⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-02-19 更新
SVBench: A Benchmark with Temporal Multi-Turn Dialogues for Streaming Video Understanding
Authors:Zhenyu Yang, Yuhang Hu, Zemin Du, Dizhan Xue, Shengsheng Qian, Jiahong Wu, Fan Yang, Weiming Dong, Changsheng Xu
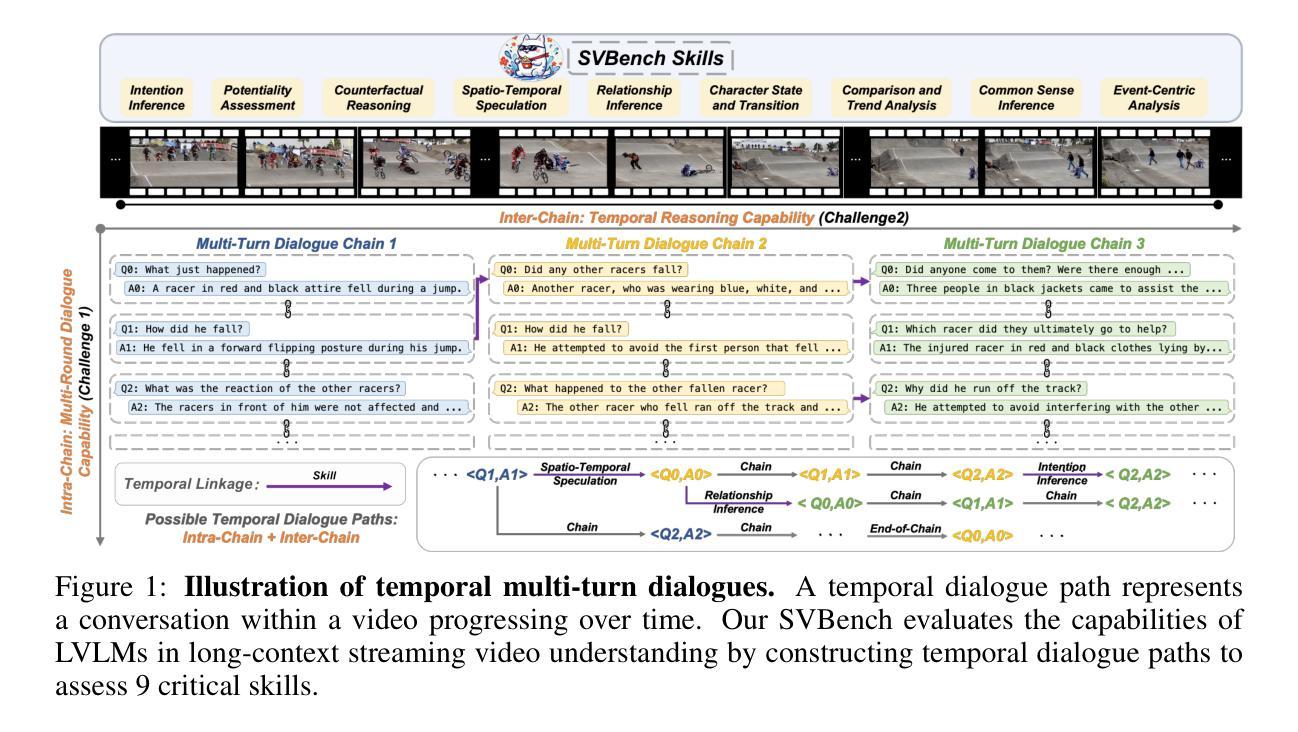
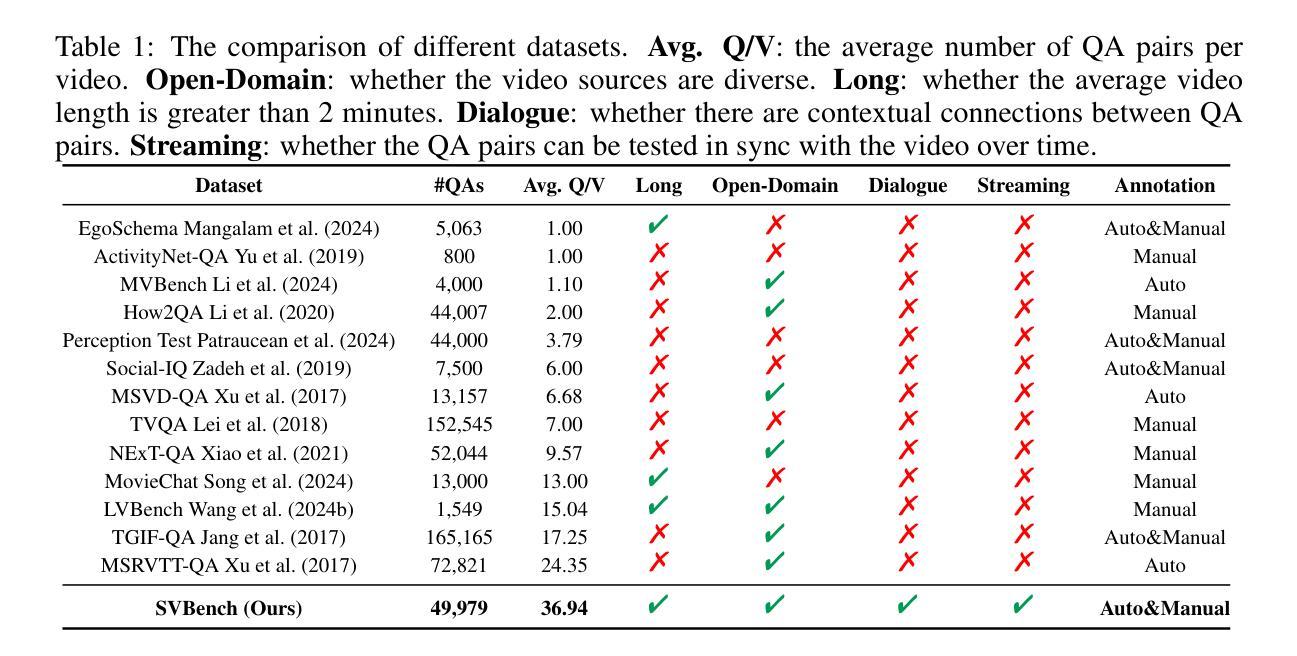
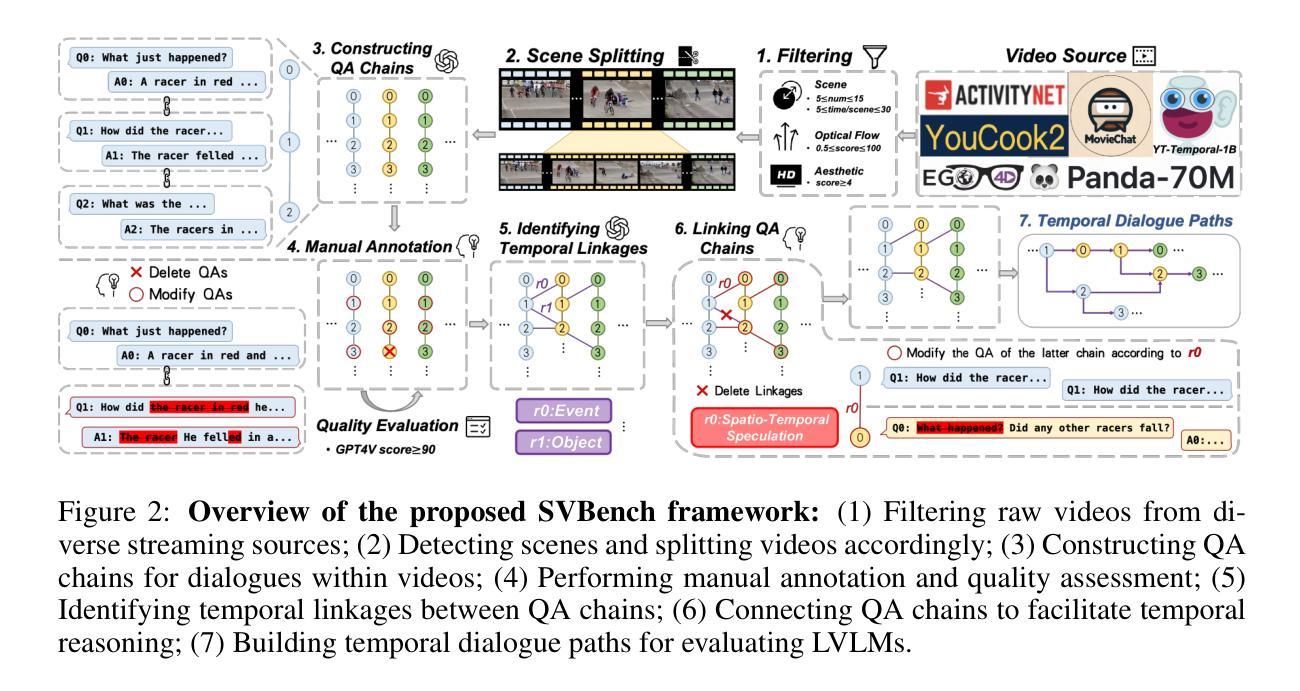
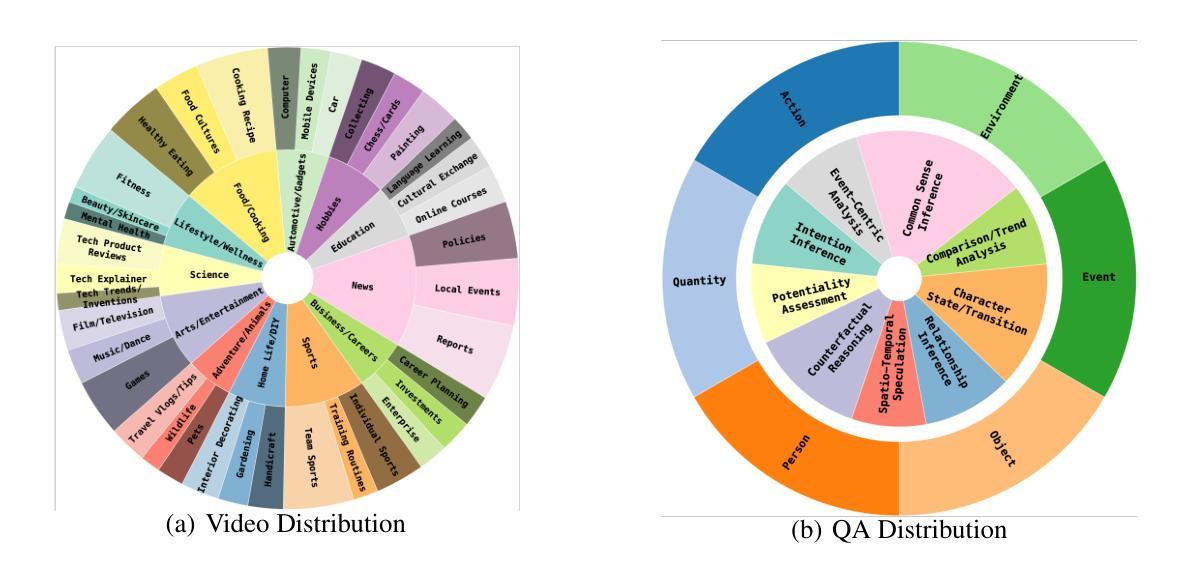
Despite the significant advancements of Large Vision-Language Models (LVLMs) on established benchmarks, there remains a notable gap in suitable evaluation regarding their applicability in the emerging domain of long-context streaming video understanding. Current benchmarks for video understanding typically emphasize isolated single-instance text inputs and fail to evaluate the capacity to sustain temporal reasoning throughout the entire duration of video streams. To address these limitations, we introduce SVBench, a pioneering benchmark with temporal multi-turn question-answering chains specifically designed to thoroughly assess the capabilities of streaming video understanding of current LVLMs. We design a semi-automated annotation pipeline to obtain 49,979 Question-Answer (QA) pairs of 1,353 streaming videos, which includes generating QA chains that represent a series of consecutive multi-turn dialogues over video segments and constructing temporal linkages between successive QA chains. Our experimental results, obtained from 14 models in dialogue and streaming evaluations, reveal that while the closed-source GPT-4o outperforms others, most open-source LVLMs struggle with long-context streaming video understanding. We also construct a StreamingChat model, which significantly outperforms open-source LVLMs on our SVBench and achieves comparable performance on diverse vision-language benchmarks. We expect SVBench to advance the research of streaming video understanding by providing a comprehensive and in-depth analysis of current LVLMs. Our benchmark and model can be accessed at https://yzy-bupt.github.io/SVBench.
尽管大型视觉语言模型(LVLMs)在既定基准测试中取得了显著进展,但在长上下文流式视频理解等新兴领域的应用评估中仍存在明显的差距。当前视频理解的基准测试通常强调孤立的单实例文本输入,无法评估在整个视频流中维持时间推理的能力。为了解决这些局限性,我们引入了SVBench,这是一个具有时间多回合问答链的开创性基准测试,专门设计用于全面评估当前LVLMs的流式视频理解能力。我们设计了一个半自动注释管道,获得了49979个问答对,涉及1353个流式视频,包括生成代表视频片段上连续多回合对话的QA链,以及在连续QA链之间建立时间联系。我们的实验结果来自对话和流式评估中的1,共十四个模型的数据表明,虽然闭源的GPT-显著优于其他模型,但大多数开源LVLMs在长上下文流式视频理解方面遇到了困难。我们还构建了一个StreamingChat模型,在我们的SVBench上,该模型显著优于开源LVLMs并实现了多样化的视觉语言基准测试中的可比性能。我们期望SVBench通过提供对当前LVLM的全面深入分析来促进流式视频理解的研究。我们的基准测试和模型可通过https://yzy-bupt.github.io/SVBench进行访问。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICLR 2025 Accept (Spotlight)
Summary
本文介绍了大型视觉语言模型(LVLMs)在处理长上下文流式视频理解方面的应用差距。针对现有视频理解基准测试未能充分评估模型在流式视频处理方面的能力,本文提出了一种新的基准测试SVBench。该基准测试通过设计包含连续多轮对话的视频片段问答链,全面评估模型对长上下文流式视频的理解能力。实验结果显示,尽管GPT-4o表现较好,但大多数开源LVLMs在处理长上下文流式视频理解方面仍有困难。本文还构建了一个StreamingChat模型,该模型在SVBench上显著优于开源LVLMs,并在多种视觉语言基准测试中表现良好。
Key Takeaways
- 当前视频理解基准测试未能充分评估大型视觉语言模型(LVLMs)在处理长上下文流式视频方面的能力。
- SVBench是一种新基准测试,设计用于评估模型在流式视频理解方面的能力,包含连续的多轮问答链。
- SVBench包含半自动注释管道,用于生成QA对和构建视频片段之间的时间链接。
- GPT-4o在基准测试中表现较好,但大多数开源LVLMs在处理长上下文流式视频理解方面遇到困难。
- 构建了一个StreamingChat模型,该模型在SVBench上表现优秀,并在多种视觉语言基准测试中达到良好性能。
点此查看论文截图

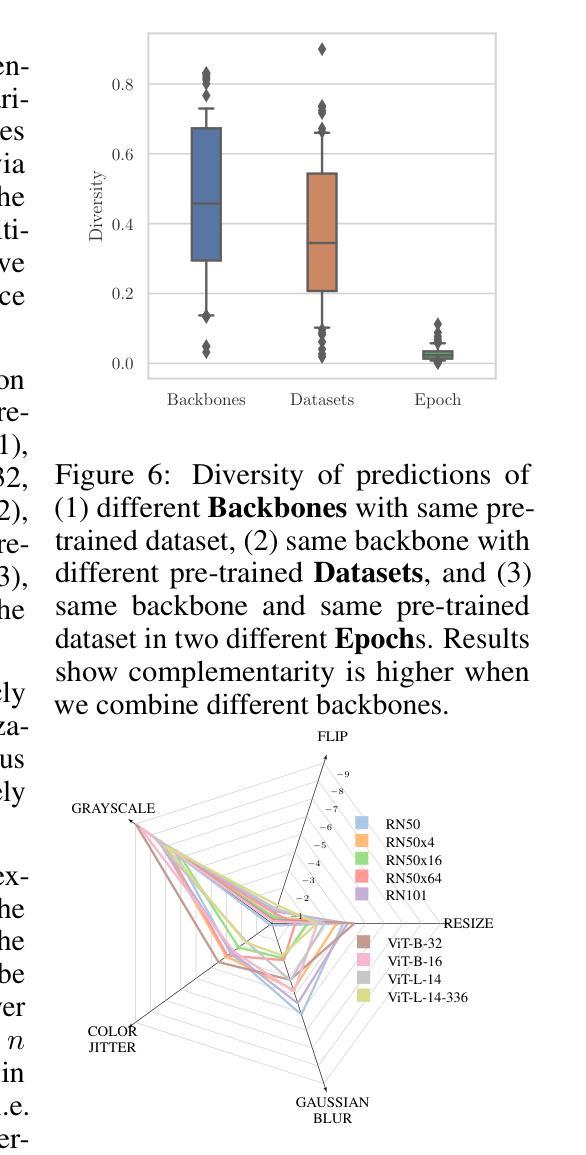
Optimizing GPT for Video Understanding: Zero-Shot Performance and Prompt Engineering
Authors:Mark Beliaev, Victor Yang, Madhura Raju, Jiachen Sun, Xinghai Hu
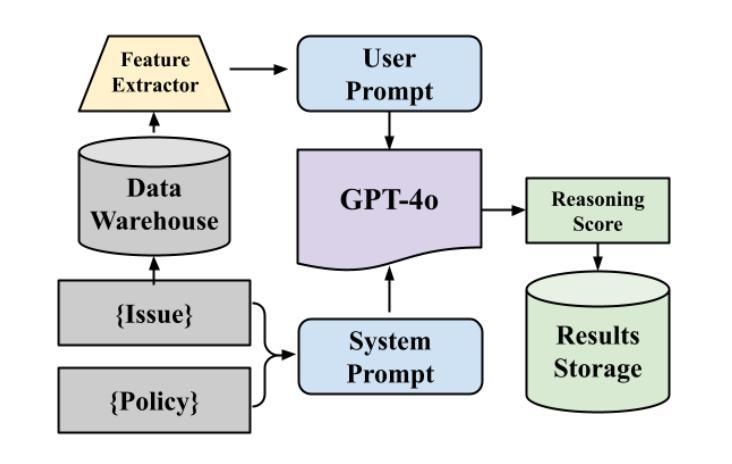
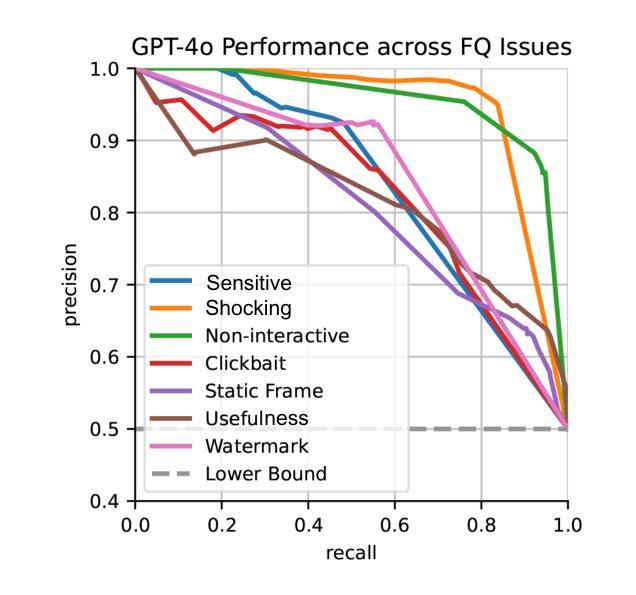
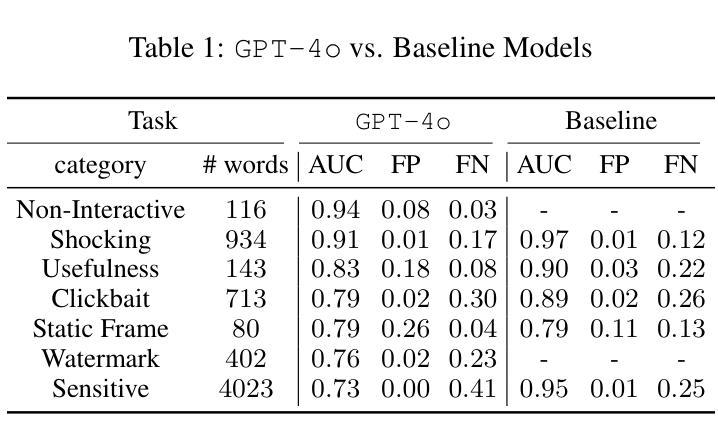
In this study, we tackle industry challenges in video content classification by exploring and optimizing GPT-based models for zero-shot classification across seven critical categories of video quality. We contribute a novel approach to improving GPT’s performance through prompt optimization and policy refinement, demonstrating that simplifying complex policies significantly reduces false negatives. Additionally, we introduce a new decomposition-aggregation-based prompt engineering technique, which outperforms traditional single-prompt methods. These experiments, conducted on real industry problems, show that thoughtful prompt design can substantially enhance GPT’s performance without additional finetuning, offering an effective and scalable solution for improving video classification systems across various domains in industry.
在这项研究中,我们通过探索和优化基于GPT的模型,解决视频内容分类行业中的挑战,实现对七个关键视频质量类别的零样本分类。我们提出了一种改进GPT性能的新方法,通过提示优化和政策完善,证明简化复杂政策可以显著降低假阴性。此外,我们引入了一种基于分解聚合的提示工程技术,它优于传统的单提示方法。这些针对真实行业问题进行的实验表明,有策略性的提示设计可以显著提高GPT的性能,而无需额外的微调,为改进各行业领域的视频分类系统提供了有效且可扩展的解决方案。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:
本研究通过探索和优化基于GPT的模型,解决视频内容分类的行业挑战,实现跨七个关键视频质量类别的零样本分类。研究通过优化提示和细化策略,提高GPT性能,发现简化复杂策略能显著降低误报。同时,引入基于分解聚合的提示工程技术,优于传统单一提示方法。基于行业实际问题的实验表明,精心设计的提示可大幅提高GPT性能,无需额外微调,为各行业领域改进视频分类系统提供有效可伸缩的解决方案。
Key Takeaways:
- 研究针对视频内容分类的行业挑战,利用GPT模型进行优化。
- 实现跨七个关键视频质量类别的零样本分类。
- 通过优化提示和策略来提高GPT的性能。
- 简化复杂策略能显著降低误报。
- 引入基于分解聚合的提示工程技术,提高分类性能。
- 精心设计的提示可大幅提高GPT性能,无需额外微调。
点此查看论文截图

VideoWebArena: Evaluating Long Context Multimodal Agents with Video Understanding Web Tasks
Authors:Lawrence Jang, Yinheng Li, Dan Zhao, Charles Ding, Justin Lin, Paul Pu Liang, Rogerio Bonatti, Kazuhito Koishida
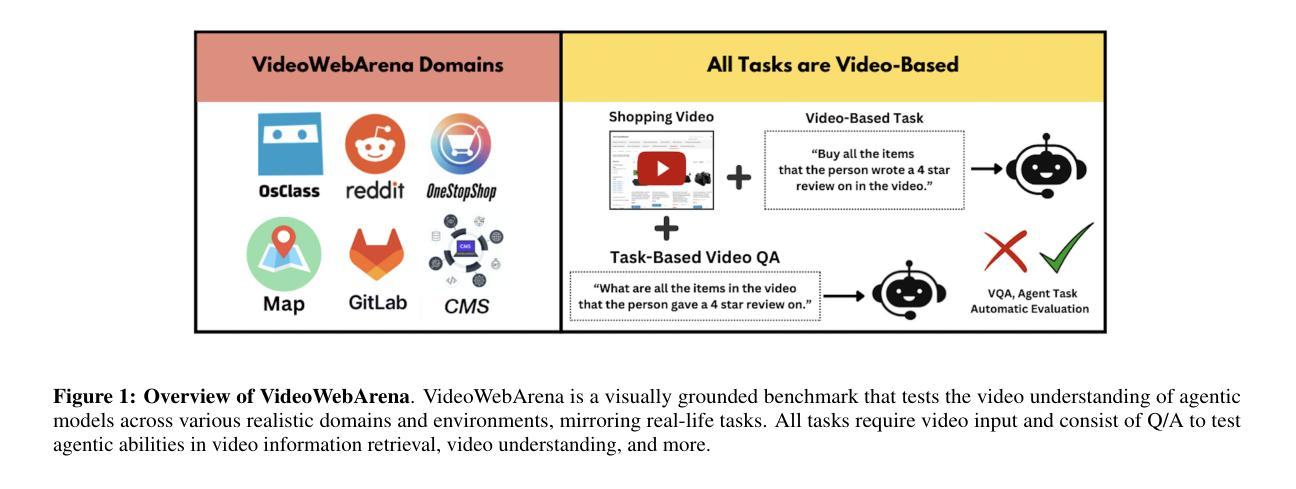
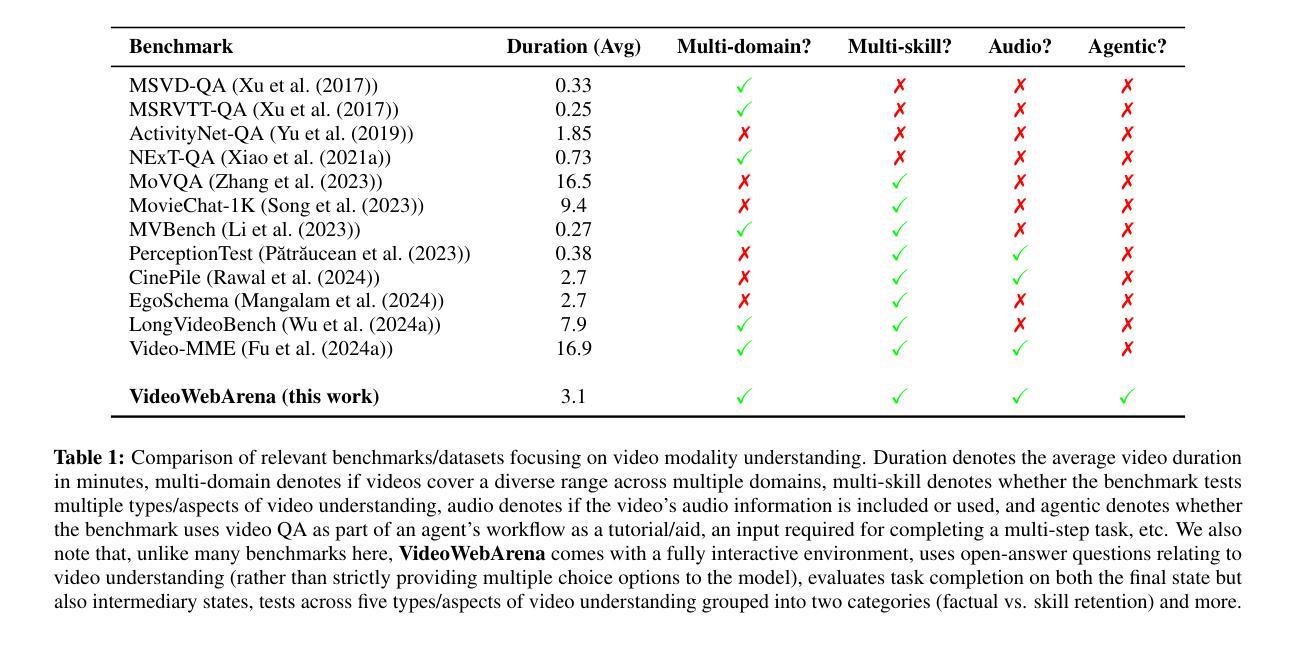
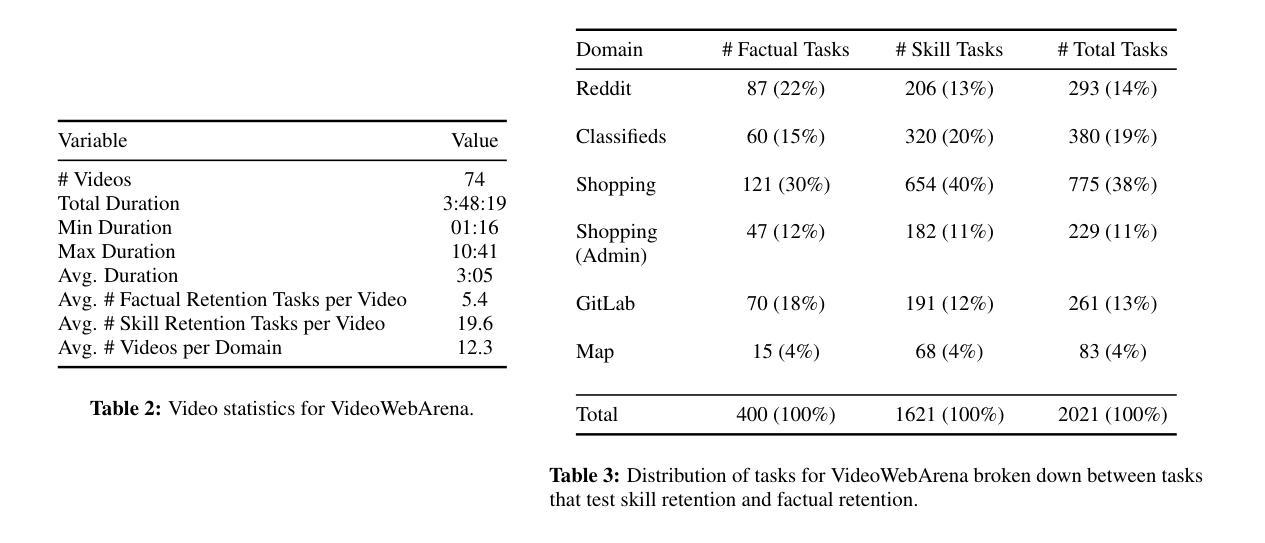
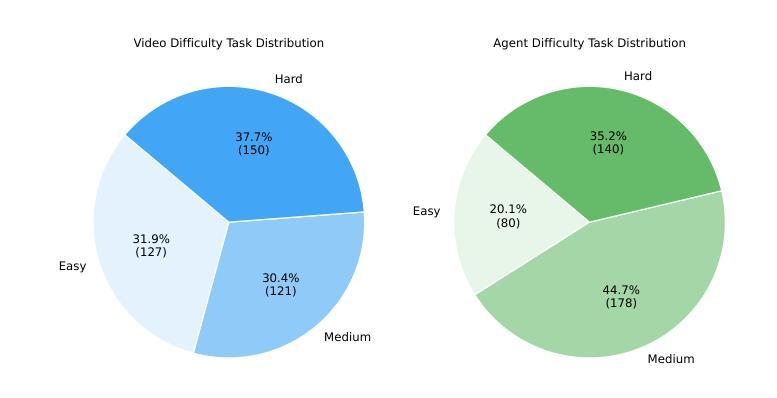
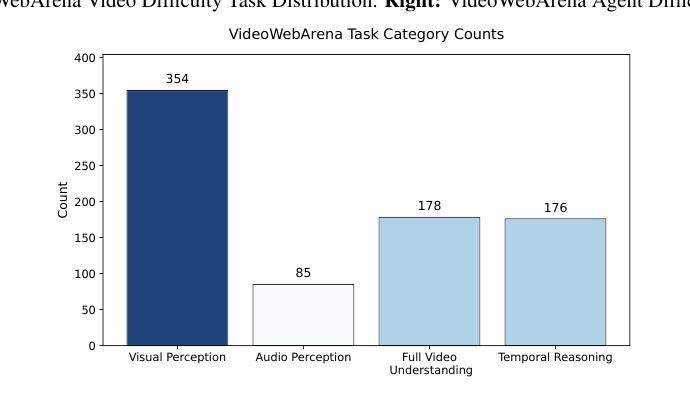
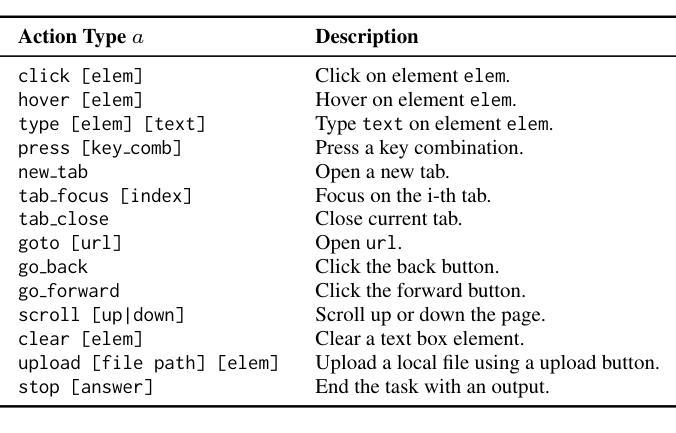
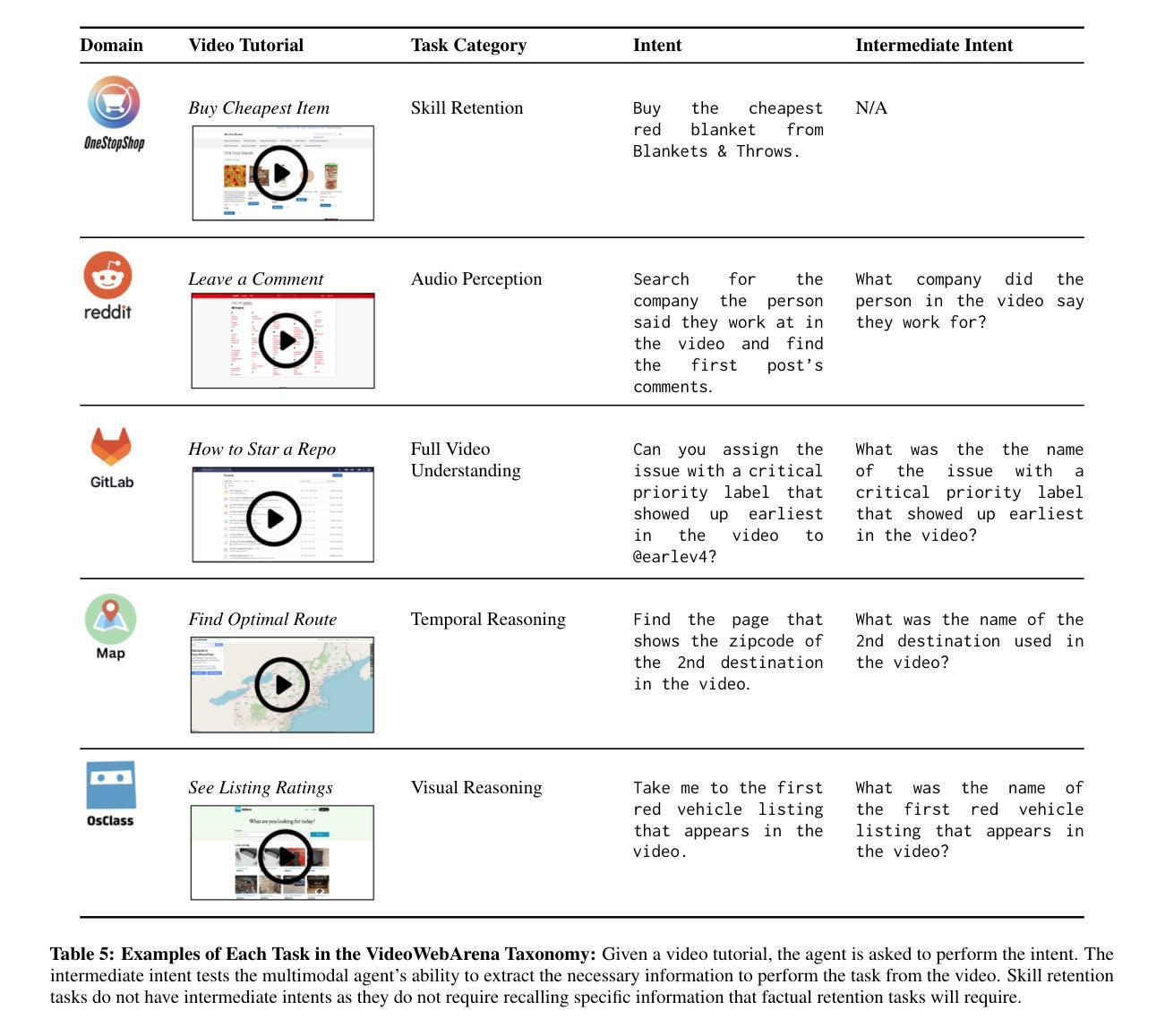
Videos are often used to learn or extract the necessary information to complete tasks in ways different than what text and static imagery alone can provide. However, many existing agent benchmarks neglect long-context video understanding, instead focusing on text or static image inputs. To bridge this gap, we introduce VideoWebArena (VideoWA), a benchmark for evaluating the capabilities of long-context multimodal agents for video understanding. VideoWA consists of 2,021 web agent tasks based on manually crafted video tutorials, which total almost four hours of content. For our benchmark, we define a taxonomy of long-context video-based agent tasks with two main areas of focus: skill retention and factual retention. While skill retention tasks evaluate whether an agent can use a given human demonstration to complete a task efficiently, the factual retention task evaluates whether an agent can retrieve instruction-relevant information from a video to complete a task. We find that the best model achieves 13.3% success on factual retention tasks and 45.8% on factual retention QA pairs, far below human performance at 73.9% and 79.3%, respectively. On skill retention tasks, long-context models perform worse with tutorials than without, exhibiting a 5% performance decrease in WebArena tasks and a 10.3% decrease in VisualWebArena tasks. Our work highlights the need to improve the agentic abilities of long-context multimodal models and provides a testbed for future development with long-context video agents.
视频通常用于以不同于文本和静态图像的方式学习或提取完成任务所需的信息。然而,许多现有的代理基准测试忽视了长语境视频理解,而是专注于文本或静态图像输入。为了弥补这一差距,我们引入了VideoWebArena(VideoWA),这是一个用于评估长语境多媒体代理视频理解能力的基准测试。VideoWA由基于手工制作的视频教程的2021个网络代理任务组成,总计近四个小时的内容。在我们的基准测试中,我们定义了长语境视频代理任务分类,重点关注两个主要领域:技能保持和事实保持。技能保持任务评估代理是否能够使用给定的人类演示有效地完成任务,而事实保持任务评估代理是否能够从视频中检索与指令相关的信息来完成任务。我们发现,最佳模型在事实保持任务上达到13.3%的成功率,在事实保持问答对上达到45.8%,远低于人类的73.9%和79.3%。在技能保持任务上,长上下文模型在有教程的情况下表现更差,在WebArena任务中性能下降5%,在VisualWebArena任务中下降10.3%。我们的工作强调了提高长语境多媒体模型代理能力的重要性,并为未来长语境视频代理的开发提供了测试平台。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了一个评估长语境视频理解能力的基准测试——VideoWebArena(VideoWA)。该基准测试包含2021个基于手工制作的视频教程的Web代理任务,总时长近四个小时。文章提出了长语境视频代理任务的分类,主要关注技能保持和事实保持两个方面。技能保持任务评估代理是否可以根据人类演示高效完成任务,而事实保持任务则评估代理是否可以从视频中检索与指令相关的信息来完成任务。研究发现,最好的模型在事实保持任务上的成功率仅为13.3%,问答对上的成功率为45.8%,远低于人类的73.9%和79.3%。技能保持任务中,长语境模型在教程下的性能不如无教程,WebArena任务和VisualWebArena任务的性能分别下降了5%和10.3%。本文强调了提高长语境多模式模型的代理能力的重要性,并为未来长语境视频代理的开发提供了测试平台。
Key Takeaways
- VideoWebArena(VideoWA)是一个评估长语境视频理解能力的基准测试。
- 该基准测试包含基于手工制作的视频教程的Web代理任务,时长近四个小时。
- 长语境视频代理任务分类主要包括技能保持和事实保持两个方面。
- 现有模型在事实保持任务上的表现远不及人类。
- 在技能保持任务中,长语境模型在有教程的情况下性能下降。
- 文章强调了提高长语境多模式模型的代理能力的重要性。
点此查看论文截图

Understanding Long Videos with Multimodal Language Models
Authors:Kanchana Ranasinghe, Xiang Li, Kumara Kahatapitiya, Michael S. Ryoo
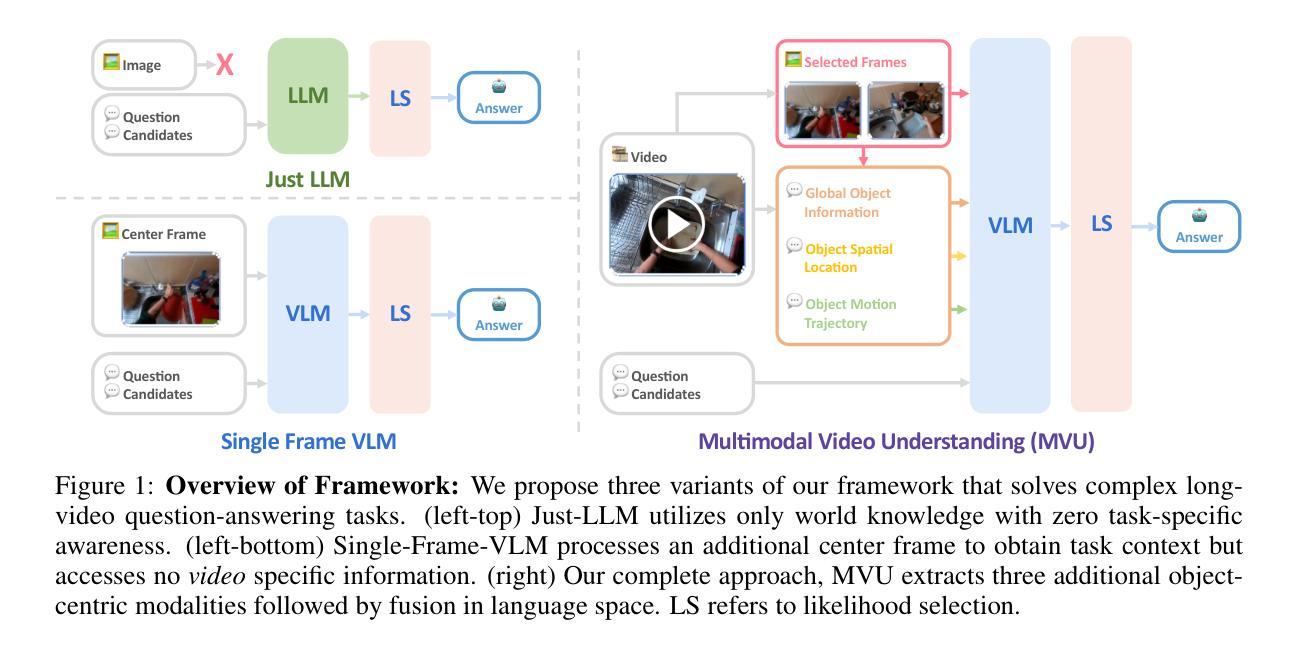
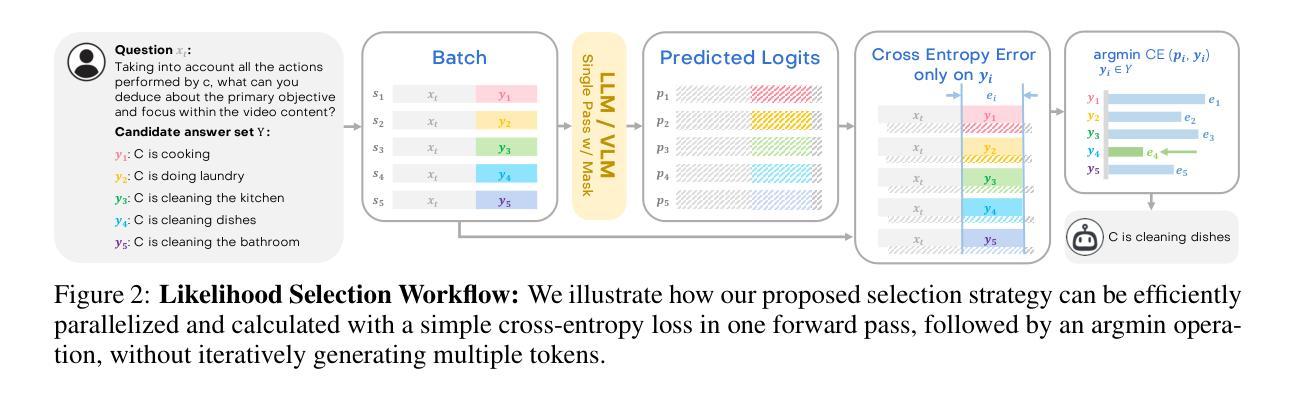
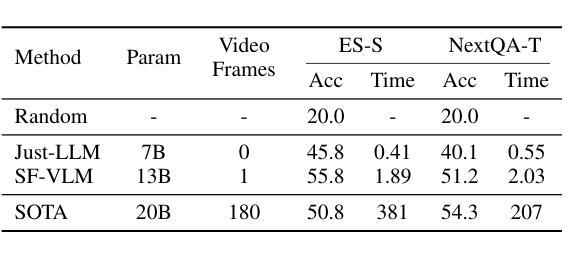
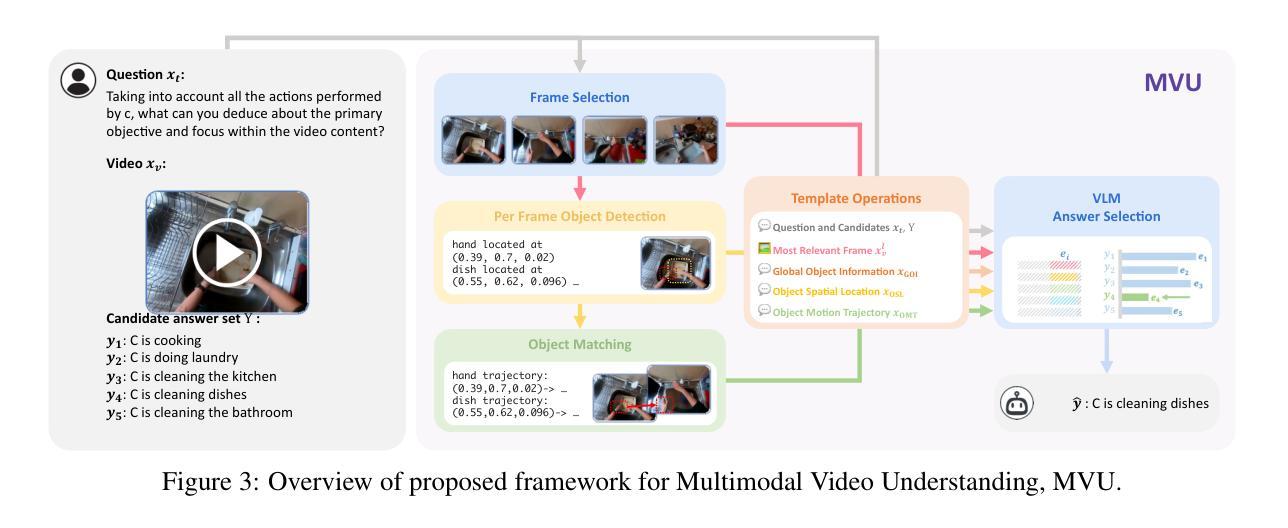
Large Language Models (LLMs) have allowed recent LLM-based approaches to achieve excellent performance on long-video understanding benchmarks. We investigate how extensive world knowledge and strong reasoning skills of underlying LLMs influence this strong performance. Surprisingly, we discover that LLM-based approaches can yield surprisingly good accuracy on long-video tasks with limited video information, sometimes even with no video specific information. Building on this, we exploring injecting video-specific information into an LLM-based framework. We utilize off-the-shelf vision tools to extract three object-centric information modalities from videos and then leverage natural language as a medium for fusing this information. Our resulting Multimodal Video Understanding (MVU) framework demonstrates state-of-the-art performance across multiple video understanding benchmarks. Strong performance also on robotics domain tasks establish its strong generality. Our code will be released publicly.
大型语言模型(LLM)使得最近的基于LLM的方法在长时间视频理解基准测试中取得了卓越的性能。我们研究了基础LLM的广泛世界知识和强大的推理能力是如何影响这一出色性能的。令人惊讶的是,我们发现基于LLM的方法在有限的视频信息,甚至有时没有任何特定视频信息的情况下,都能在长时间视频任务上产生令人惊讶的良好准确性。基于此,我们探索将特定视频信息注入基于LLM的框架中。我们使用现成的视觉工具从视频中提取三种以对象为中心的信息模式,并利用自然语言作为融合这些信息的媒介。我们由此构建的多媒体视频理解(MVU)框架在多个视频理解基准测试中展现了卓越的性能。其在机器人领域任务上的出色表现也证明了其强大的泛化能力。我们的代码将公开发布。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Code available at https://github.com/kahnchana/mvu
Summary
大型语言模型(LLM)在视频理解方面展现出卓越性能。研究发现,LLM的丰富知识及强大推理能力有助于其在长视频任务上实现高精度,即使视频信息有限或无特定视频信息亦能取得良好效果。基于这一发现,我们尝试将视频特定信息注入LLM框架中。利用现成的视觉工具提取视频中的三个以对象为中心的信息模式,并利用自然语言作为融合这些信息的媒介。我们提出的多媒体视频理解(MVU)框架在多个视频理解基准测试中表现出卓越性能,并在机器人领域任务中展现出强大的通用性。我们的代码将公开发布。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLM)在长视频理解任务中表现优异。
- LLM的丰富知识和强大推理能力有助于其性能表现。
- 在视频信息有限或无特定视频信息的情况下,LLM仍能取得良好效果。
- 提出将视频特定信息注入LLM框架的方法。
- 利用现成的视觉工具提取视频中的对象信息。
- 通过自然语言融合不同信息,形成多媒体视频理解(MVU)框架。
点此查看论文截图