⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-02-19 更新
Variable-frame CNNLSTM for Breast Nodule Classification using Ultrasound Videos
Authors:Xiangxiang Cui, Zhongyu Li, Xiayue Fan, Peng Huang, Ying Wang, Meng Yang, Shi Chang, Jihua Zhu
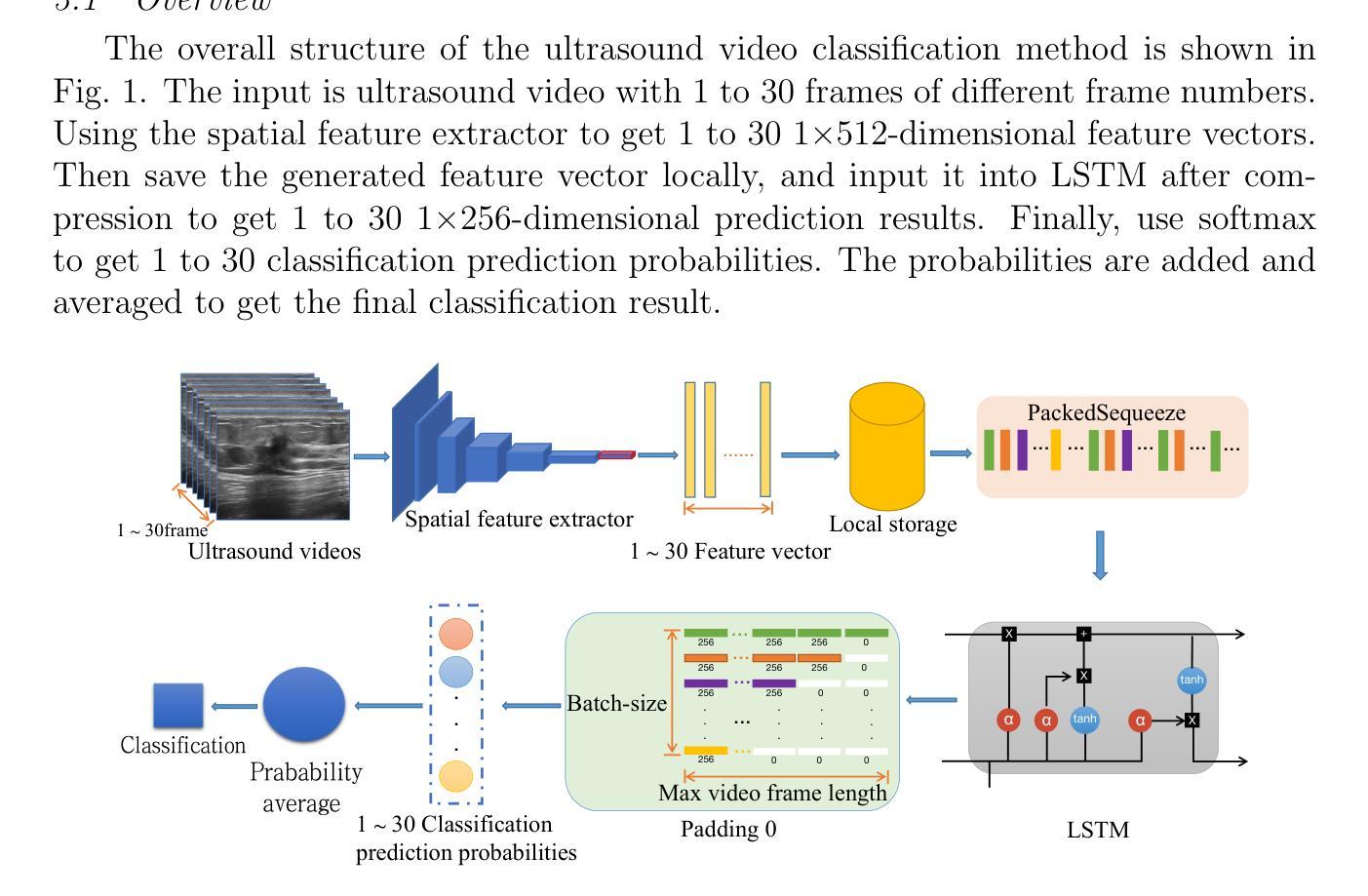
The intersection of medical imaging and artificial intelligence has become an important research direction in intelligent medical treatment, particularly in the analysis of medical images using deep learning for clinical diagnosis. Despite the advances, existing keyframe classification methods lack extraction of time series features, while ultrasonic video classification based on three-dimensional convolution requires uniform frame numbers across patients, resulting in poor feature extraction efficiency and model classification performance. This study proposes a novel video classification method based on CNN and LSTM, introducing NLP’s long and short sentence processing scheme into video classification for the first time. The method reduces CNN-extracted image features to 1x512 dimension, followed by sorting and compressing feature vectors for LSTM training. Specifically, feature vectors are sorted by patient video frame numbers and populated with padding value 0 to form variable batches, with invalid padding values compressed before LSTM training to conserve computing resources. Experimental results demonstrate that our variable-frame CNNLSTM method outperforms other approaches across all metrics, showing improvements of 3-6% in F1 score and 1.5% in specificity compared to keyframe methods. The variable-frame CNNLSTM also achieves better accuracy and precision than equal-frame CNNLSTM. These findings validate the effectiveness of our approach in classifying variable-frame ultrasound videos and suggest potential applications in other medical imaging modalities.
医学影像与人工智能的交汇已成为智能医疗治疗领域的重要研究方向,特别是在利用深度学习对医学影像进行临床分析诊断方面。然而,尽管有所进展,现有的关键帧分类方法缺乏时间序列特征的提取,而基于三维卷积的超声视频分类则要求患者间的帧数量一致,导致特征提取效率和模型分类性能较差。本研究提出了一种基于CNN和LSTM的新型视频分类方法,首次将NLP的长短句处理方案引入视频分类。该方法将CNN提取的图像特征降维至1x512,然后对特征向量进行排序和压缩,以供LSTM训练使用。具体来说,特征向量按患者视频帧号进行排序,并用填充值0形成可变批次,在LSTM训练前压缩无效填充值以节省计算资源。实验结果表明,我们的可变帧CNNLSTM方法在各项指标上均优于其他方法,与关键帧方法相比,F1得分提高了3-6%,特异性提高了1.5%。此外,可变帧CNNLSTM的准确性和精度也高于等帧CNNLSTM。这些发现验证了我们方法在分类可变帧超声视频方面的有效性,并提示其在其他医学影像模态中的潜在应用。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本研究的交集医疗影像与人工智能已经成为智能医疗的重要研究方向,特别是在利用深度学习进行医学影像分析以辅助临床诊断。本研究提出了一种基于CNN和LSTM的新型视频分类方法,引入NLP的长短句处理方案首次用于视频分类,能够高效地处理患者视频的帧序列信息,提高了特征提取效率和模型分类性能。实验结果显示,相比其他方法,该方法的F1得分提高了3-6%,特异度提高了1.5%,并且在处理不同帧数的超声视频时表现更好。这证明了该方法在超声视频分类中的有效性,并有望应用于其他医学影像模态。
Key Takeaways
- 医疗影像与人工智能的交集已成为智能医疗的重要研究方向。
- 现有方法在医学影像分类中面临时间序特征提取不足和模型性能问题。
- 本研究首次将NLP的长短句处理方案引入视频分类,以提高特征提取效率。
- 提出了一种基于CNN和LSTM的视频分类方法,适用于处理不同帧数的超声视频。
- 该方法相较于其他方法具有更高的F1得分和特异度,证明了其有效性。
- 实验结果显示该方法在超声视频分类中的优越性。
点此查看论文截图

Expert-Agnostic Learning to Defer
Authors:Joshua Strong, Pramit Saha, Yasin Ibrahim, Cheng Ouyang, Alison Noble
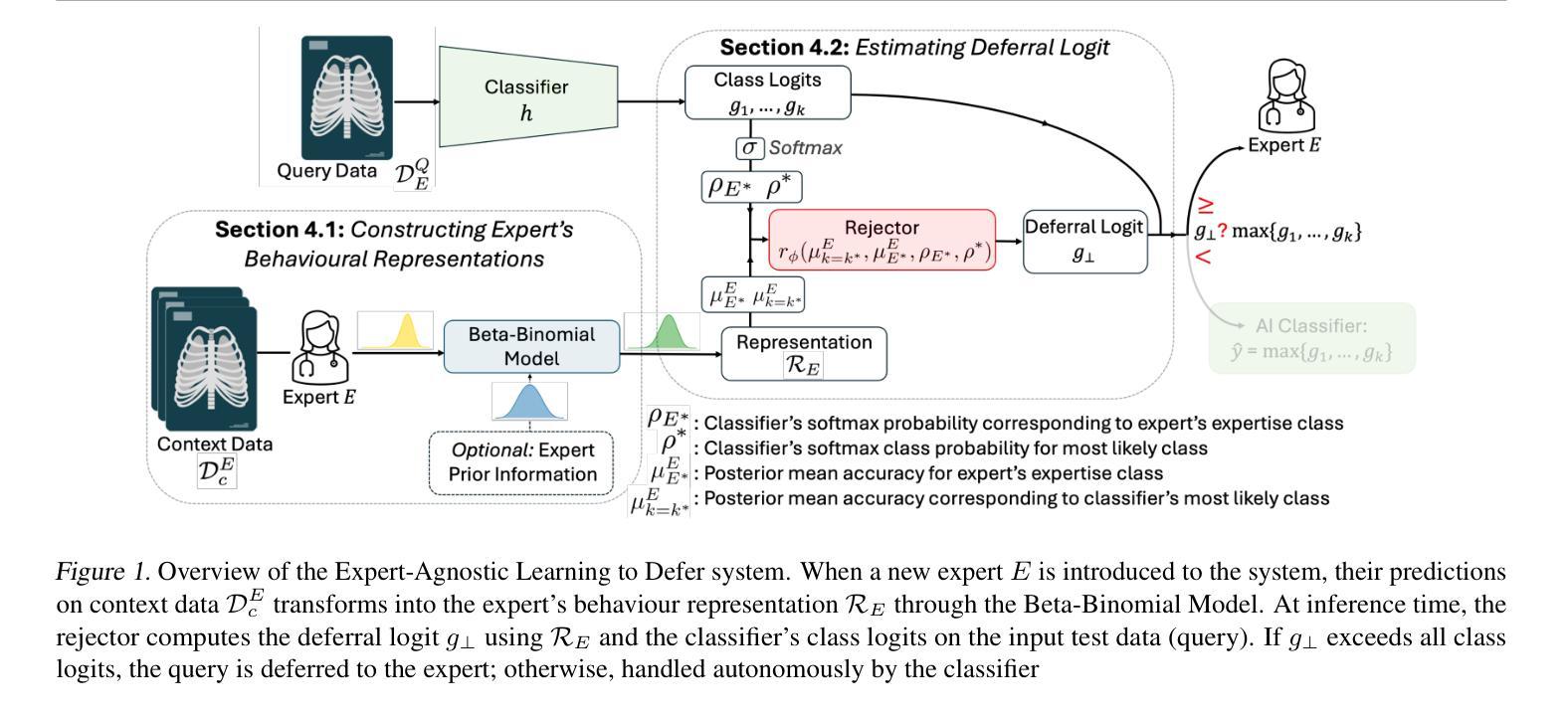
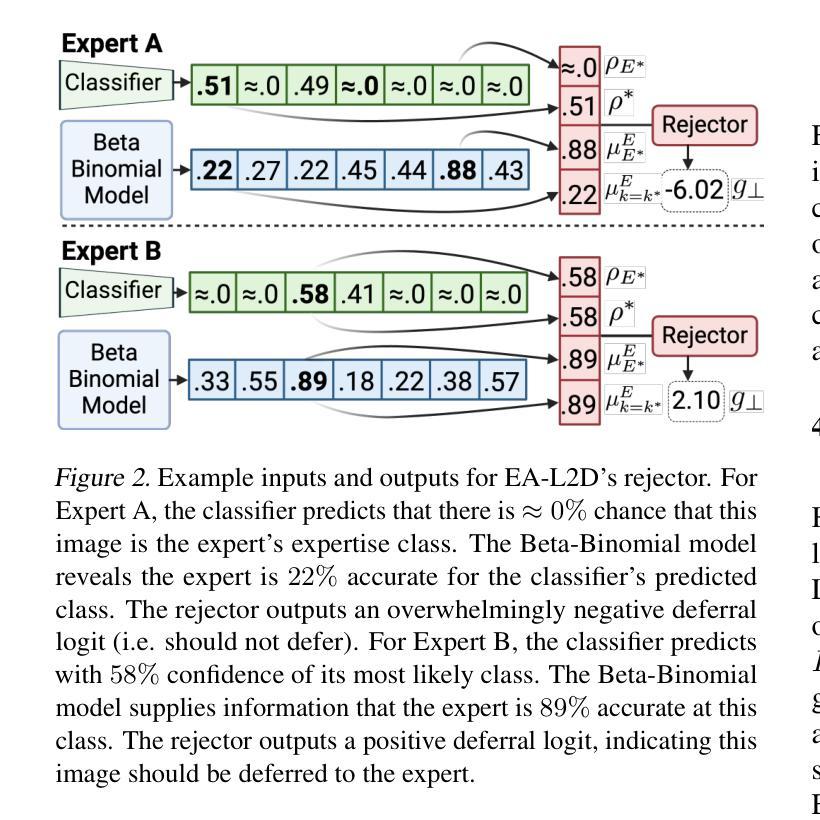
Learning to Defer (L2D) learns autonomous systems to independently manage straightforward cases, while deferring uncertain cases to human experts. Recent advancements in this field have introduced features enabling flexibility to unseen experts at test-time, but we find these approaches have significant limitations. To address these, we introduce EA-L2D: Expert-Agnostic Learning to Defer, a novel L2D framework that leverages a Bayesian approach to model expert behaviour in an expert-agnostic manner, facilitating optimal deferral decisions. EA-L2D offers several critical improvements over prior methods, including the ability to incorporate prior knowledge about experts, a reduced reliance on expert-annotated data, and robust performance when deferring to experts with expertise not seen during training. Evaluating on CIFAR-10, HAM10000, German Traffic Lights, Breast Ultrasound, Axial Organ Slices, and Blood Cell MNIST, we observe performance gains over the next state-of-the-art of 1-16% for seen experts and 4-28% for unseen experts in settings with high expert diversity.
学习延迟(L2D)旨在让自主系统能够独立处理简单案例,而将不确定的案例推迟给人类专家处理。该领域的最新进展引入了能够在测试时灵活适应未见过的专家的功能,但我们发现这些方法存在明显的局限性。为了解决这个问题,我们引入了专家无关学习延迟(EA-L2D):一种新型L2D框架,它采用贝叶斯方法来以专家无关的方式对专家行为进行建模,从而做出最佳的推迟决策。EA-L2D相对于以前的方法有几个重要的改进,包括能够融入关于专家的先验知识、减少对专家注释数据的依赖,以及在推迟给训练期间未见过的专家时保持稳健的性能。在CIFAR-10、HAM10000、德国交通灯、乳腺超声、轴向器官切片和血液细胞MNIST上进行的评估显示,与当前最新技术相比,对于已知的专家,性能提高了1-16%,对于未知的专家,在专家多样性高的环境中,性能提高了4-28%。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于文本的描述,提出了一个新的系统——EA-L2D(专家无关的自主学习推迟决策框架)。它利用贝叶斯方法以专家无关的方式模拟专家行为,使自主系统能够独立处理简单案例,并在面临不确定案例时向专家求助。相较于先前的方法,EA-L2D能够在引入专家先验知识的同时减少专家标注数据的依赖,并且在面对训练时未见到的专家时表现出稳健的性能。在多数据集上的评估表明,对于已见和未见专家,其性能相较于当前最优状态提升显著。
Key Takeaways
以下是该文本中的关键见解要点:
- EA-L2D是一种新的学习推迟决策框架,能够自主管理简单案例并在不确定时向专家求助。
- 该框架采用贝叶斯方法模拟专家行为,具有专家无关的特性。
- EA-L2D能够引入专家的先验知识,减少依赖专家标注的数据。
- 在面对训练时未见到的专家时,EA-L2D展现出稳健的性能。
- 该框架在多数据集上的评估表现出优异性能,相对于当前最优状态有明显提升。
- 无论是在已见还是未见专家的场景中,性能提升都相当显著。具体提升幅度在4%~28%之间。
- 该技术的核心优势在于能够根据环境和数据变化动态调整策略,并且在复杂的场景中仍能做出有效决策。
点此查看论文截图

MedCLIP-SAMv2: Towards Universal Text-Driven Medical Image Segmentation
Authors:Taha Koleilat, Hojat Asgariandehkordi, Hassan Rivaz, Yiming Xiao
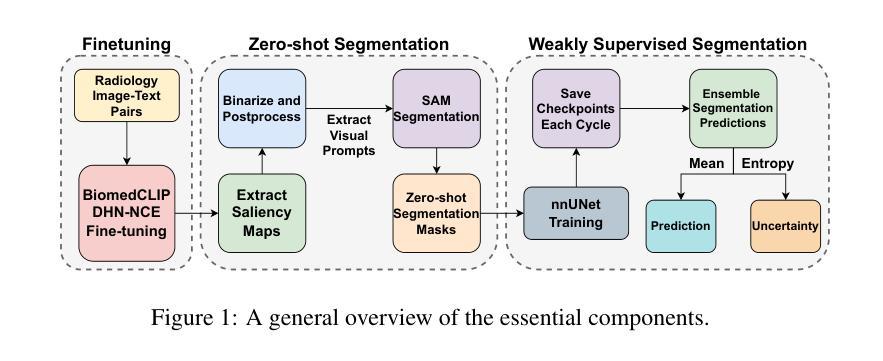
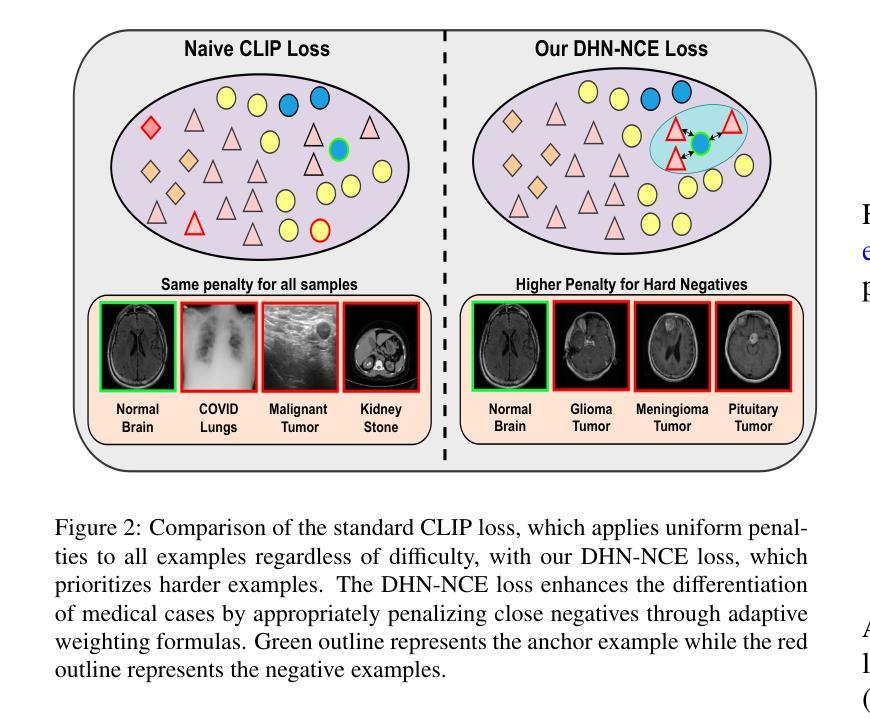
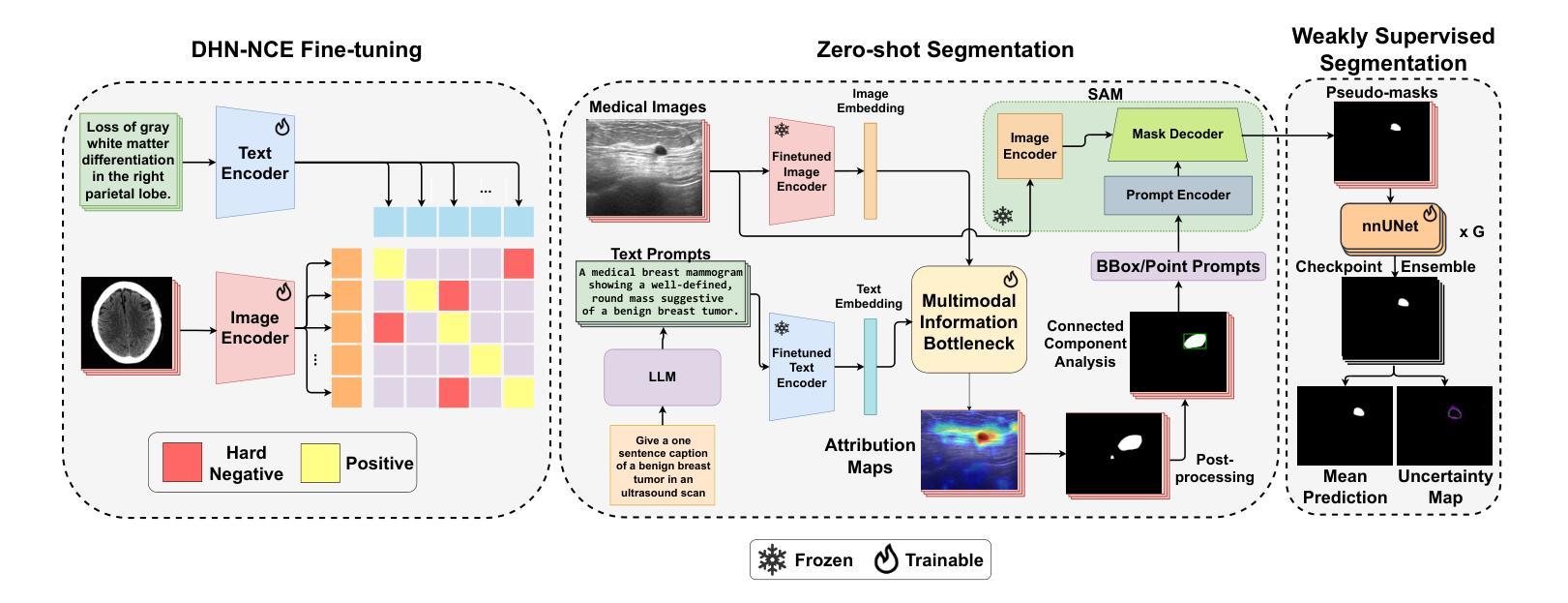
Segmentation of anatomical structures and pathological regions in medical images is essential for modern clinical diagnosis, disease research, and treatment planning. While significant advancements have been made in deep learning-based segmentation techniques, many of these methods still suffer from limitations in data efficiency, generalizability, and interactivity. As a result, developing precise segmentation methods that require fewer labeled datasets remains a critical challenge in medical image analysis. Recently, the introduction of foundation models like CLIP and Segment-Anything-Model (SAM), with robust cross-domain representations, has paved the way for interactive and universal image segmentation. However, further exploration of these models for data-efficient segmentation in medical imaging is still needed and highly relevant. In this paper, we introduce MedCLIP-SAMv2, a novel framework that integrates the CLIP and SAM models to perform segmentation on clinical scans using text prompts, in both zero-shot and weakly supervised settings. Our approach includes fine-tuning the BiomedCLIP model with a new Decoupled Hard Negative Noise Contrastive Estimation (DHN-NCE) loss, and leveraging the Multi-modal Information Bottleneck (M2IB) to create visual prompts for generating segmentation masks from SAM in the zero-shot setting. We also investigate using zero-shot segmentation labels within a weakly supervised paradigm to enhance segmentation quality further. Extensive testing across four diverse segmentation tasks and medical imaging modalities (breast tumor ultrasound, brain tumor MRI, lung X-ray, and lung CT) demonstrates the high accuracy of our proposed framework. Our code is available at https://github.com/HealthX-Lab/MedCLIP-SAMv2.
医学图像中解剖结构和病理区域的分割对于现代临床诊断、疾病研究和治疗计划制定至关重要。虽然基于深度学习的分割技术已经取得了重大进展,但许多这些方法在数据效率、通用性和交互性方面仍存在局限性。因此,开发需要较少标记数据集的高精度分割方法仍是医学图像分析中的一项关键挑战。最近,引入具有强大跨域表示能力的CLIP和Segment-Anything-Model(SAM)等基础模型,为交互式和通用图像分割铺平了道路。然而,需要进一步探索这些模型在医学成像中的数据高效分割,这仍然是非常相关和必要的。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 10 pages, 2 figures, 6 tables
Summary
该文本介绍了一种新的医学影像分割框架MedCLIP-SAMv2,它结合了CLIP和SAM模型,可以在零样本和弱监督设置下,使用文本提示对临床扫描图像进行分割。该框架通过微调BiomedCLIP模型并引入新的DHN-NCE损失和M2IB方法,提高了分割质量和效率,并在多种医学影像分割任务中表现出高准确性。
Key Takeaways
- MedCLIP-SAMv2是一个新颖的医学影像分割框架,结合了CLIP和SAM模型。
- 该框架能够在零样本和弱监督设置下使用文本提示进行临床扫描图像分割。
- MedCLIP-SAMv2通过微调BiomedCLIP模型并引入DHN-NCE损失来提高分割质量和效率。
- M2IB方法被用于创建视觉提示,以生成SAM的分割掩膜,进一步提高分割质量。
- 该框架在多种医学影像分割任务(如乳腺肿瘤超声、脑肿瘤MRI、肺部X光和CT)中表现出高准确性。
- MedCLIP-SAMv2的代码已公开发布在HealthX-Lab的GitHub仓库中。
点此查看论文截图