⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-02-19 更新
THESAURUS: Contrastive Graph Clustering by Swapping Fused Gromov-Wasserstein Couplings
Authors:Bowen Deng, Tong Wang, Lele Fu, Sheng Huang, Chuan Chen, Tao Zhang
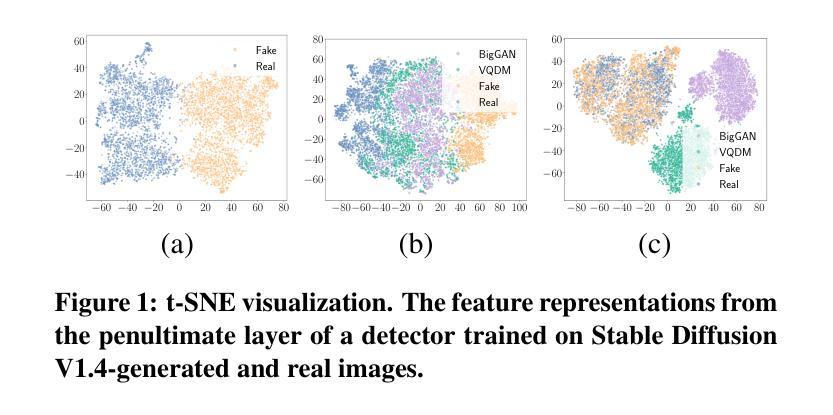
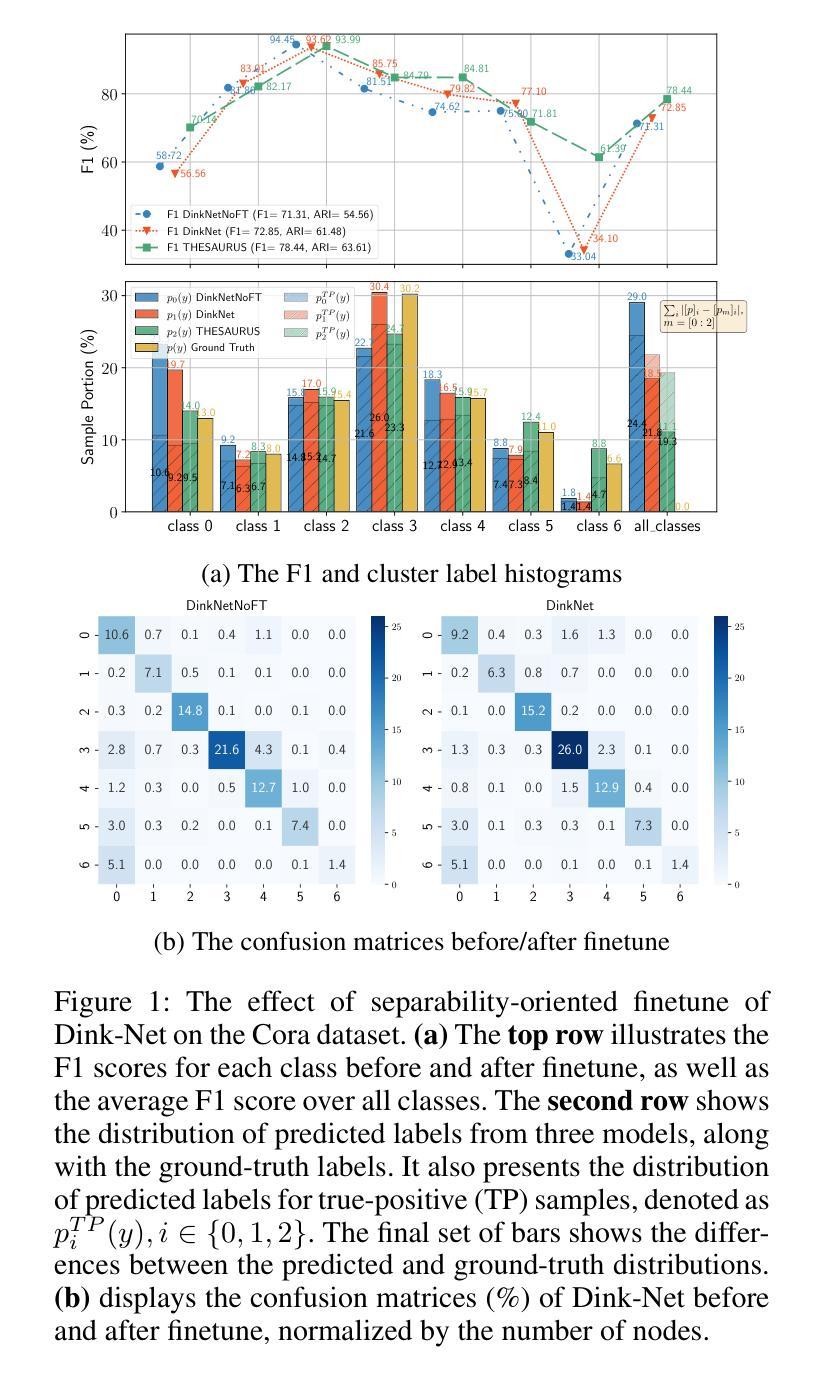
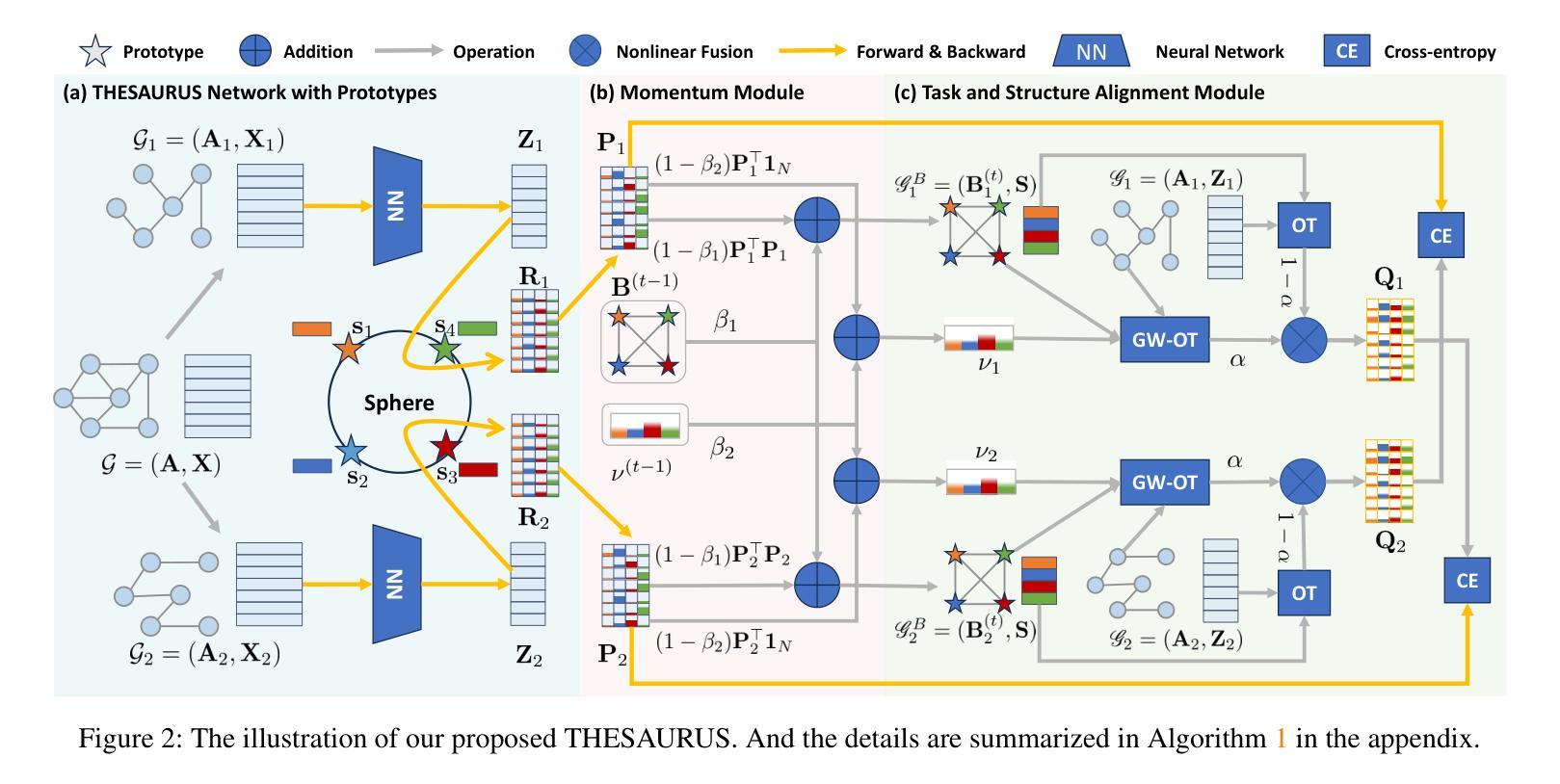
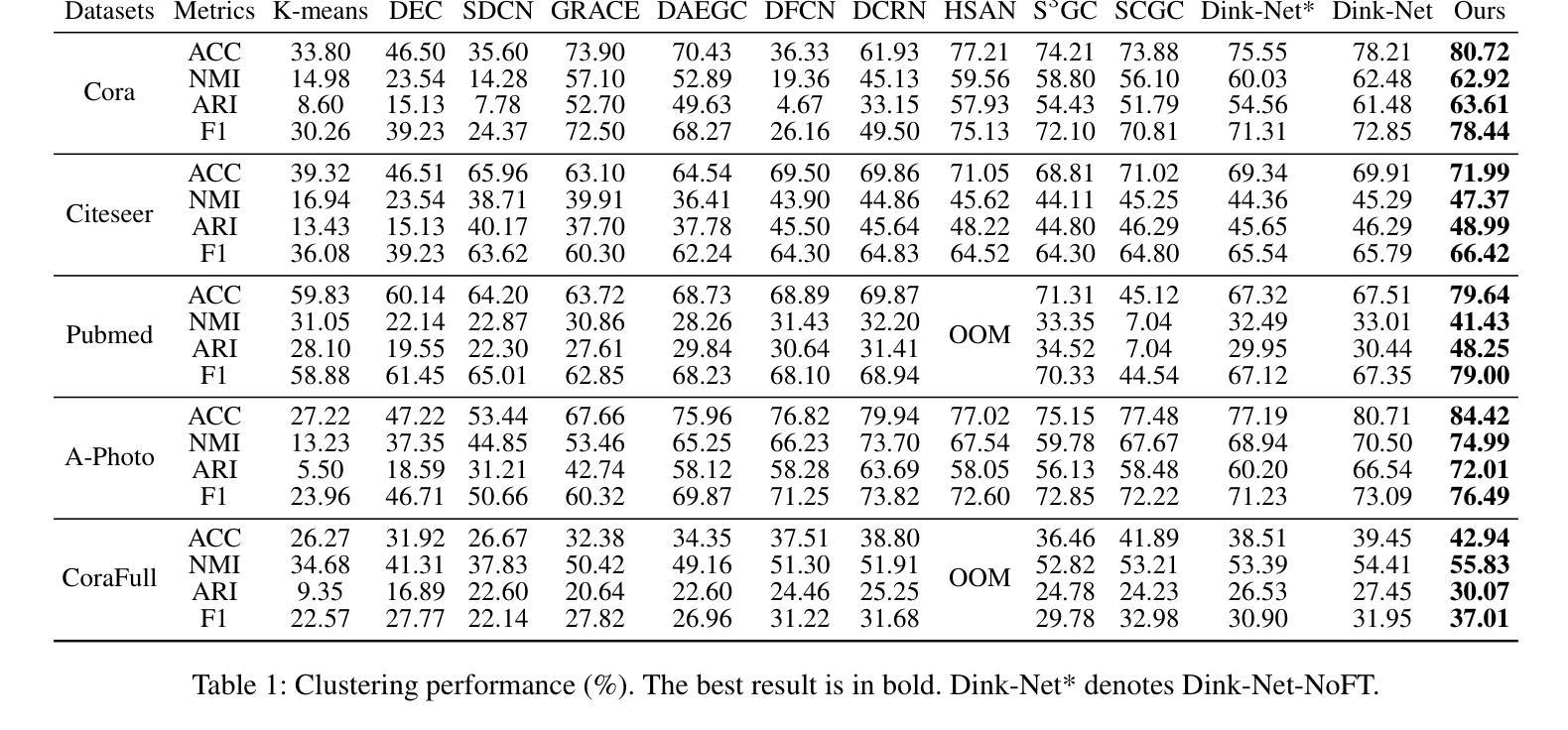
Graph node clustering is a fundamental unsupervised task. Existing methods typically train an encoder through selfsupervised learning and then apply K-means to the encoder output. Some methods use this clustering result directly as the final assignment, while others initialize centroids based on this initial clustering and then finetune both the encoder and these learnable centroids. However, due to their reliance on K-means, these methods inherit its drawbacks when the cluster separability of encoder output is low, facing challenges from the Uniform Effect and Cluster Assimilation. We summarize three reasons for the low cluster separability in existing methods: (1) lack of contextual information prevents discrimination between similar nodes from different clusters; (2) training tasks are not sufficiently aligned with the downstream clustering task; (3) the cluster information in the graph structure is not appropriately exploited. To address these issues, we propose conTrastive grapH clustEring by SwApping fUsed gRomov-wasserstein coUplingS (THESAURUS). Our method introduces semantic prototypes to provide contextual information, and employs a cross-view assignment prediction pretext task that aligns well with the downstream clustering task. Additionally, it utilizes Gromov-Wasserstein Optimal Transport (GW-OT) along with the proposed prototype graph to thoroughly exploit cluster information in the graph structure. To adapt to diverse real-world data, THESAURUS updates the prototype graph and the prototype marginal distribution in OT by using momentum. Extensive experiments demonstrate that THESAURUS achieves higher cluster separability than the prior art, effectively mitigating the Uniform Effect and Cluster Assimilation issues
图节点聚类是一项基本的无监督任务。现有方法通常通过自监督学习训练编码器,然后应用于编码器的输出进行K-均值聚类。一些方法直接使用这种聚类结果作为最终分配,而其他方法则基于这种初始聚类初始化质心,然后微调编码器和这些可学习的质心。然而,由于它们依赖于K-均值,这些方法继承了当编码器输出的聚类可分性较低时的缺点,面临着来自统一效应和集群同化等的挑战。我们总结了现有方法中低聚类可分性的三个原因:(1)缺乏上下文信息,无法区分来自不同簇的相似节点;(2)训练任务与下游聚类任务不够对齐;(3)没有适当地利用图结构中的聚类信息。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了通过交换使用图结构中的Gromov-Wasserstein耦合的对比性图聚类方法(THESAURUS)。我们的方法引入语义原型以提供上下文信息,并采用跨视图分配预测前体任务,与下游聚类任务对齐。此外,它利用Gromov-Wasserstein最优传输(GW-OT)以及提出的原型图,以彻底利用图结构中的聚类信息。为了适应多样化的现实世界数据,THESAURUS通过使用动量更新原型图和原型边际分布。大量实验表明,THESAURUS在聚类可分性方面优于先前技术,有效地减轻了统一效应和集群同化问题。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by AAAI 2025
Summary
图节点聚类是一项基本的无监督任务。现有方法通常通过自监督学习训练编码器,然后对编码器输出进行K-means处理。然而,由于依赖K-means,这些方法继承了其缺点,当编码器输出的聚类可分性较低时,面临统一效应和集群融合的挑战。为解决这些问题,我们提出通过交换使用的Gromov-Wasserstein耦合进行对比图聚类(THESAURUS)。该方法引入语义原型提供上下文信息,采用与下游聚类任务对齐的跨视图分配预测任务。同时,它利用Gromov-Wasserstein最佳传输与提出的原型图,充分利用图结构中的聚类信息。适应各种现实世界数据,THESAURUS通过动量更新原型图和原型边缘分布。实验表明,THESAURUS较之前的技术提高了聚类可分性,有效缓解了统一效应和集群融合问题。
Key Takeaways
- 图节点聚类是无监督学习任务,现有方法依赖K-means进行聚类,存在局限性。
- 现有方法聚类可分性低的原因包括缺乏上下文信息、训练任务与下游聚类任务不匹配以及图结构中的聚类信息未得到适当利用。
- THESAURUS方法通过引入语义原型提供上下文信息,改善聚类效果。
- THESAURUS采用跨视图分配预测任务,与下游聚类任务对齐,提高聚类准确性。
- Gromov-Wasserstein最佳传输与原型图结合,THESAURUS能充分利用图结构中的聚类信息。
- THESAURUS适应各种现实世界数据,通过动量更新原型图和原型边缘分布。
点此查看论文截图