⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-02-15 更新
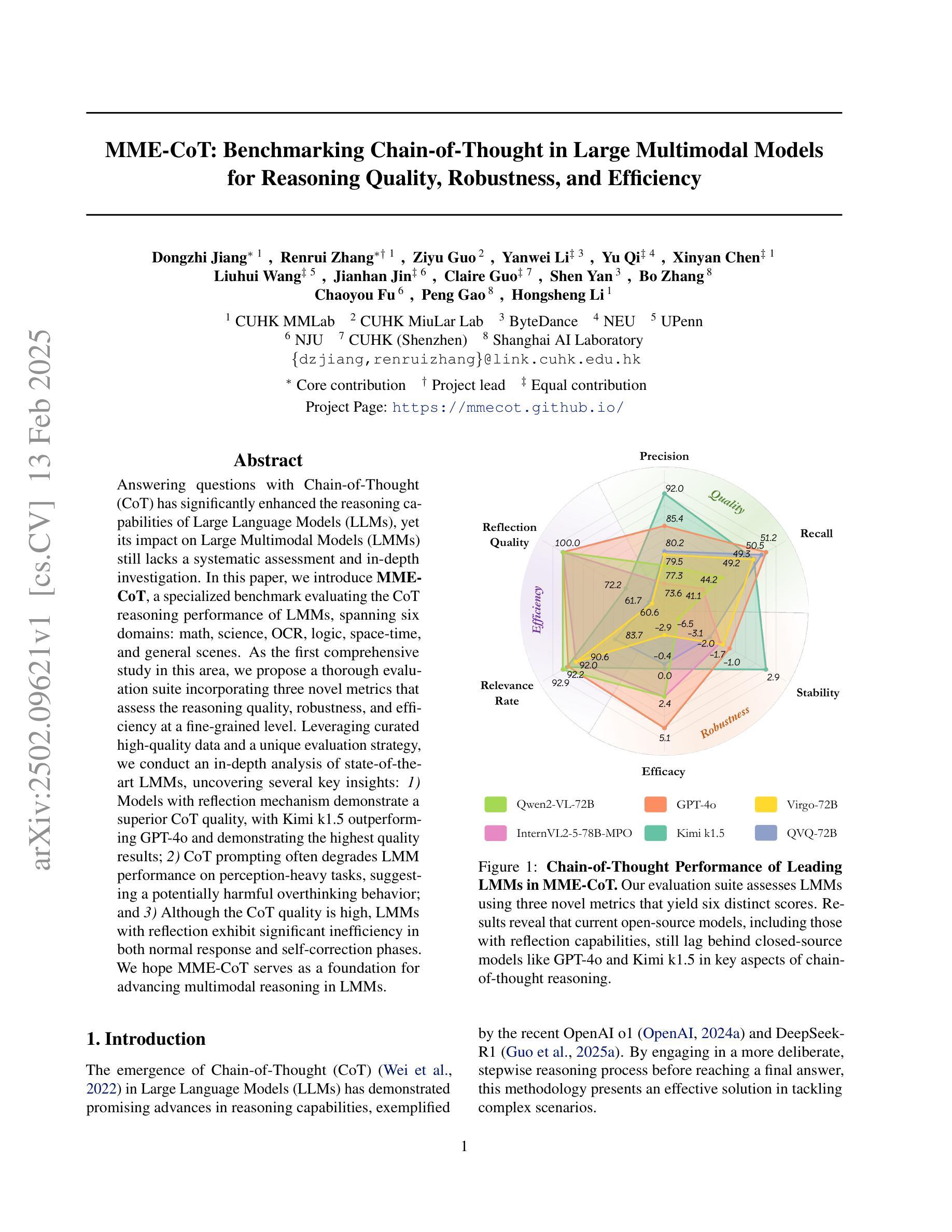
MME-CoT: Benchmarking Chain-of-Thought in Large Multimodal Models for Reasoning Quality, Robustness, and Efficiency
Authors:Dongzhi Jiang, Renrui Zhang, Ziyu Guo, Yanwei Li, Yu Qi, Xinyan Chen, Liuhui Wang, Jianhan Jin, Claire Guo, Shen Yan, Bo Zhang, Chaoyou Fu, Peng Gao, Hongsheng Li
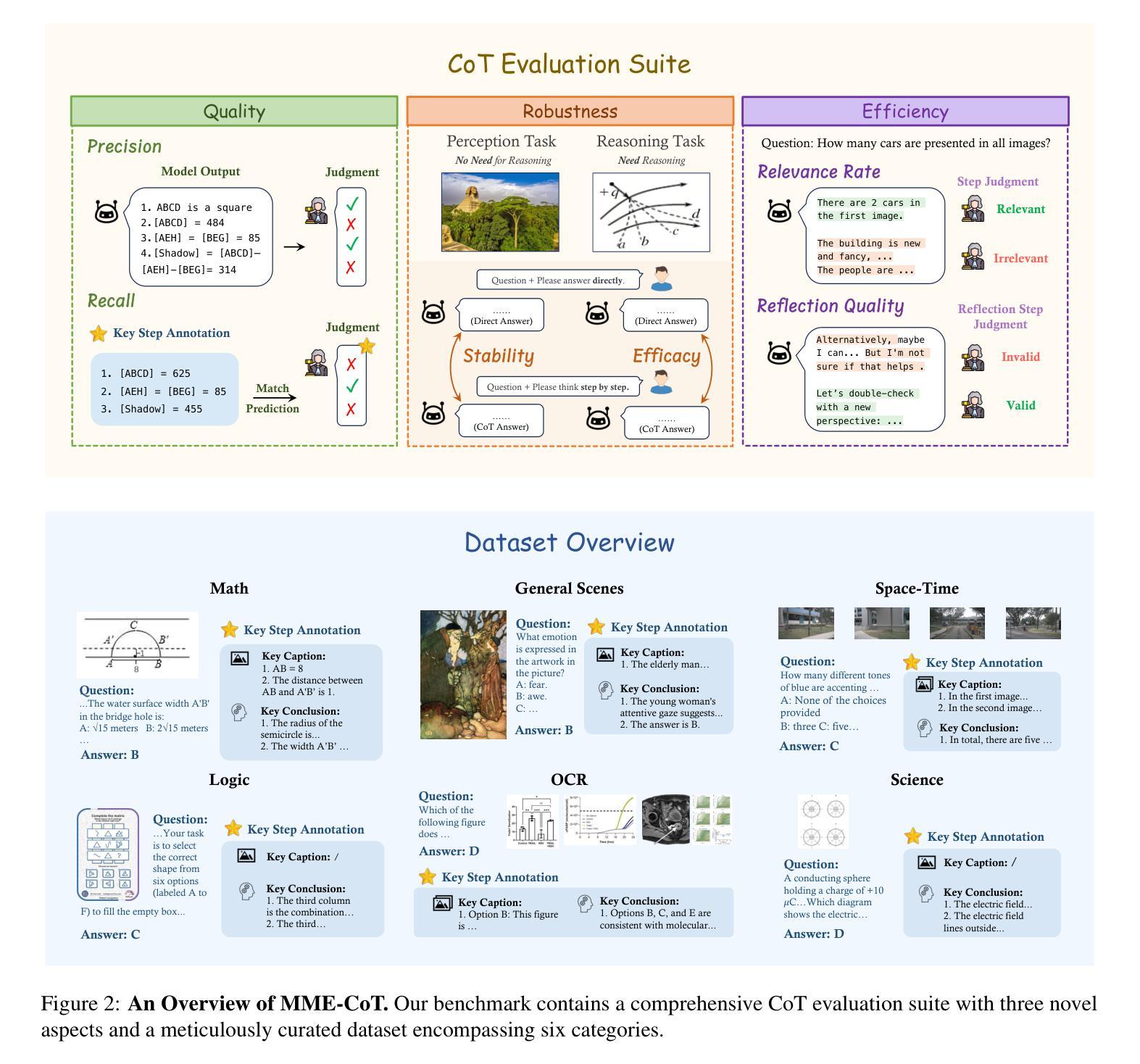
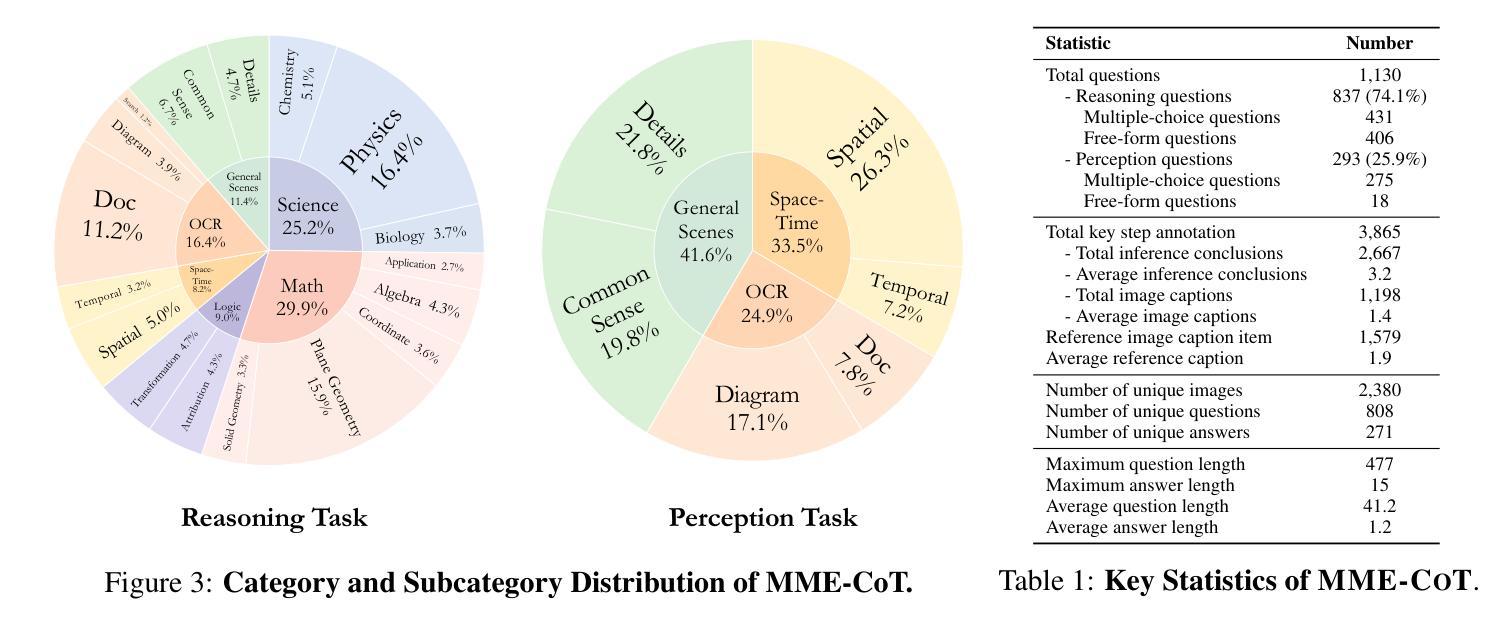
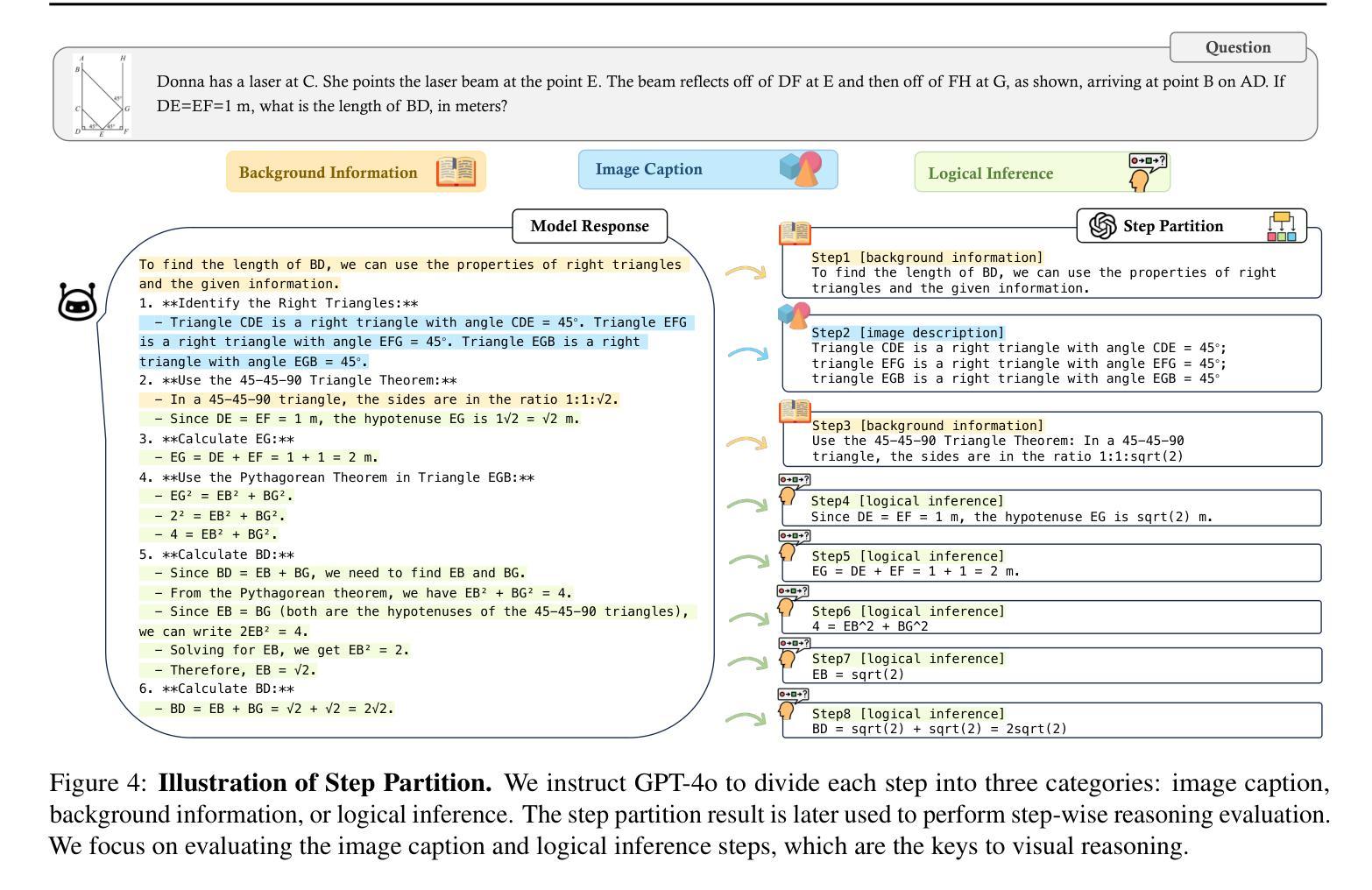
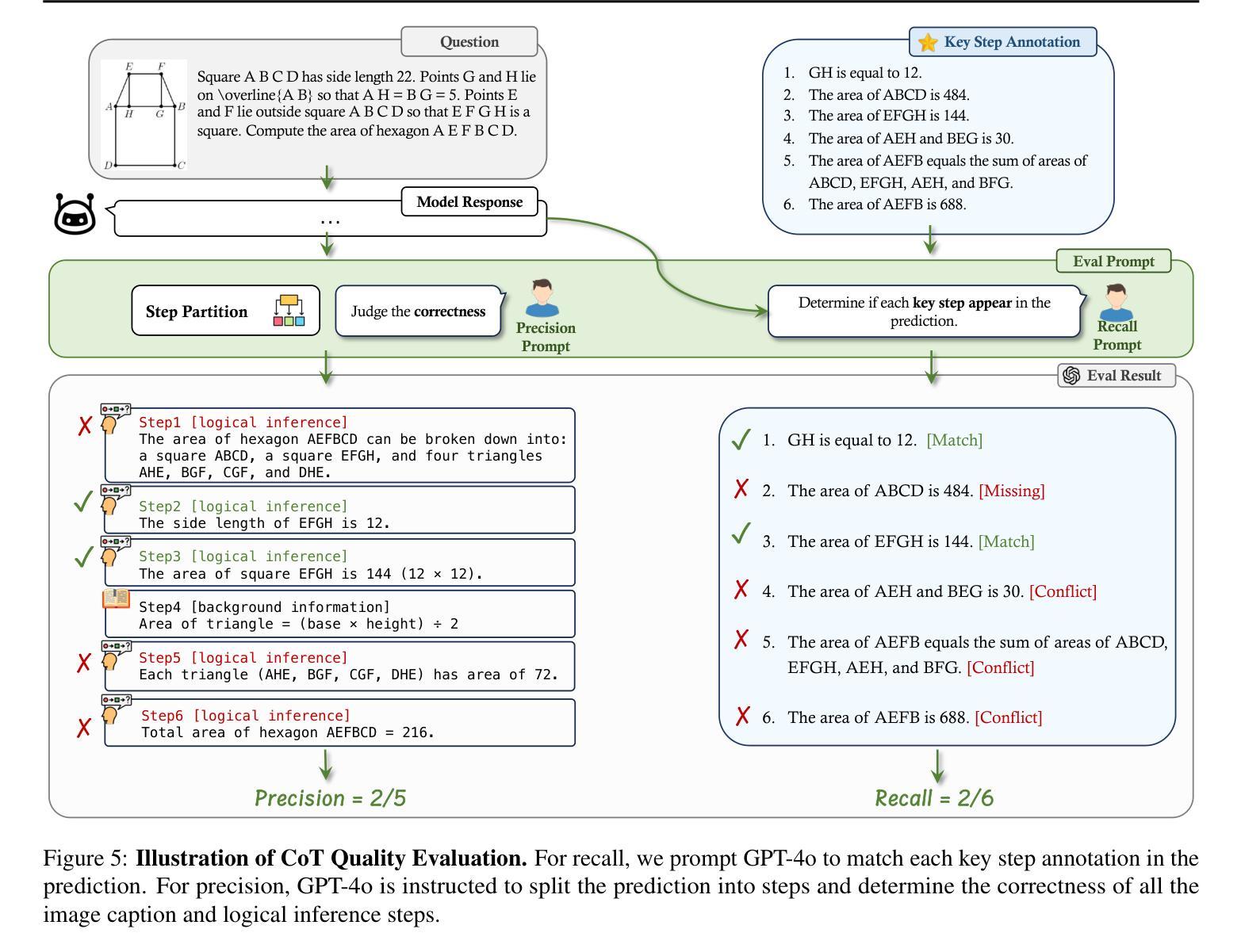
Answering questions with Chain-of-Thought (CoT) has significantly enhanced the reasoning capabilities of Large Language Models (LLMs), yet its impact on Large Multimodal Models (LMMs) still lacks a systematic assessment and in-depth investigation. In this paper, we introduce MME-CoT, a specialized benchmark evaluating the CoT reasoning performance of LMMs, spanning six domains: math, science, OCR, logic, space-time, and general scenes. As the first comprehensive study in this area, we propose a thorough evaluation suite incorporating three novel metrics that assess the reasoning quality, robustness, and efficiency at a fine-grained level. Leveraging curated high-quality data and a unique evaluation strategy, we conduct an in-depth analysis of state-of-the-art LMMs, uncovering several key insights: 1) Models with reflection mechanism demonstrate a superior CoT quality, with Kimi k1.5 outperforming GPT-4o and demonstrating the highest quality results; 2) CoT prompting often degrades LMM performance on perception-heavy tasks, suggesting a potentially harmful overthinking behavior; and 3) Although the CoT quality is high, LMMs with reflection exhibit significant inefficiency in both normal response and self-correction phases. We hope MME-CoT serves as a foundation for advancing multimodal reasoning in LMMs. Project Page: https://mmecot.github.io/
采用思维链(CoT)回答问题的方式已经显著提高了大型语言模型(LLM)的推理能力,然而它对大型多模态模型(LMM)的影响仍缺乏系统的评估和深入研究。在本文中,我们介绍了MME-CoT,这是一个专门用于评估LMM的CoT推理性能的基准测试,涵盖六个领域:数学、科学、光学字符识别、逻辑、时空和一般场景。作为该领域的首次综合研究,我们提出了一种全面的评估套件,其中包括三个新颖的指标,这些指标在细微层面上评估推理质量、稳健性和效率。我们利用精心挑选的高质量数据和独特的评估策略,对最新的LMM进行了深入分析,揭示了几个关键见解:1)具有反射机制的模型表现出优越的CoT质量,Kimi k1.5在CoT质量方面超越了GPT-4o并获得了最高质量的结果;2)CoT提示往往会降低LMM在感知密集任务上的性能,这表明可能存在有害的过度思考行为;3)尽管CoT质量很高,但具有反射的LMM在正常响应和自我纠正阶段都表现出显著的低效。我们希望MME-CoT能为推进LMM中的多模态推理奠定基础。项目页面:https://mmecot.github.io/
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project Page: https://mmecot.github.io/
Summary
基于Chain-of-Thought(CoT)的回答问题方式显著增强了大型语言模型(LLM)的推理能力,但对于大型多模态模型(LMM)的影响仍缺乏系统评估和深入研究。本文介绍了一个专门用于评估LMM的CoT推理性能的基准测试MME-CoT,涵盖六个领域:数学、科学、OCR、逻辑、时空和一般场景。作为该领域的首项综合研究,我们提出了一个细致的评价套件,包括三个新的指标,用于精细地评估推理质量、稳健性和效率。通过对最新LMM的深入分析,本文揭示了几个关键见解。
Key Takeaways
- 带有反射机制的模型在CoT质量上表现出优势,Kimi k1.5在CoT质量方面表现最佳,优于GPT-4o。
- CoT提示在感知密集型任务上可能会降低LMM的性能,表现出潜在的过度思考行为。
- 尽管CoT质量很高,但具有反射功能的LMM在常规响应和自我纠正阶段存在显著效率问题。
- MME-CoT作为基准测试,旨在为推进LMM中的多模态推理奠定基础。
- 研究涵盖了数学、科学、OCR、逻辑、时空和一般场景等六个领域的评估。
- 提出了一个评价套件,包含三个新的指标,用于评估推理质量、稳健性和效率。
点此查看论文截图
Exploring the Potential of Encoder-free Architectures in 3D LMMs
Authors:Yiwen Tang, Zoey Guo, Zhuhao Wang, Ray Zhang, Qizhi Chen, Junli Liu, Delin Qu, Zhigang Wang, Dong Wang, Xuelong Li, Bin Zhao
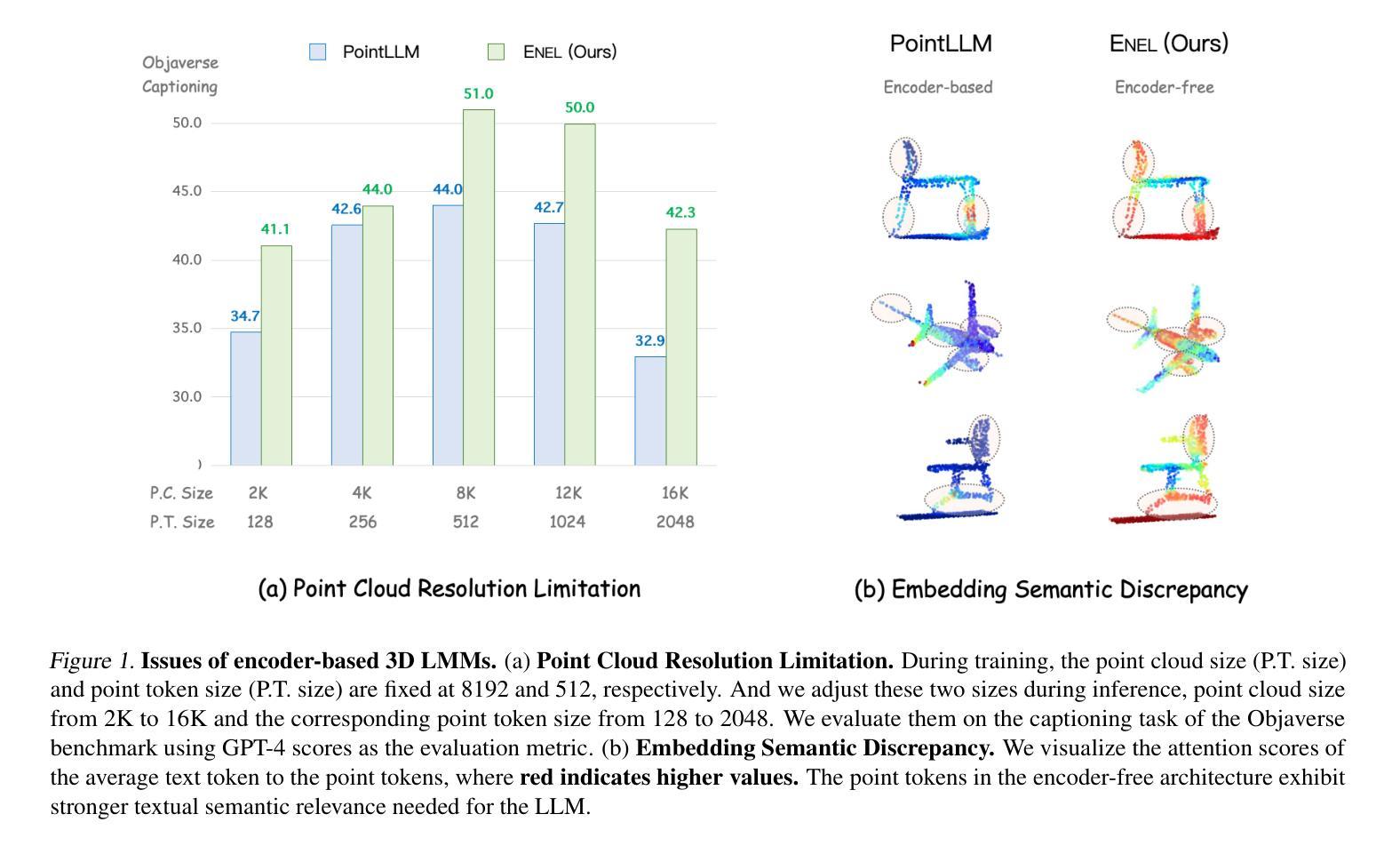
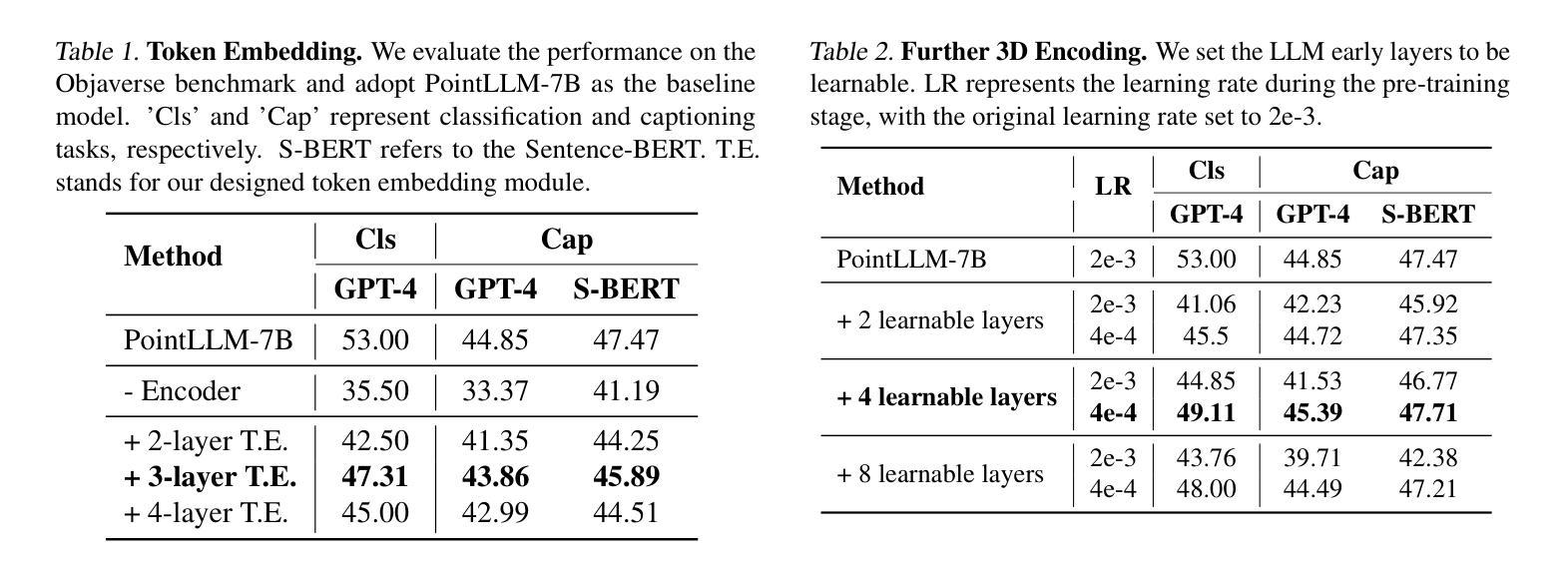
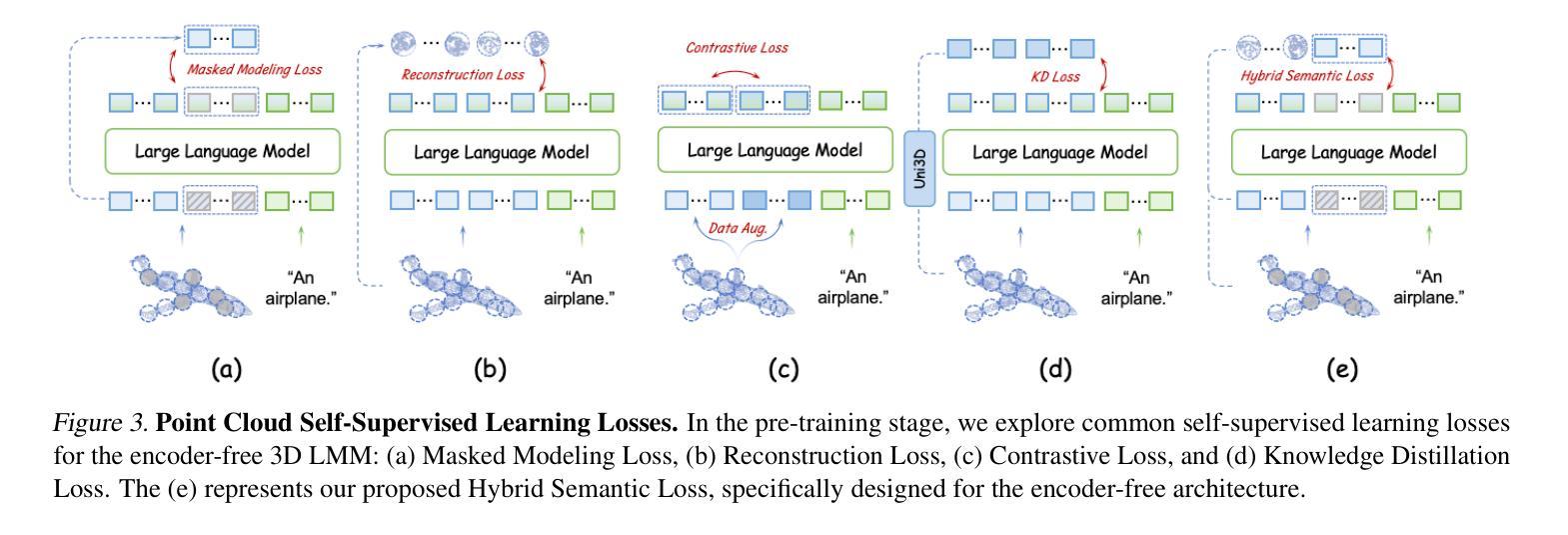
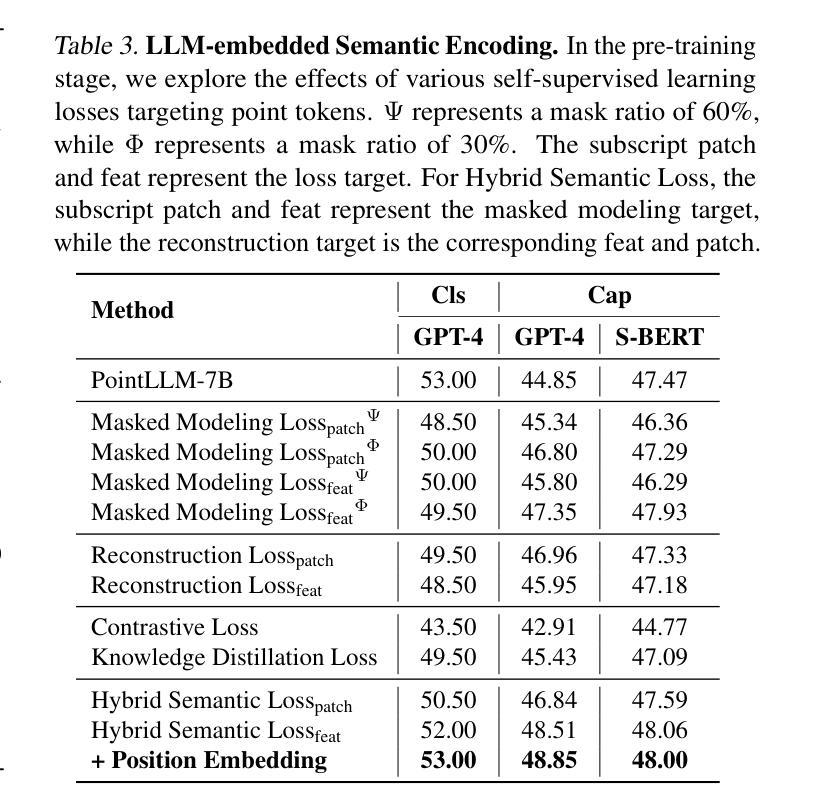
Encoder-free architectures have been preliminarily explored in the 2D visual domain, yet it remains an open question whether they can be effectively applied to 3D understanding scenarios. In this paper, we present the first comprehensive investigation into the potential of encoder-free architectures to overcome the challenges of encoder-based 3D Large Multimodal Models (LMMs). These challenges include the failure to adapt to varying point cloud resolutions and the point features from the encoder not meeting the semantic needs of Large Language Models (LLMs). We identify key aspects for 3D LMMs to remove the encoder and enable the LLM to assume the role of the 3D encoder: 1) We propose the LLM-embedded Semantic Encoding strategy in the pre-training stage, exploring the effects of various point cloud self-supervised losses. And we present the Hybrid Semantic Loss to extract high-level semantics. 2) We introduce the Hierarchical Geometry Aggregation strategy in the instruction tuning stage. This incorporates inductive bias into the LLM early layers to focus on the local details of the point clouds. To the end, we present the first Encoder-free 3D LMM, ENEL. Our 7B model rivals the current state-of-the-art model, ShapeLLM-13B, achieving 55.0%, 50.92%, and 42.7% on the classification, captioning, and VQA tasks, respectively. Our results demonstrate that the encoder-free architecture is highly promising for replacing encoder-based architectures in the field of 3D understanding. The code is released at https://github.com/Ivan-Tang-3D/ENEL
无编码器架构已在2D视觉领域进行了初步探索,然而,它们是否能有效应用于3D理解场景仍是一个悬而未决的问题。本文首次全面探讨了无编码器架构在克服基于编码器的3D大型多模态模型(LMM)的挑战方面的潜力。这些挑战包括难以适应不同的点云分辨率以及编码器提取的点特征不符合大型语言模型(LLM)的语义需求。我们确定了3D LMM去除编码器并使LLM承担3D编码器角色的关键方面:1)我们在预训练阶段提出了LLM嵌入语义编码策略,探索了各种点云自监督损失的影响。并提出了混合语义损失来提取高级语义。2)我们在指令微调阶段引入了分层几何聚合策略。这可以将归纳偏置融入LLM的早期层,以关注点云的局部细节。最终,我们提出了第一个无编码器3D LMM,ENEL。我们的7B模型与当前最先进的模型ShapeLLM-13B相竞争,在分类、描述和视觉问答任务上分别实现了55.0%、50.92%和42.7%的性能。我们的结果表明,无编码器架构在3D理解领域替代基于编码器的架构具有巨大潜力。[相关代码已发布在https://github.com/Ivan-Tang-3D/ENEL]
论文及项目相关链接
PDF The code is released at https://github.com/Ivan-Tang-3D/ENEL
摘要
本文首次全面探讨了无编码器架构在克服基于编码器的三维大型多模态模型(LMMs)挑战方面的潜力。研究提出了LLM嵌入语义编码策略与混合语义损失方法,以提取高级语义信息。此外,引入层次化几何聚合策略以专注于点云的局部细节。最终构建出无编码器架构的三维LMM——ENEL模型。在分类、描述和视觉问答任务上,ENEL模型与当前最先进的模型ShapeLLM-13B相比表现优异,展现出无编码器架构在三维理解领域的巨大潜力。相关代码已发布于开源网站。
关键见解
- 文章探索了无编码器架构在三维视觉领域的应用潜力,针对现有基于编码器的三维大型多模态模型的挑战提出了解决方案。
- 提出LLM嵌入语义编码策略,在预训练阶段探索各种点云自监督损失的影响,并引入混合语义损失以提取高级语义信息。
- 引入层次化几何聚合策略,在指令微调阶段将归纳偏见融入LLM早期层,以关注点云的局部细节。
- 成功构建首个无编码器架构的三维LMM——ENEL模型,并在分类、描述和视觉问答任务上实现了与当前最先进的模型相当的性能。
- ENEL模型显示了在处理不同点云分辨率以及满足大型语言模型语义需求方面的优势。
- 研究表明无编码器架构在三维理解领域具有巨大潜力,可能会取代基于编码器的架构。
点此查看论文截图


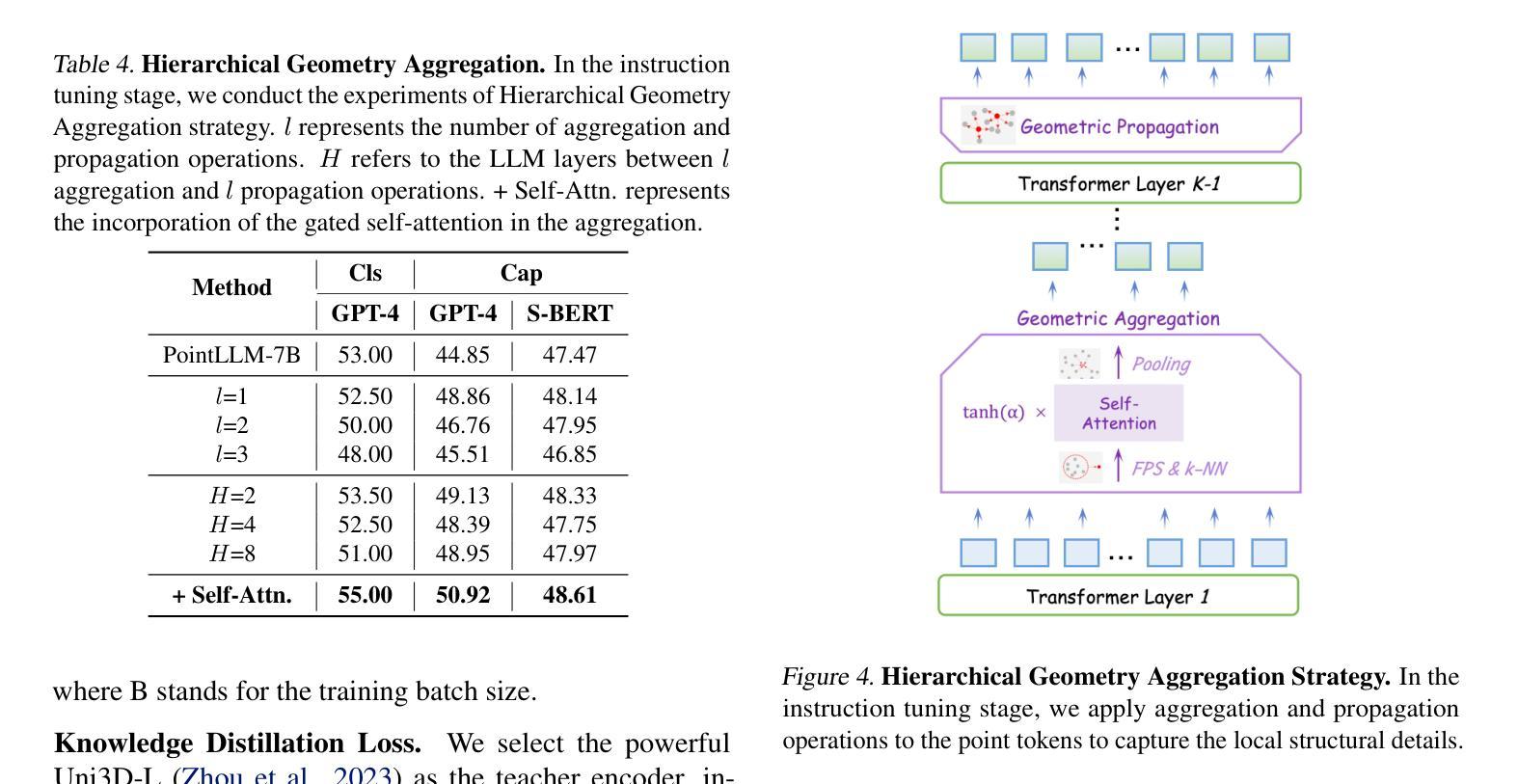
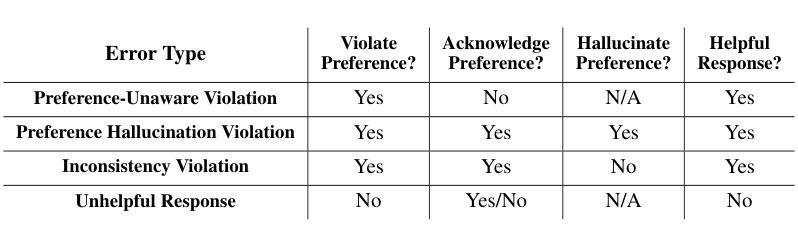
Do LLMs Recognize Your Preferences? Evaluating Personalized Preference Following in LLMs
Authors:Siyan Zhao, Mingyi Hong, Yang Liu, Devamanyu Hazarika, Kaixiang Lin
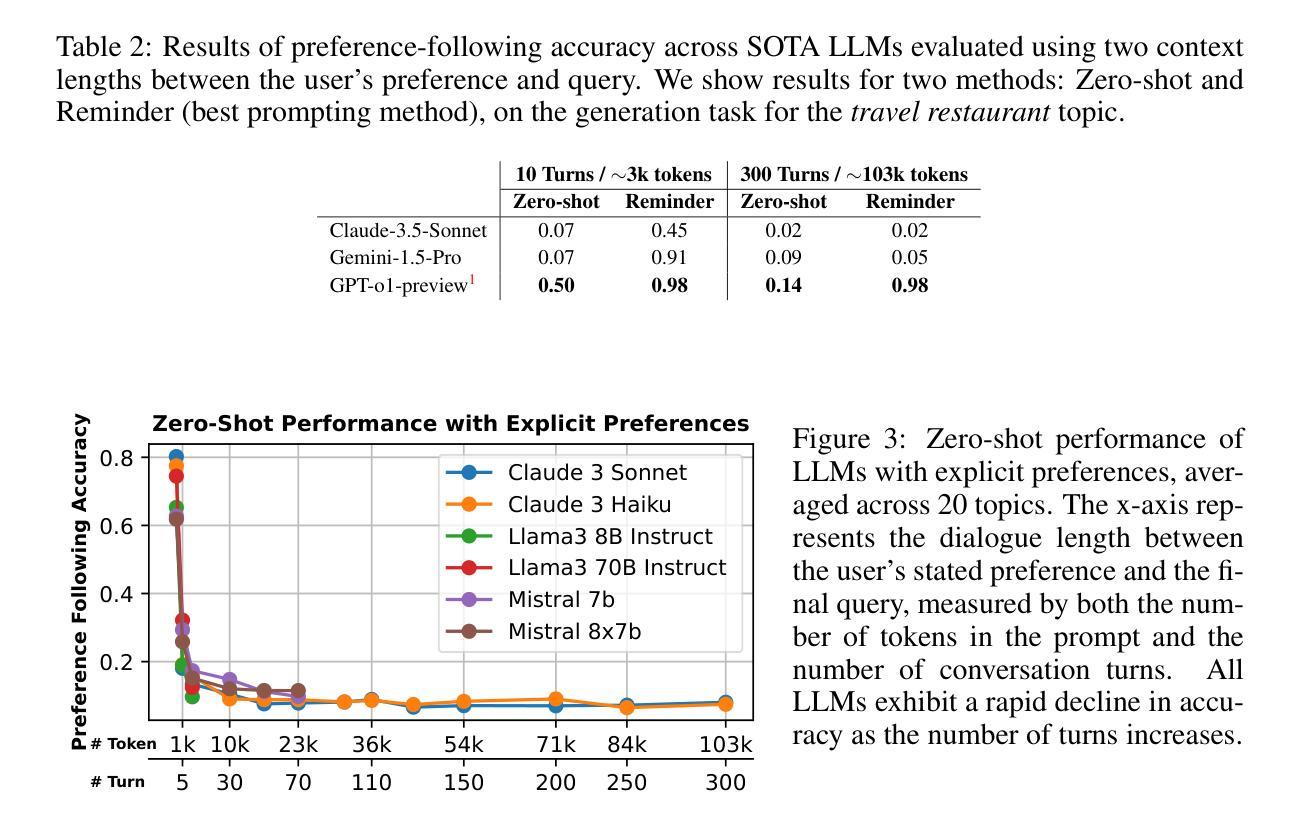
Large Language Models (LLMs) are increasingly used as chatbots, yet their ability to personalize responses to user preferences remains limited. We introduce PrefEval, a benchmark for evaluating LLMs’ ability to infer, memorize and adhere to user preferences in a long-context conversational setting. PrefEval comprises 3,000 manually curated user preference and query pairs spanning 20 topics. PrefEval contains user personalization or preference information in both explicit and implicit forms, and evaluates LLM performance using a generation and a classification task. With PrefEval, we evaluated the aforementioned preference following capabilities of 10 open-source and proprietary LLMs in multi-session conversations with varying context lengths up to 100k tokens. We benchmark with various prompting, iterative feedback, and retrieval-augmented generation methods. Our benchmarking effort reveals that state-of-the-art LLMs face significant challenges in proactively following users’ preferences during conversations. In particular, in zero-shot settings, preference following accuracy falls below 10% at merely 10 turns (~3k tokens) across most evaluated models. Even with advanced prompting and retrieval methods, preference following still deteriorates in long-context conversations. Furthermore, we show that fine-tuning on PrefEval significantly improves performance. We believe PrefEval serves as a valuable resource for measuring, understanding, and enhancing LLMs’ preference following abilities, paving the way for personalized conversational agents. Our code and dataset are available at https://prefeval.github.io/.
大规模语言模型(LLM)越来越多地被用作聊天机器人,然而它们根据用户偏好进行个性化响应的能力仍然有限。我们引入了PrefEval,这是一个用于评估LLM在长时间上下文对话环境中推断、记忆和遵守用户偏好的能力的基准测试。PrefEval包含3000个手动整理的用户偏好和查询对,涵盖20个主题。PrefEval以显式和隐式两种形式包含用户个性化或偏好信息,并使用生成任务和分类任务来评估LLM的性能。通过PrefEval,我们评估了上述10个开源和专有LLM在具有不同上下文长度(最长可达10万令牌)的多会话对话中的偏好遵循能力。我们用各种提示、迭代反馈和检索增强生成方法进行基准测试。我们的基准测试结果表明,尖端LLM在对话中主动遵循用户偏好方面面临重大挑战。特别是,在零样本情况下,大多数评估模型的偏好遵循准确率在仅10轮(约3000个令牌)内就下降到低于10%。即使在长时间上下文对话中采用先进的提示和检索方法,偏好遵循能力仍然会下降。此外,我们表明在PrefEval上进行微调可以显著提高性能。我们相信PrefEval对于衡量、理解和提高LLM的偏好遵循能力具有重要价值,为个性化聊天机器人铺平了道路。我们的代码和数据集可在https://prefeval.github.io/上找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at ICLR 2025 as oral presentation. Code and data at: https://prefeval.github.io/
Summary
LLM在聊天机器人领域的应用日益广泛,但其对用户偏好的个性化响应能力仍有局限。为此,我们推出PrefEval基准测试,旨在评估LLM在具有长期上下文对话环境中对用户偏好的推断、记忆和遵循能力。PrefEval包含涵盖20个话题的3000组人工筛选的用户偏好和查询配对,涵盖显式与隐式形式的用户个性化或偏好信息,并通过生成与分类任务来评估LLM的表现。通过PrefEval基准测试,我们评估了10款开源和专有LLM的偏好跟随能力,涉及多会话对话,上下文长度可达10万令牌。我们的研究结果表明,最先进的大型语言模型在对话中主动遵循用户偏好方面面临重大挑战。特别是在零样本环境中,大多数模型的偏好遵循准确性在仅10轮对话(约3千令牌)时就低于10%。即使使用高级提示和检索方法,在长期上下文对话中,偏好的遵循仍然会恶化。此外,我们证明在PrefEval上进行微调可以显著提高性能。我们相信PrefEval对于衡量、理解和提高LLM的偏好跟随能力具有宝贵价值,为个性化聊天机器人铺平了道路。
Key Takeaways
- LLM在作为聊天机器人应用时,对用户偏好的个性化响应能力存在局限。
- PrefEval基准测试用于评估LLM在具有长期上下文对话环境中对用户偏好的推断、记忆和遵循能力。
- PrefEval包含涵盖多种话题的用户偏好和查询配对。
- LLM面临在对话中主动遵循用户偏好的挑战,特别是在零样本环境下。
- 先进的大型语言模型在长期上下文对话中的偏好遵循能力仍然不足。
- 在PrefEval上进行微调可以显著提高LLM的性能。
点此查看论文截图

Optimizing GPT for Video Understanding: Zero-Shot Performance and Prompt Engineering
Authors:Mark Beliaev, Victor Yang, Madhura Raju, Jiachen Sun, Xinghai Hu
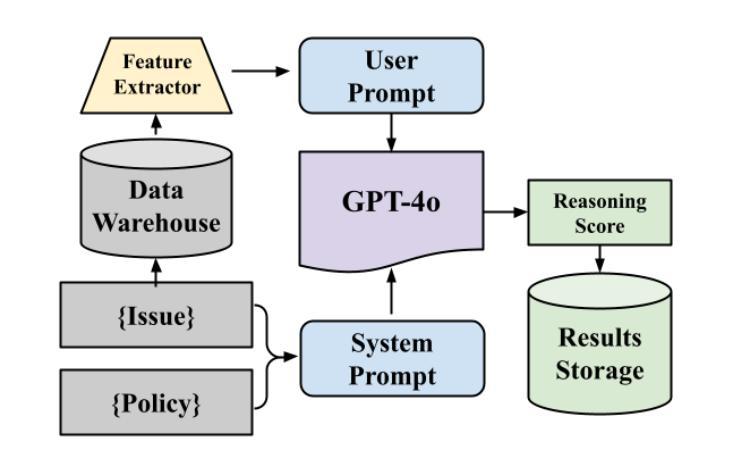
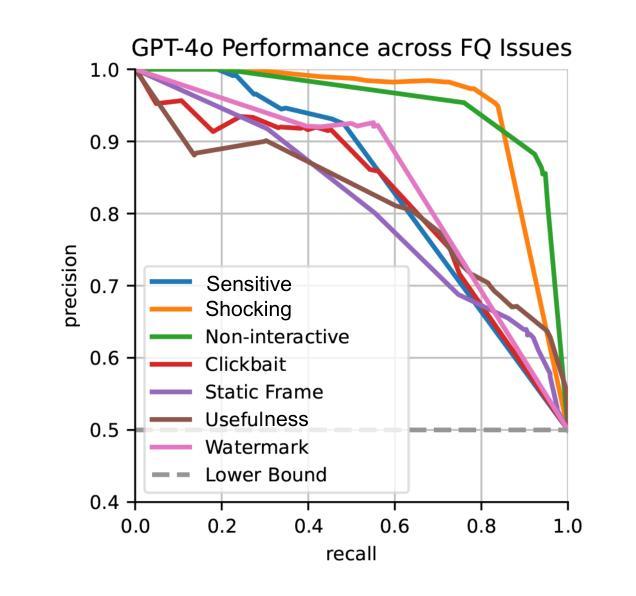
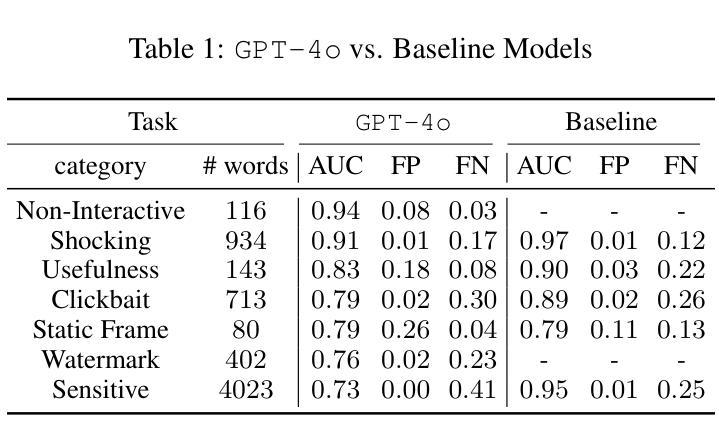
In this study, we tackle industry challenges in video content classification by exploring and optimizing GPT-based models for zero-shot classification across seven critical categories of video quality. We contribute a novel approach to improving GPT’s performance through prompt optimization and policy refinement, demonstrating that simplifying complex policies significantly reduces false negatives. Additionally, we introduce a new decomposition-aggregation-based prompt engineering technique, which outperforms traditional single-prompt methods. These experiments, conducted on real industry problems, show that thoughtful prompt design can substantially enhance GPT’s performance without additional finetuning, offering an effective and scalable solution for improving video classification systems across various domains in industry.
在这项研究中,我们通过对GPT模型的探索和优化,针对视频质量的七大关键类别,进行零样本分类来解决视频内容分类行业的挑战。我们提出了一种改进GPT性能的新方法,通过提示优化和政策完善,证明了简化复杂政策可以显著降低假阴性率。此外,我们还引入了一种基于分解聚合的提示工程技术,它优于传统的单一提示方法。这些针对真实行业问题进行的实验表明,有策略性的提示设计可以在不增加微调的情况下显著提高GPT的性能,为工业领域各种域的视频分类系统提供了有效且可扩展的解决方案。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本研究通过探索和优化GPT模型解决视频内容分类行业中的挑战,实现零样本分类视频质量的七个关键类别。研究提出了一种通过优化提示和精炼策略来提升GPT性能的新方法,证明简化复杂策略能显著降低误报。同时,研究还引入了一种基于分解聚合的提示工程技术,该技术优于传统单一提示方法。针对实际行业问题的实验表明,精心设计的提示能显著提高GPT性能,无需额外微调,为改进各行业视频分类系统提供了有效且可扩展的解决方案。
Key Takeaways
- 研究解决了视频内容分类行业的挑战,通过GPT模型实现零样本分类七个关键视频质量类别。
- 提出了一种优化GPT性能的新方法,包括优化提示和精炼策略。
- 研究发现简化复杂策略能显著降低误报。
- 引入了一种基于分解聚合的提示工程技术,表现优于传统单一提示方法。
- 实验表明精心设计的提示能显著提高GPT性能,无需额外微调。
- 该研究为改进各行业视频分类系统提供了有效且可扩展的解决方案。
点此查看论文截图

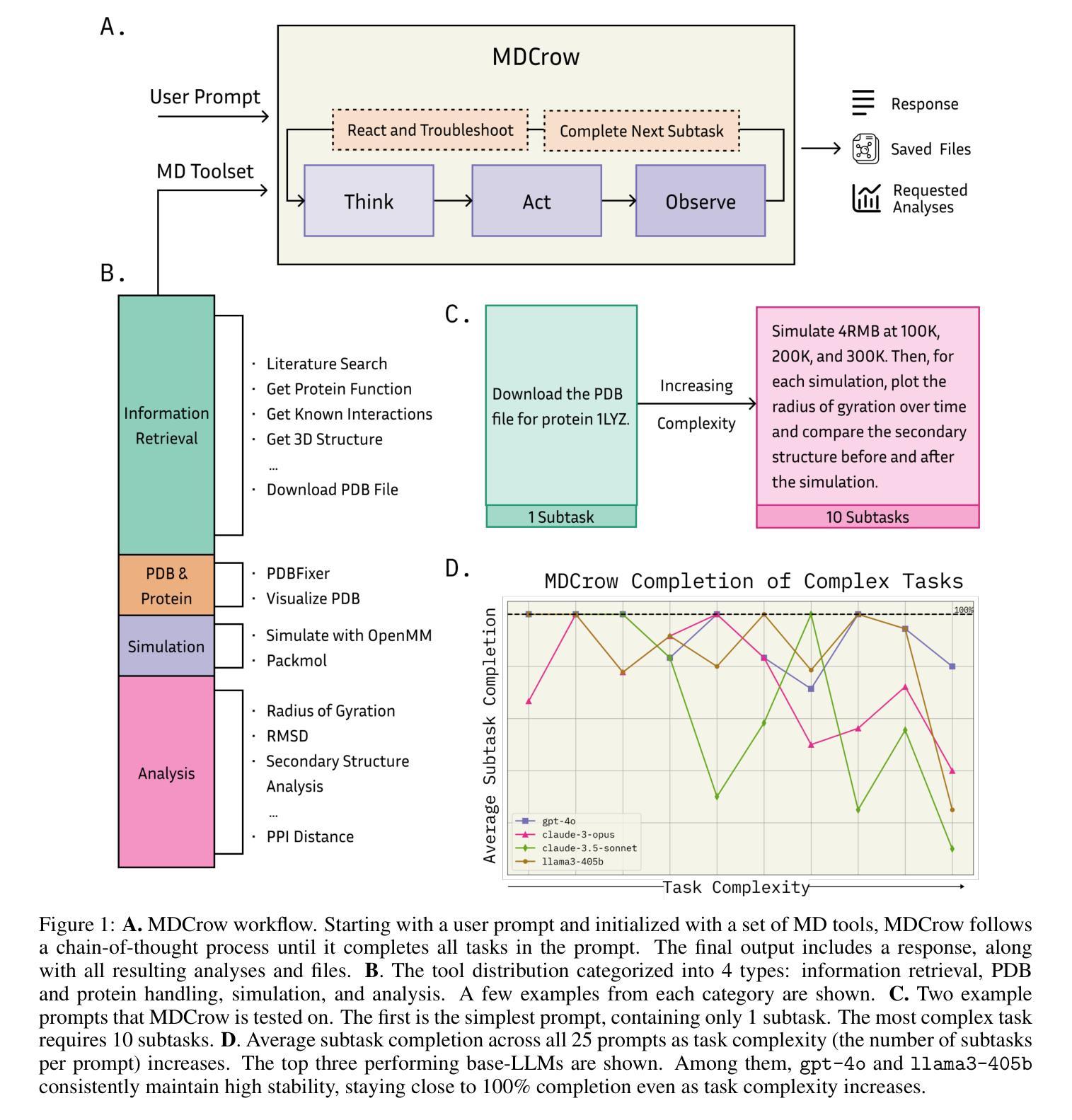
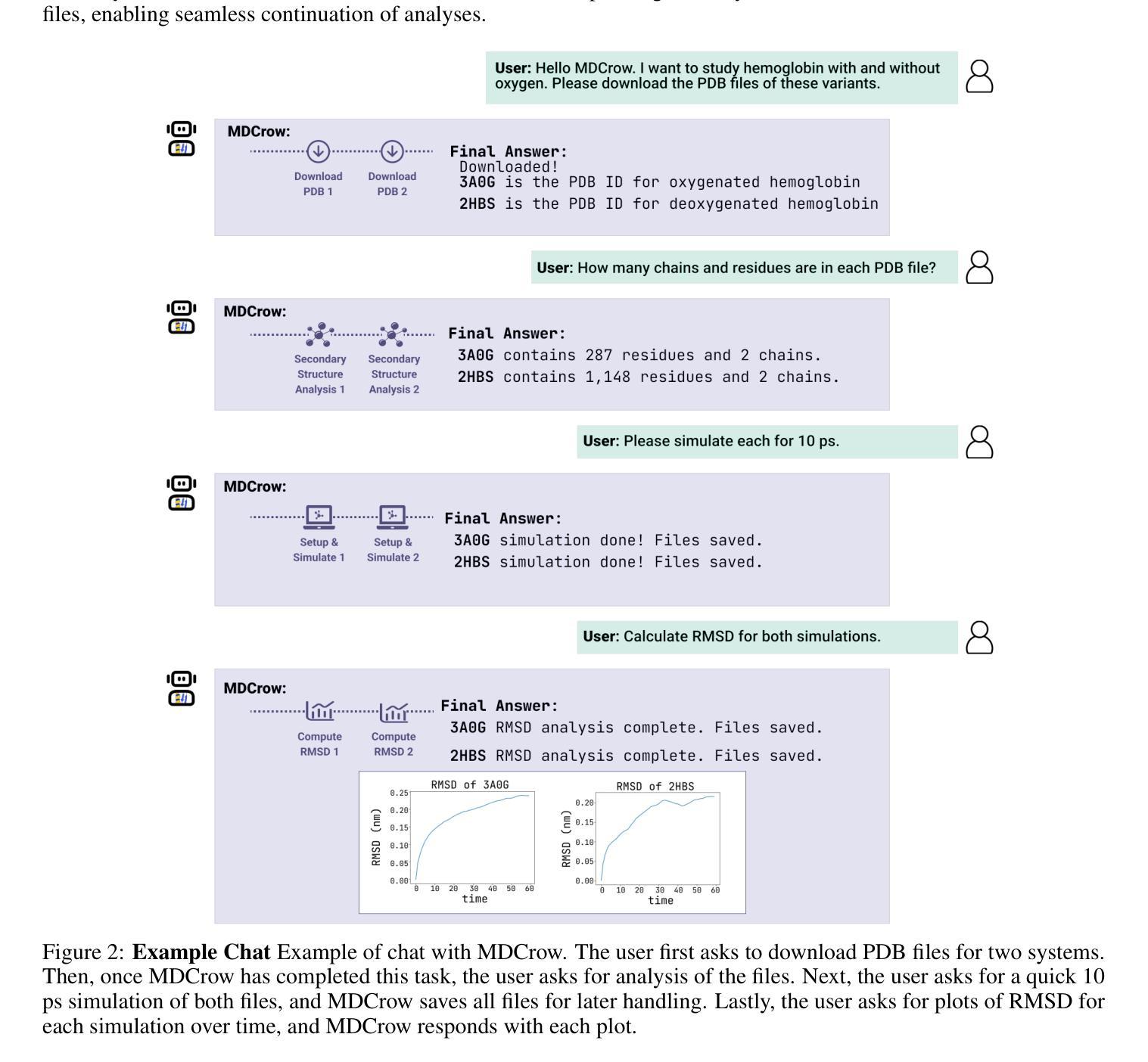
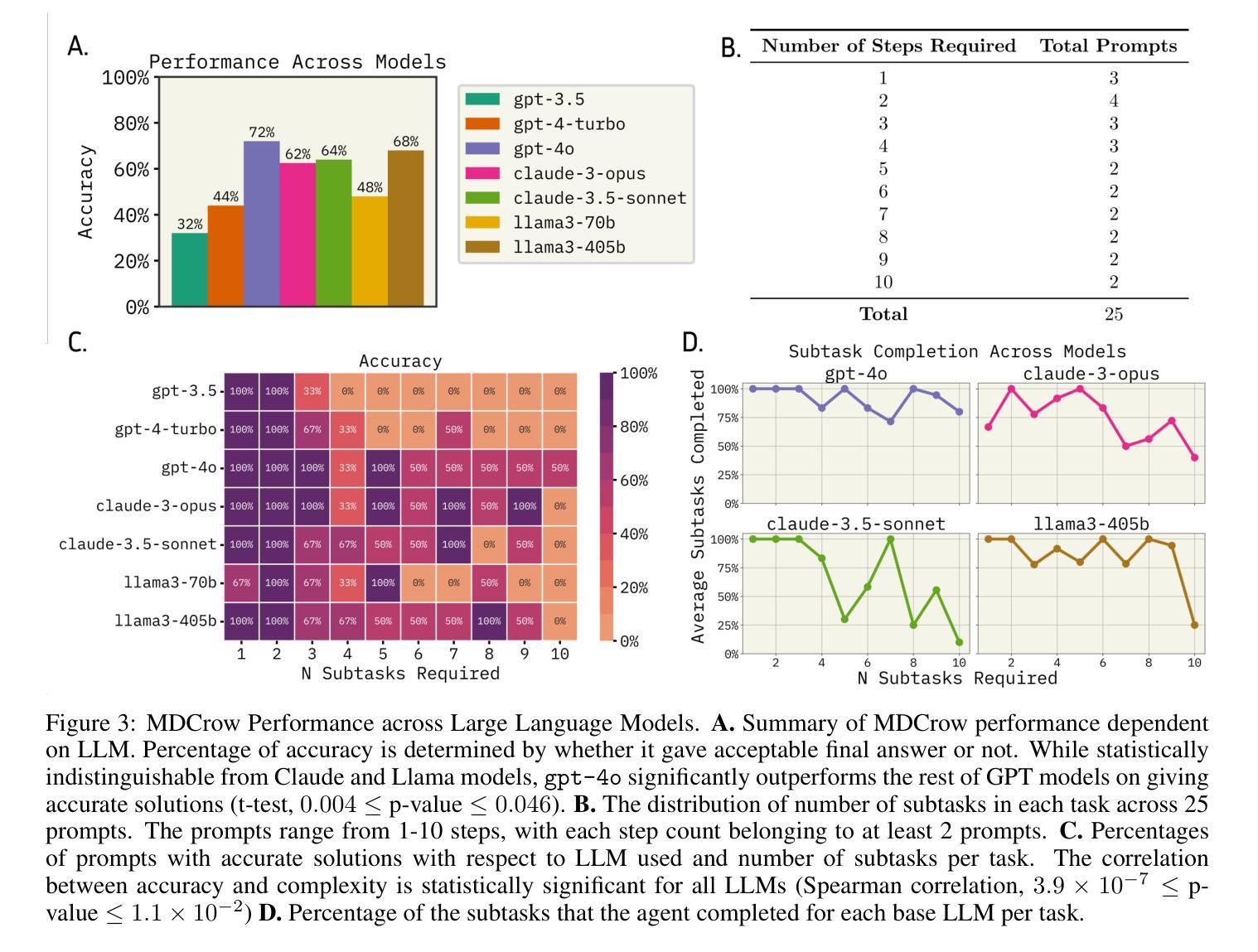
MDCrow: Automating Molecular Dynamics Workflows with Large Language Models
Authors:Quintina Campbell, Sam Cox, Jorge Medina, Brittany Watterson, Andrew D. White
Molecular dynamics (MD) simulations are essential for understanding biomolecular systems but remain challenging to automate. Recent advances in large language models (LLM) have demonstrated success in automating complex scientific tasks using LLM-based agents. In this paper, we introduce MDCrow, an agentic LLM assistant capable of automating MD workflows. MDCrow uses chain-of-thought over 40 expert-designed tools for handling and processing files, setting up simulations, analyzing the simulation outputs, and retrieving relevant information from literature and databases. We assess MDCrow’s performance across 25 tasks of varying required subtasks and difficulty, and we evaluate the agent’s robustness to both difficulty and prompt style. \texttt{gpt-4o} is able to complete complex tasks with low variance, followed closely by \texttt{llama3-405b}, a compelling open-source model. While prompt style does not influence the best models’ performance, it has significant effects on smaller models.
分子动力学(MD)模拟对于理解生物分子系统至关重要,但自动化仍然具有挑战性。最近大型语言模型(LLM)的进步表明,使用基于LLM的代理可以自动执行复杂的科学任务。在本文中,我们介绍了MDCrow,这是一款能够自动化MD工作流程的LLM助理。MDCrow使用思想链,结合了40种专家设计的工具,用于处理和加工文件、设置模拟、分析模拟输出以及从文献和数据库中检索相关信息。我们评估了MDCrow在25个不同子任务和难度的任务上的性能,并评估了该代理对难度和提示风格的稳健性。
gpt-4o能够以低方差完成复杂任务,紧随其后的是llama3-405b,这是一个引人注目的开源模型。虽然提示风格不会影响最佳模型的表现,但它对较小模型的影响是显著的。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
MD模拟自动化挑战重重,但大型语言模型(LLM)为其带来突破。本文介绍MDCrow,一款基于LLM的自动化MD工作流程助理。MDCrow利用思维链,通过四十多种专业工具处理文件、设置模拟、分析模拟输出并从文献和数据库中检索相关信息。对MDCrow在25项不同难度任务上的性能进行评估,评估模型对难度和提示风格的稳健性。其中,GPT-4o表现出色,完成复杂任务方差较低,其次是开源模型llama3-405b。提示风格对最佳模型性能影响不大,但对小型模型影响显著。
Key Takeaways
- MDCrow是基于大型语言模型的自动化MD工作流程助理,结合了众多专业工具以完成模拟过程。
- MDCrow可以在文件处理、模拟设置、结果分析和文献检索等多个环节发挥作用。
- GPT-4o在自动化MD任务中表现优秀,同时显示出对复杂任务的稳健性。
- 开源模型llama3-405b同样具备强大的自动化能力。
- MDCrow的评估跨越了多个任务级别和难度级别,以全面了解其性能范围。
- 提示风格对小型模型的性能有显著影响,但对最佳模型的性能影响不大。
点此查看论文截图

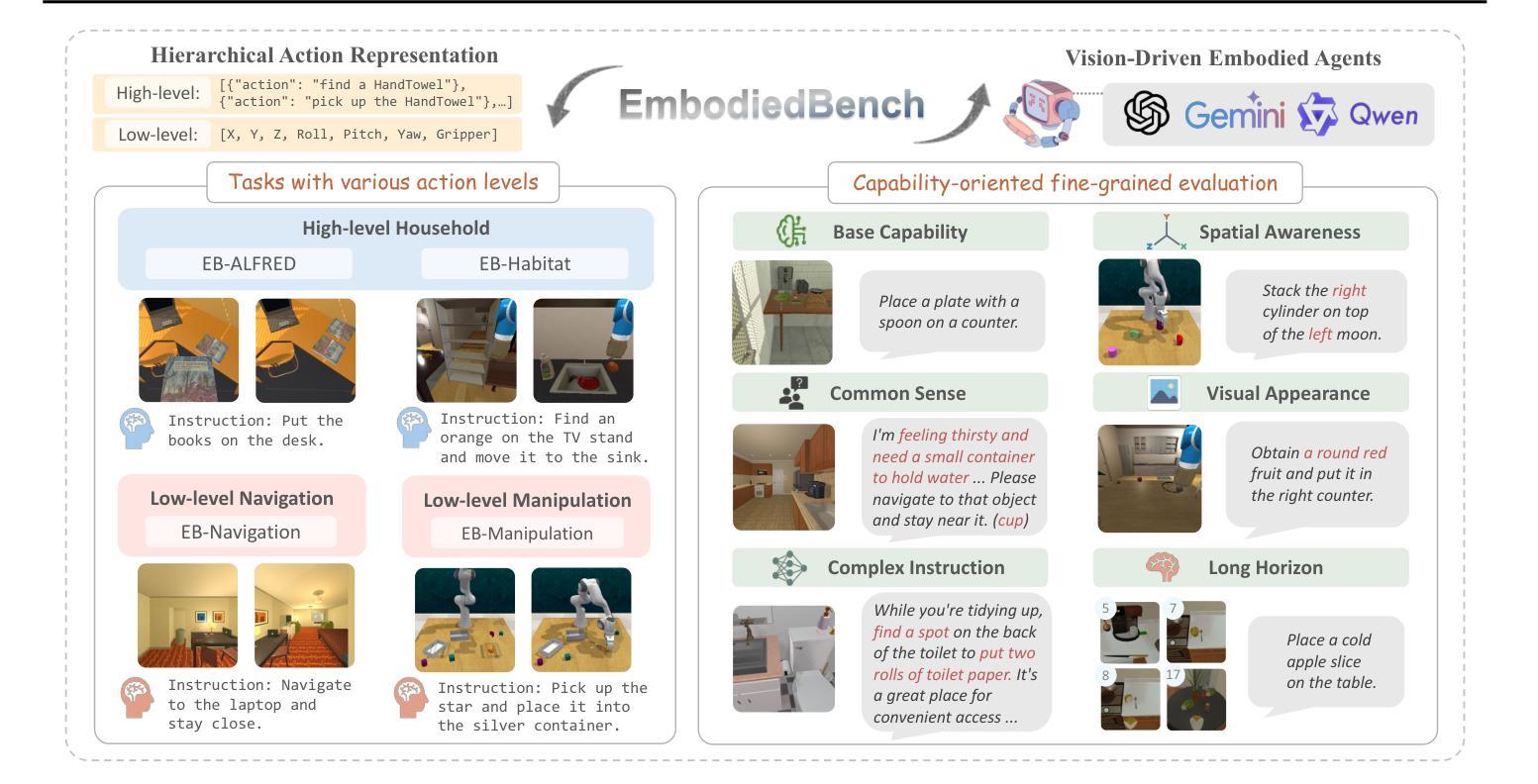
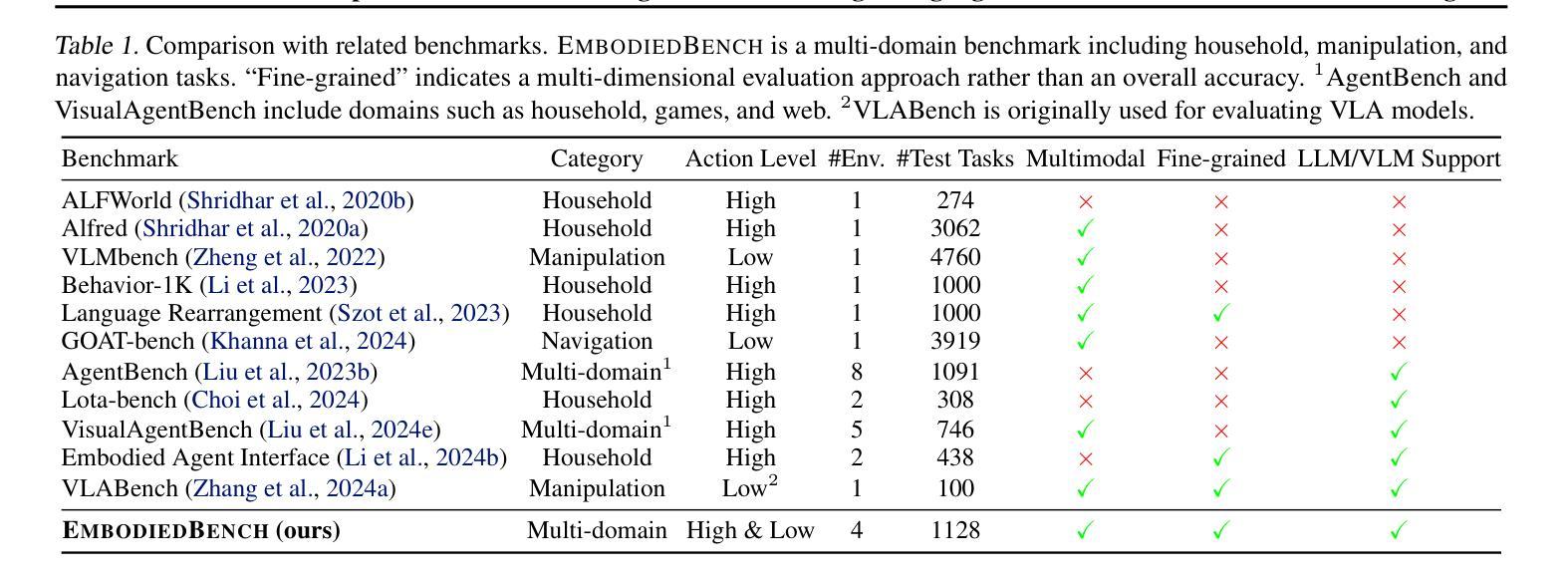
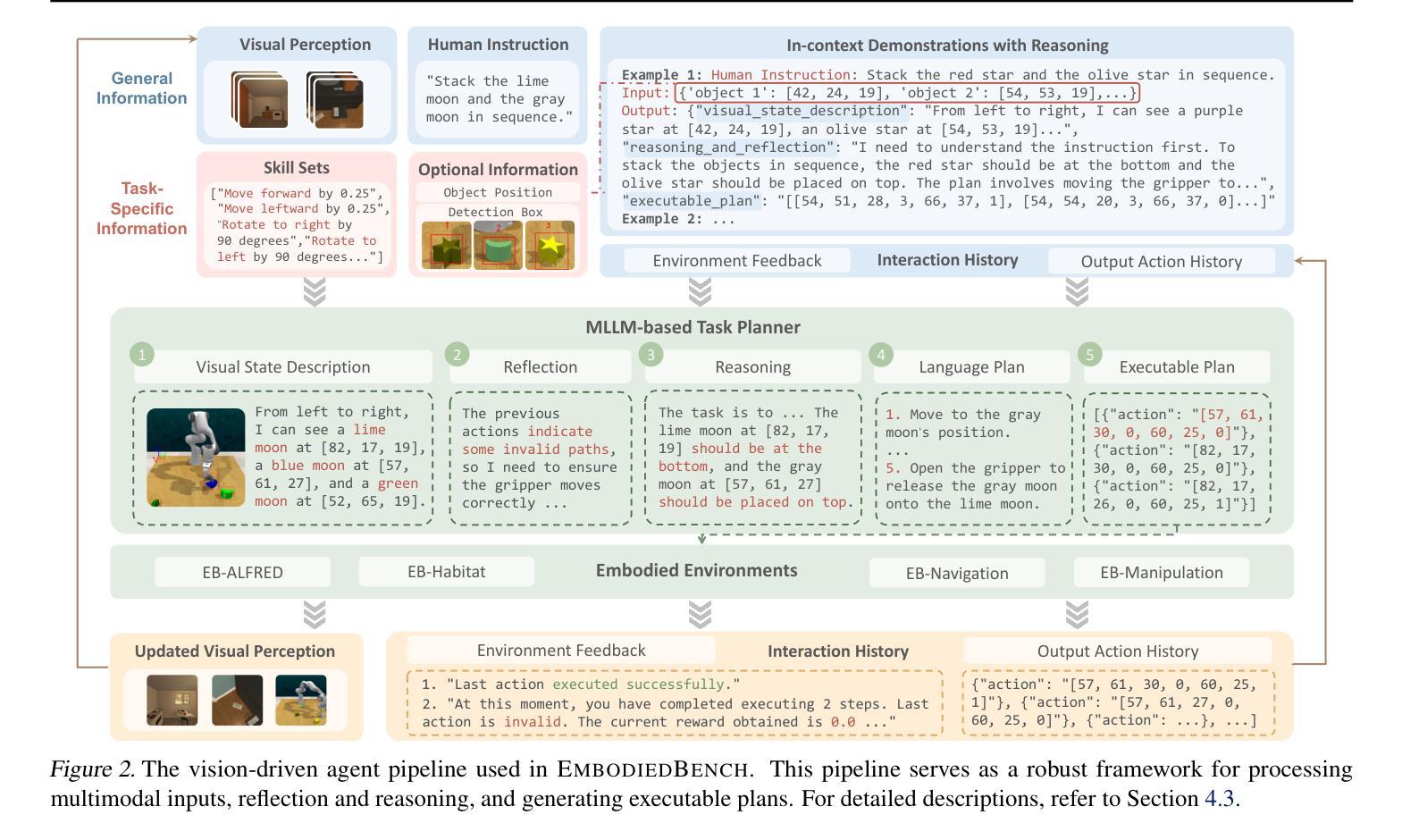
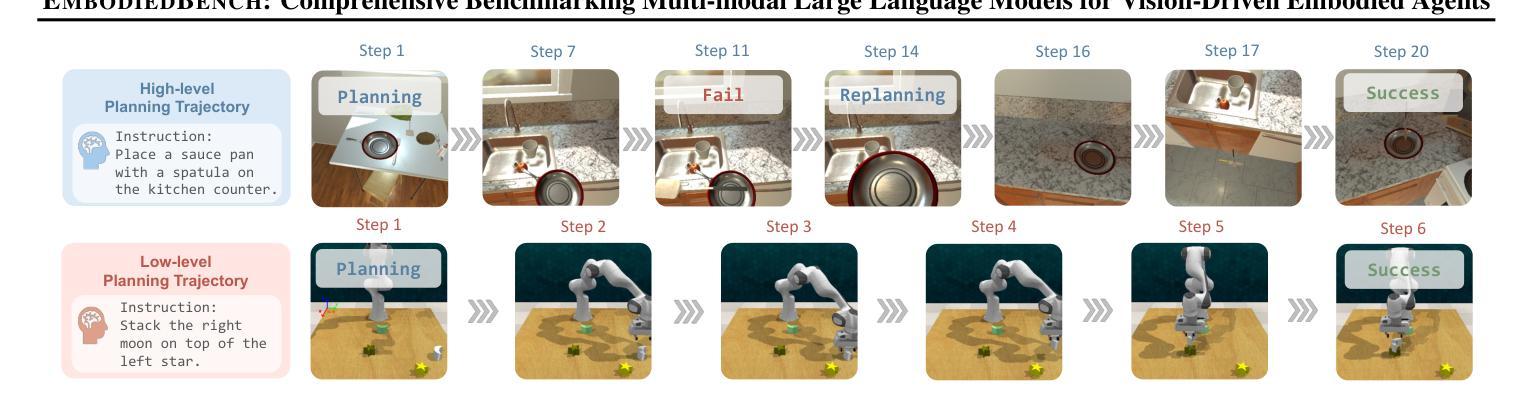
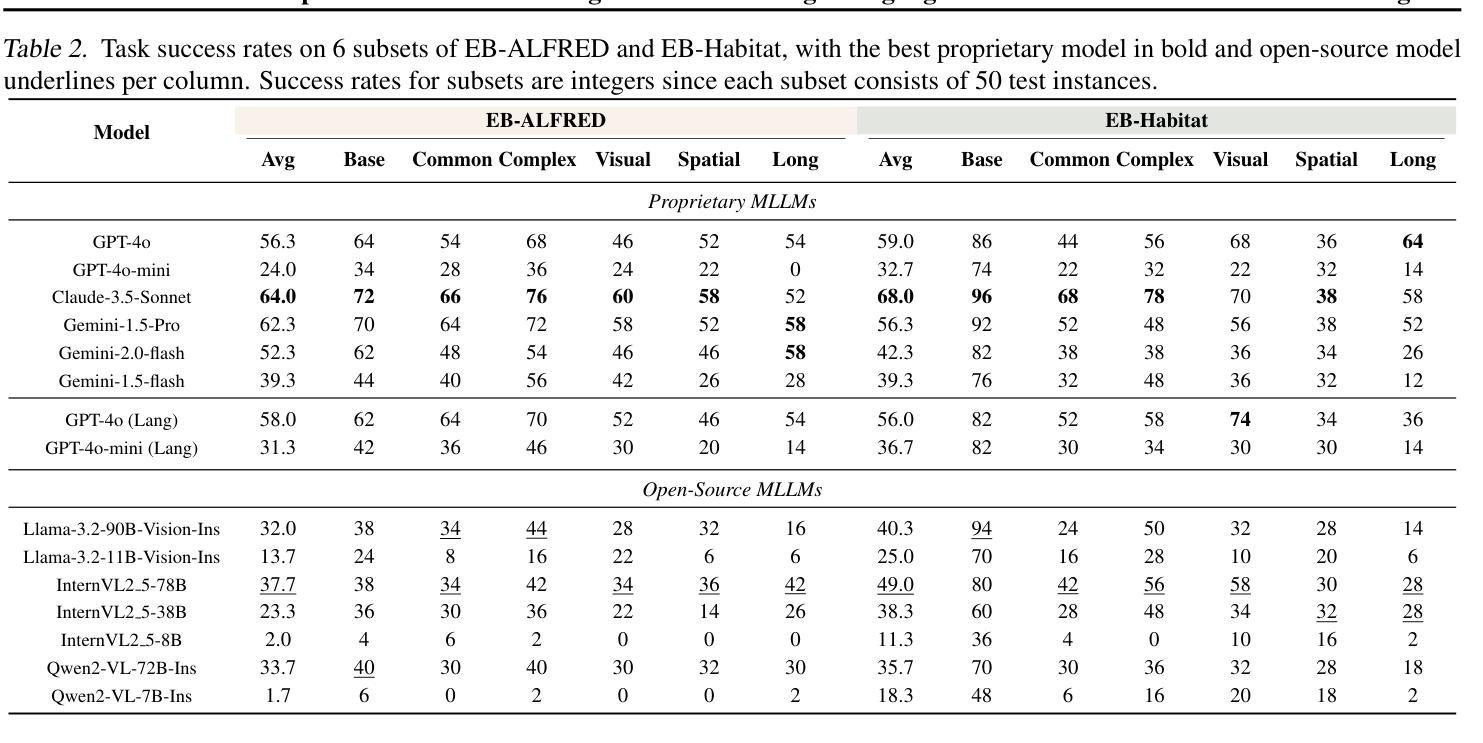
EmbodiedBench: Comprehensive Benchmarking Multi-modal Large Language Models for Vision-Driven Embodied Agents
Authors:Rui Yang, Hanyang Chen, Junyu Zhang, Mark Zhao, Cheng Qian, Kangrui Wang, Qineng Wang, Teja Venkat Koripella, Marziyeh Movahedi, Manling Li, Heng Ji, Huan Zhang, Tong Zhang
Leveraging Multi-modal Large Language Models (MLLMs) to create embodied agents offers a promising avenue for tackling real-world tasks. While language-centric embodied agents have garnered substantial attention, MLLM-based embodied agents remain underexplored due to the lack of comprehensive evaluation frameworks. To bridge this gap, we introduce EmbodiedBench, an extensive benchmark designed to evaluate vision-driven embodied agents. EmbodiedBench features: (1) a diverse set of 1,128 testing tasks across four environments, ranging from high-level semantic tasks (e.g., household) to low-level tasks involving atomic actions (e.g., navigation and manipulation); and (2) six meticulously curated subsets evaluating essential agent capabilities like commonsense reasoning, complex instruction understanding, spatial awareness, visual perception, and long-term planning. Through extensive experiments, we evaluated 13 leading proprietary and open-source MLLMs within EmbodiedBench. Our findings reveal that: MLLMs excel at high-level tasks but struggle with low-level manipulation, with the best model, GPT-4o, scoring only 28.9% on average. EmbodiedBench provides a multifaceted standardized evaluation platform that not only highlights existing challenges but also offers valuable insights to advance MLLM-based embodied agents. Our code is available at https://embodiedbench.github.io.
利用多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)创建实体代理为解决现实世界任务提供了一个有前景的途径。虽然以语言为中心的实体代理已经引起了广泛关注,但由于缺乏全面的评估框架,基于MLLM的实体代理仍然被探索得很少。为了弥补这一空白,我们引入了EmbodiedBench,这是一个旨在评估视觉驱动的实体代理的广泛基准测试。EmbodiedBench的特点包括:(1)在四个环境中包含1128个测试任务集,范围从高级语义任务(例如家务)到涉及原子动作的低级任务(例如导航和操作);(2)六个精心策划的子集评估了关键代理能力,如常识推理、复杂指令理解、空间感知、视觉感知和长期规划。通过广泛的实验,我们在EmbodiedBench中对13个领先的专业和开源MLLM进行了评估。我们发现:MLLM在高级任务上表现出色,但在低级操作任务上遇到困难,最佳模型GPT-4o的平均得分仅为28.9%。EmbodiedBench提供了一个多方面的标准化评估平台,它不仅突出了现有挑战,而且为推进基于MLLM的实体代理提供了有价值的见解。我们的代码可在https://embodiedbench.github.io获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 51 pages
Summary
基于多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)的实体代理在解决现实世界任务方面展现出巨大潜力。然而,由于缺少全面的评估框架,MLLM实体代理的研究仍处于起步阶段。为了填补这一空白,我们推出了EmbodiedBench评估平台,用于评估视觉驱动的实体代理。EmbodiedBench的特点是:(1)在四个环境中设有涵盖范围广泛的1,128项测试任务,包括高级语义任务(如家务)和低级原子动作任务(如导航和操作);(2)精心策划的六个子集评估了代理的核心能力,如常识推理、复杂指令理解、空间感知、视觉感知和长期规划等。通过广泛实验,我们对EmbodiedBench中的13款主流和开源的MLLM进行了评估。研究结果表明:MLLM擅长高级任务但难以处理低级操作任务,其中表现最好的模型GPT-4o在操作任务上的平均得分仅为28.9%。EmbodiedBench提供了一个多方面的标准化评估平台,不仅突出了现有挑战,也为推动MLLM实体代理的发展提供了宝贵见解。我们的代码可在https://embodiedbench.github.io上找到。
Key Takeaways
一、利用多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)构建实体代理为应对现实任务提供有力途径。
二、目前MLLM实体代理研究受限于缺乏全面的评估框架。
三、EmbodiedBench是一个用于评估视觉驱动实体代理的评估平台。
四、EmbodiedBench包含多样化的测试任务,涵盖高级语义任务和低级原子动作任务。
五、六个精心策划的子集评估实体代理的核心能力。
六、研究结果显示MLLM在处理低级操作任务上存在困难。
点此查看论文截图

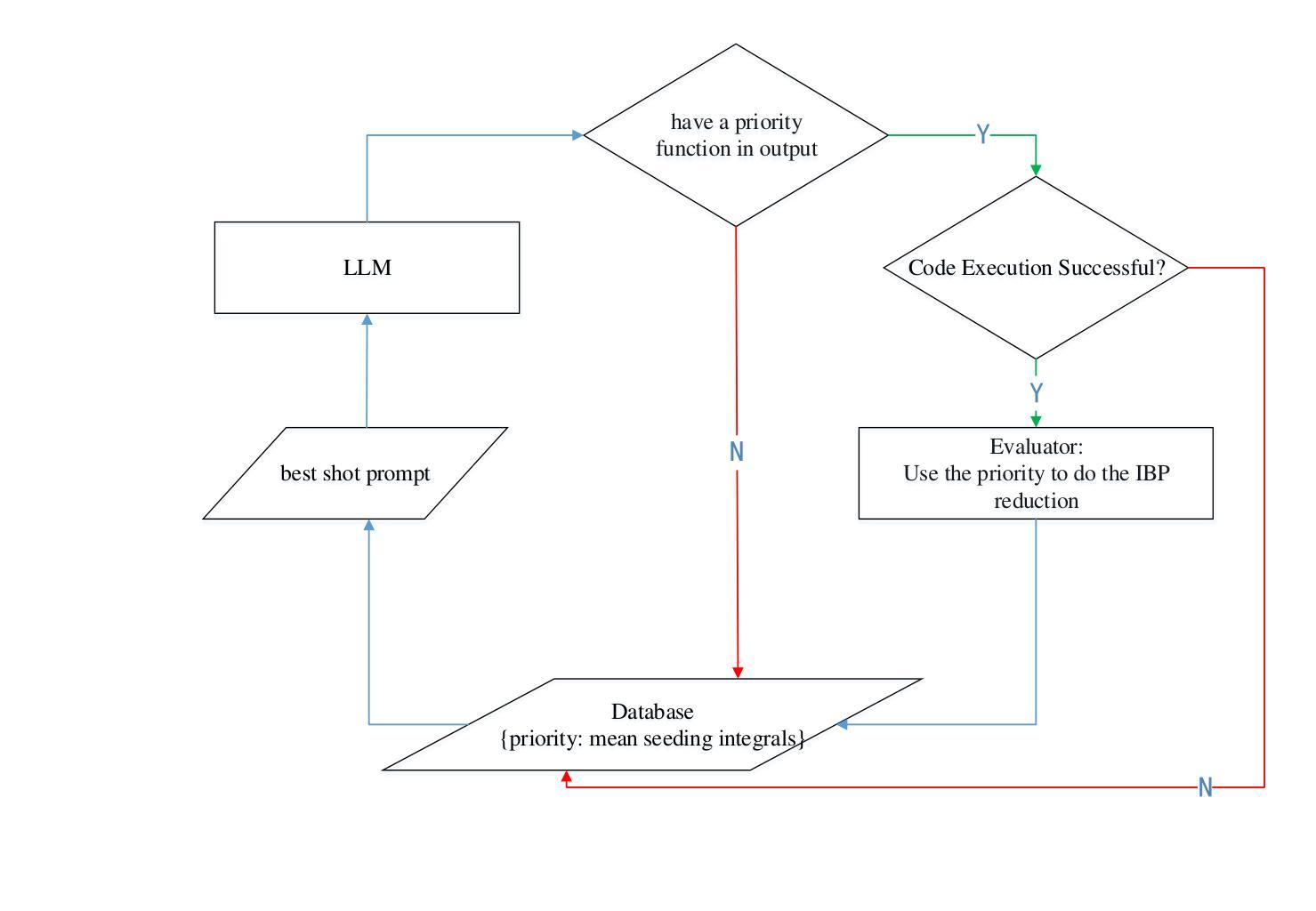
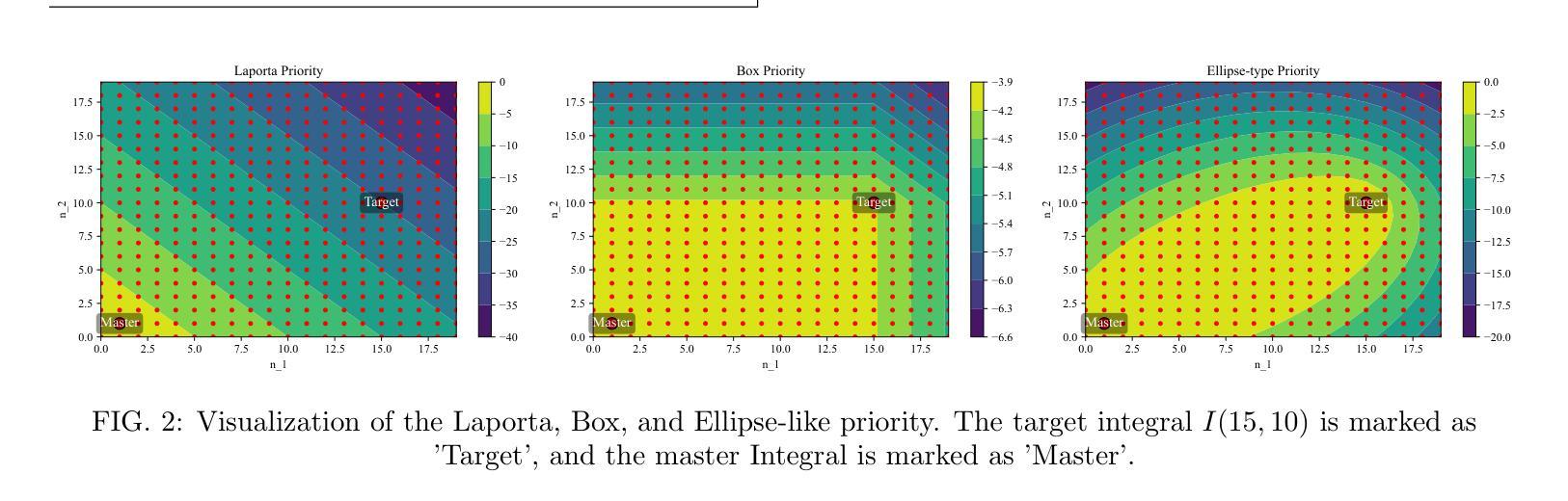
Explainable AI-assisted Optimization for Feynman Integral Reduction
Authors:Zhuo-Yang Song, Tong-Zhi Yang, Qing-Hong Cao, Ming-xing Luo, Hua Xing Zhu
We present a novel approach to optimizing the reduction of Feynman integrals using integration-by-parts identities. By developing a priority function through the FunSearch algorithm, which combines large language models and genetic algorithms, we achieve significant improvements in memory usage and computational efficiency compared to traditional methods. Our approach demonstrates substantial reductions in the required seeding integrals, making previously intractable integrals more manageable. Tested on a variety of Feynman integrals, including one-loop and multi-loop cases with planar and non-planar configurations, our method demonstrates remarkable scalability and adaptability. For reductions of certain Feynman integrals with many dots and numerators, we observed an improvement by a factor of 3058 compared to traditional methods. This work provides a powerful and interpretable framework for optimizing IBP reductions, paving the way for more efficient and practical calculations in high-energy physics.
我们提出了一种利用分部积分恒等式优化费曼积分的新方法。通过利用FunSearch算法开发优先级函数,结合大型语言模型和遗传算法,在内存使用和计算效率方面取得了显著的改进,相较于传统方法。我们的方法大幅度减少了所需的种子积分,使以前无法处理的积分更容易管理。我们在各种类型的费曼积分上进行了测试,包括具有平面和非平面配置的单循环和多循环情况,我们的方法表现出惊人的可扩展性和适应性。对于具有许多点和分子的某些费曼积分的化简,我们观察到与传统方法相比提高了3058倍。这项工作提供了一个强大且可解释的优化IBP化简框架,为高能物理的更高效和实用的计算铺平了道路。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 14 pages, 4 figures
Summary
本研究提出一种基于FunSearch算法和大型语言模型的新颖方法,用于优化费曼积分的缩减。该方法通过开发优先级函数,在内存使用和计算效率方面实现了对传统方法的显著改进。新方法在平面和非平面配置的单回路和多回路情况下测试的费曼积分中表现出良好的可扩展性和适应性。对于具有许多点和分子的某些费曼积分,与传统的缩减方法相比,观察到效率提高了高达三千多倍。该研究为优化IBP缩减提供了强大而可解释性的框架,为高能物理中的更实用和高效的计算铺平了道路。
Key Takeaways
- 提出了新的方法来优化费曼积分的减少,使用FunSearch算法结合了大型语言模型。
- 该方法通过开发优先级函数,显著改进了内存使用和计算效率。
- 方法在多种费曼积分测试中表现出良好的可扩展性和适应性,包括单回路和多回路情况,以及平面和非平面配置。
- 对于具有复杂结构和众多分子和点的费曼积分,新方法相比传统方法的效率提升显著,达到三千多倍。
- 此方法提供了一个强大的框架来优化IBP缩减。
- 此框架可能推动高能物理中更高效和实际的计算。
点此查看论文截图


Improve LLM-based Automatic Essay Scoring with Linguistic Features
Authors:Zhaoyi Joey Hou, Alejandro Ciuba, Xiang Lorraine Li
Automatic Essay Scoring (AES) assigns scores to student essays, reducing the grading workload for instructors. Developing a scoring system capable of handling essays across diverse prompts is challenging due to the flexibility and diverse nature of the writing task. Existing methods typically fall into two categories: supervised feature-based approaches and large language model (LLM)-based methods. Supervised feature-based approaches often achieve higher performance but require resource-intensive training. In contrast, LLM-based methods are computationally efficient during inference but tend to suffer from lower performance. This paper combines these approaches by incorporating linguistic features into LLM-based scoring. Experimental results show that this hybrid method outperforms baseline models for both in-domain and out-of-domain writing prompts.
自动作文评分(AES)为学生作文打分,减轻教师评分的工作量。开发一个能够处理不同提示的作文的评分系统是一个挑战,因为写作任务具有灵活性和多样性。现有方法通常分为两类:基于监督特征的方法和基于大型语言模型(LLM)的方法。基于监督特征的方法通常性能较高,但需要密集的资源进行训练。相比之下,基于LLM的方法在推理过程中计算效率高,但性能往往较低。本文结合了这两种方法,通过将语言特征纳入基于LLM的评分中。实验结果表明,这种混合方法对于领域内外(in-domain and out-of-domain)的写作提示都优于基线模型。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF To be published in the workshop Innovation and Responsibility in AI-Supported Education (iRaise) at the 2025 Conference on Artificial Intelligence (AAAI)
Summary
本文介绍了自动作文评分系统(AES)为学生作文打分,减轻教师评分工作量的功能。文章指出开发一个能够处理不同主题的自动作文评分系统是一个挑战。现有的方法主要分为两类:基于特征的监督方法和基于大型语言模型(LLM)的方法。基于特征的监督方法性能较高但需要密集的资源训练,而LLM方法虽然计算效率高但性能较低。本文结合了这两种方法,将语言特征纳入LLM评分系统中,实验结果表明这种混合方法在主题内外都优于基准模型。
Key Takeaways
- 自动作文评分系统(AES)可以为学生作文打分,减轻教师工作量。
- 开发自动作文评分系统面临处理不同主题的挑战。
- 现有方法主要包括基于特征的监督方法和基于大型语言模型(LLM)的方法。
- 基于特征的监督方法性能较高但需要密集的资源训练。
- LLM方法计算效率高但性能较低。
- 结合语言特征的LLM评分系统(混合方法)在主题内外都表现出优异性能。
点此查看论文截图

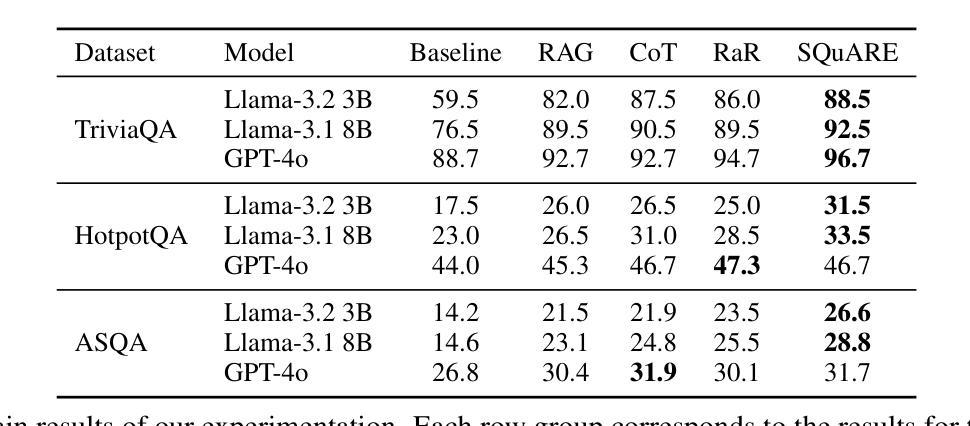
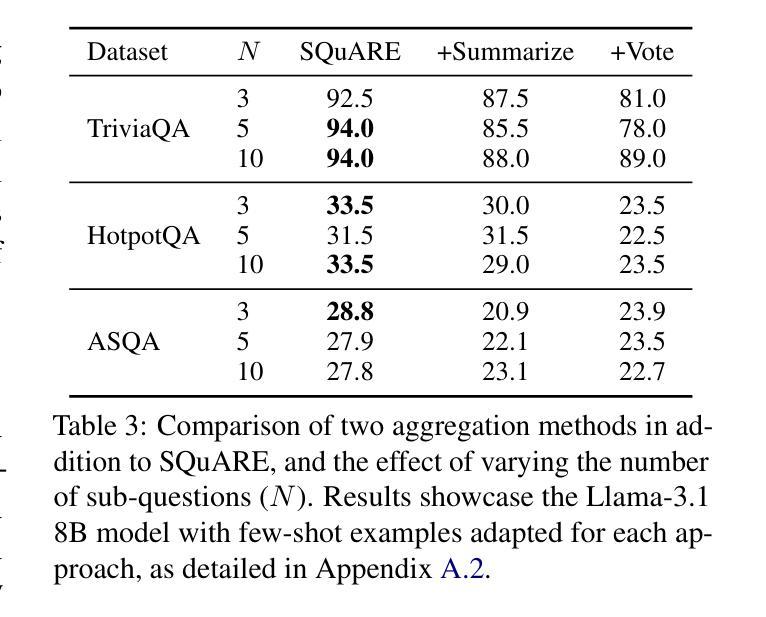
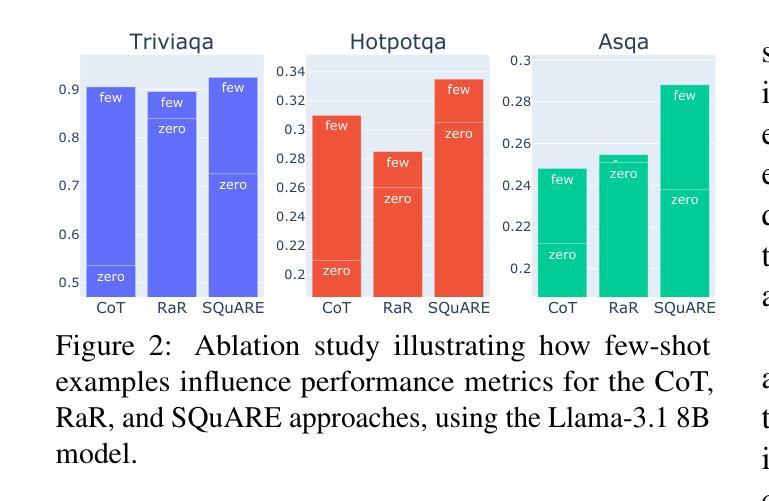
SQuARE: Sequential Question Answering Reasoning Engine for Enhanced Chain-of-Thought in Large Language Models
Authors:Daniel Fleischer, Moshe Berchansky, Gad Markovits, Moshe Wasserblat
In the rapidly evolving field of Natural Language Processing, Large Language Models (LLMs) are tasked with increasingly complex reasoning challenges. Traditional methods like chain-of-thought prompting have shown promise but often fall short in fully leveraging a model’s reasoning capabilities. This paper introduces SQuARE (Sequential Question Answering Reasoning Engine), a novel prompting technique designed to improve reasoning through a self-interrogation paradigm. Building upon CoT frameworks, SQuARE prompts models to generate and resolve multiple auxiliary questions before tackling the main query, promoting a more thorough exploration of various aspects of a topic. Our expansive evaluations, conducted with Llama 3 and GPT-4o models across multiple question-answering datasets, demonstrate that SQuARE significantly surpasses traditional CoT prompts and existing rephrase-and-respond methods. By systematically decomposing queries, SQuARE advances LLM capabilities in reasoning tasks. The code is publicly available at https://github.com/IntelLabs/RAG-FiT/tree/square.
在快速发展的自然语言处理领域,大型语言模型(LLM)面临着日益复杂的推理挑战。传统的诸如思维链提示法等方法虽然显示出了一定的潜力,但往往未能充分利用模型的推理能力。本文介绍了SQuARE(顺序问答推理引擎),这是一种新型的提示技术,旨在通过自我质问范式提高推理能力。SQuARE建立在CoT框架之上,提示模型在解决主要查询之前生成并解决多个辅助问题,从而促进对主题各方面的更全面的探索。我们在Llama 3和GPT-4o模型上进行了广泛的多问答数据集评估,证明了SQuARE显著超越了传统的CoT提示和现有的重述和回应方法。通过系统地分解查询,SQuARE提高了LLM在推理任务中的能力。代码公开在https://github.com/IntelLabs/RAG-FiT/tree/square。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 14 pages
Summary
在自然语言处理领域,大型语言模型(LLM)面临日益复杂的推理挑战。传统方法如链式思维提示法虽有潜力,但常常不能充分利用模型的推理能力。本文介绍了一种新的提示技术——SQuARE(序贯问答推理引擎),它采用自问自答模式改善推理能力。建立在CoT框架之上,SQuARE通过生成并解决多个辅助问题来应对主要查询,促进对主题各方面的全面探索。在多个问答数据集上进行的对Llama 3和GPT-4o模型的广泛评估表明,SQuARE显著超越了传统CoT提示和现有的重述与回应方法。通过系统地分解查询,SQuARE推动了LLM在推理任务中的应用能力。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLM)在自然语言处理领域面临复杂的推理挑战。
- 传统方法如链式思维提示法虽然有一定潜力,但无法充分利用模型的全部推理能力。
- SQuARE是一种新型的提示技术,采用自问自答模式来提高推理能力。
- SQuARE建立在CoT框架之上,通过生成并解决多个辅助问题来应对主要查询。
- SQuARE能系统地分解查询,促进对主题各方面的全面探索。
- 在多个问答数据集上的广泛评估显示,SQuARE显著优于传统CoT提示和重述与回应方法。
点此查看论文截图


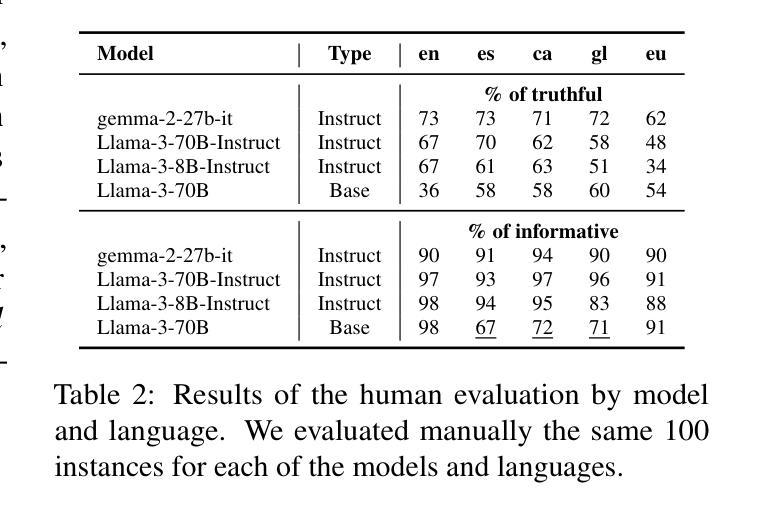
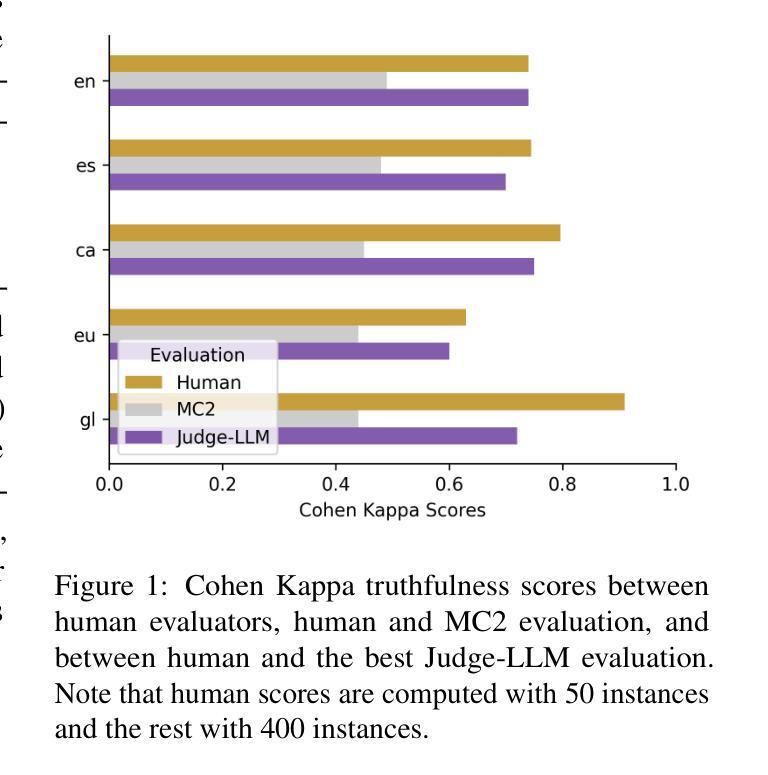
Truth Knows No Language: Evaluating Truthfulness Beyond English
Authors:Blanca Calvo Figueras, Eneko Sagarzazu, Julen Etxaniz, Jeremy Barnes, Pablo Gamallo, Iria De Dios Flores, Rodrigo Agerri
We introduce a professionally translated extension of the TruthfulQA benchmark designed to evaluate truthfulness in Basque, Catalan, Galician, and Spanish. Truthfulness evaluations of large language models (LLMs) have primarily been conducted in English. However, the ability of LLMs to maintain truthfulness across languages remains under-explored. Our study evaluates 12 state-of-the-art open LLMs, comparing base and instruction-tuned models using human evaluation, multiple-choice metrics, and LLM-as-a-Judge scoring. Our findings reveal that, while LLMs perform best in English and worst in Basque (the lowest-resourced language), overall truthfulness discrepancies across languages are smaller than anticipated. Furthermore, we show that LLM-as-a-Judge correlates more closely with human judgments than multiple-choice metrics, and that informativeness plays a critical role in truthfulness assessment. Our results also indicate that machine translation provides a viable approach for extending truthfulness benchmarks to additional languages, offering a scalable alternative to professional translation. Finally, we observe that universal knowledge questions are better handled across languages than context- and time-dependent ones, highlighting the need for truthfulness evaluations that account for cultural and temporal variability. Dataset and code are publicly available under open licenses.
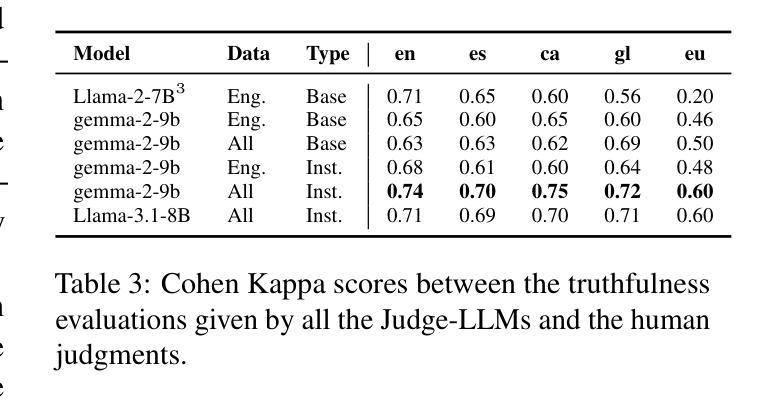
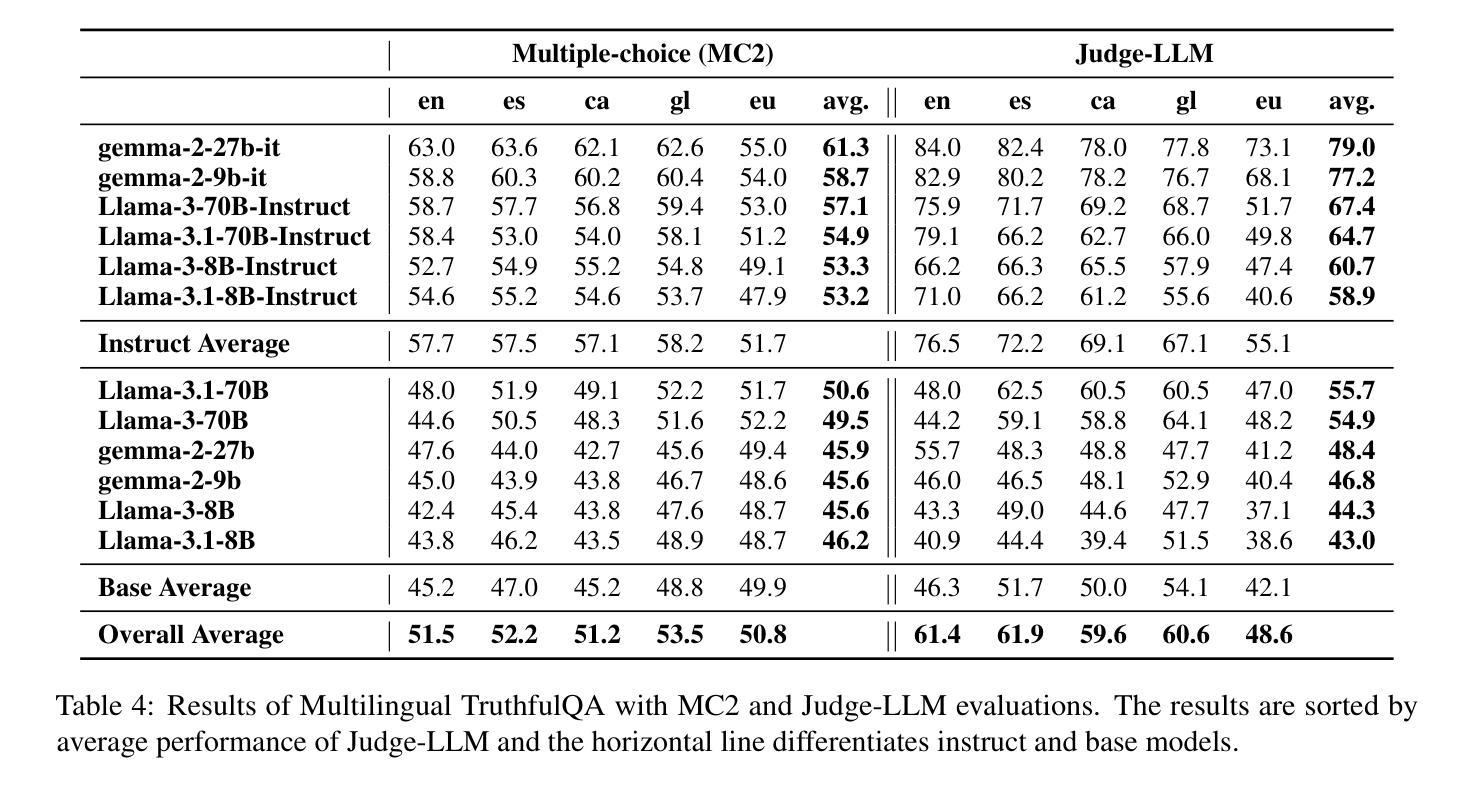
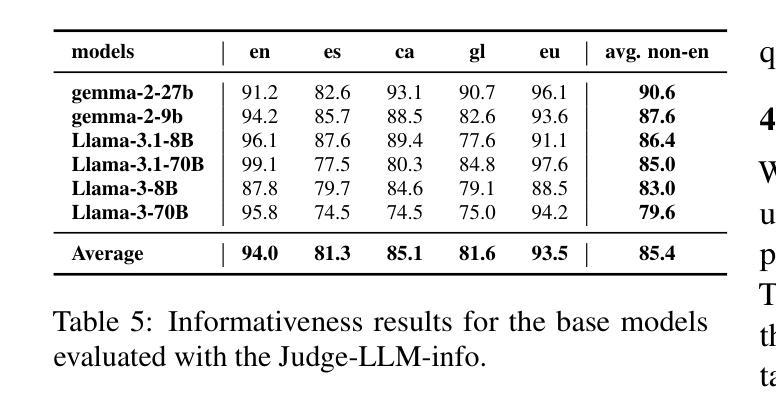
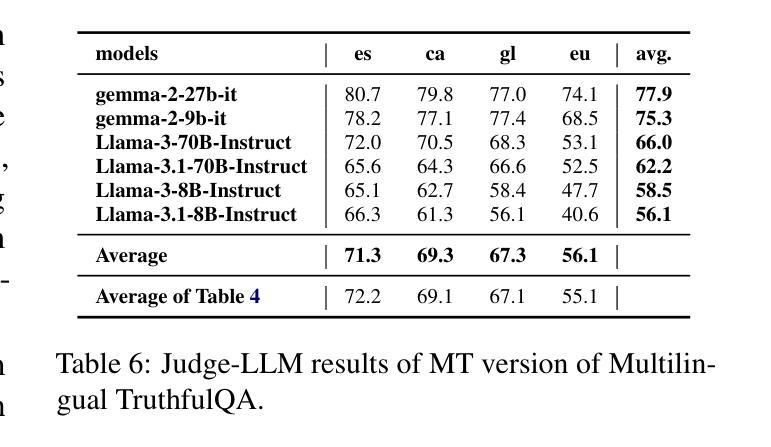
我们介绍了一个专业翻译的TruthfulQA基准测试扩展版,该版本旨在评估巴斯克语、加泰罗尼亚语、加利西亚语和西班牙语的真实性。迄今为止,对大型语言模型(LLM)的真实性评价主要都是在英语环境中进行的。然而,LLM在不同语言中保持真实性的能力仍待探索。我们的研究评估了12款最先进的开源LLM,通过人工评价、多项选择指标和LLM-as-a-Judge评分对比基础模型和指令优化模型。我们的研究发现,虽然LLM在英语中的表现最好,在巴斯克语(资源最少的语言)中的表现最差,但总体来说,不同语言间的真实性差异比预期的要小。此外,我们还发现LLM-as-a-Judge与人类判断的联系比多项选择指标更为紧密,信息在真实性评估中起着至关重要的作用。我们的结果还表明,机器翻译是扩展真实性基准测试到更多语言的一种可行方法,为专业翻译提供了一种可扩展的替代方案。最后,我们观察到,通用知识问题的跨语言处理能力优于语境和时间依赖问题,这强调了在进行真实性评估时需要考虑到文化和时间变量的必要性。数据集和代码均公开提供开放许可。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 13 pages, 5 figures, 8 tables
Summary
本文介绍了针对巴斯克语、加泰罗尼亚语、加利西亚语和西班牙语的真实性评价基准测试的专业翻译扩展版本。该研究评估了12个最先进的开源大型语言模型(LLM),对比了基础模型和指令调整模型,使用人类评估、多项选择指标和LLM-as-a-Judge评分方法。研究发现,LLM在英语中表现最好,在巴斯克语(资源最少)中表现最差,但总体来说,不同语言之间的真实性差异小于预期。此外,LLM-as-a-Judge与人类判断的相关性更高,信息性在真实性评估中起着关键作用。机器翻译可作为将真实性基准测试扩展到其他语言的可行方法,提供了一种可扩展的替代专业翻译的途径。最后,普遍知识的相关问题在不同语言中的处理情况比上下文和时间相关的问题更好,这强调了在进行真实性评估时需要考虑到文化和时间的变化性。
Key Takeaways
- 研究介绍了针对多种语言(巴斯克语、加泰罗尼亚语、加利西亚语和西班牙语)的大型语言模型(LLM)的真实性评估。
- 对比了12个先进的LLM模型在多种语言中的表现。
- 发现LLM在英语中表现最佳,在巴斯克语中表现最差,但不同语言间的真实性差异总体较小。
- LLM-as-a-Judge评分方法与人类判断的相关性更高。
- 信息性对真实性评估至关重要。
- 机器翻译可作为将真实性基准测试扩展到其他语言的可行方法。
点此查看论文截图


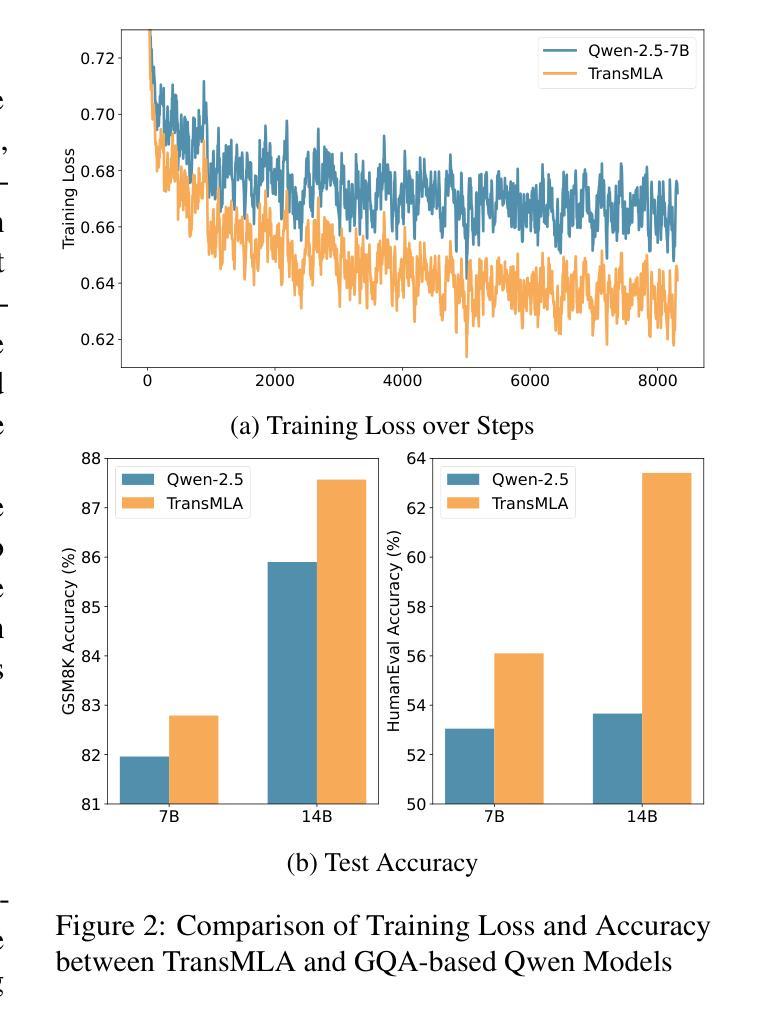
TransMLA: Multi-Head Latent Attention Is All You Need
Authors:Fanxu Meng, Zengwei Yao, Muhan Zhang
Modern large language models (LLMs) often encounter communication bottlenecks on current hardware, rather than purely computational constraints. Multi-head Latent Attention (MLA) tackles this challenge by using low-rank matrices in the key-value (KV) layers, thereby allowing compressed latent KV states to be cached. This approach significantly reduces the KV cache size relative to traditional multi-head attention, leading to faster inference. Moreover, MLA employs an up-projection matrix to increase expressiveness, trading additional computation for reduced communication overhead. Although MLA has demonstrated efficiency and effectiveness in Deepseek V2/V3/R1, many major model providers still rely on Group Query Attention (GQA) and have not announced any plans to adopt MLA. In this paper, we show that GQA can always be represented by MLA while maintaining the same KV cache overhead, but the converse does not hold. To encourage broader use of MLA, we introduce TransMLA, a post-training method that converts widely used GQA-based pre-trained models (e.g., LLaMA, Qwen, Mixtral) into MLA-based models. After conversion, the model can undergo additional training to boost expressiveness without increasing the KV cache size. Furthermore, we plan to develop MLA-specific inference acceleration techniques to preserve low latency in transformed models, thus enabling more efficient distillation of Deepseek R1.
现代大型语言模型(LLM)经常在现有硬件上遇到通信瓶颈,而不是纯粹的计算约束。多头潜在注意力(MLA)通过键值(KV)层使用低阶矩阵来解决这一挑战,从而允许压缩的潜在KV状态被缓存。这种方法显著减少了与传统的多头注意力相比的KV缓存大小,导致推理速度更快。此外,MLA采用上投影矩阵来增加表达力,以额外的计算换取减少的通信开销。尽管MLA已在Deepseek V2/V3/R1中展现了其高效性和有效性,但许多主要模型提供商仍然依赖群组查询注意力(GQA)并且没有宣布采用MLA的计划。在本文中,我们展示GQA总是可以由MLA表示,同时保持相同的KV缓存开销,但反之则不成立。为了鼓励更广泛地使用MLA,我们引入了TransMLA,这是一种后训练方法,可将广泛使用的基于GQA的预训练模型(例如LLaMA、Qwen、Mixtral)转换为基于MLA的模型。转换后,模型可以进行额外的训练以提升表达力而不会增加KV缓存大小。此外,我们计划开发针对MLA的推理加速技术,以保持转换模型中的低延迟,从而实现Deepseek R1的更有效蒸馏。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF https://github.com/fxmeng/TransMLA
Summary
大型语言模型在现代硬件上遇到的瓶颈更多是通信瓶颈而非计算约束。Multi-head Latent Attention(MLA)通过关键值层中的低秩矩阵解决此问题,允许压缩潜在关键值状态被缓存,显著减少关键值缓存大小,加快推理速度。此外,MLA使用上投影矩阵提高表达能力,以额外的计算换取减少通信开销。虽然MLA已在Deepseek V2/V3/R1中表现出高效和有效性,但许多主要模型提供商仍依赖Group Query Attention(GQA)并未宣布采用MLA的计划。本文展示了GQA可由MLA表示并保持相同的关键值缓存开销,但反之不成立。为鼓励更广泛使用MLA,我们引入了TransMLA,这是一种将广泛使用的基于GQA的预训练模型(如LLaMA、Qwen、Mixtral)转换为基于MLA的模型的后训练方法。转换后的模型可进一步进行训练以提高表达能力而不增加关键值缓存大小。我们还计划开发MLA特定的推理加速技术,以保持转换模型的低延迟,从而实现Deepseek R1更有效的蒸馏。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型在现代硬件上遇到的挑战主要是通信瓶颈而非计算约束。
- Multi-head Latent Attention (MLA) 通过使用低秩矩阵减少关键值缓存大小并加快推理速度。
- MLA采用上投影矩阵以提高表达能力并减少通信开销。
- 尽管MLA在某些情况下表现出优势,但许多主要模型提供商仍依赖Group Query Attention (GQA)。
- GQA可由MLA表示并保持相同的关键值缓存开销,但反之不成立。这意味着转换为MLA后可能有更大的优化潜力。
- TransMLA方法能将现有的基于GQA的预训练模型转换为基于MLA的模型,进一步提高效率和表达能力。
点此查看论文截图

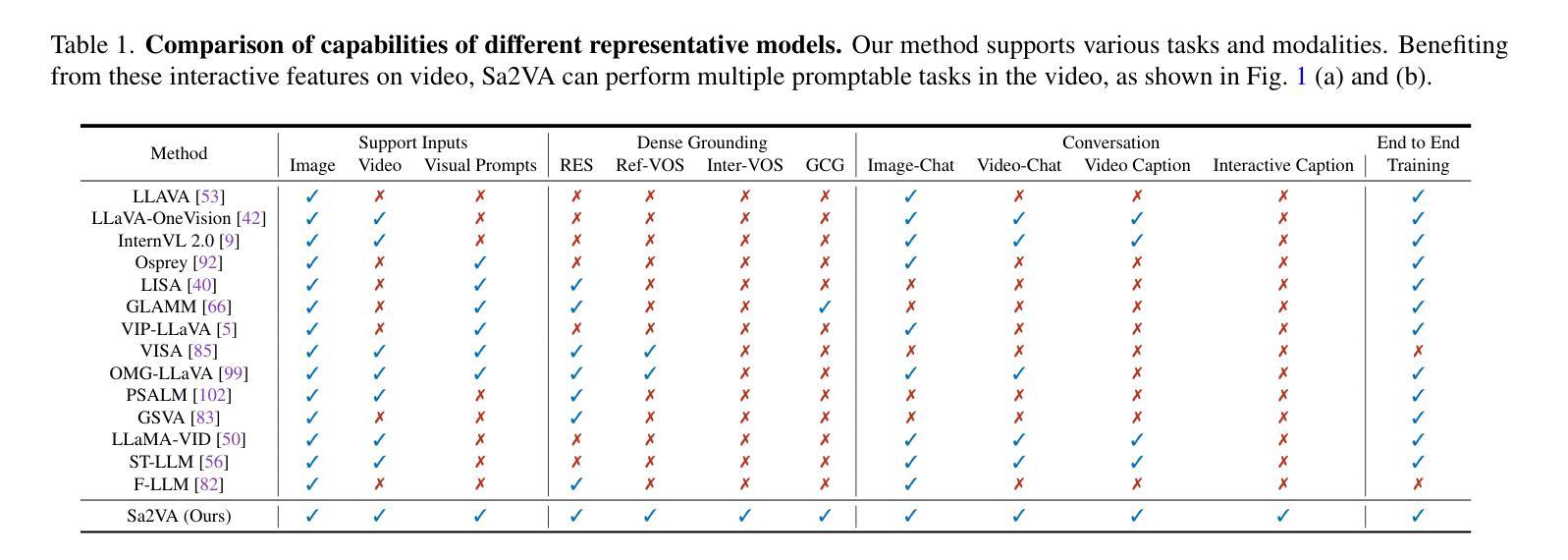
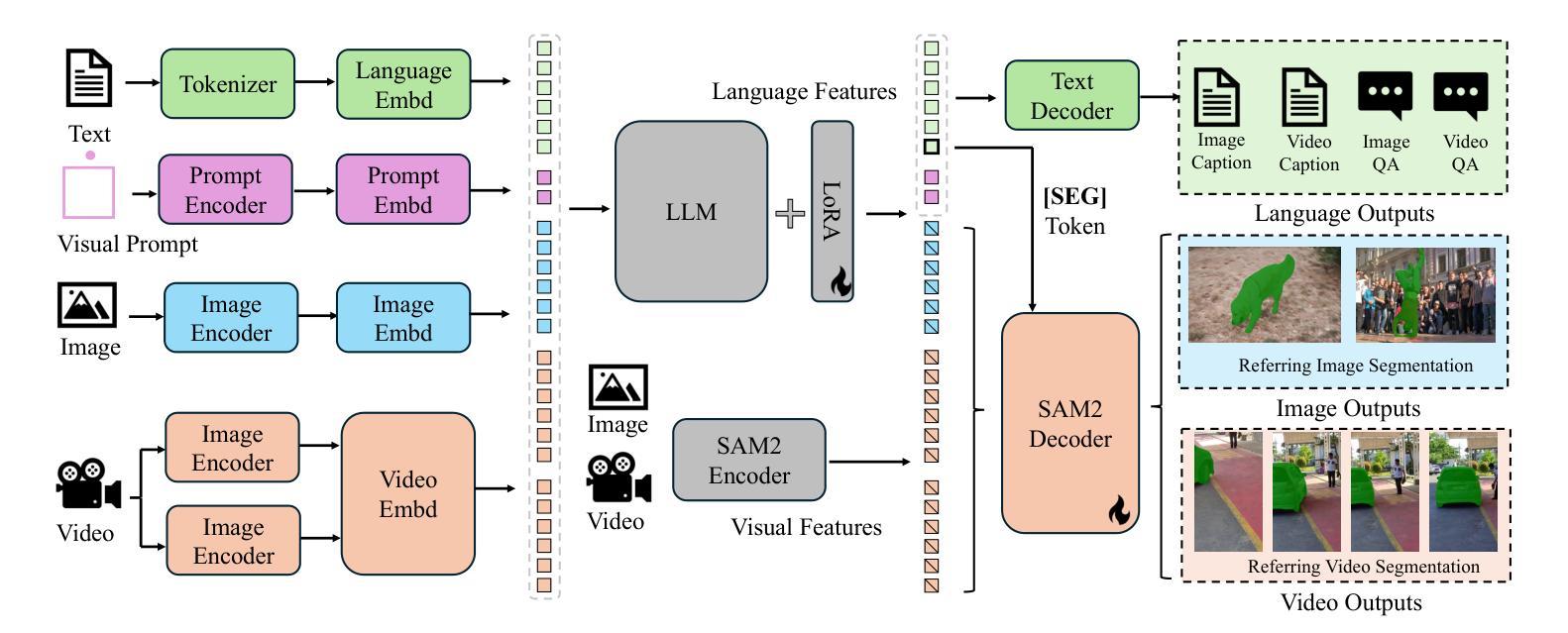
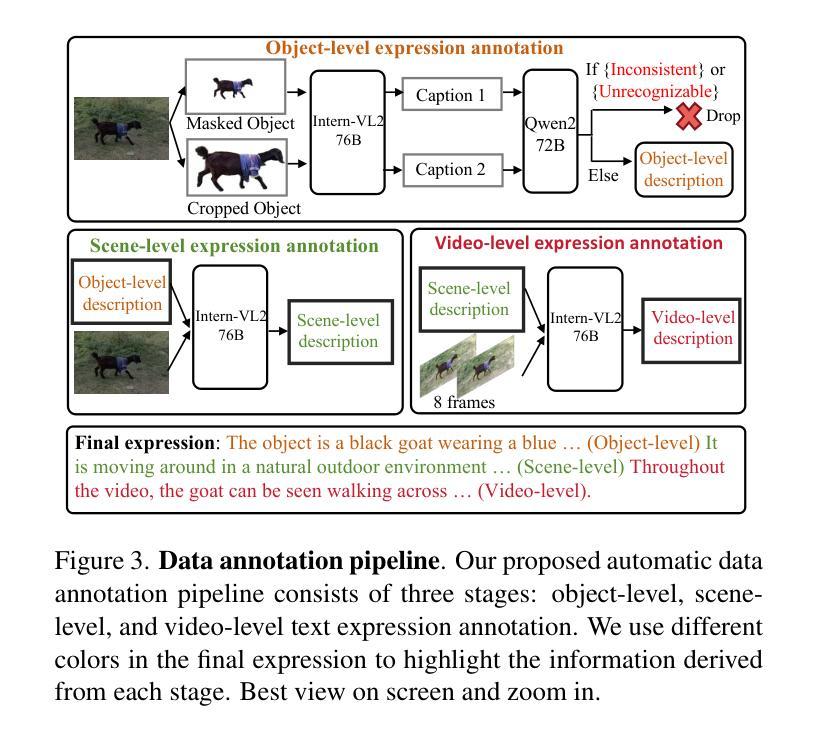
Sa2VA: Marrying SAM2 with LLaVA for Dense Grounded Understanding of Images and Videos
Authors:Haobo Yuan, Xiangtai Li, Tao Zhang, Zilong Huang, Shilin Xu, Shunping Ji, Yunhai Tong, Lu Qi, Jiashi Feng, Ming-Hsuan Yang
This work presents Sa2VA, the first unified model for dense grounded understanding of both images and videos. Unlike existing multi-modal large language models, which are often limited to specific modalities and tasks, Sa2VA supports a wide range of image and video tasks, including referring segmentation and conversation, with minimal one-shot instruction tuning. Sa2VA combines SAM-2, a foundation video segmentation model, with LLaVA, an advanced vision-language model, and unifies text, image, and video into a shared LLM token space. Using the LLM, Sa2VA generates instruction tokens that guide SAM-2 in producing precise masks, enabling a grounded, multi-modal understanding of both static and dynamic visual content. Additionally, we introduce Ref-SAV, an auto-labeled dataset containing over 72k object expressions in complex video scenes, designed to boost model performance. We also manually validate 2k video objects in the Ref-SAV datasets to benchmark referring video object segmentation in complex environments. Experiments show that Sa2VA achieves state-of-the-art across multiple tasks, particularly in referring video object segmentation, highlighting its potential for complex real-world applications.
本文介绍了Sa2VA,这是第一个统一模型,能够密集地对图像和视频进行接地理解。与现有的多模态大型语言模型不同,这些模型通常仅限于特定的模态和任务,而Sa2VA支持广泛的图像和视频任务,包括引用分割和对话,并且可以通过一次简单的指令调整来实现。Sa2VA结合了SAM-2基础视频分割模型和LLaVA高级视觉语言模型,并将文本、图像和视频统一到共享的大型语言模型标记空间中。利用大型语言模型,Sa2VA生成指令标记,指导SAM-2生成精确蒙版,实现对静态和动态视觉内容的接地多模态理解。此外,我们引入了Ref-SAV,这是一个自动标记的数据集,包含超过7万多个复杂视频场景中的对象表达式,旨在提高模型性能。我们还手动验证了Ref-SAV数据集中的2千个视频对象,以评估复杂环境中引用视频对象分割的基准。实验表明,Sa2VA在多个任务上均达到最新水平,特别是在引用视频对象分割方面,突显其在复杂现实世界应用中的潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project page: https://lxtgh.github.io/project/sa2va
Summary
本文提出了Sa2VA模型,它是首个支持图像和视频密集接地理解的一体化模型。该模型融合了SAM-2视频分割模型和LLaVA高级视觉语言模型,并将文本、图像和视频统一到共享的LLM令牌空间中。通过LLM生成指令令牌,指导SAM-2产生精确蒙版,实现静态和动态视觉内容的接地、多模态理解。此外,还介绍了用于复杂视频场景的Ref-SAV自标注数据集,用于提升模型性能。实验表明,Sa2VA在多任务中实现了业界领先水平,尤其在指代视频对象分割方面表现出巨大潜力。
Key Takeaways
- Sa2VA是首个统一模型,支持图像和视频的密集接地理解。
- Sa2VA能处理多种图像和视频任务,包括指代分割和对话。
- Sa2VA融合了SAM-2视频分割模型和LLaVA视觉语言模型。
- Sa2VA将文本、图像和视频统一到共享的LLM令牌空间中。
- LLM生成的指令令牌指导SAM-2产生精确蒙版,实现多模态理解。
- 引入了Ref-SAV自标注数据集,用于提升模型在复杂视频场景中的性能。
点此查看论文截图

WarriorCoder: Learning from Expert Battles to Augment Code Large Language Models
Authors:Huawen Feng, Pu Zhao, Qingfeng Sun, Can Xu, Fangkai Yang, Lu Wang, Qianli Ma, Qingwei Lin, Saravan Rajmohan, Dongmei Zhang, Qi Zhang
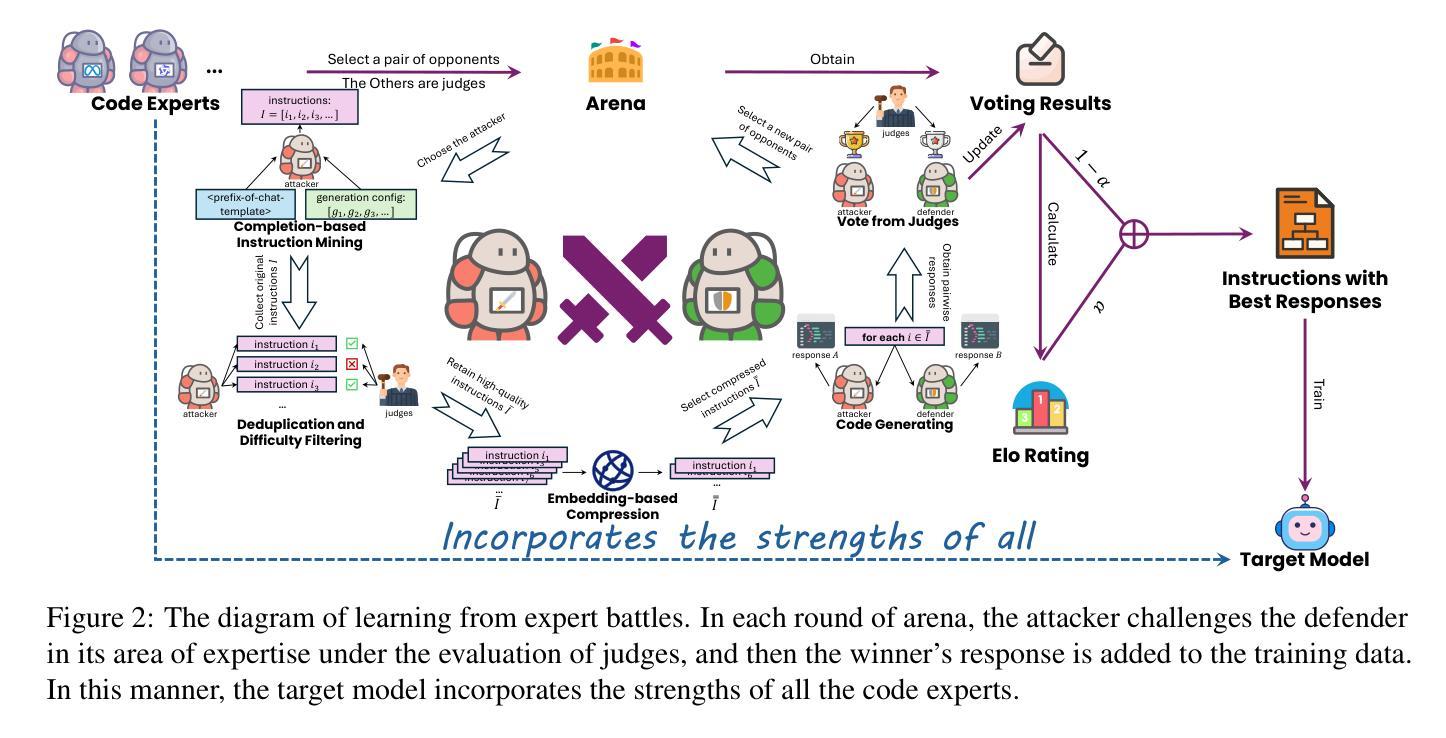
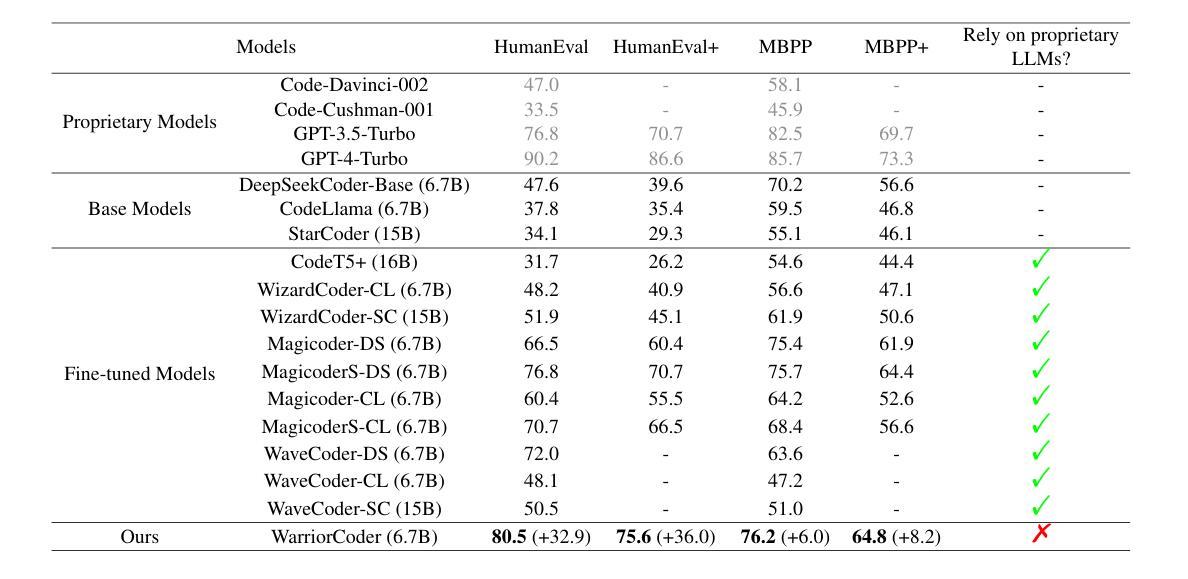
Despite recent progress achieved by code large language models (LLMs), their remarkable abilities are largely dependent on fine-tuning on the high-quality data, posing challenges for data collection and annotation. To address this, current methods often design various data flywheels to collect complex code instructions, enabling models to handle more intricate tasks. However, these approaches typically rely on off-the-shelf datasets and data augmentation from a limited set of proprietary LLMs (e.g., Claude, GPT4, and so on), which restricts the diversity of the constructed data and makes it prone to systemic biases. In this paper, we propose WarriorCoder, a novel paradigm learns from expert battles to address these limitations. Specifically, we create an arena where leading expert code LLMs challenge each other, with evaluations conducted by impartial judges. This competitive framework generates novel training data from scratch, leveraging the strengths of all participants. Experimental results show that WarriorCoder achieves state-of-the-art performance compared to previous models of the same size, even without relying on proprietary LLMs.
尽管代码大型语言模型(LLM)最近取得了进展,但它们的卓越能力在很大程度上依赖于高质量数据的微调,这给数据采集和标注带来了挑战。为了解决这一问题,当前的方法通常设计各种数据飞轮来收集复杂的代码指令,使模型能够处理更复杂的任务。然而,这些方法通常依赖于现成的数据集和有限专有LLM(如Claude、GPT4等)的数据增强,这限制了构建数据的多样性,并使其容易受系统偏见的影响。在本文中,我们提出了WarriorCoder,一种新型范式,从专家对决中学习,以解决这些限制。具体来说,我们创建一个竞技场,让领先的专家代码LLM相互挑战,由公正裁判进行评估。这个竞争框架从零开始生成新的训练数据,利用所有参与者的优势。实验结果表明,WarriorCoder在相同大小的模型中实现了最先进的性能表现,甚至不需要依赖专有LLM。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出了WarriorCoder,一个从专家对抗中学习的新型范式,以解决大型语言模型(LLMs)在数据处理和注释方面的挑战。该框架创建一个领先的专业代码LLMs竞技场,通过公正的评委进行评估,生成新的训练数据。实验结果表明,WarriorCoder在不依赖专有LLMs的情况下,实现了与相同规模的前模型的卓越性能。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLMs)虽然已经取得进展,但仍需精细化调整以处理高质量数据。
- 目前的方法通常依赖现成的数据集和有限专有LLMs的数据增强来收集复杂的代码指令。
- 专有LLMs的限制包括数据多样性不足和系统偏见。
- WarriorCoder框架通过创建领先的专业代码LLMs竞技场来解决这些问题。
- WarriorCoder利用所有参与者的优势生成新的训练数据。
- 实验结果表明,WarriorCoder在不依赖专有LLMs的情况下实现了卓越性能。
点此查看论文截图
Diffusion Transformer Policy: Scaling Diffusion Transformer for Generalist Vision-Language-Action Learning
Authors:Zhi Hou, Tianyi Zhang, Yuwen Xiong, Hengjun Pu, Chengyang Zhao, Ronglei Tong, Yu Qiao, Jifeng Dai, Yuntao Chen
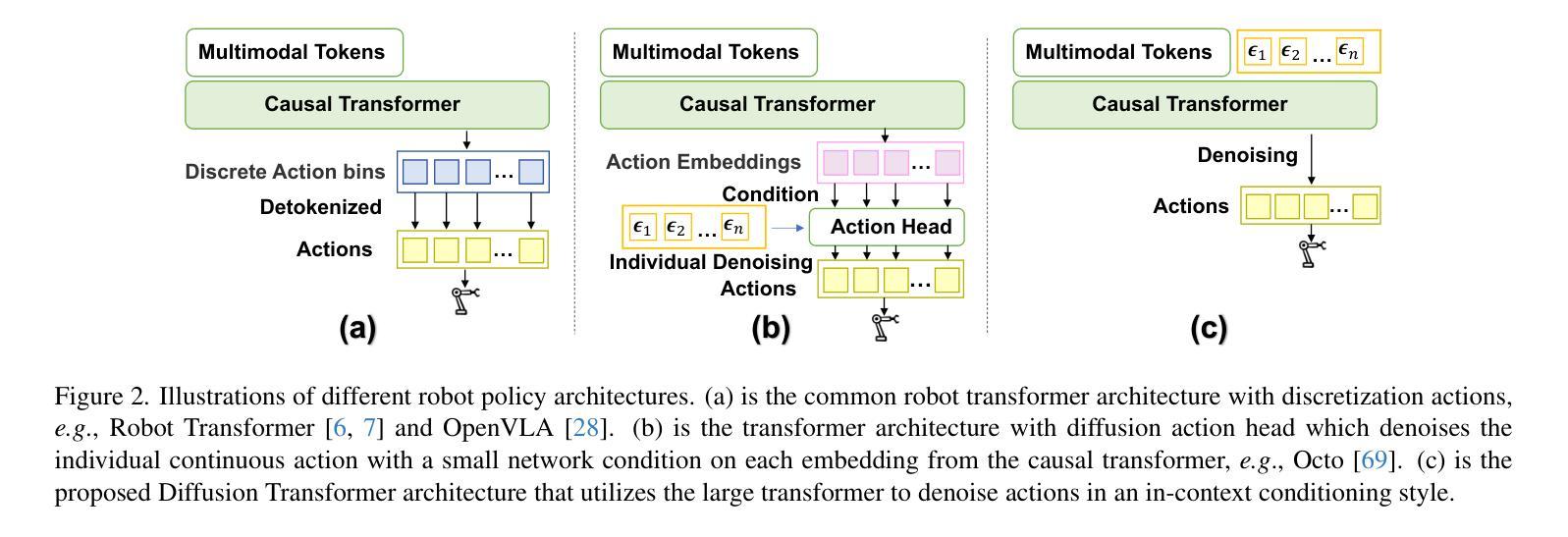
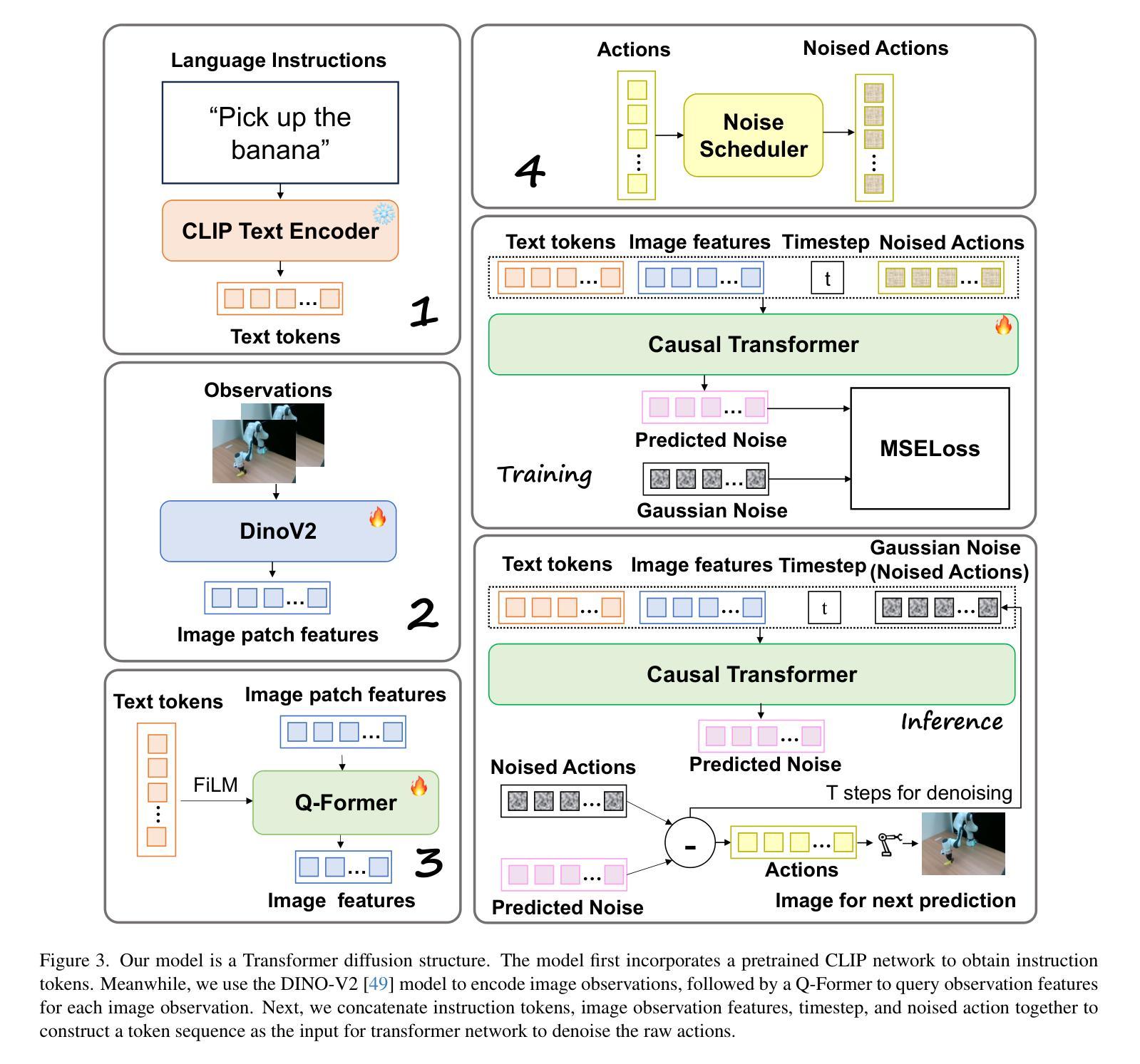
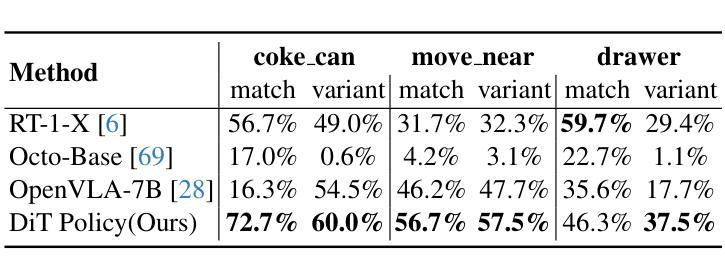
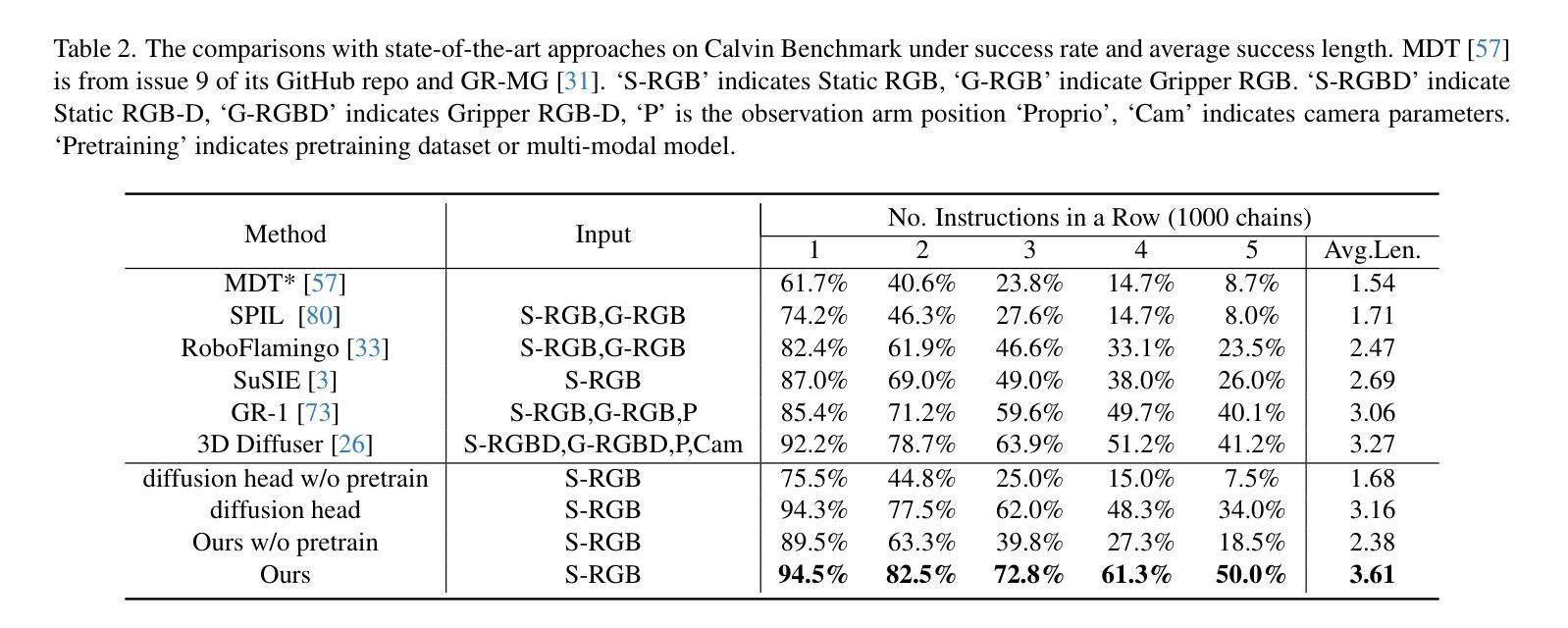
Recent large vision-language action models pretrained on diverse robot datasets have demonstrated the potential for generalizing to new environments with a few in-domain data. However, those approaches usually predict individual discretized or continuous action by a small action head, which limits the ability in handling diverse action spaces. In contrast, we model the continuous action sequence with a large multi-modal diffusion transformer, dubbed as Diffusion Transformer Policy, in which we directly denoise action chunks by a large transformer model rather than a small action head for action embedding. By leveraging the scaling capability of transformers, the proposed approach can effectively model continuous end-effector actions across large diverse robot datasets, and achieve better generalization performance. Extensive experiments demonstrate the effectiveness and generalization of Diffusion Transformer Policy on Maniskill2, Libero, Calvin and SimplerEnv, as well as the real-world Franka arm, achieving consistent better performance on Real-to-Sim benchmark SimplerEnv, real-world Franka Arm and Libero compared to OpenVLA and Octo. Specifically, without bells and whistles, the proposed approach achieves state-of-the-art performance with only a single third-view camera stream in the Calvin task ABC->D, improving the average number of tasks completed in a row of 5 to 3.6, and the pretraining stage significantly facilitates the success sequence length on the Calvin by over 1.2. Project Page: https://zhihou7.github.io/dit_policy_vla/
最近的大型视觉语言行动模型通过在各种机器人数据集上进行预训练,已经显示出在新环境中使用少量领域数据进行泛化的潜力。然而,这些方法通常通过小型动作头预测离散或连续的动作,这限制了处理多样化动作空间的能力。相比之下,我们采用大型多模态扩散变压器来模拟连续动作序列,称为扩散变压器策略。我们通过一个大型的变压器模型直接去除动作块中的噪声,而不是通过一个小型的动作头进行动作嵌入。通过利用变压器的可扩展性,所提出的方法可以有效地模拟跨大型多样化机器人数据集的连续末端执行器动作,并实现更好的泛化性能。大量实验表明,Diffusion Transformer Policy在Maniskill2、Libero、Calvin和SimplerEnv以及真实世界的Franka机械臂上的有效性和泛化能力。具体来说,与OpenVLA和Octo相比,所提出的方法在Real-to-Sim基准测试SimplerEnv、真实世界的Franka机械臂和Libero上表现一致且更好。特别的是,在不使用任何花哨的技术的情况下,所提出的方法仅在Calvin任务的ABC->D中使用单个第三人称视角的相机流就实现了最先进的性能,将连续完成任务的平均数量从5提高到3.6,而且预训练阶段显著增加了Calvin任务上的成功序列长度超过1. - 齐鸿博博士个人网站:https://zhihou7.github.io/dit_policy_vla/。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Preprint
Summary
本文介绍了一种基于大型多模态扩散变压器的新型机器人动作策略。与传统方法不同,它通过大型变压器模型直接对动作片段进行去噪,而非通过小型动作头进行动作嵌入。该方法能有效建模大型多样机器人数据集中的连续末端执行器动作,并实现更好的泛化性能。在多个数据集上的实验表明,该策略在模拟到现实环境的任务中表现出卓越的性能。
Key Takeaways
- 介绍了一种基于扩散变压器的大型视觉语言动作模型,该模型在多样机器人数据集上进行预训练。
- 模型能够泛化到新环境并处理多样化的动作空间。
- 通过大型变压器模型直接对动作片段进行去噪,提高了动作嵌入的效果。
- 模型在多个数据集上表现出卓越的性能,包括Maniskill2、Libero、Calvin和SimplerEnv等。
- 在模拟到现实环境的任务中,该策略实现了比OpenVLA和Octo更好的性能。
- 该策略仅使用单个第三人称视角相机流,在Calvin任务ABC->D中实现了最先进的性能。
点此查看论文截图

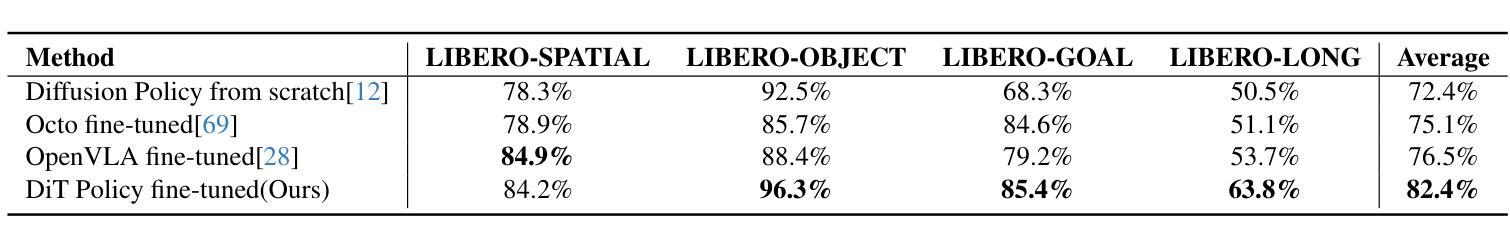
An Evolved Universal Transformer Memory
Authors:Edoardo Cetin, Qi Sun, Tianyu Zhao, Yujin Tang
Prior methods propose to offset the escalating costs of modern foundation models by dropping specific parts of their contexts with hand-designed rules, while attempting to preserve their original performance. We overcome this trade-off with Neural Attention Memory Models (NAMMs), introducing a learned network for memory management that improves both the performance and efficiency of transformers. We evolve NAMMs atop pre-trained transformers to provide different latent contexts focusing on the most relevant information for individual layers and attention heads. NAMMs are universally applicable to any model using self-attention as they condition exclusively on the values in the produced attention matrices. Learning NAMMs on a small set of problems, we achieve substantial performance improvements across multiple long-context benchmarks while cutting the model’s input contexts up to a fraction of the original sizes. We show the generality of our conditioning enables zero-shot transfer of NAMMs trained only on language to entirely new transformer architectures even across input modalities, with their benefits carrying over to vision and reinforcement learning.
先前的方法提议通过利用手工设计的规则来删除现代基础模型特定部分的上下文来抵消其不断上升的成本,同时试图保持其原始性能。我们通过神经注意力记忆模型(NAMMs)克服了这一权衡,引入了用于记忆管理的学习网络,提高了转换器的性能和效率。我们在预训练的转换器之上发展NAMMs,以提供不同的潜在上下文,专注于各层和注意力头最相关的信息。由于它们仅依赖于生成的注意力矩阵中的值,因此NAMMs可普遍适用于任何使用自注意力的模型。通过在一系列问题上学习NAMMs,我们在多个长上下文基准测试中实现了显著的性能提升,同时还将模型的输入上下文缩减到原始大小的一小部分。我们证明了我们的条件通用性使仅通过语言训练的NAMMs能够零样本迁移到全新的转换器架构,甚至跨越输入模式,它们的优势也延伸到计算机视觉和强化学习领域。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Published at ICLR 2025. Source code available at https://github.com/SakanaAI/evo-memory
Summary
本文提出一种名为神经注意力记忆模型(NAMMs)的方法,用于改进和优化变压器的性能和效率。该方法通过引入学习到的内存管理机制来克服以往方法中成本和性能之间的权衡。通过预训练的变压器,NAMMs能够生成针对不同层级和注意力头的不同潜在上下文,专注于最相关的信息。这种方法具有通用性,可应用于任何使用自注意力的模型,因为它完全依赖于产生的注意力矩阵的值。通过一系列实验,NAMMs在多个长上下文基准测试中实现了显著的性能提升,并将模型的输入上下文大小缩减至原始大小的极小部分。此外,我们还证明了其在语言训练的NAMMs可以零迁移至全新变压器架构乃至不同输入模式的一般性能力,并成功将其应用于视觉和强化学习领域。
Key Takeaways
- NAMMs通过引入学习到的内存管理机制来改进和优化变压器的性能和效率。
- NAMMs克服了以往方法中成本和性能之间的权衡问题。
- NAMMs能够生成针对不同层级和注意力头的不同潜在上下文,专注于最相关的信息。
- 该方法具有通用性,适用于任何使用自注意力的模型。
- NAMMs通过生成注意力矩阵的值进行工作,实现了更高效和灵活的模型性能。
- 在多个长上下文基准测试中,NAMMs实现了显著的性能提升,并将模型的输入上下文大小大幅缩减。
点此查看论文截图

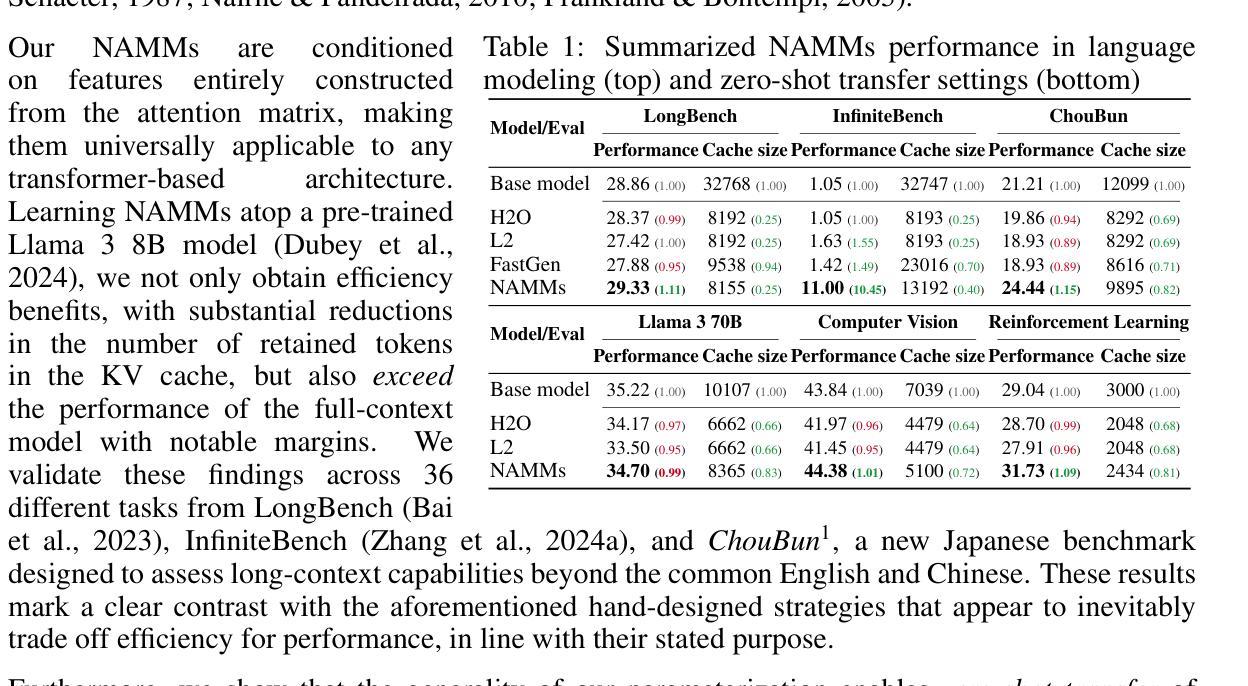
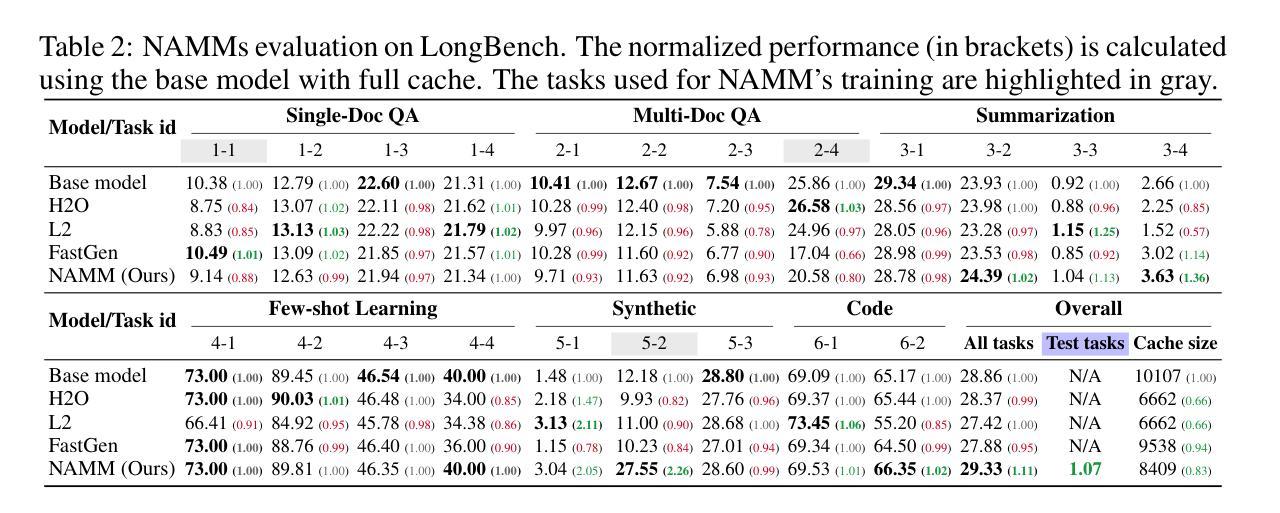
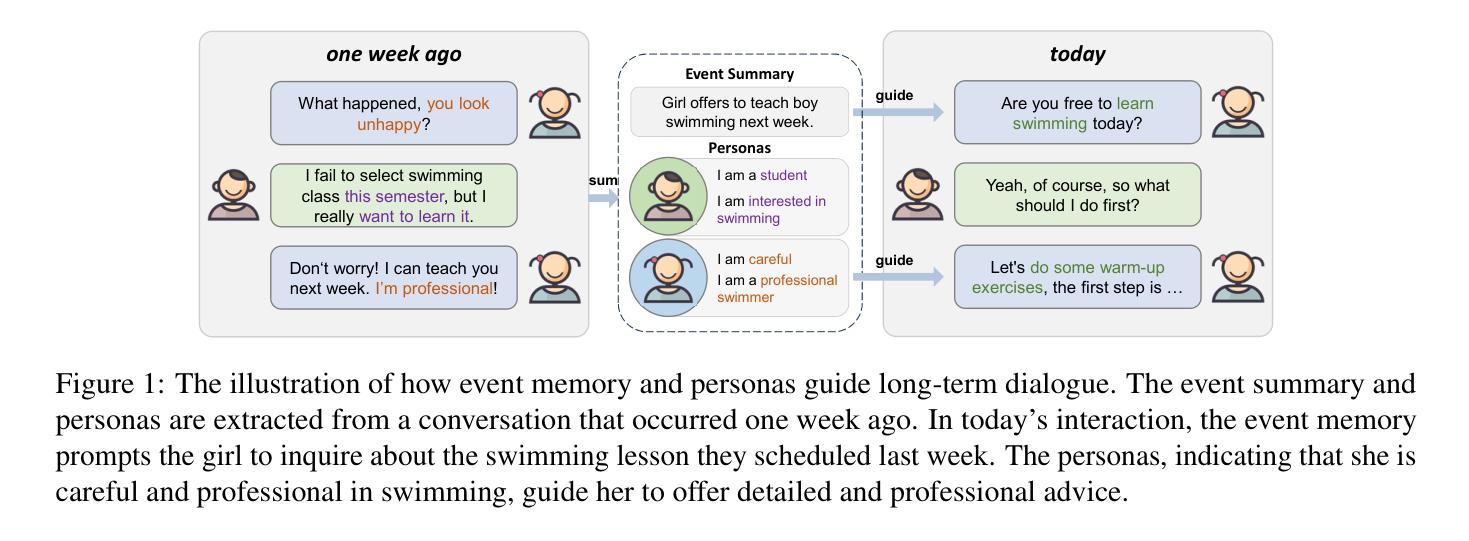
Hello Again! LLM-powered Personalized Agent for Long-term Dialogue
Authors:Hao Li, Chenghao Yang, An Zhang, Yang Deng, Xiang Wang, Tat-Seng Chua
Open-domain dialogue systems have seen remarkable advancements with the development of large language models (LLMs). Nonetheless, most existing dialogue systems predominantly focus on brief single-session interactions, neglecting the real-world demands for long-term companionship and personalized interactions with chatbots. Crucial to addressing this real-world need are event summary and persona management, which enable reasoning for appropriate long-term dialogue responses. Recent progress in the human-like cognitive and reasoning capabilities of LLMs suggests that LLM-based agents could significantly enhance automated perception, decision-making, and problem-solving. In response to this potential, we introduce a model-agnostic framework, the Long-term Dialogue Agent (LD-Agent), which incorporates three independently tunable modules dedicated to event perception, persona extraction, and response generation. For the event memory module, long and short-term memory banks are employed to separately focus on historical and ongoing sessions, while a topic-based retrieval mechanism is introduced to enhance the accuracy of memory retrieval. Furthermore, the persona module conducts dynamic persona modeling for both users and agents. The integration of retrieved memories and extracted personas is subsequently fed into the generator to induce appropriate responses. The effectiveness, generality, and cross-domain capabilities of LD-Agent are empirically demonstrated across various illustrative benchmarks, models, and tasks. The code is released at https://github.com/leolee99/LD-Agent.
随着大型语言模型(LLM)的发展,开放域对话系统已经取得了显著的进步。然而,大多数现有的对话系统主要关注短暂的单一会话互动,忽视了现实世界对长期伴侣关系和与聊天机器人的个性化互动的需求。要解决这一现实需求的关键是事件总结和人格管理,它们为适当的长期对话回应提供了推理能力。最近,LLM的人类认知和推理能力的进步表明,基于LLM的代理可以显着增强自动化感知、决策和问题解决。基于此潜力,我们引入了一个模型无关框架,即长期对话代理(LD-Agent),它包括三个独立可调模块,专门用于事件感知、人格提取和响应生成。对于事件内存模块,长短时记忆库被用来分别关注历史会话和正在进行中的会话,同时引入基于主题的检索机制来提高内存检索的准确性。此外,人格模块为用户和代理进行动态人格建模。检索到的记忆和提取的人格的整合随后被输入到生成器中,以产生适当的响应。LD-Agent的有效性、通用性和跨域能力在各种基准测试、模型和任务中得到了实证证明。代码已发布在https://github.com/leolee99/LD-Agent。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to NAACL 2025
Summary:
随着大型语言模型(LLM)的发展,开放域对话系统取得了显著的进步。然而,大多数现有对话系统主要关注短暂的单一会话互动,忽视了现实世界对长期伴侣关系和与聊天机器人的个性化互动的需求。为解决这一需求,引入了一个模型无关框架——长期对话代理(LD-Agent),包含三个独立可调模块:事件感知、人格提取和响应生成。该框架采用长短时记忆库分别关注历史和当前会话,并引入主题基于的检索机制来提高记忆检索的准确性。此外,人格模块为用户和代理进行动态人格建模。检索到的记忆和提取的人格集成后,会生成适当的响应。LD-Agent的有效性、通用性和跨域能力在各种基准测试、模型和任务中得到了实证证明。
Key Takeaways:
- 开放域对话系统借助大型语言模型(LLM)取得显著进步。
- 现有对话系统主要关注短暂单一会话互动,缺乏长期伴侣和个性化互动的能力。
- 为满足现实需求,引入长期对话代理(LD-Agent)框架。
- LD-Agent包含三个独立可调模块:事件感知、人格提取和响应生成。
- 框架采用长短时记忆库以关注历史和当前会话,提高记忆检索准确性。
- 动态人格建模为用户和代理提供个性化互动。
点此查看论文截图

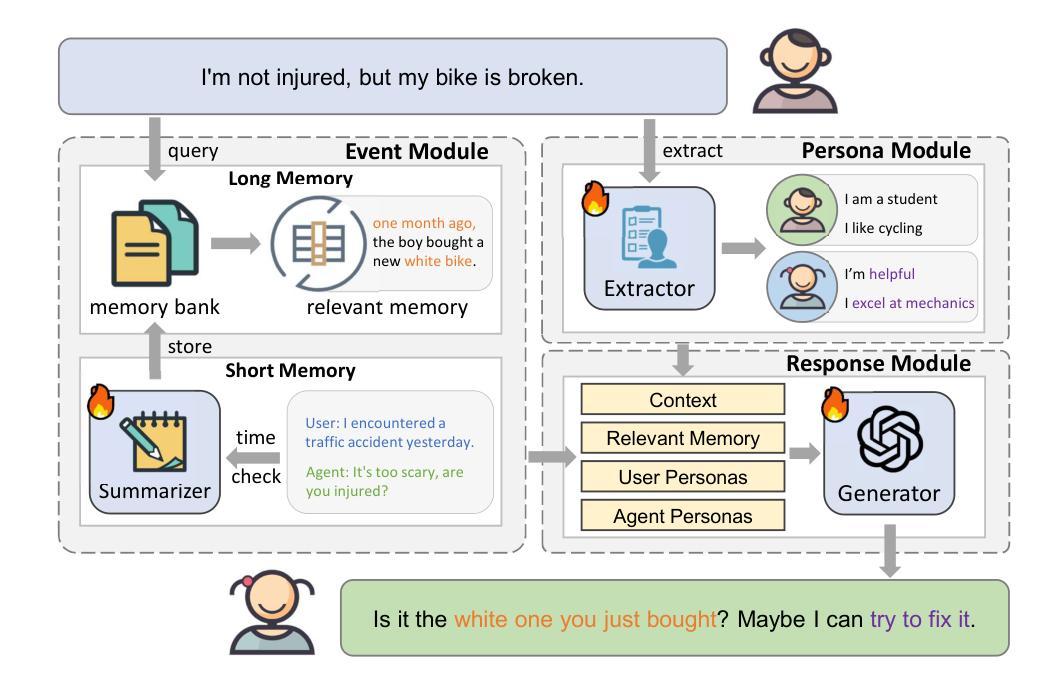
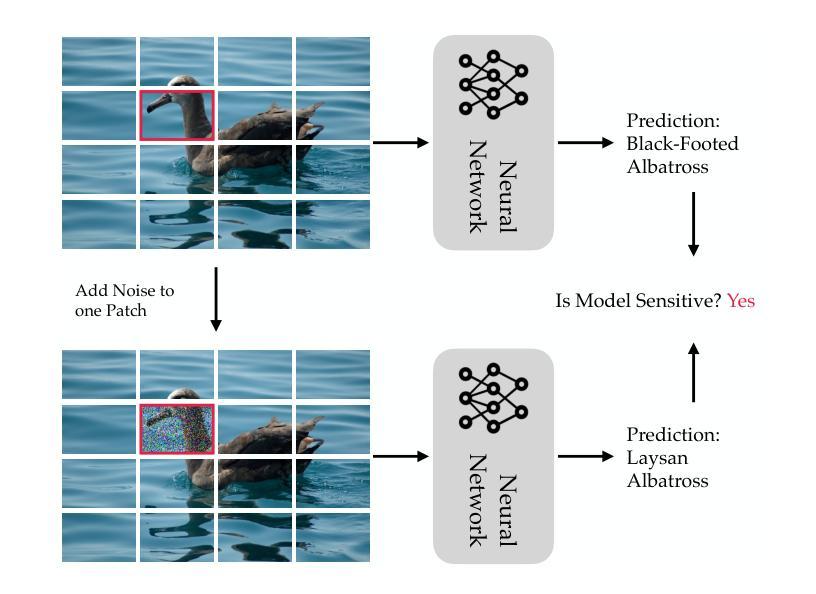
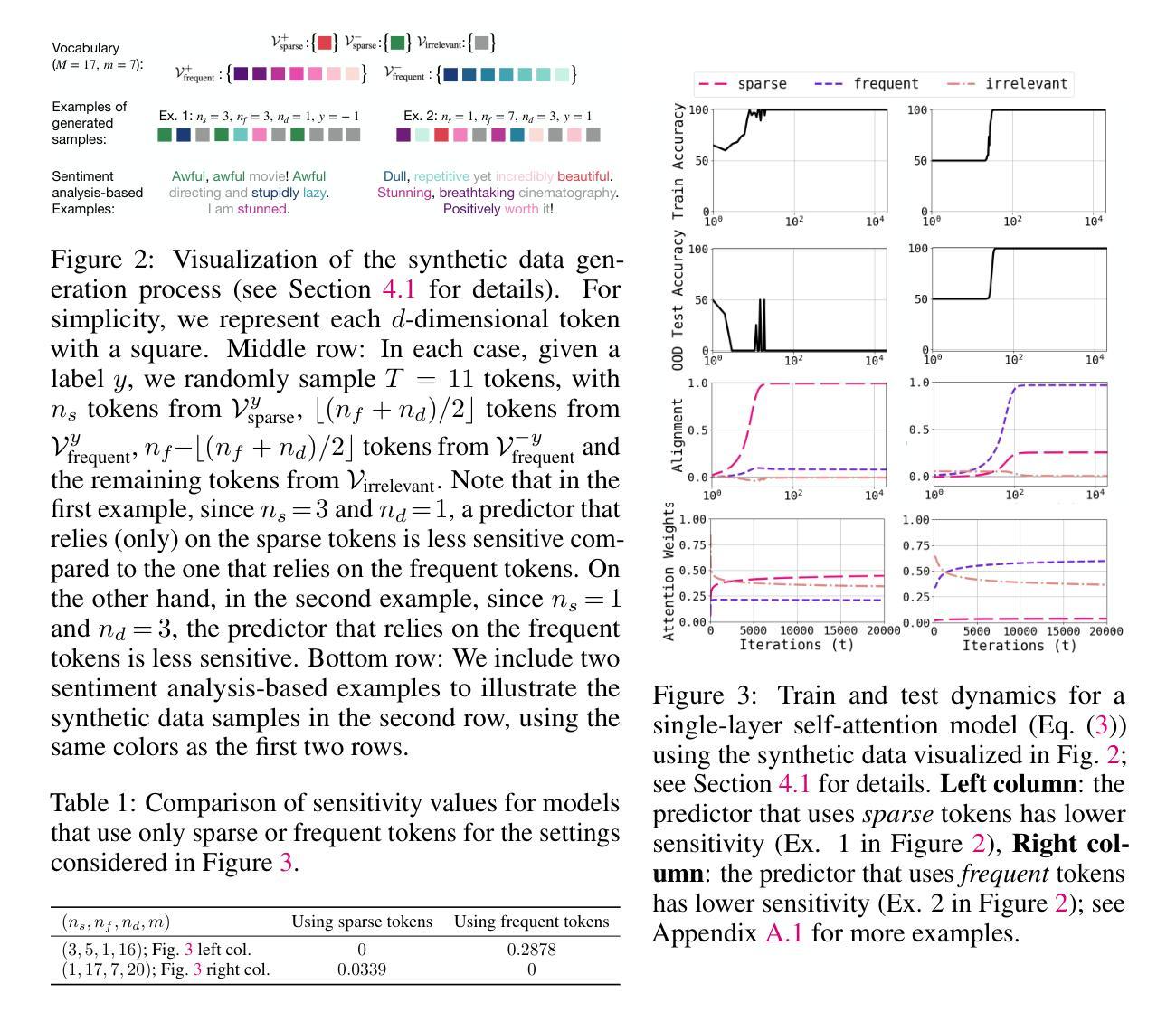
Transformers Learn Low Sensitivity Functions: Investigations and Implications
Authors:Bhavya Vasudeva, Deqing Fu, Tianyi Zhou, Elliott Kau, Youqi Huang, Vatsal Sharan
Transformers achieve state-of-the-art accuracy and robustness across many tasks, but an understanding of their inductive biases and how those biases differ from other neural network architectures remains elusive. In this work, we identify the sensitivity of the model to token-wise random perturbations in the input as a unified metric which explains the inductive bias of transformers across different data modalities and distinguishes them from other architectures. We show that transformers have lower sensitivity than MLPs, CNNs, ConvMixers and LSTMs, across both vision and language tasks. We also show that this low-sensitivity bias has important implications: i) lower sensitivity correlates with improved robustness; it can also be used as an efficient intervention to further improve the robustness of transformers; ii) it corresponds to flatter minima in the loss landscape; and iii) it can serve as a progress measure for grokking. We support these findings with theoretical results showing (weak) spectral bias of transformers in the NTK regime, and improved robustness due to the lower sensitivity. The code is available at https://github.com/estija/sensitivity.
Transformer模型在许多任务上实现了最先进的准确性和鲁棒性,但对其归纳偏置以及如何与其他神经网络架构的偏置相区别的理解仍然不明确。在这项工作中,我们将模型对输入中令牌级随机扰动的敏感性作为统一度量标准,以解释不同数据模式下Transformer的归纳偏置,并将其与其他架构区分开。我们表明,与多层感知器(MLPs)、卷积神经网络(CNNs)、ConvMixers和长短时记忆网络(LSTM)相比,Transformer在视觉和语言任务上的敏感性较低。我们还表明,这种低敏感性偏置具有重要影响:i)低敏感性与提高的鲁棒性相关;它还可以作为进一步提高Transformer鲁棒性的有效干预措施;ii)它与损失景观中的平坦最小值相对应;iii)它可以作为学习进步的一种度量。我们以理论结果支持这些发现,展示了在NTK范围内Transformer的(弱)谱偏置,以及由于低敏感性而提高了鲁棒性。代码位于 https://github.com/estija/sensitivity。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICLR 2025. 24 pages, 19 figures, 3 tables
Summary
本文探讨了Transformer模型的归纳偏见,通过统一度量输入中的token级随机扰动敏感性来解释其在不同数据模态下的归纳偏见,并将其与其他架构区分开来。研究发现,Transformer模型的敏感性低于MLPs、CNNs、ConvMixers和LSTM模型,在视觉和语言任务中均表现出较低的敏感性偏见。此外,低敏感性偏见对于提高模型的鲁棒性和在损失景观中的平坦最小点寻找有重要作用,同时可以作为改进Transformer鲁棒性的有效干预手段。本文还提供了理论支持,展示了Transformer在NTK状态下的弱谱偏向以及因低敏感性而提高的鲁棒性。代码已公开在GitHub上。
Key Takeaways
- Transformer模型具有统一的归纳偏见度量标准,即输入中的token级随机扰动敏感性。
- Transformer模型在视觉和语言任务中表现出较低的敏感性偏见,与其他网络架构相比具有优势。
- 低敏感性偏见与提高模型的鲁棒性相关,可作为进一步提高Transformer鲁棒性的干预手段。
- 低敏感性偏见与损失景观中的平坦最小点有关,有助于在优化过程中找到更好的解决方案。
- Transformer的弱谱偏向及其在NTK状态下的表现是理论支持的一部分,有助于解释其归纳偏见和鲁棒性的提高。
- 代码已公开在GitHub上,可供进一步研究和实验使用。
点此查看论文截图

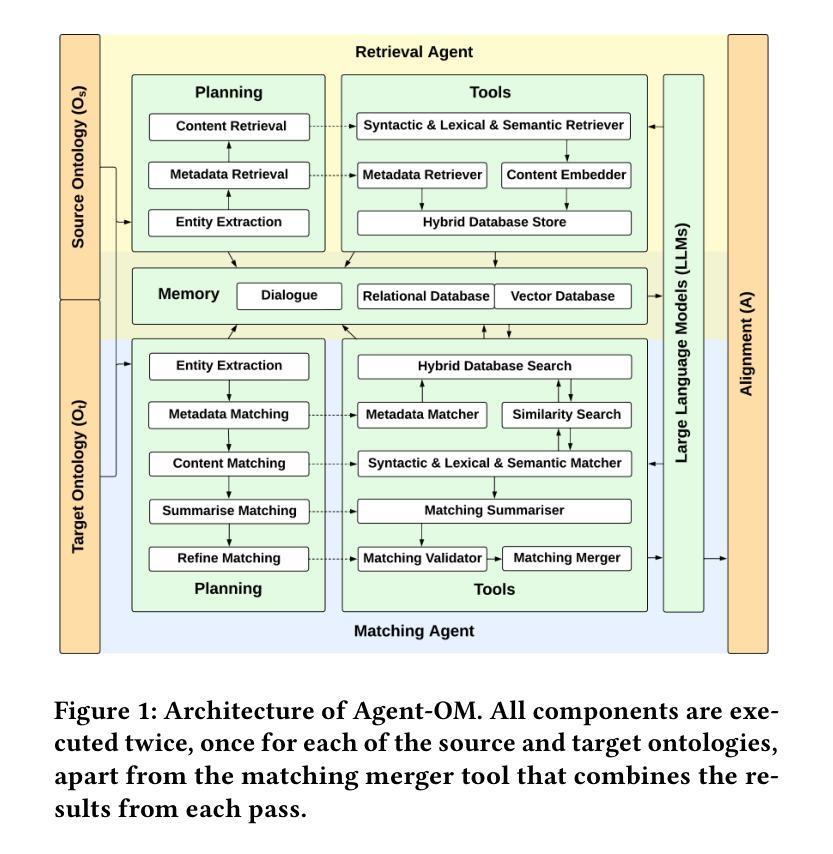
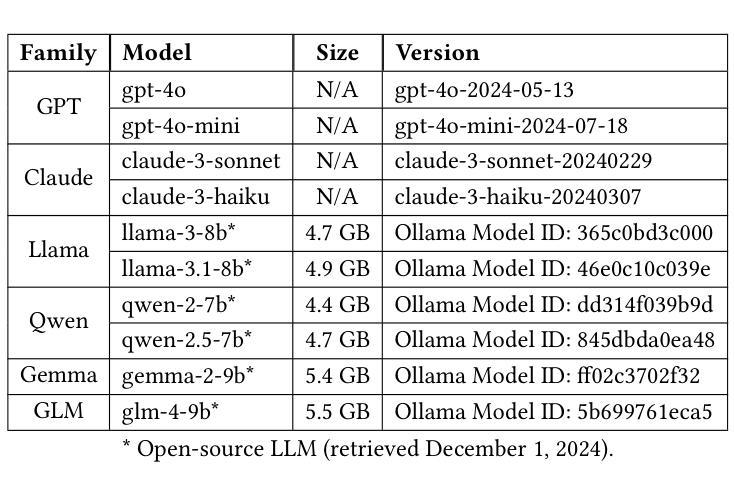
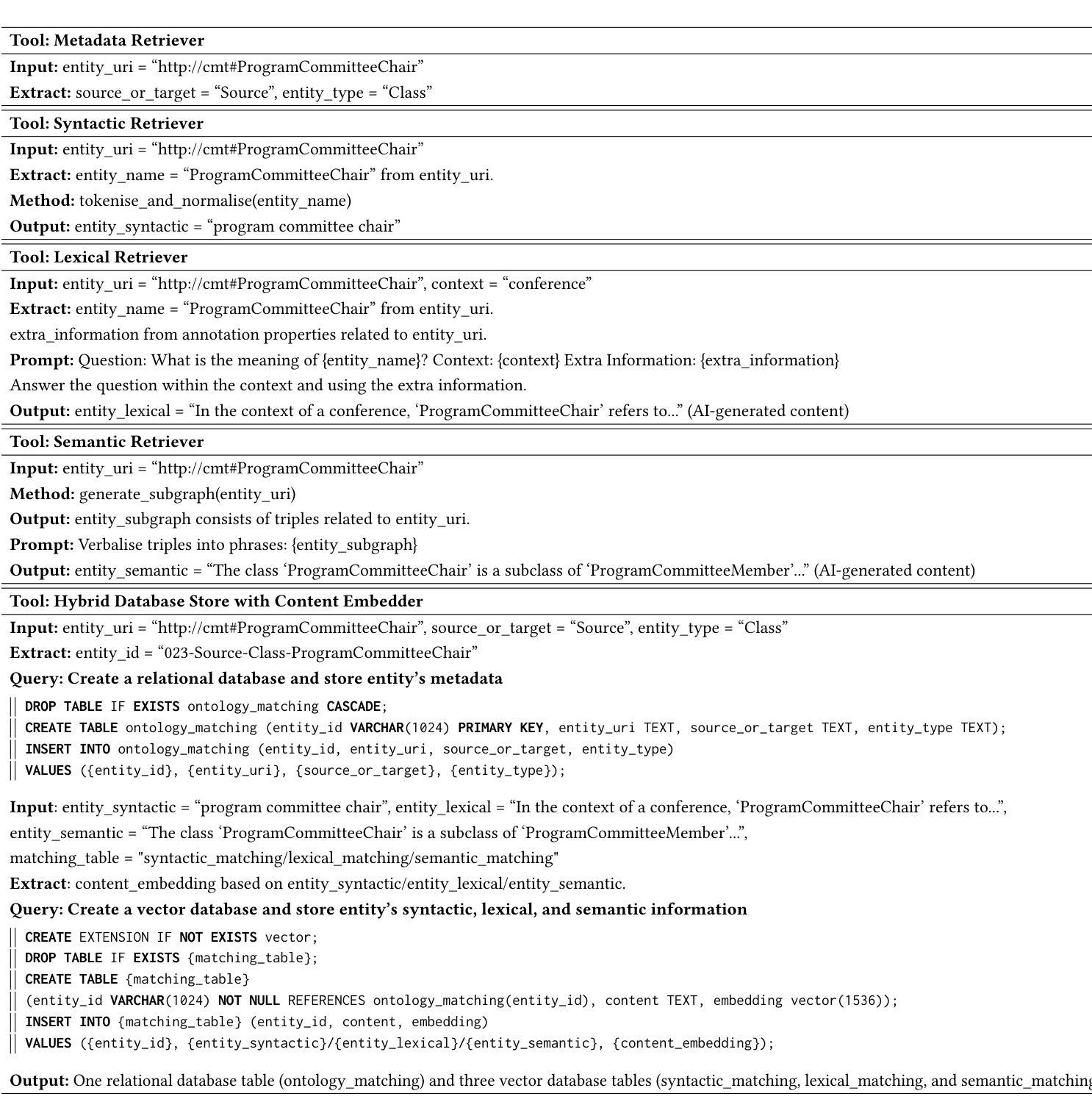
Agent-OM: Leveraging LLM Agents for Ontology Matching
Authors:Zhangcheng Qiang, Weiqing Wang, Kerry Taylor
Ontology matching (OM) enables semantic interoperability between different ontologies and resolves their conceptual heterogeneity by aligning related entities. OM systems currently have two prevailing design paradigms: conventional knowledge-based expert systems and newer machine learning-based predictive systems. While large language models (LLMs) and LLM agents have revolutionised data engineering and have been applied creatively in many domains, their potential for OM remains underexplored. This study introduces a novel agent-powered LLM-based design paradigm for OM systems. With consideration of several specific challenges in leveraging LLM agents for OM, we propose a generic framework, namely Agent-OM (Agent for Ontology Matching), consisting of two Siamese agents for retrieval and matching, with a set of OM tools. Our framework is implemented in a proof-of-concept system. Evaluations of three Ontology Alignment Evaluation Initiative (OAEI) tracks over state-of-the-art OM systems show that our system can achieve results very close to the long-standing best performance on simple OM tasks and can significantly improve the performance on complex and few-shot OM tasks.
本体匹配(OM)能够通过对齐相关实体,实现在不同本体之间的语义互操作,并解决其概念上的异质性。目前,OM系统主要有两种流行的设计范式:传统的基于知识的专家系统和较新的基于机器学习的预测系统。虽然大型语言模型(LLM)和LLM代理已经彻底改变了数据工程,并且在许多领域得到了创造性的应用,但它们在OM领域的潜力仍未得到充分探索。本研究介绍了一种新型基于LLM的代理驱动设计范式的OM系统。考虑到在利用LLM代理进行OM时面临的若干特定挑战,我们提出了一个通用框架,即Agent-OM(用于本体匹配的代理),该框架包括两个用于检索和匹配的Siamese代理和一组OM工具。我们的框架在一个概念验证系统中实现。对三个本体对齐评估倡议(OAEI)赛道与最新OM系统的评估表明,我们的系统在简单OM任务上的结果非常接近长期以来的最佳性能,并且在复杂和少样本OM任务上可以显著提高性能。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 19 pages, 12 figures, 3 tables
Summary
基于本研究的介绍,利用大型语言模型(LLM)和LLM代理人在本体匹配(OM)系统中的应用研究仍处于初级阶段。本研究提出了一种新的基于LLM代理的本体匹配设计范式,旨在解决当前OM系统面临的挑战。所提出的Agent-OM框架由两个用于检索和匹配的Siamese代理组成,结合一套OM工具。经过初步的系统验证,其性能已接近现有的先进OM系统在简单任务上的最佳表现,并在复杂和少数样本的OM任务上显著提高性能。
Key Takeaways
- 本研究提出了一种基于大型语言模型(LLM)的新型本体匹配(OM)系统设计范式。
- 该设计范式利用LLM代理来解决不同本体之间的语义互操作性和概念异质性问题。
- 提出了一种通用框架Agent-OM,包含两个用于检索和匹配的Siamese代理以及一套OM工具。
- 系统在简单的本体匹配任务上的性能接近当前最佳水平。
- 在复杂的和少量样本的本体匹配任务上,系统显著提高了性能。
- 此框架具有一定的创新性和潜力,但也需要进一步的研究和改进以优化其在实际应用中的表现。
点此查看论文截图