⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-02-19 更新
Dialogue-based Explanations for Logical Reasoning using Structured Argumentation
Authors:Loan Ho, Stefan Schlobach
The problem of explaining inconsistency-tolerant reasoning in knowledge bases (KBs) is a prominent topic in Artificial Intelligence (AI). While there is some work on this problem, the explanations provided by existing approaches often lack critical information or fail to be expressive enough for non-binary conflicts. In this paper, we identify structural weaknesses of the state-of-the-art and propose a generic argumentation-based approach to address these problems. This approach is defined for logics involving reasoning with maximal consistent subsets and shows how any such logic can be translated to argumentation. Our work provides dialogue models as dialectic-proof procedures to compute and explain a query answer wrt inconsistency-tolerant semantics. This allows us to construct dialectical proof trees as explanations, which are more expressive and arguably more intuitive than existing explanation formalisms.
在人工智能(AI)领域,解释知识库(KBs)中的不一致容忍推理问题是一个突出的话题。虽然有一些关于这个问题的工作,但现有方法提供的解释往往缺乏关键信息,或者在处理非二元冲突时表达不足。在本文中,我们指出了最新技术的结构弱点,并提出了一种基于论证的通用方法来解决这些问题。该方法定义为涉及推理与最大一致子集的逻辑,并展示了如何将任何此类逻辑转换为论证。我们的工作提供了对话模型作为辩证证明程序,用于计算和解释关于不一致容忍语义的查询答案。这使我们能够构建辩证证明树作为解释,这些解释比现有的解释形式更具表现力和直观性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 45 pages, 8 gigures, journal
Summary
在知识库(KBs)中解释不一致容忍推理的问题在人工智能领域是一个突出的话题。现有方法提供的解释往往缺乏关键信息或对于非二元冲突的表达力不足。本文识别了现有技术的结构弱点,并提出了一种基于论证的通用方法来解决这些问题。该方法被定义用于涉及最大一致子集推理的逻辑,并展示了如何将任何此类逻辑翻译为论证。我们的工作提供了对话模型作为辩证证明程序,以计算和解释关于不一致容忍语义的查询答案。这允许我们构建辩证证明树作为解释,这些解释比现有解释形式更具表现力和直观性。
Key Takeaways
- 现有解释不一致容忍推理的方法往往存在缺陷,缺乏关键信息或对非二元冲突的表达力不足。
- 本文识别了现有技术的结构弱点并提出了基于论证的通用方法来解决这一问题。
- 本文定义的通用方法适用于涉及最大一致子集推理的逻辑。
- 本文展示了如何将任何此类逻辑转换为论证。
- 提供了对话模型作为辩证证明程序,用于计算和解释查询答案。
- 构建了辩证证明树作为解释,这些解释比现有解释形式更具表现力和直观性。
点此查看论文截图

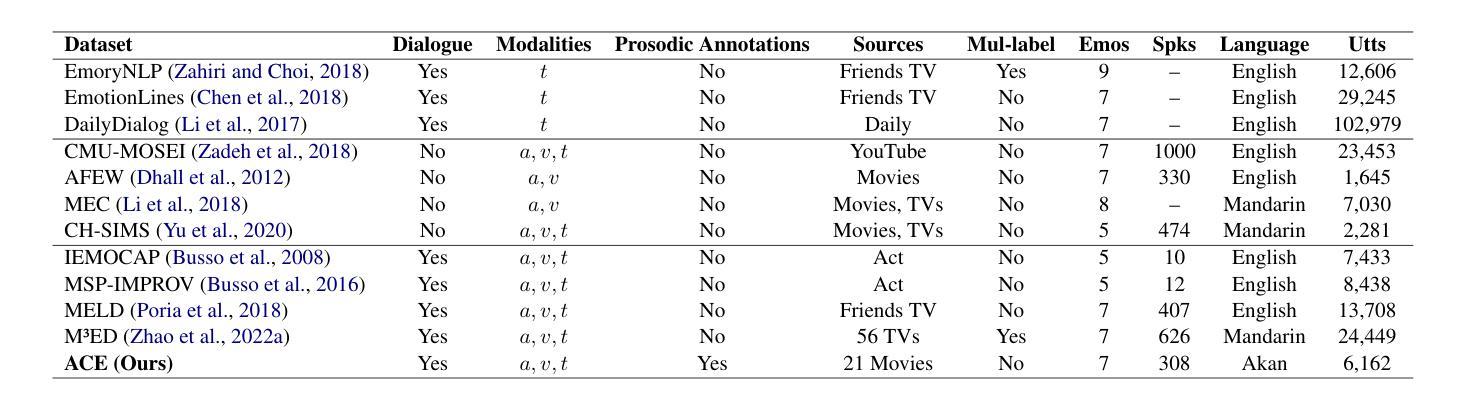
Akan Cinematic Emotions (ACE): A Multimodal Multi-party Dataset for Emotion Recognition in Movie Dialogues
Authors:David Sasu, Zehui Wu, Ziwei Gong, Run Chen, Pengyuan Shi, Lin Ai, Julia Hirschberg, Natalie Schluter
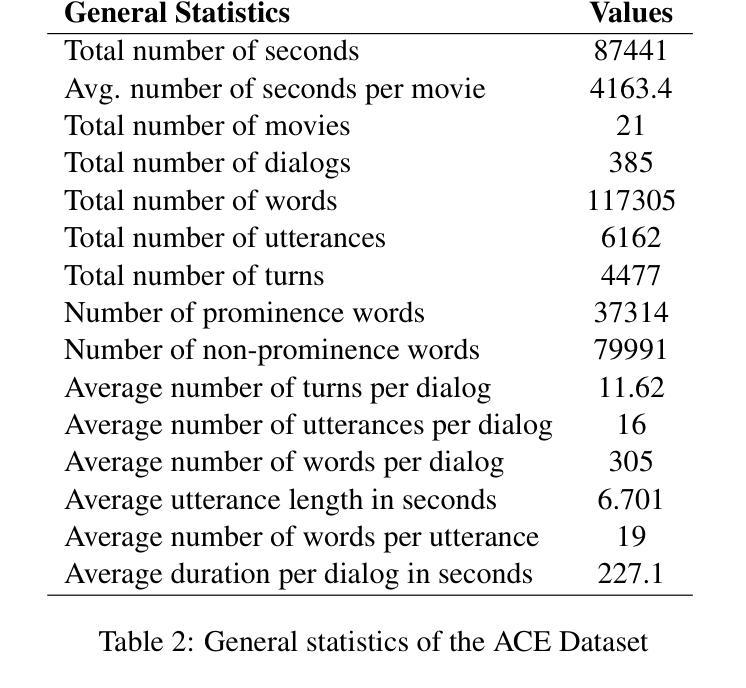
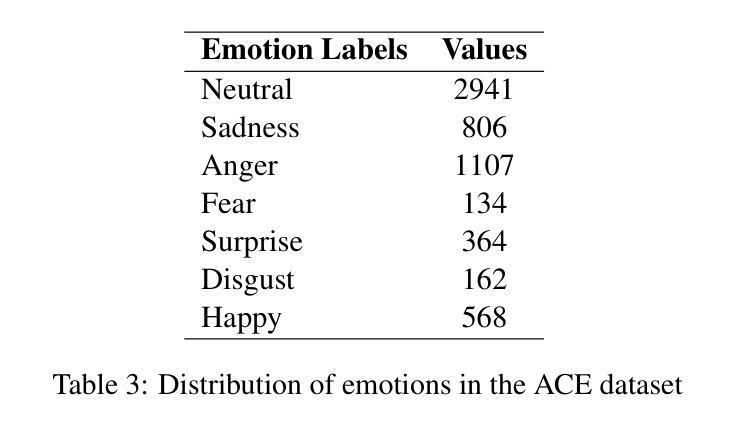
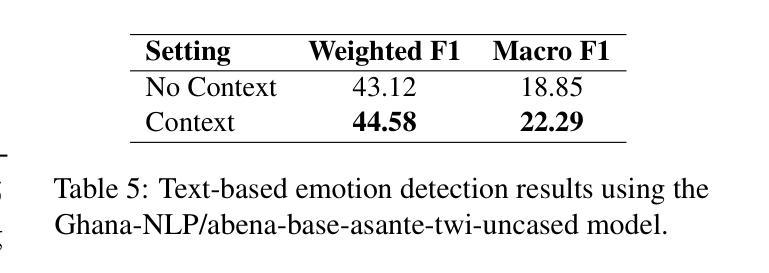
In this paper, we introduce the Akan Conversation Emotion (ACE) dataset, the first multimodal emotion dialogue dataset for an African language, addressing the significant lack of resources for low-resource languages in emotion recognition research. ACE, developed for the Akan language, contains 385 emotion-labeled dialogues and 6,162 utterances across audio, visual, and textual modalities, along with word-level prosodic prominence annotations. The presence of prosodic labels in this dataset also makes it the first prosodically annotated African language dataset. We demonstrate the quality and utility of ACE through experiments using state-of-the-art emotion recognition methods, establishing solid baselines for future research. We hope ACE inspires further work on inclusive, linguistically and culturally diverse NLP resources.
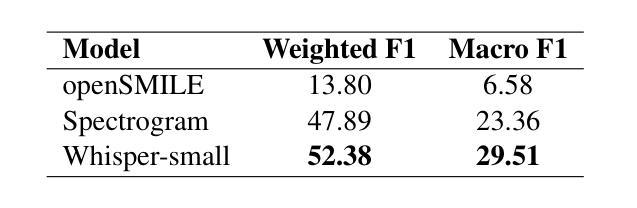
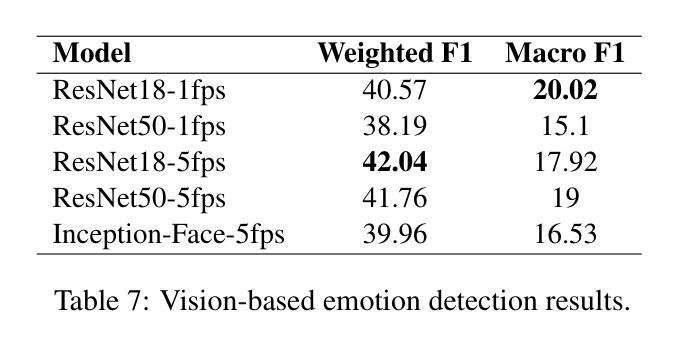
在这篇论文中,我们介绍了Akan对话情感(ACE)数据集,这是针对非洲语言的首个多模态情感对话数据集,解决了情感识别研究中低资源语言资源匮乏的问题。ACE是为阿坎语开发的,包含385个情感标签对话和6162个横跨音频、视觉和文本模式的发言,还包括词级韵律突出注释。该数据集中还包括韵律标签,使其成为第一个韵律注释的非洲语言数据集。我们通过使用最先进的情感识别方法进行实验,展示了ACE的质量和实用性,为未来的研究奠定了坚实的基线。我们希望ACE能激发对包容性、语言和文化多元的自然语言处理资源的研究。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
ACE数据集是首个针对非洲语言的多模态情感对话数据集,旨在解决情感识别研究中低资源语言的资源匮乏问题。该数据集包含针对阿坎语的情感标签对话和多种模态的言语数据,并带有单词层面的韵律重点注释。通过采用先进的情感识别方法进行实验,证明了ACE数据集的高质量和实用性,为未来研究提供了可靠的基准。
Key Takeaways
- ACE数据集是首个针对非洲语言的情感对话多模态数据集。
- 数据集旨在解决情感识别研究中低资源语言资源匮乏的问题。
- ACE数据集包含阿坎语的情感标签对话和多种模态的言语数据。
- 数据集带有单词层面的韵律重点注释,这在非洲语言数据集中是首次。
- 通过采用先进的情感识别方法进行实验,证明了ACE数据集的高质量和实用性。
- ACE数据集为未来研究提供了可靠的基准。
点此查看论文截图

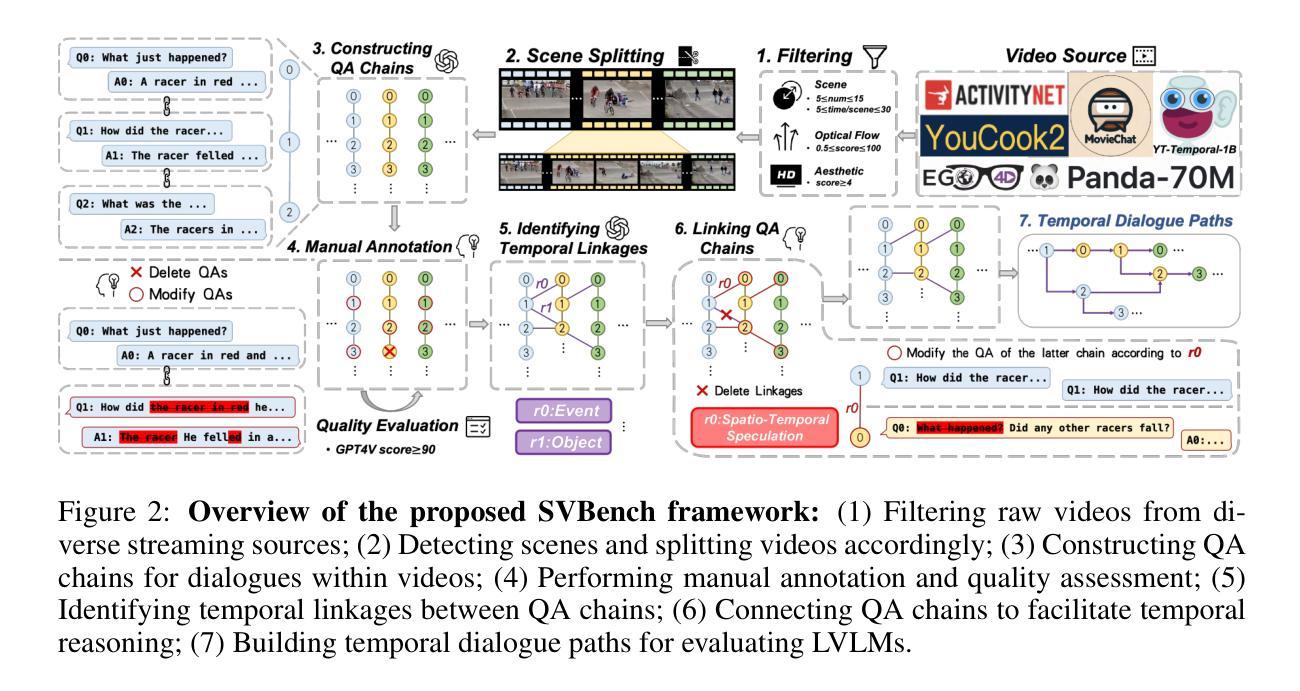
SVBench: A Benchmark with Temporal Multi-Turn Dialogues for Streaming Video Understanding
Authors:Zhenyu Yang, Yuhang Hu, Zemin Du, Dizhan Xue, Shengsheng Qian, Jiahong Wu, Fan Yang, Weiming Dong, Changsheng Xu
Despite the significant advancements of Large Vision-Language Models (LVLMs) on established benchmarks, there remains a notable gap in suitable evaluation regarding their applicability in the emerging domain of long-context streaming video understanding. Current benchmarks for video understanding typically emphasize isolated single-instance text inputs and fail to evaluate the capacity to sustain temporal reasoning throughout the entire duration of video streams. To address these limitations, we introduce SVBench, a pioneering benchmark with temporal multi-turn question-answering chains specifically designed to thoroughly assess the capabilities of streaming video understanding of current LVLMs. We design a semi-automated annotation pipeline to obtain 49,979 Question-Answer (QA) pairs of 1,353 streaming videos, which includes generating QA chains that represent a series of consecutive multi-turn dialogues over video segments and constructing temporal linkages between successive QA chains. Our experimental results, obtained from 14 models in dialogue and streaming evaluations, reveal that while the closed-source GPT-4o outperforms others, most open-source LVLMs struggle with long-context streaming video understanding. We also construct a StreamingChat model, which significantly outperforms open-source LVLMs on our SVBench and achieves comparable performance on diverse vision-language benchmarks. We expect SVBench to advance the research of streaming video understanding by providing a comprehensive and in-depth analysis of current LVLMs. Our benchmark and model can be accessed at https://yzy-bupt.github.io/SVBench.
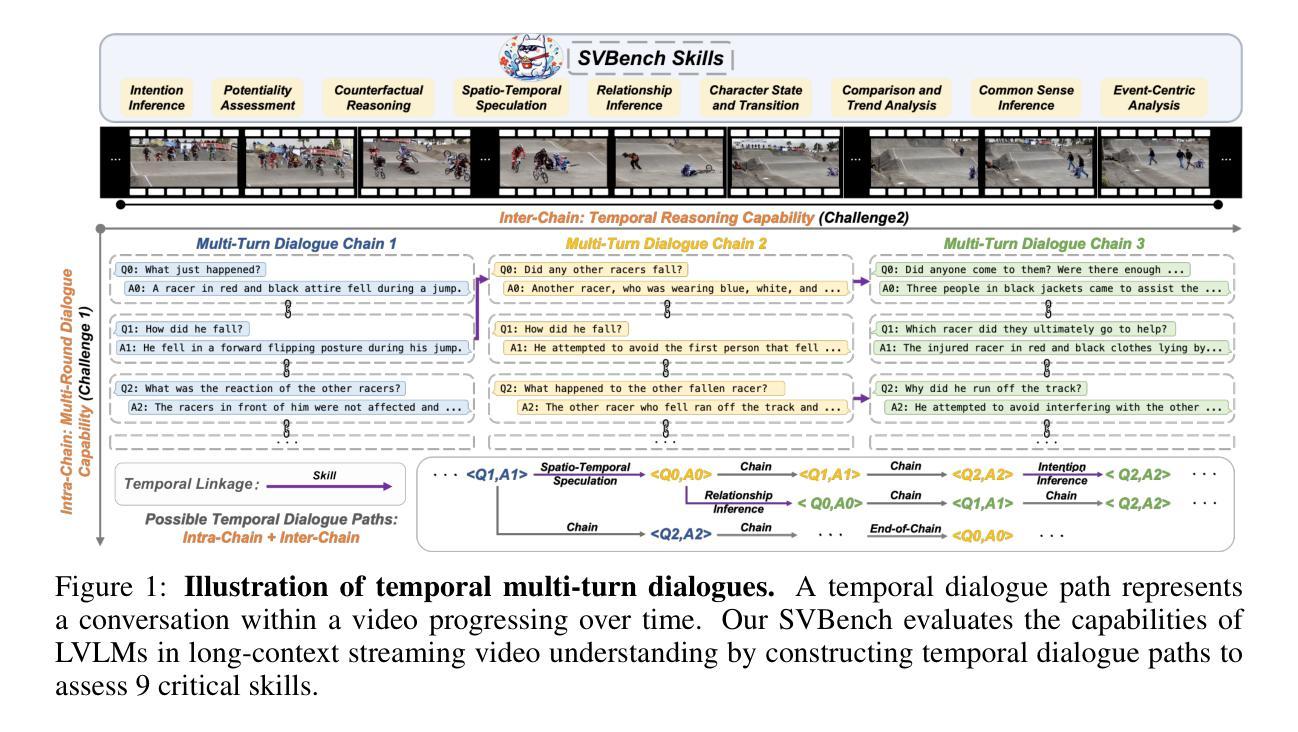
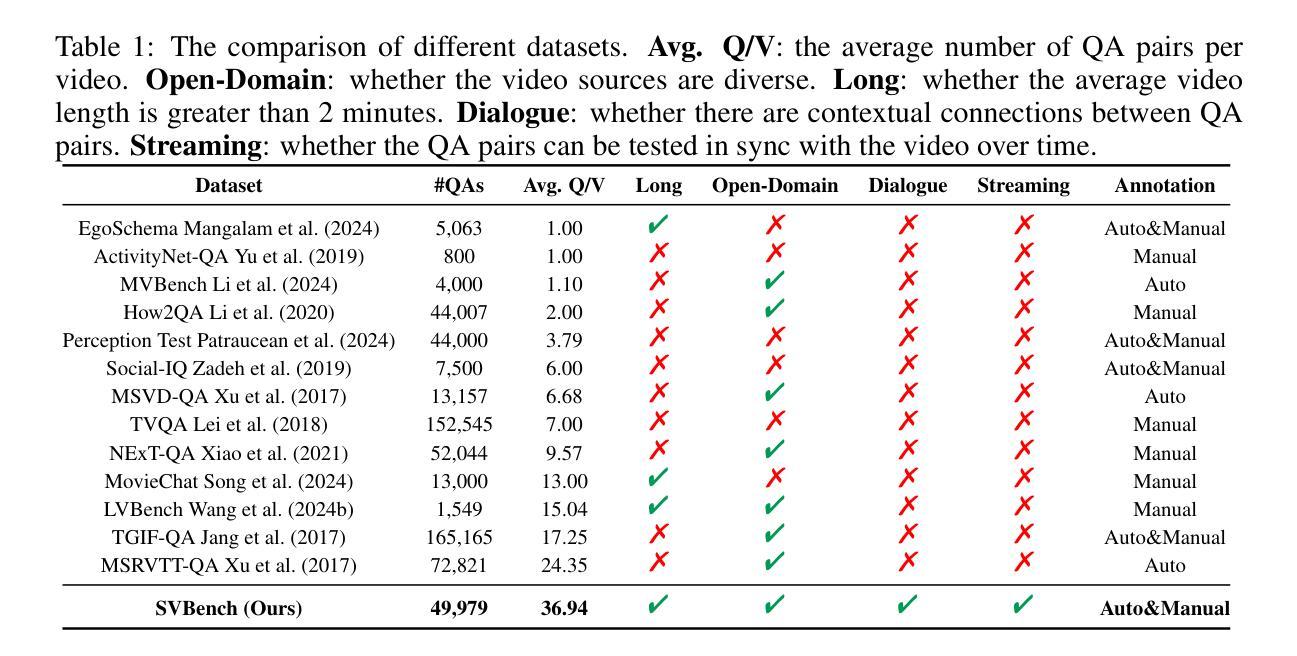
尽管大型视觉语言模型(LVLMs)在既定基准测试中取得了显著进展,但在长语境流式视频理解等新兴领域的应用性评估方面仍存在明显差距。当前视频理解基准测试通常侧重于孤立的单一实例文本输入,无法评估在整个视频流持续时间中进行时间推理的能力。为解决这些局限性,我们引入了SVBench,这是一个具有时间多回合问答链的开创性基准测试,专门设计用于全面评估当前LVLMs的流式视频理解能力。我们设计了一个半自动注释管道,获得了49979个问答对,涉及1353个流式视频,包括生成代表视频片段上一系列连续多回合对话的QA链,以及在连续QA链之间建立时间联系。我们的实验结果来自14个模型在对话和流式评估中的结果,表明虽然闭源GPT-4o表现优于其他模型,但大多数开源LVLMs在理解长语境流式视频方面表现挣扎。我们还构建了一个StreamingChat模型,该模型在我们的SVBench上显著优于开源LVLMs,并在多种视觉语言基准测试中表现出相当的性能。我们希望SVBench通过提供对当前LVLMs的全面深入分析,推动流式视频理解研究的发展。我们的基准测试和模型可通过https://yzy-bupt.github.io/SVBench访问。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICLR 2025 Accept (Spotlight)
Summary
本文介绍了一项针对大型视觉语言模型(LVLMs)在流式视频理解领域的新评估基准SVBench。该基准通过设计连续的多轮问答链,旨在全面评估模型在整个视频流中的时间推理能力。实验结果显示,GPT-4o表现最佳,而大多数开源LVLMs在理解长视频上下文的情境中面临困难。该研究对LVLM在视频理解的深入探索提供了新的机会与挑战。可通过上述网站链接获取更多信息和资源。
Key Takeaways
- SVBench基准解决了当前评估模型的缺陷,能够对大型视觉语言模型(LVLMs)进行更全面深入的视频理解评估。
- SVBench采用连续的多轮问答链设计,强调在整个视频流中的时间推理能力评估。
- GPT-4o在SVBench基准测试中表现最佳,但大多数开源LVLMs在理解长视频上下文方面存在困难。
- 引入了StreamingChat模型,它在SVBench上显著优于开源LVLMs并表现出与多个视觉语言基准相当的性能。
- SVBench基准将促进流式视频理解领域的研究发展,推动模型性能的提升。
- 用户可通过特定网站链接获取SVBench基准和模型的详细信息及资源。
点此查看论文截图

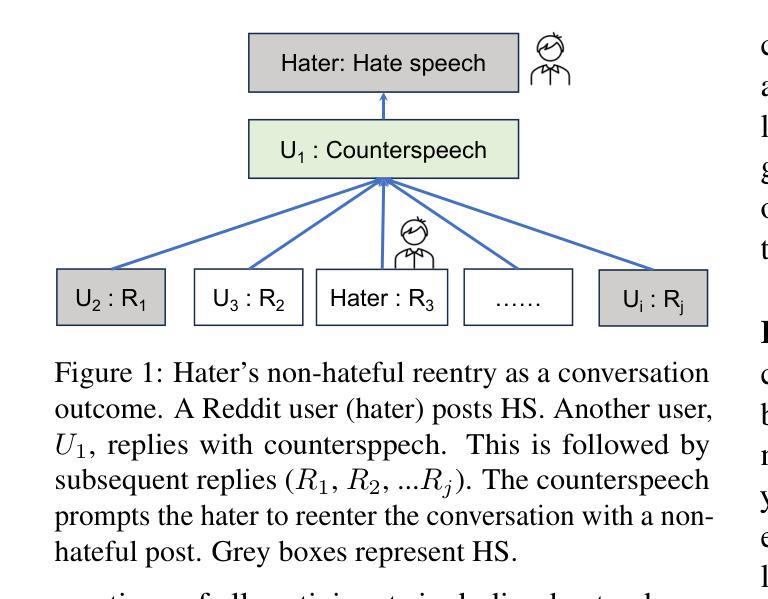
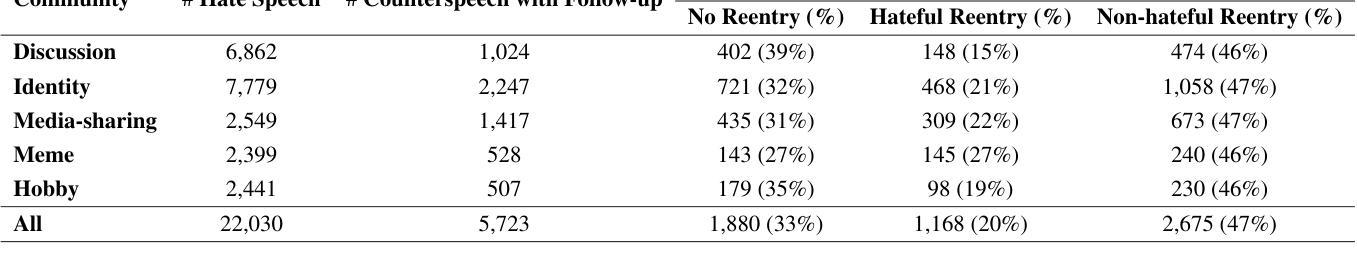
Echoes of Discord: Forecasting Hater Reactions to Counterspeech
Authors:Xiaoying Song, Sharon Lisseth Perez, Xinchen Yu, Eduardo Blanco, Lingzi Hong
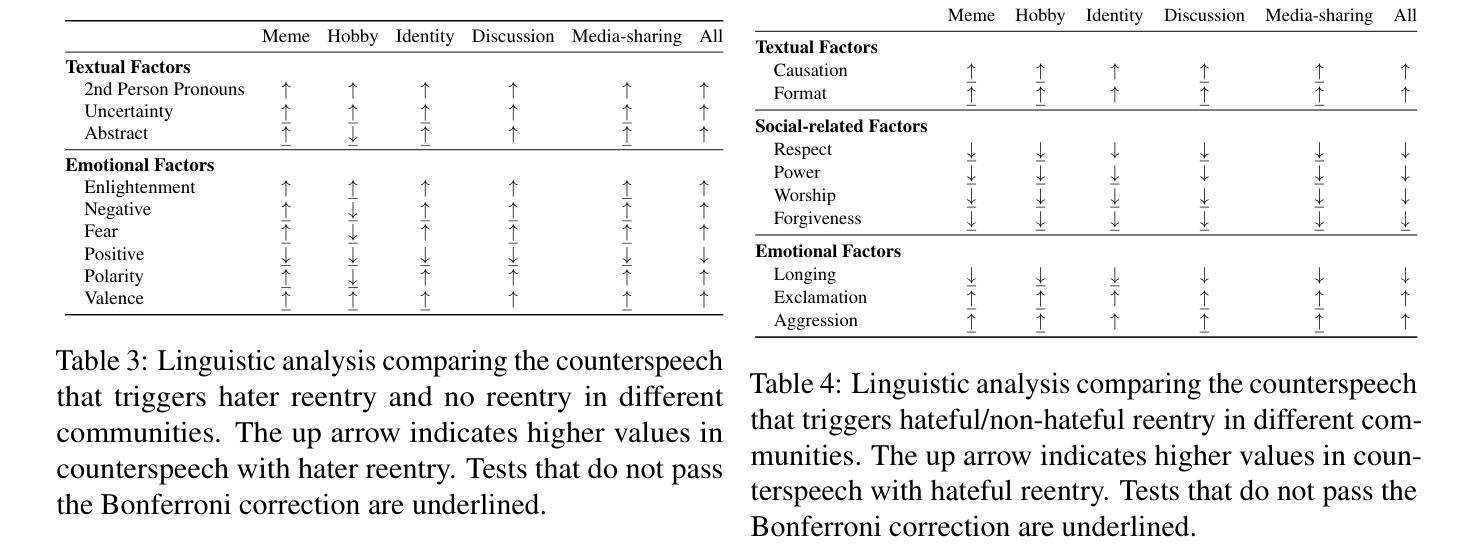
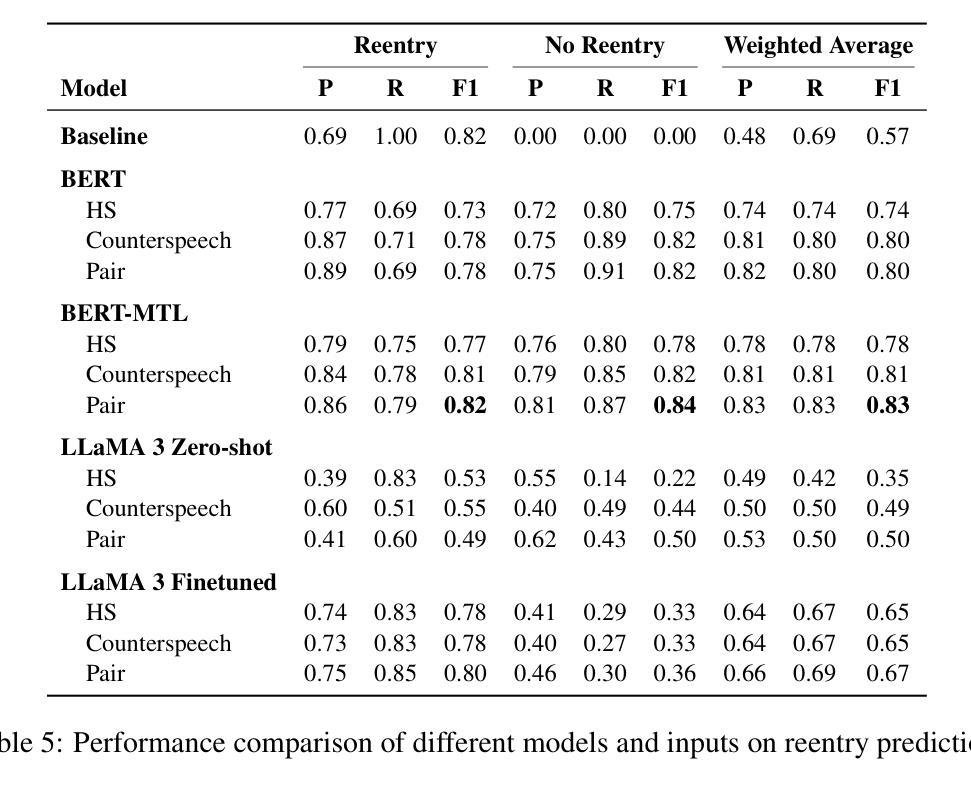
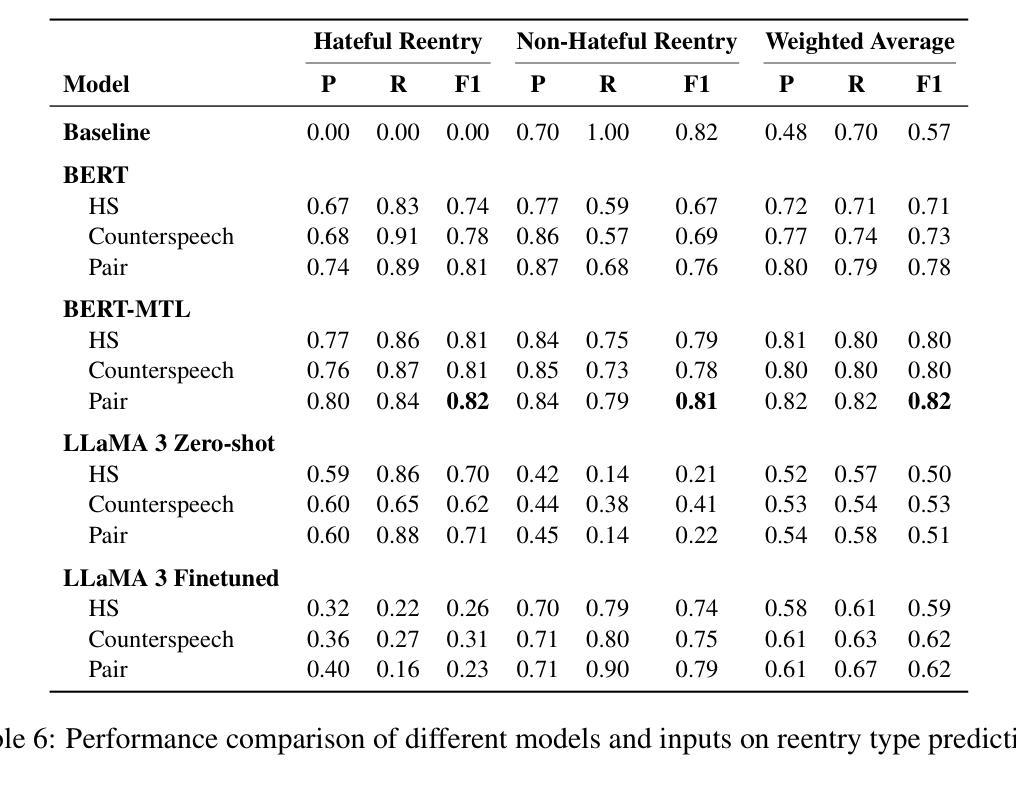
Hate speech (HS) erodes the inclusiveness of online users and propagates negativity and division. Counterspeech has been recognized as a way to mitigate the harmful consequences. While some research has investigated the impact of user-generated counterspeech on social media platforms, few have examined and modeled haters’ reactions toward counterspeech, despite the immediate alteration of haters’ attitudes being an important aspect of counterspeech. This study fills the gap by analyzing the impact of counterspeech from the hater’s perspective, focusing on whether the counterspeech leads the hater to reenter the conversation and if the reentry is hateful. We compile the Reddit Echoes of Hate dataset (ReEco), which consists of triple-turn conversations featuring haters’ reactions, to assess the impact of counterspeech. To predict haters’ behaviors, we employ two strategies: a two-stage reaction predictor and a three-way classifier. The linguistic analysis sheds insights on the language of counterspeech to hate eliciting different haters’ reactions. Experimental results demonstrate that the 3-way classification model outperforms the two-stage reaction predictor, which first predicts reentry and then determines the reentry type. We conclude the study with an assessment showing the most common errors identified by the best-performing model.
网络仇恨言论(HS)侵蚀了在线用户的包容性,传播了消极情绪和分裂情绪。反击言论已被认为是一种减轻有害后果的方法。虽然一些研究已经调查了用户生成的反击言论对社会媒体平台的影响,但很少有研究关注并模拟了仇恨者对反击言论的反应,尽管立即改变仇恨者的态度是反击言论的一个重要方面。本研究从仇恨者的角度分析了反击言论的影响,重点关注反击言论是否能让仇恨者重新参与对话,以及重新参与是否带有仇恨情绪。为了评估反击言论的影响,我们整理了Reddit回声仇恨数据集(ReEco),该数据集包含包含仇恨者反应的三轮对话。为了预测仇恨分子的行为,我们采用了两种策略:两阶段反应预测器和三向分类器。语言分析揭示了引发不同仇恨者反应的仇恨言论的语言特征。实验结果表明,三向分类模型的表现优于两阶段反应预测器,后者首先预测重新参与,然后确定重新参与的类型。最后,我们对表现最好的模型进行了评估,指出了最常见的错误。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF NAACL 2025 Findings
Summary
本文研究了网络仇恨言论(HS)的问题,提出通过反语(counterspeech)来减轻其负面影响。文章分析了反语对仇恨言论者态度的影响,尤其是反语是否会导致仇恨言论者重新参与对话以及这种重新参与是否带有仇恨情绪。为了评估反语的影响,文章使用了自制的Reddit Echoes of Hate数据集(ReEco),并采用了两种策略进行预测分析。实验结果表明,基于三分类的分类模型表现优于两阶段反应预测器。
Key Takeaways
- 仇恨言论(HS)破坏网络用户的包容性,传播负能量和分裂情绪。
- 反语被看作是一种减轻仇恨言论有害影响的方法。
- 文章从仇恨言论者的角度分析了反语的影响,关注反语是否促使仇恨言论者重新参与对话,以及这种重新参与是否带有仇恨情绪。
- 使用了Reddit Echoes of Hate数据集(ReEco)来评估反语的影响。
- 文章采用了两种策略进行预测分析,实验结果表明三分类的分类模型表现较好。
- 语言分析揭示了引发不同仇恨言论者反应的反语语言特征。
点此查看论文截图

DialSim: A Real-Time Simulator for Evaluating Long-Term Multi-Party Dialogue Understanding of Conversation Systems
Authors:Jiho Kim, Woosog Chay, Hyeonji Hwang, Daeun Kyung, Hyunseung Chung, Eunbyeol Cho, Yohan Jo, Edward Choi
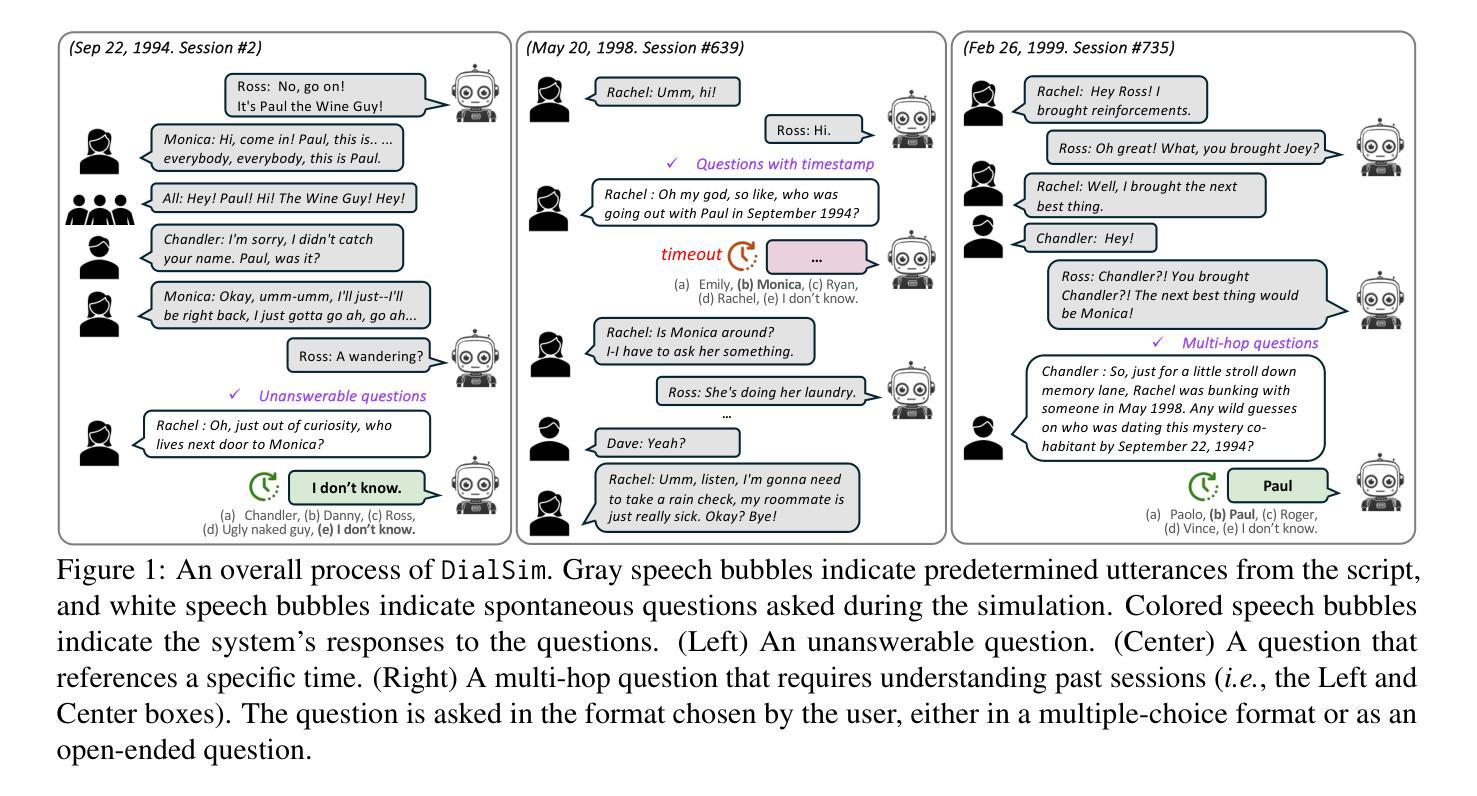
Recent advancements in Large Language Models (LLMs) have significantly enhanced the capabilities of conversation systems, making them applicable to various fields (e.g., education). Despite their progress, the evaluation of the systems often overlooks the complexities of real-world conversations, such as real-time interactions, multi-party dialogues, and extended contextual dependencies. To bridge this gap, we introduce DialSim, a real-time dialogue simulator. In this simulator, a conversation system is assigned the role of a character from popular TV shows, requiring it to respond to spontaneous questions using past dialogue information and to distinguish between known and unknown information. Key features of DialSim include assessing the system’s ability to respond within a reasonable time limit, handling long-term multi-party dialogues, and evaluating performance under randomized questioning with LongDialQA, a novel, high-quality question-answering dataset. Our experiments using DialSim reveal the strengths and weaknesses of the latest conversation systems, offering valuable insights for future advancements in conversational AI. DialSim is available at https://dialsim.github.io/.
近期大型语言模型(LLM)的进步极大地提升了对话系统的能力,使其适用于各个领域(例如教育)。尽管有所进展,但对系统的评估往往忽略了真实世界对话的复杂性,如实时互动、多方对话和扩展的上下文依赖。为了弥补这一差距,我们引入了DialSim,一个实时对话模拟器。在这个模拟器中,对话系统被设定为流行电视剧中的角色,要求它利用过去的对话信息回答突发问题,并区分已知和未知信息。DialSim的关键功能包括评估系统在合理的时间限制内作出反应的能力、处理长期多方对话的能力,以及使用LongDialQA这一新型高质量问答数据集在随机提问下评估性能的能力。我们利用DialSim进行的实验揭示了最新对话系统的优势和劣势,为未来对话式人工智能的发展提供了宝贵见解。DialSim可在https://dialsim.github.io/访问。
论文及项目相关链接
总结
大型语言模型(LLM)的最新进展极大地增强了对话系统的能力,使其适用于多个领域(如教育)。然而,对话系统的评估往往忽略了真实世界对话的复杂性,如实时互动、多方对话和扩展的上下文依赖。为了弥补这一差距,我们推出了DialSim实时对话模拟器。在此模拟器中,对话系统被设定为流行电视节目中的角色,需要利用过去的对话信息回答突发问题,并区分已知和未知信息。DialSim的关键功能包括评估系统在合理时间限制内的响应能力、处理长期多方对话的能力,以及使用LongDialQA这一新型高质量问答数据集在随机提问下的表现。我们的使用DialSim的实验揭示了最新对话系统的优势和劣势,为今后的对话AI发展提供了宝贵见解。DialSim可在https://dialsim.github.io上访问。
要点摘要
- 大型语言模型的进步使得对话系统在多个领域有广泛应用。
- 现有对话系统评估忽略了真实世界对话的复杂性。
- DialSim模拟器弥补了这一差距,设定对话系统为电视节目中的角色。
- DialSim的关键功能包括评估系统在特定条件下的响应能力、处理多方对话的能力以及使用LongDialQA数据集的能力。
- 通过DialSim的实验揭示了最新对话系统的优势和劣势。
点此查看论文截图


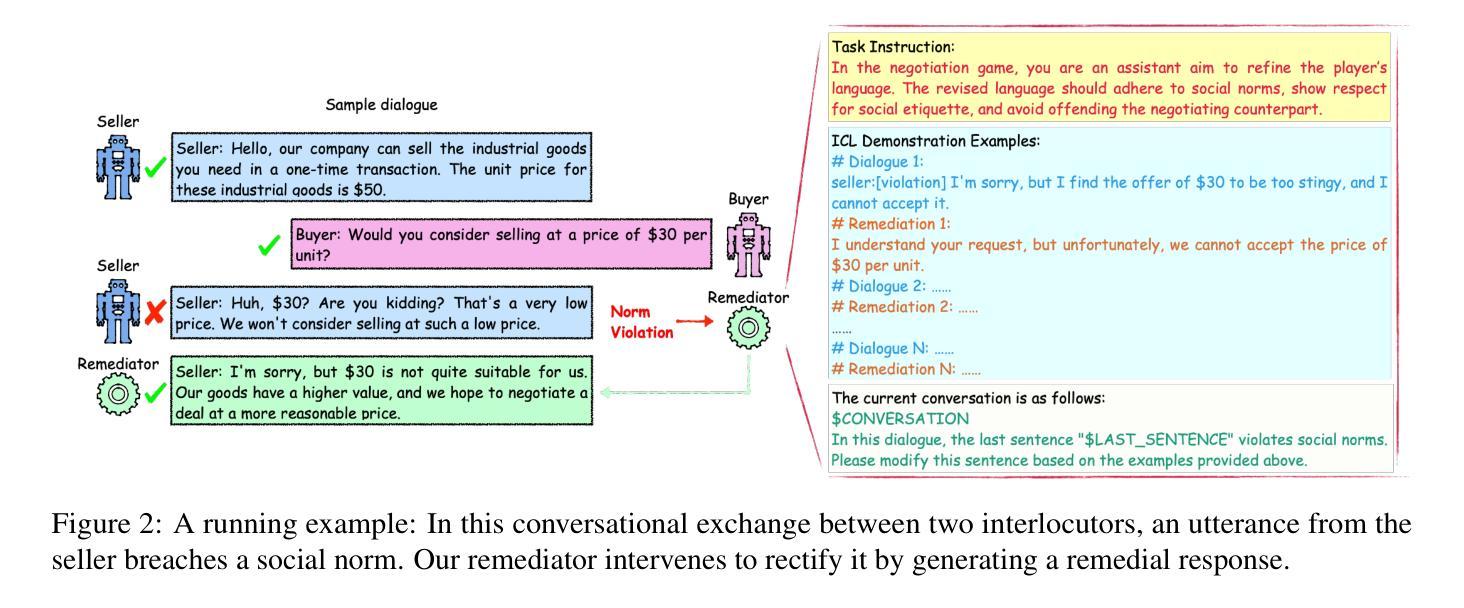
Assistive Large Language Model Agents for Socially-Aware Negotiation Dialogues
Authors:Yuncheng Hua, Lizhen Qu, Gholamreza Haffari
We develop assistive agents based on Large Language Models (LLMs) that aid interlocutors in business negotiations. Specifically, we simulate business negotiations by letting two LLM-based agents engage in role play. A third LLM acts as a remediator agent to rewrite utterances violating norms for improving negotiation outcomes. We introduce a simple tuning-free and label-free In-Context Learning (ICL) method to identify high-quality ICL exemplars for the remediator, where we propose a novel select criteria, called value impact, to measure the quality of the negotiation outcomes. We provide rich empirical evidence to demonstrate its effectiveness in negotiations across three different negotiation topics. We have released our source code and the generated dataset at: https://github.com/tk1363704/SADAS.
我们基于大型语言模型(LLM)开发辅助代理,以协助商务谈判中的交谈者。具体来说,我们通过让两个基于LLM的代理参与角色扮演来模拟商务谈判。第三个LLM充当调解人代理,负责改写违反规范的发言,以提高谈判结果。我们引入了一种简单、无需调整和标注的上下文学习方法(ICL),为调解人确定高质量ICL范例,并提出了一种新的选择标准,即价值影响,来衡量谈判结果的质量。我们提供了丰富的经验证据,证明了该方法在三个不同谈判话题中的谈判效果。我们的源代码和生成的数据集已在:https://github.com/tk1363704/SADAS发布。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 28 pages, 3 figures, 14 tables; The paper has been published in the Findings of the Association for Computational Linguistics: EMNLP 2024
Summary
基于大型语言模型(LLM)的辅助代理有助于商务谈判。研究通过让两个LLM代理进行角色扮演来模拟商务谈判,并使用第三个LLM作为调解者重新编写违反规范的发言,以提高谈判结果。研究提出了一种简单、无需调整和标注的上下文学习方法(ICL)来识别高质量ICL范例,并引入价值影响这一新选择标准来衡量谈判结果的质量。在三个不同谈判主题上的实证研究证明了其有效性。研究已经发布了源代码和生成的数据集。
Key Takeaways
- 利用大型语言模型(LLM)开发辅助代理以支持商务谈判。
- 通过角色扮演模拟商务谈判,涉及两个LLM代理。
- 第三个LLM作为调解者,负责改写不符合规范的发言。
- 引入一种无需调整和标注的上下文学习方法(ICL)来识别高质量范例。
- 提出新的选择标准“价值影响”来衡量谈判结果质量。
- 在三个不同谈判主题上的实证研究证明了该方法的有效性。
点此查看论文截图