⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-02-17 更新
Utilizing 3D Fast Spin Echo Anatomical Imaging to Reduce the Number of Contrast Preparations in $T_{1ρ}$ Quantification of Knee Cartilage Using Learning-Based Methods
Authors:Junru Zhong, Chaoxing Huang, Ziqiang Yu, Fan Xiao, Siyue Li, Tim-Yun Michael Ong, Ki-Wai Kevin Ho, Queenie Chan, James F. Griffith, Weitian Chen
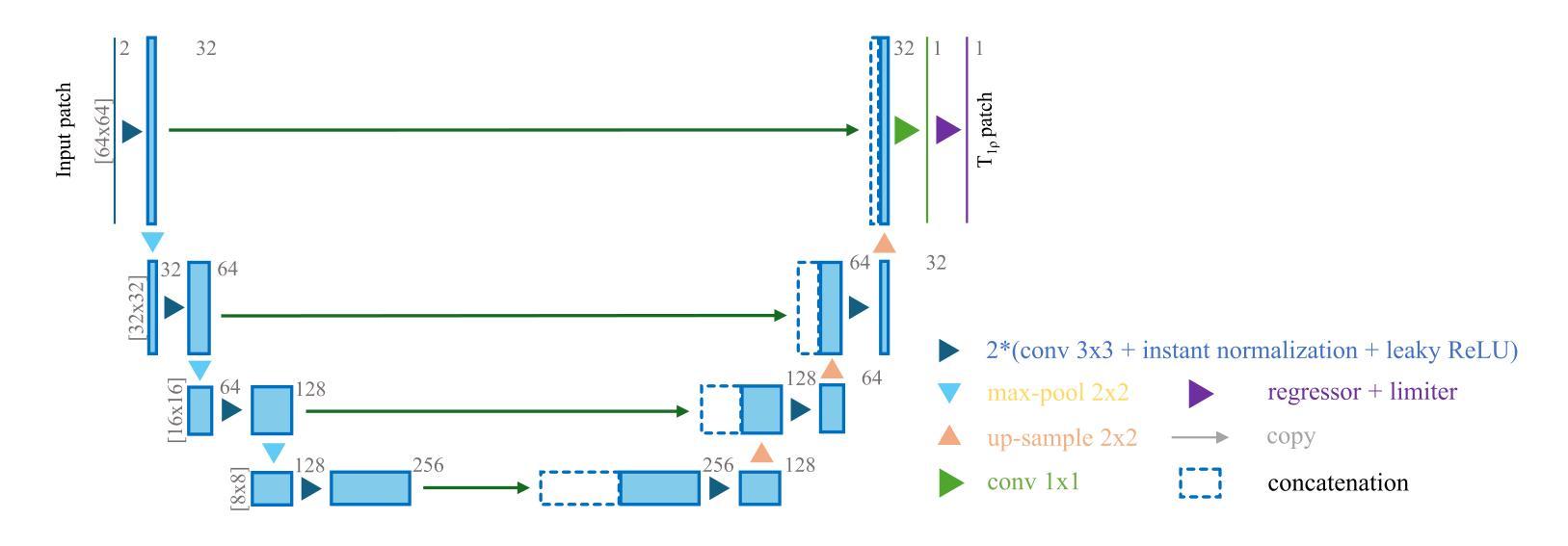
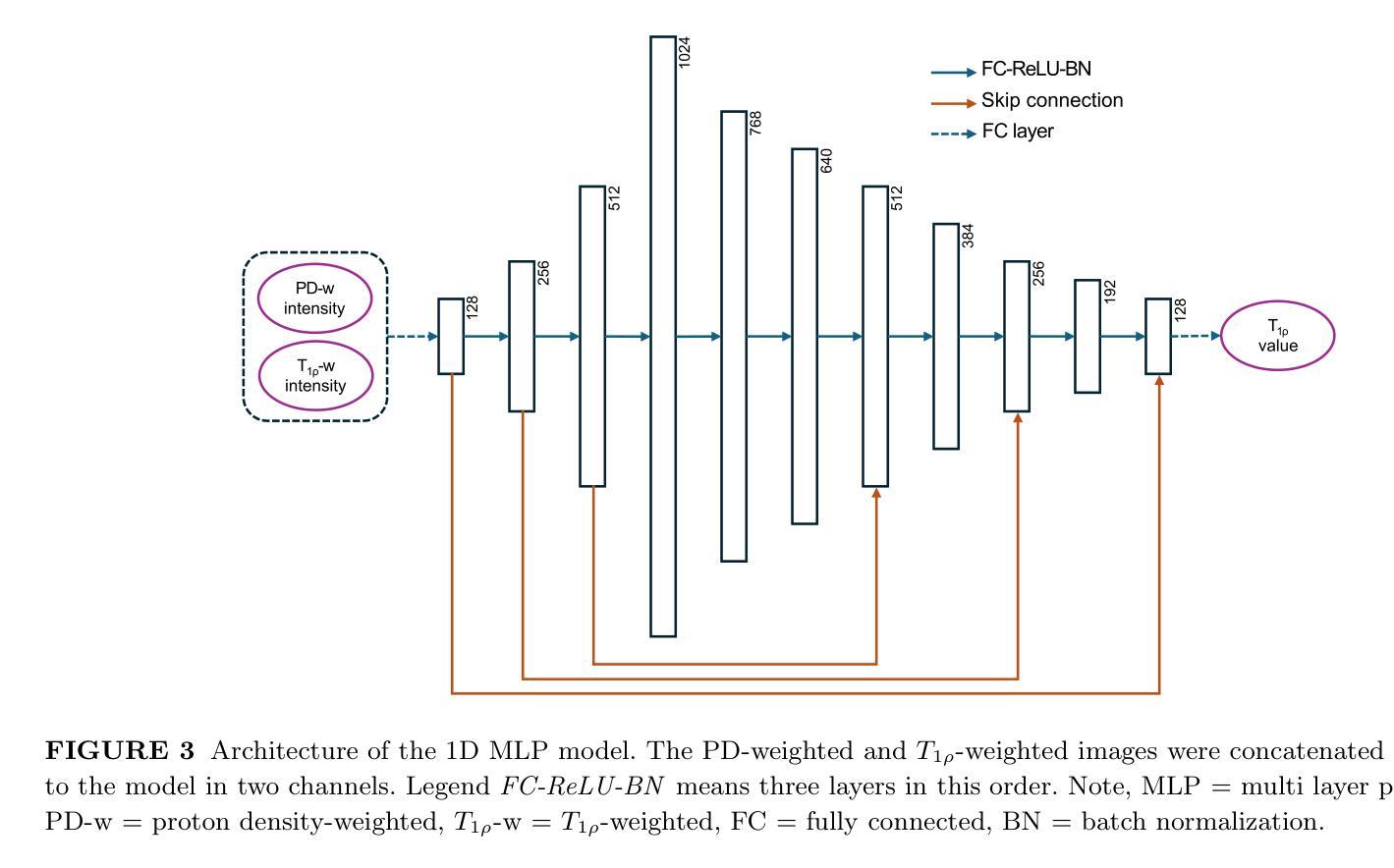
Purpose: To propose and evaluate an accelerated $T_{1\rho}$ quantification method that combines $T_{1\rho}$-weighted fast spin echo (FSE) images and proton density (PD)-weighted anatomical FSE images, leveraging deep learning models for $T_{1\rho}$ mapping. The goal is to reduce scan time and facilitate integration into routine clinical workflows for osteoarthritis (OA) assessment. Methods: This retrospective study utilized MRI data from 40 participants (30 OA patients and 10 healthy volunteers). A volume of PD-weighted anatomical FSE images and a volume of $T_{1\rho}$-weighted images acquired at a non-zero spin-lock time were used as input to train deep learning models, including a 2D U-Net and a multi-layer perceptron (MLP). $T_{1\rho}$ maps generated by these models were compared with ground truth maps derived from a traditional non-linear least squares (NLLS) fitting method using four $T_{1\rho}$-weighted images. Evaluation metrics included mean absolute error (MAE), mean absolute percentage error (MAPE), regional error (RE), and regional percentage error (RPE). Results: Deep learning models achieved RPEs below 5% across all evaluated scenarios, outperforming NLLS methods, especially in low signal-to-noise conditions. The best results were obtained using the 2D U-Net, which effectively leveraged spatial information for accurate $T_{1\rho}$ fitting. The proposed method demonstrated compatibility with shorter TSLs, alleviating RF hardware and specific absorption rate (SAR) limitations. Conclusion: The proposed approach enables efficient $T_{1\rho}$ mapping using PD-weighted anatomical images, reducing scan time while maintaining clinical standards. This method has the potential to facilitate the integration of quantitative MRI techniques into routine clinical practice, benefiting OA diagnosis and monitoring.
目的:提出并评估一种加速的$T_{1\rho}$定量方法,该方法结合了$T_{1\rho}$加权快速自旋回波(FSE)图像和质子密度(PD)加权解剖FSE图像,利用深度学习模型进行$T_{1\rho}$映射。旨在缩短扫描时间,促进定量磁共振成像技术融入临床日常工作中,用于骨关节炎(OA)的评估。
方法:这项回顾性研究使用了40名参与者(30名OA患者和10名健康志愿者)的MRI数据。使用体积PD加权解剖FSE图像和体积$T_{1\rho}$加权图像(在非零自旋锁定时间获取)来训练深度学习模型,包括二维U-Net和多层感知器(MLP)。将这些模型生成的$T_{1\rho$地图与基于四幅$T_{1\rho}$加权图像的传统非线性最小二乘(NLLS)拟合方法得出的真实地图进行比较。评估指标包括平均绝对误差(MAE)、平均绝对百分比误差(MAPE)、区域误差(RE)和区域百分比误差(RPE)。
结果:深度学习模型的RPE在所有评估场景中均低于5%,优于NLLS方法,特别是在低信噪比条件下。使用二维U-Net获得最佳结果,该网络有效利用空间信息,实现准确的$T_{1\rho}$拟合。所提出的方法证明与较短的TSL兼容,减轻了射频硬件和特定吸收率(SAR)的限制。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Submitted to Magnetic Resonance in Medicine
摘要
深度学习模型结合$T_{1\rho}$加权快速自旋回波(FSE)图像和质子密度(PD)加权解剖FSE图像,实现$T_{1\rho}$量化方法的加速,用于骨关节炎(OA)评估。通过回顾性研究利用MRI数据训练和评估模型,结果显示深度学习模型,特别是2D U-Net,在$T_{1\rho}$映射中表现优异,具有缩短扫描时间并维持临床标准的潜力。
关键见解
- 研究旨在提出并评估一种结合$T_{1\rho}$加权快速自旋回波(FSE)图像和质子密度(PD)加权解剖FSE图像的加速$T_{1\rho}$量化方法。
- 利用深度学习模型,包括2D U-Net和多层感知器(MLP),进行$T_{1\rho}$映射,以缩短扫描时间并促进在日常临床工作中的集成。
- 回顾性研究使用来自40名参与者(30名OA患者和10名健康志愿者)的MRI数据训练和评估模型。
- 深度学习模型在$T_{1\rho}$映射方面表现出优异的性能,与基于传统非线性最小二乘(NLLS)拟合方法生成的地面真实地图相比,评价指标包括平均绝对误差(MAE)、平均绝对百分比误差(MAPE)、区域误差(RE)和区域百分比误差(RPE)。
- 2D U-Net在有效利用空间信息以进行准确的$T_{1\rho}$拟合方面表现出最佳结果。
- 所提出的方法与较短的时间间隔(TSLs)兼容,减轻了射频硬件和特定吸收率(SAR)的限制。
点此查看论文截图


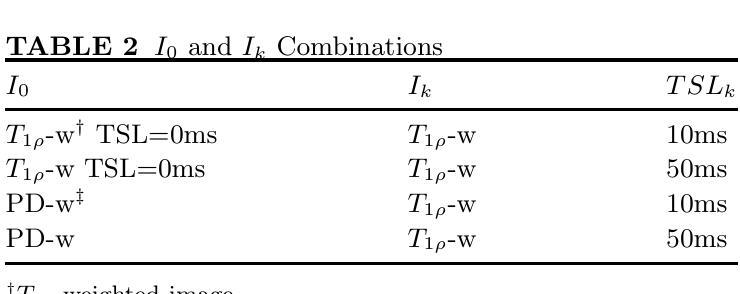
Exploring Test Time Adaptation for Subcortical Segmentation of the Fetal Brain in 3D Ultrasound
Authors:Joshua Omolegan, Pak Hei Yeung, Madeleine K. Wyburd, Linde Hesse, Monique Haak, Intergrowth-21st Consortium, Ana I. L. Namburete, Nicola K. Dinsdale
Monitoring the growth of subcortical regions of the fetal brain in ultrasound (US) images can help identify the presence of abnormal development. Manually segmenting these regions is a challenging task, but recent work has shown that it can be automated using deep learning. However, applying pretrained models to unseen freehand US volumes often leads to a degradation of performance due to the vast differences in acquisition and alignment. In this work, we first demonstrate that test time adaptation (TTA) can be used to improve model performance in the presence of both real and simulated domain shifts. We further propose a novel TTA method by incorporating a normative atlas as a prior for anatomy. In the presence of various types of domain shifts, we benchmark the performance of different TTA methods and demonstrate the improvements brought by our proposed approach, which may further facilitate automated monitoring of fetal brain development. Our code is available at https://github.com/joshuaomolegan/TTA-for-3D-Fetal-Subcortical-Segmentation.
监测胎儿大脑皮层下区域在超声(US)图像中的生长情况有助于识别异常发育的存在。手动分割这些区域是一项具有挑战性的任务,但最近的工作表明,可以使用深度学习来自动化完成。然而,将预训练模型应用于未见过的自由手超声体积常常会导致性能下降,这是由于采集和对齐方面的巨大差异。在这项工作中,我们首先证明测试时间适应(TTA)可用于在存在真实和模拟域偏移的情况下提高模型性能。我们进一步提出了一种新型的TTA方法,该方法结合规范性图谱作为解剖学的先验知识。在各种类型的域偏移存在的情况下,我们对不同的TTA方法进行了性能评估,并展示了我们所提出方法所带来的改进,这可能有助于进一步促进胎儿大脑发育的自动化监测。我们的代码可在[https://github.com/joshuaomolegan/TTA-for-3D-Fetal-Subcortical-Segmentation找到。]
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 5 pages, 5 figures
Summary
本文探讨了利用超声图像监测胎儿大脑亚皮层区域发育情况的重要性,并指出手动分割这些区域是一项挑战。然而,近期的研究显示可通过深度学习实现自动化。但当将预训练模型应用于未见的手绘超声体积数据时,性能往往会下降,因为采集和校准方面存在巨大差异。本文首先验证了测试时间适应(TTA)技术在真实和模拟域偏移情况下的模型性能提升作用。此外,本文提出了一种新的TTA方法,通过纳入规范图谱作为解剖学先验。在不同类型的域偏移情况下,本文评估了不同TTA方法的性能,并展示了所提出的方法在自动化监测胎儿大脑发育方面的改进优势。相关代码可在https://github.com/joshuaomolegan/TTA-for-3D-Fetal-Subcortical-Segmentation获取。
Key Takeaways
- 超声图像监测胎儿大脑亚皮层区域发育情况对识别异常发育具有重要意义。
- 手动分割胎儿大脑的亚皮层区域是一项挑战,但深度学习可实现自动化。
- 预训练模型应用于手绘超声体积数据时性能可能下降,原因是数据的采集和校准差异。
- 测试时间适应技术(TTA)能提升模型在真实和模拟域偏移情况下的性能。
- 本文提出了一种新的TTA方法,结合规范图谱作为解剖学先验来提升性能。
- 在不同类型的域偏移情况下,本文评估了多种TTA方法的性能。
点此查看论文截图

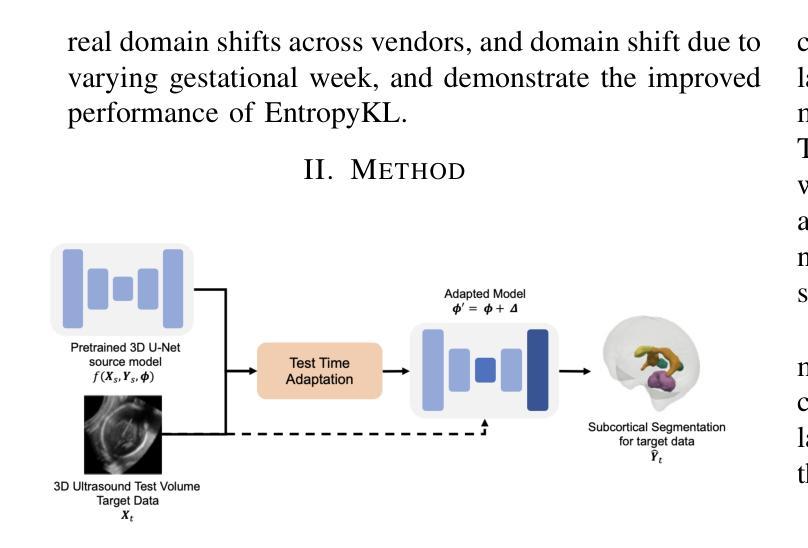
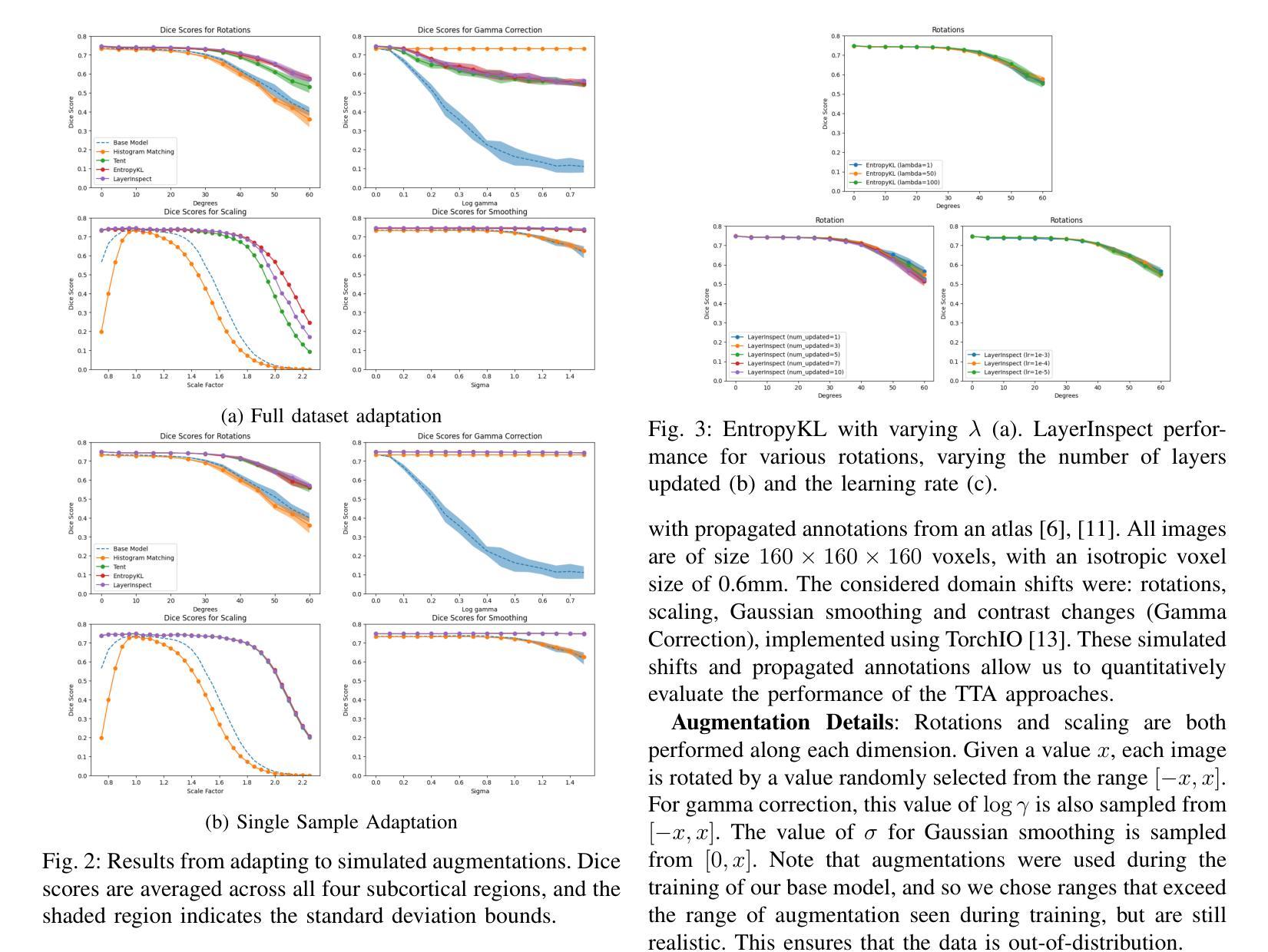
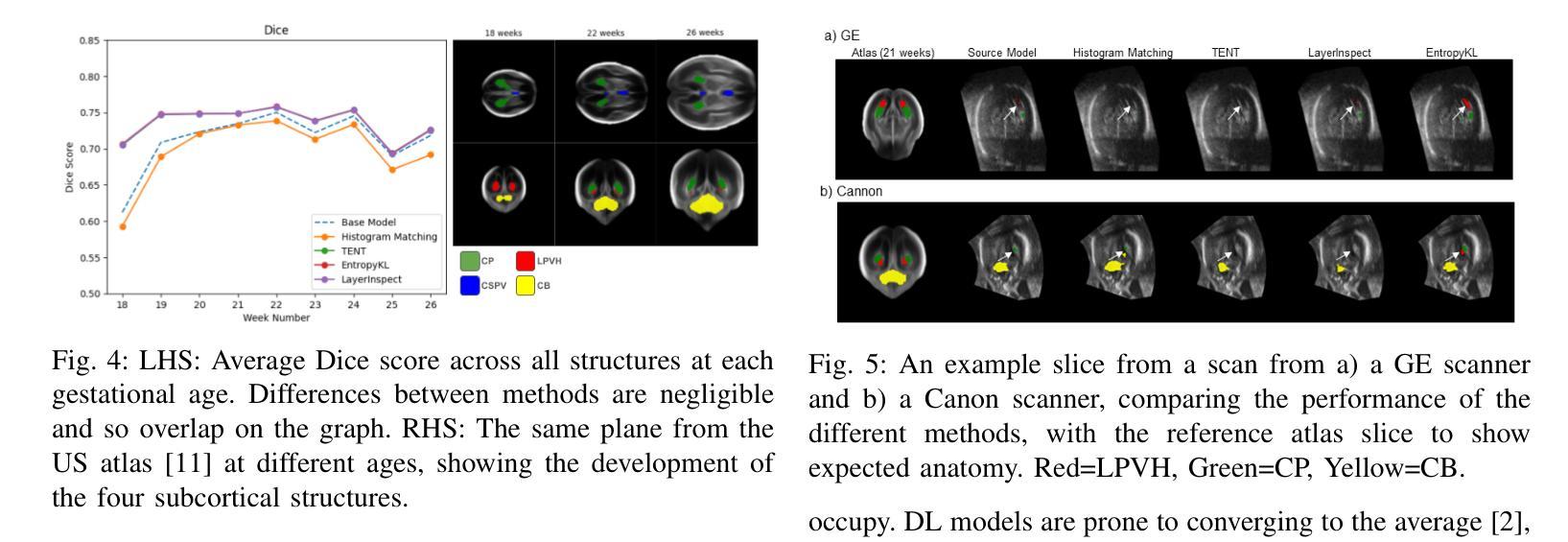
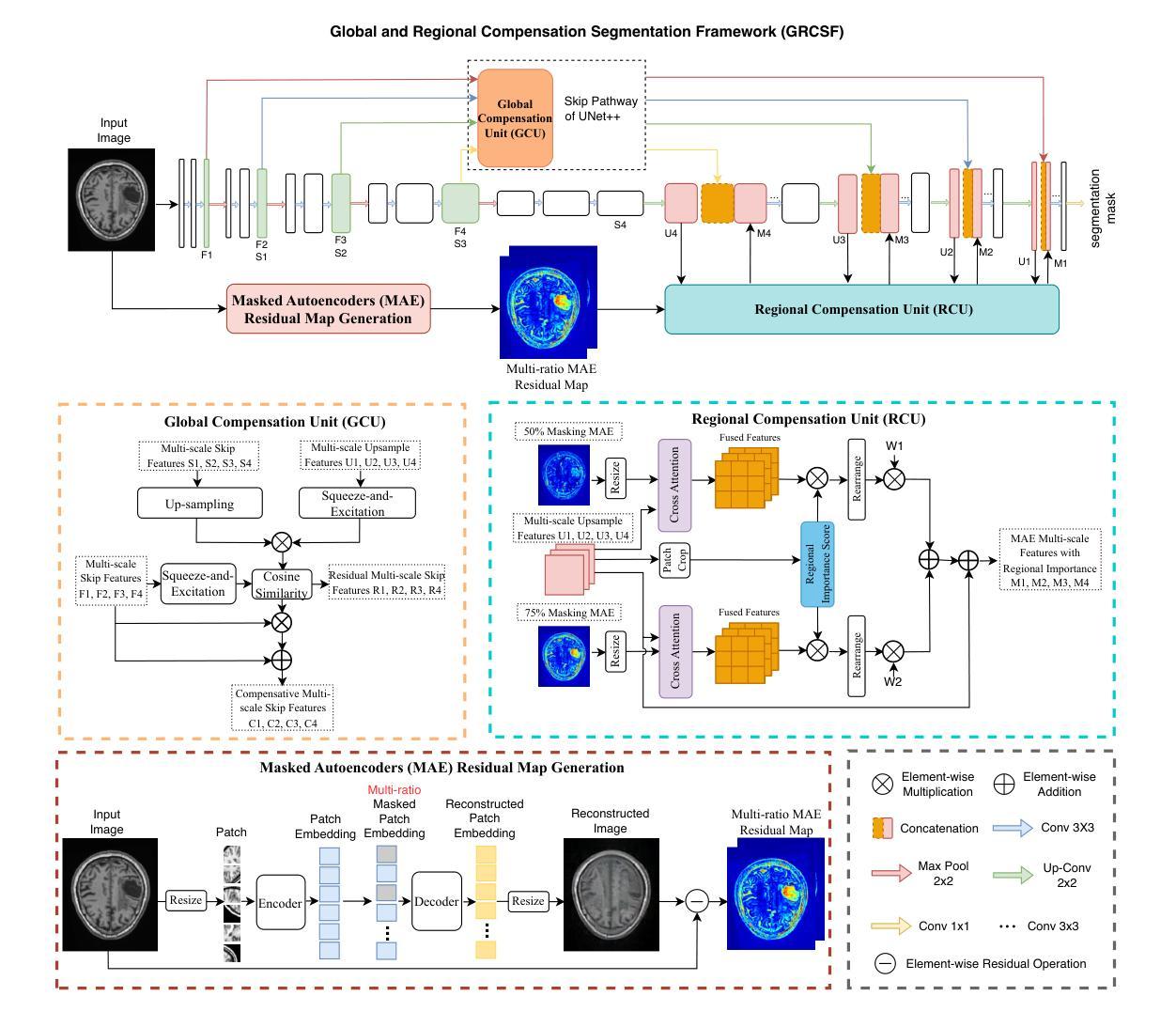
Improving Lesion Segmentation in Medical Images by Global and Regional Feature Compensation
Authors:Chuhan Wang, Zhenghao Chen, Jean Y. H. Yang, Jinman Kim
Automated lesion segmentation of medical images has made tremendous improvements in recent years due to deep learning advancements. However, accurately capturing fine-grained global and regional feature representations remains a challenge. Many existing methods obtain suboptimal performance on complex lesion segmentation due to information loss during typical downsampling operations and the insufficient capture of either regional or global features. To address these issues, we propose the Global and Regional Compensation Segmentation Framework (GRCSF), which introduces two key innovations: the Global Compensation Unit (GCU) and the Region Compensation Unit (RCU). The proposed GCU addresses resolution loss in the U-shaped backbone by preserving global contextual features and fine-grained details during multiscale downsampling. Meanwhile, the RCU introduces a self-supervised learning (SSL) residual map generated by Masked Autoencoders (MAE), obtained as pixel-wise differences between reconstructed and original images, to highlight regions with potential lesions. These SSL residual maps guide precise lesion localization and segmentation through a patch-based cross-attention mechanism that integrates regional spatial and pixel-level features. Additionally, the RCU incorporates patch-level importance scoring to enhance feature fusion by leveraging global spatial information from the backbone. Experiments on two publicly available medical image segmentation datasets, including brain stroke lesion and coronary artery calcification datasets, demonstrate that our GRCSF outperforms state-of-the-art methods, confirming its effectiveness across diverse lesion types and its potential as a generalizable lesion segmentation solution.
医学图像自动化病灶分割在最近几年由于深度学习的发展而取得了巨大的进步。然而,精准捕捉精细粒度的全局和局部特征表示仍然是一个挑战。由于典型的下采样操作过程中的信息损失以及对局部或全局特征的捕捉不足,许多现有方法在复杂病灶分割方面的表现并不理想。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了全球和区域补偿分割框架(GRCSF),它引入了两个关键的创新点:全球补偿单元(GCU)和区域补偿单元(RCU)。所提出的GCU通过在多尺度下采样过程中保留全局上下文特征和精细细节,解决了U形主干中的分辨率损失问题。同时,RCU引入了一种由Masked Autoencoders(MAE)生成的自监督学习(SSL)残差图,该图是通过重建图像和原始图像之间的像素级差异获得的,以突出潜在病灶区域。这些SSL残差图通过基于补丁的交叉注意力机制引导精确病灶定位和分割,该机制融合了局部空间特征和像素级特征。此外,RCU还结合了补丁级别的重要性评分,通过利用主干网络中的全局空间信息来增强特征融合。在包括脑卒中病灶和冠状动脉钙化数据集在内的两个公开可用的医学图像分割数据集上的实验表明,我们的GRCSF优于最新方法,证实了其在多种病灶类型中的有效性,以及其作为可推广的病灶分割解决方案的潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种名为全局与区域补偿分割框架(GRCSF)的方法,用于解决医学图像中精细粒度全局和区域特征表示捕捉的挑战。该框架包含两个关键创新点:全局补偿单元(GCU)和区域补偿单元(RCU)。GCU解决在U型骨干网络中的分辨率损失问题,通过多尺度下采样过程中保留全局上下文特征和精细细节。RCU则引入自监督学习(SSL)残差图,由Masked Autoencoders生成的像素级差异图突出潜在病变区域。这些SSL残差图通过基于补丁的交叉注意力机制引导精确病变定位和分割,融合区域空间特征和像素级特征。在公开可用的医学图像分割数据集上的实验结果表明,GRCSF方法优于当前主流方法,表现出对不同病变类型的良好泛化潜力。
Key Takeaways
- 深度学习在医学图像自动化病变分割方面取得巨大进步,但仍面临捕捉精细粒度全局和区域特征表示的难题。
- 现有方法在复杂病变分割上表现不佳,主要由于下采样操作中的信息损失以及对区域或全局特征捕捉不足。
- 提出Global and Regional Compensation Segmentation Framework (GRCSF),包含Global Compensation Unit (GCU) 和 Region Compensation Unit (RCU) 两个关键创新点。
- GCU解决U型骨干网络中的分辨率损失问题,通过多尺度下采样保留全局上下文特征和精细细节。
- RCU引入自监督学习(SSL)残差图,突出潜在病变区域,通过基于补丁的交叉注意力机制引导精确病变定位和分割。
点此查看论文截图

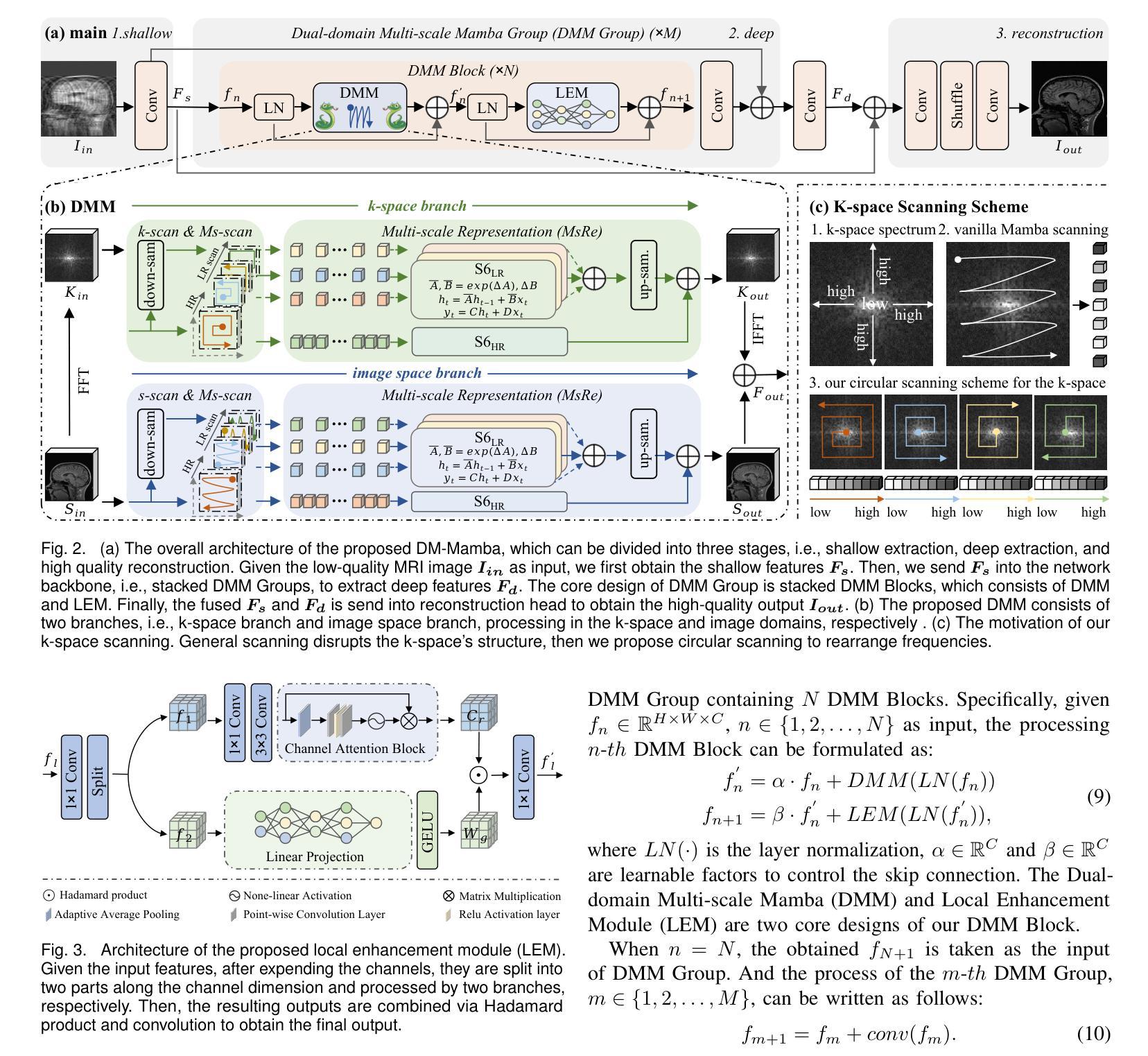
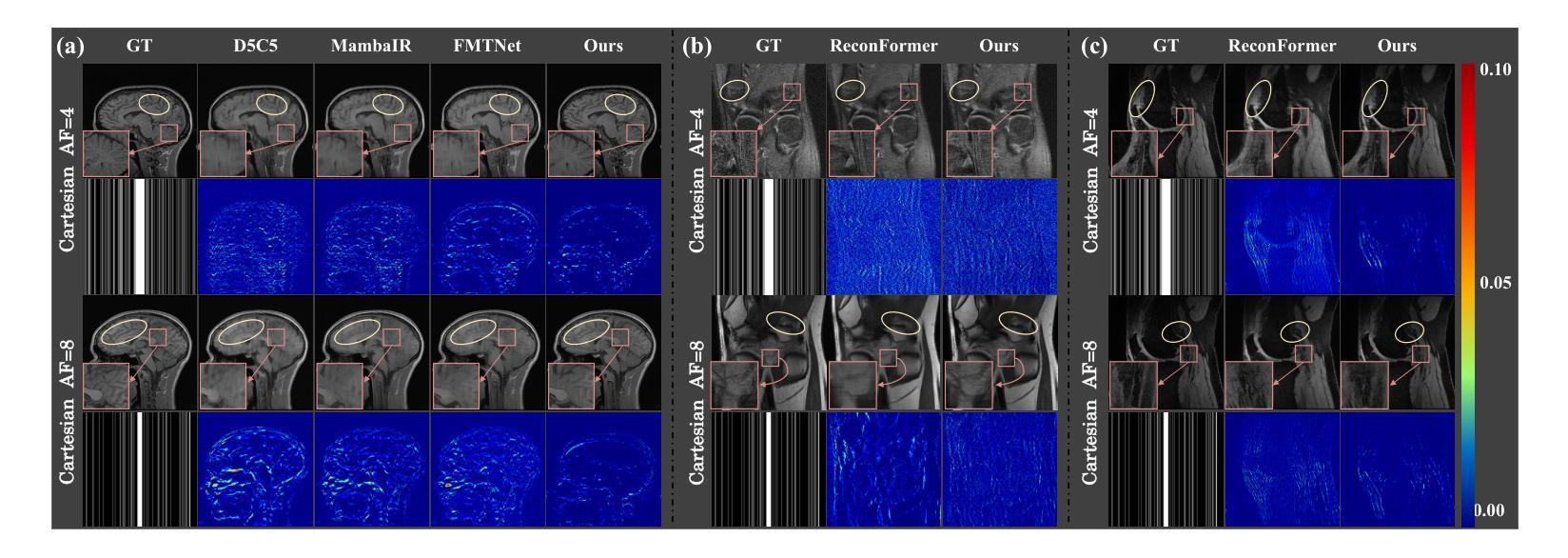
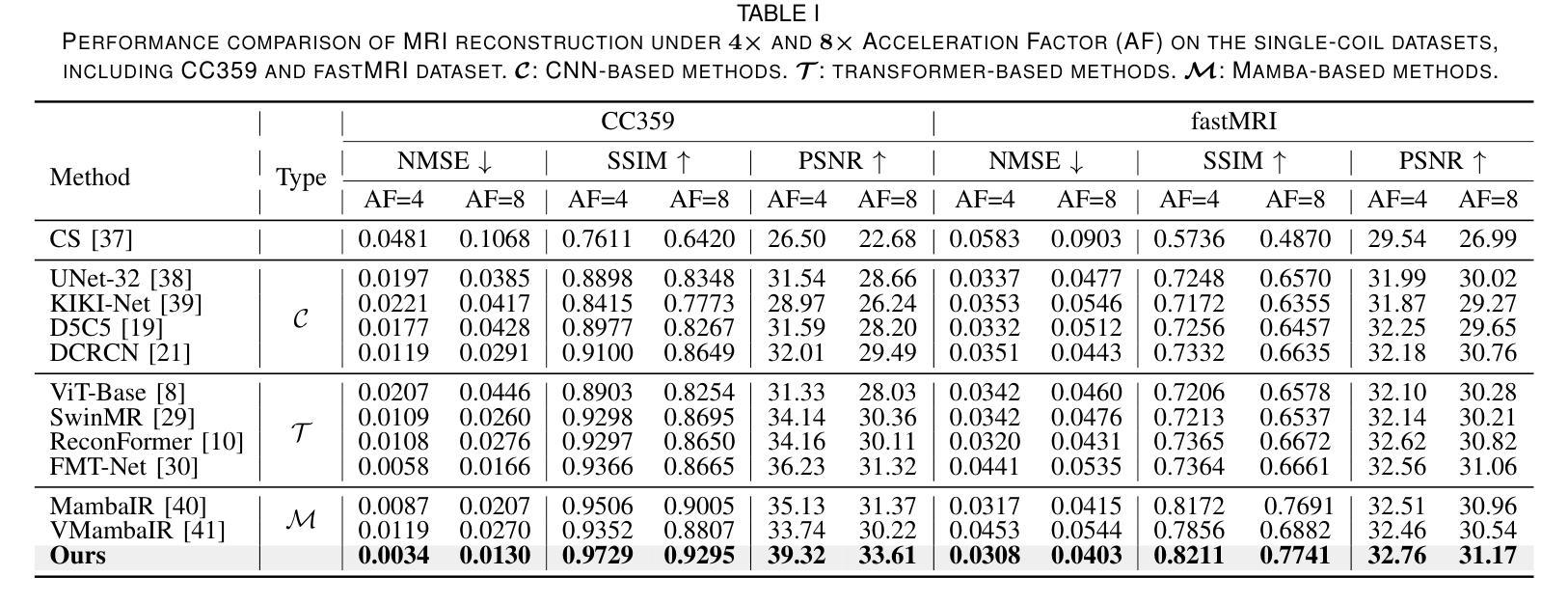
DM-Mamba: Dual-domain Multi-scale Mamba for MRI reconstruction
Authors:Yucong Meng, Zhiwei Yang, Zhijian Song, Yonghong Shi
The accelerated MRI reconstruction poses a challenging ill-posed inverse problem due to the significant undersampling in k-space. Deep neural networks, such as CNNs and ViT, have shown substantial performance improvements for this task while encountering the dilemma between global receptive fields and efficient computation. To this end, this paper pioneers exploring Mamba, a new paradigm for long-range dependency modeling with linear complexity, for efficient and effective MRI reconstruction. However, directly applying Mamba to MRI reconstruction faces three significant issues: (1) Mamba’s row-wise and column-wise scanning disrupts k-space’s unique spectrum, leaving its potential in k-space learning unexplored. (2) Existing Mamba methods unfold feature maps with multiple lengthy scanning paths, leading to long-range forgetting and high computational burden. (3) Mamba struggles with spatially-varying contents, resulting in limited diversity of local representations. To address these, we propose a dual-domain multi-scale Mamba for MRI reconstruction from the following perspectives: (1) We pioneer vision Mamba in k-space learning. A circular scanning is customized for spectrum unfolding, benefiting the global modeling of k-space. (2) We propose a multi-scale Mamba with an efficient scanning strategy in both image and k-space domains. It mitigates long-range forgetting and achieves a better trade-off between efficiency and performance. (3) We develop a local diversity enhancement module to improve the spatially-varying representation of Mamba. Extensive experiments are conducted on three public datasets for MRI reconstruction under various undersampling patterns. Comprehensive results demonstrate that our method significantly outperforms state-of-the-art methods with lower computational cost. Implementation code will be available at https://github.com/XiaoMengLiLiLi/DM-Mamba.
加速MRI重建是一个具有挑战性的不适定反问题,主要是因为k空间存在大量的欠采样。深度神经网络,如卷积神经网络(CNN)和Vision Transformer(ViT),在此任务上显示出显著的性能提升,但在全局感受野和高效计算之间遇到了困境。鉴于此,本文开创性地探索了Mamba,这是一种具有线性复杂度的长距离依赖建模新范式,用于高效且有效的MRI重建。然而,直接将Mamba应用于MRI重建面临三个主要问题:(1)Mamba的行扫描和列扫描破坏了k空间的独特频谱,使其对k空间学习的潜力尚未得到探索。(2)现有的Mamba方法展开特征映射具有多条冗长的扫描路径,导致长距离遗忘和高计算负担。(3)Mamba在空间内容变化方面遇到困难,导致局部表示多样性有限。为解决这些问题,我们从以下角度提出了用于MRI重建的双域多尺度Mamba:(1)我们开创性地提出了k空间中的视觉Mamba。针对频谱展开定制了循环扫描,有利于k空间的全局建模。(2)我们提出了一个在图像和k空间域都具有高效扫描策略的多尺度Mamba。它减轻了长距离遗忘问题,并在效率和性能之间取得了更好的平衡。(3)我们开发了一个局部多样性增强模块,以提高Mamba的空间变化表示。在三个公共数据集上进行了广泛的MRI重建实验,实验结果表明,我们的方法在较低的计算成本下显著优于最先进的方法。相关实现代码将发布在https://github.com/XiaoMengLiLiLi/DM-Mamba。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
这篇论文探讨了在MRI重建中的挑战性问题,针对k空间中显著的欠采样现象,提出了一种新的建模方法Mamba。尽管Mamba在解决长距离依赖建模方面具有线性复杂性的优势,但在直接应用于MRI重建时面临三个主要问题。为了克服这些问题,本文提出了一种双域多尺度Mamba方法,在k空间和图像域进行高效扫描策略,并开发了一个局部多样性增强模块来改善Mamba的空间变化表示。实验结果表明,该方法在降低计算成本的同时,显著优于现有技术。
关键见解
- Mamba作为一种新的长距离依赖建模方法,具有线性复杂性,在MRI重建中具有潜力。
- 直接应用Mamba于MRI重建面临三个主要问题:对k空间独特谱的干扰、特征映射展开路径过长以及空间内容变化导致的局部表示多样性有限。
- 提出了一种双域多尺度Mamba方法,首次在k空间中进行视觉Mamba学习,并定制了循环扫描以展开频谱,有利于全局k空间建模。
- 通过在图像和k空间域中采用高效扫描策略的多尺度Mamba,减轻了长距离遗忘问题,实现了效率和性能之间的更好权衡。
- 开发了局部多样性增强模块,提高了Mamba的空间变化表示。
- 在多个公共数据集上的实验表明,该方法在MRI重建方面显著优于现有技术,计算成本更低。
点此查看论文截图

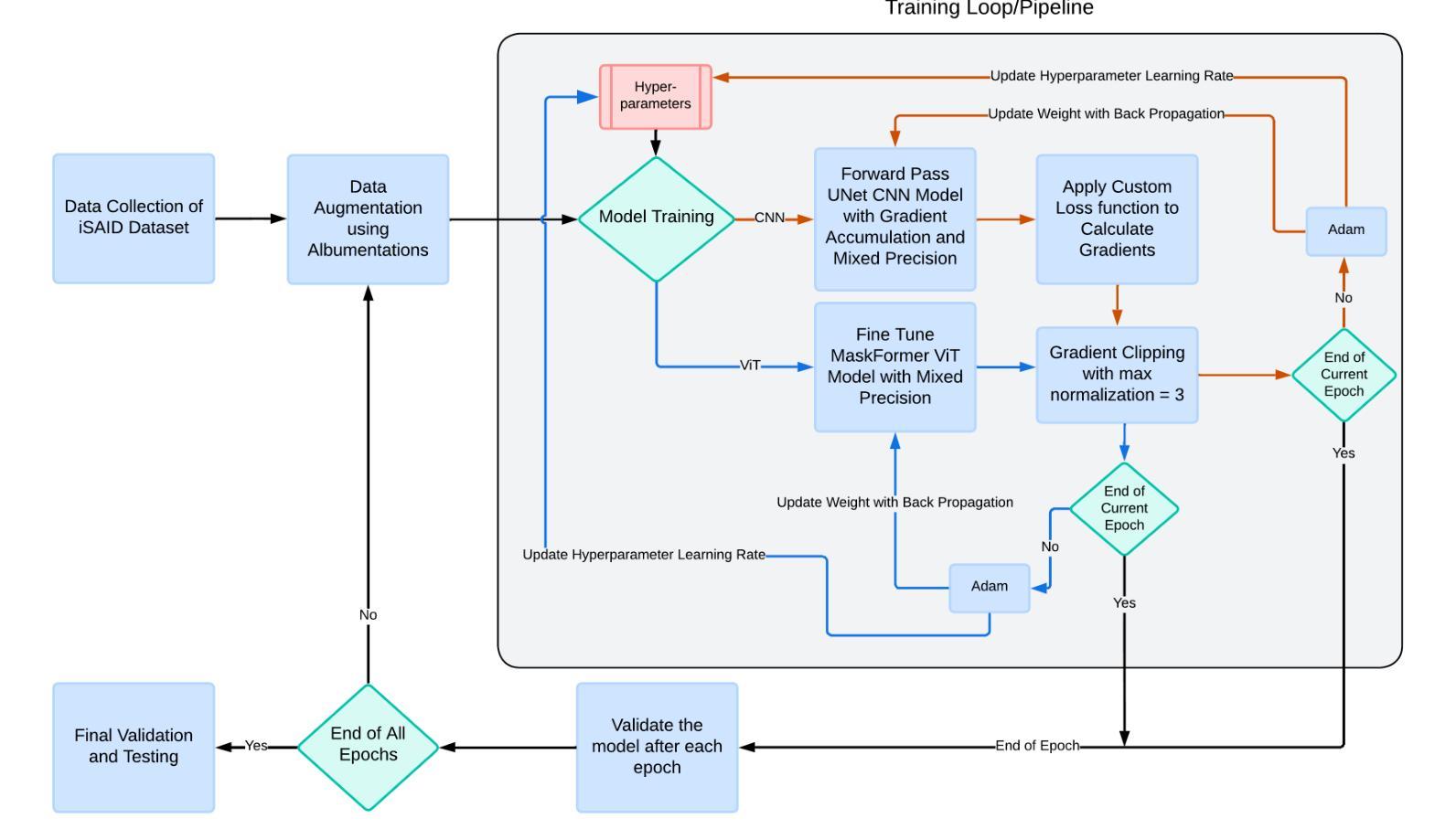
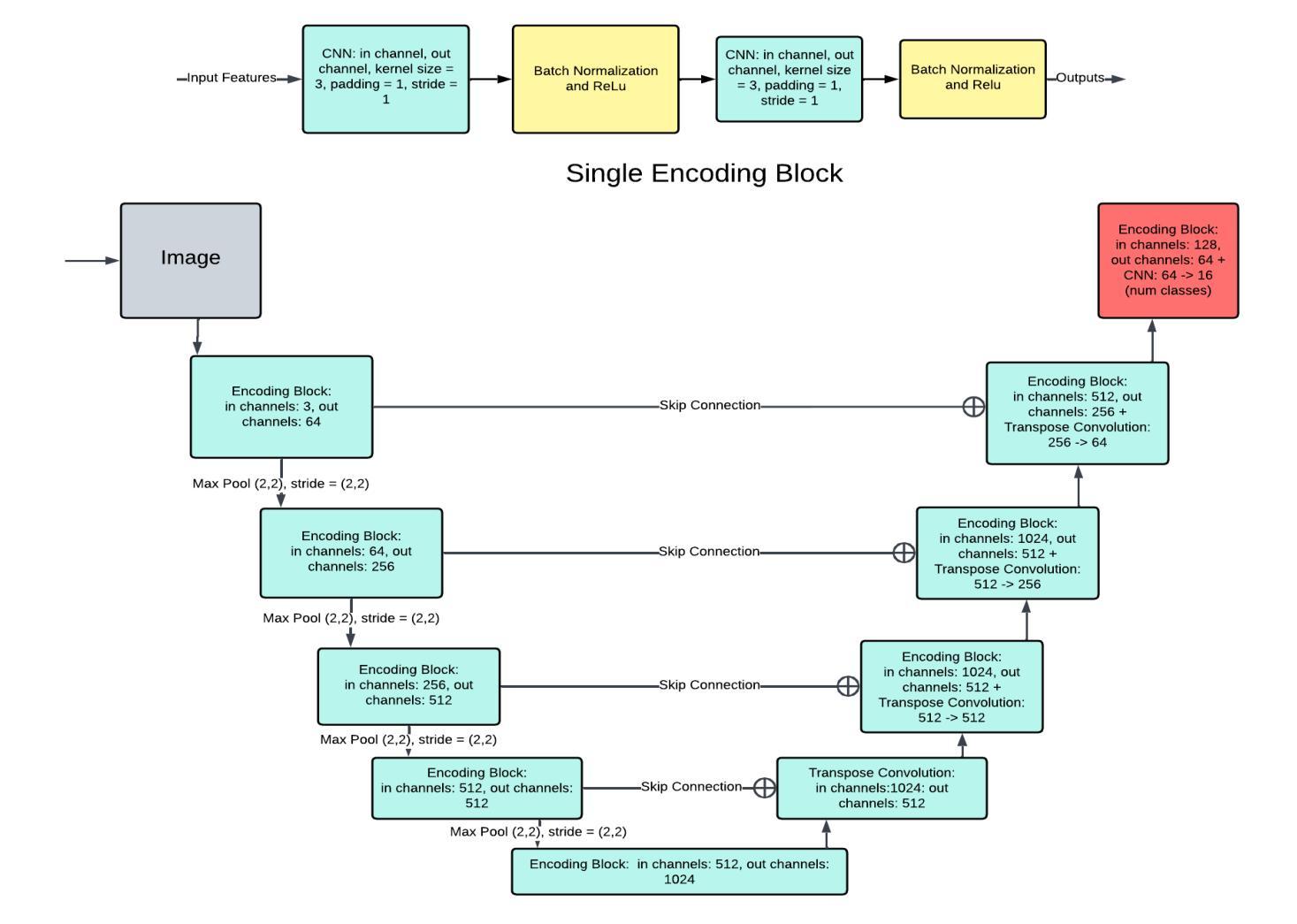
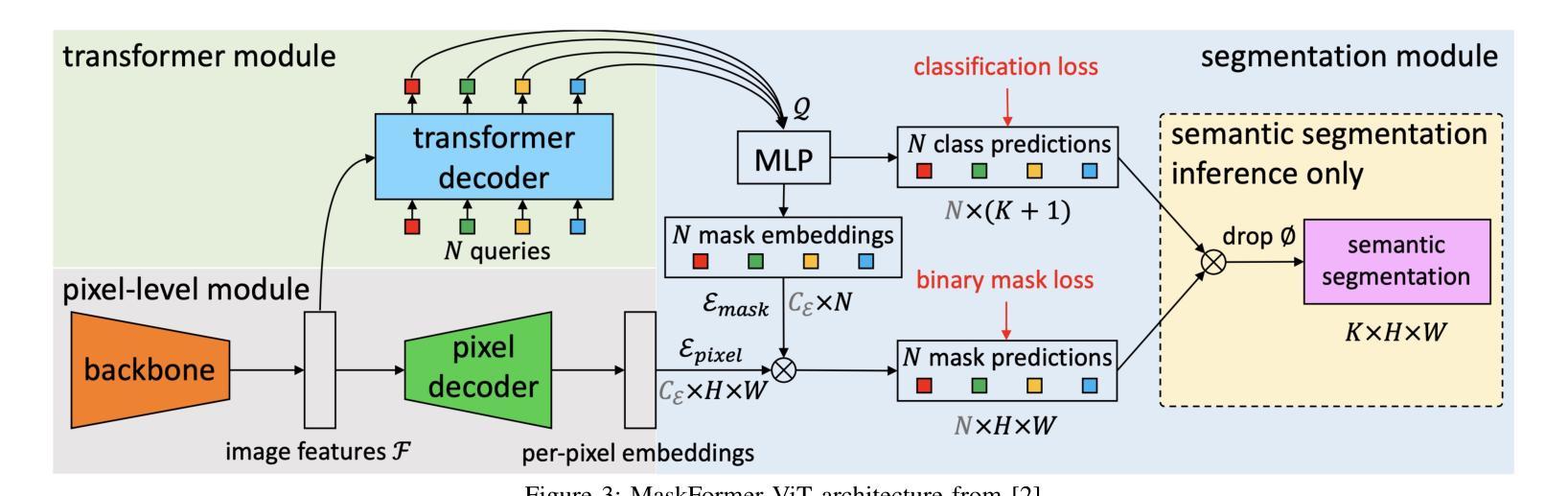
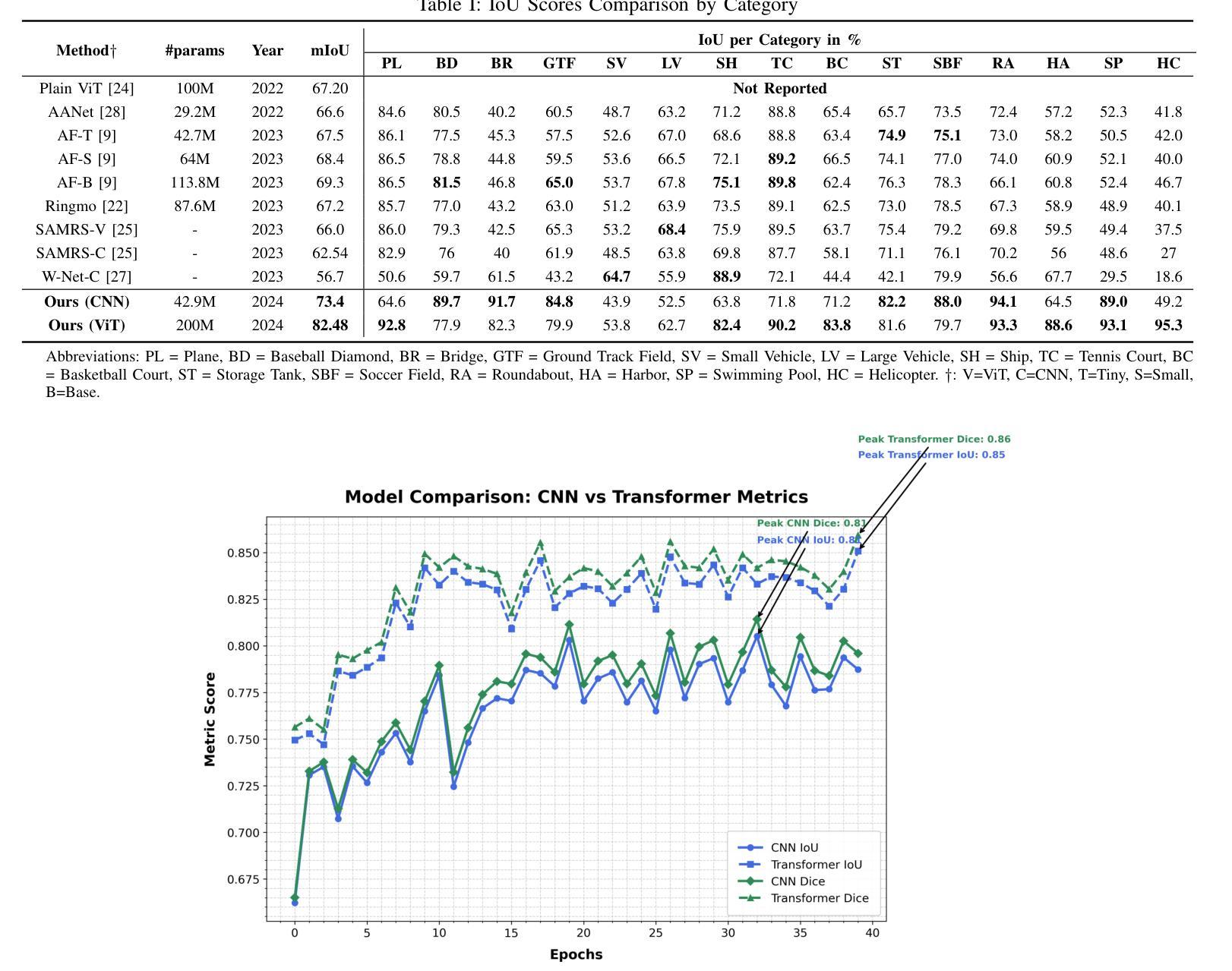
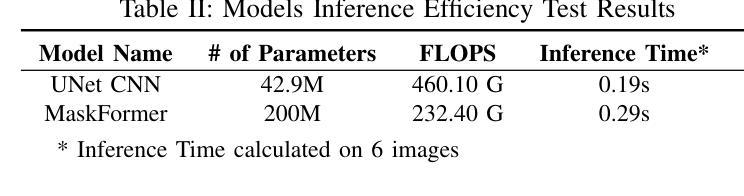
Heuristical Comparison of Vision Transformers Against Convolutional Neural Networks for Semantic Segmentation on Remote Sensing Imagery
Authors:Ashim Dahal, Saydul Akbar Murad, Nick Rahimi
Vision Transformers (ViT) have recently brought a new wave of research in the field of computer vision. These models have performed particularly well in image classification and segmentation. Research on semantic and instance segmentation has accelerated with the introduction of the new architecture, with over 80% of the top 20 benchmarks for the iSAID dataset based on either the ViT architecture or the attention mechanism behind its success. This paper focuses on the heuristic comparison of three key factors of using (or not using) ViT for semantic segmentation of remote sensing aerial images on the iSAID dataset. The experimental results observed during this research were analyzed based on three objectives. First, we studied the use of a weighted fused loss function to maximize the mean Intersection over Union (mIoU) score and Dice score while minimizing entropy or class representation loss. Second, we compared transfer learning on Meta’s MaskFormer, a ViT-based semantic segmentation model, against a generic UNet Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) based on mIoU, Dice scores, training efficiency, and inference time. Third, we examined the trade-offs between the two models in comparison to current state-of-the-art segmentation models. We show that the novel combined weighted loss function significantly boosts the CNN model’s performance compared to transfer learning with ViT. The code for this implementation can be found at: https://github.com/ashimdahal/ViT-vs-CNN-Image-Segmentation.
Vision Transformers(ViT)最近为计算机视觉领域带来了新的研究浪潮。这些模型在图像分类和分割方面表现出色。新架构的引入加速了语义分割和实例分割的研究,iSAID数据集的前20个榜单中有超过80%是基于ViT架构或其成功背后的注意力机制。本文重点关注在iSAID数据集上使用(或不使用)ViT进行遥感图像语义分割的三个关键因素的启发式比较。研究过程中的实验结果基于以下三个目标进行分析。首先,我们研究了使用加权融合损失函数,以最大化平均交并比(mIoU)得分和Dice得分,同时最小化��e或类表示损失。其次,我们比较了Meta的MaskFormer(一种基于ViT的语义分割模型)的迁移学习与基于mIoU、Dice得分、训练效率和推理时间的通用UNet卷积神经网络(CNN)的迁移学习。第三,我们比较了这两种模型与当前最先进的分割模型的得失。我们表明,与ViT的迁移学习相比,新型组合加权损失函数显著提高了CNN模型的性能。该实现的代码可在以下网址找到:https://github.com/ashimdahal/ViT-vs-CNN-Image-Segmentation。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文研究了使用Vision Transformers(ViT)进行遥感图像语义分割的优缺点,并对比了ViT架构和基于注意力机制的模型在iSAID数据集上的表现。文章重点探讨了三个关键方面:使用加权融合损失函数的效果、与基于ViT的MaskFormer模型的迁移学习对比,以及与传统CNN模型的性能对比。实验结果表明,加权损失函数能有效提升CNN模型性能,相较于ViT迁移学习有更好的表现。
Key Takeaways
Vision Transformers(ViT)在图像分类和分割领域表现优异,已成为计算机视觉领域的新研究热点。
iSAID数据集的前20名榜单中,超过80%是基于ViT架构或注意力机制的模型。
加权融合损失函数用于最大化平均交并比(mIoU)和Dice系数,同时最小化熵或类别表示损失。
对比了基于ViT的MaskFormer模型和通用UNet卷积神经网络(CNN)在mIoU、Dice系数、训练效率和推理时间上的表现。
加权损失函数显著提升CNN模型性能,相较于ViT迁移学习有更好的表现。
研究结果提供了遥感图像语义分割的新视角和方法论。
点此查看论文截图
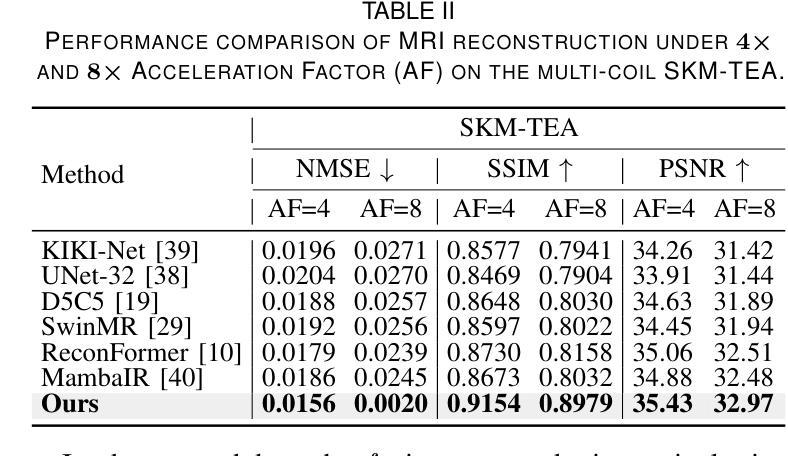
A Unified Model for Compressed Sensing MRI Across Undersampling Patterns
Authors:Armeet Singh Jatyani, Jiayun Wang, Aditi Chandrashekar, Zihui Wu, Miguel Liu-Schiaffini, Bahareh Tolooshams, Anima Anandkumar
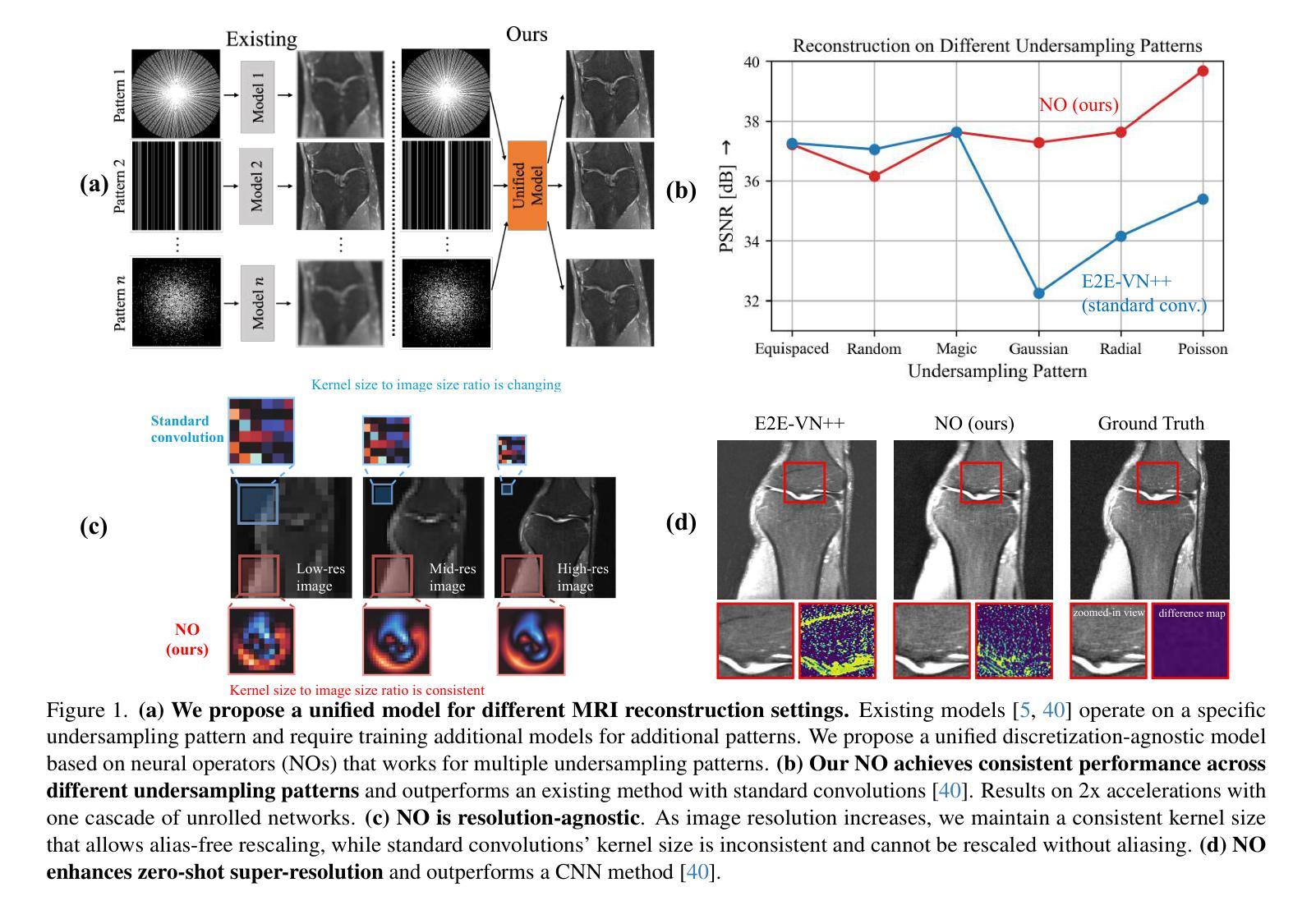
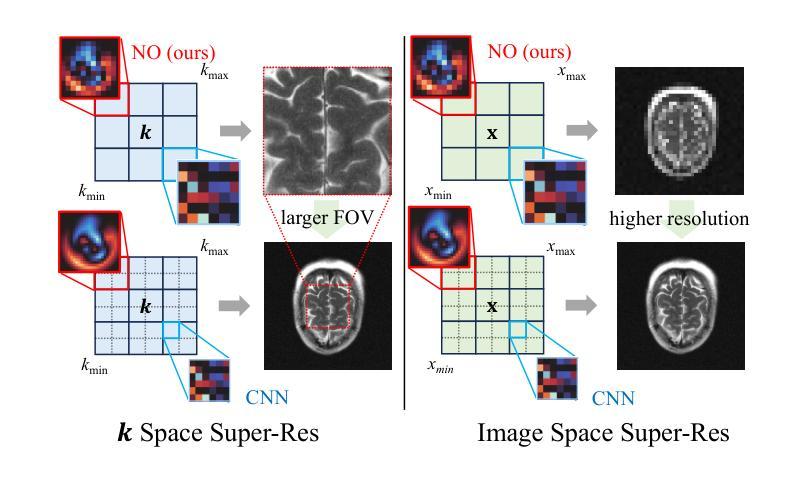
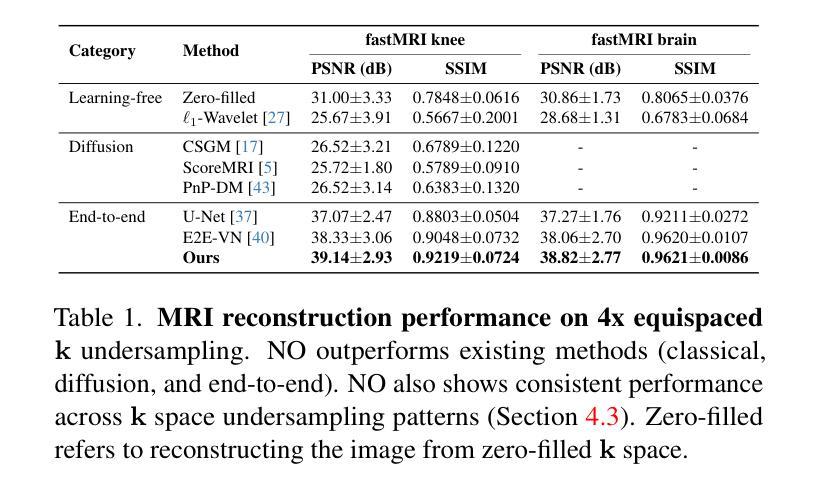
Compressed Sensing MRI reconstructs images of the body’s internal anatomy from undersampled measurements, thereby reducing the scan time - the time subjects need to remain still. Recently, deep neural networks have shown great potential for reconstructing high-fidelity images from highly undersampled measurements in the frequency space. However, one needs to train multiple models for different undersampling patterns and desired output image resolutions, since most networks operate on a fixed discretization. Such approaches are highly impractical in clinical settings, where undersampling patterns and image resolutions are frequently changed to accommodate different real-time imaging and diagnostic requirements. We propose a unified model robust to different measurement undersampling patterns and image resolutions in compressed sensing MRI. Our model is based on neural operators, a discretization-agnostic architecture. Neural operators are employed in both image and measurement space, which capture local and global image features for MRI reconstruction. Empirically, we achieve consistent performance across different undersampling rates and patterns, with an average 11 percent SSIM and 4dB PSNR improvement over a state-of-the-art CNN, End-to-End VarNet. For efficiency, our inference speed is also 1,400x faster than diffusion methods. The resolution-agnostic design also enhances zero-shot super-resolution and extended field of view in reconstructed images. Our unified model offers a versatile solution for MRI, adapting seamlessly to various measurement undersampling and imaging resolutions, making it highly effective for flexible and reliable clinical imaging. Our code is available at https://armeet.ca/nomri.
压缩感知MRI通过欠采样的测量重建人体内部解剖图像,从而减少扫描时间——即患者需要保持静止的时间。最近,深度神经网络在频率空间从高度欠采样的测量中重建高保真图像方面显示出巨大潜力。然而,由于大多数网络在固定的离散化上运行,因此需要针对不同的欠采样模式和所需的输出图像分辨率训练多个模型。在临床环境中,欠采样模式和图像分辨率经常更改以适应不同的实时成像和诊断要求,因此这种方法不太实用。我们提出了一种适用于压缩感知MRI中不同测量欠采样模式和图像分辨率的统一模型。我们的模型基于神经算子,这是一种不受离散化影响的架构。神经算子在图像和测量空间中都被采用,能够捕捉MRI重建的局部和全局图像特征。从经验上看,我们在不同的欠采样率和模式上实现了稳定的性能,与最先进的CNN End-to-End VarNet相比,平均SSIM提高了11%,PSNR提高了4dB。为了提高效率,我们的推理速度也比扩散方法快1400倍。分辨率无关的设计还提高了重建图像的零射击超分辨率和扩展视野。我们的统一模型为MRI提供了一个通用解决方案,可以无缝适应各种测量欠采样和成像分辨率,使其成为灵活可靠的临床成像的高效工具。我们的代码可在https://armeet.ca/nomri获取。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于压缩感知的MRI通过欠采样的测量重建身体内部结构图像,减少了扫描时间。近期深度神经网络在频率空间高度欠采样的测量重建高保真图像方面展现出巨大潜力。然而,大多数网络在固定离散化上操作,需要针对不同的欠采样模式和所需的输出图像分辨率训练多个模型,这在临床环境中非常不实用。我们提出一种统一的模型,适应不同的测量欠采样模式和图像分辨率。该模型基于神经算子,是一种不受离散化影响的架构。神经算子在图像和测量空间中均被采用,可捕捉局部和全局图像特征用于MRI重建。与当前先进技术相比,我们的模型在不同的欠采样率和模式上表现一致,平均SSIM提高11%,PSNR提高4dB。同时,我们的推理速度比扩散方法快1400倍。分辨率无关的设计还提高了重建图像的零射束超分辨率和扩展视野。我们的统一模型为MRI提供了通用解决方案,可轻松适应各种测量欠采样和成像分辨率,为临床成像提供了灵活可靠的选择。
Key Takeaways
- 压缩感知MRI可从欠采样测量重建图像,缩短扫描时间。
- 深度神经网络在重建高频空间高度欠采样的图像方面表现出巨大潜力。
- 现有方法需要在不同欠采样模式和输出图像分辨率上训练多个模型,缺乏实用性。
- 提出一种基于神经算子的统一模型,适应不同的测量欠采样模式和图像分辨率。
- 该模型在多种欠采样情况下表现稳定,相较于先进技术有显著的SSIM和PSNR提升。
- 模型推理速度显著提高,且具备零射束超分辨率和扩展视野能力。
点此查看论文截图


Fully Unsupervised Dynamic MRI Reconstruction via Diffeo-Temporal Equivariance
Authors:Andrew Wang, Mike Davies
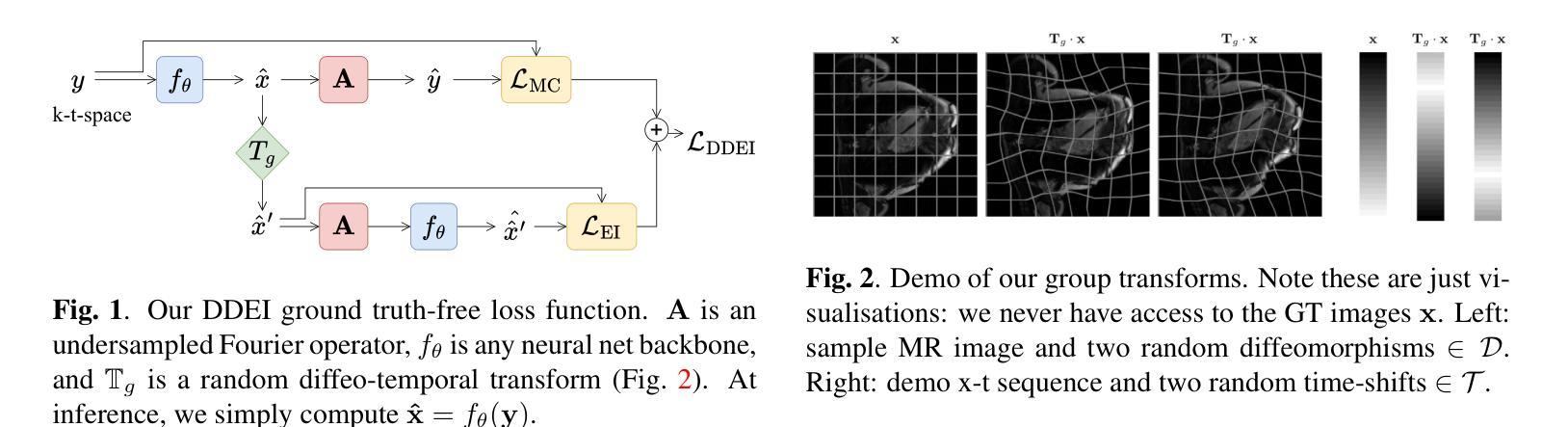
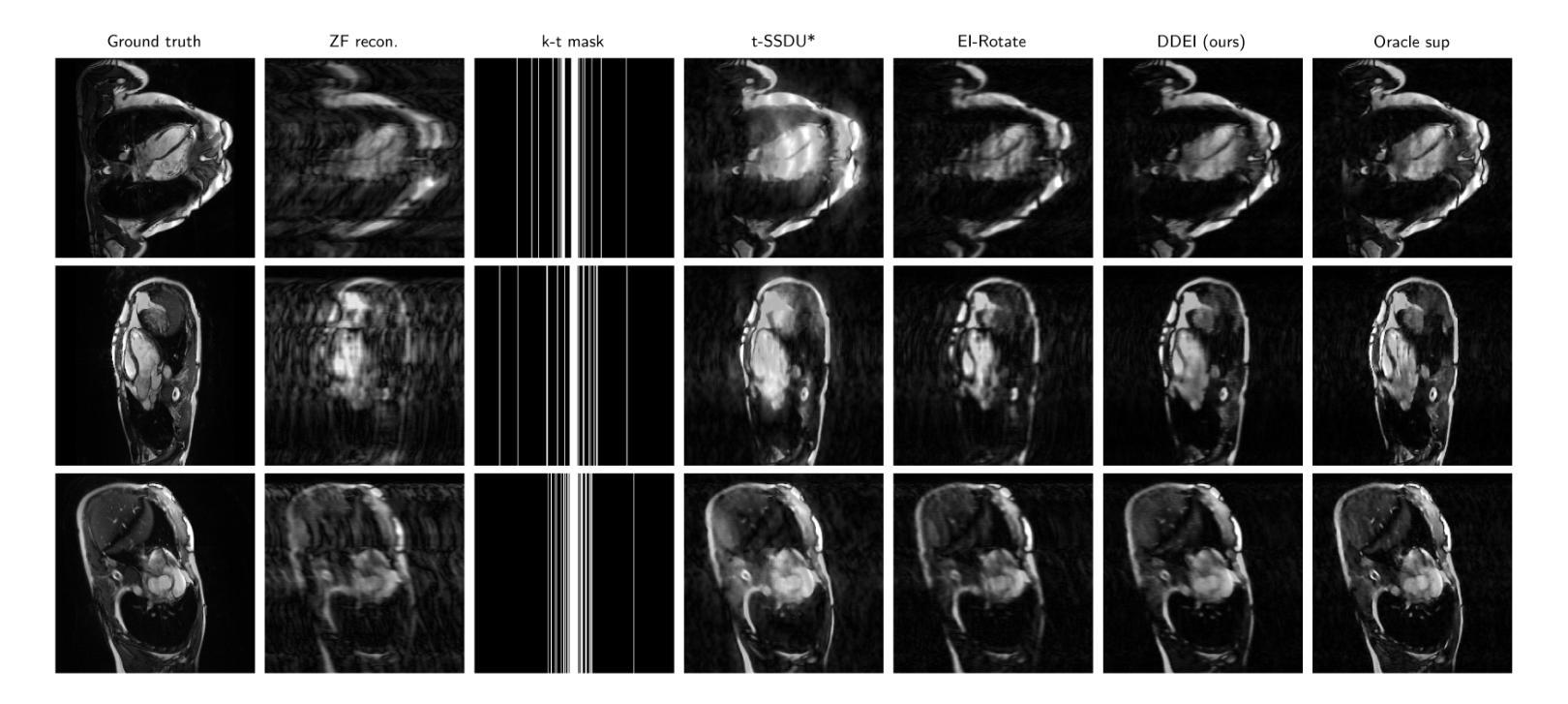
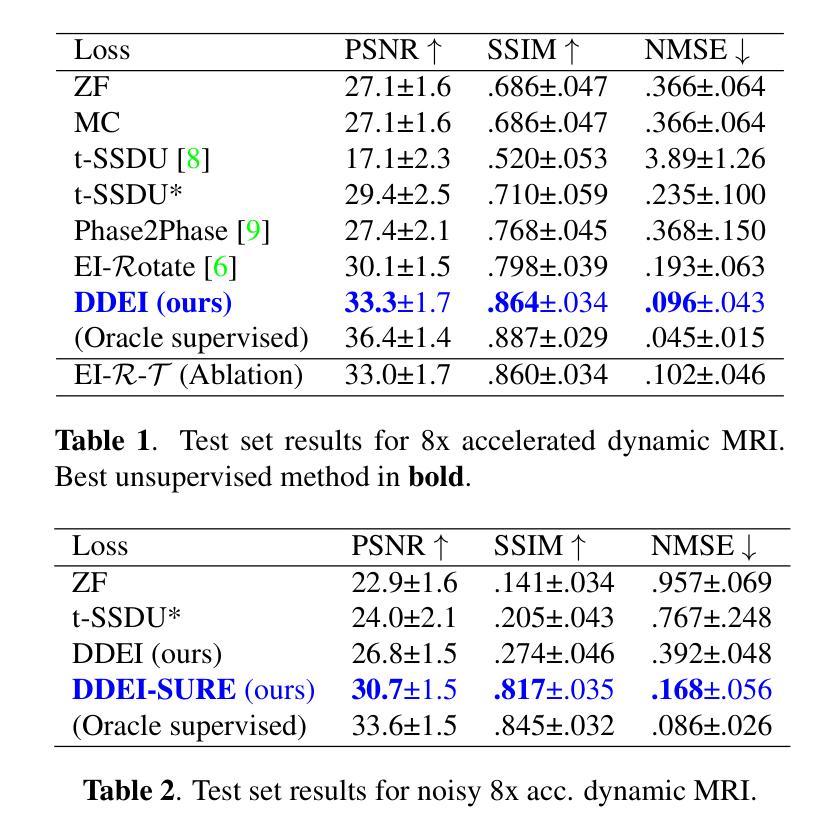
Reconstructing dynamic MRI image sequences from undersampled accelerated measurements is crucial for faster and higher spatiotemporal resolution real-time imaging of cardiac motion, free breathing motion and many other applications. Classical paradigms, such as gated cine MRI, assume periodicity, disallowing imaging of true motion. Supervised deep learning methods are fundamentally flawed as, in dynamic imaging, ground truth fully-sampled videos are impossible to truly obtain. We propose an unsupervised framework to learn to reconstruct dynamic MRI sequences from undersampled measurements alone by leveraging natural geometric spatiotemporal equivariances of MRI. Dynamic Diffeomorphic Equivariant Imaging (DDEI) significantly outperforms state-of-the-art unsupervised methods such as SSDU on highly accelerated dynamic cardiac imaging. Our method is agnostic to the underlying neural network architecture and can be used to adapt the latest models and post-processing approaches. Our code and video demos are at https://github.com/Andrewwango/ddei.
从欠采样的加速测量值重建动态MRI图像序列对于更快、更高时空分辨率的实时心脏运动成像、自由呼吸运动成像以及许多其他应用至关重要。经典的模式,如门控电影MRI,假设周期性,不允许对真实运动进行成像。监督深度学习方法存在根本缺陷,因为在动态成像中,不可能真正获得完全采样的地面真实视频。我们提出了一种无监督的框架,通过利用MRI的自然几何时空等价性,仅从欠采样测量中学习重建动态MRI序列。动态微分等价成像(DDEI)在高度加速的动态心脏成像方面显著优于最新无监督方法如SSDU。我们的方法与底层神经网络架构无关,可用于适应最新模型和后期处理方法。我们的代码和视频演示可在https://github.com/Andrewwango/ddei查看。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Conference paper at ISBI 2025
Summary
从欠采样的加速测量中重建动态MRI图像序列对于更快、更高时空分辨率的实时心脏运动成像、自由呼吸运动成像以及许多其他应用至关重要。现有的方法如门控电影MRI存在周期性假设,无法真正成像。由于无法获取动态成像的真实地面全采样视频,监督深度学习方法存在根本缺陷。我们提出了一种利用MRI自然几何时空等价性的无监督框架来重建动态MRI序列。动态微分等价成像(DDEI)在高度加速的动态心脏成像上显著优于最先进的状态无监督方法,如SSDU。我们的方法不依赖于底层神经网络架构,可用于适应最新模型和后期处理方法。我们的代码和视频演示可在https://github.com/Andrewwango/ddei查看。
Key Takeaways
- 动态MRI图像序列重建是加快实时成像速度和提高时空分辨率的关键。
- 传统方法存在周期性假设问题,无法真正捕捉运动状态。
- 由于无法获取真实的地面全采样视频,监督深度学习方法存在根本问题。
- 提出了一种无监督框架,利用MRI的自然几何时空等价性进行重建。
- 动态微分等价成像(DDEI)在高度加速的动态心脏成像上表现优异。
- DDEI方法具有通用性,不依赖于特定的神经网络架构,可适应最新模型和后期处理方法。
点此查看论文截图

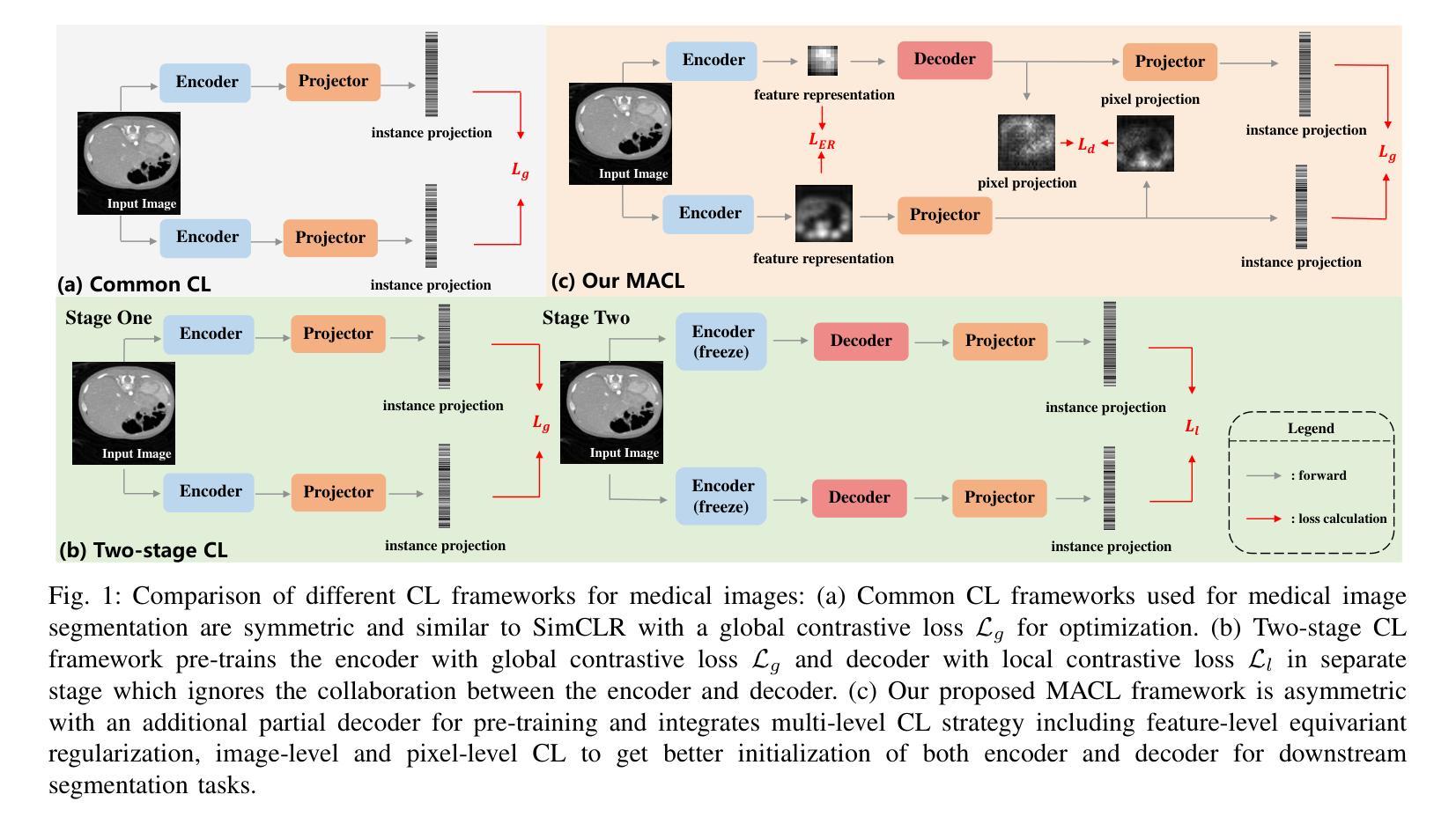
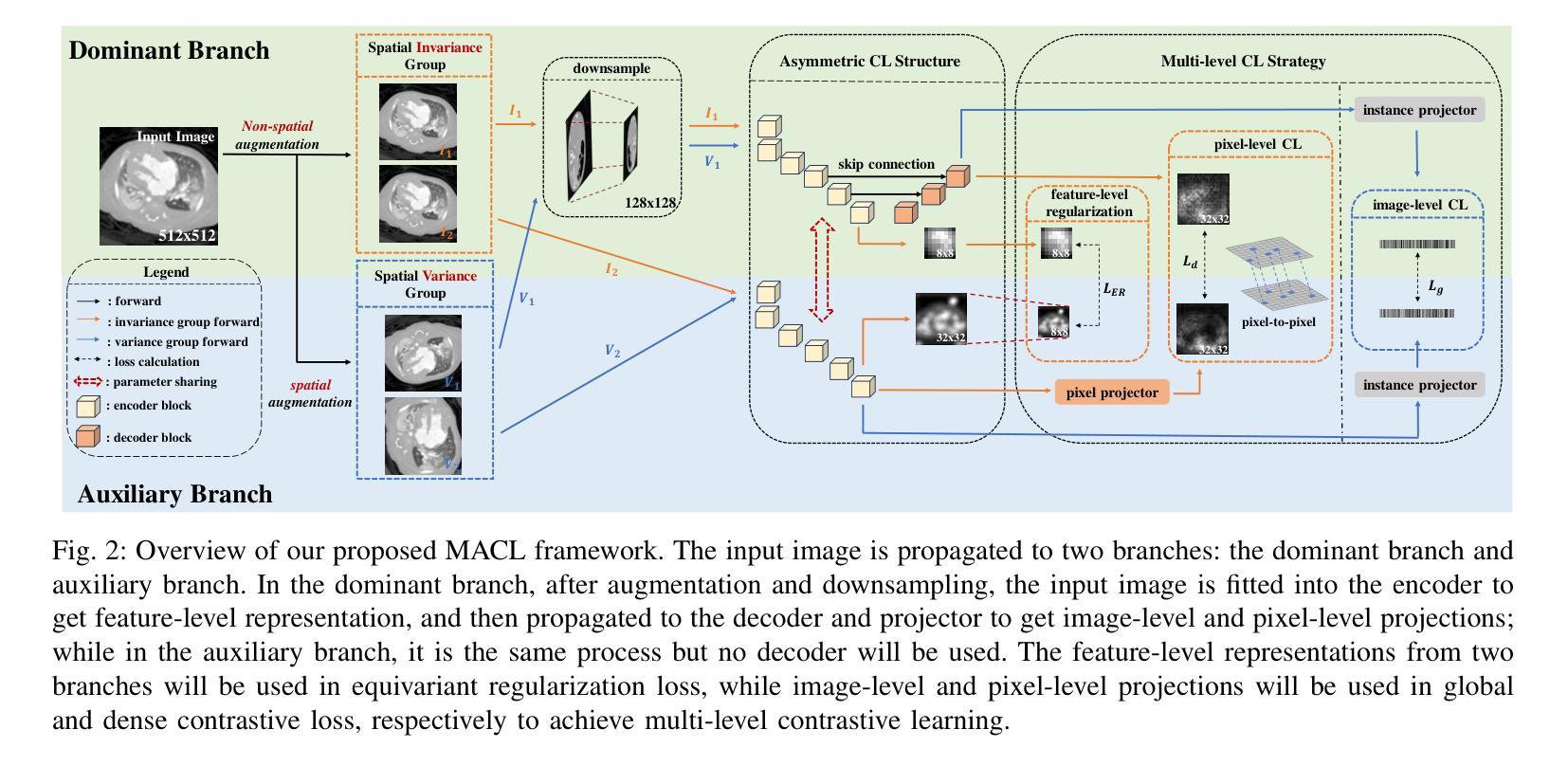
Multi-level Asymmetric Contrastive Learning for Volumetric Medical Image Segmentation Pre-training
Authors:Shuang Zeng, Lei Zhu, Xinliang Zhang, Micky C Nnamdi, Wenqi Shi, J Ben Tamo, Qian Chen, Hangzhou He, Lujia Jin, Zifeng Tian, Qiushi Ren, Zhaoheng Xie, Yanye Lu
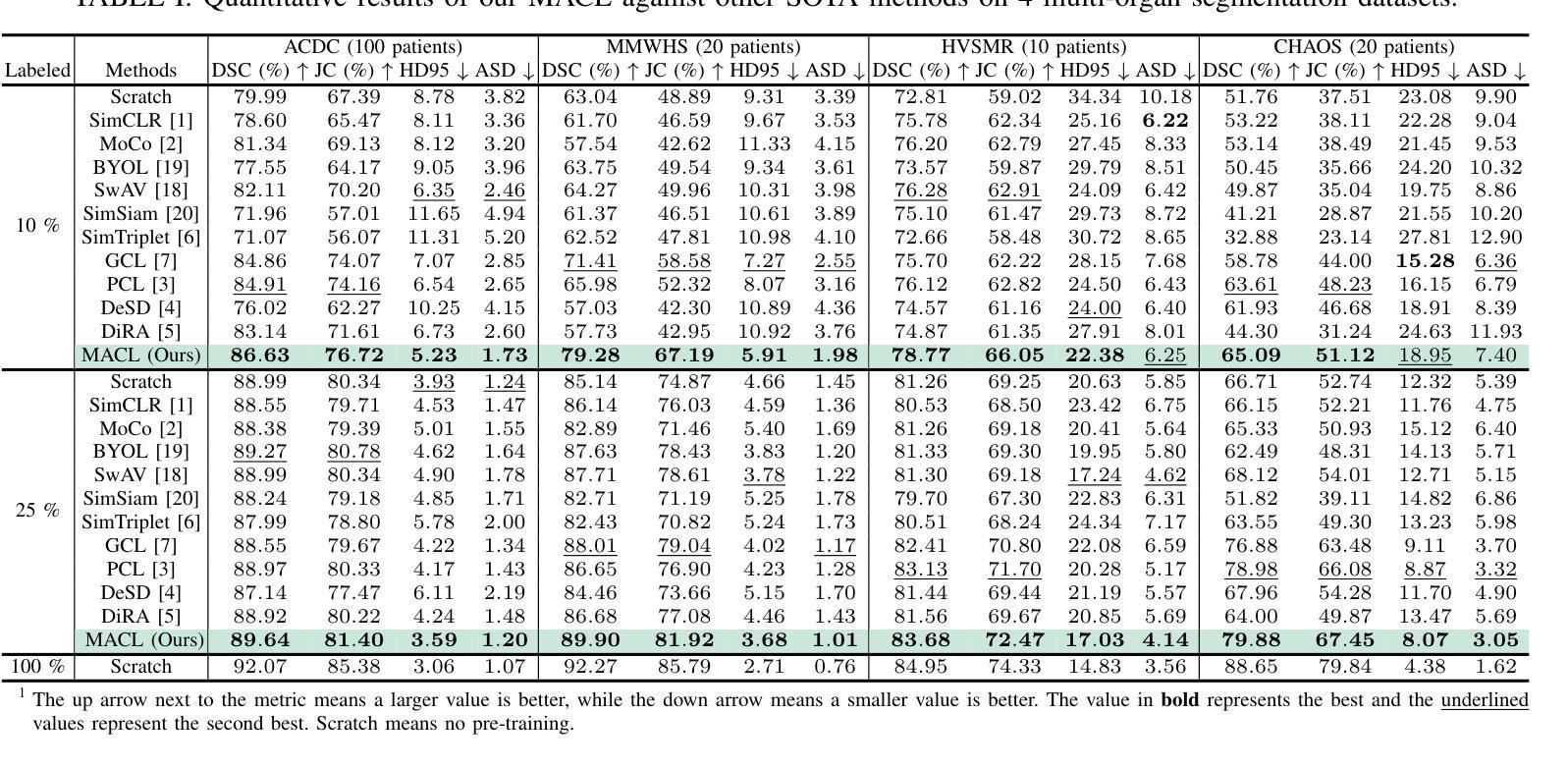
Medical image segmentation is a fundamental yet challenging task due to the arduous process of acquiring large volumes of high-quality labeled data from experts. Contrastive learning offers a promising but still problematic solution to this dilemma. Firstly existing medical contrastive learning strategies focus on extracting image-level representation, which ignores abundant multi-level representations. Furthermore they underutilize the decoder either by random initialization or separate pre-training from the encoder, thereby neglecting the potential collaboration between the encoder and decoder. To address these issues, we propose a novel multi-level asymmetric contrastive learning framework named MACL for volumetric medical image segmentation pre-training. Specifically, we design an asymmetric contrastive learning structure to pre-train encoder and decoder simultaneously to provide better initialization for segmentation models. Moreover, we develop a multi-level contrastive learning strategy that integrates correspondences across feature-level, image-level, and pixel-level representations to ensure the encoder and decoder capture comprehensive details from representations of varying scales and granularities during the pre-training phase. Finally, experiments on 8 medical image datasets indicate our MACL framework outperforms existing 11 contrastive learning strategies. i.e. Our MACL achieves a superior performance with more precise predictions from visualization figures and 1.72%, 7.87%, 2.49% and 1.48% Dice higher than previous best results on ACDC, MMWHS, HVSMR and CHAOS with 10% labeled data, respectively. And our MACL also has a strong generalization ability among 5 variant U-Net backbones. Our code will be released at https://github.com/stevezs315/MACL.
医学图像分割是一项基础且具有挑战性的任务,主要是因为从专家那里获取大量高质量标记数据的艰巨过程。对比学习为解决这一困境提供了有前景但仍有问题的解决方案。首先,现有的医学对比学习策略侧重于提取图像级别的表示,这忽略了丰富的多层次表示。此外,它们对解码器的利用不足,要么是通过随机初始化,要么是编码器独立进行预训练,从而忽略了编码器和解码器之间的潜在协作。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了一种名为MACL的新型多层次不对称对比学习框架,用于医学图像分割的预训练。具体来说,我们设计了一种不对称对比学习结构,可以同时对编码器和解码器进行预训练,为分割模型提供更好的初始化。此外,我们开发了一种多层次对比学习策略,该策略结合了特征级别、图像级别和像素级别表示之间的对应关系,以确保编码器和解码器在预训练阶段捕获不同规模和粒度的表示中的综合细节。最后,在8个医学图像数据集上的实验表明,我们的MACL框架优于现有的11种对比学习策略。例如,使用我们的MACL,可视化图预测更准确,在ACDC、MMWHS、HVSMR和CHAOS数据集上分别比之前的最佳结果高出1.72%、7.87%、2.49%和1.48%。我们的MACL还具有在5种变体U-Net骨干网中强大的泛化能力。我们的代码将在https://github.com/stevezs315/MACL上发布。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
医学图像分割是一项基础且具挑战性的任务,主要由于获取大量高质量专家标注数据的困难。对比学习为此提供了有前景的解决方案,但现有医学对比学习策略主要关注图像级别的表示,忽略了多级别的丰富表示。此外,他们未充分利用解码器,或与编码器进行独立预训练,忽视了二者的协作潜力。针对这些问题,我们提出了名为MACL的体积医学图像分割预训练的多级别不对称对比学习框架。我们设计了不对称对比学习结构,同时预训练编码器和解码器,为分割模型提供更好的初始化。同时,我们发展了多级别对比学习策略,整合特征级别、图像级别和像素级别表示的对应关系,确保编码器和解码器在预训练阶段捕获不同尺度和粒度的综合细节。在8个医学图像数据集上的实验表明,我们的MACL框架优于现有的11种对比学习策略,具有更精确预测和更高的Dice系数。
Key Takeaways
- 医学图像分割面临获取高质量标注数据的挑战。
- 现有对比学习策略主要关注图像级别表示,忽略了多级别表示。
- MACL框架通过不对称对比学习结构同时预训练编码器和解码器。
- MACL采用多级别对比学习策略,整合不同级别的表示对应关系。
- MACL在多个医学图像数据集上表现优越,具有更高的Dice系数和更精确的预测。
- MACL框架具有强大的泛化能力,适用于多种U-Net变体。
点此查看论文截图