⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-02-17 更新
TokenSynth: A Token-based Neural Synthesizer for Instrument Cloning and Text-to-Instrument
Authors:Kyungsu Kim, Junghyun Koo, Sungho Lee, Haesun Joung, Kyogu Lee
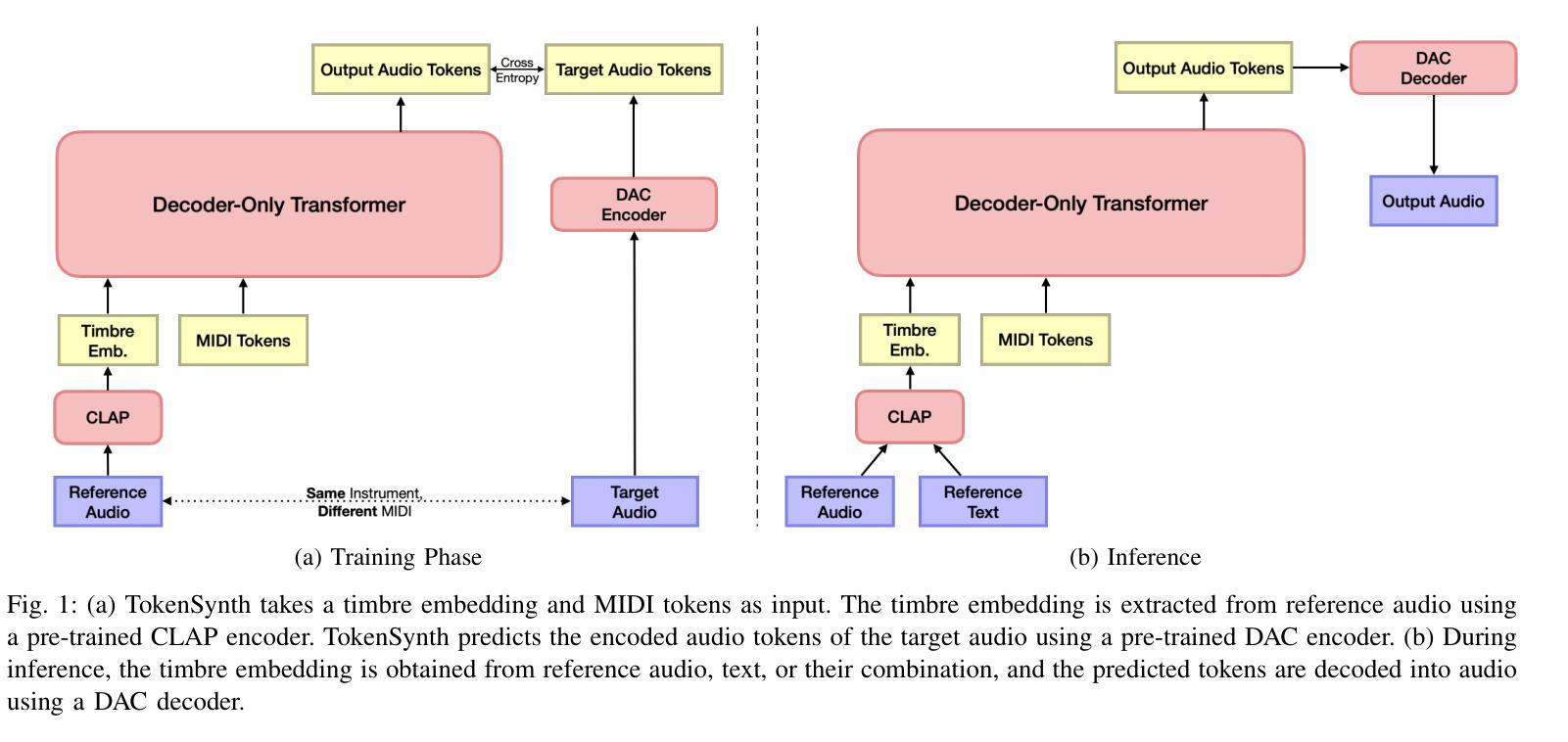
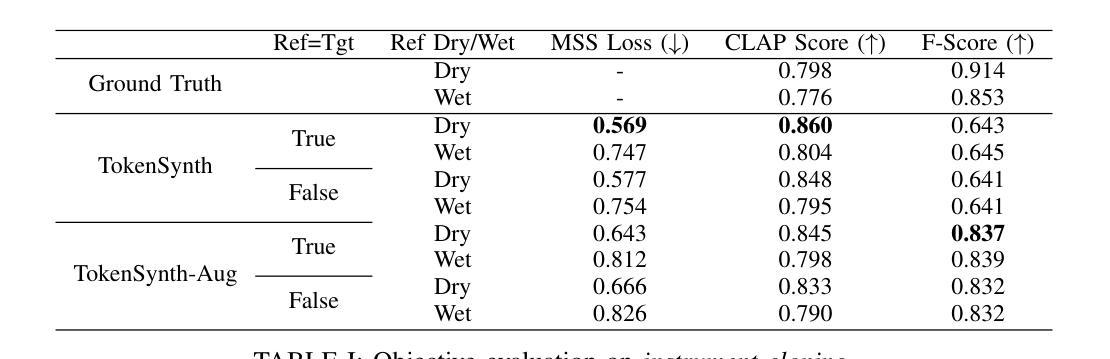
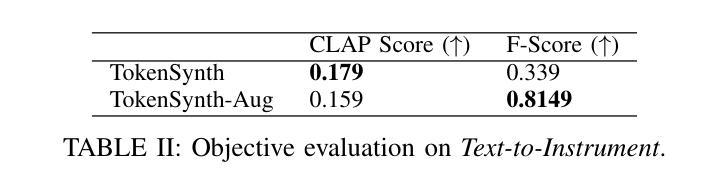
Recent advancements in neural audio codecs have enabled the use of tokenized audio representations in various audio generation tasks, such as text-to-speech, text-to-audio, and text-to-music generation. Leveraging this approach, we propose TokenSynth, a novel neural synthesizer that utilizes a decoder-only transformer to generate desired audio tokens from MIDI tokens and CLAP (Contrastive Language-Audio Pretraining) embedding, which has timbre-related information. Our model is capable of performing instrument cloning, text-to-instrument synthesis, and text-guided timbre manipulation without any fine-tuning. This flexibility enables diverse sound design and intuitive timbre control. We evaluated the quality of the synthesized audio, the timbral similarity between synthesized and target audio/text, and synthesis accuracy (i.e., how accurately it follows the input MIDI) using objective measures. TokenSynth demonstrates the potential of leveraging advanced neural audio codecs and transformers to create powerful and versatile neural synthesizers. The source code, model weights, and audio demos are available at: https://github.com/KyungsuKim42/tokensynth
近期神经音频编解码器的进展使得对音频进行标记化表示的方法得以应用于各种音频生成任务,如文本转语音、文本转音频以及文本转音乐生成。利用这一方法,我们提出了TokenSynth,这是一种新型神经合成器,它采用仅解码的转换器来根据MIDI标记和CLAP(对比语言音频预训练)嵌入生成所需的音频标记,其中包含音色相关信息。我们的模型能够执行乐器克隆、文本转乐器合成以及文本引导音色操纵,无需进行微调。这种灵活性可实现多样的声音设计和直观的音色控制。我们采用客观度量来评估合成音频的质量、合成音频与目标音频或文本之间的音色相似性,以及合成准确性(即跟随输入MIDI的程度)。TokenSynth展示了利用先进的神经音频编解码器和转换器创建强大且多功能神经合成器的潜力。源代码、模型权重和音频演示可在以下网址找到:https://github.com/KyungsuKim42/tokensynth 。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 5 pages, 1 figure, to be published in ICASSP 2025
Summary
神经音频编码器的最新进展使得在音频生成任务(如文本转语音、文本转音频和文本转音乐生成)中使用令牌化音频表示成为可能。基于此,我们提出了TokenSynth,这是一种新型神经合成器,它利用仅解码的转换器生成所需的音频令牌,这些令牌来自MIDI令牌和CLAP(对比语言-音频预训练)嵌入(包含音色相关信息)。我们的模型能够执行乐器克隆、文本转乐器合成和文本指导音色操控,无需进行微调。这灵活性实现了多样化的声音设计和直观音色控制。我们已经通过客观评估方法对合成音频的质量以及合成音色与目标音频或文本的相似度进行了评价。TokenSynth展示了利用先进的神经音频编码器和转换器创建强大且多功能神经合成器的潜力。
Key Takeaways
- 神经音频编码器的最新进展使得在音频生成任务中使用令牌化音频表示成为可能。
- TokenSynth是一种新型神经合成器,采用解码器转换器生成音频令牌。
- TokenSynth能够执行乐器克隆、文本转乐器合成和文本指导音色操控。
- TokenSynth具有灵活性,可实现多样化的声音设计和直观音色控制。
- TokenSynth通过客观评估方法对合成音频的质量进行了评价。
- TokenSynth展示了利用先进的神经音频编码器和转换器的潜力。
点此查看论文截图

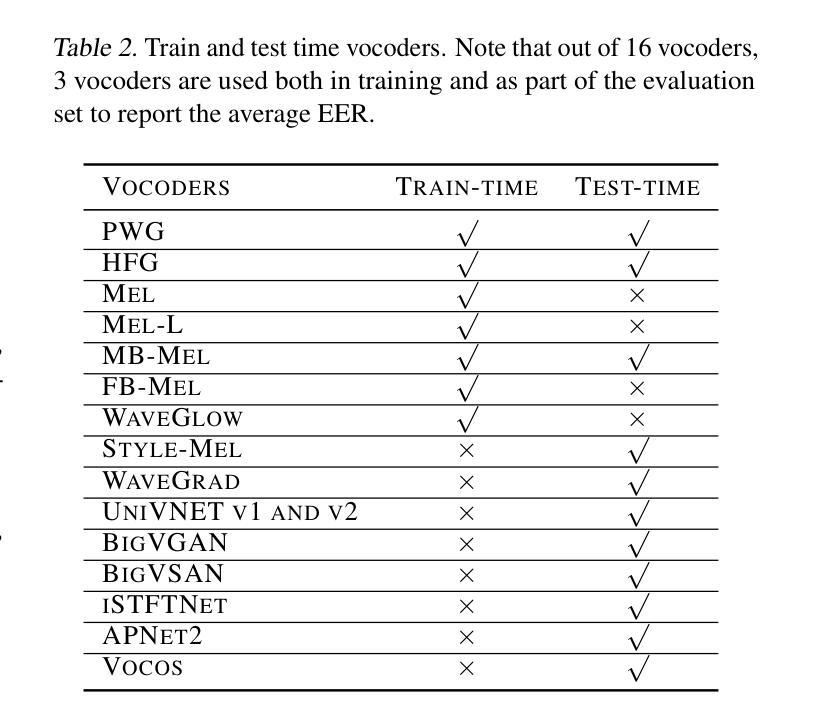
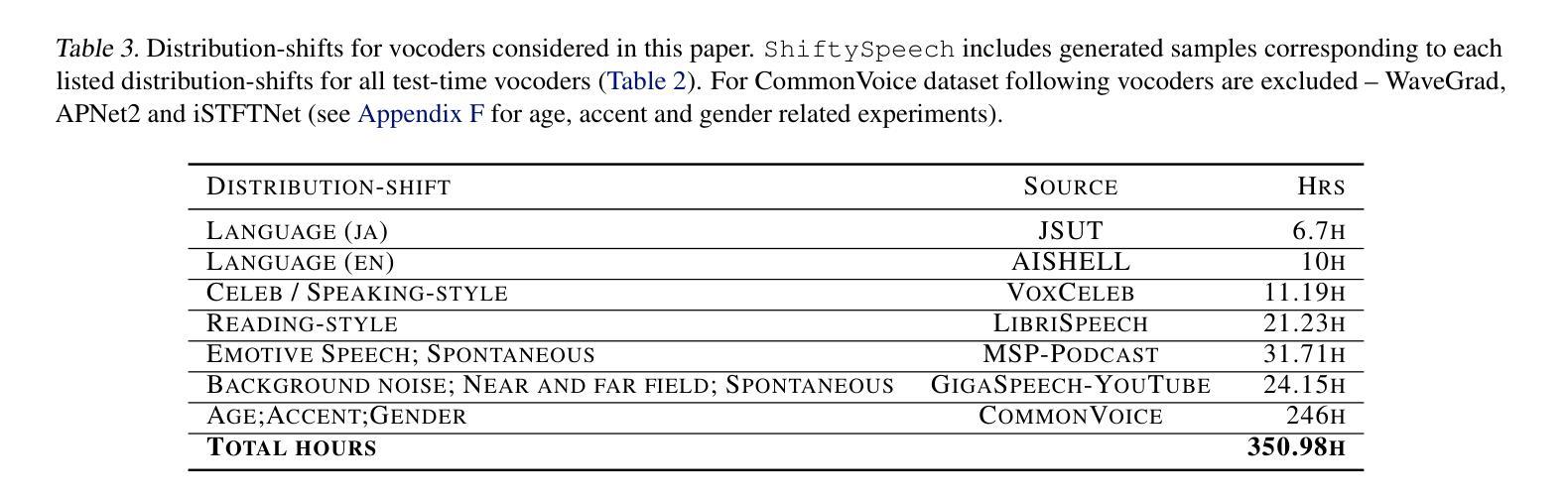
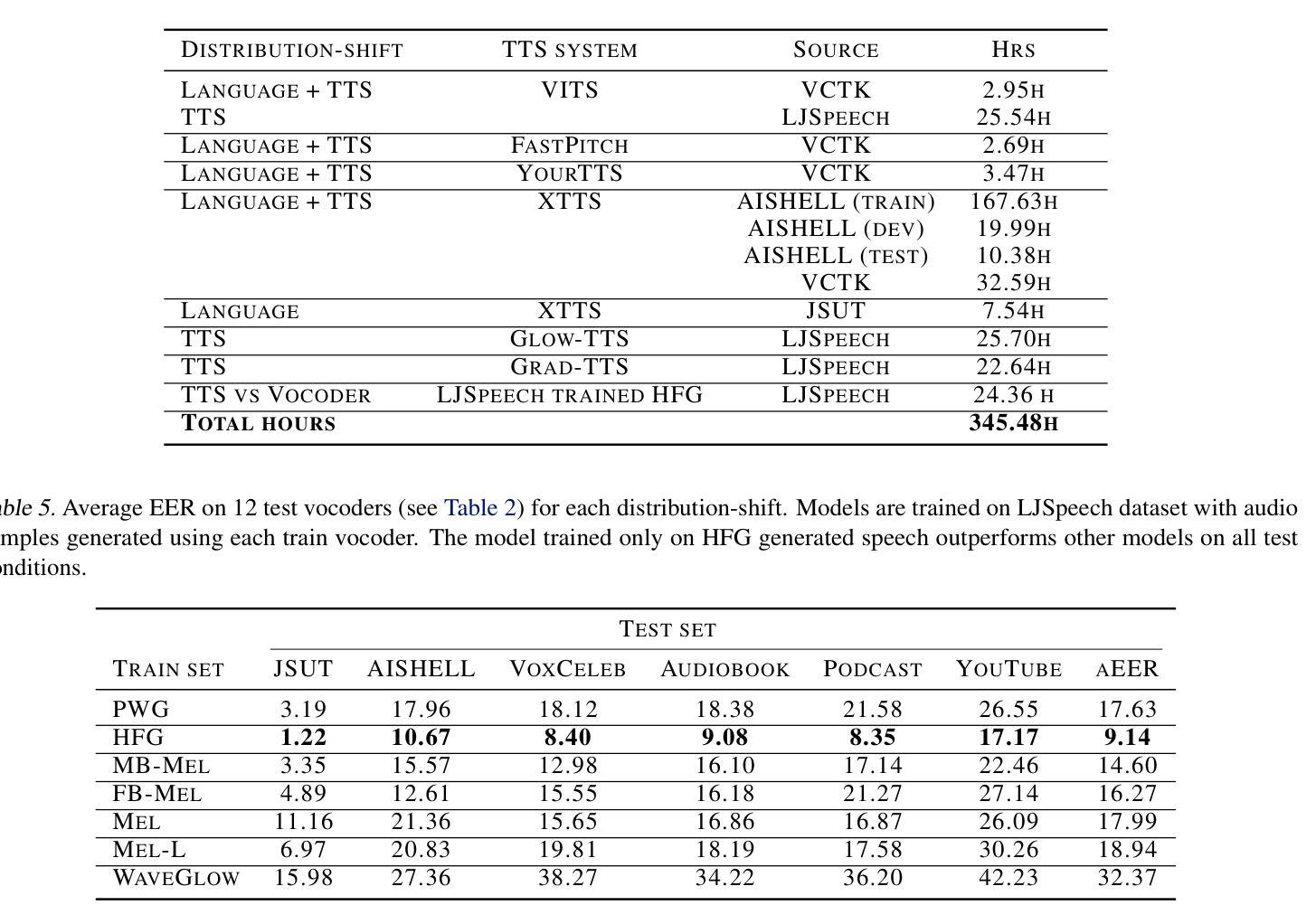
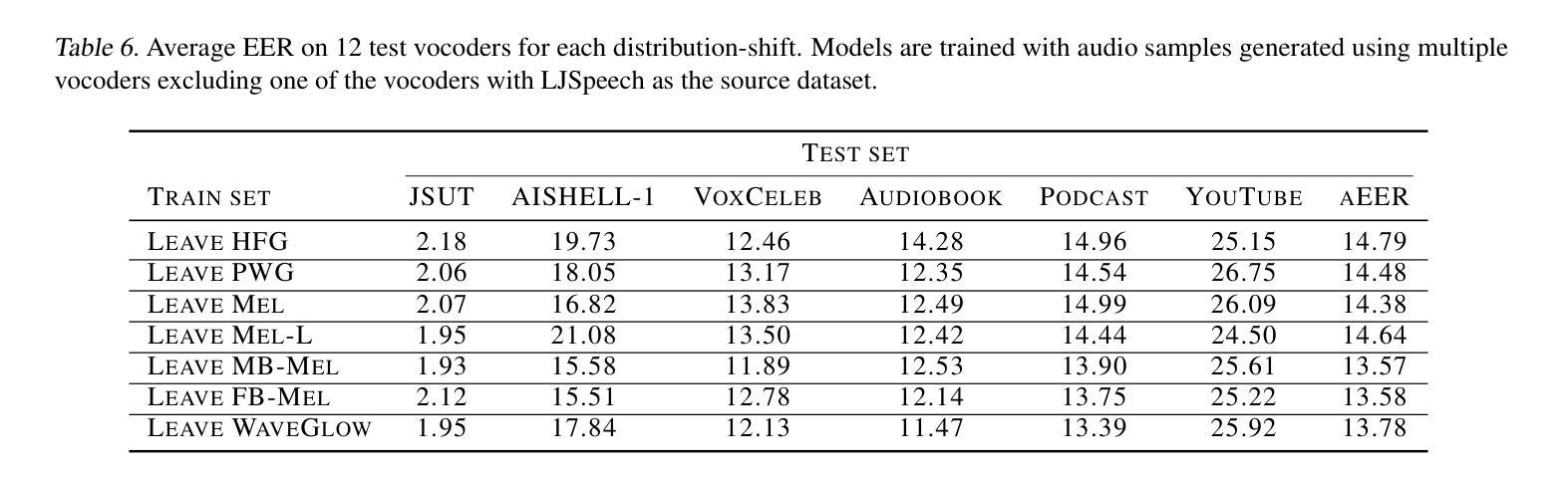
Less is More for Synthetic Speech Detection in the Wild
Authors:Ashi Garg, Zexin Cai, Henry Li Xinyuan, Leibny Paola García-Perera, Kevin Duh, Sanjeev Khudanpur, Matthew Wiesner, Nicholas Andrews
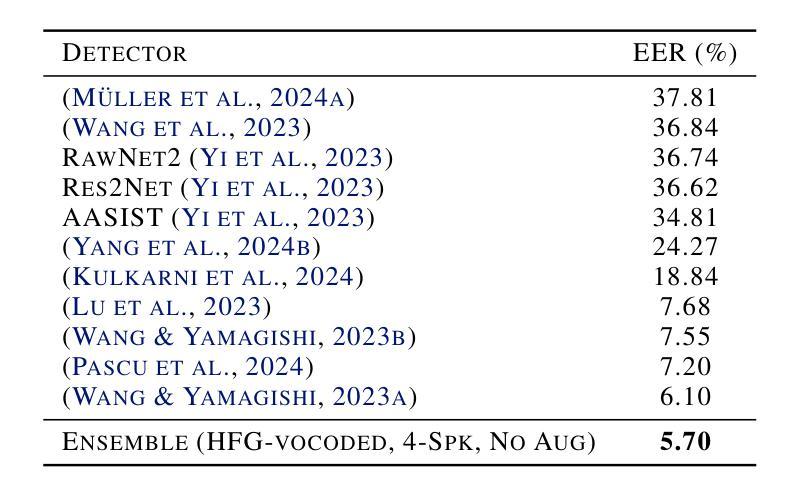
Driven by advances in self-supervised learning for speech, state-of-the-art synthetic speech detectors have achieved low error rates on popular benchmarks such as ASVspoof. However, prior benchmarks do not address the wide range of real-world variability in speech. Are reported error rates realistic in real-world conditions? To assess detector failure modes and robustness under controlled distribution shifts, we introduce ShiftySpeech, a benchmark with more than 3000 hours of synthetic speech from 7 domains, 6 TTS systems, 12 vocoders, and 3 languages. We found that all distribution shifts degraded model performance, and contrary to prior findings, training on more vocoders, speakers, or with data augmentation did not guarantee better generalization. In fact, we found that training on less diverse data resulted in better generalization, and that a detector fit using samples from a single carefully selected vocoder and a single speaker achieved state-of-the-art results on the challenging In-the-Wild benchmark.
随着语音自监督学习技术的发展,最先进的语音合成检测器已在如ASVspoof等流行基准测试上实现了低错误率。然而,先前的基准测试并未解决现实世界中语音的广泛变化。在现实世界的条件下,报告的误差率是否现实?为了评估检测器在受控分布变化下的故障模式和稳健性,我们引入了ShiftySpeech基准测试,其中包含超过3000小时的合成语音数据,涵盖7个领域、6个文本转语音系统和3种语言。我们发现所有的分布变化都会降低模型性能,与之前的研究结果相反,使用更多编码器、扬声器进行数据训练或数据增强并不能保证更好的泛化性能。事实上,我们发现使用较少多样化的数据进行训练反而能更好地实现泛化,使用单一精心挑选的编码器和单一扬声器的检测器样本在具有挑战性的In-the-Wild基准测试中取得了最先进的成果。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
最新语音合成检测器在ASVspoof等流行基准测试上实现了低错误率。然而,这些基准测试未能涵盖现实世界中语音的广泛变化。为评估检测器在受控分布变化下的失效模式和稳健性,我们推出了ShiftySpeech基准测试,包含超过3000小时来自7个领域、6种文本转语音系统和3种语言的合成语音。我们发现所有分布变化都会降低模型性能,与之前的研究结果相反,在更多编解码器、扬声器上进行训练或使用数据增强并不一定能保证更好的泛化性能。实际上,我们发现训练于较少多样数据能更好地推广使用,用一个精心挑选的编解码器和单个扬声器的样本进行训练的检测器在挑战性很大的In-the-Wild基准测试中取得了最佳成绩。
关键见解
- 最新语音合成检测器在基准测试上的错误率大幅降低。
- 现行基准测试未能涵盖现实世界中语音的广泛变化。
- 引入ShiftySpeech基准测试,模拟真实环境下的语音变化。
- 分布变化会降低语音合成检测模型的性能。
- 不同于以往观念,训练使用的编解码器、扬声器数量或数据增强并不保证更好的泛化能力。
- 训练于较少多样数据能更好地推广使用。
点此查看论文截图

Continuous Autoregressive Modeling with Stochastic Monotonic Alignment for Speech Synthesis
Authors:Weiwei Lin, Chenghan He
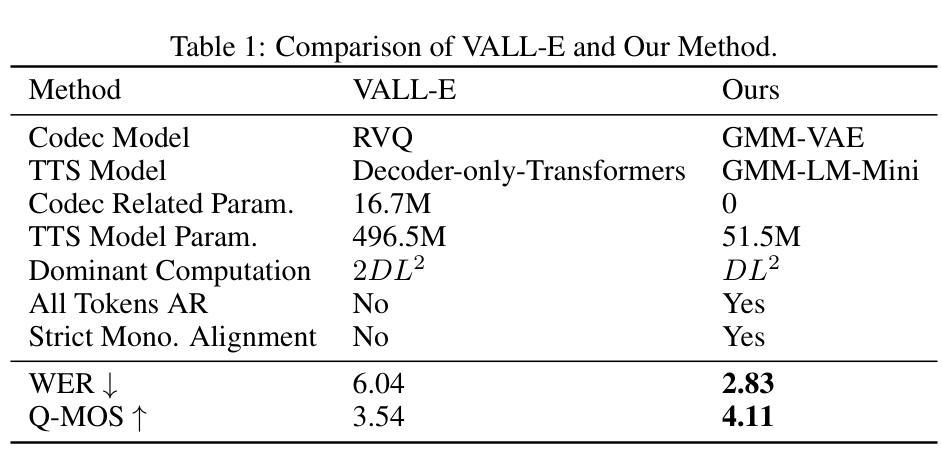
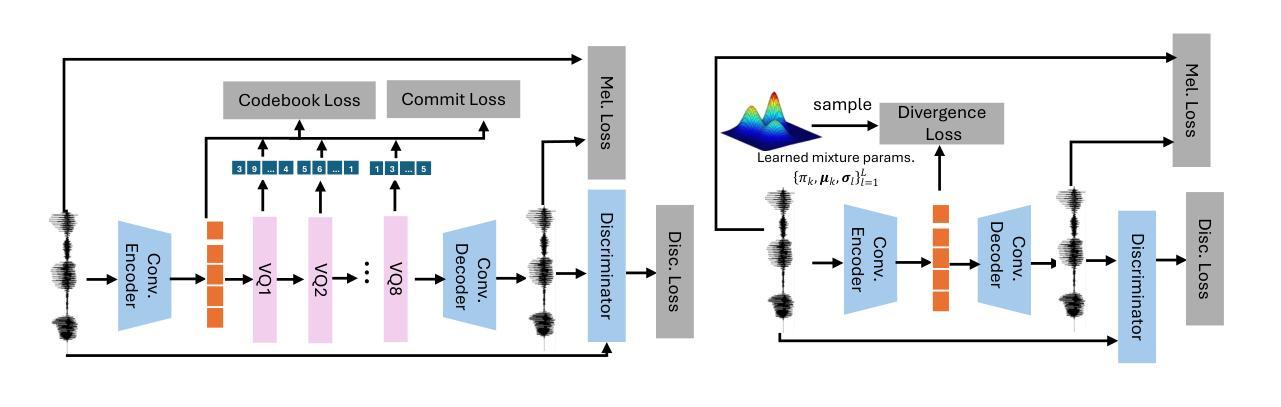
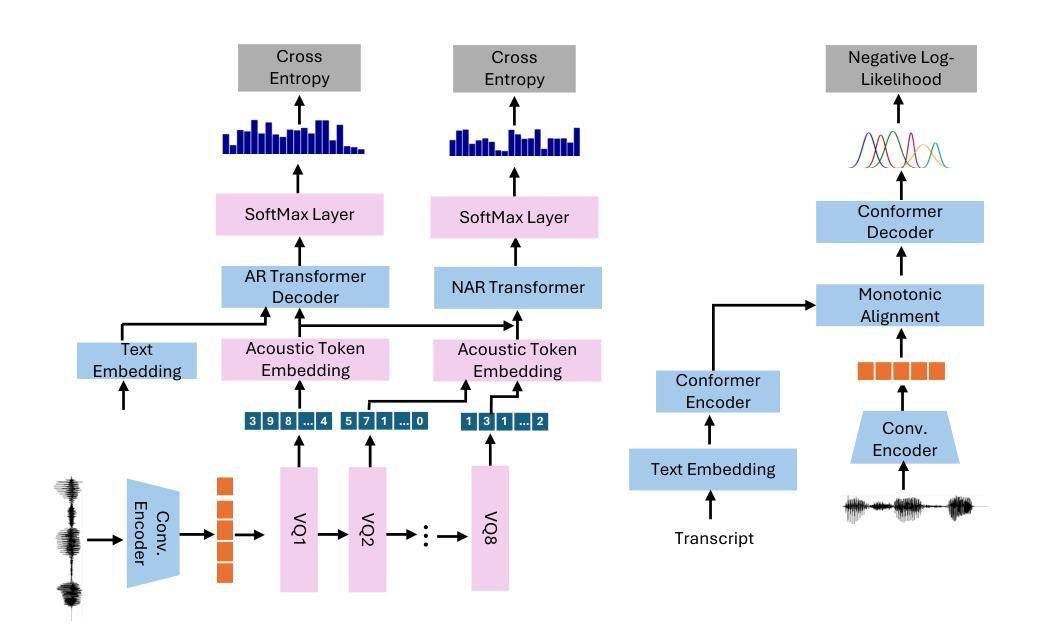
We propose a novel autoregressive modeling approach for speech synthesis, combining a variational autoencoder (VAE) with a multi-modal latent space and an autoregressive model that uses Gaussian Mixture Models (GMM) as the conditional probability distribution. Unlike previous methods that rely on residual vector quantization, our model leverages continuous speech representations from the VAE’s latent space, greatly simplifying the training and inference pipelines. We also introduce a stochastic monotonic alignment mechanism to enforce strict monotonic alignments. Our approach significantly outperforms the state-of-the-art autoregressive model VALL-E in both subjective and objective evaluations, achieving these results with only 10.3% of VALL-E’s parameters. This demonstrates the potential of continuous speech language models as a more efficient alternative to existing quantization-based speech language models. Sample audio can be found at https://tinyurl.com/gmm-lm-tts.
我们提出了一种用于语音合成的新型自回归建模方法,该方法结合了变分自编码器(VAE)的多模态潜在空间和使用高斯混合模型(GMM)作为条件概率分布的自回归模型。不同于以往依赖残差向量量化的方法,我们的模型利用VAE潜在空间中的连续语音表示,极大地简化了训练和推理流程。我们还引入了一种随机单调对齐机制,以强制执行严格的对齐规则。我们的方法在主观和客观评估上都显著优于当前最先进的自回归模型VALL-E,并以VALL-E仅有10.3%的参数取得了这些成果。这证明了连续语音语言模型作为现有基于量化的语音语言模型的更高效替代方案的潜力。相关音频样本可访问https://tinyurl.com/gmm-lm-tts。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICLR 2025
Summary
本文提出了一种结合变分自编码器(VAE)和多模态潜在空间的自回归建模方法,用于语音合成。该方法使用高斯混合模型(GMM)作为条件概率分布,并引入随机单调对齐机制来强制执行严格的对齐。该方法在主观和客观评估上都显著优于现有的自回归模型VALL-E,且仅使用VALL-E的10.3%参数即可实现这些结果。这证明了连续语音语言模型作为现有量化语音语言模型的更高效替代方案的潜力。
Key Takeaways
- 提出了结合变分自编码器(VAE)和多模态潜在空间的自回归建模方法用于语音合成。
- 使用高斯混合模型(GMM)作为条件概率分布。
- 引入随机单调对齐机制以强制执行严格的对齐。
- 方法在主观和客观评估上均显著优于VALL-E模型。
- 相比VALL-E模型,仅使用其10.3%的参数即可实现高性能。
- 潜在空间的连续语音表示简化了训练和推理流程。
- 展示了连续语音语言模型作为更高效替代方案的潜力。
点此查看论文截图