⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-02-19 更新
Idiosyncrasies in Large Language Models
Authors:Mingjie Sun, Yida Yin, Zhiqiu Xu, J. Zico Kolter, Zhuang Liu
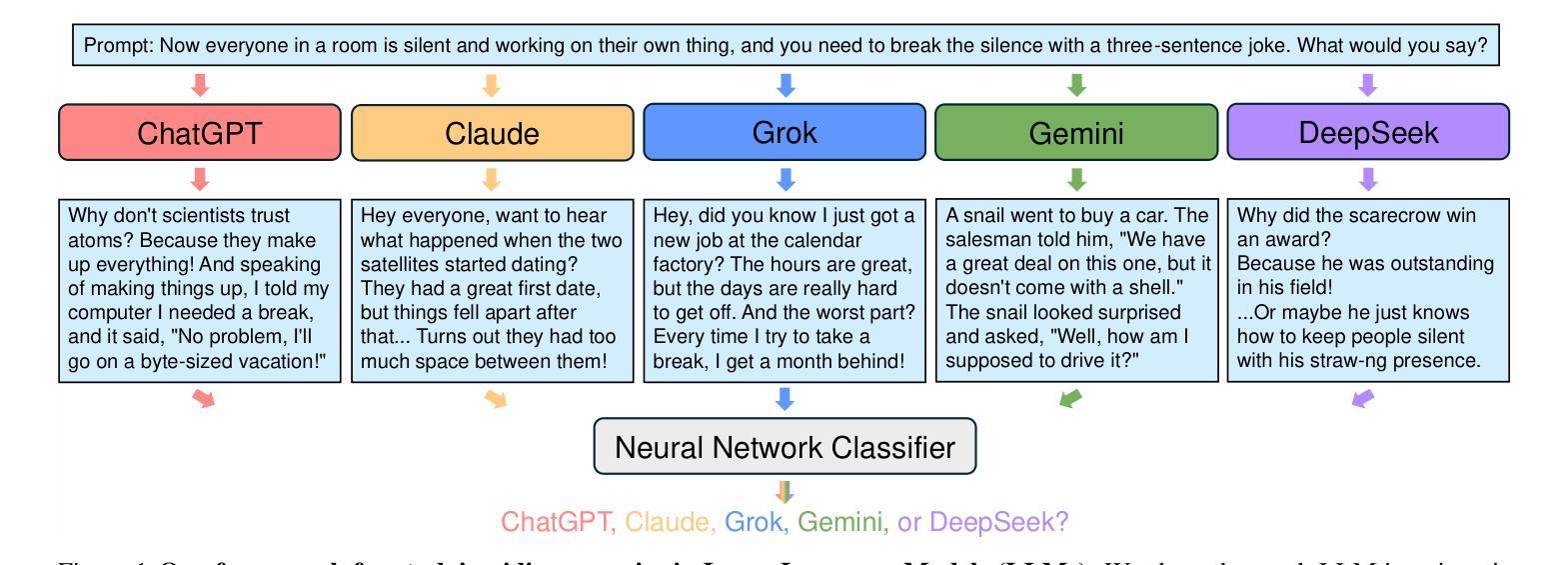
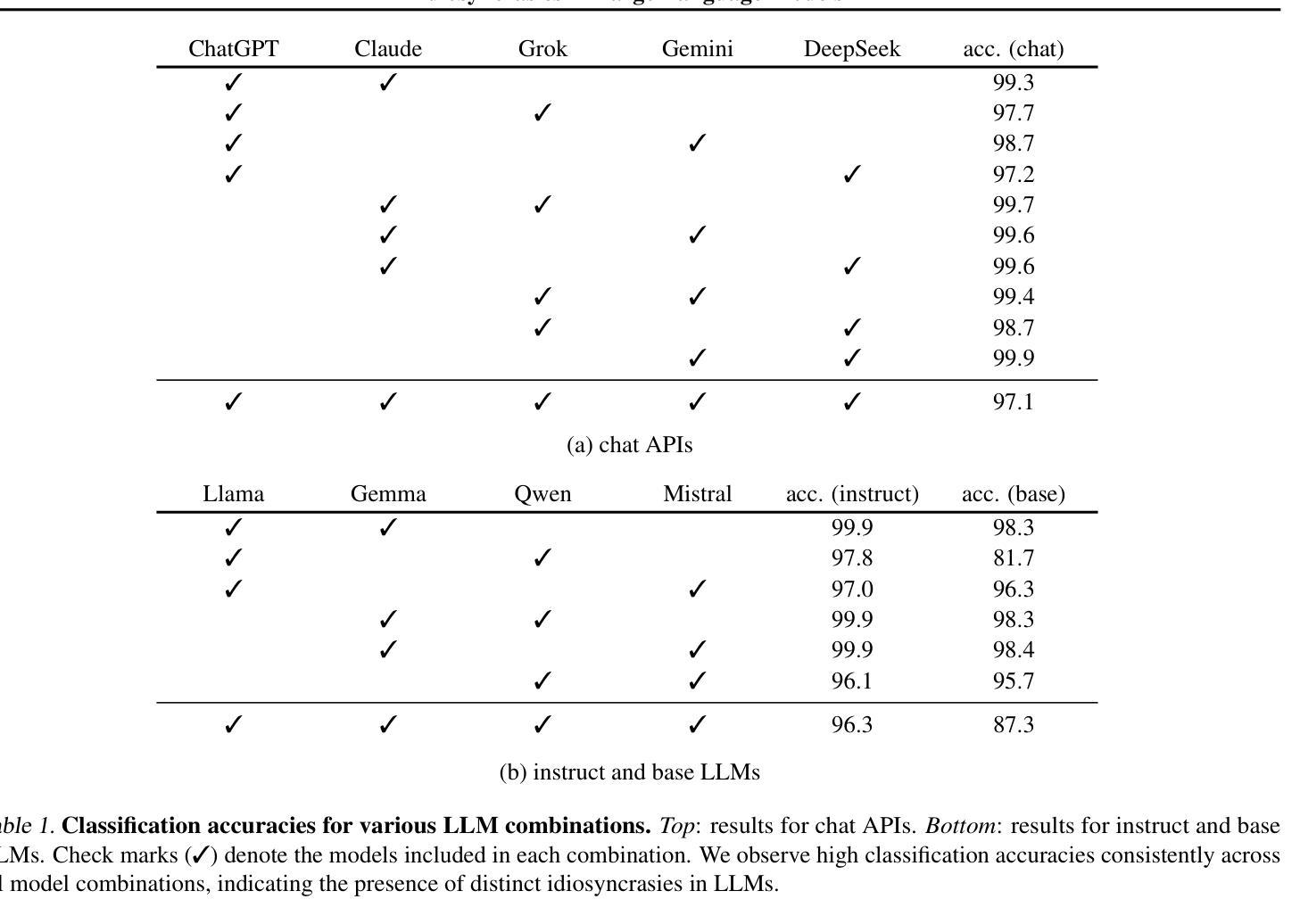
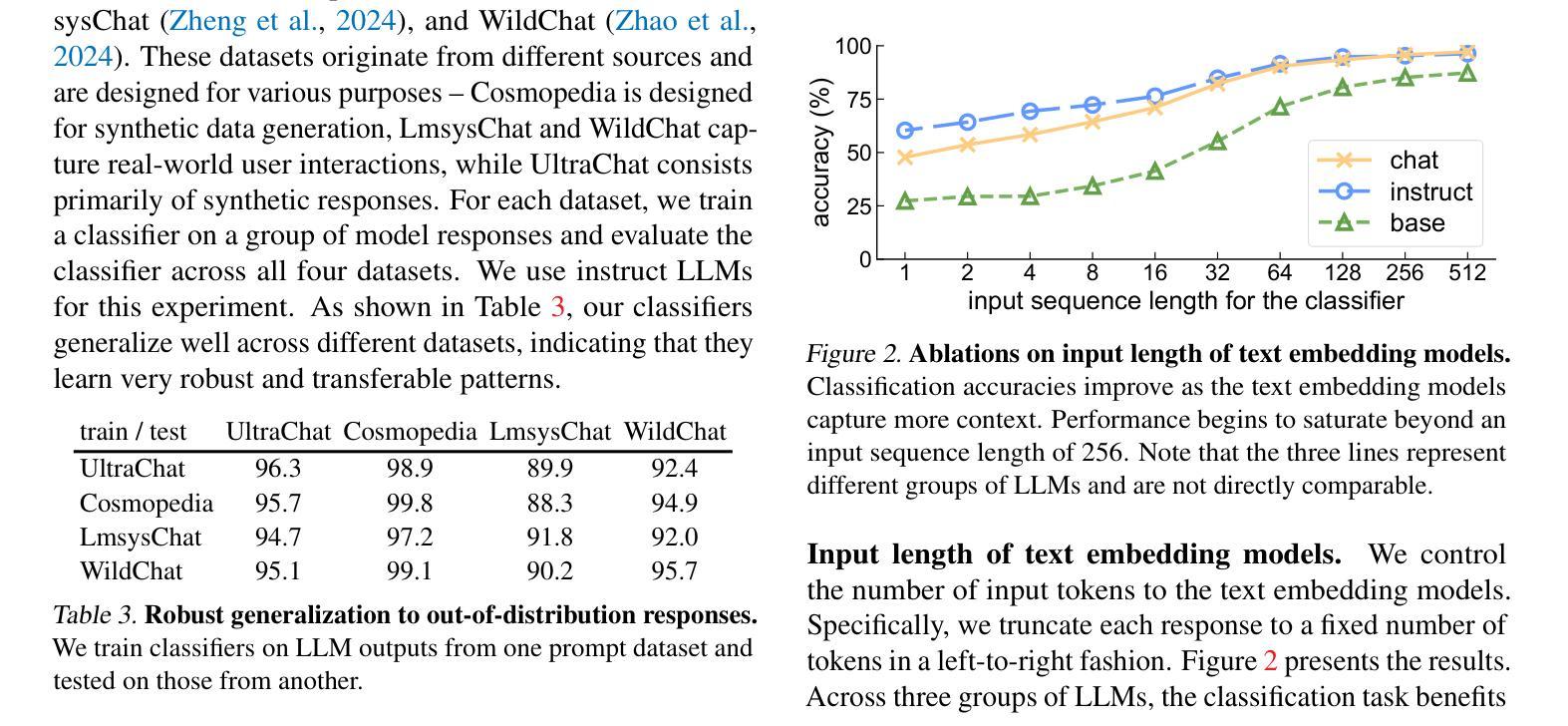
In this work, we unveil and study idiosyncrasies in Large Language Models (LLMs) – unique patterns in their outputs that can be used to distinguish the models. To do so, we consider a simple classification task: given a particular text output, the objective is to predict the source LLM that generates the text. We evaluate this synthetic task across various groups of LLMs and find that simply fine-tuning existing text embedding models on LLM-generated texts yields excellent classification accuracy. Notably, we achieve 97.1% accuracy on held-out validation data in the five-way classification problem involving ChatGPT, Claude, Grok, Gemini, and DeepSeek. Our further investigation reveals that these idiosyncrasies are rooted in word-level distributions. These patterns persist even when the texts are rewritten, translated, or summarized by an external LLM, suggesting that they are also encoded in the semantic content. Additionally, we leverage LLM as judges to generate detailed, open-ended descriptions of each model’s idiosyncrasies. Finally, we discuss the broader implications of our findings, particularly for training on synthetic data and inferring model similarity. Code is available at https://github.com/locuslab/llm-idiosyncrasies.
在这项工作中,我们揭示并研究了大语言模型(LLM)的独特性——输出中的独特模式,这些模式可用于区分模型。为此,我们考虑了一个简单的分类任务:给定特定的文本输出,目标是预测生成该文本的语言模型。我们评估了不同组LLM的这个合成任务,发现仅通过微调现有的文本嵌入模型即可在LLM生成的文本上获得出色的分类准确率。值得注意的是,在涉及ChatGPT、Claude、Grok、Gemini和DeepSeek的五分类问题中,我们在保留的验证数据上达到了97.1%的准确率。我们的进一步调查表明,这些独特性根植于单词级别的分布。这些模式在文本被重写、翻译或摘要外部LLM时仍然存在,这表明它们也编码在语义内容中。此外,我们还利用LLM作为法官来生成关于每个模型的独特性的详细、开放式描述。最后,我们讨论了我们的发现对训练合成数据和推断模型相似性的更广泛影响。代码可在 https://github.com/locuslab/llm-idiosyncrasies 找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Website at https://eric-mingjie.github.io/llm-idiosyncrasies/index.html
Summary
本文揭示并研究了大型语言模型(LLM)的特性——模型输出中的独特模式,这些模式可用于区分不同的模型。文章通过一个简单的分类任务来展示这些特性,即根据文本输出预测生成文本的LLM来源。通过在不同LLM组上评估这一合成任务发现,仅对现有文本嵌入模型进行微调即可获得出色的分类准确性。在涉及ChatGPT、Claude、Grok、Gemini和DeepSeek的五分类问题上,我们在验证数据上达到了97.1%的准确率。进一步的研究表明,这些特性根植于单词级别的分布模式,并且即使文本被重写、翻译或摘要,这些模式依然存在,这表明它们也存在于语义内容中。此外,我们还利用LLM作为法官来生成关于每个模型特性的详细开放式描述。最后,我们讨论了我们的发现对合成数据训练和推断模型相似性的更广泛影响。
Key Takeaways
- 文章揭示了大型语言模型(LLM)的特性,这些特性可用于区分不同的LLM。
- 通过简单的分类任务评估了LLM的特性,即预测文本输出对应的LLM来源。
- 通过对文本嵌入模型的微调,实现了高准确率的分类。
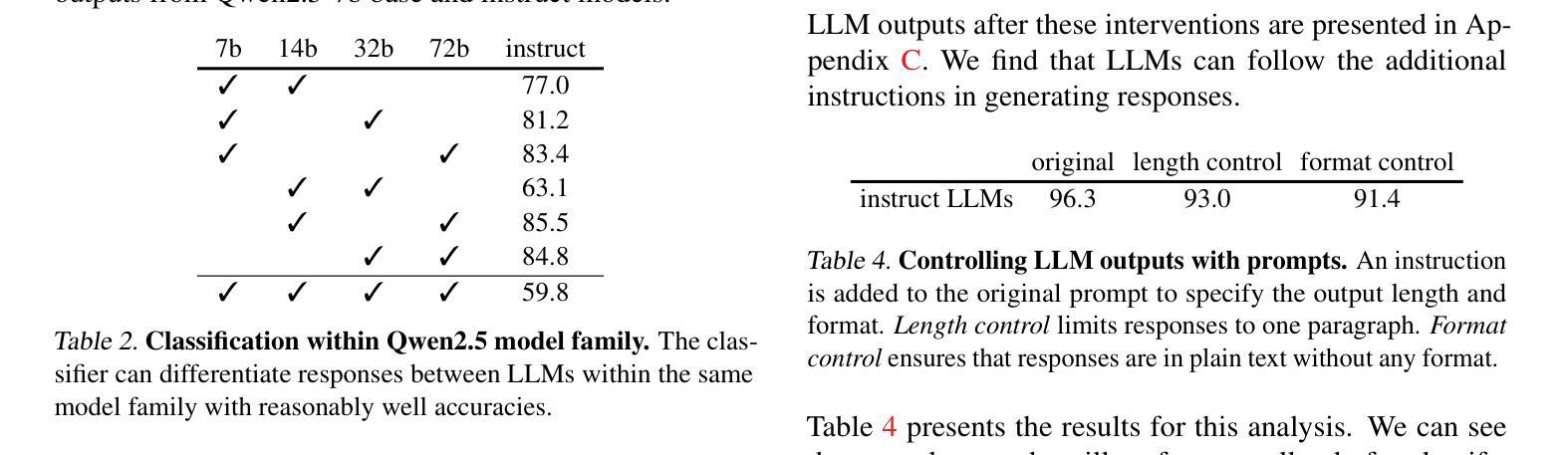
- 在涉及多个LLM的五分类问题上,验证数据准确率达到了97.1%。
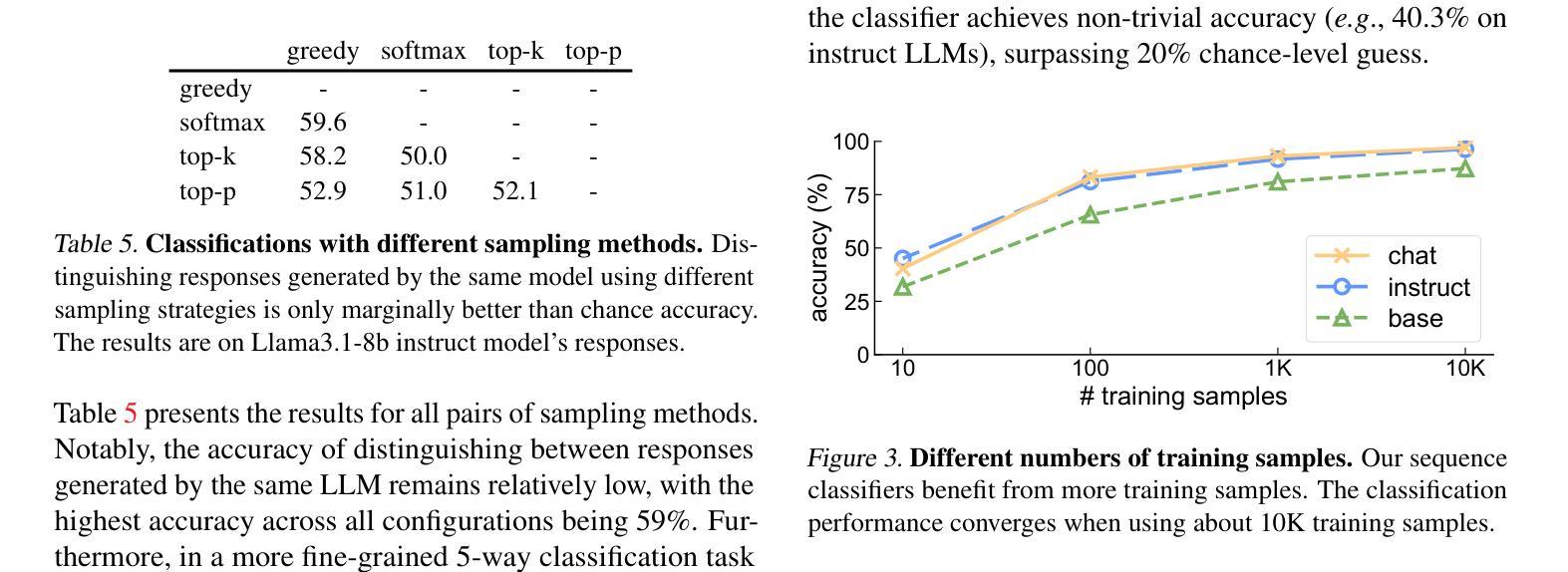
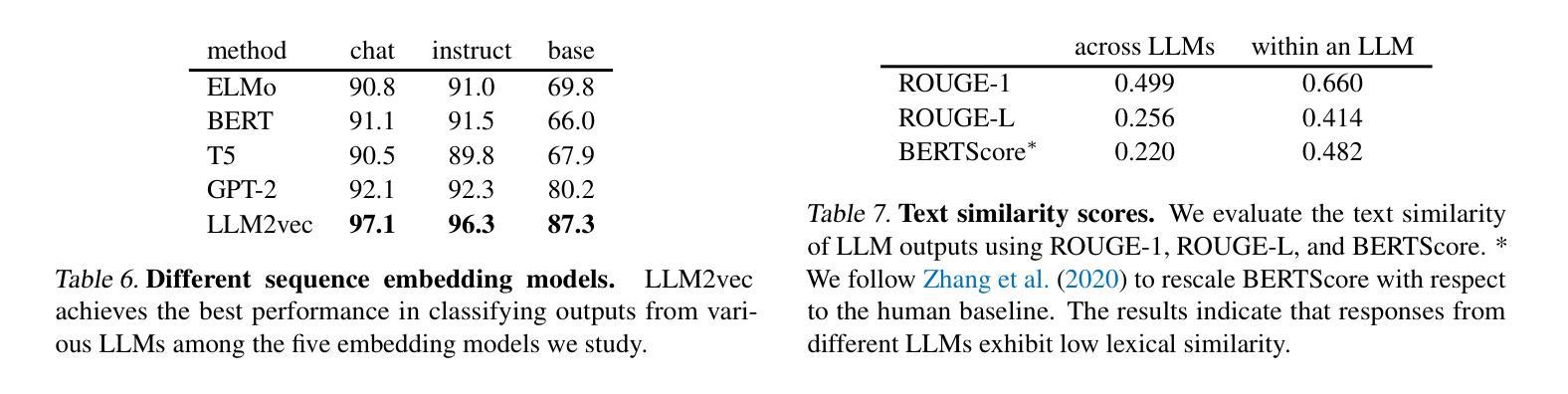
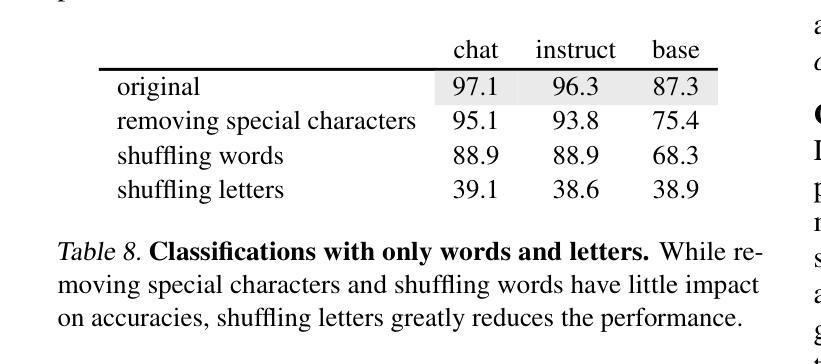
- LLM的特性源于单词级别的分布模式,且这些模式在文本重写、翻译或摘要中依然存在。
- 这些特性不仅存在于LLM的输出中,也与其语义内容有关。
点此查看论文截图

HermesFlow: Seamlessly Closing the Gap in Multimodal Understanding and Generation
Authors:Ling Yang, Xinchen Zhang, Ye Tian, Chenming Shang, Minghao Xu, Wentao Zhang, Bin Cui
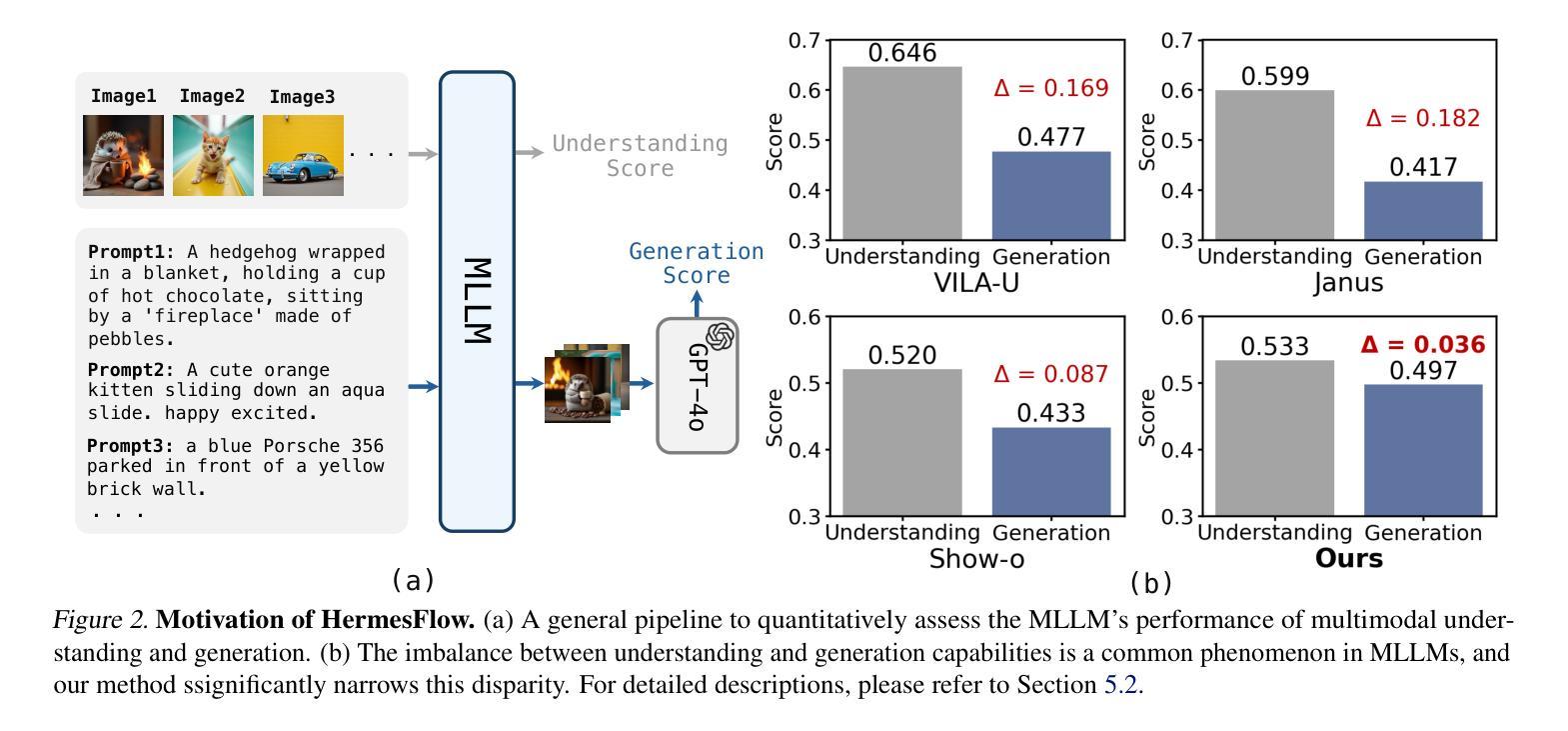
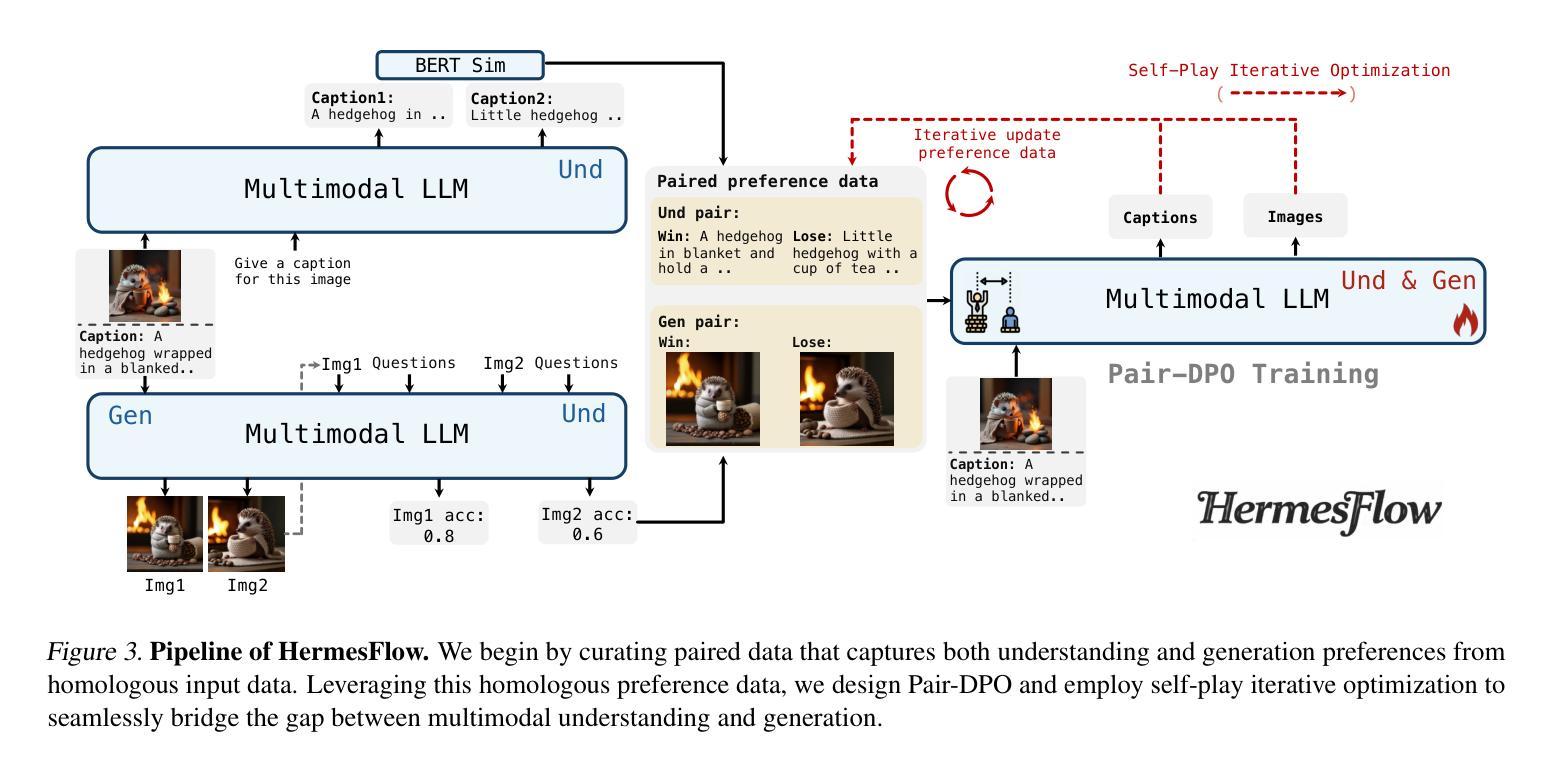
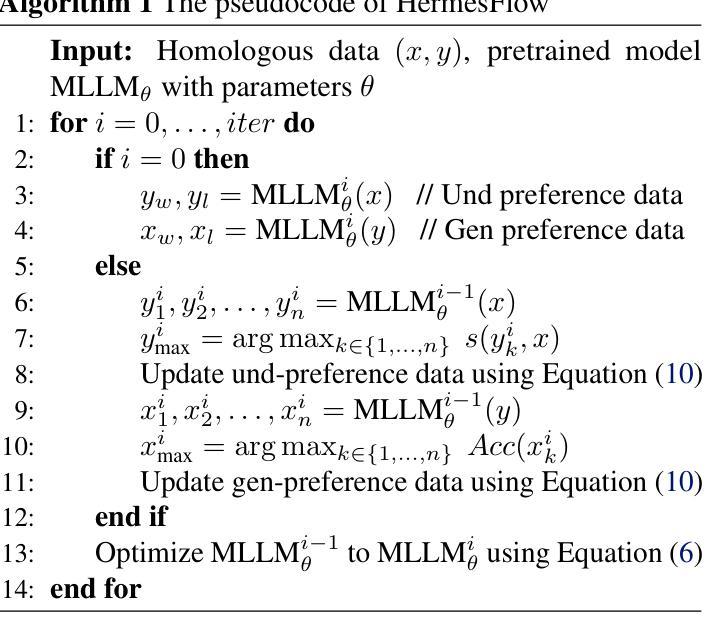
The remarkable success of the autoregressive paradigm has made significant advancement in Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs), with powerful models like Show-o, Transfusion and Emu3 achieving notable progress in unified image understanding and generation. For the first time, we uncover a common phenomenon: the understanding capabilities of MLLMs are typically stronger than their generative capabilities, with a significant gap between the two. Building on this insight, we propose HermesFlow, a simple yet general framework designed to seamlessly bridge the gap between understanding and generation in MLLMs. Specifically, we take the homologous data as input to curate homologous preference data of both understanding and generation. Through Pair-DPO and self-play iterative optimization, HermesFlow effectively aligns multimodal understanding and generation using homologous preference data. Extensive experiments demonstrate the significant superiority of our approach over prior methods, particularly in narrowing the gap between multimodal understanding and generation. These findings highlight the potential of HermesFlow as a general alignment framework for next-generation multimodal foundation models. Code: https://github.com/Gen-Verse/HermesFlow
自动回归范式的巨大成功使得多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)取得了显著进展。像Show-o、Transfusion和Emu3等强大模型在统一图像理解和生成方面取得了显著进展。我们首次发现了一个普遍现象:MLLMs的理解能力通常强于其生成能力,两者之间存在明显的差距。基于这一发现,我们提出了HermesFlow,这是一个简单而通用的框架,旨在无缝桥接MLLMs中理解与生成之间的差距。具体来说,我们以同源数据作为输入,整理出理解和生成方面的同源偏好数据。通过Pair-DPO和自我博弈迭代优化,HermesFlow有效地使用同源偏好数据对齐多模态理解和生成。大量实验证明我们的方法较之前的方法有显著的优越性,特别是在缩小多模态理解与生成的差距方面。这些发现突显了HermesFlow作为下一代多模态基础模型的一般对齐框架的潜力。代码:https://github.com/Gen-Verse/HermesFlow
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Code: https://github.com/Gen-Verse/HermesFlow
Summary
多模态大语言模型(MLLMs)的自回归范式取得了显著成功,Show-o、Transfusion和Emu3等强大模型在统一图像理解和生成方面取得了显著进展。研究发现MLLMs的理解能力通常强于生成能力,两者之间存在明显差距。基于此,提出了HermesFlow框架,旨在无缝桥接MLLMs中的理解与生成差距。通过同源数据输入、同源偏好数据整合以及Pair-DPO和自我博弈迭代优化,HermesFlow有效对齐多模态理解与生成。实验表明,该方法显著优于其他方法,特别是在缩小多模态理解与生成差距方面。这凸显了HermesFlow作为下一代多模态基础模型的通用对齐框架的潜力。
Key Takeaways
- 多模态大语言模型(MLLMs)自回归范式的成功推动了模型如Show-o、Transfusion和Emu3的进展。
- MLLMs的理解能力通常强于生成能力,存在能力差距。
- HermesFlow框架旨在桥接MLLMs中的理解与生成差距。
- HermesFlow利用同源数据输入和同源偏好数据整合。
- 通过Pair-DPO和自我博弈迭代优化,HermesFlow有效对齐多模态理解与生成。
- 实验表明HermesFlow在缩小多模态理解与生成差距方面显著优于其他方法。
点此查看论文截图
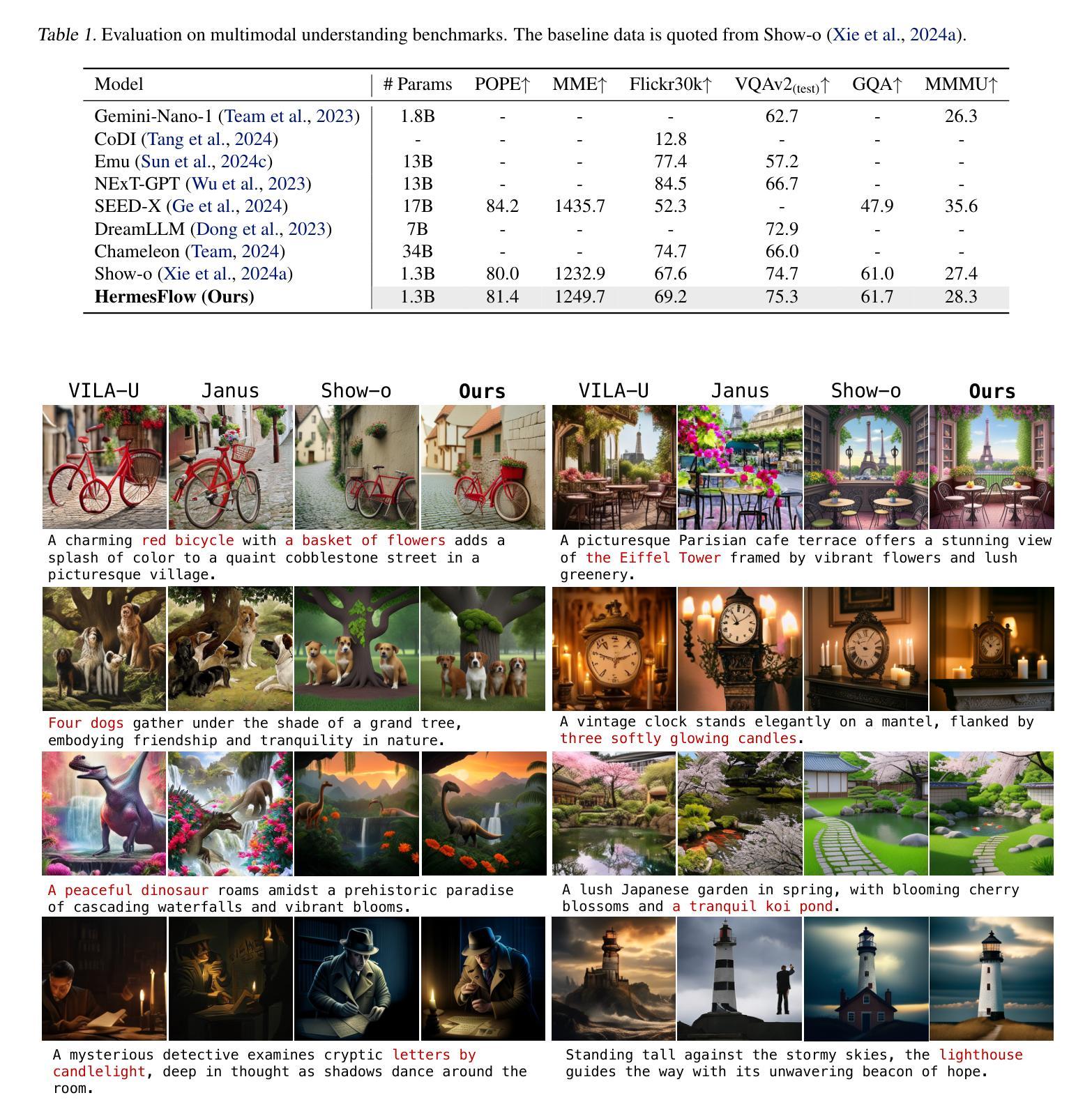
SoftCoT: Soft Chain-of-Thought for Efficient Reasoning with LLMs
Authors:Yige Xu, Xu Guo, Zhiwei Zeng, Chunyan Miao
Chain-of-Thought (CoT) reasoning enables Large Language Models (LLMs) to solve complex reasoning tasks by generating intermediate reasoning steps. However, most existing approaches focus on hard token decoding, which constrains reasoning within the discrete vocabulary space and may not always be optimal. While recent efforts explore continuous-space reasoning, they often suffer from catastrophic forgetting, limiting their applicability to state-of-the-art LLMs that already perform well in zero-shot settings with a proper instruction. To address this challenge, we propose a novel approach for continuous-space reasoning that does not require modifying the underlying LLM. Specifically, we employ a lightweight assistant model to generate instance-specific soft thought tokens speculatively as the initial chain of thoughts, which are then mapped into the LLM’s representation space via a projection module. Experimental results on five reasoning benchmarks demonstrate that our method enhances LLM reasoning performance through supervised, parameter-efficient fine-tuning.
链式思维(CoT)推理通过生成中间推理步骤,使大型语言模型(LLM)能够解决复杂的推理任务。然而,大多数现有方法侧重于硬令牌解码,这限制了推理在离散词汇空间内,并不总是最优的。虽然最近的努力探索连续空间推理,但它们经常遭受灾难性遗忘的问题,限制了它们在已经表现良好的零样本设置的最新LLM中的应用。为了应对这一挑战,我们提出了一种不需要修改基础LLM的连续空间推理新方法。具体来说,我们采用轻量级助理模型来生成实例特定的软思维令牌作为初始的思维链,然后通过投影模块将其映射到LLM的表示空间。在五个推理基准测试上的实验结果表明,我们的方法通过监督、参数高效的微调,提高了LLM的推理性能。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于Chain-of-Thought(CoT)推理的大型语言模型(LLM)能够解决复杂的推理任务,通过生成中间推理步骤来实现。然而,现有方法大多集中在硬令牌解码上,这限制了推理在离散词汇空间内的进行,并不总是最优。尽管最近有努力探索连续空间推理,但它们经常遭受灾难性遗忘的问题。为了解决这个问题,我们提出了一种不需要修改基础LLM的连续空间推理新方法。特别是,我们采用轻量级助理模型来生成实例特定的软思维令牌作为初步思维链,然后通过投影模块映射到LLM的表示空间。在五个推理基准测试上的实验结果表明,我们的方法通过监督、参数有效的微调提高了LLM的推理性能。
Key Takeaways
- CoT推理使LLM能够解决复杂的推理任务,通过生成中间推理步骤实现。
- 现有方法主要集中在硬令牌解码上,这可能限制推理的优化。
- 连续空间推理是最近的研究方向,但存在灾难性遗忘的问题。
- 提出了一种新的连续空间推理方法,不需要修改基础LLM。
- 采用轻量级助理模型生成实例特定的软思维令牌作为初步思维链。
- 通过投影模块将软思维令牌映射到LLM的表示空间。
点此查看论文截图

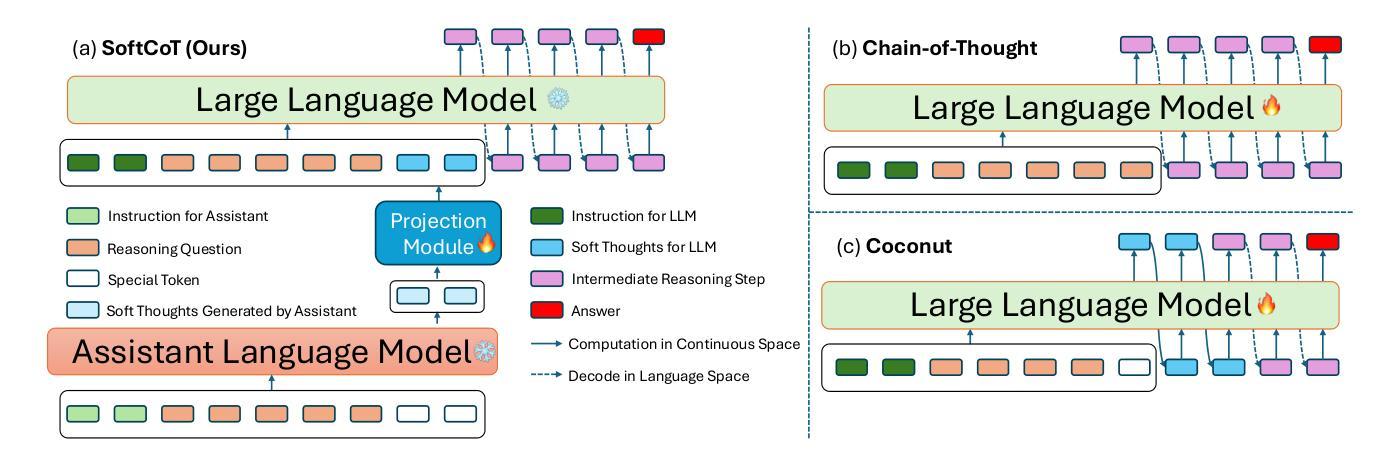
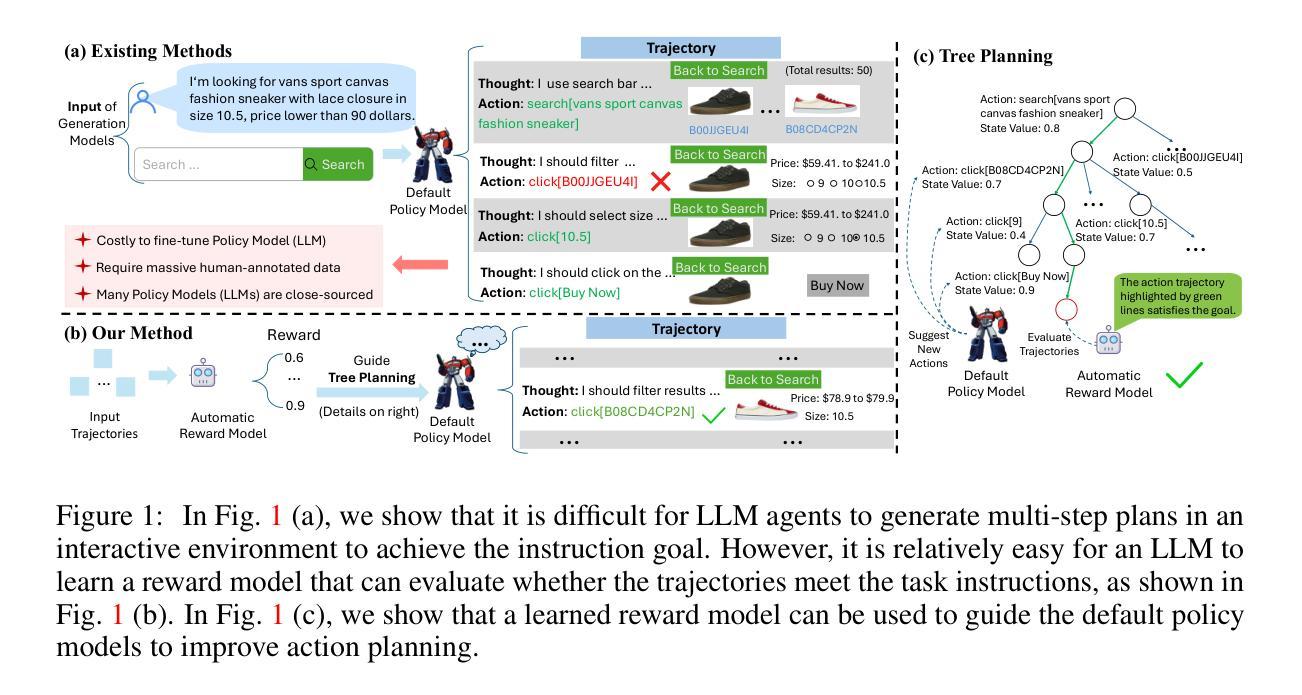
Scaling Autonomous Agents via Automatic Reward Modeling And Planning
Authors:Zhenfang Chen, Delin Chen, Rui Sun, Wenjun Liu, Chuang Gan
Large language models (LLMs) have demonstrated remarkable capabilities across a range of text-generation tasks. However, LLMs still struggle with problems requiring multi-step decision-making and environmental feedback, such as online shopping, scientific reasoning, and mathematical problem-solving. Unlike pure text data, collecting large-scale decision-making data is challenging. Moreover, many powerful LLMs are only accessible through APIs, which hinders their fine-tuning for agent tasks due to cost and complexity. To address LLM agents’ limitations, we propose a framework that can automatically learn a reward model from the environment without human annotations. This model can be used to evaluate the action trajectories of LLM agents and provide heuristics for task planning. Specifically, our approach involves employing one LLM-based agent to navigate an environment randomly, generating diverse action trajectories. Subsequently, a separate LLM is leveraged to assign a task intent and synthesize a negative response alongside the correct response for each trajectory. These triplets (task intent, positive response, and negative response) are then utilized as training data to optimize a reward model capable of scoring action trajectories. The effectiveness and generalizability of our framework are demonstrated through evaluations conducted on different agent benchmarks. In conclusion, our proposed framework represents a significant advancement in enhancing LLM agents’ decision-making capabilities. By automating the learning of reward models, we overcome the challenges of data scarcity and API limitations, potentially revolutionizing the application of LLMs in complex and interactive environments. This research paves the way for more sophisticated AI agents capable of tackling a wide range of real-world problems requiring multi-step decision-making.
大型语言模型(LLM)在多种文本生成任务中表现出了出色的能力。然而,LLM仍然在处理需要多步骤决策和环境反馈的问题上遇到挑战,如在在线购物、科学推理和数学问题解决等领域。与纯文本数据不同,收集大规模决策数据是一项挑战。此外,许多强大的LLM只能通过API访问,这增加了对代理任务的微调成本并带来复杂性。为了解决LLM代理人的局限性,我们提出了一种可以自动从环境中学习奖励模型的框架,无需人工注释。该模型可用于评估LLM代理的行动轨迹,并为任务规划提供启发式信息。具体来说,我们的方法包括使用一个基于LLM的代理在环境中随机导航,生成各种行动轨迹。然后利用另一个LLM为每条轨迹分配任务意图,并合成一个与正确响应相对应的负面响应。这些三元组(任务意图、正向响应和负面响应)随后被用作训练数据,以优化能够评估行动轨迹的奖励模型。我们的框架在不同代理基准测试上的评估结果证明了其有效性和通用性。总之,我们提出的框架在增强LLM代理的决策能力方面取得了重大进展。通过自动学习奖励模型,我们克服了数据稀缺和API限制的挑战,有可能彻底改变LLM在复杂和交互式环境中的应用。这项研究为能够处理需要多步骤决策的各种现实世界问题的更高级AI代理铺平了道路。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICLR2025, Project page: https://armap-agent.github.io
Summary
大型语言模型(LLM)在文本生成任务中表现出卓越的能力,但在需要多步骤决策、环境反馈的情境,如在线购物、科学推理和数学问题解决中仍面临挑战。针对LLM代理的局限性,提出了一种能够自动从环境中学习奖励模型的框架,无需人工注释即可评估LLM代理的行动轨迹,为任务规划提供启发式信息。该框架通过LLM代理在环境中随机导航生成多样的行动轨迹,并利用另一LLM为每条轨迹分配任务意图和合成负面响应及正确响应,形成训练数据来优化能够评分行动轨迹的奖励模型。该框架在多个代理基准测试上的评估结果证明了其有效性和通用性。总之,该框架显著提高了LLM代理的决策能力,通过自动化奖励模型的学习克服了数据稀缺和API限制的挑战,有望为复杂、交互式环境中的LLM应用带来革命性变革。
Key Takeaways
- LLM在文本生成任务中表现出卓越的能力,但在需要多步骤决策和环境反馈的问题中仍存在挑战。
- 提出的框架能自动从环境中学习奖励模型,无需人工注释即可评估LLM代理的行动轨迹。
- 框架通过LLM代理在环境中随机导航生成多样的行动轨迹,并利用LLM合成训练数据来优化奖励模型。
- 框架的有效性在多个代理基准测试上得到证明。
- 该框架克服了数据稀缺和API限制的挑战。
- 该框架有望为复杂、交互式环境中的LLM应用带来变革。
点此查看论文截图

SWE-Lancer: Can Frontier LLMs Earn $1 Million from Real-World Freelance Software Engineering?
Authors:Samuel Miserendino, Michele Wang, Tejal Patwardhan, Johannes Heidecke
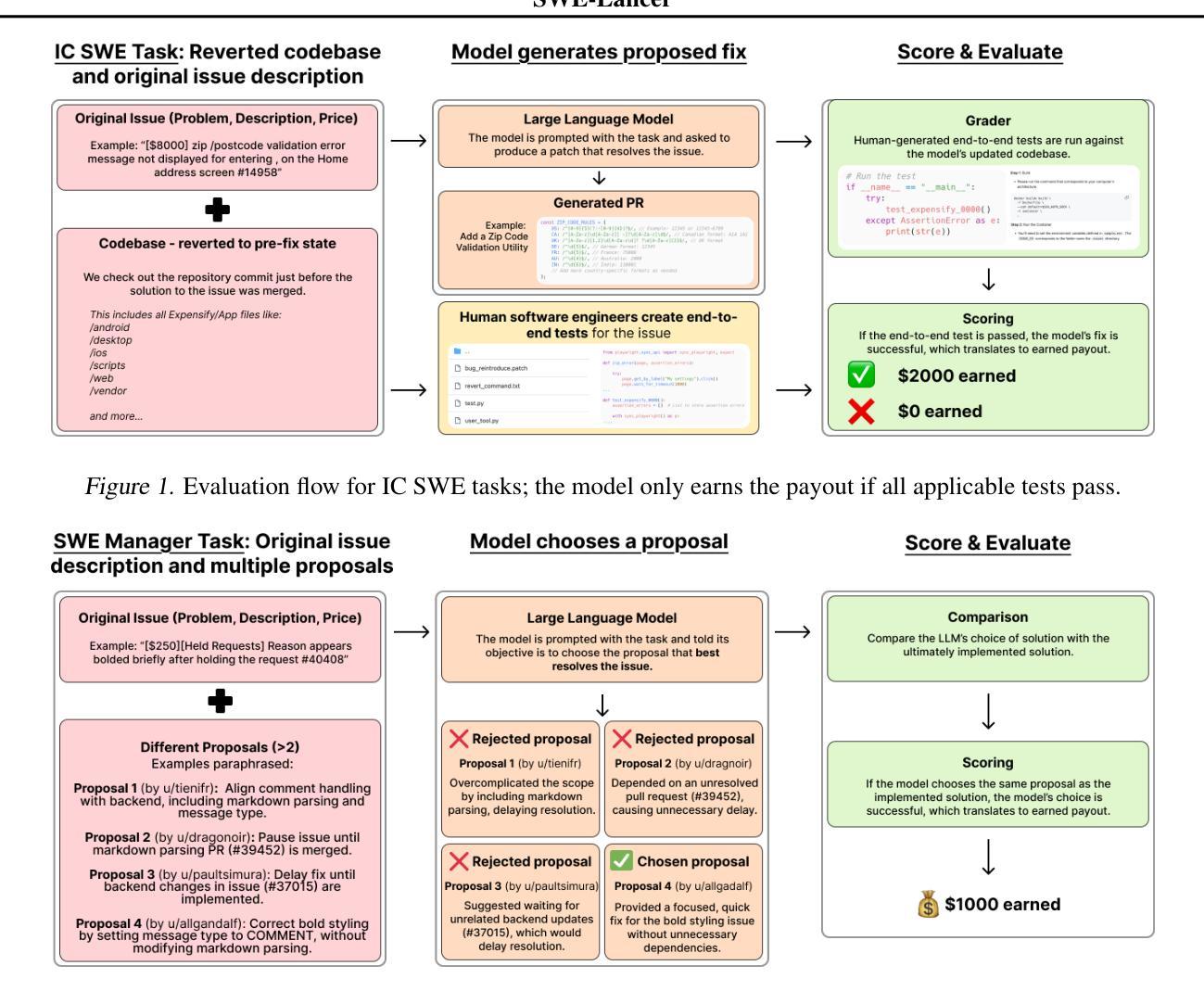
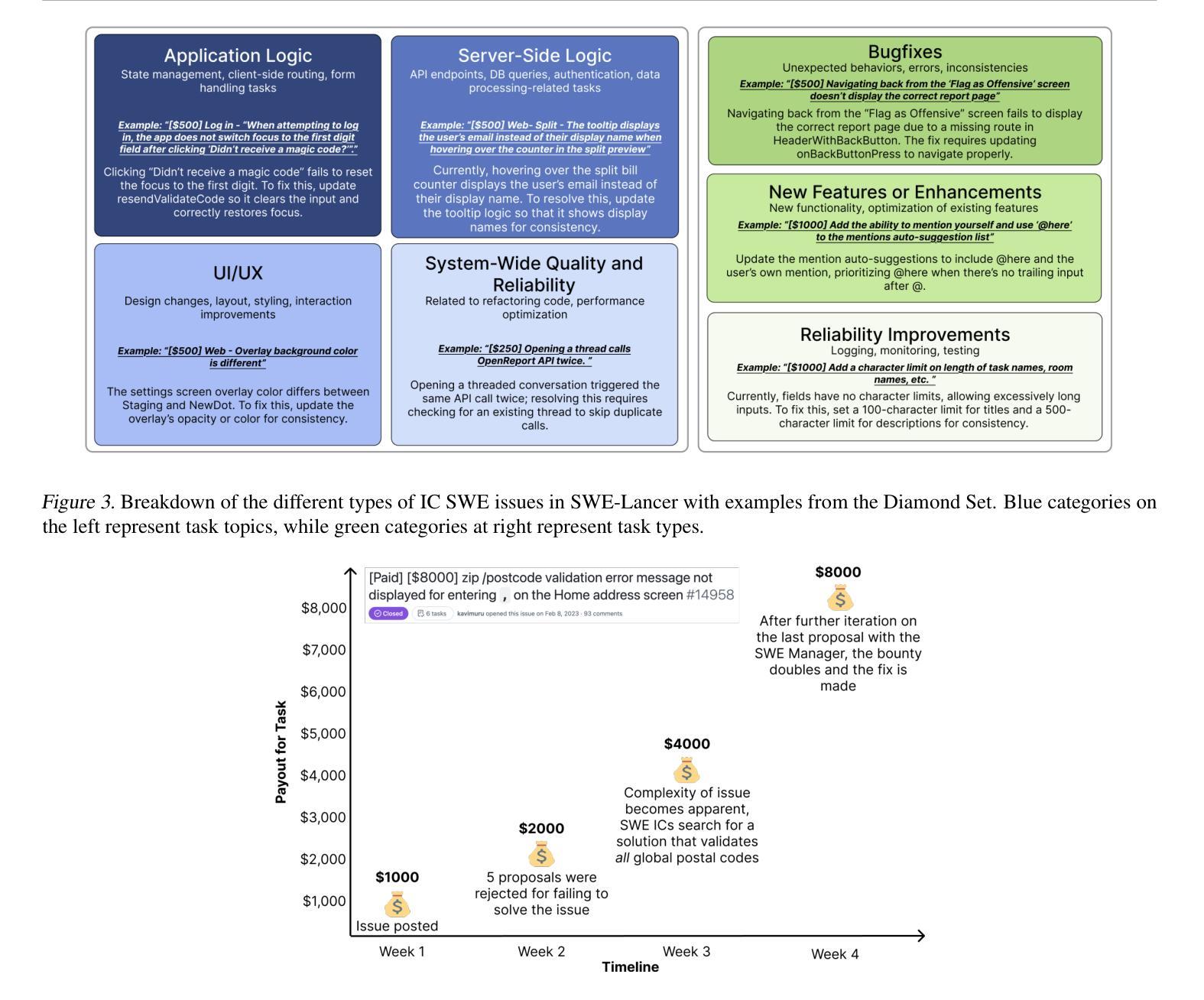
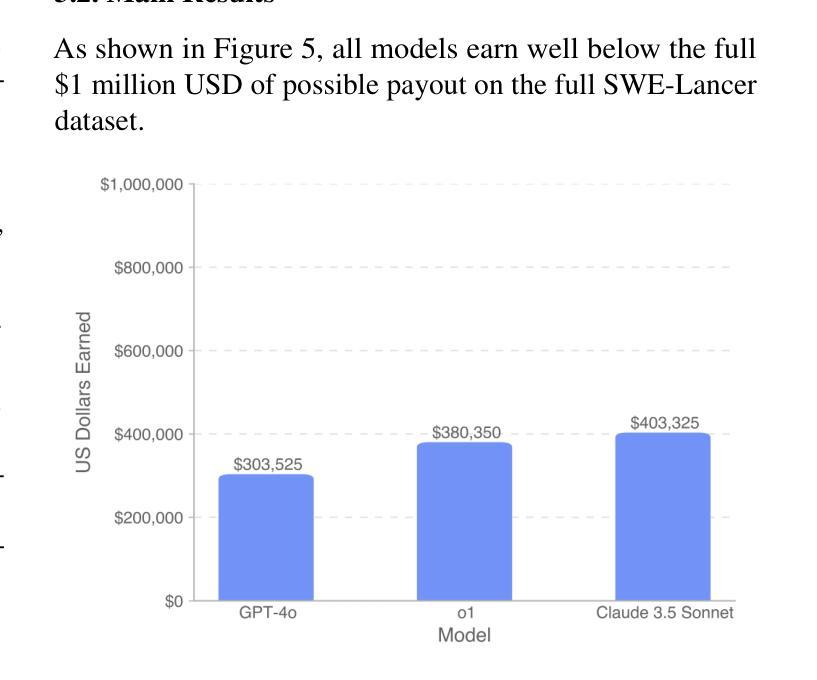
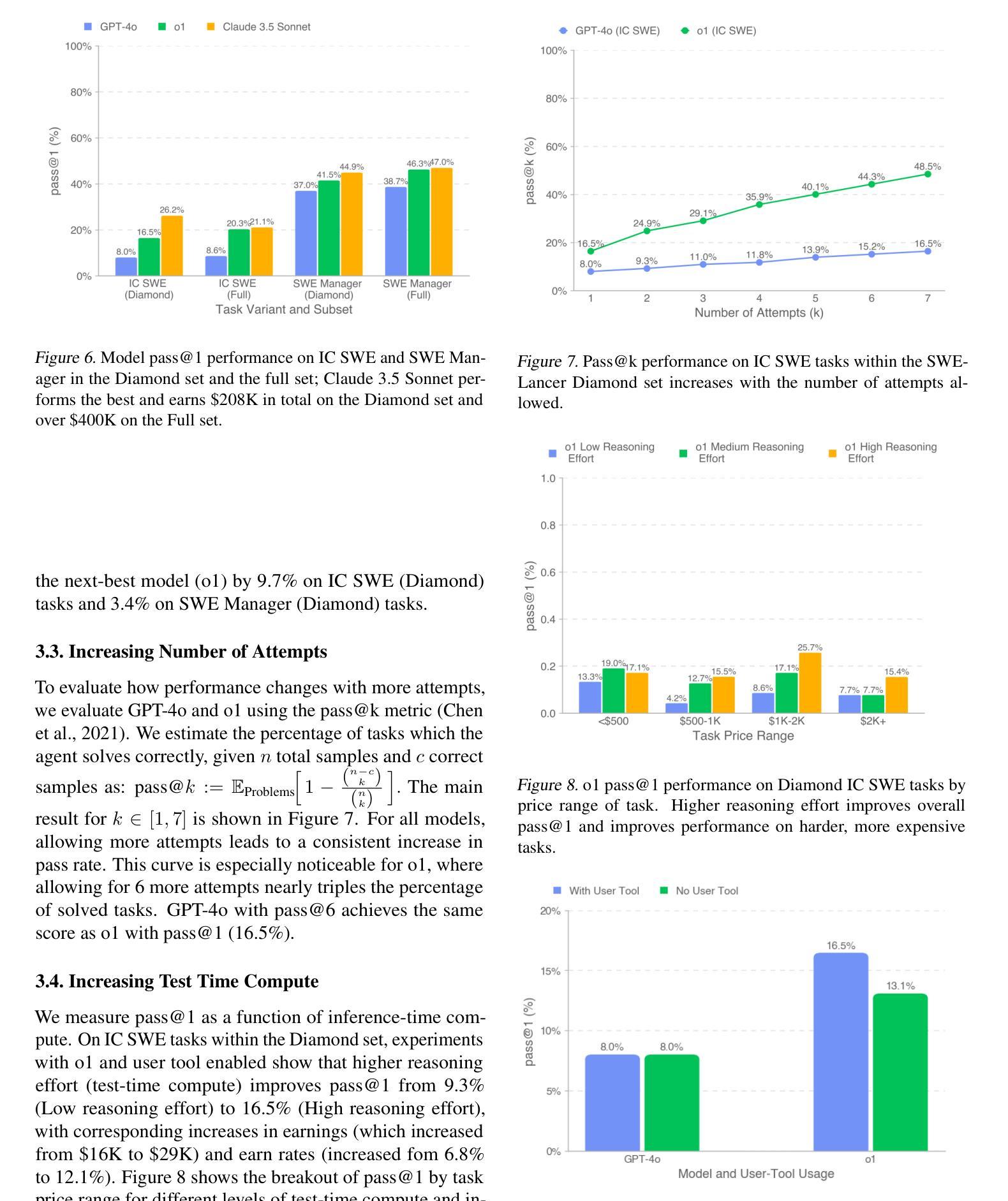
We introduce SWE-Lancer, a benchmark of over 1,400 freelance software engineering tasks from Upwork, valued at $1 million USD total in real-world payouts. SWE-Lancer encompasses both independent engineering tasks–ranging from $50 bug fixes to $32,000 feature implementations–and managerial tasks, where models choose between technical implementation proposals. Independent tasks are graded with end-to-end tests triple-verified by experienced software engineers, while managerial decisions are assessed against the choices of the original hired engineering managers. We evaluate model performance and find that frontier models are still unable to solve the majority of tasks. To facilitate future research, we open-source a unified Docker image and a public evaluation split, SWE-Lancer Diamond (https://github.com/openai/SWELancer-Benchmark). By mapping model performance to monetary value, we hope SWE-Lancer enables greater research into the economic impact of AI model development.
我们推出了SWE-Lancer,这是一个来自Upwork的自由职业软件工程项目基准测试,包含超过1400项任务,总价值百万美元级别的真实世界支付金额。SWE-Lancer不仅包括从价值50美元的bug修复到价值高达3万2千美元的功能开发等独立工程任务,还包括管理任务,在这些任务中,模型需要在技术实施方案之间进行选择。独立任务通过经验丰富的软件工程师进行端到端测试的三重验证进行评分,而管理决策则根据最初雇佣的工程经理的选择进行评估。我们评估模型性能并发现前沿模型仍然无法解决大多数任务。为了方便未来研究,我们公开了一个统一的Docker镜像和一个公共评估版本SWE-Lancer Diamond(https://github.com/openai/SWELancer-Benchmark)。通过把模型性能映射到货币价值上,我们希望SWE-Lancer能够促进对AI模型开发经济影响的研究。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 9 pages, 24 pages appendix
Summary
SWE-Lancer是来自于Upwork的真实世界软件开发任务的基准测试,涵盖超过1400项任务,总价值达百万美元。它包括独立工程任务和管理任务,模型需在技术实施提案中进行选择。独立任务通过经验丰富的软件工程师进行端到端测试的三重验证进行分级,管理决策则与最初雇佣的工程经理的选择相对比进行评估。作者评估了模型性能,发现前沿模型仍无法解决大多数任务。为了方便未来研究,作者开源了统一的Docker镜像和公共评估版本SWE-Lancer Diamond,通过将模型性能映射为货币价值,为人工智能模型开发的经济研究提供了新的方向。
Key Takeaways
- SWE-Lancer是一个包含超过1400项真实世界软件开发任务的基准测试,涵盖独立工程和管理任务。
- 独立任务通过端到端测试的三重验证进行分级,管理决策则与工程经理的选择相对比进行评估。
- 前沿模型仍无法解决大多数任务,说明在复杂的软件开发任务中仍存在挑战。
- SWE-Lancer开放了一个公共评估版本SWE-Lancer Diamond,并提供统一的Docker镜像,方便未来研究。
- 通过将模型性能映射为货币价值,SWE-Lancer有助于评估模型的经济影响。
- 这个基准测试可以为AI模型在真实世界软件开发任务中的应用提供有价值的参考。
点此查看论文截图

A-MEM: Agentic Memory for LLM Agents
Authors:Wujiang Xu, Zujie Liang, Kai Mei, Hang Gao, Juntao Tan, Yongfeng Zhang
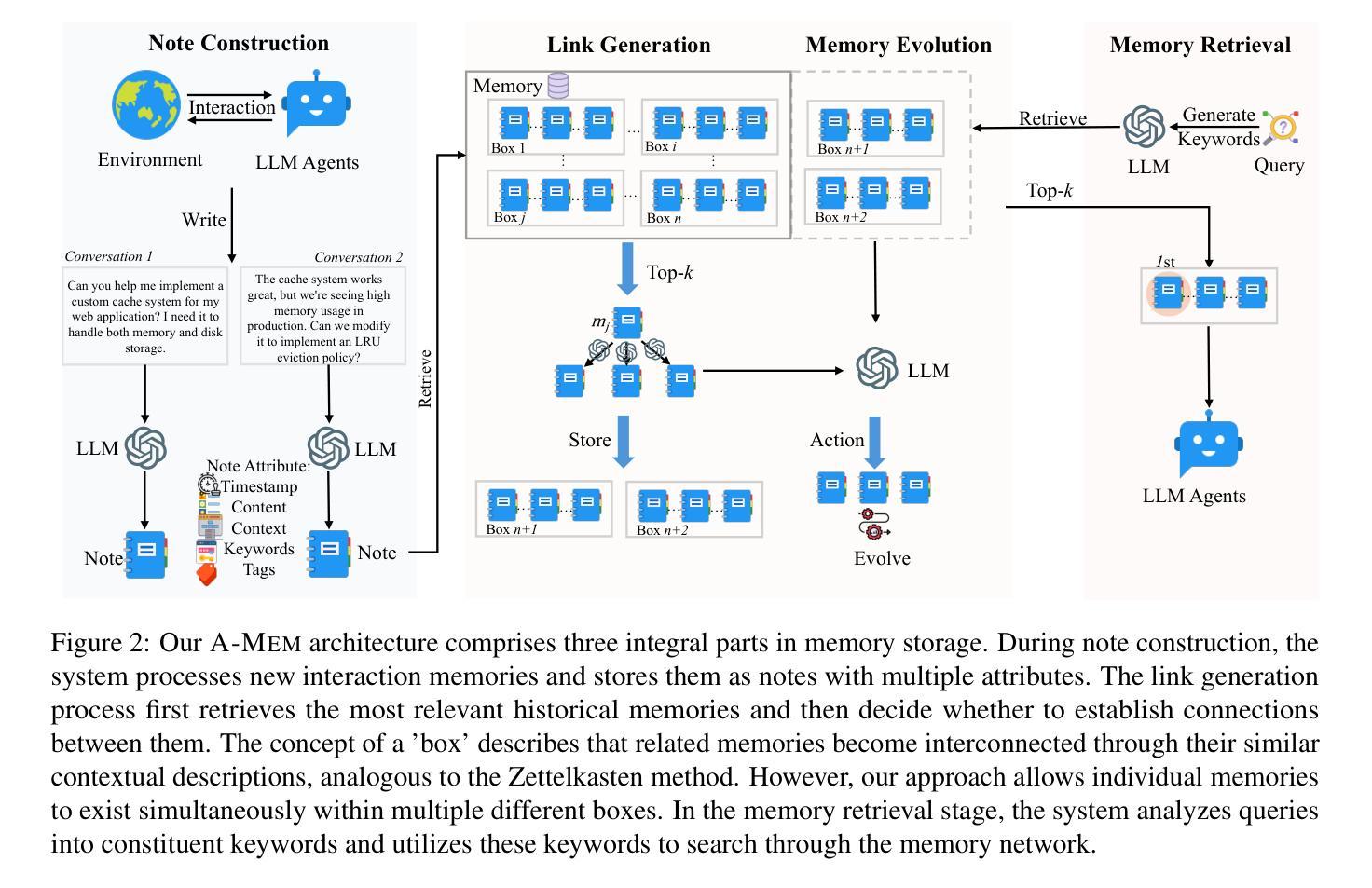
While large language model (LLM) agents can effectively use external tools for complex real-world tasks, they require memory systems to leverage historical experiences. Current memory systems enable basic storage and retrieval but lack sophisticated memory organization, despite recent attempts to incorporate graph databases. Moreover, these systems’ fixed operations and structures limit their adaptability across diverse tasks. To address this limitation, this paper proposes a novel agentic memory system for LLM agents that can dynamically organize memories in an agentic way. Following the basic principles of the Zettelkasten method, we designed our memory system to create interconnected knowledge networks through dynamic indexing and linking. When a new memory is added, we generate a comprehensive note containing multiple structured attributes, including contextual descriptions, keywords, and tags. The system then analyzes historical memories to identify relevant connections, establishing links where meaningful similarities exist. Additionally, this process enables memory evolution - as new memories are integrated, they can trigger updates to the contextual representations and attributes of existing historical memories, allowing the memory network to continuously refine its understanding. Our approach combines the structured organization principles of Zettelkasten with the flexibility of agent-driven decision making, allowing for more adaptive and context-aware memory management. Empirical experiments on six foundation models show superior improvement against existing SOTA baselines. The source code is available at https://github.com/WujiangXu/AgenticMemory.
虽然大型语言模型(LLM)代理可以有效地利用外部工具完成复杂的现实世界任务,但它们需要记忆系统来利用历史经验。当前的记忆系统虽然实现了基本的存储和检索功能,但缺乏高级的记忆组织功能,尽管最近有尝试融入图形数据库。此外,这些系统的固定操作和结构限制了它们在多样化任务中的适应性。为了解决这一限制,本文提出了一种新型的大型语言模型代理记忆系统,该系统能够以动态的方式组织记忆。
遵循Zettelkasten方法的基本原则,我们设计的记忆系统通过动态索引和链接创建相互关联的知识网络。每当添加新记忆时,我们会生成一个包含多个结构化属性的综合笔记,包括上下文描述、关键词和标签。然后,系统分析历史记忆以识别相关连接,在存在有意义的相似性时建立链接。此外,这个过程使记忆得以进化——随着新记忆的融入,它们可以触发对现有历史记忆的上下文表示和属性的更新,使记忆网络能够持续不断地优化其理解。我们的方法结合了Zettelkasten的结构化组织原则与代理驱动的决策灵活性,从而实现更适应上下文变化的记忆管理。在六个基础模型上的实证实验表明,与现有的最新技术基准相比,有明显的改进。源代码可在https://github.com/WujiangXu/AgenticMemory找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大型语言模型(LLM)需要记忆系统来利用历史经验以完成复杂的现实世界任务。当前记忆系统虽能进行基本存储和检索,但在组织记忆方面缺乏高级功能,且固定操作和结构的限制影响了其在不同任务中的适应性。为解决这一问题,本文提出了一种新型的语言模型记忆系统,采用动态索引和链接的方式创建知识网络。新记忆被添加时,系统生成包含上下文描述、关键词和标签的综合性笔记,并分析历史记忆以识别关联,建立有意义的链接。新记忆的融入可触发现有历史记忆的更新,使记忆网络不断完善理解。结合Zettelkasten的结构化组织原则和代理驱动的决策灵活性,实现更适应上下文变化的记忆管理。在六种基础模型上的实验显示,该方法优于现有最先进基线方法。
Key Takeaways
- LLM需要大量记忆系统来利用历史经验完成复杂任务。
- 当前记忆系统缺乏高级组织功能,不能适应多样化任务需求。
- 本文提出一种新型的记忆系统,采用动态组织方式创建知识网络。
- 新记忆生成时,系统生成综合性笔记并识别历史记忆中的关联。
- 新记忆的融入能够触发历史记忆的更新,增强记忆网络的理解能力。
- 该方法结合Zettelkasten的结构化组织和代理决策的灵活性。
点此查看论文截图

APB: Accelerating Distributed Long-Context Inference by Passing Compressed Context Blocks across GPUs
Authors:Yuxiang Huang, Mingye Li, Xu Han, Chaojun Xiao, Weilin Zhao, Sun Ao, Hao Zhou, Jie Zhou, Zhiyuan Liu, Maosong Sun
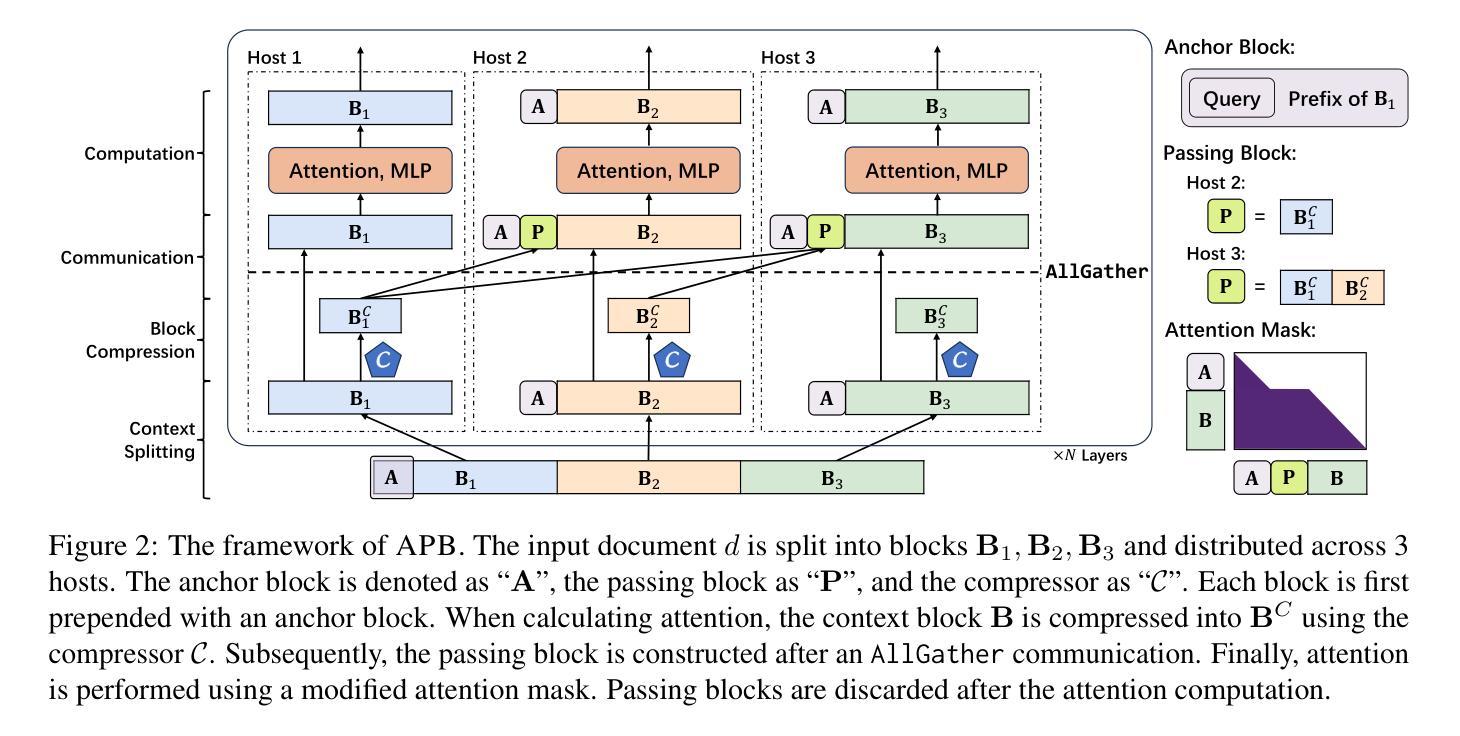
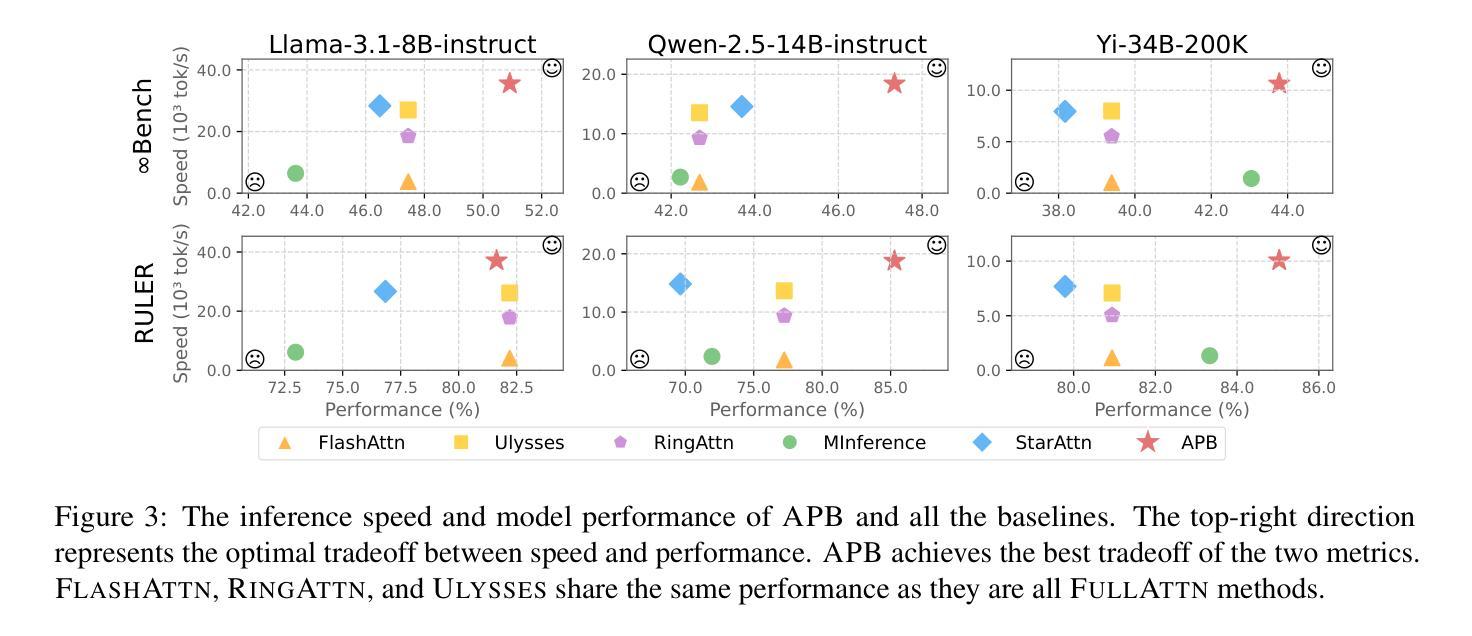
While long-context inference is crucial for advancing large language model (LLM) applications, its prefill speed remains a significant bottleneck. Current approaches, including sequence parallelism strategies and compute reduction through approximate attention mechanisms, still fall short of delivering optimal inference efficiency. This hinders scaling the inputs to longer sequences and processing long-context queries in a timely manner. To address this, we introduce APB, an efficient long-context inference framework that leverages multi-host approximate attention to enhance prefill speed by reducing compute and enhancing parallelism simultaneously. APB introduces a communication mechanism for essential key-value pairs within a sequence parallelism framework, enabling a faster inference speed while maintaining task performance. We implement APB by incorporating a tailored FlashAttn kernel alongside optimized distribution strategies, supporting diverse models and parallelism configurations. APB achieves speedups of up to 9.2x, 4.2x, and 1.6x compared with FlashAttn, RingAttn, and StarAttn, respectively, without any observable task performance degradation. We provide the implementation and experiment code of APB in https://github.com/thunlp/APB.
虽然长上下文推理对于推动大型语言模型(LLM)应用的进步至关重要,但其预填充速度仍然是一个重要的瓶颈。当前的方法,包括序列并行策略和通过近似注意力机制减少计算,仍然未能实现最佳的推理效率。这阻碍了扩展到更长的序列输入并及时处理长上下文查询。为了解决这一问题,我们引入了APB,这是一种有效的长上下文推理框架,它通过利用多主机近似注意力机制同时提高计算效率和并行性来提高预填充速度。APB在序列并行框架内引入了一种关键键值对的通信机制,以更快的推理速度维持任务性能。我们通过结合定制的FlashAttn内核和优化的分布策略来实现APB,支持不同的模型和并行配置。与FlashAttn、RingAttn和StarAttn相比,APB分别实现了最高达9.2倍、4.2倍和1.6倍的加速,且无任何任务性能下降的可观察结果。我们在https://github.com/thunlp/APB上提供了APB的实现和实验代码。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Preprint
摘要
为解决大型语言模型(LLM)应用中长文本推理的预填充速度瓶颈问题,提出了APB高效长文本推理框架。该框架利用多主机近似注意力机制,同时减少计算并增强并行性,提高了预填充速度。通过引入序列并行框架内的关键键值对通信机制,实现在保持任务性能的同时加快推理速度。APB通过定制的FlashAttn内核和优化分布策略实现,支持多种模型和并行配置。与FlashAttn、RingAttn和StarAttn相比,APB分别实现了最高达9.2倍、4.2倍和1.6倍的加速,且任务性能无明显下降。
要点
- 长文本推理的预填充速度是LLM应用中的瓶颈。
- 当前方法如序列并行策略和近似注意力机制仍未能实现最优推理效率。
- APB框架利用多主机近似注意力机制提高预填充速度。
- APB通过引入序列并行框架内的关键键值对通信机制,加快推理速度,同时保持任务性能。
- APB通过定制化的FlashAttn内核和优化分布策略实现。
- APB与现有方法相比实现了显著的加速效果。
- APB的实现和实验代码已在GitHub上公开。
点此查看论文截图


On the robustness of ChatGPT in teaching Korean Mathematics
Authors:Phuong-Nam Nguyen, Quang Nguyen-The, An Vu-Minh, Diep-Anh Nguyen, Xuan-Lam Pham
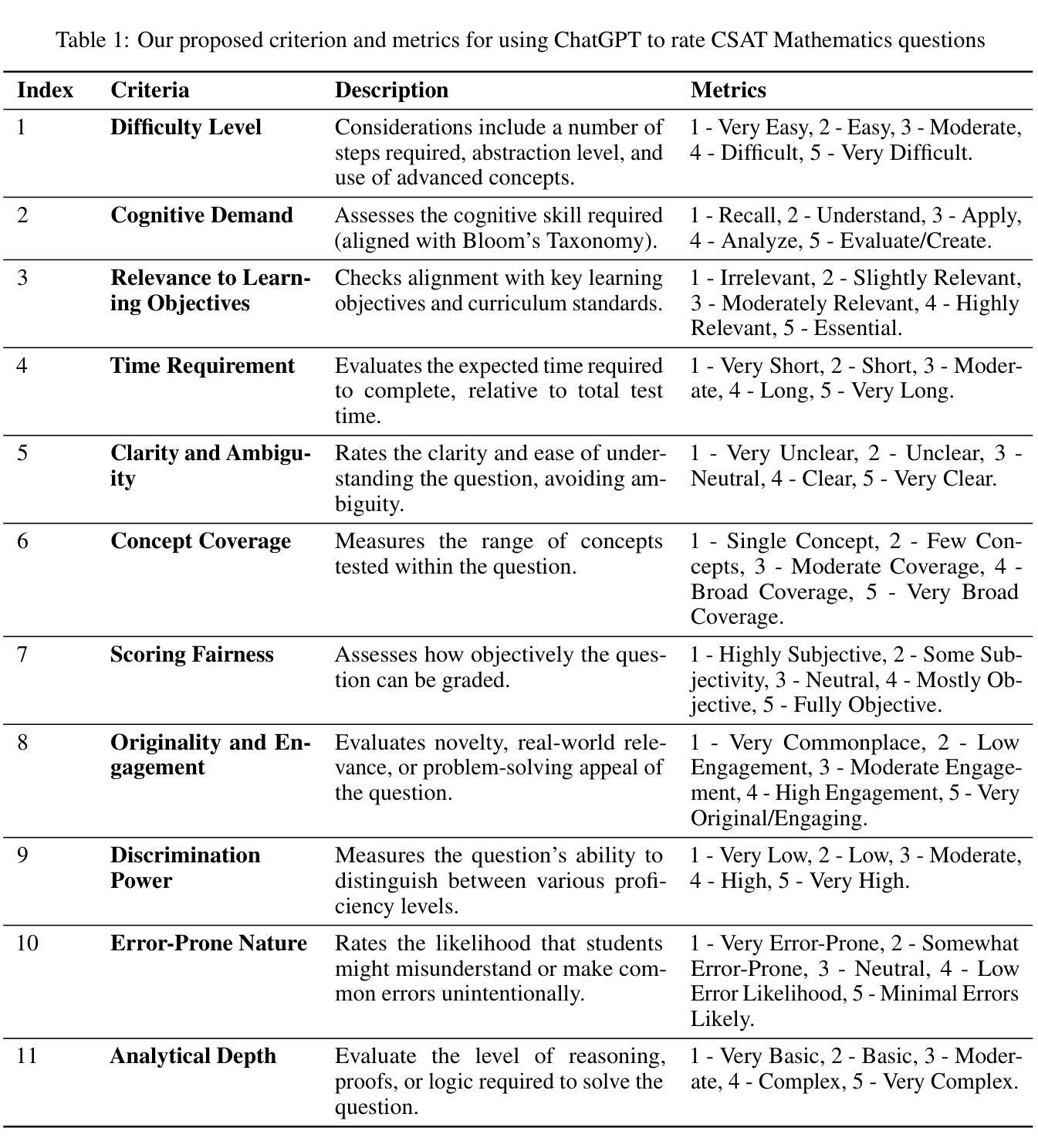
ChatGPT, an Artificial Intelligence model, has the potential to revolutionize education. However, its effectiveness in solving non-English questions remains uncertain. This study evaluates ChatGPT’s robustness using 586 Korean mathematics questions. ChatGPT achieves 66.72% accuracy, correctly answering 391 out of 586 questions. We also assess its ability to rate mathematics questions based on eleven criteria and perform a topic analysis. Our findings show that ChatGPT’s ratings align with educational theory and test-taker perspectives. While ChatGPT performs well in question classification, it struggles with non-English contexts, highlighting areas for improvement. Future research should address linguistic biases and enhance accuracy across diverse languages. Domain-specific optimizations and multilingual training could improve ChatGPT’s role in personalized education.
ChatGPT作为一种人工智能模型,具有颠覆教育的潜力。然而,其在解决非英语问题时的有效性尚不确定。本研究使用586道韩国数学题目对ChatGPT的稳健性进行了评估。ChatGPT准确率为66.72%,回答了其中的391个问题。我们还对其根据十一个标准对数学题目进行评分的能力进行了评估,并进行了主题分析。我们的研究结果表明,ChatGPT的评分与教育理论及测试者的观点一致。虽然ChatGPT在问题分类方面表现良好,但在非英语环境中却感到困难,这凸显了需要改进的领域。未来的研究应解决语言偏见问题,提高在不同语言环境中的准确性。针对特定领域的优化和多语言训练可以提高ChatGPT在个性化教育中的角色。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 21 pages, 12 figures, includes statistical analysis of ChatGPT’s robustness in solving and rating multilingual mathematics questions. Focus on Korean CSAT Mathematics. Evaluates AI accuracy, rating effectiveness, and topic analysis
Summary
ChatGPT在解决非英语问题方面的效果尚待验证。本研究通过586道韩国数学题目对ChatGPT的稳健性进行了评估。ChatGPT准确率为66.72%,即正确回答了391个问题。此外,还评估了其根据11项标准对数学题目进行评分的能力并进行了主题分析。研究发现ChatGPT的评分与教育理论及考生观点相符。ChatGPT在问题分类方面表现良好,但在非英语环境下表现欠佳,未来研究应解决语言偏见问题并提升其在多种语言环境下的准确性。
Key Takeaways
- ChatGPT在解决韩国数学题目时表现出一定的准确性,正确率为66.72%。
- ChatGPT能够根据教育理论和考生观点对数学题目进行评分。
- ChatGPT在非英语环境下的表现尚待提升,特别是在解决非英语数学题目时存在挑战。
- ChatGPT在问题分类方面展现出了良好的能力。
- 研究发现ChatGPT在某些方面存在语言偏见,未来研究需要解决这一问题。
- 通过域特定优化和多语言训练,ChatGPT在个性化教育中的角色有望得到提升。
点此查看论文截图

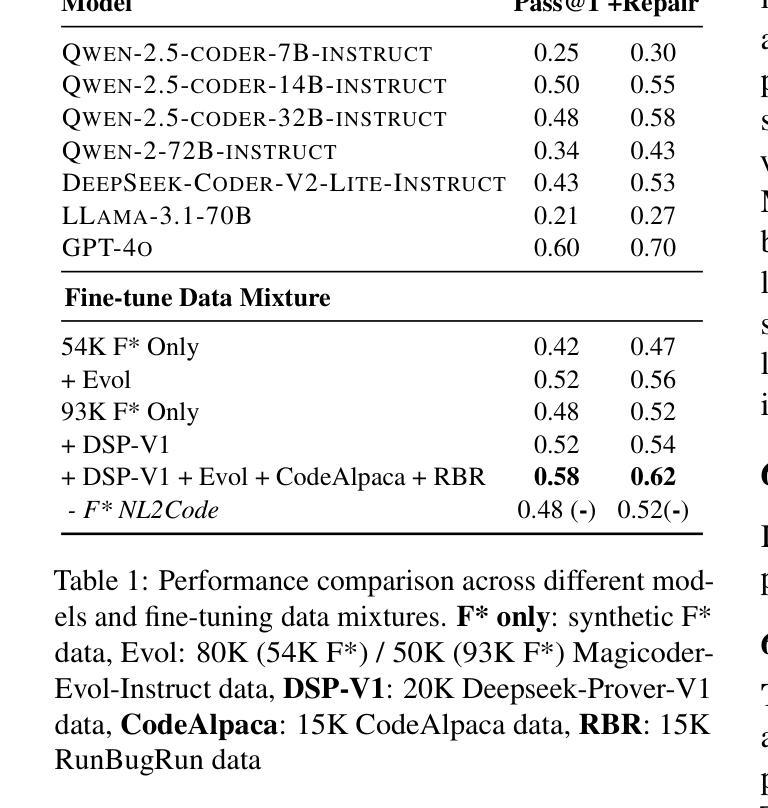
Building A Proof-Oriented Programmer That Is 64% Better Than GPT-4o Under Data Scarsity
Authors:Dylan Zhang, Justin Wang, Tianran Sun
Existing LMs struggle with proof-oriented programming due to data scarcity, which manifest in two key ways: (1) a lack of sufficient corpora for proof-oriented programming languages such as F*, and (2) the absence of large-scale, project-level proof-oriented implementations that can teach the model the intricate reasoning process when performing proof-oriented programming. We present the first on synthetic data augmentation for project level proof oriented programming for both generation and repair. Our method addresses data scarcity by synthesizing basic proof-oriented programming problems for proficiency in that language; incorporating diverse coding data for reasoning capability elicitation and creating new proofs and repair data within existing repositories. This approach enables language models to both synthesize and repair proofs for function- and repository-level code. We show that our fine-tuned 14B parameter model, PoPilot, can exceed the performance of the models that outperforms GPT-4o in project-level proof-oriented programming by 64% relative margin, and can improve GPT-4o’s performance by 54% by repairing its outputs over GPT-4o’s self-repair.
现有的语言模型(LMs)在面向证明编程方面存在困难,这主要是由于数据稀缺导致的,主要体现在两个方面:(1)缺乏足够的面向证明编程语言的语料库,如F*,以及(2)缺乏大规模的项目级面向证明的编程实现,这些实现可以教授模型在进行面向证明编程时的复杂推理过程。我们首次介绍了项目级面向证明的编程的合成数据增强方法,包括生成和修复两个方面。我们的方法通过合成基本的面向证明的编程问题来解决该语言的熟练程度问题;通过引入多样化的编码数据来激发推理能力,并在现有存储库中创建新的证明和修复数据。这种方法使语言模型能够合成和修复函数级和存储库级的代码证明。我们展示了经过微调拥有14B参数的模型PoPilot,在面向项目级别的证明编程上能够超越GPT-4o模型的表现,相对性能提升高达64%,并且在修复输出方面相较于GPT-4o的自我修复性能提升了54%。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
大型语言模型在处理证明导向编程时面临数据稀缺的问题,表现为缺乏足够的针对证明导向编程语言(如F*)的语料库以及缺乏大规模的项目级证明导向实现。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了一种合成数据增强方法,用于生成和修复证明导向编程的项目级代码。该方法通过合成基本的证明导向编程问题来训练模型在该语言中的熟练程度,同时引入多样化的编码数据来激发模型的推理能力,并在现有存储库中创建新的证明和修复数据。我们的实验结果显示,经过精细训练的PoPilot模型(参数为14B)在面向项目的证明导向编程任务上的性能超过了GPT-4o模型,相对性能提升幅度达到64%,并且在修复输出方面比GPT-4o的自我修复功能提高了54%。
关键见解
- 大型语言模型在处理证明导向编程时面临数据稀缺的问题。
- 缺乏足够的针对证明导向编程语言的语料库以及缺乏大规模的项目级证明导向实现是数据稀缺的两个主要表现。
- 提出了一种合成数据增强方法来解决数据稀缺问题,包括合成证明导向编程问题的训练、引入多样化的编码数据和在现有存储库中创建新的证明和修复数据。
- 实验结果表明PoPilot模型的性能超过了GPT-4o模型在面向项目的证明导向编程任务上的表现,相对性能提升幅度达到64%。
点此查看论文截图


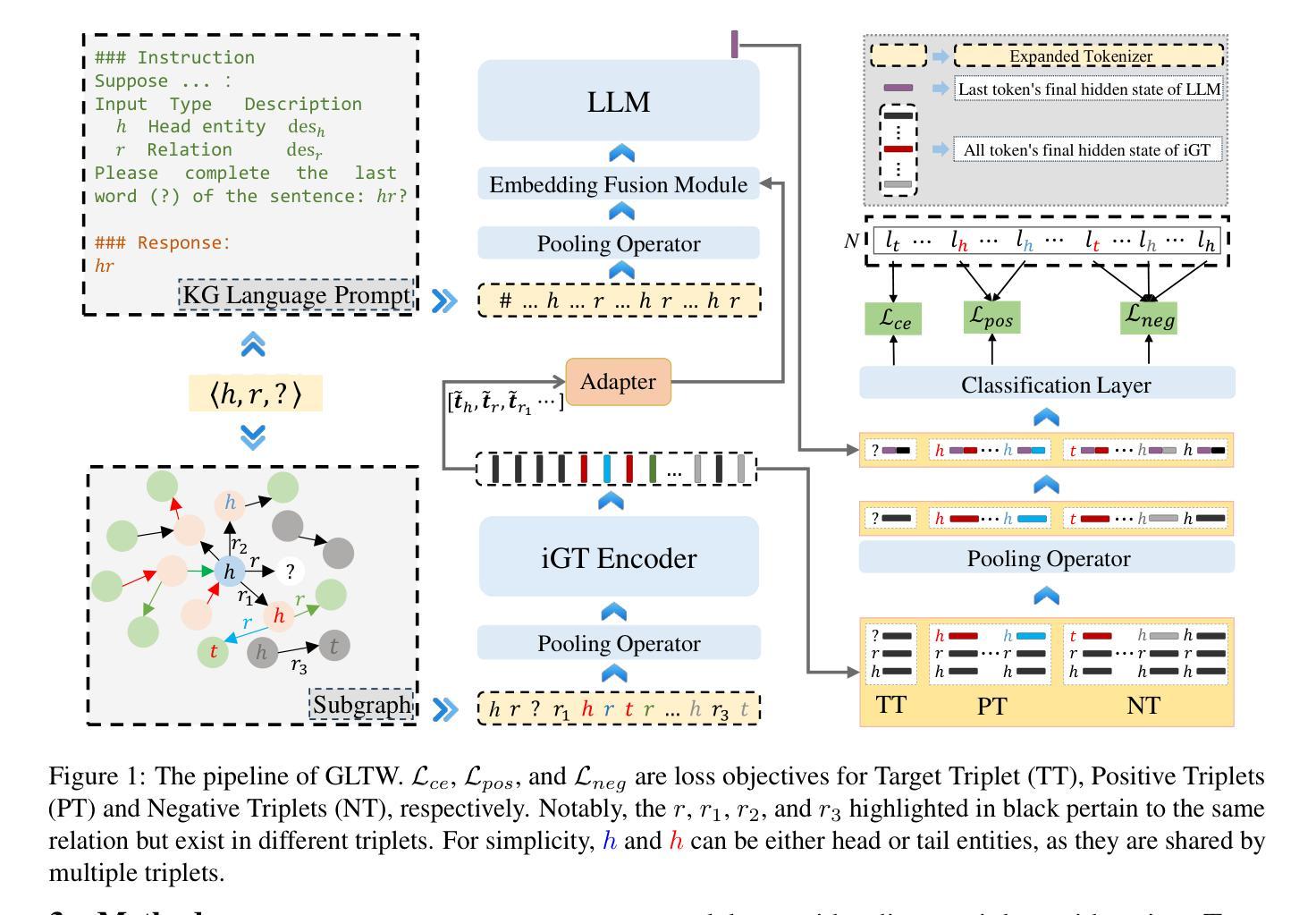
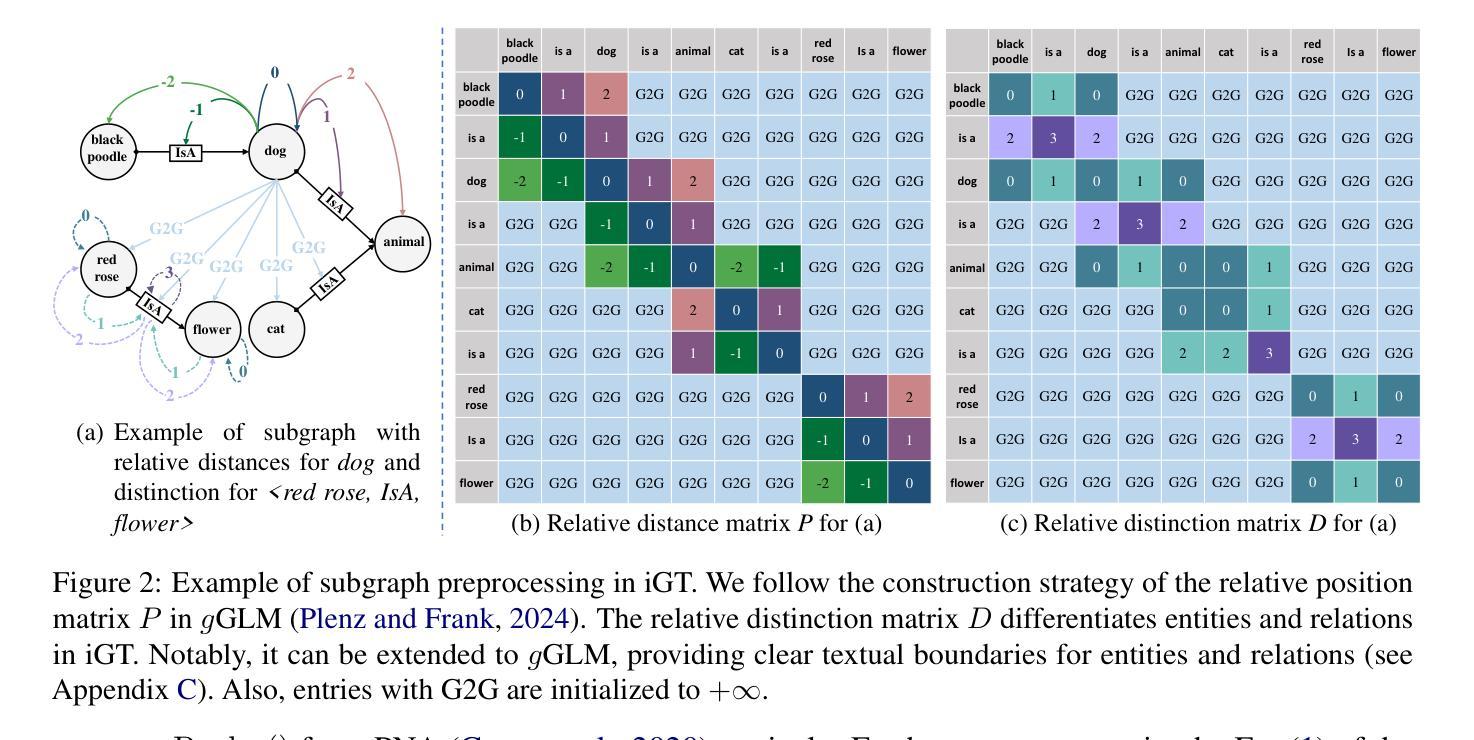
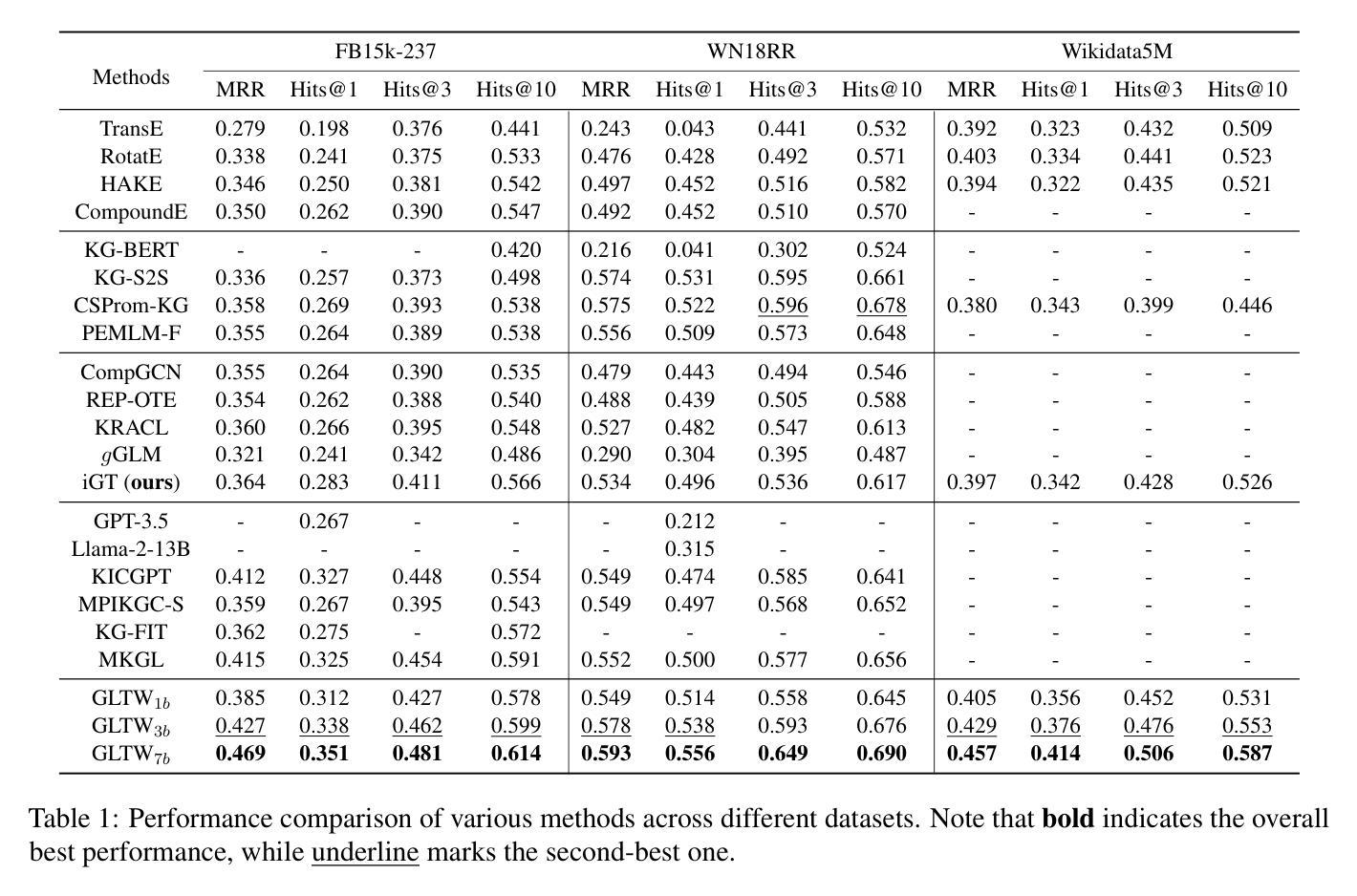
GLTW: Joint Improved Graph Transformer and LLM via Three-Word Language for Knowledge Graph Completion
Authors:Kangyang Luo, Yuzhuo Bai, Cheng Gao, Shuzheng Si, Yingli Shen, Zhu Liu, Zhitong Wang, Cunliang Kong, Wenhao Li, Yufei Huang, Ye Tian, Xuantang Xiong, Lei Han, Maosong Sun
Knowledge Graph Completion (KGC), which aims to infer missing or incomplete facts, is a crucial task for KGs. However, integrating the vital structural information of KGs into Large Language Models (LLMs) and outputting predictions deterministically remains challenging. To address this, we propose a new method called GLTW, which encodes the structural information of KGs and merges it with LLMs to enhance KGC performance. Specifically, we introduce an improved Graph Transformer (iGT) that effectively encodes subgraphs with both local and global structural information and inherits the characteristics of language model, bypassing training from scratch. Also, we develop a subgraph-based multi-classification training objective, using all entities within KG as classification objects, to boost learning efficiency.Importantly, we combine iGT with an LLM that takes KG language prompts as input.Our extensive experiments on various KG datasets show that GLTW achieves significant performance gains compared to SOTA baselines.
知识图谱补全(KGC)旨在推断缺失或不完整的事实,是知识图谱(KG)中的一项关键任务。然而,将知识图谱中的重要结构信息整合到大型语言模型(LLM)中并确定性地输出预测仍然是一个挑战。为了解决这个问题,我们提出了一种新的方法,称为GLTW,该方法对知识图谱的结构信息进行编码,并与LLM合并,以提高KGC的性能。具体来说,我们引入了一种改进的图转换器(iGT),它能有效地编码具有局部和全局结构信息的子图,并继承语言模型的特性,无需从零开始训练。此外,我们开发了一种基于子图的多元分类训练目标,使用知识图谱中的所有实体作为分类对象,以提高学习效率。重要的是,我们将iGT与一种大型语言模型相结合,该模型以知识图谱语言提示作为输入。我们在各种知识图谱数据集上的广泛实验表明,与最新基线相比,GLTW实现了显著的性能提升。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
知识图谱补全(KGC)旨在推断缺失或不完整的事实,是知识图谱(KG)中的关键任务。然而,将知识图谱的重要结构信息整合到大型语言模型(LLM)中并确定性地输出预测仍然具有挑战性。为解决此问题,我们提出了一种新的方法GLTW,该方法编码知识图谱的结构信息并将其与LLM合并,以提高KGC性能。我们引入了改进的图转换器(iGT),它有效地编码具有局部和全局结构信息的子图,并继承语言模型的特性,无需从零开始训练。此外,我们开发了一种基于子图的多元分类训练目标,以知识图谱中的所有实体作为分类对象,以提高学习效率。最重要的是,我们将iGT与接受知识图谱语言提示作为输入的LLM相结合。在多个知识图谱数据集上的广泛实验表明,GLTW与最新基线相比实现了显著的性能提升。
Key Takeaways
- 知识图谱补全(KGC)是知识图谱中的关键任务,旨在推断缺失或不完整的事实。
- 整合知识图谱的结构信息到大型语言模型(LLM)中并确定性地输出预测具有挑战性。
- 提出了一种新的方法GLTW,通过编码知识图谱的结构信息并与LLM合并,以提高KGC性能。
- 引入改进的图转换器(iGT),有效编码子图的局部和全局结构信息,并继承语言模型的特性。
- 开发基于子图的多元分类训练目标,利用知识图谱中的所有实体作为分类对象,提高学习效率。
- iGT与接受知识图谱语言提示作为输入的LLM相结合。
点此查看论文截图

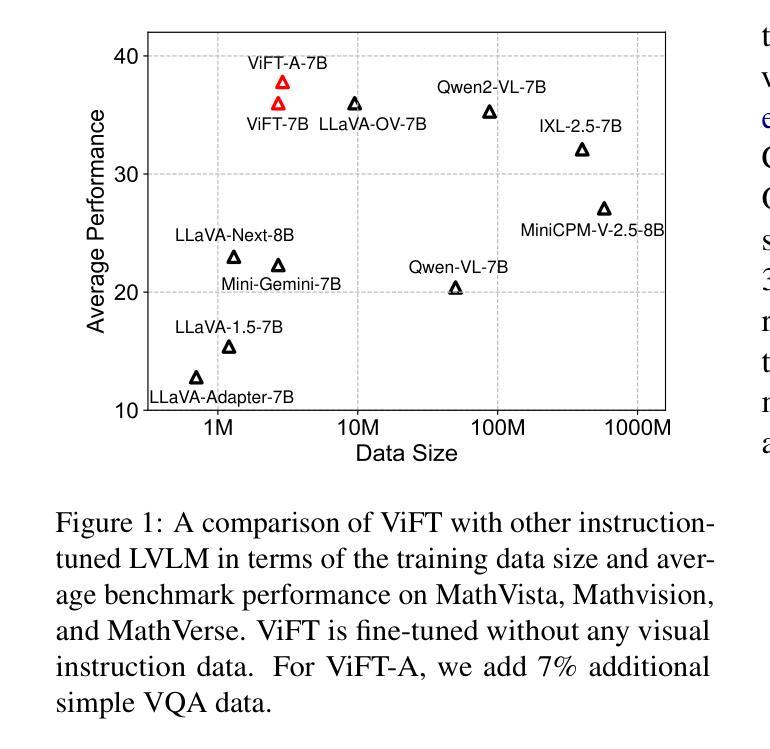
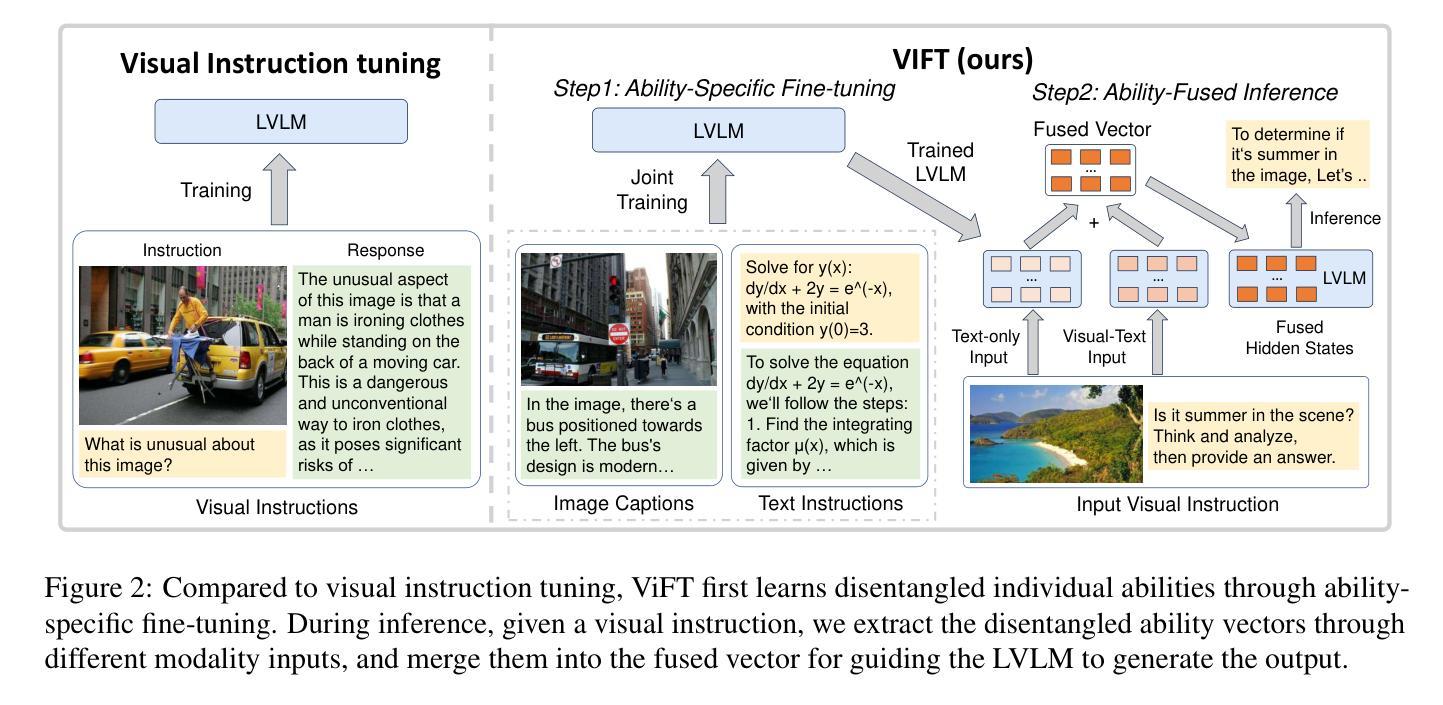
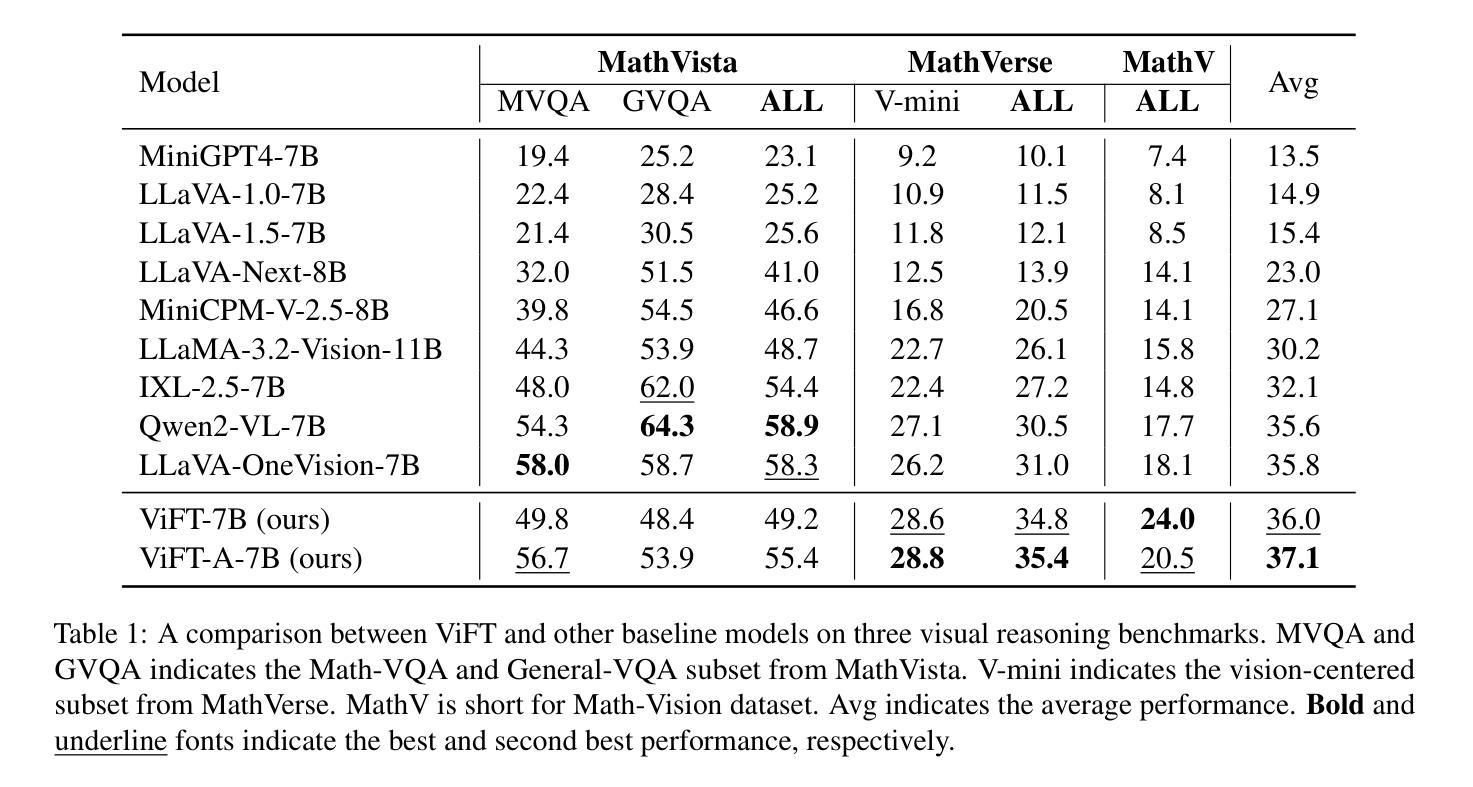
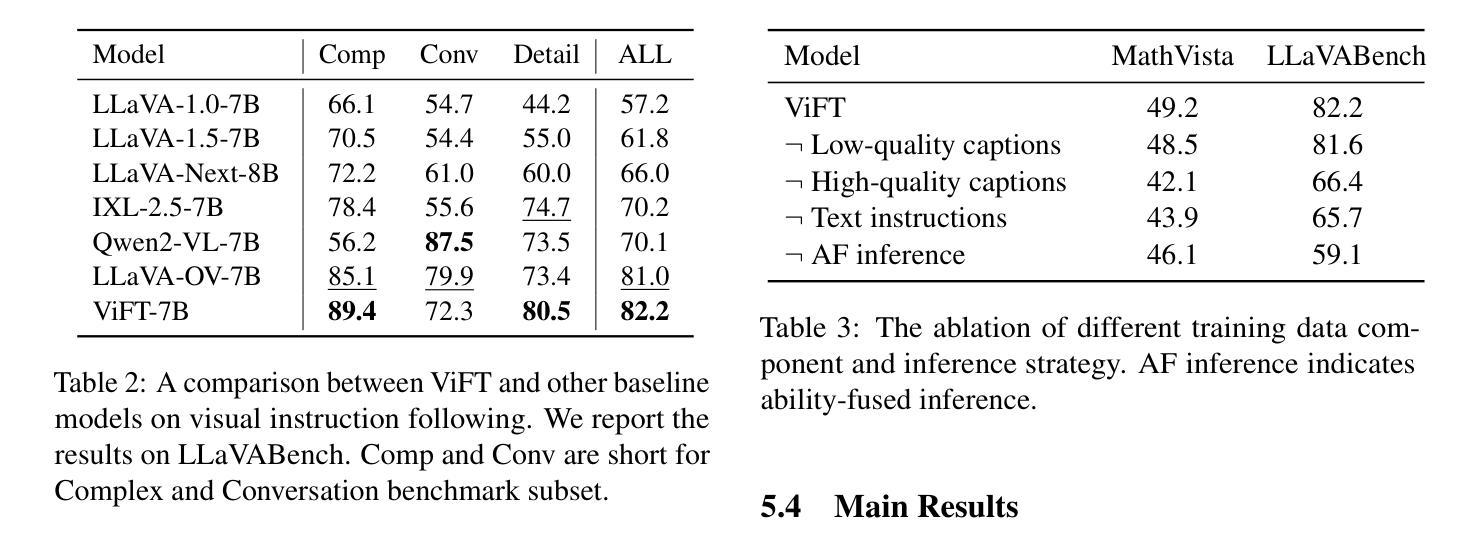
Do we Really Need Visual Instructions? Towards Visual Instruction-Free Fine-tuning for Large Vision-Language Models
Authors:Zikang Liu, Kun Zhou, Wayne Xin Zhao, Dawei Gao, Yaliang Li, Ji-Rong Wen
Visual instruction tuning has become the predominant technology in eliciting the multimodal task-solving capabilities of large vision-language models (LVLMs). Despite the success, as visual instructions require images as the input, it would leave the gap in inheriting the task-solving capabilities from the backbone LLMs, and make it costly to collect a large-scale dataset. To address it, we propose ViFT, a visual instruction-free fine-tuning framework for LVLMs. In ViFT, we only require the text-only instructions and image caption data during training, to separately learn the task-solving and visual perception abilities. During inference, we extract and combine the representations of the text and image inputs, for fusing the two abilities to fulfill multimodal tasks. Experimental results demonstrate that ViFT can achieve state-of-the-art performance on several visual reasoning and visual instruction following benchmarks, with rather less training data. Our code and data will be publicly released.
视觉指令调整已成为激发大型视觉语言模型(LVLMs)的多模式任务解决能力的主导技术。尽管取得了成功,但由于视觉指令需要图像作为输入,这将留下从主干LLMs继承任务解决能力的空白,并且收集大规模数据集的成本很高。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了ViFT,这是一种用于LVLMs的视觉指令免费微调框架。在ViFT中,我们只需要在训练期间使用纯文本指令和图像标题数据,以分别学习任务解决和视觉感知能力。在推理期间,我们提取并结合文本和图像输入的代表,融合这两种能力来完成多模式任务。实验结果表明,ViFT可以在几个视觉推理和视觉指令遵循基准测试上实现最先进的性能表现,且所需的训练数据较少。我们的代码和数据将公开发布。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF under review
Summary
大型视觉语言模型(LVLMs)的视讯指令调整是启发多任务解决能力的主要技术。然而,由于视讯指令需要图像作为输入,导致无法继承主干大型语言模型(LLMs)的任务解决能力,并且收集大规模数据集的成本高昂。为解决这一问题,我们提出ViFT,这是一种无需视觉指令的LVLMs精细调整框架。在ViFT中,我们仅需在训练期间使用纯文本指令和图像描述数据,以分别学习任务解决能力和视觉感知能力。在推理过程中,我们提取并结合文本和图像输入的表示形式,融合两种能力来完成多模式任务。实验结果表明,ViFT在多个视觉推理和视觉指令遵循基准测试上能达到最先进的性能表现,且使用较少的训练数据。我们的代码和数据将公开发布。
Key Takeaways
- 视觉指令调整是启发大型视觉语言模型多任务解决能力的主要技术,但需要图像作为输入。
- 无需视觉指令的ViFT框架旨在解决该问题,允许使用纯文本指令和图像描述数据进行训练。
- ViFT分别学习任务解决能力和视觉感知能力。
- 在推理阶段,ViFT融合文本和图像输入的表示形式,以完成多模式任务。
- 实验证明ViFT在视觉推理和视觉指令遵循方面达到先进性能,且使用较少的训练数据。
- 公开发布代码和数据以便他人使用和研究。
点此查看论文截图

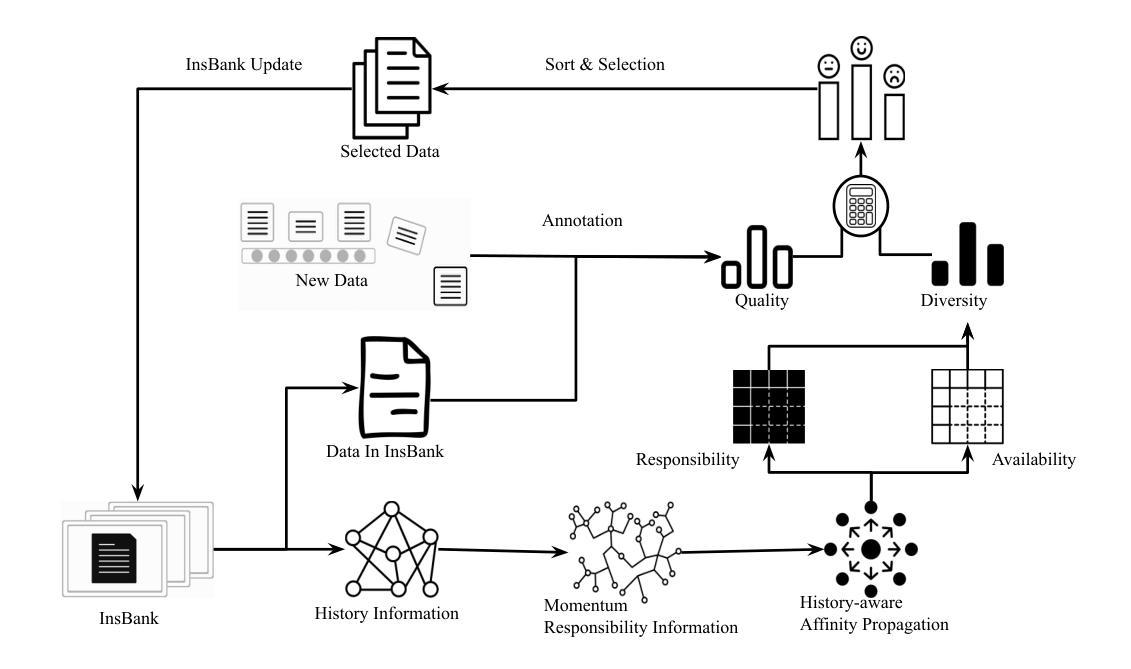
InsBank: Evolving Instruction Subset for Ongoing Alignment
Authors:Jiayi Shi, Yiwei Li, Shaoxiong Feng, Peiwen Yuan, Xinglin Wang, Yueqi Zhang, Chuyi Tan, Boyuan Pan, Huan Ren, Yao Hu, Kan Li
Large language models (LLMs) typically undergo instruction tuning to enhance alignment. Recent studies emphasize that quality and diversity of instruction data are more crucial than quantity, highlighting the need to select diverse, high-quality subsets to reduce training costs. However, how to evolve these selected subsets alongside the development of new instruction data remains insufficiently explored. To achieve LLMs’ ongoing alignment, we introduce Instruction Bank (InsBank), a continuously updated repository that integrates the latest valuable instruction data. We further propose Progressive Instruction Bank Evolution (PIBE), a novel framework designed to evolve InsBank effectively and efficiently over time. PIBE employs a gradual data selection strategy to maintain long-term efficiency, leveraging a representation-based diversity score to capture relationships between data points and retain historical information for comprehensive diversity evaluation. This also allows for flexible combination of diversity and quality scores during data selection and ranking. Extensive experiments demonstrate that PIBE significantly outperforms baselines in InsBank evolution and is able to extract budget-specific subsets, demonstrating its effectiveness and adaptability.
大型语言模型(LLM)通常通过指令微调来增强对齐效果。最近的研究强调,指令数据的质量和多样性比数量更重要,这凸显了选择多样、高质量子集的需要,以降低训练成本。然而,如何随着新指令数据的发展而发展这些选定子集仍然没有得到充分的探索。为了实现LLM的持续对齐,我们引入了指令库(InsBank),这是一个不断更新的存储库,集成了最新的宝贵指令数据。我们进一步提出了渐进式指令库进化(PIBE)这一新型框架,旨在实现InsBank的有效和高效长期进化。PIBE采用渐进的数据选择策略来维持长期效率,利用基于表示的多样性分数来捕捉数据点之间的关系并保留历史信息进行全面的多样性评估。这也允许在数据选择和排名过程中灵活结合多样性和质量分数。大量实验表明,PIBE在InsBank进化方面显著优于基线,并且能够提取特定预算的子集,证明了其有效性和适应性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大型语言模型(LLM)通过指令调整增强对齐效果。研究表明,指令数据的质量和多样性比数量更重要,需要选择多样且高质量的子集来降低训练成本。为配合新指令数据的发展,本文提出了持续更新的指令库Instruction Bank(InsBank),以及新型的指令库进化框架Progressive Instruction Bank Evolution(PIBE)。PIBE采用渐进的数据选择策略,以长期保持效率,并利用基于表示的多样性得分来捕捉数据点之间的关系,保留历史信息进行全面的多样性评估。实验表明,PIBE在指令库进化方面显著优于基准方法,并能够提取预算特定的子集,展现出其有效性和适应性。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLM)通过指令调整增强对齐效果。
- 指令数据的质量和多样性比数量更重要。
- 需要选择多样且高质量的子集来降低训练成本。
- 提出了Instruction Bank(InsBank)作为持续更新的指令库。
- 介绍了Progressive Instruction Bank Evolution(PIBE)框架,用于有效和高效地进化InsBank。
- PIBE采用渐进的数据选择策略和基于表示的多样性得分来捕捉数据点之间的关系。
点此查看论文截图

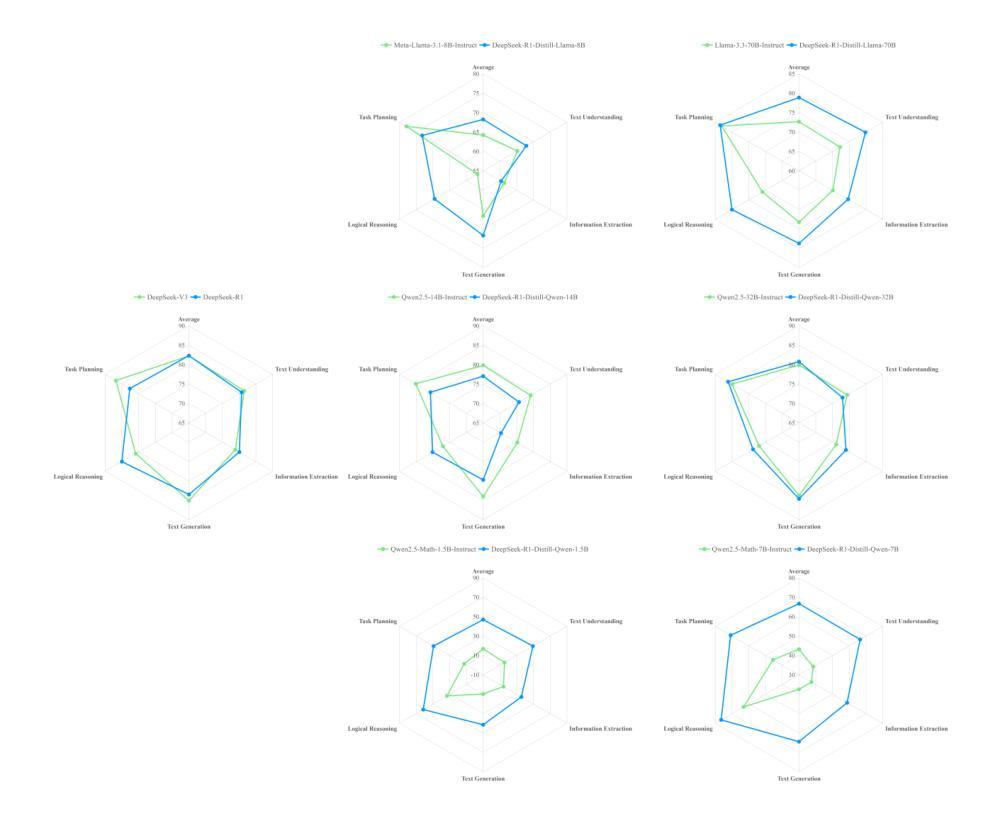
Quantifying the Capability Boundary of DeepSeek Models: An Application-Driven Performance Analysis
Authors:Shiguo Lian, Kaikai Zhao, Xuejiao Lei, Ning Wang, Zhenhong Long, Peijun Yang, Minjie Hua, Chaoyang Ma, Wen Liu, Kai Wang, Zhaoxiang Liu
DeepSeek-R1, known for its low training cost and exceptional reasoning capabilities, has achieved state-of-the-art performance on various benchmarks. However, detailed evaluations from the perspective of real-world applications are lacking, making it challenging for users to select the most suitable DeepSeek models for their specific needs. To address this gap, we evaluate the DeepSeek-V3, DeepSeek-R1, DeepSeek-R1-Distill-Qwen series, and DeepSeek-R1-Distill-Llama series on A-Eval, an application-driven benchmark. By comparing original instruction-tuned models with their distilled counterparts, we analyze how reasoning enhancements impact performance across diverse practical tasks. Our results show that reasoning-enhanced models, while generally powerful, do not universally outperform across all tasks, with performance gains varying significantly across tasks and models. To further assist users in model selection, we quantify the capability boundary of DeepSeek models through performance tier classifications and intuitive line charts. Specific examples provide actionable insights to help users select and deploy the most cost-effective DeepSeek models, ensuring optimal performance and resource efficiency in real-world applications.
DeepSeek-R1以其低训练成本和出色的推理能力而著称,已在各种基准测试中达到最新技术水平。然而,从现实世界应用的角度进行的详细评估仍然缺乏,这使得用户难以为其特定需求选择最合适的DeepSeek模型。为了弥补这一空白,我们对DeepSeek-V3、DeepSeek-R1、DeepSeek-R1-Distill-Qwen系列和DeepSeek-R1-Distill-Llama系列在A-Eval这一应用驱动的基准测试上进行了评估。通过比较原始指令调整模型与其蒸馏对应模型,我们分析了推理增强如何影响各种实际任务的性能。我们的结果表明,虽然推理增强模型通常强大,但并不在所有任务上都表现最佳,不同任务和模型之间的性能提升差异很大。为了进一步帮助用户进行模型选择,我们通过性能分级和直观的线形图来量化DeepSeek模型的能力边界。具体示例提供了可操作性的见解,有助于用户选择和部署最经济实惠的DeepSeek模型,确保在真实世界应用中实现最佳性能和资源效率。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大模型在各个基准测试中表现卓越,但其在现实世界应用中的性能评价仍缺乏详细的研究。为了填补这一空白,我们对DeepSeek系列模型进行了评估,对比了原始指令调优模型与蒸馏模型在多种实用任务中的表现。结果显示,推理增强模型整体强大,但并非所有任务都表现最佳,性能和收益在不同任务和模型中差异显著。我们进一步通过性能等级分类和直观图表量化DeepSeek模型的能力边界,以帮助用户选择最适合的模型。
Key Takeaways
- 大模型在基准测试中表现优秀,但在现实世界应用中的性能评价尚待深入研究。
- 对DeepSeek系列模型的评估表明,推理增强模型整体强大。
- 不同模型和任务中,推理增强模型的性能增益存在差异。
- 原始指令调优模型与蒸馏模型在实用任务中的表现有对比价值。
- 通过性能等级分类和直观图表,可量化DeepSeek模型的能力边界。
- 用户在选择和部署模型时,应关注成本效益、性能及资源效率。
点此查看论文截图


SyncSpeech: Low-Latency and Efficient Dual-Stream Text-to-Speech based on Temporal Masked Transformer
Authors:Zhengyan Sheng, Zhihao Du, Shiliang Zhang, Zhijie Yan, Yexin Yang, Zhenhua Ling
This paper presents a dual-stream text-to-speech (TTS) model, SyncSpeech, capable of receiving streaming text input from upstream models while simultaneously generating streaming speech, facilitating seamless interaction with large language models. SyncSpeech has the following advantages: Low latency, as it begins generating streaming speech upon receiving the second text token; High efficiency, as it decodes all speech tokens corresponding to the each arrived text token in one step. To achieve this, we propose a temporal masked transformer as the backbone of SyncSpeech, combined with token-level duration prediction to predict speech tokens and the duration for the next step. Additionally, we design a two-stage training strategy to improve training efficiency and the quality of generated speech. We evaluated the SyncSpeech on both English and Mandarin datasets. Compared to the recent dual-stream TTS models, SyncSpeech significantly reduces the first packet delay of speech tokens and accelerates the real-time factor. Moreover, with the same data scale, SyncSpeech achieves performance comparable to that of traditional autoregressive-based TTS models in terms of both speech quality and robustness. Speech samples are available at https://SyncSpeech.github.io/}{https://SyncSpeech.github.io/.
本文提出了一种双流文本到语音(TTS)模型SyncSpeech,它能够从上游模型接收流式文本输入,同时生成流式语音,便于与大语言模型无缝交互。SyncSpeech具有以下优点:低延迟,因为在接收到第二个文本标记时就开始生成流式语音;高效率,因为它可以在一步中解码每个到达文本标记对应的所有语音标记。为了实现这一点,我们提出了一个时间掩码转换器作为SyncSpeech的骨干,结合标记级持续时间预测来预测语音标记和下一个步骤的持续时间。此外,我们设计了一个两阶段训练策略来提高训练效率和生成的语音质量。我们在英语和普通话数据集上评估了SyncSpeech。与最近的双流TTS模型相比,SyncSpeech显著减少了语音标记的第一包延迟并加速了实时因子。此外,在相同的数据规模下,SyncSpeech在语音质量和稳健性方面达到了与传统基于自回归的TTS模型相当的性能。语音样本可在https://SyncSpeech.github.io上找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
该论文提出了一种双流文本到语音(TTS)模型SyncSpeech,能够接收来自上游模型的流式文本输入,同时生成流式语音,便于与大型语言模型无缝交互。SyncSpeech具有低延迟和高效率的优点,能够在接收到第二个文本标记时开始生成流式语音,并在一步中解码每个到达文本标记的所有语音标记。为实现这一目标,我们提出了以时间掩码转换器为SyncSpeech的骨干,结合标记级时长预测,预测语音标记和下一步的时长。此外,我们设计了两阶段训练策略,以提高训练效率和生成的语音质量。我们在英语和普通话数据集上评估了SyncSpeech的表现。与最近的双流TTS模型相比,SyncSpeech显著降低了语音标记的第一包延迟并加速了实时因子。即使在相同的数据规模下,SyncSpeech在语音质量和稳健性方面都实现了与传统基于自回归的TTS模型相当的性能。
Key Takeaways
- SyncSpeech是一种双流文本到语音(TTS)模型,能够实现流式文本输入和语音生成的无缝交互。
- SyncSpeech具有低延迟和高效率的优点,可快速生成语音。
- SyncSpeech采用时间掩码转换器作为骨干,结合标记级时长预测来生成语音。
- 两阶段训练策略用于提高训练效率和语音生成质量。
- SyncSpeech在英语和普通话数据集上进行了评估,表现良好。
- 与其他双流TTS模型相比,SyncSpeech降低了语音标记的第一包延迟并加速了实时性能。
点此查看论文截图



Beyond Similarity: A Gradient-based Graph Method for Instruction Tuning Data Selection
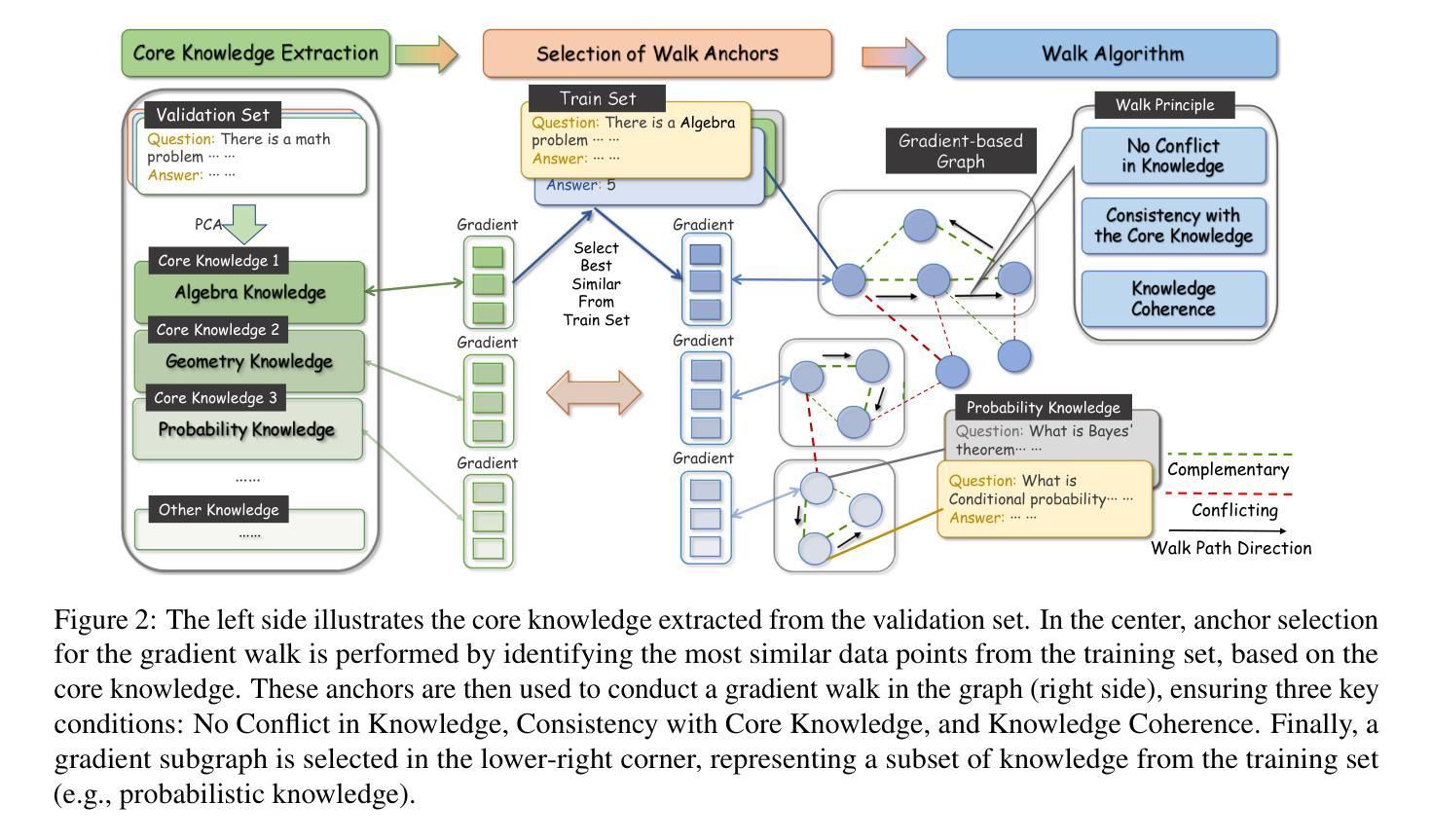
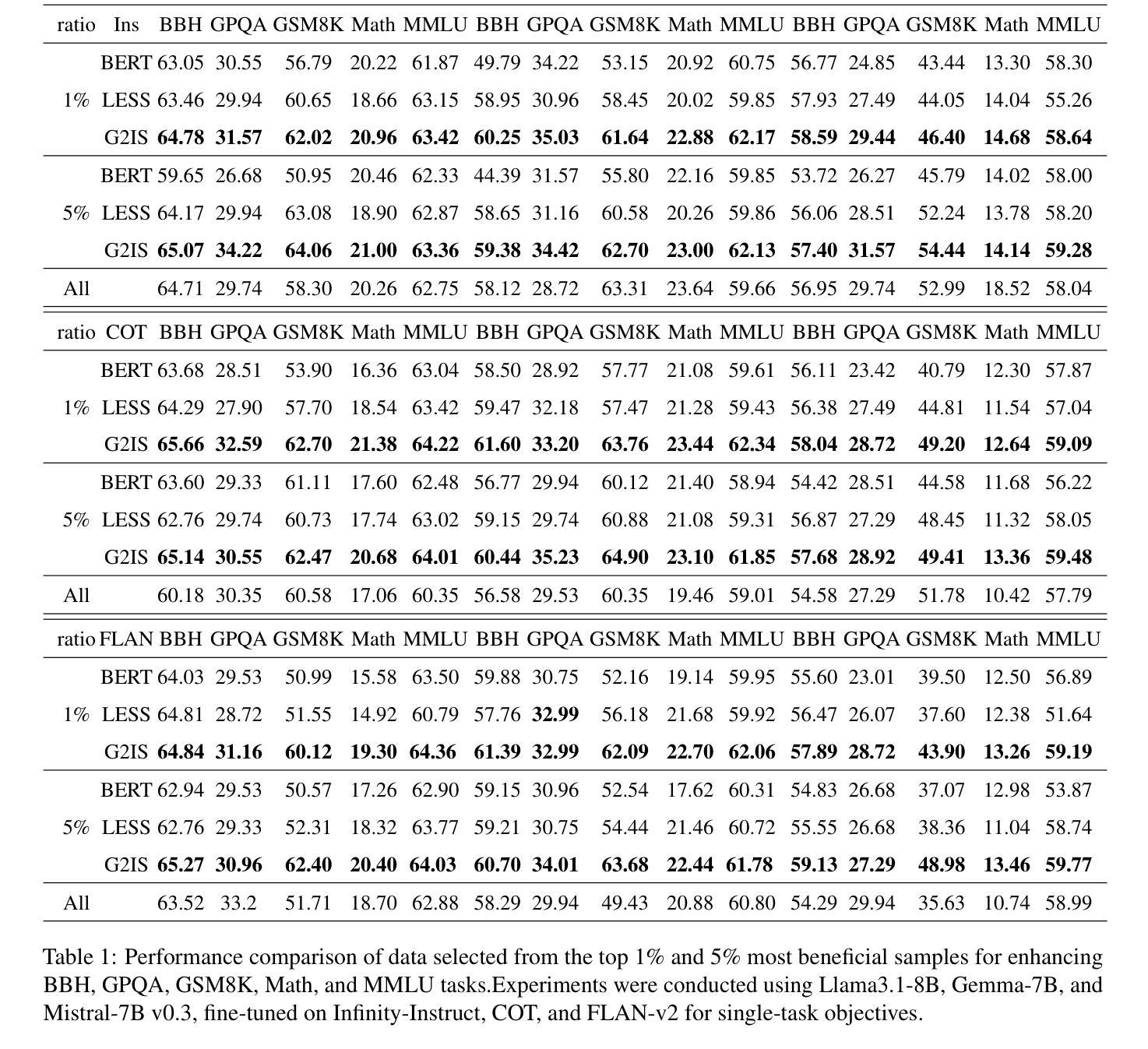
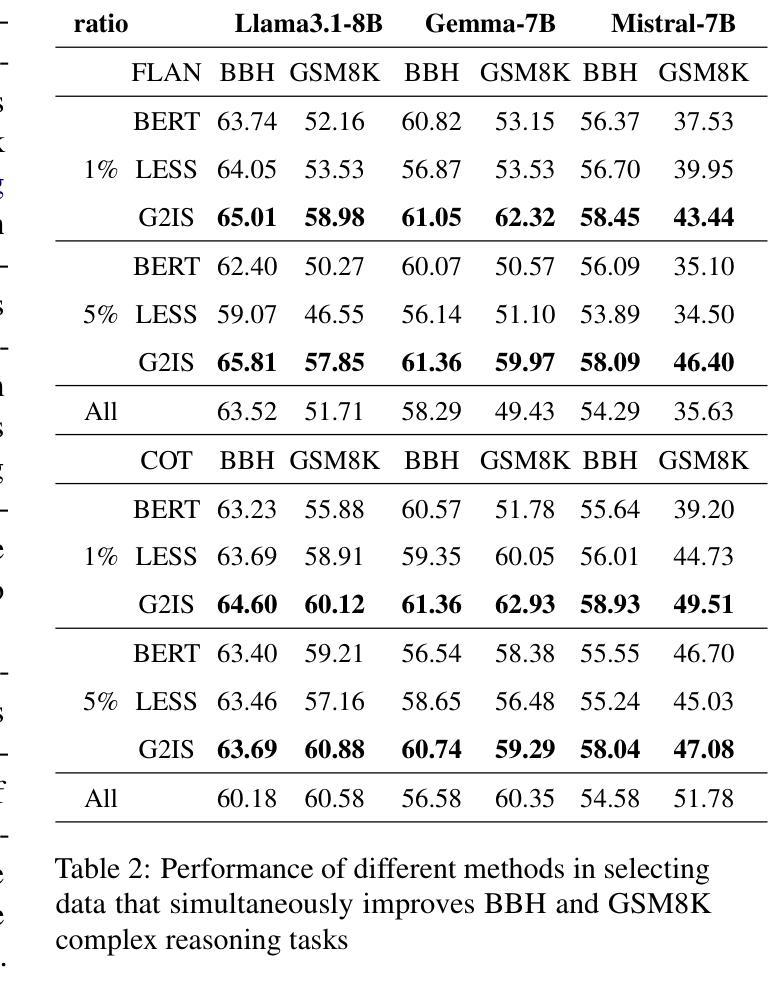
Authors:Yang Zhao, Li Du, Xiao Ding, Yangou Ouyang, Hepeng Wang, Kai Xiong, Jinglong Gao, Zhouhao Sun, Dongliang Xu, Yang Qing, Dongchen Li, Bing Qin, Ting Liu
Large language models (LLMs) have shown great potential across various industries due to their remarkable ability to generalize through instruction tuning. However, the limited availability of domain-specific data significantly hampers their performance on specialized tasks. While existing methods primarily focus on selecting training data from general datasets that are similar to the target domain, they often fail to consider the joint distribution of instructions, resulting in inefficient learning and suboptimal knowledge transfer. To address these challenges, we introduce G2IS (Gradient-based Graph Instruction Selection), a novel method that constructs a mixed gradient-based instruction graph to capture the joint distribution and interdependencies between instructions. By accounting for the relationships between instructions, G2IS improves domain adaptation efficiency. Additionally, we propose a gradient walk algorithm to refine the data selection process, enhancing both training effectiveness and efficiency. Our experiments demonstrate that G2IS outperforms traditional methods across various domain adaptation tasks, yielding significant performance gains, particularly in complex, data-scarce scenarios. These results underscore the potential of G2IS in advancing the development of large, domain-specific models.
大型语言模型(LLM)因其通过指令调整实现泛化的显著能力而在各行各业展现出巨大潜力。然而,特定领域数据的有限可用性显著阻碍了它们在专业任务上的性能。现有方法主要关注从与目标域相似的通用数据集中选择训练数据,但它们往往忽略了指令的联合分布,导致学习效率低下和知识转移不佳。为了解决这些挑战,我们引入了G2IS(基于梯度的图指令选择)这一新方法,它构建了一个基于混合梯度的指令图来捕捉指令之间的联合分布和相互依赖性。通过考虑指令之间的关系,G2IS提高了域适应效率。此外,我们提出了一种梯度步行算法来改进数据选择过程,提高训练和效率。我们的实验表明,G2IS在各种域适应任务上优于传统方法,产生了显著的性能提升,特别是在复杂、数据稀缺的场景中。这些结果突出了G2IS在推动大型特定领域模型开发方面的潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大型语言模型(LLM)具有通过指令调整进行泛化的能力,因此在各行业具有巨大潜力。然而,领域特定数据的有限可用性对模型在专项任务上的表现构成了显著障碍。现有方法主要关注从类似目标域的通用数据集中选择训练数据,却忽视了指令的联合分布,导致学习效率低下和知识转移不佳。为解决这些挑战,我们提出了G2IS(基于梯度的图指令选择)方法,构建了一个基于梯度的混合指令图来捕捉指令之间的联合分布和互依赖性。通过考虑指令之间的关系,G2IS提高了领域适应效率。此外,我们还提出了一种梯度步行算法来优化数据选择过程,提高了训练和效率。实验表明,G2IS在多种领域适应任务上优于传统方法,特别是在复杂、数据稀缺的场景下性能提升显著。这突显了G2IS在开发大型领域特定模型中的潜力。
Key Takeaways
- LLMs具有通过指令调整进行泛化的能力,但在领域特定任务上的表现受限于数据可用性。
- 现有方法主要关注从通用数据集中选择训练数据,忽略了指令的联合分布。
- G2IS方法通过构建混合梯度指令图来捕捉指令之间的联合分布和互依赖性,提高领域适应效率。
- G2IS采用梯度步行算法优化数据选择,提高训练和效率。
- 实验表明,G2IS在多种领域适应任务上表现优于传统方法,尤其在数据稀缺的复杂场景下。
- G2IS具有开发大型领域特定模型的潜力。
点此查看论文截图

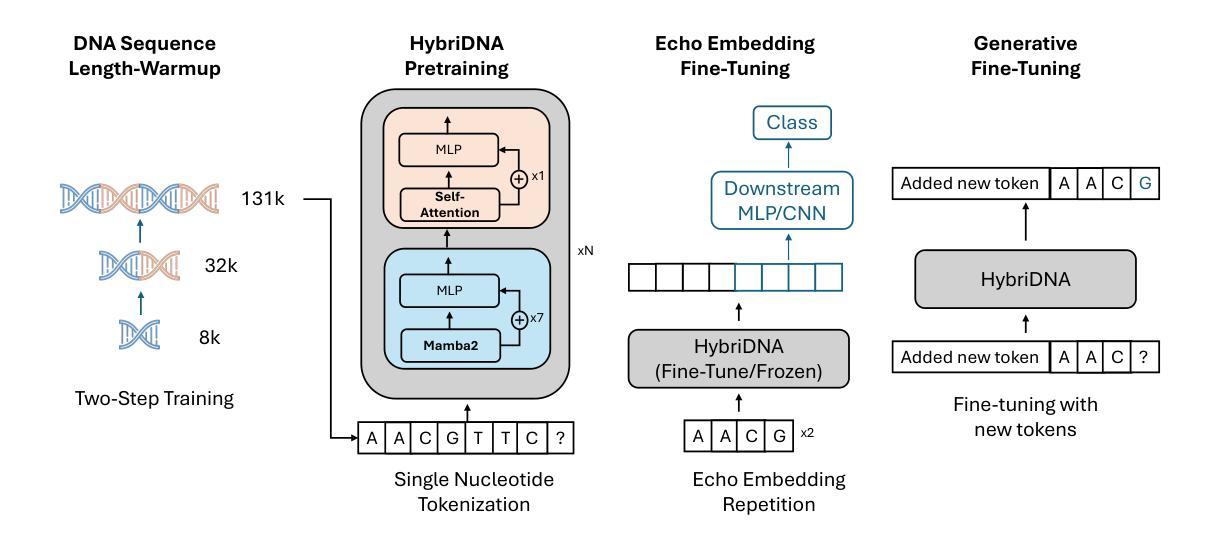
HybriDNA: A Hybrid Transformer-Mamba2 Long-Range DNA Language Model
Authors:Mingqian Ma, Guoqing Liu, Chuan Cao, Pan Deng, Tri Dao, Albert Gu, Peiran Jin, Zhao Yang, Yingce Xia, Renqian Luo, Pipi Hu, Zun Wang, Yuan-Jyue Chen, Haiguang Liu, Tao Qin
Advances in natural language processing and large language models have sparked growing interest in modeling DNA, often referred to as the “language of life”. However, DNA modeling poses unique challenges. First, it requires the ability to process ultra-long DNA sequences while preserving single-nucleotide resolution, as individual nucleotides play a critical role in DNA function. Second, success in this domain requires excelling at both generative and understanding tasks: generative tasks hold potential for therapeutic and industrial applications, while understanding tasks provide crucial insights into biological mechanisms and diseases. To address these challenges, we propose HybriDNA, a decoder-only DNA language model that incorporates a hybrid Transformer-Mamba2 architecture, seamlessly integrating the strengths of attention mechanisms with selective state-space models. This hybrid design enables HybriDNA to efficiently process DNA sequences up to 131kb in length with single-nucleotide resolution. HybriDNA achieves state-of-the-art performance across 33 DNA understanding datasets curated from the BEND, GUE, and LRB benchmarks, and demonstrates exceptional capability in generating synthetic cis-regulatory elements (CREs) with desired properties. Furthermore, we show that HybriDNA adheres to expected scaling laws, with performance improving consistently as the model scales from 300M to 3B and 7B parameters. These findings underscore HybriDNA’s versatility and its potential to advance DNA research and applications, paving the way for innovations in understanding and engineering the “language of life”.
随着自然语言处理和大型语言模型的进步,对DNA的建模,常被称为“生命的语言”,引发了越来越多的兴趣。然而,DNA建模存在独特的挑战。首先,它需要在保持单核苷酸分辨率的同时处理超长的DNA序列,因为单个核苷酸在DNA功能中发挥关键作用。其次,在这个领域取得成功需要在生成和理解任务上都表现出色:生成任务在治疗和工业应用方面具有潜力,而理解任务则提供了对生物机制和疾病的深刻见解。为了应对这些挑战,我们提出了HybriDNA,这是一个仅解码的DNA语言模型,它结合了混合Transformer-Mamba2架构,无缝集成了注意力机制的选择状态空间模型的优点。这种混合设计使HybriDNA能够高效处理长达131kb的DNA序列,并保留单核苷酸分辨率。HybriDNA在来自BEND、GUE和LRB基准测试的33个DNA理解数据集上实现了最先进的性能,并显示出生成具有所需特性的合成顺式调控元件(CREs)的卓越能力。此外,我们证明HybriDNA遵循预期的比例定律,随着模型从3亿参数扩展到7亿参数,其性能一直在不断提高。这些发现强调了HybriDNA的通用性以及其在推动DNA研究与应用方面的潜力,为理解和工程化“生命的语言”铺平了道路。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
自然语言处理和大型语言模型的进步激发了人们对DNA建模的兴趣,DNA被称为“生命的语言”。然而,DNA建模存在挑战。HybriDNA模型结合Transformer和Mamba2架构,实现了超长DNA序列的单核苷酸分辨率处理,同时完成生成和理解任务。模型性能在多个DNA理解数据集上达到领先水平,能生成具有所需属性的合成顺式调控元件(CREs)。随着模型规模从3亿到3千亿和7千亿参数的扩大,性能不断提高。这显示了HybriDNA的通用性和潜力。
Key Takeaways
- DNA建模被称为“生命的语言”,受到自然语言处理领域发展的启发。
- DNA建模面临处理超长序列并保持单核苷酸分辨率的挑战。
- HybriDNA结合了Transformer和Mamba2架构,实现了高效DNA序列处理。
- HybriDNA能在多个DNA理解数据集上达到领先水平。
- HybriDNA能生成具有所需属性的合成顺式调控元件(CREs)。
- 随着模型规模的扩大,HybriDNA的性能持续提高。
点此查看论文截图

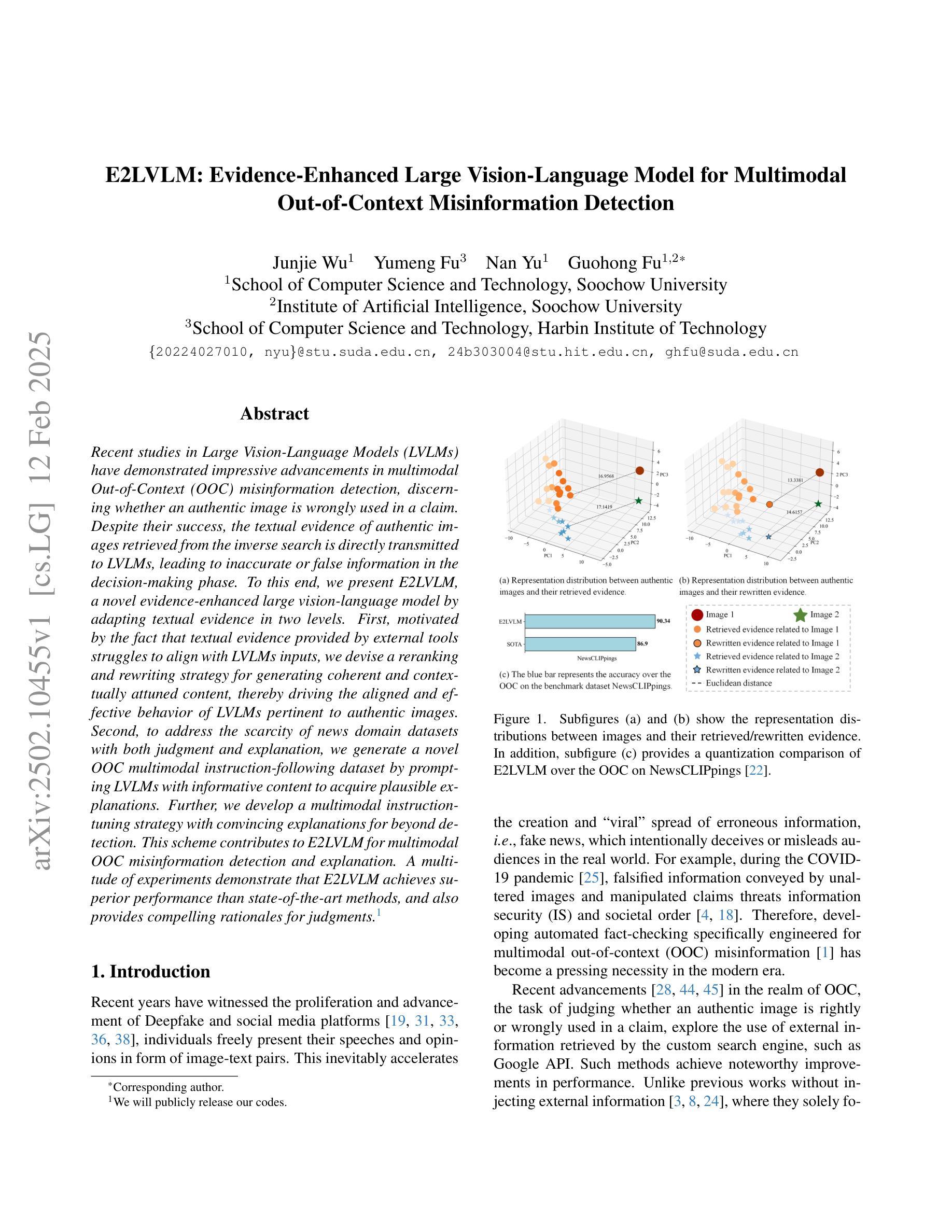
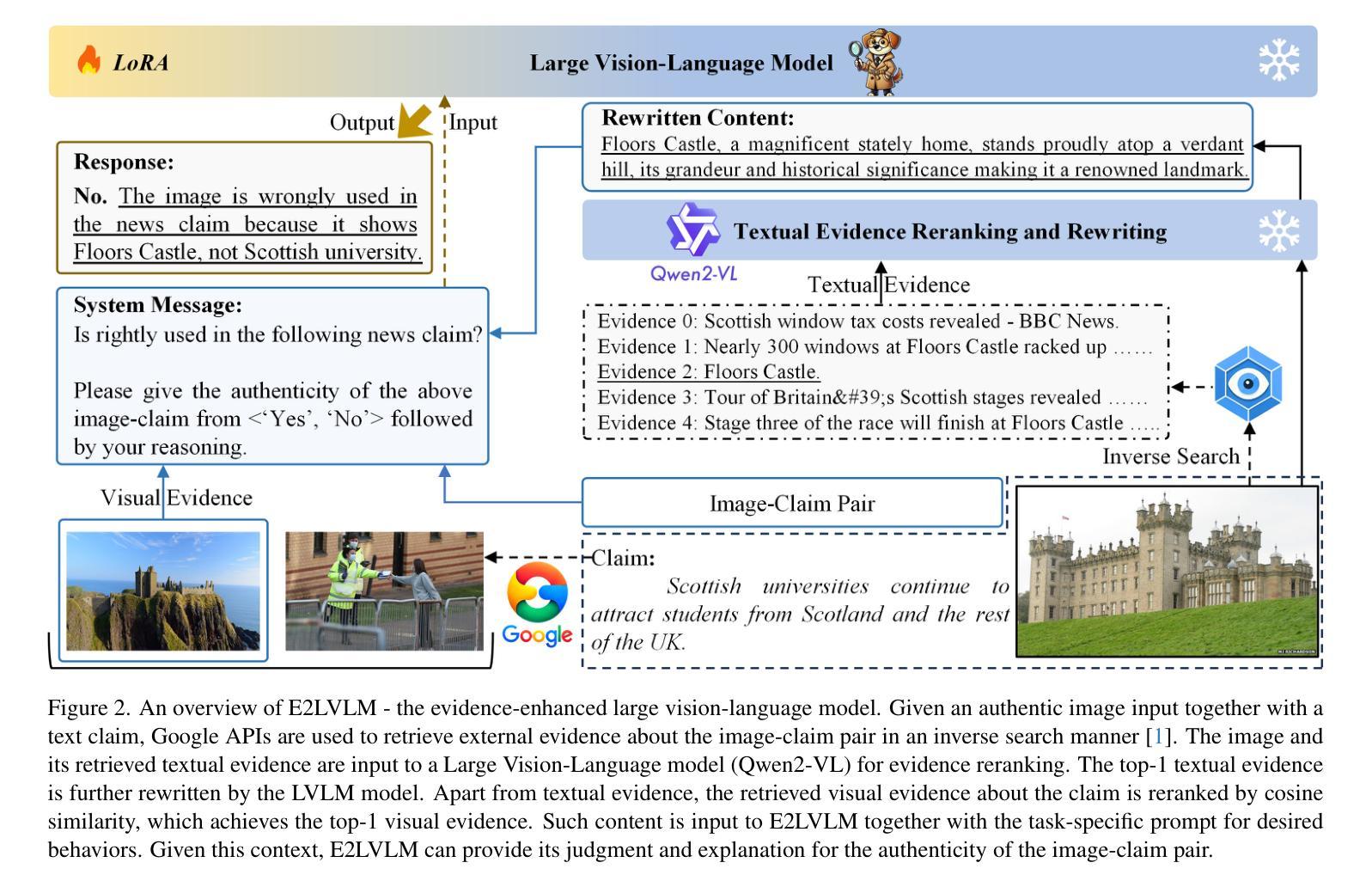
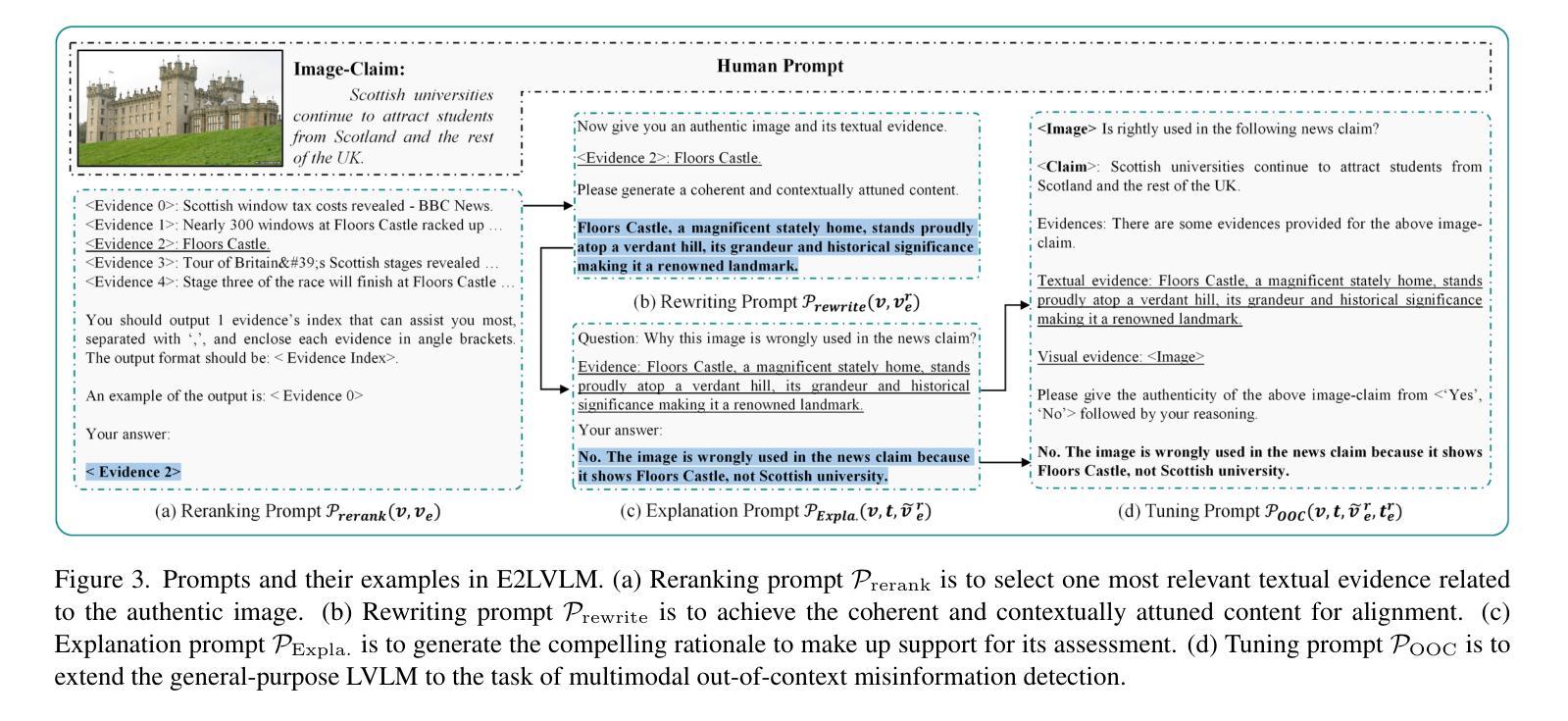
E2LVLM:Evidence-Enhanced Large Vision-Language Model for Multimodal Out-of-Context Misinformation Detection
Authors:Junjie Wu, Yumeng Fu, Nan Yu, Guohong Fu
Recent studies in Large Vision-Language Models (LVLMs) have demonstrated impressive advancements in multimodal Out-of-Context (OOC) misinformation detection, discerning whether an authentic image is wrongly used in a claim. Despite their success, the textual evidence of authentic images retrieved from the inverse search is directly transmitted to LVLMs, leading to inaccurate or false information in the decision-making phase. To this end, we present E2LVLM, a novel evidence-enhanced large vision-language model by adapting textual evidence in two levels. First, motivated by the fact that textual evidence provided by external tools struggles to align with LVLMs inputs, we devise a reranking and rewriting strategy for generating coherent and contextually attuned content, thereby driving the aligned and effective behavior of LVLMs pertinent to authentic images. Second, to address the scarcity of news domain datasets with both judgment and explanation, we generate a novel OOC multimodal instruction-following dataset by prompting LVLMs with informative content to acquire plausible explanations. Further, we develop a multimodal instruction-tuning strategy with convincing explanations for beyond detection. This scheme contributes to E2LVLM for multimodal OOC misinformation detection and explanation. A multitude of experiments demonstrate that E2LVLM achieves superior performance than state-of-the-art methods, and also provides compelling rationales for judgments.
在大型视觉语言模型(LVLMs)的最新研究中,多模态脱离上下文(OOC)的虚假信息检测取得了令人印象深刻的进展,能够辨别真实图像是否被错误地用于某个声明中。然而,尽管取得了成功,通过反向搜索检索到的真实图像的文字证据会直接传递给LVLMs,导致决策阶段出现不准确或错误的信息。为此,我们提出了E2LVLM,这是一种新的增强型大型视觉语言模型,它通过两个层次适应文本证据。首先,受到外部工具提供的文本证据难以与LVLMs输入对齐的事实的启发,我们设计了一种重新排序和重写策略,以生成连贯且上下文协调的内容,从而驱动与真实图像相关的LVLMs的对齐和有效行为。其次,为了解决同时包含判断和解释的新闻领域数据集的稀缺问题,我们通过提示LVLMs以包含信息的内容来生成一个新的OOC多模态指令遵循数据集,以获得合理的解释。此外,我们开发了一种具有说服力的解释的多模态指令调整策略,不仅限于检测。这一方案为E2LVLM多模态OOC虚假信息检测和解释做出了贡献。大量实验表明,E2LVLM较现有方法取得了优越性,并为判断提供了令人信服的依据。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
近期关于大型视觉语言模型(LVLM)的研究在脱离上下文的多媒体信息检测方面取得了显著进展,能够判断图像是否被错误使用。然而,现有方法直接将通过反向搜索获取的图像文本证据传递给LVLM,导致决策阶段可能出现不准确或错误信息。为此,提出一种新型的证据增强大型视觉语言模型E2LVLM,通过两个层级适应文本证据。首先,针对外部工具提供的文本证据与LVLM输入对齐困难的问题,设计了一种重新排序和重写策略,生成连贯且符合上下文的内容,从而驱动LVLM对真实图像的相关性和有效性行为。其次,为解决新闻领域数据集判断与解释兼备的稀缺问题,通过引导LVLMs获取合理解释,生成新型脱离上下文的多媒体指令跟随数据集。此外,还开发了一种具有说服力的解释的多模态指令微调策略。实验表明,E2LVLM相较于现有方法表现出卓越性能,并为判断提供了有力依据。
Key Takeaways
- 大型视觉语言模型(LVLM)在脱离上下文的多媒体信息检测方面取得显著进展。
- 现有方法直接将图像文本证据传递给LVLM,可能导致决策阶段的不准确或错误信息。
- E2LVLM通过两个层级适应文本证据,解决文本证据与LVLM输入对齐困难的问题。
- E2LVLM采用重新排序和重写策略,生成连贯且符合上下文的内容,以驱动LVLM的相关性和有效性行为。
- 针对新闻领域数据集判断与解释兼备的稀缺问题,E2LVLM生成新型脱离上下文的多媒体指令跟随数据集。
- E2LVLM开发了一种具有说服力的解释的多模态指令微调策略。
- 实验表明,E2LVLM相较于现有方法表现出卓越性能。
点此查看论文截图
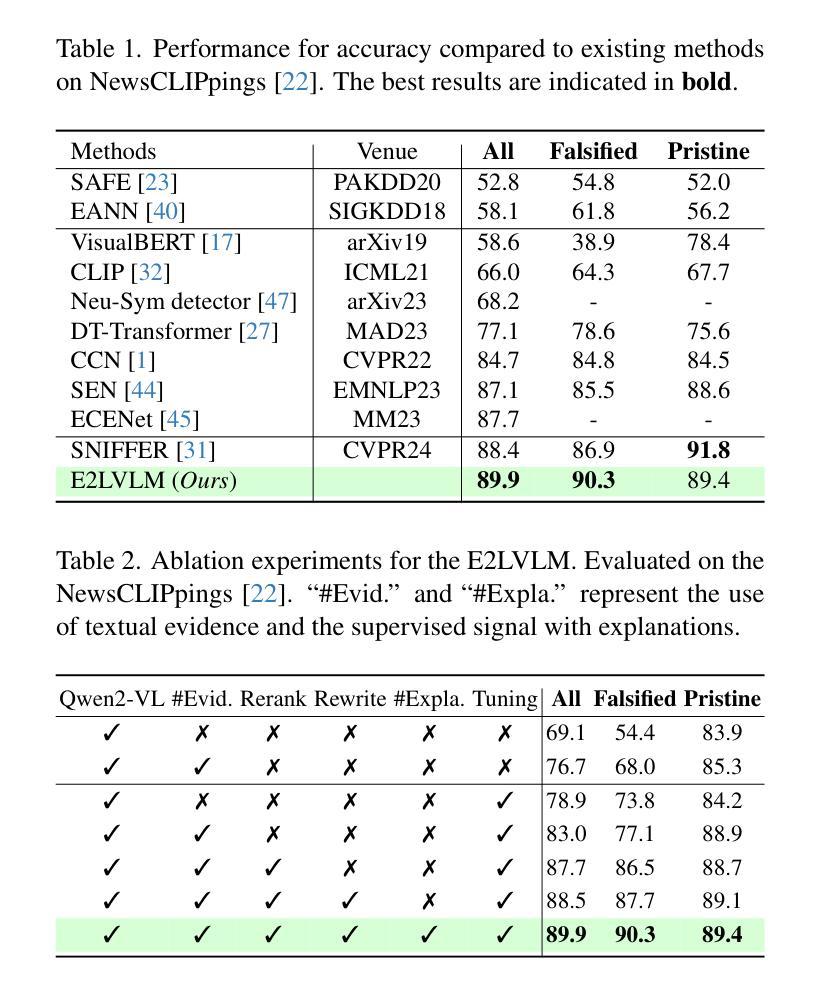
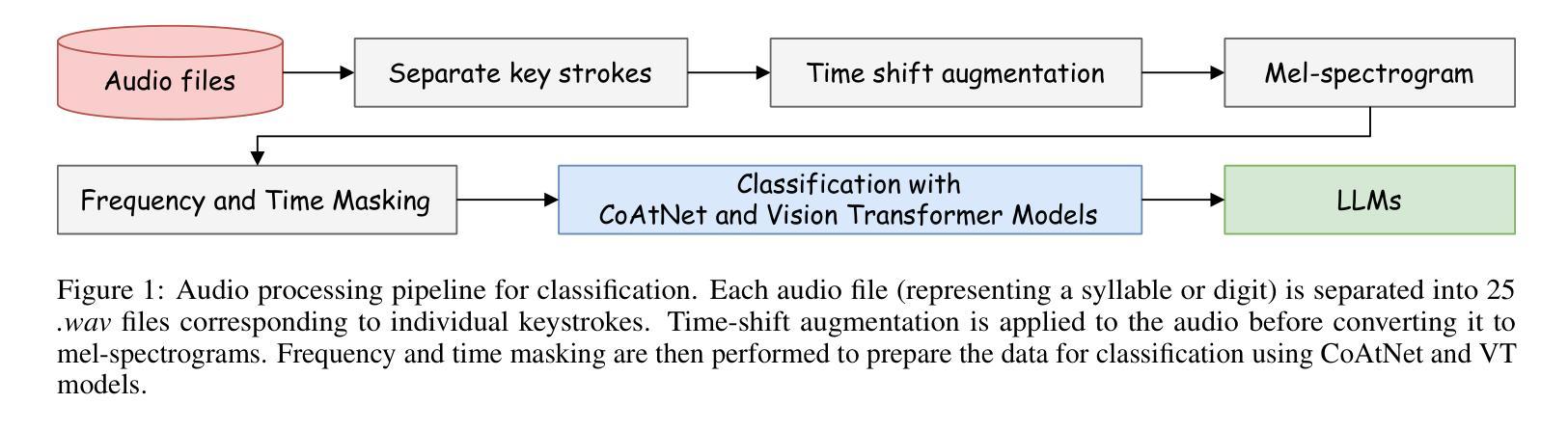
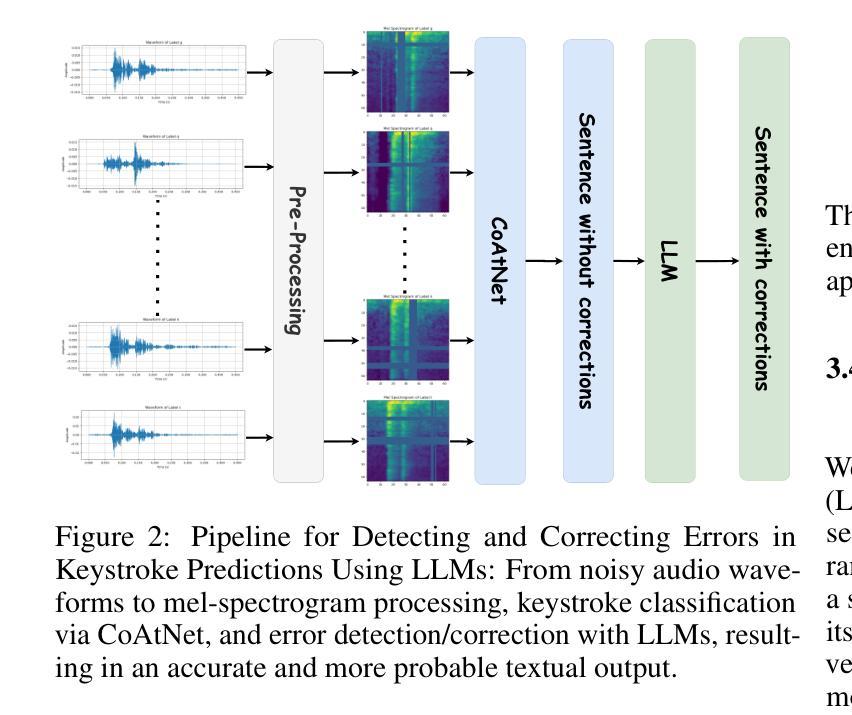
Improving Acoustic Side-Channel Attacks on Keyboards Using Transformers and Large Language Models
Authors:Jin Hyun Park, Seyyed Ali Ayati, Yichen Cai
The increasing prevalence of microphones in everyday devices and the growing reliance on online services have amplified the risk of acoustic side-channel attacks (ASCAs) targeting keyboards. This study explores deep learning techniques, specifically vision transformers (VTs) and large language models (LLMs), to enhance the effectiveness and applicability of such attacks. We present substantial improvements over prior research, with the CoAtNet model achieving state-of-the-art performance. Our CoAtNet shows a 5.0% improvement for keystrokes recorded via smartphone (Phone) and 5.9% for those recorded via Zoom compared to previous benchmarks. We also evaluate transformer architectures and language models, with the best VT model matching CoAtNet’s performance. A key advancement is the introduction of a noise mitigation method for real-world scenarios. By using LLMs for contextual understanding, we detect and correct erroneous keystrokes in noisy environments, enhancing ASCA performance. Additionally, fine-tuned lightweight language models with Low-Rank Adaptation (LoRA) deliver comparable performance to heavyweight models with 67X more parameters. This integration of VTs and LLMs improves the practical applicability of ASCA mitigation, marking the first use of these technologies to address ASCAs and error correction in real-world scenarios.
日常设备中麦克风的使用越来越普遍,对在线服务的依赖程度也越来越高,这加大了针对键盘的声侧信道攻击(ASCAs)的风险。本研究探讨了深度学习技术,特别是视觉变压器(VTs)和大型语言模型(LLMs)在提高此类攻击的有效性和适用性方面的应用。我们在先前研究的基础上取得了重大改进,CoAtNet模型达到了最先进的性能。我们的CoAtNet在通过智能手机(Phone)记录的键击上实现了5.0%的改进,在通过Zoom记录的键击上实现了5.9%的改进,超过了先前的基准测试。我们还评估了变压器架构和语言模型,最佳VT模型与CoAtNet的性能相匹配。一个关键的进步是引入了用于现实世界的噪声缓解方法。我们通过使用LLMs进行上下文理解,检测和纠正嘈杂环境中的错误键击,提高了ASCA的性能。此外,使用低秩适应(LoRA)进行微调的小型语言模型可产生与具有67倍以上参数的大型模型相当的性能。VTs和LLMs的集成提高了ASCA缓解的实际适用性,标志着这些技术在应对现实世界的ASCAs和错误纠正方面的首次应用。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF We will reflect comments from the reviewers and re-submit
Summary
本文探讨了日益普及的麦克风在日常设备中的风险以及在线服务增长的背景下,针对键盘的声学侧信道攻击(ASCAs)问题。研究利用深度学习的视觉变压器(VTs)和大型语言模型(LLMs)技术来提升此类攻击的有效性和适用性。CoAtNet模型实现了业界领先的性能,与先前的研究相比,在智能手机和Zoom记录的关键字输入方面分别提高了5.0%和5.9%。研究还评估了变压器架构和语言模型,并引入了一种用于真实场景的噪声缓解方法。通过利用LLMs进行上下文理解,可以在嘈杂环境中检测和纠正错误的键击,提高ASCA性能。此外,使用低秩适配(LoRA)的微调轻量级语言模型可实现与具有更多参数的重量级模型相当的性能。VTs和LLMs的结合提高了ASCA缓解的实际适用性,标志着这些技术首次被用于解决真实场景中的ASCA和错误纠正问题。
Key Takeaways
- 麦克风在日常设备中的普及和在线服务的增长增加了声学侧信道攻击(ASCAs)的风险。
- 研究利用深度学习的视觉变压器(VTs)和大型语言模型(LLMs)来增强ASCAs的有效性和适用性。
- CoAtNet模型实现了业界最佳性能,相比先前研究,在关键输入记录方面有所改善。
- 引入了一种针对真实场景的噪声缓解方法。
- 利用LLMs进行上下文理解,能在嘈杂环境中检测和纠正错误的键击。
- 使用低秩适配(LoRA)的轻量级语言模型可实现与重量级模型相当的性能。
点此查看论文截图


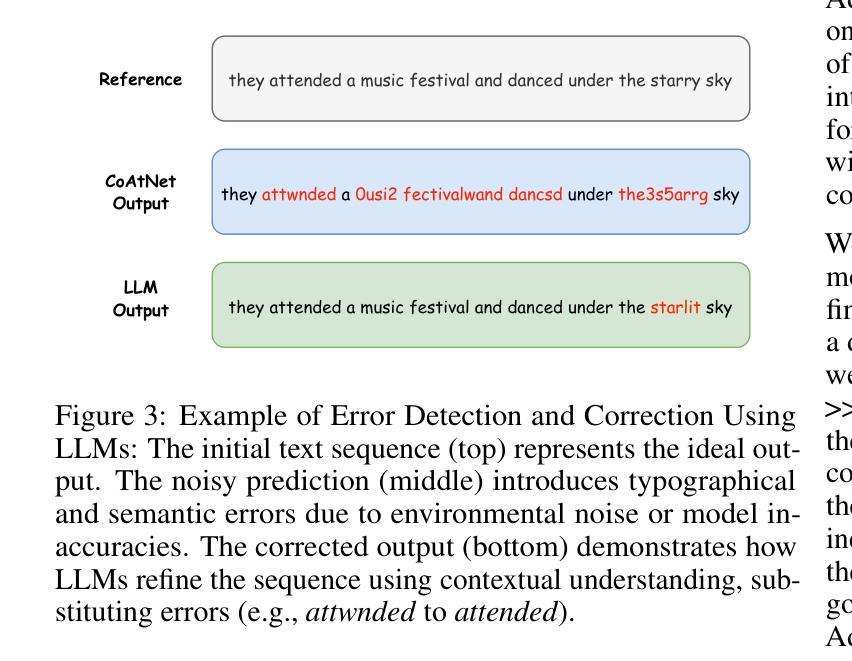
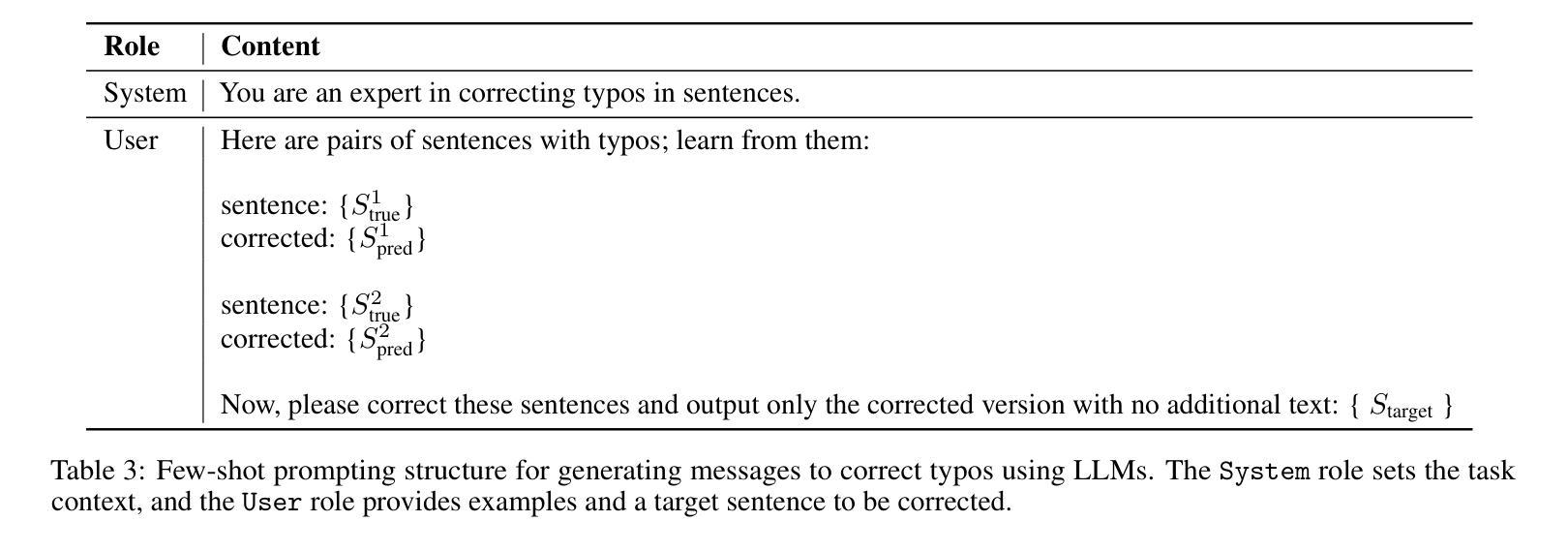
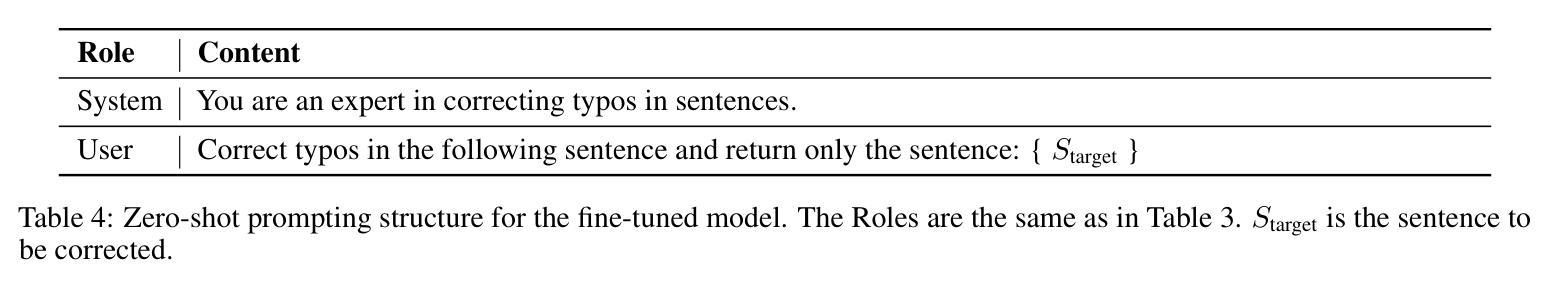
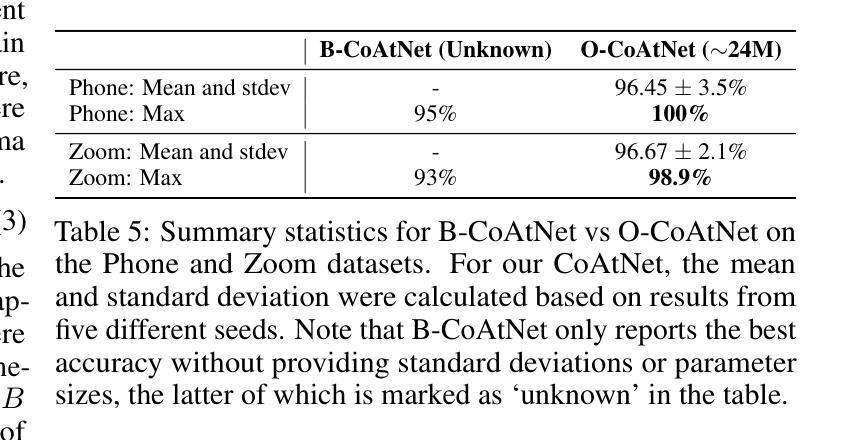
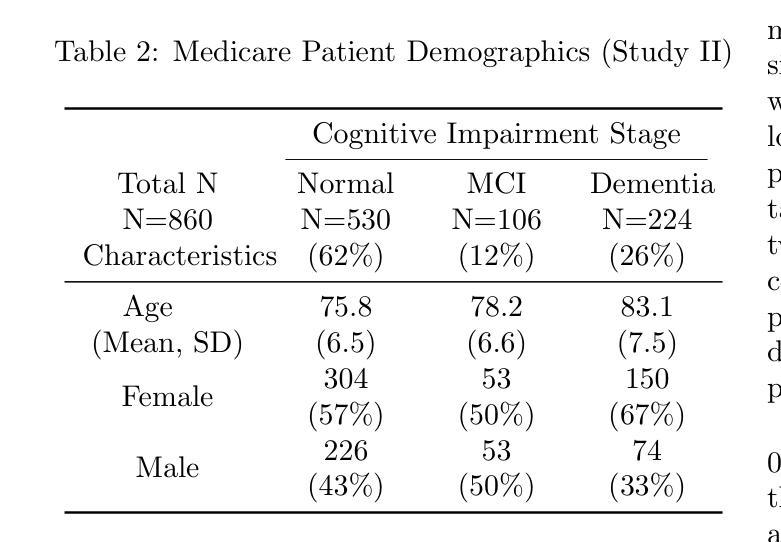
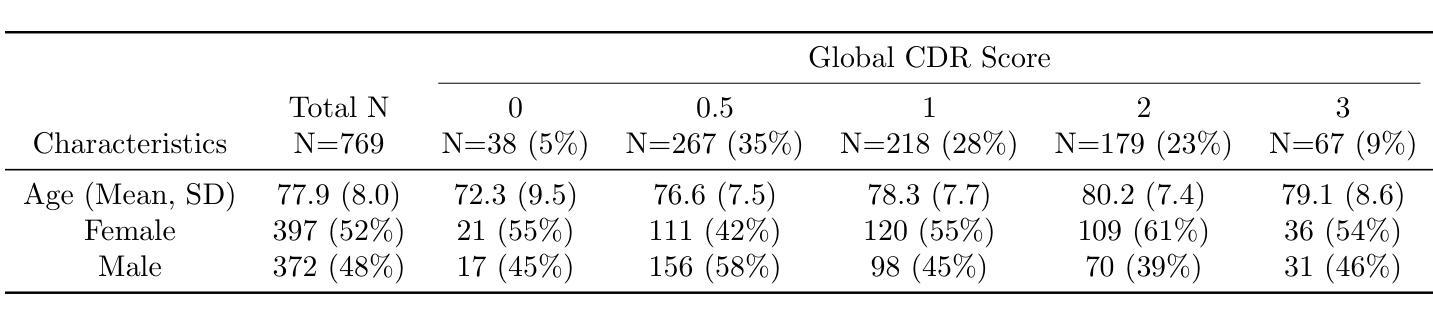
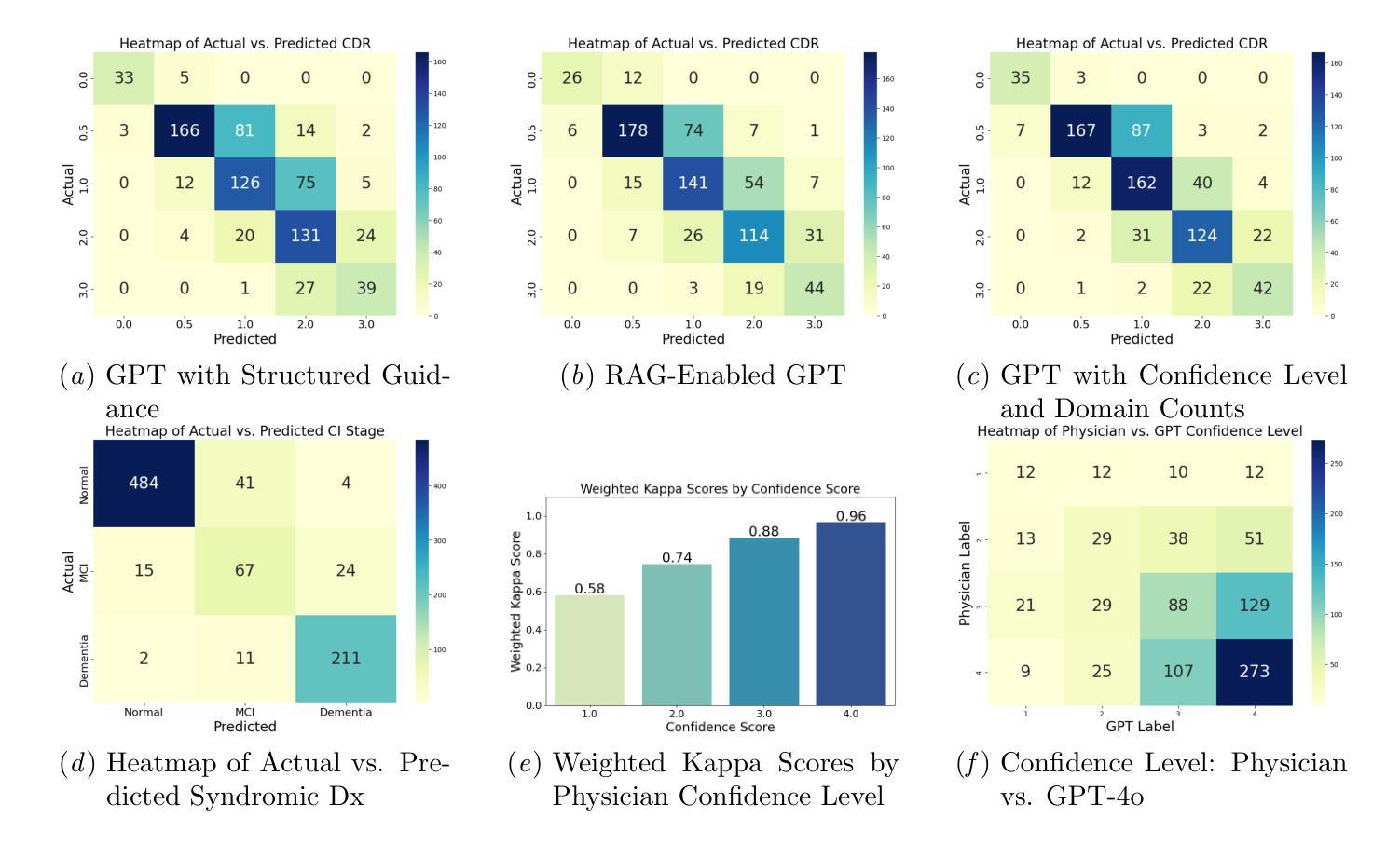
Evaluating GPT’s Capability in Identifying Stages of Cognitive Impairment from Electronic Health Data
Authors:Yu Leng, Yingnan He, Colin Magdamo, Ana-Maria Vranceanu, Christine S. Ritchie, Shibani S. Mukerji, Lidia M. V. R. Moura, John R. Dickson, Deborah Blacker, Sudeshna Das
Identifying cognitive impairment within electronic health records (EHRs) is crucial not only for timely diagnoses but also for facilitating research. Information about cognitive impairment often exists within unstructured clinician notes in EHRs, but manual chart reviews are both time-consuming and error-prone. To address this issue, our study evaluates an automated approach using zero-shot GPT-4o to determine stage of cognitive impairment in two different tasks. First, we evaluated the ability of GPT-4o to determine the global Clinical Dementia Rating (CDR) on specialist notes from 769 patients who visited the memory clinic at Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH), and achieved a weighted kappa score of 0.83. Second, we assessed GPT-4o’s ability to differentiate between normal cognition, mild cognitive impairment (MCI), and dementia on all notes in a 3-year window from 860 Medicare patients. GPT-4o attained a weighted kappa score of 0.91 in comparison to specialist chart reviews and 0.96 on cases that the clinical adjudicators rated with high confidence. Our findings demonstrate GPT-4o’s potential as a scalable chart review tool for creating research datasets and assisting diagnosis in clinical settings in the future.
识别电子健康记录(EHRs)中的认知障碍不仅对于及时诊断至关重要,而且对于促进研究也至关重要。关于认知障碍的信息通常存在于EHRs中的非结构化医生笔记中,但手动图表审查既耗时又容易出错。为了解决这一问题,我们的研究评估了一种使用零样本GPT-4o的自动化方法,以确定两个不同任务中的认知障碍阶段。首先,我们评估了GPT-4o确定来自马萨诸塞州总医院(MGH)记忆诊所的769名患者的全局临床痴呆评分(CDR)的能力,加权kappa得分为0.83。其次,我们评估了GPT-4o区分来自860名医疗保险患者三年所有记录的常规认知、轻度认知障碍(MCI)和痴呆的能力。GPT-4o与专业图表审查的加权kappa得分为0.91,而在临床裁定者高度评价的案例中达到了0.96。我们的研究结果表明,GPT-4o具有作为可伸缩的图表审查工具在未来创建研究数据集和协助临床环境中诊断的潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Findings paper presented at Machine Learning for Health (ML4H) symposium 2024, December 15-16, 2024, Vancouver, Canada, 7 pages
Summary:本研究利用GPT-4o自动化方法,通过两个任务评估其在电子健康记录中识别认知障碍阶段的性能。首先,在记忆诊所患者数据集中,GPT-4o能够确定临床痴呆评分,加权kappa得分为0.83。其次,在医保患者数据集中,GPT-4o能区分正常认知、轻度认知障碍和痴呆,加权kappa得分为0.91。研究结果表明GPT-4o具有作为可规模化图表审查工具在未来创建研究数据集和辅助临床诊疗的潜力。
Key Takeaways:
- GPT-4o被用于自动化识别电子健康记录中的认知障碍阶段。
- 在记忆诊所患者数据集中,GPT-4o的临床痴呆评分加权kappa得分为0.83。
- GPT-4o在医保患者数据集中能够区分正常认知、轻度认知障碍和痴呆,加权kappa得分为0.91。
- GPT-4o的表现在高置信度病例中尤其出色,与专家评审的加权kappa得分达到0.96。
- 此方法能够提高诊断时效性和准确性,对于研究和临床实践具有重要意义。
- GPT-4o的潜力在于可作为可规模化图表审查工具,便于创建研究数据集。
点此查看论文截图

Optimizing GPT for Video Understanding: Zero-Shot Performance and Prompt Engineering
Authors:Mark Beliaev, Victor Yang, Madhura Raju, Jiachen Sun, Xinghai Hu
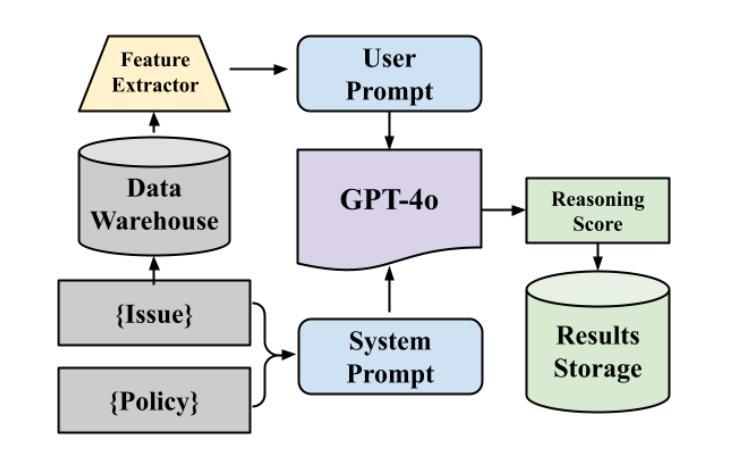
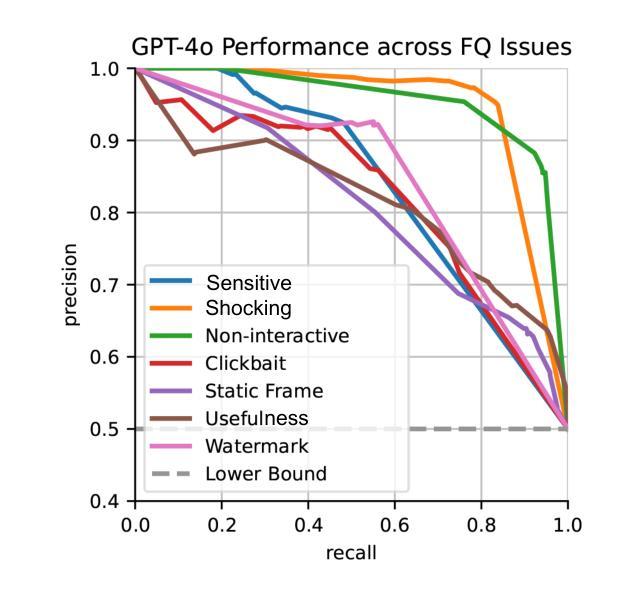
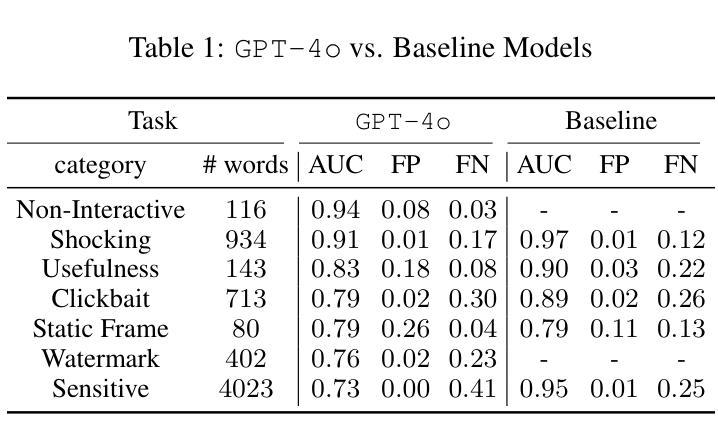
In this study, we tackle industry challenges in video content classification by exploring and optimizing GPT-based models for zero-shot classification across seven critical categories of video quality. We contribute a novel approach to improving GPT’s performance through prompt optimization and policy refinement, demonstrating that simplifying complex policies significantly reduces false negatives. Additionally, we introduce a new decomposition-aggregation-based prompt engineering technique, which outperforms traditional single-prompt methods. These experiments, conducted on real industry problems, show that thoughtful prompt design can substantially enhance GPT’s performance without additional finetuning, offering an effective and scalable solution for improving video classification systems across various domains in industry.
在本次研究中,我们通过对GPT为基础模型的探索与优化,针对视频质量的七大关键类别,实现零样本分类的视频内容分类行业挑战。我们提出了一种改进GPT性能的新方法,通过提示优化和政策完善,证明简化复杂政策可以显著降低假阴性。此外,我们还引入了一种基于分解聚合的提示工程技术,它优于传统的单一提示方法。这些实验是在真实的行业问题上进行的,表明有策略的提示设计可以在不增加微调的情况下显著提高GPT的性能,为改善工业各领域视频分类系统提供了有效且可扩展的解决方案。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本研究通过探索和优化GPT模型为基础的方法,解决视频内容分类行业中的挑战,实现了零样本分类在七个关键视频质量类别中的应用。研究通过改进GPT性能,提出优化提示和政策精炼的新方法,简化复杂政策以降低误报率。同时引入基于分解聚合技术的提示工程技术,超越传统单一提示方法。实验证明,无需额外微调,精心设计提示可以显著提高GPT性能,为工业界各领域改进视频分类系统提供了有效可伸缩的解决方案。
Key Takeaways
- 研究针对视频内容分类行业的挑战,采用GPT模型进行优化。
- 实现零样本分类在七个关键视频质量类别中的应用。
- 提出优化提示和政策精炼的新方法,以提高GPT的性能。
- 简化复杂政策以降低误报率。
- 引入基于分解聚合技术的提示工程技术,提高分类准确性。
- 实验证明精心设计提示可以显著提高GPT性能,无需额外微调。
点此查看论文截图