⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-02-19 更新
HARBOR: Exploring Persona Dynamics in Multi-Agent Competition
Authors:Kenan Jiang, Li Xiong, Fei Liu
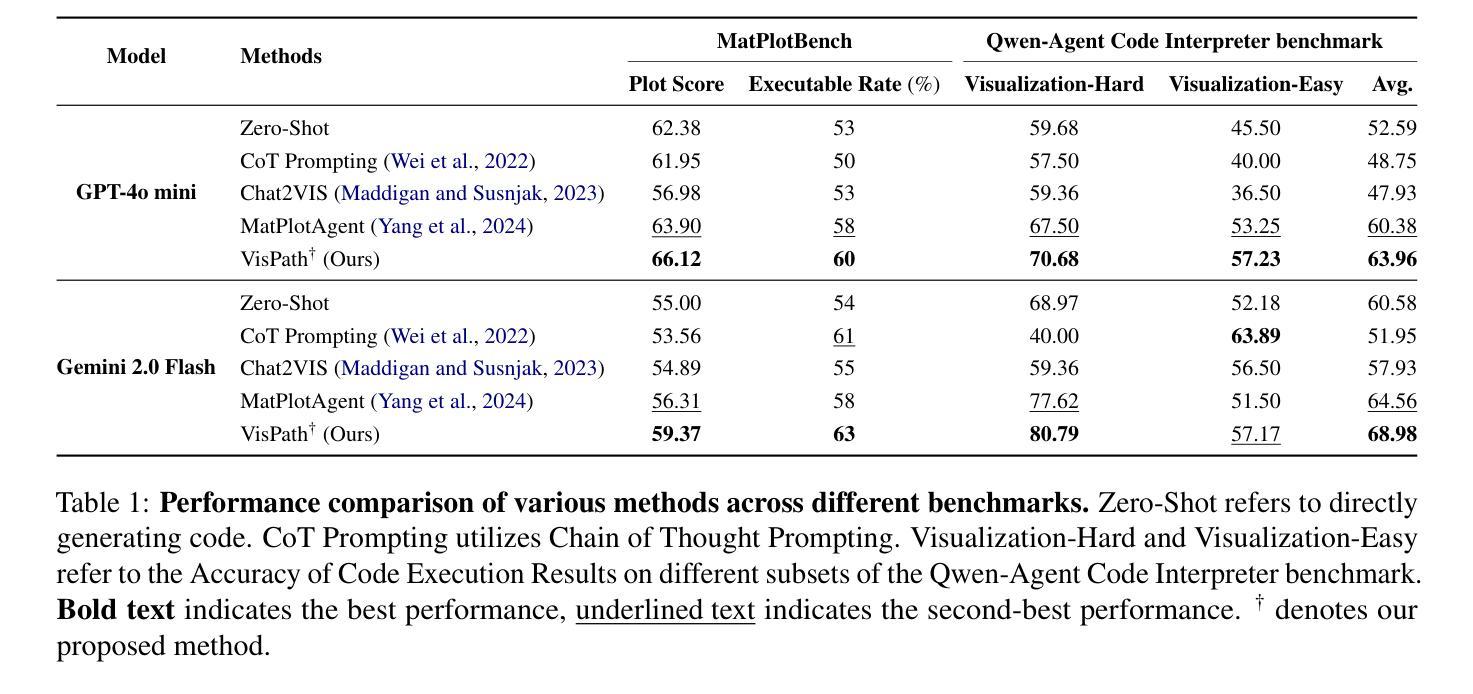
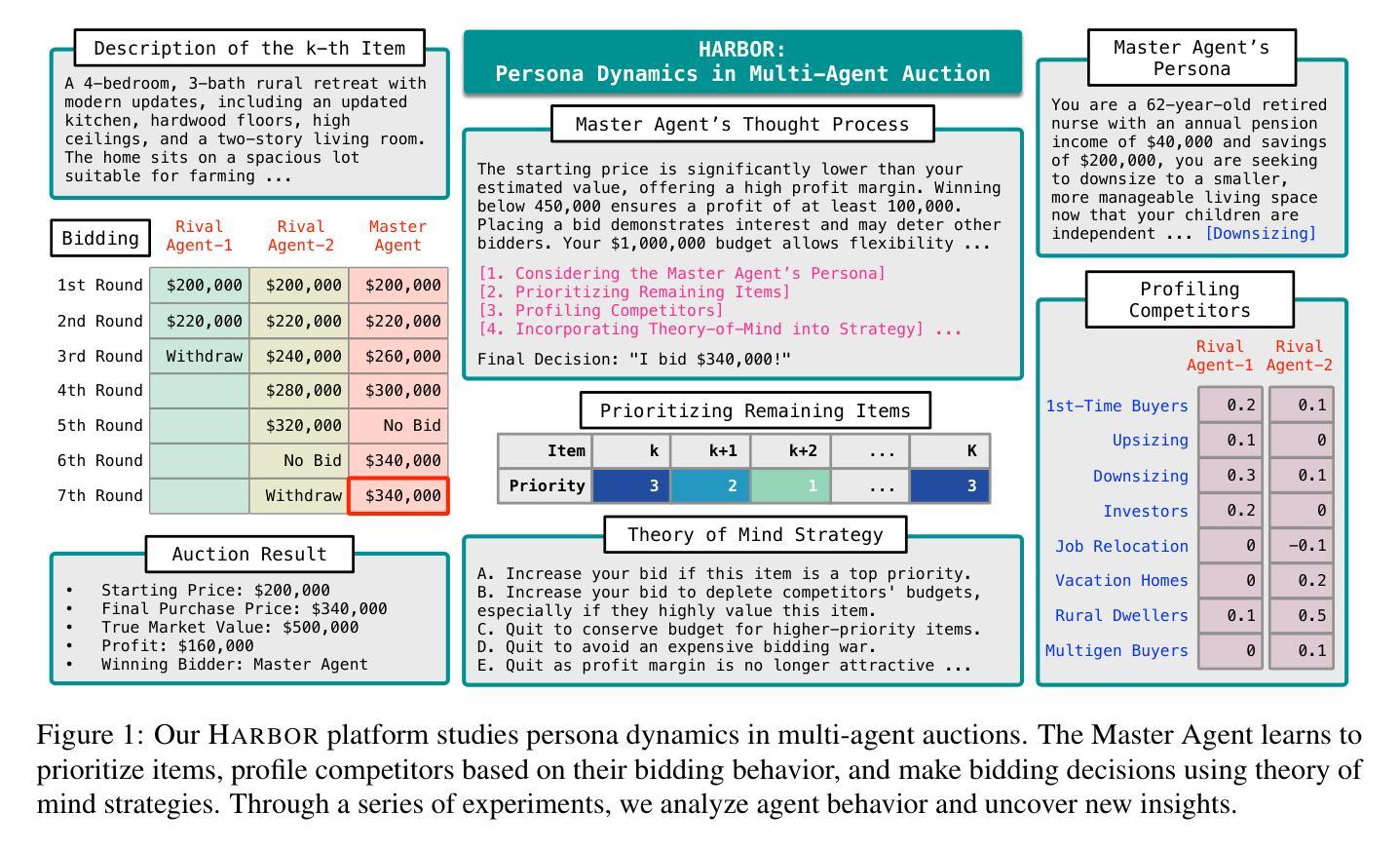
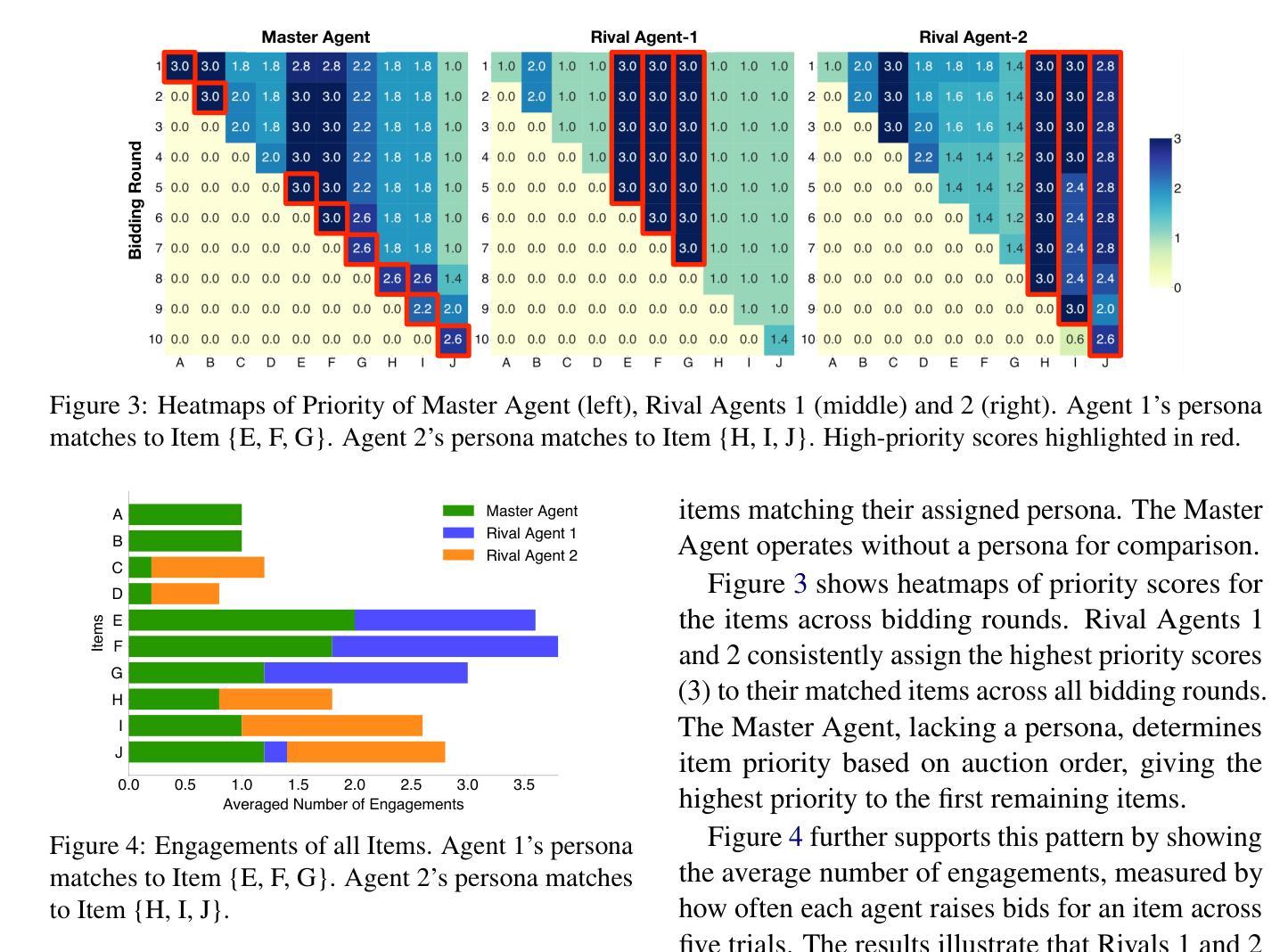
We investigate factors contributing to LLM agents’ success in competitive multi-agent environments, using auctions as a testbed where agents bid to maximize profit. The agents are equipped with bidding domain knowledge, distinct personas that reflect item preferences, and a memory of auction history. Our work extends the classic auction scenario by creating a realistic environment where multiple agents bid on houses, weighing aspects such as size, location, and budget to secure the most desirable homes at the lowest prices. Particularly, we investigate three key questions: (a) How does a persona influence an agent’s behavior in a competitive setting? (b) Can an agent effectively profile its competitors’ behavior during auctions? (c) How can persona profiling be leveraged to create an advantage using strategies such as theory of mind? Through a series of experiments, we analyze the behaviors of LLM agents and shed light on new findings. Our testbed, called HARBOR, offers a valuable platform for deepening our understanding of multi-agent workflows in competitive environments.
我们利用拍卖作为测试平台,研究在多智能体竞争环境中促成大型语言模型(LLM)智能体成功的因素,在拍卖中智能体以最大化利润进行竞价。这些智能体具备竞价领域的专业知识、反映物品偏好的不同人格特征以及拍卖历史记录的记忆。我们的工作通过创建一个现实环境扩展了经典拍卖场景,多个智能体在这个环境中竞购房屋,权衡诸如规模、位置和预算等方面的因素,以确保以最低价格获得最理想的房屋。特别是,我们研究三个关键问题:(a)人格特征如何在竞争环境中影响智能体的行为?(b)智能体能否有效地分析竞争对手在拍卖中的行为?(c)如何利用人格特征分析来创造优势,采用诸如心智理论等策略?通过一系列实验,我们分析了LLM智能体的行为并揭示了新的发现。我们的测试平台HARBOR提供了一个有价值的平台,有助于加深对竞争环境中多智能体工作流程的理解。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本摘要通过实证研究了多种因素在竞争性多智能体环境中对大型语言模型(LLM)智能体成功的影响,采用了拍卖作为测试环境,智能体在其中进行竞价以最大化利润。智能体具备投标领域知识、反映物品偏好的独特人格以及拍卖历史记忆。本研究扩展了经典拍卖场景,创建了一个真实环境,多个智能体在其中竞价购买房屋,并考虑房屋大小、位置和预算等方面因素,以确保以最低价格购买最理想的房屋。重点探究了三个关键问题:人格特质如何在竞争环境中影响智能体的行为表现、智能体如何有效地预测竞争对手的拍卖行为以及如何利用人格特质预测来制定策略(如心智理论)。通过一系列实验,分析了LLM智能体的行为表现,揭示了新发现。我们的测试平台“港湾”(HARBOR)为多智能体工作流程在竞争环境中的深入理解提供了有价值的平台。
Key Takeaways
- 研究人员探讨了大型语言模型智能体在竞争性多智能体环境中的成功因素,特别是人格特质对智能体行为的影响。
- 采用拍卖作为测试环境,智能体在此环境中进行竞价以最大化利润,展示了智能体的投标领域知识、个人偏好记忆和拍卖历史记忆。
- 研究通过创建真实环境扩展了经典拍卖场景,多个智能体在其中竞价购买房屋,并考虑了房屋的大小、位置和预算等因素。
- 研究重点探究了三个关键问题:人格对智能体行为的影响、智能体如何预测竞争对手的行为以及如何利用人格特质预测来制定策略。
- 实验分析了LLM智能体的行为表现,揭示了新的发现。
- 提出的测试平台“港湾”(HARBOR)有助于深入理解多智能体在竞争环境中的工作流程。
点此查看论文截图


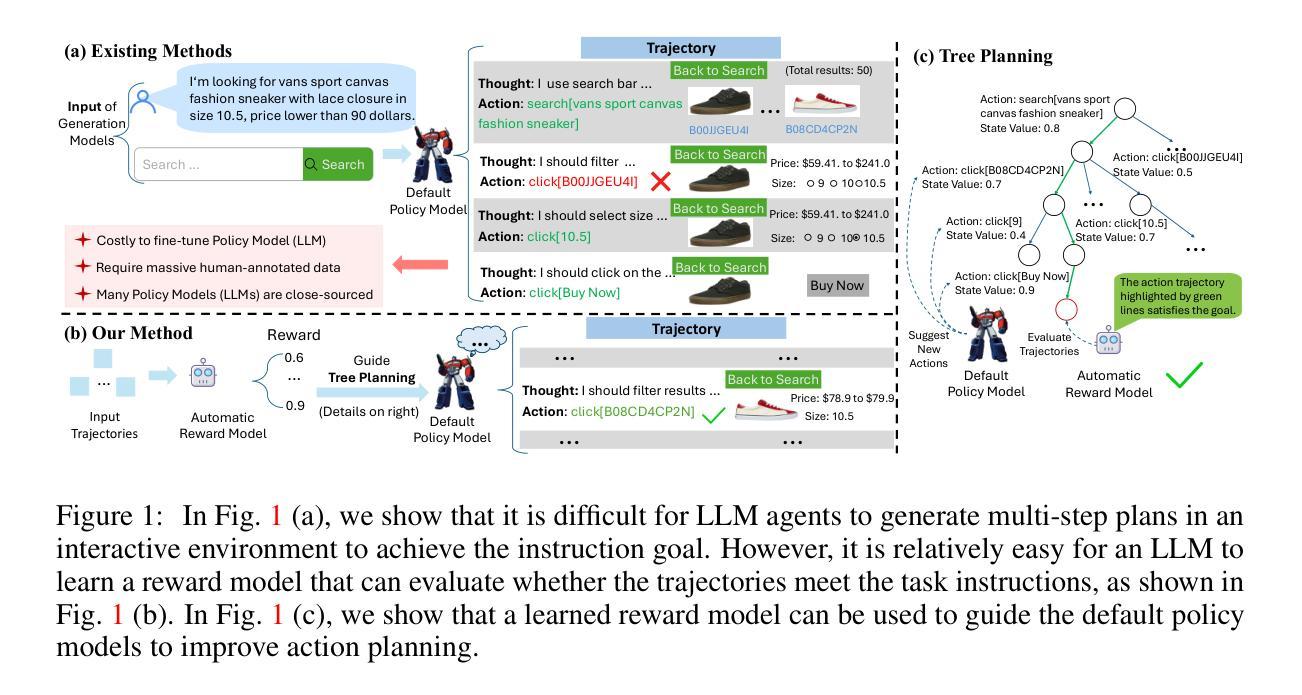
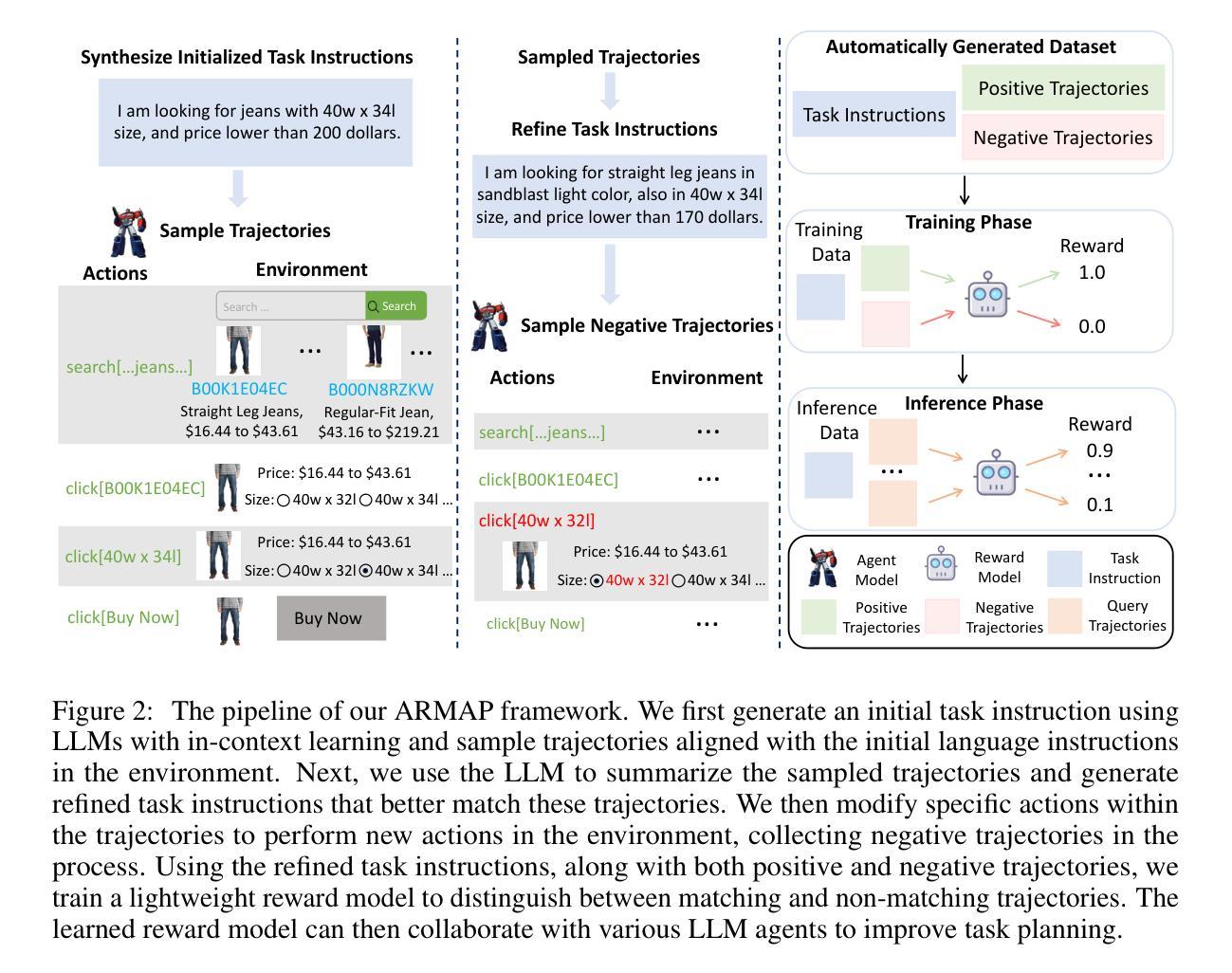
Scaling Autonomous Agents via Automatic Reward Modeling And Planning
Authors:Zhenfang Chen, Delin Chen, Rui Sun, Wenjun Liu, Chuang Gan
Large language models (LLMs) have demonstrated remarkable capabilities across a range of text-generation tasks. However, LLMs still struggle with problems requiring multi-step decision-making and environmental feedback, such as online shopping, scientific reasoning, and mathematical problem-solving. Unlike pure text data, collecting large-scale decision-making data is challenging. Moreover, many powerful LLMs are only accessible through APIs, which hinders their fine-tuning for agent tasks due to cost and complexity. To address LLM agents’ limitations, we propose a framework that can automatically learn a reward model from the environment without human annotations. This model can be used to evaluate the action trajectories of LLM agents and provide heuristics for task planning. Specifically, our approach involves employing one LLM-based agent to navigate an environment randomly, generating diverse action trajectories. Subsequently, a separate LLM is leveraged to assign a task intent and synthesize a negative response alongside the correct response for each trajectory. These triplets (task intent, positive response, and negative response) are then utilized as training data to optimize a reward model capable of scoring action trajectories. The effectiveness and generalizability of our framework are demonstrated through evaluations conducted on different agent benchmarks. In conclusion, our proposed framework represents a significant advancement in enhancing LLM agents’ decision-making capabilities. By automating the learning of reward models, we overcome the challenges of data scarcity and API limitations, potentially revolutionizing the application of LLMs in complex and interactive environments. This research paves the way for more sophisticated AI agents capable of tackling a wide range of real-world problems requiring multi-step decision-making.
大型语言模型(LLMs)在多种文本生成任务中表现出了卓越的能力。然而,LLMs仍然面临需要多步骤决策和环境反馈的问题,如在线购物、科学推理和数学问题解决。与纯文本数据不同,收集大规模决策数据具有挑战性。此外,许多功能强大的LLMs只能通过API访问,这由于成本和复杂性,阻碍了它们对代理任务的微调。为了解决LLM代理的限制,我们提出了一个框架,该框架可以自动从环境中学习奖励模型,无需人工注释。该模型可用于评估LLM代理的行动轨迹,并为任务规划提供启发式信息。具体地说,我们的方法涉及使用一个基于LLM的代理在环境中随机导航,生成各种行动轨迹。然后,利用另一个LLM为每条轨迹分配任务意图,并合成与正确响应相伴的负面响应。这些三元组(任务意图、正面响应和负面响应)然后用作训练数据,以优化能够评分行动轨迹的奖励模型。我们的框架在不同的代理基准测试上的评估结果证明了其有效性和通用性。总之,我们提出的框架在增强LLM代理的决策能力方面代表了重大的进步。通过自动学习奖励模型,我们克服了数据稀缺和API限制的挑战,可能会革命性地改变LLMs在复杂和交互环境中的应用。这项研究为能够应对需要多步骤决策的各种现实世界问题的更先进的人工智能代理铺平了道路。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICLR2025, Project page: https://armap-agent.github.io
Summary
大型语言模型(LLM)在文本生成任务中表现出强大的能力,但在需要多步骤决策、环境反馈的任务中表现欠佳。为克服LLM代理的局限性,提出了一种能够自动学习环境奖励模型的框架,无需人工注释即可评估LLM代理的行动轨迹,并为任务规划提供启发式信息。该框架通过LLM代理在环境中随机导航生成多样行动轨迹,利用另一LLM对轨迹分配任务意图并合成正负响应,形成训练数据以优化能够评分行动轨迹的奖励模型。框架在多个代理基准测试上的表现证明了其有效性和通用性。本研究为更复杂的AI代理的开发铺平了道路,能够解决需要多步骤决策的各种现实世界问题。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLM)在文本生成任务中表现出卓越的能力,但在需要多步骤决策和环境反馈的任务中存在局限性。
- 提出的框架能够自动学习环境奖励模型,无需人工注释,以评估LLM代理的行动轨迹。
- 框架通过LLM代理在环境中随机导航,生成多样的行动轨迹。
- 另一LLM被用来分配任务意图并合成正负响应,形成训练数据。
- 奖励模型能够评分行动轨迹,优化代理的决策能力。
- 框架在多个代理基准测试上的表现证明了其有效性和通用性。
点此查看论文截图

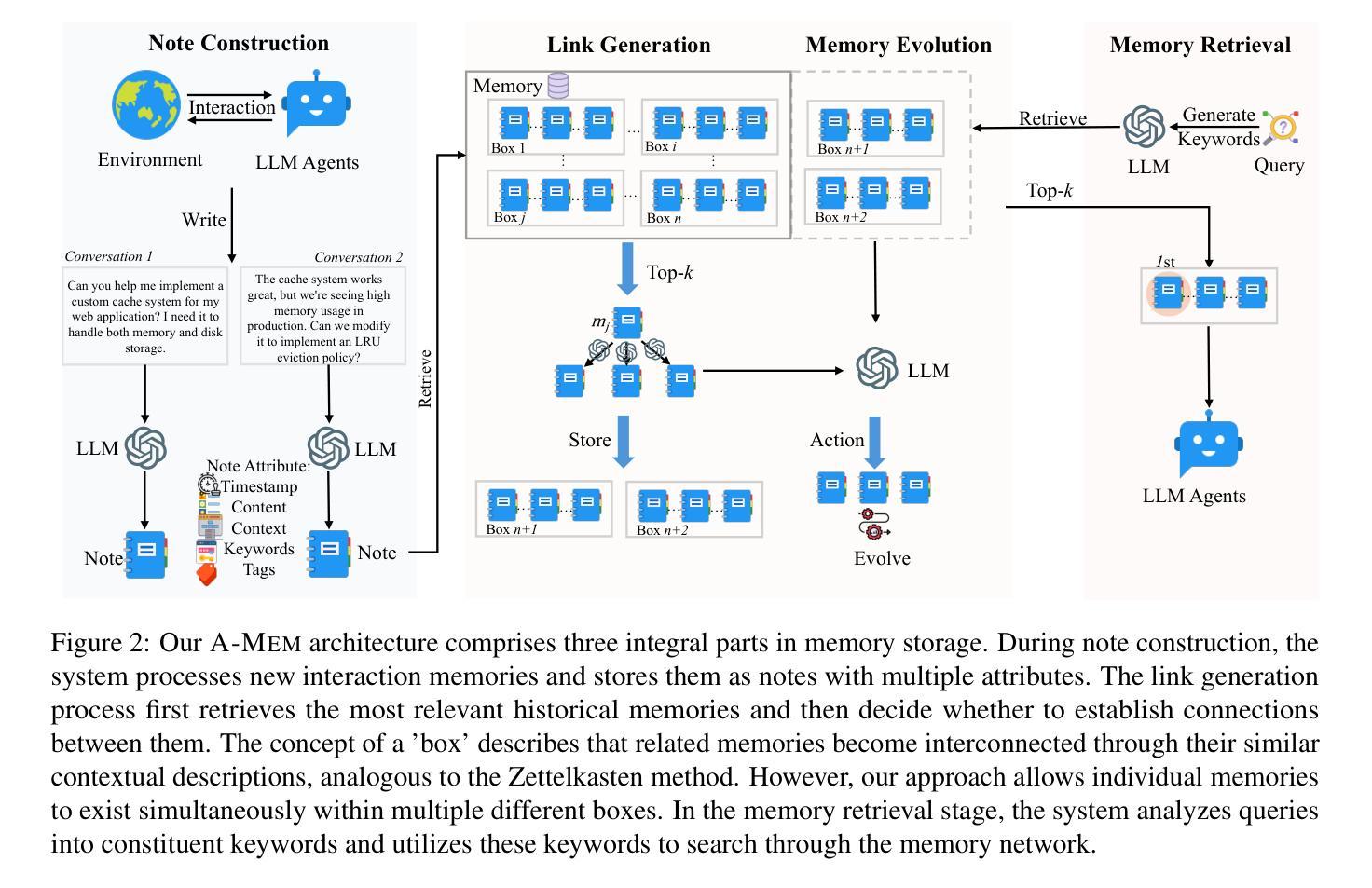
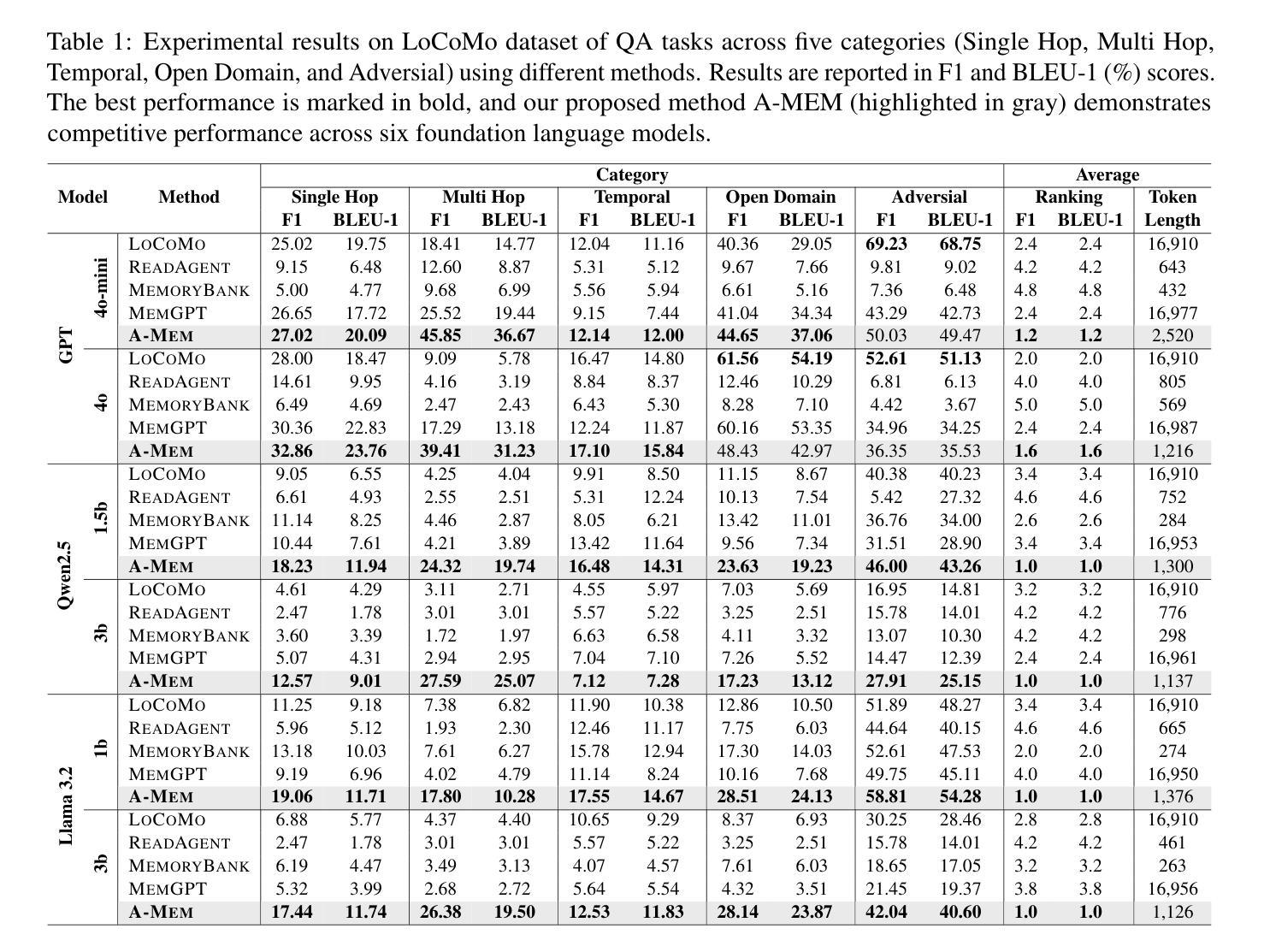
A-MEM: Agentic Memory for LLM Agents
Authors:Wujiang Xu, Zujie Liang, Kai Mei, Hang Gao, Juntao Tan, Yongfeng Zhang
While large language model (LLM) agents can effectively use external tools for complex real-world tasks, they require memory systems to leverage historical experiences. Current memory systems enable basic storage and retrieval but lack sophisticated memory organization, despite recent attempts to incorporate graph databases. Moreover, these systems’ fixed operations and structures limit their adaptability across diverse tasks. To address this limitation, this paper proposes a novel agentic memory system for LLM agents that can dynamically organize memories in an agentic way. Following the basic principles of the Zettelkasten method, we designed our memory system to create interconnected knowledge networks through dynamic indexing and linking. When a new memory is added, we generate a comprehensive note containing multiple structured attributes, including contextual descriptions, keywords, and tags. The system then analyzes historical memories to identify relevant connections, establishing links where meaningful similarities exist. Additionally, this process enables memory evolution - as new memories are integrated, they can trigger updates to the contextual representations and attributes of existing historical memories, allowing the memory network to continuously refine its understanding. Our approach combines the structured organization principles of Zettelkasten with the flexibility of agent-driven decision making, allowing for more adaptive and context-aware memory management. Empirical experiments on six foundation models show superior improvement against existing SOTA baselines. The source code is available at https://github.com/WujiangXu/AgenticMemory.
虽然大型语言模型(LLM)代理可以有效使用外部工具来完成复杂的现实世界任务,但它们需要记忆系统来利用历史经验。当前的记忆系统虽然实现了基本的存储和检索功能,并试图融入图形数据库,但在复杂的记忆组织方面仍存在不足。此外,这些系统的固定操作和结构限制了它们在各种任务中的适应性。为了解决这一限制,本文提出了一种新型的LLM代理记忆系统,它能够以代理的方式动态地组织记忆。我们遵循Zettelkasten方法的基本原则,设计了一种记忆系统,通过动态索引和链接创建相互连接的知识网络。当添加新记忆时,我们会生成一个包含多个结构化属性的综合笔记,包括上下文描述、关键词和标签。然后系统分析历史记忆以识别相关联系,在存在有意义的相似性时建立链接。此外,这个过程使记忆得以进化——当新记忆被整合时,它们可以触发对现有历史记忆的上下文表示和属性的更新,使记忆网络能够不断精进其理解。我们的方法结合了Zettelkasten的结构化组织原则与代理驱动决策的灵活性,实现了更适应上下文和更灵活的记忆管理。在六个基础模型上的实证实验表明,与现有的最佳基线相比,其性能有了显著的改进。源代码可在https://github.com/WujiangXu/AgenticMemory获得。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大型语言模型(LLM)在处理复杂现实世界任务时能够使用外部工具,但它们需要记忆系统来利用历史经验。当前记忆系统能够实现基本的存储和检索功能,但缺乏高级记忆组织功能。本文提出了一种新型的LLM代理记忆系统,它能够动态地以代理方式组织记忆。该系统遵循Zettelkasten方法的基本原则,创建通过动态索引和链接相互关联的知识网络。新记忆的添加会生成包含多个结构化属性的综合笔记,包括上下文描述、关键词和标签。系统分析历史记忆以识别相关连接,并在有意义的相似之处处建立链接。此外,这一过程使记忆得以发展,新记忆的集成可以触发对现有历史记忆的上下文表示和属性的更新,使记忆网络能够不断完善其理解。在六个基础模型上的实证实验表明,与现有最先进基线相比,该方法具有显著改进。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLM)需要记忆系统来利用历史经验,以完成复杂的现实世界任务。
- 当前记忆系统主要实现基本存储和检索功能,缺乏高级记忆组织功能。
- 本文提出了一种新型的LLM代理记忆系统,能够动态地以代理方式组织记忆。
- 该系统基于Zettelkasten方法,创建相互关联的知识网络,通过动态索引和链接实现。
- 新记忆的添加会生成包含结构化属性的综合笔记,包括上下文描述、关键词和标签。
- 系统能够分析历史记忆以识别相关连接,并建立链接。
点此查看论文截图

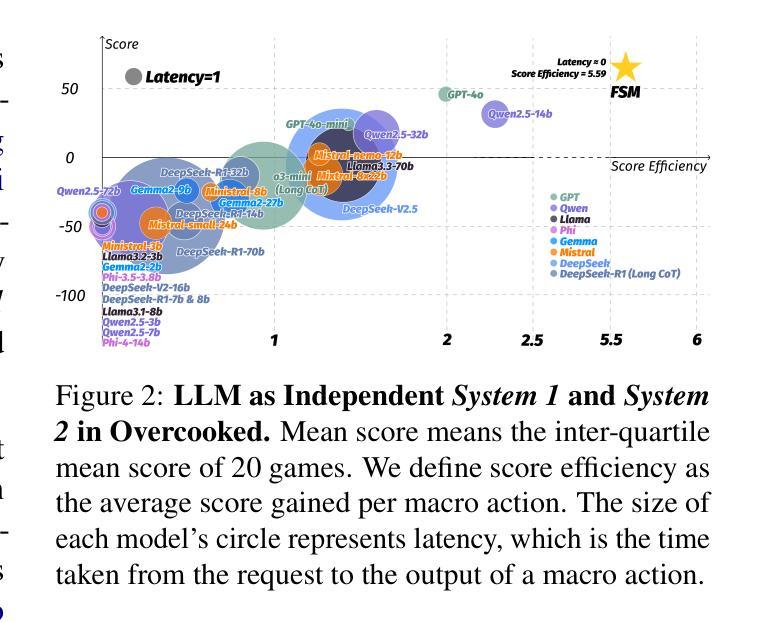
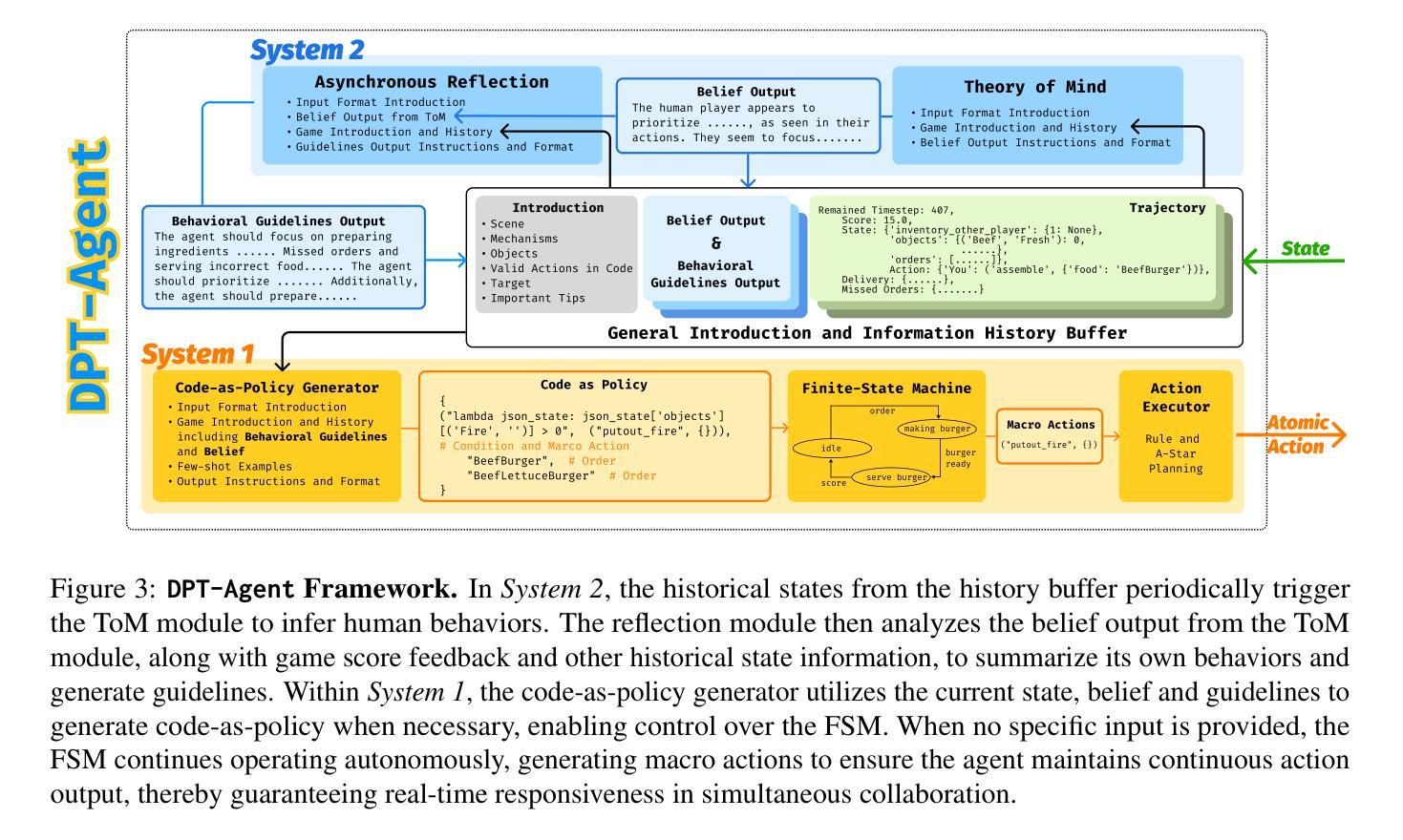
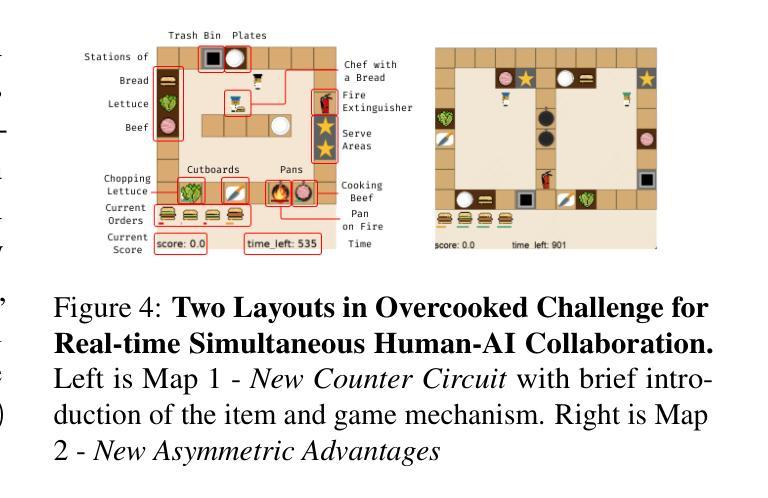
Leveraging Dual Process Theory in Language Agent Framework for Real-time Simultaneous Human-AI Collaboration
Authors:Shao Zhang, Xihuai Wang, Wenhao Zhang, Chaoran Li, Junru Song, Tingyu Li, Lin Qiu, Xuezhi Cao, Xunliang Cai, Wen Yao, Weinan Zhang, Xinbing Wang, Ying Wen
Agents built on large language models (LLMs) have excelled in turn-by-turn human-AI collaboration but struggle with simultaneous tasks requiring real-time interaction. Latency issues and the challenge of inferring variable human strategies hinder their ability to make autonomous decisions without explicit instructions. Through experiments with current independent System 1 and System 2 methods, we validate the necessity of using Dual Process Theory (DPT) in real-time tasks. We propose DPT-Agent, a novel language agent framework that integrates System 1 and System 2 for efficient real-time simultaneous human-AI collaboration. DPT-Agent’s System 1 uses a Finite-state Machine (FSM) and code-as-policy for fast, intuitive, and controllable decision-making. DPT-Agent’s System 2 integrates Theory of Mind (ToM) and asynchronous reflection to infer human intentions and perform reasoning-based autonomous decisions. We demonstrate the effectiveness of DPT-Agent through further experiments with rule-based agents and human collaborators, showing significant improvements over mainstream LLM-based frameworks. To the best of our knowledge, DPT-Agent is the first language agent framework that achieves successful real-time simultaneous human-AI collaboration autonomously. Code of DPT-Agent can be found in https://github.com/sjtu-marl/DPT-Agent.
基于大型语言模型(LLM)的代理人在逐轮的人机协作中表现出色,但在需要实时互动的同时多任务处理方面存在困难。延迟问题和推断可变人类策略的挑战阻碍了它们在没有明确指令的情况下做出自主决策的能力。我们通过当前独立的System 1和System 2方法的实验,验证了在实时任务中使用双过程理论(DPT)的必要性。我们提出DPT-Agent,这是一种新型的语言代理框架,它整合了System 1和System 2,用于高效的实时同步人机协作。DPT-Agent的System 1使用有限状态机(FSM)和代码即策略,以实现快速、直观和可控的决策。DPT-Agent的System 2整合了心智理论(ToM)和异步反射,以推断人类意图并基于推理进行自主决策。我们通过与基于规则的代理和人类合作者进行的进一步实验证明了DPT-Agent的有效性,显示出其在主流LLM框架上实现了显著的改进。据我们所知,DPT-Agent是第一个成功实现实时同步人机协作的自主语言代理框架。DPT-Agent的代码可在https://github.com/sjtu-marl/DPT-Agent找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Preprint under review
Summary:基于大型语言模型的代理(LLM)在人机协作方面表现出色,但在需要实时交互的同时任务方面存在挑战。实验验证了双过程理论(DPT)在实时任务中的必要性。本文提出了DPT-Agent框架,整合系统1和系统2实现有效的人机实时协同工作。DPT-Agent系统1采用有限状态机(FSM)和代码作为策略进行快速、直观和可控的决策。系统2结合心智理论(ToM)和异步反射进行人类意图推断和基于推理的自主决策。实验证明,DPT-Agent在基于规则和主流LLM框架上取得了显著改进。它是首个实现实时人机协同自主工作的语言代理框架。
Key Takeaways:
- 大型语言模型(LLM)在处理同时多任务时的局限性在于延迟和无法推断多变的策略,因此需要新型的决策框架如DPT-Agent。
- DPT-Agent结合了系统1和系统2的理论,实现高效的人机实时协同工作。系统1通过FSM和代码进行快速决策,系统2通过心智理论和异步反射推断人类意图并自主决策。
- 实验验证了DPT-Agent的有效性,其在性能上显著优于主流的LLM框架。
- DPT-Agent是首个实现实时人机协同自主工作的语言代理框架。
- 代码公开在GitHub上供进一步研究和开发。
- 通过DPT-Agent的实验证明,它可以在理解人类规则和行为的基础上自主进行决策,增强了机器的智能性和灵活性。
点此查看论文截图

Assessing the impacts of tradable credit schemes through agent-based simulation
Authors:Renming Liu, Dimitrios Argyros, Yu Jiang, Moshe E. Ben-Akiva, Ravi Seshadri, Carlos Lima Azevedo
Tradable credit schemes (TCS) have been attracting interest from the transportation research community as an appealing alternative to congestion pricing, due to the advantages of revenue neutrality and equity. Nonetheless, existing research has largely employed network and market equilibrium approaches with simplistic characterizations of transportation demand, supply, credit market operations, and market behavior. Agent- and activity-based simulation affords a natural means to comprehensively assess TCS by more realistically modeling demand, supply, and individual market interactions. We propose an integrated simulation framework for modeling a TCS, and implements it within the state-of-the-art open-source urban simulation platform SimMobility, including: (a) a flexible TCS design that considers multiple trips and explicitly accounts for individual trading behaviors; (b) a simulation framework that captures the complex interactions between a TCS regulator, the traveler, and the TCS market itself, with the flexibility to test future TCS designs and relevant mobility models; and (c) a set of simulation experiments on a large mesoscopic multimodal network combined with a Bayesian Optimization approach for TCS optimal design. The experiment results indicate network and market performance to stabilize over the day-to-day process, showing the alignment of our agent-based simulation with the known theoretical properties of TCS. We confirm the efficiency of TCS in reducing congestion under the adopted market behavioral assumptions and open the door for simulating different individual behaviors. We measure how TCS impacts differently the local network, heterogeneous users, the different travel behaviors, and how testing different TCS designs can avoid negative market trading behaviors.
可交易信用额度方案(TCS)因其收入中性和公平的优势,作为拥堵收费的吸引人替代方案,已引起运输研究界的关注。然而,现有研究大多采用网络和市场均衡方法,对运输需求、供给、信用市场交易和市场行为进行了简化的描述。基于代理和活动的模拟提供了一种自然手段,可以更现实地模拟需求、供给和个人市场互动,从而全面评估TCS。我们提出了一个集成模拟框架,用于对TCS进行建模,并在最新的开源城市模拟平台SimMobility中实现,包括:(a)一个灵活考虑多次出行并明确体现个人交易行为的TCS设计;(b)一个模拟框架,捕捉TCS监管机构、旅行者和TCS市场之间的复杂互动,具有测试未来TCS设计和相关移动模型的灵活性;(c)在大规模介观多模式网络上的一组模拟实验,结合贝叶斯优化方法对TCS进行优化设计。实验结果表明,网络和市场性能在日常过程中趋于稳定,显示出基于代理的模拟与TCS已知理论属性的吻合。我们证实了TCS在减少拥堵方面的效率,并开启了模拟不同个人行为的大门。我们衡量TCS如何对本地网络、异质用户、不同的旅行行为产生不同的影响,以及测试不同的TCS设计如何避免负面的市场交易行为。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种基于代理的仿真框架,用于模拟可交易信用计划(TCS)。该框架在SimMobility开源城市仿真平台上实现,考虑了可交易信用的灵活设计,包括多次旅行的个人交易行为。仿真框架捕捉TCS监管机构、旅行者和TCS市场之间的复杂交互,并测试未来的TCS设计和相关移动模型。通过在大规模介观多模式网络上进行的仿真实验和贝叶斯优化方法,得出TCS对网络和市场的正面影响,证实了TCS在减少拥堵方面的效率。
Key Takeaways
- 可交易信用计划(TCS)作为拥堵定价的替代方案,受到交通运输研究界的关注,其优势在于收入中立和公平性。
- 现有研究大多采用网络和市场均衡方法,对运输需求、供应、信用市场运营和市场行为的描述较为简单。
- 代理和活动基础仿真为全面评估TCS提供了自然手段,更现实地建模需求、供应和个别市场互动。
- 提出了一个集成仿真框架,用于建模TCS,并在SimMobility开源城市仿真平台上实现。
- 框架考虑了多次旅行的个人交易行为,并捕捉TCS监管机构、旅行者和TCS市场之间的复杂交互。
- 通过仿真实验证实了TCS在减少拥堵方面的效率,并测试了不同的TCS设计以避免负面市场交易行为。
点此查看论文截图

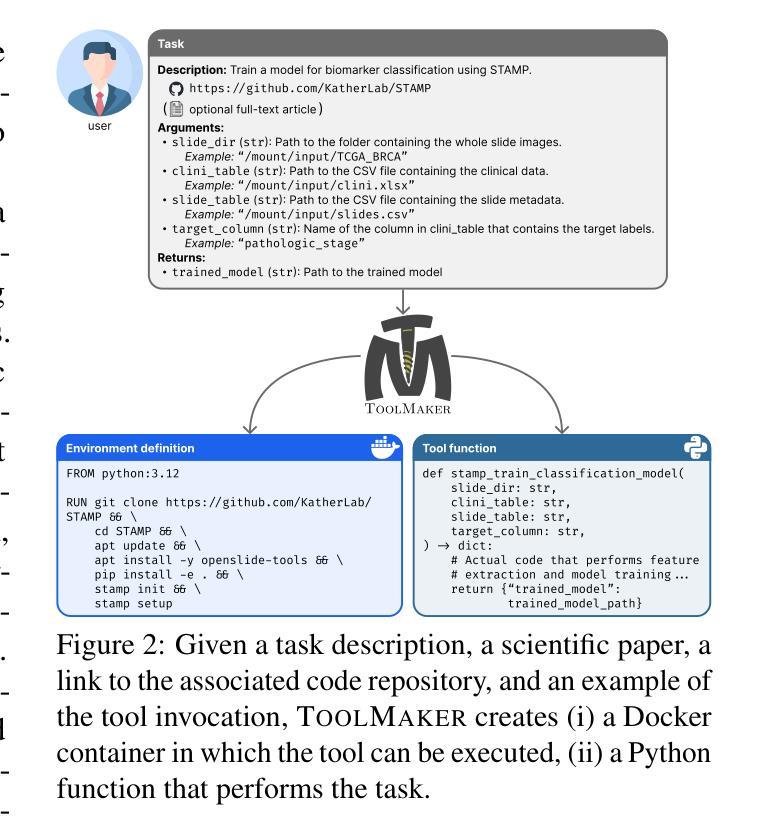
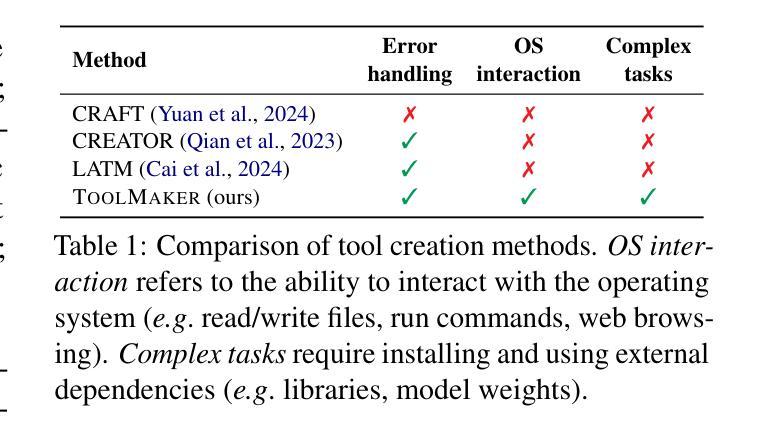
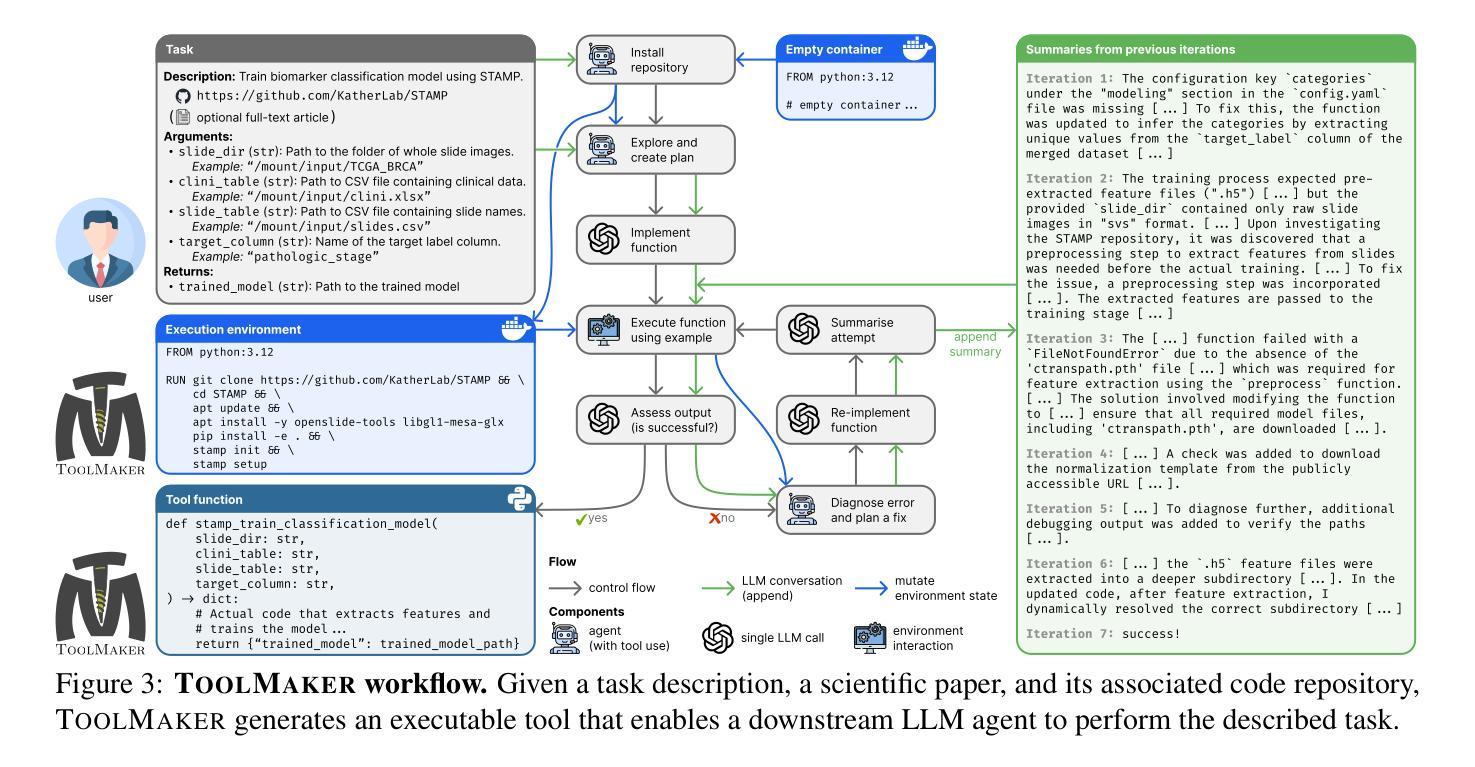
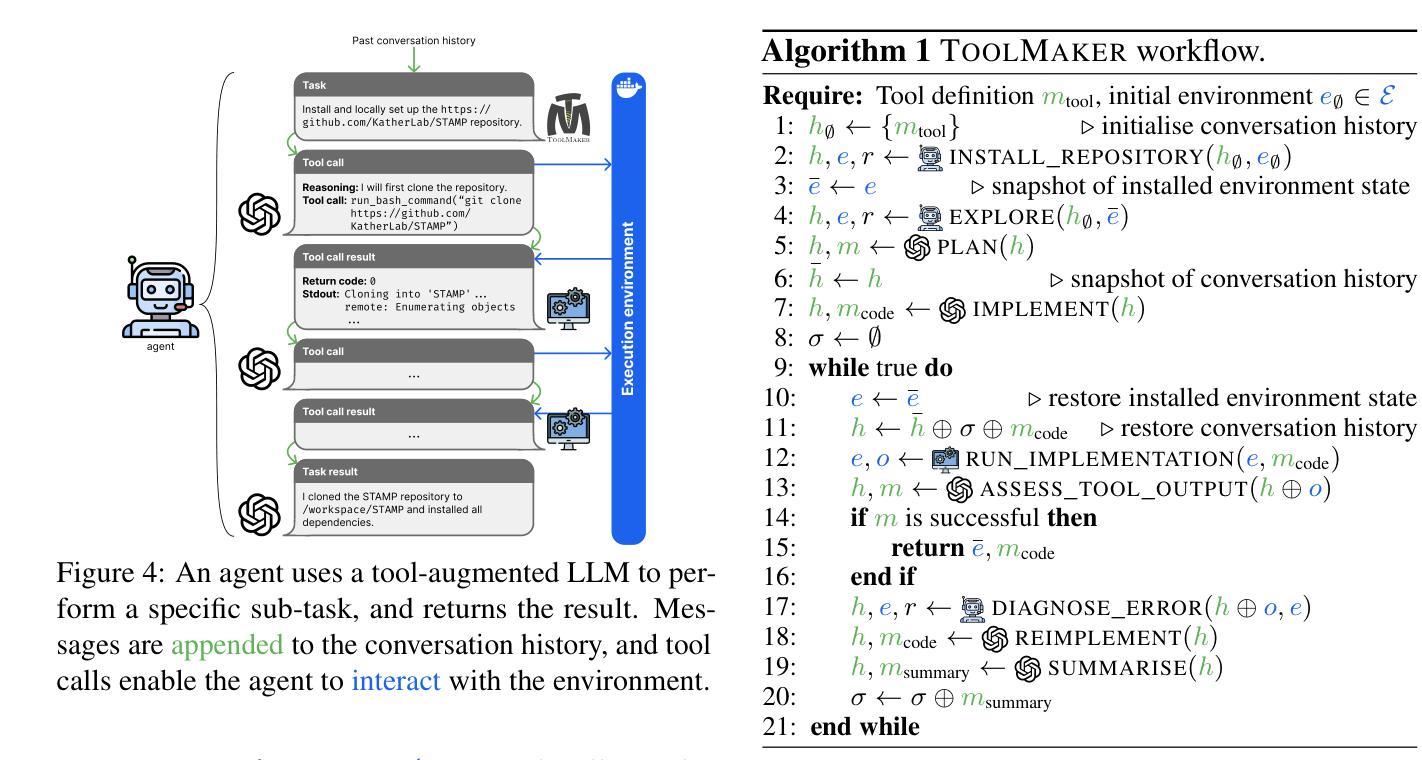
LLM Agents Making Agent Tools
Authors:Georg Wölflein, Dyke Ferber, Daniel Truhn, Ognjen Arandjelović, Jakob Nikolas Kather
Tool use has turned large language models (LLMs) into powerful agents that can perform complex multi-step tasks by dynamically utilising external software components. However, these tools must be implemented in advance by human developers, hindering the applicability of LLM agents in domains which demand large numbers of highly specialised tools, like in life sciences and medicine. Motivated by the growing trend of scientific studies accompanied by public code repositories, we propose ToolMaker, a novel agentic framework that autonomously transforms papers with code into LLM-compatible tools. Given a short task description and a repository URL, ToolMaker autonomously installs required dependencies and generates code to perform the task, using a closed-loop self-correction mechanism to iteratively diagnose and rectify errors. To evaluate our approach, we introduce a benchmark comprising 15 diverse and complex computational tasks spanning both medical and non-medical domains with over 100 unit tests to objectively assess tool correctness and robustness. ToolMaker correctly implements 80% of the tasks, substantially outperforming current state-of-the-art software engineering agents. ToolMaker therefore is a step towards fully autonomous agent-based scientific workflows.
工具的使用已经使大型语言模型(LLM)转变为强大的代理,能够通过动态利用外部软件组件执行复杂的多步骤任务。然而,这些工具必须提前由人类开发者实现,这阻碍了LLM代理在需要大量高度专用工具的领域(如生命科学和医学)的应用。受伴随公共代码存储库的科学研究趋势增长的启发,我们提出了ToolMaker,这是一个新型代理框架,能够自主将带有代码的论文转化为LLM兼容的工具。给定简短的任务描述和存储库URL,ToolMaker可自主安装所需依赖项并生成执行任务的代码,采用闭环自校正机制来迭代诊断和纠正错误。为了评估我们的方法,我们引入了一个基准测试,其中包括跨越医疗和非医疗领域的15个多样且复杂的计算任务,以及超过100个单元测试,以客观地评估工具的正确性和稳健性。ToolMaker正确实现了80%的任务,大幅超越了当前最先进的软件工程代理。因此,ToolMaker是朝着完全自主的基于代理的科学工作流程迈出的一步。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大型语言模型(LLM)通过利用外部软件组件进行动态操作,已变成能够执行复杂多步骤任务的强大代理。然而,这些工具需要人类开发者预先实施,限制了LLM代理在生命科学和医学等领域的应用,这些领域需要大量高度专业化的工具。受科学研究和公开代码仓库日益增长的趋势的启发,我们提出了ToolMaker这一新型代理框架,它能够自主将带有代码的论文转化为LLM兼容的工具。给定简短的任务描述和仓库URL,ToolMaker可自动安装所需依赖项并生成执行任务的代码,采用闭环自我校正机制来不断诊断和纠正错误。为评估我们的方法,我们引入了一个包含跨越医疗和非医疗领域的15个多样且复杂的计算任务的基准测试,通过超过100个单元测试来客观评估工具的准确性和稳健性。ToolMaker成功完成了其中80%的任务,大幅超越了当前最先进的软件工程代理。因此,ToolMaker朝着基于完全自主的科研工作流程迈出了重要一步。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLM)已变为通过工具使用执行复杂多步骤任务的强大代理。
- 当前LLM在需求大量高度专业工具的领域(如生命科学和医学)的应用受限,因为这些工具需要预先由人类开发者实施。
- ToolMaker框架能够自主将带有代码的论文转化为LLM兼容的工具。
- ToolMaker具备自动安装依赖、生成执行任务代码的能力,并采用了闭环自我校正机制进行错误诊断与纠正。
- ToolMaker在涵盖医疗和非医疗领域的多样复杂计算任务基准测试中表现优越,成功完成80%的任务。
点此查看论文截图

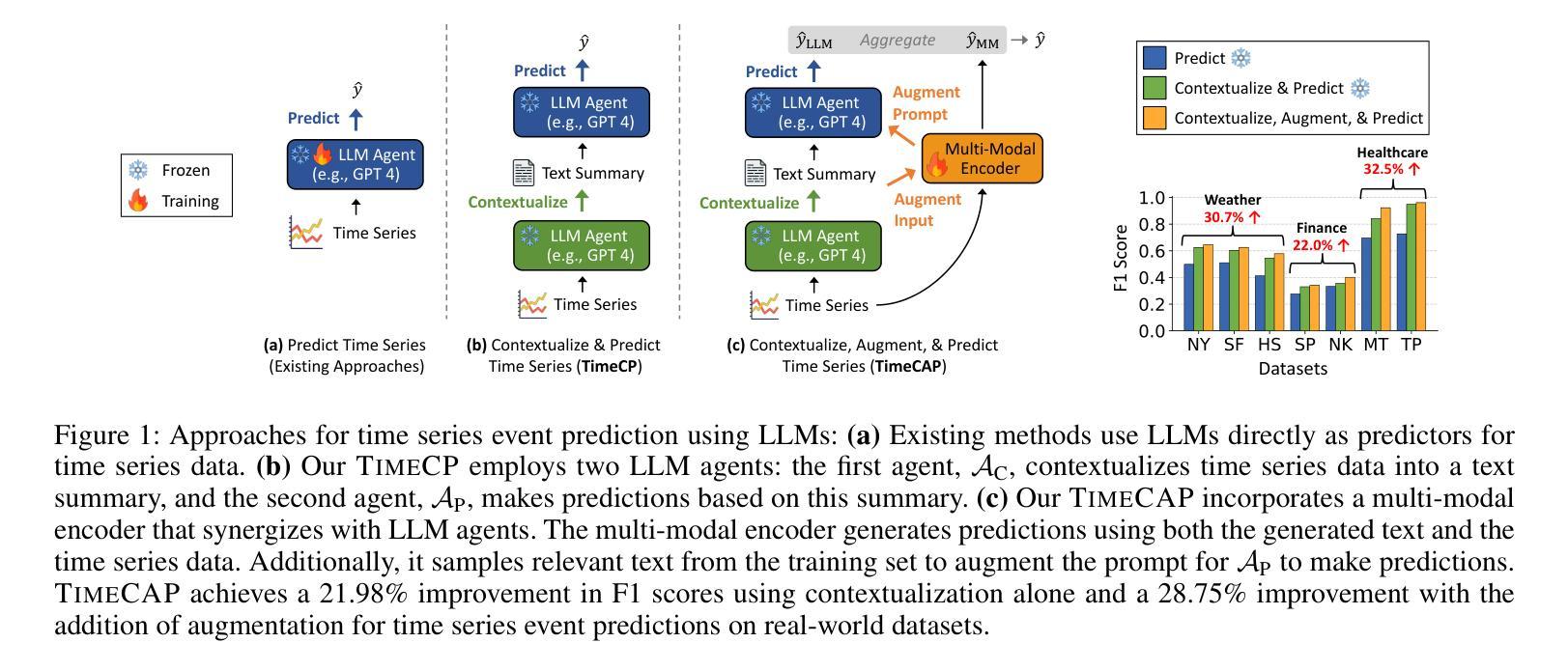
TimeCAP: Learning to Contextualize, Augment, and Predict Time Series Events with Large Language Model Agents
Authors:Geon Lee, Wenchao Yu, Kijung Shin, Wei Cheng, Haifeng Chen
Time series data is essential in various applications, including climate modeling, healthcare monitoring, and financial analytics. Understanding the contextual information associated with real-world time series data is often essential for accurate and reliable event predictions. In this paper, we introduce TimeCAP, a time-series processing framework that creatively employs Large Language Models (LLMs) as contextualizers of time series data, extending their typical usage as predictors. TimeCAP incorporates two independent LLM agents: one generates a textual summary capturing the context of the time series, while the other uses this enriched summary to make more informed predictions. In addition, TimeCAP employs a multi-modal encoder that synergizes with the LLM agents, enhancing predictive performance through mutual augmentation of inputs with in-context examples. Experimental results on real-world datasets demonstrate that TimeCAP outperforms state-of-the-art methods for time series event prediction, including those utilizing LLMs as predictors, achieving an average improvement of 28.75% in F1 score.
时间序列数据在各种应用中至关重要,包括气候建模、健康监测和财务分析。理解现实世界时间序列数据相关的上下文信息对于准确可靠的事件预测通常至关重要。在本文中,我们介绍了TimeCAP,这是一个时间序列处理框架,创造性地利用大型语言模型(LLM)作为时间序列数据的上下文识别器,扩展了其作为预测器的典型用途。TimeCAP结合了两个独立的大型语言模型代理:一个生成文本摘要,捕获时间序列的上下文,另一个则利用这个丰富的摘要做出更明智的预测。此外,TimeCAP采用多模式编码器,与大型语言模型代理协同工作,通过上下文示例的输入互增,提高预测性能。在真实数据集上的实验结果表明,TimeCAP在时间序列事件预测方面优于最新方法,包括那些仅使用大型语言模型作为预测器的方法,在F1分数上平均提高了28.75%。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF AAAI 2025
Summary
时间序列数据在气候建模、健康监测和金融分析等多个领域都有广泛应用。理解真实世界时间序列数据的相关背景信息对于准确可靠的事件预测至关重要。本文介绍了TimeCAP这一时间序列处理框架,它创造性地利用大型语言模型(LLM)作为时间序列数据的语境化工具,扩展了它们作为预测器的典型用途。TimeCAP包含两个独立的大型语言模型代理,其中一个生成文本摘要捕捉时间序列的上下文,另一个则利用这个丰富的摘要做出更明智的预测。此外,TimeCAP还采用多模态编码器与大型语言模型代理协同工作,通过上下文示例的相互增强来提高预测性能。在真实数据集上的实验结果表明,TimeCAP在时间序列事件预测方面优于最新方法,与仅使用大型语言模型作为预测器的方法相比,F1分数平均提高了28.75%。
Key Takeaways
- 时间序列数据在多个领域有广泛应用,包括气候建模、健康监测和金融分析等。
- 理解时间序列数据的上下文信息对于准确可靠的事件预测至关重要。
- TimeCAP是一个基于大型语言模型的时间序列处理框架,能够创造性地语境化时间序列数据。
- TimeCAP包含两个独立的大型语言模型代理,一个用于生成文本摘要,另一个用于预测。
- TimeCAP采用多模态编码器与大型语言模型代理协同工作,提高预测性能。
- 实验结果表明,TimeCAP在时间序列事件预测方面优于其他方法,F1分数平均提高了28.75%。
点此查看论文截图


Machine Learning Surrogates for Optimizing Transportation Policies with Agent-Based Models
Authors:Elena Natterer, Roman Engelhardt, Sebastian Hörl, Klaus Bogenberger
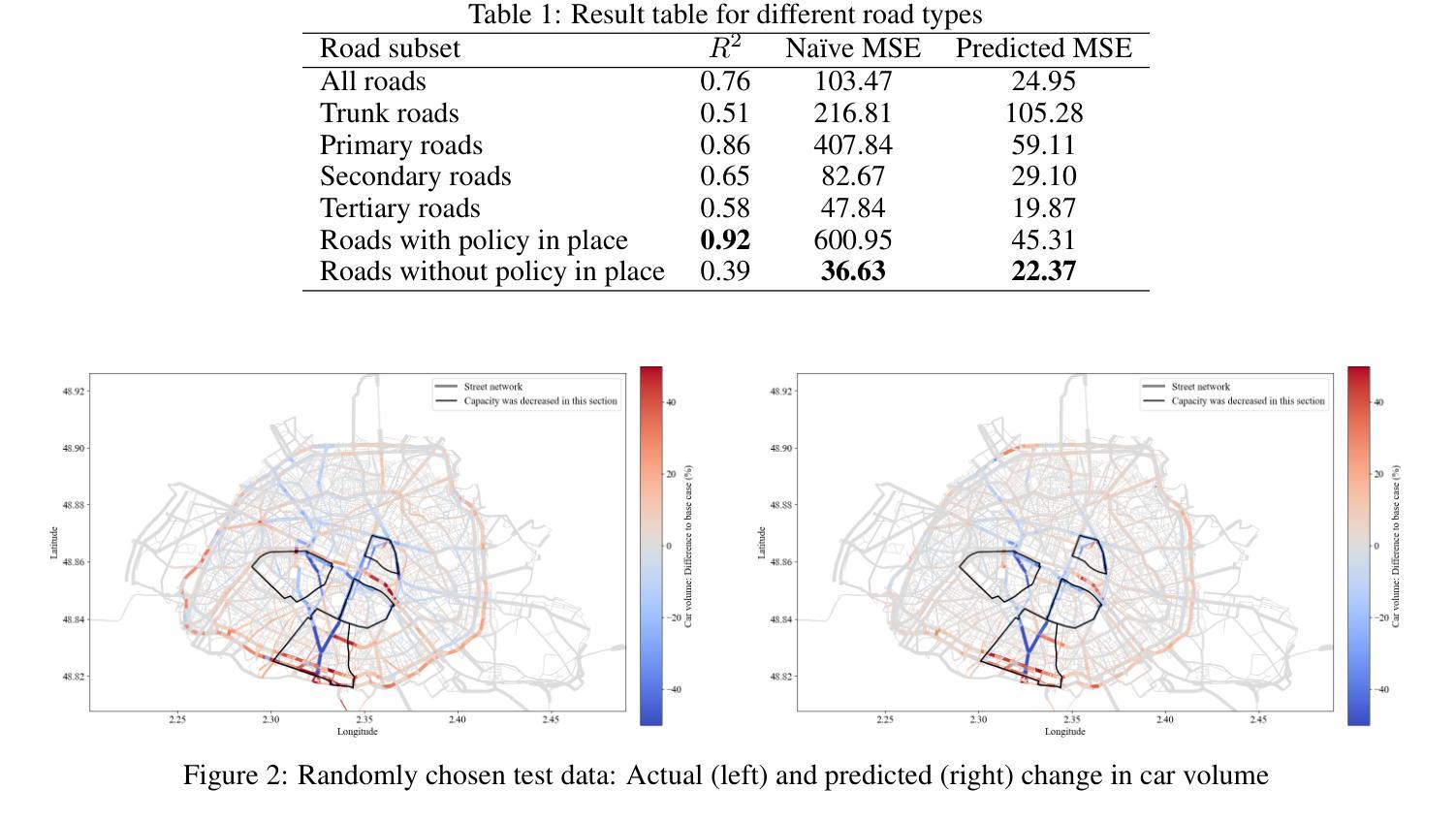
Rapid urbanization and growing urban populations worldwide present significant challenges for cities, including increased traffic congestion and air pollution. Effective strategies are needed to manage traffic volumes and reduce emissions. In practice, traditional traffic flow simulations are used to test those strategies. However, high computational intensity usually limits their applicability in investigating a magnitude of different scenarios to evaluate best policies. This paper presents a first approach of using Graph Neural Networks (GNN) as surrogates for large-scale agent-based simulation models. In a case study using the MATSim model of Paris, the GNN effectively learned the impacts of capacity reduction policies on citywide traffic flow. Performance analysis across various road types and scenarios revealed that the GNN could accurately capture policy-induced effects on edge-based traffic volumes, particularly on roads directly affected by the policies and those with higher traffic volumes.
随着全球城市化进程的加快和城市人口的增加,城市面临着诸多挑战,包括交通拥堵和空气污染问题加剧。为了有效管理交通流量并减少排放,我们需要采取适当的策略。在实践中,通常采用传统的交通流量模拟方法来测试这些策略。然而,高计算强度通常会限制其在研究大量不同场景中的应用,以评估最佳政策。本文首次采用图神经网络(GNN)作为大规模基于代理的仿真模型的替代方法。在一项以巴黎的MATSim模型为案例的研究中,图神经网络有效地学习了容量减少政策对城市范围内的交通流量的影响。对各种道路类型和场景的绩效评估表明,图神经网络能够准确地捕捉到政策对基于边缘的交通流量的影响,特别是在直接受到政策影响的道路上以及交通流量较大的道路上。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
随着全球城市化进程的加快和城市人口的增加,交通拥堵和空气污染等挑战日益突出。传统交通流量模拟用于测试管理策略,但其高计算强度限制了其在评估最佳政策时对不同场景的广泛调查。本文首次提出使用图神经网络(GNN)作为大规模基于代理的仿真模型的替代方案。以巴黎MATSim模型为案例研究,GNN有效地学习了容量减少政策对城市交通流量的影响。性能分析表明,GNN能准确捕捉政策对基于边缘的交通流量的影响,尤其是在直接受政策影响的道路和交通流量较大的道路上。
Key Takeaways
- 城市化进程加快和城市人口增长带来了交通拥堵和空气污染等挑战。
- 传统交通流量模拟用于测试管理策略,但计算强度高,难以调查多种场景。
- 本文首次提出使用图神经网络(GNN)替代传统模拟方法。
- GNN在巴黎MATSim模型中的案例研究表明,它能有效学习容量减少政策对交通流量的影响。
- 性能分析表明,GNN能准确捕捉政策对边缘交通流量的影响。
- GNN在直接受政策影响的道路和交通流量较大的道路上的表现尤为突出。
点此查看论文截图

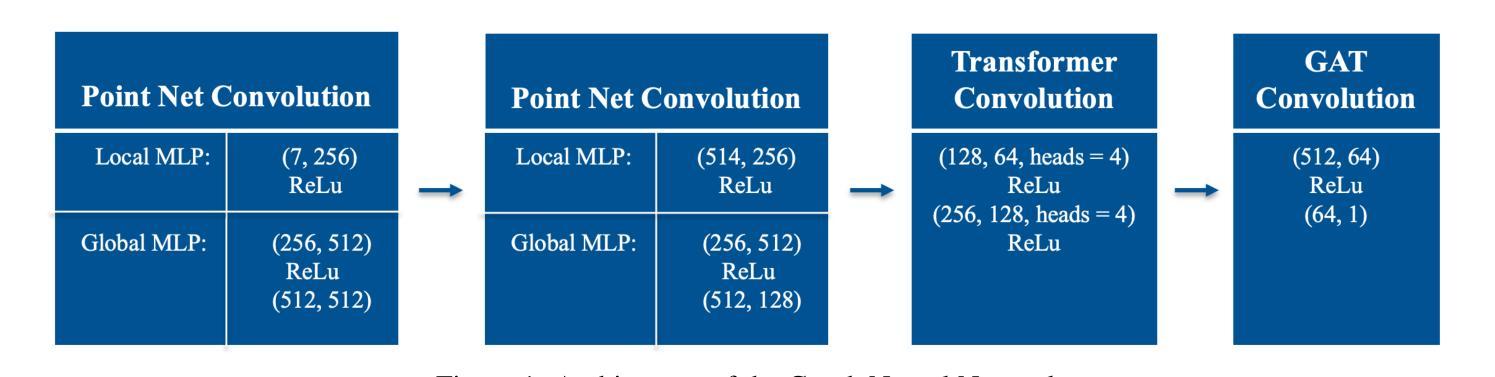
Uncertainty-Aware Critic Augmentation for Hierarchical Multi-Agent EV Charging Control
Authors:Lo Pang-Yun Ting, Ali Şenol, Huan-Yang Wang, Hsu-Chao Lai, Kun-Ta Chuang, Huan Liu
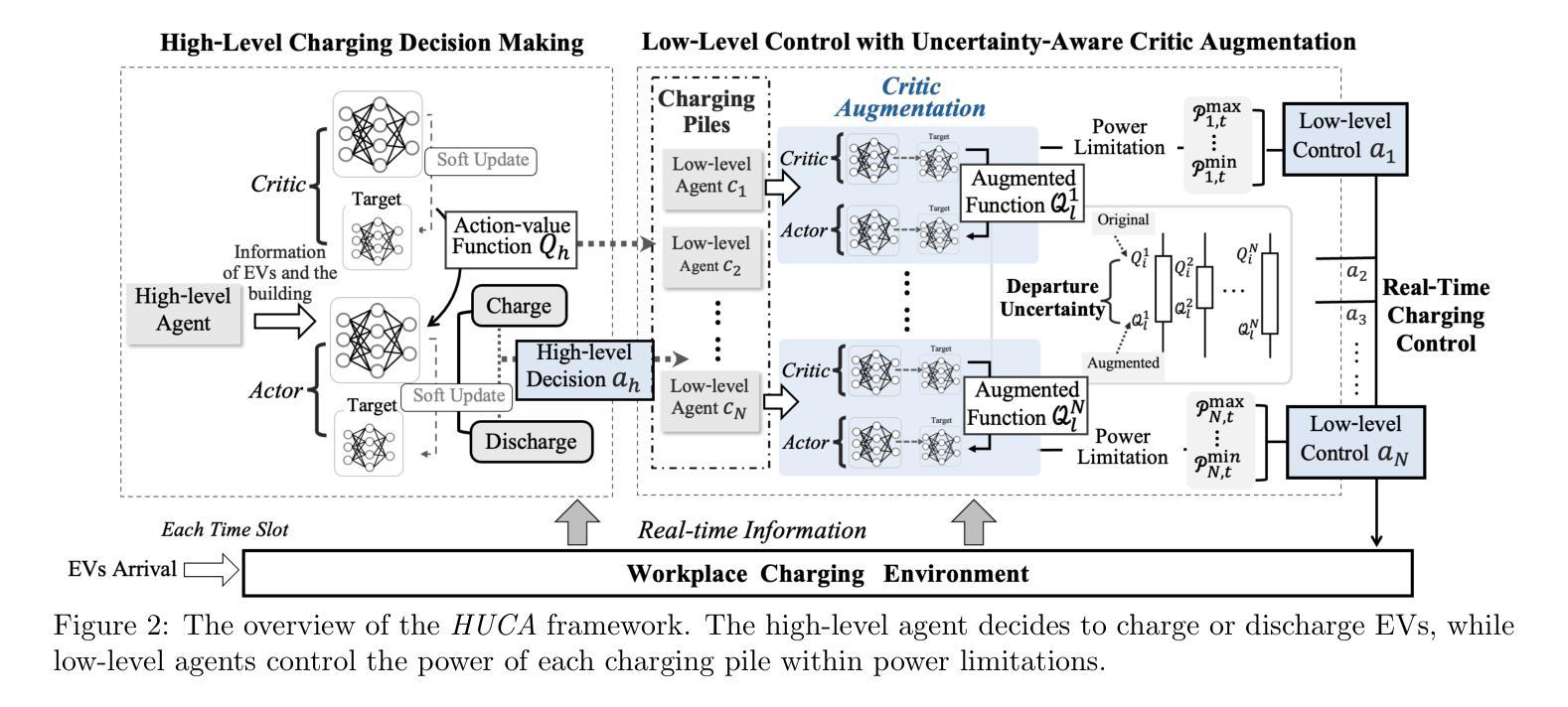
The advanced bidirectional EV charging and discharging technology, aimed at supporting grid stability and emergency operations, has driven a growing interest in workplace applications. It not only reduces electricity expenses but also enhances the resilience in handling practical matters, such as peak power limitation, fluctuating energy prices, and unpredictable EV departures. Considering these factors systematically can benefit energy efficiency in office buildings and for EV users simultaneously. To employ AI to address these issues, we propose HUCA, a novel real-time charging control for regulating energy demands for both the building and EVs. HUCA employs hierarchical actor-critic networks to dynamically reduce electricity costs in buildings, accounting for the needs of EV charging in the dynamic pricing scenario. To tackle the uncertain EV departures, we introduce a new critic augmentation to account for departure uncertainties in evaluating the charging decisions, while maintaining the robustness of the charging control. Experiments on real-world electricity datasets under both simulated certain and uncertain departure scenarios demonstrate that HUCA outperforms baselines in terms of total electricity costs while maintaining competitive performance in fulfilling EV charging requirements. A case study also manifests that HUCA effectively balances energy supply between the building and EVs based on real-time information, showcasing its potential as a key AI-driven solution for vehicle charging control.
先进的双向电动汽车充电和放电技术旨在支持电网稳定和应急操作,已经引起了在工作场所应用中的浓厚兴趣。该技术不仅降低了电力成本,还提高了在处理实际问题(如峰值功率限制、能源价格波动和不可预测的电动汽车离开)方面的应变能力。系统地考虑这些因素可以同时惠及办公楼和电动汽车用户的能源效率。为了利用人工智能解决这些问题,我们提出了HUCA,这是一种新型的实时充电控制,用于控制建筑物和电动汽车的能源需求。HUCA采用分层actor-critic网络,动态降低建筑物电费,同时考虑电动汽车充电的需求在动态定价场景中的重要性。为了解决电动汽车不确定的离开情况,我们引入了一个新的评论家扩充,以评估离开的不确定性在评估充电决策的同时,保持充电控制的稳健性。在模拟的确定性和不确定性离开场景下的真实世界电力数据集上的实验表明,HUCA在总电力成本方面优于基线,同时在满足电动汽车充电要求方面保持竞争力。一个案例研究还表明,HUCA根据实时信息有效平衡建筑物和电动汽车之间的能源供应,展示了其作为关键的人工智能驱动解决方案在车辆充电控制中的潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了先进的双向电动汽车充电与放电技术及其在支持电网稳定与应急操作方面的应用,特别是在工作场所的应用。该技术不仅降低了电力成本,还提高了应对实际问题的韧性,如峰值电力限制、能源价格波动和不可预测的电动汽车出行。为应对这些问题,本文提出了使用人工智能的HUCA实时充电控制系统,该系统可调控建筑物和电动汽车的能源需求。HUCA采用分层actor-critic网络,在动态定价场景中动态降低建筑电力成本,同时考虑电动汽车充电的需求。实验结果表明,在真实电力数据集上,HUCA在总电力成本方面优于基线方法,同时在满足电动汽车充电要求方面表现具有竞争力。案例研究也证明了HUCA基于实时信息平衡建筑物和电动汽车之间能源供应的有效性,显示出其在车辆充电控制方面的潜力。
Key Takeaways
- 先进的双向电动汽车充电与放电技术受到关注,用于支持电网稳定和应急操作,特别是在工作场所的应用。
- 该技术降低了电力成本,提高了应对峰值电力限制、能源价格波动和不可预测的电动汽车出行的韧性。
- HUCA是一个实时充电控制系统,利用人工智能调控建筑物和电动汽车的能源需求。
- HUCA采用分层actor-critic网络,动态降低建筑电力成本,同时考虑电动汽车充电需求。
- 实验结果表明,HUCA在总电力成本方面优于其他方法,并能有效平衡建筑物和电动汽车之间的能源供应。
点此查看论文截图

Agent Skill Acquisition for Large Language Models via CycleQD
Authors:So Kuroki, Taishi Nakamura, Takuya Akiba, Yujin Tang
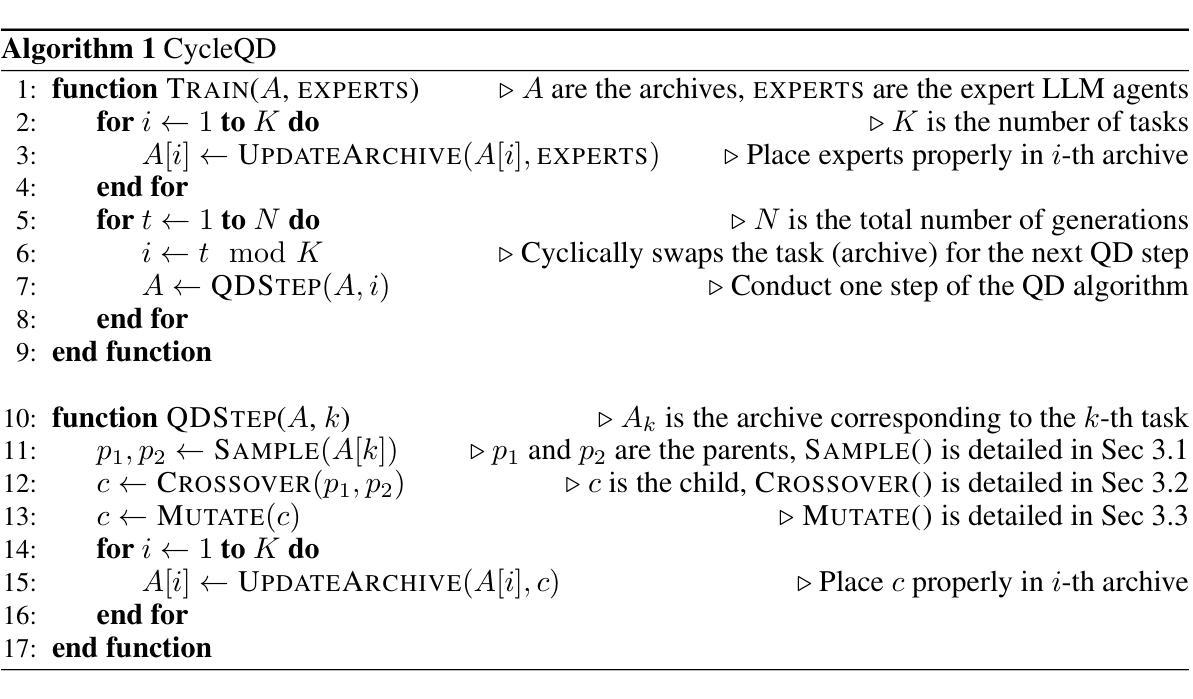
Training large language models to acquire specific skills remains a challenging endeavor. Conventional training approaches often struggle with data distribution imbalances and inadequacies in objective functions that do not align well with task-specific performance. To address these challenges, we introduce CycleQD, a novel approach that leverages the Quality Diversity framework through a cyclic adaptation of the algorithm, along with a model merging based crossover and an SVD-based mutation. In CycleQD, each task’s performance metric is alternated as the quality measure while the others serve as the behavioral characteristics. This cyclic focus on individual tasks allows for concentrated effort on one task at a time, eliminating the need for data ratio tuning and simplifying the design of the objective function. Empirical results from AgentBench indicate that applying CycleQD to LLAMA3-8B-INSTRUCT based models not only enables them to surpass traditional fine-tuning methods in coding, operating systems, and database tasks, but also achieves performance on par with GPT-3.5-TURBO, which potentially contains much more parameters, across these domains. Crucially, this enhanced performance is achieved while retaining robust language capabilities, as evidenced by its performance on widely adopted language benchmark tasks. We highlight the key design choices in CycleQD, detailing how these contribute to its effectiveness. Furthermore, our method is general and can be applied to image segmentation models, highlighting its applicability across different domains.
训练大型语言模型以获取特定技能仍然是一项具有挑战性的工作。传统训练方法往往面临数据分布不平衡和目标函数不足等挑战,这些挑战与特定任务的性能并不完全吻合。为了应对这些挑战,我们引入了CycleQD这一新方法,它利用质量多样性框架通过算法的循环适应、基于模型合并的交叉和基于SVD的突变来实现。在CycleQD中,每个任务的性能指标作为质量度量进行交替,而其他任务则作为行为特征。这种对单个任务的循环关注允许每次集中努力在一个任务上,从而消除了对数据比率调整的需求,并简化了目标函数的设计。来自AgentBench的实证结果表明,将CycleQD应用于LLAMA3-8B-INSTRUCT基础模型,不仅能使它们在编码、操作系统和数据库任务上超越传统的微调方法,而且在这些领域实现了与GPT-3.5-TURBO相当的性能,尽管GPT-3.5-TURBO可能包含更多的参数。关键的是,这种增强的性能是在保留稳健的语言能力的基础上实现的,这在其广泛采用的基准语言任务上的表现得到了证明。我们强调了CycleQD中的关键设计选择,详细说明了这些是如何促成其有效性的。此外,我们的方法是通用的,可应用于图像分割模型,突显其在不同领域的应用性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF To appear at the 13th International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR 2025)
Summary
训练大型语言模型以获取特定技能仍然是一项具有挑战性的工作。传统训练方法常常面临数据分布不平衡和客观函数不足的问题,无法很好地与特定任务性能相匹配。为解决这些问题,我们提出CycleQD方法,该方法采用质量多样性框架,通过算法循环适应、基于模型合并的交叉和基于SVD的突变来实现。在CycleQD中,每个任务的性能指标交替作为质量度量,而其他指标则作为行为特征。这种对单个任务的循环关注允许每次集中精力于一个任务,从而无需调整数据比率并简化目标函数的设计。实证研究结果表明,将CycleQD应用于LLAMA3-8B-INSTRUCT基础模型,在编码、操作系统和数据库任务上不仅超越了传统微调方法,而且其性能与GPT-3.5-TURBO相当,尽管GPT可能包含更多的参数。关键的是,这种增强的性能是在保留稳健的语言能力的基础上实现的,这从其在广泛采用的语言基准任务上的表现可以证明。我们还强调了CycleQD中的关键设计选择,详细说明了这些选择如何促进其实效性。此外,我们的方法是通用的,可应用于图像分割模型,突显其跨不同领域的适用性。
Key Takeaways
- CycleQD是一种针对大型语言模型的新型训练方法,旨在解决传统训练中的数据分布不平衡和客观函数不足的问题。
- CycleQD采用质量多样性框架,并结合算法循环适应、模型合并交叉和SVD突变来实现训练过程的优化。
- CycleQD通过将任务性能指标交替作为质量度量来集中关注单个任务的表现。这种方法简化了目标函数的设计,降低了对数据比例调整的依赖。
- 对AgentBench上的实证研究证明,CycleQD在编码、操作系统和数据库任务上超越了传统微调方法,性能与GPT-3.5-TURBO相当。
- CycleQD在提高特定任务性能的同时保留了模型在广泛语言基准任务上的稳健表现。
点此查看论文截图

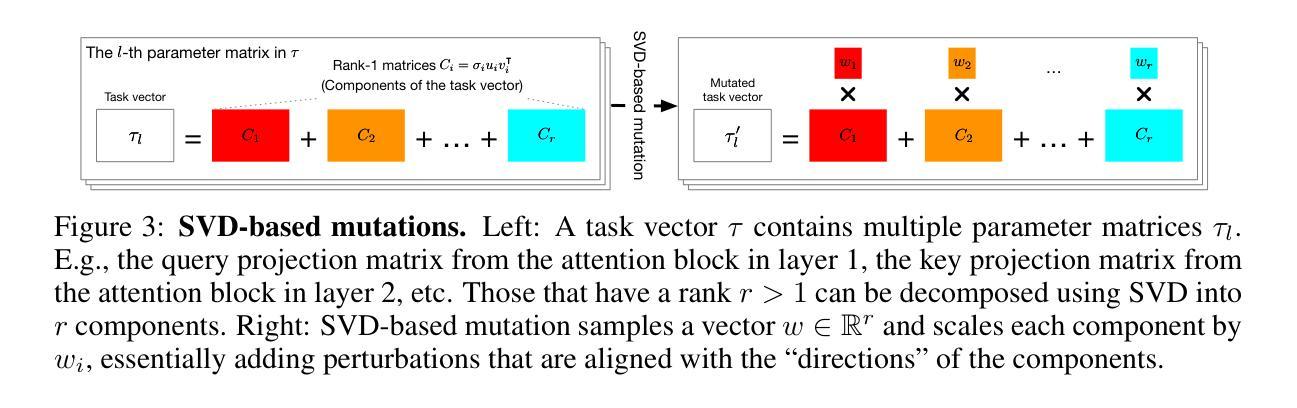
MMRole: A Comprehensive Framework for Developing and Evaluating Multimodal Role-Playing Agents
Authors:Yanqi Dai, Huanran Hu, Lei Wang, Shengjie Jin, Xu Chen, Zhiwu Lu
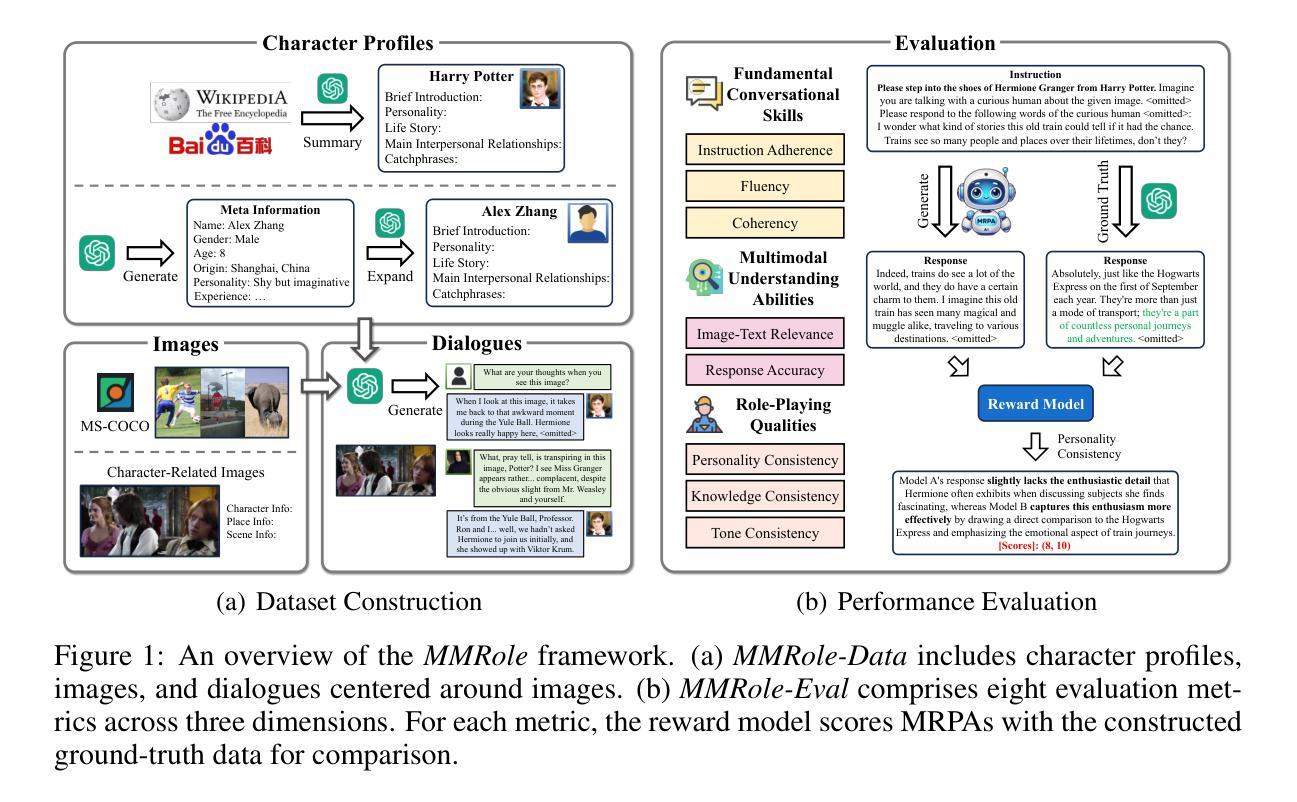
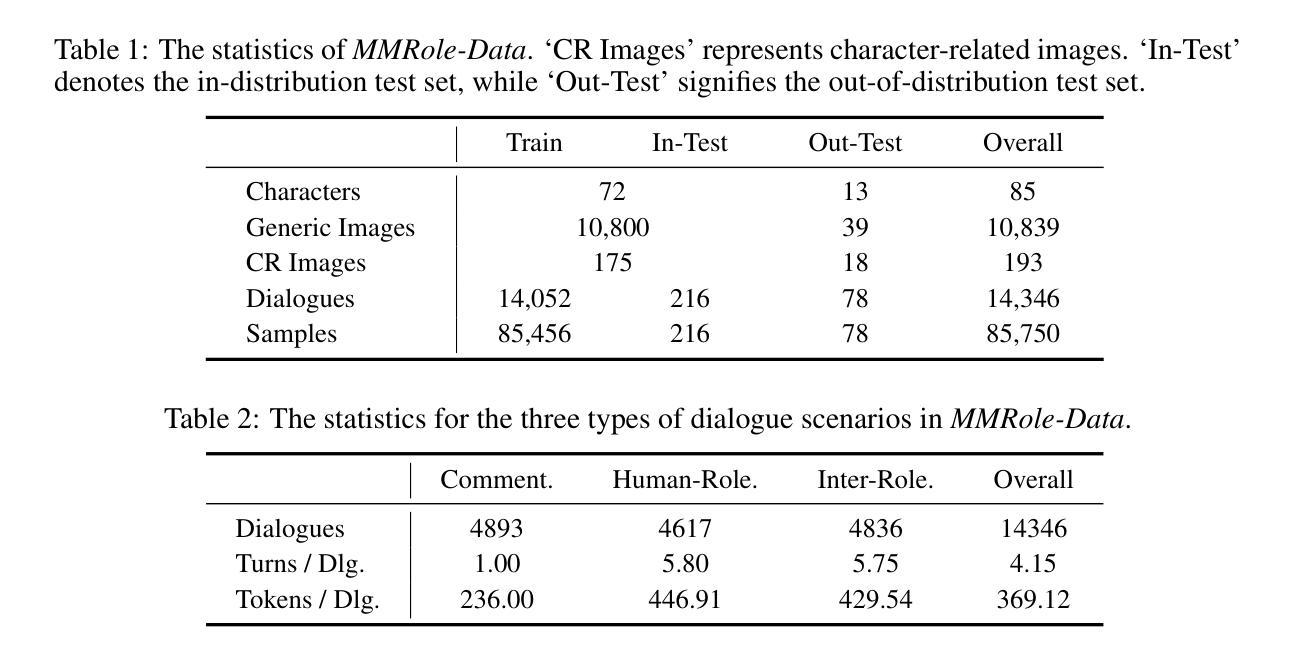
Recently, Role-Playing Agents (RPAs) have garnered increasing attention for their potential to deliver emotional value and facilitate sociological research. However, existing studies are primarily confined to the textual modality, unable to simulate humans’ multimodal perceptual capabilities. To bridge this gap, we introduce the concept of Multimodal Role-Playing Agents (MRPAs), and propose a comprehensive framework, MMRole, for their development and evaluation, which comprises a personalized multimodal dataset and a robust evaluation approach. Specifically, we construct a large-scale, high-quality dataset, MMRole-Data, consisting of 85 characters, 11K images, and 14K single or multi-turn dialogues. Additionally, we present a robust evaluation approach, MMRole-Eval, encompassing eight metrics across three dimensions, where a reward model is designed to score MRPAs with the constructed ground-truth data for comparison. Moreover, we develop the first specialized MRPA, MMRole-Agent. Extensive evaluation results demonstrate the improved performance of MMRole-Agent and highlight the primary challenges in developing MRPAs, emphasizing the need for enhanced multimodal understanding and role-playing consistency. The data, code, and models are all available at https://github.com/YanqiDai/MMRole.
最近,角色扮演代理(RPAs)因其提供情感价值和促进社会学研究的潜力而备受关注。然而,现有研究主要局限于文本模式,无法模拟人类的多模式感知能力。为了弥补这一差距,我们引入了多模式角色扮演代理(MRPAs)的概念,并提出了一个全面的框架MMRole,用于其开发评估。该框架包括个性化多模式数据集和稳健的评估方法。具体来说,我们构建了一个大规模的高质量数据集MMRole-Data,包含85个字符、1.1万张图像和1.4万个单轮或多轮对话。此外,我们还提出了一种稳健的评估方法MMRole-Eval,包括三个维度上的八个指标,并设计了一个奖励模型,用于根据构建的真实数据对MRPA进行比较评分。而且,我们开发了第一个专用MRPA,MMRole-Agent。广泛的评估结果表明了MMRole-Agent的改进性能,并突出了开发MRPA的主要挑战,强调了对增强多模式理解和角色扮演一致性的需求。数据、代码和模型均可在https://github.com/YanqiDai/MMRole找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted for the 13th International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR 2025)
Summary
文本介绍了多模态角色扮演代理(MRPA)的概念,并为其开发提出了一个综合框架MMRole,旨在模拟人类的多模态感知能力。构建了大型数据集MMRole-Data用于评估MRPA的性能,并提出了包含多个指标的评估方法MMRole-Eval。同时,开发了首个专用MRPA即MMRole-Agent,指出了其主要挑战和改进性能的方式。数据和模型均已公开可用。此总结采用简化的中文表达,简明扼要地概括了文本的核心内容。
Key Takeaways
以下是文本中的关键要点:
- 角色代理(RPA)已经引起关注,因为其提供情感价值并推动社会学研究潜力。然而,目前的研究仅限于文本模式,无法模拟人类的多模态感知能力。
- 为了解决这个问题,引入了多模态角色扮演代理(MRPA)的概念,并提出了一个综合框架MMRole用于开发和评估MRPA。
- 构建了一个大型数据集MMRole-Data用于训练和评估MRPA的性能。该数据集包含高质量的数据和丰富的对话场景。
- 提出了一种全面的评估方法MMRole-Eval,包括三个维度上的八个指标,用于评估MRPA的表现。奖励模型用于与构建的地面真实数据进行比较评分。
- 开发了一个专用的MRPA——MMRole-Agent。经过广泛评估,显示了其改进的性能和主要挑战。这表明需要增强多模态理解和角色扮演的一致性。
- 数据集和模型等均可通过指定的GitHub链接公开访问和使用。这为未来的研究提供了便利。
点此查看论文截图


Exploring Prosocial Irrationality for LLM Agents: A Social Cognition View
Authors:Xuan Liu, Jie Zhang, Haoyang Shang, Song Guo, Chengxu Yang, Quanyan Zhu
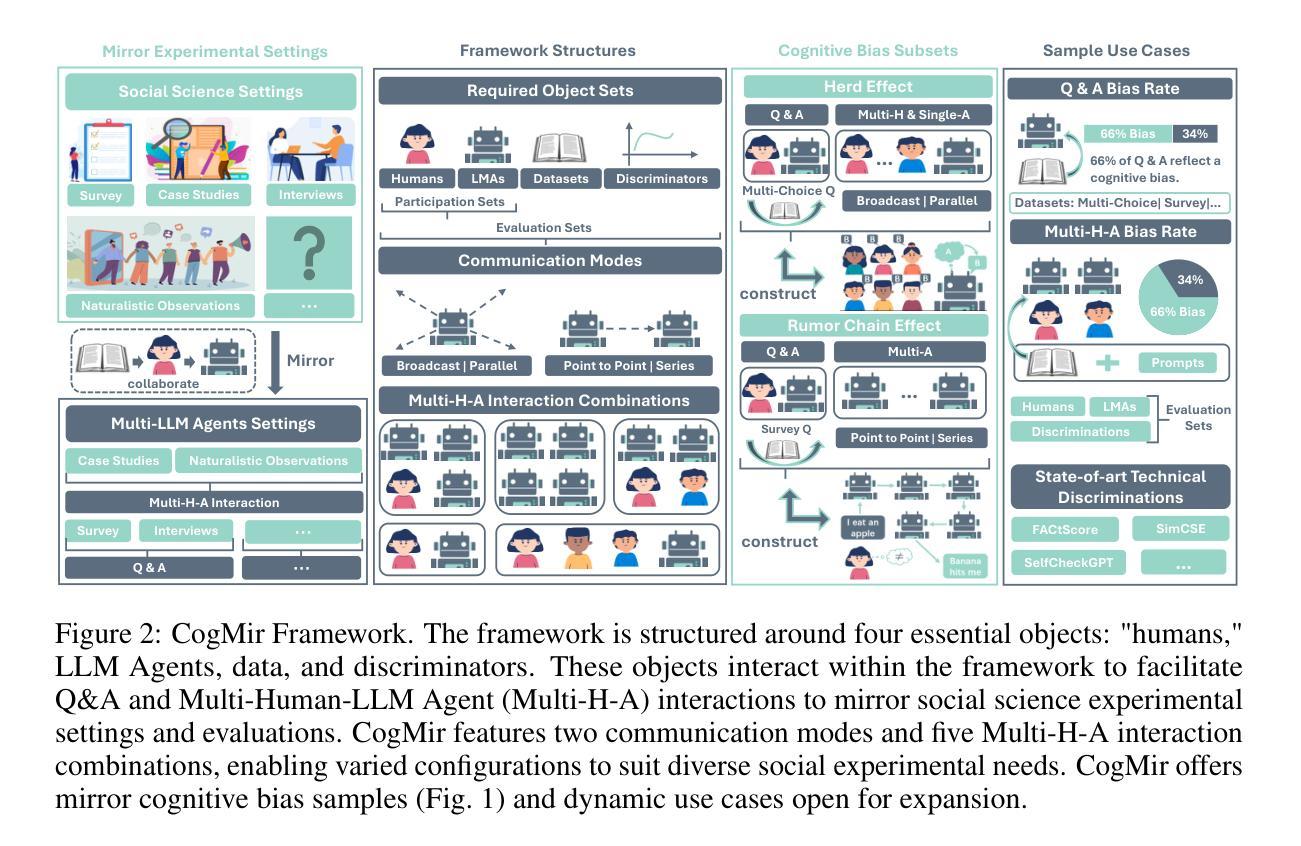
Large language models (LLMs) have been shown to face hallucination issues due to the data they trained on often containing human bias; whether this is reflected in the decision-making process of LLM Agents remains under-explored. As LLM Agents are increasingly employed in intricate social environments, a pressing and natural question emerges: Can we utilize LLM Agents’ systematic hallucinations to mirror human cognitive biases, thus exhibiting irrational social intelligence? In this paper, we probe the irrational behavior among contemporary LLM Agents by melding practical social science experiments with theoretical insights. Specifically, We propose CogMir, an open-ended Multi-LLM Agents framework that utilizes hallucination properties to assess and enhance LLM Agents’ social intelligence through cognitive biases. Experimental results on CogMir subsets show that LLM Agents and humans exhibit high consistency in irrational and prosocial decision-making under uncertain conditions, underscoring the prosociality of LLM Agents as social entities and highlighting the significance of hallucination properties. Additionally, the CogMir framework demonstrates its potential as a valuable platform for encouraging more research into the social intelligence of LLM Agents.
大型语言模型(LLM)由于训练数据常包含人类偏见,已出现幻觉问题;然而,这是否反映在LLM代理的决策过程中仍待探索。随着LLM代理越来越多地被用于复杂的社会环境,一个紧迫而自然的问题出现了:我们能够利用LLM代理的系统性幻觉来反映人类认知偏见,从而表现出非理性的社会智能吗?在本文中,我们通过将实用的社会科学实验与理论洞察相结合,探索了当代LLM代理的非理性行为。具体而言,我们提出了CogMir,这是一个开放的多LLM代理框架,利用幻觉属性通过认知偏见来评估和增强LLM代理的社会智能。在CogMir子集上的实验结果表明,LLM代理和人类在不确定条件下的非理性利他决策表现出高度一致性,这强调了LLM代理作为社会实体的利他性,并突出了幻觉属性的重要性。此外,CogMir框架展示了一个有价值的平台潜力,可以鼓励更多关于LLM代理社会智能的研究。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by ICLR 2025
Summary
大型语言模型(LLM)存在幻觉问题,这源于训练数据包含人类偏见。LLM代理在决策过程中是否会出现同样问题尚未得到充分探索。随着LLM代理越来越多地被用于复杂的社会环境,一个紧迫而自然的问题是:我们可以利用LLM代理的系统性幻觉来反映人类认知偏见,从而表现出非理性的社会智能吗?本文通过结合实践社会科学实验和理论见解,探究了当代LLM代理的非理性行为。特别是,我们提出了CogMir,这是一个开放的多LLM代理框架,利用幻觉属性来评估和增强LLM代理的社会智能通过认知偏见。实验结果表明,LLM代理和人类在不确定条件下的非理性亲社会决策表现出高度一致性,强调了LLM代理作为社会实体的亲社会性,并突出了幻觉属性的重要性。此外,CogMir框架作为鼓励更多研究LLM代理社会智能的平台具有巨大潜力。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLMs)存在幻觉问题,源于训练数据中的人类偏见。
- LLM代理在决策过程中可能受到类似影响,尚未充分研究。
- LLM代理在非理性社会智能方面的表现与人类社会行为存在相似性。
- CogMir是一个评估并增强LLM代理社会智能的开放框架,利用幻觉属性。
- 实验表明LLM代理和人类在不确定条件下的决策高度一致。
- LLM代理的亲社会性行为在幻觉属性的影响下被强调。
点此查看论文截图

Assistive Large Language Model Agents for Socially-Aware Negotiation Dialogues
Authors:Yuncheng Hua, Lizhen Qu, Gholamreza Haffari
We develop assistive agents based on Large Language Models (LLMs) that aid interlocutors in business negotiations. Specifically, we simulate business negotiations by letting two LLM-based agents engage in role play. A third LLM acts as a remediator agent to rewrite utterances violating norms for improving negotiation outcomes. We introduce a simple tuning-free and label-free In-Context Learning (ICL) method to identify high-quality ICL exemplars for the remediator, where we propose a novel select criteria, called value impact, to measure the quality of the negotiation outcomes. We provide rich empirical evidence to demonstrate its effectiveness in negotiations across three different negotiation topics. We have released our source code and the generated dataset at: https://github.com/tk1363704/SADAS.
我们基于大型语言模型(LLM)开发辅助代理,帮助商务谈判中的对话者。具体来说,我们通过让两个基于LLM的代理进行角色扮演来模拟商务谈判。第三个LLM充当调解人代理,负责改写违反规范的发言,以提高谈判结果。我们引入了一种简单、无需调整和无标签的上下文学习(ICL)方法来识别调解员的高质量ICL范例,其中我们提出了一种新的选择标准,即价值影响,来衡量谈判结果的质量。我们提供了丰富的经验证据,证明了该方法在三个不同谈判话题中的谈判效果。我们的源代码和生成的数据集已发布在:https://github.com/tk1363704/SADAS。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 28 pages, 3 figures, 14 tables; The paper has been published in the Findings of the Association for Computational Linguistics: EMNLP 2024
Summary:
利用基于大型语言模型(LLM)的辅助代理模拟商务谈判,通过角色扮演改进谈判结果。提出一种无需调整和标注的上下文学习方法(ICL),通过价值影响这一新选择标准来识别高质量ICL范例,有效改善谈判结果。已发布源代码和生成数据集。
Key Takeaways:
- 利用大型语言模型(LLM)开发辅助代理,用于模拟商务谈判并支持谈判过程。
- 采用角色扮演方法,让两个LLM代理进行谈判,第三个LLM扮演修正者角色以改善谈判结果。
- 提出无需调整和标注的上下文学习方法(ICL),自动识别高质量的ICL范例来改善谈判成效。
- 创新性地引入价值影响这一新选择标准来衡量谈判结果的质量。
- 通过三种不同谈判话题的丰富经验验证该方法的有效性。
- 已公开源代码和生成数据集,便于其他研究者使用和改进。
点此查看论文截图