⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-02-19 更新
A Survey on Bridging EEG Signals and Generative AI: From Image and Text to Beyond
Authors:Shreya Shukla, Jose Torres, Abhijit Mishra, Jacek Gwizdka, Shounak Roychowdhury
Integration of Brain-Computer Interfaces (BCIs) and Generative Artificial Intelligence (GenAI) has opened new frontiers in brain signal decoding, enabling assistive communication, neural representation learning, and multimodal integration. BCIs, particularly those leveraging Electroencephalography (EEG), provide a non-invasive means of translating neural activity into meaningful outputs. Recent advances in deep learning, including Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) and Transformer-based Large Language Models (LLMs), have significantly improved EEG-based generation of images, text, and speech. This paper provides a literature review of the state-of-the-art in EEG-based multimodal generation, focusing on (i) EEG-to-image generation through GANs, Variational Autoencoders (VAEs), and Diffusion Models, and (ii) EEG-to-text generation leveraging Transformer based language models and contrastive learning methods. Additionally, we discuss the emerging domain of EEG-to-speech synthesis, an evolving multimodal frontier. We highlight key datasets, use cases, challenges, and EEG feature encoding methods that underpin generative approaches. By providing a structured overview of EEG-based generative AI, this survey aims to equip researchers and practitioners with insights to advance neural decoding, enhance assistive technologies, and expand the frontiers of brain-computer interaction.
脑机接口(BCIs)与生成式人工智能(GenAI)的融合为脑信号解码开辟了新的前沿领域,能够实现辅助通信、神经表征学习和多模式融合。特别是利用脑电图(EEG)的脑机接口为非侵入性地转换神经活动为有意义的输出提供了一种手段。深度学习领域的最新进展,包括生成对抗网络(GANs)和基于变压器的自然语言大型模型(LLMs),已经极大地提高了基于EEG的图像、文本和语音生成。本文综述了基于EEG的多模式生成的最新研究状况,重点关注(i)通过GANs、变分自动编码器(VAEs)和扩散模型实现的EEG到图像生成,(ii)利用基于变压器的语言模型和对比学习方法实现的EEG到文本生成。此外,我们还讨论了新兴的EEG到语音合成领域,这是一个不断发展的多模式前沿领域。本文强调了关键数据集、用例、挑战以及支撑生成方法的基础EEG特征编码方法。通过对基于EEG的生成式人工智能的结构性概述,本综述旨在为研究人员和实践者提供洞察力,以推动神经解码的发展,提高辅助技术的效能,并拓展脑机交互的边界。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
该论文探讨了脑机接口(BCIs)与生成式人工智能(GenAI)的融合,在脑信号解码方面开创了新的前沿领域。论文重点介绍了利用脑电图(EEG)的脑机接口,通过深度学习技术生成图像、文本和语音的应用。论文回顾了EEG基于多模态生成的研究现状,讨论了关键数据集、用例、挑战和EEG特征编码方法。旨在为研究人员和实践者提供洞察,以推动神经解码的发展,提高辅助技术的性能,并拓展脑机交互的边界。
Key Takeaways
- 脑机接口(BCIs)与生成式人工智能(GenAI)的融合为脑信号解码提供了新的机会。
- 利用脑电图(EEG)的脑机接口可实现非侵入式神经活动翻译。
- 深度学习技术,包括生成对抗网络(GANs)、基于Transformer的大型语言模型(LLMs)等,已显著改善EEG生成的图像、文本和语音的质量。
- EEG基于多模态生成的研究已成为热点,包括EEG转图像和EEG转文本生成。
- EEG转语音合成是一个新兴的多模态前沿领域。
- 论文回顾了关键数据集、用例、挑战和EEG特征编码方法,以提供对EEG基于生成式人工智能的深入理解。
点此查看论文截图

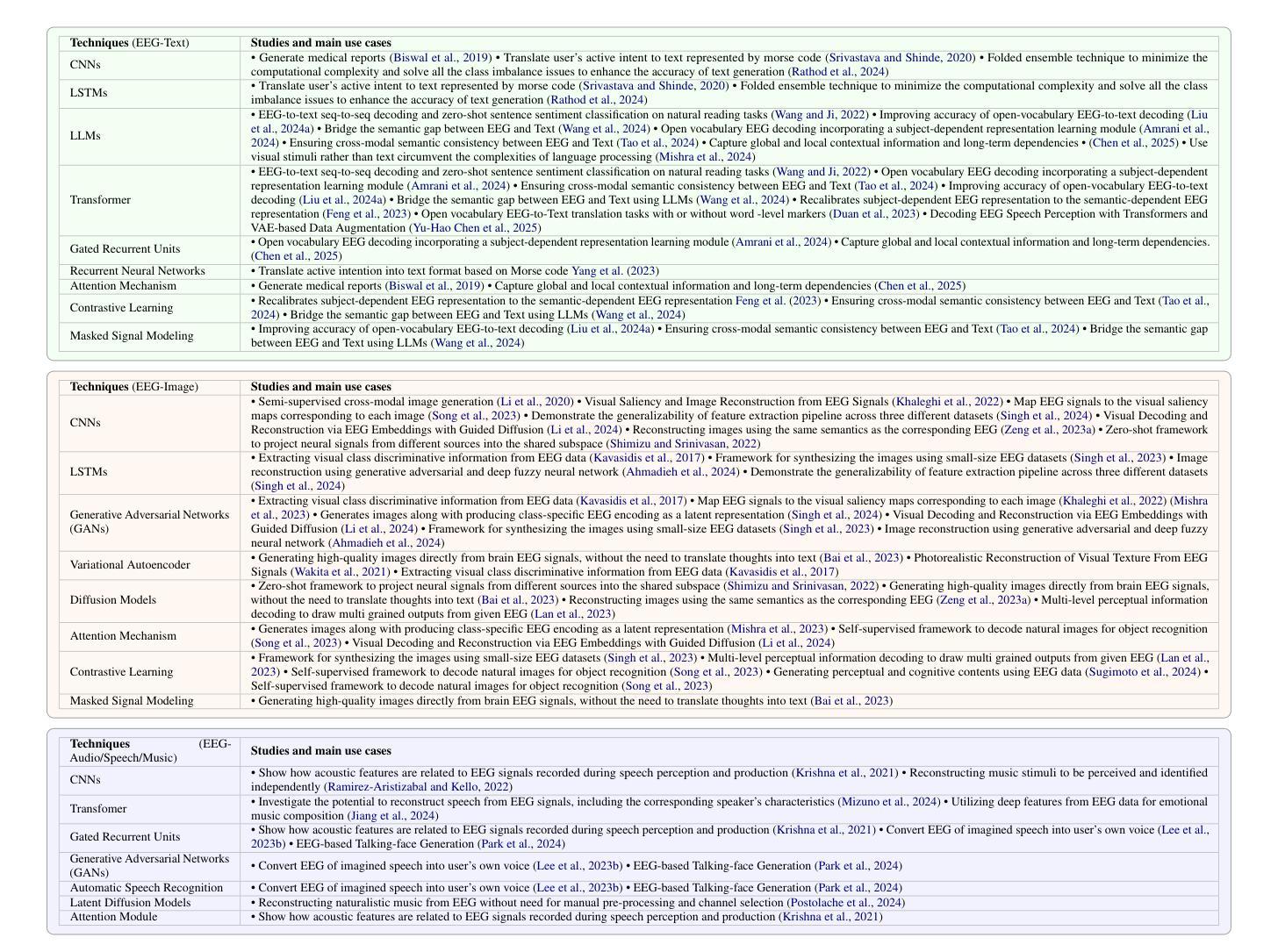
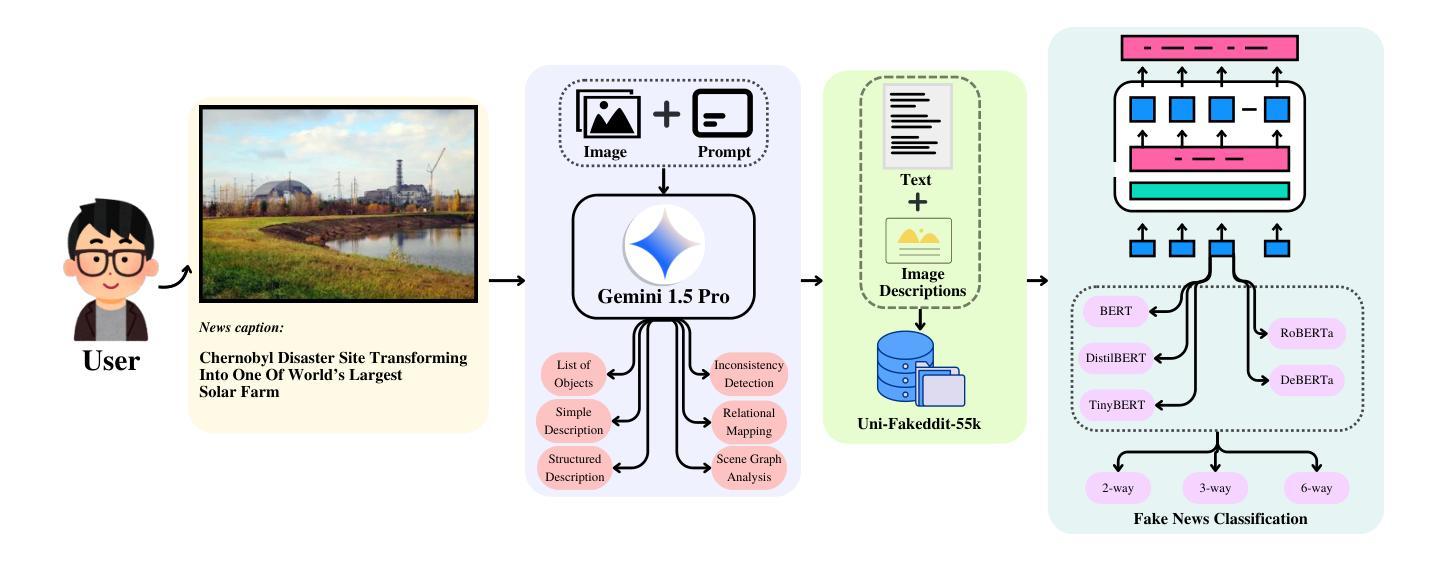
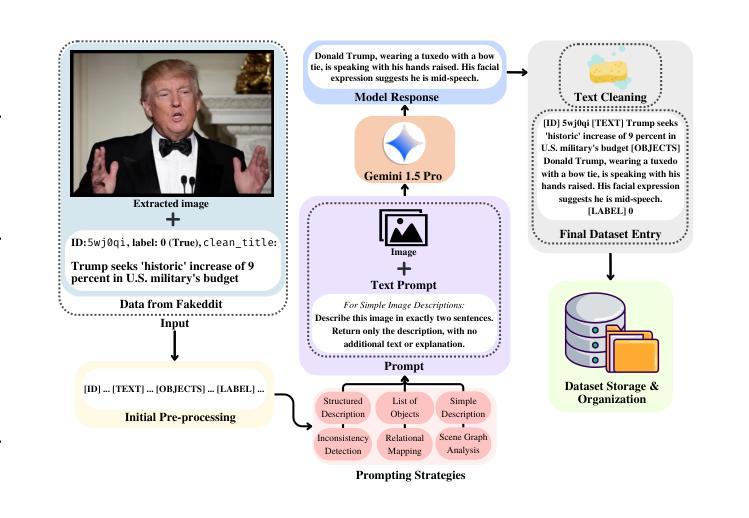
UNITE-FND: Reframing Multimodal Fake News Detection through Unimodal Scene Translation
Authors:Arka Mukherjee, Shreya Ghosh
Multimodal fake news detection typically demands complex architectures and substantial computational resources, posing deployment challenges in real-world settings. We introduce UNITE-FND, a novel framework that reframes multimodal fake news detection as a unimodal text classification task. We propose six specialized prompting strategies with Gemini 1.5 Pro, converting visual content into structured textual descriptions, and enabling efficient text-only models to preserve critical visual information. To benchmark our approach, we introduce Uni-Fakeddit-55k, a curated dataset family of 55,000 samples each, each processed through our multimodal-to-unimodal translation framework. Experimental results demonstrate that UNITE-FND achieves 92.52% accuracy in binary classification, surpassing prior multimodal models while reducing computational costs by over 10x (TinyBERT variant: 14.5M parameters vs. 250M+ in SOTA models). Additionally, we propose a comprehensive suite of five novel metrics to evaluate image-to-text conversion quality, ensuring optimal information preservation. Our results demonstrate that structured text-based representations can replace direct multimodal processing with minimal loss of accuracy, making UNITE-FND a practical and scalable alternative for resource-constrained environments.
多模态虚假新闻检测通常需要复杂的架构和大量的计算资源,这在现实世界的部署中构成了挑战。我们引入了UNITE-FND,这是一个将多模态虚假新闻检测重新定位为单模态文本分类任务的新型框架。我们提出了六种专业的提示策略与双子座1.5专业版相结合,将视觉内容转换为结构化文本描述,使文本模型能够高效保存关键视觉信息。为了对我们的方法进行基准测试,我们引入了Uni-Fakeddit-55k数据集家族,包含经过我们多模态到单模态翻译框架处理的每个样本为55000个样本的数据集。实验结果表明,UNITE-FND在二分类中的准确度达到了92.52%,超越了先前的多模态模型,并将计算成本降低了超过十倍(TinyBERT变体:参数为14.5M与SOTA模型中的超过2.5亿相比)。此外,我们还提出了一个综合的五个新指标来评估图像到文本的转换质量,确保信息的最佳保存。我们的结果表明,基于结构化文本的表示可以替代直接的多模态处理而不会产生显著的精度损失,这使得UNITE-FND成为资源受限环境的实用且可扩展的替代方案。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 28 pages, 16 figures
Summary
多媒体假新闻检测通常要求复杂的架构和大量的计算资源,这对真实环境中的部署提出了挑战。我们推出了UNITE-FND,这是一种将多媒体假新闻检测重新定位为单模态文本分类任务的新框架。通过六种专门的提示策略和Gemini 1.5 Pro,我们将视觉内容转换为结构化文本描述,使文本模型能够保留关键视觉信息。为了评估我们的方法,我们引入了Uni-Fakeddit-55k数据集,包含55000个样本,每个样本都通过我们的多媒体到单模态翻译框架进行处理。实验结果表明,UNITE-FND在二元分类中达到了92.52%的准确率,超越了先前的多媒体模型,同时降低了超过10倍的计算成本。此外,我们还提出了一个综合的五种新型指标来评估图像到文本的转换质量,确保最优的信息保留。我们的研究结果表明,基于结构化文本的表示可以替代直接的多模态处理,且不会造成显著的精度损失,这使得UNITE-FND成为资源受限环境中的实用和可扩展的替代方案。
Key Takeaways
- UNITE-FND框架将多媒体假新闻检测重新定位为单模态文本分类任务,简化了检测过程。
- 提出了六种专门的提示策略,将视觉内容转换为结构化文本描述,便于文本模型处理。
- 引入了Uni-Fakeddit-55k数据集,用于评估多媒体到单模态翻译框架的性能。
- UNITE-FND在二元分类中实现了高准确率(92.52%),同时显著降低了计算成本。
- 与现有模型相比,UNITE-FND的计算成本降低了10倍以上,具有更好的实用性。
- 提出了五种新型指标来评估图像到文本的转换质量,确保信息保留的完整性。
点此查看论文截图

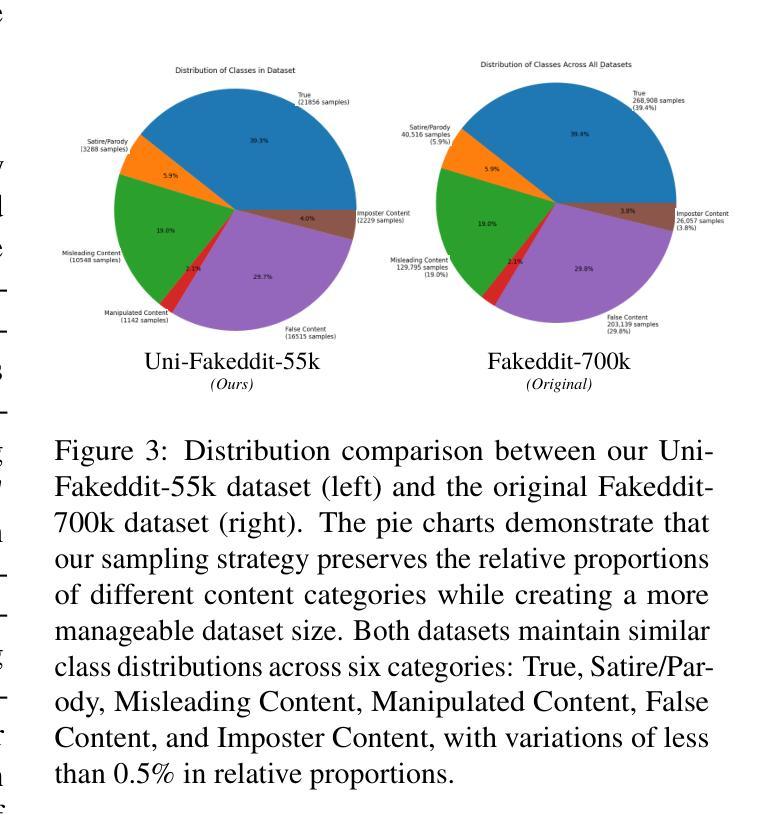

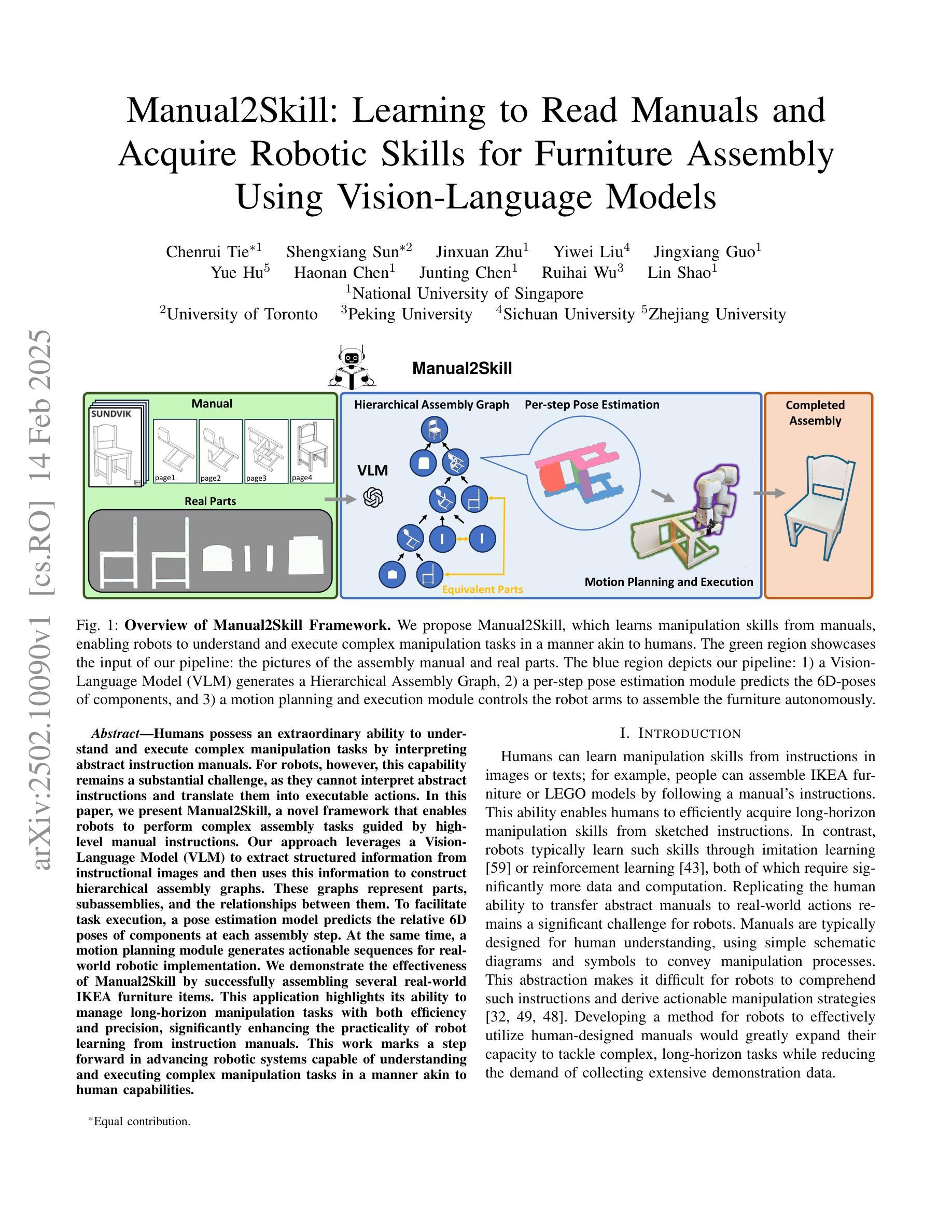
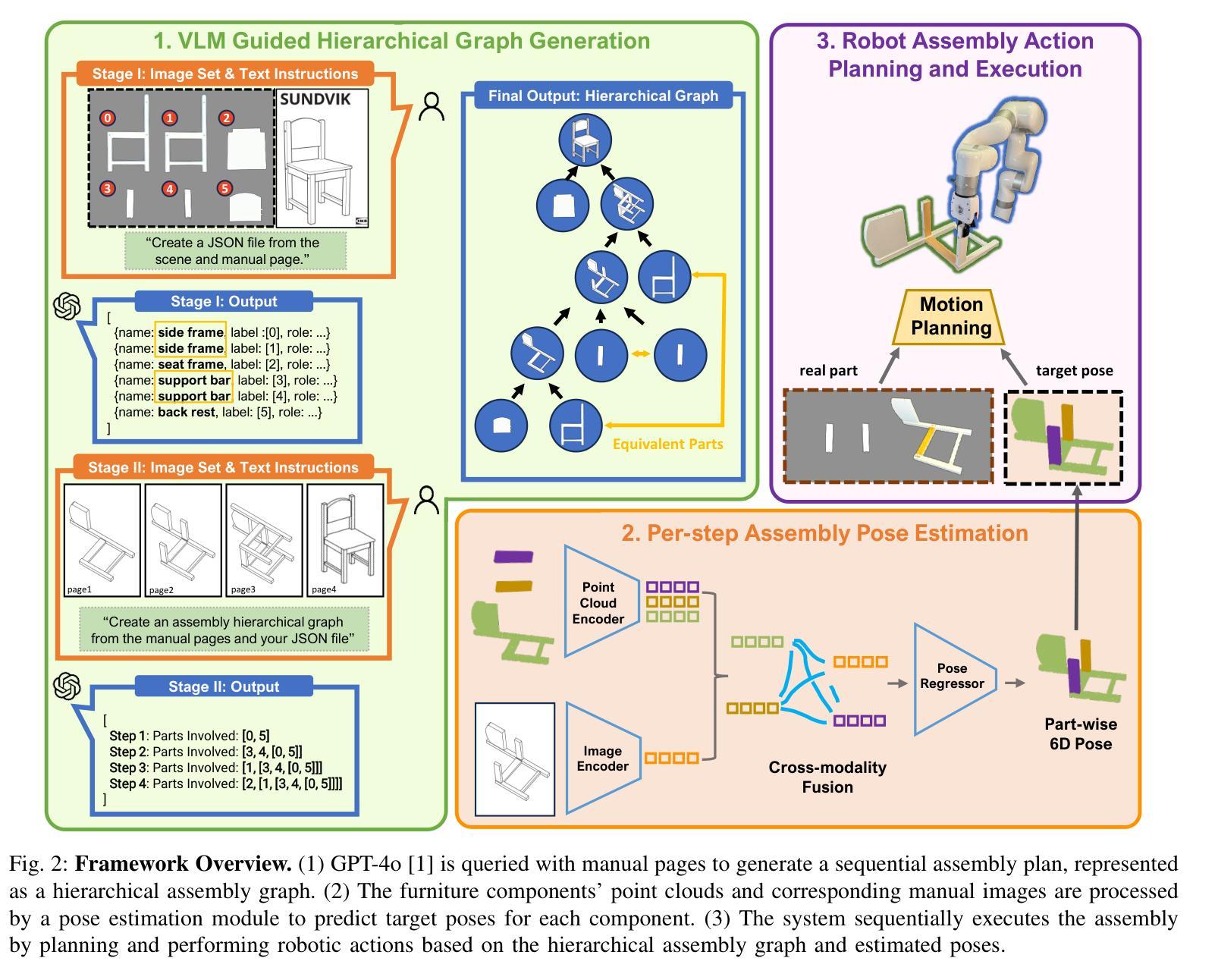
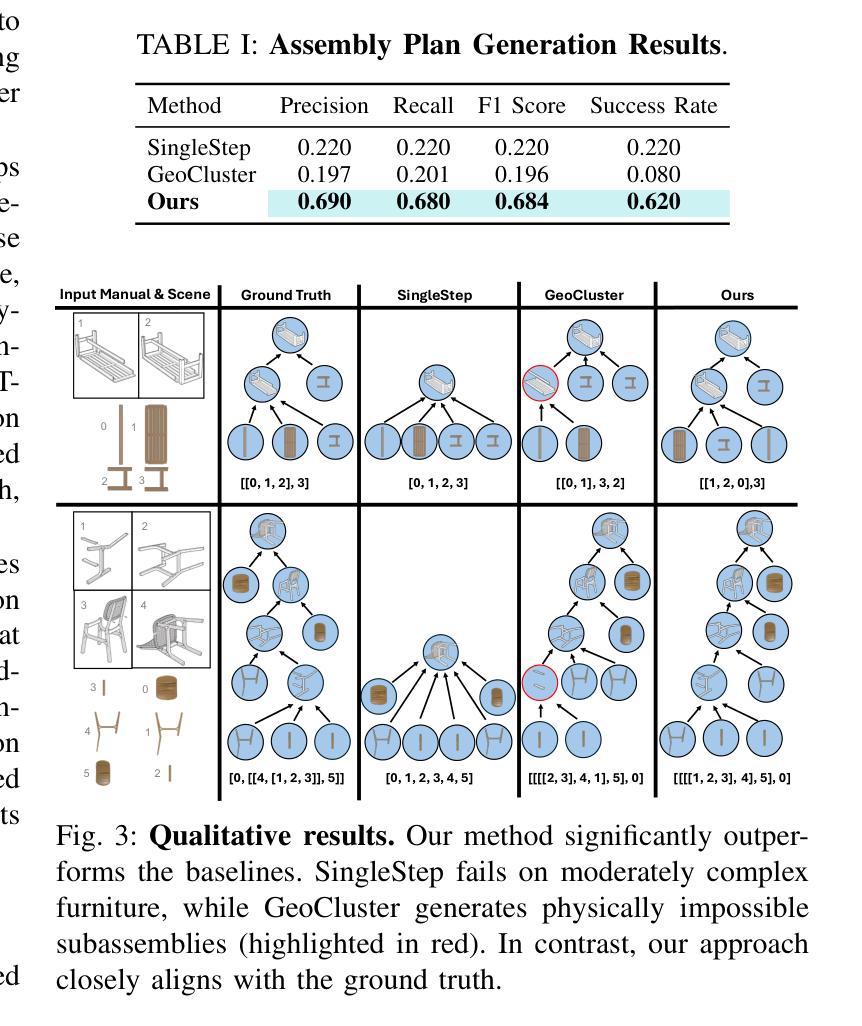
Manual2Skill: Learning to Read Manuals and Acquire Robotic Skills for Furniture Assembly Using Vision-Language Models
Authors:Chenrui Tie, Shengxiang Sun, Jinxuan Zhu, Yiwei Liu, Jingxiang Guo, Yue Hu, Haonan Chen, Junting Chen, Ruihai Wu, Lin Shao
Humans possess an extraordinary ability to understand and execute complex manipulation tasks by interpreting abstract instruction manuals. For robots, however, this capability remains a substantial challenge, as they cannot interpret abstract instructions and translate them into executable actions. In this paper, we present Manual2Skill, a novel framework that enables robots to perform complex assembly tasks guided by high-level manual instructions. Our approach leverages a Vision-Language Model (VLM) to extract structured information from instructional images and then uses this information to construct hierarchical assembly graphs. These graphs represent parts, subassemblies, and the relationships between them. To facilitate task execution, a pose estimation model predicts the relative 6D poses of components at each assembly step. At the same time, a motion planning module generates actionable sequences for real-world robotic implementation. We demonstrate the effectiveness of Manual2Skill by successfully assembling several real-world IKEA furniture items. This application highlights its ability to manage long-horizon manipulation tasks with both efficiency and precision, significantly enhancing the practicality of robot learning from instruction manuals. This work marks a step forward in advancing robotic systems capable of understanding and executing complex manipulation tasks in a manner akin to human capabilities.
人类拥有一种非凡的能力,可以通过解读抽象说明书来理解和执行复杂的操作任务。然而,对于机器人来说,这一能力仍然是一个巨大的挑战,因为它们无法解读抽象指令并将其转化为可执行的行动。在本文中,我们提出了Manual2Skill这一新型框架,使机器人能够在高级手册指令的引导下完成复杂的装配任务。我们的方法利用视觉语言模型(VLM)从教学图像中提取结构信息,然后使用这些信息来构建层次化的装配图。这些图代表了部件、子组件和它们之间的关系。为了促进任务执行,姿态估计模型预测了每个装配步骤中组件的6D相对姿态。同时,运动规划模块为现实世界的机器人实现生成可操作序列。我们通过成功组装几个现实世界的宜家家具产品来证明Manual2Skill的有效性。这一应用凸显了其在长周期操作任务中的效率和精确度,显著提高了机器人从说明书学习的实用性。这项工作标志着机器人系统在理解和执行复杂操作任务方面的能力向前迈进了一步,以一种类似于人类能力的方式。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
机器人执行复杂操作任务的能力一直是其面临的一大挑战,特别是它们无法解读抽象指令并将其转化为可执行动作。本文提出了Manual2Skill框架,使机器人能够依据高级手册指令执行复杂的装配任务。该框架通过视觉语言模型从教学图像中提取结构化信息,构建层次化的装配图,展示部件、子组件及其关系。同时,姿态估计模型预测每个装配步骤中组件的6D相对姿态,运动规划模块则生成可用于实际机器人操作的行动序列。通过成功装配宜家家具等实例,展示了Manual2Skill在管理和执行长期操作任务中的高效性和精确度,显著提高了机器人从说明书学习的实用性。本研究标志着机器人在理解和执行复杂操作任务方面取得了进展,与人类能力相媲美。
Key Takeaways
- 机器人执行复杂操作任务是一大挑战,无法直接解读抽象指令。
- Manual2Skill框架使机器人能够依据高级手册指令执行复杂的装配任务。
- Manual2Skill通过视觉语言模型从教学图像中提取结构化信息。
- 姿态估计模型和运动规划模块共同促进任务执行。
- 通过成功装配宜家家具,展示了Manual2Skill的高效性和精确度。
- Manual2Skill增强了机器人从说明书学习的实用性。
点此查看论文截图
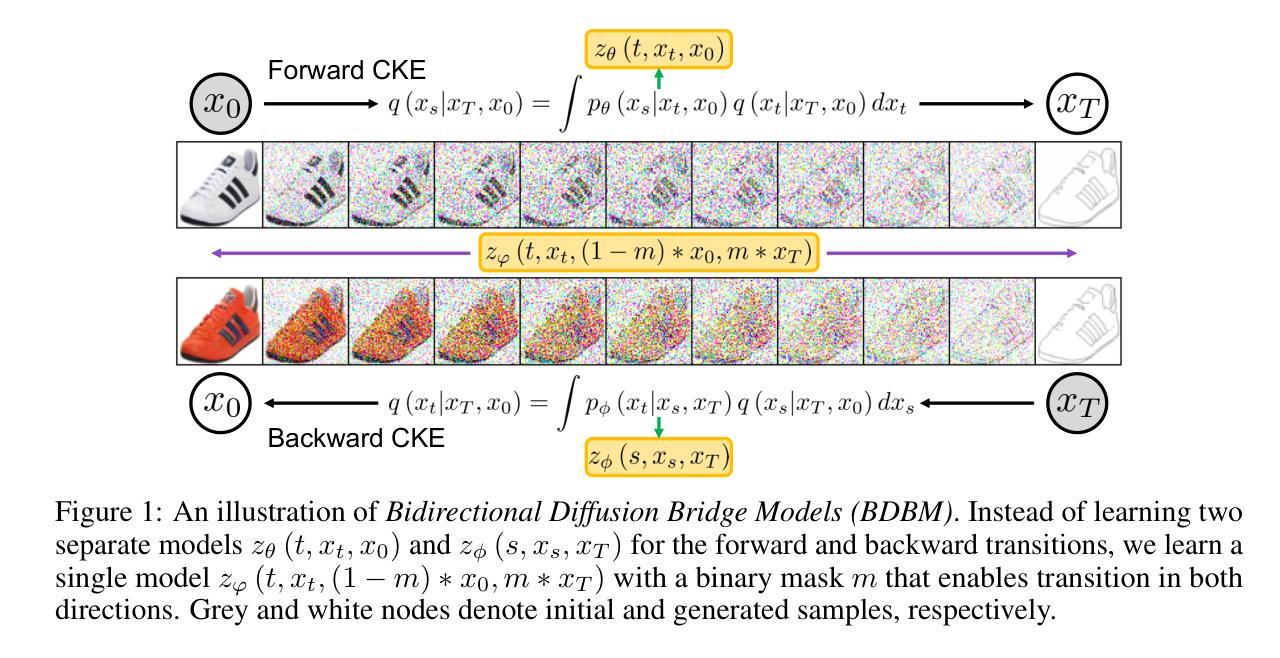
Bidirectional Diffusion Bridge Models
Authors:Duc Kieu, Kien Do, Toan Nguyen, Dang Nguyen, Thin Nguyen
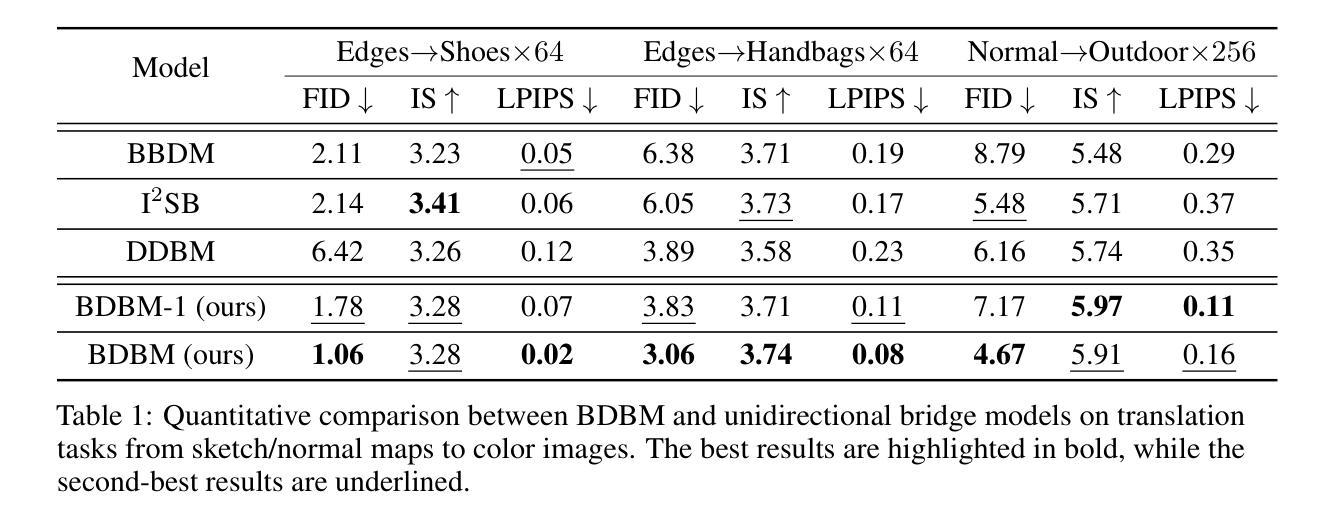
Diffusion bridges have shown potential in paired image-to-image (I2I) translation tasks. However, existing methods are limited by their unidirectional nature, requiring separate models for forward and reverse translations. This not only doubles the computational cost but also restricts their practicality. In this work, we introduce the Bidirectional Diffusion Bridge Model (BDBM), a scalable approach that facilitates bidirectional translation between two coupled distributions using a single network. BDBM leverages the Chapman-Kolmogorov Equation for bridges, enabling it to model data distribution shifts across timesteps in both forward and backward directions by exploiting the interchangeability of the initial and target timesteps within this framework. Notably, when the marginal distribution given endpoints is Gaussian, BDBM’s transition kernels in both directions possess analytical forms, allowing for efficient learning with a single network. We demonstrate the connection between BDBM and existing bridge methods, such as Doob’s h-transform and variational approaches, and highlight its advantages. Extensive experiments on high-resolution I2I translation tasks demonstrate that BDBM not only enables bidirectional translation with minimal additional cost but also outperforms state-of-the-art bridge models. Our source code is available at [https://github.com/kvmduc/BDBM||https://github.com/kvmduc/BDBM].
扩散桥在配对图像到图像(I2I)翻译任务中显示出潜力。然而,现有方法受到其单向性质的限制,需要单独的模型进行正向和反向翻译。这不仅使计算成本翻倍,而且限制了它们的实用性。在这项工作中,我们引入了双向扩散桥模型(BDBM),这是一种可扩展的方法,使用一个网络实现两个耦合分布之间的双向翻译。BDBM利用Chapman-Kolmogorov方程构建桥梁,能够在框架内初始和目标时间点互换,以在两个方向上建模数据分布变化的时序迁移。值得注意的是,当给定端点的边缘分布为高斯分布时,BDBM在双向的转换内核具有分析形式,允许使用单个网络进行有效学习。我们展示了BDBM与现有桥梁方法(如Doob的h变换和变分方法)之间的联系,并强调了其优势。在高分辨率I2I翻译任务上的大量实验表明,BDBM不仅实现了双向翻译且几乎没有额外的成本,而且还优于最新的桥梁模型。我们的源代码可在https://github.com/kvmduc/BDBM访问。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Source code: https://github.com/kvmduc/BDBM
Summary
本文介绍了双向扩散桥梁模型(BDBM),该模型可实现两个耦合分布之间的双向翻译,且仅使用一个网络。它利用Chapman-Kolmogorov方程构建桥梁,能在前后方向上模拟数据分布的时间步移,并通过此框架内初始和目标时间步的互换性来实现。当给定端点的边际分布为高斯分布时,BDBM在双向的过渡核具有解析形式,使得单网络的学习更为高效。实验证明,BDBM在图像到图像(I2I)翻译任务上表现优异,不仅实现了双向翻译且成本增加极小,还优于现有桥梁模型。
Key Takeaways
- BDBM模型可以实现两个耦合分布之间的双向翻译,并仅使用一个网络。
- BDBM利用Chapman-Kolmogorov方程构建桥梁,实现前后方向上的数据分布时间步移模拟。
- 当边际分布为高斯分布时,BDBM的过渡核具有解析形式,提高学习效率。
- BDBM与现有的桥梁方法如Doob的h-transform和变分方法有联系。
- BDBM在图像到图像(I2I)翻译任务上表现优异。
- BDBM实现了双向翻译且成本增加极小。
点此查看论文截图

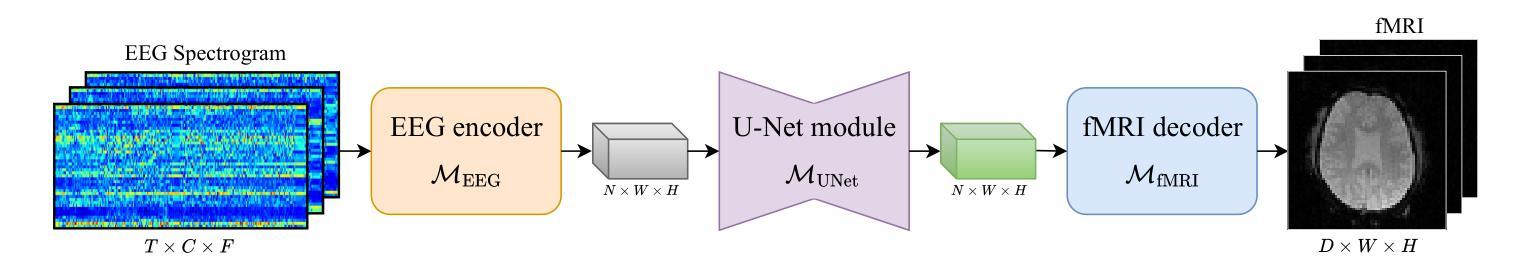
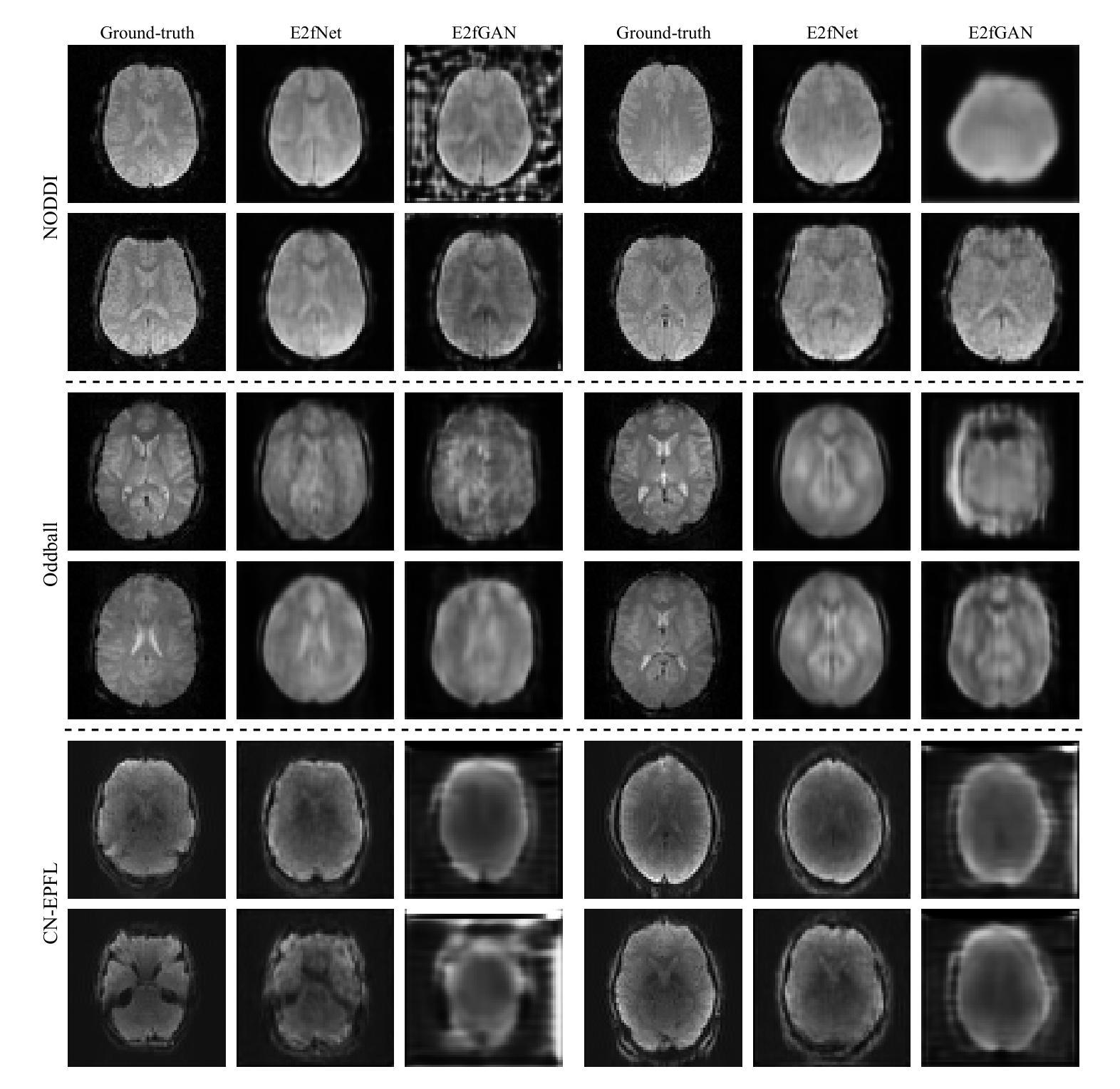
From Brainwaves to Brain Scans: A Robust Neural Network for EEG-to-fMRI Synthesis
Authors:Kristofer Grover Roos, Atsushi Fukuda, Quan Huu Cap
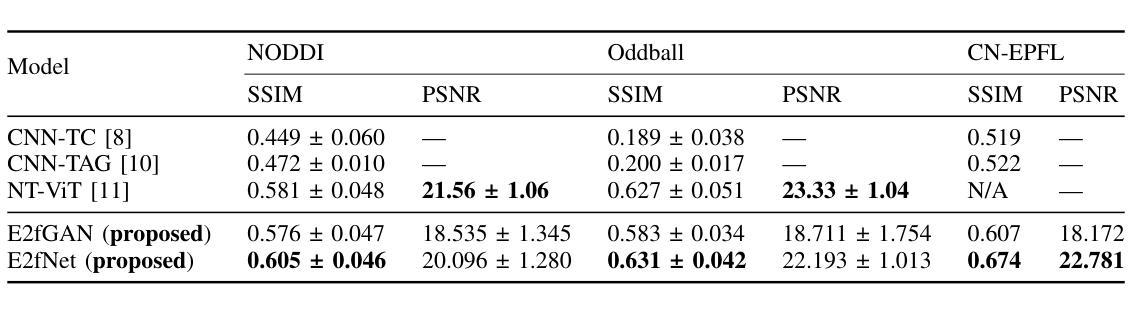
While functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) offers rich spatial resolution, it is limited by high operational costs and significant infrastructural demands. In contrast, electroencephalography (EEG) provides millisecond-level precision in capturing electrical activity but lacks the spatial resolution necessary for precise neural localization. To bridge these gaps, we introduce E2fNet, a simple yet effective deep learning model for synthesizing fMRI images from low-cost EEG data. E2fNet is specifically designed to capture and translate meaningful features from EEG across electrode channels into accurate fMRI representations. Extensive evaluations across three datasets demonstrate that E2fNet consistently outperforms existing methods, achieving state-of-the-art results in terms of the structural similarity index measure (SSIM). Our findings suggest that E2fNet is a promising, cost-effective solution for enhancing neuroimaging capabilities. The code is available at https://github.com/kgr20/E2fNet.
功能磁共振成像(fMRI)虽然提供了丰富的空间分辨率,但由于操作成本高和对基础设施的巨大需求而受到限制。相比之下,脑电图(EEG)在捕捉电活动方面提供了毫秒级的精确度,但缺乏精确神经定位所需的空间分辨率。为了弥补这些差距,我们引入了E2fNet,这是一个简单有效的深度学习模型,可以从低成本的EEG数据中合成fMRI图像。E2fNet专门设计用于捕获和翻译EEG跨电极通道的有意义特征,转化为准确的fMRI表示。在三个数据集上的广泛评估表明,E2fNet始终优于现有方法,在结构相似性指数度量(SSIM)方面达到最新结果。我们的研究结果表明,E2fNet是一个有前景的、经济实惠的解决方案,可增强神经成像能力。代码可在https://github.com/kgr20/E2fNet找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:
EEG与fMRI融合研究取得突破,通过深度学习模型E2fNet实现从低成本EEG数据合成fMRI图像。E2fNet设计精巧,能有效捕捉EEG数据中的有意义特征并转化为准确的fMRI表示。评估显示其表现超越现有方法,具有成为增强神经影像学能力的潜力且经济实惠。代码已公开分享。
Key Takeaways:
- E2fNet是一个深度学习模型,旨在解决低成本EEG数据与富空间分辨率的fMRI图像之间的差距。
- E2fNet可以从EEG数据中捕捉有意义特征并将其转化为fMRI图像表示。
- 通过在三组数据集上的评估,E2fNet在结构相似性指数度量(SSIM)方面达到了业界最佳表现。
- E2fNet表现超越现有方法,有望为神经影像学提供更经济高效的解决方案。
- 该模型能够实现精准的神经定位并丰富空间分辨率。
- 模型可以通过公开的GitHub仓库获得并应用于进一步研究和实际应用中。
点此查看论文截图

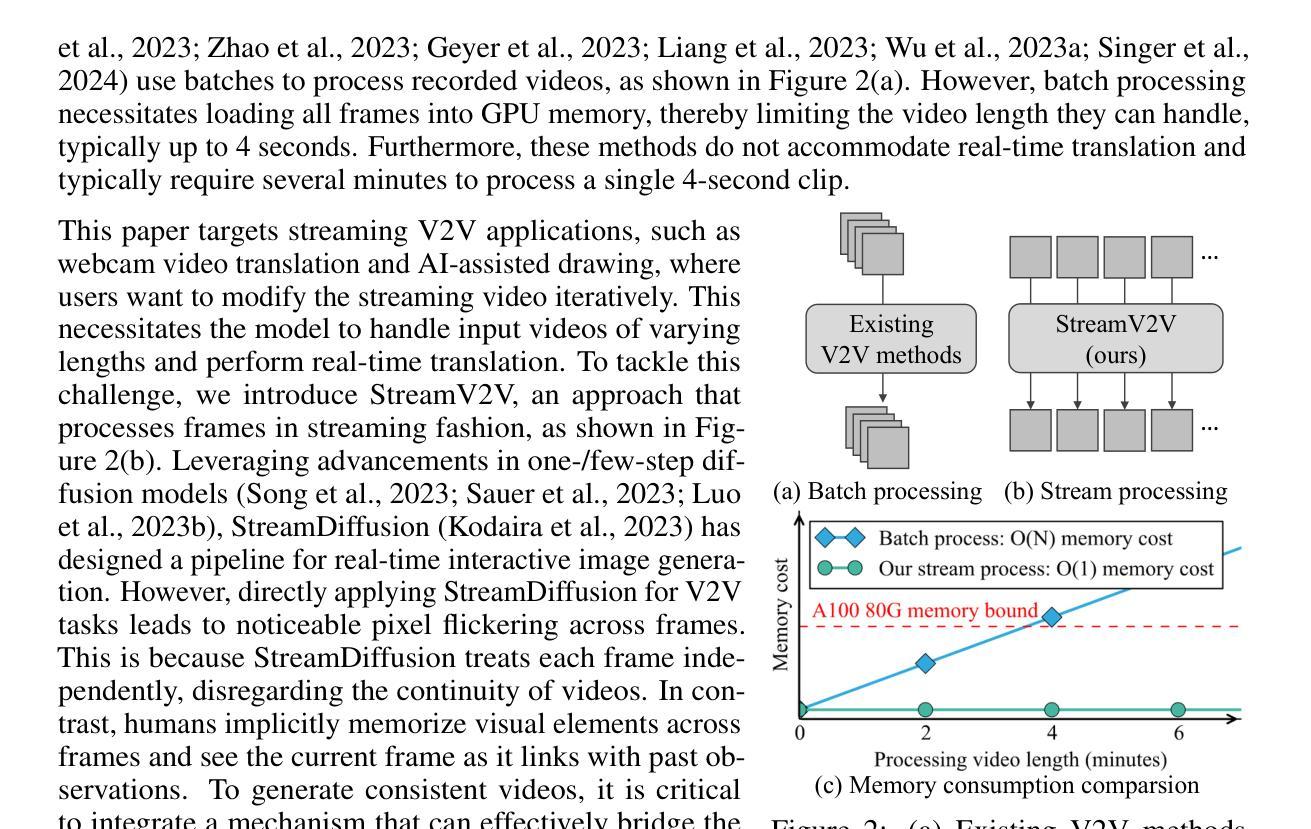
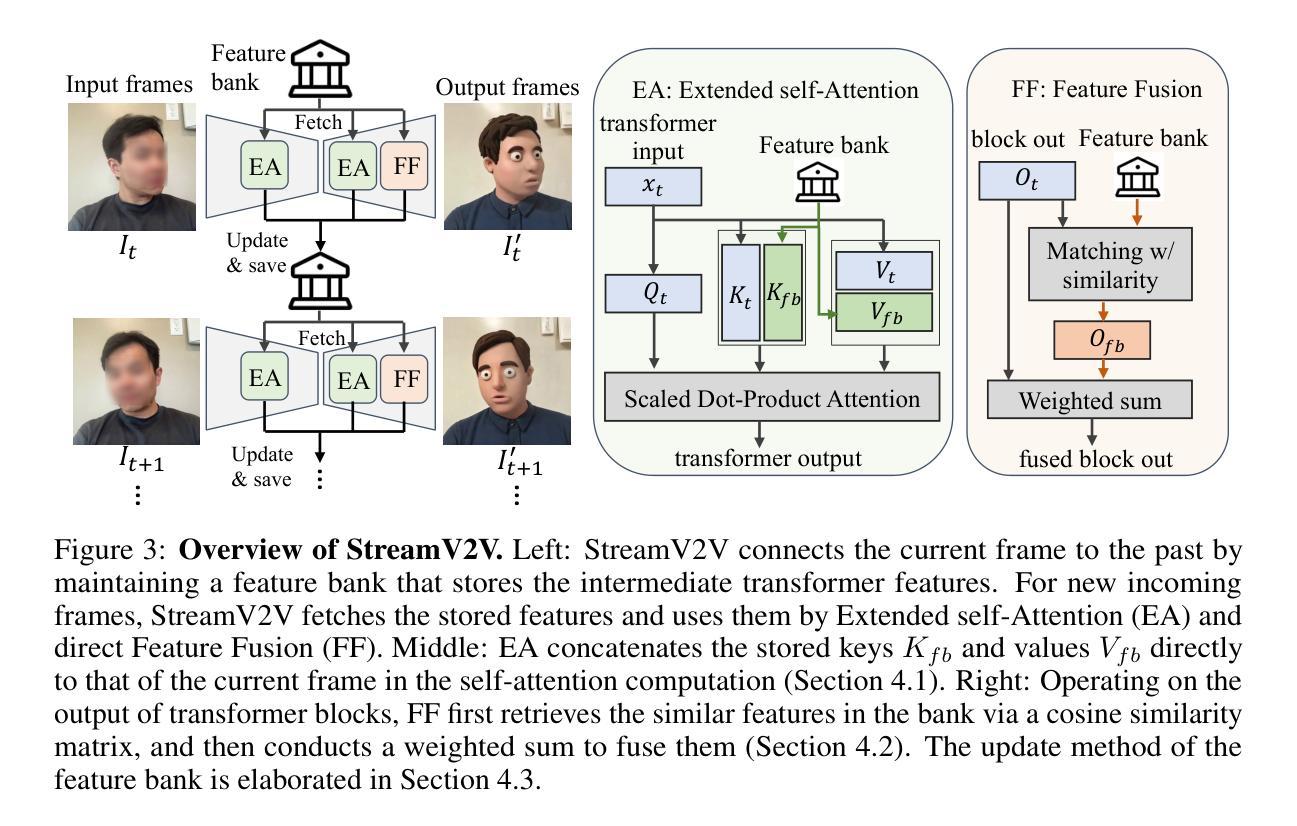
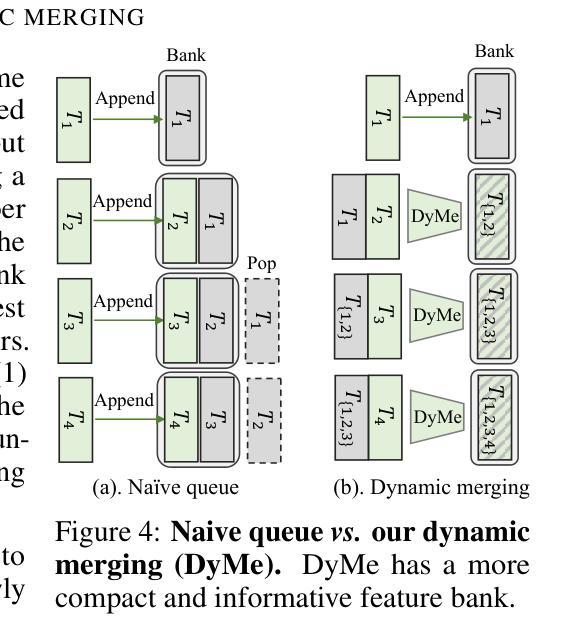
Looking Backward: Streaming Video-to-Video Translation with Feature Banks
Authors:Feng Liang, Akio Kodaira, Chenfeng Xu, Masayoshi Tomizuka, Kurt Keutzer, Diana Marculescu
This paper introduces StreamV2V, a diffusion model that achieves real-time streaming video-to-video (V2V) translation with user prompts. Unlike prior V2V methods using batches to process limited frames, we opt to process frames in a streaming fashion, to support unlimited frames. At the heart of StreamV2V lies a backward-looking principle that relates the present to the past. This is realized by maintaining a feature bank, which archives information from past frames. For incoming frames, StreamV2V extends self-attention to include banked keys and values and directly fuses similar past features into the output. The feature bank is continually updated by merging stored and new features, making it compact but informative. StreamV2V stands out for its adaptability and efficiency, seamlessly integrating with image diffusion models without fine-tuning. It can run 20 FPS on one A100 GPU, being 15x, 46x, 108x, and 158x faster than FlowVid, CoDeF, Rerender, and TokenFlow, respectively. Quantitative metrics and user studies confirm StreamV2V’s exceptional ability to maintain temporal consistency.
本文介绍了StreamV2V,这是一种扩散模型,通过用户提示实现实时流式视频到视频(V2V)的翻译。不同于之前使用批次处理有限帧的V2V方法,我们选择以流式方式处理帧,以支持无限帧。StreamV2V的核心在于一个后顾原则,将现在与过去联系起来。这是通过维护一个特征银行来实现的,该银行存档过去帧的信息。对于传入帧,StreamV2V将自注意力扩展到包括银行密钥和值,并直接将相似的过去特征融合到输出中。特征银行通过合并存储的新特征来不断更新,使其紧凑而富有信息。StreamV2V以其适应性和效率而脱颖而出,无需微调即可无缝集成到图像扩散模型中。它可以在一个A100 GPU上以每秒20帧的速度运行,比FlowVid、CoDeF、Rerender和TokenFlow分别快15倍、46倍、108倍和158倍。定量指标和用户研究证实了StreamV2V在保持时间一致性方面的出色能力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICLR 2025. Project page: https://jeff-liangf.github.io/projects/streamv2v
Summary
本文提出了StreamV2V模型,这是一个基于扩散的视频转视频(V2V)实时翻译模型,通过用户提示实现。与传统的批处理方式的V2V方法不同,StreamV2V采用流式处理方式支持无限帧数的处理。其核心原理是利用向后观察原则将当前与过去相联系,通过维护特征库存储过去帧的信息。对于新进入的帧,StreamV2V扩展了自注意力机制,包括存储的关键字和值,并将相似的过去特征直接融合到输出中。该特征库通过合并存储的新特征不断更新,使其紧凑且信息丰富。StreamV2V具有适应性和效率,可无缝集成图像扩散模型而无需微调。它在A100 GPU上的运行速度为每秒20帧,相较于其他模型有显著的速度优势。其卓越的临时一致性能力得到了定量指标和用户研究的证实。
Key Takeaways
- StreamV2V是一个实时视频转视频翻译模型,支持无限帧处理。
- 采用流式处理方法,维护一个特征库存储过去帧的信息。
- 利用向后观察原则将当前与过去相联系。
- 扩展自注意力机制以包括存储的关键字和值,融合相似的过去特征到输出中。
- 特征库通过合并新旧特征不断更新,保持紧凑且信息丰富。
- StreamV2V适应性强、效率高,可无缝集成图像扩散模型。
点此查看论文截图

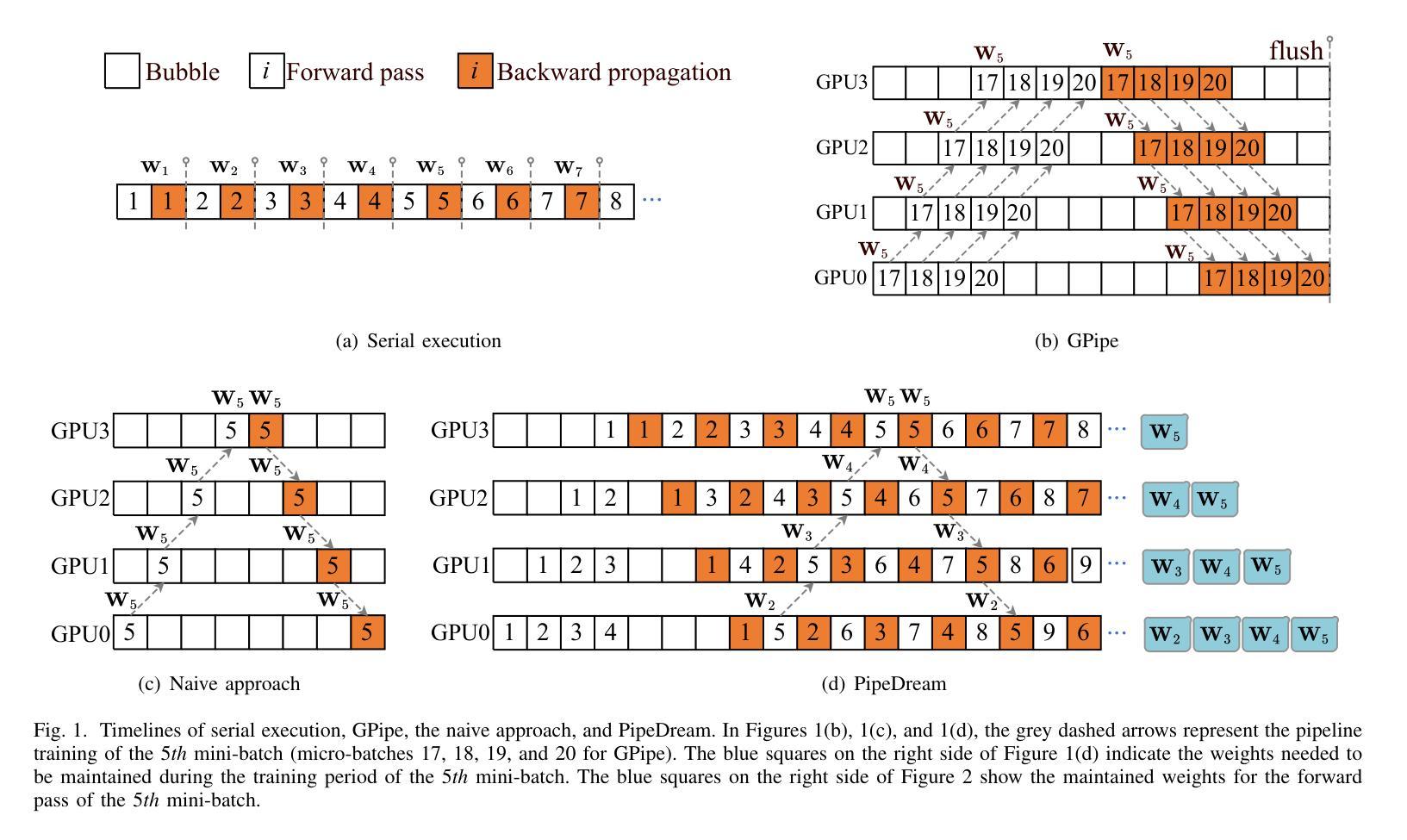
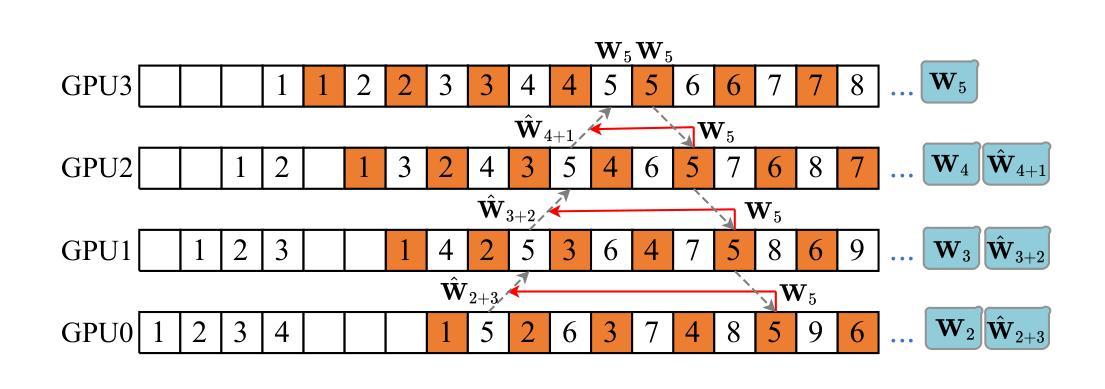
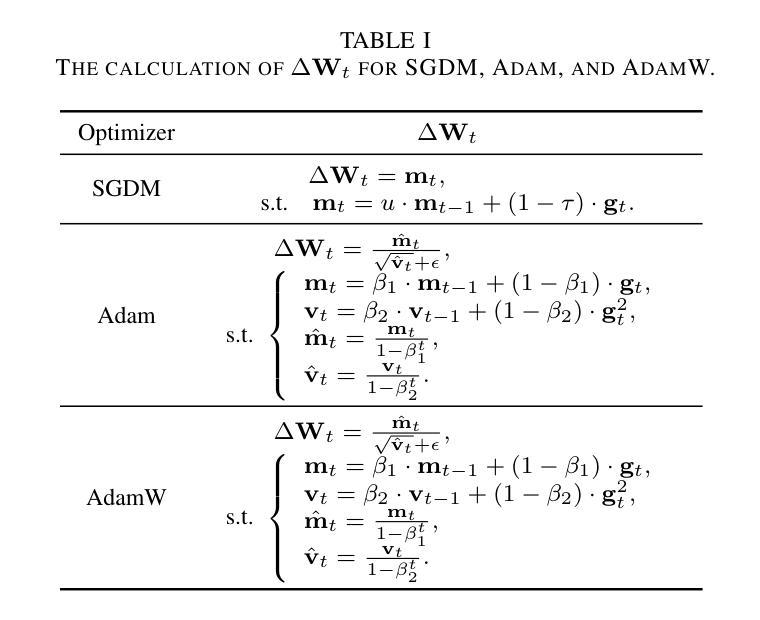
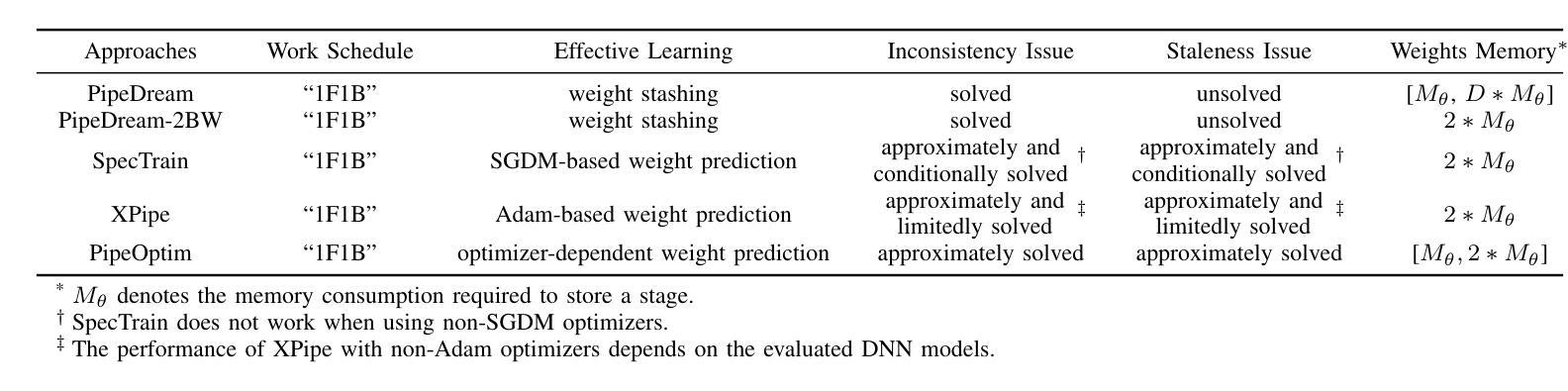
PipeOptim: Ensuring Effective 1F1B Schedule with Optimizer-Dependent Weight Prediction
Authors:Lei Guan, Dongsheng Li, Yongle Chen, Jiye Liang, Wenjian Wang, Xicheng Lu
Asynchronous pipeline model parallelism with a “1F1B” (one forward, one backward) schedule generates little bubble overhead and always provides quite a high throughput. However, the “1F1B” schedule inevitably leads to weight inconsistency and weight staleness issues due to the cross-training of different mini-batches across GPUs. To simultaneously address these two problems, in this paper, we propose an optimizer-dependent weight prediction strategy (a.k.a PipeOptim) for asynchronous pipeline training. The key insight of our proposal is that we employ a weight prediction strategy in the forward pass to ensure that each mini-batch uses consistent and staleness-free weights to compute the forward pass. To be concrete, we first construct the weight prediction scheme based on the update rule of the used optimizer when training the deep neural network models. Then throughout the “1F1B” pipelined training, each mini-batch is mandated to execute weight prediction ahead of the forward pass, subsequently employing the predicted weights to perform the forward pass. As a result, PipeOptim 1) inherits the advantage of the “1F1B” schedule and generates pretty high throughput, and 2) can ensure effective parameter learning regardless of the type of the used optimizer. To verify the effectiveness of our proposal, we conducted extensive experimental evaluations using eight different deep-learning models spanning three machine-learning tasks including image classification, sentiment analysis, and machine translation. The experiment results demonstrate that PipeOptim outperforms the popular pipelined approaches including GPipe, PipeDream, PipeDream-2BW, and SpecTrain. The code of PipeOptim can be accessible at https://github.com/guanleics/PipeOptim.
采用异步流水线模型并行性的”1F1B”(一前一后)时间表,会产生较少的冒泡开销,并且始终提供较高的吞吐量。然而,“1F1B”时间表不可避免地会导致权重不一致和权重陈旧问题,这是由于不同小批量数据在GPU之间的交叉训练造成的。为了解决这两个问题,本文提出了一种依赖于优化器的权重预测策略(也称为PipeOptim),用于异步流水线训练。我们提案的关键见解是,我们在前向传播过程中采用权重预测策略,以确保每个小批量数据使用一致且无陈旧的权重进行计算。具体来说,我们首先基于所用优化器的更新规则构建权重预测方案,用于训练深度神经网络模型。然后在“1F1B”流水线训练中,每个小批量数据必须在前向传播之前执行权重预测,随后使用预测的权重执行前向传播。因此,PipeOptim 1)继承了“1F1B”时间表的优点,并产生了较高的吞吐量,2)无论使用哪种优化器,都可以确保有效的参数学习。为了验证我们提案的有效性,我们使用涵盖三项机器学习任务(包括图像分类、情感分析和机器翻译)的八个不同深度学习模型进行了广泛的实验评估。实验结果表明,PipeOptim优于流行的流水线方法,包括GPipe、PipeDream、PipeDream-2BW和SpecTrain。PipeOptim的代码可在[https://github.com/guanleics/PipeOptim访问。]
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 15 pages
Summary
本文提出了一种针对异步流水线训练的优化器依赖权重预测策略(PipeOptim)。该策略在“1F1B”(一前一后)调度的基础上,通过在正向传播过程中采用权重预测策略,确保每个小批次使用一致且无陈旧权重的计算。PipeOptim不仅继承了“1F1B”调度的高吞吐量优势,还能确保各种优化器的有效参数学习。实验结果表明,PipeOptim在图像分类、情感分析和机器翻译等任务上的表现优于其他流行的流水线方法。
Key Takeaways
- 异步流水线模型并行性采用“1F1B”调度在高吞吐量方面表现出色,但存在权重不一致和陈旧问题。
- PipeOptim通过优化器依赖的权重预测策略解决上述问题,确保每个小批次使用一致且无陈旧的权重进行计算。
- PipeOptim继承了“1F1B”调度的优势,并确保了各种优化器的有效参数学习。
- 实验结果表明,PipeOptim在多种深度学习模型和任务上优于其他流水线方法。
- PipeOptim的代码已公开,可访问https://github.com/guanleics/PipeOptim。
- 该策略适用于图像分类、情感分析和机器翻译等任务。
点此查看论文截图