⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-02-15 更新
EmbodiedBench: Comprehensive Benchmarking Multi-modal Large Language Models for Vision-Driven Embodied Agents
Authors:Rui Yang, Hanyang Chen, Junyu Zhang, Mark Zhao, Cheng Qian, Kangrui Wang, Qineng Wang, Teja Venkat Koripella, Marziyeh Movahedi, Manling Li, Heng Ji, Huan Zhang, Tong Zhang
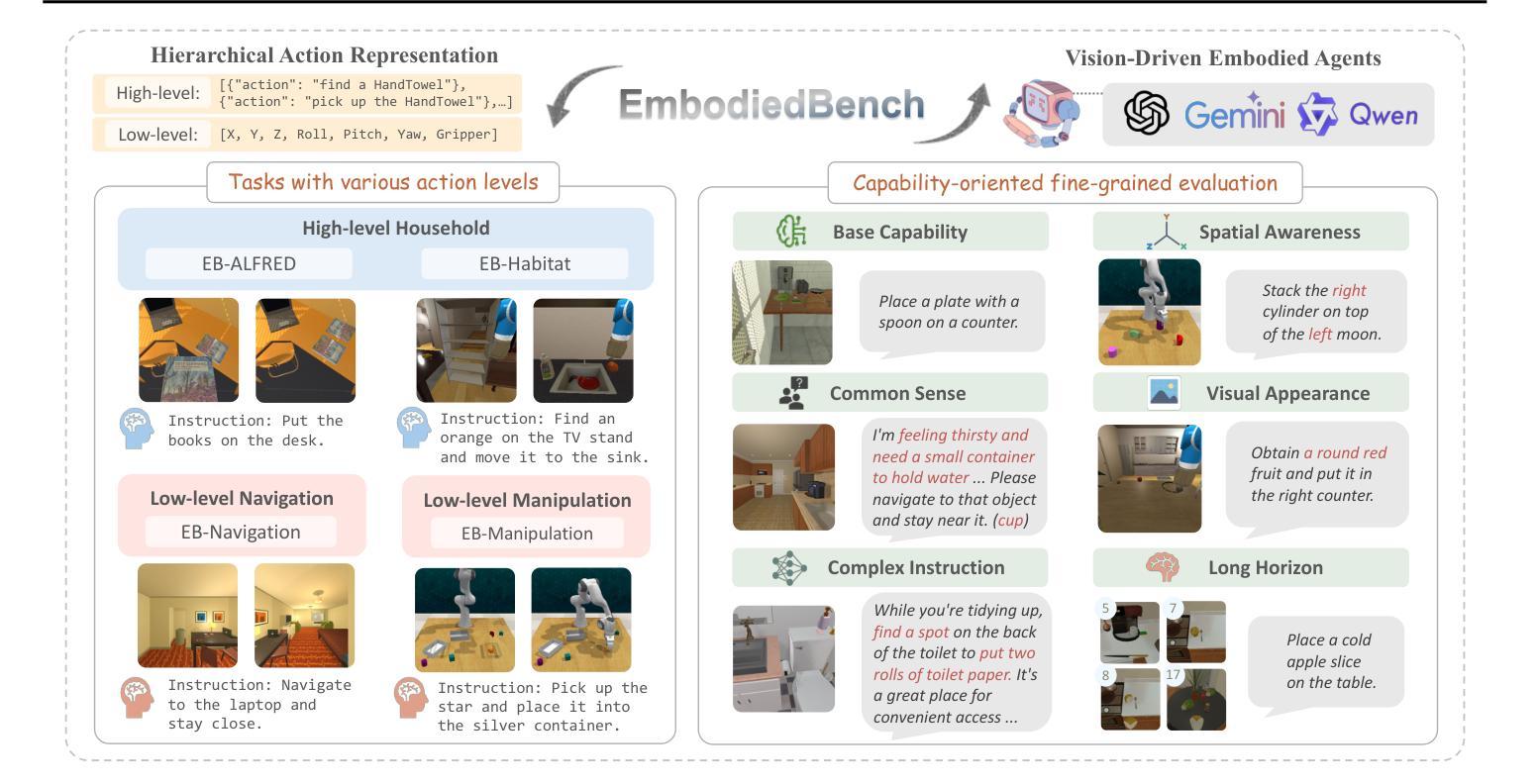
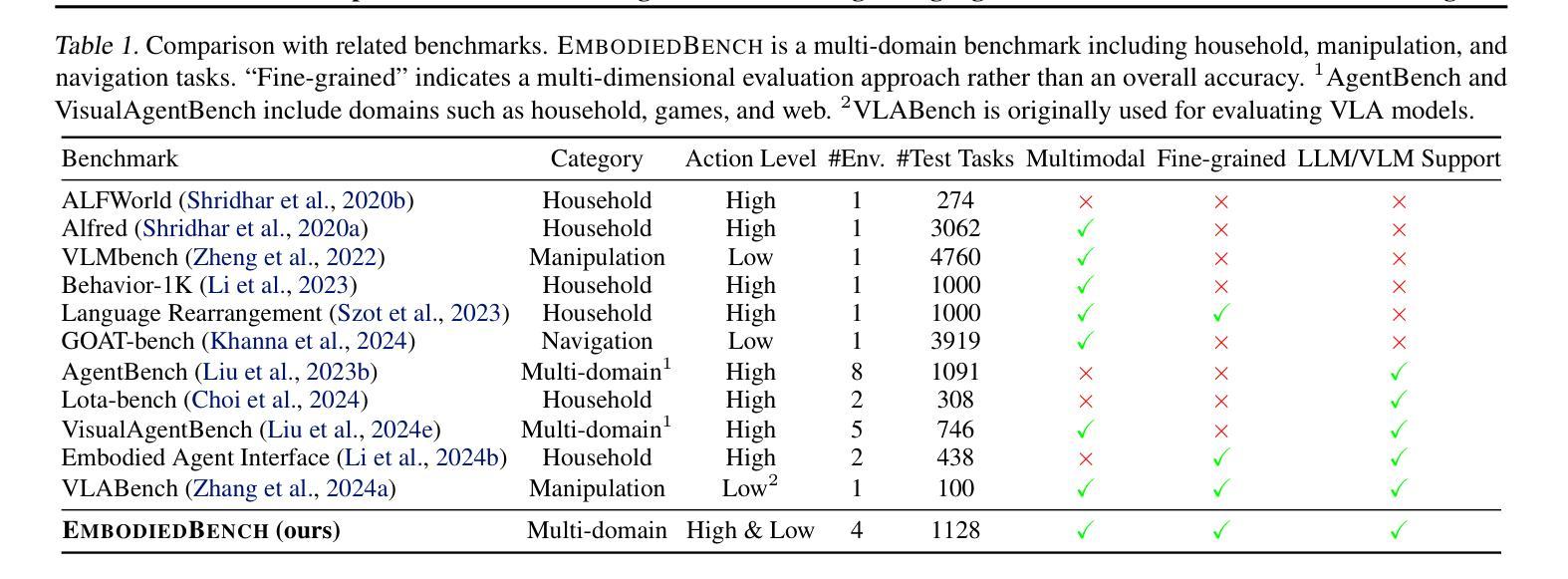
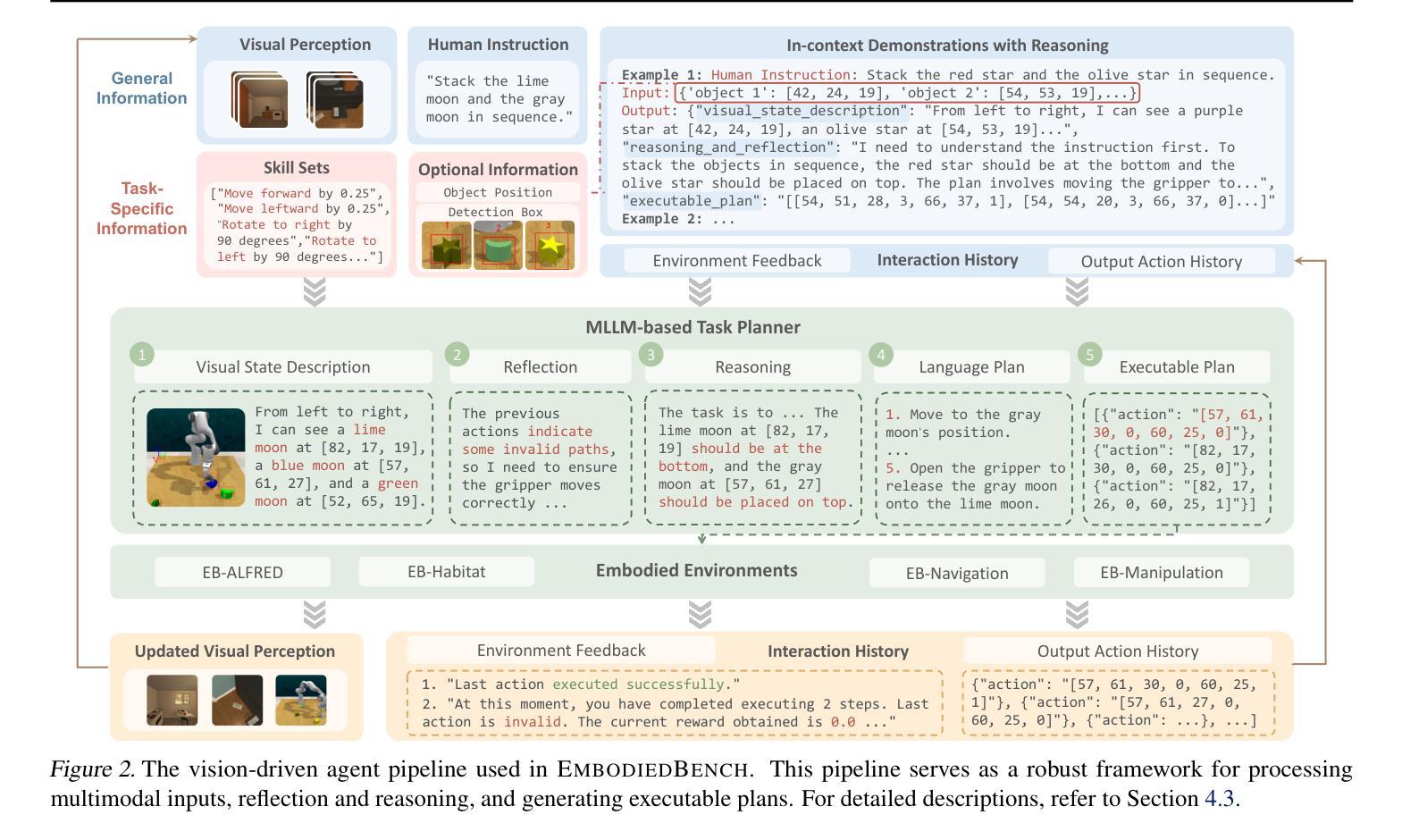
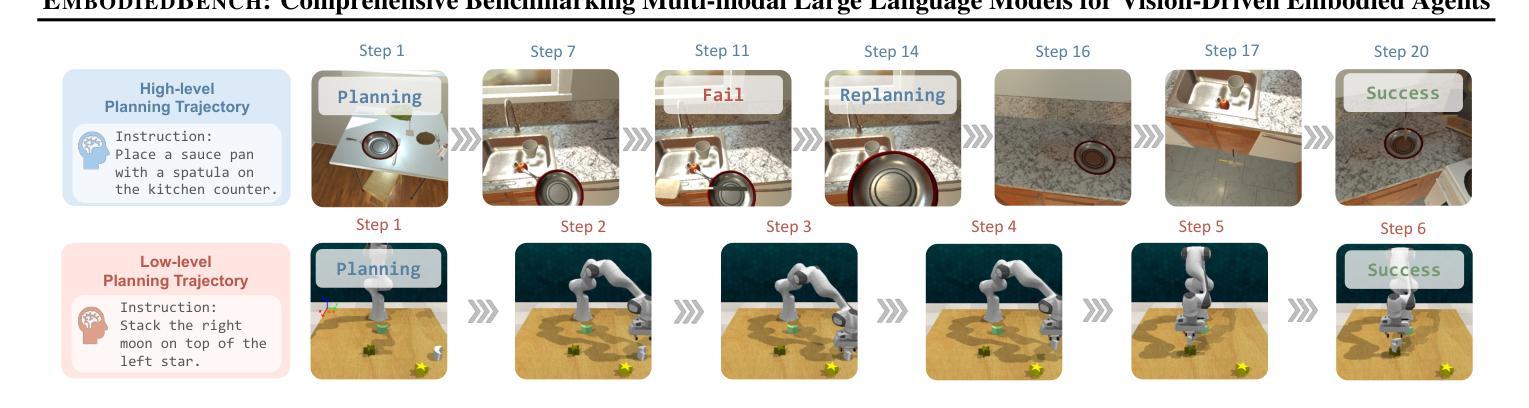
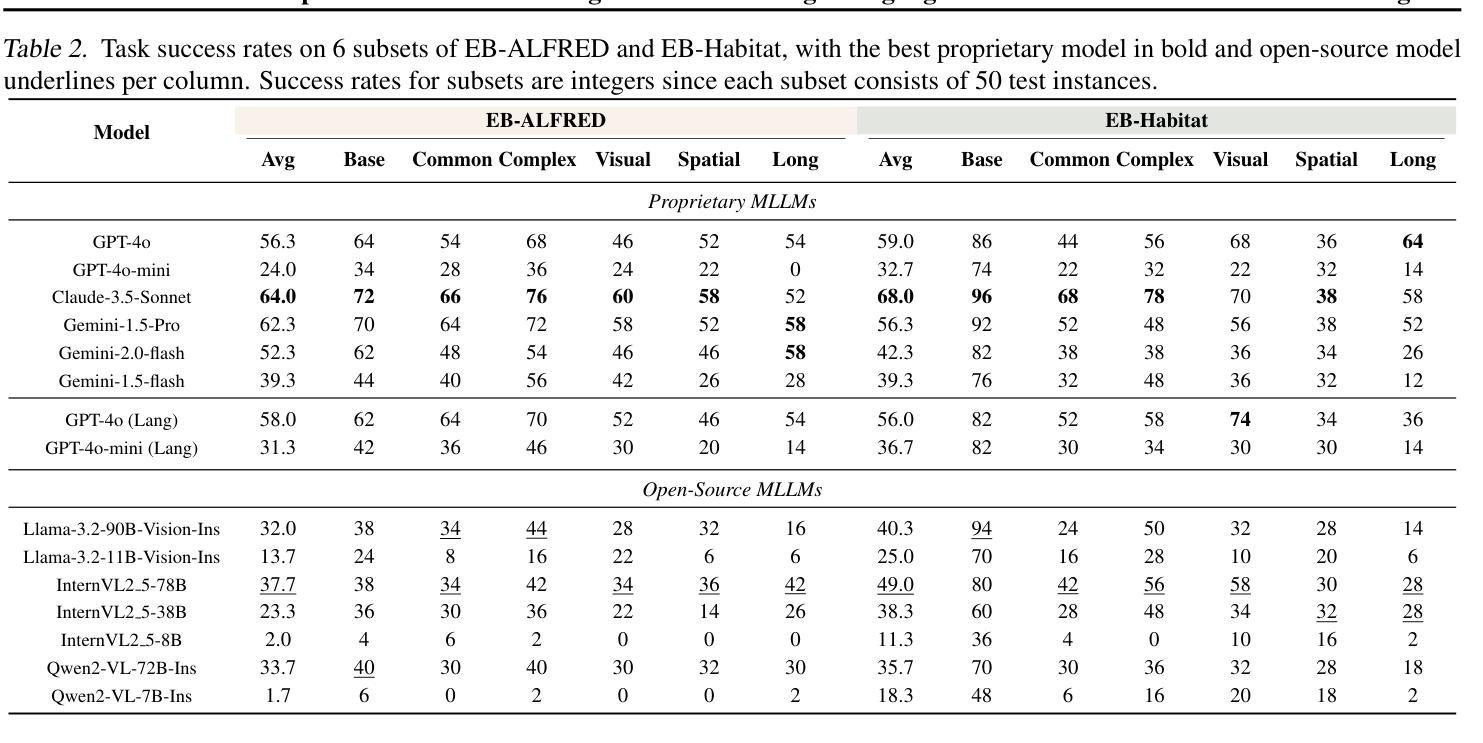
Leveraging Multi-modal Large Language Models (MLLMs) to create embodied agents offers a promising avenue for tackling real-world tasks. While language-centric embodied agents have garnered substantial attention, MLLM-based embodied agents remain underexplored due to the lack of comprehensive evaluation frameworks. To bridge this gap, we introduce EmbodiedBench, an extensive benchmark designed to evaluate vision-driven embodied agents. EmbodiedBench features: (1) a diverse set of 1,128 testing tasks across four environments, ranging from high-level semantic tasks (e.g., household) to low-level tasks involving atomic actions (e.g., navigation and manipulation); and (2) six meticulously curated subsets evaluating essential agent capabilities like commonsense reasoning, complex instruction understanding, spatial awareness, visual perception, and long-term planning. Through extensive experiments, we evaluated 13 leading proprietary and open-source MLLMs within EmbodiedBench. Our findings reveal that: MLLMs excel at high-level tasks but struggle with low-level manipulation, with the best model, GPT-4o, scoring only 28.9% on average. EmbodiedBench provides a multifaceted standardized evaluation platform that not only highlights existing challenges but also offers valuable insights to advance MLLM-based embodied agents. Our code is available at https://embodiedbench.github.io.
利用多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)创建实体代理为解决现实世界任务提供了一条充满希望的道路。虽然以语言为中心的实体代理已经引起了广泛关注,但基于MLLM的实体代理由于缺乏全面的评估框架而尚未得到充分探索。为了弥补这一空白,我们引入了EmbodiedBench,这是一个旨在评估视觉驱动的实体代理的广泛基准测试。EmbodiedBench的特点包括:(1)在四个环境中包含1,128个测试任务,范围从高级语义任务(例如家庭任务)到涉及原子动作的低级任务(例如导航和操作);(2)六个精心策划的子集,评估代理的必要能力,如常识推理、复杂指令理解、空间感知、视觉感知和长期规划。通过广泛的实验,我们在EmbodiedBench中对13个领先的专业和开源MLLM进行了评估。研究结果表明:MLLM在高级任务上表现出色,但在低级操作任务上遇到困难,其中最佳模型GPT-4o的平均得分仅为28.9%。EmbodiedBench提供了一个多方面的标准化评估平台,它不仅突出了现有挑战,而且为推进基于MLLM的实体代理提供了宝贵见解。我们的代码可在https://embodiedbench.github.io找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 51 pages
Summary
利用多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)创建实体代理为解决现实世界任务提供了有效途径。虽然语言为中心的实体代理受到了广泛关注,但基于MLLM的实体代理由于缺乏全面的评估框架而尚未得到充分探索。为了弥补这一空白,我们引入了EmbodiedBench,这是一个旨在评估视觉驱动实体代理的广泛基准测试。EmbodiedBench的特点包括:(1)在四个环境中包含1,128个测试任务,涵盖从高级语义任务(如家庭任务)到涉及原子动作的低级任务(如导航和操作);(2)六个精心策划的子集评估代理的核心能力,如常识推理、复杂指令理解、空间意识、视觉感知和长期规划。通过广泛实验,我们在EmbodiedBench中评估了13个领先的专有和开源MLLMs。我们发现:MLLMs在高级任务方面表现出色,但在低级操作任务方面遇到困难,最佳模型GPT-4o的平均得分仅为28.9%。EmbodiedBench提供了一个多方面的标准化评估平台,它不仅突出了现有挑战,而且为推进基于MLLM的实体代理提供了宝贵见解。
Key Takeaways
- 多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)在创建实体代理以完成现实世界任务方面具有潜力。
- 视觉驱动实体代理的评估缺乏全面基准测试。
- EmbodiedBench是一个广泛基准测试,旨在评估实体代理在多种任务和环境中的性能。
- MLLMs在高级任务上表现良好,但在低级操作任务上遇到困难。
- 最佳模型GPT-4o在平均得分仅为28.9%,说明在实体代理的低级操作任务上仍有很大改进空间。
- EmbodiedBench平台突出了现有挑战,并为改进基于MLLM的实体代理提供了有价值的信息。
点此查看论文截图

Reliable Conversational Agents under ASP Control that Understand Natural Language
Authors:Yankai Zeng
Efforts have been made to make machines converse like humans in the past few decades. The recent techniques of Large Language Models (LLMs) make it possible to have human-like conversations with machines, but LLM’s flaws of lacking understanding and reliability are well documented. We believe that the best way to eliminate this problem is to use LLMs only as parsers to translate text to knowledge and vice versa and carry out the conversation by reasoning over this knowledge using the answer set programming. I have been developing a framework based on LLMs and ASP to realize reliable chatbots that “understand” human conversation. This framework has been used to develop task-specific chatbots as well as socialbots. My future research is focused on making these chatbots scalable and trainable.
在过去的几十年里,人们一直在努力让机器像人类一样进行对话。最近的大型语言模型(LLM)技术使得与机器进行类似人类的对话成为可能,但LLM在理解和可靠性方面的缺陷已经得到了很好的记录。我们相信消除这个问题的最佳方法是仅将LLM用作解析器,将文本转换为知识反之亦然,并通过答案集编程对这种知识进行推理以进行对话。我一直在基于LLM和ASP开发一个框架,以实现可靠的聊天机器人,让它们“理解”人类对话。该框架已被用于开发针对特定任务的聊天机器人以及社交机器人。我未来的研究重点是使这些聊天机器人可扩展和可训练。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF In Proceedings ICLP 2024, arXiv:2502.08453
Summary
过去几十年,人们一直在努力让机器像人类一样进行对话。虽然大型语言模型(LLM)技术使人与机器之间的对话变得人性化,但其缺乏理解和可靠性的问题也被广泛记录。最佳解决方案是使用LLM仅作为文本与知识之间的转换器,并通过答案集编程(ASP)在知识上进行推理来进行对话。我已经开发了一个基于LLM和ASP的框架,用于实现可靠的聊天机器人,它们可以“理解”人类对话。此框架已用于开发任务特定的聊天机器人和社会机器人。我未来的研究重点是使这些聊天机器人更具可扩展性和可训练性。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLM)技术使得机器对话更加人性化。
- LLM存在缺乏理解和可靠性的问题。
- 使用LLM作为文本与知识之间的转换器,并通过答案集编程(ASP)进行推理是实现可靠聊天机器人的方法。
- 开发者已经创建了一个基于LLM和ASP的框架来实现理解人类对话的聊天机器人。
- 此框架可用于开发任务特定的聊天机器人和社会机器人。
- 未来的研究重点是提高聊天机器人的可扩展性和可训练性。
点此查看论文截图

AIDE: Agentically Improve Visual Language Model with Domain Experts
Authors:Ming-Chang Chiu, Fuxiao Liu, Karan Sapra, Andrew Tao, Yaser Jacoob, Xuezhe Ma, Zhiding Yu, Guilin Liu
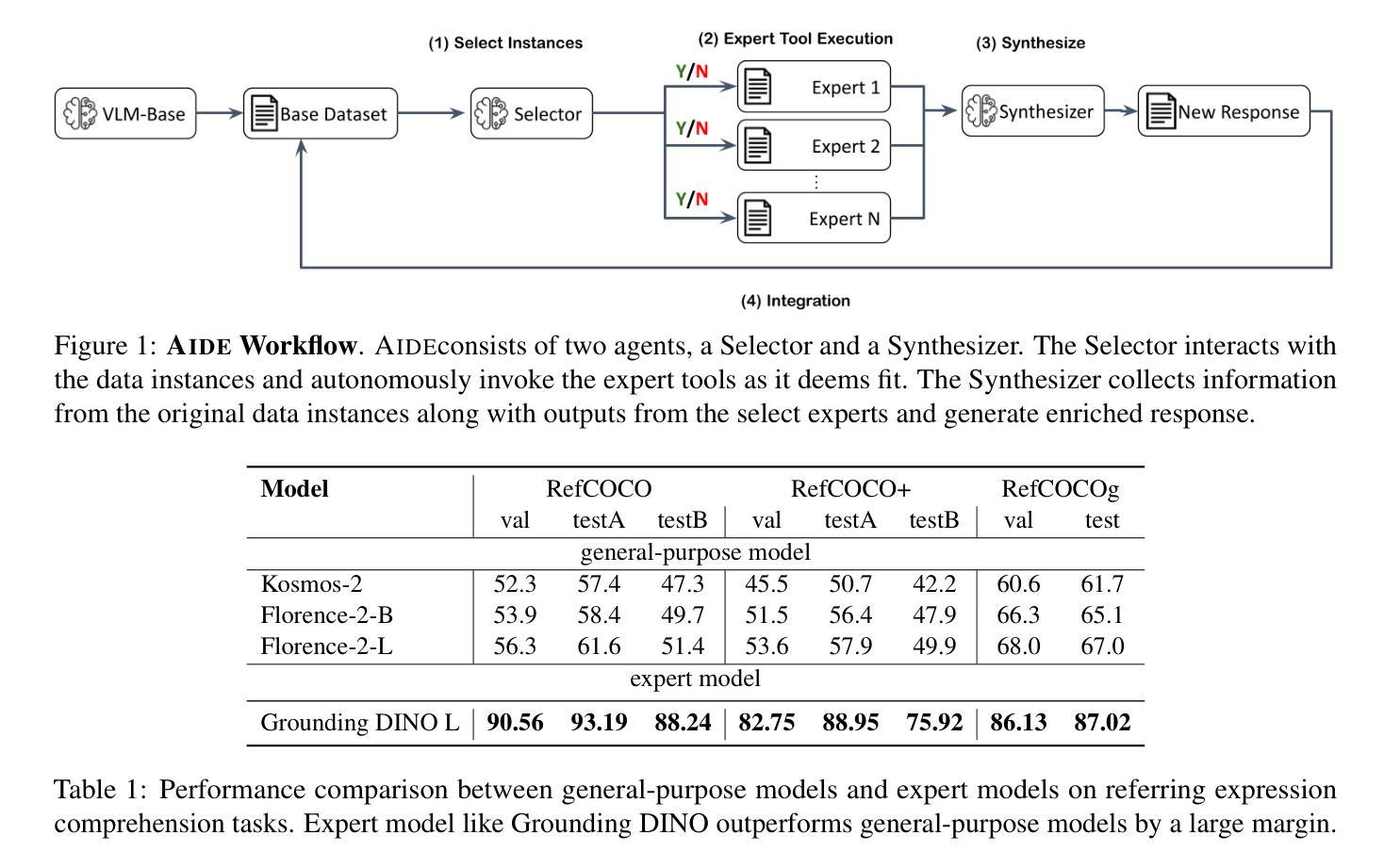
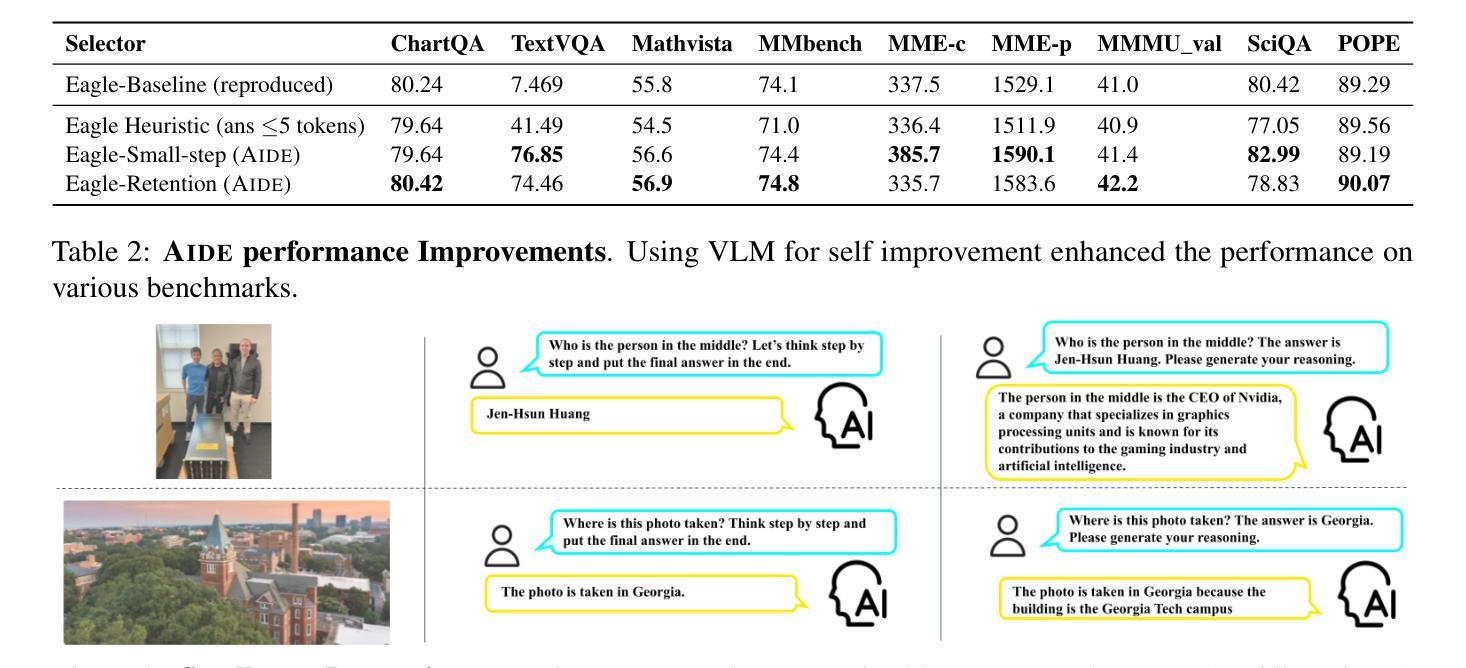
The enhancement of Visual Language Models (VLMs) has traditionally relied on knowledge distillation from larger, more capable models. This dependence creates a fundamental bottleneck for improving state-of-the-art systems, particularly when no superior models exist. We introduce AIDE (Agentic Improvement through Domain Experts), a novel framework that enables VLMs to autonomously enhance their capabilities by leveraging specialized domain expert models. AIDE operates through a four-stage process: (1) identifying instances for refinement, (2) engaging domain experts for targeted analysis, (3) synthesizing expert outputs with existing data, and (4) integrating enhanced instances into the training pipeline. Experiments on multiple benchmarks, including MMMU, MME, MMBench, etc., demonstrate AIDE’s ability to achieve notable performance gains without relying on larger VLMs nor human supervision. Our framework provides a scalable, resource-efficient approach to continuous VLM improvement, addressing critical limitations in current methodologies, particularly valuable when larger models are unavailable to access.
视觉语言模型(VLMs)的增强传统上依赖于更大、更强大的模型的知识蒸馏。这种依赖为改进最新系统创造了根本性的瓶颈,特别是在不存在更优秀模型的情况下。我们引入了AIDE(通过领域专家进行智能改进),这是一种新型框架,它能够使VLMs利用专业的领域专家模型自主增强其能力。AIDE通过四个阶段的流程进行操作:(1)识别需要改进的情况,(2)邀请领域专家进行有针对性的分析,(3)将专家输出与现有数据进行合成,(4)将增强的实例集成到训练管道中。在包括MMMU、MME、MMBench等多个基准测试上的实验表明,AIDE能够在不依赖更大的VLMs和人类监督的情况下实现显著的性能提升。我们的框架提供了一种可扩展、资源高效的方法,用于持续改进VLM,解决了当前方法的关键局限性,特别是在无法访问大型模型时尤为有价值。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 6 pages, 4 figures, 2 tables
Summary
AIDE框架通过利用专业领域专家模型,实现了视觉语言模型(VLMs)的自主能力提升。该框架通过四个阶段操作:识别改进实例、邀请领域专家进行针对性分析、合成专家输出与现有数据,以及将增强实例集成到训练流程中。实验证明,AIDE在多个基准测试中实现了显著的性能提升,且无需依赖更大的VLMs和人类监督。此框架为解决当前方法的关键局限性提供了一种可扩展且资源高效的方法,尤其在无法访问大型模型时尤为有价值。
Key Takeaways
- AIDE框架利用专业领域专家模型,使VLMs能够自主提升能力。
- AIDE通过四个阶段操作实现能力提升:识别改进实例、领域专家分析、合成专家输出与现有数据,以及集成增强实例。
- AIDE框架在多个基准测试中表现出显著性能提升。
- AIDE不需要依赖更大的VLMs和人类监督。
- AIDE框架解决了当前方法的关键局限性。
- AIDE提供了一种可扩展且资源高效的方法,用于持续改进VLMs。
点此查看论文截图

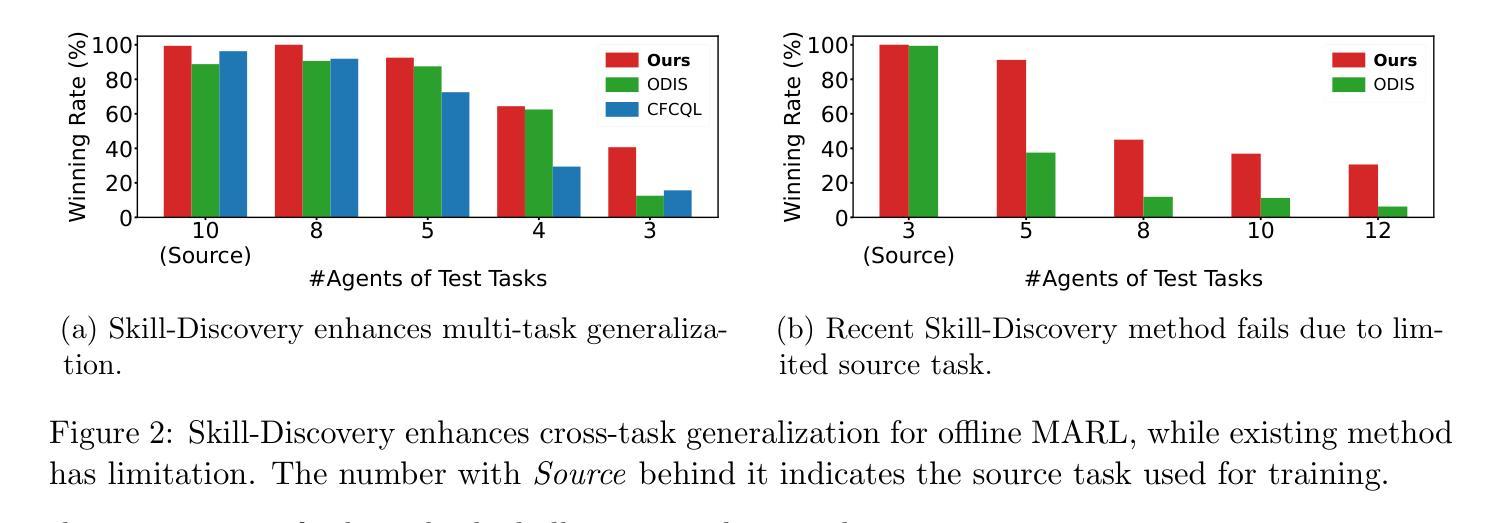
Few is More: Task-Efficient Skill-Discovery for Multi-Task Offline Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning
Authors:Xun Wang, Zhuoran Li, Hai Zhong, Longbo Huang
As a data-driven approach, offline MARL learns superior policies solely from offline datasets, ideal for domains rich in historical data but with high interaction costs and risks. However, most existing methods are task-specific, requiring retraining for new tasks, leading to redundancy and inefficiency. To address this issue, in this paper, we propose a task-efficient multi-task offline MARL algorithm, Skill-Discovery Conservative Q-Learning (SD-CQL). Unlike existing offline skill-discovery methods, SD-CQL discovers skills by reconstructing the next observation. It then evaluates fixed and variable actions separately and employs behavior-regularized conservative Q-learning to execute the optimal action for each skill. This approach eliminates the need for local-global alignment and enables strong multi-task generalization from limited small-scale source tasks. Substantial experiments on StarCraftII demonstrates the superior generalization performance and task-efficiency of SD-CQL. It achieves the best performance on $\textbf{10}$ out of $14$ task sets, with up to $\textbf{65%}$ improvement on individual task sets, and is within $4%$ of the best baseline on the remaining four.
作为一种数据驱动的方法,离线多智能体强化学习(Offline MARL)仅从离线数据集中学习卓越的策略,这对于历史数据丰富但交互成本高和风险高的领域尤为理想。然而,大多数现有方法是针对特定任务的,需要针对新任务进行再训练,导致冗余和效率低下。为了解决这一问题,本文提出了一种任务高效的多任务离线MARL算法——技能发现保守Q学习(SD-CQL)。不同于现有的离线技能发现方法,SD-CQL通过重建下一个观察结果来发现技能。然后,它分别评估固定动作和可变动作,并采用行为正则化保守Q学习来执行每个技能的最佳动作。这种方法消除了对局部-全局对齐的需求,并实现了从有限的小规模源任务到强大的多任务泛化。在StarCraftII上的大量实验证明了SD-CQL出色的泛化性能和任务效率。它在14个任务集中的10个任务上取得了最佳性能,在个别任务集上最多提高了65%,其余四个任务的性能与最佳基准值相差不到4%。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
离线多智能体强化学习(Offline MARL)从离线数据集中学习优质策略,适用于历史数据丰富但交互成本高、风险大的领域。现有方法多为针对特定任务的,对新任务需重新训练,导致冗余和效率低。为解决此问题,本文提出一种任务高效的多任务离线MARL算法——技能发现保守Q学习(SD-CQL)。SD-CQL通过重建下一个观察结果来发现技能,并分别评估固定和可变动作,采用行为正则化的保守Q学习来执行每项技能的最优动作。这消除了对局部-全局对齐的需求,并实现了从有限小规模源任务到多任务强泛化。在StarCraftII上的大量实验表明SD-CQL的优越泛化性能和任务效率,在14个任务集中最佳表现于其中10个,个别任务集上最多提升了65%,其余四个任务集与最佳基准差距在4%以内。
Key Takeaways
- 离线多智能体强化学习(Offline MARL)适用于历史数据丰富的领域,能够基于离线数据集学习优质策略。
- 当前方法多存在任务特定性,需要针对新任务重新训练,导致效率不高。
- SD-CQL算法通过重建下一个观察结果发现技能,解决了这一问题。
- SD-CQL能够分别评估固定和可变动作,并采用行为正则化的保守Q学习执行每项技能的最优动作。
- 该算法实现了从有限小规模源任务到多任务强泛化,无需局部-全局对齐。
- 在StarCraftII上的实验证明SD-CQL具有良好的泛化性能和任务效率。
点此查看论文截图


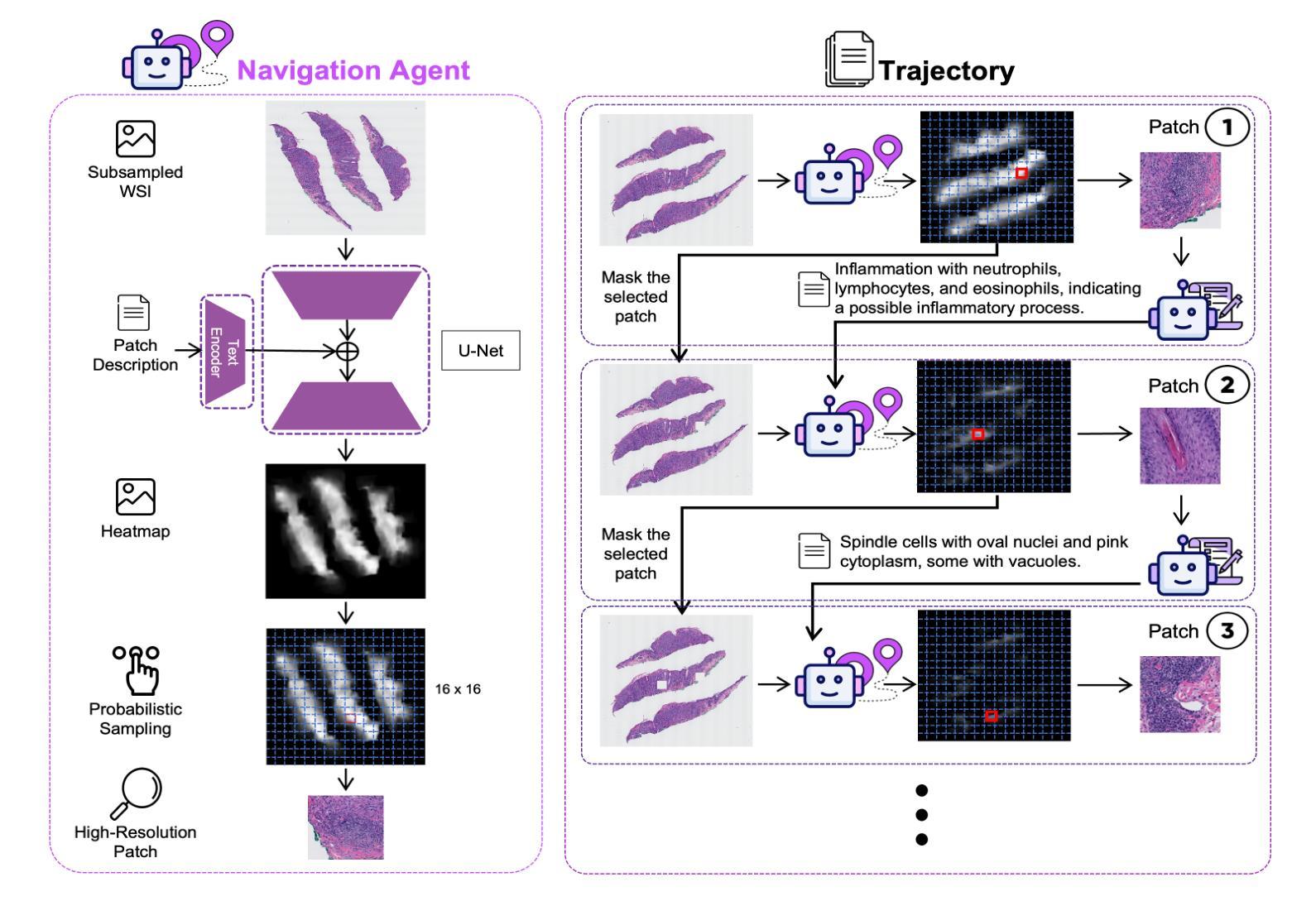
PathFinder: A Multi-Modal Multi-Agent System for Medical Diagnostic Decision-Making Applied to Histopathology
Authors:Fatemeh Ghezloo, Mehmet Saygin Seyfioglu, Rustin Soraki, Wisdom O. Ikezogwo, Beibin Li, Tejoram Vivekanandan, Joann G. Elmore, Ranjay Krishna, Linda Shapiro
Diagnosing diseases through histopathology whole slide images (WSIs) is fundamental in modern pathology but is challenged by the gigapixel scale and complexity of WSIs. Trained histopathologists overcome this challenge by navigating the WSI, looking for relevant patches, taking notes, and compiling them to produce a final holistic diagnostic. Traditional AI approaches, such as multiple instance learning and transformer-based models, fail short of such a holistic, iterative, multi-scale diagnostic procedure, limiting their adoption in the real-world. We introduce PathFinder, a multi-modal, multi-agent framework that emulates the decision-making process of expert pathologists. PathFinder integrates four AI agents, the Triage Agent, Navigation Agent, Description Agent, and Diagnosis Agent, that collaboratively navigate WSIs, gather evidence, and provide comprehensive diagnoses with natural language explanations. The Triage Agent classifies the WSI as benign or risky; if risky, the Navigation and Description Agents iteratively focus on significant regions, generating importance maps and descriptive insights of sampled patches. Finally, the Diagnosis Agent synthesizes the findings to determine the patient’s diagnostic classification. Our Experiments show that PathFinder outperforms state-of-the-art methods in skin melanoma diagnosis by 8% while offering inherent explainability through natural language descriptions of diagnostically relevant patches. Qualitative analysis by pathologists shows that the Description Agent’s outputs are of high quality and comparable to GPT-4o. PathFinder is also the first AI-based system to surpass the average performance of pathologists in this challenging melanoma classification task by 9%, setting a new record for efficient, accurate, and interpretable AI-assisted diagnostics in pathology. Data, code and models available at https://pathfinder-dx.github.io/
通过组织病理学全切片图像(WSI)诊断疾病是现代病理学中的基本方法,但受到WSI千兆像素规模和复杂性的挑战。经过训练的组织病理学家通过浏览WSI,寻找相关斑块,做笔记,并对其进行整理以产生最终的全面诊断来克服这一挑战。传统的AI方法,如多实例学习和基于变压器模型的AI方法,未能实现这种全面、迭代、多尺度的诊断程序,限制了它们在现实世界中的应用。我们引入了PathFinder,这是一个多模式、多代理框架,模拟专家病理学家的决策过程。PathFinder集成了四个AI代理,即分拣代理、导航代理、描述代理和诊断代理,它们协同浏览WSI,收集证据并提供全面的诊断以及自然语言解释。分拣代理将WSI分类为良性或风险性;如果为风险性,导航和描述代理将迭代关注重要区域,生成重要性地图和采样斑块的描述性见解。最后,诊断代理综合这些发现以确定患者的诊断分类。我们的实验表明,在皮肤黑色素瘤诊断中,PathFinder较最新方法高出8%,同时提供通过自然语言描述诊断相关斑块的内生解释性。病理学家进行的定性分析表明,描述代理的输出质量高,与GPT-4o相当。PathFinder也是第一个在此具有挑战性的黑色素瘤分类任务中超越病理学家平均性能的AI系统,在高效、准确和可解释的AI辅助诊断病理学中创造了新纪录。数据和模型可在https://pathfinder-dx.github.io/找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于人工智能技术的PathFinder框架在模拟病理专家诊断过程中表现出色。PathFinder通过多模态、多智能体协作导航WSIs,提供全面的诊断及自然语言解释。在皮肤黑色素瘤诊断中,PathFinder超越现有技术,具备出色的诊断性能及解释性。相关数据和模型可访问官网了解。
Key Takeaways
- PathFinder通过模拟病理专家的诊断过程来解决挑战。
- 它集成了四个AI智能体进行协同工作:分类智能体、导航智能体、描述智能体和诊断智能体。
- PathFinder框架能生成重要性地图和采样斑块的描述性见解,从而为黑色素瘤等疾病的诊断提供全面的视角。
- 实验显示,PathFinder在皮肤黑色素瘤诊断方面比当前技术领先了8%,并且在解释性方面也有优势。
- 定性分析表明,描述智能体的输出质量高,与GPT-4相当。
点此查看论文截图

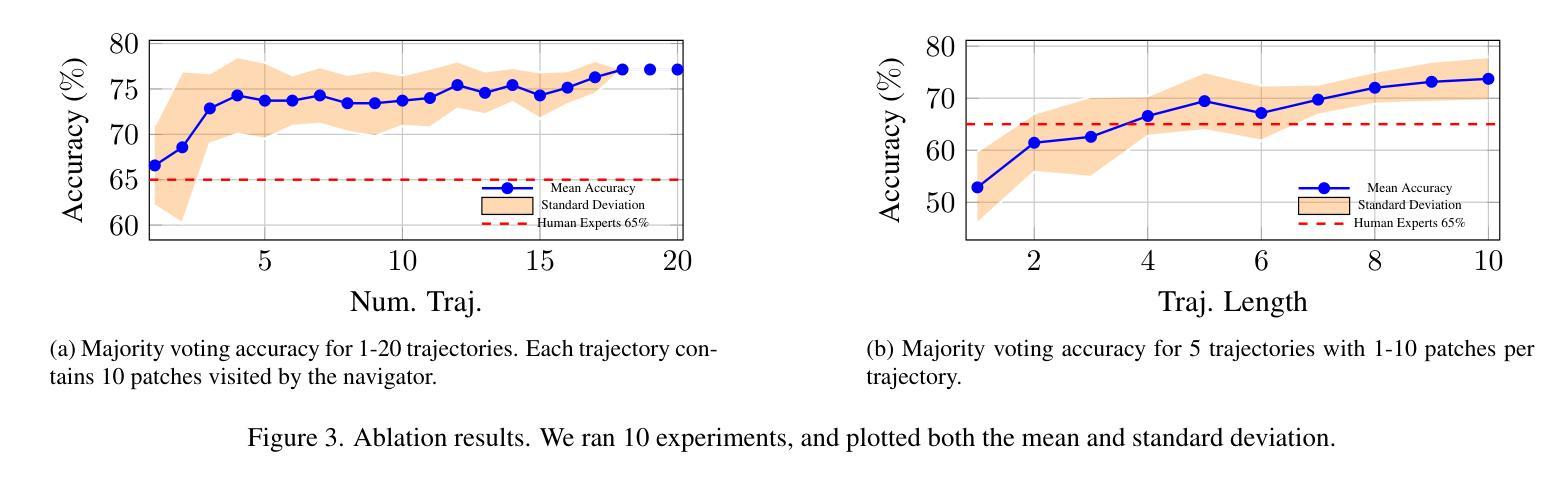
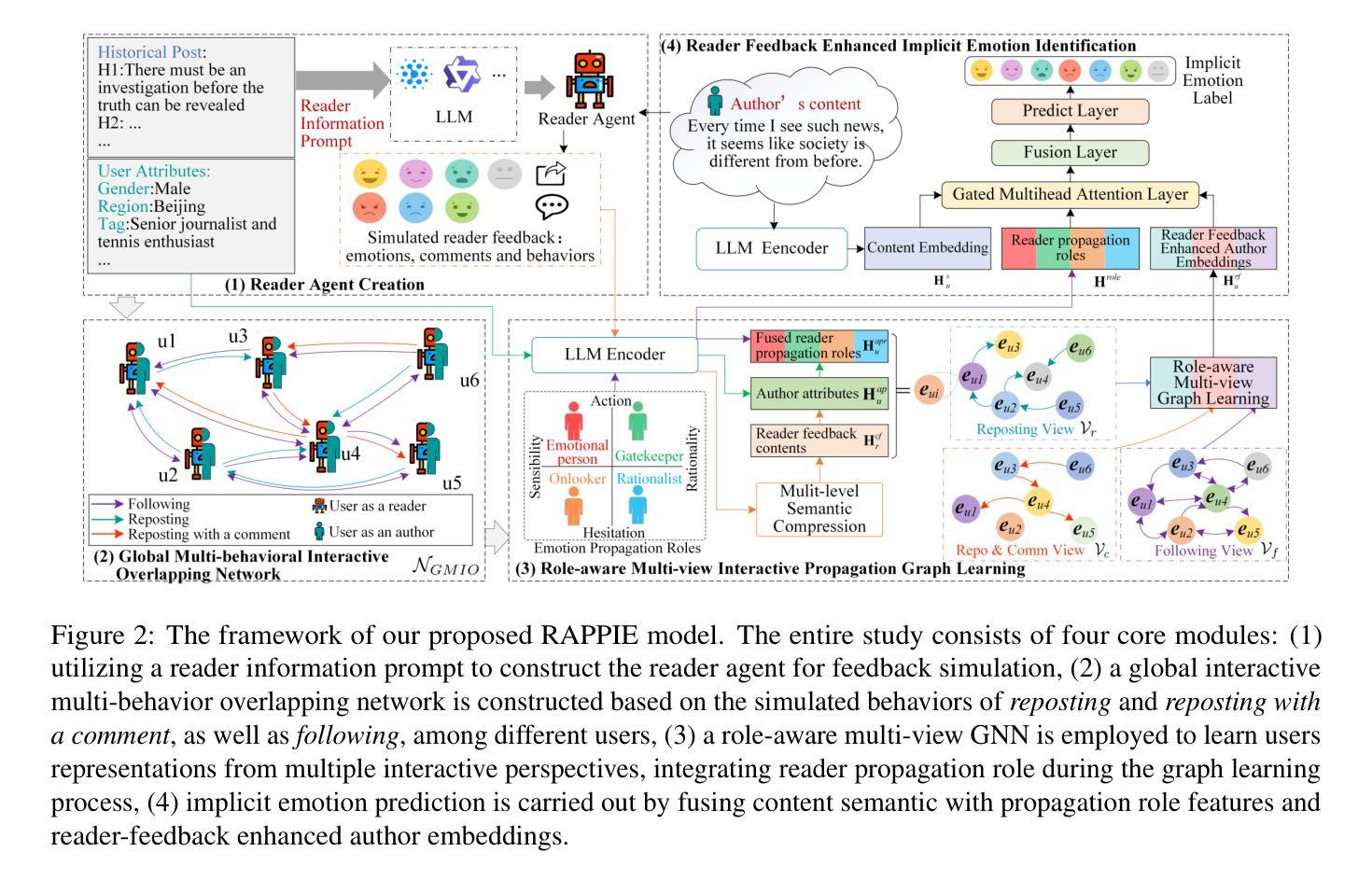
My Words Imply Your Opinion: Reader Agent-Based Propagation Enhancement for Personalized Implicit Emotion Analysis
Authors:Jian Liao, Yu Feng, Yujin Zheng, Jun Zhao, Suge Wang, Jianxing Zheng
The subtlety of emotional expressions makes implicit emotion analysis (IEA) particularly sensitive to user-specific characteristics. Current studies personalize emotion analysis by focusing on the author but neglect the impact of the intended reader on implicit emotional feedback. In this paper, we introduce Personalized IEA (PIEA) and present the RAPPIE model, which addresses subjective variability by incorporating reader feedback. In particular, (1) we create reader agents based on large language models to simulate reader feedback, overcoming the issue of ``spiral of silence effect’’ and data incompleteness of real reader reaction. (2) We develop a role-aware multi-view graph learning to model the emotion interactive propagation process in scenarios with sparse reader information. (3) We construct two new PIEA datasets covering English and Chinese social media with detailed user metadata, addressing the text-centric limitation of existing datasets. Extensive experiments show that RAPPIE significantly outperforms state-of-the-art baselines, demonstrating the value of incorporating reader feedback in PIEA.
情感表达的细微之处使得隐式情感分析(IEA)特别关注用户特定特征。当前的研究通过关注作者来实现情感分析的个性化,但忽视了目标读者对隐式情感反馈的影响。在本文中,我们介绍了个性化IEA(PIEA)并提出了RAPPIE模型,该模型通过融入读者反馈来解决主观变化性的问题。具体来说,(1)我们基于大型语言模型创建读者代理来模拟读者反馈,克服了“沉默螺旋效应”和真实读者反应数据不完整的问题。(2)我们开发了角色感知多视图图学习,以在读者信息稀疏的场景中建模情感交互传播过程。(3)我们构建了两个新的PIEA数据集,涵盖了英语和中文社交媒体,并包含详细的用户元数据,解决了现有数据集以文本为中心的限制。大量实验表明,RAPPIE显著优于最新基线,证明了在PIEA中融入读者反馈的价值。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
文本介绍了个性化隐式情感分析(PIEA)的新方法,包括创建读者代理模拟读者反馈、开发角色感知多视角图学习以及构建包含详细用户元数据的PIEA数据集。该方法克服了真实读者反应的数据不完整性和“沉默螺旋效应”的问题,并通过实验证明,在融入读者反馈后,PIEA的效果显著提升。
Key Takeaways
- 隐式情感分析(IEA)因情感表达的微妙性而特别关注用户特定特征。
- 当前研究主要通过聚焦作者个性化情感分析,但忽视了预期读者对隐式情感反馈的影响。
- 引入个性化隐式情感分析(PIEA)和RAPPIE模型,通过融入读者反馈来解决主观差异性问题。
- 创建基于大型语言模型的读者代理,模拟读者反馈,克服真实读者反应的数据不完整性和“沉默螺旋效应”。
- 开发角色感知多视角图学习,建模稀疏读者信息情境下的情感交互传播过程。
- 构建包含英语和中文社交媒体的新PIEA数据集,包含详细用户元数据,解决现有数据集过于侧重文本的问题。
点此查看论文截图

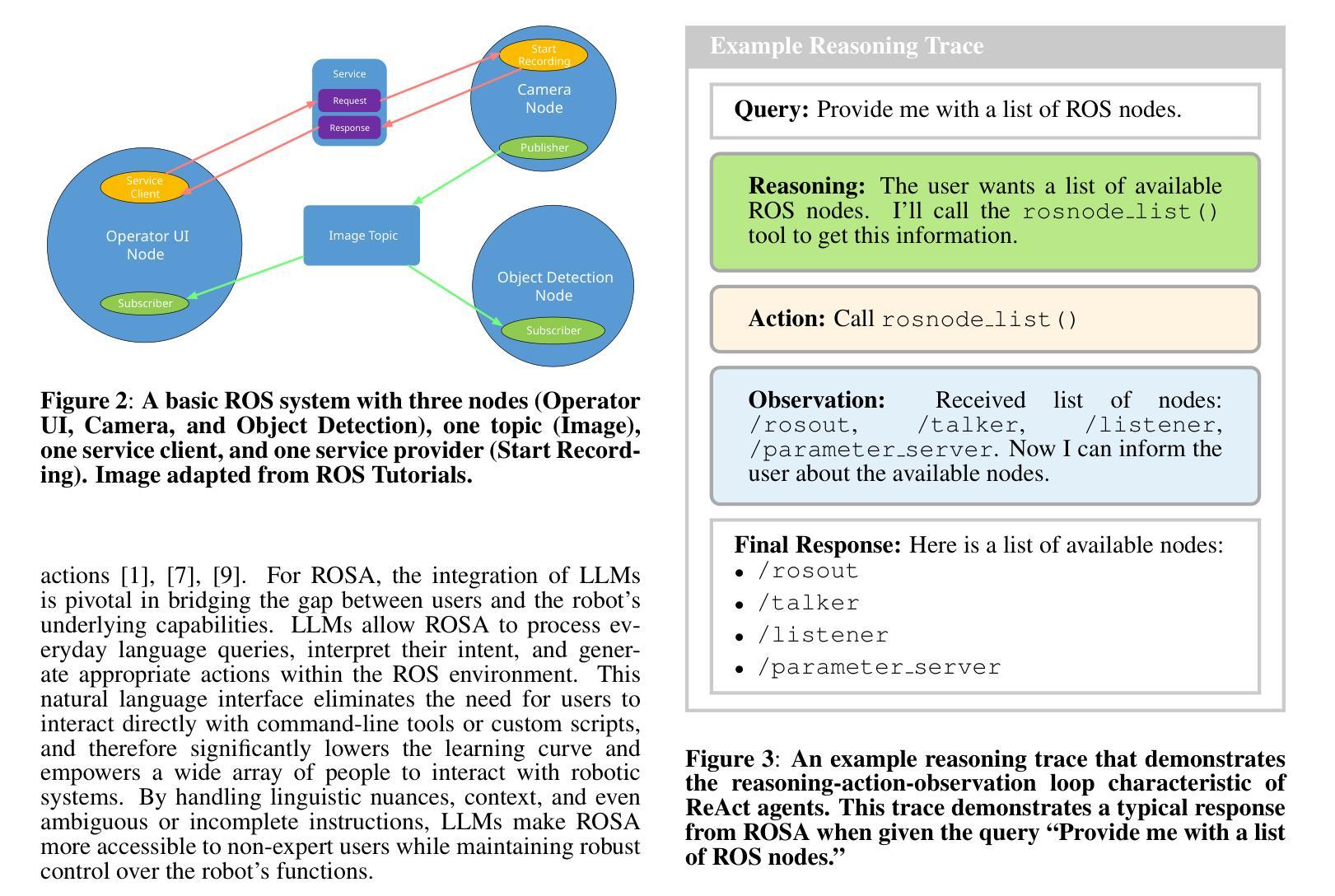
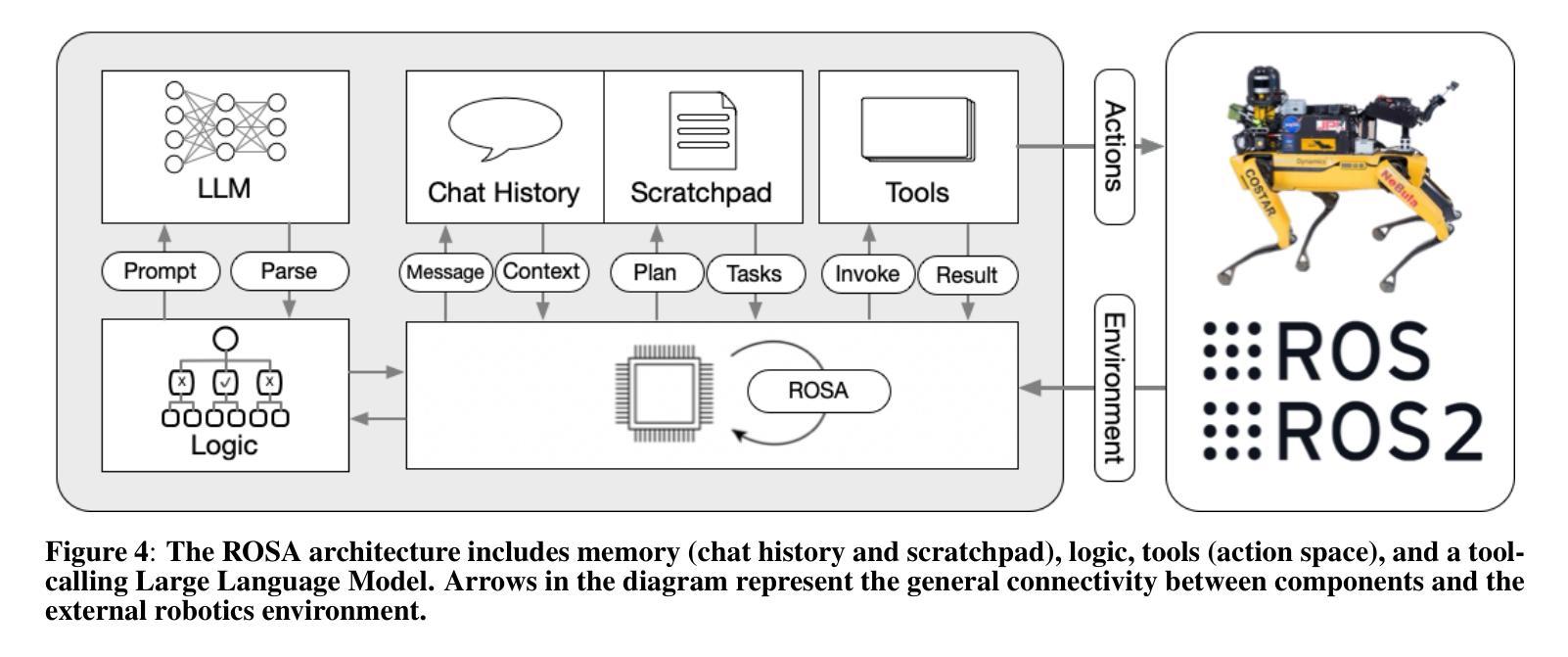
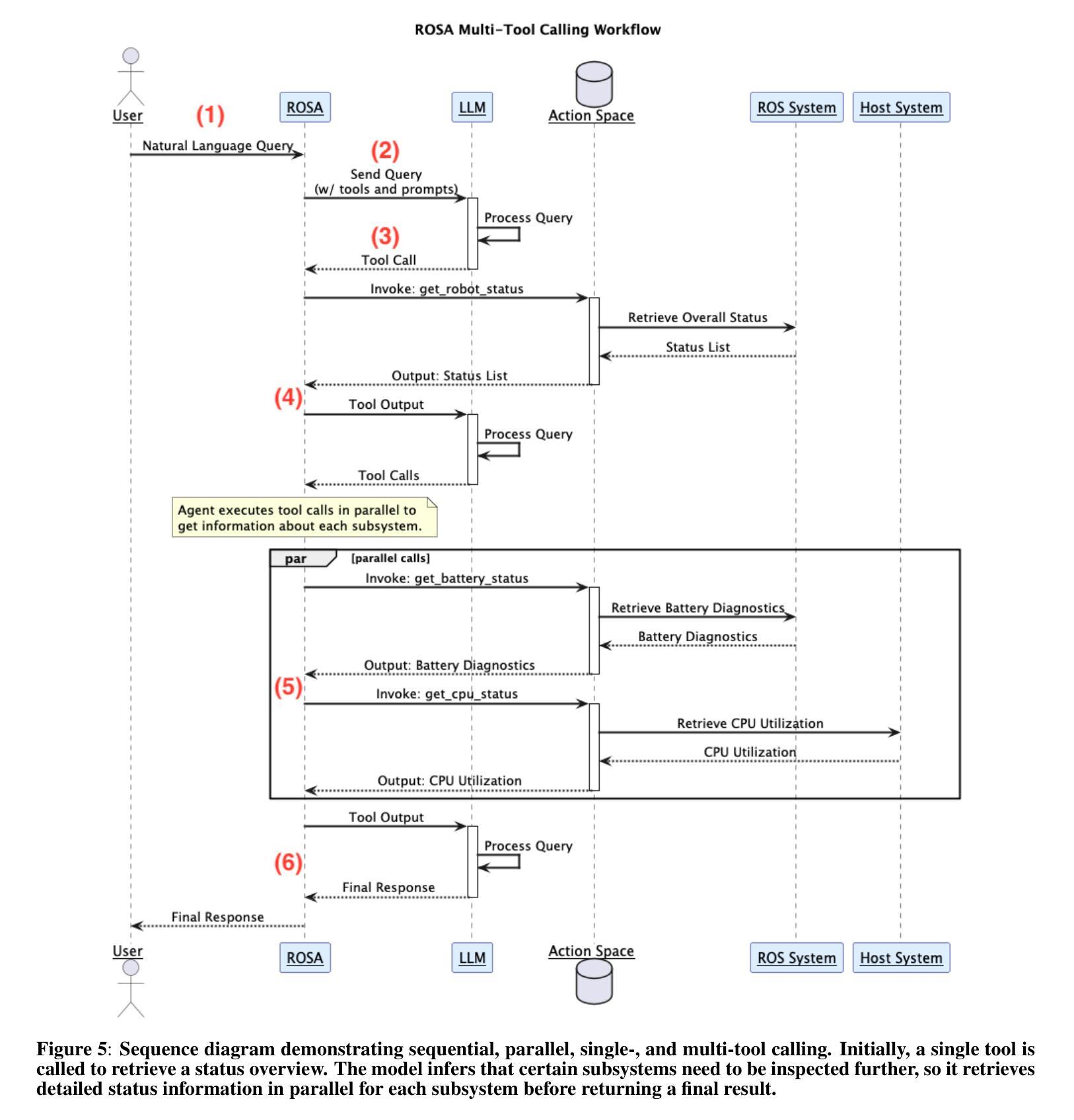
Enabling Novel Mission Operations and Interactions with ROSA: The Robot Operating System Agent
Authors:Rob Royce, Marcel Kaufmann, Jonathan Becktor, Sangwoo Moon, Kalind Carpenter, Kai Pak, Amanda Towler, Rohan Thakker, Shehryar Khattak
The advancement of robotic systems has revolutionized numerous industries, yet their operation often demands specialized technical knowledge, limiting accessibility for non-expert users. This paper introduces ROSA (Robot Operating System Agent), an AI-powered agent that bridges the gap between the Robot Operating System (ROS) and natural language interfaces. By leveraging state-of-the-art language models and integrating open-source frameworks, ROSA enables operators to interact with robots using natural language, translating commands into actions and interfacing with ROS through well-defined tools. ROSA’s design is modular and extensible, offering seamless integration with both ROS1 and ROS2, along with safety mechanisms like parameter validation and constraint enforcement to ensure secure, reliable operations. While ROSA is originally designed for ROS, it can be extended to work with other robotics middle-wares to maximize compatibility across missions. ROSA enhances human-robot interaction by democratizing access to complex robotic systems, empowering users of all expertise levels with multi-modal capabilities such as speech integration and visual perception. Ethical considerations are thoroughly addressed, guided by foundational principles like Asimov’s Three Laws of Robotics, ensuring that AI integration promotes safety, transparency, privacy, and accountability. By making robotic technology more user-friendly and accessible, ROSA not only improves operational efficiency but also sets a new standard for responsible AI use in robotics and potentially future mission operations. This paper introduces ROSA’s architecture and showcases initial mock-up operations in JPL’s Mars Yard, a laboratory, and a simulation using three different robots. The core ROSA library is available as open-source.
机器人系统的进步已经颠覆了许多行业,然而它们的操作通常需要专业的技术知识,这对于非专业用户来说有一定的使用门槛。本文介绍了 ROSA(机器人操作系统代理),这是一个由人工智能驱动的代理,能够弥补机器人操作系统(ROS)和自然语言界面之间的鸿沟。通过利用最先进的语言模型并整合开源框架,ROSA允许操作者使用自然语言与机器人进行交互,将命令翻译成动作,并通过定义良好的工具与ROS进行接口。ROSA的设计具有模块化和可扩展性,可以与ROS1和ROS2无缝集成,同时提供参数验证和强制约束等安全机制,以确保安全、可靠的操作。虽然ROSA最初是为ROS设计的,但它可以扩展到与其他机器人中间件一起使用,以最大限度地提高跨任务的兼容性。ROSA通过使复杂的机器人系统民主化,增强了人机互动,赋予所有技能水平的用户多模式功能,如语音集成和视觉感知。伦理问题得到了充分的解决,由阿西莫夫的三大机器人定律等基本原则引导,确保人工智能的整合促进安全、透明、隐私和问责制。通过使机器人技术更加用户友好和可访问,ROSA不仅提高了操作效率,而且为机器人和潜在未来任务操作中的负责任的人工智能使用设定了新的标准。本文介绍了ROSA的架构,并在JPL的火星场(实验室)以及使用三种不同机器人的模拟环境中展示了初步模拟操作。ROSA核心库现已作为开源提供。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Preprint. Accepted at IEEE Aerospace Conference 2025, 16 pages, 12 figures
摘要
机器人操作系统代理(ROSA)通过运用先进语言模型和集成开源框架,实现了机器人操作系统与自然语言接口的衔接。ROSA支持操作人员用自然语言与机器人交互,将命令转化为行动,并通过明确工具与ROS交互。ROSA设计模块化、可扩展,可无缝集成ROS1和ROS2,同时有参数验证和约束执行等安全机制,确保安全、可靠的操作。ROSA增强了人机交互,通过多模式能力如语音集成和视觉感知,让所有水平的用户都能使用复杂的机器人系统。本文介绍了ROSA的架构,并在模拟火星场地上展示了初步操作。ROSA提高了操作效率并设定了负责任的AI使用新标准。
关键见解
- ROSA是首个实现机器人操作系统与自然语言交互的桥梁的人工智能代理。
- 通过运用先进语言模型和集成开源框架,ROSA支持用户使用自然语言与机器人交互。
- ROSA设计模块化、可扩展,能无缝集成ROS1和ROS2,并保证操作的安全性和可靠性。
- ROSA具备多模式能力,包括语音集成和视觉感知,适用于各种水平的用户。
- ROSA在模拟火星场地进行了初步操作展示,证明了其在实际应用中的潜力。
- ROSA提高了操作效率,特别是对于非专业用户。
- ROSA的开源特性有助于推动负责任的AI在机器人技术中的使用和发展。
点此查看论文截图


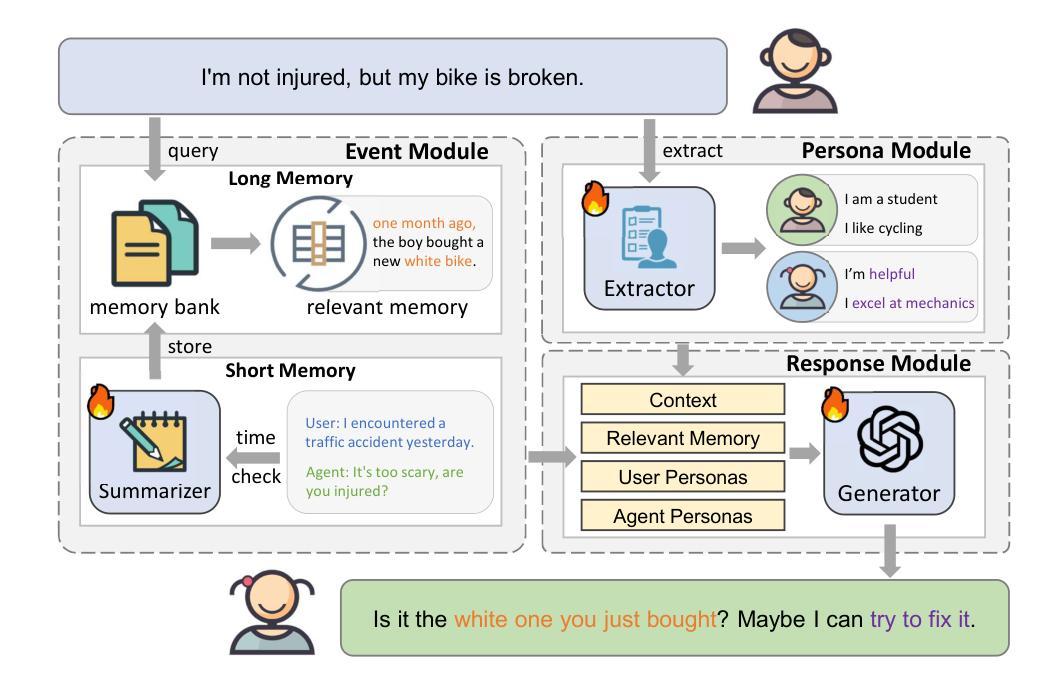
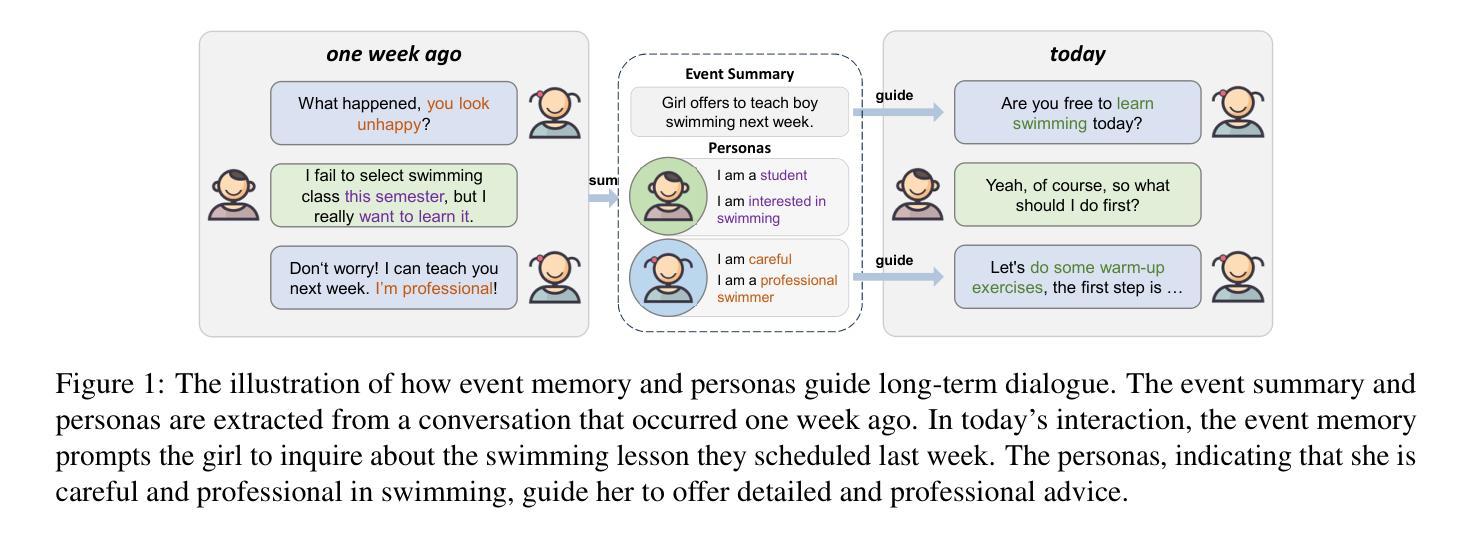
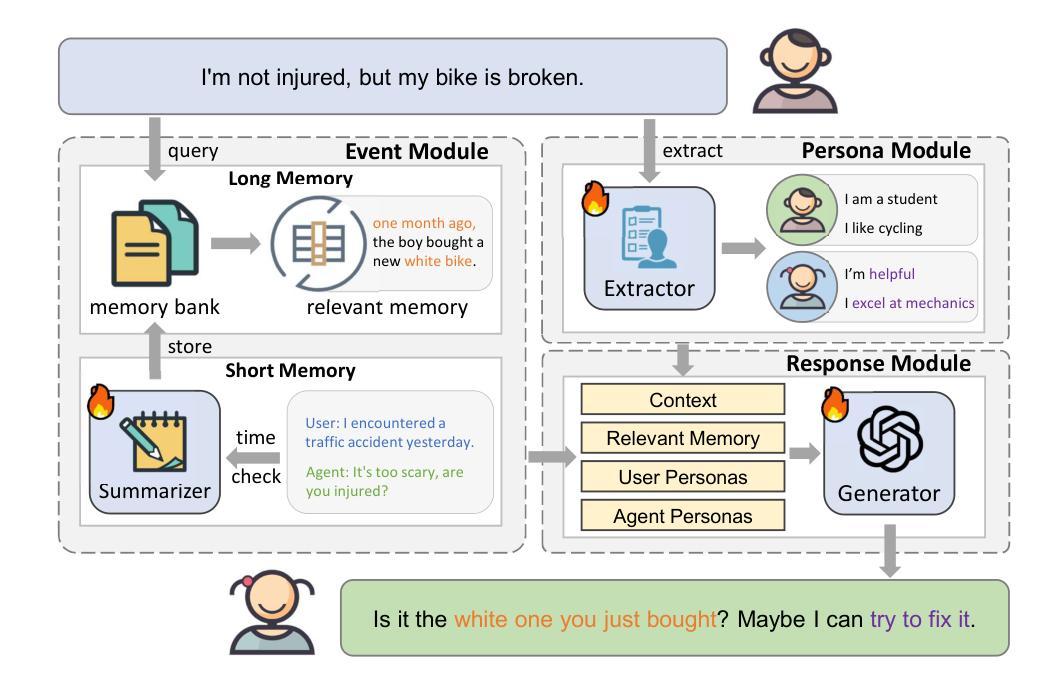
Hello Again! LLM-powered Personalized Agent for Long-term Dialogue
Authors:Hao Li, Chenghao Yang, An Zhang, Yang Deng, Xiang Wang, Tat-Seng Chua
Open-domain dialogue systems have seen remarkable advancements with the development of large language models (LLMs). Nonetheless, most existing dialogue systems predominantly focus on brief single-session interactions, neglecting the real-world demands for long-term companionship and personalized interactions with chatbots. Crucial to addressing this real-world need are event summary and persona management, which enable reasoning for appropriate long-term dialogue responses. Recent progress in the human-like cognitive and reasoning capabilities of LLMs suggests that LLM-based agents could significantly enhance automated perception, decision-making, and problem-solving. In response to this potential, we introduce a model-agnostic framework, the Long-term Dialogue Agent (LD-Agent), which incorporates three independently tunable modules dedicated to event perception, persona extraction, and response generation. For the event memory module, long and short-term memory banks are employed to separately focus on historical and ongoing sessions, while a topic-based retrieval mechanism is introduced to enhance the accuracy of memory retrieval. Furthermore, the persona module conducts dynamic persona modeling for both users and agents. The integration of retrieved memories and extracted personas is subsequently fed into the generator to induce appropriate responses. The effectiveness, generality, and cross-domain capabilities of LD-Agent are empirically demonstrated across various illustrative benchmarks, models, and tasks. The code is released at https://github.com/leolee99/LD-Agent.
随着大型语言模型(LLM)的发展,开放域对话系统已经取得了显著的进步。然而,大多数现有的对话系统主要关注短暂的单一会话互动,忽视了现实世界对长期伴侣关系和与聊天机器人的个性化互动的需求。要解决这一现实需求的关键是事件总结和人格管理,它们能够推理出适当的长期对话回应。最近,LLM在人类似的认知和推理能力方面的进步表明,基于LLM的代理可以大大增强自动化感知、决策和问题解决。基于此潜力,我们引入了一个模型无关框架,即长期对话代理(LD-Agent),它包括三个独立可调模块,分别用于事件感知、人格提取和响应生成。在事件记忆模块中,长期和短期记忆银行被用来分别关注历史会话和正在进行中的会话,同时引入基于主题的检索机制来提高记忆检索的准确性。此外,人格模块为用户和代理进行动态人格建模。检索到的记忆和提取的人格的集成随后被输入生成器,以引导适当的响应。LD-Agent的有效性、通用性和跨域能力在各种基准测试、模型和任务中得到了实证证明。代码已发布在https://github.com/leolee99/LD-Agent。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to NAACL 2025
总结
随着大型语言模型(LLM)的发展,开放域对话系统取得了显著的进步。然而,大多数现有的对话系统主要关注短暂的单一会话互动,忽视了现实世界对长期伴侣关系和与聊天机器人个性化互动的需求。为解决这一需求,事件总结和人格管理成为关键,它们能够使对话响应更加适当和长期。基于近期LLM在模拟人类认知和推理能力方面的进展,LLM代理可显著增强自动化感知、决策和问题解决。为此,我们引入了一个模型无关框架——长期对话代理(LD-Agent),包含三个独立可调模块,分别用于事件感知、人格提取和响应生成。该框架的事件记忆模块采用长短时记忆库,分别关注历史会话和当前会话,并引入基于主题的检索机制提高记忆检索的准确性。此外,人格模块为用户和代理进行动态人格建模。随后将检索到的记忆和提取的人格集成并输入生成器,以产生适当的响应。LD-Agent的有效性、通用性和跨域能力已在各种基准测试、模型和任务中得到了实证。相关代码已发布在https://github.com/leolee99/LD-Agent。
要点
- 开放域对话系统借助大型语言模型(LLM)取得显著进步。
- 现有系统主要关注短暂单一会话,忽视长期和个性化互动需求。
- 事件总结和人格管理是解决长期对话的关键要素。
- LLM的认知和推理能力显著提高自动化感知、决策和问题解决的可能性。
- 引入LD-Agent模型无关框架,包含事件感知、人格提取和响应生成三个独立可调模块。
- LD-Agent采用长短时记忆库来关注历史与当前会话,采用基于主题的检索机制提升记忆检索准确性。
点此查看论文截图

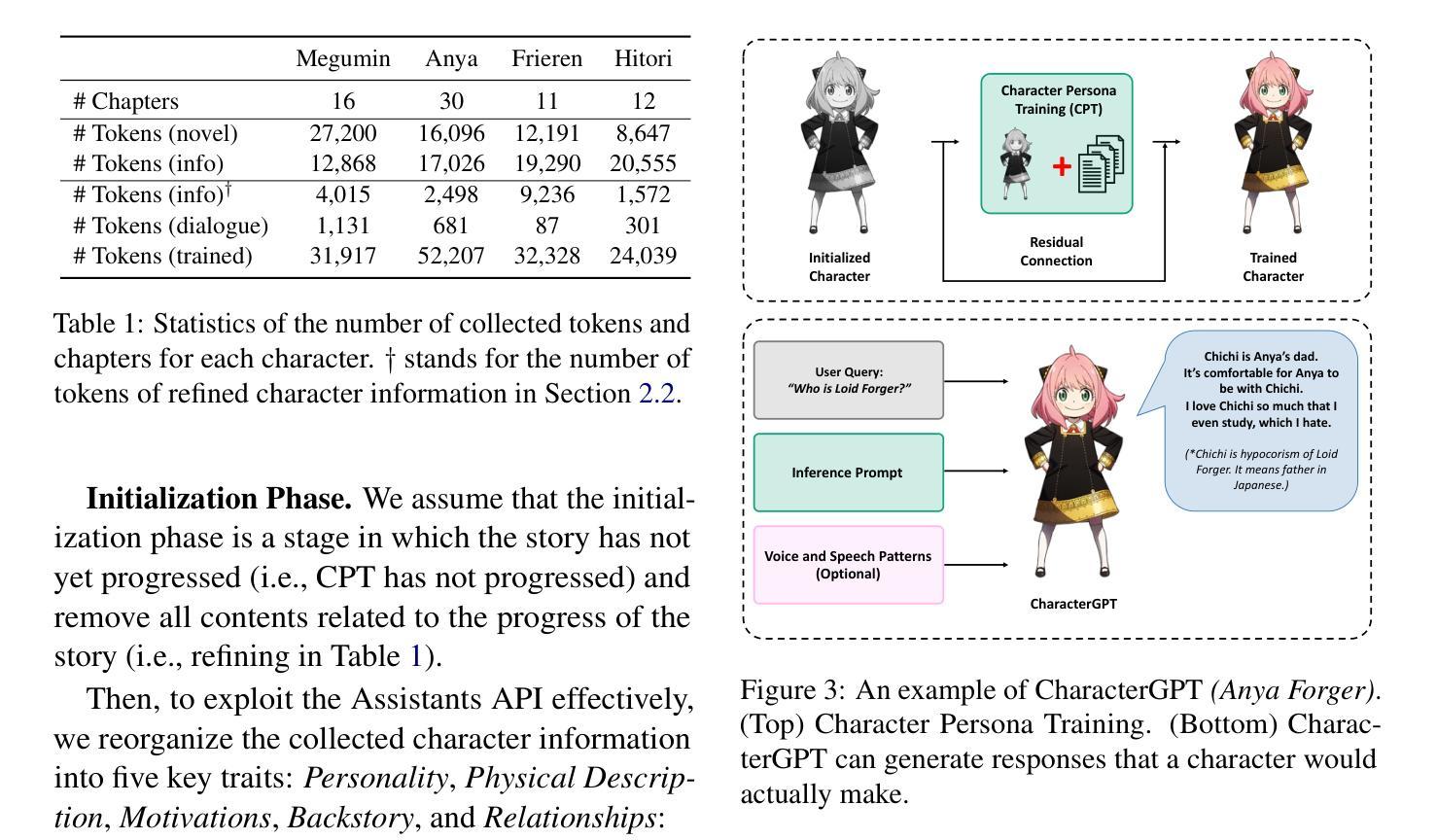
CharacterGPT: A Persona Reconstruction Framework for Role-Playing Agents
Authors:Jeiyoon Park, Chanjun Park, Heuiseok Lim
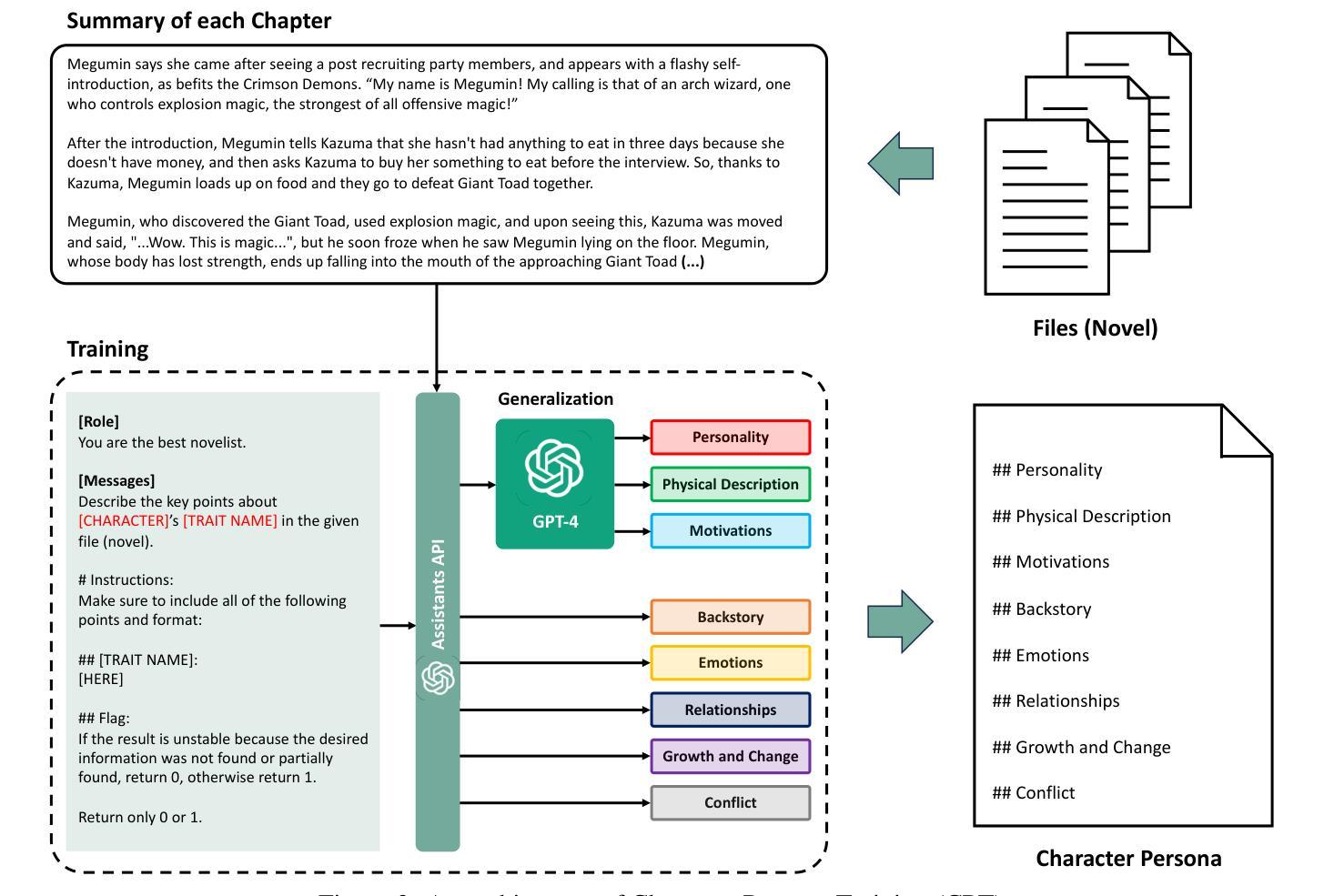
With the recent introduction of Assistants API, it is expected that document-based language models will be actively used in various domains, especially Role-playing. However, a key challenge lies in utilizing protagonist’s persona: Assistants API often fails to achieve with its search because the information extraction part is different each time and it often omits important information such as protagonist’s backstory or relationships. It is hard to maintain a consistent persona simply by using the persona document as input to the Assistants API. To address the challenge of achieving stable persona consistency, we propose CharacterGPT, a novel persona reconstruction framework to alleviate the shortcomings of the Assistants API. Our method involves Character Persona Training (CPT), an effective persona rebuilding process that updates the character persona by extracting the character’s traits from given summary of the novel for each character as if the story in a novel progresses. In our experiments, we ask each character to take the Big Five Inventory personality test in various settings and analyze the results. To assess whether it can think outside the box, we let each character generate short novels. Extensive experiments and human evaluation demonstrate that CharacterGPT presents new possibilities for role-playing agent research. Code and results are available at: https://github.com/Jeiyoon/charactergpt
随着最近Assistant API的引入,预计基于文档的模型将在各种领域中得到广泛应用,特别是在角色扮演方面。然而,关键挑战在于如何利用主角的人设:由于每次信息提取部分都不同,并且经常遗漏重要信息,如主角的背景故事或关系,因此Assistant API的搜索往往无法达到目的。仅仅将人设文档作为输入提供给Assistant API,很难保持一致性的人设。为了解决实现稳定人设一致性的挑战,我们提出了CharacterGPT,这是一种新型的人设重建框架,旨在缓解Assistant API的缺点。我们的方法包括Character Persona Training(CPT),这是一种有效的重建过程,通过从给定的小说摘要中提取每个角色的特征来更新角色的人设,就像小说情节进展一样。在我们的实验中,我们要求每个角色在各种情境下接受五大人格测验并分析其测试结果。为了评估它是否拥有跳跃式思维的能力,我们让各个角色创作短篇小说。广泛的实验和人类评估表明,CharacterGPT为角色扮演代理研究提供了新的可能性。代码和结果可通过以下链接获取:https://github.com/Jeiyoon/charactergpt
论文及项目相关链接
PDF NAACL 2025 Industry Track (Oral)
Summary:随着Assistants API的引入,文档型语言模型在角色扮演等领域的应用前景广阔,但如何利用主角人设是一个挑战。Assistants API在信息提取方面存在缺陷,难以维持人设一致性。为解决这个问题,提出了CharacterGPT框架,通过Character Persona Training(CPT)进行人设重建,从小说概述中提取角色特性来更新角色人设。实验证明,CharacterGPT为角色扮演代理研究提供了新的可能性。
Key Takeaways:
- Assistants API在文档型语言模型的应用中,特别是在角色扮演领域,有着广阔的应用前景。
- 利用主角的人设是应用Assistants API的一个关键挑战。
- Assistants API在信息提取方面存在缺陷,每次提取的信息不同,且容易遗漏重要信息,如主角的背景故事和人际关系。
- CharacterGPT是一个新颖的人设重建框架,旨在缓解Assistants API的短板。
- CharacterGPT通过Character Persona Training(CPT)进行人设重建,随着故事进展,从给定的小说概述中提取角色特性来更新角色人设。
- 实验证明,CharacterGPT能够让角色在多种情境下接受Big Five Inventory性格测试,并展现出思考创新能力。
点此查看论文截图


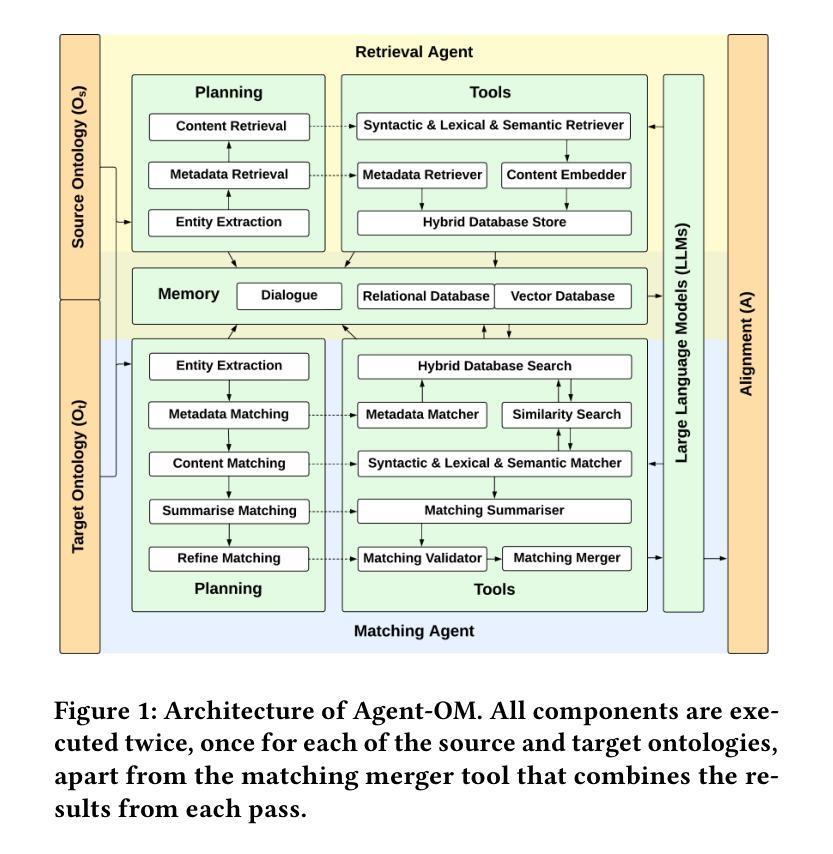
Agent-OM: Leveraging LLM Agents for Ontology Matching
Authors:Zhangcheng Qiang, Weiqing Wang, Kerry Taylor
Ontology matching (OM) enables semantic interoperability between different ontologies and resolves their conceptual heterogeneity by aligning related entities. OM systems currently have two prevailing design paradigms: conventional knowledge-based expert systems and newer machine learning-based predictive systems. While large language models (LLMs) and LLM agents have revolutionised data engineering and have been applied creatively in many domains, their potential for OM remains underexplored. This study introduces a novel agent-powered LLM-based design paradigm for OM systems. With consideration of several specific challenges in leveraging LLM agents for OM, we propose a generic framework, namely Agent-OM (Agent for Ontology Matching), consisting of two Siamese agents for retrieval and matching, with a set of OM tools. Our framework is implemented in a proof-of-concept system. Evaluations of three Ontology Alignment Evaluation Initiative (OAEI) tracks over state-of-the-art OM systems show that our system can achieve results very close to the long-standing best performance on simple OM tasks and can significantly improve the performance on complex and few-shot OM tasks.
本体匹配(OM)能够在不同的本体之间实现语义互操作性,并通过对齐相关实体解决其概念上的异质性。目前,OM系统主要有两种流行的设计范式:传统的基于知识的专家系统和较新的基于机器学习的预测系统。虽然大型语言模型(LLM)和LLM代理已经彻底改变了数据工程,并在许多领域得到了创造性的应用,但它们在OM中的潜力仍未得到充分探索。本研究引入了一种基于新型代理驱动的LLM的OM系统设计范式。考虑到利用LLM代理进行OM所面临的若干特定挑战,我们提出了一个通用框架,即Agent-OM(用于本体匹配的代理),该框架包含两个用于检索和匹配的Siamese代理以及一组OM工具。我们的框架在一个概念验证系统中得到了实现。对最先进的OM系统进行了三次本体对齐评估倡议(OAEI)跟踪评估表明,我们的系统在简单OM任务上取得了接近长期最佳性能的结果,并在复杂和少量OM任务上能显著提高性能。
论文及项目相关链接
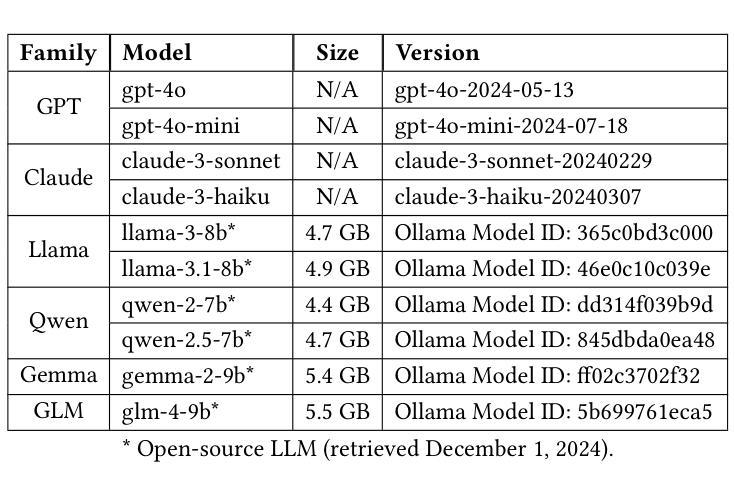
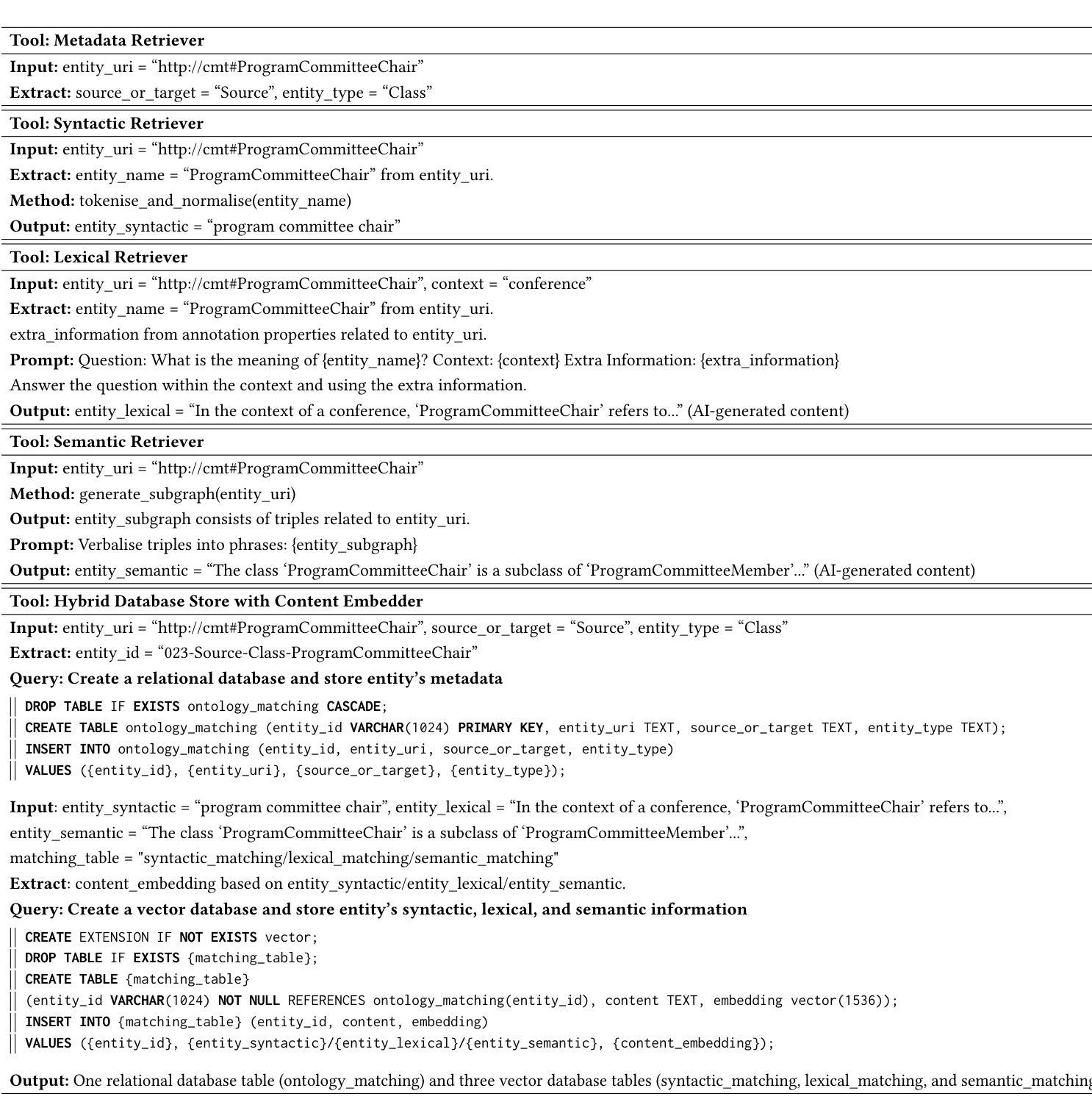
PDF 19 pages, 12 figures, 3 tables
Summary
本体匹配(OM)通过语义互联不同本体,解决其概念异质性,实现实体对齐。当前OM系统主要有传统知识型专家系统和新兴机器学习预测系统两种设计范式。大型语言模型(LLM)及其代理人在数据工程领域应用广泛,但在OM方面的潜力尚未得到充分探索。本研究引入新型基于LLM的代理设计范式OM系统。在考虑利用LLM代理人进行OM所面临的特定挑战的基础上,我们提出一个通用框架——Agent-OM(用于本体匹配的代理),包含两个用于检索和匹配的Siamese代理人及一套OM工具。框架在概念验证系统中实现,对最新OM系统的三项OAEI轨迹评估表明,该系统在简单OM任务上表现接近最佳,并在复杂和少量OM任务上显著提高性能。
Key Takeaways
- 本体匹配(OM)是通过语义互联不同本体来解决其概念异质性,实现实体对齐的关键技术。
- 当前OM系统的两种主要设计范式包括传统知识型专家系统和机器学习预测系统。
- 大型语言模型(LLM)在数据工程领域应用广泛,但在本体匹配方面的潜力尚未被充分探索。
- 本研究提出一种新型的基于LLM的代理设计范式OM系统——Agent-OM。
- Agent-OM框架包含用于检索和匹配的Siamese代理人及一套OM工具。
- Agent-OM系统性能评估显示,在简单OM任务上表现接近最佳,复杂和少量OM任务上显著提高性能。
- 此研究为利用LLM在OM领域的进一步发展提供了有力的基础和启示。
点此查看论文截图