⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-02-19 更新
A Survey on Bridging EEG Signals and Generative AI: From Image and Text to Beyond
Authors:Shreya Shukla, Jose Torres, Abhijit Mishra, Jacek Gwizdka, Shounak Roychowdhury
Integration of Brain-Computer Interfaces (BCIs) and Generative Artificial Intelligence (GenAI) has opened new frontiers in brain signal decoding, enabling assistive communication, neural representation learning, and multimodal integration. BCIs, particularly those leveraging Electroencephalography (EEG), provide a non-invasive means of translating neural activity into meaningful outputs. Recent advances in deep learning, including Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) and Transformer-based Large Language Models (LLMs), have significantly improved EEG-based generation of images, text, and speech. This paper provides a literature review of the state-of-the-art in EEG-based multimodal generation, focusing on (i) EEG-to-image generation through GANs, Variational Autoencoders (VAEs), and Diffusion Models, and (ii) EEG-to-text generation leveraging Transformer based language models and contrastive learning methods. Additionally, we discuss the emerging domain of EEG-to-speech synthesis, an evolving multimodal frontier. We highlight key datasets, use cases, challenges, and EEG feature encoding methods that underpin generative approaches. By providing a structured overview of EEG-based generative AI, this survey aims to equip researchers and practitioners with insights to advance neural decoding, enhance assistive technologies, and expand the frontiers of brain-computer interaction.
脑机接口(BCI)与生成式人工智能(GenAI)的融合为脑信号解码开辟了新的领域,实现了辅助通信、神经表征学习和多模态融合。特别是利用脑电图(EEG)的BCI为神经活动提供了一种非侵入性的翻译手段,转化为有意义的输出。深度学习领域的最新进展,包括生成对抗网络(GANs)和基于Transformer的大型语言模型(LLMs),已经极大地提高了基于EEG的图像、文本和语音生成能力。本文综述了基于EEG的多模态生成的最新进展,重点关注(i)通过GANs、变分自动编码器(VAEs)和扩散模型实现EEG到图像生成;(ii)利用基于Transformer的语言模型和对比学习方法实现EEG到文本的生成。此外,我们还讨论了新兴的EEG语音合成领域,这是一个不断发展的多模态前沿领域。本文强调了关键数据集、用例、挑战和EEG特征编码方法,这些方法是生成式人工智能的基础。通过对基于EEG的生成式人工智能的结构性概述,本综述旨在为研究人员和实践者提供洞察力,以推动神经解码的发展,提高辅助技术的性能,并拓展脑机交互的边界。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:脑机接口(BCI)与生成性人工智能(GenAI)的融合为脑信号解码打开了新纪元,助力辅助沟通、神经表征学习和多模式整合。借助脑电图(EEG)的BCI为非侵入式地转化神经活动为有意义输出提供了手段。最近深度学习的进步,包括生成对抗网络(GANs)和基于Transformer的大型语言模型(LLMs),已显著改进基于EEG的图像、文本和语音生成。本文综述了基于EEG的多模式生成的最新进展,重点介绍了通过GANs、变分自编码器(VAEs)和扩散模型实现EEG到图像生成,以及利用基于Transformer的语言模型和对比学习方法实现EEG到文本生成。我们还讨论了新兴的EEG语音合成领域,这是一个不断发展的多模式前沿领域。
Key Takeaways:
- BCI与GenAI融合为脑信号解码带来新纪元,助力辅助沟通、神经表征学习和多模式整合。
- EEG为非侵入式地转化神经活动为有意义输出提供了手段。
- 深度学习,包括GANs和LLMs,已改进基于EEG的图像、文本和语音生成。
- EEG到图像生成的方法包括GANs、VAEs和扩散模型。
- EEG到文本生成利用了基于Transformer的语言模型和对比学习方法。
- EEG语音合成是一个新兴且不断发展的多模式前沿领域。
点此查看论文截图

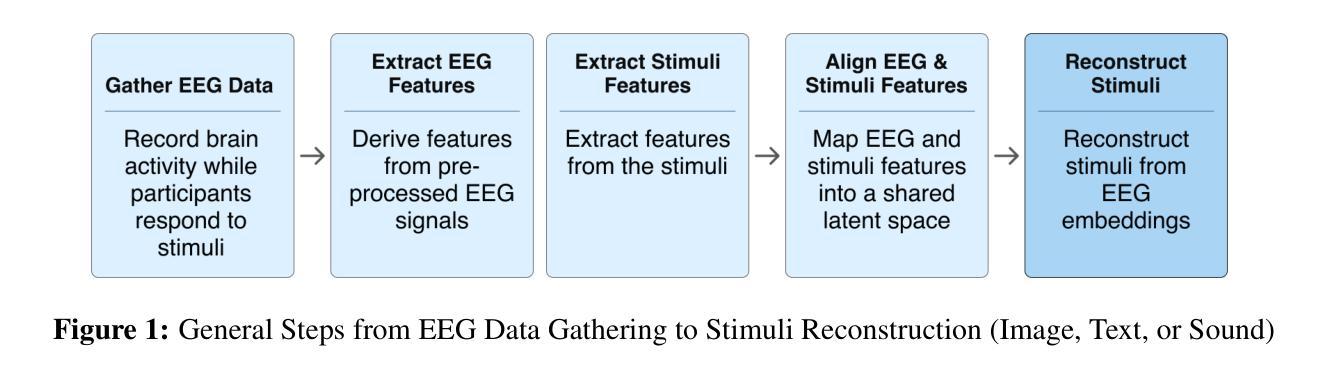
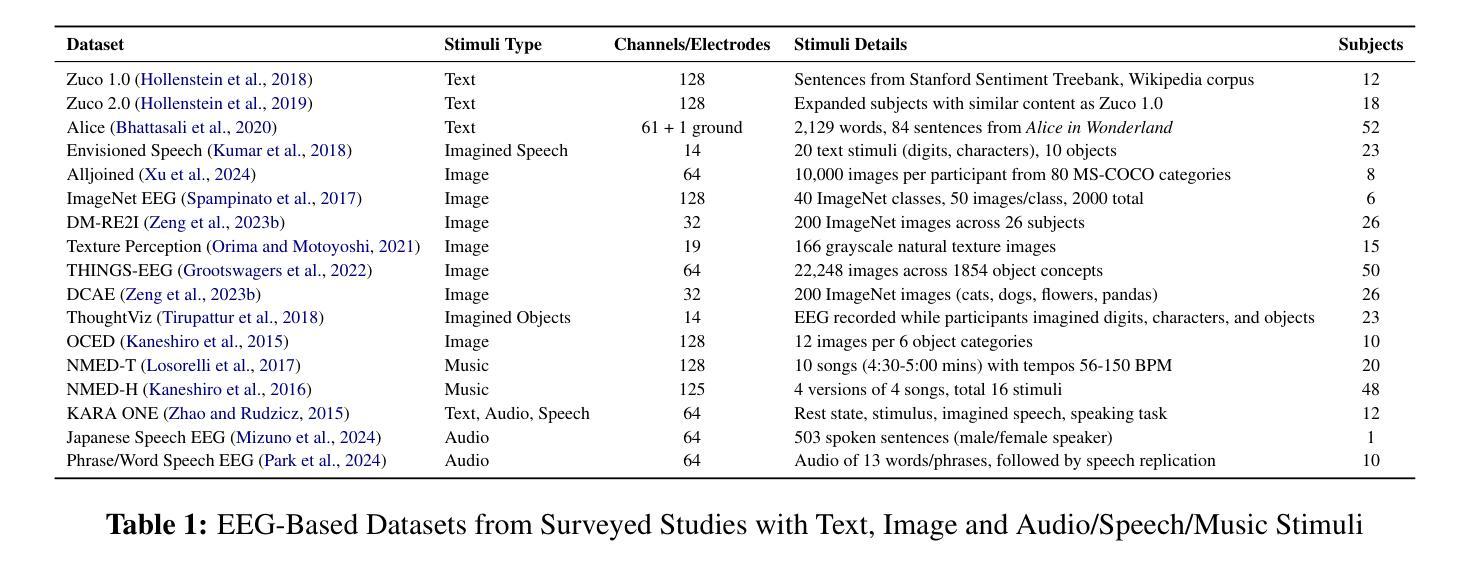
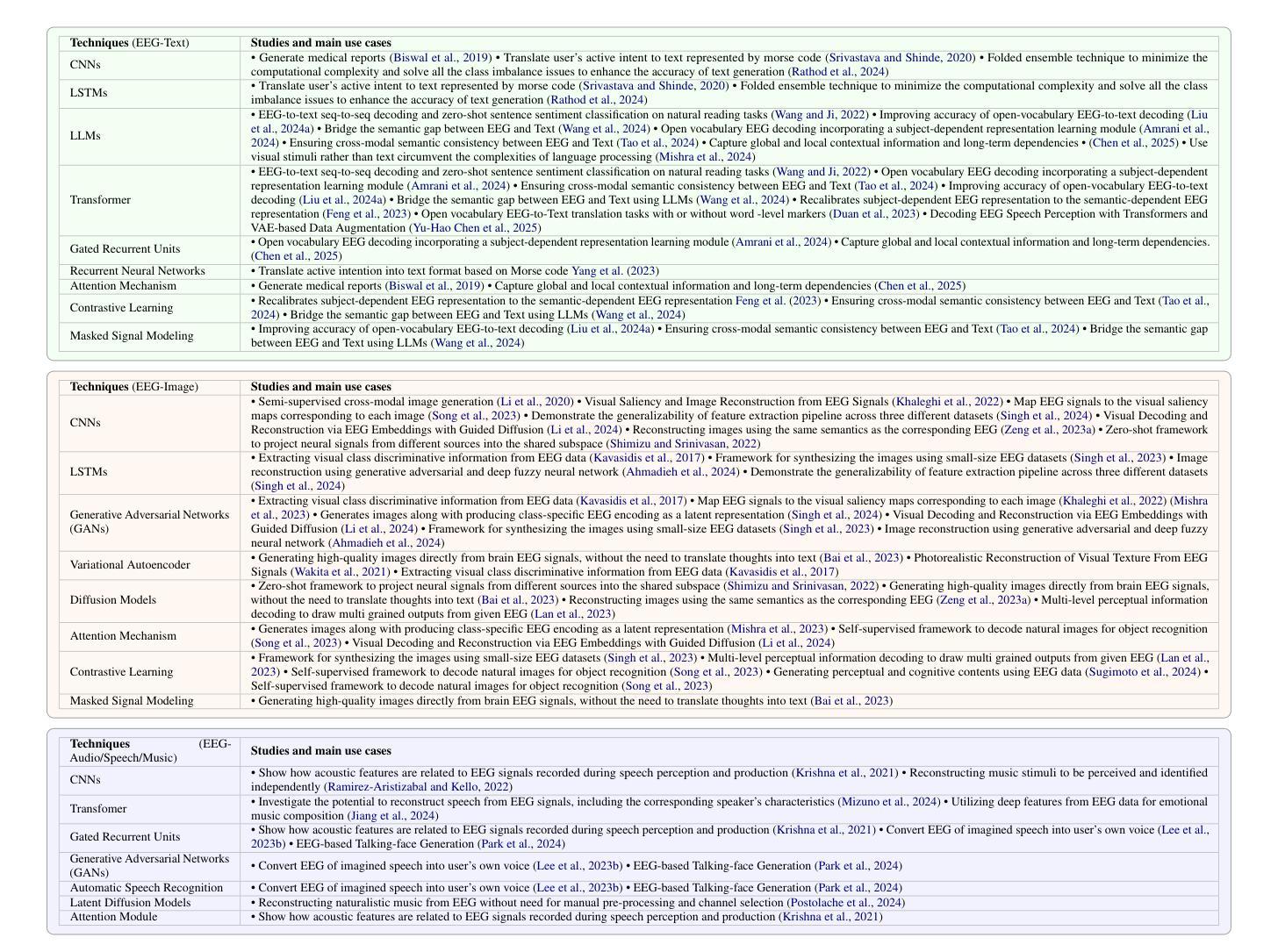
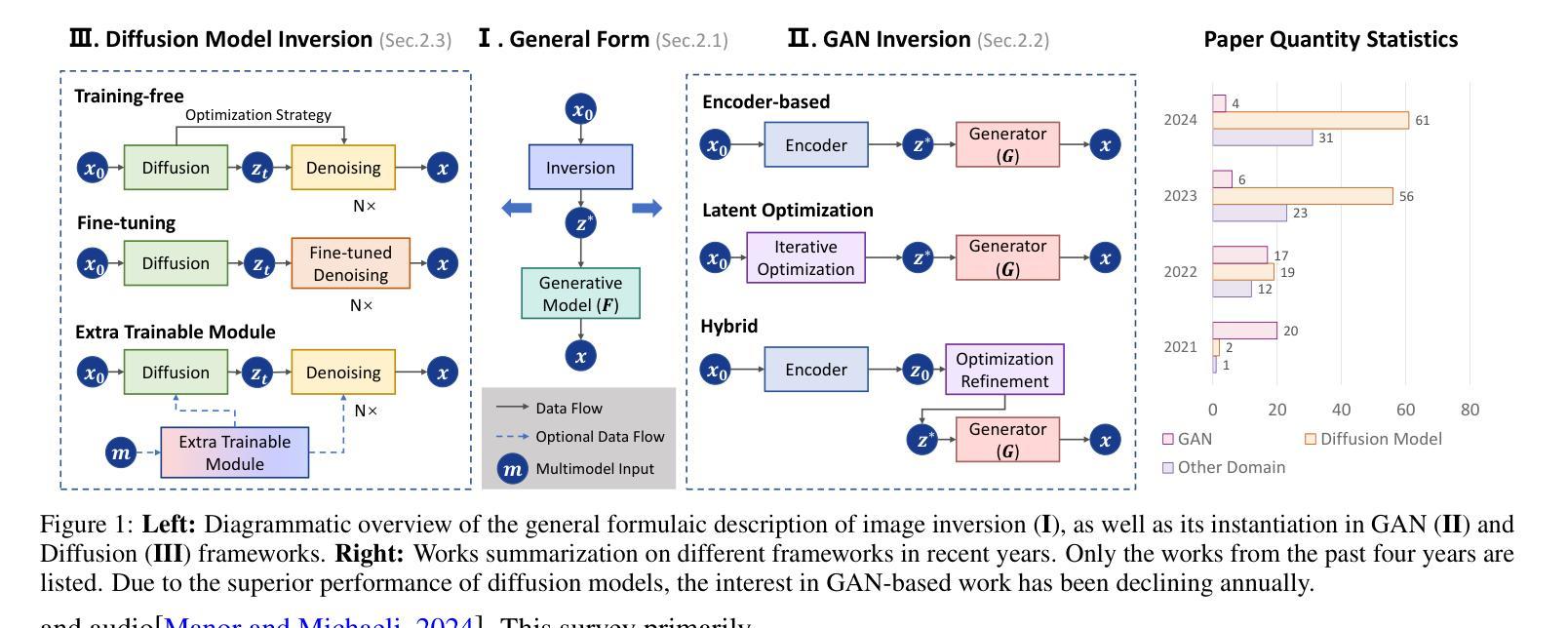
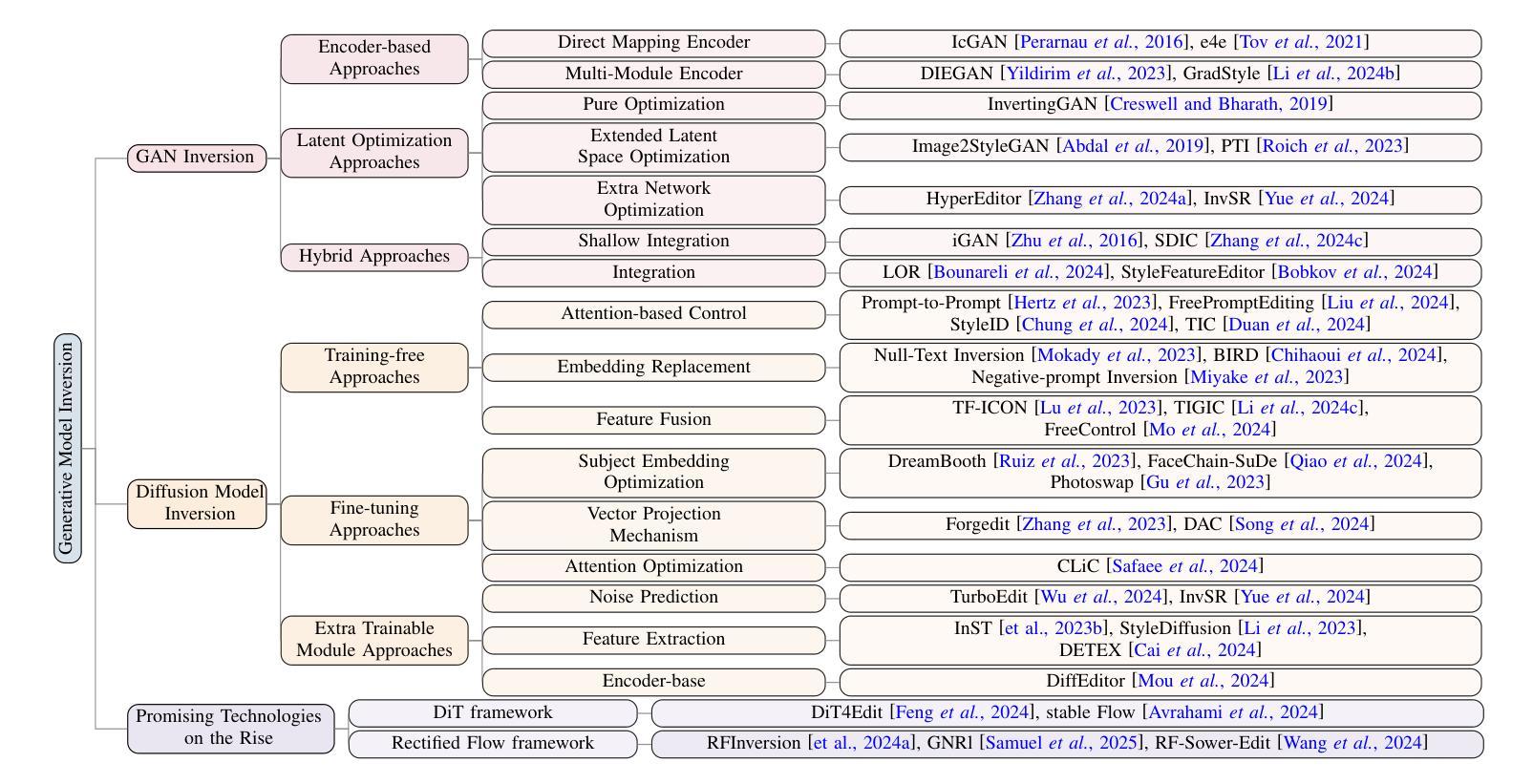
Image Inversion: A Survey from GANs to Diffusion and Beyond
Authors:Yinan Chen, Jiangning Zhang, Yali Bi, Xiaobin Hu, Teng Hu, Zhucun Xue, Ran Yi, Yong Liu, Ying Tai
Image inversion is a fundamental task in generative models, aiming to map images back to their latent representations to enable downstream applications such as editing, restoration, and style transfer. This paper provides a comprehensive review of the latest advancements in image inversion techniques, focusing on two main paradigms: Generative Adversarial Network (GAN) inversion and diffusion model inversion. We categorize these techniques based on their optimization methods. For GAN inversion, we systematically classify existing methods into encoder-based approaches, latent optimization approaches, and hybrid approaches, analyzing their theoretical foundations, technical innovations, and practical trade-offs. For diffusion model inversion, we explore training-free strategies, fine-tuning methods, and the design of additional trainable modules, highlighting their unique advantages and limitations. Additionally, we discuss several popular downstream applications and emerging applications beyond image tasks, identifying current challenges and future research directions. By synthesizing the latest developments, this paper aims to provide researchers and practitioners with a valuable reference resource, promoting further advancements in the field of image inversion. We keep track of the latest works at https://github.com/RyanChenYN/ImageInversion
图像反转是生成模型中的一项基本任务,旨在将图像映射回其潜在表示,以支持后续应用,例如编辑、恢复和风格转换。本文对图像反转技术的最新进展进行了全面回顾,重点介绍了两种主要方法:生成对抗网络(GAN)反转和扩散模型反转。我们根据优化方法对技术进行分类。对于GAN反转,我们系统地总结了现有方法,将其分为基于编码器的方法、潜在优化方法和混合方法,分析了它们的理论基础、技术创新和实际应用中的权衡。对于扩散模型反转,我们探讨了无训练策略、微调方法和附加训练模块的设计,突出了它们的独特优势和局限性。此外,我们还讨论了流行的下游应用和图像任务以外的其他新兴应用,确定了当前挑战和未来研究方向。通过综合最新发展,本文旨在为研究人员和实践者提供有价值的参考资料,推动图像反转领域的进一步发展。我们在 https://github.com/RyanChenYN/ImageInversion 上跟踪最新作品。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 10 pages, 2 figures
Summary
图像反演是生成模型中的基础任务,旨在将图像映射回其潜在表示形式,以支持编辑、修复和风格转换等下游应用。本文综述了最新的图像反演技术进展,主要关注生成对抗网络(GAN)反演和扩散模型反演两种主要范式。基于优化方法,对GAN反演和扩散模型反演技术进行了分类,并对理论背景、技术创新和实用权衡进行了系统分析。本文旨在为研究人员和实践者提供参考资源,促进图像反演领域的进一步发展。
Key Takeaways
- 图像反演是生成模型的基础任务,旨在将图像映射回其潜在表示。
- GAN反演和扩散模型反演是图像反演的两种主要技术范式。
- GAN反演技术分为编码器方法、潜在优化方法和混合方法。
- 扩散模型反演涉及无训练策略、微调方法和可训练模块的设计。
- 图像反演支持下游应用如编辑、修复和风格转换等。
- 当前挑战和未来研究方向包括新兴应用的拓展和理论研究的深化等。
点此查看论文截图

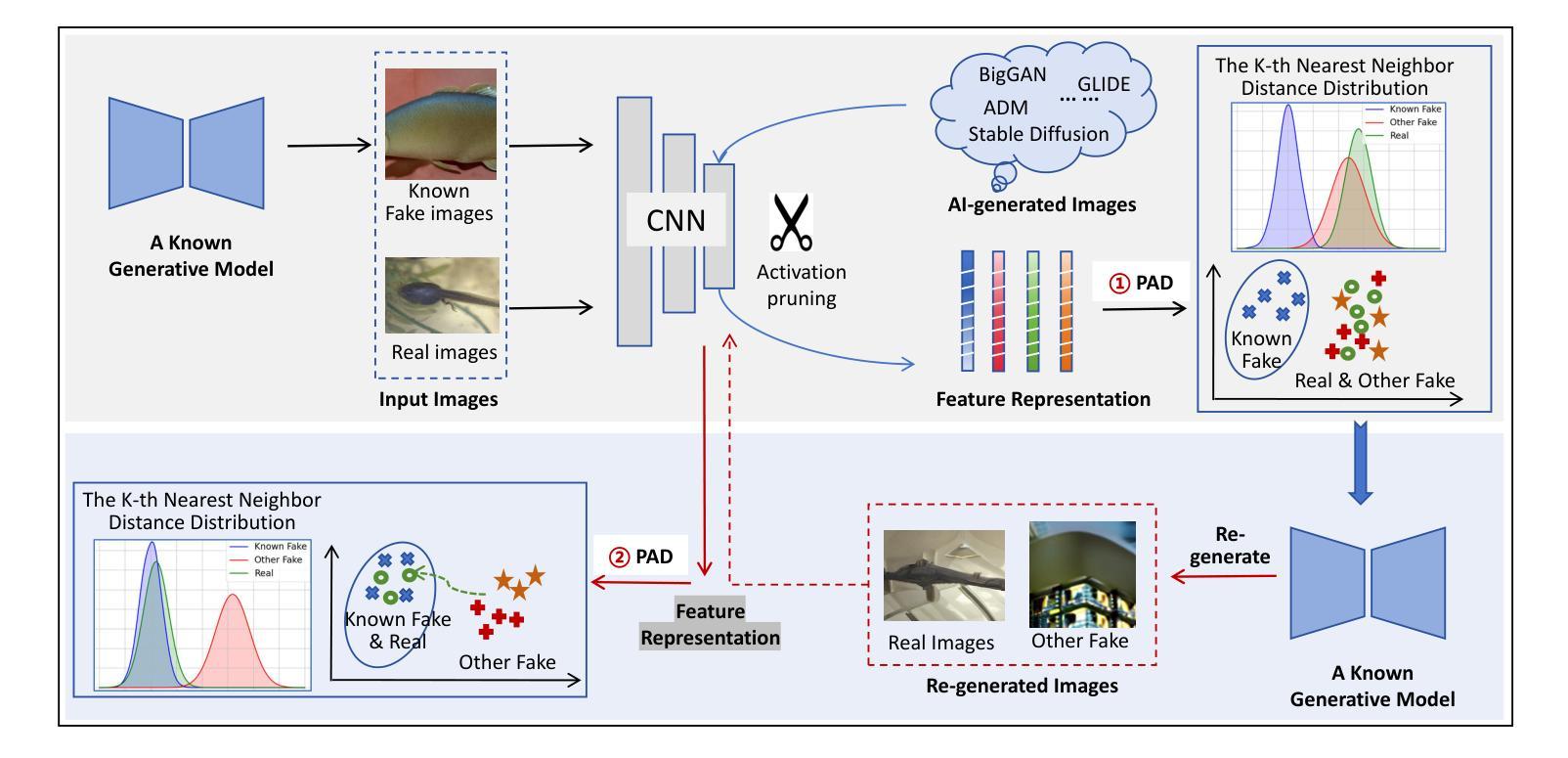
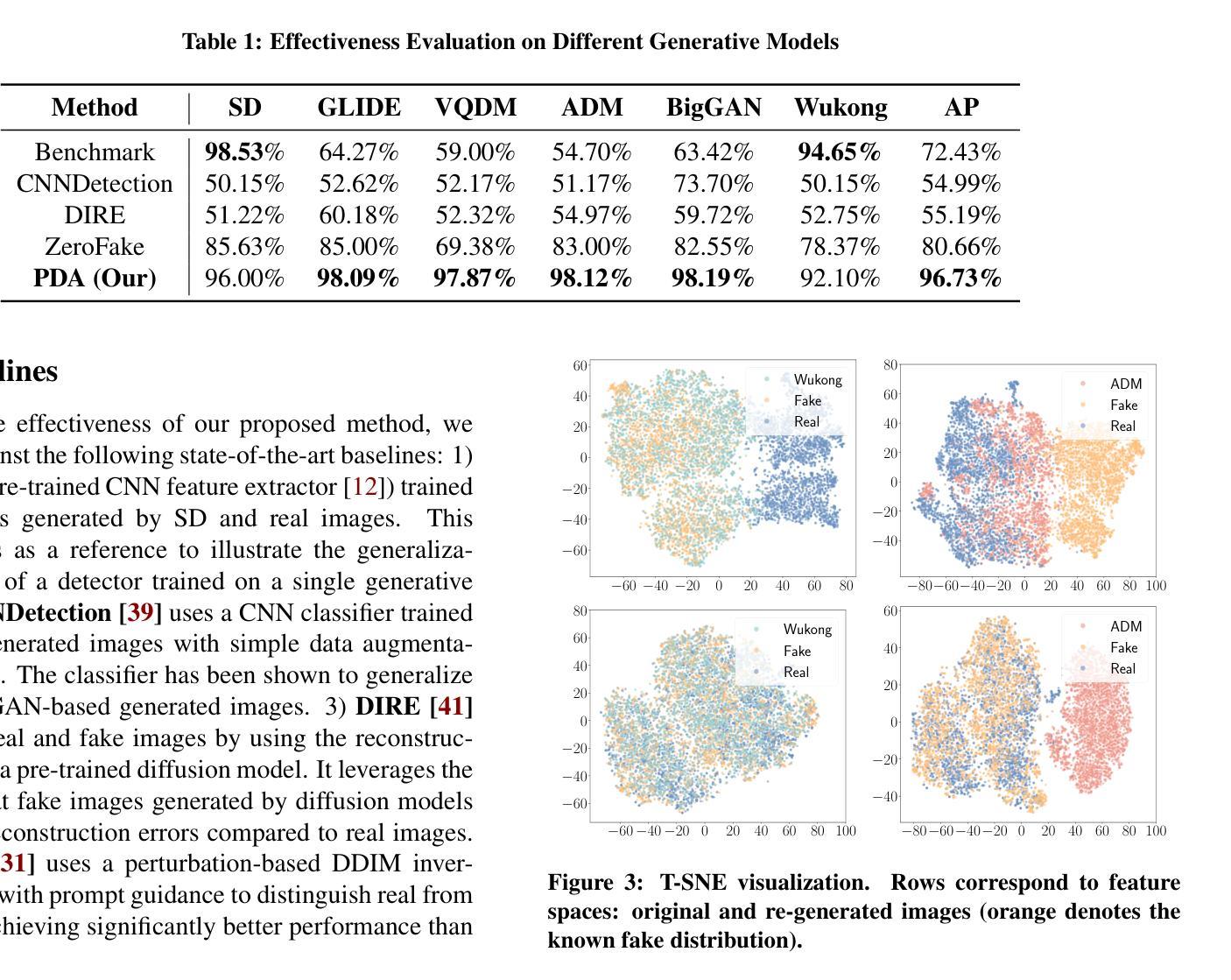
PDA: Generalizable Detection of AI-Generated Images via Post-hoc Distribution Alignment
Authors:Li Wang, Wenyu Chen, Zheng Li, Shanqing Guo
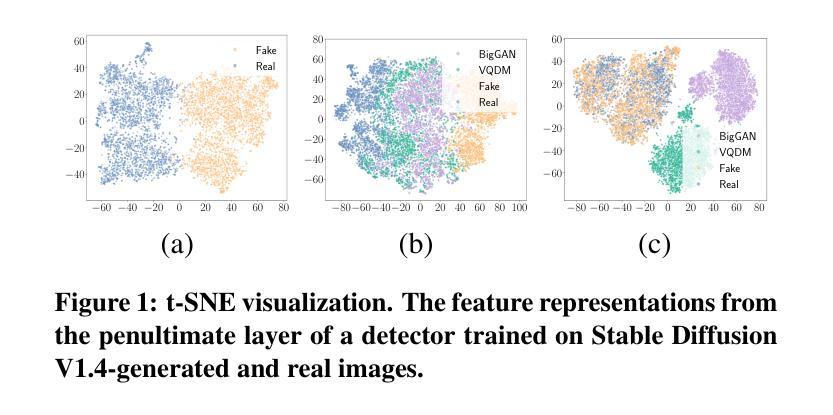
The rapid advancement of generative models has led to the proliferation of highly realistic AI-generated images, posing significant challenges for detection methods to generalize across diverse and evolving generative techniques. Existing approaches often fail to adapt to unknown models without costly retraining, limiting their practicability. To fill this gap, we propose Post-hoc Distribution Alignment (PDA), a novel approach for the generalizable detection for AI-generated images. The key idea is to use the known generative model to regenerate undifferentiated test images. This process aligns the distributions of the re-generated real images with the known fake images, enabling effective distinction from unknown fake images. PDA employs a two-step detection framework: 1) evaluating whether a test image aligns with the known fake distribution based on deep k-nearest neighbor (KNN) distance, and 2) re-generating test images using known generative models to create pseudo-fake images for further classification. This alignment strategy allows PDA to effectively detect fake images without relying on unseen data or requiring retraining. Extensive experiments demonstrate the superiority of PDA, achieving 96.73% average accuracy across six state-of-the-art generative models, including GANs, diffusion models, and text-to-image models, and improving by 16.07% over the best baseline. Through t-SNE visualizations and KNN distance analysis, we provide insights into PDA’s effectiveness in separating real and fake images. Our work provides a flexible and effective solution for real-world fake image detection, advancing the generalization ability of detection systems.
生成模型的快速发展导致了高度逼真的AI生成图像的大量涌现,这给检测方法的通用性带来了重大挑战,因为生成技术多种多样且不断演变。现有方法往往无法适应未知模型,而无需进行昂贵的重新训练,从而限制了其实用性。为了填补这一空白,我们提出了事后分布对齐(PDA)方法,这是一种用于AI生成图像的可泛化检测的新方法。其核心思想是利用已知的生成模型对未分类的测试图像进行重新生成。这个过程将对重新生成的真实图像与已知伪造图像的分布进行对齐,从而实现从未知伪造图像的有效区分。PDA采用两步检测框架:首先评估测试图像是否与已知伪造分布对齐,基于深度k近邻(KNN)距离进行评估;然后利用已知生成模型对测试图像进行重新生成以创建伪造的伪图像用于进一步分类。这种对齐策略使得PDA能够检测伪造图像,无需依赖未见过的数据或重新训练。大量实验表明,PDA在六种最先进的生成模型上表现出卓越的性能,包括GANs、扩散模型和文本到图像模型,并且在平均准确度上较最佳基线提高了16.07%。通过t-SNE可视化和KNN距离分析,我们深入了解了PDA在区分真实和伪造图像方面的有效性。我们的工作提供了一种灵活有效的解决方案来解决现实生活中的伪造图像检测问题,提高了检测系统的泛化能力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
该文提出一种针对AI生成图像的可泛化检测方案,名为后处理分布对齐(PDA)。它使用已知的生成模型重新生成测试图像,并通过对齐真实图像的分布与已知虚假图像,实现对未知虚假图像的有效鉴别。该方法采用两步检测框架:首先基于深度k近邻距离评估测试图像是否与已知虚假分布相符;然后利用已知生成模型重新生成测试图像以创建伪虚假图像进行进一步分类。实验证明,PDA在六种先进的生成模型上平均准确率达到了96.73%,相较于最佳基线提高了16.07%。通过t-SNE可视化和KNN距离分析,揭示了PDA在区分真实和虚假图像方面的有效性。本研究为真实世界中的虚假图像检测提供了灵活有效的解决方案,提高了检测系统的泛化能力。
Key Takeaways
- PDA方法利用已知的生成模型重新生成测试图像,实现真实与虚假图像分布的对齐。
- PDA采用两步检测框架:基于深度k近邻距离评估图像与已知虚假分布的一致性,并通过再生图像进行分类。
- PDA在多种先进生成模型上表现出优异的检测性能,平均准确率高达96.73%。
- 与最佳基线相比,PDA的准确率提高了16.07%,显示出显著的优势。
- t-SNE可视化和KNN距离分析为PDA的有效性提供了深入的理解。
- PDA方法对于真实世界中的虚假图像检测具有实际应用价值。
点此查看论文截图


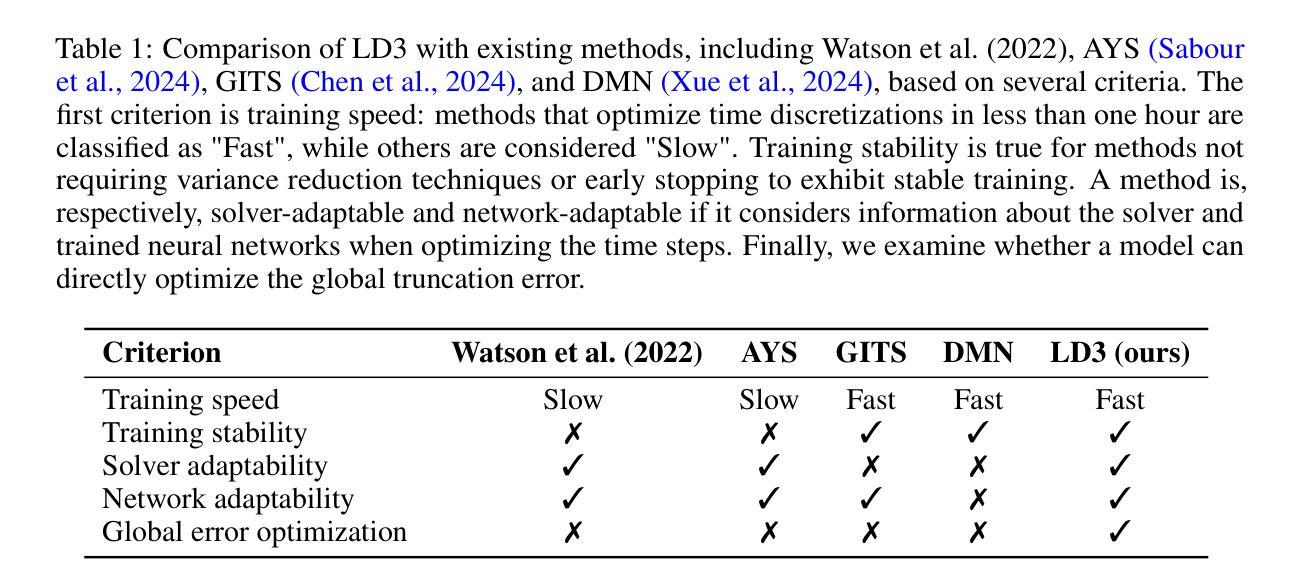
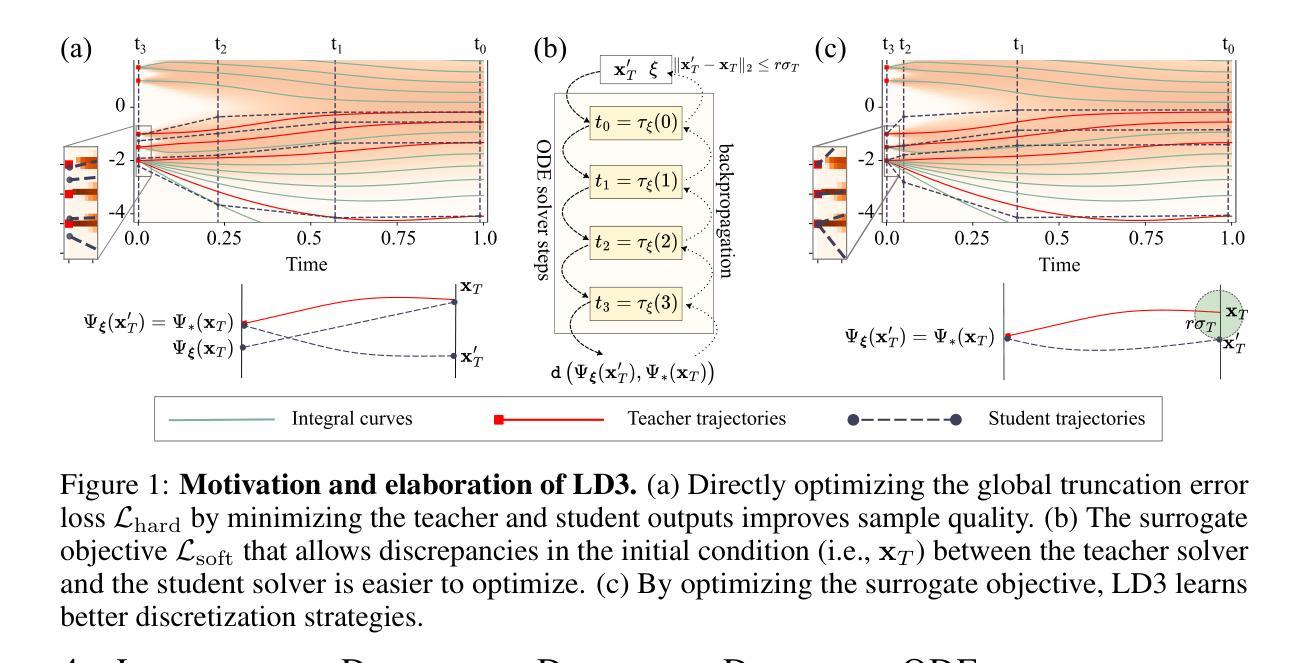
Learning to Discretize Denoising Diffusion ODEs
Authors:Vinh Tong, Trung-Dung Hoang, Anji Liu, Guy Van den Broeck, Mathias Niepert
Diffusion Probabilistic Models (DPMs) are generative models showing competitive performance in various domains, including image synthesis and 3D point cloud generation. Sampling from pre-trained DPMs involves multiple neural function evaluations (NFEs) to transform Gaussian noise samples into images, resulting in higher computational costs compared to single-step generative models such as GANs or VAEs. Therefore, reducing the number of NFEs while preserving generation quality is crucial. To address this, we propose LD3, a lightweight framework designed to learn the optimal time discretization for sampling. LD3 can be combined with various samplers and consistently improves generation quality without having to retrain resource-intensive neural networks. We demonstrate analytically and empirically that LD3 improves sampling efficiency with much less computational overhead. We evaluate our method with extensive experiments on 7 pre-trained models, covering unconditional and conditional sampling in both pixel-space and latent-space DPMs. We achieve FIDs of 2.38 (10 NFE), and 2.27 (10 NFE) on unconditional CIFAR10 and AFHQv2 in 5-10 minutes of training. LD3 offers an efficient approach to sampling from pre-trained diffusion models. Code is available at https://github.com/vinhsuhi/LD3.
扩散概率模型(DPMs)是一类在各种领域表现出竞争力的生成模型,包括图像合成和3D点云生成。从预训练的DPMs中进行采样,需要通过多次神经网络功能评估(NFEs)将高斯噪声样本转换为图像,这导致与一次性生成模型(如GANs或VAEs)相比,计算成本更高。因此,在保持生成质量的同时减少NFEs的数量至关重要。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了LD3,这是一个轻量级的框架,旨在学习采样的最佳时间离散化。LD3可以与各种采样器相结合,能够在不重新训练资源密集型的神经网络的情况下,持续提高生成质量。我们从分析和实证两个方面证明,LD3可以提高采样效率,同时大大降低计算开销。我们在7个预训练模型上进行了广泛实验,涵盖了像素空间和潜在空间的DPMs的无条件和有条件的采样。我们在无条件CIFAR10和AFHQv2上实现了FID为2.38(10 NFE)和2.27(10 NFE),在5-10分钟的训练时间内达到这一效果。LD3为从预训练的扩散模型中采样提供了一种高效的方法。代码可在https://github.com/vinhsuhi/LD3找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
DPM(扩散概率模型)是一种在各种领域表现出竞争性能的生成模型,但在采样过程中需要进行多次神经函数评估(NFE),导致计算成本较高。为解决这个问题,提出了LD3这一轻量级框架,旨在学习采样的最优时间离散化。LD3可与各种采样器结合,能在不重新训练资源密集型神经网络的情况下提高生成质量。经分析和实证,LD3能提高采样效率且计算开销较小。在7个预训练模型上进行实验,无条件与条件采样的DPMs在像素空间和潜在空间均取得良好效果。
Key Takeaways
- DPMs在图像合成和3D点云生成等领域展现出竞争力,但采样过程的计算成本较高。
- LD3框架旨在减少DPMs采样的神经函数评估次数(NFE),同时保持生成质量。
- LD3可与各种采样器结合使用,无需重新训练神经网络即可提高生成质量。
- LD3通过学习和优化时间离散化来提高采样效率。
- LD3在预训练模型上的实验表明,无条件与条件采样的DPMs在像素空间和潜在空间均取得良好效果。
- LD3方法能在短时间内(5-10分钟)达到良好的生成质量,如CIFAR10和AFHQv2的FID分别为2.38和2.27(10 NFE)。
点此查看论文截图

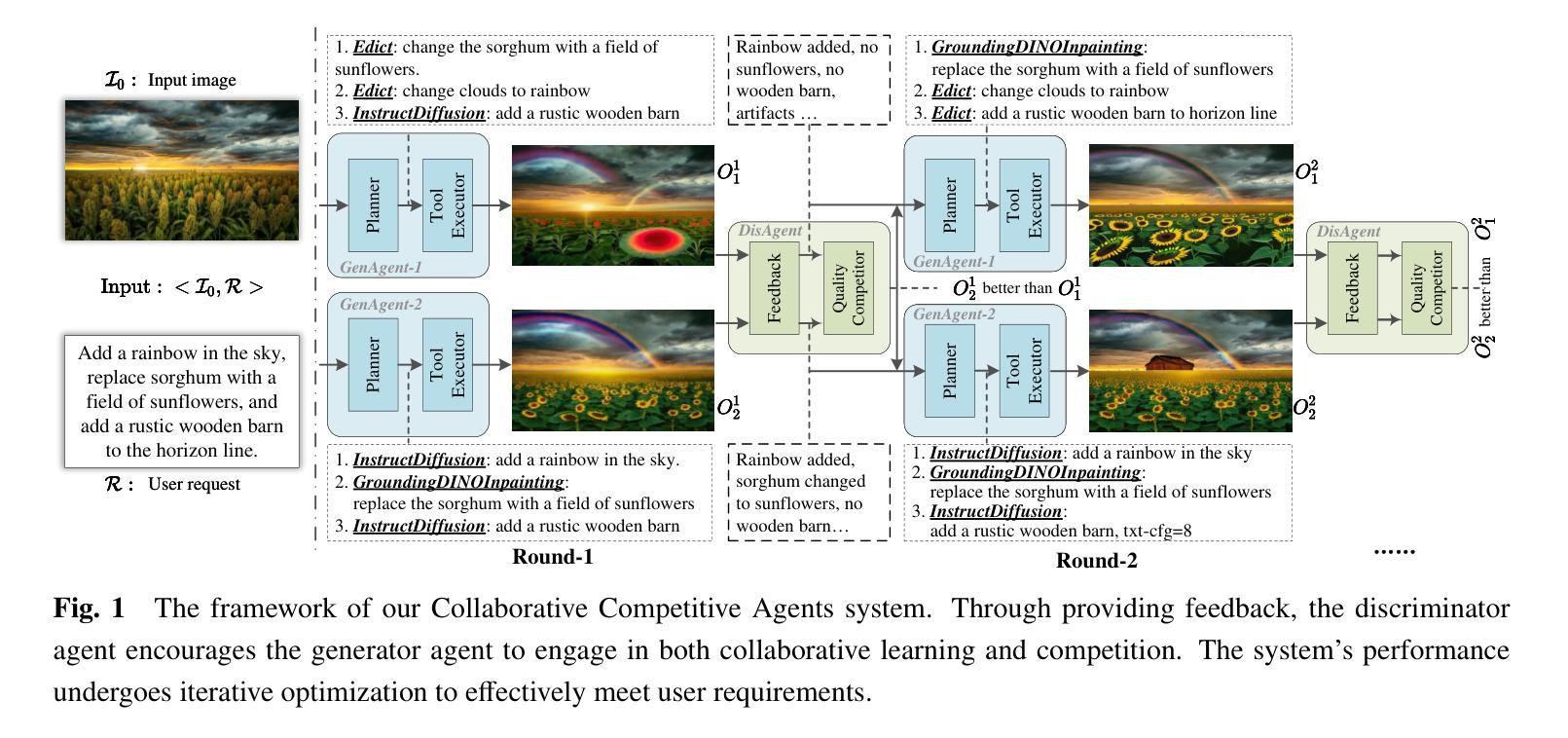
CCA: Collaborative Competitive Agents for Image Editing
Authors:Tiankai Hang, Shuyang Gu, Dong Chen, Xin Geng, Baining Guo
This paper presents a novel generative model, Collaborative Competitive Agents (CCA), which leverages the capabilities of multiple Large Language Models (LLMs) based agents to execute complex tasks. Drawing inspiration from Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs), the CCA system employs two equal-status generator agents and a discriminator agent. The generators independently process user instructions and generate results, while the discriminator evaluates the outputs, and provides feedback for the generator agents to further reflect and improve the generation results. Unlike the previous generative model, our system can obtain the intermediate steps of generation. This allows each generator agent to learn from other successful executions due to its transparency, enabling a collaborative competition that enhances the quality and robustness of the system’s results. The primary focus of this study is image editing, demonstrating the CCA’s ability to handle intricate instructions robustly. The paper’s main contributions include the introduction of a multi-agent-based generative model with controllable intermediate steps and iterative optimization, a detailed examination of agent relationships, and comprehensive experiments on image editing. Code is available at \href{https://github.com/TiankaiHang/CCA}{https://github.com/TiankaiHang/CCA}.
本文介绍了一种新型生成模型——协作竞争代理(CCA),该模型利用多个基于大型语言模型(LLM)的代理执行复杂任务的能力。该CCA系统从生成对抗网络(GANs)中汲取灵感,采用两个地位平等的生成器代理和一个判别器代理。生成器独立处理用户指令并生成结果,而判别器则评估输出,并为生成器代理提供反馈,以便进一步反思和改进生成结果。与传统的生成模型不同,我们的系统可以获得生成的中间步骤。这使得每个生成器代理都可以从其他成功的执行中学习,因其透明度而实现协作竞争,提高了系统结果的质量和稳健性。本研究的主要重点是图像编辑,展示了CCA在处理复杂指令方面的稳健能力。论文的主要贡献包括引入具有可控中间步骤和迭代优化的多代理生成模型、对代理关系的详细考察以及关于图像编辑的综合实验。代码可在https://github.com/TiankaiHang/CCA获得。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF The article has been accepted by Frontiers of Computer Science (FCS), with the DOI: {10.1007/s11704-025-41244-0}
Summary
该论文提出了一种新型生成模型——协作竞争代理(CCA),它利用多个基于大型语言模型(LLM)的代理执行复杂任务。该模型借鉴生成对抗网络(GANs)的思想,采用两个地位平等的生成器代理和一个判别器代理。生成器独立处理用户指令并生成结果,判别器评估输出结果为生成器代理提供反馈,以进一步反思和改进生成结果。与之前生成模型不同的是,该系统可获得生成的中间步骤,使得每个生成器代理能够学习其他成功执行的结果,通过其透明性实现协作竞争,提高系统结果的品质和稳健性。该研究主要关注图像编辑,展示了CCA在处理复杂指令时的强大能力。
Key Takeaways
- 引入了一种新型生成模型——协作竞争代理(CCA)。
- CCA利用多个大型语言模型(LLM)的代理来执行复杂任务。
- CCA借鉴生成对抗网络(GANs)的思想,包含两个生成器代理和一个判别器代理。
- 生成器能够独立处理用户指令并生成结果,判别器则评估这些结果并为生成器提供反馈。
- CCA系统能够获取生成的中间步骤,促进各生成器代理之间的学习和协作竞争。
- 该模型的透明性使得每个代理能够借鉴其他成功执行的结果,从而提高系统结果的品质和稳健性。
- 该研究主要关注图像编辑领域,展示了CCA在处理复杂指令时的强大能力。
点此查看论文截图