⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-02-15 更新
Advances in Microphone Array Processing and Multichannel Speech Enhancement
Authors:Gongping Huang, Jesper R. Jensen, Jingdong Chen, Jacob Benesty, Mads G. Christensen, Akihiko Sugiyama, Gary Elko, Tomas Gaensler
This paper reviews pioneering works in microphone array processing and multichannel speech enhancement, highlighting historical achievements, technological evolution, commercialization aspects, and key challenges. It provides valuable insights into the progression and future direction of these areas. The paper examines foundational developments in microphone array design and optimization, showcasing innovations that improved sound acquisition and enhanced speech intelligibility in noisy and reverberant environments. It then introduces recent advancements and cutting-edge research in the field, particularly the integration of deep learning techniques such as all-neural beamformers. The paper also explores critical applications, discussing their evolution and current state-of-the-art technologies that significantly impact user experience. Finally, the paper outlines future research directions, identifying challenges and potential solutions that could drive further innovation in these fields. By providing a comprehensive overview and forward-looking perspective, this paper aims to inspire ongoing research and contribute to the sustained growth and development of microphone arrays and multichannel speech enhancement.
本文综述了麦克风阵列处理和多通道语音增强的开创性工作,重点介绍了历史成就、技术演变、商业化方面和关键挑战。本文为这些领域的进展和未来发展方向提供了宝贵的见解。文章研究了麦克风阵列设计和优化的基础发展,展示了在嘈杂和混响环境中提高声音采集和增强语音清晰度的创新。然后介绍了该领域的最新进展和尖端研究,特别是全神经网络波束成形器等深度学习技术的集成。本文还探讨了关键应用,讨论了它们的演变和当前最新技术,这些技术对用户体验产生了重大影响。最后,本文概述了未来的研究方向,确定了可能推动这些领域进一步创新的挑战和潜在解决方案。本文旨在提供全面的概述和前瞻性的观点,以激发持续的研究,为麦克风阵列和多通道语音增强的持续增长和发展做出贡献。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF accepted by ICASSP 2025
Summary
本论文全面回顾了麦克风阵列处理和多通道语音增强的开创性工作,介绍了历史成就、技术演变、商业化方面和关键挑战,为这些领域的发展及未来方向提供了宝贵见解。论文详细探讨了麦克风阵列设计和优化的基础发展,展示了提高声音采集质量和增强噪声和混响环境中语音清晰度的创新。此外,论文还介绍了最新的进展和尖端研究,特别是全神经网络波束形成器等深度学习技术的集成。论文也探讨了关键应用及其当前最新技术,这些技术对用户体验产生了重大影响。最后,论文概述了未来的研究方向,确定了推动这些领域进一步创新的挑战和潜在解决方案。
Key Takeaways
- 论文回顾了麦克风阵列处理和多通道语音增强的历史成就和技术演变。
- 论文探讨了麦克风阵列设计和优化的基础发展。
- 论文展示了提高声音采集质量和增强噪声环境中语音清晰度的创新。
- 论文介绍了最新的进展和尖端研究,包括全神经网络波束形成器的集成。
- 论文讨论了关键应用及其当前最新技术对用户体验的影响。
- 论文概述了未来的研究方向,包括挑战和潜在解决方案。
点此查看论文截图

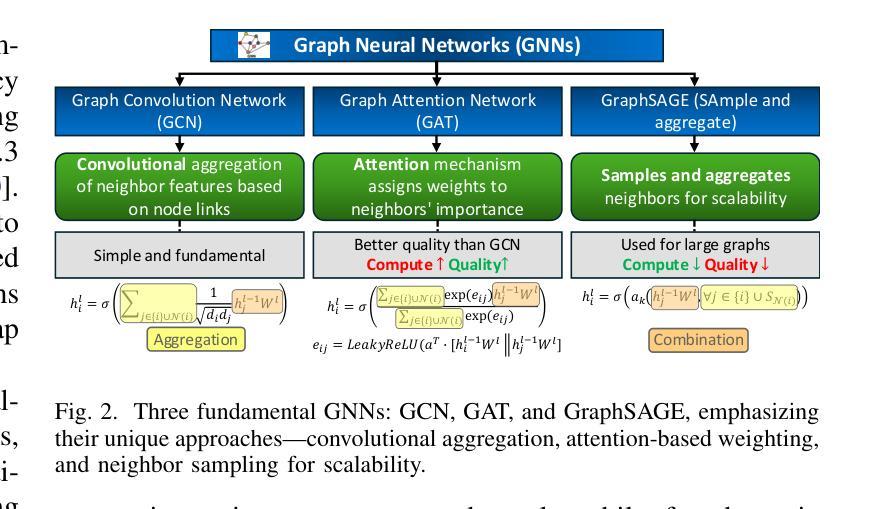
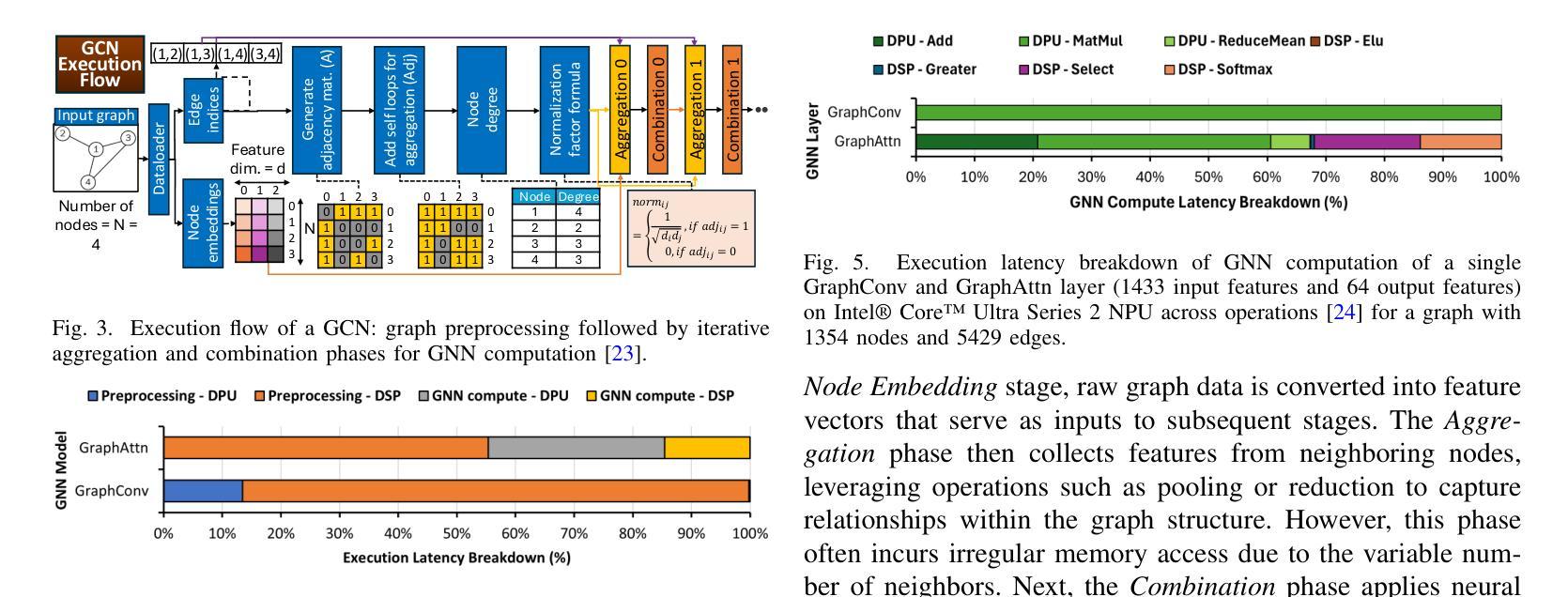
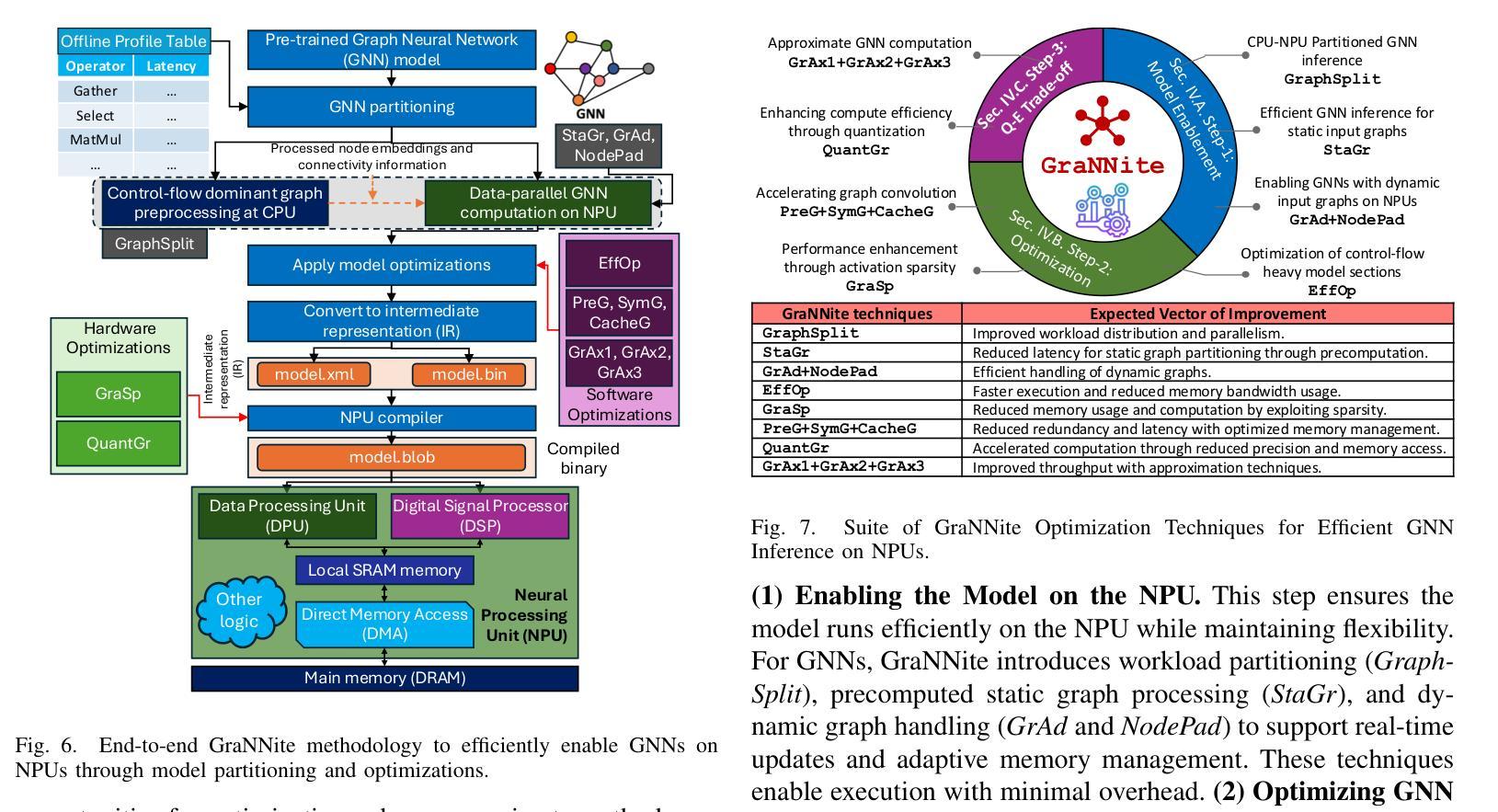
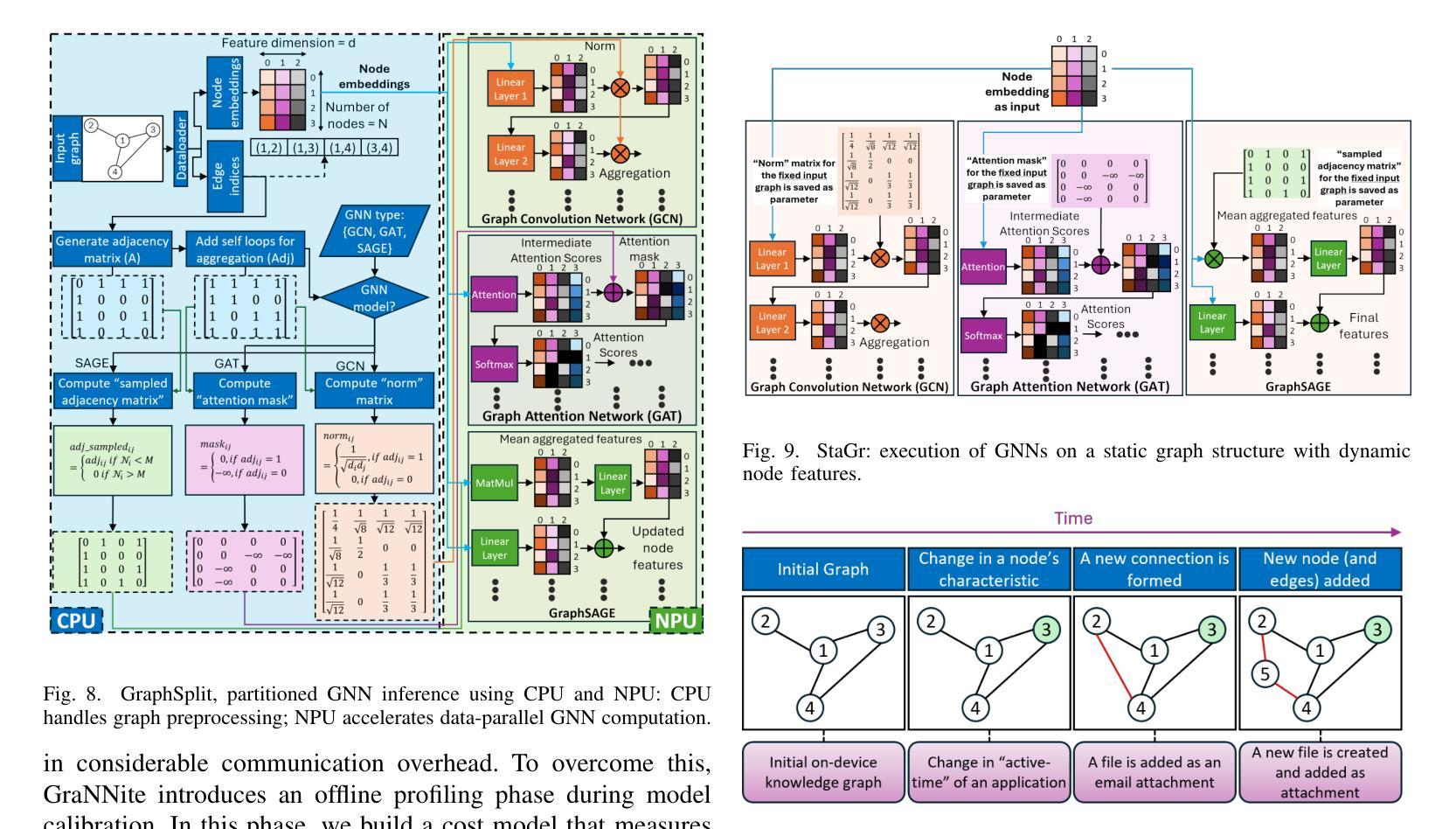
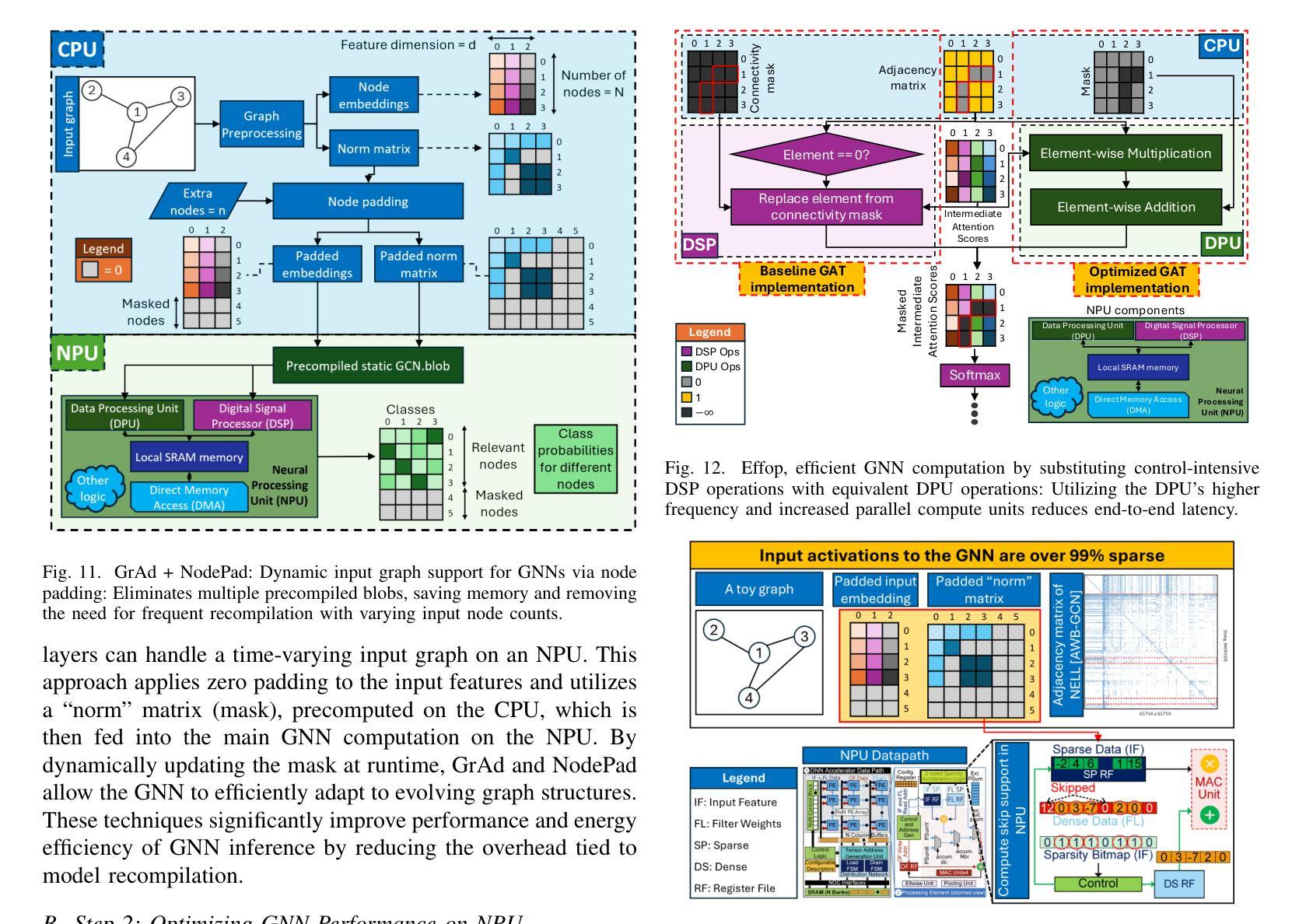
GraNNite: Enabling High-Performance Execution of Graph Neural Networks on Resource-Constrained Neural Processing Units
Authors:Arghadip Das, Shamik Kundu, Arnab Raha, Soumendu Ghosh, Deepak Mathaikutty, Vijay Raghunathan
Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) are vital for learning from graph-structured data, enabling applications in network analysis, recommendation systems, and speech analytics. Deploying them on edge devices like client PCs and laptops enhances real-time processing, privacy, and cloud independence. GNNs aid Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) for Large Language Models (LLMs) and enable event-based vision tasks. However, irregular memory access, sparsity, and dynamic structures cause high latency and energy overhead on resource-constrained devices. While modern edge processors integrate CPUs, GPUs, and NPUs, NPUs designed for data-parallel tasks struggle with irregular GNN computations. We introduce GraNNite, the first hardware-aware framework optimizing GNN execution on commercial-off-the-shelf (COTS) SOTA DNN accelerators via a structured three-step methodology: (1) enabling NPU execution, (2) optimizing performance, and (3) trading accuracy for efficiency gains. Step 1 employs GraphSplit for workload distribution and StaGr for static aggregation, while GrAd and NodePad handle dynamic graphs. Step 2 boosts performance using EffOp for control-heavy tasks and GraSp for sparsity exploitation. Graph Convolution optimizations PreG, SymG, and CacheG reduce redundancy and memory transfers. Step 3 balances quality versus efficiency, where QuantGr applies INT8 quantization, and GrAx1, GrAx2, and GrAx3 accelerate attention, broadcast-add, and SAGE-max aggregation. On Intel Core Ultra AI PCs, GraNNite achieves 2.6X to 7.6X speedups over default NPU mappings and up to 8.6X energy gains over CPUs and GPUs, delivering 10.8X and 6.7X higher performance than CPUs and GPUs, respectively, across GNN models.
图神经网络(GNNs)对于从图形结构数据中学习至关重要,可应用于网络分析、推荐系统和语音分析等应用。在客户端PC和笔记本电脑等边缘设备上部署它们,可提高实时处理、隐私和云独立性。GNNs有助于大型语言模型的检索增强生成(RAG),并可用于基于事件的视觉任务。然而,不规则内存访问、稀疏性和动态结构会在资源受限的设备上导致高延迟和能源开销。虽然现代边缘处理器集成了CPU、GPU和NPU,但为数据并行任务设计的NPU在处理不规则GNN计算时感到困难。我们引入了GraNNite,这是第一个硬件感知框架,通过结构化三步方法优化在商用现货(COTS)SOTA深度神经网络(DNN)加速器上执行GNN:(1)实现NPU执行,(2)优化性能,(3)以效率增益换取准确性。第1步采用GraphSplit进行工作量分配和StaGr进行静态聚合,而GrAd和NodePad处理动态图。第2步使用EffOp进行控制密集型任务的性能提升和GraSp进行稀疏性利用。图卷积优化PreG、SymG和CacheG减少冗余和内存传输。第3步平衡质量与效率,其中QuantGr应用INT8量化,GrAx1、GrAx2和GrAx3加速注意力、广播加法和SAGE-max聚合。在Intel Core Ultra AI PC上,GraNNite相对于默认的NPU映射实现了2.6倍至7.6倍的加速,并在CPU和GPU上实现了高达8.6倍的能源效益。相较于CPU和GPU,GraNNite在GNN模型上的性能分别提高了10.8倍和6.7倍。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
图神经网络(GNNs)对于从图形结构数据中学习至关重要,可应用于网络分析、推荐系统和语音分析等。在边缘设备上部署它们可提高实时处理、隐私和云独立性。然而,由于不规则的内存访问、稀疏性和动态结构,它们在资源受限的设备上会造成高延迟和能源开销。GraNNite是一个硬件感知框架,通过三步法优化在商品现货(COTS)上的图神经网络执行。它在最先进的深度神经网络加速器上实现了2.6至7.6倍的速度提升和高达8.6倍的能源效益。
关键见解
- 图神经网络对于从图形结构数据中学习至关重要,可广泛应用于网络分析、推荐系统和语音分析等领域。
- 在边缘设备上部署图神经网络可提高实时处理、隐私保护和云独立性。
- 图神经网络在资源受限的设备上运行面临高延迟和能源开销的挑战。
- GraNNite是首个硬件感知框架,优化了图神经网络在商品现货(COTS)上的执行。
- GraNNite通过三步法实现性能优化,包括启用NPU执行、性能优化以及权衡精度与效率。
- GraNNite在Intel Core Ultra AI PC上实现了显著的性能提升,相对于默认NPU映射实现2.6至7.6倍的速度提升和高达8.6倍的能源效益。
点此查看论文截图
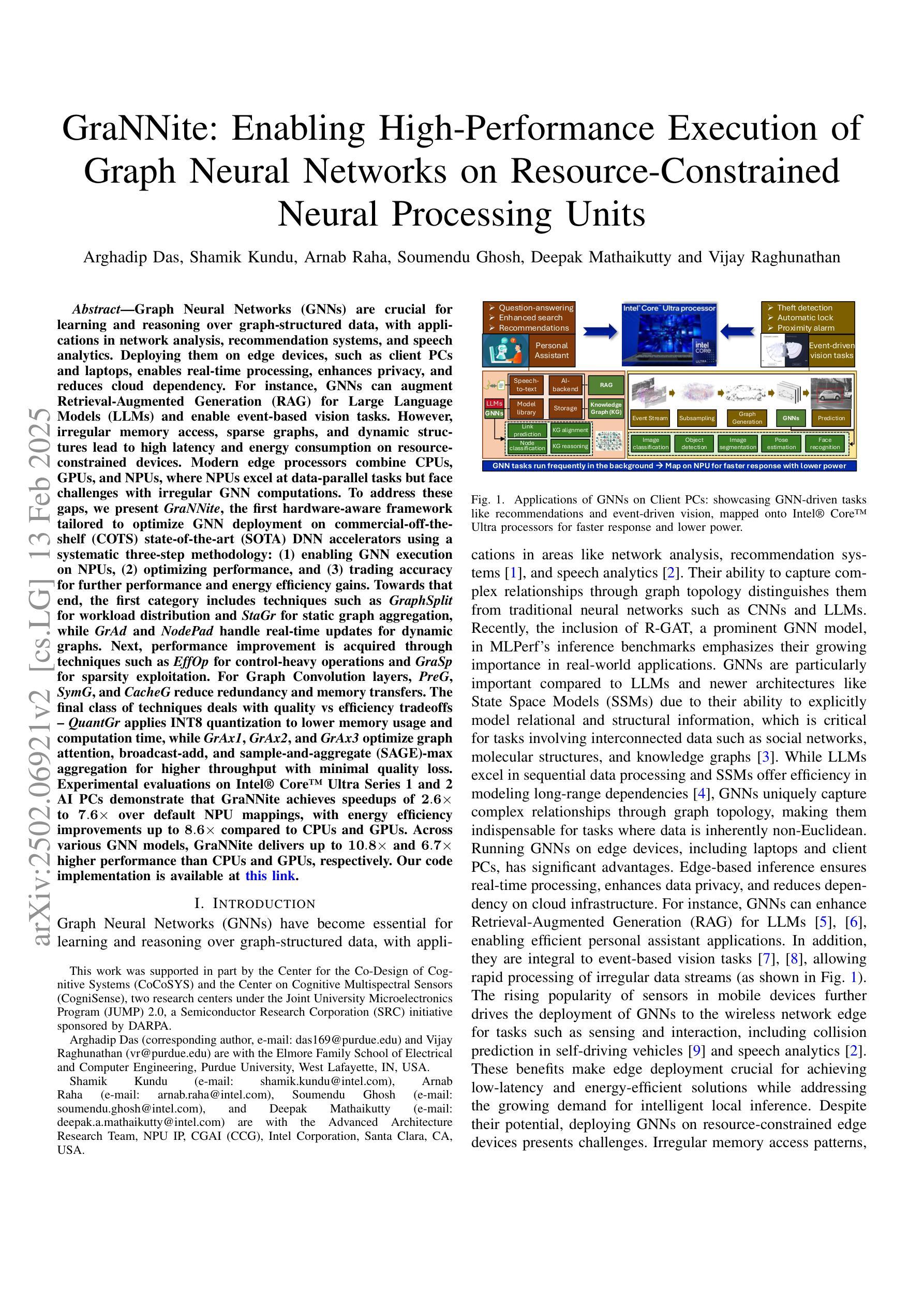
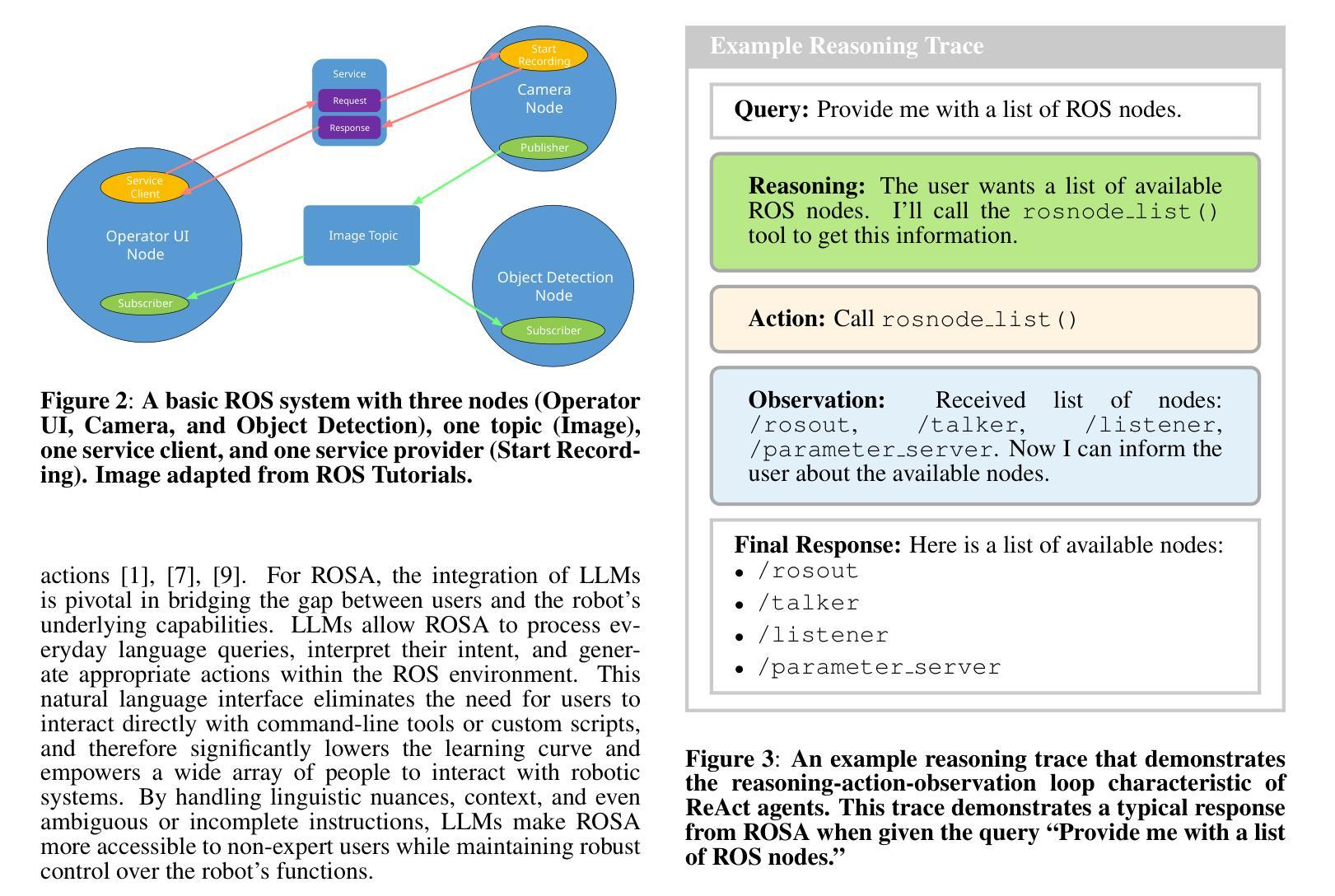
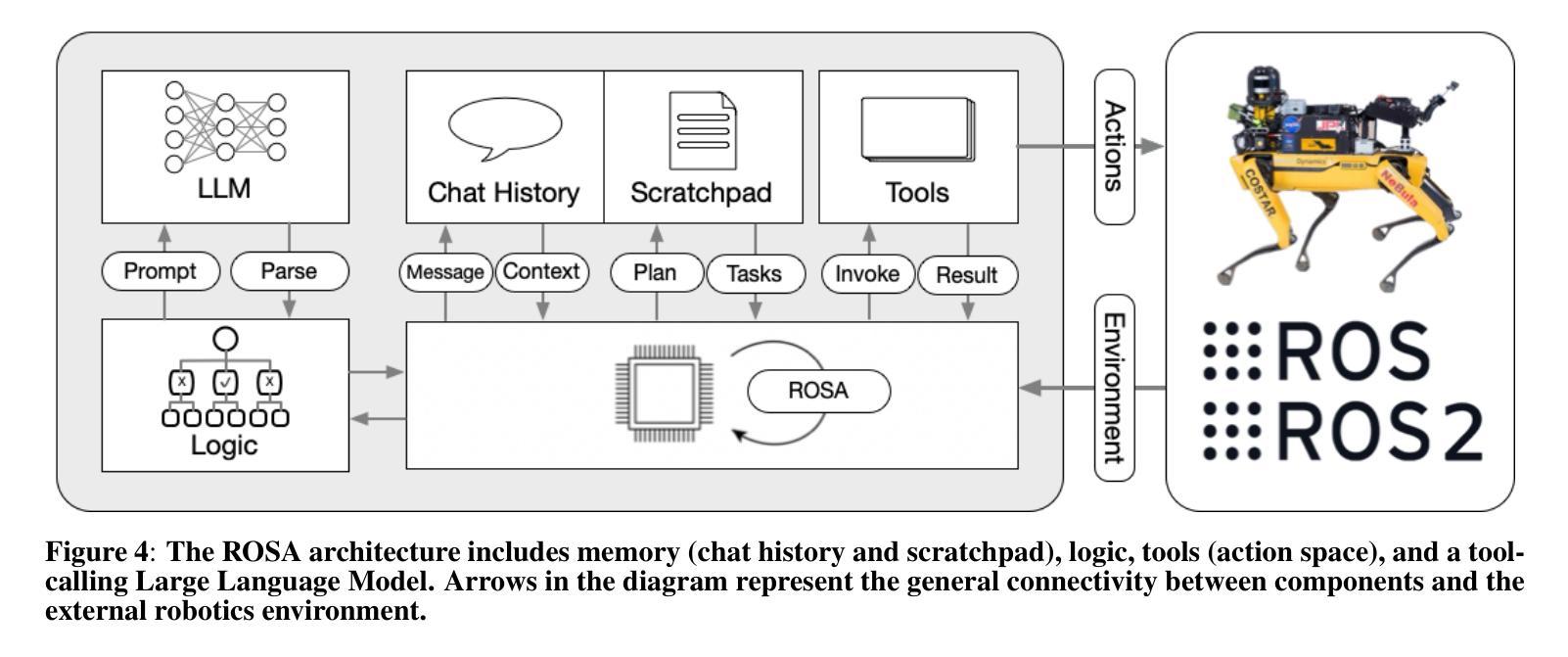
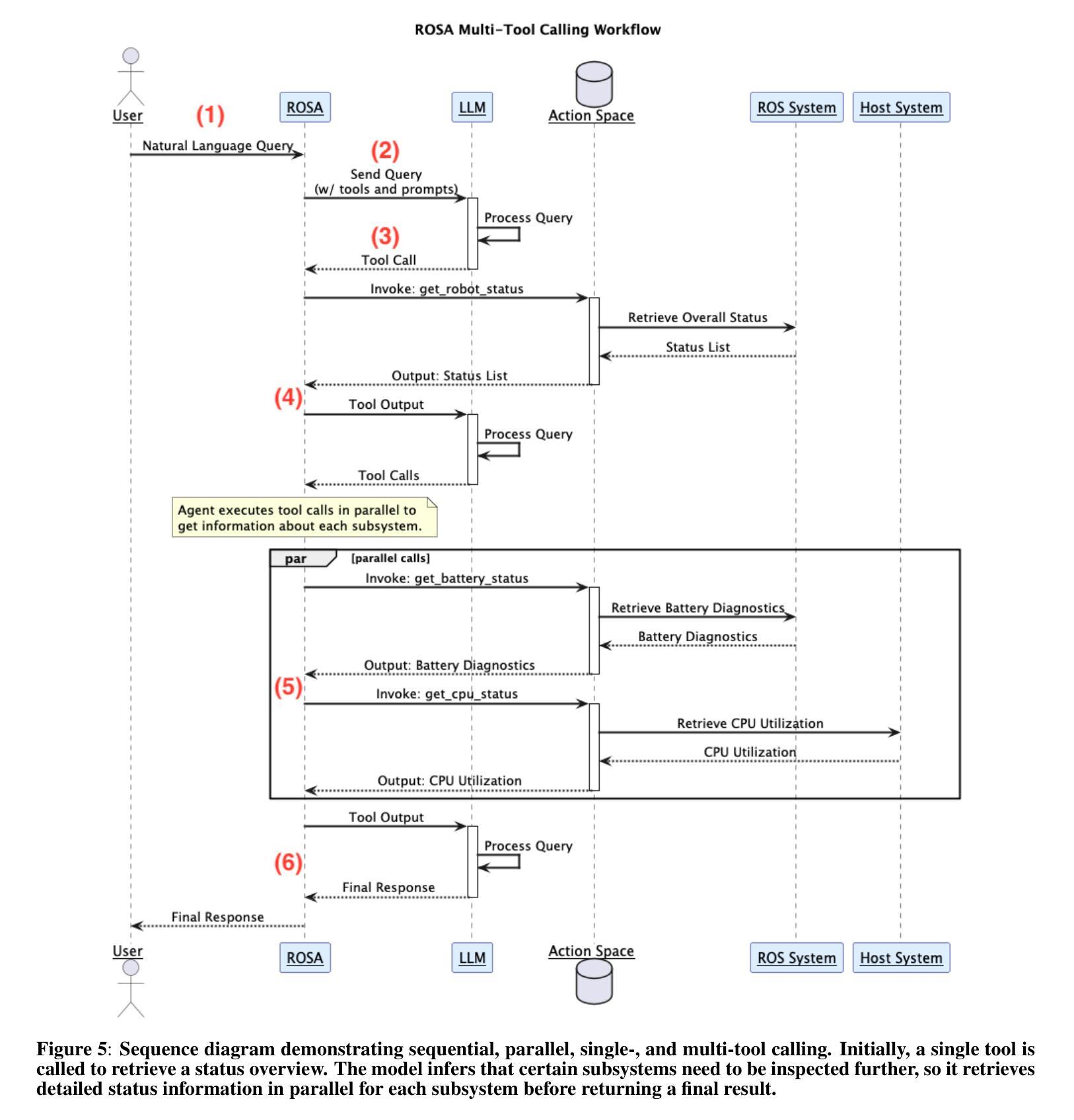
Enabling Novel Mission Operations and Interactions with ROSA: The Robot Operating System Agent
Authors:Rob Royce, Marcel Kaufmann, Jonathan Becktor, Sangwoo Moon, Kalind Carpenter, Kai Pak, Amanda Towler, Rohan Thakker, Shehryar Khattak
The advancement of robotic systems has revolutionized numerous industries, yet their operation often demands specialized technical knowledge, limiting accessibility for non-expert users. This paper introduces ROSA (Robot Operating System Agent), an AI-powered agent that bridges the gap between the Robot Operating System (ROS) and natural language interfaces. By leveraging state-of-the-art language models and integrating open-source frameworks, ROSA enables operators to interact with robots using natural language, translating commands into actions and interfacing with ROS through well-defined tools. ROSA’s design is modular and extensible, offering seamless integration with both ROS1 and ROS2, along with safety mechanisms like parameter validation and constraint enforcement to ensure secure, reliable operations. While ROSA is originally designed for ROS, it can be extended to work with other robotics middle-wares to maximize compatibility across missions. ROSA enhances human-robot interaction by democratizing access to complex robotic systems, empowering users of all expertise levels with multi-modal capabilities such as speech integration and visual perception. Ethical considerations are thoroughly addressed, guided by foundational principles like Asimov’s Three Laws of Robotics, ensuring that AI integration promotes safety, transparency, privacy, and accountability. By making robotic technology more user-friendly and accessible, ROSA not only improves operational efficiency but also sets a new standard for responsible AI use in robotics and potentially future mission operations. This paper introduces ROSA’s architecture and showcases initial mock-up operations in JPL’s Mars Yard, a laboratory, and a simulation using three different robots. The core ROSA library is available as open-source.
机器人系统的进步已经彻底改变了许多行业,然而,它们的操作通常需要专业的技术知识,这对非专业用户构成了可达性限制。本文介绍了 ROSA(机器人操作系统代理),这是一个由人工智能驱动的代理,能够在机器人操作系统(ROS)和自然语言接口之间建立桥梁。它通过利用最先进的语言模型并整合开源框架,使操作者能够通过自然语言与机器人进行交互,将命令翻译成动作,并通过定义良好的工具与ROS进行接口。ROSA的设计具有模块化和可扩展性,可以与ROS1和ROS2无缝集成,并提供参数验证和约束执行等安全机制,以确保安全、可靠的操作。虽然ROSA最初是为ROS设计的,但可以通过扩展到其他机器人中间件来适应各种任务,最大限度地提高跨任务的兼容性。ROSA通过普及复杂机器人系统的访问权限,增强了人机互动,使用户能够利用多模式功能(如语音集成和视觉感知),无论其专业程度如何。本文充分探讨了伦理问题,遵循阿西莫夫机器人三大定律等基本原则,确保人工智能的集成促进安全、透明、隐私和问责制。通过使机器人技术更加用户友好和可访问,ROSA不仅提高了操作效率,还为机器人和潜在未来任务操作中的负责任的人工智能使用设定了新的标准。本文介绍了ROSA的架构,并在JPL的火星场、实验室以及使用三种不同机器人的模拟环境中展示了初步的模拟操作。ROSA核心库作为开源提供。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Preprint. Accepted at IEEE Aerospace Conference 2025, 16 pages, 12 figures
Summary
机器人操作系统代理(ROSA)通过自然语言接口与机器人操作系统(ROS)之间的桥梁,实现了机器人的自然语言交互。它使用最新的语言模型和开源框架,能够安全有效地翻译命令为操作。ROSA的设计具有模块化特点且可扩展,可以与ROS1和ROS2无缝集成,同时提供参数验证和约束执行等安全机制。ROSA不仅提高了人机互动,还通过多模态能力使复杂机器人系统更加用户友好和可访问。此外,它还考虑了伦理问题,遵循如阿西莫夫的机器人三大定律等基本原则,确保AI集成促进安全、透明、隐私和问责制。此论文展示了ROSA架构和实验室火星基地的初步模拟操作成果。它是开源的。
Key Takeaways
- ROSA是一个AI驱动的代理,实现了机器人操作系统与自然语言接口之间的衔接,让用户使用自然语言与机器人交互成为可能。
- ROSA通过利用最先进的语言模型和集成开源框架来实现命令到动作的转换。
- ROSA设计具有模块化特点且可扩展,支持ROS1和ROS2的无缝集成。
- ROSA提供安全机制,如参数验证和约束执行,确保机器人操作的可靠性和安全性。
- ROSA增强了人机互动,通过多模态能力使复杂机器人系统更加用户友好,适用于各种专业水平的用户。
- ROSA考虑了伦理问题,遵循基本原则如阿西莫夫的机器人三大定律,确保AI集成符合安全、透明、隐私和问责制的要求。
点此查看论文截图


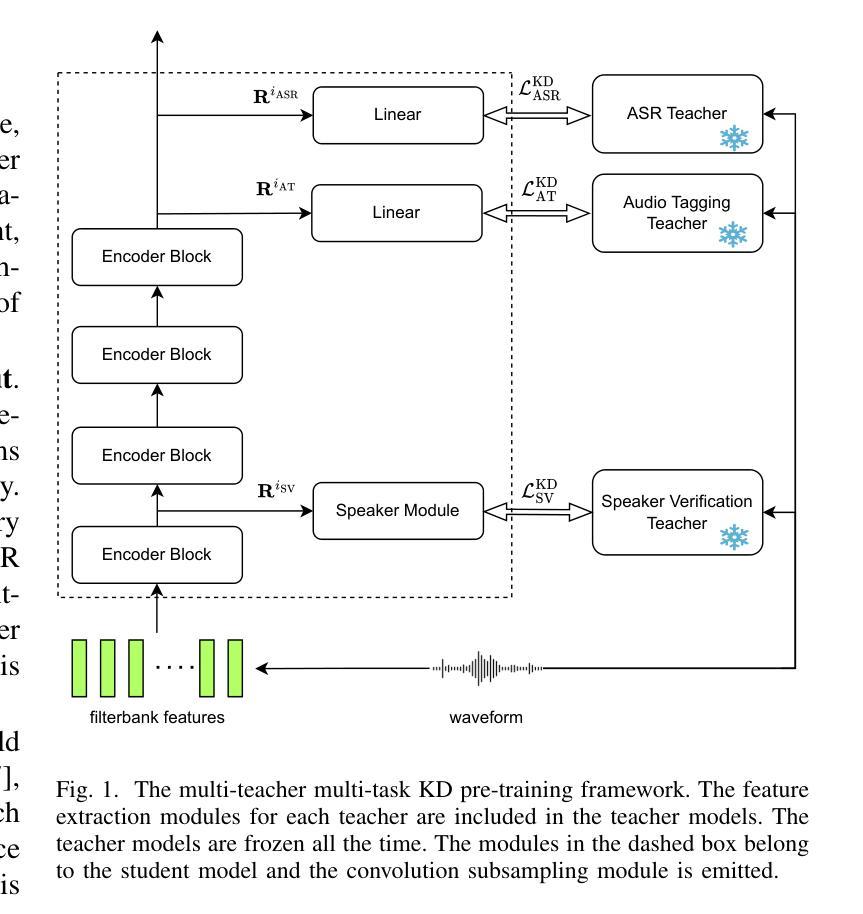
MT2KD: Towards A General-Purpose Encoder for Speech, Speaker, and Audio Events
Authors:Xiaoyu Yang, Qiujia Li, Chao Zhang, Phil Woodland
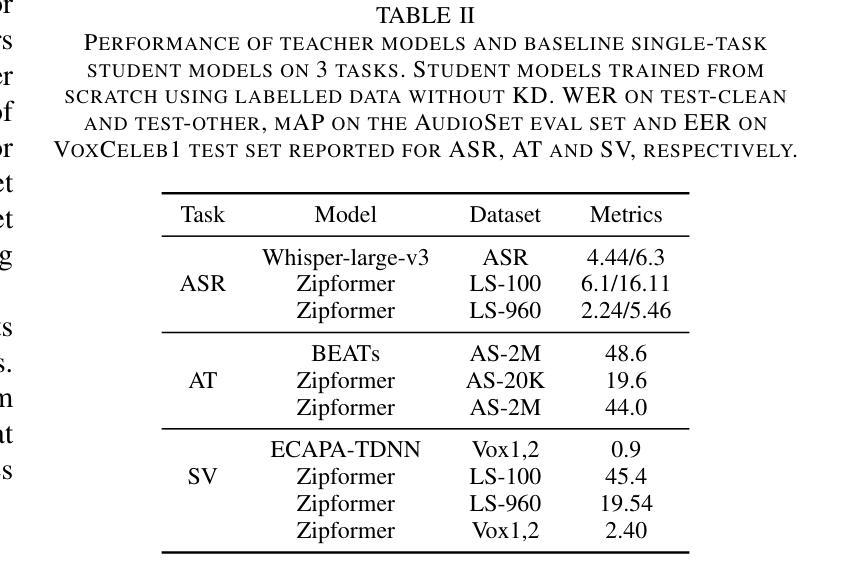
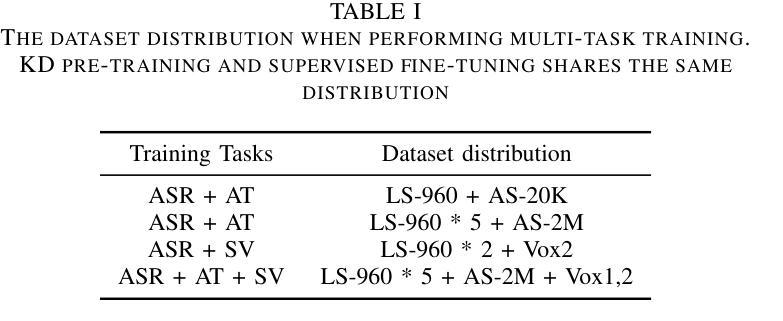
With the advances in deep learning, the performance of end-to-end (E2E) single-task models for speech and audio processing has been constantly improving. However, it is still challenging to build a general-purpose model with high performance on multiple tasks, since different speech and audio processing tasks usually require different training data, input features, or model architectures to achieve optimal performance. In this work, MT2KD, a novel two-stage multi-task learning framework is proposed to build a general-purpose speech and audio encoder that jointly performs three fundamental tasks: automatic speech recognition (ASR), audio tagging (AT) and speaker verification (SV). In the first stage, multi-teacher knowledge distillation (KD) is applied to align the feature spaces of three single-task high-performance teacher encoders into a single student encoder using the same unlabelled data. In the second stage, multi-task supervised fine-tuning is carried out by initialising the model from the first stage and training on the separate labelled data of each single task. Experiments demonstrate that the proposed multi-task training pipeline significantly outperforms a baseline model trained with multi-task learning from scratch. The final system achieves good performance on ASR, AT and SV: with less than 4% relative word-error-rate increase on ASR, only 1.9 lower mean averaged precision on AT and 0.23% absolute higher equal error rate on SV compared to the best-performing single-task encoders, using only a 66M total model parameters.
随着深度学习的发展,端到端(E2E)单任务模型在语音和音频处理方面的性能不断提升。然而,构建能够在多个任务上实现高性能的通用模型仍然是一个挑战,因为不同的语音和音频处理任务通常需要不同的训练数据、输入特征或模型架构来实现最佳性能。在此工作中,提出了MT2KD这一新型两阶段多任务学习框架,用于构建通用语音和音频编码器,该编码器可联合执行三个基本任务:自动语音识别(ASR)、音频标签(AT)和说话人验证(SV)。在第一阶段,应用多教师知识蒸馏(KD)技术,使用相同的无标签数据将三个高性能单任务教师编码器的特征空间对齐到一个单一的学生编码器中。在第二阶段,通过初始化第一阶段的模型,并在每个单独任务的标记数据上进行训练,进行多任务监督微调。实验表明,所提出的多任务训练流程显著优于从头开始进行多任务学习的基线模型。最终系统在ASR、AT和SV上均表现出良好性能:ASR的单词错误率增加不到4%,AT的平均精度仅下降1.9,SV的绝对等错误率提高0.23%,而总模型参数仅使用66M。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Disclaimer: This work has been submitted to the IEEE for possible publication
摘要
随着深度学习的发展,端到端单一任务模型在语音和音频处理方面的性能不断提升。然而,构建能在多个任务上表现优异的通用模型仍然是一个挑战。本文提出MT2KD,一种新型两阶段多任务学习框架,用于构建联合执行三项基本任务的通用语音和音频编码器:自动语音识别(ASR)、音频标签(AT)和说话人验证(SV)。第一阶段采用多教师知识蒸馏(KD)技术,使用相同未标记的数据将三个高性能教师编码器的特征空间对齐到一个单一的学生编码器。第二阶段进行多任务监督微调,从第一阶段模型初始化并在每个单一任务的标记数据上进行训练。实验表明,本文提出的多任务训练流水线显著优于从头开始训练的基于多任务学习的基线模型。最终系统在高分辨率光谱影像的烟囱探测方面取得了良好性能,相对于自动语音识别任务的最优单任务编码器而言,其相对词错误率增加了不到4%,音频标签的均值平均精度下降了仅1.9%,而说话人验证任务有稍微降低的等高误差率。总体来看,该模型实现了高效的多任务性能并具有出色的参数效率,仅使用总计66M的参数。
关键见解
- 端到端单一任务模型在语音和音频处理上的性能随深度学习发展而提升。
- 构建能在多个任务上表现优异的通用模型存在挑战,因为不同任务通常需要不同的训练数据、输入特征或模型架构。
- 提出了一种新型的两阶段多任务学习框架MT2KD,用于构建联合执行ASR、AT和SV任务的一般性语音和音频编码器。
- 第一阶段通过多教师知识蒸馏技术对齐教师编码器的特征空间至单一学生编码器。
- 第二阶段在多任务监督微调中进行训练,优化了模型的性能。
- 实验结果表明,MT2KD显著优于多任务学习的基线模型。在ASR、AT和SV任务上的性能良好,相较于最优单任务编码器仅有微小性能差异。
点此查看论文截图

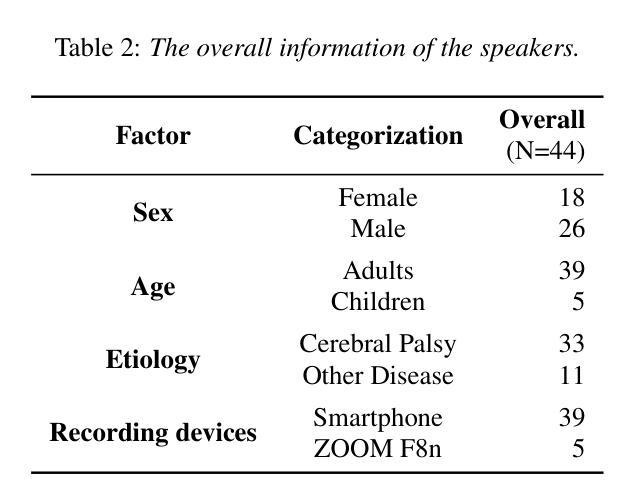
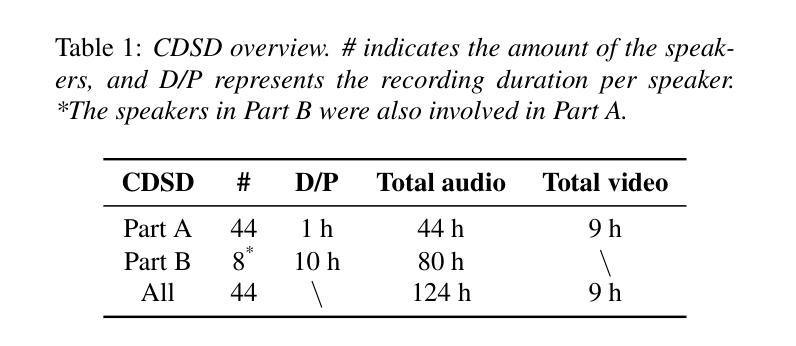
CDSD: Chinese Dysarthria Speech Database
Authors:Yan Wang, Mengyi Sun, Xinchen Kang, Jingting Li, Pengfei Guo, Ming Gao, Su-Jing Wang
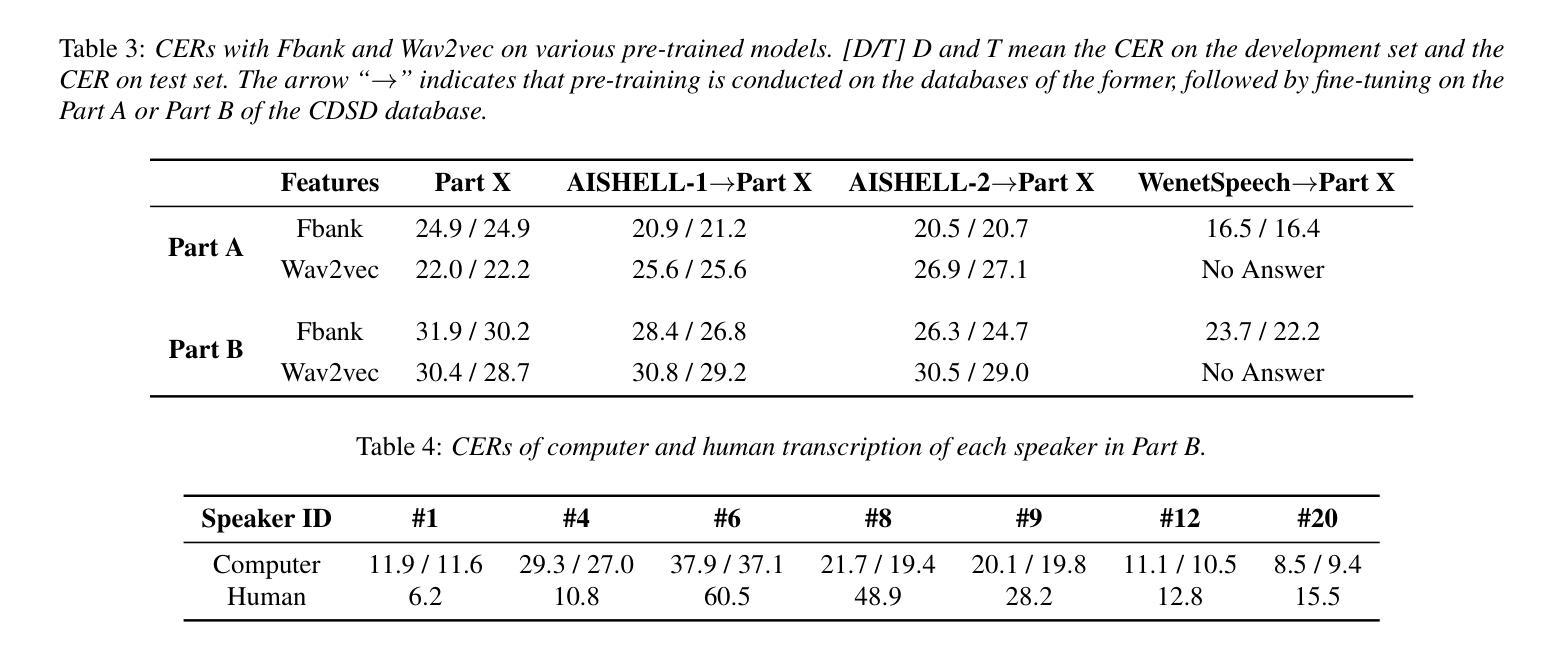
Dysarthric speech poses significant challenges for individuals with dysarthria, impacting their ability to communicate socially. Despite the widespread use of Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR), accurately recognizing dysarthric speech remains a formidable task, largely due to the limited availability of dysarthric speech data. To address this gap, we developed the Chinese Dysarthria Speech Database (CDSD), the most extensive collection of Chinese dysarthria data to date, featuring 133 hours of recordings from 44 speakers. Our benchmarks reveal a best Character Error Rate (CER) of 16.4%. Compared to the CER of 20.45% from our additional human experiments, Dysarthric Speech Recognition (DSR) demonstrates its potential in significant improvement of communication for individuals with dysarthria. The CDSD database will be made publicly available at http://melab.psych.ac.cn/CDSD.html.
构音障碍者的语音为社会交际带来了很大的挑战。尽管自动语音识别(ASR)技术广泛应用,但由于构音障碍语音数据的有限性,准确识别构音障碍语音仍然是一项艰巨的任务。为了解决这一差距,我们建立了中国构音障碍语音数据库(CDSD),迄今为止最大规模的中国构音障碍数据集合,包含来自44名发言人的133小时录音。我们的基准测试显示,最佳字符错误率为16.4%。与我们额外的对比人类实验相比,构音障碍语音识别(DSR)的字符错误率为20.45%,显示出其在改善构音障碍者的沟通方面的潜力。CDSD数据库将在http://melab.psych.ac.cn/CDSD.html上公开提供。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at INTERSPEECH 2024 Yan Wang and Mengyi Sun contributed equally to this research
Summary:中文构音障碍者的语音给个人沟通带来挑战。尽管自动语音识别(ASR)技术广泛应用,但识别构音障碍者的语音仍是一大难题,原因在于构音障碍语音数据的缺乏。为解决这一问题,我们建立了中国构音障碍语音数据库(CDSD),包含来自44名说话者的133小时录音,是目前最大的中文构音障碍数据库。基准测试显示最佳字符错误率为16.4%。与人类实验相比,构音障碍语音识别(DSR)显示出改善构音障碍者沟通的潜力。CDSD数据库将在http://melab.psych.ac.cn/CDSD.html公开提供。
Key Takeaways:
- 中文构音障碍者的语音沟通存在挑战。
- 自动语音识别技术在识别构音障碍语音时面临难题,主要原因在于构音障碍语音数据的有限性。
- 为解决此问题,建立了中国构音障碍语音数据库(CDSD),包含大量的构音障碍语音数据。
- 基准测试显示,中国构音障碍语音数据库的最佳字符错误率为16.4%。
- 与人类实验相比,构音障碍语音识别技术显示出改善构音障碍者沟通的潜力。
- CDSD数据库将公开提供,以便研究者和开发者使用。
点此查看论文截图