⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-02-15 更新
AnomalyGFM: Graph Foundation Model for Zero/Few-shot Anomaly Detection
Authors:Hezhe Qiao, Chaoxi Niu, Ling Chen, Guansong Pang
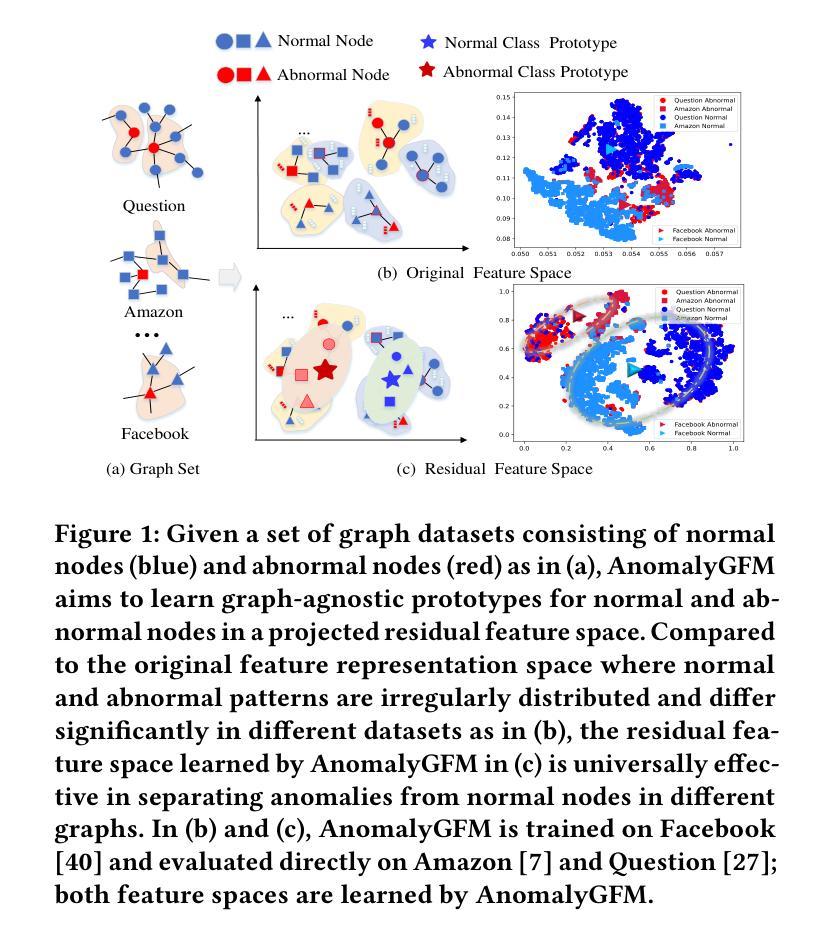
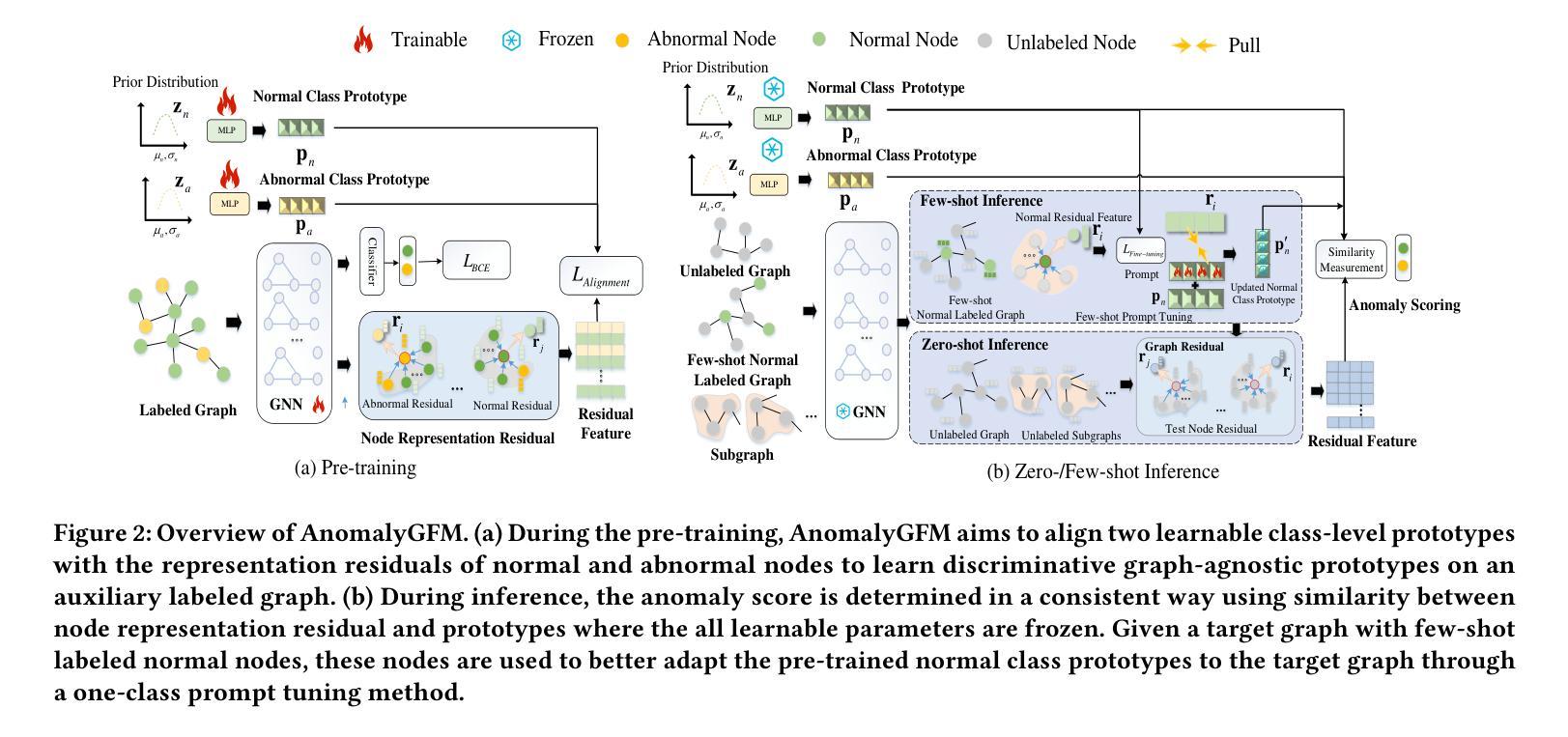
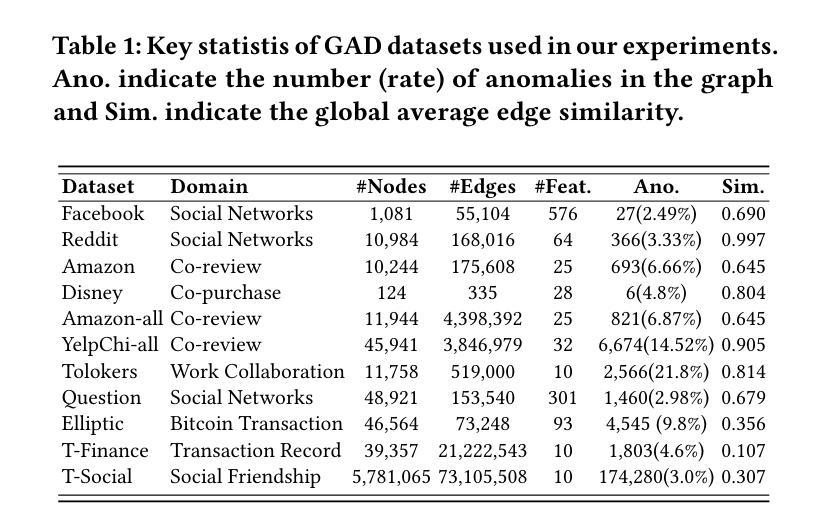
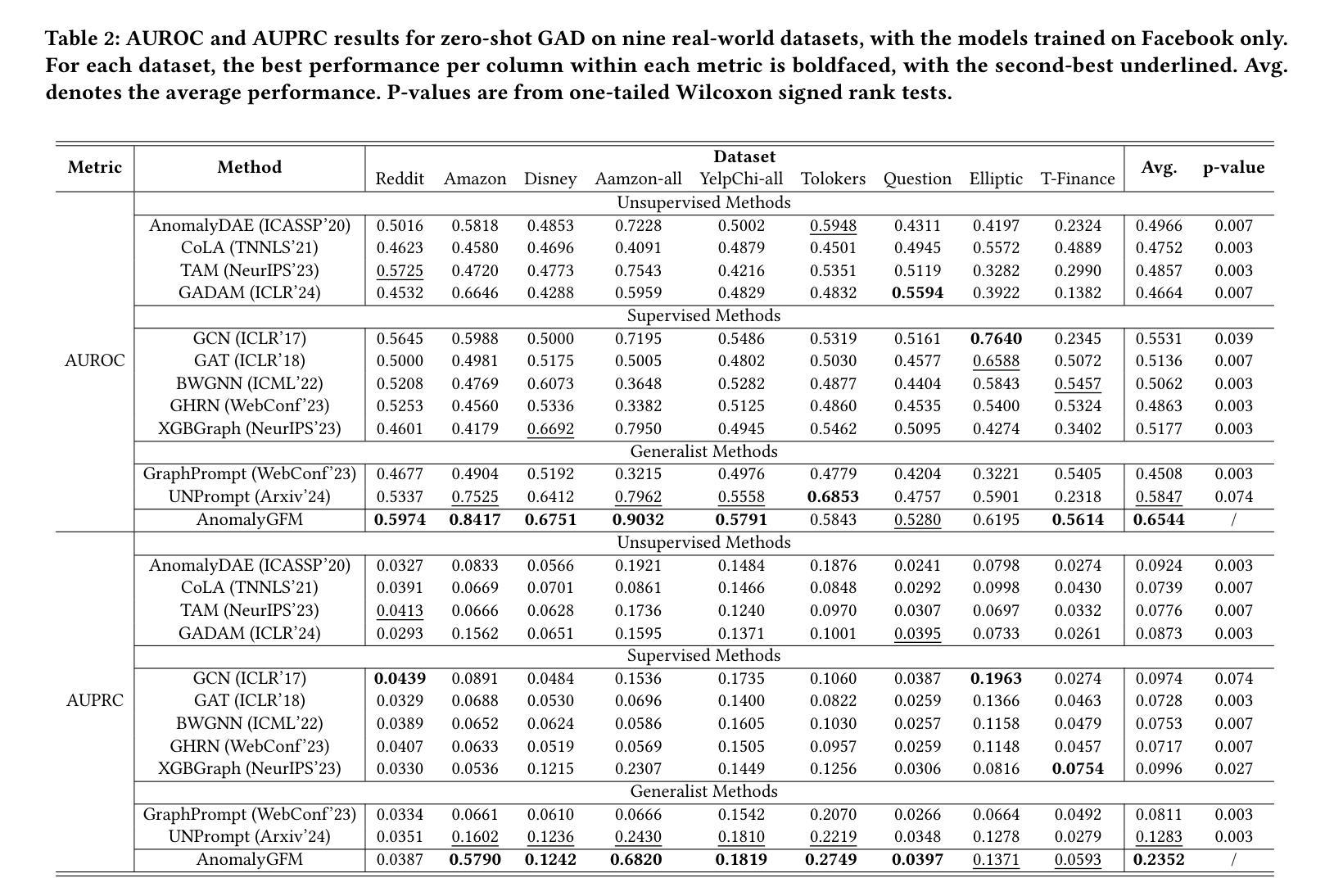
Graph anomaly detection (GAD) aims to identify abnormal nodes that differ from the majority of the nodes in a graph, which has been attracting significant attention in recent years. Existing generalist graph models have achieved remarkable success in different graph tasks but struggle to generalize to the GAD task. This limitation arises from their difficulty in learning generalized knowledge for capturing the inherently infrequent, irregular and heterogeneous abnormality patterns in graphs from different domains. To address this challenge, we propose AnomalyGFM, a GAD-oriented graph foundation model that supports zero-shot inference and few-shot prompt tuning for GAD in diverse graph datasets. One key insight is that graph-agnostic representations for normal and abnormal classes are required to support effective zero/few-shot GAD across different graphs. Motivated by this, AnomalyGFM is pre-trained to align data-independent, learnable normal and abnormal class prototypes with node representation residuals (i.e., representation deviation of a node from its neighbors). The residual features essentially project the node information into a unified feature space where we can effectively measure the abnormality of nodes from different graphs in a consistent way. This provides a driving force for the learning of graph-agnostic, discriminative prototypes for the normal and abnormal classes, which can be used to enable zero-shot GAD on new graphs, including very large-scale graphs. If there are few-shot labeled normal nodes available in the new graphs, AnomalyGFM can further support prompt tuning to leverage these nodes for better adaptation. Comprehensive experiments on 11 widely-used GAD datasets with real anomalies, demonstrate that AnomalyGFM significantly outperforms state-of-the-art competing methods under both zero- and few-shot GAD settings.
图异常检测(GAD)旨在识别图中与大多数节点不同的异常节点,这近年来引起了广泛关注。现有的通用图模型在不同的图任务中取得了显著的成功,但在GAD任务中却难以推广。这一局限性源于它们在捕捉来自不同领域的图中固有的稀少、不规则和异质异常模式时学习通用知识的困难。为了解决这一挑战,我们提出了AnomalyGFM,一个面向GAD的图基础模型,支持零样本推理和少量样本提示调整,用于处理各种图数据集中的GAD。一个重要的见解是,为了支持在不同图上进行有效的零/少量样本GAD,需要针对正常和异常类别的图无关表示。受此启发,AnomalyGFM进行了预训练,以将独立于数据的学习到的正常和异常类别原型与节点表示残差(即节点与其邻居的表示偏差)对齐。残差特征本质上将节点信息投影到一个统一的特征空间,我们可以有效地测量不同节点的异常值。这为学习正常和异常类别的图无关判别原型提供了动力,这些原型可用于在新图上进行零样本GAD,包括大规模图。如果新图中只有少量标记的正常节点可用,AnomalyGFM还可以进一步支持提示调整,以利用这些节点进行更好的适应。在具有真实异常的11个广泛使用的GAD数据集上的实验表明,AnomalyGFM在零样本和少量样本GAD设置下均显著优于最新竞争方法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 14 pages
Summary
本文介绍了针对图异常检测(GAD)任务的新型图基础模型AnomalyGFM。该模型支持零样本推理和少样本提示调优,旨在解决现有图模型在应对多样化和跨领域图的异常检测时存在的局限性。AnomalyGFM通过对节点表示残差的训练,实现对正常和异常类数据无关的通用表示,并利用这些表示实现零样本和少样本条件下的图异常检测。实验证明,AnomalyGFM在多个GAD数据集上的表现显著优于现有方法。
Key Takeaways
- Graph anomaly detection (GAD)面临现有图模型的通用化挑战。
- AnomalyGFM是一种针对GAD任务的图基础模型,支持零样本推理和少样本提示调优。
- AnomalyGFM通过对节点表示残差的训练,实现正常和异常类的数据无关通用表示。
- 模型利用这些表示在统一特征空间中测量不同图中节点的异常性。
- AnomalyGFM通过驱动学习正常和异常类的鉴别原型,实现零样本GAD在新图上的应用。
- 当新图中存在少量标记的正常节点时,AnomalyGFM可通过提示调整进行适应利用。
点此查看论文截图

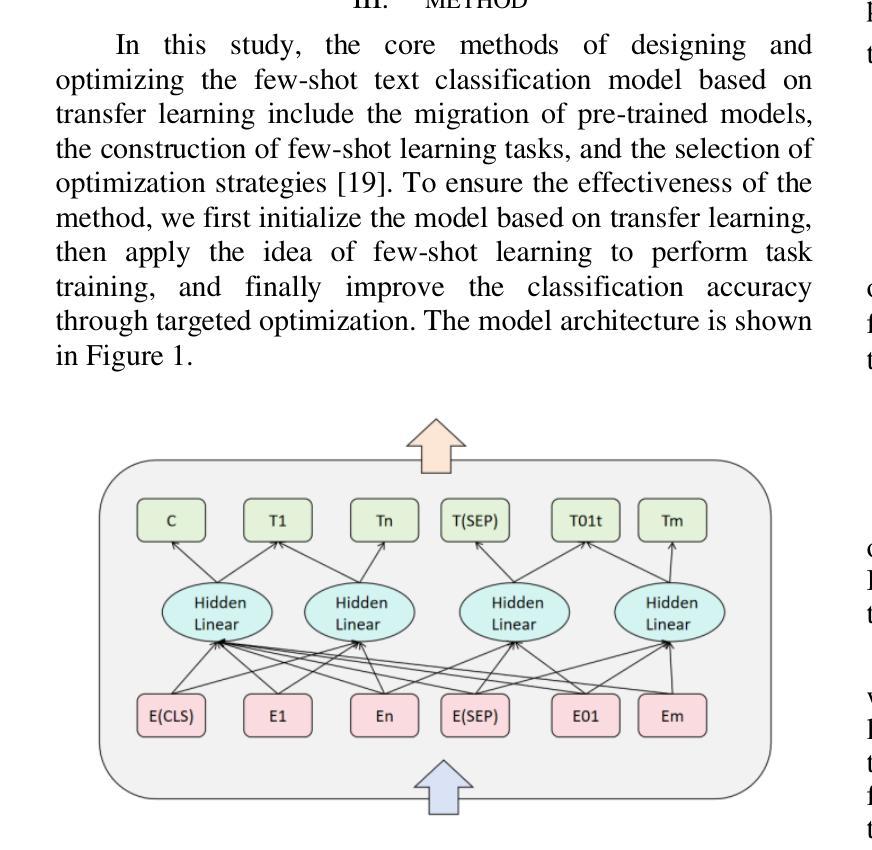
A Hybrid Model for Few-Shot Text Classification Using Transfer and Meta-Learning
Authors:Jia Gao, Shuangquan Lyu, Guiran Liu, Binrong Zhu, Hongye Zheng, Xiaoxuan Liao
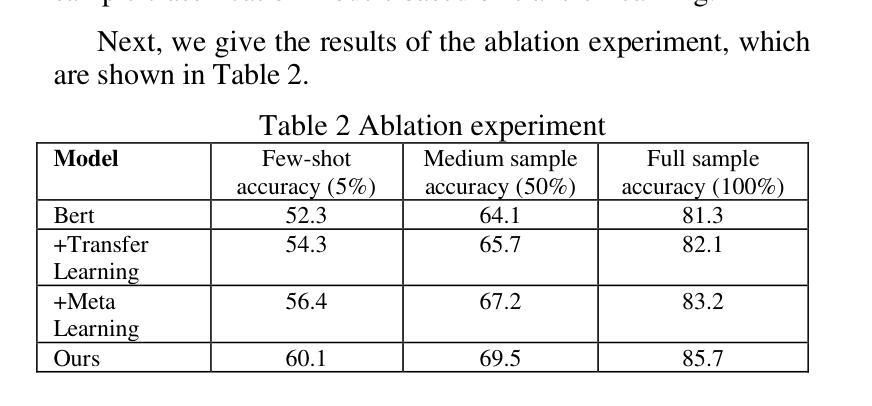
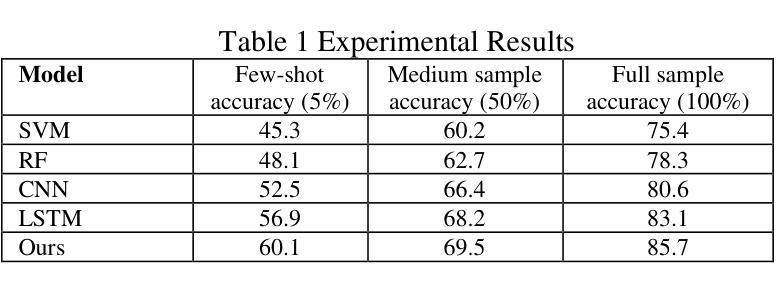
With the continuous development of natural language processing (NLP) technology, text classification tasks have been widely used in multiple application fields. However, obtaining labeled data is often expensive and difficult, especially in few-shot learning scenarios. To solve this problem, this paper proposes a few-shot text classification model based on transfer learning and meta-learning. The model uses the knowledge of the pre-trained model for transfer and optimizes the model’s rapid adaptability in few-sample tasks through a meta-learning mechanism. Through a series of comparative experiments and ablation experiments, we verified the effectiveness of the proposed method. The experimental results show that under the conditions of few samples and medium samples, the model based on transfer learning and meta-learning significantly outperforms traditional machine learning and deep learning methods. In addition, ablation experiments further analyzed the contribution of each component to the model performance and confirmed the key role of transfer learning and meta-learning in improving model accuracy. Finally, this paper discusses future research directions and looks forward to the potential of this method in practical applications.
随着自然语言处理(NLP)技术的不断发展,文本分类任务已广泛应用于多个应用领域。然而,获取标注数据通常既昂贵又困难,尤其在少样本学习场景中更是如此。为了解决这一问题,本文提出了一种基于迁移学习和元学习的少样本文本分类模型。该模型利用预训练模型的知识进行迁移,并通过元学习机制优化模型在少量样本任务中的快速适应能力。通过一系列对比实验和消融实验,我们验证了所提出方法的有效性。实验结果表明,在少量样本和中量样本的条件下,基于迁移学习和元学习的模型显著优于传统的机器学习和深度学习方法。此外,消融实验进一步分析了各个组件对模型性能的贡献,并证实了迁移学习和元学习在提高模型准确性方面的关键作用。最后,本文讨论了未来的研究方向,并期待该方法在实际应用中的潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于迁移学习和元学习的少样本文本分类模型被提出,利用预训练模型知识实现迁移,并通过元学习机制优化模型的快速适应能力。实验证明,该模型在少量样本和中量样本条件下显著优于传统机器学习和深度学习方法。
Key Takeaways
- 该论文针对少样本学习场景下的文本分类任务,提出了基于迁移学习和元学习的模型。
- 模型利用预训练模型的知识进行迁移学习,以提高对未知数据的适应能力。
- 通过元学习机制,模型能够在新任务中快速适应并优化性能。
- 实验证明,该模型在少量样本和中量样本条件下显著优于传统机器学习和深度学习模型。
- 迁移学习和元学习在提升模型准确性方面起到了关键作用。
- 论文通过消融实验分析了模型中各组件的贡献。
点此查看论文截图


Vision-Language In-Context Learning Driven Few-Shot Visual Inspection Model
Authors:Shiryu Ueno, Yoshikazu Hayashi, Shunsuke Nakatsuka, Yusei Yamada, Hiroaki Aizawa, Kunihito Kato
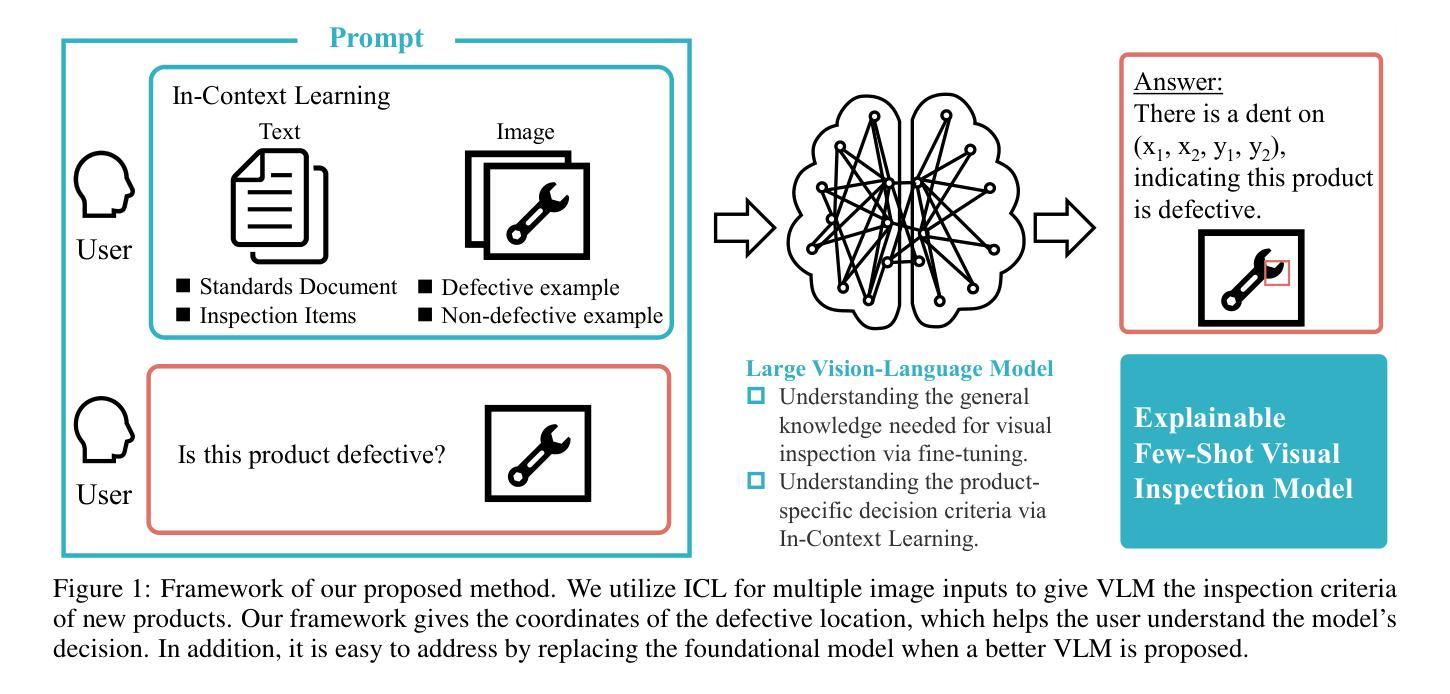
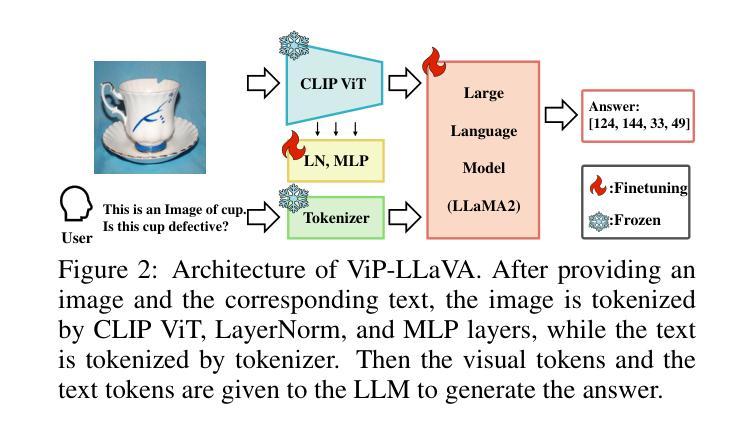
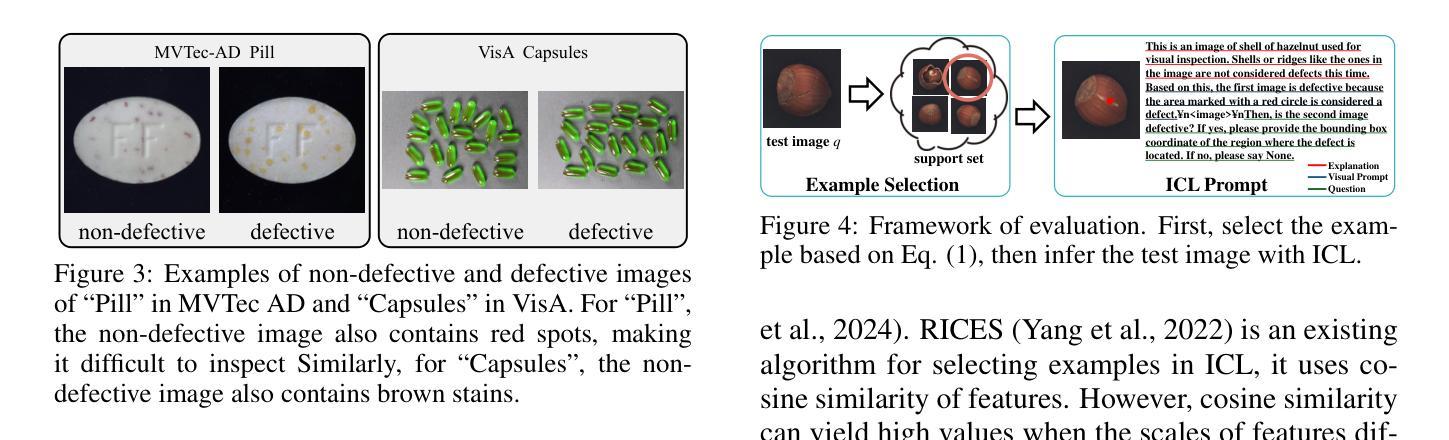
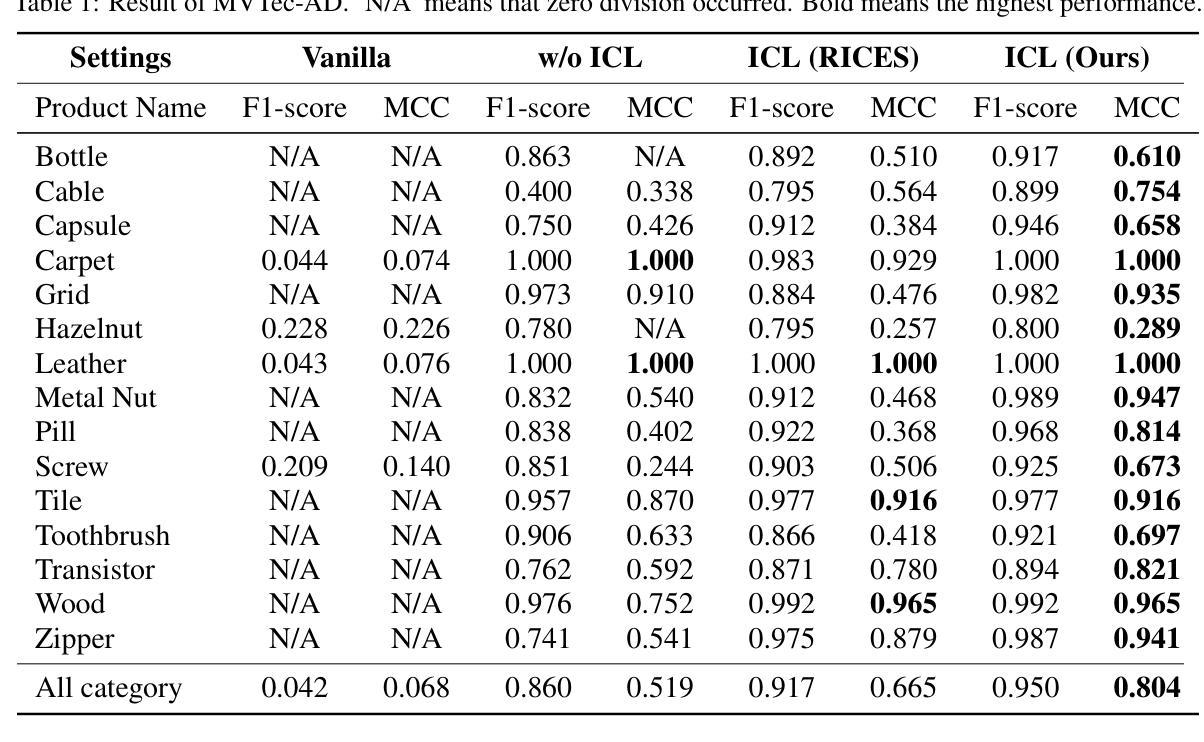
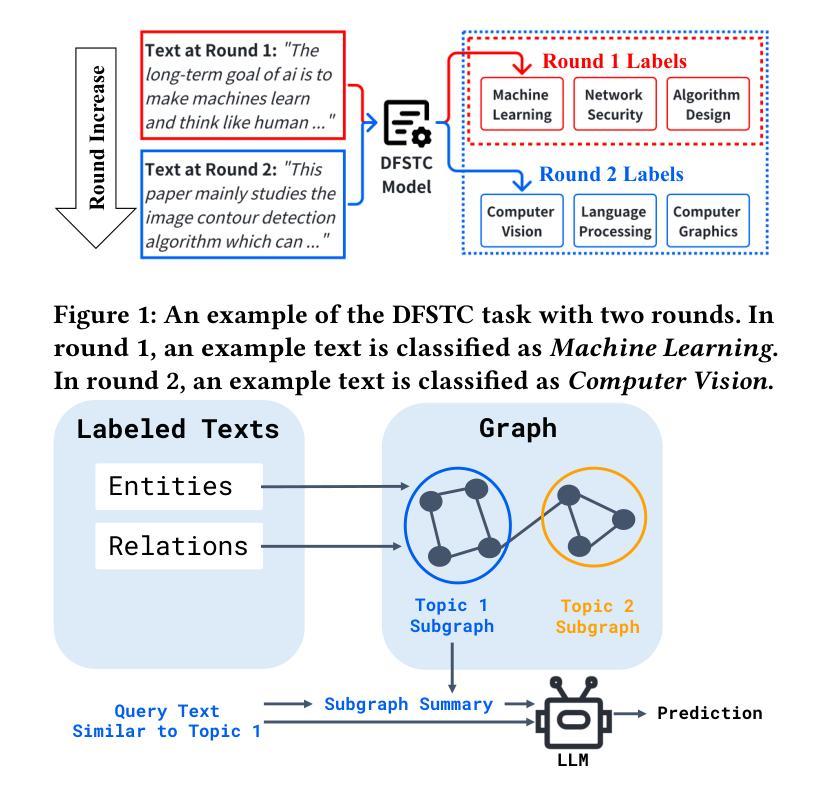
We propose general visual inspection model using Vision-Language Model(VLM) with few-shot images of non-defective or defective products, along with explanatory texts that serve as inspection criteria. Although existing VLM exhibit high performance across various tasks, they are not trained on specific tasks such as visual inspection. Thus, we construct a dataset consisting of diverse images of non-defective and defective products collected from the web, along with unified formatted output text, and fine-tune VLM. For new products, our method employs In-Context Learning, which allows the model to perform inspections with an example of non-defective or defective image and the corresponding explanatory texts with visual prompts. This approach eliminates the need to collect a large number of training samples and re-train the model for each product. The experimental results show that our method achieves high performance, with MCC of 0.804 and F1-score of 0.950 on MVTec AD in a one-shot manner. Our code is available athttps://github.com/ia-gu/Vision-Language-In-Context-Learning-Driven-Few-Shot-Visual-Inspection-Model.
我们提出了一种基于视觉语言模型(VLM)的通用视觉检测模型。该模型使用少数非缺陷或缺陷产品的图像以及作为检测标准的解释性文本。尽管现有的VLM在各种任务中表现出高性能,但它们并未针对视觉检测等特定任务进行训练。因此,我们构建了一个数据集,其中包含从网上收集的非缺陷和缺陷产品的多样化图像,以及统一格式的输出文本,并对VLM进行了微调。对于新产品,我们的方法采用上下文学习(In-Context Learning),该方法允许模型通过非缺陷或缺陷图像的示例以及相应的解释性文本和视觉提示进行检查。这种方法消除了需要收集大量训练样本并为每个产品重新训练模型的需求。实验结果表明,我们的方法取得了高性能,在MVTec AD上的一次性检测方式下,MCC为0.804,F1分数为0.950。我们的代码可从https://github.com/ia-gu/Vision-Language-In-Context-Learning-Driven-Few-Shot-Visual-Inspection-Model获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF VISAPP 2025
Summary
基于视觉语言模型(VLM)的非缺陷和缺陷产品少样本视觉检查模型被提出。通过使用少量的图片样本和作为检查标准的解释性文本,构建数据集并对VLM进行微调。对于新产品,采用上下文学习方法,只需一个非缺陷或缺陷产品的示例图像和相应的解释性文本即可完成检查,无需收集大量训练样本并重新训练模型。实验结果显示,该方法在MVTec AD数据集上实现了高性能,一次拍摄的平均MCC为0.804,F1分数为0.950。
Key Takeaways
- 提出了基于视觉语言模型(VLM)的通用视觉检查模型。
- 使用少量非缺陷和缺陷产品的图像样本,结合解释性文本作为检查标准。
- 对VLM进行微调以适应特定的视觉检查任务。
- 采用上下文学习方法,无需为每个产品重新收集大量训练样本。
- 通过实例展示,新方法具有高效率和高性能。
- 在MVTec AD数据集上的实验结果显示,一次拍摄的平均MCC为0.804,F1分数为0.950。
- 代码已公开可访问。
点此查看论文截图


Graph-based Retrieval Augmented Generation for Dynamic Few-shot Text Classification
Authors:Yubo Wang, Haoyang Li, Fei Teng, Lei Chen
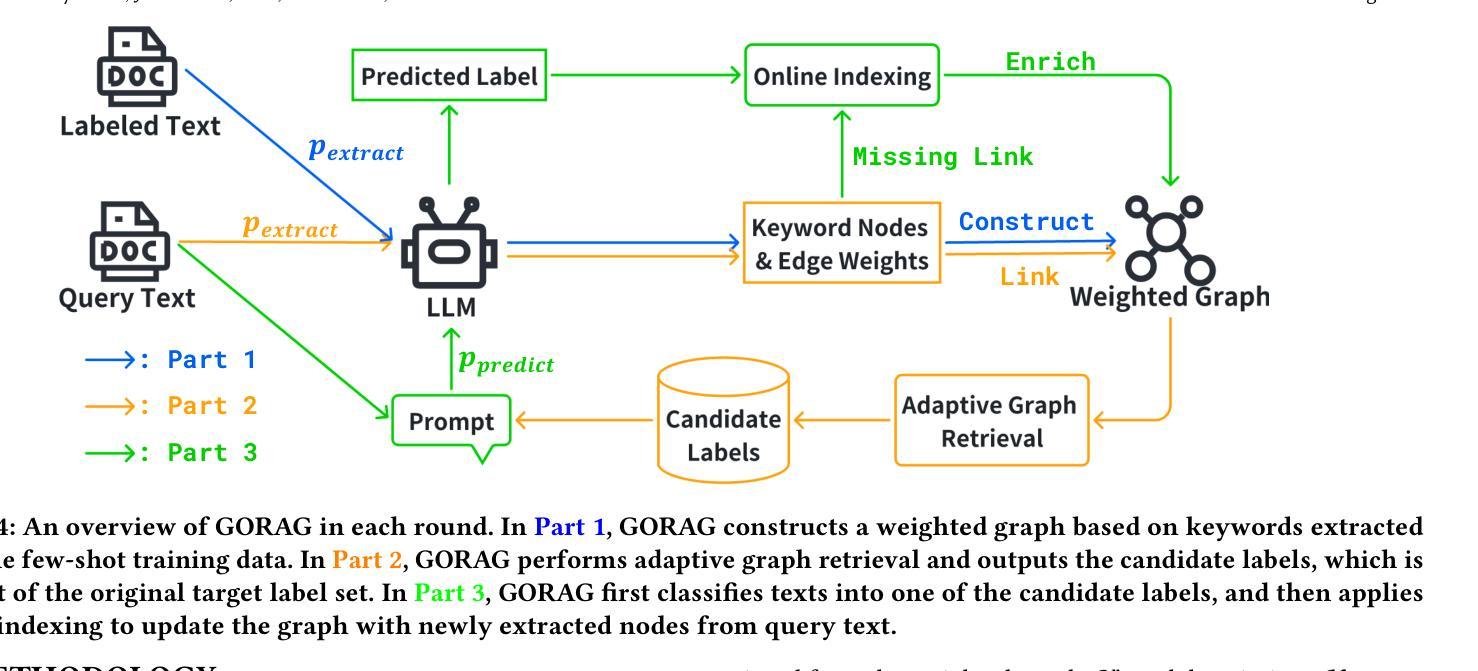
Text classification is a fundamental task in data mining, pivotal to various applications such as tabular understanding and recommendation. Although neural network-based models, such as CNN and BERT, have demonstrated remarkable performance in text classification, their effectiveness heavily relies on abundant labeled training data. This dependency makes these models less effective in dynamic few-shot text classification, where labeled data is scarce, and new target labels frequently appear based on application needs. Recently, large language models (LLMs) have shown promise due to their extensive pretraining and contextual understanding ability. Current approaches provide LLMs with text inputs, candidate labels, and additional side information (e.g., descriptions) to classify texts. However, their effectiveness is hindered by the increased input size and the noise introduced through side information processing. To address these limitations, we propose a graph-based online retrieval-augmented generation framework, namely GORAG, for dynamic few-shot text classification. Rather than treating each input independently, GORAG constructs and maintains a weighted graph by extracting side information across all target texts. In this graph, text keywords and labels are represented as nodes, with edges indicating the correlations between them. To model these correlations, GORAG employs an edge weighting mechanism to prioritize the importance and reliability of extracted information and dynamically retrieves relevant context using a minimum-cost spanning tree tailored for each text input. Empirical evaluations demonstrate that GORAG outperforms existing approaches by providing more comprehensive and precise contextual information.
文本分类是数据挖掘中的一项基本任务,对于诸如表格理解和推荐等应用程序至关重要。尽管基于神经网络模型(例如CNN和BERT)在文本分类方面表现出了显著的性能,但它们的有效性严重依赖于大量的标记训练数据。这种依赖性使得这些模型在动态少样本文本分类中的效果较差,这里的标记数据稀缺,并且基于应用需求,新的目标标签经常出现。最近,由于大型语言模型的广泛预训练和上下文理解能力,它们显示出了一定的潜力。当前的方法为大型语言模型提供文本输入、候选标签和额外的侧面信息(例如描述)来进行文本分类。然而,其有效性受到了输入大小增加和通过侧信息处理引入的噪声的阻碍。为了解决这些局限性,我们提出了一种基于图的在线检索增强生成框架,名为GORAG,用于动态少样本文本分类。GORAG不是独立处理每个输入,而是构建并维护一个加权图,通过提取所有目标文本之间的侧面信息。在此图中,文本关键词和标签被表示为节点,边表示它们之间的关联。为了对这些关联进行建模,GORAG采用边加权机制来优先处理提取信息的重要性和可靠性,并使用针对每个文本输入定制的最低成本生成树动态检索相关上下文。经验评估表明,GORAG通过提供更全面和精确的背景信息,优于现有方法。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
文本分类是数据挖掘中的基础任务,对表格理解和推荐等应用至关重要。尽管神经网络模型如CNN和BERT在文本分类中表现出卓越性能,但它们严重依赖于大量标注训练数据。在动态少样本文本分类中,由于标注数据稀缺且新目标标签频繁出现,这些模型的效能受限。大型语言模型(LLMs)因其在预训练和上下文理解方面的优势而展现出潜力。当前方法为LLMs提供文本输入、候选标签和附加的侧信息来进行文本分类。然而,其效能受到输入大小增加和侧信息处理中引入的噪声的阻碍。为解决这些局限性,本文提出一种基于图的在线检索增强生成框架——GORAG,用于动态少样本文本分类。GORAG构建并维护一个加权图,通过提取所有目标文本的侧信息来建模文本关键词和标签之间的关系。通过边缘加权机制来优先处理提取信息的重要性和可靠性,并针对每个文本输入动态检索相关上下文,使用最小成本生成树。经验评估表明,GORAG通过提供更全面和精确的背景信息,表现优于现有方法。
Key Takeaways
- 文本分类是数据挖掘中的核心任务,对多种应用至关重要。
- 神经网络模型在文本分类中表现出色,但依赖大量标注数据,这在少样本情况下成为挑战。
- 大型语言模型(LLMs)在预训练和上下文理解方面具有优势,成为少样本文本分类的有前途的方法。
- 当前方法受到输入大小增加和侧信息处理中噪声的制约。
- GORAG框架是一个基于图的在线检索增强生成模型,用于动态少样本文本分类。
- GORAG通过构建加权图来建模文本关键词和标签之间的关系,并优先处理提取信息的重要性和可靠性。
点此查看论文截图


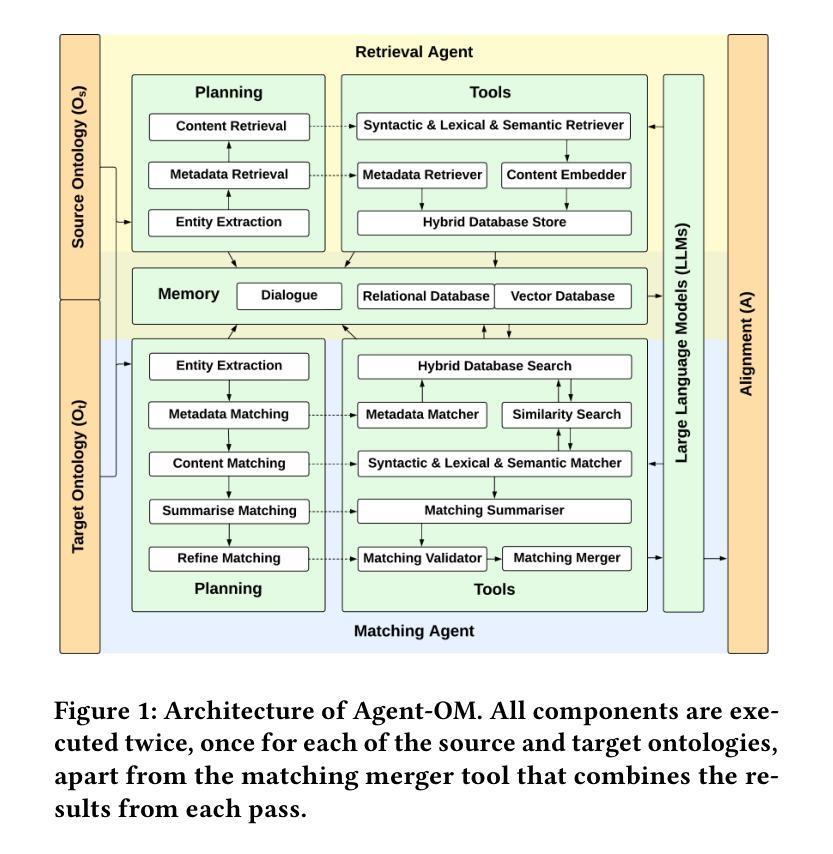
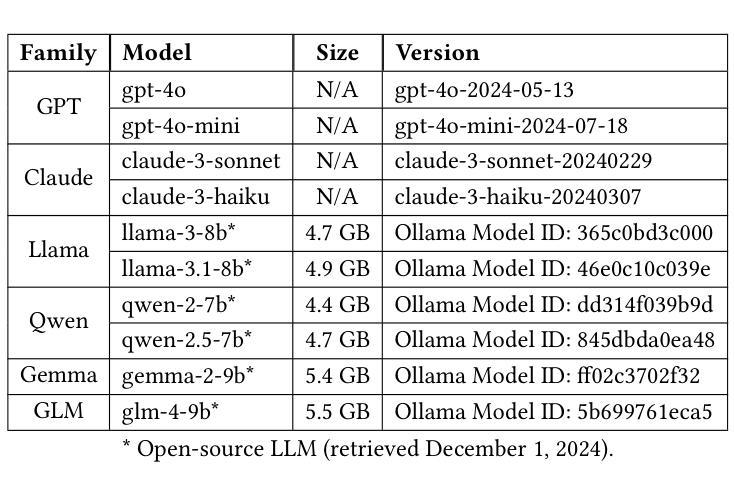
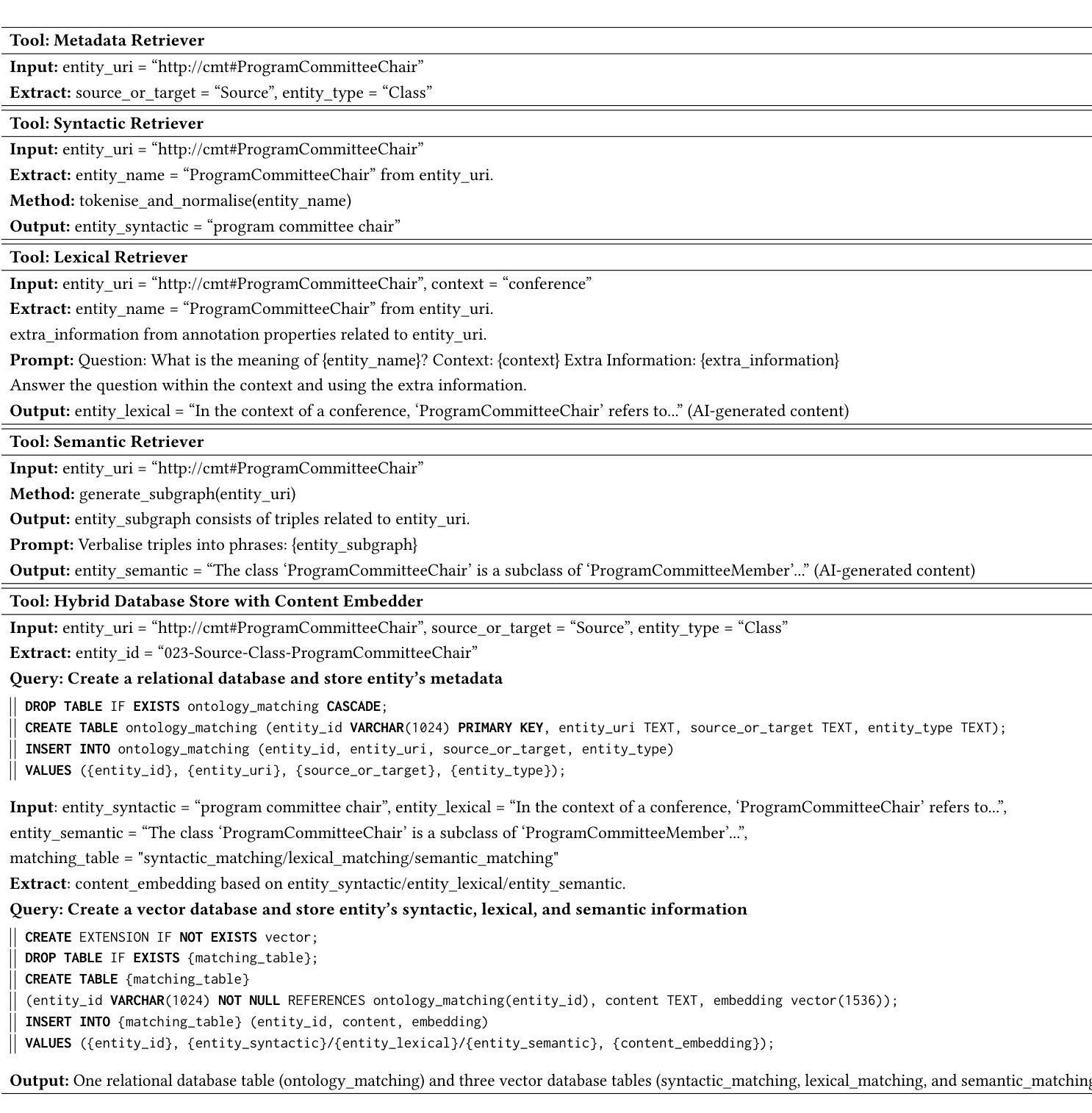
Agent-OM: Leveraging LLM Agents for Ontology Matching
Authors:Zhangcheng Qiang, Weiqing Wang, Kerry Taylor
Ontology matching (OM) enables semantic interoperability between different ontologies and resolves their conceptual heterogeneity by aligning related entities. OM systems currently have two prevailing design paradigms: conventional knowledge-based expert systems and newer machine learning-based predictive systems. While large language models (LLMs) and LLM agents have revolutionised data engineering and have been applied creatively in many domains, their potential for OM remains underexplored. This study introduces a novel agent-powered LLM-based design paradigm for OM systems. With consideration of several specific challenges in leveraging LLM agents for OM, we propose a generic framework, namely Agent-OM (Agent for Ontology Matching), consisting of two Siamese agents for retrieval and matching, with a set of OM tools. Our framework is implemented in a proof-of-concept system. Evaluations of three Ontology Alignment Evaluation Initiative (OAEI) tracks over state-of-the-art OM systems show that our system can achieve results very close to the long-standing best performance on simple OM tasks and can significantly improve the performance on complex and few-shot OM tasks.
本体匹配(OM)通过使不同本体之间实现语义互操作性,并通过对齐相关实体解决其概念上的异质性。目前,OM系统主要有两种流行的设计范式:传统的基于知识的专家系统和较新的基于机器学习的预测系统。虽然大型语言模型(LLM)和LLM代理已经彻底改变了数据工程并且在许多领域得到了创造性的应用,但它们在OM中的潜力仍未得到充分探索。本研究引入了一种新型基于LLM的代理驱动设计范式用于OM系统。考虑到在利用LLM代理进行OM时面临的若干特定挑战,我们提出了一个通用框架,即Agent-OM(用于本体匹配的代理),该框架由两个用于检索和匹配的Siamese代理和一组OM工具组成。我们的框架在一个概念验证系统中实现。对三个本体对齐评估倡议(OAEI)赛道上的最新OM系统的评估表明,我们的系统在简单OM任务上的结果非常接近长期以来的最佳性能,并且在复杂和少量数据的OM任务上可以显著提高性能。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 19 pages, 12 figures, 3 tables
总结
本研究介绍了一种新型基于LLM代理的OM系统设计范式。该范式利用大规模语言模型的能力,通过两个Siamese代理进行检索和匹配,并配备一套OM工具,以解决本体匹配中的挑战。该系统已在证明概念的系统中得到实现。通过对最新OM系统的评价发现,本系统在简单任务上表现接近最佳性能,并在复杂和少量任务上显著提高性能。
关键见解
- 本体匹配(OM)通过对齐相关实体,实现不同本体之间的语义互操作性并解决其概念异质性。
- 当前OM系统主要有两种设计范式:传统的知识型专家系统和新兴的基于机器学习的预测系统。
- 大型语言模型(LLM)和LLM代理在数据工程领域的潜力巨大,但在OM方面的潜力尚未得到充分探索。
- 提出了一种基于LLM的新型代理驱动OM系统设计范式来解决特定挑战。
- 介绍了一个名为Agent-OM(用于本体匹配的代理)的通用框架,包括用于检索和匹配的Siamese代理。
- 该系统在证明概念的系统中得到实现,并在多个OM系统评价中表现优异。
点此查看论文截图