CacheG reduce redundancy and memory transfers. Step 3 balances quality versus efficiency, where QuantGr applies INT8 quantization, and GrAx1, GrAx2, and GrAx3 accelerate attention, broadcast-add, and SAGE-max aggregation. On Intel Core Ultra AI PCs, GraNNite achieves 2.6X to 7.6X speedups over default NPU mappings and up to 8.6X energy gains over CPUs and GPUs, delivering 10.8X and 6.7X higher performance than CPUs and GPUs, respectively, across GNN models.
图神经网络(GNNs)对于从图结构数据中学习至关重要,可应用于网络分析、推荐系统和语音分析等应用。在客户端PC和笔记本电脑等边缘设备上部署它们,增强了实时处理、隐私和云独立性。GNNs有助于大型语言模型的检索增强生成(RAG),并可用于基于事件的视觉任务。然而,不规则内存访问、稀疏性和动态结构会在资源受限的设备上造成高延迟和能源开销。尽管现代边缘处理器融合了CPU、GPU和NPU,但为数据并行任务设计的NPU在处理不规则GNN计算时却表现挣扎。我们引入了GraNNite,这是第一个硬件感知框架,通过结构化三步方法优化在商用现货(COTS)SOTA DNN加速器上执行GNN:(1)实现NPU执行,(2)优化性能,(3)以效率增益换取准确性。第1步采用GraphSplit进行工作量分配和StaGr进行静态聚合,而GrAd和NodePad处理动态图。第2步使用EffOp控制密集型任务并提高性能,并使用GraSp进行稀疏性利用。图卷积优化PreG、SymG和CacheG减少冗余和内存传输。第3步平衡质量与效率,其中QuantGr应用INT8量化,GrAx1、GrAx2和GrAx3加速注意力、广播加法和SAGE-max聚合。在Intel Core Ultra AI PC上,GraNNite相对于默认的NPU映射实现了2.6倍至7.6倍的加速,并且相对于CPU和GPU实现了高达8.6倍的能源效益。相对于CPU和GPU,GraNNite在GNN模型上的性能分别提高了10.8倍和6.7倍。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
图神经网络(GNNs)对于从图形结构数据中学习至关重要,被广泛应用于网络分析、推荐系统和语音分析等领域。它们在边缘设备上部署有助于提升实时处理性能、隐私保护和云独立性。然而,由于不规则内存访问、稀疏性和动态结构等问题,在资源受限的设备上执行GNNs会产生高延迟和能源开销。GraNNite是一个硬件感知框架,通过结构化三步方法优化在现成的最先进的深度神经网络加速器上执行GNNs的任务。三步包括启用NPU执行、优化性能和权衡精度与效率收益。它在Intel Core Ultra AI PC上取得了显著的速度和能源效率提升。
关键见解
- 图神经网络(GNNs)在图形结构数据学习中起关键作用,广泛应用于网络分析、推荐系统和语音分析。
- 在边缘设备上部署GNNs可提升实时处理、隐私保护和云独立性。
- GNNs在资源受限的设备上执行面临高延迟和能源开销的挑战。
- GraNNite是首个硬件感知框架,优化在深度神经网络加速器上执行GNNs的任务。
- GraNNite采用结构化三步方法:启用NPU执行、优化性能和权衡精度与效率。
- GraNNite在Intel Core Ultra AI PC上实现了显著的速度提升和能源效率。
- GraNNite相对于默认NPU映射实现了2.6倍至7.6倍的加速,相对于CPU和GPU实现了最高8.6倍的能源效率提升。
点此查看论文截图
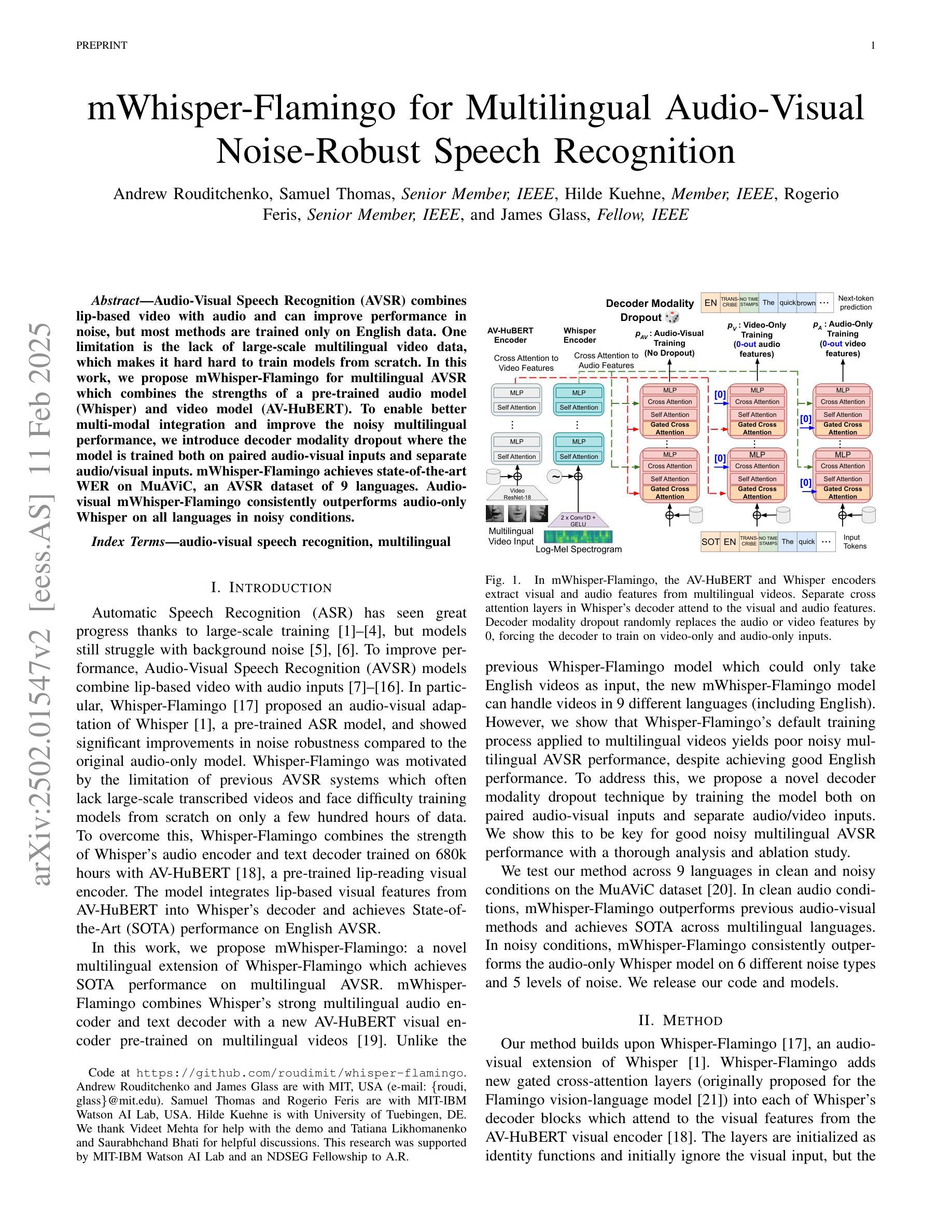
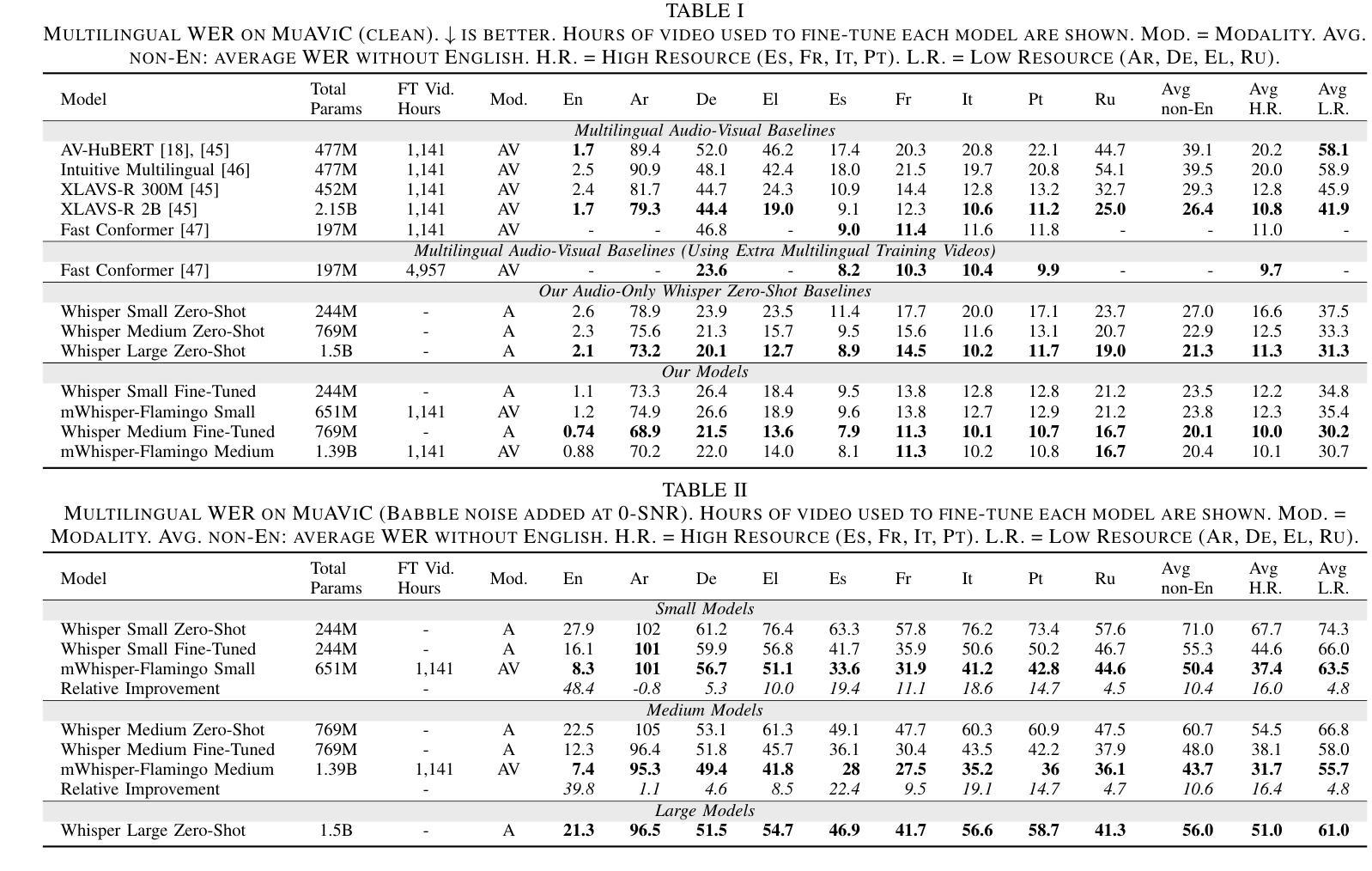
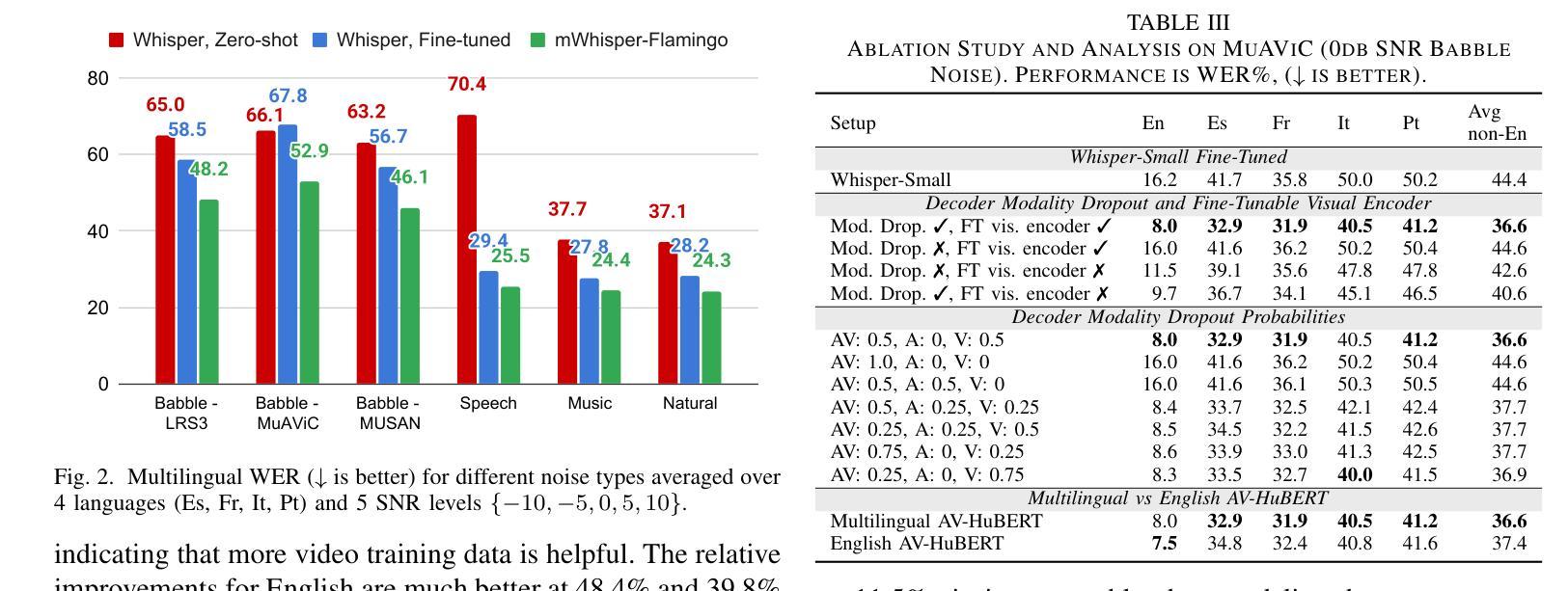
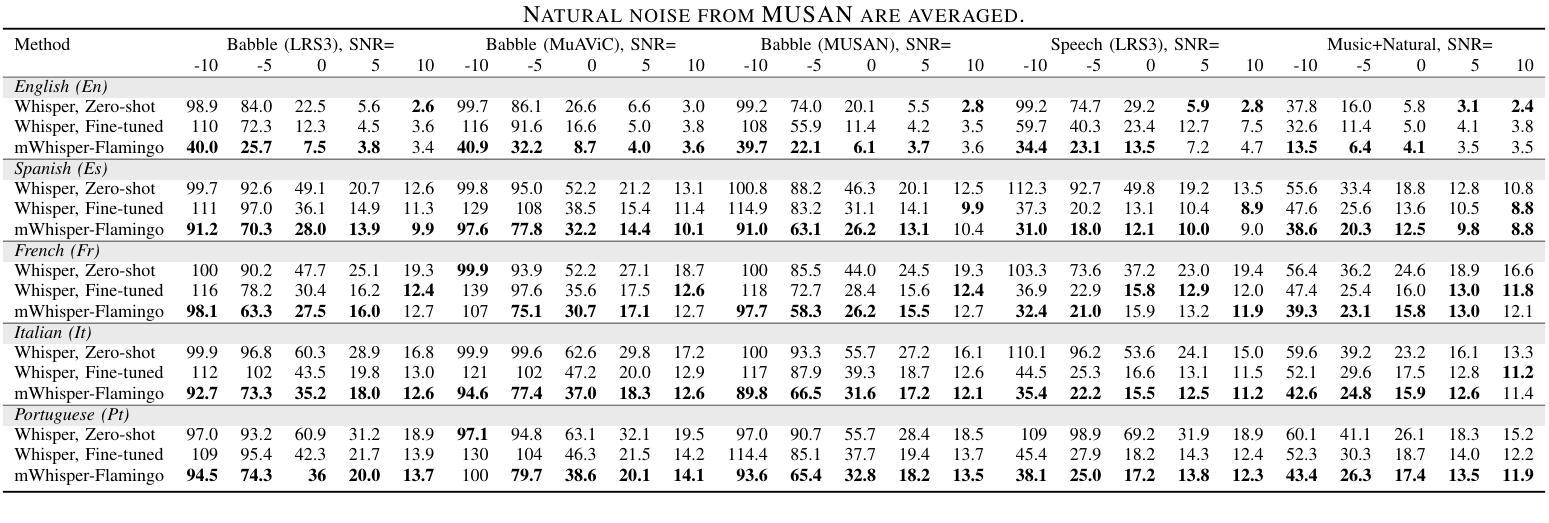
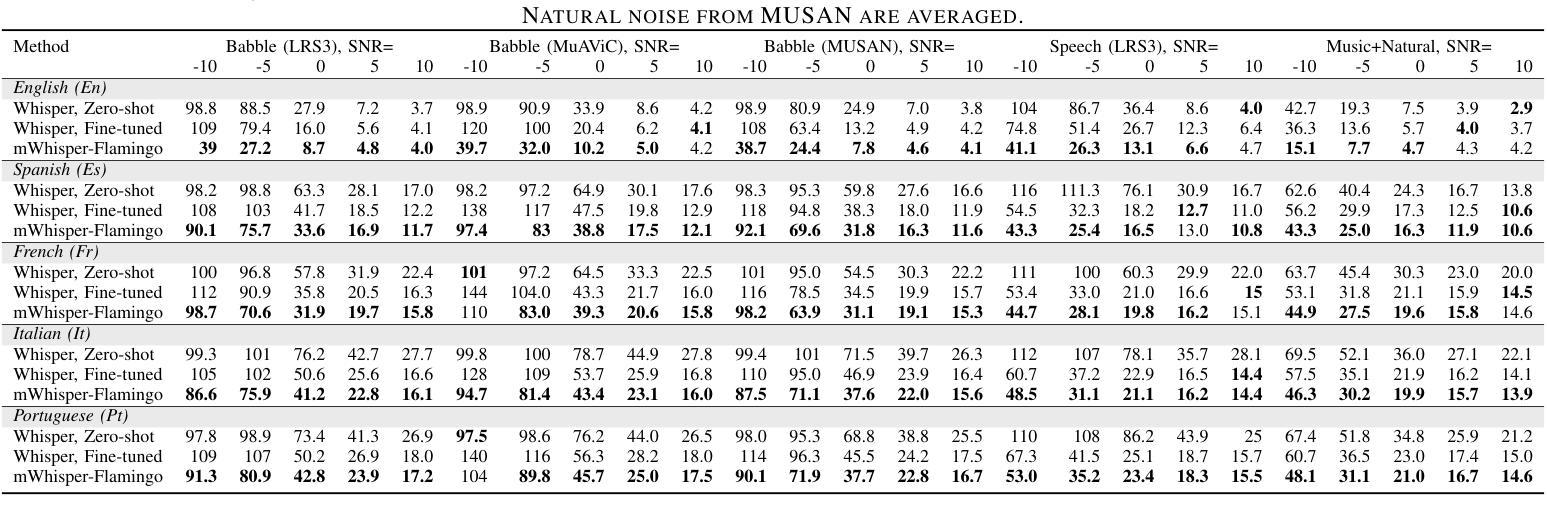
mWhisper-Flamingo for Multilingual Audio-Visual Noise-Robust Speech Recognition
Authors:Andrew Rouditchenko, Samuel Thomas, Hilde Kuehne, Rogerio Feris, James Glass
Audio-Visual Speech Recognition (AVSR) combines lip-based video with audio and can improve performance in noise, but most methods are trained only on English data. One limitation is the lack of large-scale multilingual video data, which makes it hard hard to train models from scratch. In this work, we propose mWhisper-Flamingo for multilingual AVSR which combines the strengths of a pre-trained audio model (Whisper) and video model (AV-HuBERT). To enable better multi-modal integration and improve the noisy multilingual performance, we introduce decoder modality dropout where the model is trained both on paired audio-visual inputs and separate audio/visual inputs. mWhisper-Flamingo achieves state-of-the-art WER on MuAViC, an AVSR dataset of 9 languages. Audio-visual mWhisper-Flamingo consistently outperforms audio-only Whisper on all languages in noisy conditions.
视听语音识别(AVSR)结合了基于唇语的视频和音频,可以提高噪声中的性能,但大多数方法仅针对英语数据进行训练。一个局限性在于缺乏大规模的多语言视频数据,这使得从头开始训练模型变得困难。在这项工作中,我们针对多语言AVSR提出了mWhisper-Flamingo,它结合了预训练音频模型(Whisper)和视频模型(AV-HuBERT)的优点。为了实更好的多模式集成并提高嘈杂的多语言性能,我们引入了解码器模态丢弃训练策略,即模型同时接受配对音频视觉输入和单独的音频/视觉输入。mWhisper-Flamingo在MuAViC上实现了最先进的词错误率(WER),MuAViC是一个包含9种语言的AVSR数据集。在嘈杂条件下,视听mWhisper-Flamingo在所有语言上的性能均优于仅使用音频的Whisper。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了音频视觉语音识别(AVSR)结合唇语视频与音频,在噪声环境下可提高性能。然而,大多数方法仅针对英语数据进行训练,缺乏大规模多语言视频数据,使得从头开始训练模型变得困难。为此,本文提出了多语言AVSR模型mWhisper-Flamingo,结合了预训练音频模型(Whisper)和视频模型(AV-HuBERT)的优势。通过引入解码器模态丢弃(decoder modality dropout),使模型能够在配对音频视觉输入和单独音频/视觉输入上进行训练,实现更好的多模态集成并改善噪声多语言环境性能。在MuAViC数据集上,mWhisper-Flamingo实现了最先进的词错误率(WER),该数据集包含9种语言。在噪声条件下,视听mWhisper-Flamingo在所有语言上的表现均优于仅音频的Whisper。
Key Takeaways
- 音频视觉语音识别(AVSR)结合了唇语视频与音频,以改善噪声环境下的性能。
- 现有方法主要针对英语数据训练,缺乏多语言视频数据,导致训练困难。
- 提出mWhisper-Flamingo模型,结合预训练音频模型(Whisper)和视频模型(AV-HuBERT)的优势。
- 通过引入解码器模态丢弃(decoder modality dropout),提高多模态集成效果,并改善噪声多语言环境性能。
- mWhisper-Flamingo在MuAViC数据集上实现最先进的词错误率(WER),涵盖9种语言。
- 在噪声条件下,mWhisper-Flamingo在所有语言上的表现均优于仅使用音频的识别模型。
点此查看论文截图
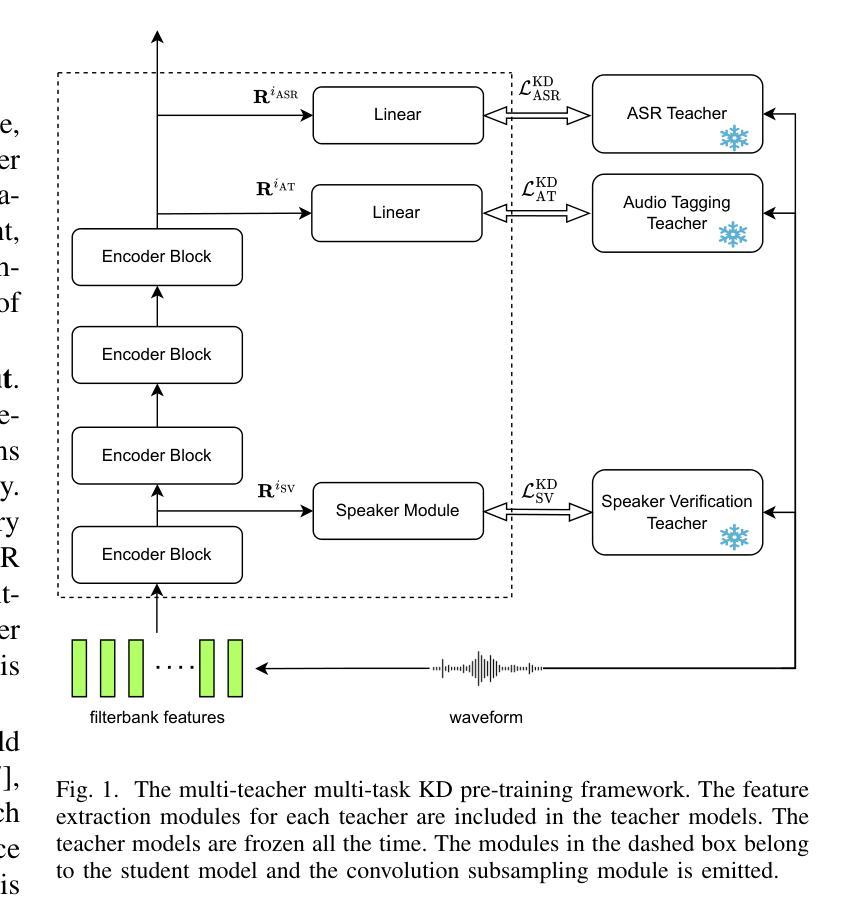
MT2KD: Towards A General-Purpose Encoder for Speech, Speaker, and Audio Events
Authors:Xiaoyu Yang, Qiujia Li, Chao Zhang, Phil Woodland
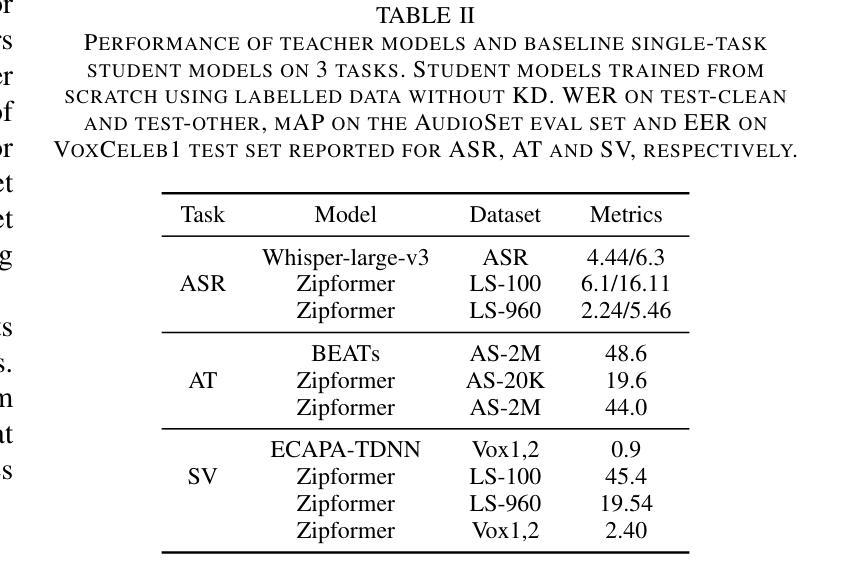
With the advances in deep learning, the performance of end-to-end (E2E) single-task models for speech and audio processing has been constantly improving. However, it is still challenging to build a general-purpose model with high performance on multiple tasks, since different speech and audio processing tasks usually require different training data, input features, or model architectures to achieve optimal performance. In this work, MT2KD, a novel two-stage multi-task learning framework is proposed to build a general-purpose speech and audio encoder that jointly performs three fundamental tasks: automatic speech recognition (ASR), audio tagging (AT) and speaker verification (SV). In the first stage, multi-teacher knowledge distillation (KD) is applied to align the feature spaces of three single-task high-performance teacher encoders into a single student encoder using the same unlabelled data. In the second stage, multi-task supervised fine-tuning is carried out by initialising the model from the first stage and training on the separate labelled data of each single task. Experiments demonstrate that the proposed multi-task training pipeline significantly outperforms a baseline model trained with multi-task learning from scratch. The final system achieves good performance on ASR, AT and SV: with less than 4% relative word-error-rate increase on ASR, only 1.9 lower mean averaged precision on AT and 0.23% absolute higher equal error rate on SV compared to the best-performing single-task encoders, using only a 66M total model parameters.
随着深度学习的发展,端到端(E2E)单任务模型在语音和音频处理方面的性能不断提升。然而,构建能够在多个任务上实现高性能的通用模型仍然是一个挑战,因为不同的语音和音频处理任务通常需要不同的训练数据、输入特征或模型架构来实现最佳性能。在此工作中,提出了MT2KD这一新型两阶段多任务学习框架,用于构建通用语音和音频编码器,该编码器可联合执行三个基本任务:自动语音识别(ASR)、音频标签(AT)和说话人验证(SV)。在第一阶段,应用多教师知识蒸馏(KD)技术,使用相同的无标签数据将三个高性能单任务教师编码器的特征空间对齐到一个单一的学生编码器中。在第二阶段,通过初始化第一阶段的模型,并在每个单独任务的标记数据上进行训练,进行多任务监督微调。实验表明,所提出的多任务训练流程显著优于从头开始进行多任务学习的基线模型。最终系统在ASR、AT和SV方面取得了良好的性能:与最佳性能的单任务编码器相比,ASR的相对词错误率增加不到4%,AT的平均精度仅低1.9,SV的等错误率绝对提高0.23%,而总模型参数仅为66M。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Disclaimer: This work has been submitted to the IEEE for possible publication
摘要
随着深度学习的发展,端到端单一任务模型在语音和音频处理方面的性能不断提升。然而,构建能在多个任务上表现良好的通用模型仍然是一个挑战。不同的语音和音频处理任务通常需要不同的训练数据、输入特征或模型架构来达到最佳性能。本研究提出了MT2KD,一种新型两阶段多任务学习框架,用于构建通用语音和音频编码器,可联合执行三个基本任务:自动语音识别(ASR)、音频标签(AT)和说话人验证(SV)。第一阶段采用多教师知识蒸馏(KD),使用相同的无标签数据,将三个高性能教师编码器的特征空间对齐到一个单一的学生编码器。第二阶段,通过初始化第一阶段的模型,并在每个单一任务的标记数据上进行训练,进行多任务监督微调。实验表明,与从头开始训练的多任务学习基线模型相比,所提出的多任务训练流程具有显著优势。最终系统在与最佳的单任务编码器相比时,在ASR上的相对单词错误率增加不到4%,在AT上的平均精度仅下降1.9,在SV上的等错误率绝对提高仅为0.23%,而总模型参数仅为66M。
关键见解
- 端到端单一任务模型在语音和音频处理方面的性能随深度学习的发展而提升。
- 构建能在多个任务上表现良好的通用模型仍然是一个挑战。
- 不同语音和音频处理任务需要不同的训练数据、输入特征和模型架构来达到最佳性能。
- 研究提出了MT2KD两阶段多任务学习框架,包括多教师知识蒸馏和多任务监督微调。
- 使用无标签数据对齐教师编码器的特征空间,再初始化到单一学生编码器。
- 与基线模型相比,所提出的多任务训练流程具有显著优势。
- 最终系统在与最佳单任务编码器相比时,在ASR、AT和SV任务上的性能损失较小。
点此查看论文截图