⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-02-15 更新
Utilizing 3D Fast Spin Echo Anatomical Imaging to Reduce the Number of Contrast Preparations in $T_{1ρ}$ Quantification of Knee Cartilage Using Learning-Based Methods
Authors:Junru Zhong, Chaoxing Huang, Ziqiang Yu, Fan Xiao, Siyue Li, Tim-Yun Michael Ong, Ki-Wai Kevin Ho, Queenie Chan, James F. Griffith, Weitian Chen
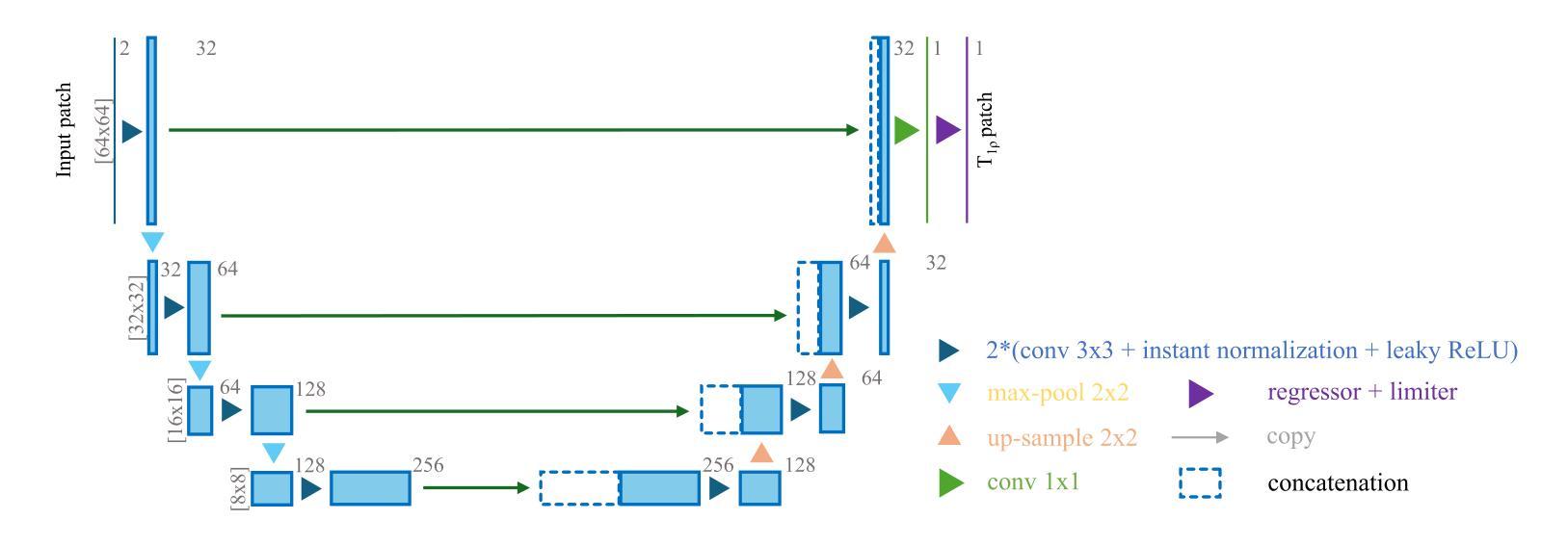
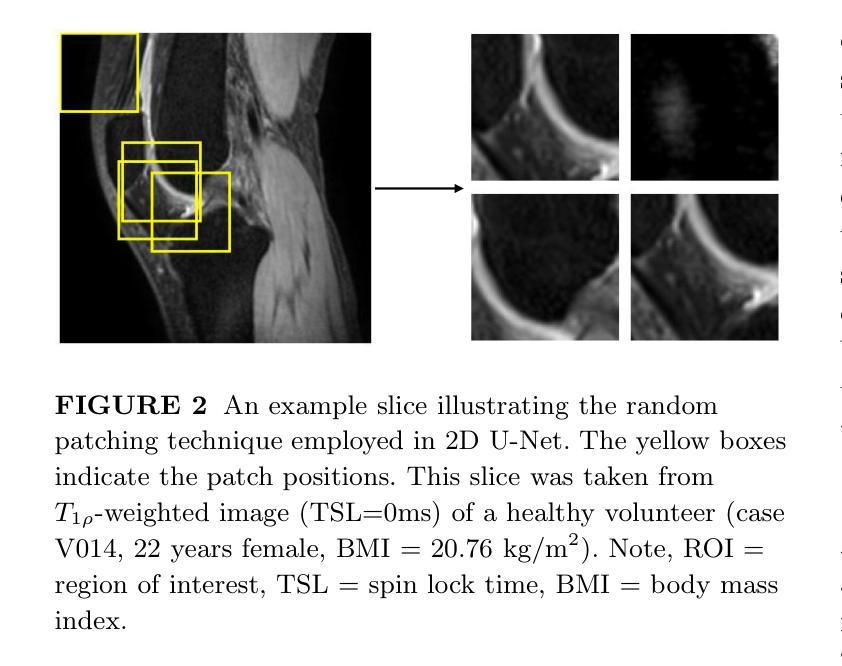
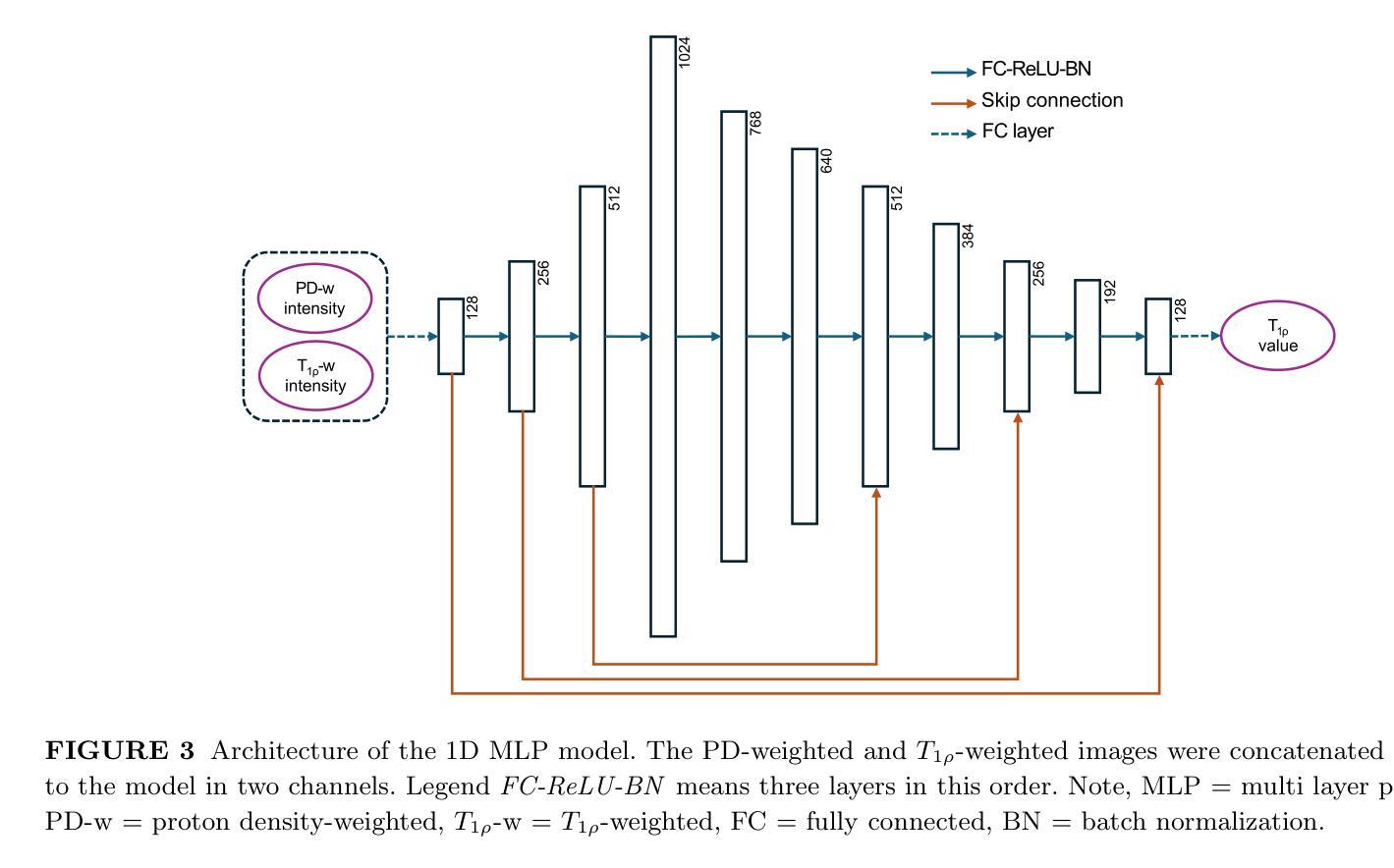
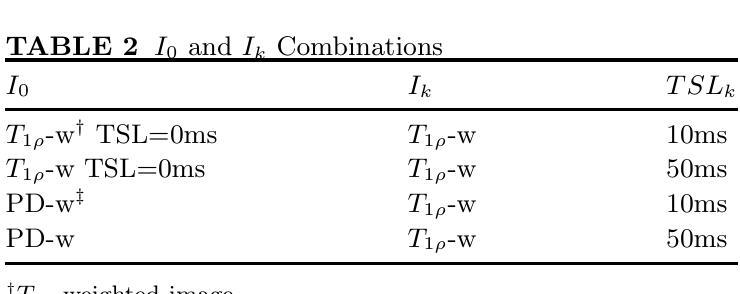
Purpose: To propose and evaluate an accelerated $T_{1\rho}$ quantification method that combines $T_{1\rho}$-weighted fast spin echo (FSE) images and proton density (PD)-weighted anatomical FSE images, leveraging deep learning models for $T_{1\rho}$ mapping. The goal is to reduce scan time and facilitate integration into routine clinical workflows for osteoarthritis (OA) assessment. Methods: This retrospective study utilized MRI data from 40 participants (30 OA patients and 10 healthy volunteers). A volume of PD-weighted anatomical FSE images and a volume of $T_{1\rho}$-weighted images acquired at a non-zero spin-lock time were used as input to train deep learning models, including a 2D U-Net and a multi-layer perceptron (MLP). $T_{1\rho}$ maps generated by these models were compared with ground truth maps derived from a traditional non-linear least squares (NLLS) fitting method using four $T_{1\rho}$-weighted images. Evaluation metrics included mean absolute error (MAE), mean absolute percentage error (MAPE), regional error (RE), and regional percentage error (RPE). Results: Deep learning models achieved RPEs below 5% across all evaluated scenarios, outperforming NLLS methods, especially in low signal-to-noise conditions. The best results were obtained using the 2D U-Net, which effectively leveraged spatial information for accurate $T_{1\rho}$ fitting. The proposed method demonstrated compatibility with shorter TSLs, alleviating RF hardware and specific absorption rate (SAR) limitations. Conclusion: The proposed approach enables efficient $T_{1\rho}$ mapping using PD-weighted anatomical images, reducing scan time while maintaining clinical standards. This method has the potential to facilitate the integration of quantitative MRI techniques into routine clinical practice, benefiting OA diagnosis and monitoring.
目的:提出并评估一种结合$T_{1\rho}$加权快速自旋回波(FSE)图像和质子密度(PD)加权解剖FSE图像的加速$T_{1\rho}$定量方法,利用深度学习模型进行$T_{1\rho}$映射。旨在缩短扫描时间,便于骨关节炎(OA)评估的常规临床工作流程集成。方法:这项回顾性研究使用了来自40名参与者(30名OA患者和10名健康志愿者)的MRI数据。使用PD加权解剖FSE图像体积和在不同自旋锁定时间获得的$T_{1\rho}$加权图像体积来训练深度学习模型,包括二维U-Net和多层感知器(MLP)。通过传统非线性最小二乘(NLLS)拟合方法使用四张$T_{1\rho}$加权图像得出的真实地图比较这些模型生成的$T_{1\rho}$图。评估指标包括平均绝对误差(MAE)、平均绝对百分比误差(MAPE)、区域误差(RE)和区域百分比误差(RPE)。结果:深度学习模型的RPE在所有评估场景中低于5%,优于NLLS方法,特别是在低信噪比条件下。使用二维U-Net获得了最佳结果,该网络有效利用空间信息进行准确的$T_{1\rho}$拟合。所提出的方法证明了与较短TSL的兼容性,缓解了射频硬件和特定吸收率(SAR)的限制。结论:所提出的方法利用PD加权解剖图像有效地进行$T_{1\rho}$映射,缩短了扫描时间,同时保持了临床标准。这种方法有可能促进定量MRI技术融入常规临床实践,有益于OA的诊断和监测。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Submitted to Magnetic Resonance in Medicine
Summary
本文提出了一种结合$T_{1\rho}$加权快速自旋回波(FSE)图像和质子密度(PD)加权解剖FSE图像的加速$T_{1\rho}$定量方法,利用深度学习模型进行$T_{1\rho}$映射。该研究旨在减少扫描时间,促进定量核磁共振成像技术融入日常临床实践中,以评估骨关节炎(OA)。深度学习模型表现出优异性能,特别是在低信噪比条件下,能够有效进行$T_{1\rho}$拟合。此方法具有潜力推动临床诊断和治疗的发展。
Key Takeaways
- 研究提出了结合$T_{1\rho}$-加权和PD-加权图像的深度学习模型用于$T_{1\rho}$定量分析的方法。
- 该方法旨在减少扫描时间,并促进在临床实践中对骨关节炎(OA)的评估。
- 深度学习模型在$T_{1\rho}$映射方面表现出优异性能,特别是在低信噪比条件下。
- 2D U-Net模型能有效利用空间信息进行$T_{1\rho}$拟合,获得最佳结果。
- 该方法兼容较短的TSL,减轻了射频硬件和特定吸收率(SAR)的限制。
- 此方法具有潜力推动定量MRI技术融入日常临床实践,有助于OA的诊断和监测。
点此查看论文截图


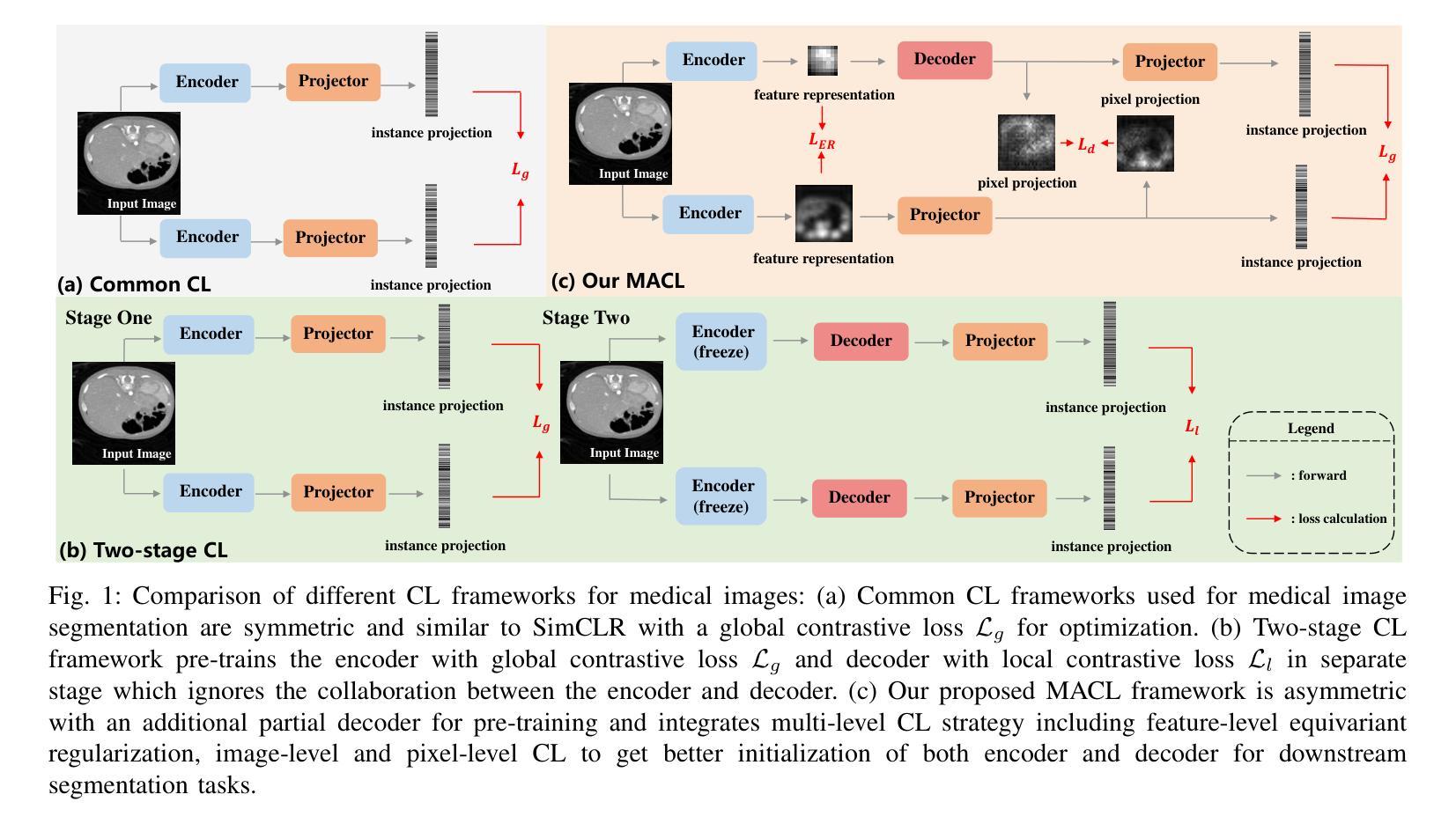
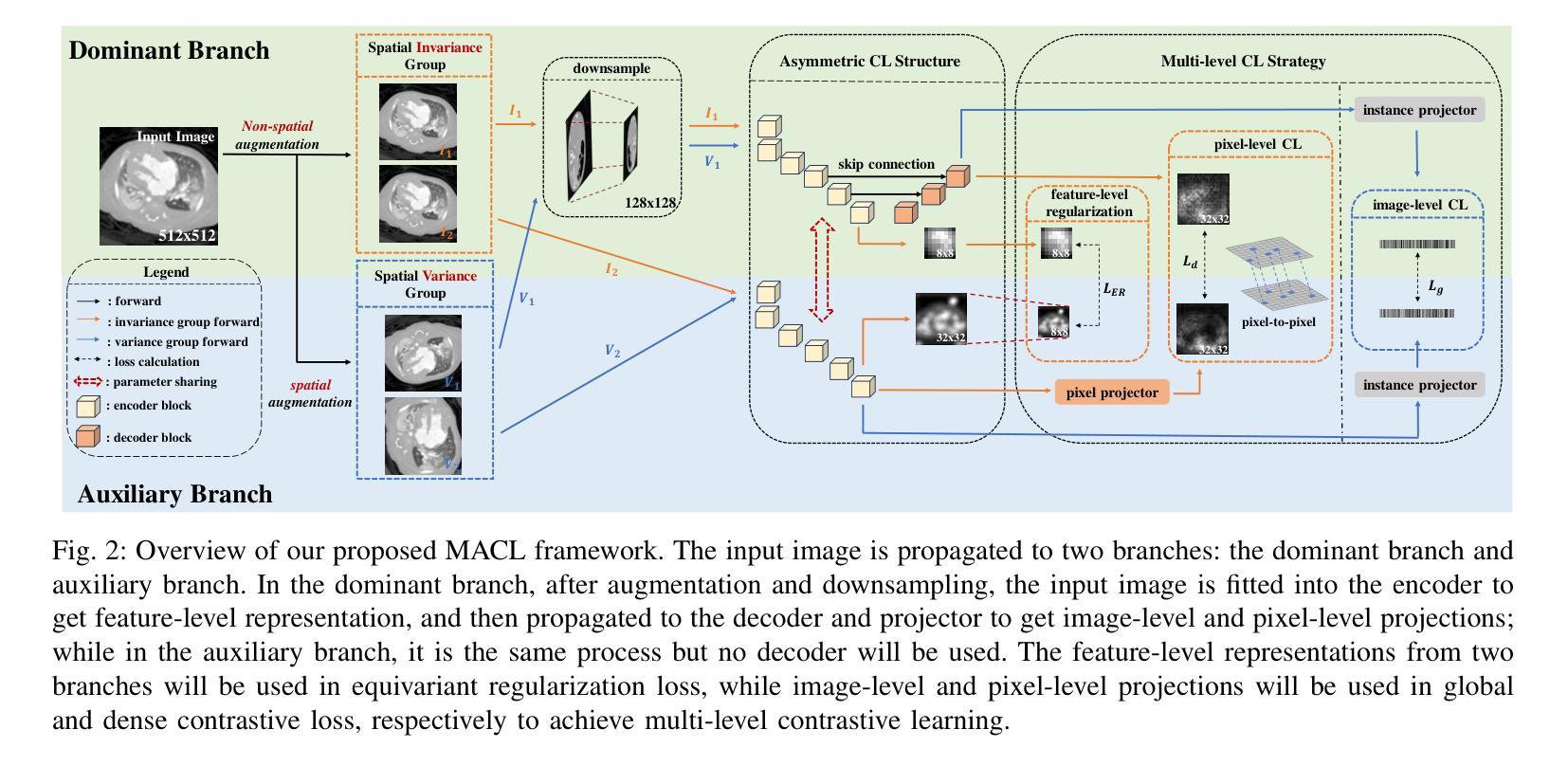
Multi-level Asymmetric Contrastive Learning for Volumetric Medical Image Segmentation Pre-training
Authors:Shuang Zeng, Lei Zhu, Xinliang Zhang, Micky C Nnamdi, Wenqi Shi, J Ben Tamo, Qian Chen, Hangzhou He, Lujia Jin, Zifeng Tian, Qiushi Ren, Zhaoheng Xie, Yanye Lu
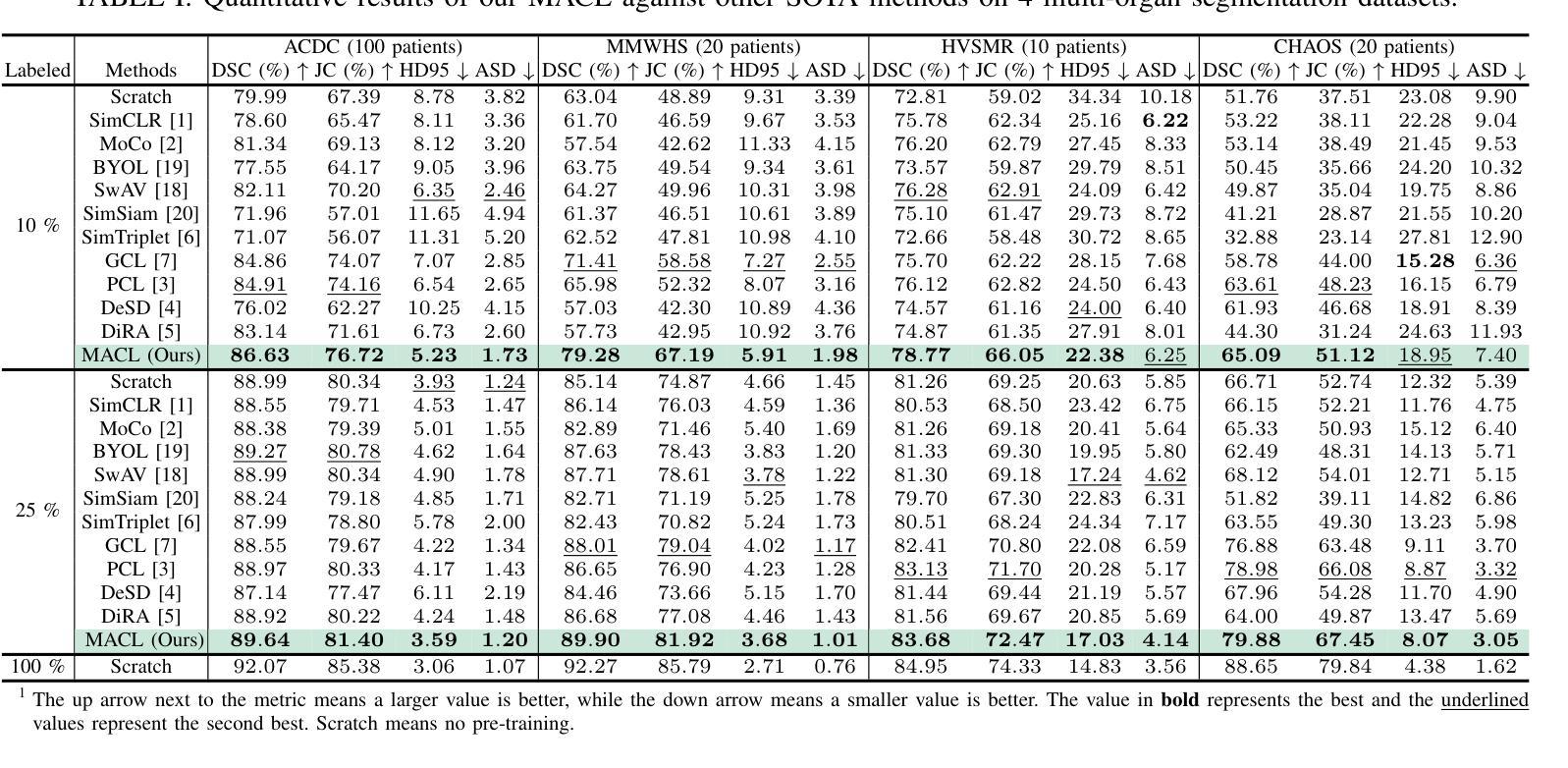
Medical image segmentation is a fundamental yet challenging task due to the arduous process of acquiring large volumes of high-quality labeled data from experts. Contrastive learning offers a promising but still problematic solution to this dilemma. Firstly existing medical contrastive learning strategies focus on extracting image-level representation, which ignores abundant multi-level representations. Furthermore they underutilize the decoder either by random initialization or separate pre-training from the encoder, thereby neglecting the potential collaboration between the encoder and decoder. To address these issues, we propose a novel multi-level asymmetric contrastive learning framework named MACL for volumetric medical image segmentation pre-training. Specifically, we design an asymmetric contrastive learning structure to pre-train encoder and decoder simultaneously to provide better initialization for segmentation models. Moreover, we develop a multi-level contrastive learning strategy that integrates correspondences across feature-level, image-level, and pixel-level representations to ensure the encoder and decoder capture comprehensive details from representations of varying scales and granularities during the pre-training phase. Finally, experiments on 8 medical image datasets indicate our MACL framework outperforms existing 11 contrastive learning strategies. i.e. Our MACL achieves a superior performance with more precise predictions from visualization figures and 1.72%, 7.87%, 2.49% and 1.48% Dice higher than previous best results on ACDC, MMWHS, HVSMR and CHAOS with 10% labeled data, respectively. And our MACL also has a strong generalization ability among 5 variant U-Net backbones. Our code will be released at https://github.com/stevezs315/MACL.
医学图像分割是一项基础且具有挑战性的任务,因为从专家那里获取大量高质量标注数据的过程非常艰难。对比学习为解决这一难题提供了有前景但仍有问题的解决方案。首先,现有的医学对比学习策略侧重于提取图像级别的表示,这忽略了丰富的多层次表示。此外,它们要么通过随机初始化来利用解码器,要么将编码器进行预先训练,从而忽略了编码器和解码器之间的潜在协作。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了一种名为MACL的新型多层次不对称对比学习框架,用于医学图像分割的预训练。具体来说,我们设计了一种不对称对比学习结构,同时预训练编码器和解码器,为分割模型提供更好的初始化。此外,我们开发了一种多层次对比学习策略,该策略结合了特征级、图像级和像素级表示的对应关系,以确保编码器和解码器在预训练阶段从各种规模和粒度的表示中捕获全面的细节。最后,在8个医学图像数据集上的实验表明,我们的MACL框架优于现有的11种对比学习策略。例如,我们的MACL实现了更高的性能,预测结果更为精确,并且在ACDC、MMWHS、HVSMR和CHAOS数据集上的Dice值分别比之前的最佳结果高出1.72%、7.87%、2.49%和1.48%,在标注数据为10%的情况下亦然。此外,我们的MACL在五种变体U-Net骨干网中具有强大的泛化能力。我们的代码将在https://github.com/stevezs315/MACL上发布。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种名为MACL的多层次不对称对比学习框架,用于解决医学图像分割任务中数据标注困难的问题。MACL框架通过设计不对称对比学习结构,同时预训练编码器和解码器,提供更佳的分割模型初始化。此外,MACL采用多层次对比学习策略,整合特征级、图像级和像素级的表示对应,确保编码器和解码器在预训练阶段捕捉不同尺度和粒度的综合细节。实验结果显示,MACL框架在8个医学图像数据集上的表现优于现有的11种对比学习策略,特别是在ACDC、MMWHS、HVSMR和CHAOS数据集上取得了较高的Dice系数。此外,MACL框架具有强大的泛化能力,适用于多种U-Net变体。
Key Takeaways
- MACL框架采用多层次不对称对比学习策略,同时预训练编码器和解码器,以提升医学图像分割模型的性能。
- MACL通过整合多层次(特征级、图像级和像素级)的对比学习,捕捉不同尺度和粒度的细节信息。
- 实验结果显示MACL在多个医学图像数据集上表现优异,特别是在ACDC、MMWHS、HVSMR和CHAOS数据集上的Dice系数较高。
- MACL框架具有较强的泛化能力,适用于多种U-Net变体。
- 该研究提出的MACL框架代码将公开在https://github.com/stevezs315/MACL。
点此查看论文截图