⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-02-19 更新
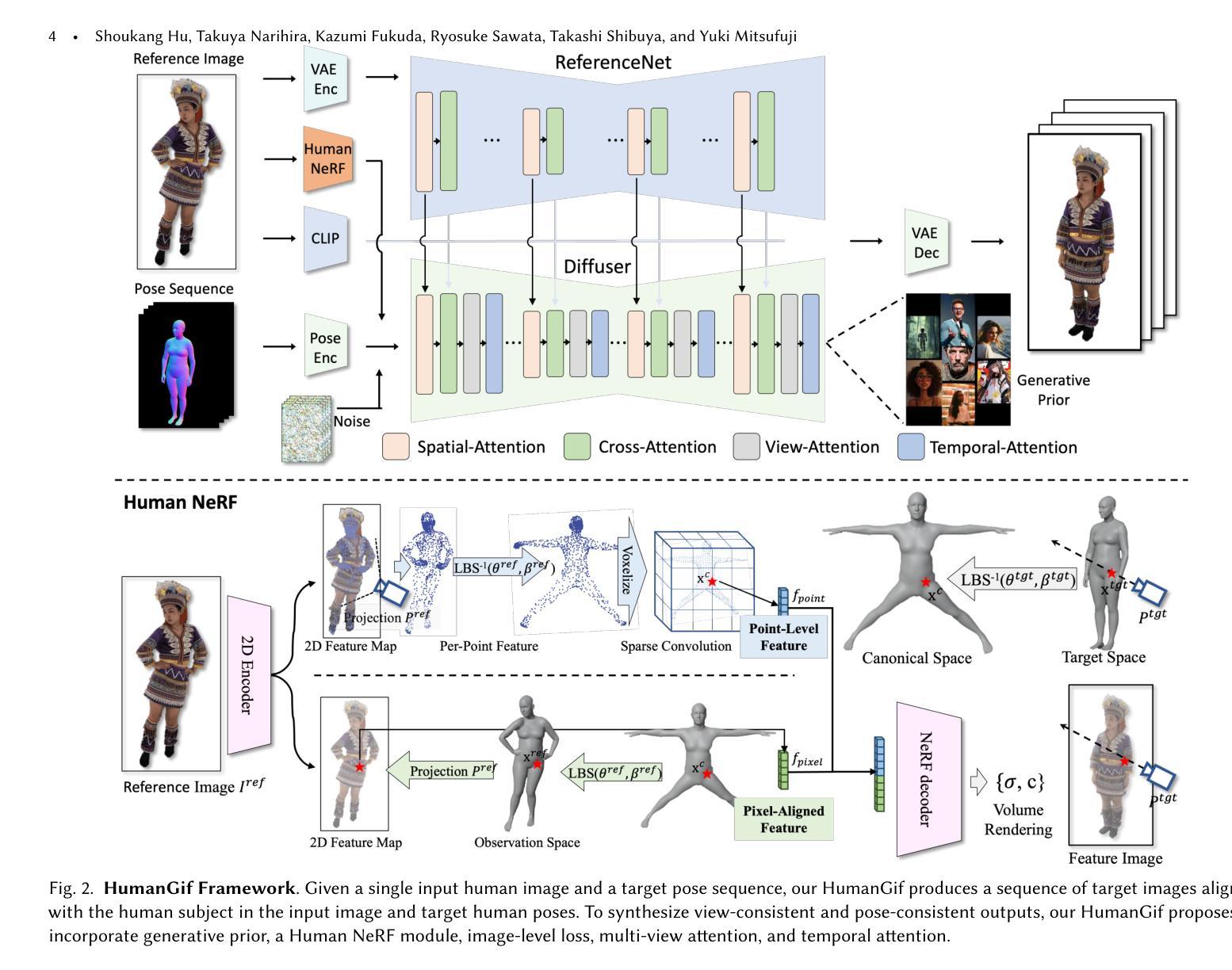
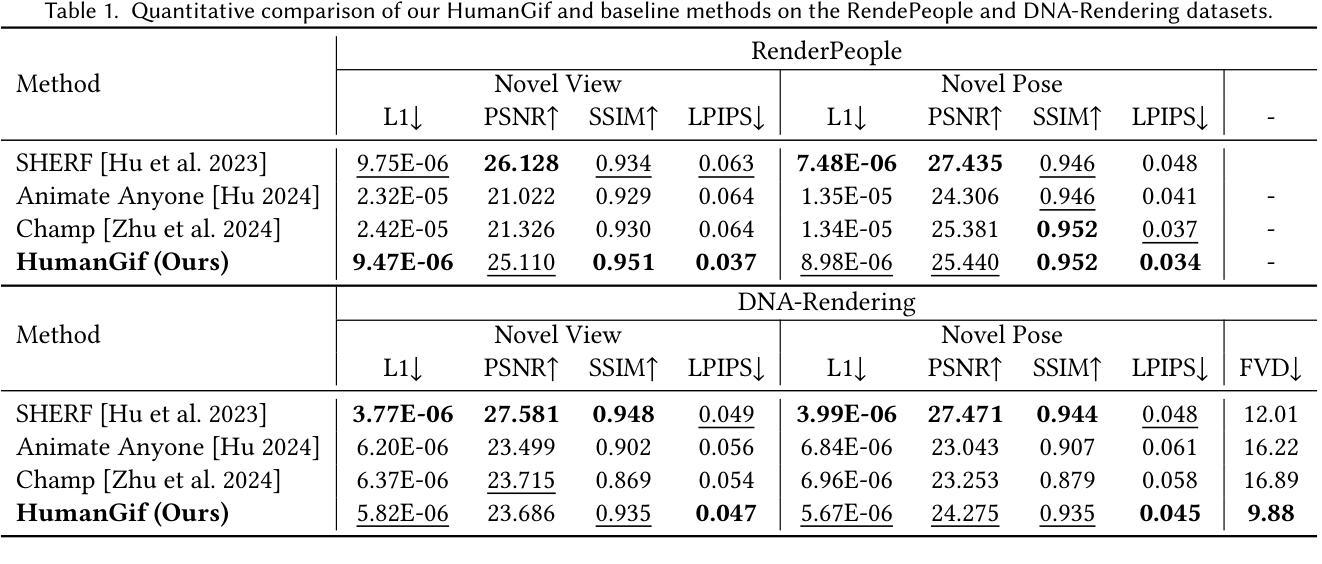
HumanGif: Single-View Human Diffusion with Generative Prior
Authors:Shoukang Hu, Takuya Narihira, Kazumi Fukuda, Ryosuke Sawata, Takashi Shibuya, Yuki Mitsufuji
While previous single-view-based 3D human reconstruction methods made significant progress in novel view synthesis, it remains a challenge to synthesize both view-consistent and pose-consistent results for animatable human avatars from a single image input. Motivated by the success of 2D character animation, we propose HumanGif, a single-view human diffusion model with generative prior. Specifically, we formulate the single-view-based 3D human novel view and pose synthesis as a single-view-conditioned human diffusion process, utilizing generative priors from foundational diffusion models. To ensure fine-grained and consistent novel view and pose synthesis, we introduce a Human NeRF module in HumanGif to learn spatially aligned features from the input image, implicitly capturing the relative camera and human pose transformation. Furthermore, we introduce an image-level loss during optimization to bridge the gap between latent and image spaces in diffusion models. Extensive experiments on RenderPeople and DNA-Rendering datasets demonstrate that HumanGif achieves the best perceptual performance, with better generalizability for novel view and pose synthesis.
虽然之前的基于单视角的3D人体重建方法在新型视角合成方面取得了显著进展,但仍然存在从单一图像输入合成与视角和姿态都一致的可动画人体角色的挑战。受到二维角色动画成功的启发,我们提出了具有生成先验的单视角人体扩散模型——HumanGif。具体来说,我们将基于单视角的3D人体新型视角和姿态合成表述为单视角条件下的人体扩散过程,利用基础扩散模型的生成先验。为确保精细且一致的全新视角和姿态合成,我们在HumanGif中引入了一个Human NeRF模块,用于从输入图像中学习空间对齐特征,从而隐式捕获相对相机和人体姿态变换。此外,在优化过程中我们引入了图像级损失,以缩小扩散模型中的潜在空间和图像空间之间的差距。在RenderPeople和DNA-Rendering数据集上的大量实验表明,HumanGif在感知性能上表现最佳,并且在新型视角和姿态合成方面表现出更好的泛化能力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project page: https://skhu101.github.io/HumanGif/
Summary
本文提出了一种基于单视图的人类扩散模型HumanGif,用于生成具有视图一致性和姿态一致性的动画人物模型。该模型结合2D角色动画的成功经验,利用基础扩散模型的生成先验信息,将单视图下的3D人类新视图和姿态合成定义为受单视图条件约束的人类扩散过程。为精细且一致地合成新视图和姿态,HumanGif引入了Human NeRF模块来从输入图像中学习空间对齐特征,并隐含地捕捉相对相机和人类姿态变换。此外,优化过程中引入了图像级损失,以缩小扩散模型中潜空间和图像空间之间的差距。在RenderPeople和DNA-Rendering数据集上的广泛实验表明,HumanGif在感知性能上达到最佳,对于新视图和姿态的合成具有更好的泛化能力。
Key Takeaways
- 提出了一种新的基于单视图的人类扩散模型HumanGif,用于生成动画人物模型。
- 结合2D角色动画的成功经验,利用基础扩散模型的生成先验信息。
- 将单视图下的3D人类新视图和姿态合成定义为受单视图条件约束的人类扩散过程。
- 引入了Human NeRF模块,从输入图像中学习空间对齐特征,并隐含地捕捉相对相机和姿态变换。
- 在优化过程中引入了图像级损失,以缩小潜空间和图像空间之间的差距。
- 在多个数据集上的实验表明,HumanGif在感知性能上优于其他方法。
点此查看论文截图

A Survey on Bridging EEG Signals and Generative AI: From Image and Text to Beyond
Authors:Shreya Shukla, Jose Torres, Abhijit Mishra, Jacek Gwizdka, Shounak Roychowdhury
Integration of Brain-Computer Interfaces (BCIs) and Generative Artificial Intelligence (GenAI) has opened new frontiers in brain signal decoding, enabling assistive communication, neural representation learning, and multimodal integration. BCIs, particularly those leveraging Electroencephalography (EEG), provide a non-invasive means of translating neural activity into meaningful outputs. Recent advances in deep learning, including Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) and Transformer-based Large Language Models (LLMs), have significantly improved EEG-based generation of images, text, and speech. This paper provides a literature review of the state-of-the-art in EEG-based multimodal generation, focusing on (i) EEG-to-image generation through GANs, Variational Autoencoders (VAEs), and Diffusion Models, and (ii) EEG-to-text generation leveraging Transformer based language models and contrastive learning methods. Additionally, we discuss the emerging domain of EEG-to-speech synthesis, an evolving multimodal frontier. We highlight key datasets, use cases, challenges, and EEG feature encoding methods that underpin generative approaches. By providing a structured overview of EEG-based generative AI, this survey aims to equip researchers and practitioners with insights to advance neural decoding, enhance assistive technologies, and expand the frontiers of brain-computer interaction.
脑机接口(BCI)与生成式人工智能(GenAI)的融合为脑信号解码开辟了新的领域,实现了辅助通信、神经表征学习和多模态融合。特别是利用脑电图(EEG)的脑机接口,提供了一种将神经活动转化为有意义输出的非侵入性手段。深度学习领域的最新进展,包括生成对抗网络(GANs)和基于变压器的自然语言模型(LLMs),极大地改进了基于EEG的图像、文本和语音生成。本文对基于EEG的多模态生成的最新研究进行了文献综述,重点关注(i)通过GANs、变分自动编码器(VAEs)和扩散模型实现EEG到图像生成,以及(ii)利用基于Transformer的自然语言模型和对比学习方法实现EEG到文本的生成。此外,我们还讨论了新兴的基于EEG的语音合成领域,这是一个不断发展的多模态前沿领域。本文重点介绍了关键数据集、应用场景、挑战以及支持生成方法的EEG特征编码方法。通过对基于EEG的生成式人工智能进行全面概述,本综述旨在为研究人员和实践者提供洞察力,以推动神经解码的发展,提高辅助技术水平,并拓展脑机交互的边界。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
脑机接口(BCI)与生成式人工智能(GenAI)的融合为脑信号解码开创了新纪元,助力辅助沟通、神经表征学习与多媒体融合。借助脑电图(EEG)的BCI实现了神经活动至图像、文本和语音的生成。本文综述了基于EEG的多模态生成最新进展,关注EEG转图像和EEG转文本生成,并探讨了新兴的EEG语音合成领域。
Key Takeaways
- BCIs与GenAI融合推动了脑信号解码的发展。
- EEG为BCI提供了非侵入式的神经活动翻译方式。
- 深度学习进步促进了基于EEG的图像、文本和语音生成。
- GANs、VAEs和Diffusion Models用于EEG转图像生成。
- Transformer基础的语言模型和对比学习方法用于EEG转文本生成。
- EEG语音合成是新兴的多模态领域。
- 文章讨论了关键数据集、用例、挑战和EEG特征编码方法。
点此查看论文截图

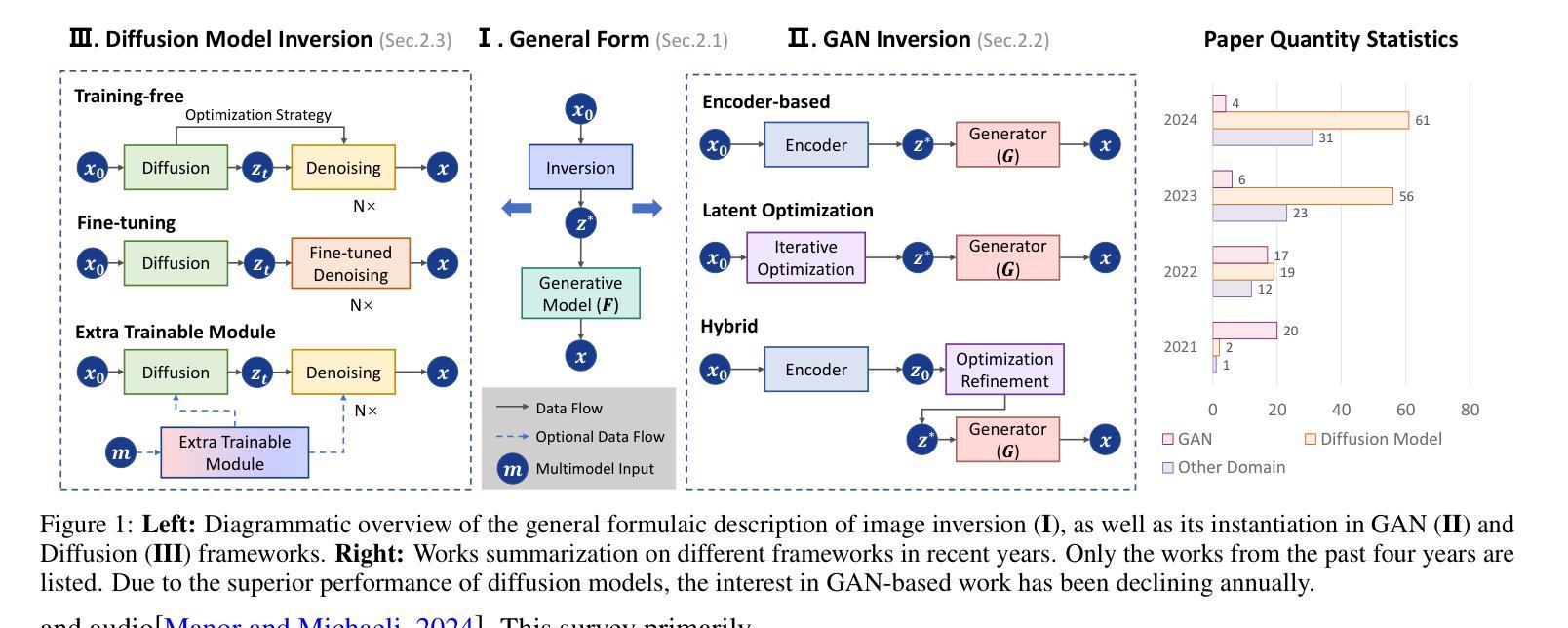
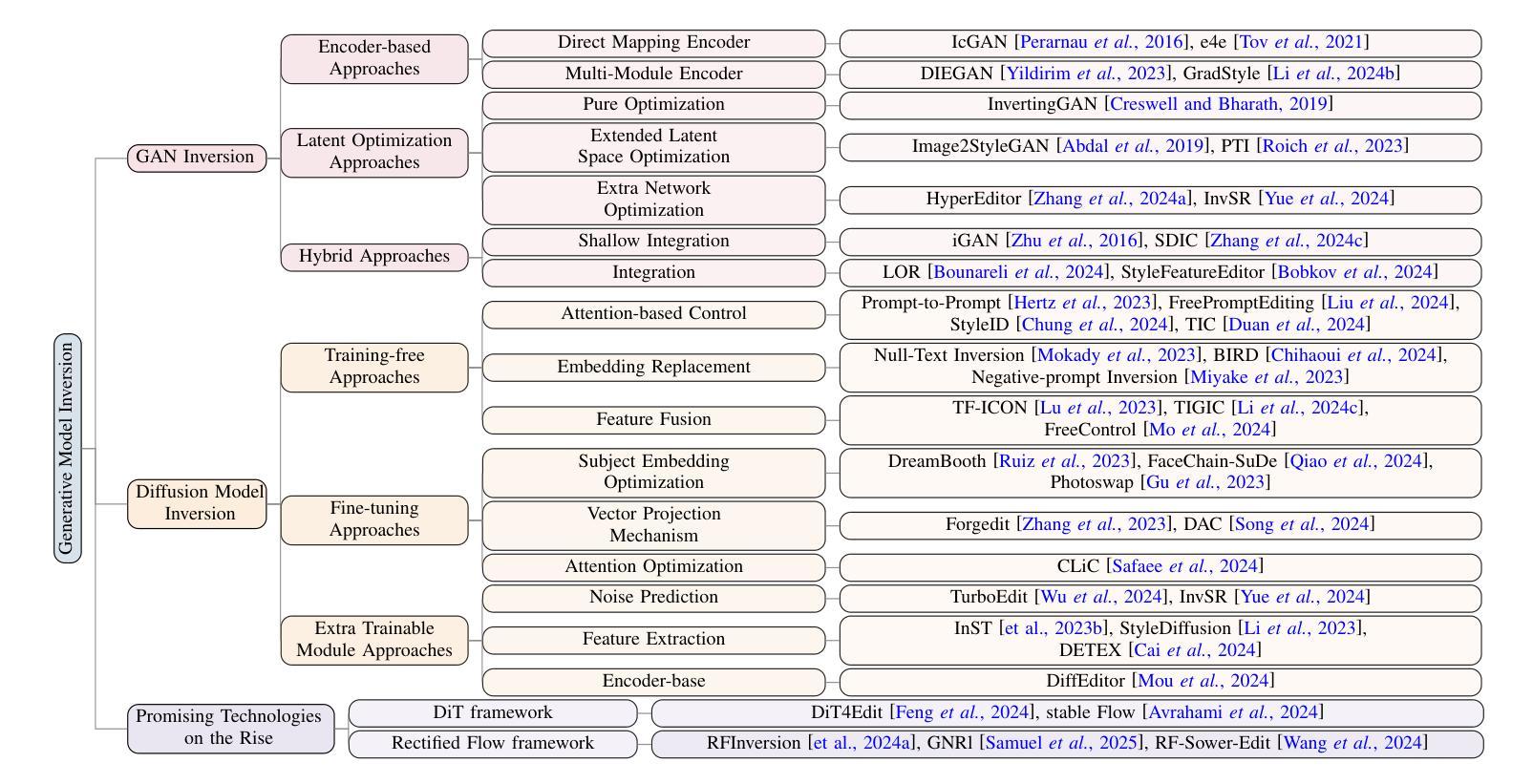
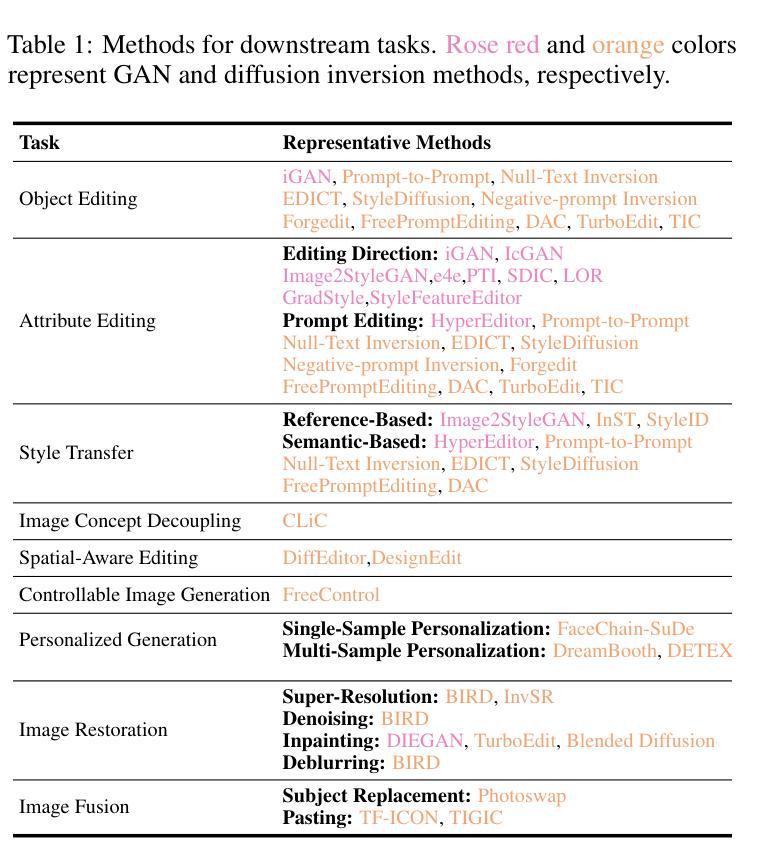
Image Inversion: A Survey from GANs to Diffusion and Beyond
Authors:Yinan Chen, Jiangning Zhang, Yali Bi, Xiaobin Hu, Teng Hu, Zhucun Xue, Ran Yi, Yong Liu, Ying Tai
Image inversion is a fundamental task in generative models, aiming to map images back to their latent representations to enable downstream applications such as editing, restoration, and style transfer. This paper provides a comprehensive review of the latest advancements in image inversion techniques, focusing on two main paradigms: Generative Adversarial Network (GAN) inversion and diffusion model inversion. We categorize these techniques based on their optimization methods. For GAN inversion, we systematically classify existing methods into encoder-based approaches, latent optimization approaches, and hybrid approaches, analyzing their theoretical foundations, technical innovations, and practical trade-offs. For diffusion model inversion, we explore training-free strategies, fine-tuning methods, and the design of additional trainable modules, highlighting their unique advantages and limitations. Additionally, we discuss several popular downstream applications and emerging applications beyond image tasks, identifying current challenges and future research directions. By synthesizing the latest developments, this paper aims to provide researchers and practitioners with a valuable reference resource, promoting further advancements in the field of image inversion. We keep track of the latest works at https://github.com/RyanChenYN/ImageInversion
图像反演是生成模型中的一项基本任务,旨在将图像映射回其潜在表示,以支持下游应用,如编辑、恢复和风格转换。本文对图像反演技术的最新进展进行了全面综述,重点介绍了两种主要范式:生成对抗网络(GAN)反演和扩散模型反演。我们根据优化方法对这些技术进行分类。对于GAN反演,我们系统地将其分为基于编码器的方法、潜在优化方法和混合方法,并对其理论基础、技术创新和实际应用进行了深入的分析和讨论。对于扩散模型反演,我们探讨了无训练策略、微调方法和附加训练模块的设计,突出了它们的独特优势和局限性。此外,我们还介绍了几个流行的下游应用和超越图像任务的新兴应用,确定了当前面临的挑战和未来研究方向。通过综合最新发展,本文旨在为研究人员和实践者提供有价值的参考资源,推动图像反演领域的进一步发展。有关最新研究成果的最新信息请参见:[https://github.com/RyanChenYN/ImageInversion](点击链接可查看详细信息)。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 10 pages, 2 figures
Summary
本文综述了图像反转任务中的最新进展,特别是生成对抗网络(GAN)反转和扩散模型反转的两种主要范式。文章对这两种方法进行了系统的分类,并分析了它们的理论框架、技术创新和实践中的权衡。此外,还探讨了图像反转在下游应用中的热门领域以及超出现有图像任务的新兴应用,指出了当前面临的挑战和未来研究方向。
Key Takeaways
- 图像反转是生成模型中的基础任务,旨在将图像映射回其潜在表示,以支持下游应用,如编辑、恢复和风格转换。
- GAN反转和扩散模型反转是图像反转中的两种主要方法,本文进行了详细综述。
- GAN反转方法包括基于编码器的方法、潜在优化方法和混合方法,各有其理论、技术和实践上的特点。
- 扩散模型反转策略涉及无训练策略、微调方法和可训练模块的设计,具有独特的优势和局限性。
- 图像反转在下游应用中的热门领域包括编辑、恢复和风格转换等,同时也有超出现有图像任务的新兴应用。
- 当前图像反转领域仍面临一些挑战,包括模型的稳定性、效率、以及跨模态的应用等。
点此查看论文截图

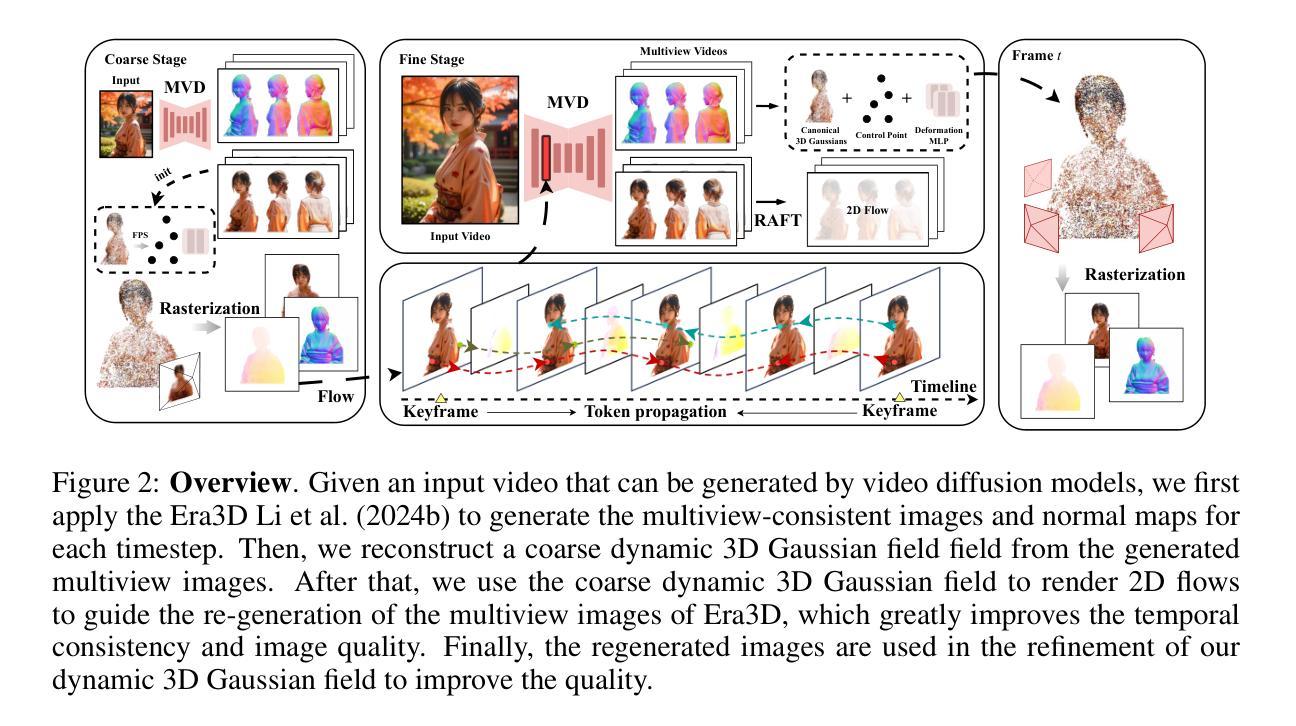
MVTokenFlow: High-quality 4D Content Generation using Multiview Token Flow
Authors:Hanzhuo Huang, Yuan Liu, Ge Zheng, Jiepeng Wang, Zhiyang Dou, Sibei Yang
In this paper, we present MVTokenFlow for high-quality 4D content creation from monocular videos. Recent advancements in generative models such as video diffusion models and multiview diffusion models enable us to create videos or 3D models. However, extending these generative models for dynamic 4D content creation is still a challenging task that requires the generated content to be consistent spatially and temporally. To address this challenge, MVTokenFlow utilizes the multiview diffusion model to generate multiview images on different timesteps, which attains spatial consistency across different viewpoints and allows us to reconstruct a reasonable coarse 4D field. Then, MVTokenFlow further regenerates all the multiview images using the rendered 2D flows as guidance. The 2D flows effectively associate pixels from different timesteps and improve the temporal consistency by reusing tokens in the regeneration process. Finally, the regenerated images are spatiotemporally consistent and utilized to refine the coarse 4D field to get a high-quality 4D field. Experiments demonstrate the effectiveness of our design and show significantly improved quality than baseline methods.
本文介绍了MVTokenFlow,用于从单目视频中创建高质量4D内容。最近的生成模型(如视频扩散模型和多视图扩散模型)的进步使我们能够创建视频或3D模型。然而,将这些生成模型扩展到动态4D内容创建仍然是一项具有挑战性的任务,需要确保生成的内容在空间和时间上保持一致。为了解决这一挑战,MVTokenFlow利用多视图扩散模型在不同的时间步长上生成多视图图像,这实现了不同视点之间的空间一致性,并使我们能够重建合理的粗略4D场。然后,MVTokenFlow进一步以渲染的2D流为引导,重新生成所有多视图图像。2D流有效地关联了来自不同时间步长的像素,并在再生过程中重用令牌,提高了时间一致性。最后,再生图像具有时空一致性,并用于细化粗略的4D场,以获得高质量的4D场。实验证明了我们设计的有效性,并显示出比基线方法显著提高的质量。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICLR 2025. Project page: https://soolab.github.io/MVTokenFlow
Summary
本论文提出了MVTokenFlow,一种用于高质量四维内容创建的技术。该技术基于单目视频,利用先进的生成模型如视频扩散模型和多视角扩散模型,生成具有时空一致性的多视角图像,进而构建合理的粗略四维场。通过利用渲染的二维流作为指导,MVTokenFlow能够改善时间一致性并再生所有多视角图像。最终,使用时空一致的再生图像对粗略四维场进行精细化处理,以获得高质量的四维场。实验证明了该设计的有效性,显著优于基准方法。
Key Takeaways
- MVTokenFlow是一种用于高质量四维内容创建的技术,能够从单目视频中生成多视角图像。
- 利用先进的生成模型如视频扩散模型和多视角扩散模型为基础构建技术框架。
- 通过构建多视角图像在不同时间点的生成,实现空间一致性。
- 利用渲染的二维流作为指导,改善时间一致性并再生多视角图像。
- 通过时空一致的再生图像对粗略四维场进行精细化处理。
- 实验证明了MVTokenFlow设计的有效性,显著提高了四维内容创建的质量。
点此查看论文截图


Learning to Sample Effective and Diverse Prompts for Text-to-Image Generation
Authors:Taeyoung Yun, Dinghuai Zhang, Jinkyoo Park, Ling Pan
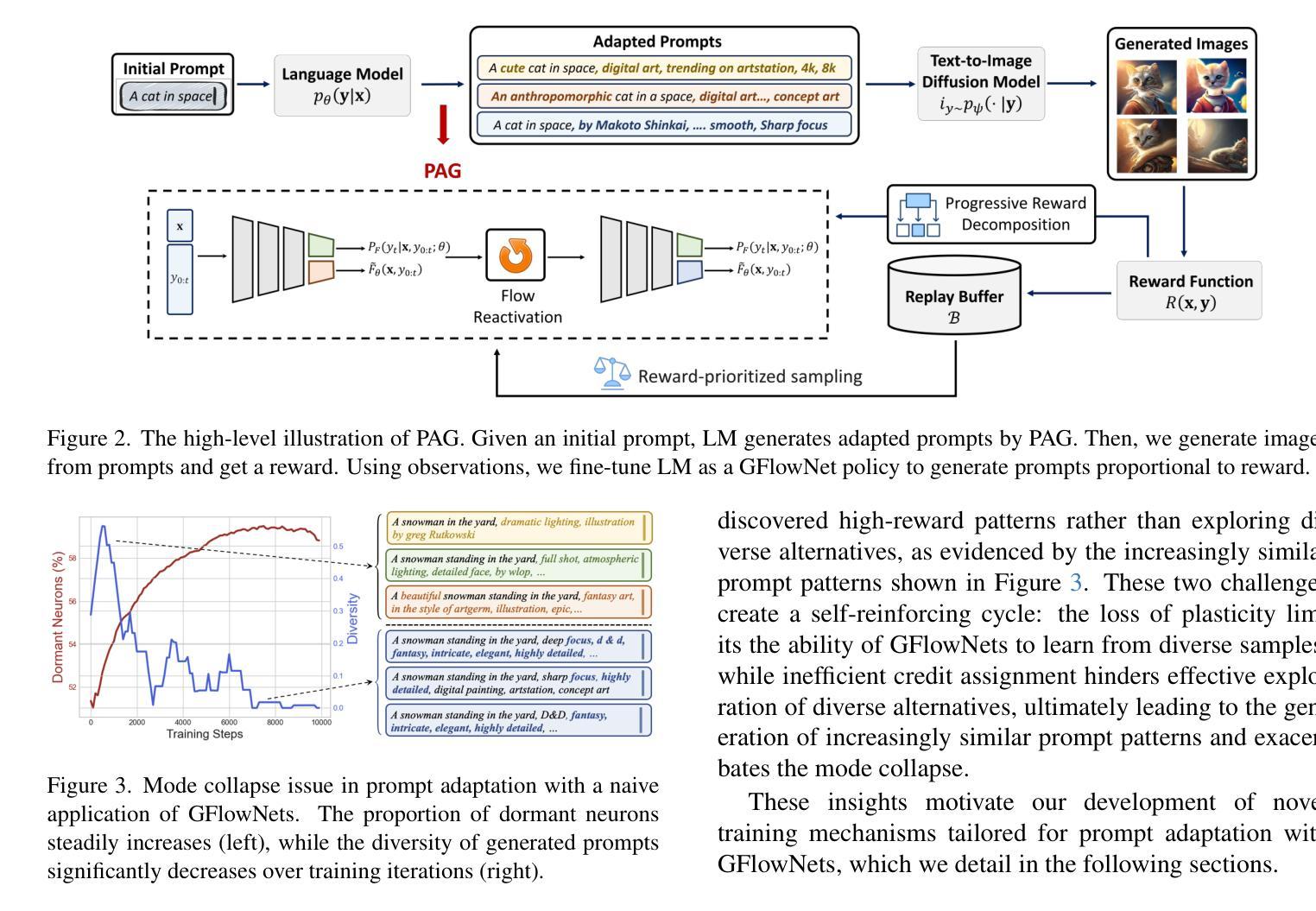
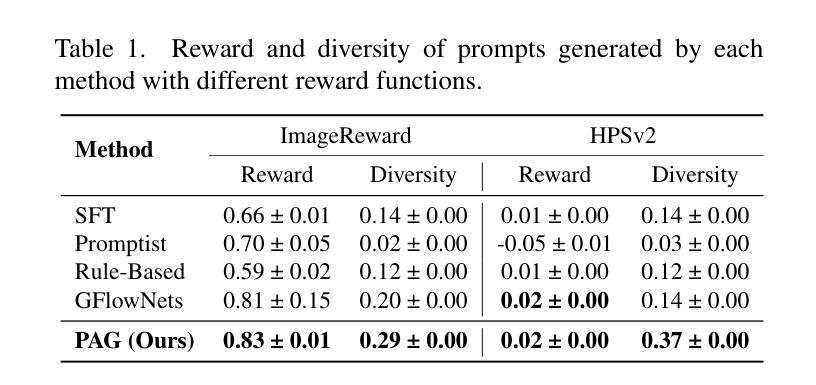
Recent advances in text-to-image diffusion models have achieved impressive image generation capabilities. However, it remains challenging to control the generation process with desired properties (e.g., aesthetic quality, user intention), which can be expressed as black-box reward functions. In this paper, we focus on prompt adaptation, which refines the original prompt into model-preferred prompts to generate desired images. While prior work uses reinforcement learning (RL) to optimize prompts, we observe that applying RL often results in generating similar postfixes and deterministic behaviors. To this end, we introduce \textbf{P}rompt \textbf{A}daptation with \textbf{G}FlowNets (\textbf{PAG}), a novel approach that frames prompt adaptation as a probabilistic inference problem. Our key insight is that leveraging Generative Flow Networks (GFlowNets) allows us to shift from reward maximization to sampling from an unnormalized density function, enabling both high-quality and diverse prompt generation. However, we identify that a naive application of GFlowNets suffers from mode collapse and uncovers a previously overlooked phenomenon: the progressive loss of neural plasticity in the model, which is compounded by inefficient credit assignment in sequential prompt generation. To address this critical challenge, we develop a systematic approach in PAG with flow reactivation, reward-prioritized sampling, and reward decomposition for prompt adaptation. Extensive experiments validate that PAG successfully learns to sample effective and diverse prompts for text-to-image generation. We also show that PAG exhibits strong robustness across various reward functions and transferability to different text-to-image models.
近期文本到图像扩散模型的进展已经实现了令人印象深刻的图像生成能力。然而,使用期望的属性(如美学质量、用户意图)来控制生成过程仍然是一个挑战,这些属性可以表示为黑盒奖励函数。在本文中,我们专注于提示适应,它将原始提示细化为模型偏好的提示以生成所需的图像。虽然先前的工作使用强化学习(RL)来优化提示,但我们发现应用RL通常会导致生成相似的后缀和确定性行为。为此,我们引入了带有GFlowNets的提示适应(PAG),这是一种将提示适应框架化为概率推理问题的新方法。我们的关键见解是利用生成流网络(GFlowNets)允许我们从奖励最大化转向从未归一化的密度函数中进行采样,从而实现高质量和多样化的提示生成。然而,我们发现GFlowNets的朴素应用存在模式崩溃的问题,并揭示了一个以前被忽视的现象:模型中神经可塑性的逐步丧失,这是由顺序提示生成中的低效信用分配所加剧的。为了解决这一关键挑战,我们在PAG中开发了一种系统方法,包括流复活、奖励优先采样和奖励分解来进行提示适应。大量实验验证,PAG成功学会了对文本到图像生成进行有效且多样化的提示采样。我们还表明,PAG在各种奖励函数之间表现出强大的稳健性,并且可转移到不同的文本到图像模型。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 18 pages, 14 figures, 6 tables
Summary
文本到图像扩散模型的最新进展已实现了令人印象深刻的图像生成能力。然而,如何控制生成过程以获取具有特定属性(如美学质量、用户意图)的图像仍然是一个挑战。本文关注提示适应(Prompt Adaptation)技术,该技术将原始提示细化为模型偏好的提示,以生成所需的图像。本文引入了一种新的方法PAG(利用GFlowNets的提示适应),将提示适应视为概率推理问题。我们的关键见解是利用GFlowNets从非标准化密度函数中采样,以实现高质量和多样化的提示生成。然而,我们发现单纯应用GFlowNets会出现模式崩溃的问题,并揭示了一个被忽视的现象:模型中神经可塑性的逐步丧失,这在序列提示生成中的信用分配效率低下时更为严重。为解决这一关键挑战,我们在PAG中采用了流再激活、奖励优先采样和奖励分解的方法。实验证明,PAG成功学习了对文本到图像生成的有效和多样化的提示进行采样。我们还表明,PAG在不同的奖励函数之间表现出强大的稳健性,并可在不同的文本到图像模型中进行转移。
Key Takeaways
- 文本到图像扩散模型在图像生成方面取得了显著进展,但控制生成过程以获取具有特定属性的图像仍存在挑战。
- 提示适应技术通过细化原始提示为模型偏好的提示,提高了图像生成的效率和质量。
- 引入新的方法PAG,将提示适应视为概率推理问题,利用GFlowNets进行非标准化密度函数采样,实现高质量和多样化的提示生成。
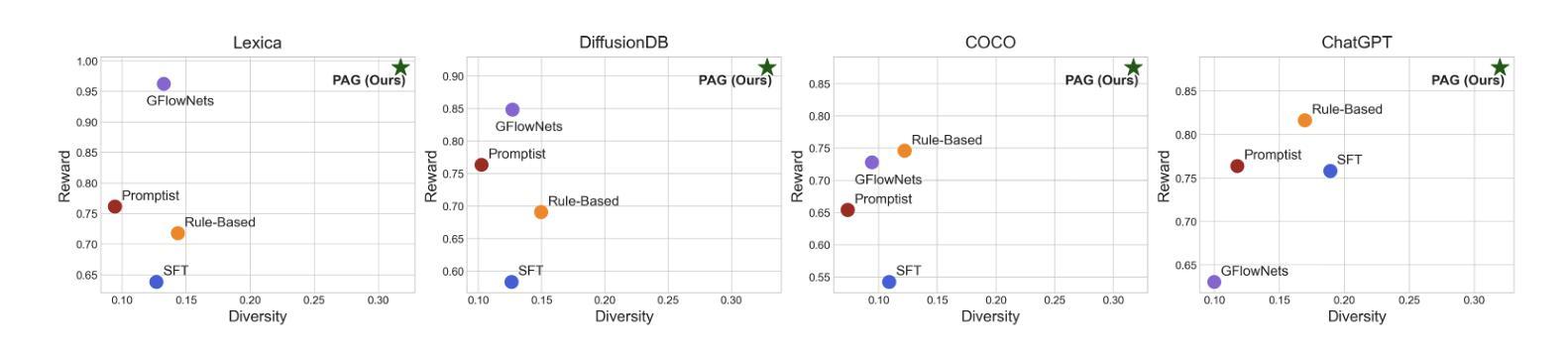
- 发现单纯应用GFlowNets会导致模式崩溃,并揭示模型中神经可塑性的丧失和序列提示生成中的信用分配问题。
- 为解决这些问题,PAG采用了流再激活、奖励优先采样和奖励分解的方法。
- 实验证明,PAG能有效学习对文本到图像生成过程中的提示进行采样,表现出强大的稳健性和在不同模型中的可转移性。
点此查看论文截图


PDA: Generalizable Detection of AI-Generated Images via Post-hoc Distribution Alignment
Authors:Li Wang, Wenyu Chen, Zheng Li, Shanqing Guo
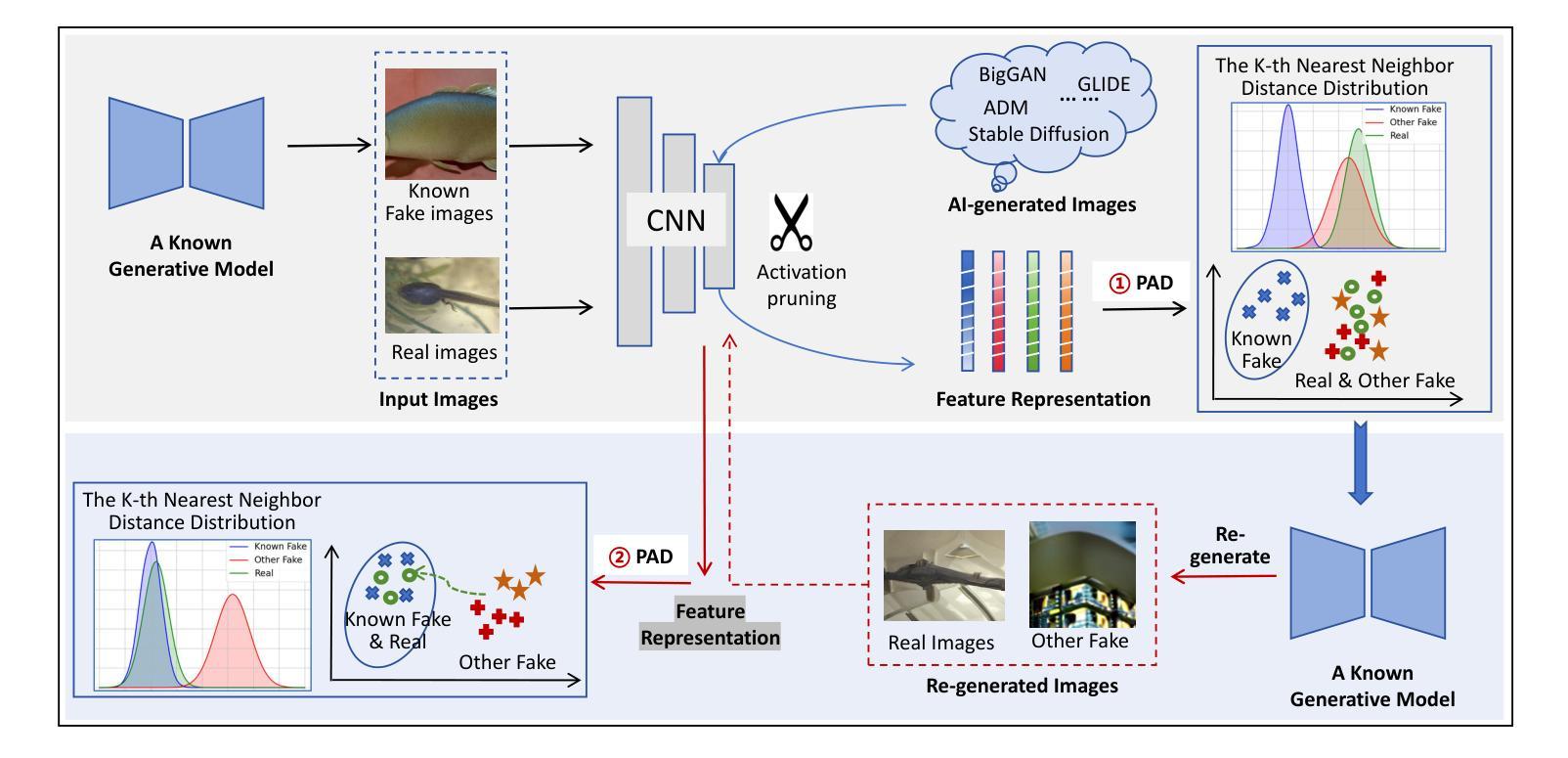
The rapid advancement of generative models has led to the proliferation of highly realistic AI-generated images, posing significant challenges for detection methods to generalize across diverse and evolving generative techniques. Existing approaches often fail to adapt to unknown models without costly retraining, limiting their practicability. To fill this gap, we propose Post-hoc Distribution Alignment (PDA), a novel approach for the generalizable detection for AI-generated images. The key idea is to use the known generative model to regenerate undifferentiated test images. This process aligns the distributions of the re-generated real images with the known fake images, enabling effective distinction from unknown fake images. PDA employs a two-step detection framework: 1) evaluating whether a test image aligns with the known fake distribution based on deep k-nearest neighbor (KNN) distance, and 2) re-generating test images using known generative models to create pseudo-fake images for further classification. This alignment strategy allows PDA to effectively detect fake images without relying on unseen data or requiring retraining. Extensive experiments demonstrate the superiority of PDA, achieving 96.73% average accuracy across six state-of-the-art generative models, including GANs, diffusion models, and text-to-image models, and improving by 16.07% over the best baseline. Through t-SNE visualizations and KNN distance analysis, we provide insights into PDA’s effectiveness in separating real and fake images. Our work provides a flexible and effective solution for real-world fake image detection, advancing the generalization ability of detection systems.
随着生成模型的快速发展,高度逼真的AI生成图像大量涌现,这为检测方法的通用性带来了重大挑战,因为生成技术多种多样且不断演变。现有方法往往无法适应未知模型,而无需进行昂贵的重新训练,这限制了它们的实用性。为了填补这一空白,我们提出了事后分布对齐(PDA)方法,这是一种用于AI生成图像的可泛化检测的新方法。关键思想是利用已知的生成模型重新生成未分化的测试图像。这个过程将重新生成的真实图像分布与已知的虚假图像对齐,从而能够有效地区分未知的虚假图像。PDA采用两步检测框架:1)基于深度k最近邻(KNN)距离评估测试图像是否与已知虚假分布对齐;2)使用已知生成模型重新生成测试图像以创建伪假图像进行进一步分类。这种对齐策略允许PDA有效地检测虚假图像,而无需依赖未见过的数据或进行重新训练。大量实验表明,PDA在六种最先进的生成模型上表现出卓越的性能,包括GANs、扩散模型和文本到图像模型,并比最佳基线提高了16.07%。通过t-SNE可视化和KNN距离分析,我们深入了解了PDA在分离真实和虚假图像方面的有效性。我们的工作提供了一种灵活有效的解决方案,用于真实世界的虚假图像检测,提高了检测系统的通用性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
针对生成模型快速发展带来的AI生成图像检测挑战,本文提出了一种后验分布对齐(PDA)的通用检测方法。它通过已知生成模型重新生成测试图像来对齐真实与生成图像的分布,从而实现未知生成模型下生成图像的有效鉴别。该策略通过评估测试图像与已知假图像分布的匹配程度,并利用已知生成模型重新生成测试图像进行分类,无需未见数据或重新训练即可实现检测。实验证明,PDA在六种先进的生成模型上取得了平均准确率高达96.73%的效果,相较于最佳基线提高了16.07%。它为真实世界的假图像检测提供了灵活有效的解决方案。
Key Takeaways
- 生成模型的快速发展带来了AI生成图像的检测挑战,因为现有方法难以适应未知模型。
- PDA方法通过已知生成模型重新生成测试图像,实现真实与生成图像分布的对齐。
- PDA利用深度k近邻(KNN)距离评估测试图像与已知假分布的匹配程度。
- PDA在多种生成模型上实现了高效的假图像检测,平均准确率高达96.73%。
- PDA相较于最佳基线提高了16.07%,显示出其显著优势。
- PDA方法通过t-SNE可视化和KNN距离分析证明了其有效性。
点此查看论文截图


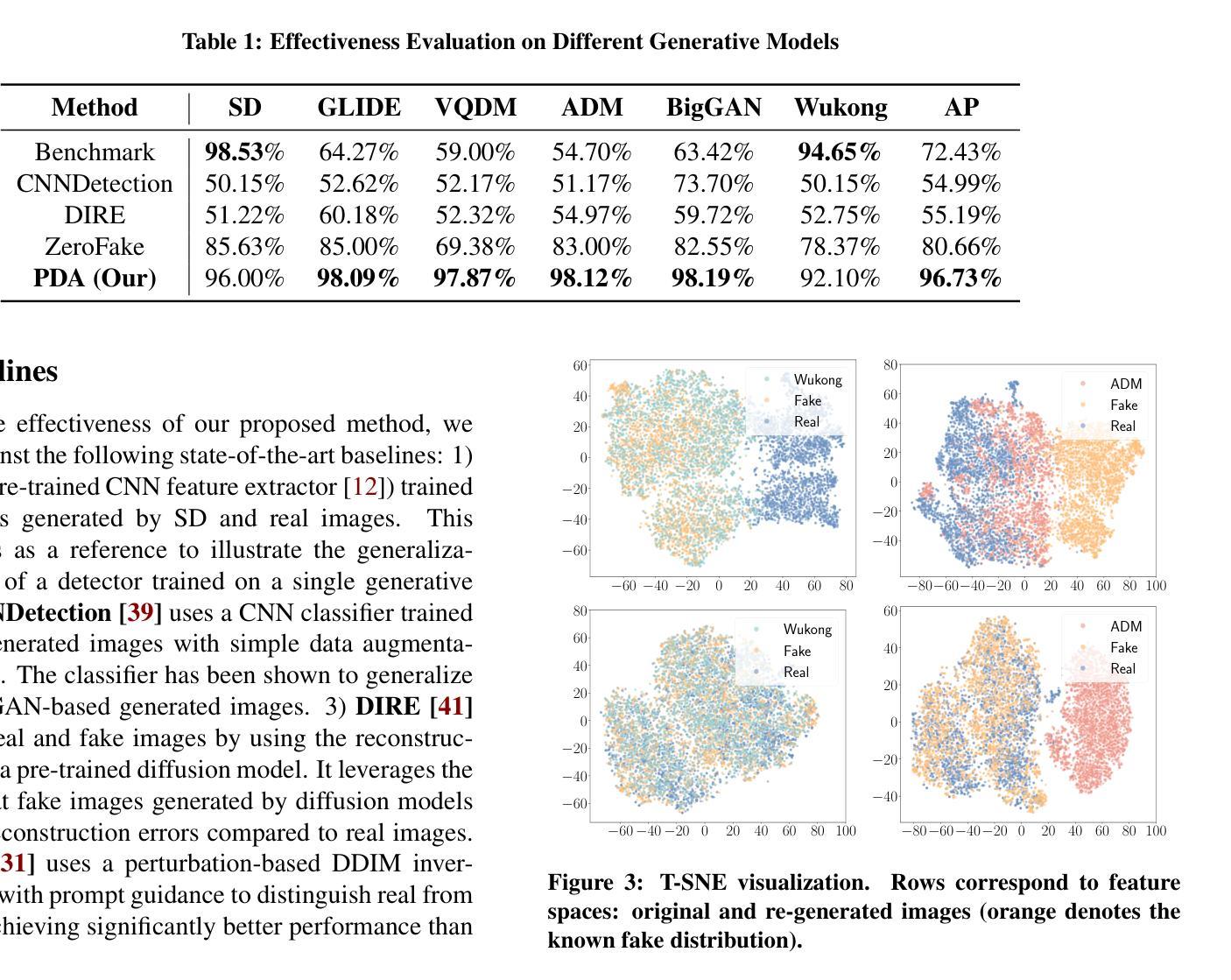
Diffusing DeBias: a Recipe for Turning a Bug into a Feature
Authors:Massimiliano Ciranni, Vito Paolo Pastore, Roberto Di Via, Enzo Tartaglione, Francesca Odone, Vittorio Murino
Deep learning model effectiveness in classification tasks is often challenged by the quality and quantity of training data which, whenever containing strong spurious correlations between specific attributes and target labels, can result in unrecoverable biases in model predictions. Tackling these biases is crucial in improving model generalization and trust, especially in real-world scenarios. This paper presents Diffusing DeBias (DDB), a novel approach acting as a plug-in for common methods in model debiasing while exploiting the inherent bias-learning tendency of diffusion models. Our approach leverages conditional diffusion models to generate synthetic bias-aligned images, used to train a bias amplifier model, to be further employed as an auxiliary method in different unsupervised debiasing approaches. Our proposed method, which also tackles the common issue of training set memorization typical of this type of tech- niques, beats current state-of-the-art in multiple benchmark datasets by significant margins, demonstrating its potential as a versatile and effective tool for tackling dataset bias in deep learning applications.
深度学习模型在分类任务中的有效性常常受到训练数据质量和数量的挑战。训练数据中特定属性与目标标签之间存在强烈的虚假关联时,可能导致模型预测中出现无法挽回的偏见。解决这些偏见对于提高模型的通用性和信任度至关重要,尤其是在现实场景中应用尤为重要。本文提出了Diffusing DeBias(DDB),这是一种新型方法,可作为通用模型去偏方法的插件,同时利用扩散模型固有的偏学习倾向。我们的方法利用条件扩散模型生成合成偏置对齐图像,用于训练偏置放大器模型,进一步用于不同的无监督去偏方法中作为辅助方法。我们提出的方法还解决了此类技术典型的训练集记忆化问题,在多个基准数据集上大幅度地超越了当前最先进的水平,证明了其在深度学习应用中解决数据集偏见的潜力和有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 29 Pages, 12 Figures
Summary
深度学习模型在分类任务中的有效性经常受到训练数据的质量和数量的挑战。当训练数据包含特定属性与目标标签之间的强烈虚假关联时,会导致模型预测中出现不可挽回的偏见。本论文提出了一种名为Diffusing DeBias(DDB)的新方法,它利用扩散模型的固有偏见学习倾向,作为通用方法的一个插件来解决偏见问题。DDB通过生成合成偏见对齐图像来训练偏见放大器模型,并进一步用于不同的无监督去偏见方法。该方法还解决了此类技术中常见的训练集记忆问题,在多个基准数据集上显著优于当前最新技术,表明其在深度学习应用中解决数据集潜力的巨大潜力。
Key Takeaways
- 深度学习模型在分类任务中易受训练数据质量和数量的影响。
- 当训练数据存在虚假关联时,会导致模型预测出现偏见。
- Diffusing DeBias(DDB)是一种新的去偏见方法,利用扩散模型的倾向性。
- DDB通过生成合成偏见对齐图像来训练偏见放大器模型。
- DDB可作为插件用于不同的无监督去偏见方法。
- 该方法解决了现有技术中的训练集记忆问题。
点此查看论文截图

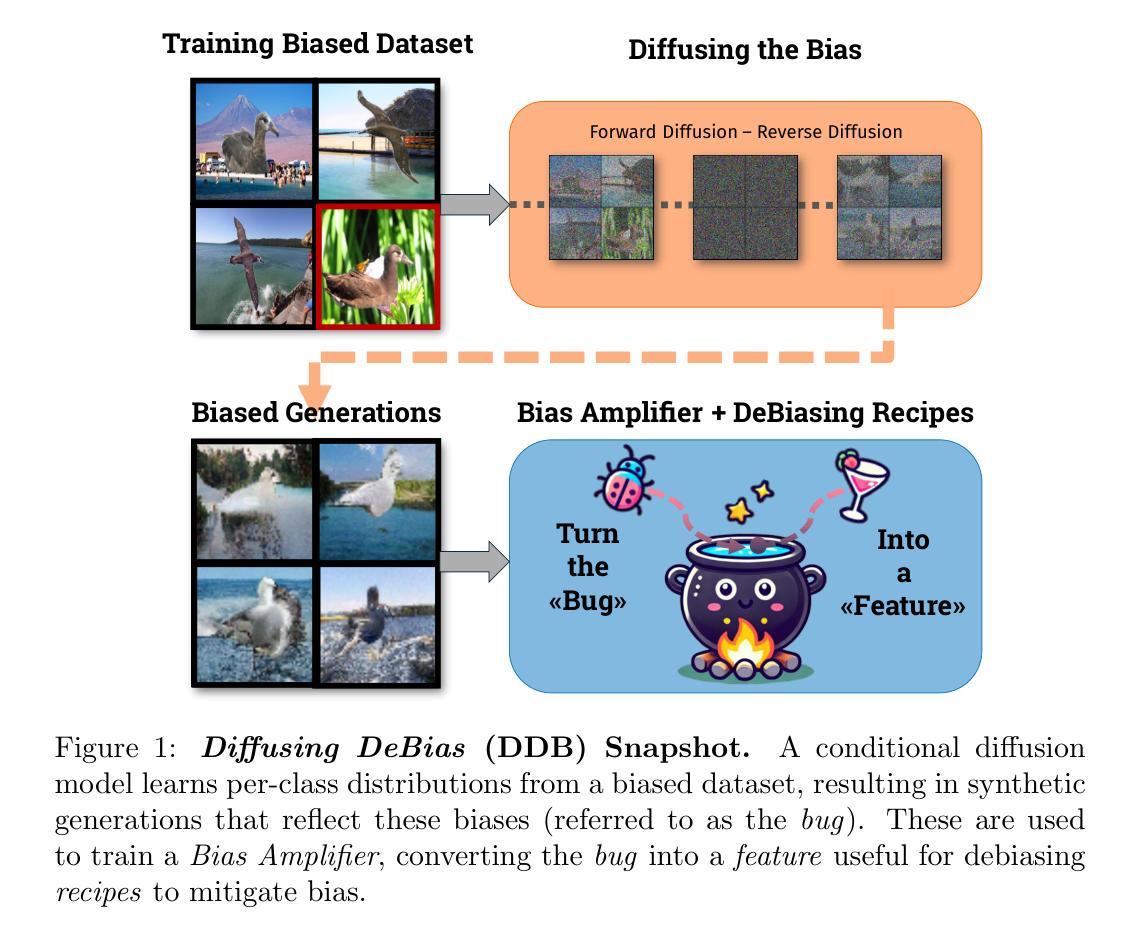
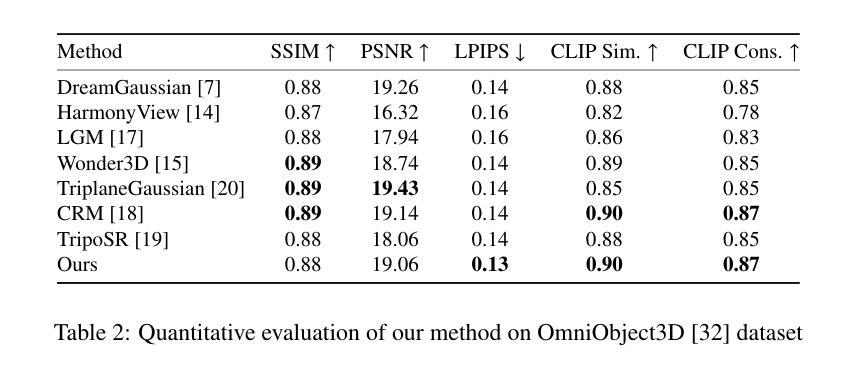
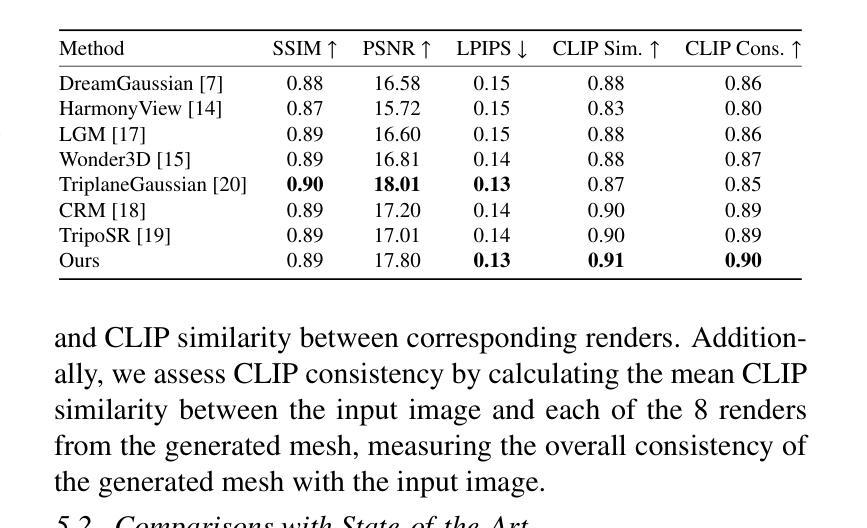
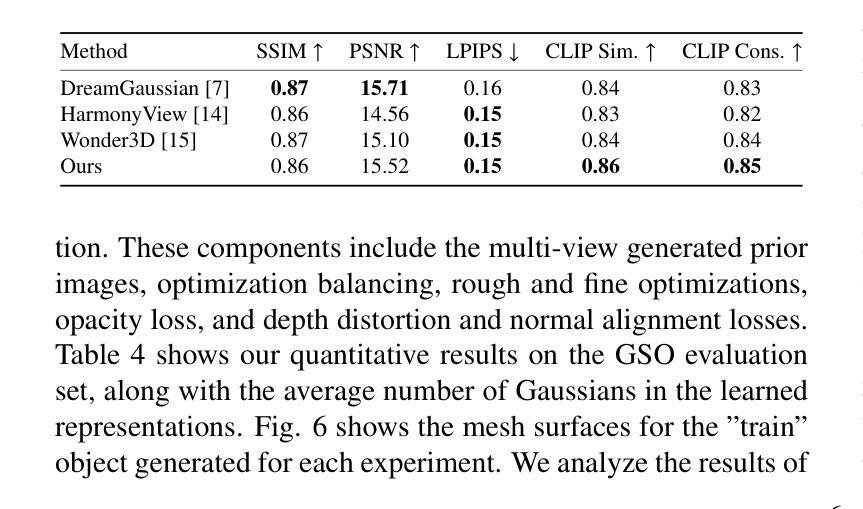
ConsistentDreamer: View-Consistent Meshes Through Balanced Multi-View Gaussian Optimization
Authors:Onat Şahin, Mohammad Altillawi, George Eskandar, Carlos Carbone, Ziyuan Liu
Recent advances in diffusion models have significantly improved 3D generation, enabling the use of assets generated from an image for embodied AI simulations. However, the one-to-many nature of the image-to-3D problem limits their use due to inconsistent content and quality across views. Previous models optimize a 3D model by sampling views from a view-conditioned diffusion prior, but diffusion models cannot guarantee view consistency. Instead, we present ConsistentDreamer, where we first generate a set of fixed multi-view prior images and sample random views between them with another diffusion model through a score distillation sampling (SDS) loss. Thereby, we limit the discrepancies between the views guided by the SDS loss and ensure a consistent rough shape. In each iteration, we also use our generated multi-view prior images for fine-detail reconstruction. To balance between the rough shape and the fine-detail optimizations, we introduce dynamic task-dependent weights based on homoscedastic uncertainty, updated automatically in each iteration. Additionally, we employ opacity, depth distortion, and normal alignment losses to refine the surface for mesh extraction. Our method ensures better view consistency and visual quality compared to the state-of-the-art.
近期扩散模型的新进展极大地改进了3D生成,使得可以使用从图像生成的资产进行实体AI模拟。然而,图像到3D的一对多性质由于从不同视角的不一致内容和质量而限制了其使用。以前的模型会通过从视角调节的扩散先验中采样视角来优化3D模型,但扩散模型无法保证视角的一致性。相反,我们提出了ConsistentDreamer,我们首先生成一组固定的多视角先验图像,并在它们之间通过评分蒸馏采样(SDS)损失使用另一个扩散模型进行随机视角采样。因此,我们通过SDS损失指导的视图限制了差异,并确保了一致的粗略形状。在每次迭代中,我们还使用生成的多视角先验图像进行细节重建。为了平衡粗略形状和细节优化之间的权衡,我们引入了基于异方差不确定性的动态任务依赖权重,并在每次迭代中自动更新。此外,我们还采用了透明度、深度失真和法线对齐损失来完善表面网格提取。我们的方法相较于最新技术确保了更好的视角一致性和视觉质量。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Manuscript accepted by Pattern Recognition Letters
Summary
扩散模型的最新进展已显著提高3D生成能力,可实现从图像生成资产用于实体AI模拟。然而,图像到3D的一对多问题导致其内容在不同视角上不一致,影响使用。之前的方法通过从视角调节的扩散先验中采样视角优化3D模型,但扩散模型无法保证视角一致性。因此,我们提出ConsistentDreamer,首先生成一组固定的多视角先验图像,并在它们之间通过另一个扩散模型进行随机视角采样,通过得分蒸馏采样(SDS)损失来限制视角之间的差异,确保一致的粗略形状。每次迭代中,我们还使用生成的多视角先验图像进行细节重建。为了平衡粗略形状和细节优化的平衡,我们引入了基于同方差不确定性的动态任务依赖权重,并在每次迭代中自动更新。此外,我们还采用透明度、深度失真和法线对齐损失来优化表面以进行网格提取。我们的方法相较于现有技术,在视角一致性和视觉质量上表现更佳。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型的最新进展促进了从图像生成资产在AI模拟中的应用。
- 图像到3D的一对多问题导致内容在不同视角上的不一致性。
- ConsistentDreamer通过生成固定多视角先验图像和得分蒸馏采样(SDS)损失来解决视角一致性问题。
- 多视角先验图像用于细节重建,并在迭代中自动更新权重以平衡形状和细节优化。
- 利用同方差不确定性的动态任务依赖权重来平衡粗略形状和精细细节的优化。
- 采用透明度、深度失真和法线对齐损失来优化表面以进行高质量的网格提取。
点此查看论文截图


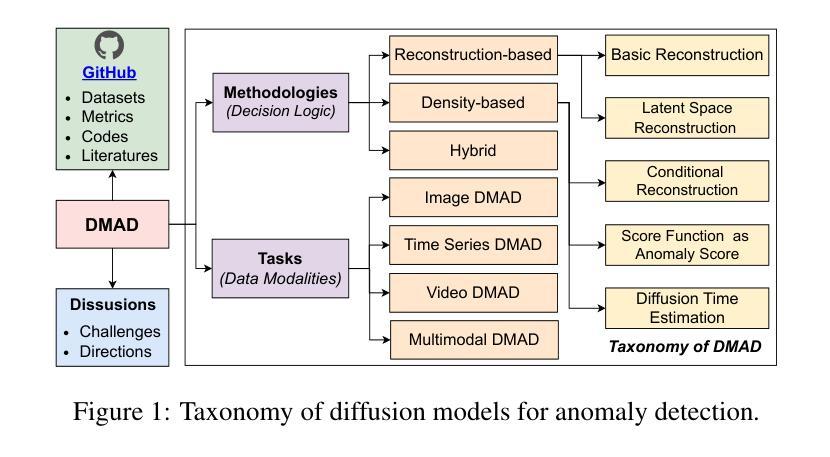
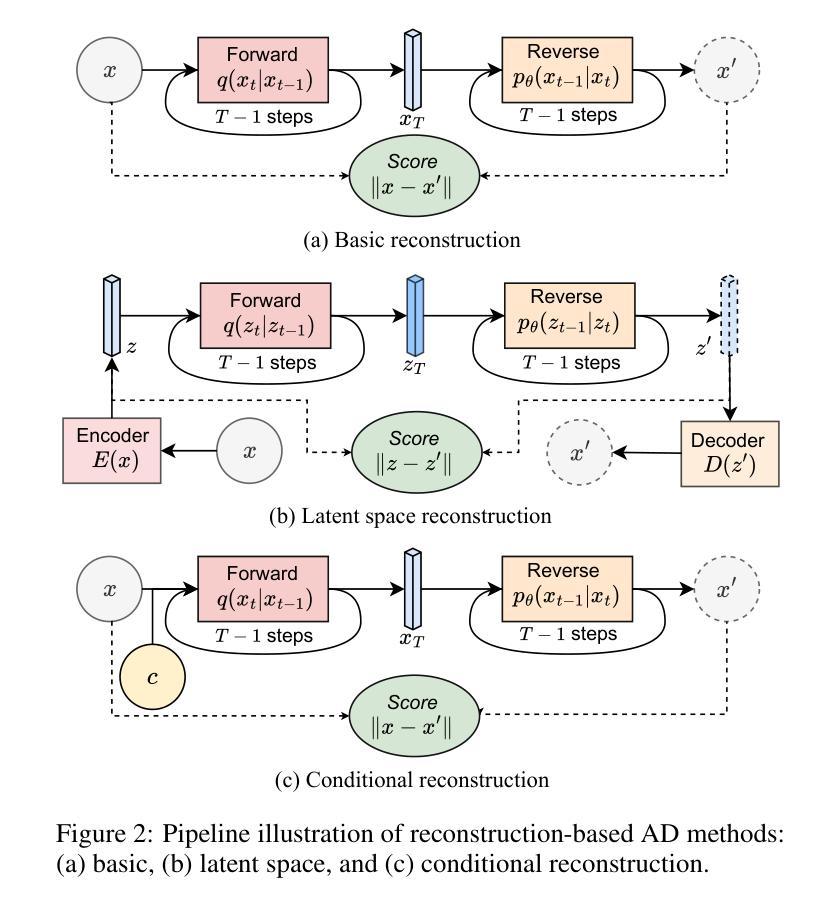
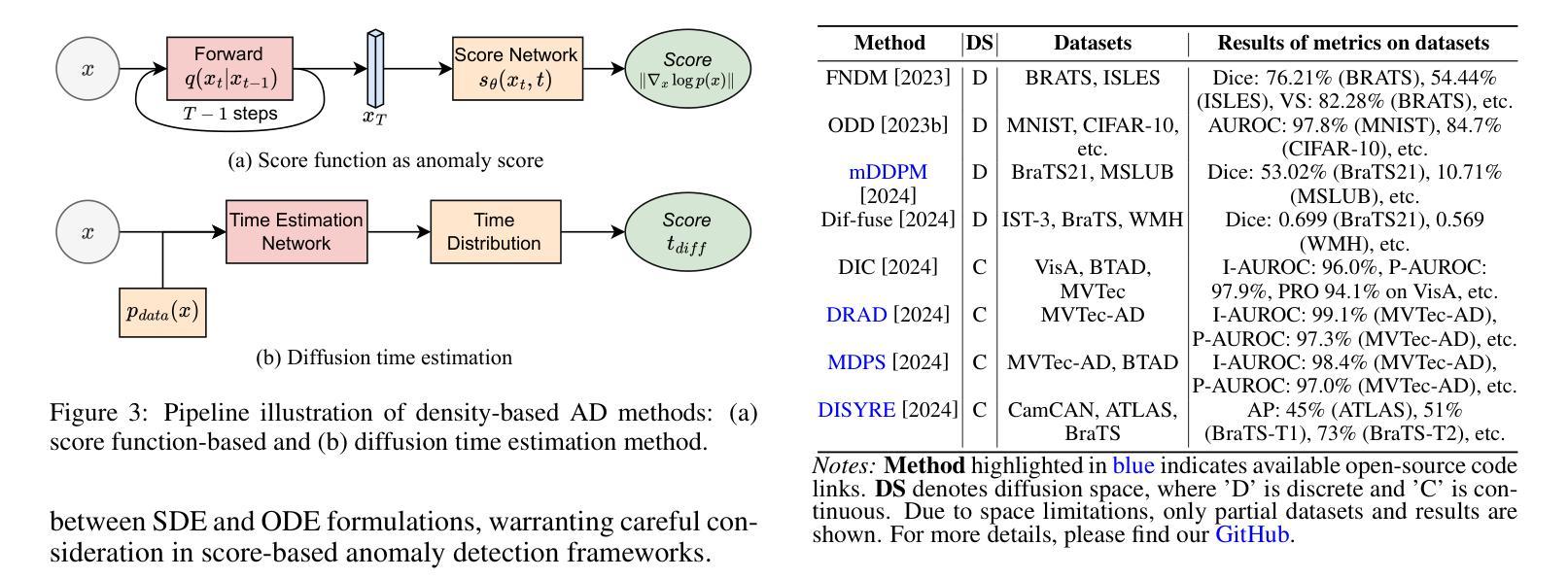
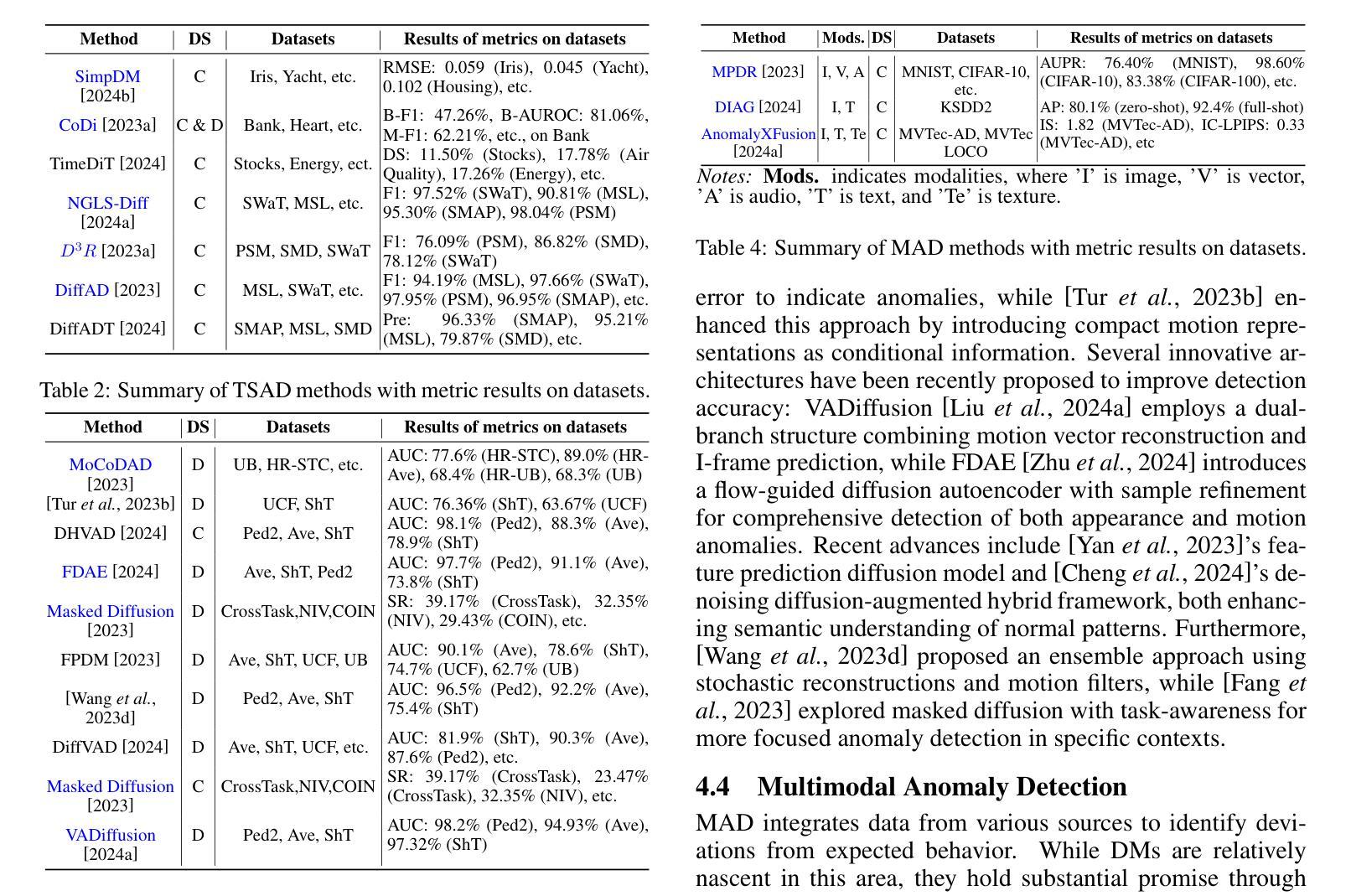
A Survey on Diffusion Models for Anomaly Detection
Authors:Jing Liu, Zhenchao Ma, Zepu Wang, Chenxuanyin Zou, Jiayang Ren, Zehua Wang, Liang Song, Bo Hu, Yang Liu, Victor C. M. Leung
Diffusion models (DMs) have emerged as a powerful class of generative AI models, showing remarkable potential in anomaly detection (AD) tasks across various domains, such as cybersecurity, fraud detection, healthcare, and manufacturing. The intersection of these two fields, termed diffusion models for anomaly detection (DMAD), offers promising solutions for identifying deviations in increasingly complex and high-dimensional data. In this survey, we review recent advances in DMAD research. We begin by presenting the fundamental concepts of AD and DMs, followed by a comprehensive analysis of classic DM architectures including DDPMs, DDIMs, and Score SDEs. We further categorize existing DMAD methods into reconstruction-based, density-based, and hybrid approaches, providing detailed examinations of their methodological innovations. We also explore the diverse tasks across different data modalities, encompassing image, time series, video, and multimodal data analysis. Furthermore, we discuss critical challenges and emerging research directions, including computational efficiency, model interpretability, robustness enhancement, edge-cloud collaboration, and integration with large language models. The collection of DMAD research papers and resources is available at https://github.com/fdjingliu/DMAD.
扩散模型(DMs)作为一类强大的生成人工智能模型已经崭露头角,在异常检测(AD)任务中显示出显著潜力,涉及多个领域,如网络安全、欺诈检测、医疗保健和制造等。这两个领域的交集,被称为用于异常检测的扩散模型(DMAD),为识别日益复杂和高维数据中的偏差提供了有前途的解决方案。在这篇综述中,我们回顾了DMAD研究的最新进展。首先,我们介绍AD和DM的基本概念,然后对经典的DM架构进行全面的分析,包括DDPMs、DDIMS和Score SDEs。我们将现有的DMAD方法进一步分为基于重建的、基于密度的和混合方法,并对其方法创新进行详细的研究。我们还探讨了不同数据模态的多样化任务,包括图像、时间序列、视频和多模态数据分析。此外,我们还讨论了关键的挑战和新兴的研究方向,包括计算效率、模型可解释性、增强稳健性、边缘云协作以及与大型语言模型的集成。DMAD研究论文和资源集可在https://github.com/fdjingliu/DMAD找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
扩散模型(DMs)作为生成式人工智能模型的新兴强大类别,在异常检测(AD)任务中展现出巨大潜力,广泛应用于网络安全、欺诈检测、医疗保健和制造等领域。本文综述了扩散模型在异常检测方面的最新研究进展,介绍了异常检测和扩散模型的基本概念,分析了经典的扩散模型架构,如DDPMs、DDIIMs和Score SDEs,并将现有的扩散模型异常检测方法分为重建型、密度型和混合型方法,详细探讨了它们的方法创新。此外,还介绍了不同数据模态的任务,包括图像、时间序列、视频和多模态数据分析。文章最后讨论了关键挑战和新兴研究方向,包括计算效率、模型可解释性、鲁棒性增强、边缘云协作以及与大型语言模型的集成。相关资源可通过链接访问。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型(DMs)在异常检测(AD)任务中展现出巨大潜力,适用于多个领域。
- 扩散模型用于异常检测(DMAD)是识别高维数据中偏差的有前途的解决方案。
- 经典扩散模型架构包括DDPMs、DDIIMs和Score SDEs。
- 现有的扩散模型异常检测方法可分为重建型、密度型和混合型方法。
- 扩散模型可处理图像、时间序列、视频和多模态数据等多种类型的数据。
- 面临的挑战包括计算效率、模型可解释性和鲁棒性增强等。
点此查看论文截图

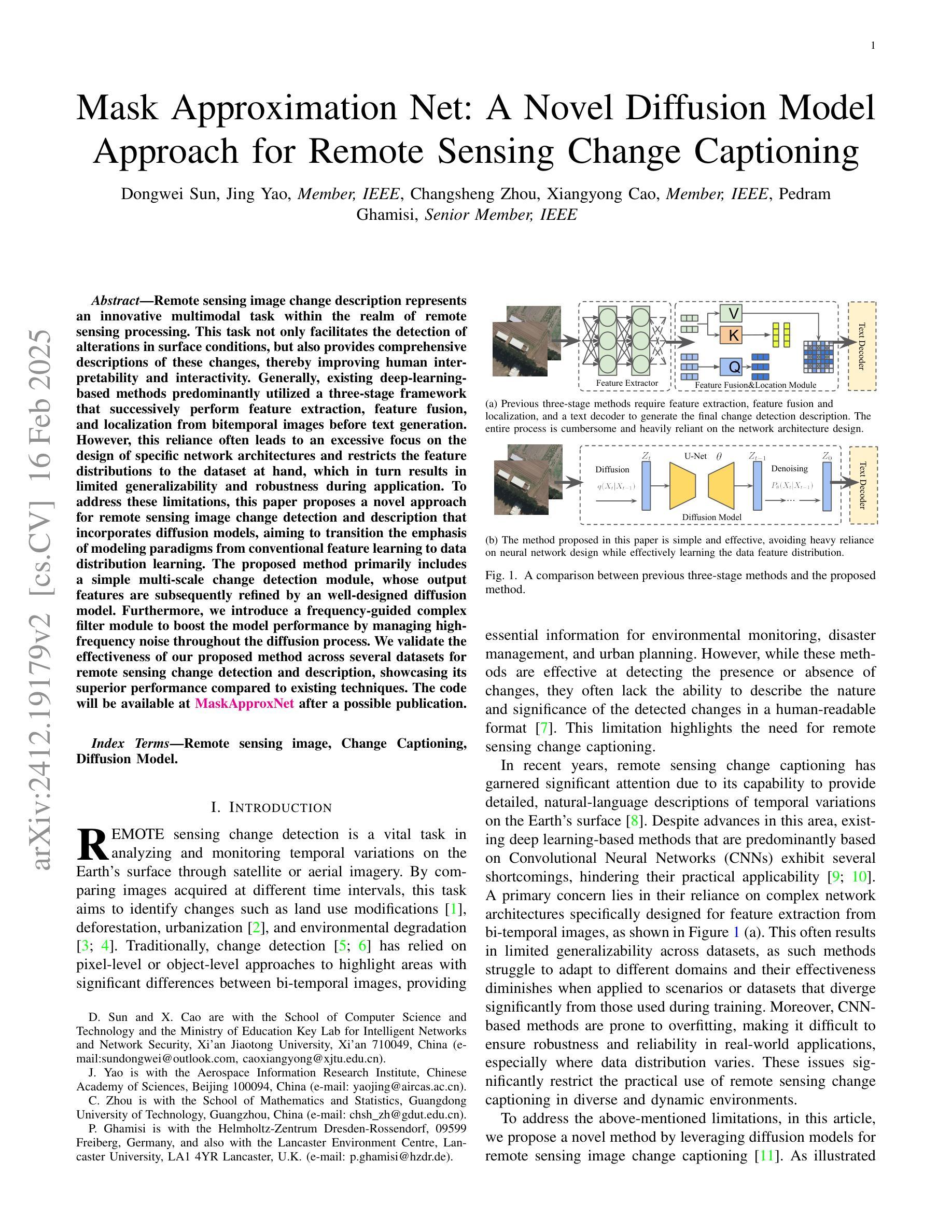
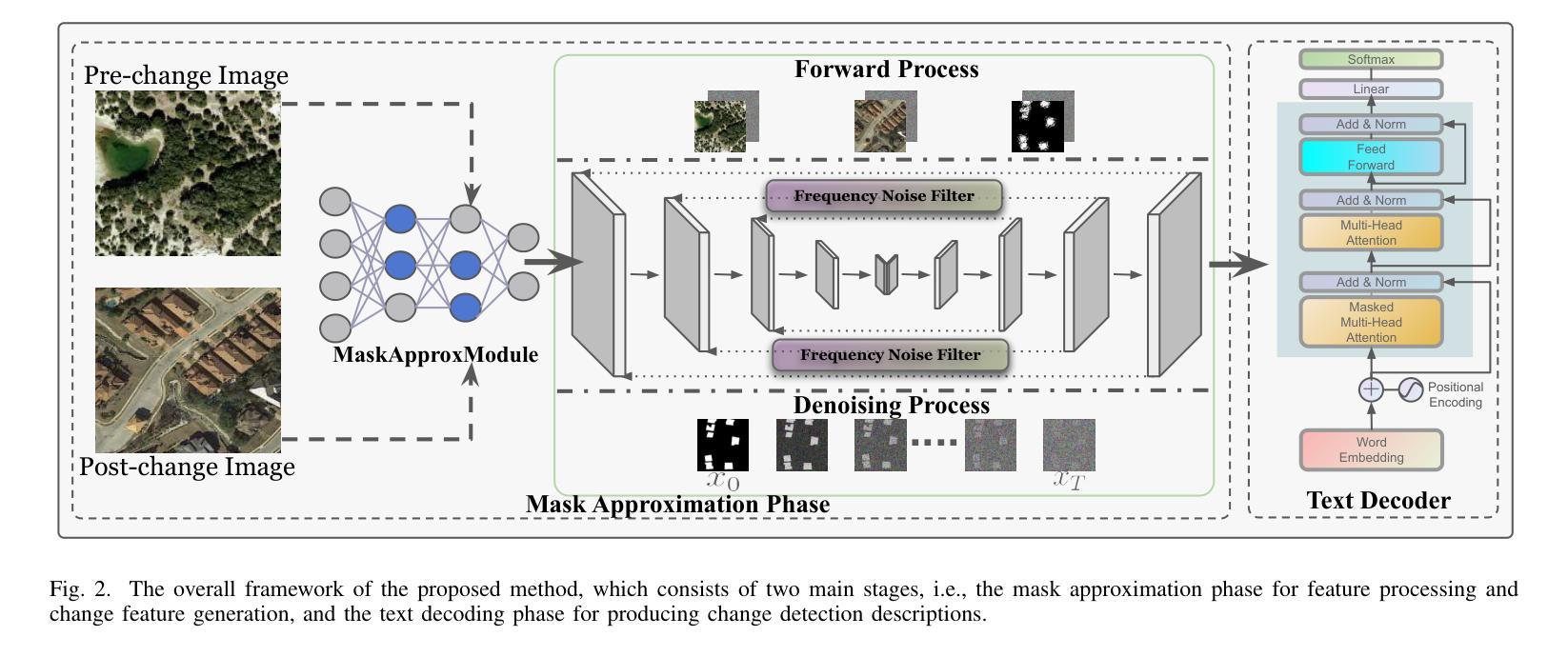
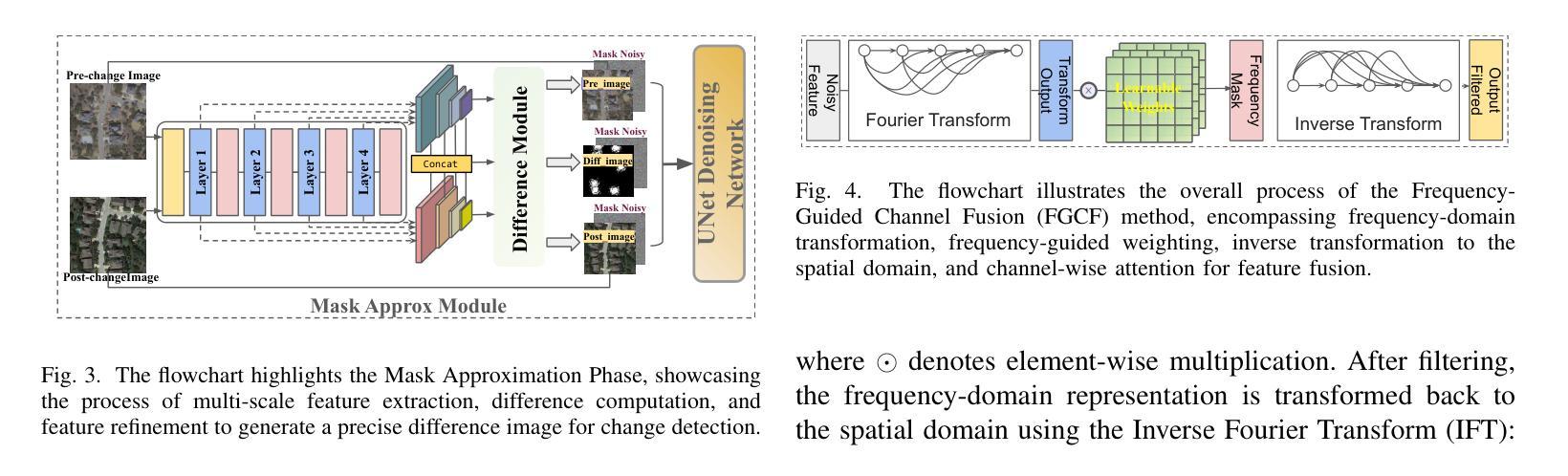
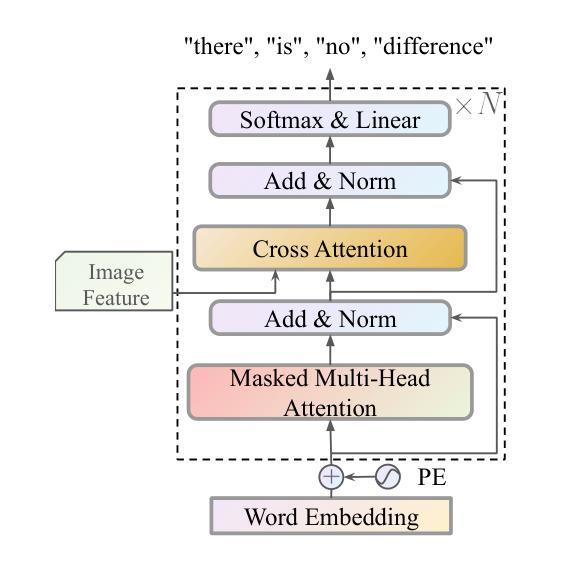
Mask Approximation Net: A Novel Diffusion Model Approach for Remote Sensing Change Captioning
Authors:Dongwei Sun, Jing Yao, Changsheng Zhou, Xiangyong Cao, Pedram Ghamisi
Remote sensing image change description represents an innovative multimodal task within the realm of remote sensing processing. This task not only facilitates the detection of alterations in surface conditions, but also provides comprehensive descriptions of these changes, thereby improving human interpretability and interactivity.Generally, existing deep-learning-based methods predominantly utilized a three-stage framework that successively perform feature extraction, feature fusion, and localization from bitemporal images before text generation. However, this reliance often leads to an excessive focus on the design of specific network architectures and restricts the feature distributions to the dataset at hand, which in turn results in limited generalizability and robustness during application.To address these limitations, this paper proposes a novel approach for remote sensing image change detection and description that incorporates diffusion models, aiming to transition the emphasis of modeling paradigms from conventional feature learning to data distribution learning. The proposed method primarily includes a simple multi-scale change detection module, whose output features are subsequently refined by an well-designed diffusion model. Furthermore, we introduce a frequency-guided complex filter module to boost the model performance by managing high-frequency noise throughout the diffusion process. We validate the effectiveness of our proposed method across several datasets for remote sensing change detection and description, showcasing its superior performance compared to existing techniques. The code will be available at \href{https://github.com/sundongwei}{MaskApproxNet} after a possible publication.
遥感图像变化描述是遥感处理领域的一项创新的多模式任务。这一任务不仅有助于检测地表条件的变化,而且提供了对这些变化的全面描述,从而提高了人类可解释性和交互性。目前,现有的基于深度学习的方法主要采用了三阶段的框架,依次从双时序图像中进行特征提取、特征融合和定位,然后进行文本生成。然而,这种依赖往往导致过于专注于特定网络架构的设计,并限制特征分布到当前数据集,从而在应用过程中导致有限的通用性和稳健性。为了解决这个问题,本文提出了一种结合扩散模型进行遥感图像变化检测与描述的新方法,旨在将建模范式的重点从传统特征学习转向数据分布学习。该方法主要包括一个简单的多尺度变化检测模块,其输出特征随后被一个精心设计的扩散模型所优化。此外,我们引入了一个频率引导复杂滤波器模块,通过管理扩散过程中的高频噪声来提高模型性能。我们在多个遥感变化检测和描述的数据集上验证了所提出方法的有效性,展示了其相较于现有技术的优越性能。代码将在可能发表后于MaskApproxNet(https://github.com/sundongwei)上提供。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
远程遥感图像变化描述是遥感处理中的一种创新的多模式任务。此任务不仅促进了地表条件变化的检测,而且提供了这些变化的全面描述,提高了人类可解释性和交互性。现有基于深度学习的方法主要使用三阶段框架,依次从双时态图像进行特征提取、特征融合和定位,然后进行文本生成。然而,这种方法过于依赖特定网络架构的设计,限制了特征分布对数据集的依赖,导致在应用中的通用性和鲁棒性有限。本文提出一种结合扩散模型的新方法来解决这一问题,旨在从传统的特征学习转向数据分布学习。新方法包括一个简单多尺度变化检测模块和精心设计扩散模型来优化特征输出。此外,引入频率引导复杂滤波器模块,通过管理扩散过程中的高频噪声来提升模型性能。通过遥感变化检测和描述的几个数据集验证了该方法的优越性。相关代码将在可能发布后于MaskApproxNet网站上公开。
Key Takeaways
- 遥感图像变化描述是多模式遥感处理任务之一,能提高人类解释性和交互性。
- 传统方法主要依赖特定网络架构设计,限制了模型的通用性和鲁棒性。
- 新方法结合扩散模型,从数据分布角度进行建模,提高了模型的性能。
- 新方法包括简单多尺度变化检测模块和频率引导复杂滤波器模块来优化性能。
- 该方法在多个数据集上进行了验证,展示了其优越性。
- 相关代码将在发布后公开于MaskApproxNet网站上供公众访问和使用。
点此查看论文截图
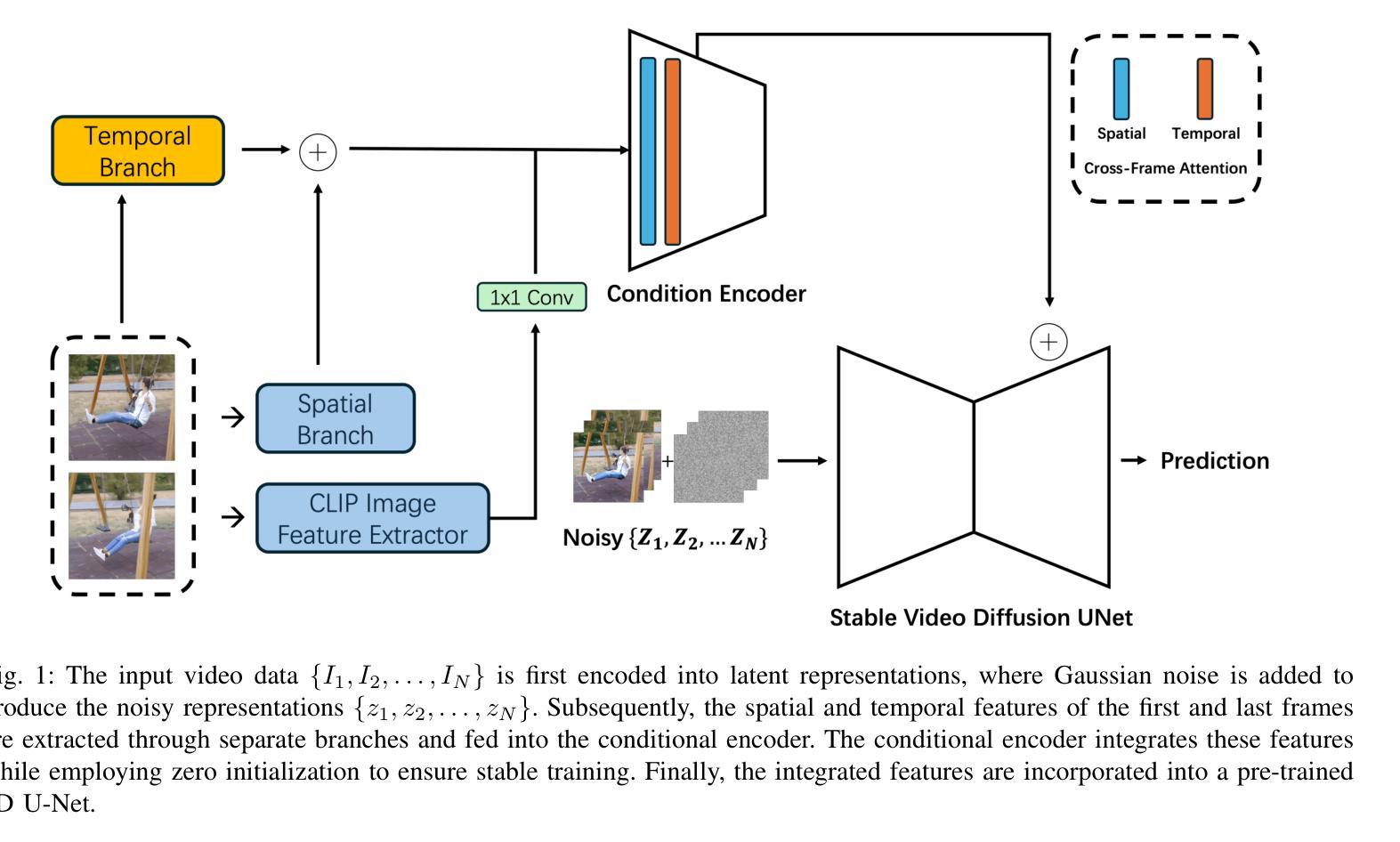
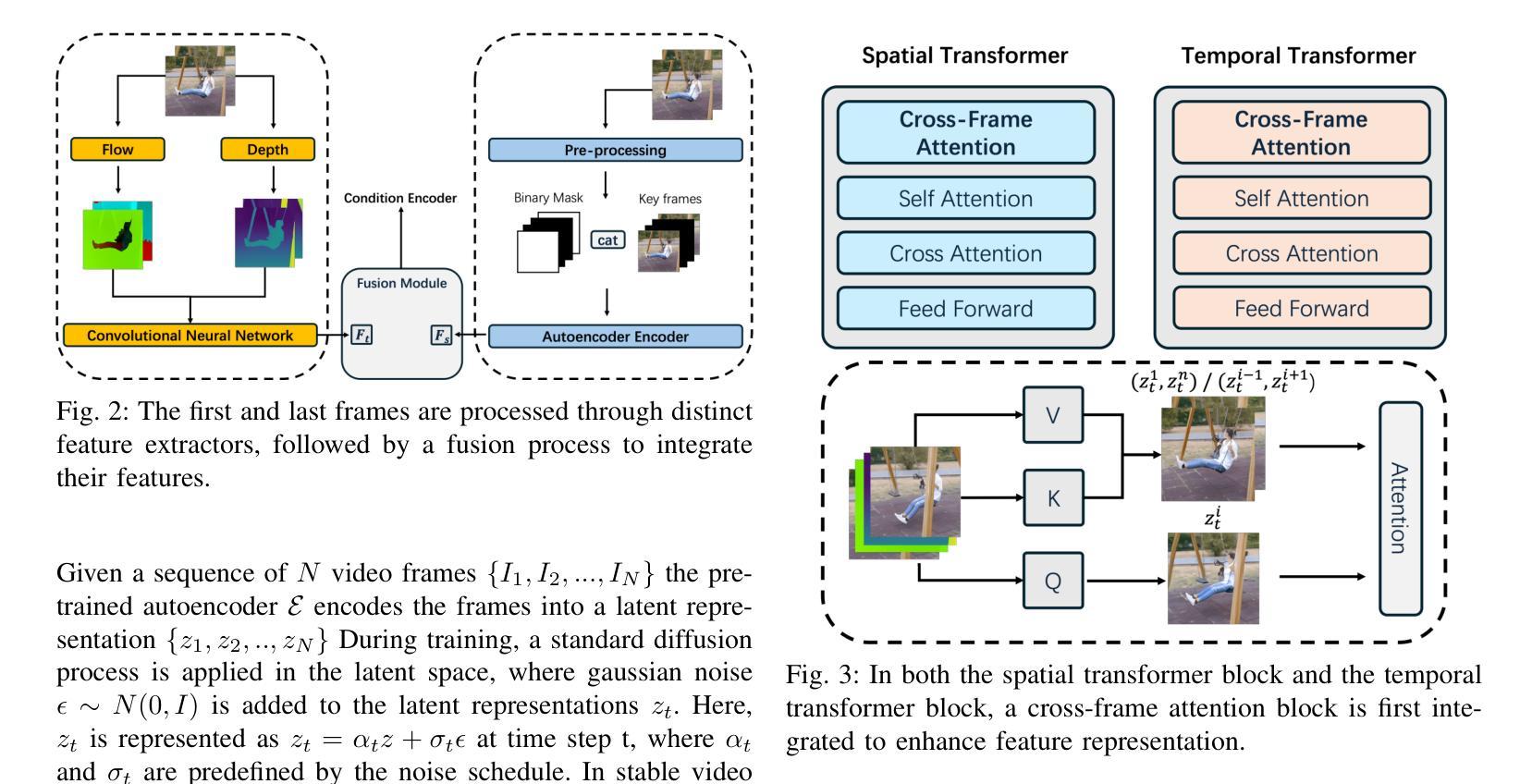
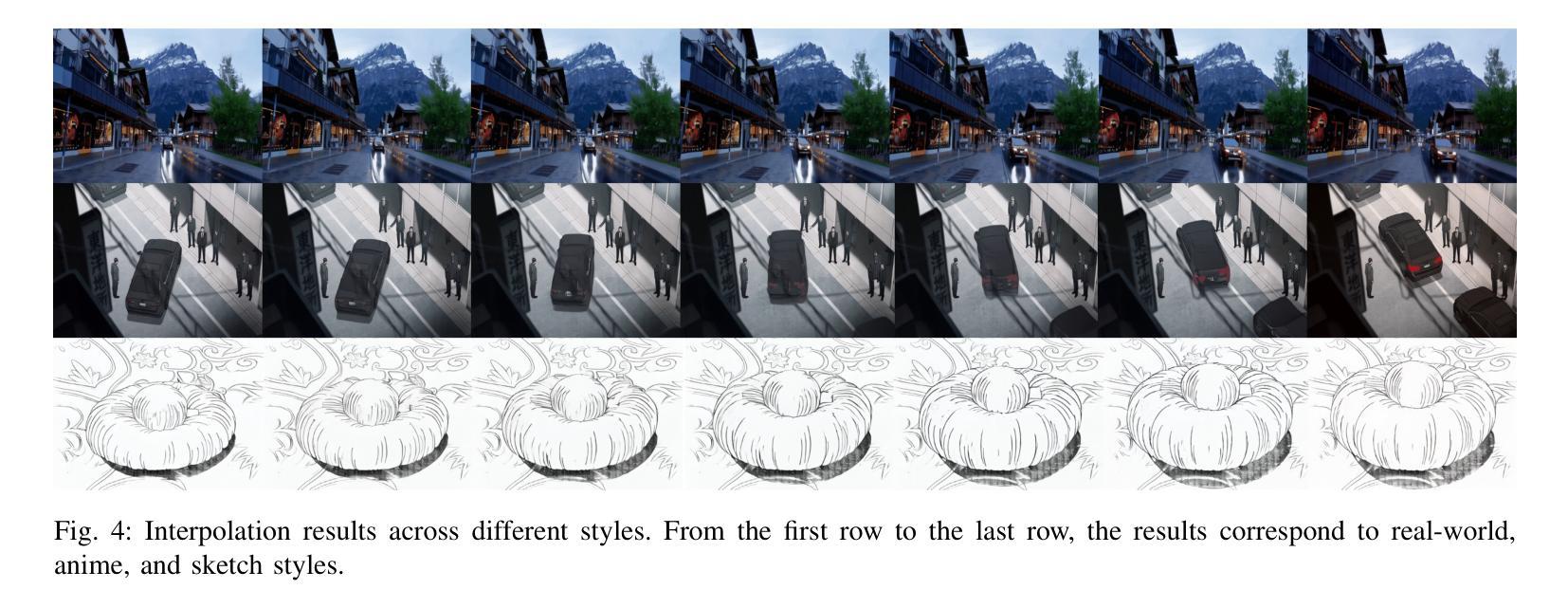
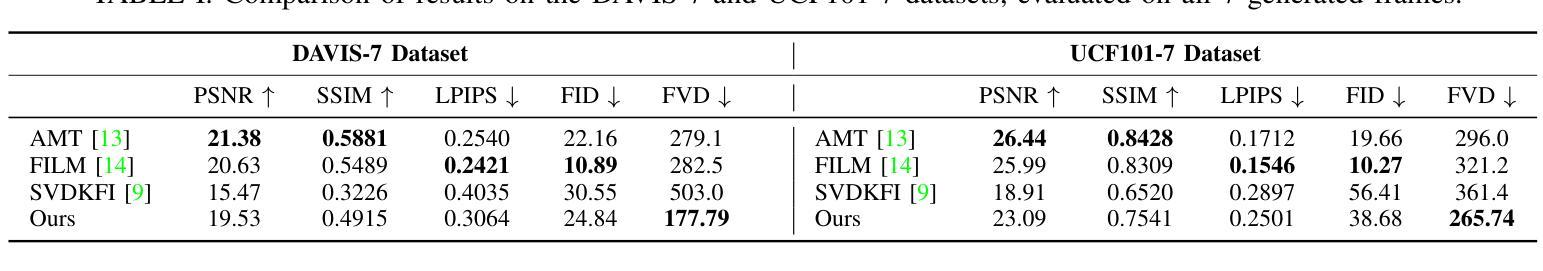
Adapting Image-to-Video Diffusion Models for Large-Motion Frame Interpolation
Authors:Luoxu Jin, Hiroshi Watanabe
With the development of video generation models has advanced significantly in recent years, we adopt large-scale image-to-video diffusion models for video frame interpolation. We present a conditional encoder designed to adapt an image-to-video model for large-motion frame interpolation. To enhance performance, we integrate a dual-branch feature extractor and propose a cross-frame attention mechanism that effectively captures both spatial and temporal information, enabling accurate interpolations of intermediate frames. Our approach demonstrates superior performance on the Fr'echet Video Distance (FVD) metric when evaluated against other state-of-the-art approaches, particularly in handling large motion scenarios, highlighting advancements in generative-based methodologies.
随着视频生成模型近年来显著发展,我们采用大规模图像到视频的扩散模型进行视频帧插值。我们提出了一种条件编码器,旨在适应图像到视频模型进行大运动帧插值。为了提高性能,我们整合了双分支特征提取器,并提出了一种跨帧注意力机制,该机制能够有效地捕捉空间和时间信息,从而实现中间帧的准确插值。与其他最新方法相比,我们的方法在Fréchet视频距离(FVD)指标上表现出卓越的性能,特别是在处理大运动场景时,突显了基于生成的方法的进步。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:随着视频生成模型的不断发展,我们采用了大规模的图像到视频的扩散模型进行视频帧插值。我们提出了一种条件编码器,旨在适应图像到视频模型进行大运动帧插值。为提高性能,我们整合了双分支特征提取器,并提出了跨帧注意力机制,能有效捕捉空间和时间信息,实现中间帧的准确插值。与其他最新方法相比,我们的方法在Fréchet视频距离(FVD)指标上表现出卓越性能,特别是在处理大运动场景时,凸显了基于生成方法的技术进步。
Key Takeaways:
- 视频生成模型近年来有显著发展。
- 采用大规模图像到视频的扩散模型进行视频帧插值。
- 提出了一种条件编码器,适应图像到视频模型进行大运动帧插值。
- 整合双分支特征提取器提高性能。
- 跨帧注意力机制能有效捕捉空间和时间信息。
- 方法在Fréchet视频距离(FVD)指标上表现出卓越性能。
点此查看论文截图

How to Backdoor Consistency Models?
Authors:Chengen Wang, Murat Kantarcioglu
Consistency models are a new class of models that generate images by directly mapping noise to data, allowing for one-step generation and significantly accelerating the sampling process. However, their robustness against adversarial attacks has not yet been thoroughly investigated. In this work, we conduct the first study on the vulnerability of consistency models to backdoor attacks. While previous research has explored backdoor attacks on diffusion models, those studies have primarily focused on conventional diffusion models, employing a customized backdoor training process and objective, whereas consistency models have distinct training processes and objectives. Our proposed framework demonstrates the vulnerability of consistency models to backdoor attacks. During image generation, poisoned consistency models produce images with a Fr'echet Inception Distance (FID) comparable to that of a clean model when sampling from Gaussian noise. However, once the trigger is activated, they generate backdoor target images. We explore various trigger and target configurations to evaluate the vulnerability of consistency models, including the use of random noise as a trigger. This novel trigger is visually inconspicuous, more challenging to detect, and aligns well with the sampling process of consistency models. Across all configurations, our framework successfully compromises the consistency models while maintaining high utility and specificity. We also examine the stealthiness of our proposed attack, which is attributed to the unique properties of consistency models and the elusive nature of the Gaussian noise trigger. Our code is available at \href{https://github.com/chengenw/backdoorCM}{https://github.com/chengenw/backdoorCM}.
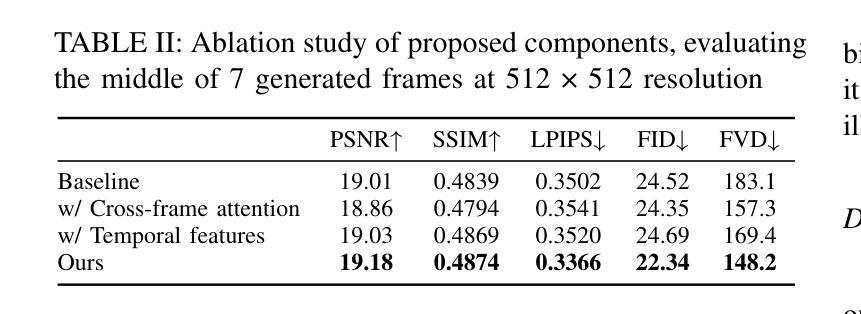
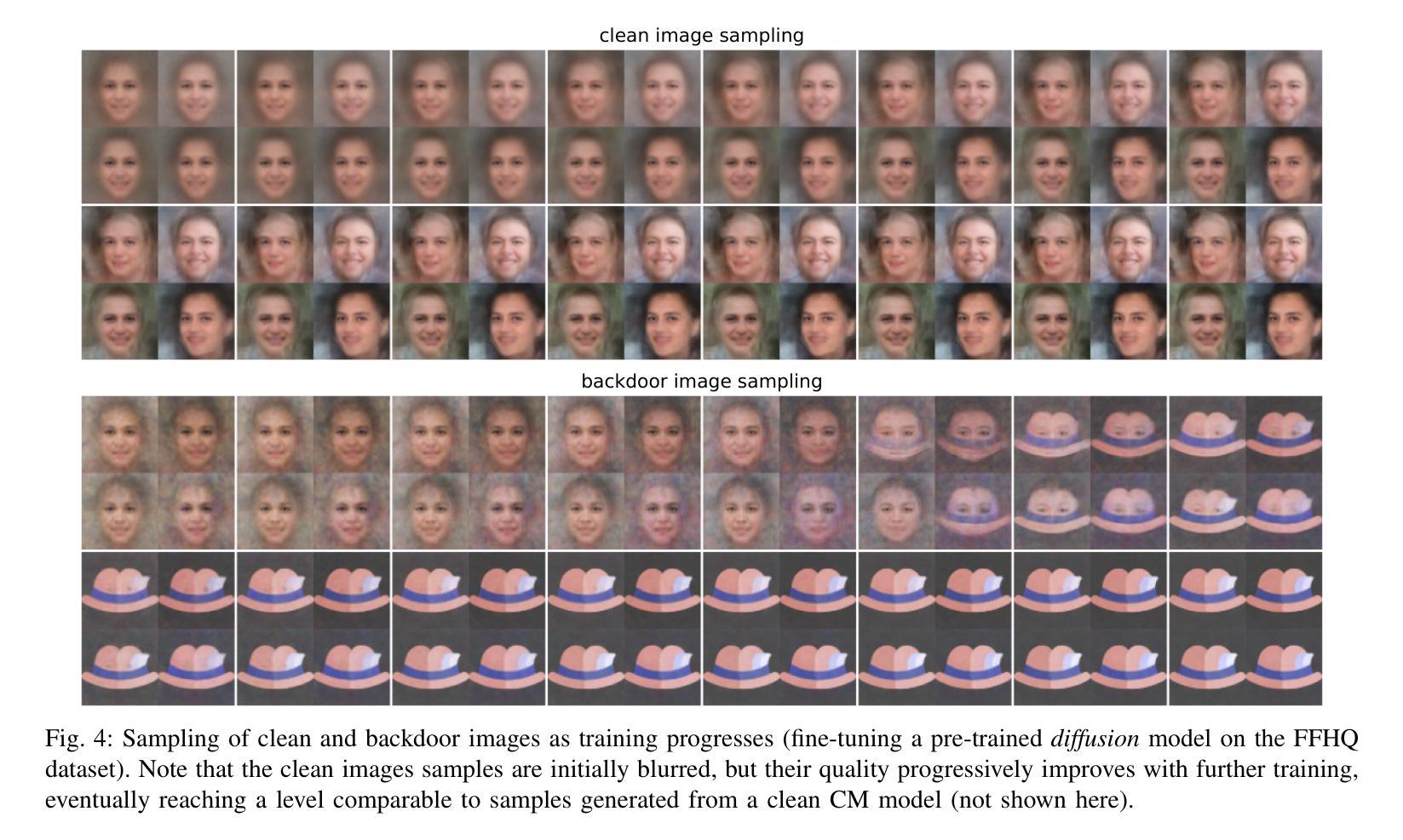
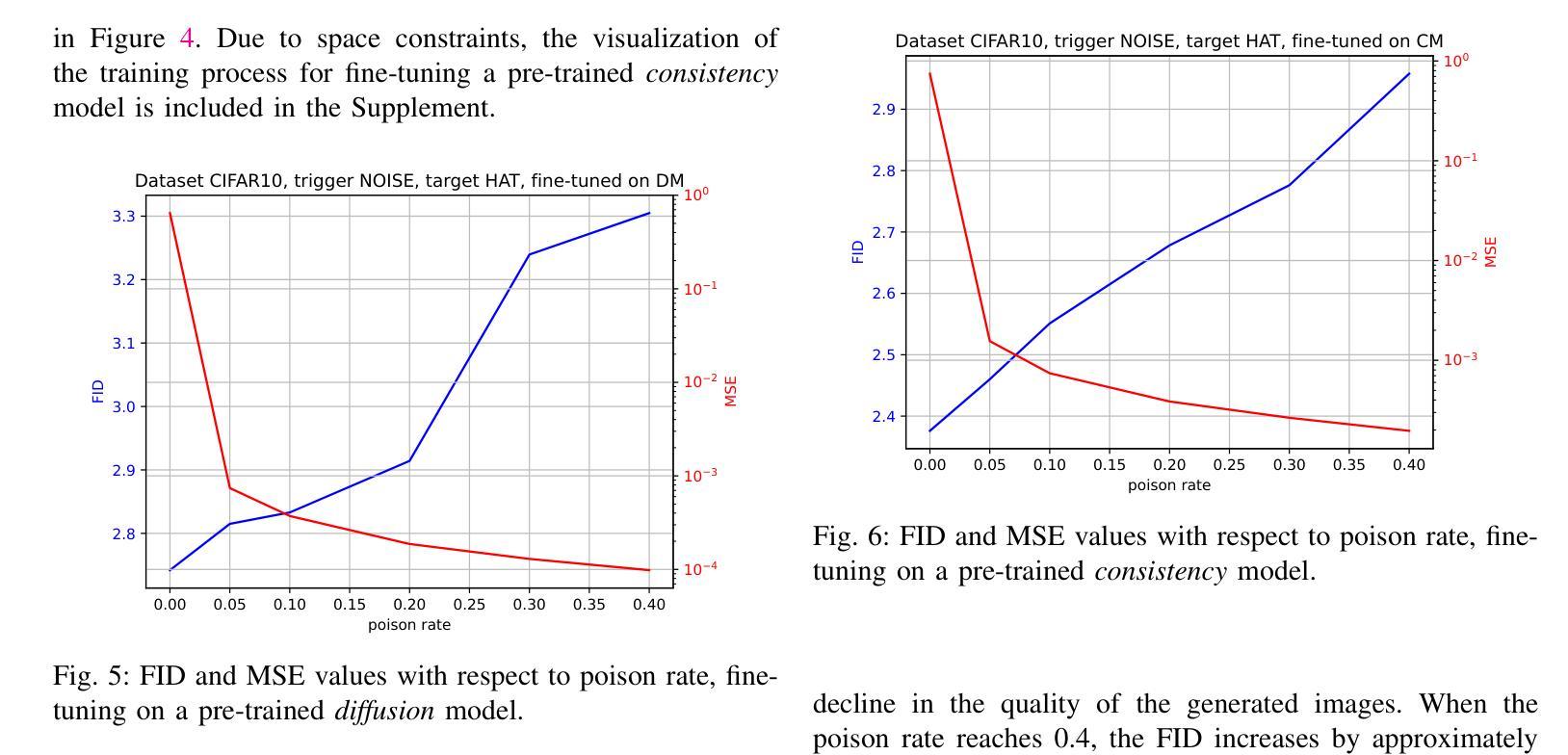
一致性模型是一类新的模型,它们通过直接将噪声映射到数据来生成图像,实现了一步生成,并显著加速了采样过程。然而,它们对抗对抗性攻击的鲁棒性尚未得到彻底研究。在这项工作中,我们对一致性模型对后门攻击的脆弱性进行了首次研究。虽然之前的研究已经探索了扩散模型上的后门攻击,但这些研究主要集中在传统的扩散模型上,采用定制的后门训练过程和目标,而一致性模型具有不同的训练过程和目标。我们提出的框架证明了一致性模型对后门攻击的脆弱性。在图像生成过程中,中毒的一致性模型在从高斯噪声采样时产生的图像与干净模型的Fréchet Inception Distance (FID)相当。然而,一旦触发条件被激活,它们就会生成后门目标图像。我们探索了各种触发器和目标配置来评估一致性模型的脆弱性,包括使用随机噪声作为触发器。这种新型触发器在视觉上并不显眼,更难以检测,并且与一致性模型的采样过程非常契合。在所有配置中,我们的框架成功攻击了一致性模型,同时保持了高实用性和特异性。我们还检查了所提出的攻击的隐蔽性,这归功于一致性模型的独特属性和高斯噪声触发器的隐蔽性。我们的代码可在https://github.com/chengenw/backdoorCM处获得。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
一致性模型是一类新的图像生成模型,它们通过直接将噪声映射到数据来生成图像,实现了一步生成,并显著加速了采样过程。然而,它们对抗恶意攻击的稳定性尚未得到充分研究。本研究首次探讨了一致性模型对后门攻击的脆弱性。虽然之前的研究已经探索了扩散模型的后门攻击,但这些研究主要集中在采用定制后门训练过程和目标的传统扩散模型上,而一致性模型具有不同的训练过程和目标。本研究提出的框架证明了一致性模型对后门攻击的脆弱性。在图像生成过程中,中毒的一致性模型产生的图像的Fr´echet Inception Distance (FID)与干净模型的FID相当,这是从高斯噪声中采样得到的。然而,一旦触发条件被激活,它们就会生成后门目标图像。我们探索了各种触发器和目标配置,以评估一致性模型的脆弱性,包括使用随机噪声作为触发器。这种新型触发器在视觉上并不显眼,更难检测,且与一致性模型的采样过程非常契合。在所有配置中,我们的框架成功地攻击了一致性模型,同时保持了高实用性和特异性。我们还检查了我们提出的攻击的隐蔽性,这归功于一致性模型的独特属性和高斯噪声触发器的难以捉摸。我们的代码可在https://github.com/chengenw/backdoorCM获取。
关键见解
- 一致性模型是一种新的图像生成模型,通过直接映射噪声到数据来生成图像,加速采样过程。
- 目前对于一致性模型对抗恶意攻击的稳定性研究尚不充分。
- 本研究首次探究了一致性模型对后门攻击的脆弱性。
- 提出的框架成功展示了一致性模型在图像生成过程中的后门攻击脆弱性。
- 中毒的一致性模型在采样过程中产生的图像与干净模型的图像相似,但在触发条件激活后生成目标后门图像。
- 研究采用了各种触发器和目标配置来评估一致性模型的脆弱性,包括使用视觉上不显眼的随机噪声作为触发器。
点此查看论文截图


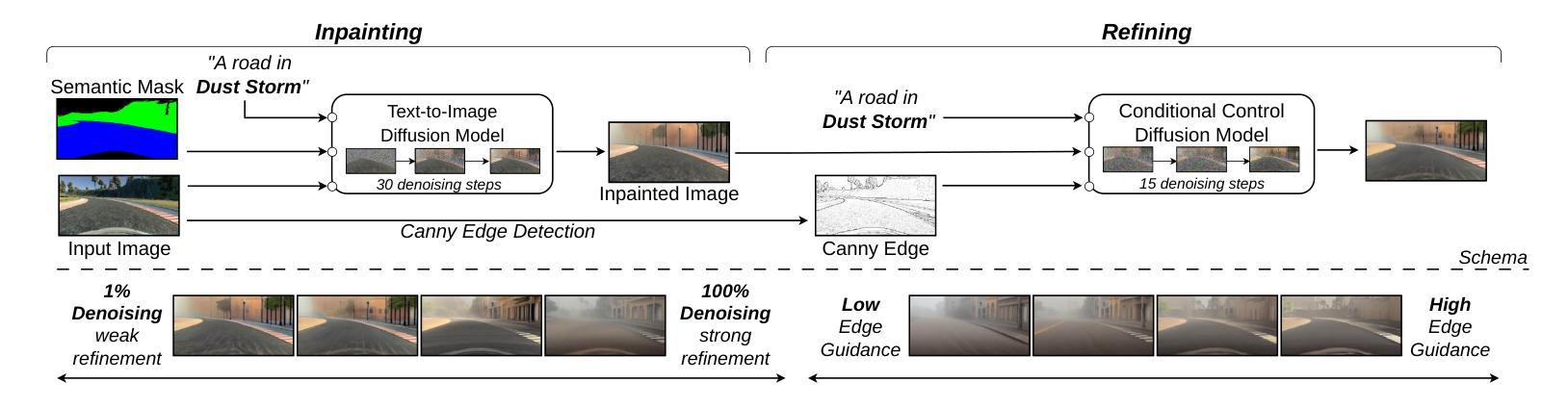
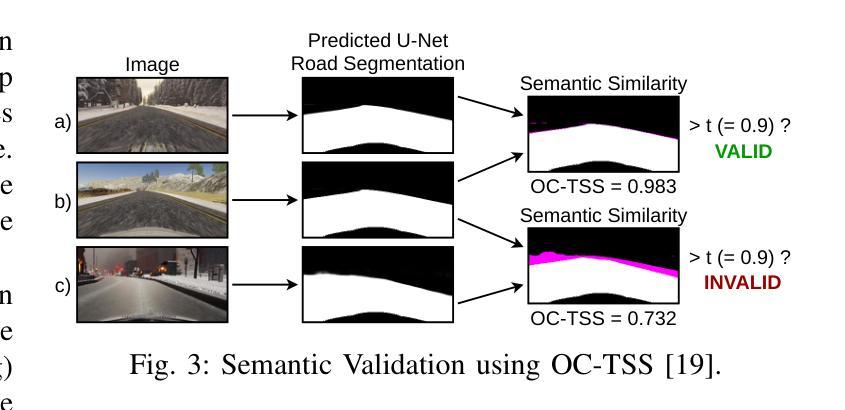
Efficient Domain Augmentation for Autonomous Driving Testing Using Diffusion Models
Authors:Luciano Baresi, Davide Yi Xian Hu, Andrea Stocco, Paolo Tonella
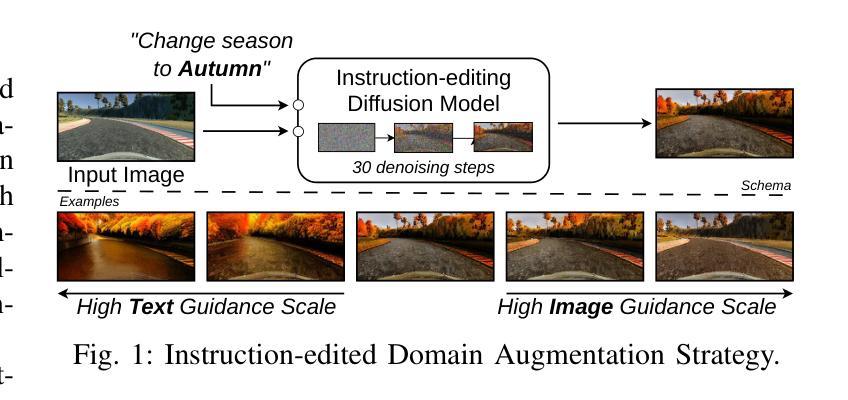
Simulation-based testing is widely used to assess the reliability of Autonomous Driving Systems (ADS), but its effectiveness is limited by the operational design domain (ODD) conditions available in such simulators. To address this limitation, in this work, we explore the integration of generative artificial intelligence techniques with physics-based simulators to enhance ADS system-level testing. Our study evaluates the effectiveness and computational overhead of three generative strategies based on diffusion models, namely instruction-editing, inpainting, and inpainting with refinement. Specifically, we assess these techniques’ capabilities to produce augmented simulator-generated images of driving scenarios representing new ODDs. We employ a novel automated detector for invalid inputs based on semantic segmentation to ensure semantic preservation and realism of the neural generated images. We then perform system-level testing to evaluate the ADS’s generalization ability to newly synthesized ODDs. Our findings show that diffusion models help increase the ODD coverage for system-level testing of ADS. Our automated semantic validator achieved a percentage of false positives as low as 3%, retaining the correctness and quality of the generated images for testing. Our approach successfully identified new ADS system failures before real-world testing.
基于模拟器的测试是评估自动驾驶系统(ADS)可靠性的常用方法,但其有效性受限于模拟器中可用的操作设计域(ODD)条件。为了解决这个问题,在这项工作中,我们探索了将生成式人工智能技术与基于物理的模拟器相结合,以提高ADS系统级测试的效果。我们的研究评估了三种基于扩散模型的生成策略的有效性和计算开销,分别是指令编辑、图像补全和精细图像补全。具体来说,我们评估了这些技术在生成代表新ODD的驾驶场景模拟器图像方面的能力。我们采用了一种基于语义分割的新型自动化检测器,以确保神经生成图像语义的保留和真实性。然后,我们进行系统级测试,以评估ADS对新合成ODD的泛化能力。我们的研究发现,扩散模型有助于增加系统级测试中对ADS的ODD覆盖。我们的自动语义验证器实现了高达3%的误报率,保持了测试图像生成的质量和正确性。我们的方法成功地在真实世界测试之前识别出了新的ADS系统故障。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted for publication at the 47th International Conference on Software Engineering (ICSE 2025). This research was partially supported by project EMELIOT, funded by MUR under the PRIN 2020 program (n. 2020W3A5FY), by the Bavarian Ministry of Economic Affairs, Regional Development and Energy, by the TUM Global Incentive Fund, and by the EU Project Sec4AI4Sec (n. 101120393)
Summary
基于扩散模型的生成技术在自主驾驶系统仿真测试中的应用摘要:为解决仿真测试在评估自主驾驶系统可靠性时受限于操作设计域条件的问题,本研究探讨了生成式人工智能技术与基于物理的仿真器的融合,以提升自主驾驶系统级别的测试水平。研究评估了三种基于扩散模型的生成策略,包括指令编辑、补全及带精修的补全方法,在生成代表新操作设计域驾驶场景图像方面的有效性及计算开销。采用新型自动化无效输入检测器确保神经生成图像语义的完整性和真实性。系统级测试显示,扩散模型有助于提高自主驾驶系统对新合成操作设计域的覆盖能力,自动语义验证器的误报率低于3%,确保了测试图像的质量和正确性。本研究方法可在真实世界测试前成功识别出新的自主驾驶系统故障。
Key Takeaways
- 仿真测试在评估自主驾驶系统可靠性时受到操作设计域的限制。
- 生成式人工智能技术与物理仿真器的结合能提升自主驾驶系统级别的测试。
- 研究评估了三种基于扩散模型的生成策略在生成新操作设计域驾驶场景图像方面的有效性。
- 采用自动化无效输入检测器确保神经生成图像语义的完整性和真实性。
- 扩散模型提高了自主驾驶系统对新合成操作设计域的覆盖能力。
- 自动语义验证器的误报率低于3%,确保测试图像的质量和正确性。
- 该方法能够在真实世界测试前识别出新的自主驾驶系统故障。
点此查看论文截图

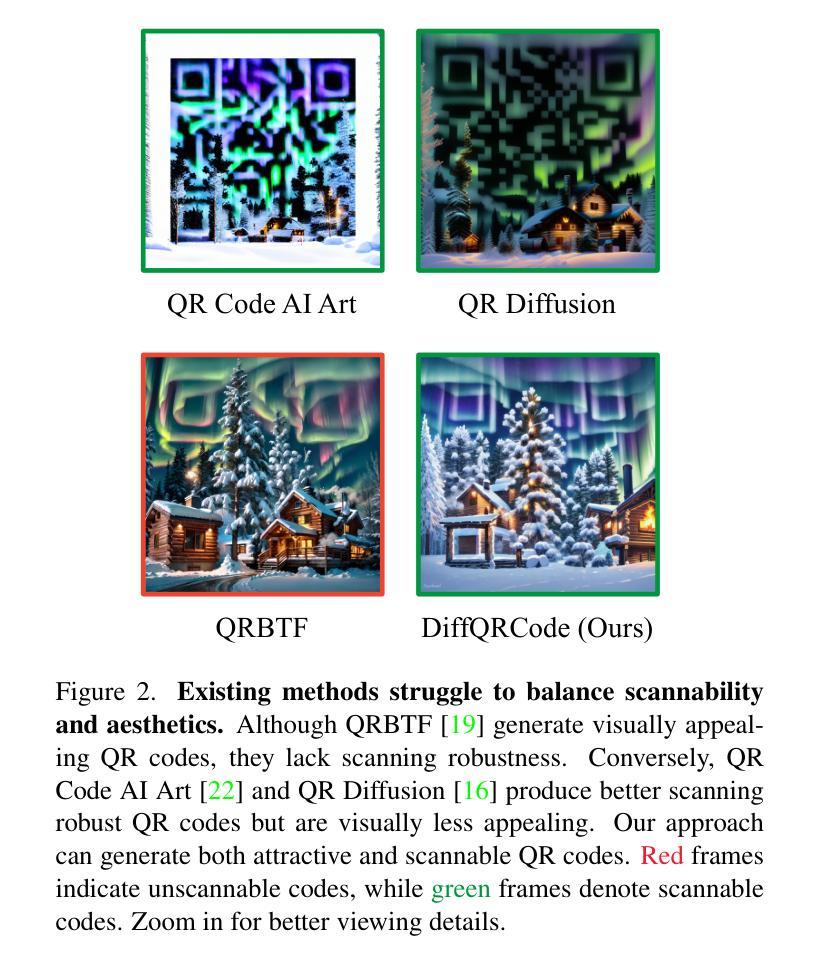
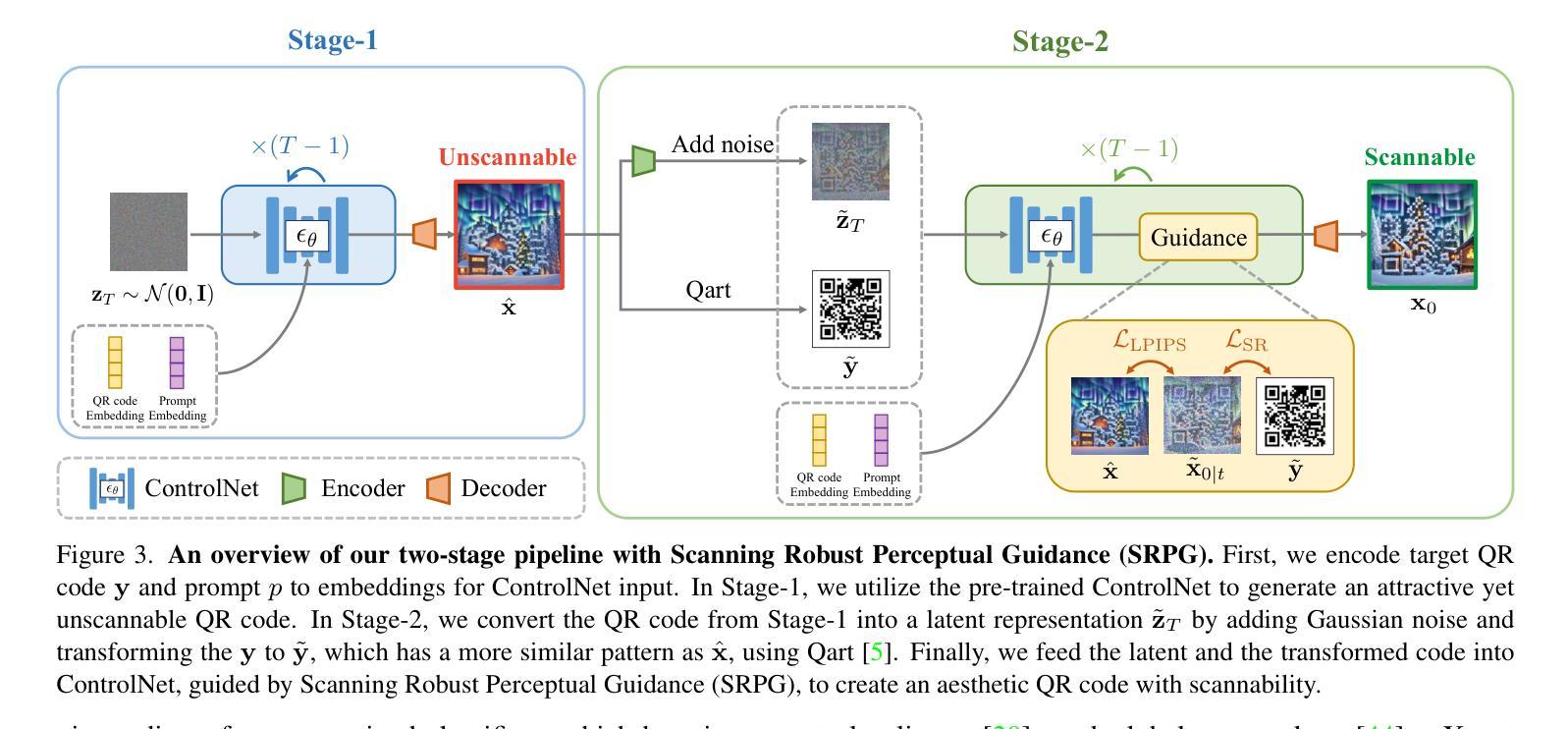
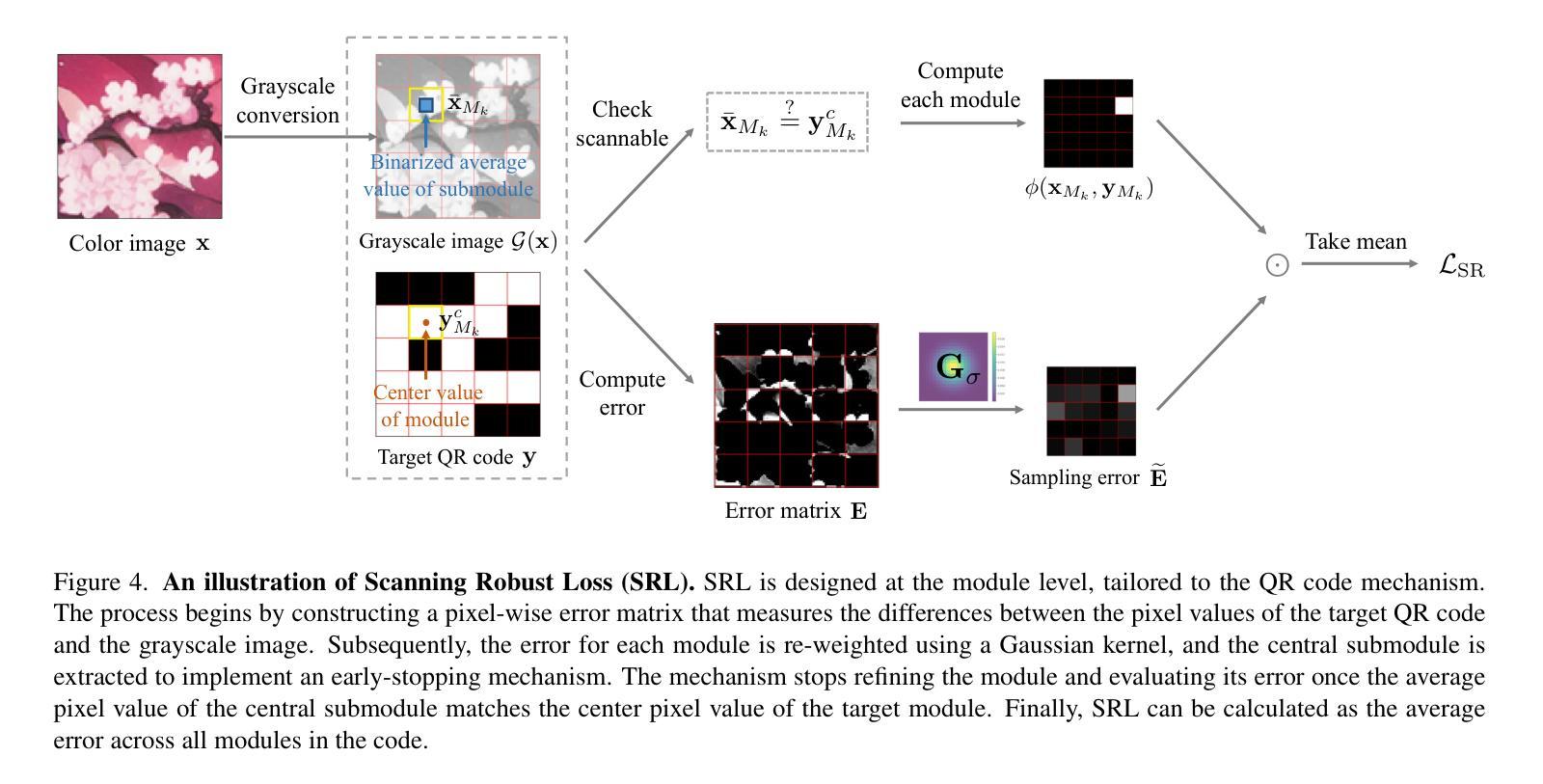
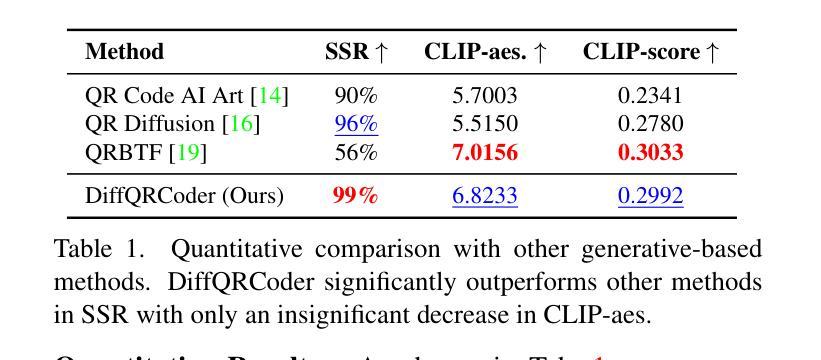
DiffQRCoder: Diffusion-based Aesthetic QR Code Generation with Scanning Robustness Guided Iterative Refinement
Authors:Jia-Wei Liao, Winston Wang, Tzu-Sian Wang, Li-Xuan Peng, Ju-Hsuan Weng, Cheng-Fu Chou, Jun-Cheng Chen
With the success of Diffusion Models for image generation, the technologies also have revolutionized the aesthetic Quick Response (QR) code generation. Despite significant improvements in visual attractiveness for the beautified codes, their scannabilities are usually sacrificed and thus hinder their practical uses in real-world scenarios. To address this issue, we propose a novel training-free Diffusion-based QR Code generator (DiffQRCoder) to effectively craft both scannable and visually pleasing QR codes. The proposed approach introduces Scanning-Robust Perceptual Guidance (SRPG), a new diffusion guidance for Diffusion Models to guarantee the generated aesthetic codes to obey the ground-truth QR codes while maintaining their attractiveness during the denoising process. Additionally, we present another post-processing technique, Scanning Robust Manifold Projected Gradient Descent (SR-MPGD), to further enhance their scanning robustness through iterative latent space optimization. With extensive experiments, the results demonstrate that our approach not only outperforms other compared methods in Scanning Success Rate (SSR) with better or comparable CLIP aesthetic score (CLIP-aes.) but also significantly improves the SSR of the ControlNet-only approach from 60% to 99%. The subjective evaluation indicates that our approach achieves promising visual attractiveness to users as well. Finally, even with different scanning angles and the most rigorous error tolerance settings, our approach robustly achieves over 95% SSR, demonstrating its capability for real-world applications. Our project page is available at https://jwliao1209.github.io/DiffQRCoder.
随着扩散模型在图像生成领域的成功,该技术也深刻影响了美学快速响应(QR)码生成。尽管在美化代码的视觉吸引力方面取得了重大改进,但它们的可扫描性通常会被牺牲,从而阻碍了它们在现实场景中的实际应用。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了一种无需训练的基于扩散的QR码生成器(DiffQRCoder),能够生成既可扫描又具有视觉吸引力的QR码。该方法引入了扫描鲁棒感知指导(SRPG),这是一种新的扩散模型指导方法,可保证生成的美学代码遵循真实QR代码,同时在去噪过程中保持其吸引力。此外,我们还介绍了另一种后处理技术,扫描鲁棒流形投影梯度下降法(SR-MPGD),通过迭代潜在空间优化进一步提高其扫描稳健性。大量实验结果表明,我们的方法不仅在扫描成功率(SSR)上优于其他对比方法,且CLIP美学评分(CLIP-aes.)更好或相当;同时,与仅使用ControlNet的方法相比,我们将SSR从60%提高到99%。主观评估表明,我们的方法在视觉吸引力方面对用户具有很大潜力。最后,即使在不同的扫描角度和最严格的错误容忍设置下,我们的方法仍然稳健地实现了超过95%的SSR,证明了其在现实世界应用中的能力。我们的项目页面可在https://jwliao1209.github.io/DiffQRCoder访问。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
扩散模型在图像生成方面的成功也推动了美化二维码生成的技术革命。为解决美观二维码扫描性能差的问题,我们提出了一种无需训练的扩散式二维码生成器(DiffQRCoder),能够生成既美观又实用的二维码。通过引入扫描稳健感知指导(SRPG)和扫描稳健流形投影梯度下降法(SR-MPGD),确保生成的二维码在保持美观的同时具备良好的扫描性能。实验结果表明,该方法不仅在其他方法的扫描成功率(SSR)上具有更高的表现或与之持平的CLIP美学得分(CLIP-aes.),还能显著提高仅使用ControlNet方法的SSR值从60%提升至99%。主观评价显示,我们的方法对用户具有吸引力。在不同扫描角度和严格的容错设置下,我们的方法依然稳健地实现了超过95%的SSR,表明其在真实世界应用中的能力。更多详情可见项目网页。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型已应用于二维码生成,实现了美观与实用性的结合。
- 提出了一种新型的无需训练的扩散式二维码生成器(DiffQRCoder)。
- 引入扫描稳健感知指导(SRPG)保证生成的二维码在美观同时保持良好扫描性能。
- 采用扫描稳健流形投影梯度下降法(SR-MPGD)进一步提高二维码的扫描稳健性。
- 该方法在扫描成功率(SSR)上表现优异,显著提高仅使用ControlNet方法的SSR值。
- 主观评价显示,该方法对用户具有吸引力。
点此查看论文截图

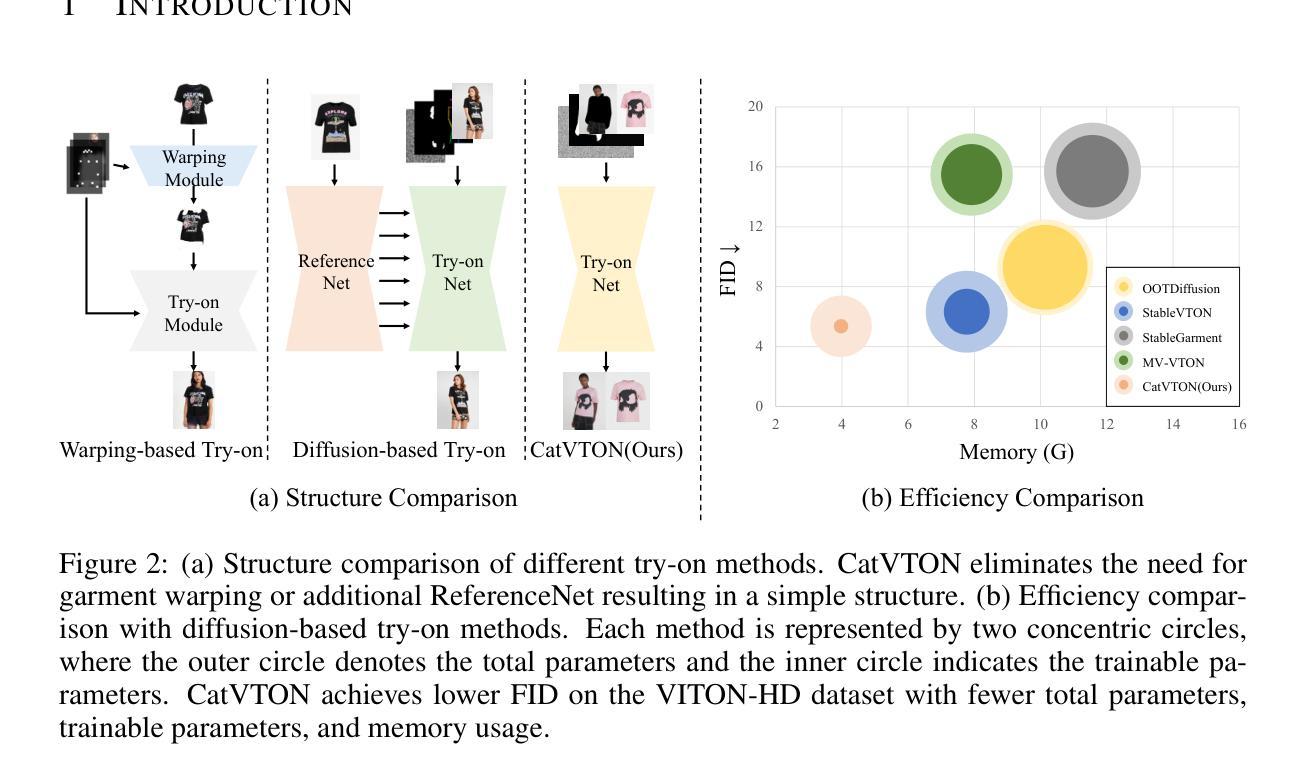
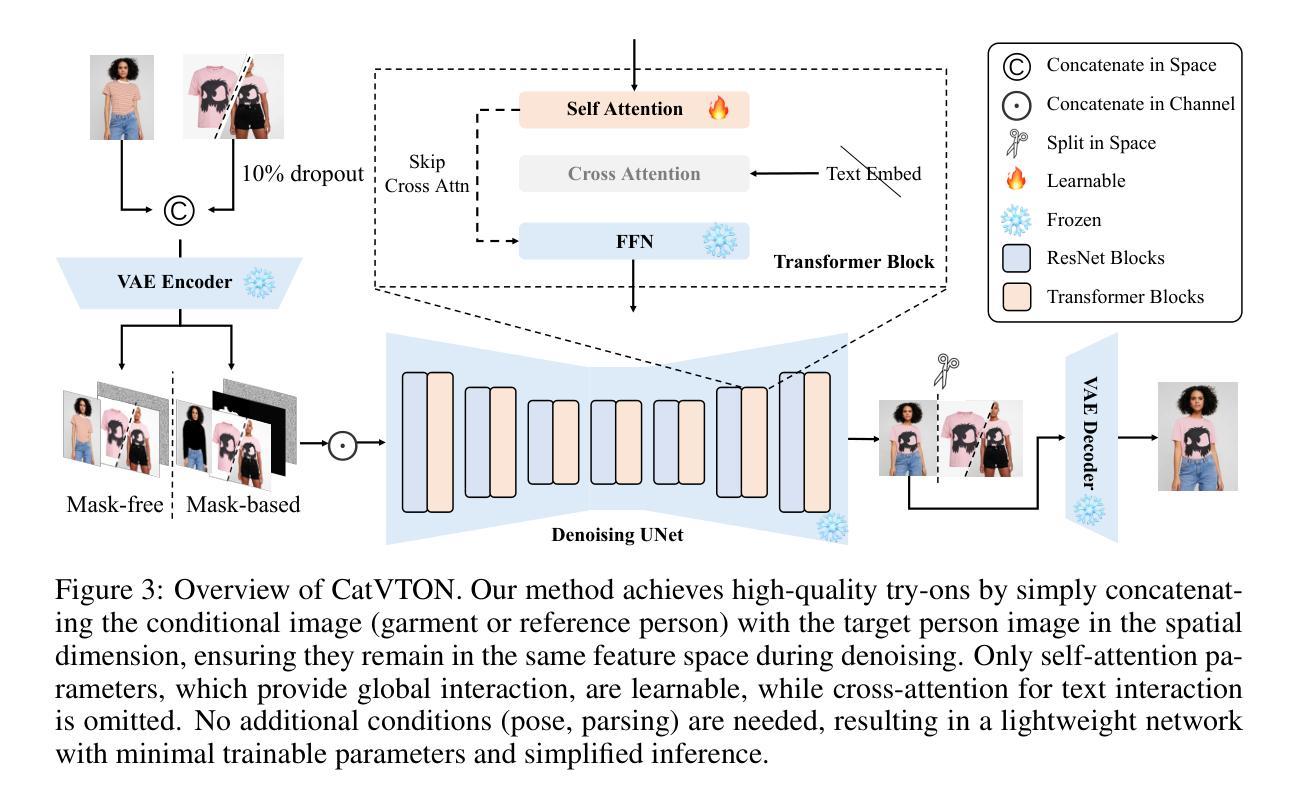
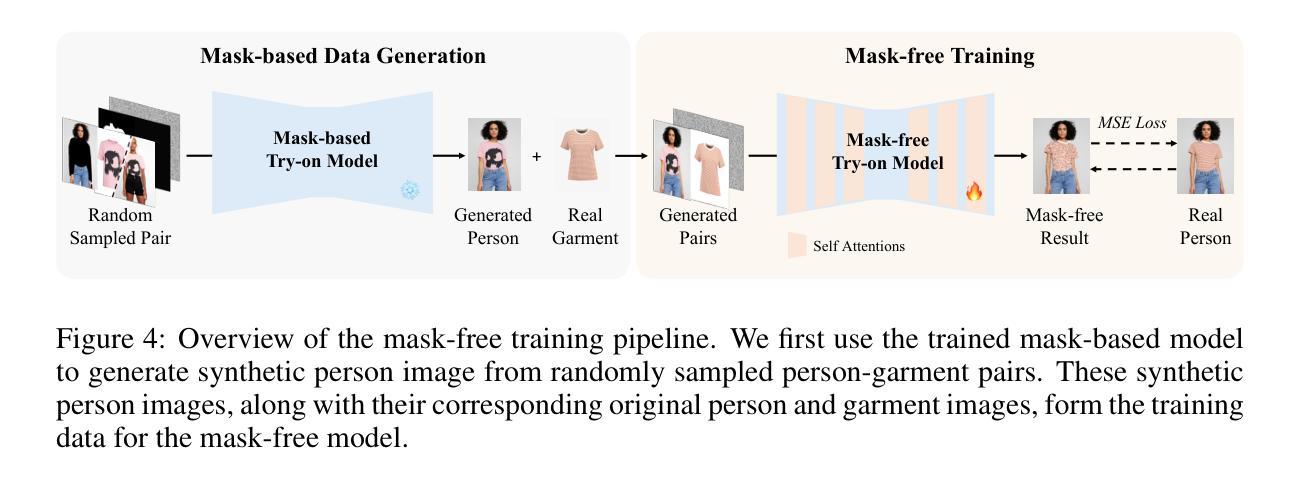
CatVTON: Concatenation Is All You Need for Virtual Try-On with Diffusion Models
Authors:Zheng Chong, Xiao Dong, Haoxiang Li, Shiyue Zhang, Wenqing Zhang, Xujie Zhang, Hanqing Zhao, Dongmei Jiang, Xiaodan Liang
Virtual try-on methods based on diffusion models achieve realistic effects but often require additional encoding modules, a large number of training parameters, and complex preprocessing, which increases the burden on training and inference. In this work, we re-evaluate the necessity of additional modules and analyze how to improve training efficiency and reduce redundant steps in the inference process. Based on these insights, we propose CatVTON, a simple and efficient virtual try-on diffusion model that transfers in-shop or worn garments of arbitrary categories to target individuals by concatenating them along spatial dimensions as inputs of the diffusion model. The efficiency of CatVTON is reflected in three aspects: (1) Lightweight network. CatVTON consists only of a VAE and a simplified denoising UNet, removing redundant image and text encoders as well as cross-attentions, and includes just 899.06M parameters. (2) Parameter-efficient training. Through experimental analysis, we identify self-attention modules as crucial for adapting pre-trained diffusion models to the virtual try-on task, enabling high-quality results with only 49.57M training parameters. (3) Simplified inference. CatVTON eliminates unnecessary preprocessing, such as pose estimation, human parsing, and captioning, requiring only a person image and garment reference to guide the virtual try-on process, reducing over 49% memory usage compared to other diffusion-based methods. Extensive experiments demonstrate that CatVTON achieves superior qualitative and quantitative results compared to baseline methods and demonstrates strong generalization performance in in-the-wild scenarios, despite being trained solely on public datasets with 73K samples.
基于扩散模型的虚拟试穿方法虽然可以实现逼真的效果,但通常需要额外的编码模块、大量的训练参数和复杂的预处理,这增加了训练和推理的负担。在这项工作中,我们重新评估了额外模块的必要性,并分析了如何提高训练效率和减少推理过程中的冗余步骤。基于这些见解,我们提出了CatVTON,这是一种简单高效的虚拟试穿扩散模型。它通过沿空间维度拼接店内或穿着的任意类别的服装作为扩散模型的输入,将服装转移到目标个体上。CatVTON的效率体现在三个方面:
(1) 轻量化网络:CatVTON仅由VAE和简化的去噪UNet组成,去除了冗余的图像和文本编码器以及跨注意力模块,仅包含899.06M参数。
(2) 参数高效训练:通过实验分析,我们认定自注意力模块对于适应虚拟试穿任务至关重要,仅使用49.57M训练参数即可实现高质量结果。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by ICLR 2025
Summary
基于扩散模型(Diffusion Models)的虚拟试穿技术旨在实现逼真的效果,但在构建额外编码模块时往往涉及大量的训练参数和复杂的预处理步骤,从而增加了训练和推理的负担。本研究重新评估了额外模块的必要性,并分析了如何优化训练效率并简化推理过程中的冗余步骤。基于此,我们提出了CatVTON,这是一个简单高效的虚拟试穿扩散模型,它通过沿空间维度拼接店内或已穿上的任意类别的服装到目标个体上,实现了高效的虚拟试穿效果。CatVTON的优势体现在三个方面:轻量级网络、参数高效训练和简化推理。它通过去除冗余的图像和文本编码器以及跨注意力机制,实现了网络的轻量化;并通过实验分析确定了自注意力模块对于适应虚拟试穿任务的重要性,实现了高质量的结果;最后,它简化了不必要的预处理步骤,如姿态估计、人体解析和字幕生成等,只需人物图像和服装参考即可引导虚拟试穿过程。实验结果证明了CatVTON相较于基线方法具有卓越的性能表现,并且在公开数据集上具有强大的泛化性能。
Key Takeaways
- 基于扩散模型的虚拟试穿技术可实现逼真效果,但需额外编码模块和复杂预处理。
- CatVTON模型提出简化虚拟试穿过程的方法,通过沿空间维度拼接服装到目标个体上实现高效试穿。
- CatVTON具有轻量级网络设计,通过去除冗余模块降低网络复杂性。
- 参数高效训练是关键,自注意力模块对适应虚拟试穿任务至关重要。
- CatVTON简化了不必要的预处理步骤,减少了内存使用并提高推理效率。
- CatVTON在实验中表现出卓越的性能,相较于基线方法具有优势。
点此查看论文截图


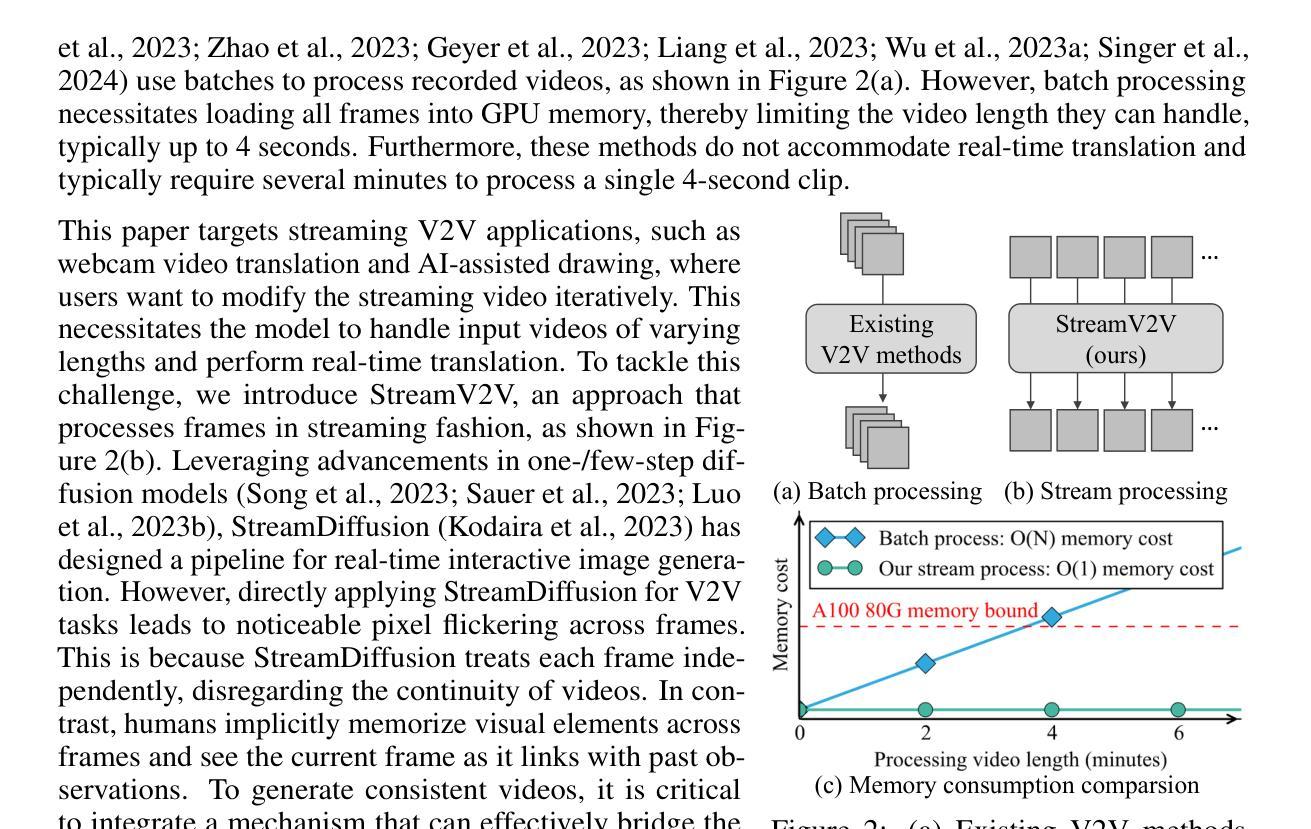
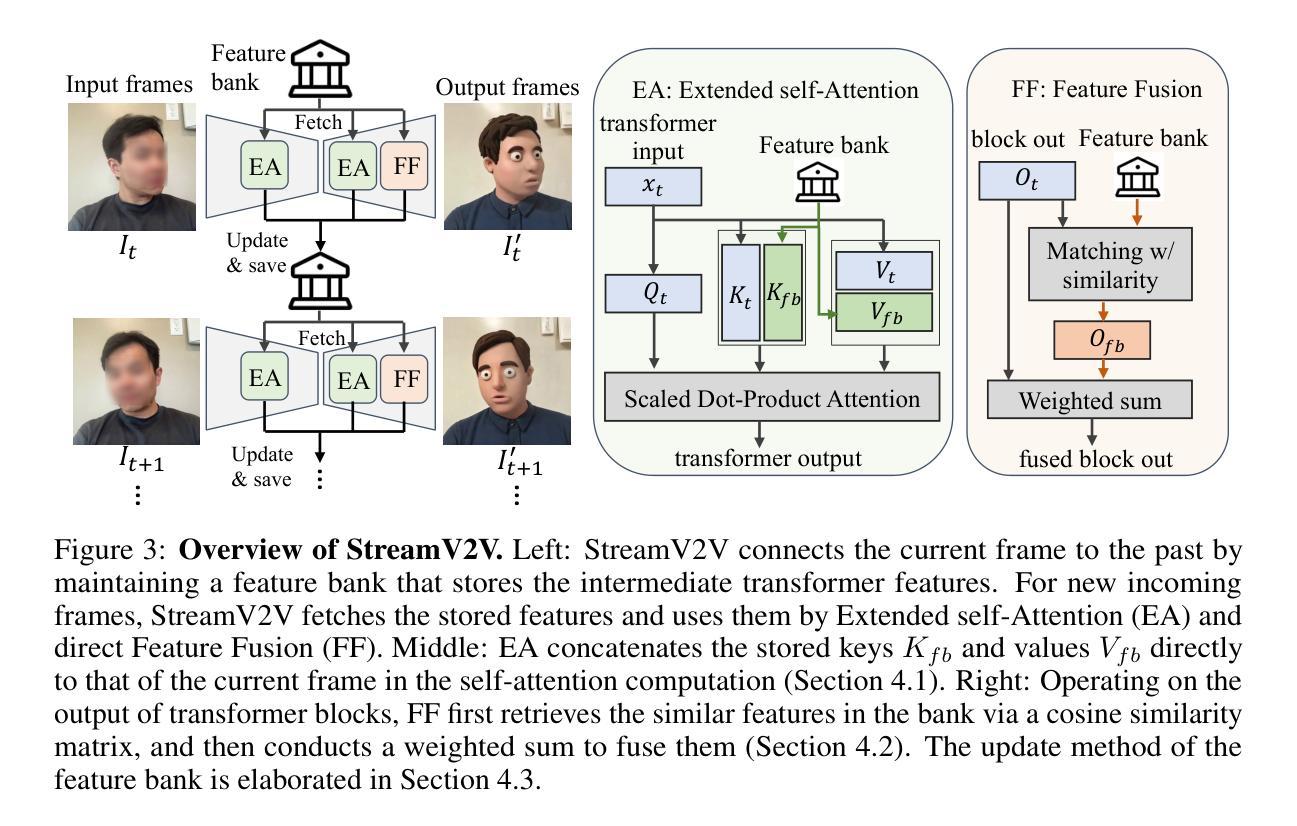
Looking Backward: Streaming Video-to-Video Translation with Feature Banks
Authors:Feng Liang, Akio Kodaira, Chenfeng Xu, Masayoshi Tomizuka, Kurt Keutzer, Diana Marculescu
This paper introduces StreamV2V, a diffusion model that achieves real-time streaming video-to-video (V2V) translation with user prompts. Unlike prior V2V methods using batches to process limited frames, we opt to process frames in a streaming fashion, to support unlimited frames. At the heart of StreamV2V lies a backward-looking principle that relates the present to the past. This is realized by maintaining a feature bank, which archives information from past frames. For incoming frames, StreamV2V extends self-attention to include banked keys and values and directly fuses similar past features into the output. The feature bank is continually updated by merging stored and new features, making it compact but informative. StreamV2V stands out for its adaptability and efficiency, seamlessly integrating with image diffusion models without fine-tuning. It can run 20 FPS on one A100 GPU, being 15x, 46x, 108x, and 158x faster than FlowVid, CoDeF, Rerender, and TokenFlow, respectively. Quantitative metrics and user studies confirm StreamV2V’s exceptional ability to maintain temporal consistency.
本文介绍了StreamV2V,这是一种扩散模型,它借助用户提示实现了实时流式视频到视频(V2V)的翻译。不同于之前使用批次处理有限帧的V2V方法,我们选择以流式方式处理帧,以支持无限帧。StreamV2V的核心在于一个后视原则,将现在与过去联系起来。这是通过维护一个特征银行来实现的,该银行存档过去帧的信息。对于传入的帧,StreamV2V将自注意力扩展到包括银行密钥和值,并直接将相似的过去特征融合到输出中。特征银行通过合并存储的新特征来不断更新,使其既紧凑又富有信息。StreamV2V以其适应性和效率而脱颖而出,无需微调即可无缝集成到图像扩散模型中。它可以在一个A100 GPU上以每秒20帧的速度运行,比FlowVid、CoDeF、Rerender和TokenFlow分别快15倍、46倍、108倍和158倍。定量指标和用户研究证实了StreamV2V在保持时间一致性方面的出色能力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICLR 2025. Project page: https://jeff-liangf.github.io/projects/streamv2v
Summary
本文介绍了StreamV2V,一种支持用户提示的实时流式视频到视频(V2V)翻译模型。它通过采用流式处理框架,实现了对无限帧的支持,并采用了后视原则,将当前帧与过去帧相关联。其核心机制是特征银行,可以存储过去帧的信息,并用于当前帧的自注意力计算和特征融合。StreamV2V具有适应性和效率,可无缝集成图像扩散模型,无需微调。它在性能上远超其他方法,可在单个A100 GPU上以每秒运行达到高达二十帧的速度运行。此外,通过定量指标和用户研究证实其保持良好的时间一致性。
Key Takeaways
- StreamV2V是一个实时流式视频到视频的翻译模型。
- 它使用流式处理框架以支持无限帧处理。
- StreamV2V采用后视原则,将当前帧与过去帧相关联。
- 特征银行是模型的核心机制,用于存储和更新过去帧的信息。
- StreamV2V具有高效性能,可以在一个A100 GPU上以每秒运行高达二十帧的速度运行。
- 它可无缝集成图像扩散模型,无需微调。
点此查看论文截图

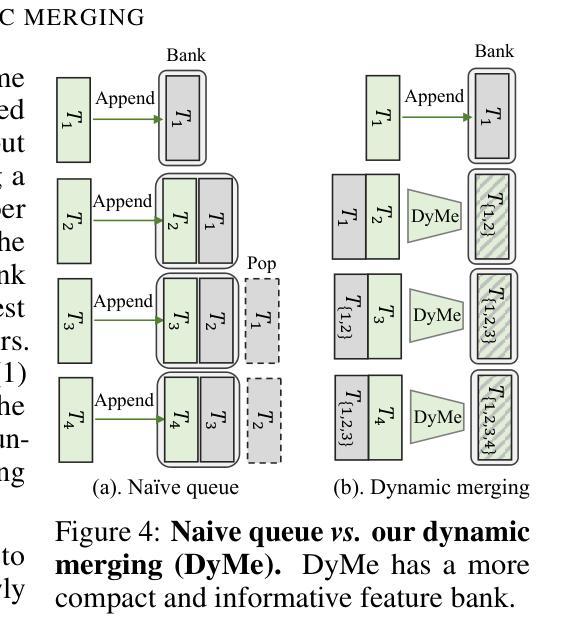
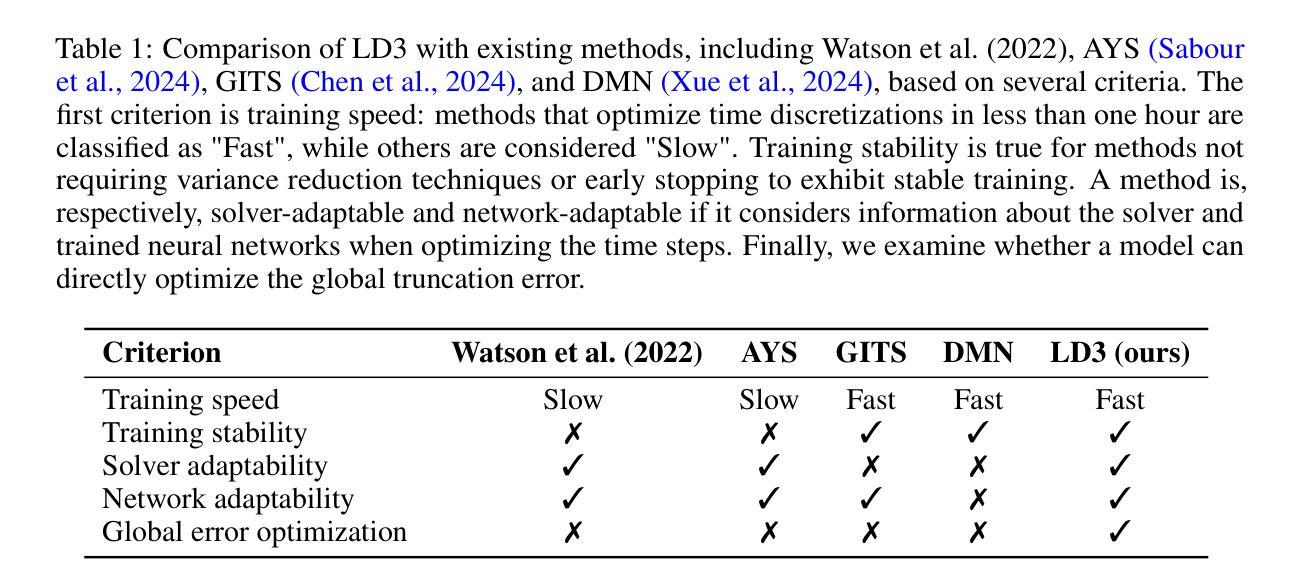
Learning to Discretize Denoising Diffusion ODEs
Authors:Vinh Tong, Trung-Dung Hoang, Anji Liu, Guy Van den Broeck, Mathias Niepert
Diffusion Probabilistic Models (DPMs) are generative models showing competitive performance in various domains, including image synthesis and 3D point cloud generation. Sampling from pre-trained DPMs involves multiple neural function evaluations (NFEs) to transform Gaussian noise samples into images, resulting in higher computational costs compared to single-step generative models such as GANs or VAEs. Therefore, reducing the number of NFEs while preserving generation quality is crucial. To address this, we propose LD3, a lightweight framework designed to learn the optimal time discretization for sampling. LD3 can be combined with various samplers and consistently improves generation quality without having to retrain resource-intensive neural networks. We demonstrate analytically and empirically that LD3 improves sampling efficiency with much less computational overhead. We evaluate our method with extensive experiments on 7 pre-trained models, covering unconditional and conditional sampling in both pixel-space and latent-space DPMs. We achieve FIDs of 2.38 (10 NFE), and 2.27 (10 NFE) on unconditional CIFAR10 and AFHQv2 in 5-10 minutes of training. LD3 offers an efficient approach to sampling from pre-trained diffusion models. Code is available at https://github.com/vinhsuhi/LD3.
扩散概率模型(DPMs)是一种生成模型,在图像合成和3D点云生成等各个领域都有着不俗的表现。从预训练的DPMs中进行采样,需要通过多次神经网络功能评估(NFEs)将高斯噪声样本转化为图像,相较于生成对抗网络(GANs)或变分自编码器(VAEs)等单步生成模型,其计算成本更高。因此,在保持生成质量的同时减少NFEs的数量至关重要。针对这一问题,我们提出了LD3,一个轻量级的框架,旨在学习采样的最优时间离散化。LD3可以与各种采样器相结合,能够在不重新训练资源密集型的神经网络的情况下,持续改善生成质量。我们分析和实证地证明,LD3能提高采样效率,且计算开销较小。我们在7个预训练模型上进行了大量实验,涵盖了像素空间和潜在空间DPMs的无条件和有条件的采样。我们在无条件CIFAR10和AFHQv2上实现了FID为2.38(10次NFE)和2.27(10次NFE),训练时间只需5-10分钟。LD3为从预训练的扩散模型中进行采样提供了一种高效的方法。代码可在https://github.com/vinhsuhi/LD3找到。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
DPM(扩散概率模型)是一种表现强劲的生成模型,广泛应用于图像合成和三维点云生成等领域。然而,由于其采样过程涉及多次神经网络功能评估(NFE),导致计算成本较高。为此,本文提出LD3这一轻量级框架,旨在学习最佳采样时间离散化策略。LD3能与多种采样器结合使用,在不重新训练资源密集型神经网络的情况下提高生成质量。经分析与实证验证,LD3能提高采样效率且计算开销较小。在7个预训练模型上进行的大量实验表明,我们的方法在无条件CIFAR10和AFHQv2上的FID达到2.38(10次NFE)和2.27(10次NFE),训练时间仅需5-10分钟。LD3为从预训练扩散模型中进行采样提供了一种高效方法。
关键见解
- DPMs在图像合成和三维点云生成等领域具有竞争力。
- 采样从预训练的DPMs涉及多次NFE,导致高计算成本。
- LD3框架旨在学习最佳采样时间离散化策略,以提高生成质量并降低计算成本。
- LD3可与各种采样器结合使用,无需重新训练资源密集型神经网络。
- LD3通过减少NFE次数提高了采样效率。
- 在多个预训练模型上的实验表明,LD3在FID指标上实现了显著的性能提升。
- LD3方法具有高效性,训练时间短,代码已公开。
点此查看论文截图

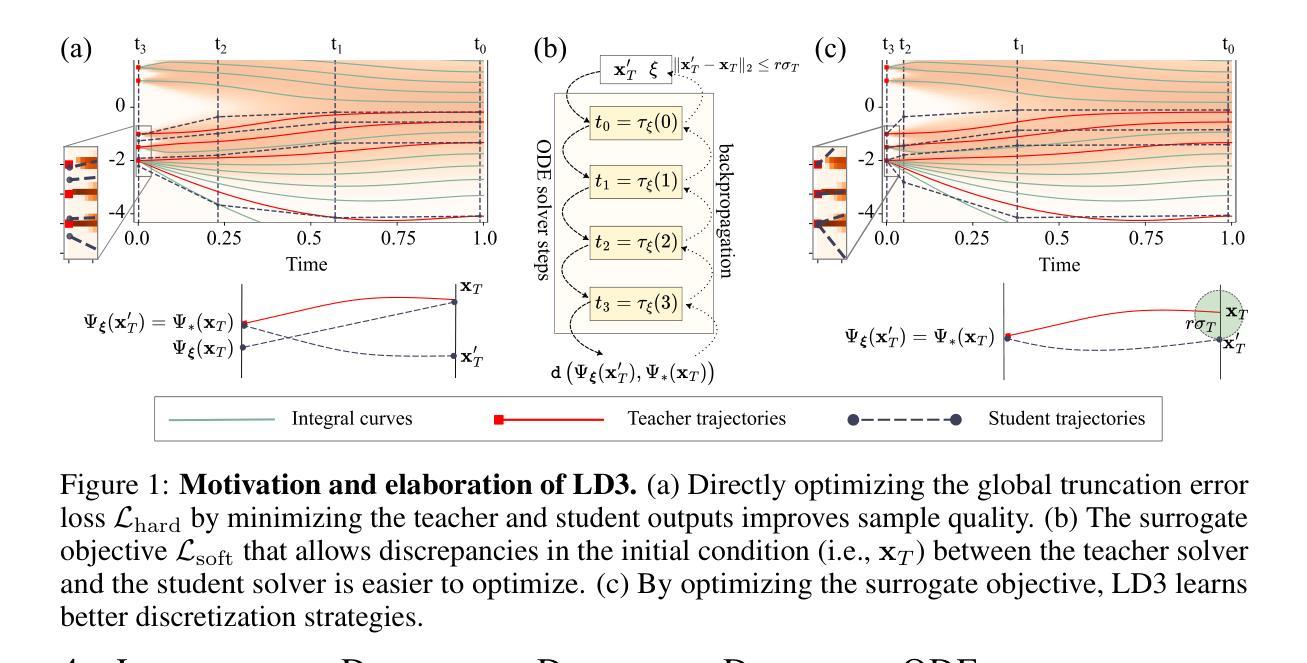
Zero-Reference Lighting Estimation Diffusion Model for Low-Light Image Enhancement
Authors:Jinhong He, Minglong Xue, Aoxiang Ning, Chengyun Song
Diffusion model-based low-light image enhancement methods rely heavily on paired training data, leading to limited extensive application. Meanwhile, existing unsupervised methods lack effective bridging capabilities for unknown degradation. To address these limitations, we propose a novel zero-reference lighting estimation diffusion model for low-light image enhancement called Zero-LED. It utilizes the stable convergence ability of diffusion models to bridge the gap between low-light domains and real normal-light domains and successfully alleviates the dependence on pairwise training data via zero-reference learning. Specifically, we first design the initial optimization network to preprocess the input image and implement bidirectional constraints between the diffusion model and the initial optimization network through multiple objective functions. Subsequently, the degradation factors of the real-world scene are optimized iteratively to achieve effective light enhancement. In addition, we explore a frequency-domain based and semantically guided appearance reconstruction module that encourages feature alignment of the recovered image at a fine-grained level and satisfies subjective expectations. Finally, extensive experiments demonstrate the superiority of our approach to other state-of-the-art methods and more significant generalization capabilities. We will open the source code upon acceptance of the paper.
基于扩散模型的低光图像增强方法严重依赖于配对训练数据,导致其广泛应用受限。同时,现有的无监督方法缺乏对未知降解的有效桥梁作用。为了解决这些局限性,我们提出了一种用于低光图像增强的新型无参考光照估计扩散模型,名为Zero-LED。它利用扩散模型的稳定收敛能力,弥合了低光领域和真实正常光领域之间的差距,并通过无参考学习成功减轻了对配对训练数据的依赖。具体来说,我们首先设计初始优化网络对输入图像进行预处理,并通过多个目标函数在扩散模型和初始优化网络之间实现双向约束。随后,优化现实世界场景的降解因素,以迭代的方式实现有效的光照增强。此外,我们探索了一种基于频域和语义引导的外观重建模块,该模块鼓励恢复图像的特在细粒度层次对齐,并满足主观预期。最后,大量实验表明我们的方法优于其他最先进的方法,并且具有更显著的泛化能力。论文被接受后,我们将公开源代码。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
本文提出了一种基于扩散模型的无参考低光图像增强方法,名为Zero-LED。该方法利用扩散模型的稳定收敛能力,桥接低光域和正常光域,通过无参考学习减轻对配对训练数据的依赖。通过设计初始优化网络对输入图像进行预处理,并在扩散模型和初始优化网络之间通过多个目标函数实现双向约束。迭代优化真实场景中的退化因素,实现有效的光照增强。此外,还探索了基于频域和语义引导的外观重建模块,使恢复的特征在精细层面上对齐,满足主观期望。实验表明,该方法优于其他先进方法,具有更强的泛化能力。
关键见解
- 扩散模型在低光图像增强中广泛应用,但仍存在对配对训练数据的依赖问题。
- 现有无监督方法在未知退化方面的桥梁作用不足。
- 提出了名为Zero-LED的新扩散模型,以减轻对配对训练数据的依赖,并通过稳定收敛能力桥接不同光照域。
- 设计了初始优化网络进行图像预处理,并通过多个目标函数实现扩散模型和初始优化网络之间的双向约束。
- 通过迭代优化真实场景中的退化因素,实现了有效的光照增强。
- 引入了基于频域和语义引导的外观重建模块,提高了恢复图像的特征对齐精度。
- 实验结果表明,该方法在性能上优于其他先进方法,并展示了更强的泛化能力。
点此查看论文截图


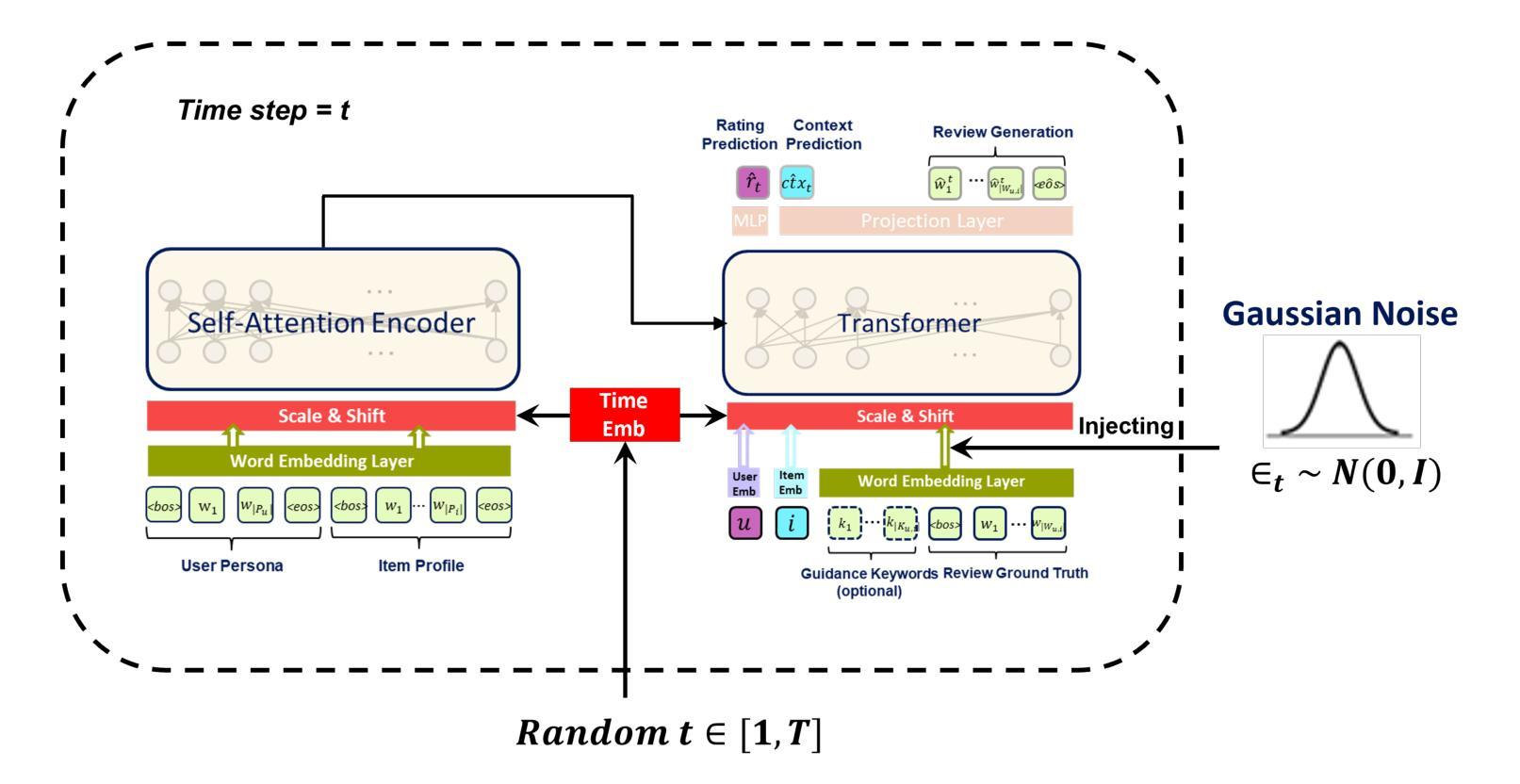
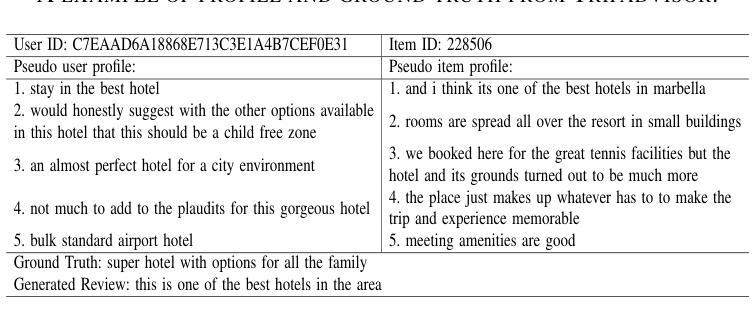
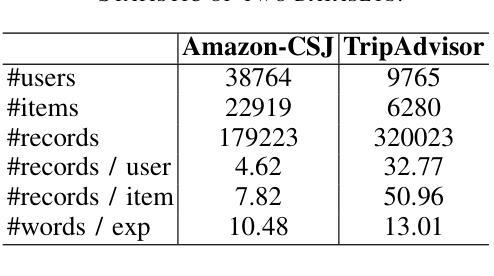
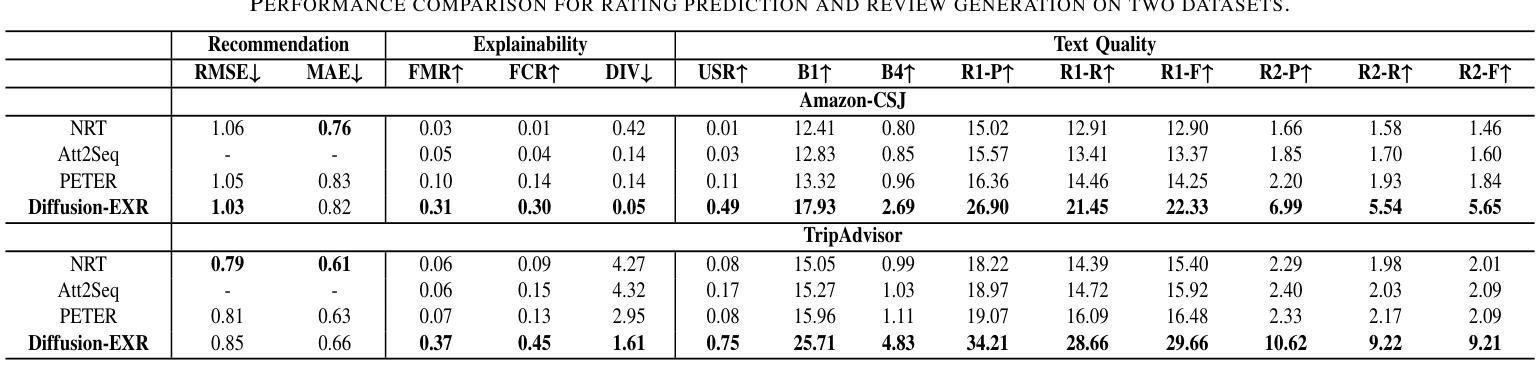
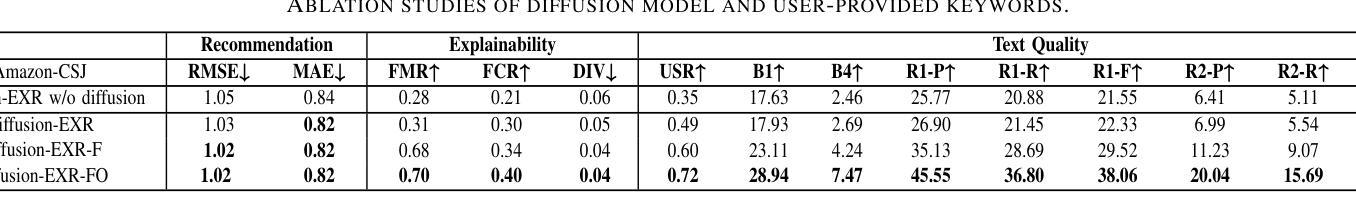
Diffusion-EXR: Controllable Review Generation for Explainable Recommendation via Diffusion Models
Authors:Ling Li, Shaohua Li, Winda Marantika, Alex C. Kot, Huijing Zhan
Denoising Diffusion Probabilistic Model (DDPM) has shown great competence in image and audio generation tasks. However, there exist few attempts to employ DDPM in the text generation, especially review generation under recommendation systems. Fueled by the predicted reviews explainability that justifies recommendations could assist users better understand the recommended items and increase the transparency of recommendation system, we propose a Diffusion Model-based Review Generation towards EXplainable Recommendation named Diffusion-EXR. Diffusion-EXR corrupts the sequence of review embeddings by incrementally introducing varied levels of Gaussian noise to the sequence of word embeddings and learns to reconstruct the original word representations in the reverse process. The nature of DDPM enables our lightweight Transformer backbone to perform excellently in the recommendation review generation task. Extensive experimental results have demonstrated that Diffusion-EXR can achieve state-of-the-art review generation for recommendation on two publicly available benchmark datasets.
去噪扩散概率模型(DDPM)在图像和音频生成任务中表现出了巨大的竞争力。然而,很少有尝试将DDPM应用于文本生成,尤其是在推荐系统的评论生成方面。我们以可解释的推荐预测为基础,推动用户更好地理解推荐项目并增加推荐系统的透明度,提出了一种基于扩散模型的面向可解释推荐的评论生成方法,名为Diffusion-EXR。Diffusion-EXR通过逐步向评论嵌入序列引入不同级别的高斯噪声来破坏评论嵌入序列,并在反向过程中学习重建原始单词表示。DDPM的特性使我们的轻量级Transformer骨干在推荐评论生成任务中表现出色。大量实验结果表明,Diffusion-EXR在两个公开可用的基准数据集上实现了先进的评论生成推荐效果。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF We request to withdraw our paper from the archive due to significant errors identified in the analysis and conclusions. Upon further review, we realized that these errors undermine the validity of our findings. We plan to conduct additional research to correct these issues and resubmit a revised version in the future
Summary
基于DDPM的扩散模型在图像和音频生成任务中展现出卓越的性能,但用于文本生成、特别是推荐系统下的评论生成的尝试仍较少。本文提出一种名为Diffusion-EXR的扩散模型评论生成方法,旨在通过预测的评论解释性来解释推荐并帮助用户更好地理解推荐商品,增加推荐系统的透明度。它通过逐步在序列的词嵌入中加入不同程度的高斯噪声来破坏评论序列,并在逆向过程中学习重建原始词表示。实验结果表明,Diffusion-EXR在两个公开基准数据集上的推荐评论生成任务表现优异。
Key Takeaways
- DDPM在图像和音频生成中性能优越,但用于文本生成特别是在推荐系统的评论生成方面应用较少。
- Diffusion-EXR是一种基于扩散模型的评论生成方法,旨在提高推荐系统的透明度。
- Diffusion-EXR通过逐步加入高斯噪声破坏评论序列,并在逆向过程中重建原始词表示。
- Diffusion-EXR利用轻量级Transformer作为骨干网,使其在推荐评论生成任务中表现优秀。
- Diffusion-EXR在两个公开数据集上实现了先进的评论生成效果。
- 该方法通过预测的评论解释性来解释推荐,帮助用户更好地理解推荐商品。
点此查看论文截图