⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-02-19 更新
Supervised contrastive learning for cell stage classification of animal embryos
Authors:Yasmine Hachani, Patrick Bouthemy, Elisa Fromont, Sylvie Ruffini, Ludivine Laffont, Alline de Paula Reis
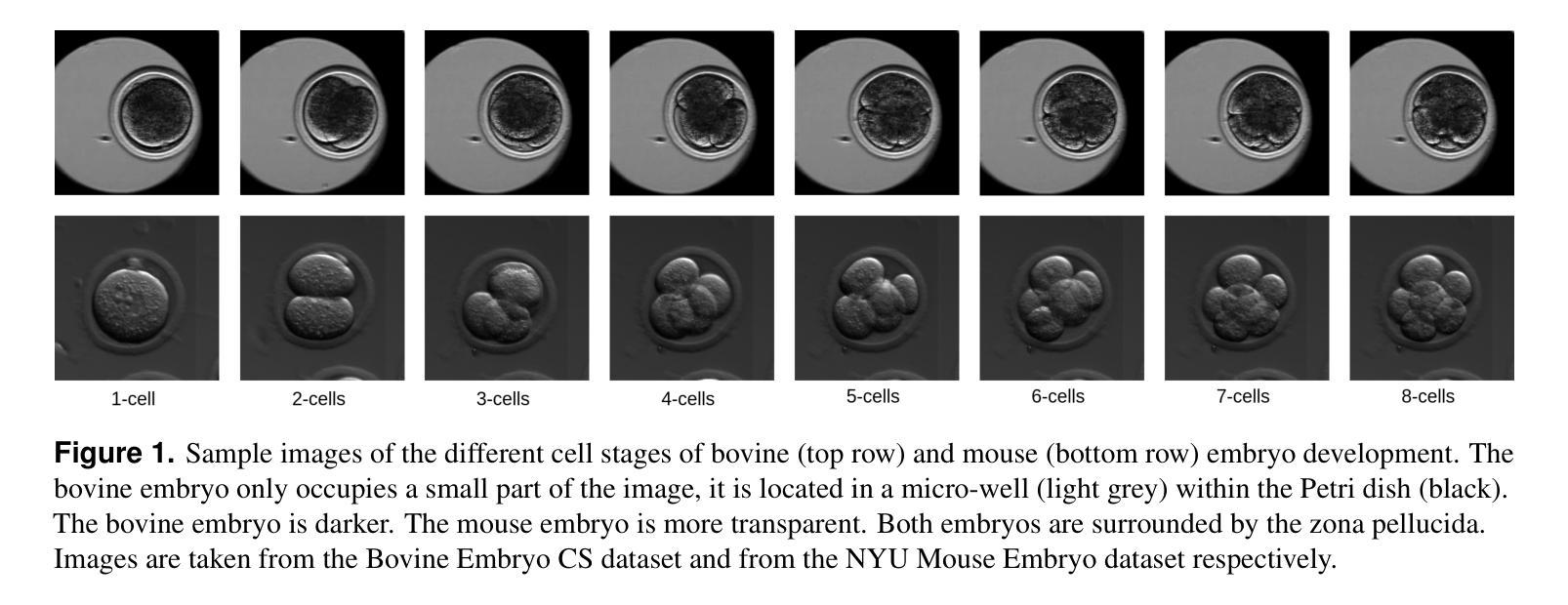
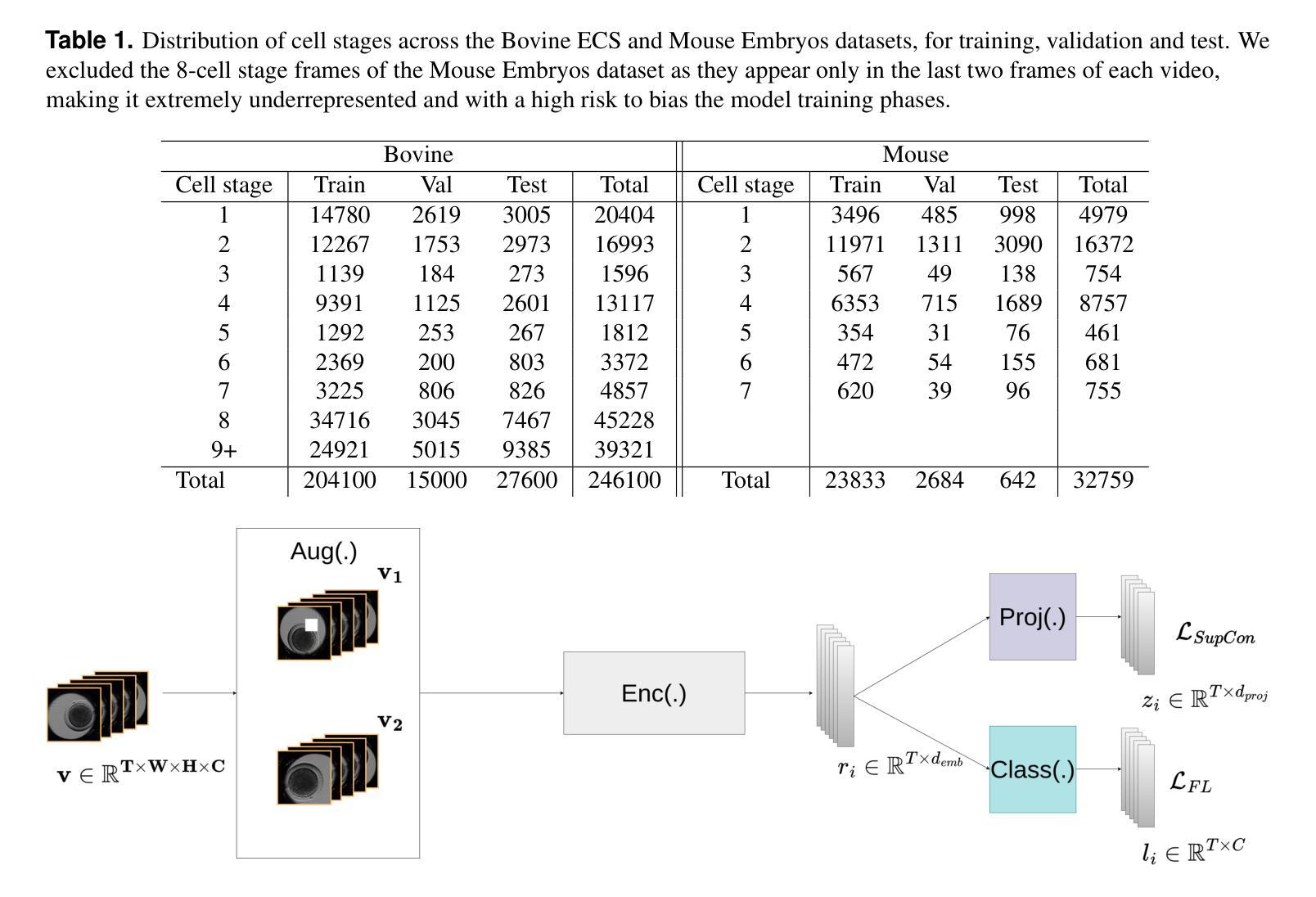
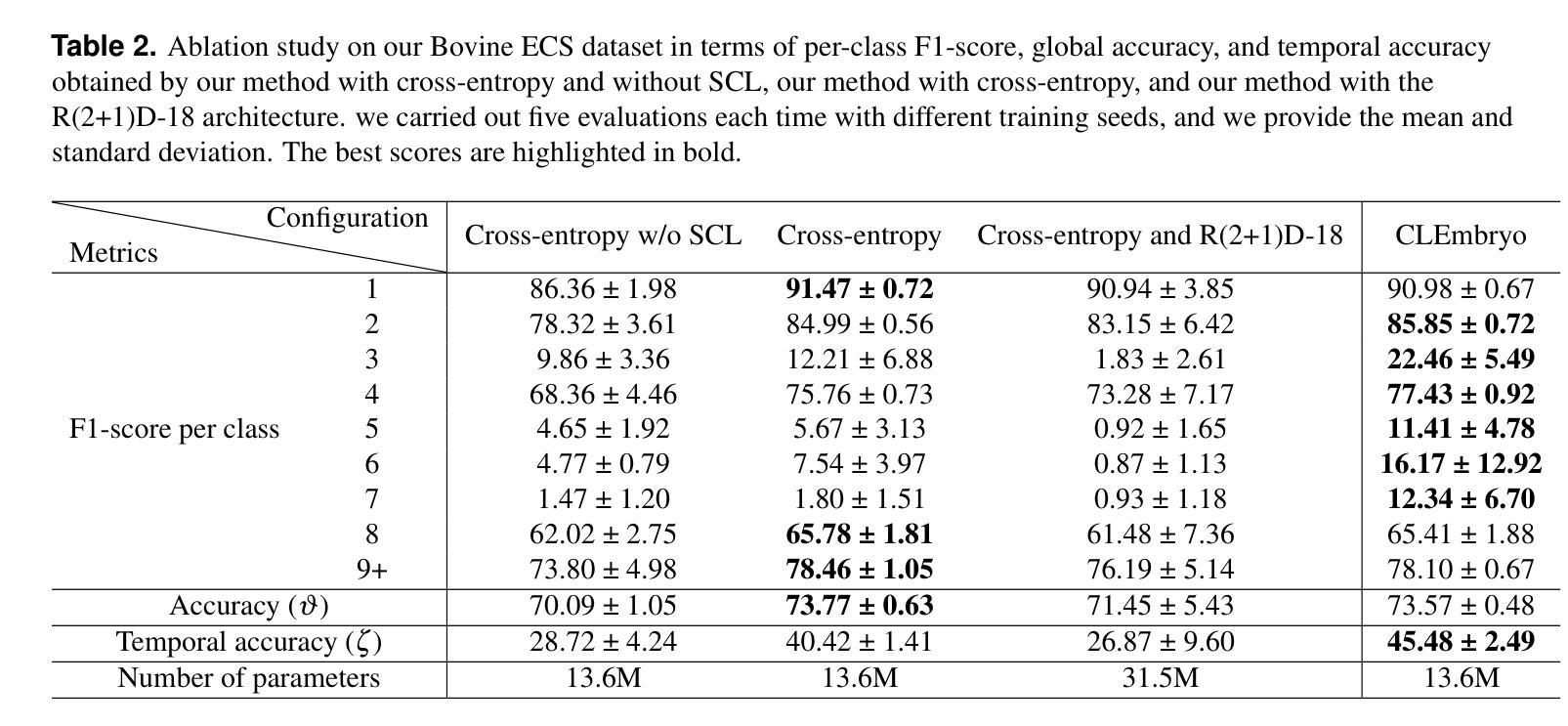
Video microscopy, when combined with machine learning, offers a promising approach for studying the early development of in vitro produced (IVP) embryos. However, manually annotating developmental events, and more specifically cell divisions, is time-consuming for a biologist and cannot scale up for practical applications. We aim to automatically classify the cell stages of embryos from 2D time-lapse microscopy videos with a deep learning approach. We focus on the analysis of bovine embryonic development using video microscopy, as we are primarily interested in the application of cattle breeding, and we have created a Bovine Embryos Cell Stages (ECS) dataset. The challenges are three-fold: (1) low-quality images and bovine dark cells that make the identification of cell stages difficult, (2) class ambiguity at the boundaries of developmental stages, and (3) imbalanced data distribution. To address these challenges, we introduce CLEmbryo, a novel method that leverages supervised contrastive learning combined with focal loss for training, and the lightweight 3D neural network CSN-50 as an encoder. We also show that our method generalizes well. CLEmbryo outperforms state-of-the-art methods on both our Bovine ECS dataset and the publicly available NYU Mouse Embryos dataset.
视频显微镜结合机器学习为研究体外生产(IVP)胚胎的早期发育提供了一个有前途的方法。然而,生物学家手动标注发育事件,尤其是细胞分裂,既耗时又无法规模化应用于实际应用。我们的目标是使用深度学习的方法自动对胚胎的细胞阶段进行分类,这些胚胎来自二维延时显微镜视频。我们重点关注牛胚胎发育的分析,因为我们主要对牛育种的应用感兴趣,并且我们已经创建了牛胚胎细胞阶段(ECS)数据集。所面临的挑战有三个:(1)图像质量低下和牛的暗细胞使得细胞阶段的识别变得困难;(2)发育阶段边界的类别模糊性;(3)数据分布不平衡。为了应对这些挑战,我们引入了CLEmbryo这一新方法,它利用有监督对比学习结合焦点损失进行训练,并使用轻量级三维神经网络CSN-50作为编码器。我们还展示了我们的方法具有良好的泛化能力。在牛ECS数据集和公开可用的NYU小鼠胚胎数据集上,CLEmbryo都优于目前最先进的方法。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
在体视显微镜结合机器学习为研究体外培养胚胎的早期发育提供了一种有前景的方法。为自动分类胚胎细胞阶段,研究采用深度学习分析牛胚胎发育的体视显微镜视频。研究中面临图像质量低、细胞暗以及发育阶段边界模糊和不平衡数据分布等挑战。为应对这些挑战,提出CLEmbryo方法,该方法结合了监督对比学习与聚焦损失训练以及轻量级三维神经网络CSN-50编码器。此外,该方法在公开数据集上的表现良好,且相较于其他前沿方法,在牛胚胎细胞阶段数据集和公开可用的纽约大学小鼠胚胎数据集上的表现更优。
Key Takeaways
- 结合视频显微镜与机器学习为研究体外培养胚胎的早期发育提供了前景。
- 研究旨在自动分类胚胎细胞阶段,使用深度学习分析牛胚胎的体视显微镜视频。
- 研究中面临图像质量低和细胞暗以及发育阶段边界模糊和不平衡数据分布的挑战。
- 为应对这些挑战,提出了CLEmbryo方法,结合了监督对比学习与聚焦损失训练。
- CLEmbryo方法使用了轻量级三维神经网络CSN-50作为编码器。
- CLEmbryo在牛胚胎细胞阶段数据集上的表现优于其他前沿方法。
点此查看论文截图

One Leaf Reveals the Season: Occlusion-Based Contrastive Learning with Semantic-Aware Views for Efficient Visual Representation
Authors:Xiaoyu Yang, Lijian Xu, Hongsheng Li, Shaoting Zhang
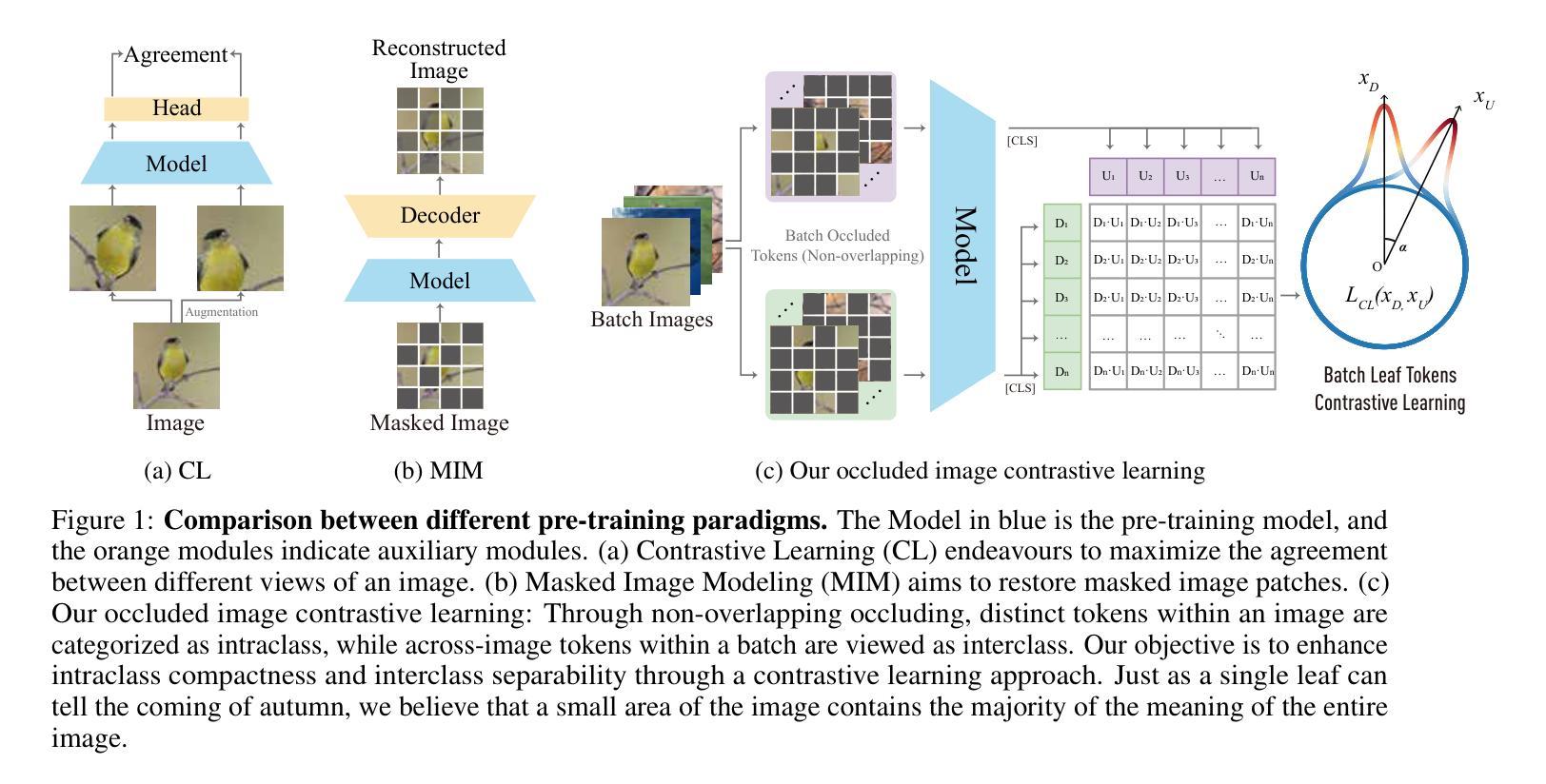
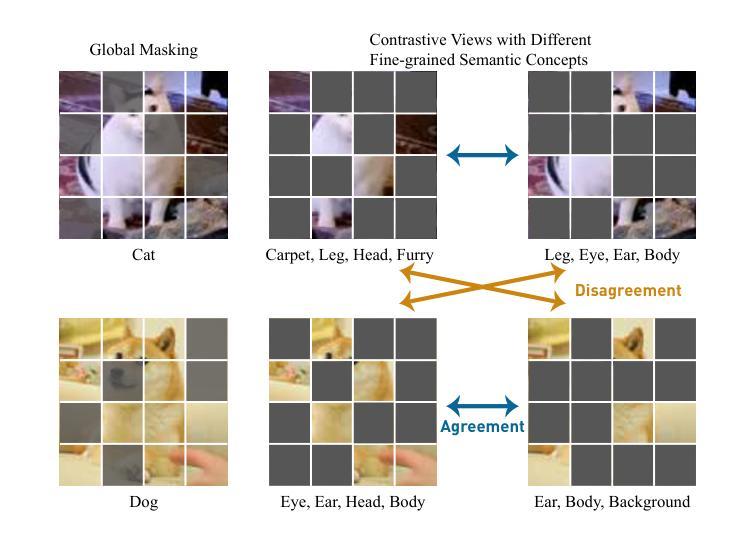
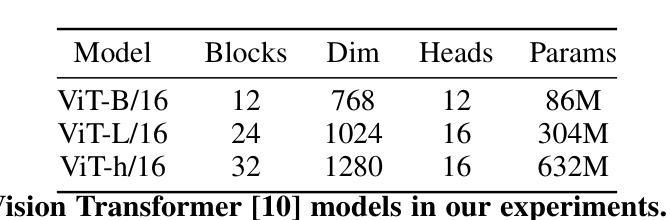
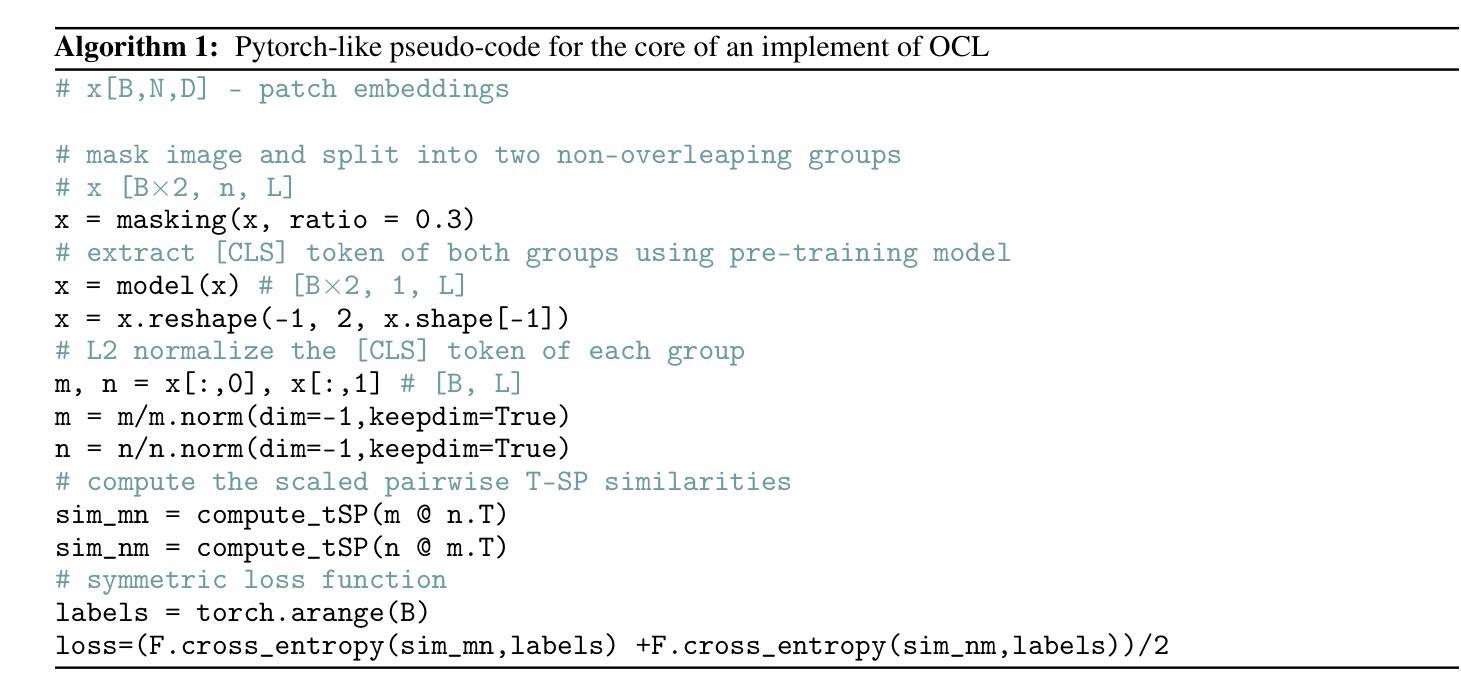
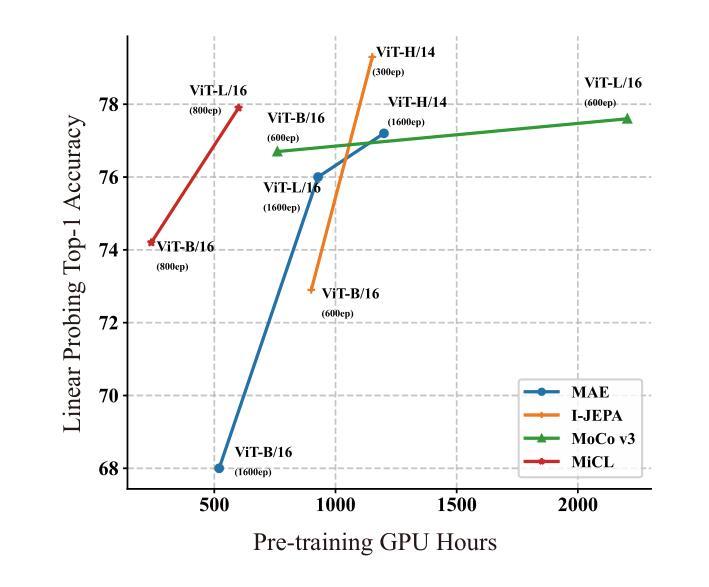
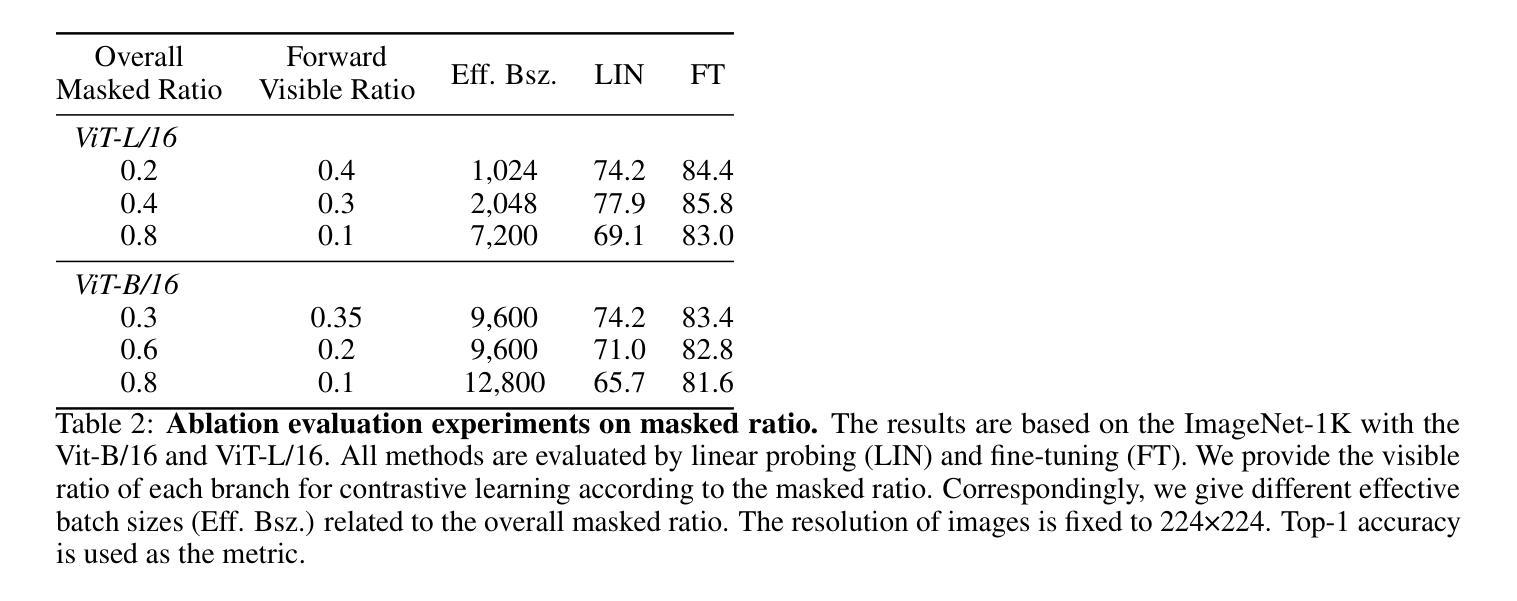
This paper proposes a scalable and straightforward pre-training paradigm for efficient visual conceptual representation called occluded image contrastive learning (OCL). Our OCL approach is simple: we randomly mask patches to generate different views within an image and contrast them among a mini-batch of images. The core idea behind OCL consists of two designs. First, masked tokens have the potential to significantly diminish the conceptual redundancy inherent in images, and create distinct views with substantial fine-grained differences on the semantic concept level instead of the instance level. Second, contrastive learning is adept at extracting high-level semantic conceptual features during the pre-training, circumventing the high-frequency interference and additional costs associated with image reconstruction. Importantly, OCL learns highly semantic conceptual representations efficiently without relying on hand-crafted data augmentations or additional auxiliary modules. Empirically, OCL demonstrates high scalability with Vision Transformers, as the ViT-L/16 can complete pre-training in 133 hours using only 4 A100 GPUs, achieving 85.8% accuracy in downstream fine-tuning tasks. Code is available at https://anonymous.4open.science/r/OLRS/.
本文提出了一种名为遮挡图像对比学习(OCL)的可扩展和直观的预训练范式,用于高效视觉概念表示。我们的OCL方法很简单:我们随机遮挡图像区域以生成不同的视图,并在一批图像之间进行对比。OCL背后的核心理念包括两个设计。首先,遮挡的标记具有减少图像中固有的概念冗余的潜力,并在语义概念层面上创建具有显著细微差别的独特视图,而不是实例层面。其次,对比学习擅长在预训练过程中提取高级语义概念特征,避免了与图像重建相关的高频干扰和额外成本。重要的是,OCL能够高效地学习高度语义化的概念表示,无需依赖手工制作的数据增强或额外的辅助模块。从经验上讲,OCL在视觉转换器上具有高度的可扩展性,例如ViT-L/16可以在仅使用4个A100 GPU的情况下在133小时内完成预训练,并在下游微调任务中实现85.8%的准确率。相关代码可通过https://anonymous.4open.science/r/OLRS/访问。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 16 pages
Summary
本文提出了一种可扩展且简单的预训练模式——遮挡图像对比学习(OCL),用于高效视觉概念表示。OCL方法通过随机遮挡图像中的区块来生成不同的视图,并在小批量图像之间进行对比。其核心思想包括两个设计:一是遮挡标记有助于减少图像中的概念冗余,在语义概念层面而非实例层面创建具有细微差异的独特视图;二是对比学习擅长在预训练过程中提取高级语义概念特征,避免了图像重建的高频干扰和额外成本。OCL能够高效地学习高度语义化的概念表示,无需依赖手工制作的数据增强或额外的辅助模块。实验表明,OCL在视觉转换器(ViT-L/16)上具有高度的可扩展性,只需使用四个A100 GPU即可在133小时内完成预训练,并在下游微调任务中实现85.8%的准确率。
Key Takeaways
- OCL通过遮挡图像区块生成不同视图,实现高效的视觉概念表示学习。
- 遮挡标记有助于减少图像中的概念冗余,强调语义概念层面的细微差异。
- 对比学习在预训练中擅长提取高级语义概念特征。
- OCL避免了图像重建的高频干扰和额外成本。
- OCL不依赖手工制作的数据增强或额外的辅助模块。
- OCL在视觉转换器上具有高可扩展性,ViT-L/16可在短时间内完成预训练。
点此查看论文截图

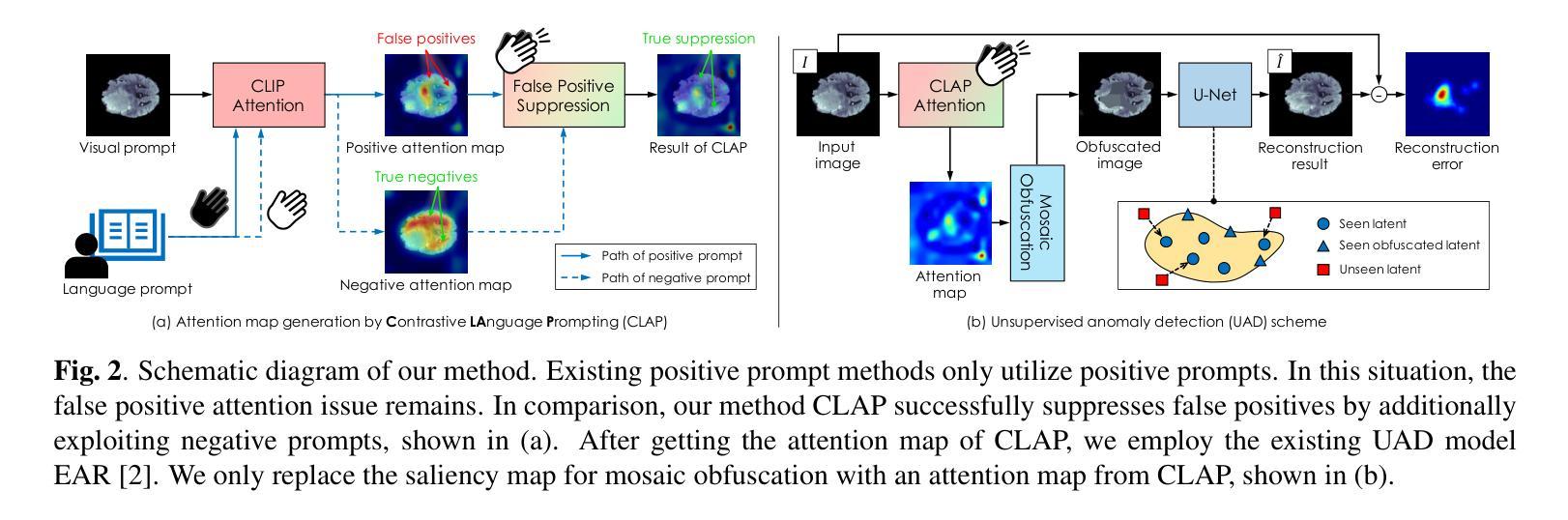
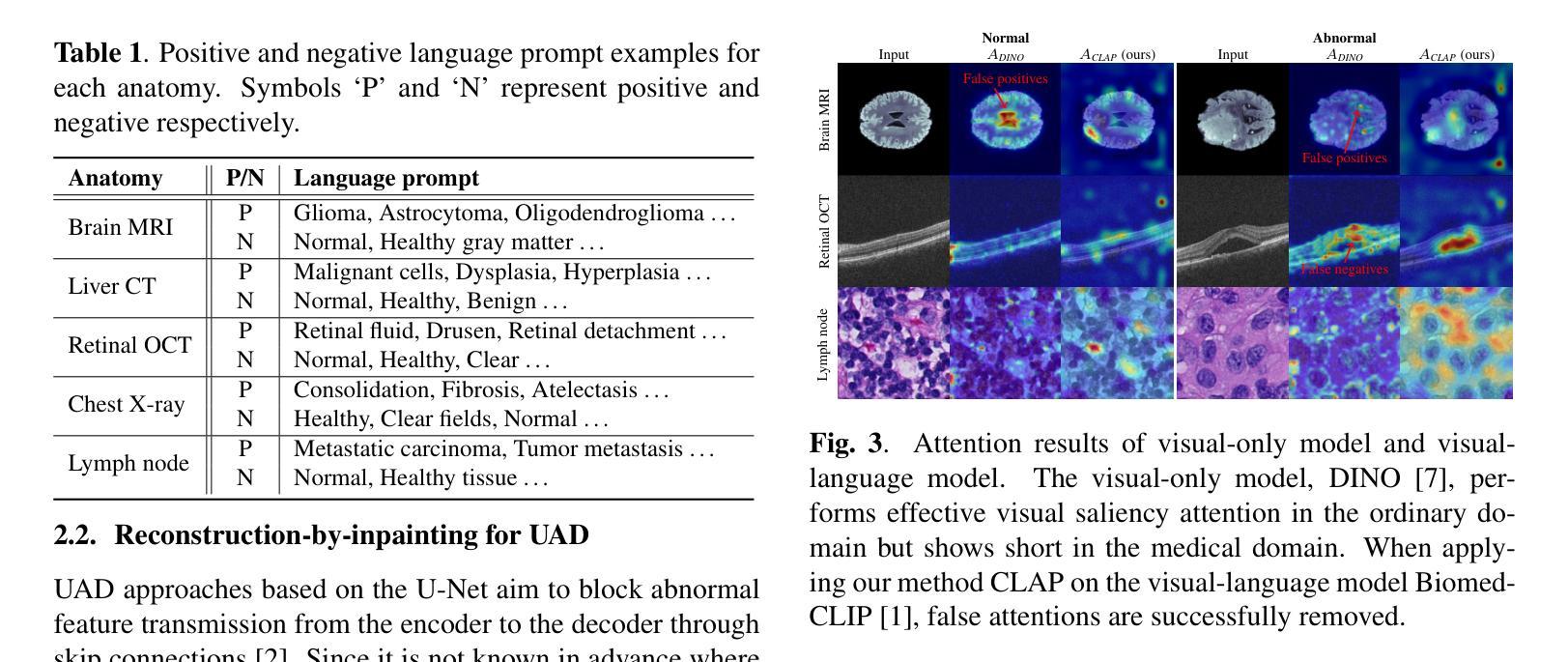
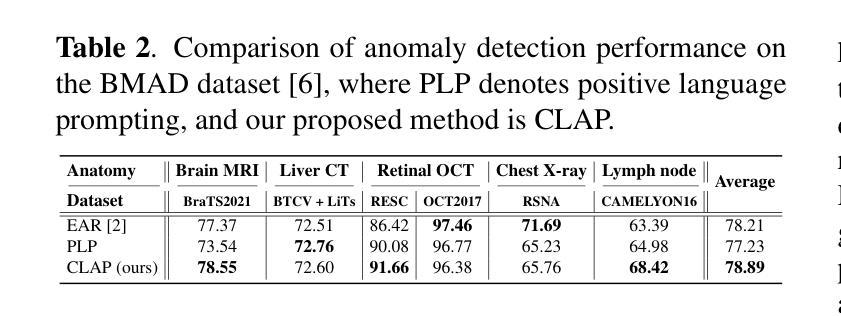
Contrastive Language Prompting to Ease False Positives in Medical Anomaly Detection
Authors:YeongHyeon Park, Myung Jin Kim, Hyeong Seok Kim
A pre-trained visual-language model, contrastive language-image pre-training (CLIP), successfully accomplishes various downstream tasks with text prompts, such as finding images or localizing regions within the image. Despite CLIP’s strong multi-modal data capabilities, it remains limited in specialized environments, such as medical applications. For this purpose, many CLIP variants-i.e., BioMedCLIP, and MedCLIP-SAMv2-have emerged, but false positives related to normal regions persist. Thus, we aim to present a simple yet important goal of reducing false positives in medical anomaly detection. We introduce a Contrastive LAnguage Prompting (CLAP) method that leverages both positive and negative text prompts. This straightforward approach identifies potential lesion regions by visual attention to the positive prompts in the given image. To reduce false positives, we attenuate attention on normal regions using negative prompts. Extensive experiments with the BMAD dataset, including six biomedical benchmarks, demonstrate that CLAP method enhances anomaly detection performance. Our future plans include developing an automated fine prompting method for more practical usage.
预训练的视觉语言模型——对比语言图像预训练(CLIP)能够通过文本提示成功完成各种下游任务,如查找图像或定位图像内的区域。尽管CLIP在多媒体数据方面表现出强大的能力,但在特定环境(例如医疗应用)中仍存在局限性。为此,已经出现了许多CLIP变体,如BioMedCLIP和MedCLIP-SAMv2等,但与正常区域相关的误报仍然存在。因此,我们旨在提出降低医疗异常检测中误报率这一简单而重要的目标。我们引入了一种对比语言提示(CLAP)方法,该方法利用正面和负面文本提示。通过视觉关注给定图像中的正面提示,此直观的方法可以识别出潜在的病变区域。为了减少误报,我们使用负面提示来减弱对正常区域的关注。在包括六个生物医学基准测试在内的BMAD数据集上的大量实验表明,CLAP方法提高了异常检测性能。我们未来的计划包括开发一种更实用的自动化精细提示方法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 4 pages, 3 figures, 2 tables
Summary:
预训练视觉语言模型CLIP在多模态数据处理方面表现出强大的能力,但在特定环境如医疗应用中仍存在限制。为减少医疗异常检测中的误报,本文提出了利用正负文本提示的对比语言提示(CLAP)方法。该方法通过正向提示识别潜在病变区域,并通过负向提示减少对正常区域的关注,从而提高异常检测性能。在BMAD数据集上的实验证明,CLAP方法能够有效增强异常检测的准确性。
Key Takeaways:
- CLIP模型虽具备强大的多模态数据处理能力,但在特定环境如医疗应用中仍存在挑战。
- 为解决医疗异常检测中的误报问题,本文提出了CLAP方法,结合正负文本提示。
- CLAP方法通过正向提示识别病变区域,并借助负向提示减少对正常区域的关注。
- 在BMAD数据集上的实验证明CLAP方法能够提高异常检测性能。
- CLAP方法具有潜力应用于其他领域,未来计划开发更实用的自动化精细提示方法。
- CLAP方法对于降低医疗诊断中的误报风险具有重要意义。
点此查看论文截图