⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-02-14 更新
A General Pipeline for Glomerulus Whole-Slide Image Segmentation
Authors:Quan Huu Cap
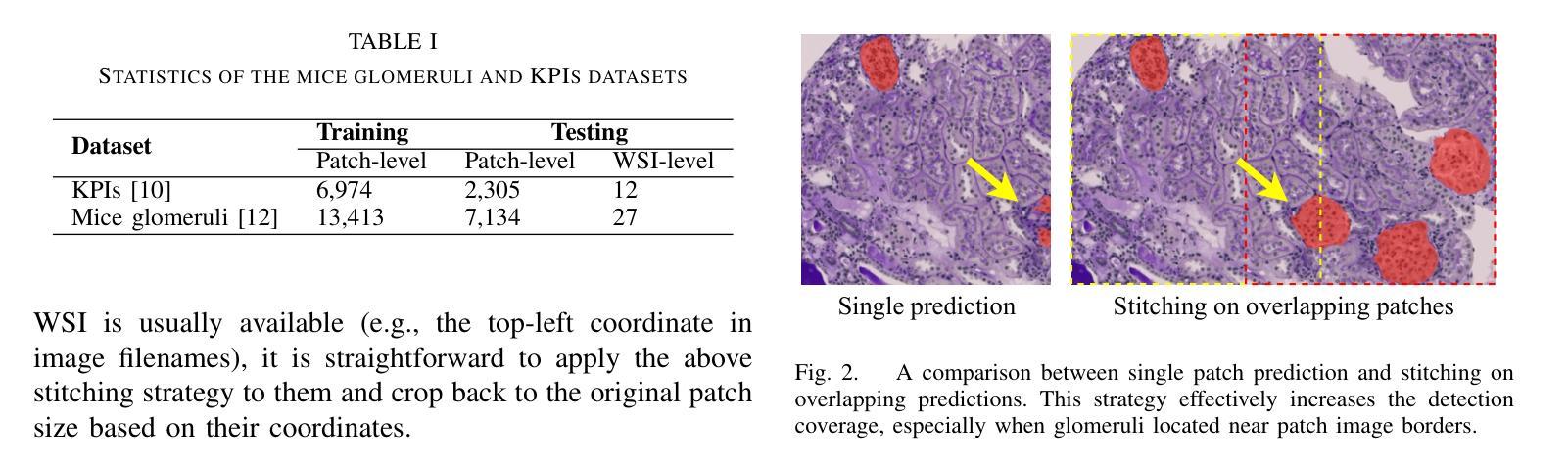
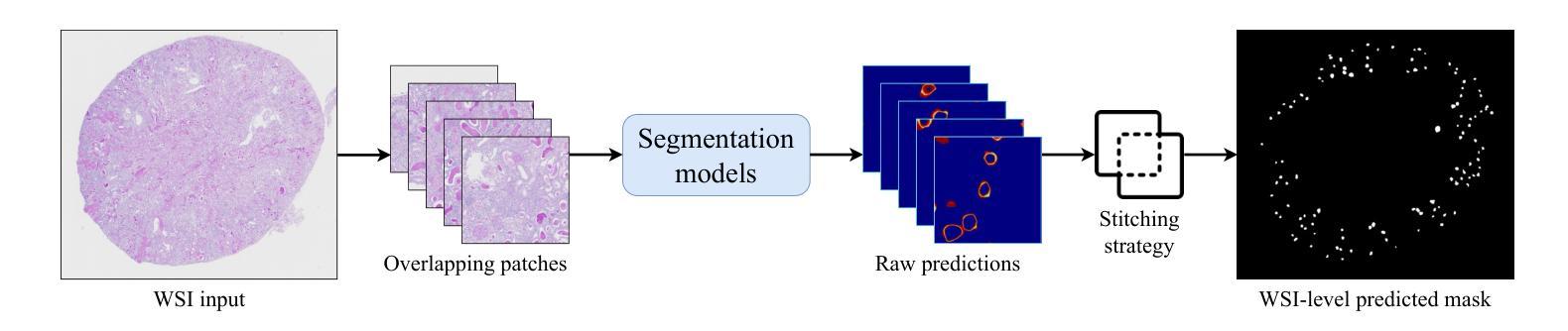
Whole-slide images (WSI) glomerulus segmentation is essential for accurately diagnosing kidney diseases. In this work, we propose a general and practical pipeline for glomerulus segmentation that effectively enhances both patch-level and WSI-level segmentation tasks. Our approach leverages stitching on overlapping patches, increasing the detection coverage, especially when glomeruli are located near patch image borders. In addition, we conduct comprehensive evaluations from different segmentation models across two large and diverse datasets with over 30K glomerulus annotations. Experimental results demonstrate that models using our pipeline outperform the previous state-of-the-art method, achieving superior results across both datasets and setting a new benchmark for glomerulus segmentation in WSIs. The code and pre-trained models are available at https://github.com/huuquan1994/wsi_glomerulus_seg.
全景图像(WSI)中的肾小球分割对于准确诊断肾脏疾病至关重要。在这项工作中,我们提出了一种用于肾小球分割的通用实用流程,该流程可有效提高补丁级别和全景图像级别的分割任务。我们的方法利用重叠补丁上的拼接技术,提高了检测覆盖率,尤其是当肾小球位于补丁图像边缘时。此外,我们在两个大型、多样化的数据集上对不同分割模型进行了全面评估,数据集包含超过三万张肾小球注释。实验结果表明,使用我们流程的模型优于以前的最先进方法,在两个数据集上都取得了优越的结果,并为全景图像中的肾小球分割设定了新的基准。代码和预训练模型可在 https://github.com/huuquan1994/wsi_glomerulus_seg 找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种通用且实用的肾小球分割流水线,可有效提升补丁级别和全幻灯片级别图像的肾小球分割任务。该方法通过重叠补丁的拼接,提高了检测覆盖率,特别是在肾小球位于补丁图像边缘时。同时,本文在两个大型、多样化的数据集上进行了全面的评估,包含超过3万张肾小球标注图像。实验结果表明,采用本文流水线的模型优于先前最先进的方法,在两个数据集上都取得了优异的结果,为全幻灯片图像中的肾小球分割设定了新的基准。
Key Takeaways
- 提出了一种用于肾小球分割的通用和实用流水线。
- 通过重叠补丁的拼接,提高了肾小球检测的覆盖率。
- 流水线设计有效提升了补丁级别和全幻灯片级别图像的肾小球分割任务。
- 在两个大型、多样化的数据集上进行了全面的评估。
- 实验结果证明该流水线模型在分割效果上优于先前最先进的方法。
- 公开了代码和预训练模型,便于其他研究者使用。
点此查看论文截图

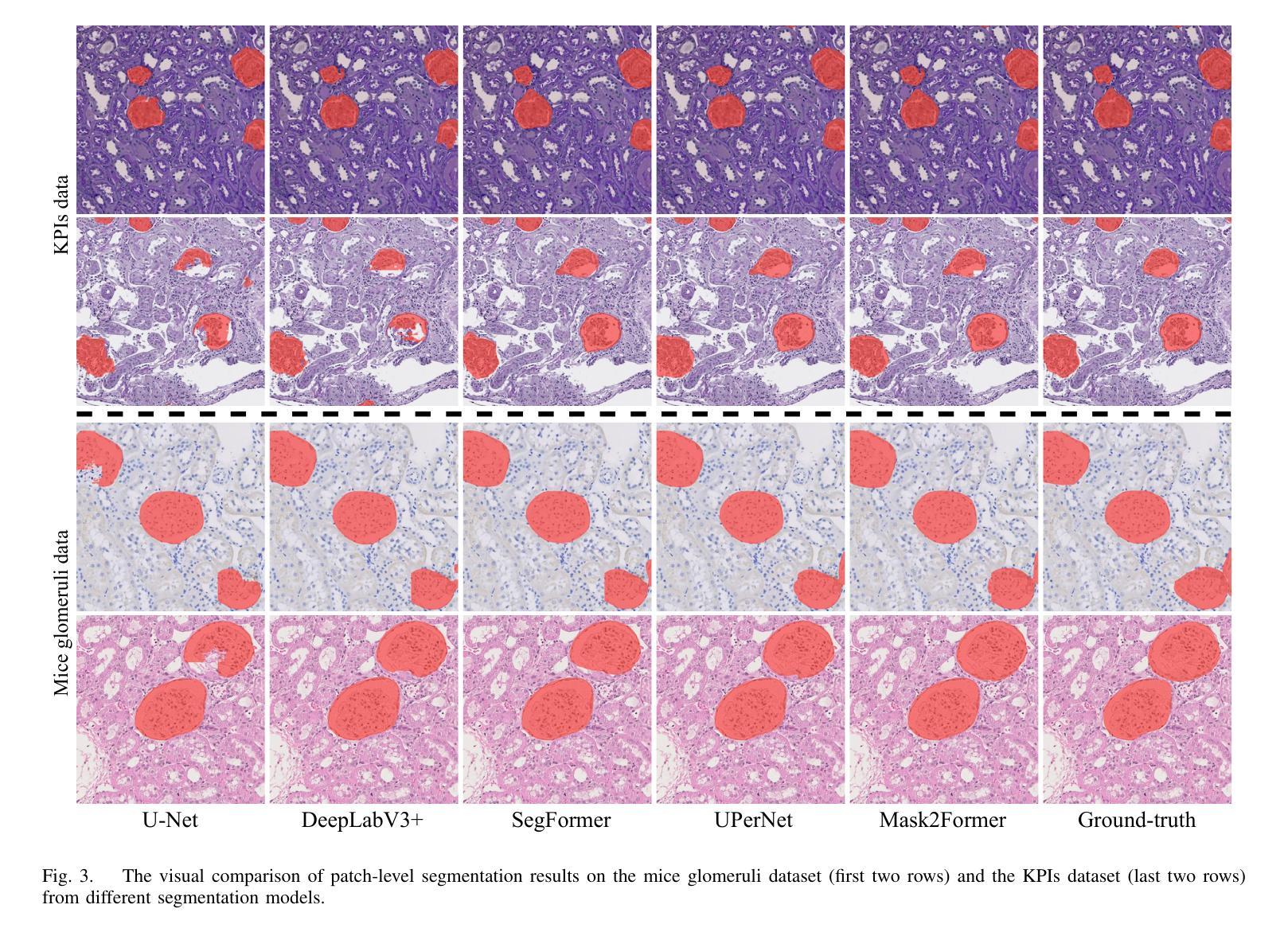
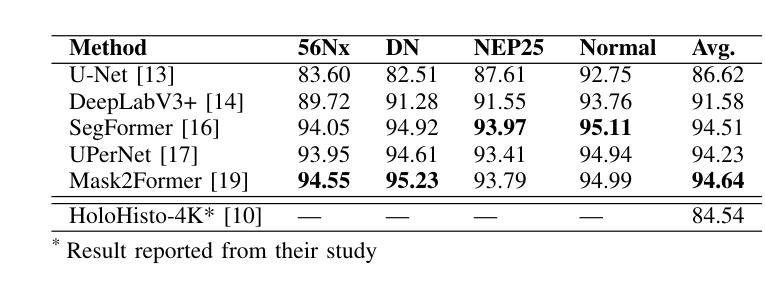
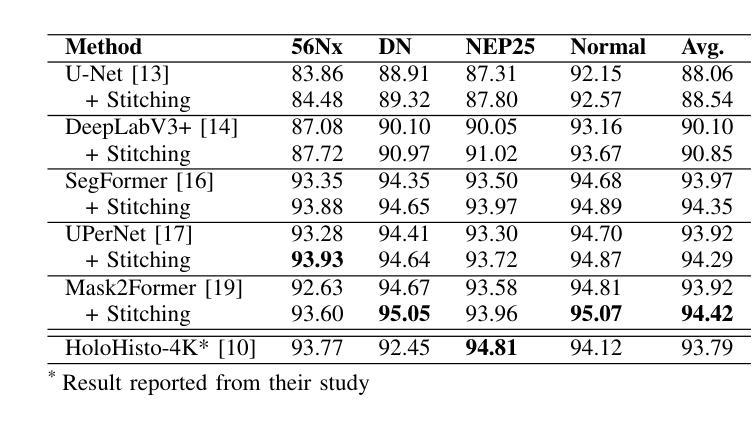
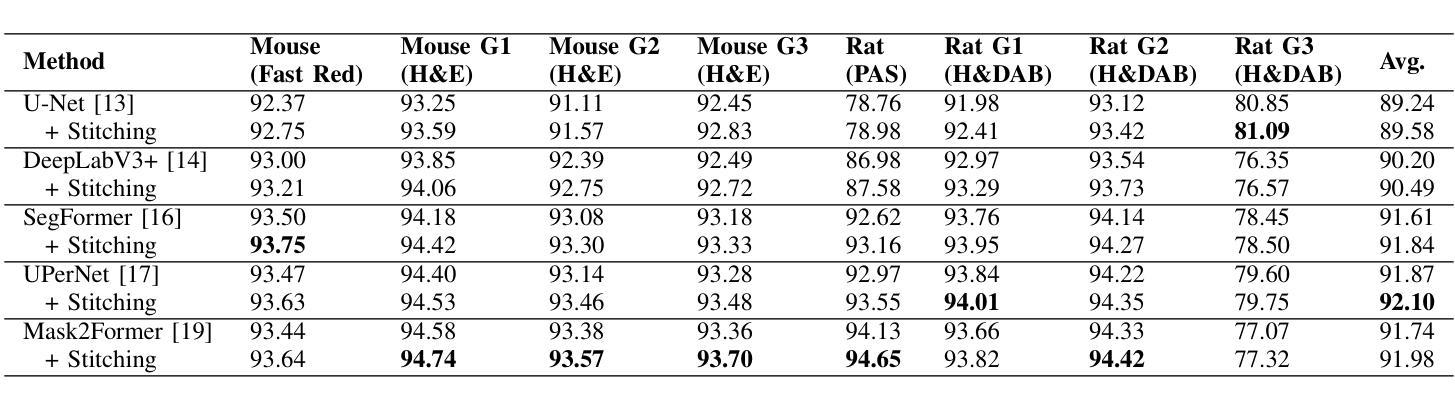
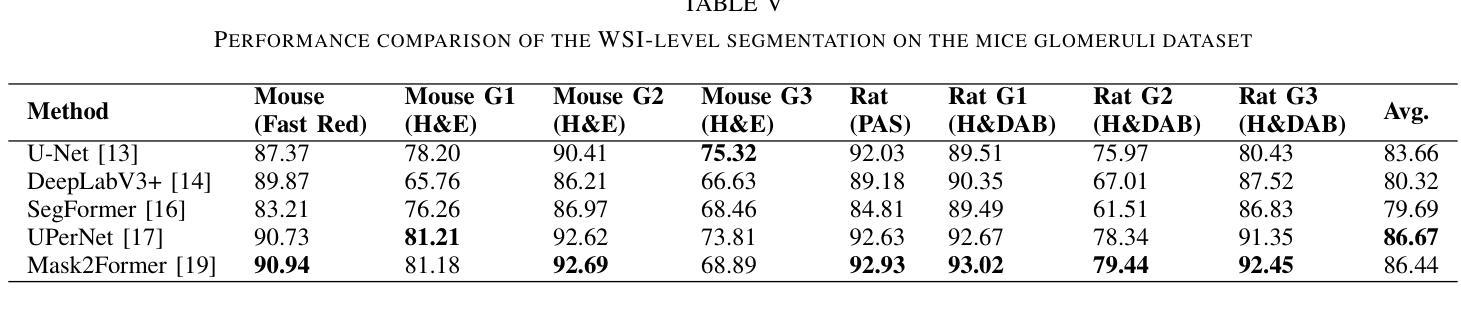
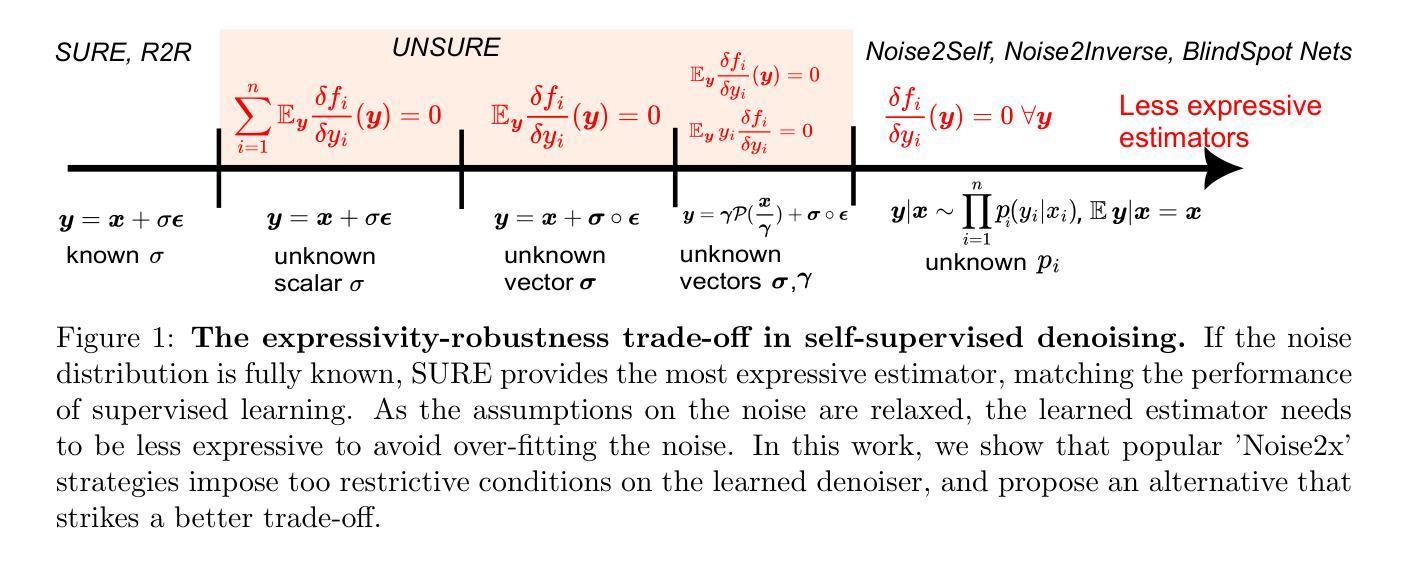
UNSURE: self-supervised learning with Unknown Noise level and Stein’s Unbiased Risk Estimate
Authors:Julián Tachella, Mike Davies, Laurent Jacques
Recently, many self-supervised learning methods for image reconstruction have been proposed that can learn from noisy data alone, bypassing the need for ground-truth references. Most existing methods cluster around two classes: i) Stein’s Unbiased Risk Estimate (SURE) and similar approaches that assume full knowledge of the noise distribution, and ii) Noise2Self and similar cross-validation methods that require very mild knowledge about the noise distribution. The first class of methods tends to be impractical, as the noise level is often unknown in real-world applications, and the second class is often suboptimal compared to supervised learning. In this paper, we provide a theoretical framework that characterizes this expressivity-robustness trade-off and propose a new approach based on SURE, but unlike the standard SURE, does not require knowledge about the noise level. Throughout a series of experiments, we show that the proposed estimator outperforms other existing self-supervised methods on various imaging inverse problems.
最近,许多用于图像重建的自我监督学习方法已被提出,这些学习方法可以从单独的噪声数据中学习,无需真实参考数据。现有的大多数方法集中在两类上:i) Stein的无偏风险估计(SURE)和假设对噪声分布有充分了解的类似方法;以及ii) Noise2Self和需要轻微了解噪声分布的类似交叉验证方法。第一类方法往往不切实际,因为在现实世界的应用中,噪声水平通常是未知的;而第二类方法与监督学习相比往往表现不佳。在本文中,我们提供了一个理论框架,描述了这种表达性稳健性权衡的特点,并提出了一种基于SURE的新方法,但与标准的SURE不同的是,它不需要了解噪声水平。通过一系列实验,我们证明了所提出的估计器在各种成像逆问题上优于其他现有的自监督方法。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出了一种基于Stein的无偏风险估计(SURE)的自监督学习方法用于图像重建,无需了解噪声水平信息即可实现自监督学习,并在各种成像逆问题上表现出优越性能。
Key Takeaways
- 文章讨论了现有的自监督学习在图像重建中的应用,包括基于Stein的Unbiased Risk Estimate的方法和Noise2Self等交叉验证方法。
- 第一种方法需要了解噪声分布的全貌,这在现实应用中往往难以实现;第二种方法相较于有监督学习表现常欠佳。
- 提出了一种基于理论框架的表叙灵活性与稳健性之间的权衡,并为一种新的自监督学习方法提供了理论基础。
- 新方法与标准的SURE方法不同,无需了解噪声水平信息。
- 通过一系列实验验证,新方法在各种成像逆问题上的表现优于其他现有自监督学习方法。
- 此方法能够在无参考真实数据的情况下学习从噪声数据中重建图像。
点此查看论文截图

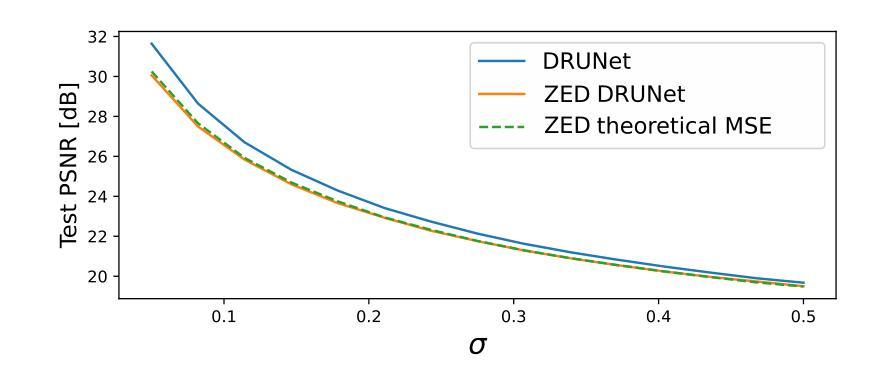
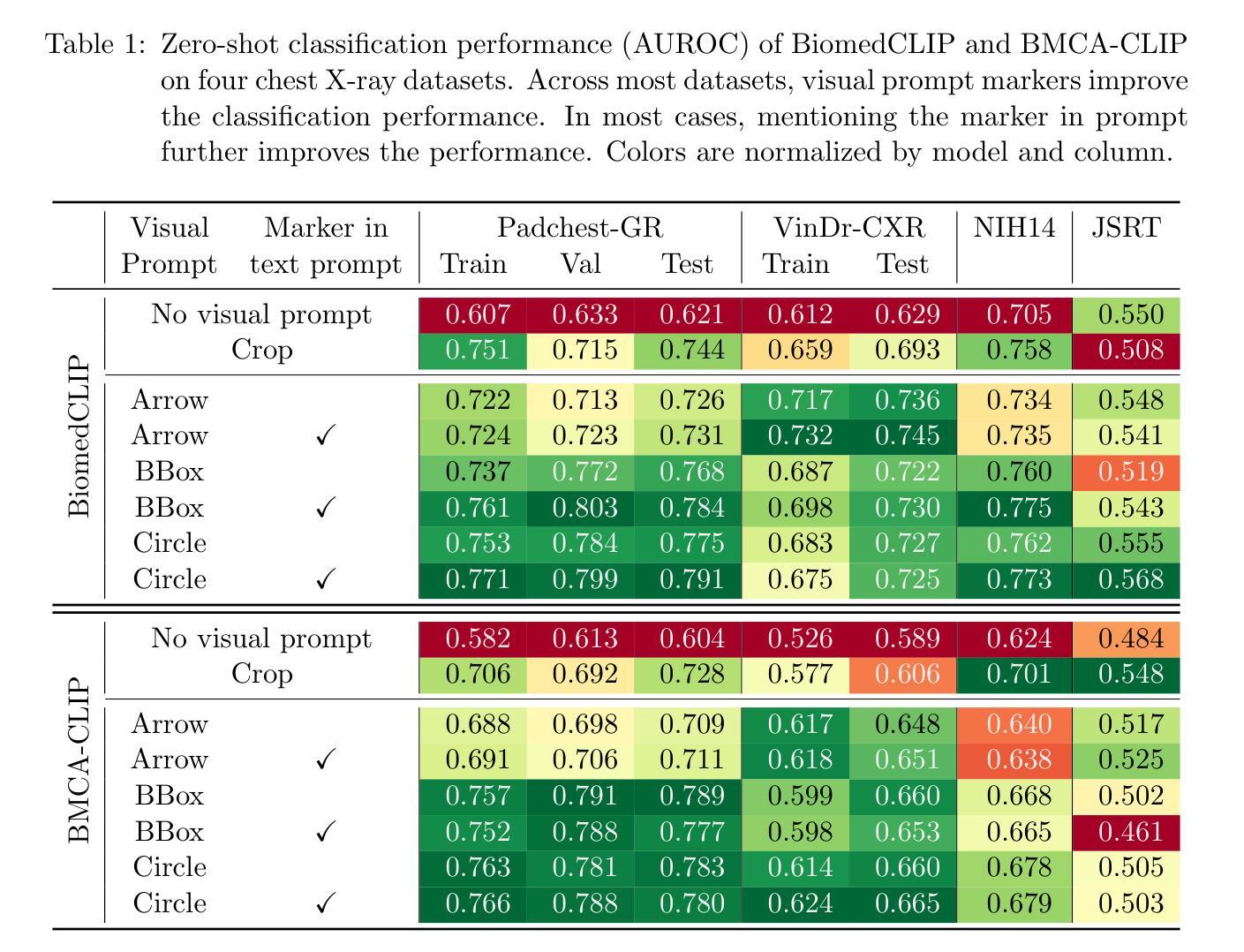
Visual Prompt Engineering for Vision Language Models in Radiology
Authors:Stefan Denner, Markus Bujotzek, Dimitrios Bounias, David Zimmerer, Raphael Stock, Klaus Maier-Hein
Medical image classification plays a crucial role in clinical decision-making, yet most models are constrained to a fixed set of predefined classes, limiting their adaptability to new conditions. Contrastive Language-Image Pretraining (CLIP) offers a promising solution by enabling zero-shot classification through multimodal large-scale pretraining. However, while CLIP effectively captures global image content, radiology requires a more localized focus on specific pathology regions to enhance both interpretability and diagnostic accuracy. To address this, we explore the potential of incorporating visual cues into zero-shot classification, embedding visual markers $\unicode{x2013}$ such as arrows, bounding boxes, and circles $\unicode{x2013}$ directly into radiological images to guide model attention. Evaluating across four public chest X-ray datasets, we demonstrate that visual markers improve AUROC by up to 0.185, highlighting their effectiveness in enhancing classification performance. Furthermore, attention map analysis confirms that visual cues help models focus on clinically relevant areas, leading to more interpretable predictions. To support further research, we use public datasets and will release our code and preprocessing pipeline, providing a reference point for future work on localized classification in medical imaging.
医学图像分类在临床决策中起着至关重要的作用,但大多数模型仅限于一组预定义的类别,这使得它们对新条件的适应性受到限制。对比语言图像预训练(CLIP)通过多模式大规模预训练提供零样本分类的有前途的解决方案。然而,虽然CLIP有效地捕获了全局图像内容,但放射学需要更加侧重于特定病理区域的本地化关注,以提高解释能力和诊断准确性。为了解决这个问题,我们探索了将视觉线索融入零样本分类的潜力,通过在放射图像中嵌入视觉标记(如箭头、边界框和圆圈)来引导模型注意力。在四个公共胸部X射线数据集上的评估表明,视觉标记提高了AUROC值高达0.185,突显了它们在提高分类性能方面的有效性。此外,注意力地图分析证实,视觉线索有助于模型关注临床相关区域,从而做出更可解释的预测。为了支持进一步研究,我们使用公共数据集,并将发布我们的代码和预处理管道,为未来医学成像中局部化分类的研究提供参考点。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at ECCV 2024 Workshop on Emergent Visual Abilities and Limits of Foundation Models
Summary
医学图像分类在临床决策中至关重要,但大多数模型受限于预设类别,难以适应新情况。对比语言图像预训练(CLIP)通过多模态大规模预训练实现零样本分类,为解决此问题提供了希望。然而,CLIP主要捕捉图像全局内容,而放射学需要更侧重于特定病理区域的视觉提示,以提高解释性和诊断准确性。本研究探索将视觉提示融入零样本分类的潜力,通过在放射图像中嵌入视觉标记(如箭头、边界框和圆圈)来引导模型注意力。在四个公共胸部X射线数据集上的评估表明,视觉标记提高了AUROC值达0.185,证明了其在提高分类性能方面的有效性。此外,注意力地图分析证实视觉线索有助于模型关注临床相关区域,产生更可解释的预测。
Key Takeaways
- 医学图像分类在临床决策中具有重要作用,但模型受限于预设类别,需要适应新情况的解决方案。
- 对比语言图像预训练(CLIP)可以实现零样本分类,但其在捕捉图像全局内容方面有所局限。
- 放射学需要更关注特定病理区域的视觉提示,以提高解释性和诊断准确性。
- 通过在放射图像中嵌入视觉标记(如箭头、边界框和圆圈)来引导模型注意力是一种有效的解决方案。
- 在四个公共胸部X射线数据集上的评估显示,视觉标记提高了分类性能。
- 注意力地图分析证实视觉线索有助于模型关注临床相关区域。
点此查看论文截图

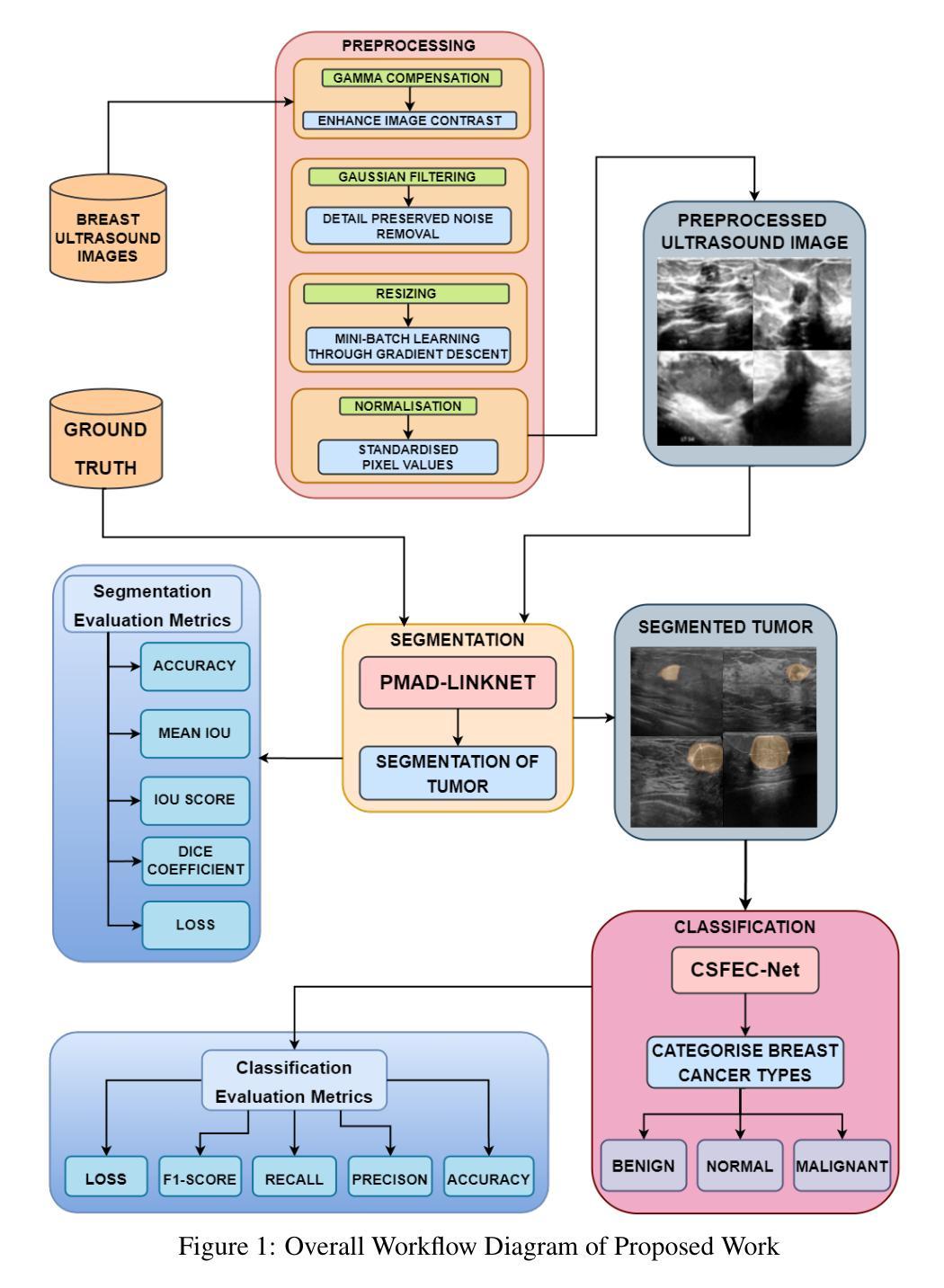
Exploiting Precision Mapping and Component-Specific Feature Enhancement for Breast Cancer Segmentation and Identification
Authors:Pandiyaraju V, Shravan Venkatraman, Pavan Kumar S, Santhosh Malarvannan, Kannan A
Breast cancer is one of the leading causes of death globally, and thus there is an urgent need for early and accurate diagnostic techniques. Although ultrasound imaging is a widely used technique for breast cancer screening, it faces challenges such as poor boundary delineation caused by variations in tumor morphology and reduced diagnostic accuracy due to inconsistent image quality. To address these challenges, we propose novel Deep Learning (DL) frameworks for breast lesion segmentation and classification. We introduce a precision mapping mechanism (PMM) for a precision mapping and attention-driven LinkNet (PMAD-LinkNet) segmentation framework that dynamically adapts spatial mappings through morphological variation analysis, enabling precise pixel-level refinement of tumor boundaries. Subsequently, we introduce a component-specific feature enhancement module (CSFEM) for a component-specific feature-enhanced classifier (CSFEC-Net). Through a multi-level attention approach, the CSFEM magnifies distinguishing features of benign, malignant, and normal tissues. The proposed frameworks are evaluated against existing literature and a diverse set of state-of-the-art Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) architectures. The obtained results show that our segmentation model achieves an accuracy of 98.1%, an IoU of 96.9%, and a Dice Coefficient of 97.2%. For the classification model, an accuracy of 99.2% is achieved with F1-score, precision, and recall values of 99.1%, 99.3%, and 99.1%, respectively.
乳腺癌是全球主要的致死原因之一,因此亟需早期准确诊断技术。超声成像虽然广泛应用于乳腺癌筛查,但仍面临因肿瘤形态变化导致的边界界定不清以及图像质量不一致导致的诊断准确性降低等挑战。为了应对这些挑战,我们提出了用于乳腺病灶分割和分类的新型深度学习(DL)框架。我们引入了一种精度映射机制(PMM),用于精度映射和注意力驱动LinkNet(PMAD-LinkNet)分割框架,通过形态变化分析动态适应空间映射,实现对肿瘤边界的精确像素级细化。接着,我们针对组件特定特征增强分类器(CSFEC-Net)引入了一个组件特定特征增强模块(CSFEM)。通过多级注意力方法,CSFEM放大了良性、恶性及正常组织的区别特征。所提出的框架与现有文献和一系列先进的卷积神经网络(CNN)架构进行了评估比较。获得的结果显示,我们的分割模型准确率达到了98.1%,IoU为96.9%,Dice系数为97.2%。分类模型则实现了99.2%的准确率,F1分数、精确度和召回率分别为99.1%、99.3%和99.1%。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 27 pages, 18 figures, 6 tables
Summary
针对乳腺癌超声成像中面临的边界模糊和诊断准确性问题,提出基于深度学习的新框架进行病灶分割和分类。通过精确映射机制和组件特定特征增强模块,实现对肿瘤边界的精确像素级分割和对良恶性及正常组织的特征增强分类。评估结果显示,分割模型准确率为98.1%,IoU为96.9%,Dice系数为97.2%;分类模型准确率为99.2%,F1分数、精确度和召回率分别为99.1%、99.3%和99.1%。
Key Takeaways
- 乳腺癌是全球主要的死亡原因之一,需要早期和准确的诊断技术。
- 超声成像在乳腺癌筛查中广泛应用,但存在边界模糊和图像质量不一致等挑战。
- 引入基于深度学习的新框架,包括精确映射机制和组件特定特征增强模块,以提高诊断准确性。
- 精确映射机制能够动态适应空间映射,实现肿瘤边界的精确像素级分割。
- 组件特定特征增强模块通过多级别注意力方法放大良恶性及正常组织间的特征差异。
- 分割模型准确率高达98.1%,IoU为96.9%,Dice系数为97.2%。
点此查看论文截图

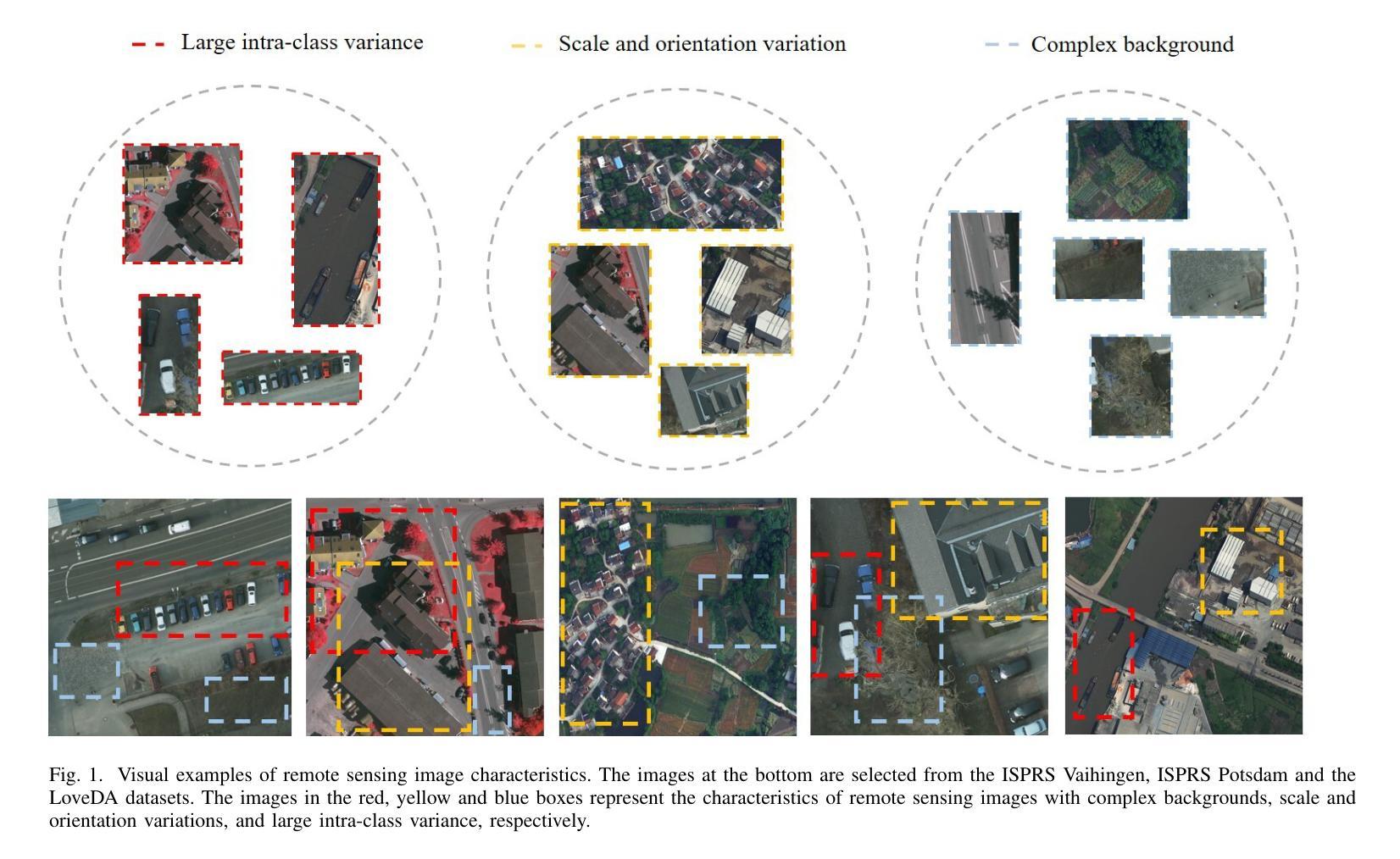
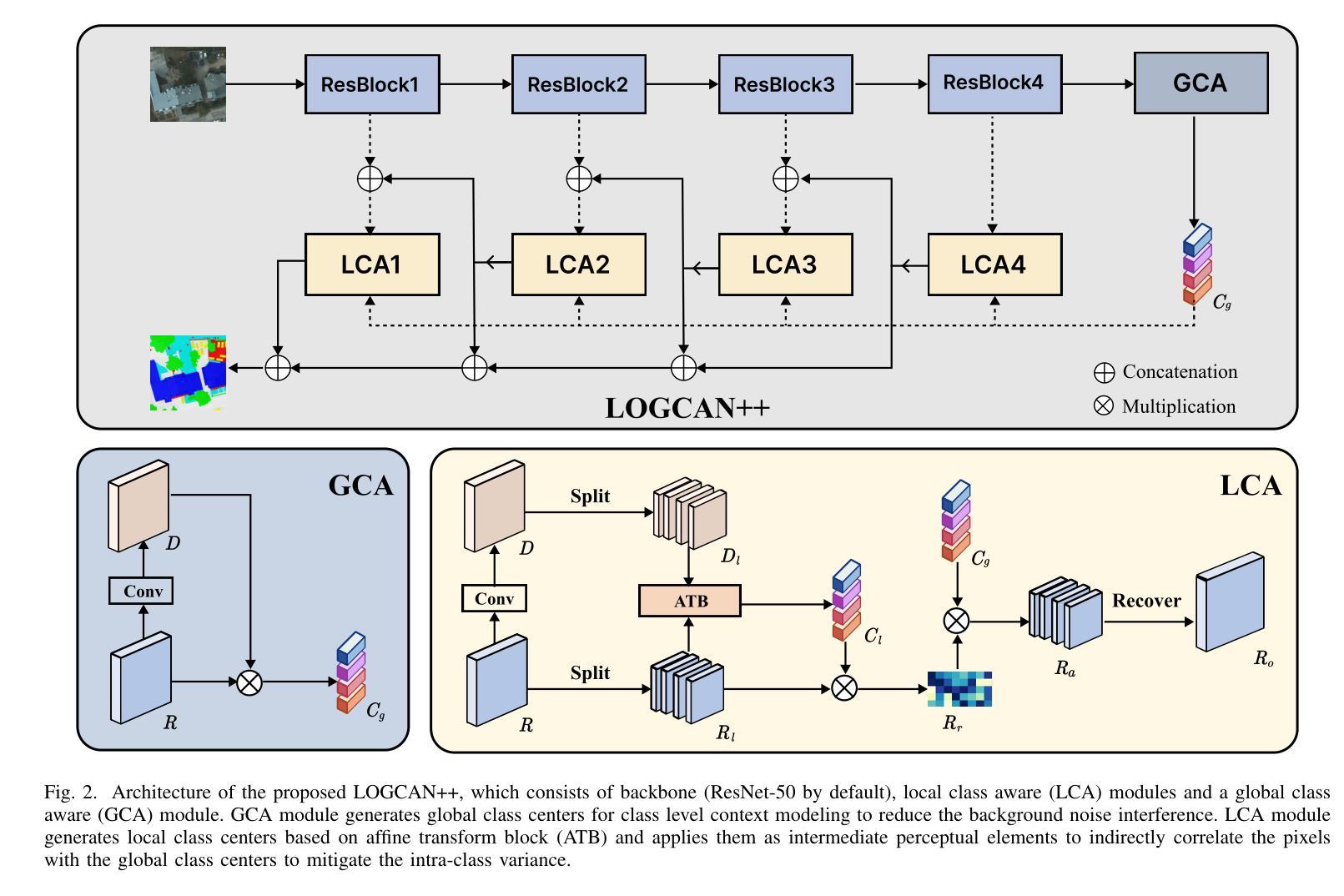
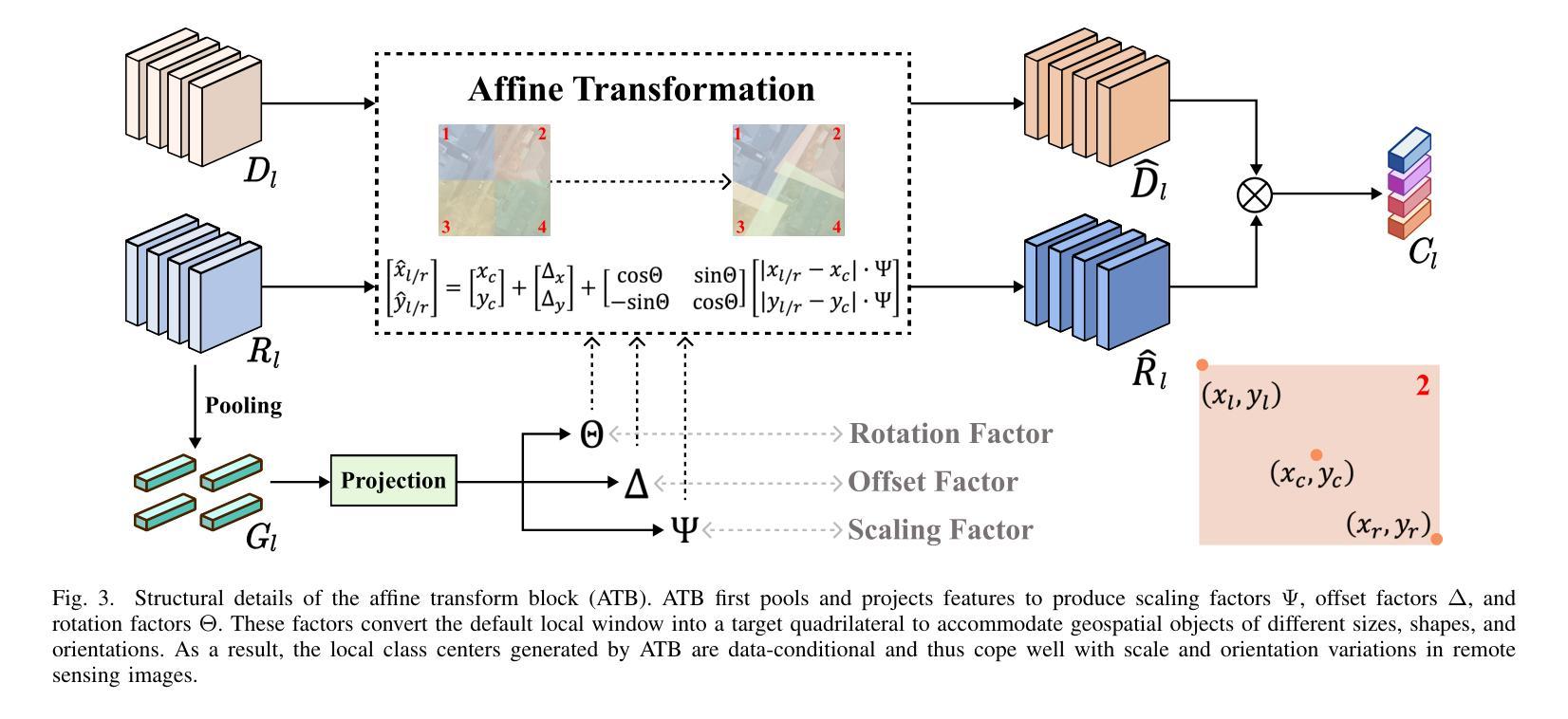
LOGCAN++: Adaptive Local-global class-aware network for semantic segmentation of remote sensing imagery
Authors:Xiaowen Ma, Rongrong Lian, Zhenkai Wu, Hongbo Guo, Mengting Ma, Sensen Wu, Zhenhong Du, Siyang Song, Wei Zhang
Remote sensing images usually characterized by complex backgrounds, scale and orientation variations, and large intra-class variance. General semantic segmentation methods usually fail to fully investigate the above issues, and thus their performances on remote sensing image segmentation are limited. In this paper, we propose our LOGCAN++, a semantic segmentation model customized for remote sensing images, which is made up of a Global Class Awareness (GCA) module and several Local Class Awareness (LCA) modules. The GCA module captures global representations for class-level context modeling to reduce the interference of background noise. The LCA module generates local class representations as intermediate perceptual elements to indirectly associate pixels with the global class representations, targeting at dealing with the large intra-class variance problem. In particular, we introduce affine transformations in the LCA module for adaptive extraction of local class representations to effectively tolerate scale and orientation variations in remotely sensed images. Extensive experiments on three benchmark datasets show that our LOGCAN++ outperforms current mainstream general and remote sensing semantic segmentation methods and achieves a better trade-off between speed and accuracy. Code is available at https://github.com/xwmaxwma/rssegmentation.
遥感图像通常具有复杂的背景、尺度和方向变化以及较大的类内差异。一般的语义分割方法通常无法完全解决上述问题,因此在遥感图像分割方面的性能有限。在本文中,我们提出了针对遥感图像的语义分割模型LOGCAN++,它由全局类意识(GCA)模块和多个局部类意识(LCA)模块组成。GCA模块捕获全局表示来进行类上下文建模,以减少背景噪声的干扰。LCA模块生成局部类表示作为中间感知元素,间接地将像素与全局类表示关联起来,以处理较大的类内差异问题。特别是,我们在LCA模块中引入了仿射变换,以进行局部类表示的自适应提取,从而有效地容忍遥感图像中的尺度和方向变化。在三个基准数据集上的大量实验表明,我们的LOGCAN++在速度和准确性之间取得了更好的权衡,并超越了当前主流的一般和遥感语义分割方法。代码可在https://github.com/xwmaxwma/rssegmentation上找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by TGRS2025
Summary
远程遥感图像具有复杂背景、尺度与方向变化以及大类内差异大的特点。通用语义分割方法难以充分应对上述问题,在遥感图像分割中的表现受限。本文提出针对遥感图像的定制语义分割模型LOGCAN++,包括全局类别感知模块和多个局部类别感知模块。全局类别感知模块捕捉全局类别上下文表示,降低背景噪声干扰;局部类别感知模块生成局部类别表示,作为中间感知元素间接关联像素与全局类别表示,以解决大类内差异问题。特别是我们在局部类别感知模块中引入了仿射变换,用于自适应提取局部类别表示,有效容忍遥感图像中的尺度和方向变化。在三个基准数据集上的广泛实验表明,我们的LOGCAN++在主流通用和遥感语义分割方法中表现优越,实现了速度和准确度的良好平衡。
Key Takeaways
- 遥感图像具有复杂背景、尺度与方向变化以及大类内差异大的特性。
- 通用语义分割方法在遥感图像分割中表现受限。
- LOGCAN++是一个针对遥感图像的定制语义分割模型,包含全局类别感知模块和局部类别感知模块。
- 全局类别感知模块捕捉全局类别上下文表示,降低背景噪声干扰。
- 局部类别感知模块解决大类内差异问题,通过生成局部类别表示间接关联像素与全局类别表示。
- 局部类别感知模块中引入仿射变换,用于自适应提取局部类别表示,有效应对遥感图像中的尺度和方向变化。
点此查看论文截图


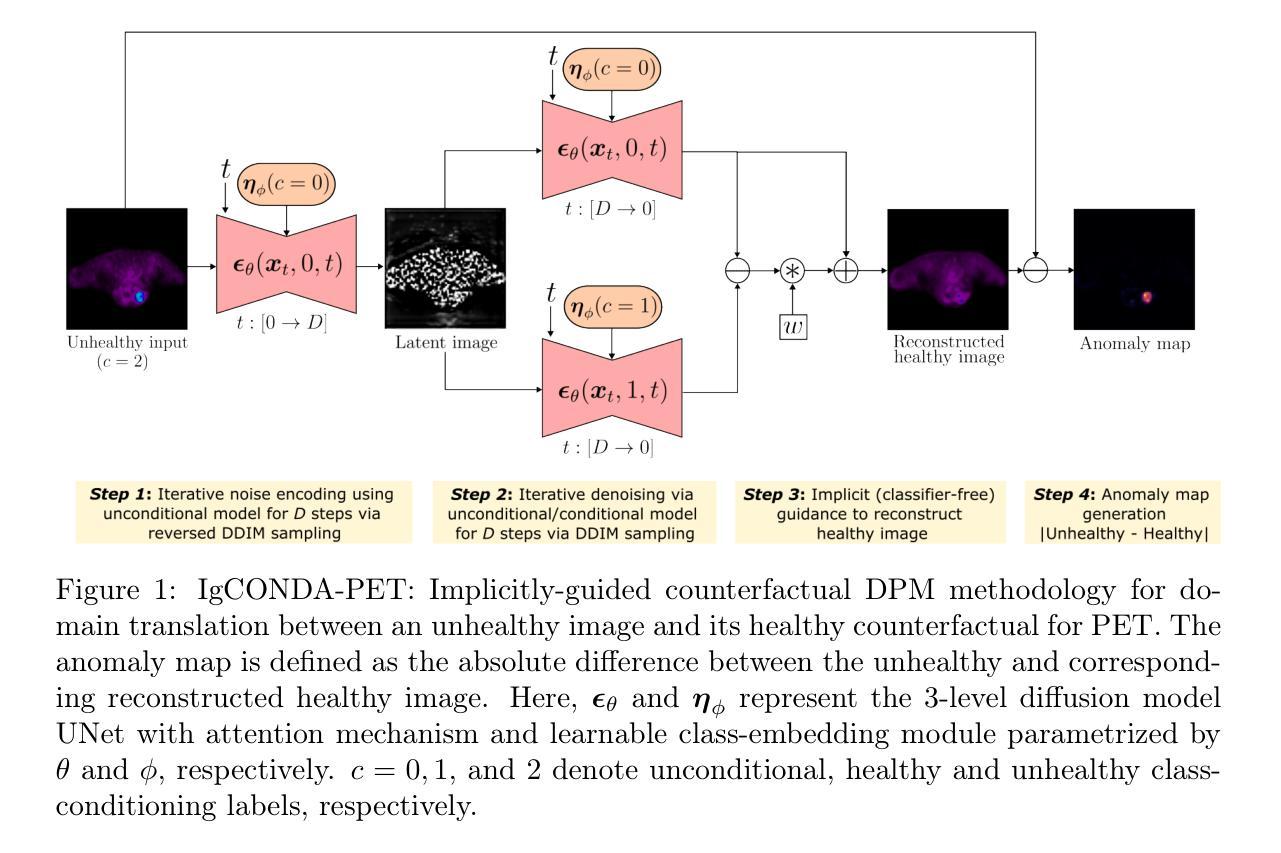
Weakly-Supervised PET Anomaly Detection using Implicitly-Guided Attention-Conditional Counterfactual Diffusion Modeling: a Multi-Center, Multi-Cancer, and Multi-Tracer Study
Authors:Shadab Ahamed, Arman Rahmim
Minimizing the need for pixel-level annotated data to train PET lesion detection and segmentation networks is highly desired and can be transformative, given time and cost constraints associated with expert annotations. Current un-/weakly-supervised anomaly detection methods rely on autoencoder or generative adversarial networks trained only on healthy data; however GAN-based networks are more challenging to train due to issues with simultaneous optimization of two competing networks, mode collapse, etc. In this paper, we present the weakly-supervised Implicitly guided COuNterfactual diffusion model for Detecting Anomalies in PET images (IgCONDA-PET). The solution is developed and validated using PET scans from six retrospective cohorts consisting of a total of 2652 cases containing both local and public datasets. The training is conditioned on image class labels (healthy vs. unhealthy) via attention modules, and we employ implicit diffusion guidance. We perform counterfactual generation which facilitates “unhealthy-to-healthy” domain translation by generating a synthetic, healthy version of an unhealthy input image, enabling the detection of anomalies through the calculated differences. The performance of our method was compared against several other deep learning based weakly-supervised or unsupervised methods as well as traditional methods like 41% SUVmax thresholding. We also highlight the importance of incorporating attention modules in our network for the detection of small anomalies. The code is publicly available at: https://github.com/ahxmeds/IgCONDA-PET.git.
最小化对像素级标注数据的需求,以训练PET图像中的病变检测和分割网络是非常理想的,并能够在时间和成本受限的专家标注下产生革命性变化。当前的无监督或弱监督异常检测方法依赖于仅使用健康数据的自编码器或生成对抗网络;然而,基于GAN的网络由于同时优化两个竞争网络、模式崩溃等问题而更具挑战性。在本文中,我们提出了用于PET图像异常检测的弱监督隐式引导计数器扩散模型(IgCONDA-PET)。该解决方案使用来自六个回顾性队列的PET扫描进行开发和验证,其中包括本地和公开数据集总共包含2652个病例。训练通过注意力模块对图像类别标签(健康与否)进行条件设置,并采用隐式扩散引导。我们执行反事实生成,通过生成不健康输入图像的合成健康版本,促进“不健康到健康”的领域转换,并通过计算差异来检测异常。我们的方法与基于深度学习的其他弱监督或无监督方法以及传统的如SUVmax阈值法等方法进行了比较。我们还强调了在网络中融入注意力模块对小异常检测的重要性。代码可在https://github.com/ahxmeds/IgCONDA-PET.git上公开访问。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 32 pages, 6 figures, 4 tables
Summary
本研究提出了一种基于弱监督的PET图像异常检测模型IgCONDA-PET。该模型采用注意力模块,利用隐扩散指导机制进行训练,无需像素级标注数据。模型可生成合成健康图像并比较其与异常输入图像的差异来检测异常。模型性能已与其他弱监督或无监督深度学习方法及传统方法进行比较验证。代码已公开。
Key Takeaways
- 提出了一种基于弱监督的PET图像异常检测模型IgCONDA-PET。
- 模型采用注意力模块,利用隐扩散指导机制进行训练,无需像素级标注数据。
- 模型通过生成合成健康图像并比较其与异常输入图像的差异来检测异常。
- 模型性能已与其他弱监督或无监督深度学习方法及传统方法进行比较验证。
- 公开了模型代码以便他人使用和研究。
- 强调了在网络检测小型异常时,注意力模块的重要性。
点此查看论文截图

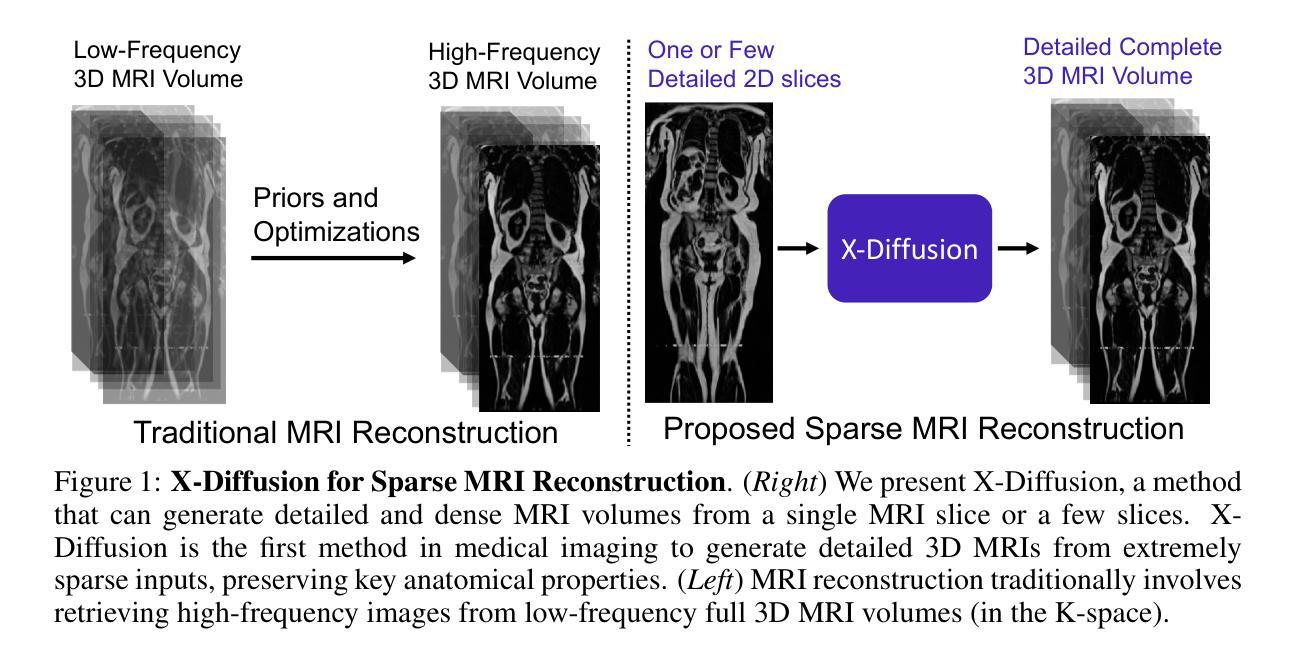
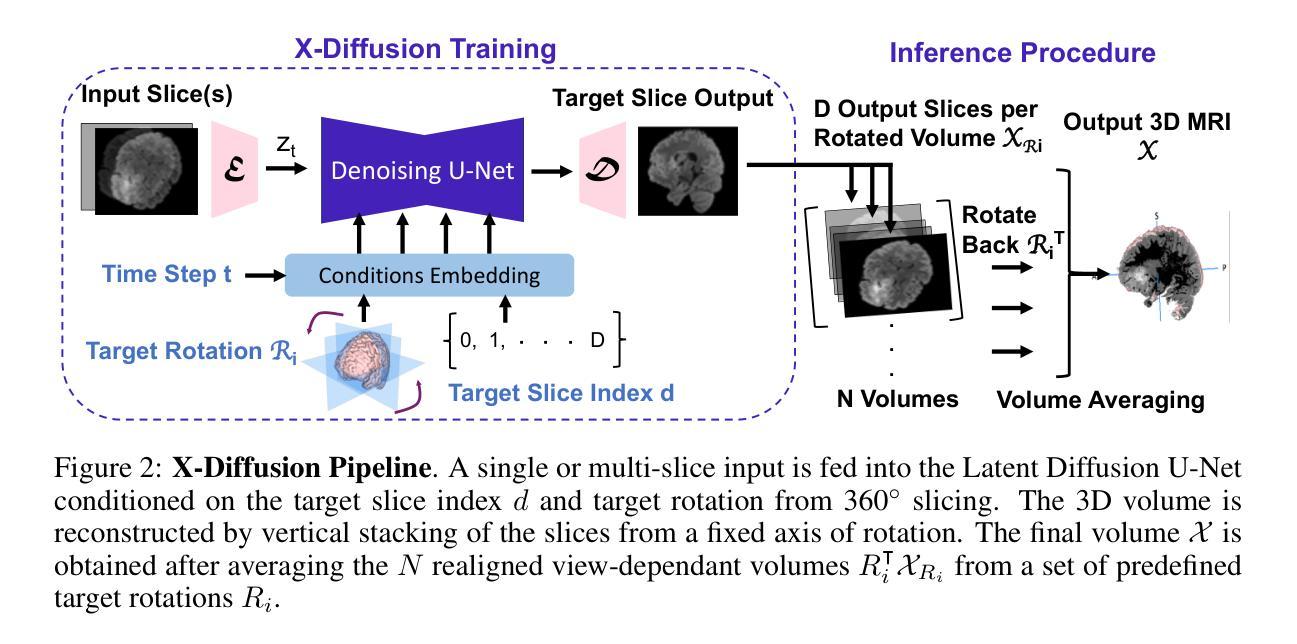
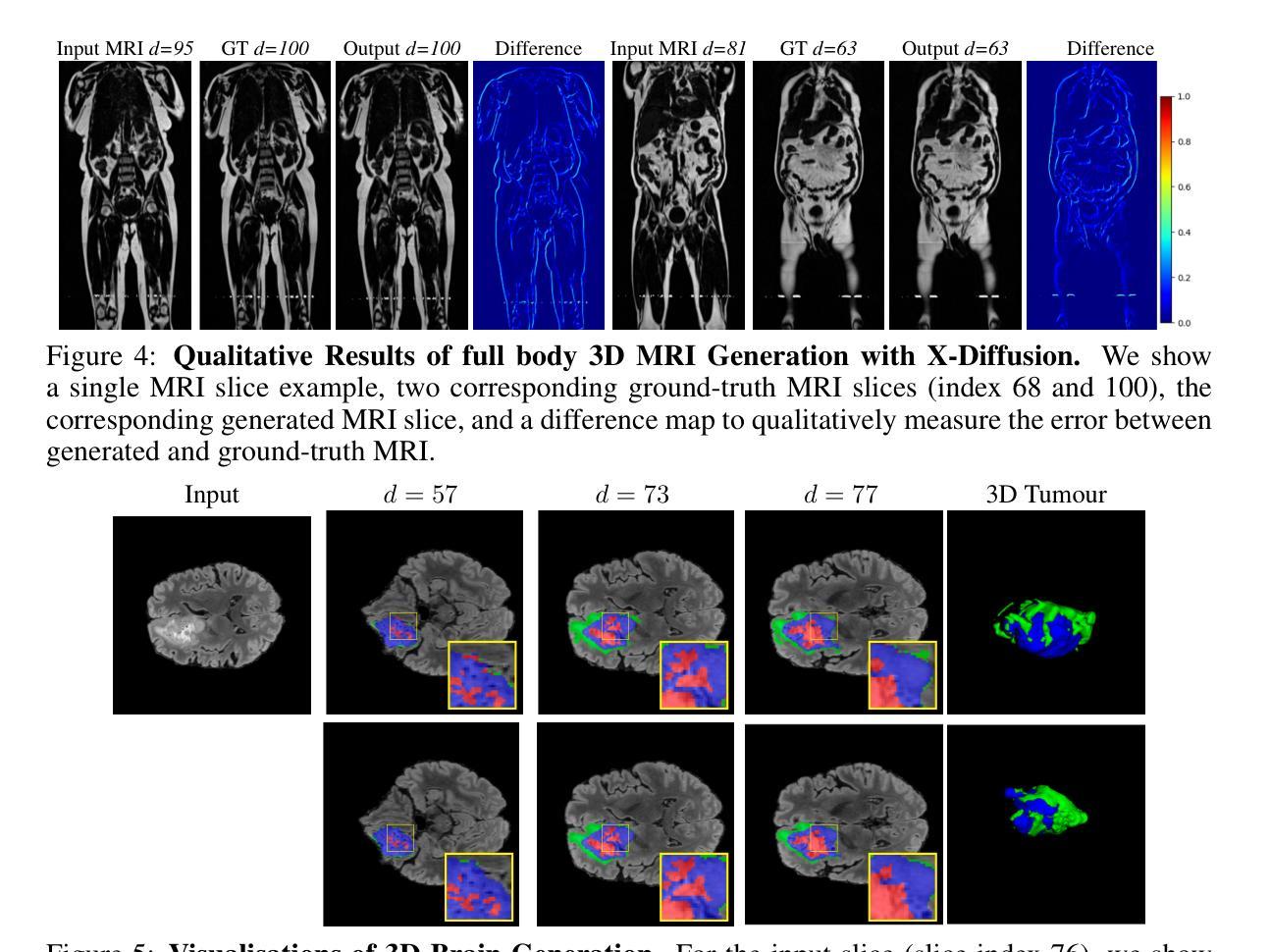
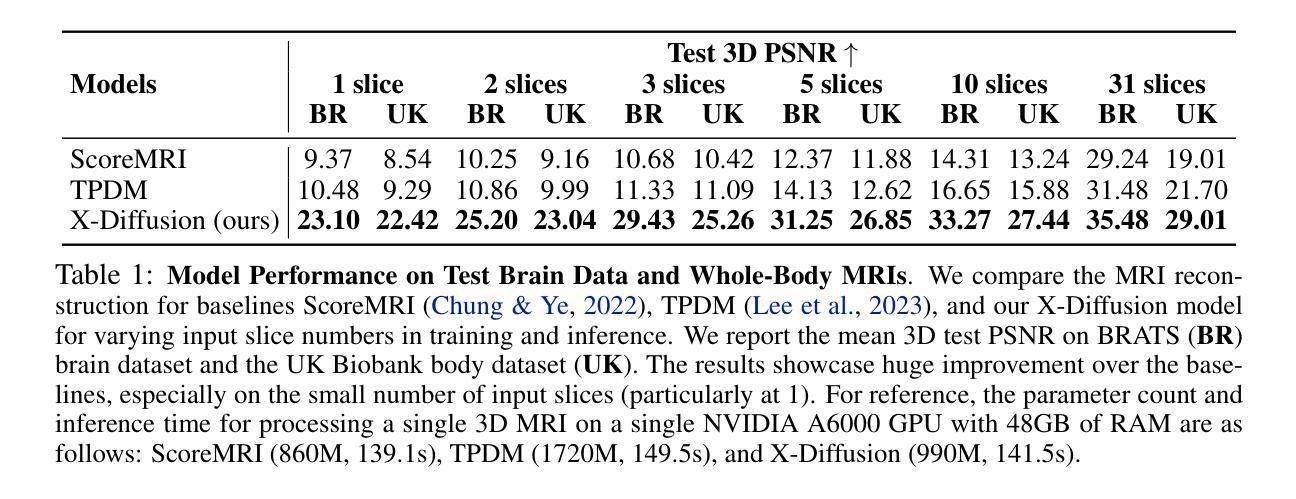
X-Diffusion: Generating Detailed 3D MRI Volumes From a Single Image Using Cross-Sectional Diffusion Models
Authors:Emmanuelle Bourigault, Abdullah Hamdi, Amir Jamaludin
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) is a crucial diagnostic tool, but high-resolution scans are often slow and expensive due to extensive data acquisition requirements. Traditional MRI reconstruction methods aim to expedite this process by filling in missing frequency components in the K-space, performing 3D-to-3D reconstructions that demand full 3D scans. In contrast, we introduce X-Diffusion, a novel cross-sectional diffusion model that reconstructs detailed 3D MRI volumes from extremely sparse spatial-domain inputs, achieving 2D-to-3D reconstruction from as little as a single 2D MRI slice or few slices. A key aspect of X-Diffusion is that it models MRI data as holistic 3D volumes during the cross-sectional training and inference, unlike previous learning approaches that treat MRI scans as collections of 2D slices in standard planes (coronal, axial, sagittal). We evaluated X-Diffusion on brain tumor MRIs from the BRATS dataset and full-body MRIs from the UK Biobank dataset. Our results demonstrate that X-Diffusion not only surpasses state-of-the-art methods in quantitative accuracy (PSNR) on unseen data but also preserves critical anatomical features such as tumor profiles, spine curvature, and brain volume. Remarkably, the model generalizes beyond the training domain, successfully reconstructing knee MRIs despite being trained exclusively on brain data. Medical expert evaluations further confirm the clinical relevance and fidelity of the generated images.To our knowledge, X-Diffusion is the first method capable of producing detailed 3D MRIs from highly limited 2D input data, potentially accelerating MRI acquisition and reducing associated costs. The code is available on the project website https://emmanuelleb985.github.io/XDiffusion/ .
磁共振成像(MRI)是一种重要的诊断工具,但高分辨率扫描通常由于需要大量数据采集而缓慢且昂贵。传统的MRI重建方法旨在通过填充K空间中的缺失频率成分来加快这一过程,进行需要完整3D扫描的3D-to-3D重建。相比之下,我们引入了X-Diffusion,这是一种新型截面扩散模型,能够从极稀疏的空间域输入中重建详细的3DMRI体积,仅使用少量或单个2DMRI切片即可实现2D-to-3D重建。X-Diffusion的一个关键方面是,它在截面训练和推断过程中将MRI数据建模为整体3D体积,不同于以往的学习方法将MRI扫描视为标准平面(冠状面、轴面、矢状面)中的2D切片集合。我们对BRATS数据集中的脑肿瘤MRI和UK Biobank数据集中的全身MRI进行了X-Diffusion评估。结果表明,X-Diffusion不仅在未见数据上的定量准确性(PSNR)上超越了最先进的方法,而且还保留了关键解剖特征,如肿瘤概况、脊柱曲度和脑容量。值得注意的是,该模型在训练领域之外也具有泛化能力,能够成功重建膝盖MRI,尽管它只接受脑部数据训练。医学专家评估进一步证实了生成图像的临床相关性和保真度。据我们所知,X-Diffusion是第一种能够从高度有限的2D输入数据生成详细的3DMRI的方法,有望加速MRI采集并降低相关成本。代码可在项目网站https://emmanuelleb985.github.io/XDiffusion/上获得。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF preprint, project website: https://emmanuelleb985.github.io/XDiffusion/
Summary
基于深度学习技术的X-Diffusion模型,能够从极少的二维MRI切片重建出详细的三维图像,实现快速且经济的三维MRI重建。该方法突破了传统方法的局限,为MRI诊断提供了新的可能性。
Key Takeaways
- X-Diffusion是一种新型交叉扩散模型,能够从极稀疏的空间域输入重建详细的三维MRI体积。
- 该方法实现了从单个或少数二维MRI切片的二维到三维重建。
- X-Diffusion将MRI数据视为整体三维体积进行训练和推断,与以往将MRI扫描视为二维切片集合的学习方法不同。
- 在BRATS和UK Biobank数据集上的实验结果表明,X-Diffusion在定量准确性(PSNR)上超越了现有方法,并保留了关键解剖特征。
- X-Diffusion能够推广到训练域之外,成功重建膝盖MRI,尽管只经过大脑数据训练。
- 医疗专家评估进一步证实了生成图像的临床相关性和保真度。
点此查看论文截图


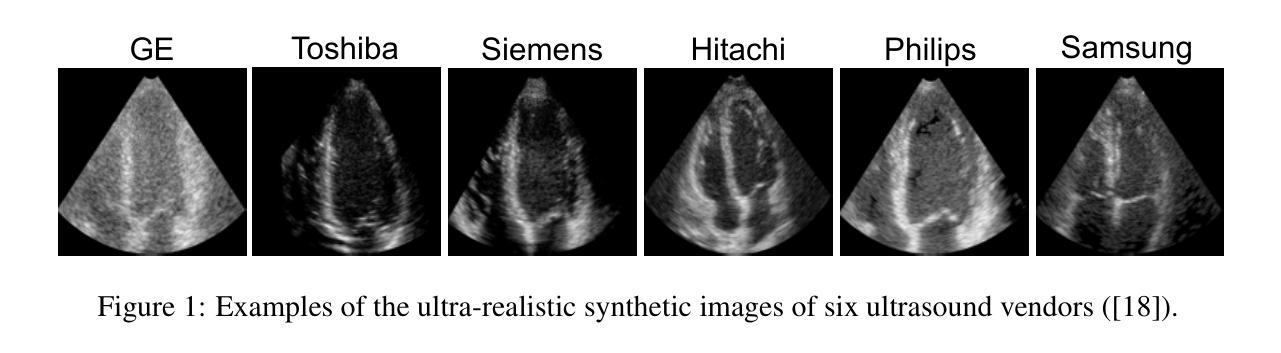
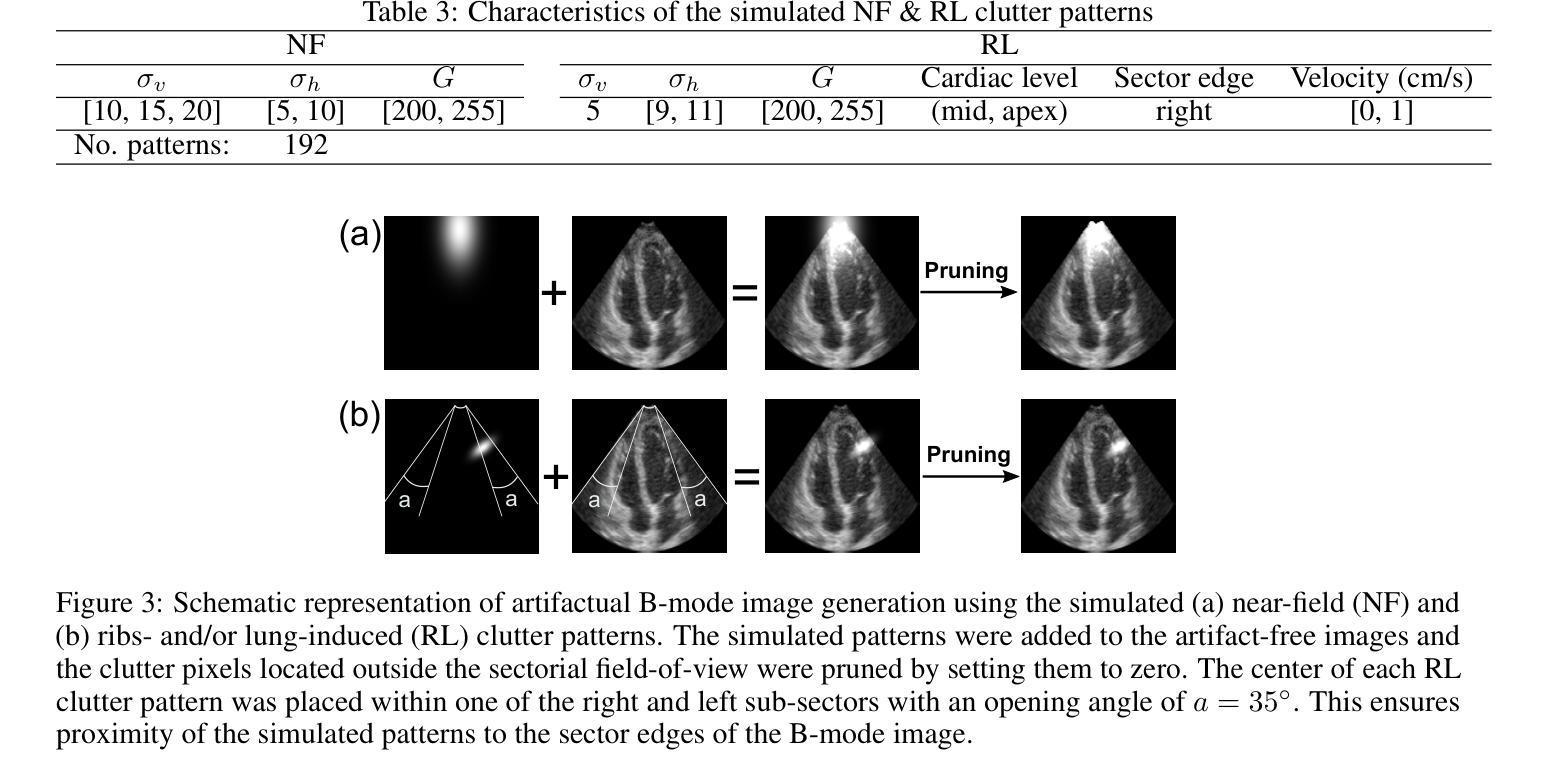
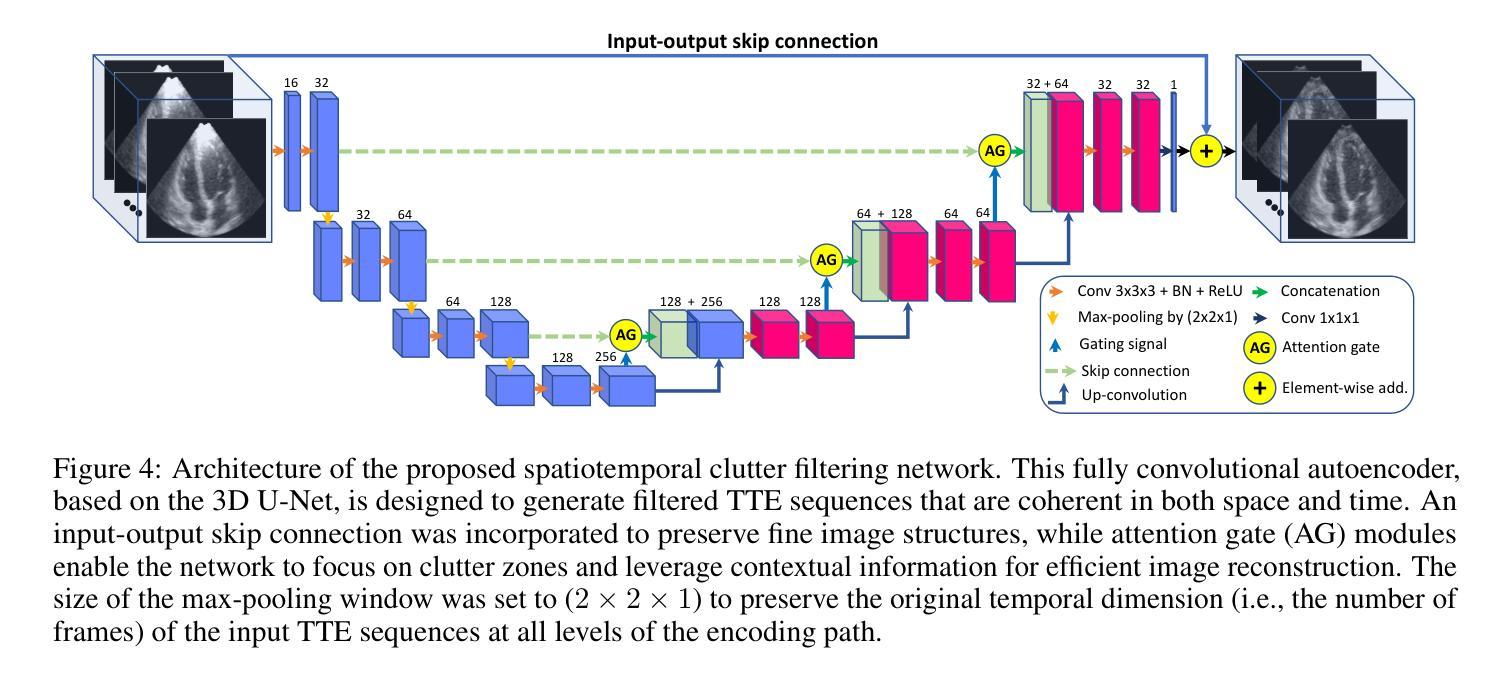
Deep Spatiotemporal Clutter Filtering of Transthoracic Echocardiographic Images: Leveraging Contextual Attention and Residual Learning
Authors:Mahdi Tabassian, Somayeh Akbari, Sandro Queirós, Jan D’hooge
This study presents a deep convolutional autoencoder network for filtering reverberation clutter from transthoracic echocardiographic (TTE) image sequences. Given the spatiotemporal nature of this type of clutter, the filtering network employs 3D convolutional layers to suppress it throughout the cardiac cycle. The design of the network incorporates two key features that contribute to the effectiveness of the filter: 1) an attention mechanism for focusing on cluttered regions and leveraging contextual information, and 2) residual learning for preserving fine image structures. To train the network, a diverse set of artifact patterns was simulated and superimposed onto ultra-realistic synthetic TTE sequences from six ultrasound vendors, generating input for the filtering network. The artifact-free sequences served as ground-truth. Performance of the filtering network was evaluated using unseen synthetic and in vivo artifactual sequences. Results from the in vivo dataset confirmed the network’s strong generalization capabilities, despite being trained solely on synthetic data and simulated artifacts. The suitability of the filtered sequences for downstream processing was assessed by computing segmental strain curves. A significant reduction in the discrepancy between strain profiles computed from cluttered and clutter-free segments was observed after filtering the cluttered sequences with the proposed network. The trained network processes a TTE sequence in a fraction of a second, enabling real-time clutter filtering and potentially improving the precision of clinically relevant indices derived from TTE sequences. The source code of the proposed method and example video files of the filtering results are available at: \href{https://github.com/MahdiTabassian/Deep-Clutter-Filtering/tree/main}{https://github.com/MahdiTabassian/Deep-Clutter-Filtering/tree/main}.
本研究提出了一种深度卷积自编码器网络,用于从胸部超声心动图(TTE)图像序列中过滤回声干扰。考虑到这种干扰的时空特性,过滤网络采用3D卷积层,在整个心动周期内抑制干扰。该网络的设计结合了两个关键特征,为过滤器的有效性做出了贡献:1)一种关注干扰区域的注意力机制和利用上下文信息;2)残差学习,以保留精细的图像结构。为了训练网络,模拟了各种伪影模式并将其叠加在来自六个超声供应商的超高真实度合成TTE序列上,以为过滤网络提供输入。无伪影序列作为地面实况(ground-truth)。过滤网络的性能通过未见过的合成和体内伪影序列进行了评估。体内数据集的结果证实了该网络强大的泛化能力,尽管它只接受合成数据和模拟伪影的训练。通过计算分段应变曲线评估了过滤序列对于下游处理的适用性。观察发现,在过滤带有干扰的序列后,与无干扰片段计算的应变曲线相比,干扰曲线之间的差异显著减少。训练后的网络能够在几分之一秒内处理一个TTE序列,实现了实时干扰过滤,并可能提高了从TTE序列中得出的临床相关指标的精度。所提出方法的源代码和过滤结果的示例视频文件可在以下网址找到:https://github.com/MahdiTabassian/Deep-Clutter-Filtering/tree/main。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 19 pages, 14 figures
摘要
本研究提出了一种深度卷积自编码器网络,用于从胸部超声心动图(TTE)图像序列中过滤混响干扰。该网络采用三维卷积层来抑制整个心动周期中的时空干扰。网络设计融入了两个关键特性,提高了滤波效果:一是关注干扰区域的注意力机制和利用上下文信息,二是保留图像细节的残差学习。为训练网络,模拟了多种伪影模式并将其叠加在来自六个超声供应商的超高真实度合成TTE序列上,作为滤波网络的输入。无伪影序列作为地面真实情况来评估滤波网络性能。通过未经验过的合成和体内干扰序列的评估结果证实,该网络在仅使用合成数据和模拟伪影进行训练的情况下仍具有强大的泛化能力。通过计算分段应变曲线评估过滤序列的下游处理适宜性。观察发现,与使用传统方法处理的干扰序列相比,使用所提网络过滤后,从干扰段计算的应变曲线之间的偏差显著降低。所训练的网络可在几分之一秒内处理TTE序列,实现实时干扰滤波,并可能提高从TTE序列派生的临床相关指标的精度。所提出方法的源代码和过滤结果示例视频文件可在https://github.com/MahdiTabassian/Deep-Clutter-Filtering/tree/main获得。
要点解析
- 本研究设计了一种深度卷积自编码器网络,旨在从胸部超声心动图(TTE)图像序列中去除混响干扰。
- 网络利用三维卷积层在心脏周期中抑制时空干扰。
- 网络设计的两大关键特性:注意力机制和残差学习,分别用于聚焦干扰区域、利用上下文信息及保留图像细节。
- 为训练网络,研究模拟多种伪影模式并将其添加到合成TTE序列中。
- 通过合成和体内数据评估网络性能,显示其在仅使用合成数据和模拟伪影训练时的强大泛化能力。
- 滤波后的序列在下游处理中的适用性通过计算分段应变曲线进行评估,显示明显改进。
点此查看论文截图



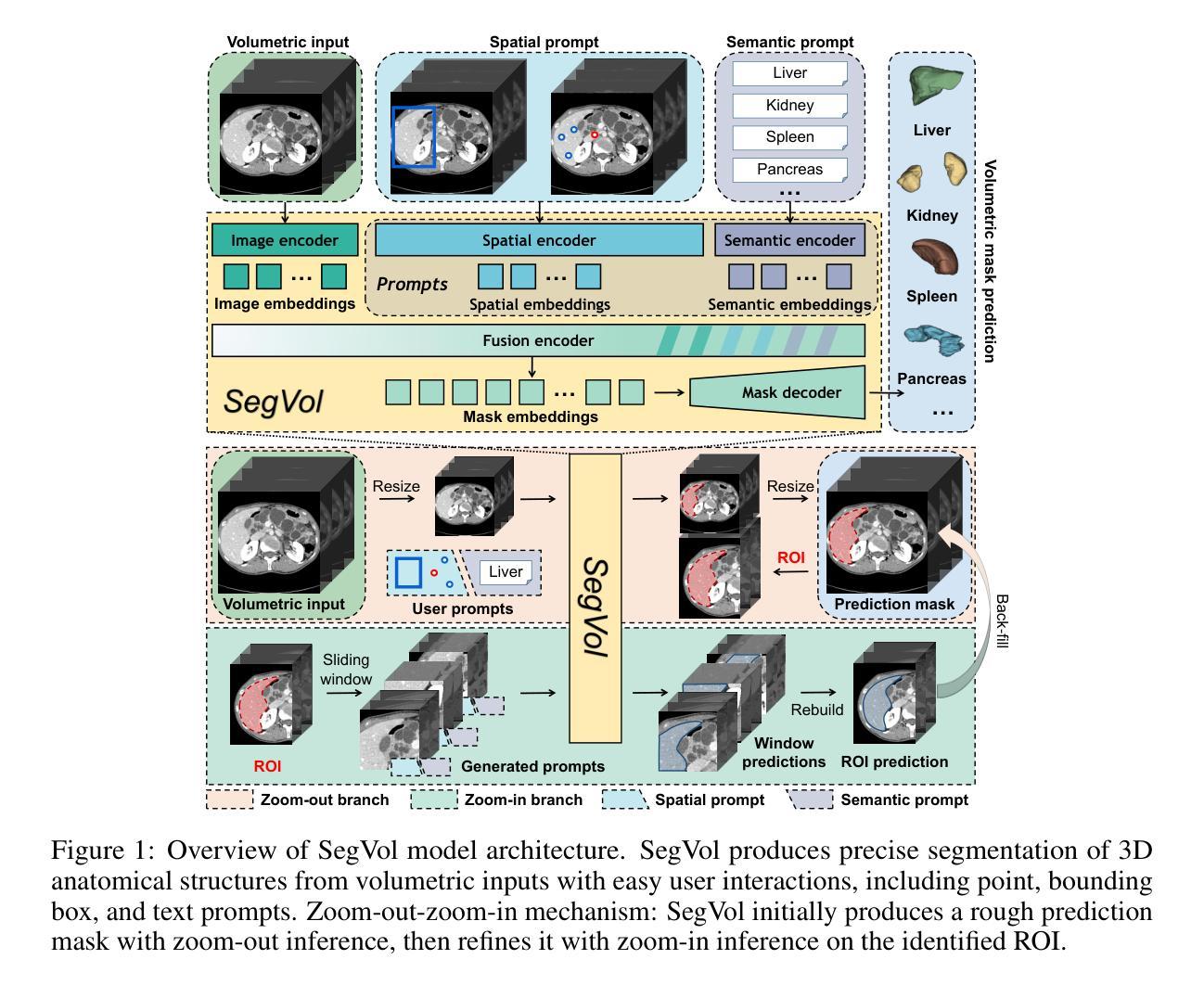
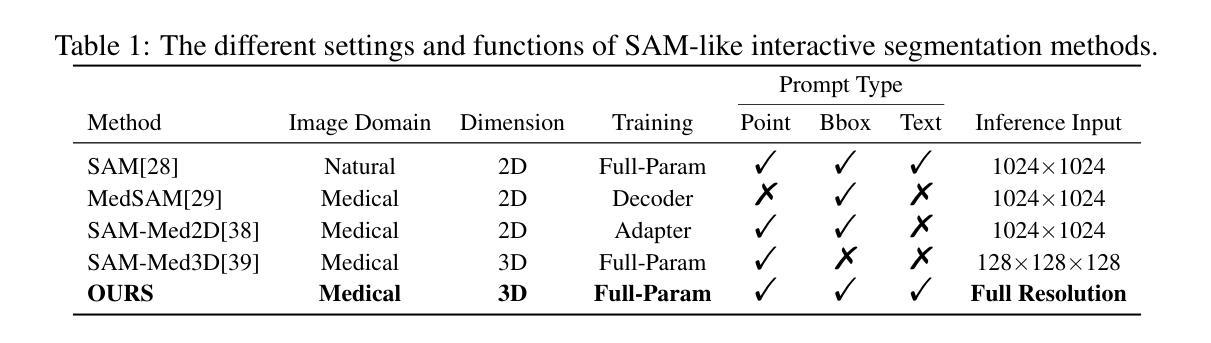
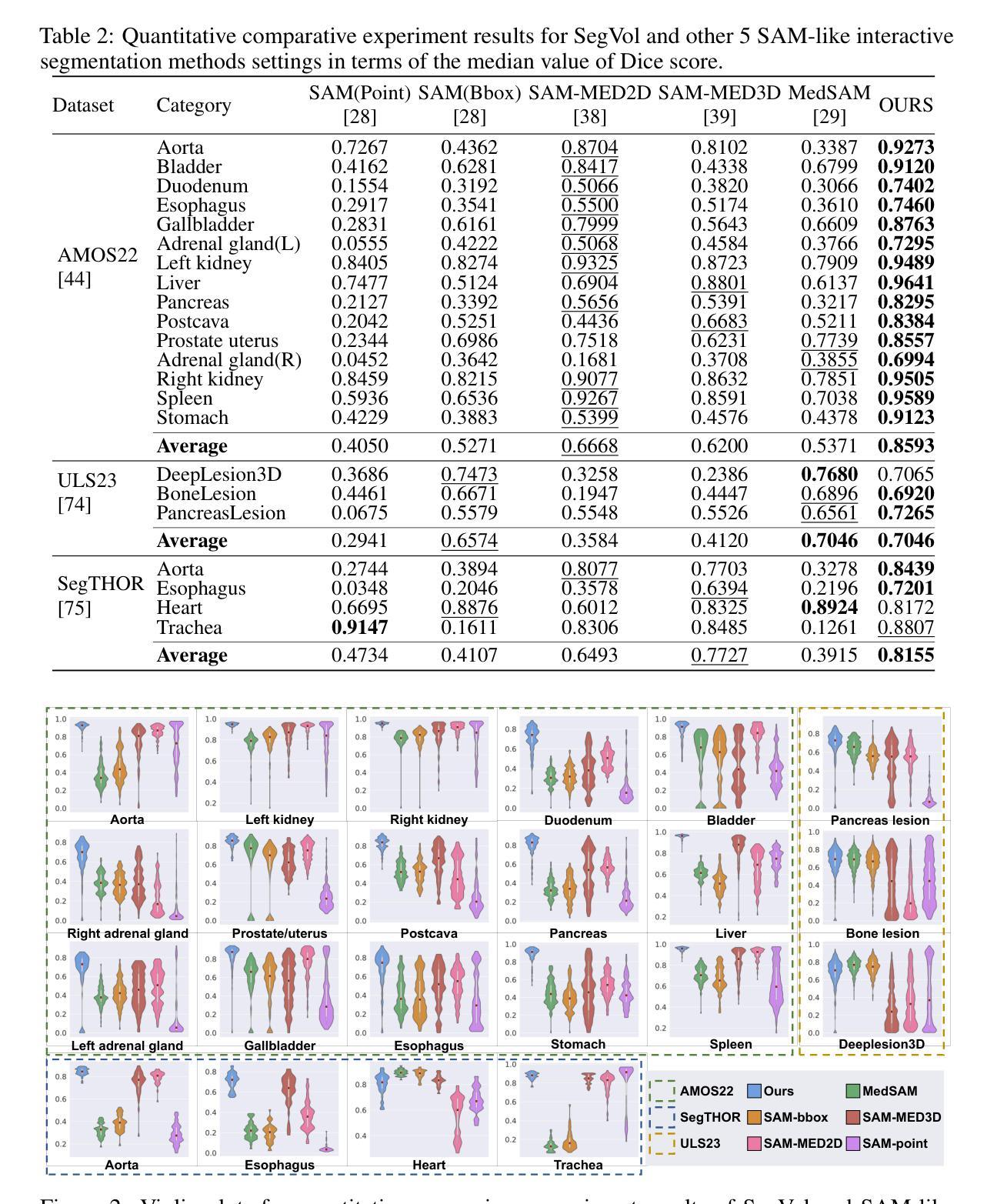
SegVol: Universal and Interactive Volumetric Medical Image Segmentation
Authors:Yuxin Du, Fan Bai, Tiejun Huang, Bo Zhao
Precise image segmentation provides clinical study with instructive information. Despite the remarkable progress achieved in medical image segmentation, there is still an absence of a 3D foundation segmentation model that can segment a wide range of anatomical categories with easy user interaction. In this paper, we propose a 3D foundation segmentation model, named SegVol, supporting universal and interactive volumetric medical image segmentation. By scaling up training data to 90K unlabeled Computed Tomography (CT) volumes and 6K labeled CT volumes, this foundation model supports the segmentation of over 200 anatomical categories using semantic and spatial prompts. To facilitate efficient and precise inference on volumetric images, we design a zoom-out-zoom-in mechanism. Extensive experiments on 22 anatomical segmentation tasks verify that SegVol outperforms the competitors in 19 tasks, with improvements up to 37.24% compared to the runner-up methods. We demonstrate the effectiveness and importance of specific designs by ablation study. We expect this foundation model can promote the development of volumetric medical image analysis. The model and code are publicly available at: https://github.com/BAAI-DCAI/SegVol.
精确图像分割为临床研究提供了指导性信息。尽管医学图像分割已经取得了显著的进展,但仍然缺乏一种3D基础分割模型,该模型能够在广泛的解剖类别中进行分割,并具备简单的用户交互功能。在本文中,我们提出了一种名为SegVol的3D基础分割模型,支持通用和交互式体积医学图像分割。通过扩大训练数据至9万份无标签计算机断层扫描(CT)体积数据和6千份标记CT体积数据,该基础模型支持超过200个解剖类别的分割,使用语义和空间提示。为了方便对体积图像进行高效和精确的推理,我们设计了一种缩放退出和缩放进入机制。在22个解剖分割任务上的大量实验表明,SegVol在19个任务中超过了竞争对手,相较于排名第二的方法改进了高达37.24%。我们通过消融研究证明了特定设计的有效性和重要性。我们预计这个基础模型可以促进体积医学图像分析的发展。模型和代码公开可用:https://github.com/BAAI-DCAI/SegVol。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF NeurIPS 2024 Spotlight
Summary
医学图像分割在临床研究中提供重要信息。尽管医学图像分割取得了显著进展,但仍缺乏一个能在广泛解剖类别中进行分割的3D基础分割模型,且需要易于用户交互。本文提出了一种名为SegVol的3D基础分割模型,支持通用和交互式体积医学图像分割。通过扩大训练数据至9万无标签计算机断层扫描(CT)体积和6千标记CT体积,该基础模型使用语义和空间提示支持超过200个解剖类别的分割。为在体积图像上进行高效和精确推理,我们设计了缩放机制。在22个解剖分割任务上的大量实验表明,SegVol在19个任务中优于竞争对手,相较于次优方法,改进率高达37.24%。我们通过消融研究证明了特定设计的有效性和重要性。期望此基础模型能促进体积医学图像分析的发展。模型和代码公开于:https://github.com/BAAI-DCAI/SegVol。
Key Takeaways
- 医学图像分割为临床研究提供关键信息。
- 当前缺乏一个能在广泛解剖类别中进行分割的3D基础分割模型,需改进以易于用户交互。
- SegVol是一个新的3D基础分割模型,支持通用和交互式体积医学图像分割。
- SegVol通过扩大训练数据至大量CT体积图像来提高性能。
- SegVol在多数解剖分割任务上表现优于竞争对手,改进效果显著。
- SegVol设计包括缩放机制以高效和精确地进行体积图像推理。
点此查看论文截图

Volumetric medical image segmentation through dual self-distillation in U-shaped networks
Authors:Soumyanil Banerjee, Nicholas Summerfield, Ming Dong, Carri Glide-Hurst
U-shaped networks and its variants have demonstrated exceptional results for medical image segmentation. In this paper, we propose a novel dual self-distillation (DSD) framework in U-shaped networks for volumetric medical image segmentation. DSD distills knowledge from the ground-truth segmentation labels to the decoder layers. Additionally, DSD also distills knowledge from the deepest decoder and encoder layer to the shallower decoder and encoder layers respectively of a single U-shaped network. DSD is a generalized training strategy that could be attached to the backbone architecture of any U-shaped network to further improve its segmentation performance. We attached DSD on several state-of-the-art U-shaped backbones, and extensive experiments on various public 3D medical image segmentation datasets (cardiac substructure, brain tumor and Hippocampus) demonstrated significant improvement over the same backbones without DSD. On average, after attaching DSD to the U-shaped backbones, we observed an increase of 2.82%, 4.53% and 1.3% in Dice similarity score, a decrease of 7.15 mm, 6.48 mm and 0.76 mm in the Hausdorff distance, for cardiac substructure, brain tumor and Hippocampus segmentation, respectively. These improvements were achieved with negligible increase in the number of trainable parameters and training time. Our proposed DSD framework also led to significant qualitative improvements for cardiac substructure, brain tumor and Hippocampus segmentation over the U-shaped backbones. The source code is publicly available at https://github.com/soumbane/DualSelfDistillation.
U形网络及其变体在医学图像分割方面表现出了卓越的结果。在本文中,我们在U形网络中提出了一种新型的双自蒸馏(DSD)框架,用于体积医学图像分割。DSD从真实的分割标签中提炼知识并将其传递给解码器层。此外,DSD还从最深层的解码器和编码器层提炼知识,并将其分别传递给较浅层的解码器和编码器层,在同一U形网络中。DSD是一种通用的训练策略,可以附加到任何U形网络的骨干架构上,以进一步提高其分割性能。我们在一些最先进的U形骨干网络上附加了DSD,在各种公共3D医学图像分割数据集(心脏子结构、脑肿瘤和海马体)上进行的大量实验表明,与没有DSD的相同骨干网络相比,DSD取得了显著的改进。平均而言,在U形骨干网络上附加DSD后,我们观察到Dice相似度得分提高了2.82%、4.53%和1.3%,心脏子结构、脑肿瘤和海马体分割的Hausdorff距离分别减少了7.15毫米、6.48毫米和0.76毫米。这些改进是在可训练参数数量和训练时间增加甚微的情况下实现的。我们提出的DSD框架还导致心脏子结构、脑肿瘤和海马体分割的定性显著改进,超过了U形骨干网络。源代码可在https://github.com/soumbane/DualSelfDistillation公开获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 27 pages, 5 figures, 7 tables, preliminary version accepted at IEEE ISBI 2024
Summary
本文提出一种新型的双重自蒸馏(DSD)框架,应用于U型网络,用于体积医学图像分割。DSD从地面真实分割标签中提炼知识并传输到解码器层,同时也将最深解码器和编码器的知识传输到较浅的解码器和编码器层。DSD是一种通用训练策略,可附加到任何U型网络的骨干架构上,以进一步提高其分割性能。在多个公共3D医学图像分割数据集上进行的实验表明,与没有DSD的相同骨干相比,添加DSD后性能显著提升。
Key Takeaways
- 双重自蒸馏(DSD)框架被提出并应用于U型网络,用于体积医学图像分割。
- DSD从地面真实分割标签和最深解码器与编码器层中提炼知识。
- DSD可附加到任何U型网络的骨干架构上,以提高分割性能。
- 在多个公共3D医学图像分割数据集上,添加DSD后,Dice相似度得分平均提高2.82%、4.53%和1.3%,Hausdorff距离平均减少7.15mm、6.48mm和0.76mm。
- DSD导致的参数增加和训练时间延长微乎其微。
- DSD框架在医学图像分割质量上有显著改进。
- 源代码已公开发布在https://github.com/soumbane/DualSelfDistillation。
点此查看论文截图