⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-02-13 更新
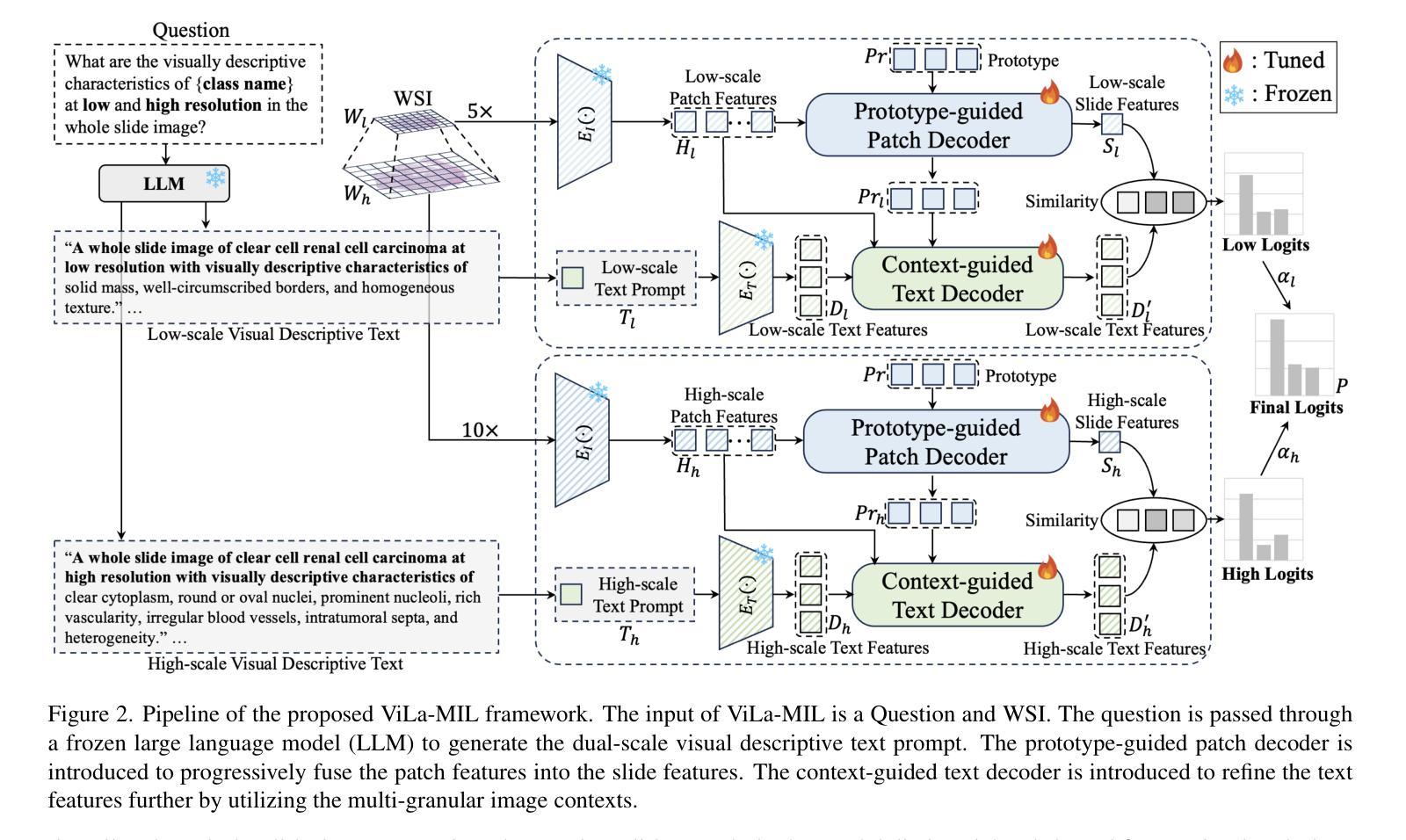
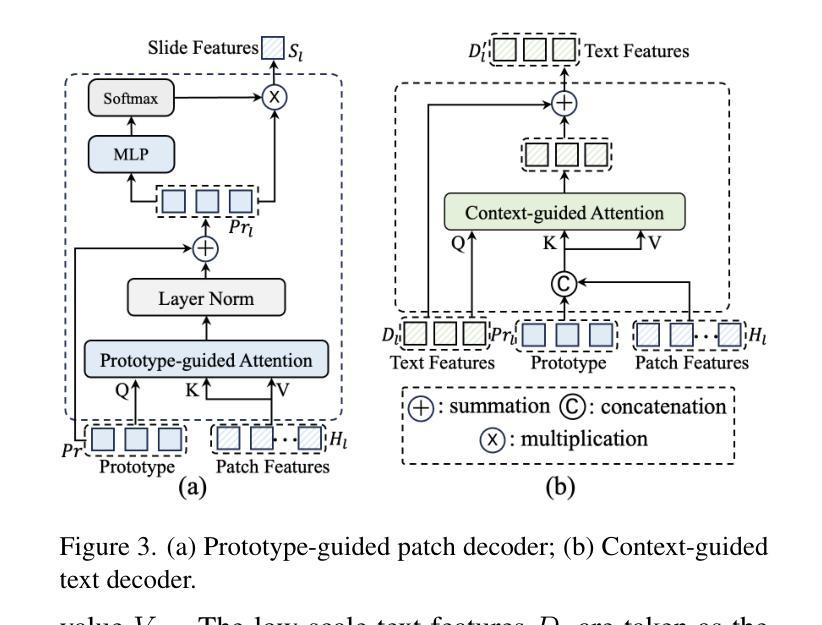
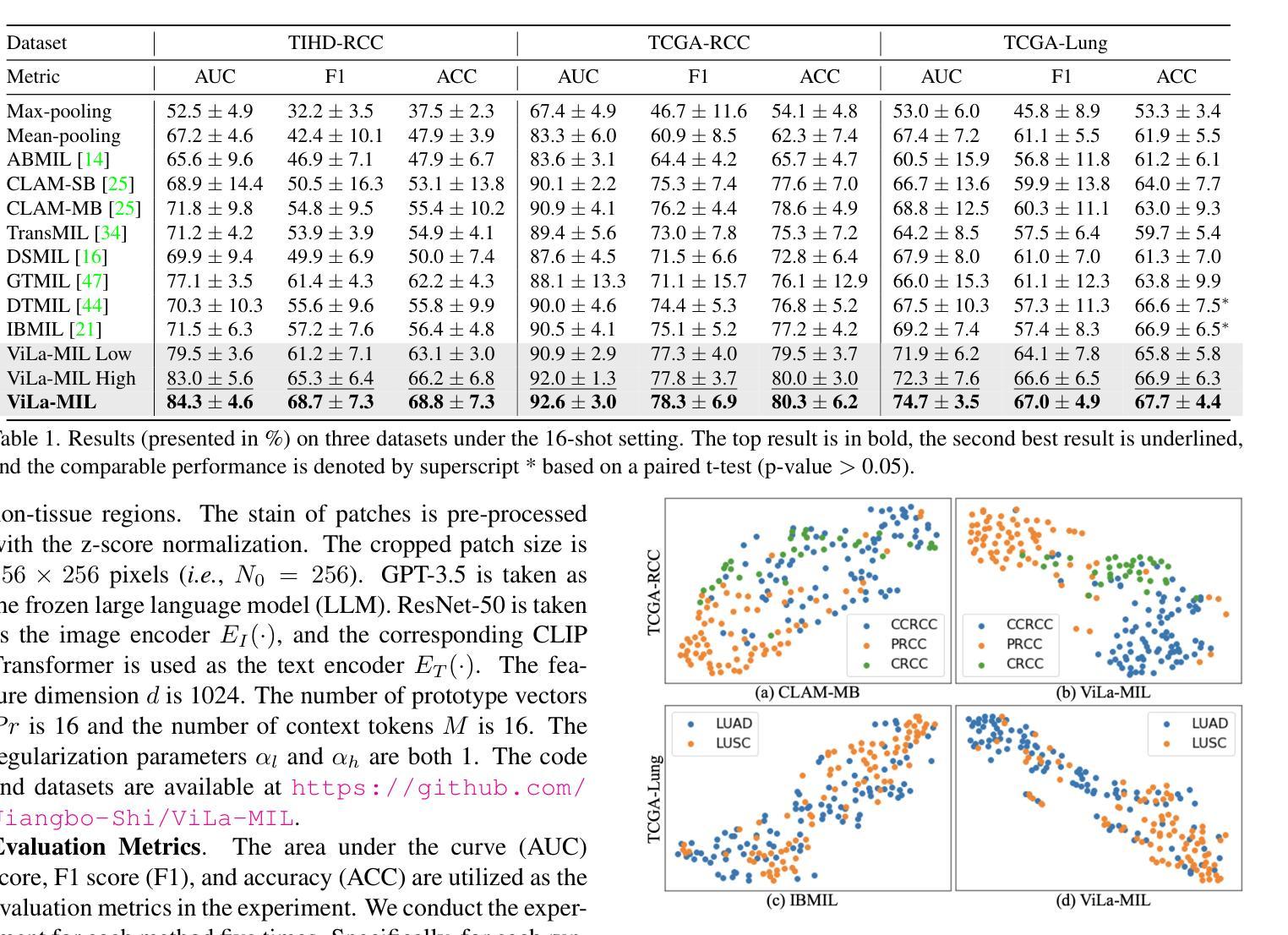
ViLa-MIL: Dual-scale Vision-Language Multiple Instance Learning for Whole Slide Image Classification
Authors:Jiangbo Shi, Chen Li, Tieliang Gong, Yefeng Zheng, Huazhu Fu
Multiple instance learning (MIL)-based framework has become the mainstream for processing the whole slide image (WSI) with giga-pixel size and hierarchical image context in digital pathology. However, these methods heavily depend on a substantial number of bag-level labels and solely learn from the original slides, which are easily affected by variations in data distribution. Recently, vision language model (VLM)-based methods introduced the language prior by pre-training on large-scale pathological image-text pairs. However, the previous text prompt lacks the consideration of pathological prior knowledge, therefore does not substantially boost the model’s performance. Moreover, the collection of such pairs and the pre-training process are very time-consuming and source-intensive.To solve the above problems, we propose a dual-scale vision-language multiple instance learning (ViLa-MIL) framework for whole slide image classification. Specifically, we propose a dual-scale visual descriptive text prompt based on the frozen large language model (LLM) to boost the performance of VLM effectively. To transfer the VLM to process WSI efficiently, for the image branch, we propose a prototype-guided patch decoder to aggregate the patch features progressively by grouping similar patches into the same prototype; for the text branch, we introduce a context-guided text decoder to enhance the text features by incorporating the multi-granular image contexts. Extensive studies on three multi-cancer and multi-center subtyping datasets demonstrate the superiority of ViLa-MIL.
基于多实例学习(MIL)的框架已成为处理具有千兆像素大小和分层图像上下文的全幻灯片图像(WSI)的主流方法,在数字病理学中广泛应用。然而,这些方法严重依赖于大量的包级标签,并且仅从原始幻灯片中学习,这很容易受到数据分布变化的影响。最近,基于视觉语言模型(VLM)的方法通过大规模病理学图像文本对进行预训练,引入了语言先验知识。然而,之前的文本提示没有考虑到病理先验知识,因此并没有显著提高模型性能。此外,此类对的收集以及预训练过程非常耗时且资源密集。为了解决上述问题,我们提出了用于全幻灯片图像分类的双尺度视觉语言多实例学习(ViLa-MIL)框架。具体来说,我们基于冻结的大型语言模型(LLM)提出了双尺度视觉描述文本提示,以有效提高VLM的性能。为了有效地将VLM用于处理WSI,对于图像分支,我们提出了原型引导补丁解码器,通过将相似的补丁分组到同一原型中来逐步聚合补丁特征;对于文本分支,我们引入了上下文引导文本解码器,通过结合多粒度图像上下文来增强文本特征。在三个多癌和多中心亚型数据集上的广泛研究表明,ViLa-MIL具有优越性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF CVPR 2024 (Updated version with corrections for typos and errors.)
Summary
在数字病理学中,处理具有千兆像素大小和层次图像上下文的全幻灯片图像(WSI)的主流方法是基于多实例学习(MIL)的框架。然而,这些方法严重依赖于大量的包级标签,并仅从原始幻灯片中学习,容易受到数据分布变化的影响。最近,基于视觉语言模型(VLM)的方法通过在大规模病理图像文本对上预训练引入了语言先验。然而,由于之前的文本提示缺乏病理先验知识考虑,未能显著提高模型性能。此外,此类对的收集和预训练过程非常耗时和耗费资源。为解决上述问题,我们提出了用于全幻灯片图像分类的双尺度视觉语言多实例学习(ViLa-MIL)框架。通过基于大型语言模型(LLM)的双尺度视觉描述文本提示有效增强VLM性能。为了将VLM有效地应用于WSI处理,我们在图像分支中提出了原型引导补丁解码器,通过逐步聚合补丁特征将相似的补丁分组到同一原型中;在文本分支中,我们引入了上下文引导文本解码器,通过结合多粒度图像上下文增强文本特征。在三个多癌和多中心亚型数据集上的广泛研究表明,ViLa-MIL具有优越性。
Key Takeaways
- 多实例学习(MIL)是当前处理数字病理学中的全幻灯片图像(WSI)的主流方法。
- MIL方法存在对大量包级标签的依赖和数据分布变化的敏感性。
- 视觉语言模型(VLM)引入语言先验,但之前的方法缺乏病理先验知识的考虑。
- ViLa-MIL框架结合双尺度视觉描述文本提示和原型引导补丁解码器,增强VLM性能。
- 图像分支采用原型引导补丁解码器,通过分组相似补丁到同一原型来聚合特征。
- 文本分支引入上下文引导文本解码器,结合多粒度图像上下文增强文本特征。
点此查看论文截图

Hi-End-MAE: Hierarchical encoder-driven masked autoencoders are stronger vision learners for medical image segmentation
Authors:Fenghe Tang, Qingsong Yao, Wenxin Ma, Chenxu Wu, Zihang Jiang, S. Kevin Zhou
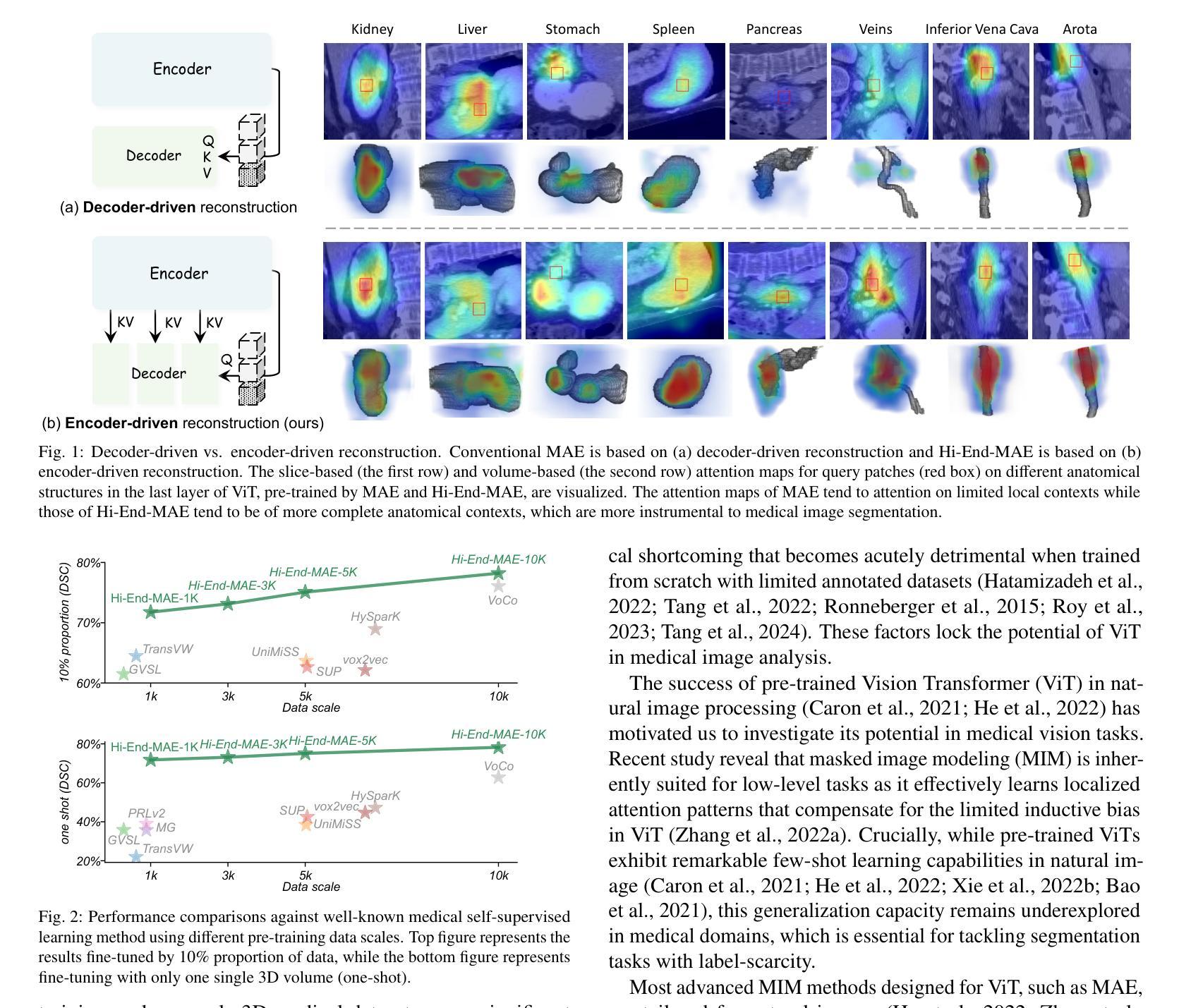
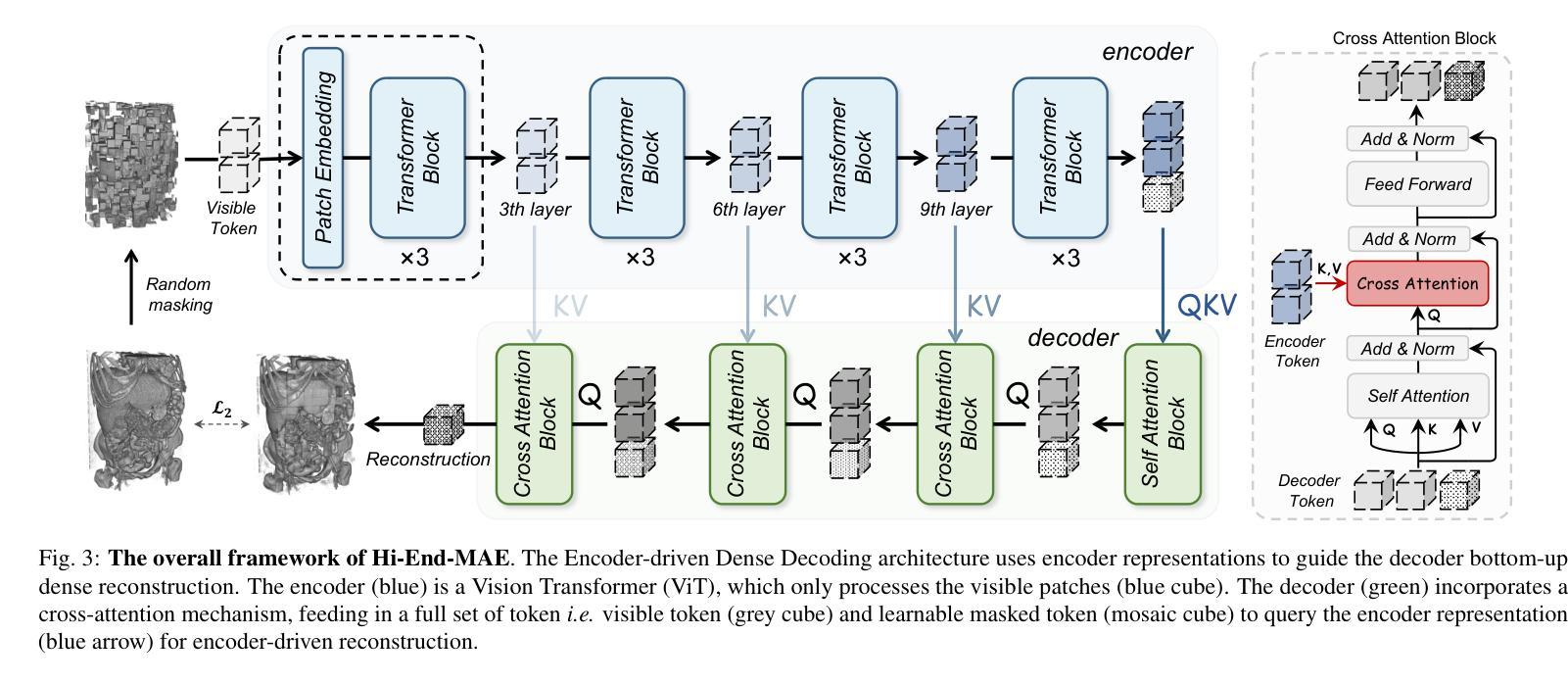
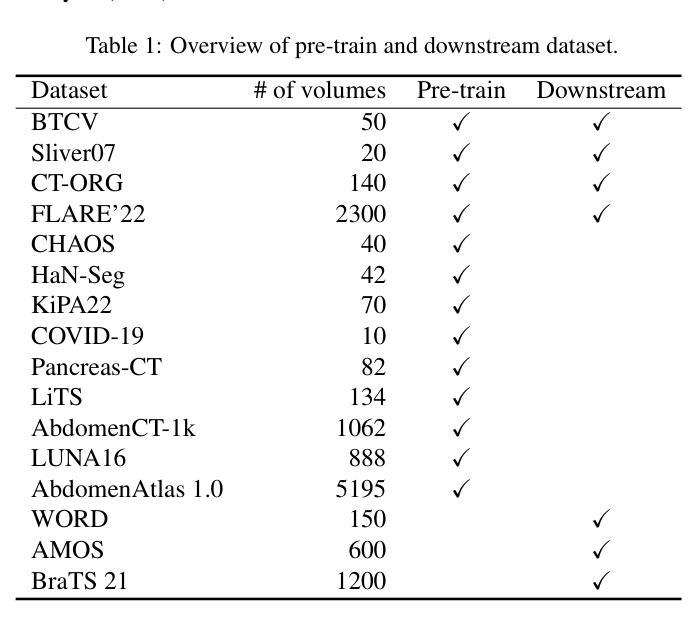
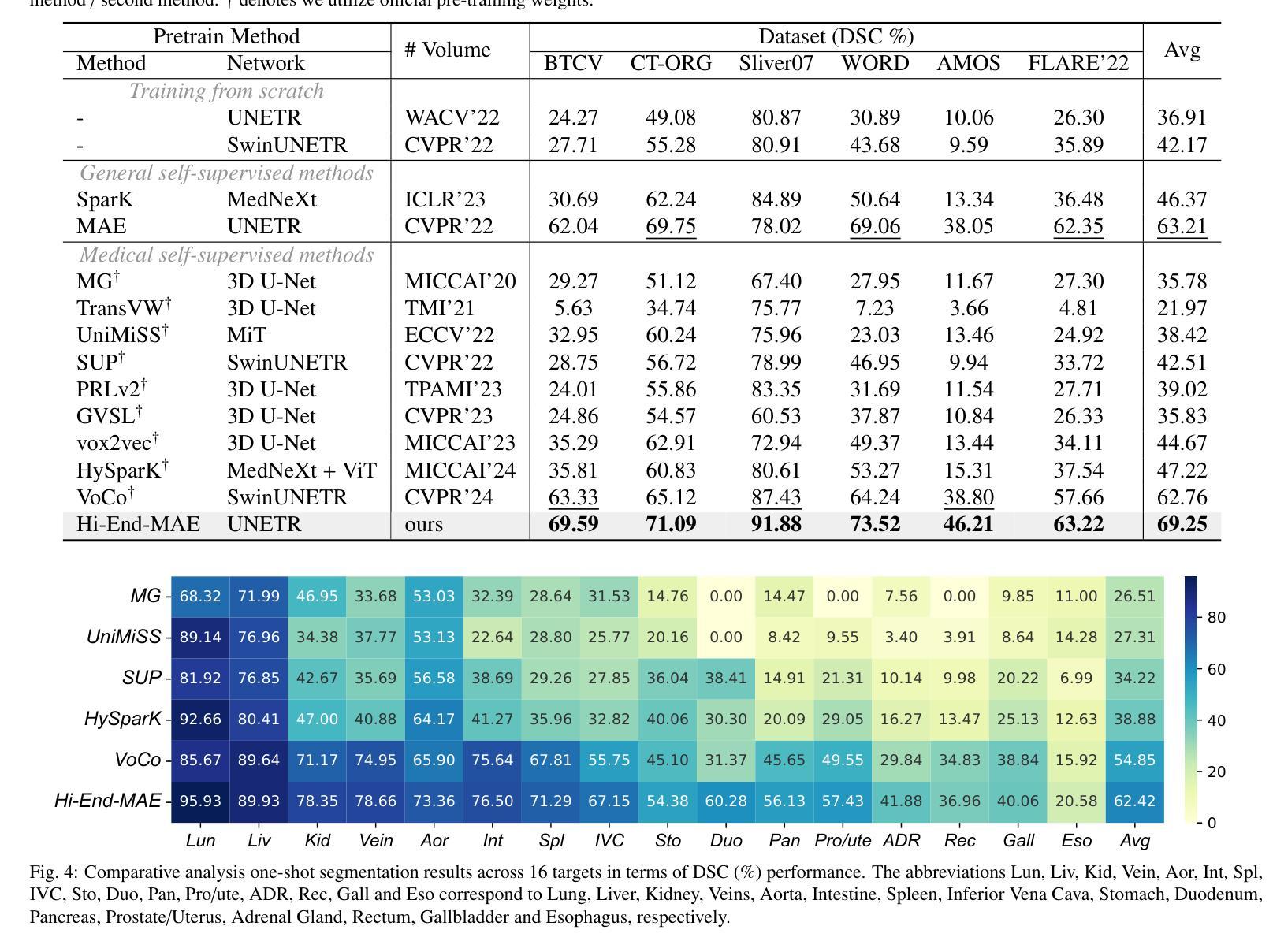
Medical image segmentation remains a formidable challenge due to the label scarcity. Pre-training Vision Transformer (ViT) through masked image modeling (MIM) on large-scale unlabeled medical datasets presents a promising solution, providing both computational efficiency and model generalization for various downstream tasks. However, current ViT-based MIM pre-training frameworks predominantly emphasize local aggregation representations in output layers and fail to exploit the rich representations across different ViT layers that better capture fine-grained semantic information needed for more precise medical downstream tasks. To fill the above gap, we hereby present Hierarchical Encoder-driven MAE (Hi-End-MAE), a simple yet effective ViT-based pre-training solution, which centers on two key innovations: (1) Encoder-driven reconstruction, which encourages the encoder to learn more informative features to guide the reconstruction of masked patches; and (2) Hierarchical dense decoding, which implements a hierarchical decoding structure to capture rich representations across different layers. We pre-train Hi-End-MAE on a large-scale dataset of 10K CT scans and evaluated its performance across seven public medical image segmentation benchmarks. Extensive experiments demonstrate that Hi-End-MAE achieves superior transfer learning capabilities across various downstream tasks, revealing the potential of ViT in medical imaging applications. The code is available at: https://github.com/FengheTan9/Hi-End-MAE
医学图像分割仍然是一个由于标签稀缺而难以应对的挑战。通过大规模无标签医学数据集进行掩模图像建模(MIM)的预训练视觉转换器(ViT)为这一问题提供了有前景的解决方案,为各种下游任务提供了计算效率和模型泛化能力。然而,当前的基于ViT的MIM预训练框架主要侧重于输出层的局部聚合表示,并未能充分利用不同ViT层中的丰富表示,这些层能更好地捕获用于更精确医学下游任务的细粒度语义信息。为了填补上述空白,我们特此推出层次编码器驱动MAE(Hi-End-MAE),这是一种简单有效的基于ViT的预训练解决方案,其核心包含两个关键创新点:(1)编码器驱动重建,这鼓励编码器学习更多信息特征以指导掩码补丁的重建;(2)层次密集解码,它实现了层次解码结构以捕获不同层次的丰富表示。我们在包含一万次CT扫描的大规模数据集上预训练了Hi-End-MAE,并在七个公开医学图像分割基准上评估了其性能。大量实验表明,Hi-End-MAE在各种下游任务上实现了卓越的迁移学习能力,展现了ViT在医学成像应用中的潜力。代码可访问于:https://github.com/FengheTan9/Hi-End-MAE
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 19 pages, Code: https://github.com/FengheTan9/Hi-End-MAE
Summary:
医学图像分割因标签稀缺而面临挑战。通过大规模无标签医学数据集对视觉转换器(ViT)进行预训练,采用掩膜图像建模(MIM)的方法展现出了一种有前途的解决方案,提高了计算效率和模型对各种下游任务的泛化能力。然而,现有的基于ViT的MIM预训练框架主要侧重于输出层的局部聚合表示,并未充分利用不同ViT层中的丰富表示,这些层能更好地捕捉精细的语义信息,对于更精确的医学下游任务至关重要。为了弥补上述空白,我们提出了基于分层编码器的MAE(Hi-End-MAE),这是一种简单有效的ViT预训练解决方案,它聚焦于两个关键创新点:(1)编码器驱动的重构,鼓励编码器学习更有信息的特征来指导遮挡补丁的重构;(2)分层密集解码,实现分层解码结构,以捕获不同层的丰富表示。我们在包含1万张CT扫描的大规模数据集上预训练了Hi-End-MAE,并在七个公共医学图像分割基准上评估了其性能。实验表明,Hi-End-MAE在多种下游任务上实现了卓越的迁移学习能力,展现了ViT在医学成像应用中的潜力。
Key Takeaways:
- 医学图像分割面临标签稀缺的挑战。
- 预训练Vision Transformer(ViT)通过掩膜图像建模(MIM)在大型无标签医学数据集上是一种有前途的解决方案。
- 现有ViT-based MIM预训练框架主要侧重于输出层的局部聚合表示,需要改进。
- Hi-End-MAE提出一种基于分层编码器的预训练解决方案,包括编码器驱动的重构和分层密集解码。
- Hi-End-MAE在大型数据集上进行预训练,并在多个公共医学图像分割基准测试中表现出优异的性能。
- Hi-End-MAE的实现显示出ViT在医学成像应用中的潜力。
点此查看论文截图

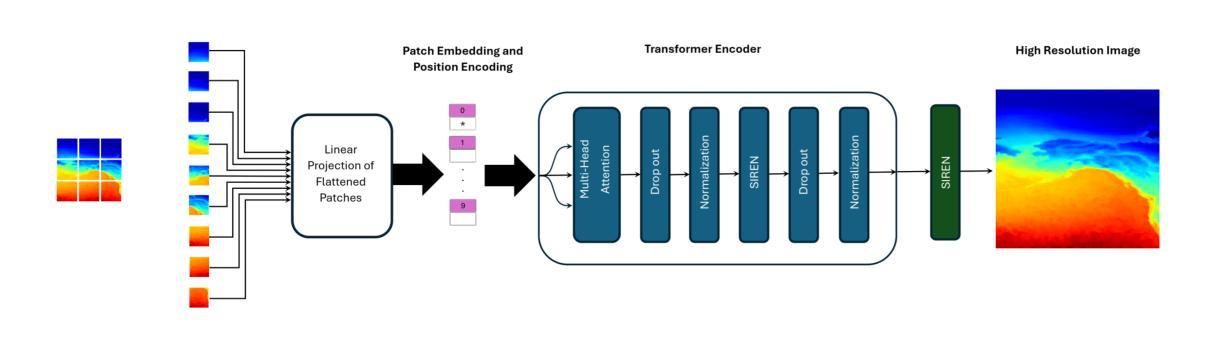
ViSIR: Vision Transformer Single Image Reconstruction Method for Earth System Models
Authors:Ehsan Zeraatkar, Salah Faroughi, Jelena Tešić
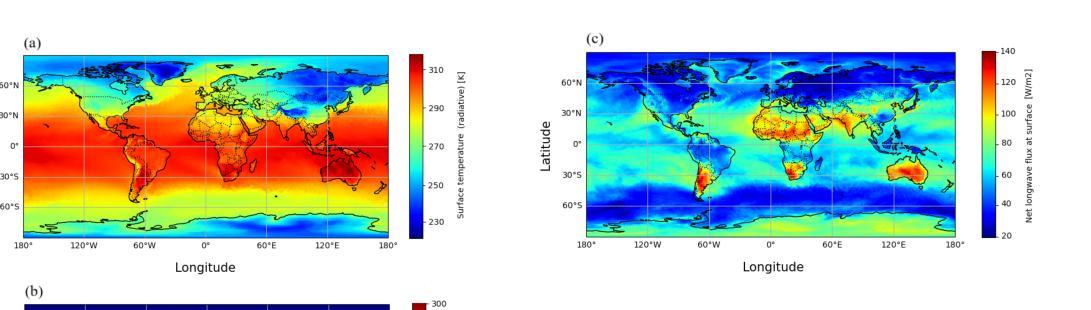
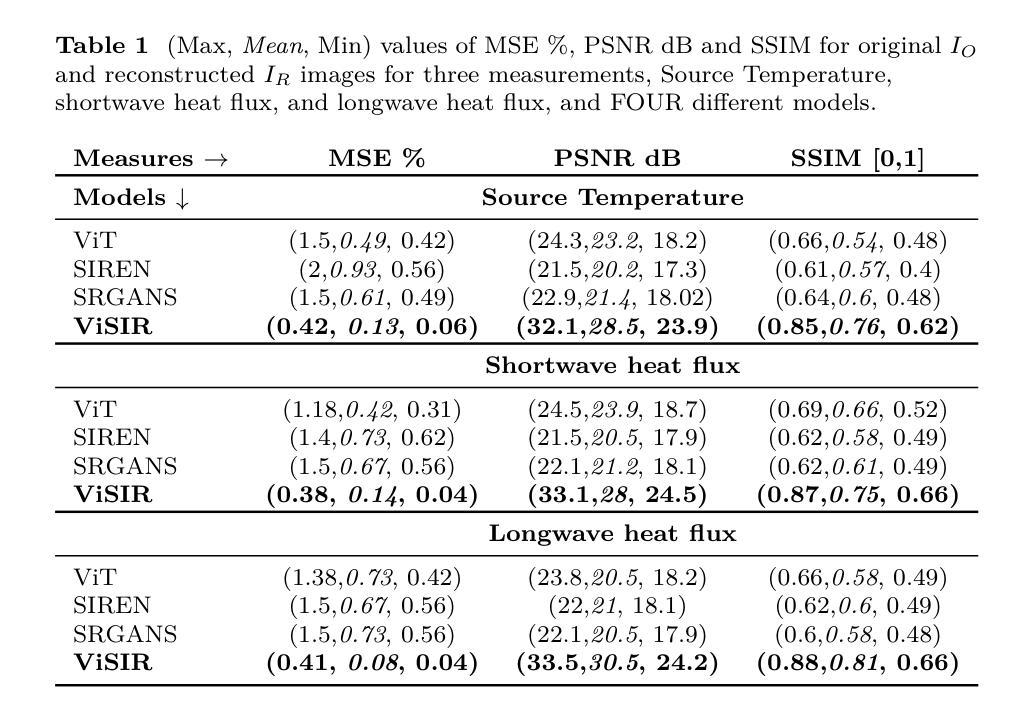
Purpose: Earth system models (ESMs) integrate the interactions of the atmosphere, ocean, land, ice, and biosphere to estimate the state of regional and global climate under a wide variety of conditions. The ESMs are highly complex, and thus, deep neural network architectures are used to model the complexity and store the down-sampled data. In this paper, we propose the Vision Transformer Sinusoidal Representation Networks (ViSIR) to improve the single image SR (SR) reconstruction task for the ESM data. Methods: ViSIR combines the SR capability of Vision Transformers (ViT) with the high-frequency detail preservation of the Sinusoidal Representation Network (SIREN) to address the spectral bias observed in SR tasks. Results: The ViSIR outperforms ViT by 4.1 dB, SIREN by 7.5 dB, and SR-Generative Adversarial (SR-GANs) by 7.1dB PSNR on average for three different measurements. Conclusion: The proposed ViSIR is evaluated and compared with state-of-the-art methods. The results show that the proposed algorithm is outperforming other methods in terms of Mean Square Error(MSE), Peak-Signal-to-Noise-Ratio(PSNR), and Structural Similarity Index Measure(SSIM).
目的:地球系统模型(ESM)整合了大气、海洋、陆地、冰川和生物圈的相互作用,以在多种条件下估计区域和全球气候的状态。由于ESM高度复杂,因此使用深度神经网络架构来对其复杂性进行建模并存储降采样数据。在本文中,我们提出Vision Transformer正弦表示网络(ViSIR)来改进ESM数据的单图像超分辨率(SR)重建任务。方法:ViSIR结合了Vision Transformer(ViT)的超分辨率能力与正弦表示网络(SIREN)的高频细节保留功能,以解决SR任务中观察到的光谱偏差。结果:ViSIR在三个不同测量指标上的平均PSNR值比ViT高出4.1 dB,比SIREN高出7.5 dB,比SR-生成对抗网络(SR-GANs)高出7.1 dB。结论:所提出的ViSIR与最新技术方法进行了评估比较。结果表明,在均方误差(MSE)、峰值信噪比(PSNR)和结构相似性指数度量(SSIM)方面,该算法的性能优于其他方法。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了地球系统模型(ESMs)的复杂性及其利用深度神经网络架构进行建模的方法。为此,提出了结合Vision Transformer和Sinusoidal Representation Network的ViSIR网络,以改进地球系统数据的单图像超分辨率(SR)重建任务。ViSIR通过结合Vision Transformer的SR能力和Sinusoidal Representation Network的高频细节保留能力,解决了SR任务中的光谱偏差问题。实验结果表明,ViSIR在PSNR指标上较ViT、SIREN和SR-GANs分别提高了4.1dB、7.5dB和7.1dB。总体而言,ViSIR表现出优秀的性能,能够有效处理地球系统模型的复杂数据。
Key Takeaways
- 地球系统模型(ESMs)利用深度神经网络架构对大气、海洋、陆地、冰和生物圈之间的相互作用进行建模,以估算各种条件下的区域和全球气候状态。
- 提出的ViSIR网络结合了Vision Transformer和Sinusoidal Representation Network的优势,旨在改进地球系统数据的单图像超分辨率(SR)重建任务。
- ViSIR通过解决SR任务中的光谱偏差问题,实现了良好的性能。
- 实验结果显示,ViSIR在PSNR、MSE和SSIM等评价指标上较其他先进方法表现出更好的性能。
- ViSIR能够处理地球系统模型的复杂数据,具有广泛的应用前景。
- 深度神经网络在地球系统模型数据建模中的应用展示了其强大的处理复杂数据的能力。
点此查看论文截图

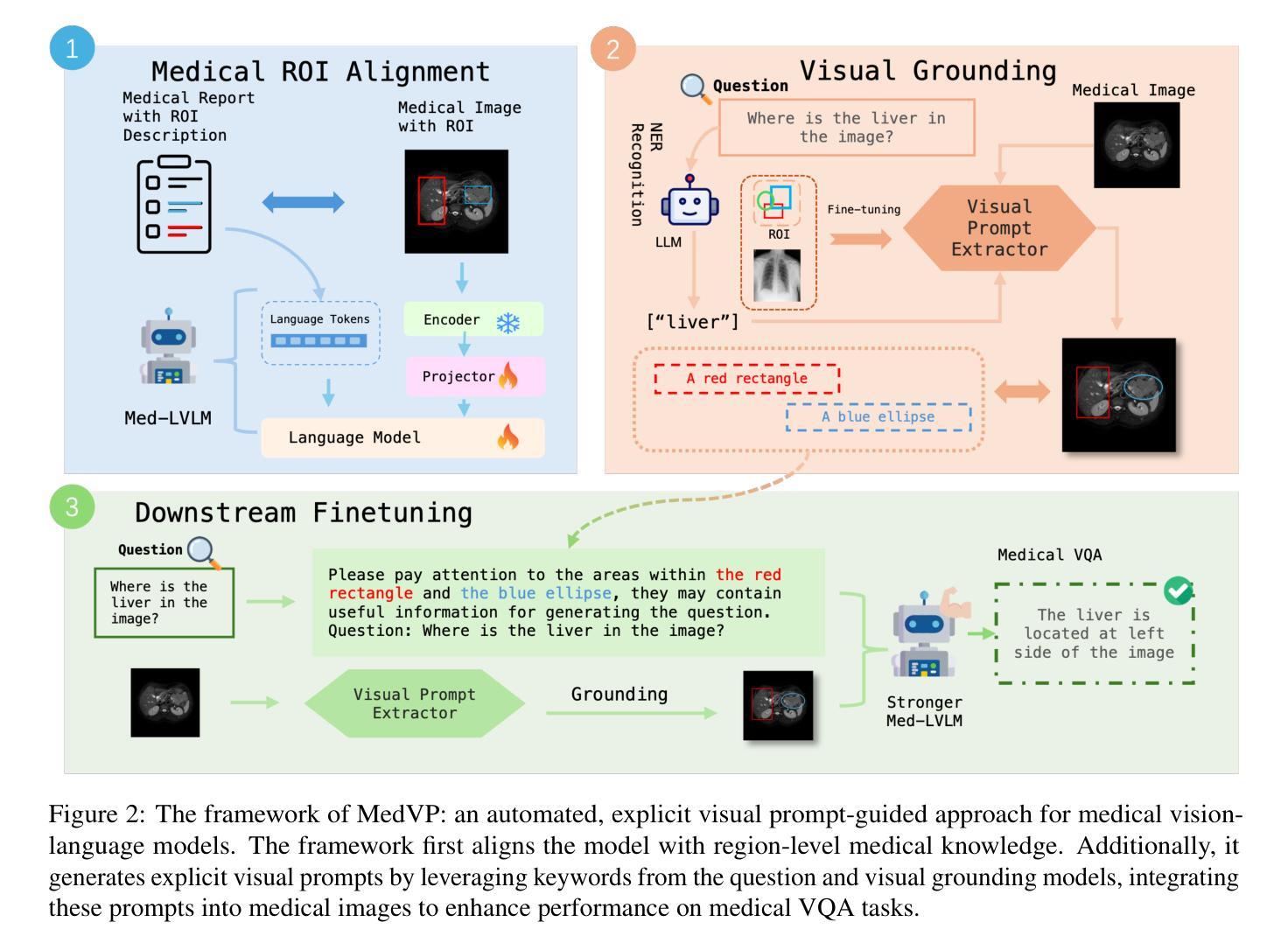
Guiding Medical Vision-Language Models with Explicit Visual Prompts: Framework Design and Comprehensive Exploration of Prompt Variations
Authors:Kangyu Zhu, Ziyuan Qin, Huahui Yi, Zekun Jiang, Qicheng Lao, Shaoting Zhang, Kang Li
While mainstream vision-language models (VLMs) have advanced rapidly in understanding image level information, they still lack the ability to focus on specific areas designated by humans. Rather, they typically rely on large volumes of high-quality image-text paired data to learn and generate posterior attention maps. To address this critical issue, we propose leveraging visual prompts:simple visual markers in various forms to guide and enhance the formation of region-specific attention. Thus, we introduce MedVP, a pioneering framework that integrates medical entity extraction, visual prompt generation, and dataset adaptation for visual prompt guided fine-tuning. We successfully outperform recent state-of-the-art large models across multiple medical VQA datasets. Extensive experiments and Human evaluation are conducted to analyze the impact of different visual prompt forms and how they contribute to performance improvement. The results demonstrate both the effectiveness and clinical significance of our approach.
主流的视觉语言模型(VLMs)虽然在理解图像级别的信息方面取得了快速发展,但它们仍然缺乏关注人类指定的特定区域的能。相反,它们通常依赖于大量高质量图像文本配对数据来学习和生成后续注意力图。为了解决这一关键问题,我们提出利用视觉提示:以各种形式的简单视觉标记来引导和增强特定区域的注意力形成。因此,我们引入了MedVP,这是一个开创性的框架,它融合了医学实体提取、视觉提示生成和数据集自适应,用于视觉提示引导的微调。我们在多个医学VQA数据集上成功超越了最新的最先进的大型模型。进行了大量实验和人类评估,分析了不同视觉提示形式的影响,以及它们如何有助于性能提升。结果证明了我们方法的有效性和临床意义。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to NAACL 2025 Main Conference
Summary
在这个文本中,介绍了针对主流视觉语言模型(VLMs)在图像层面信息处理上存在的不足而提出的一个解决方案。该方案通过利用视觉提示(Visual Prompts)来增强模型对特定区域的注意力,从而改进模型的表现。为此,他们提出了MedVP框架,该框架结合了医学实体提取、视觉提示生成和针对视觉提示引导微调的数据集适配技术。经过在多个医学VQA数据集上的实验和人文评估,证明该方法既有效又具有临床意义。
Key Takeaways
- 主流视觉语言模型虽然能迅速理解图像级别的信息,但难以聚焦于人类指定的特定区域。
- 视觉提示是一种简单的视觉标记,用于指导和增强模型对特定区域的注意力。
- MedVP框架结合了医学实体提取、视觉提示生成和针对视觉提示引导微调的数据集适配技术。
- 通过在多个医学VQA数据集上的实验和人文评估,证明该方法的优越性和临床意义。
- 该方法利用视觉提示来改善模型的表现,特别是通过增强模型对关键区域的注意力来实现这一点。
- 视觉提示的形式对模型性能有影响,文章探讨了不同形式视觉提示的影响。
点此查看论文截图

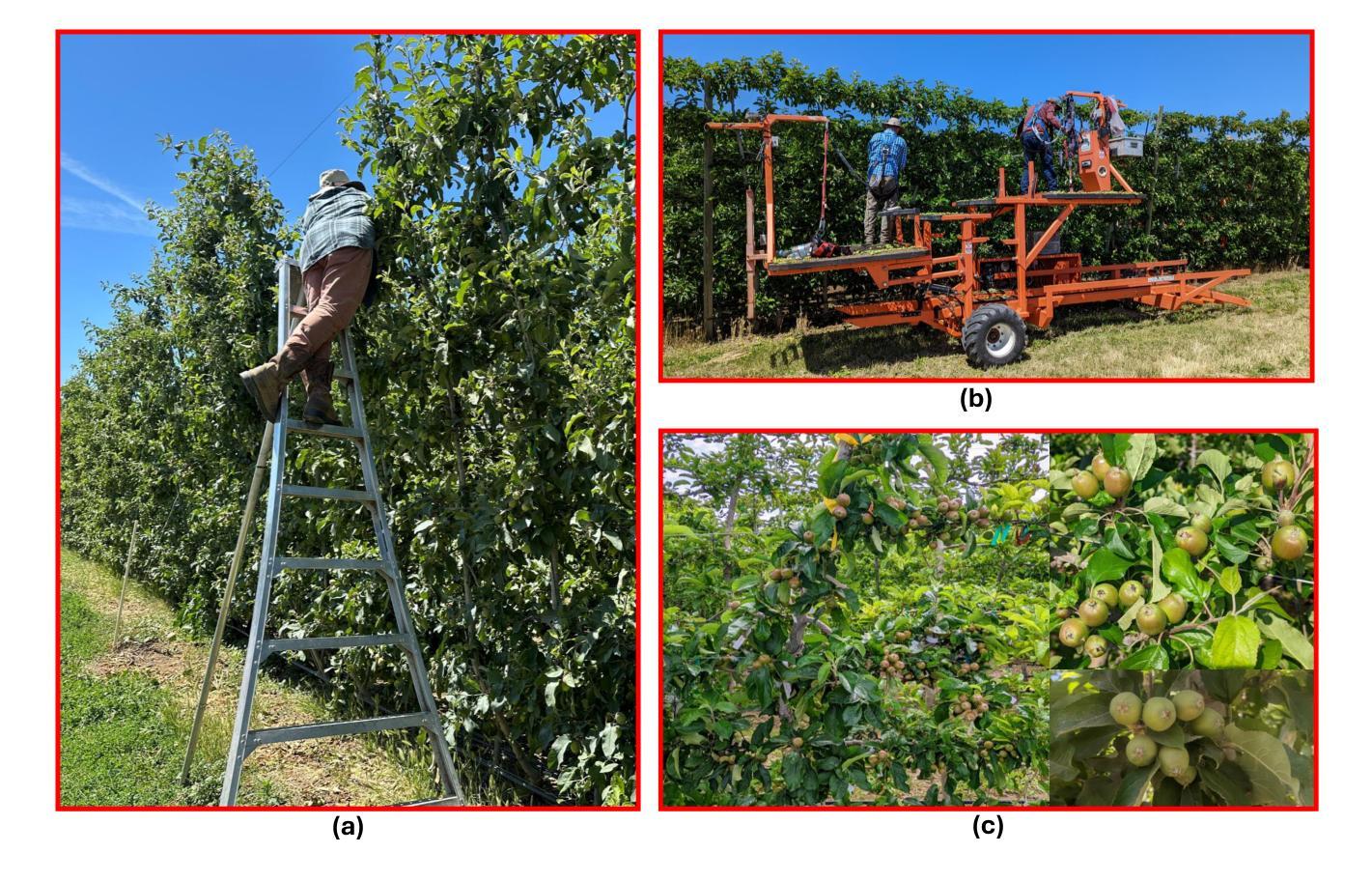
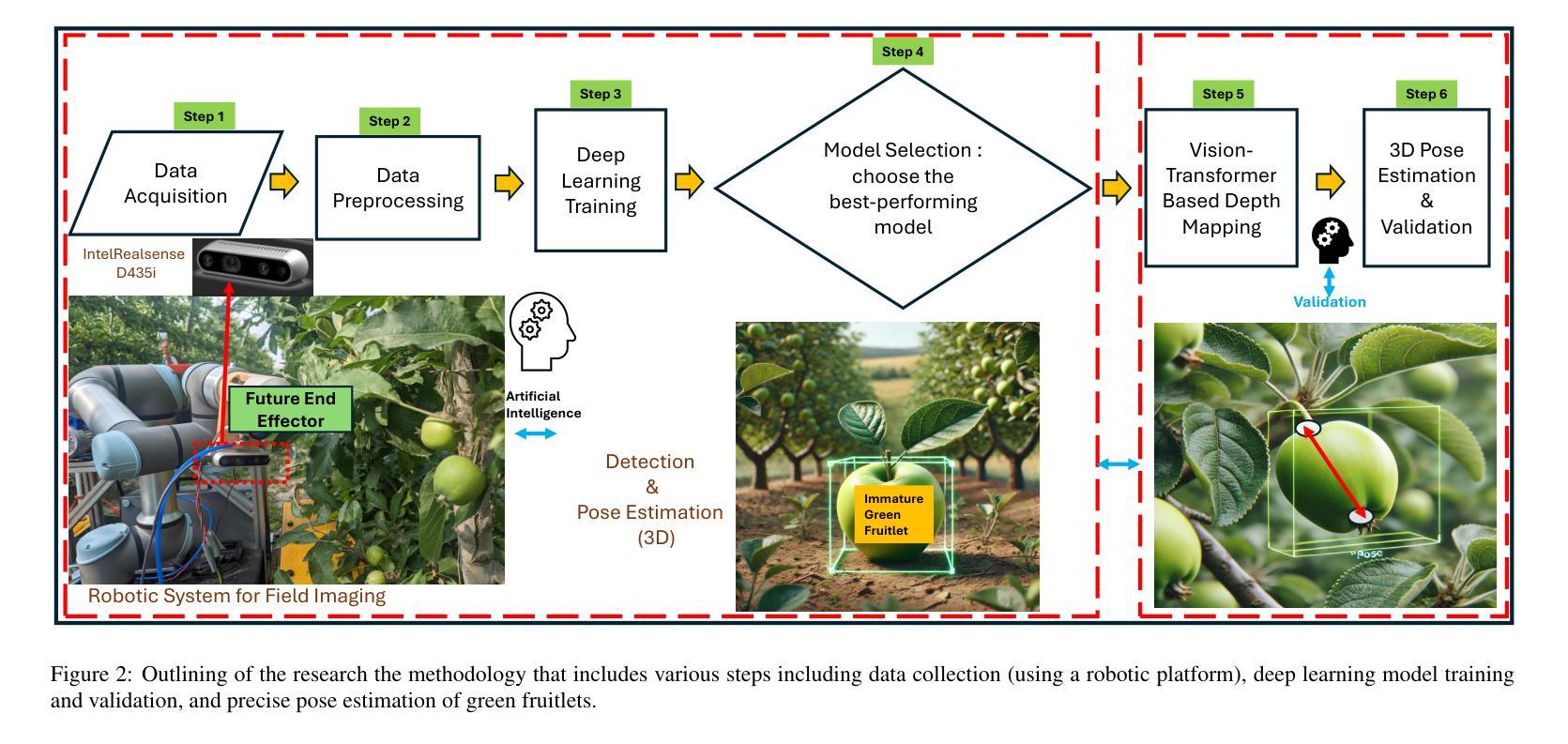
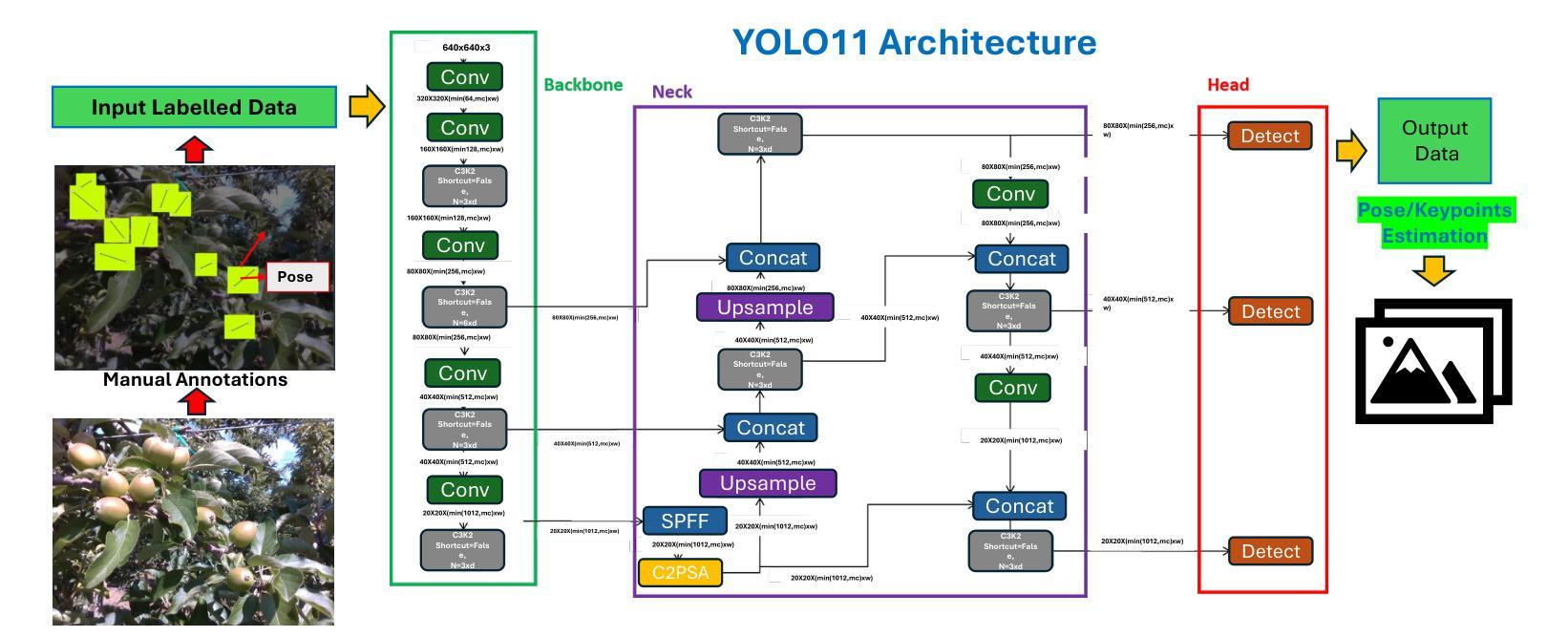
YOLO11 and Vision Transformers based 3D Pose Estimation of Immature Green Fruits in Commercial Apple Orchards for Robotic Thinning
Authors:Ranjan Sapkota, Manoj Karkee
In this study, a robust method for 3D pose estimation of immature green apples (fruitlets) in commercial orchards was developed, utilizing the YOLO11(or YOLOv11) object detection and pose estimation algorithm alongside Vision Transformers (ViT) for depth estimation (Dense Prediction Transformer (DPT) and Depth Anything V2). For object detection and pose estimation, performance comparisons of YOLO11 (YOLO11n, YOLO11s, YOLO11m, YOLO11l and YOLO11x) and YOLOv8 (YOLOv8n, YOLOv8s, YOLOv8m, YOLOv8l and YOLOv8x) were made under identical hyperparameter settings among the all configurations. It was observed that YOLO11n surpassed all configurations of YOLO11 and YOLOv8 in terms of box precision and pose precision, achieving scores of 0.91 and 0.915, respectively. Conversely, YOLOv8n exhibited the highest box and pose recall scores of 0.905 and 0.925, respectively. Regarding the mean average precision at 50% intersection over union (mAP@50), YOLO11s led all configurations with a box mAP@50 score of 0.94, while YOLOv8n achieved the highest pose mAP@50 score of 0.96. In terms of image processing speed, YOLO11n outperformed all configurations with an impressive inference speed of 2.7 ms, significantly faster than the quickest YOLOv8 configuration, YOLOv8n, which processed images in 7.8 ms. Subsequent integration of ViTs for the green fruit’s pose depth estimation revealed that Depth Anything V2 outperformed Dense Prediction Transformer in 3D pose length validation, achieving the lowest Root Mean Square Error (RMSE) of 1.52 and Mean Absolute Error (MAE) of 1.28, demonstrating exceptional precision in estimating immature green fruit lengths. Integration of YOLO11 and Depth Anything Model provides a promising solution to 3D pose estimation of immature green fruits for robotic thinning applications. (YOLOv11 pose detection, YOLOv11 Pose, YOLOv11 Keypoints detection, YOLOv11 pose estimation)
在这项研究中,开发了一种利用YOLO11(或YOLOv11)目标检测与姿态估计算法以及用于深度估计的Vision Transformers(ViT)(包括Dense Prediction Transformer(DPT)和Depth Anything V2)进行商用果园中未成熟青苹果(幼果)的3D姿态估计的稳健方法。在目标检测和姿态估计方面,在相同的超参数设置下,对YOLO11(YOLO11n、YOLO1s、YOLO11m、YOLO11l和YOLO1lx)和YOLOv8(YOLOv8n、YOLOv8s、YOLOv8m、YOLOv8l和YOLOv8x)的所有配置进行了性能比较。观察发现,YOLO1ln在框精度和姿态精度方面超越了所有YOLO11和YOLOv8的配置,分别达到了0.91和0.915。相反,YOLOv8n在盒和姿态召回率方面表现出最高得分,分别为0.905和0.925。在50%交集联合的平均精度(mAP@50)方面,YOLO1ls在所有配置中表现最佳,盒mAP@50得分为0.94,而YOLOv8n则取得了最高的姿态mAP@50得分,为0.96。在图像处理速度方面,YOLO1ln表现最佳,推理速度为2.7毫秒,比最快的YOLOv8配置YOLOv8n快得多,后者处理图像需要7.8毫秒。随后对绿色果实姿态深度估计的ViTs集成显示,Depth Anything V2在3D姿态长度验证中优于Dense Prediction Transformer,实现了最低的均方根误差(RMSE)为1.52和平均绝对误差(MAE)为1.28,显示出在估算未成熟绿色果实长度方面的出色精确度。YOLO11与Depth Anything模型的融合为解决机器人修剪应用的未成熟绿色果实3D姿态估计问题提供了有前途的解决方案。(YOLOvll姿态检测、YOLOvll姿态、YOLOvll关键点检测、YOLOvll姿态估计)
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 24 Pages, 13 Figures, 1 Table
Summary
本研究利用YOLOv11进行苹果幼果的三维姿态估计,结合Vision Transformers中的Dense Prediction Transformer和Depth Anything V2进行深度预测。YOLOv11中的YOLO11n在box精度和姿态精度上表现最佳,而YOLOv8n在召回率上表现最佳。Depth Anything V2在估算绿色幼果长度方面表现出较高精确度。结合YOLO11和Depth Anything Model可为机器人自动疏果应用提供可靠的三维姿态估计解决方案。
Key Takeaways
- 研究采用YOLOv11进行苹果幼果的三维姿态估计,具有多种配置用于比较性能。
- YOLO11n在box精度和姿态精度上超越其他配置,而YOLOv8n在召回率方面表现最佳。
- Depth Anything V2在估算绿色幼果长度方面表现出较高精确度,相较于Dense Prediction Transformer有更好的性能。
- Vision Transformers被成功应用于深度估计。
- YOLOv11结合Depth Anything Model展现出在估算不成熟绿果三维姿态方面的潜力。
- 该研究为机器人自动疏果应用提供了可靠的三维姿态估计解决方案。
点此查看论文截图


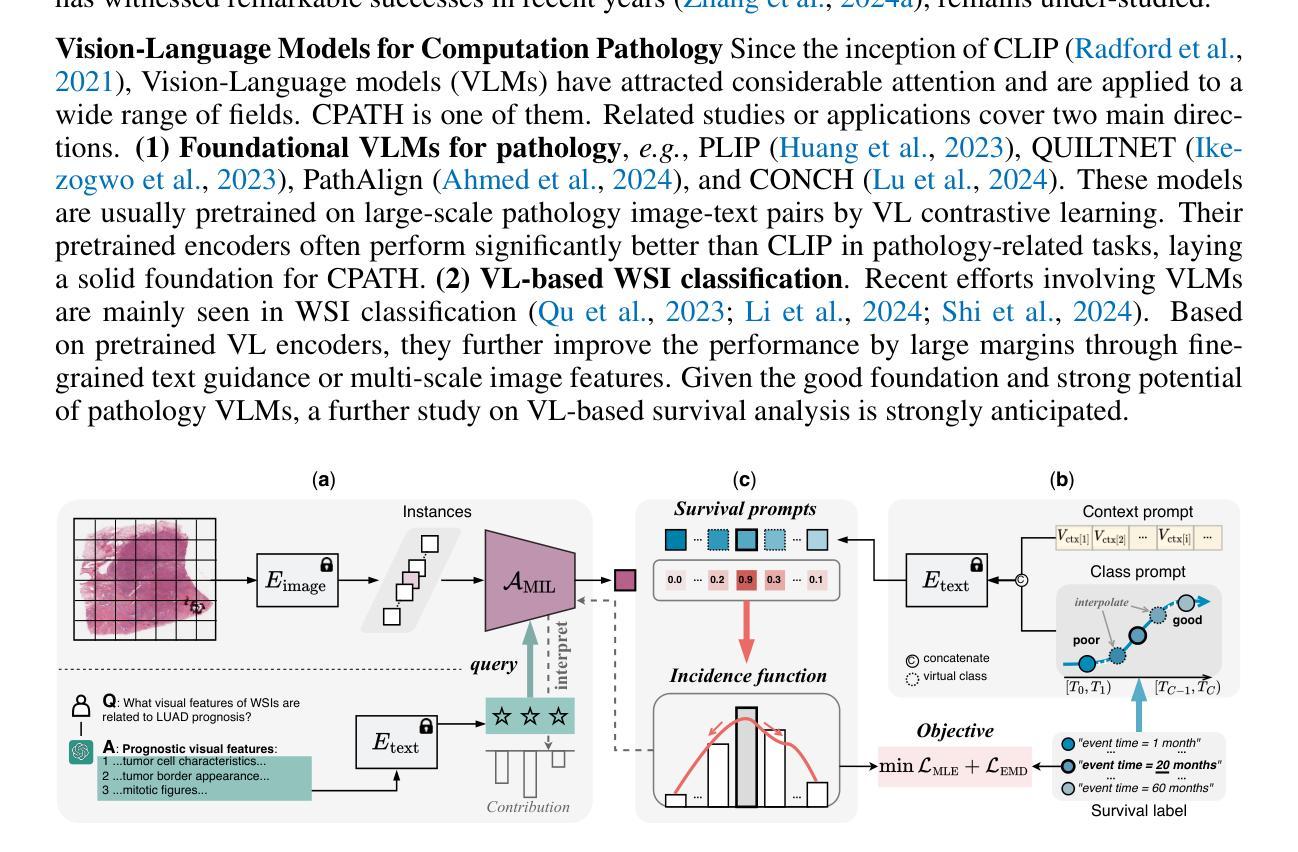
Interpretable Vision-Language Survival Analysis with Ordinal Inductive Bias for Computational Pathology
Authors:Pei Liu, Luping Ji, Jiaxiang Gou, Bo Fu, Mao Ye
Histopathology Whole-Slide Images (WSIs) provide an important tool to assess cancer prognosis in computational pathology (CPATH). While existing survival analysis (SA) approaches have made exciting progress, they are generally limited to adopting highly-expressive network architectures and only coarse-grained patient-level labels to learn visual prognostic representations from gigapixel WSIs. Such learning paradigm suffers from critical performance bottlenecks, when facing present scarce training data and standard multi-instance learning (MIL) framework in CPATH. To overcome it, this paper, for the first time, proposes a new Vision-Language-based SA (VLSA) paradigm. Concretely, (1) VLSA is driven by pathology VL foundation models. It no longer relies on high-capability networks and shows the advantage of data efficiency. (2) In vision-end, VLSA encodes textual prognostic prior and then employs it as auxiliary signals to guide the aggregating of visual prognostic features at instance level, thereby compensating for the weak supervision in MIL. Moreover, given the characteristics of SA, we propose i) ordinal survival prompt learning to transform continuous survival labels into textual prompts; and ii) ordinal incidence function as prediction target to make SA compatible with VL-based prediction. Notably, VLSA’s predictions can be interpreted intuitively by our Shapley values-based method. The extensive experiments on five datasets confirm the effectiveness of our scheme. Our VLSA could pave a new way for SA in CPATH by offering weakly-supervised MIL an effective means to learn valuable prognostic clues from gigapixel WSIs. Our source code is available at https://github.com/liupei101/VLSA.
组织病理学全切片图像(Whole-Slide Images, WSI)为计算病理学(CPATH)中评估癌症预后提供了一种重要工具。尽管现有的生存分析(Survival Analysis, SA)方法已经取得了令人兴奋的进展,但它们通常仅限于采用高度表达的神经网络架构,并且仅使用粗粒度的患者级标签来学习来自gigapixel WSI的视觉预后表示。当面临当前稀缺的训练数据和CPATH中的标准多实例学习(Multiple Instance Learning, MIL)框架时,这种学习模式面临关键的性能瓶颈。为了克服这一点,本文首次提出了一种基于视觉语言模型的生存分析(Vision-Language-based SA, VLSA)新方法。具体而言,(1)VLSA由病理学视觉语言基础模型驱动,不再依赖高性能网络,并显示出数据效率的优势。(2)在视觉端,VLSA编码文本预后先验,然后将其作为辅助信号来指导实例级视觉预后特征的聚合,从而弥补了MIL中的弱监督。此外,考虑到生存分析的特点,我们提出i)有序生存提示学习,将连续生存标签转换为文本提示;以及ii)以有序发生率函数作为预测目标,使生存分析与基于视觉语言的预测兼容。值得注意的是,VLSA的预测可以通过我们基于沙普利值的方法直观地解释。在五套数据集上的广泛实验证实了我们的方案的有效性。我们的VLSA可能为CPATH中的生存分析开辟一条新路,通过为弱监督MIL提供一种从gigapixel WSI学习有价值预后线索的有效手段。我们的源代码可在https://github.com/liupei101/VLSA获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to ICLR 2025
Summary
本文提出了一个全新的基于视觉和自然语言的生存分析(VLSA)范式,解决了计算病理学中对全切片图像(WSI)的精细分析挑战。通过引入自然语言模型到病理学的结合,该方法提升了在训练数据稀缺情况下模型的数据利用效率,并在标准的多实例学习框架内解决了标签弱化的问题。新方法还包括将连续生存标签转化为文本提示,并利用基于Shapley值的解释方法直观地解释预测结果。实验证明,该方案在五个数据集上均有效。
Key Takeaways
- VLSA首次将视觉和自然语言结合用于生存分析,解决计算病理学中的挑战。
- 利用现有的自然语言模型提高数据利用效率,减少对高度专业化的网络架构的依赖。
- 提出使用文本预后先验信息来指导视觉预后特征的聚合,强化多实例学习中的弱监督。
- 通过将连续生存标签转化为文本提示以及采用有序发生率函数作为预测目标,使生存分析与基于视觉语言模型的预测相兼容。
- 采用基于Shapley值的解释方法直观地解释预测结果,增强了模型的解释性。
- 实验结果证明,VLSA方案在五个数据集上均表现优异。
点此查看论文截图