⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-02-15 更新
Vision-Language In-Context Learning Driven Few-Shot Visual Inspection Model
Authors:Shiryu Ueno, Yoshikazu Hayashi, Shunsuke Nakatsuka, Yusei Yamada, Hiroaki Aizawa, Kunihito Kato
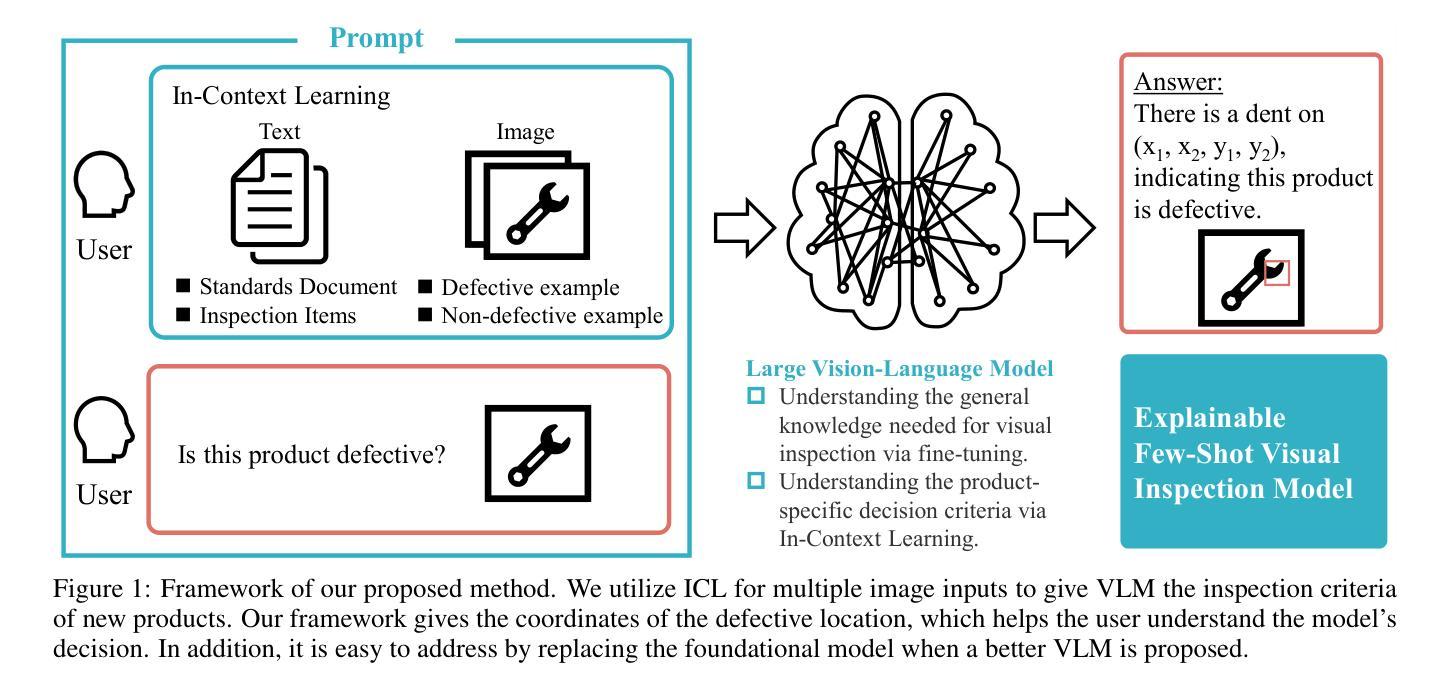
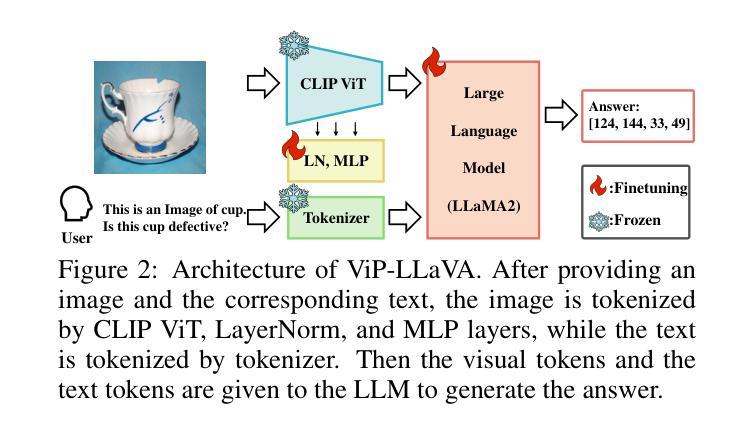
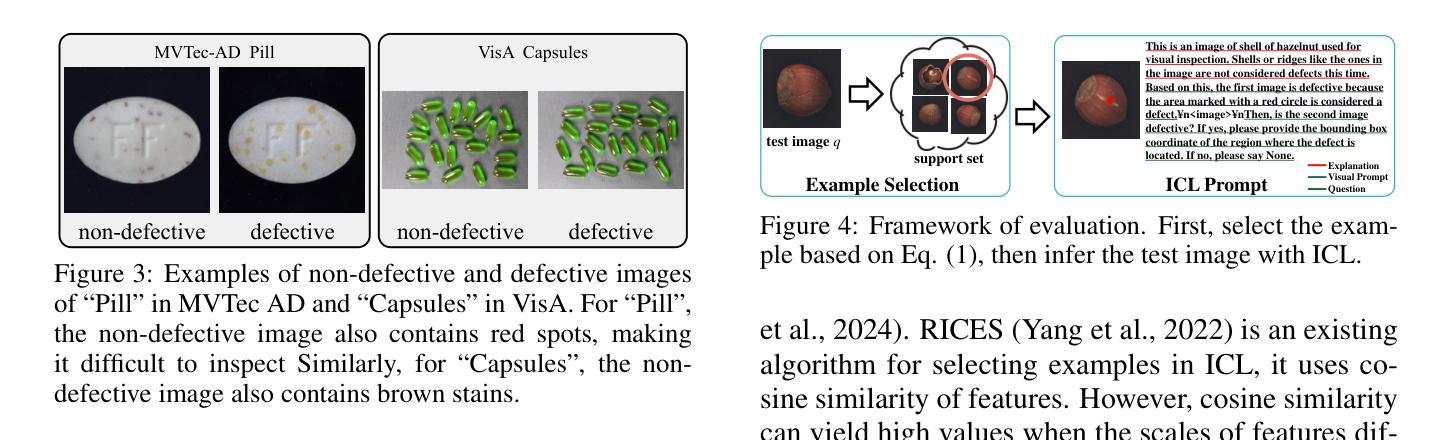
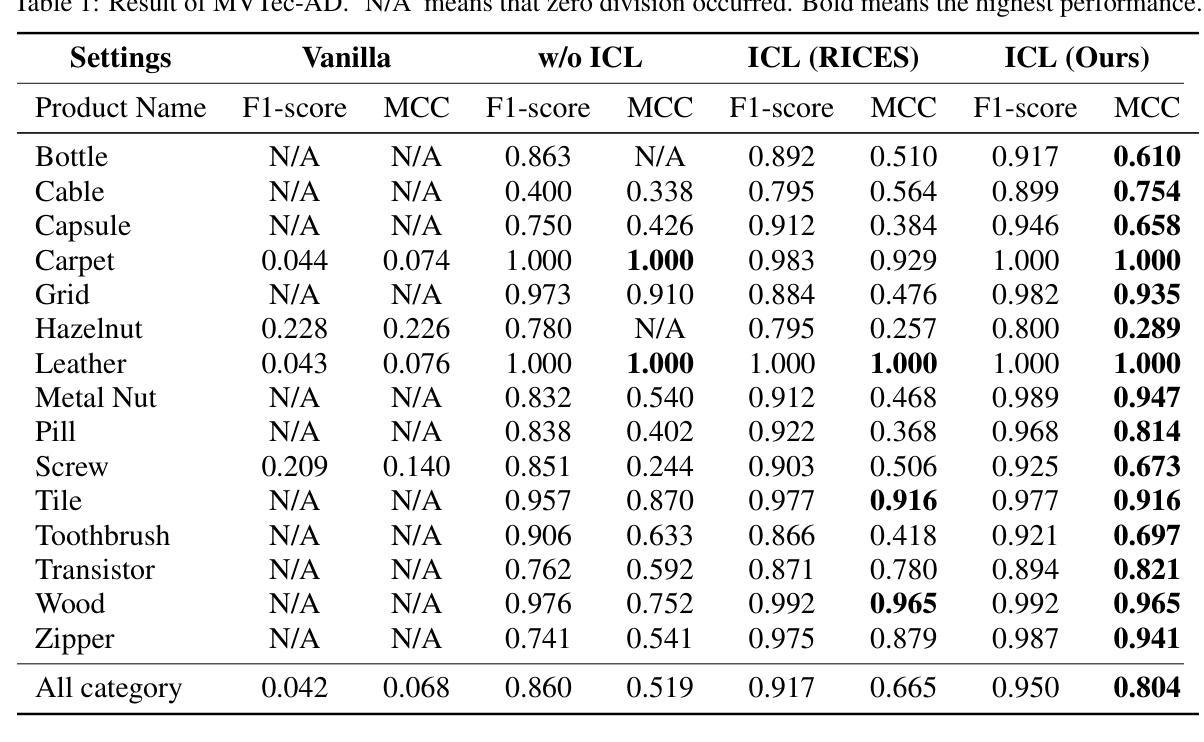
We propose general visual inspection model using Vision-Language Model(VLM) with few-shot images of non-defective or defective products, along with explanatory texts that serve as inspection criteria. Although existing VLM exhibit high performance across various tasks, they are not trained on specific tasks such as visual inspection. Thus, we construct a dataset consisting of diverse images of non-defective and defective products collected from the web, along with unified formatted output text, and fine-tune VLM. For new products, our method employs In-Context Learning, which allows the model to perform inspections with an example of non-defective or defective image and the corresponding explanatory texts with visual prompts. This approach eliminates the need to collect a large number of training samples and re-train the model for each product. The experimental results show that our method achieves high performance, with MCC of 0.804 and F1-score of 0.950 on MVTec AD in a one-shot manner. Our code is available athttps://github.com/ia-gu/Vision-Language-In-Context-Learning-Driven-Few-Shot-Visual-Inspection-Model.
我们提出了一种通用的视觉检查模型,该模型使用基于视觉语言的模型(VLM),并结合少数非缺陷或缺陷产品的图像以及作为检查标准的解释性文本。尽管现有的VLM在各种任务中表现出高性能,但它们并未针对视觉检查等特定任务进行训练。因此,我们构建了一个数据集,其中包含从网络上收集的各种非缺陷和缺陷产品的图像,以及统一格式的输出文本,并对VLM进行了微调。对于新产品,我们的方法采用上下文学习(In-Context Learning),该方法允许模型通过非缺陷或缺陷图像的示例以及相应的解释性文本和视觉提示进行检查。这种方法消除了需要收集大量训练样本并为每个产品重新训练模型的需求。实验结果表明,我们的方法在一击方式下实现了高性能,在MVTec AD上的MCC为0.804,F1分数为0.950。我们的代码可在https://github.com/ia-gu/Vision-Language-In-Context-Learning-Driven-Few-Shot-Visual-Inspection-Model找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF VISAPP 2025
Summary
本文提出了一种基于视觉语言模型(VLM)的通用视觉检查模型,该模型使用少数非缺陷或缺陷产品的图像以及作为检查标准的解释性文本。通过构建包含从网络收集的非缺陷和缺陷产品的多样化图像数据集,以及统一格式的输出文本,对VLM进行微调。对于新产品,该方法采用上下文学习方法,只需一个非缺陷或缺陷图像示例以及相应的解释性文本作为视觉提示,即可进行检验。实验结果显示,该方法在一击模式下,在MVTec AD上的MCC达到0.804,F1分数达到0.950,取得了较高的性能。
Key Takeaways
- 提出了基于视觉语言模型(VLM)的视觉检查模型。
- 使用少数非缺陷或缺陷产品的图像和解释性文本作为检查标准。
- 构建了包含多样化产品图像的数据集,并对VLM进行微调。
- 采用上下文学习方法,仅需要少量示例即可进行新产品的检验。
- 实验结果显示,该方法在一击模式下性能优异。
- 该方法的代码已公开可用。
- 该方法适用于视觉检查任务,提高了模型在新产品上的适应性并减少了训练样本的需求。
点此查看论文截图


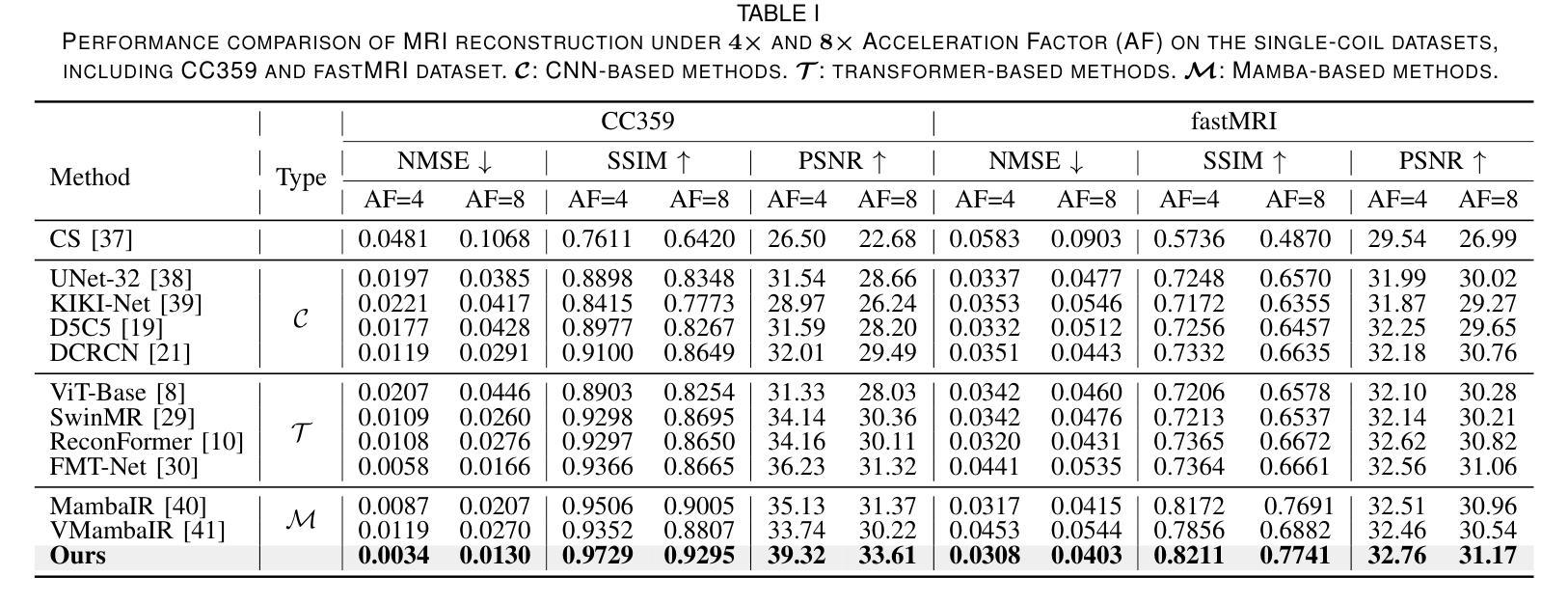
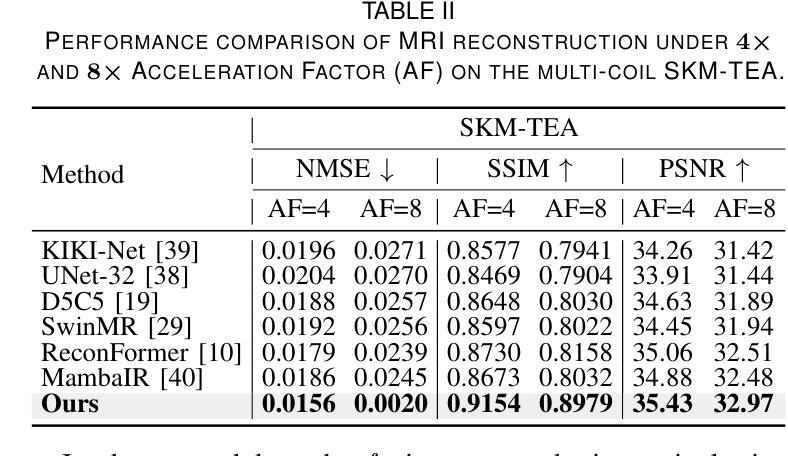
DM-Mamba: Dual-domain Multi-scale Mamba for MRI reconstruction
Authors:Yucong Meng, Zhiwei Yang, Zhijian Song, Yonghong Shi
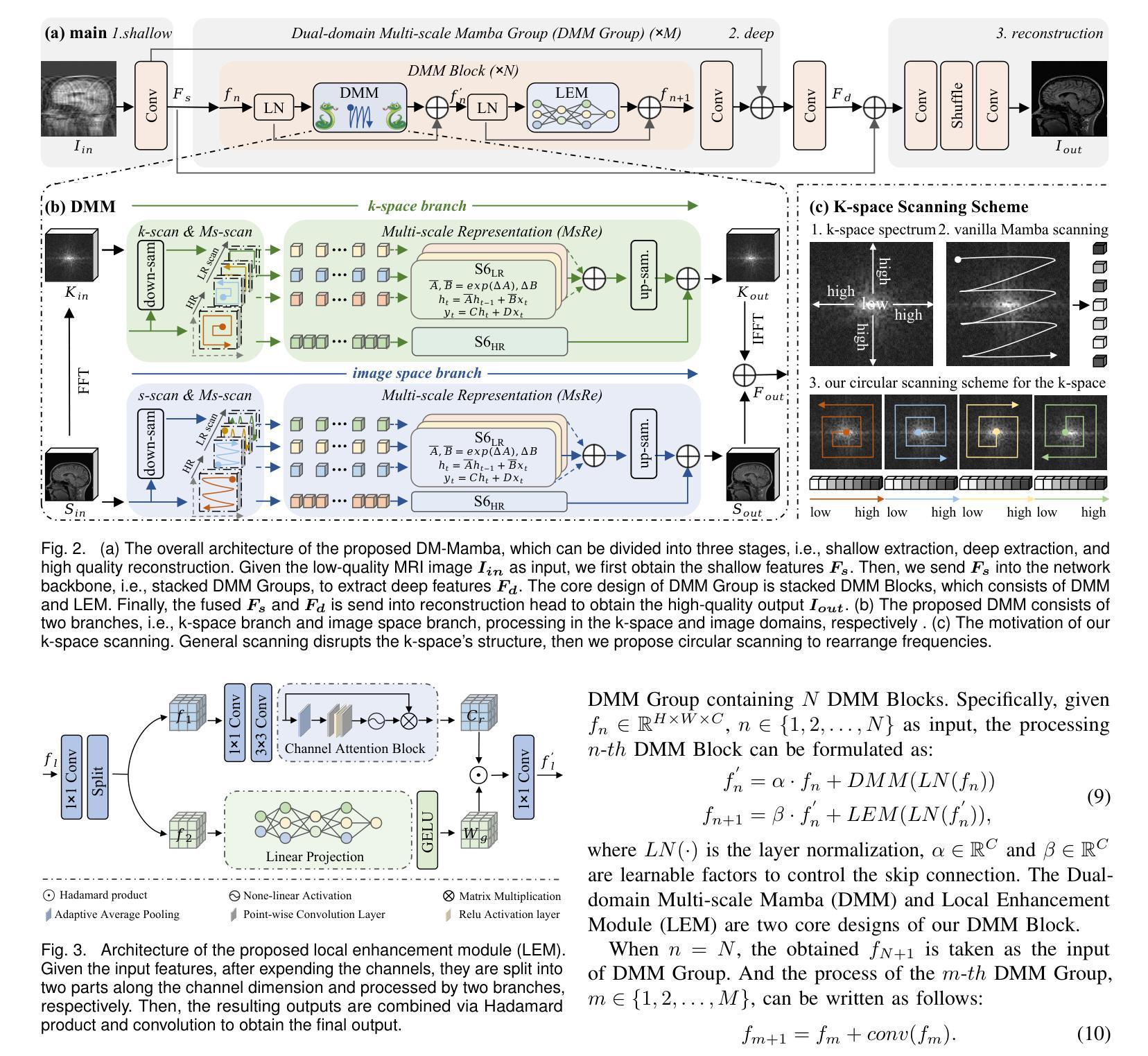
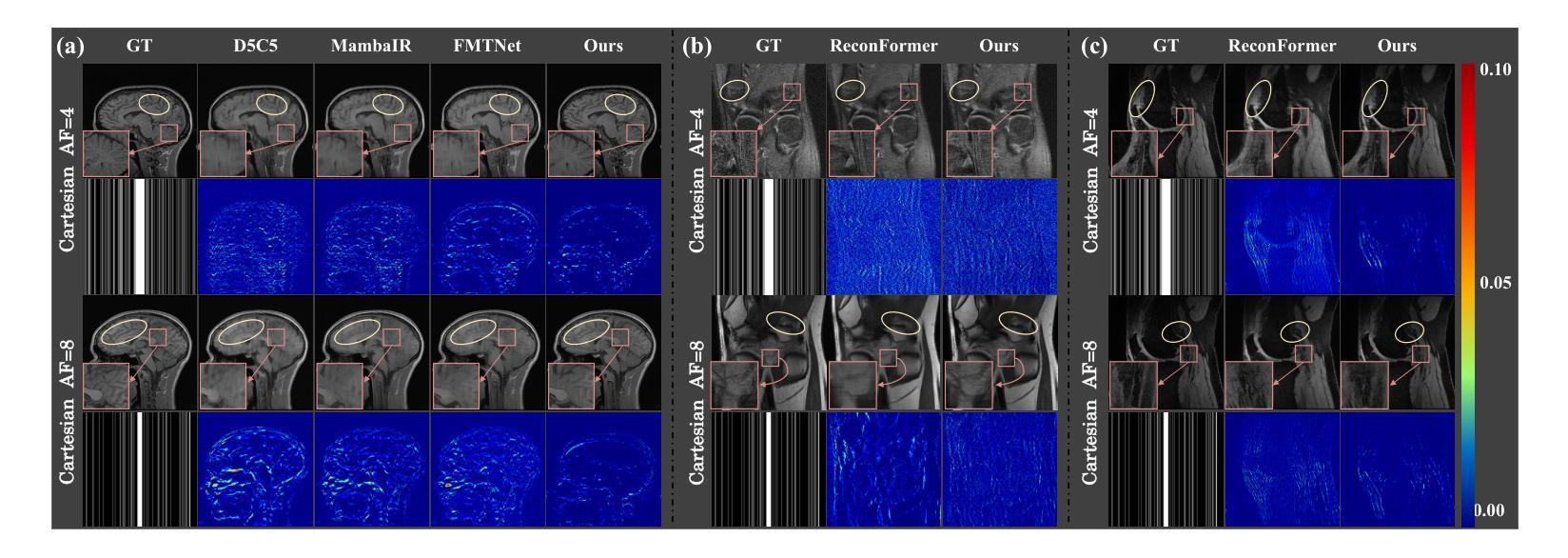
The accelerated MRI reconstruction poses a challenging ill-posed inverse problem due to the significant undersampling in k-space. Deep neural networks, such as CNNs and ViT, have shown substantial performance improvements for this task while encountering the dilemma between global receptive fields and efficient computation. To this end, this paper pioneers exploring Mamba, a new paradigm for long-range dependency modeling with linear complexity, for efficient and effective MRI reconstruction. However, directly applying Mamba to MRI reconstruction faces three significant issues: (1) Mamba’s row-wise and column-wise scanning disrupts k-space’s unique spectrum, leaving its potential in k-space learning unexplored. (2) Existing Mamba methods unfold feature maps with multiple lengthy scanning paths, leading to long-range forgetting and high computational burden. (3) Mamba struggles with spatially-varying contents, resulting in limited diversity of local representations. To address these, we propose a dual-domain multi-scale Mamba for MRI reconstruction from the following perspectives: (1) We pioneer vision Mamba in k-space learning. A circular scanning is customized for spectrum unfolding, benefiting the global modeling of k-space. (2) We propose a multi-scale Mamba with an efficient scanning strategy in both image and k-space domains. It mitigates long-range forgetting and achieves a better trade-off between efficiency and performance. (3) We develop a local diversity enhancement module to improve the spatially-varying representation of Mamba. Extensive experiments are conducted on three public datasets for MRI reconstruction under various undersampling patterns. Comprehensive results demonstrate that our method significantly outperforms state-of-the-art methods with lower computational cost. Implementation code will be available at https://github.com/XiaoMengLiLiLi/DM-Mamba.
磁共振成像(MRI)的加速重建面临一个具有挑战性的不适定反问题,这主要是由于k空间中的显著欠采样所导致的。深度神经网络,如卷积神经网络(CNNs)和视觉转换器(ViT),在此任务上显示出显著的性能改进,但在全局感受野和高效计算之间遇到了困境。为此,本文率先探索Mamba这一具有线性复杂度的长距离依赖建模新范式,以实现高效且有效的MRI重建。然而,直接将Mamba应用于MRI重建面临三个主要问题:(1)Mamba的行和列扫描会破坏k空间的独特频谱,使得其在k空间学习中的潜力尚未被探索。(2)现有的Mamba方法展开特征映射具有多条冗长的扫描路径,导致长距离遗忘和高计算负担。(3)Mamba在空间内容变化方面表现挣扎,导致局部表示多样性有限。为了解决这些问题,我们从以下几个角度提出用于MRI重建的双域多尺度Mamba:(1)我们率先在k空间学习中探索视觉Mamba。针对频谱展开定制循环扫描,有利于k空间的全局建模。(2)我们提出了一种多尺度Mamba,在图像和k空间域中都采用有效的扫描策略。它减轻了长距离遗忘问题,并在效率和性能之间实现了更好的权衡。(3)我们开发了一个局部多样性增强模块,以提高Mamba的空间变化表示。在三个公共数据集上进行了广泛的MRI重建实验,实验结果表明,我们的方法在更低的计算成本下显著优于最新技术。相关实现代码将在https://github.com/XiaoMengLiLiLi/DM-Mamba上提供。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文探索了一种新的用于MRI重建的方法,名为Mamba,它具有长距离依赖建模的优势。但Mamba直接应用于MRI重建存在一些问题,如扫描方式会破坏k-空间的独特光谱,且其在空间内容处理上存在局限。为此,提出了一个结合了双域多尺度的Mamba框架来应对这些挑战,包括改进了扫描策略以提升性能与效率、提升局部多样性增强模块来处理空间内容的变化等。该方法在各种欠采样模式下表现优越。代码将公开于链接 https://github.com/XiaoMengLiLiLi/DM-Mamba。
Key Takeaways
以下是七个关于文本的关键见解:
- Mamba是一个具有线性复杂性的新模型,适用于长距离依赖建模。
- 直接应用Mamba于MRI重建面临三个主要问题:破坏k-空间独特光谱、长距离遗忘和计算负担大以及处理空间内容变化的局限性。
- 为解决这些问题,提出了双域多尺度Mamba框架,其中包括在k-空间学习中的视觉Mamba创新使用。
- 采用定制的循环扫描方式有利于k-空间的全球建模。
- 提出了一种多尺度Mamba,通过图像和k-空间域的有效扫描策略,减轻了长距离遗忘问题并实现了效率和性能之间的平衡。
- 开发了一个局部多样性增强模块,提高了Mamba在空间变化表示方面的性能。
点此查看论文截图

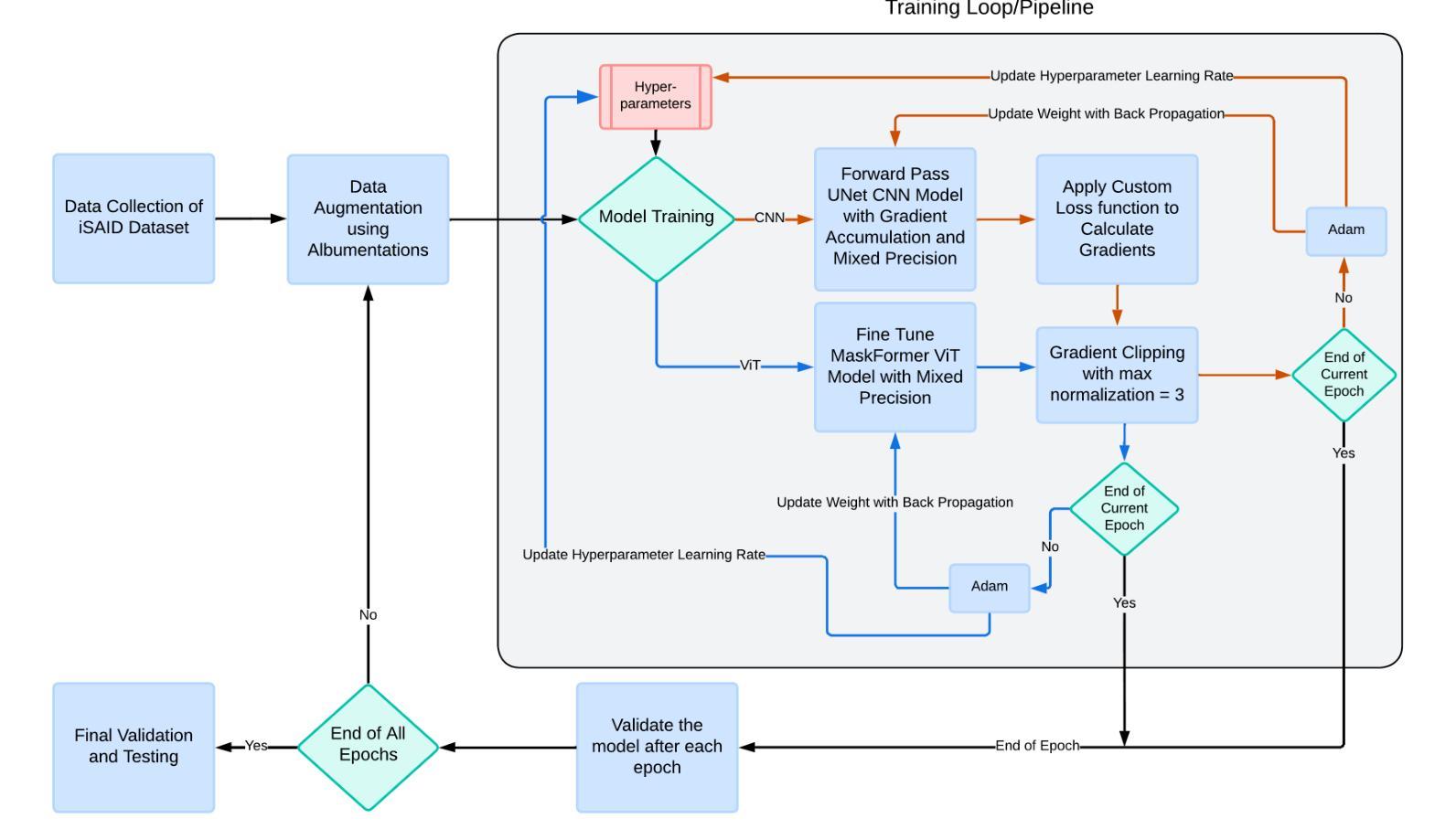
Heuristical Comparison of Vision Transformers Against Convolutional Neural Networks for Semantic Segmentation on Remote Sensing Imagery
Authors:Ashim Dahal, Saydul Akbar Murad, Nick Rahimi
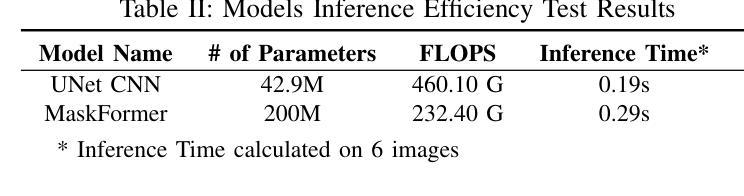
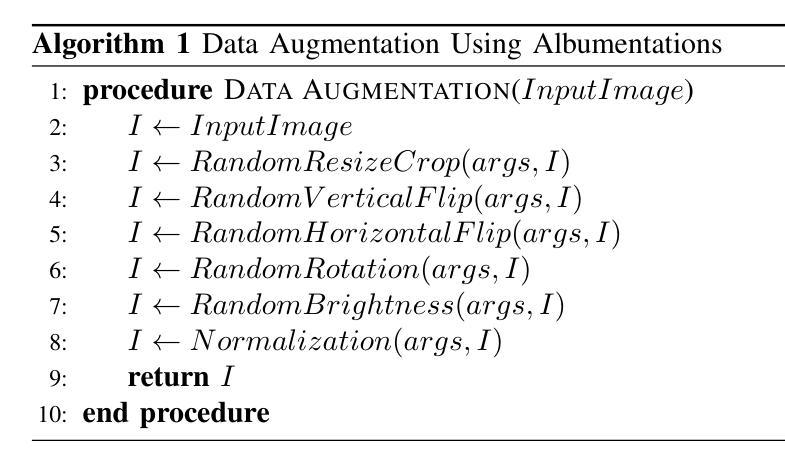
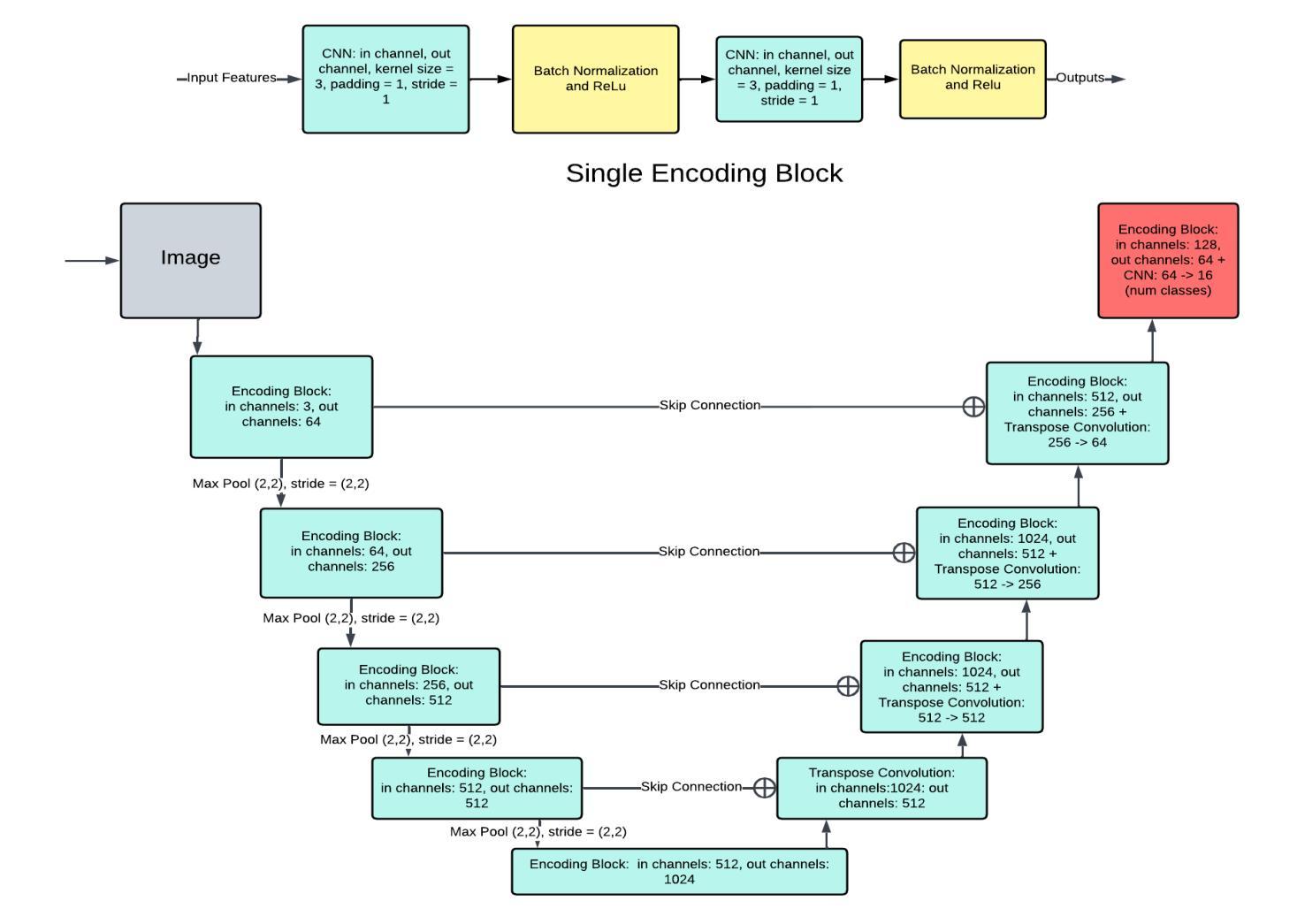
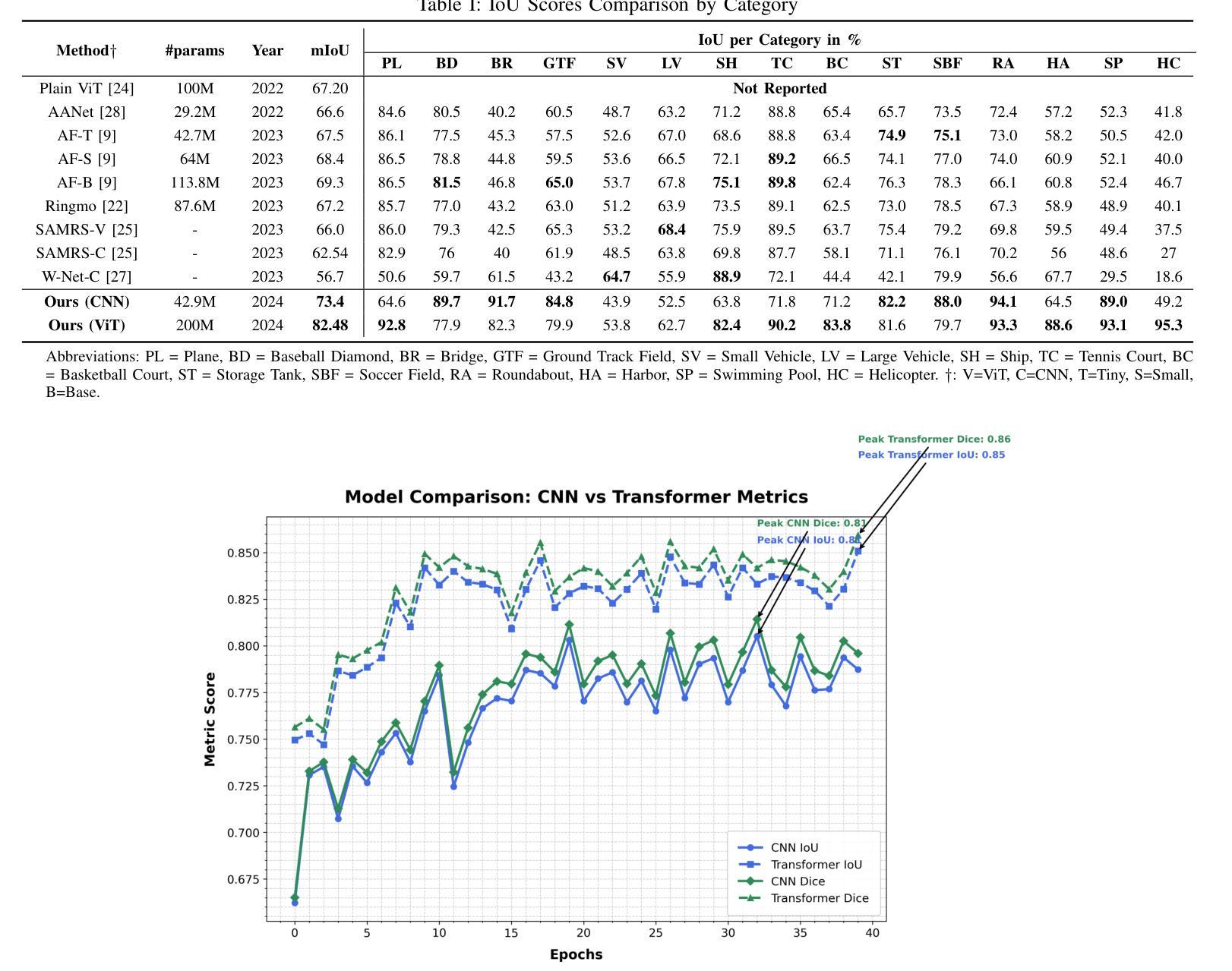
Vision Transformers (ViT) have recently brought a new wave of research in the field of computer vision. These models have performed particularly well in image classification and segmentation. Research on semantic and instance segmentation has accelerated with the introduction of the new architecture, with over 80% of the top 20 benchmarks for the iSAID dataset based on either the ViT architecture or the attention mechanism behind its success. This paper focuses on the heuristic comparison of three key factors of using (or not using) ViT for semantic segmentation of remote sensing aerial images on the iSAID dataset. The experimental results observed during this research were analyzed based on three objectives. First, we studied the use of a weighted fused loss function to maximize the mean Intersection over Union (mIoU) score and Dice score while minimizing entropy or class representation loss. Second, we compared transfer learning on Meta’s MaskFormer, a ViT-based semantic segmentation model, against a generic UNet Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) based on mIoU, Dice scores, training efficiency, and inference time. Third, we examined the trade-offs between the two models in comparison to current state-of-the-art segmentation models. We show that the novel combined weighted loss function significantly boosts the CNN model’s performance compared to transfer learning with ViT. The code for this implementation can be found at: https://github.com/ashimdahal/ViT-vs-CNN-Image-Segmentation.
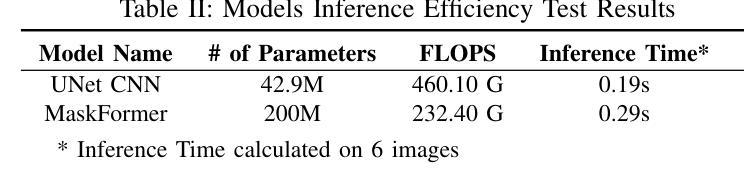
视觉Transformer(ViT)为计算机视觉领域带来了新的研究热潮。这些模型在图像分类和分割方面表现特别出色。新架构的引入加速了语义分割和实例分割的研究,在iSAID数据集的前20个标杆中,有超过80%是基于ViT架构或其背后成功的注意力机制。本文聚焦于在iSAID数据集上,使用(或不使用)ViT进行遥感航空图像语义分割的三个关键因素的启发式比较。研究过程中的实验结果基于以下三个目标进行分析。首先,我们研究了使用加权融合损失函数,以最大化平均交并比(mIoU)得分和Dice得分,同时最小化熵或类表示损失。其次,我们比较了Meta的MaskFormer(一种基于ViT的语义分割模型)的迁移学习与基于mIoU、Dice得分、训练效率和推理时间的通用UNet卷积神经网络(CNN)的迁移学习。第三,我们考察了这两种模型与当前最先进的分割模型的权衡。我们表明,与ViT的迁移学习相比,新型组合加权损失函数显著提高了CNN模型的性能。该实现的代码可在以下网址找到:https://github.com/ashimdahal/ViT-vs-CNN-Image-Segmentation。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文研究了使用Vision Transformer(ViT)对远程感测航空图像进行语义分割的效果。通过实验对比了使用加权融合损失函数优化的卷积神经网络(CNN)模型与基于ViT的MaskFormer模型在iSAID数据集上的表现。结果显示,加权损失函数能显著提升CNN模型的性能,相较于ViT的迁移学习有更好的表现。
Key Takeaways
- Vision Transformers(ViT)在计算机视觉领域引起新的研究热潮,特别是在图像分类和分割方面表现优异。
- 在iSAID数据集上,超过80%的前20名榜单是基于ViT架构或其背后的注意力机制。
- 论文重点比较了在远程感测航空图像语义分割中使用(或不使用)ViT的三个关键因素。
- 通过实验研究了使用加权融合损失函数的效果,旨在最大化mIoU和Dice得分,同时最小化熵或类别表示损失。
- 对比了基于ViT的MaskFormer模型与通用CNN模型的迁移学习效果。
- 加权损失函数显著提升了CNN模型性能,相较于ViT的迁移学习更有优势。
- 论文实现的代码可访问特定GitHub仓库。
点此查看论文截图
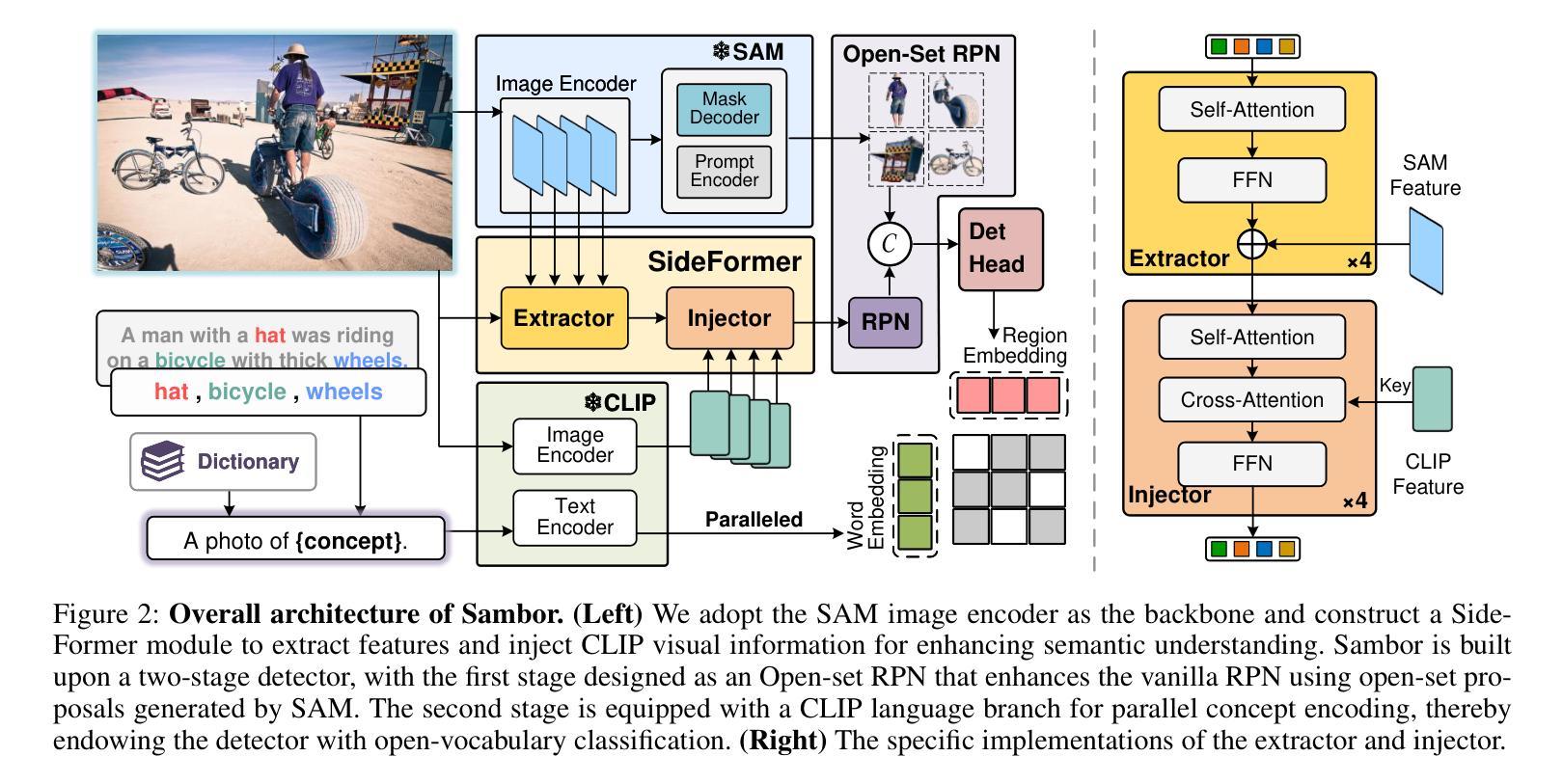
Boosting Segment Anything Model Towards Open-Vocabulary Learning
Authors:Xumeng Han, Longhui Wei, Xuehui Yu, Zhiyang Dou, Xin He, Kuiran Wang, Yingfei Sun, Zhenjun Han, Qi Tian
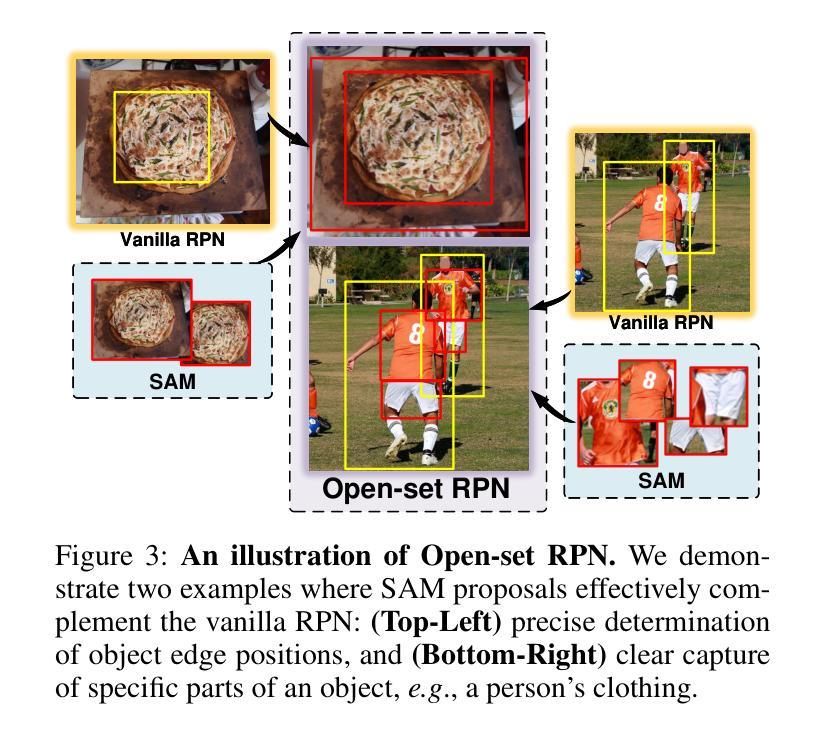
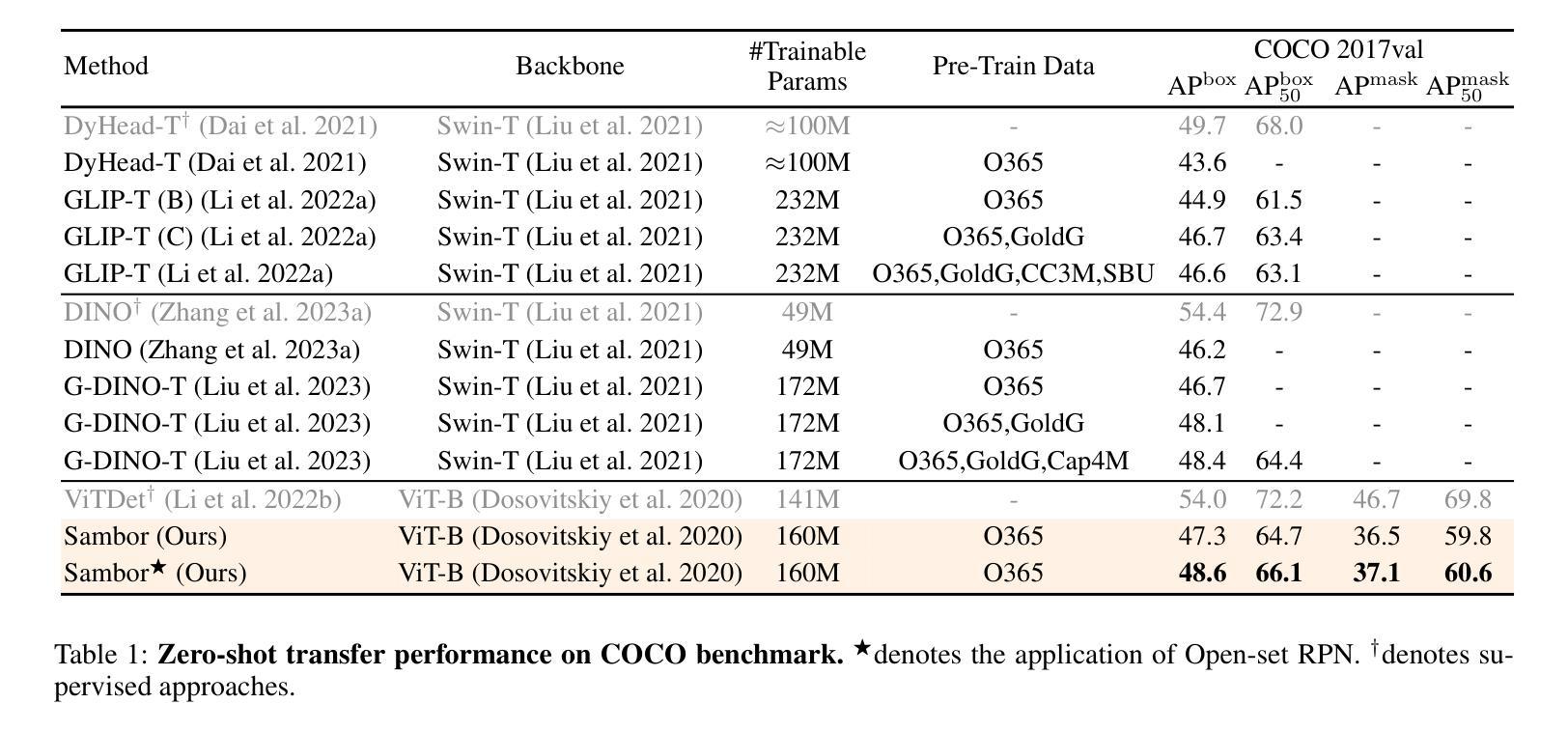
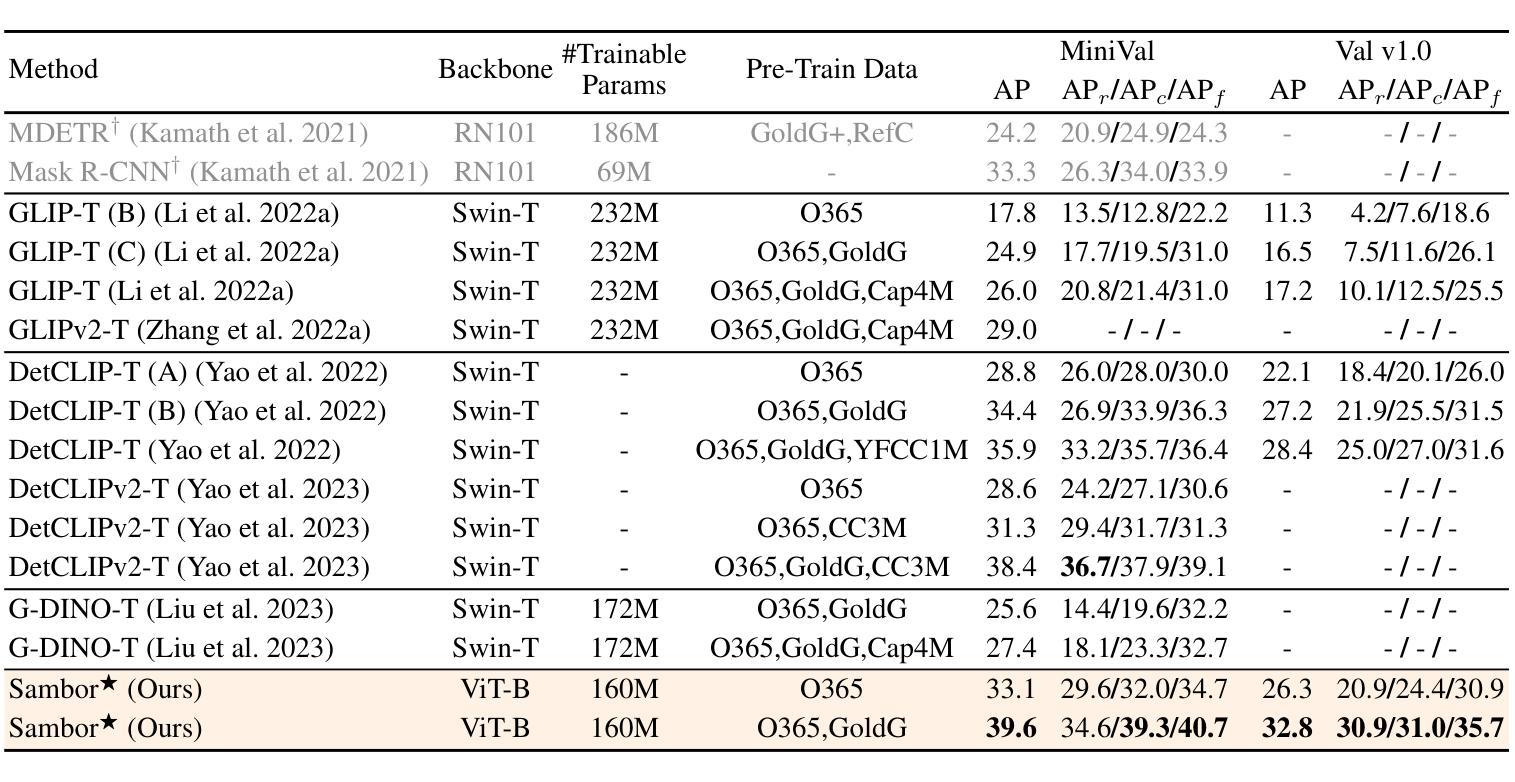
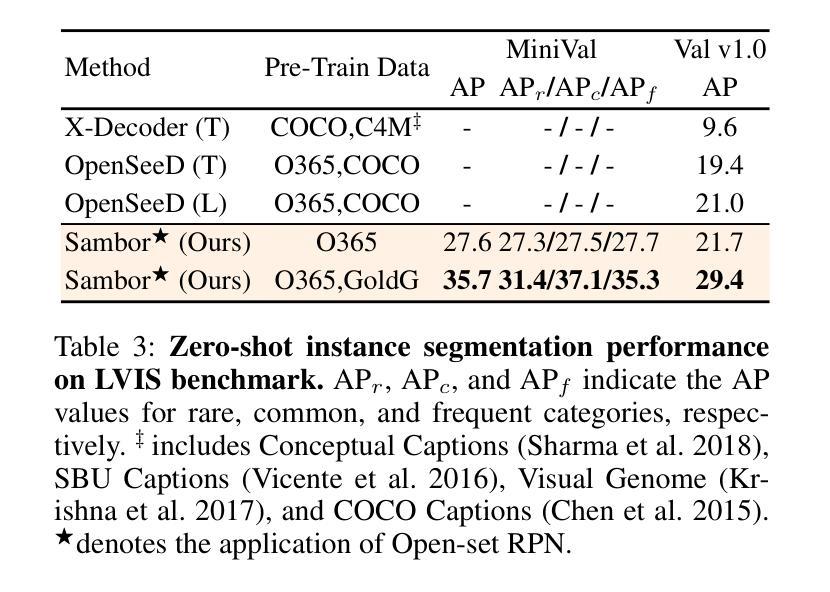
The recent Segment Anything Model (SAM) has emerged as a new paradigmatic vision foundation model, showcasing potent zero-shot generalization and flexible prompting. Despite SAM finding applications and adaptations in various domains, its primary limitation lies in the inability to grasp object semantics. In this paper, we present Sambor to seamlessly integrate SAM with the open-vocabulary object detector in an end-to-end framework. While retaining all the remarkable capabilities inherent to SAM, we boost it to detect arbitrary objects from human inputs like category names or reference expressions. Building upon the SAM image encoder, we introduce a novel SideFormer module designed to acquire SAM features adept at perceiving objects and inject comprehensive semantic information for recognition. In addition, we devise an Open-set RPN that leverages SAM proposals to assist in finding potential objects. Consequently, Sambor enables the open-vocabulary detector to equally focus on generalizing both localization and classification sub-tasks. Our approach demonstrates superior zero-shot performance across benchmarks, including COCO and LVIS, proving highly competitive against previous state-of-the-art methods. We aspire for this work to serve as a meaningful endeavor in endowing SAM to recognize diverse object categories and advancing open-vocabulary learning with the support of vision foundation models.
最近的Segment Anything Model(SAM)作为一种新的范式视觉基础模型出现,展示了强大的零样本泛化和灵活提示。尽管SAM在各种领域找到了应用和适应,但其主要局限性在于无法掌握对象语义。在本文中,我们提出Sambor,将SAM无缝集成到端到端框架中的开放词汇对象检测器中。在保留SAM固有的所有卓越功能的同时,我们将其提升为可以检测来自人类输入的任意对象,如类别名称或参考表达式。基于SAM图像编码器,我们引入了一种新型SideFormer模块,旨在获取擅长感知对象的SAM特征,并注入全面的语义信息进行识别。此外,我们设计了一个开放集RPN,利用SAM提案来帮助寻找潜在对象。因此,Sambor使开放词汇检测器能够同样专注于泛化定位和分类子任务。我们的方法在各种基准测试上表现出卓越的零样本性能,包括COCO和LVIS,证明与之前的最新方法高度竞争。我们希望这项工作能为赋予SAM识别多种对象类别的能力,以及借助视觉基础模型推进开放词汇学习,成为一次有意义的努力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by AAAI 2025
Summary
基于Segment Anything Model(SAM)的Sambor模型通过整合开放词汇对象检测器,形成了一个端到端的新框架。Sambor保留了SAM的所有出色功能,并增强了其检测能力,可以检测来自人类输入的任意对象,如类别名称或参考表达式。通过引入SideFormer模块和Open-set RPN,Sambor可以更好地获取对象的特征,注入全面的语义信息用于识别,并在定位子任务和分类子任务上都展现出卓越的泛化能力。在COCO和LVIS等基准测试中,Sambor的零样本性能优越,证明其高度竞争前沿技术。这项工作旨在为SAM赋予识别多种对象类别的能力,并推动借助视觉基础模型的开放词汇学习进步。
Key Takeaways
- Sambor模型是基于Segment Anything Model(SAM)构建,形成了一种新的端到端框架。
- 它解决了SAM无法捕获对象语义的主要限制。
- 通过引入SideFormer模块和Open-set RPN来增强SAM的特征获取和语义识别能力。
- Sambor能够检测来自人类输入的任意对象。
- 该模型在定位子任务和分类子任务上都展现出卓越的泛化能力。
- 在多个基准测试中,Sambor的零样本性能优于其他前沿技术。
点此查看论文截图