⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-02-19 更新
HumanGif: Single-View Human Diffusion with Generative Prior
Authors:Shoukang Hu, Takuya Narihira, Kazumi Fukuda, Ryosuke Sawata, Takashi Shibuya, Yuki Mitsufuji
While previous single-view-based 3D human reconstruction methods made significant progress in novel view synthesis, it remains a challenge to synthesize both view-consistent and pose-consistent results for animatable human avatars from a single image input. Motivated by the success of 2D character animation, we propose HumanGif, a single-view human diffusion model with generative prior. Specifically, we formulate the single-view-based 3D human novel view and pose synthesis as a single-view-conditioned human diffusion process, utilizing generative priors from foundational diffusion models. To ensure fine-grained and consistent novel view and pose synthesis, we introduce a Human NeRF module in HumanGif to learn spatially aligned features from the input image, implicitly capturing the relative camera and human pose transformation. Furthermore, we introduce an image-level loss during optimization to bridge the gap between latent and image spaces in diffusion models. Extensive experiments on RenderPeople and DNA-Rendering datasets demonstrate that HumanGif achieves the best perceptual performance, with better generalizability for novel view and pose synthesis.
虽然基于单视角的3D人体重建方法在新型视图合成方面取得了显著进展,但从单张图像输入中合成既符合视图又符合姿态的可动人体角色仍然是一个挑战。受到2D角色动画成功的启发,我们提出了HumanGif,这是一个带有生成先验的单视角人体扩散模型。具体来说,我们将基于单视角的3D人体新型视图和姿态合成制定为单视角条件下的人体扩散过程,利用基础扩散模型的生成先验。为了确保精细且一致的新型视图和姿态合成,我们在HumanGif中引入了Human NeRF模块,以从输入图像中学习空间对齐特征,隐式捕获相对相机和人体姿态变换。此外,在优化过程中,我们引入了图像级损失,以缩小扩散模型中潜在空间和图像空间之间的差距。在RenderPeople和DNA-Rendering数据集上的大量实验表明,HumanGif达到了最佳的感知性能,对于新型视图和姿态合成具有更好的泛化能力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project page: https://skhu101.github.io/HumanGif/
Summary
本文提出一种基于单视图的人像扩散模型HumanGif,用于合成具有一致性和可动画性的三维人类角色。通过引入Human NeRF模块,该模型可从输入图像中学习空间对齐特征,并隐式捕获相对相机和人体姿态变换。此外,采用图像级损失优化扩散模型中的潜在与图像空间差距。实验证明,HumanGif在视图和姿态合成方面具有最佳感知性能和良好的泛化能力。
Key Takeaways
- HumanGif是一个基于单视图的人像扩散模型,用于合成三维人类角色。
- 模型将单视图条件的三维人类新视角和姿态合成制定为单视图条件的人像扩散过程。
- 引入Human NeRF模块,从输入图像中学习空间对齐特征,隐式捕获相对相机和人体姿态变换。
- 采用图像级损失优化模型,缩小潜在与图像空间的差距。
- 模型在RenderPeople和DNA-Rendering数据集上的实验表现出最佳感知性能。
- 模型具有良好的泛化能力,尤其在新型视角和姿态合成方面。
点此查看论文截图

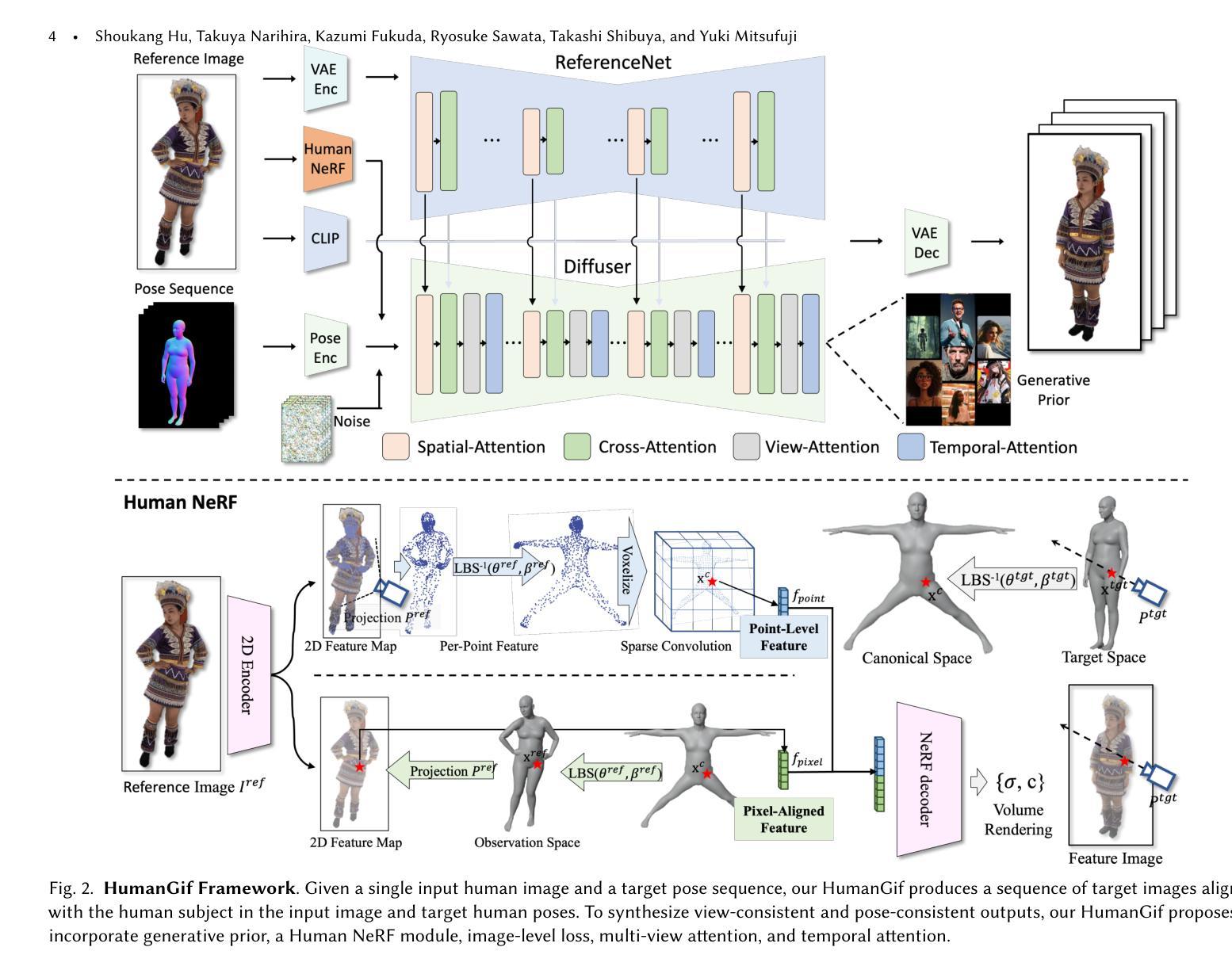
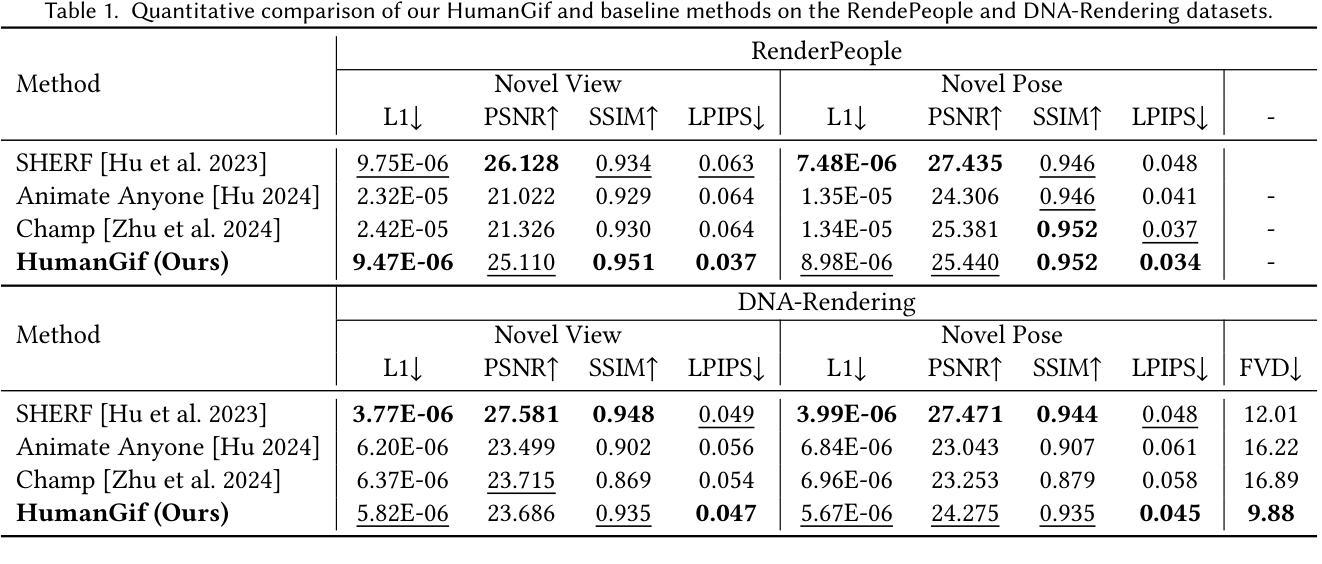
Image Inversion: A Survey from GANs to Diffusion and Beyond
Authors:Yinan Chen, Jiangning Zhang, Yali Bi, Xiaobin Hu, Teng Hu, Zhucun Xue, Ran Yi, Yong Liu, Ying Tai
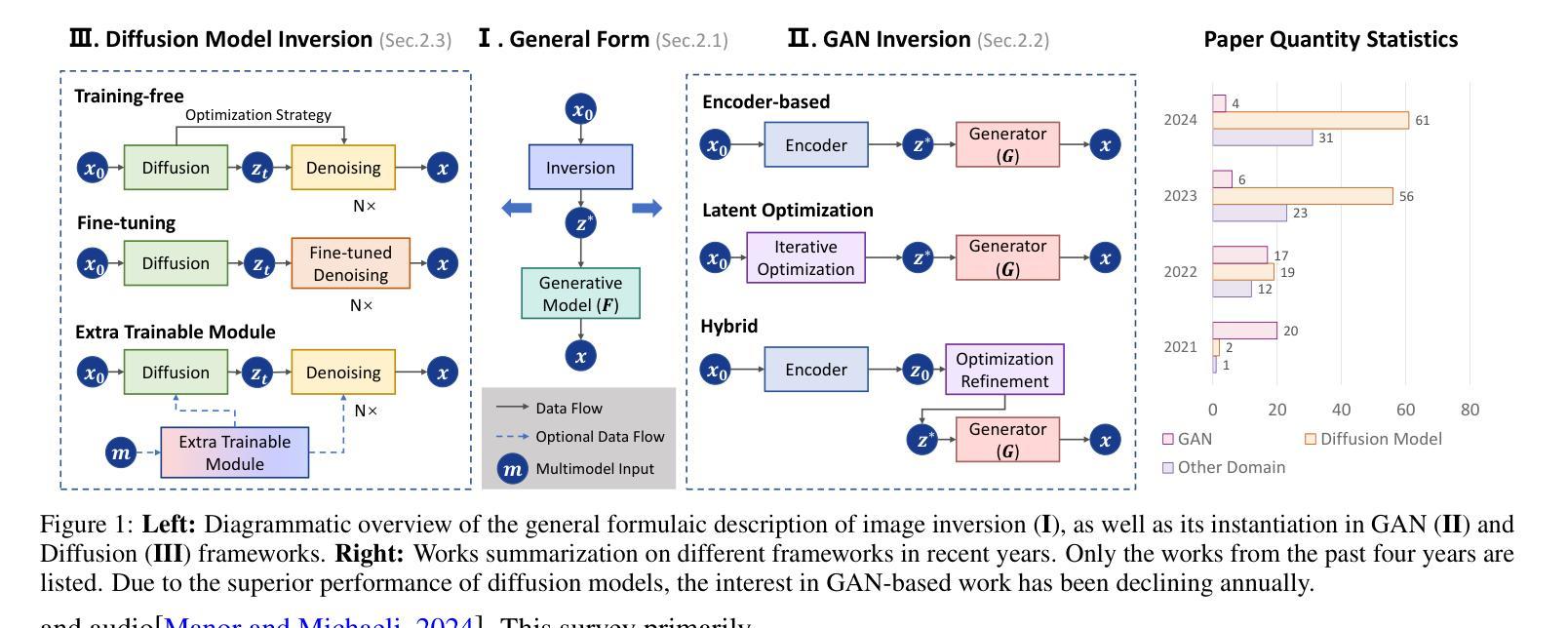
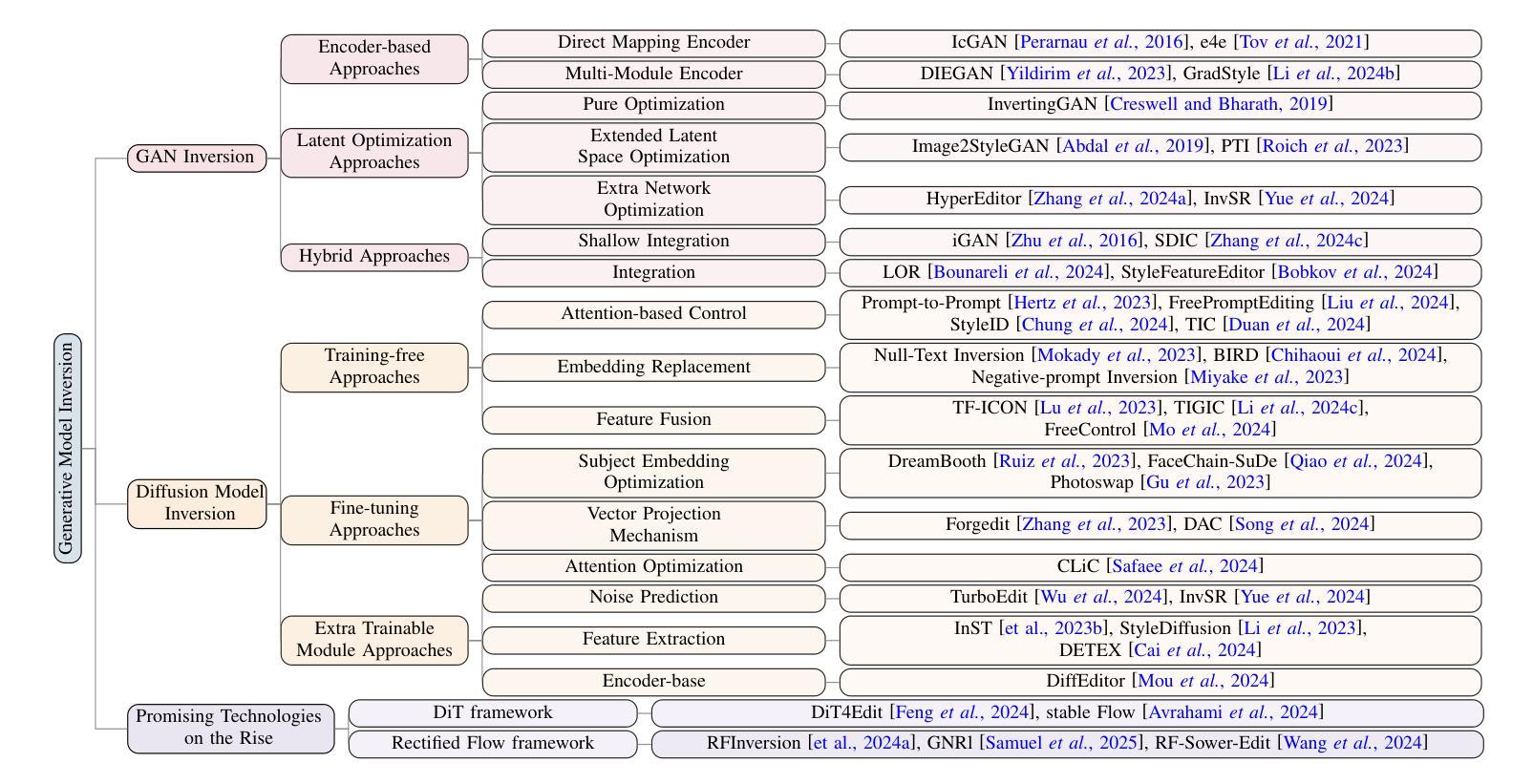
Image inversion is a fundamental task in generative models, aiming to map images back to their latent representations to enable downstream applications such as editing, restoration, and style transfer. This paper provides a comprehensive review of the latest advancements in image inversion techniques, focusing on two main paradigms: Generative Adversarial Network (GAN) inversion and diffusion model inversion. We categorize these techniques based on their optimization methods. For GAN inversion, we systematically classify existing methods into encoder-based approaches, latent optimization approaches, and hybrid approaches, analyzing their theoretical foundations, technical innovations, and practical trade-offs. For diffusion model inversion, we explore training-free strategies, fine-tuning methods, and the design of additional trainable modules, highlighting their unique advantages and limitations. Additionally, we discuss several popular downstream applications and emerging applications beyond image tasks, identifying current challenges and future research directions. By synthesizing the latest developments, this paper aims to provide researchers and practitioners with a valuable reference resource, promoting further advancements in the field of image inversion. We keep track of the latest works at https://github.com/RyanChenYN/ImageInversion
图像反转是生成模型中的一项基本任务,旨在将图像映射回其潜在表示形式,以实现下游应用,如编辑、修复和风格转换。本文全面回顾了图像反转技术的最新进展,重点介绍了两种主要范式:生成对抗网络(GAN)反转变和扩散模型反转变。我们根据优化方法对这些技术进行分类。对于GAN反转变,我们将现有方法系统地分类为基于编码器的方法、潜在优化方法和混合方法,分析其理论基础、技术创新和实用折衷。对于扩散模型反转变,我们探讨了无训练策略、微调方法和附加可训练模块的设计,突出了它们的独特优势和局限性。此外,我们还讨论了几个流行的下游应用和图像任务之外的新兴应用,确定了当前挑战和未来研究方向。通过综合最新发展,本文旨在为研究人员和实践者提供有价值的参考资料,推动图像反转领域的进一步发展。我们在https://github.com/RyanChenYN/ImageInversion上跟踪最新工作。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 10 pages, 2 figures
Summary
最新图像反转技术综述,详细介绍了生成对抗网络(GAN)反转和扩散模型反转两大主流方法。分析了各自的优化方法、理论根据、技术创新和实践中的权衡。还提供对图像反转下游应用的洞察,展望了未来研究方向。
Key Takeaways
- 图像反转是生成模型的基本任务,旨在将图像映射回其潜在表示,以支持编辑、修复和风格转换等下游应用。
- GAN反转和扩散模型反转是当前图像反转技术的两大主要方法。
- GAN反转分为基于编码器的方法、潜在优化方法和混合方法,每种方法都有其理论基础、技术新颖性和实用性权衡。
- 扩散模型反转探讨无训练策略、微调方法和可训练模块的设计,突出了它们的独特优势和局限性。
- 图像反转技术广泛应用于下游应用,包括编辑、修复和风格转换等,并扩展到其他领域。
点此查看论文截图

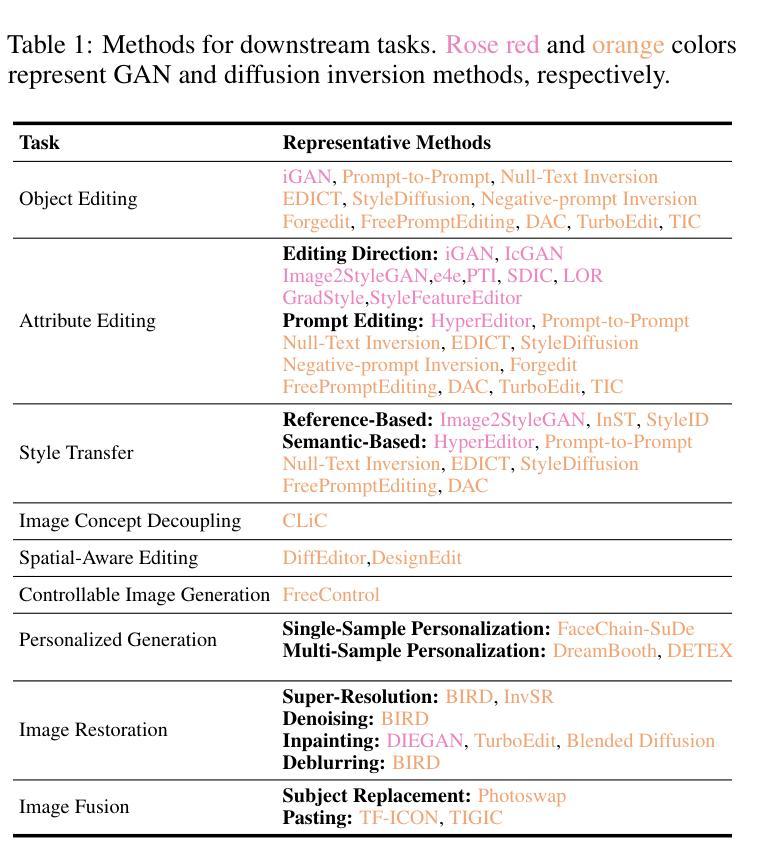
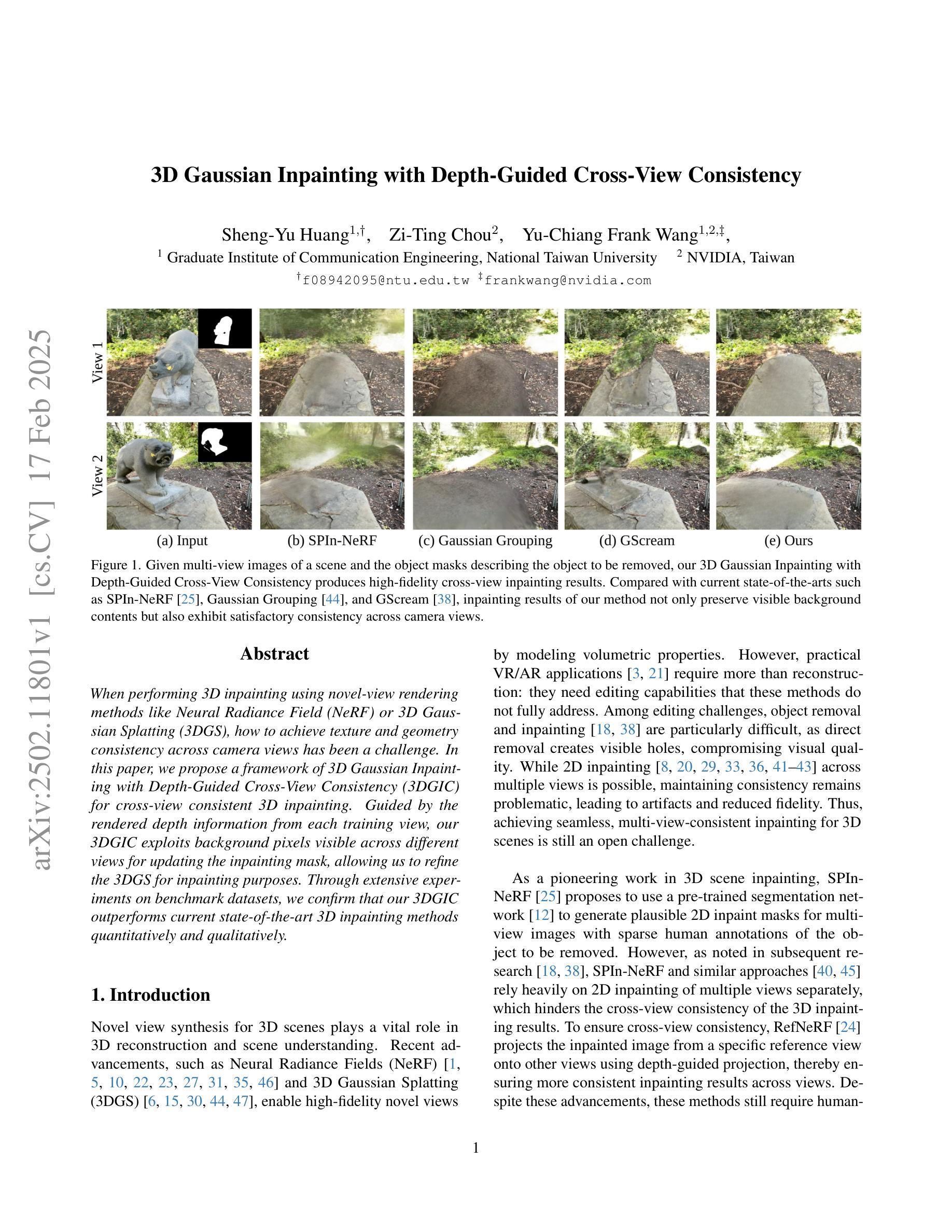
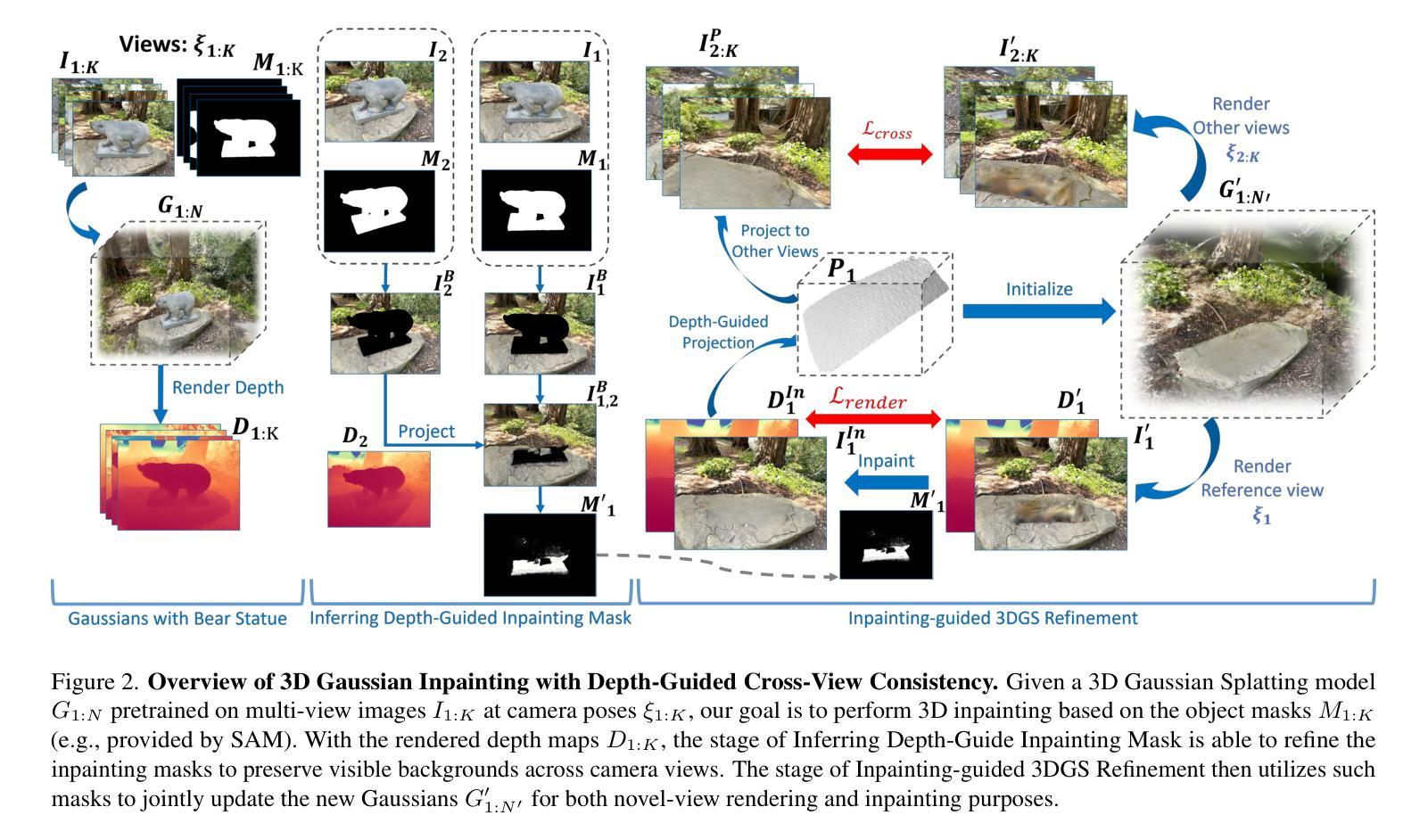
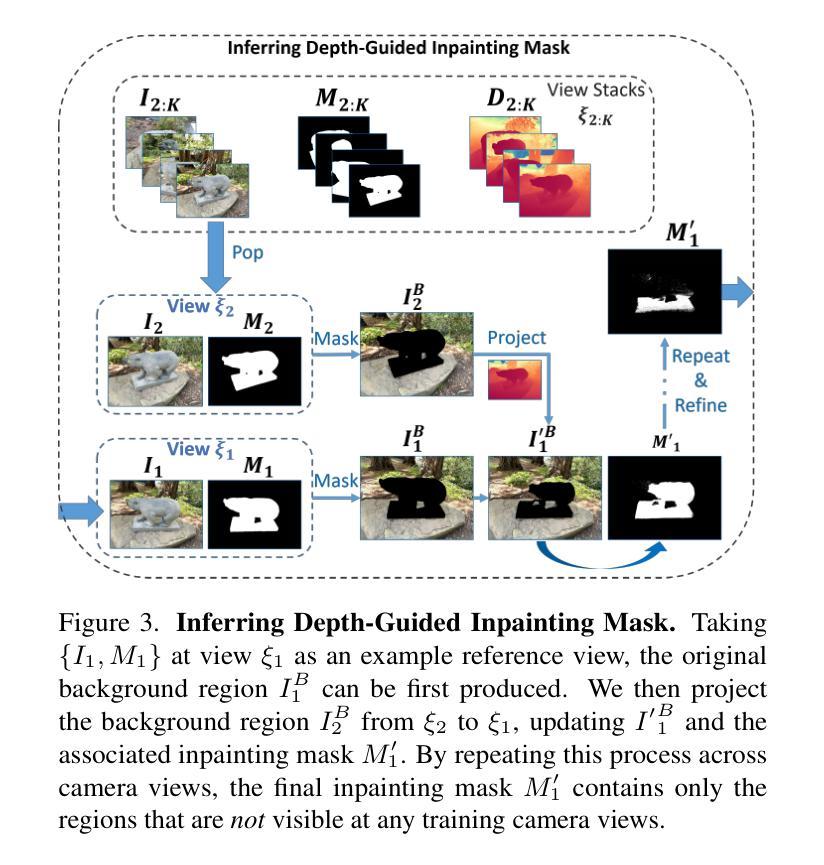
3D Gaussian Inpainting with Depth-Guided Cross-View Consistency
Authors:Sheng-Yu Huang, Zi-Ting Chou, Yu-Chiang Frank Wang
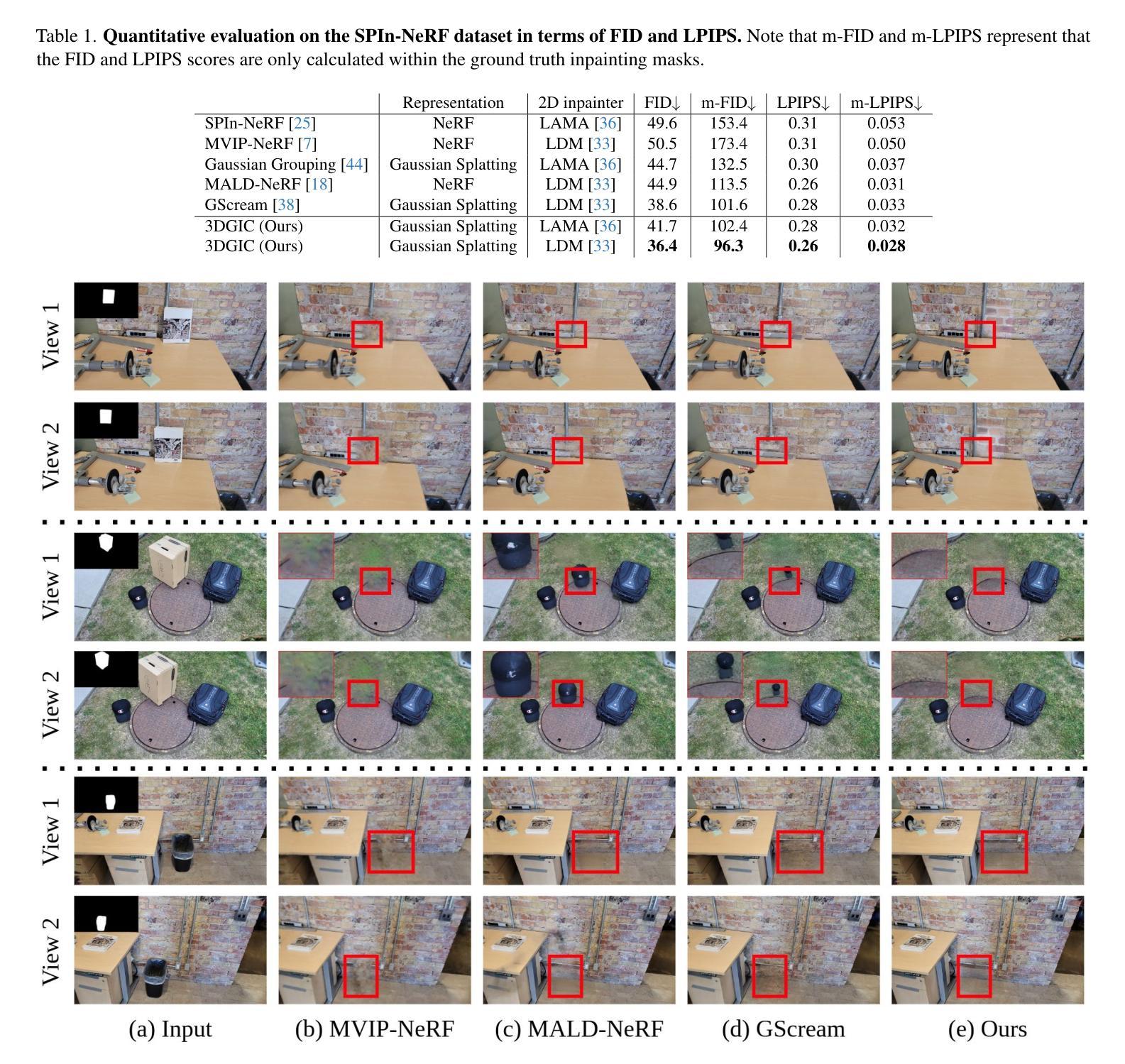
When performing 3D inpainting using novel-view rendering methods like Neural Radiance Field (NeRF) or 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS), how to achieve texture and geometry consistency across camera views has been a challenge. In this paper, we propose a framework of 3D Gaussian Inpainting with Depth-Guided Cross-View Consistency (3DGIC) for cross-view consistent 3D inpainting. Guided by the rendered depth information from each training view, our 3DGIC exploits background pixels visible across different views for updating the inpainting mask, allowing us to refine the 3DGS for inpainting purposes.Through extensive experiments on benchmark datasets, we confirm that our 3DGIC outperforms current state-of-the-art 3D inpainting methods quantitatively and qualitatively.
在使用如Neural Radiance Field(NeRF)或3D Gaussian Splatting(3DGS)等新视角渲染方法进行3D补全时,如何在不同相机视角间实现纹理和几何一致性一直是一个挑战。在本文中,我们提出了一种名为3D Gaussian补全与深度引导跨视图一致性(3DGIC)的框架,以实现跨视图一致的3D补全。通过来自每个训练视图的渲染深度信息作为指导,我们的3DGIC利用不同视图中可见的背景像素来更新补全掩模,使我们能够优化用于补全的3DGS。通过对基准数据集的大量实验,我们确认我们的3DGIC在数量和质量上都优于当前最先进的3D补全方法。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出了一种基于深度引导跨视图一致性(Depth-Guided Cross-View Consistency,简称3DGIC)的3D高斯补全框架,用于实现跨视图一致的3D补全。通过利用来自训练视图的渲染深度信息来引导,该方法可以利用不同视图可见的背景像素来更新补全掩膜,从而优化用于补全的3D高斯技术。在基准数据集上的实验证明,该方法在数量和质量上均优于当前最先进的3D补全技术。
Key Takeaways
- 介绍了使用深度引导跨视图一致性进行三维补全的框架(称为3DGIC)。此框架可实现跨不同视图的纹理和几何一致性。
- 该方法利用从训练视图中渲染的深度信息来指导补全过程。深度信息对于确保不同视图之间的几何一致性至关重要。
点此查看论文截图

Dynamic Scene Understanding through Object-Centric Voxelization and Neural Rendering
Authors:Yanpeng Zhao, Yiwei Hao, Siyu Gao, Yunbo Wang, Xiaokang Yang
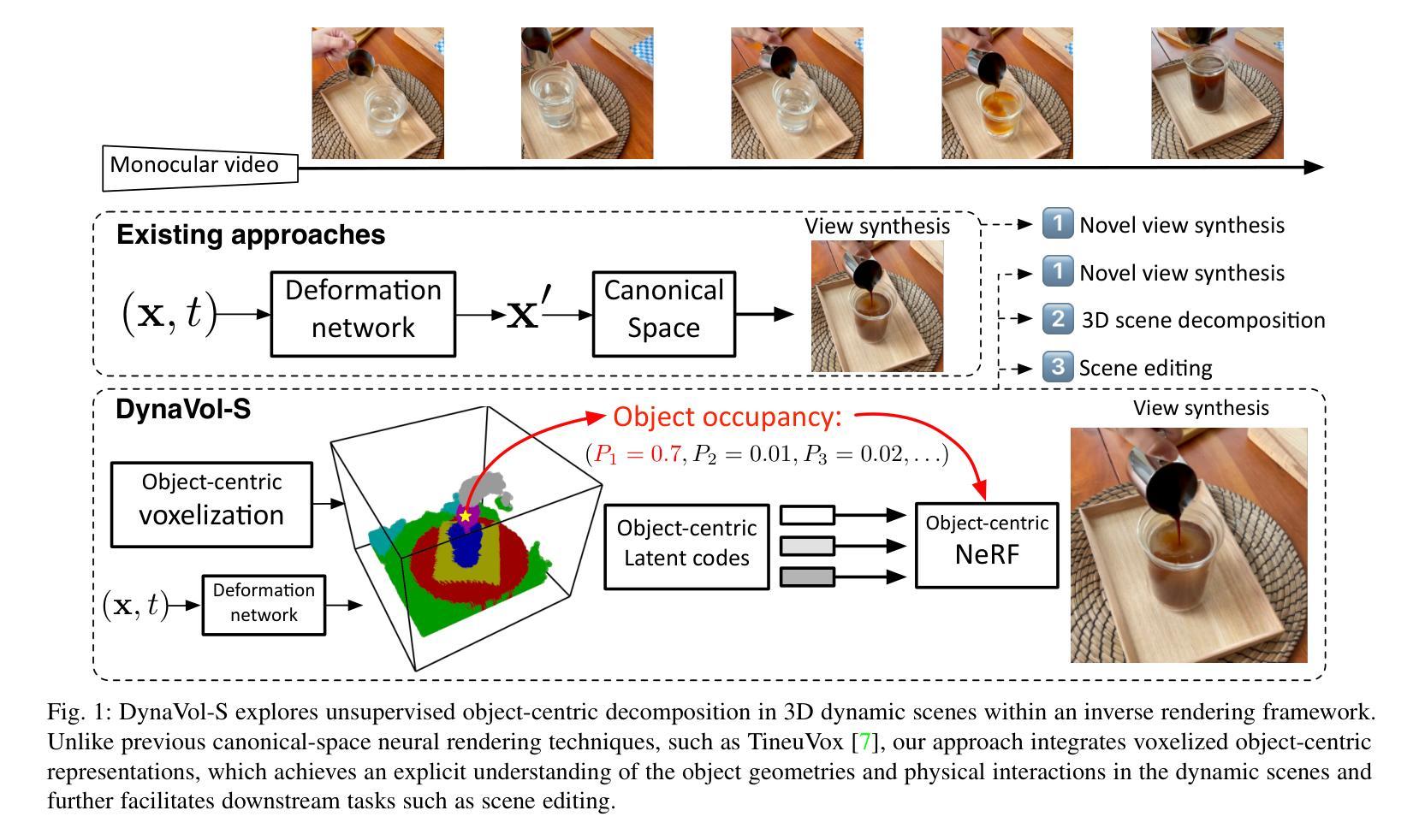
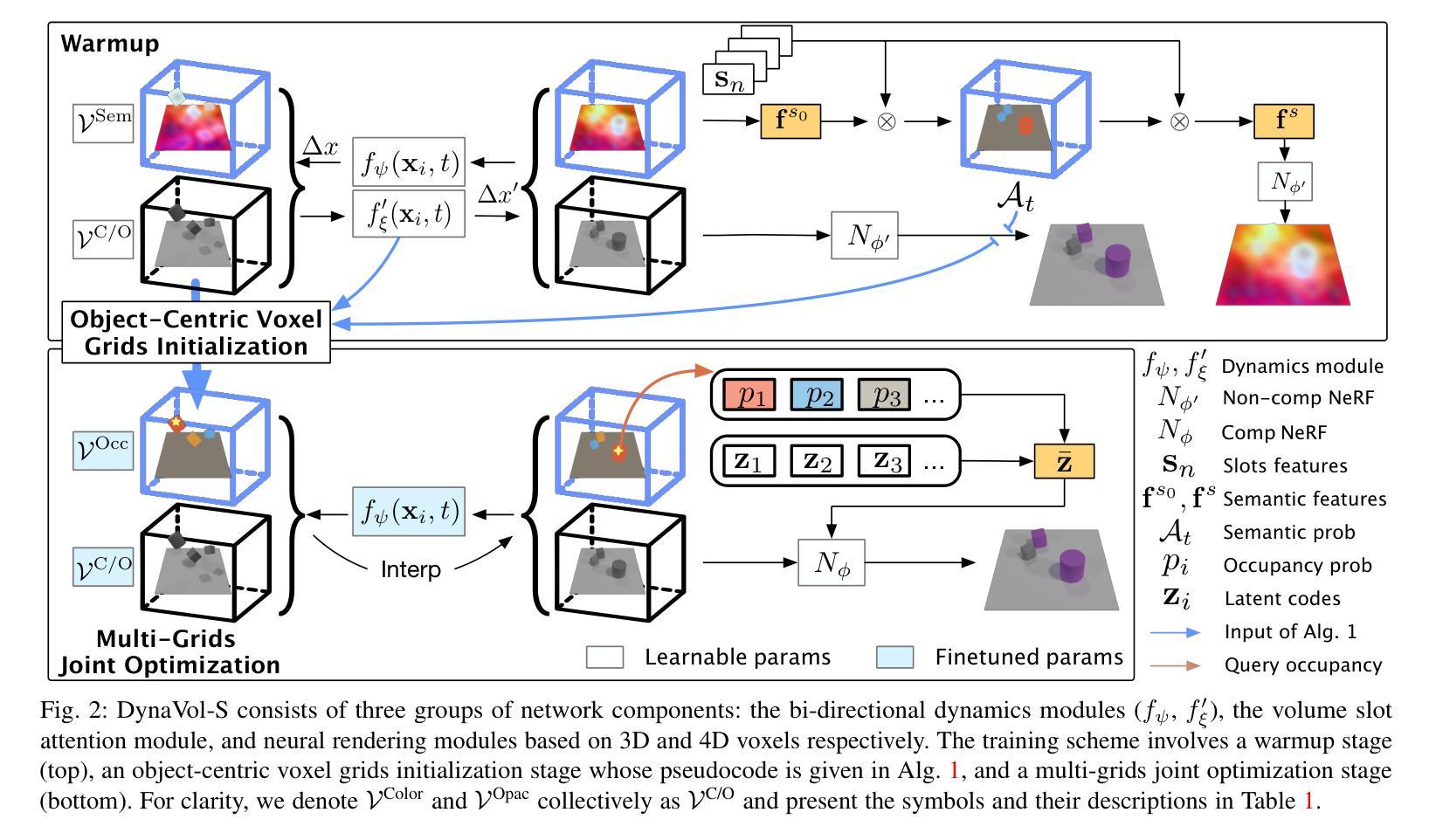
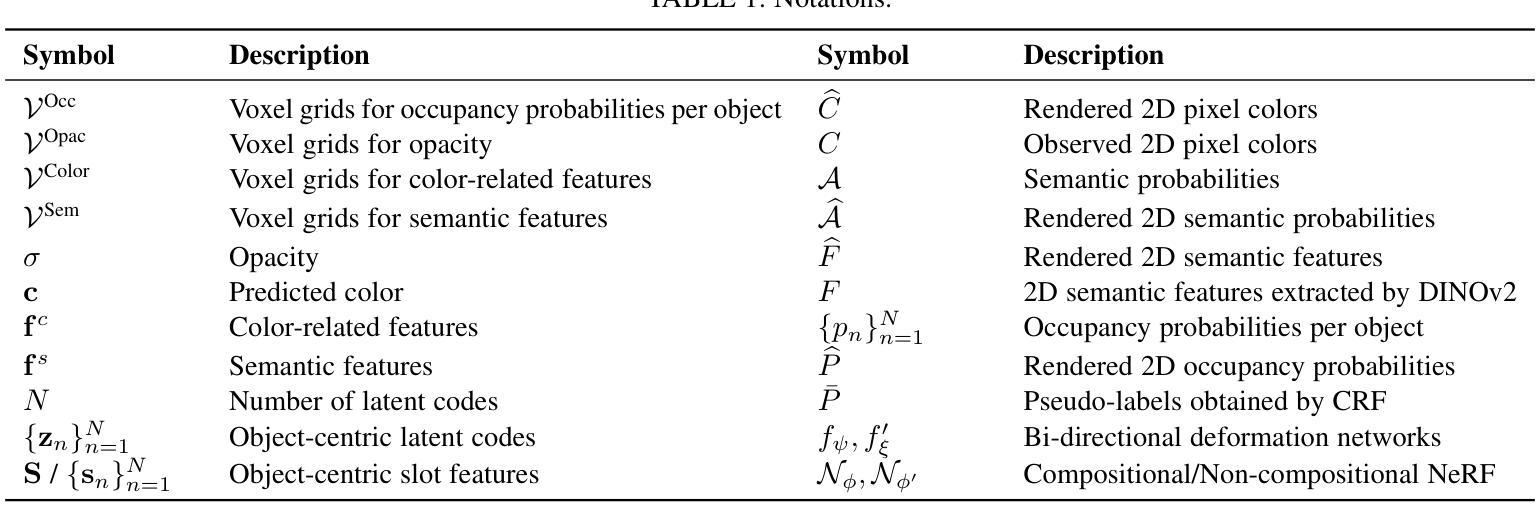
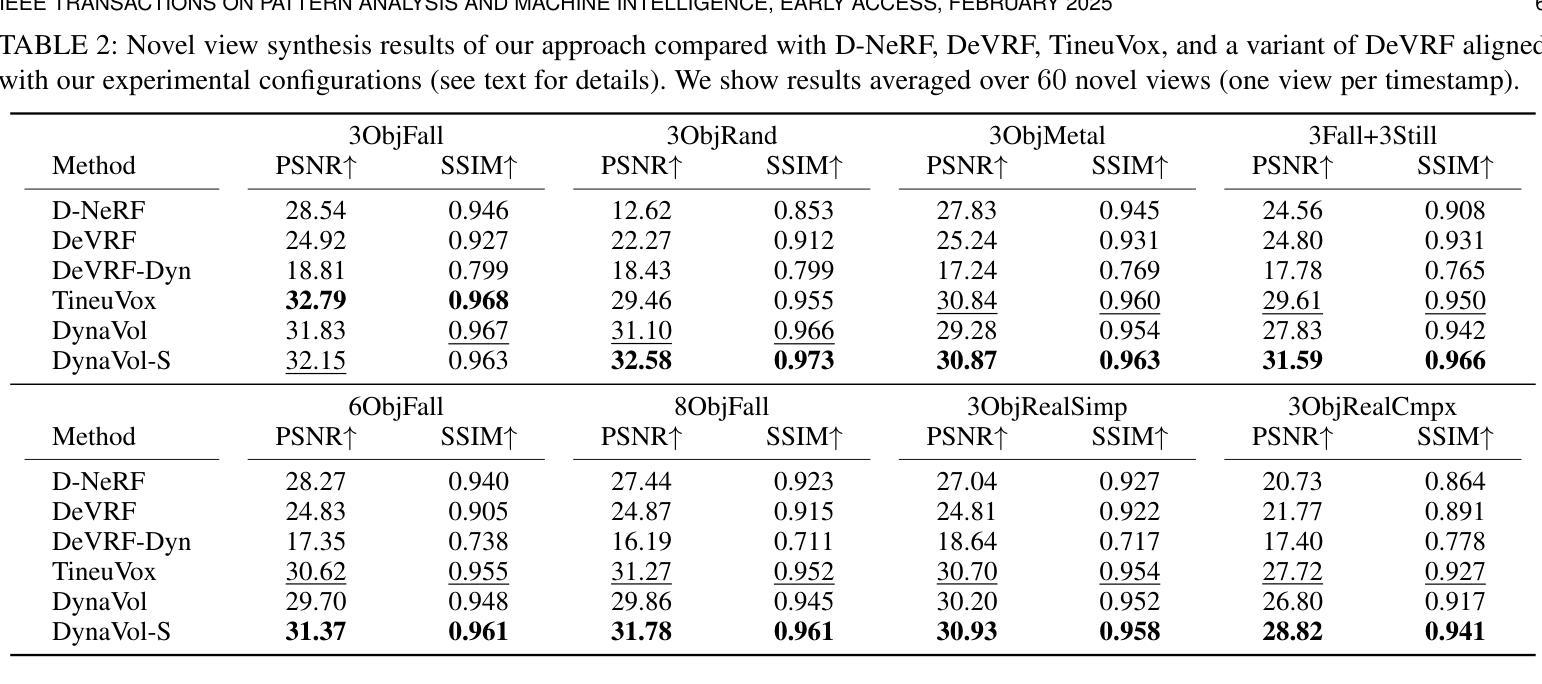
Learning object-centric representations from unsupervised videos is challenging. Unlike most previous approaches that focus on decomposing 2D images, we present a 3D generative model named DynaVol-S for dynamic scenes that enables object-centric learning within a differentiable volume rendering framework. The key idea is to perform object-centric voxelization to capture the 3D nature of the scene, which infers per-object occupancy probabilities at individual spatial locations. These voxel features evolve through a canonical-space deformation function and are optimized in an inverse rendering pipeline with a compositional NeRF. Additionally, our approach integrates 2D semantic features to create 3D semantic grids, representing the scene through multiple disentangled voxel grids. DynaVol-S significantly outperforms existing models in both novel view synthesis and unsupervised decomposition tasks for dynamic scenes. By jointly considering geometric structures and semantic features, it effectively addresses challenging real-world scenarios involving complex object interactions. Furthermore, once trained, the explicitly meaningful voxel features enable additional capabilities that 2D scene decomposition methods cannot achieve, such as novel scene generation through editing geometric shapes or manipulating the motion trajectories of objects.
从非监督视频中学习对象中心的表示是一项挑战。不同于大多数以前主要关注2D图像分解的方法,我们提出了一种用于动态场景的3D生成模型DynaVol-S,它能在可微分体积渲染框架内进行对象中心的学习。关键思想是通过对象中心的体素化捕捉场景的3D特性,推断出每个空间位置的单个对象的占用概率。这些体素特征通过规范空间变形函数进行演化,并在逆向渲染管道中与组合NeRF一起进行优化。此外,我们的方法融合了2D语义特征来创建3D语义网格,通过多个解纠缠的体素网格表示场景。DynaVol-S在动态场景的新视角合成和无监督分解任务上都显著优于现有模型。通过联合考虑几何结构和语义特征,它有效地解决了涉及复杂对象交互的挑战性现实世界场景问题。此外,一旦训练完成,明确的体素特征将具备2D场景分解方法无法实现的其他功能,如通过编辑几何形状或操作物体的运动轨迹来生成新场景。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by TPAMI2025
摘要
从无监督视频中学习对象中心表示具有挑战性。不同于大多数仅关注二维图像分解的方法,我们提出了一种名为DynaVol-S的三维生成模型,用于动态场景的对象中心学习。其核心思想是通过对象中心的体素化捕捉场景的三维特性,推断单个空间位置的每个对象的占用概率。这些体素特征通过规范空间变形函数演化,并在逆向渲染管道中与组合NeRF一起优化。此外,我们的方法结合了二维语义特征来创建三维语义网格,通过多个解耦的体素网格表示场景。DynaVol-S在动态场景的新视角合成和无监督分解任务上显著优于现有模型。通过综合考虑几何结构和语义特征,它有效地解决了涉及复杂对象交互的挑战性现实世界场景问题。此外,训练后的明确有意义的体素特征实现了二维场景分解方法无法实现的新功能,例如通过编辑几何形状或操作物体的运动轨迹来生成新场景。
要点
- 提出了一个名为DynaVol-S的3D生成模型,用于动态场景的对象中心学习。
- 通过对象中心的体素化捕捉场景的三维特性。
- 结合了二维语义特征创建三维语义网格,表示场景。
- 在新视角合成和无监督分解任务上,DynaVol-S显著优于现有模型。
- 综合考虑几何结构和语义特征,有效处理复杂对象交互的挑战性场景。
- 训练后的体素特征支持新功能,如编辑几何形状或操作物体运动轨迹来生成新场景。
- DynaVol-S模型具有更强的场景理解和生成能力。
点此查看论文截图
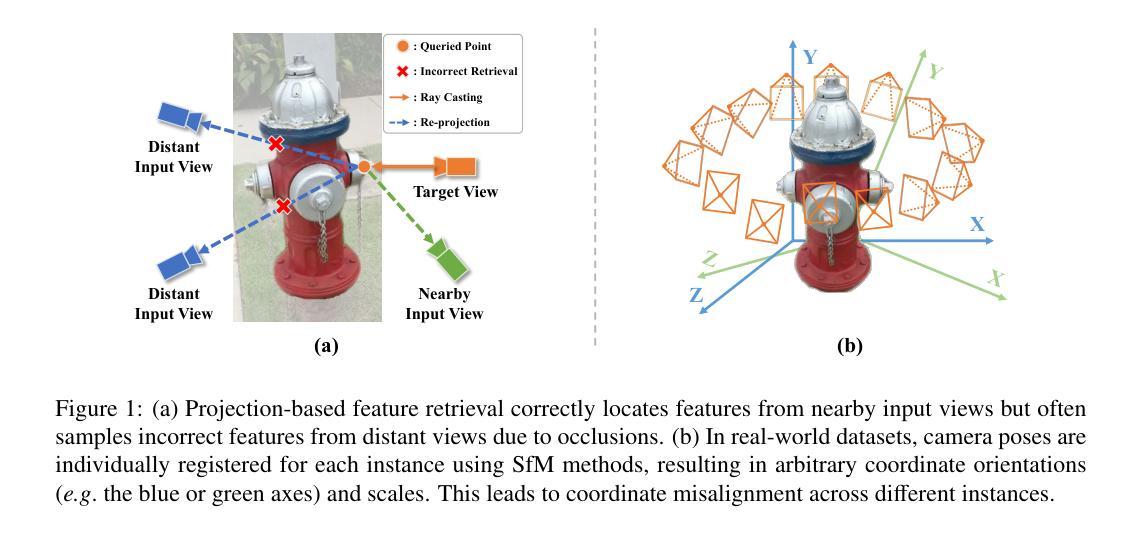
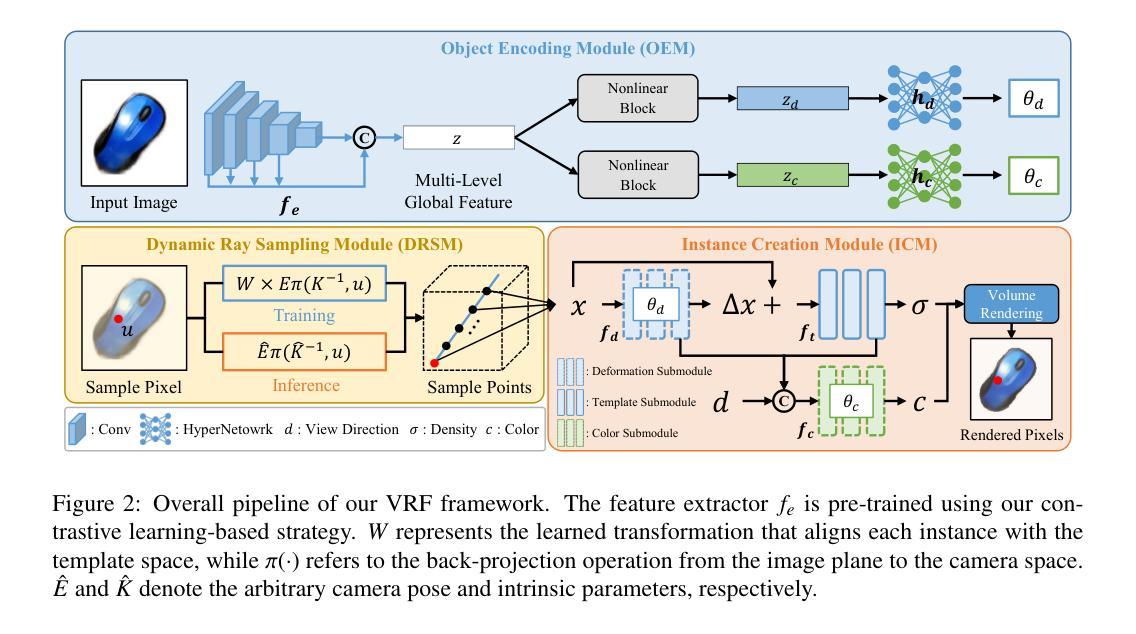
Variable Radiance Field for Real-World Category-Specific Reconstruction from Single Image
Authors:Kun Wang, Zhiqiang Yan, Zhenyu Zhang, Xiang Li, Jun Li, Jian Yang
Reconstructing category-specific objects using Neural Radiance Field (NeRF) from a single image is a promising yet challenging task. Existing approaches predominantly rely on projection-based feature retrieval to associate 3D points in the radiance field with local image features from the reference image. However, this process is computationally expensive, dependent on known camera intrinsics, and susceptible to occlusions. To address these limitations, we propose Variable Radiance Field (VRF), a novel framework capable of efficiently reconstructing category-specific objects without requiring known camera intrinsics and demonstrating robustness against occlusions. First, we replace the local feature retrieval with global latent representations, generated through a single feed-forward pass, which improves efficiency and eliminates reliance on camera intrinsics. Second, to tackle coordinate inconsistencies inherent in real-world dataset, we define a canonical space by introducing a learnable, category-specific shape template and explicitly aligning each training object to this template using a learnable 3D transformation. This approach also reduces the complexity of geometry prediction to modeling deformations from the template to individual instances. Finally, we employ a hyper-network-based method for efficient NeRF creation and enhance the reconstruction performance through a contrastive learning-based pretraining strategy. Evaluations on the CO3D dataset demonstrate that VRF achieves state-of-the-art performance in both reconstruction quality and computational efficiency.
使用神经辐射场(NeRF)从单幅图像重建特定类别的物体是一项充满前景但具有挑战性的任务。现有方法主要依赖于基于投影的特征检索,将辐射场中的3D点与参考图像中的局部图像特征相关联。然而,这个过程计算量大,依赖于已知的相机内参,并容易受到遮挡的影响。为了解决这些局限性,我们提出了可变辐射场(VRF)这一新型框架,能够高效重建特定类别的物体,无需已知相机内参,并对遮挡表现出稳健性。首先,我们用全局潜在表示替换局部特征检索,通过一次前向传递生成全局潜在表示,提高了效率,消除了对相机内参的依赖。其次,为了解决真实世界数据集固有的坐标不一致问题,我们通过引入可学习的特定类别形状模板来定义规范空间,并通过可学习的3D变换显式地将每个训练对象与此模板对齐。这种方法还降低了几何预测的复杂性,即建模从模板到各个实例的变形。最后,我们采用基于超网络的方法来实现高效的NeRF创建,并通过基于对比学习的预训练策略提高重建性能。在CO3D数据集上的评估表明,VRF在重建质量和计算效率方面都达到了最新技术水平。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:
利用神经辐射场(NeRF)从单幅图像重建特定类别的物体是一项有前途但具有挑战性的任务。现有方法主要依赖基于投影的特征检索,将三维点与参考图像中的局部图像特征相关联。然而,这种方法计算量大,依赖于已知相机参数,并容易受到遮挡的影响。为解决这些问题,我们提出了可变辐射场(VRF)这一新型框架,能够高效重建特定类别的物体,无需已知相机参数,对遮挡具有鲁棒性。我们通过全局潜在表示替换局部特征检索,通过单前向传递生成,提高效率并消除对相机参数的依赖。此外,我们定义了一个规范空间,通过引入可学习的特定类别形状模板,显式地将每个训练对象与模板进行对齐。最后,我们采用超网络方法创建高效的NeRF,并通过对比学习增强重建性能。在CO3D数据集上的评估表明,VRF在重建质量和计算效率方面均达到最佳性能。
Key Takeaways:
- 利用NeRF从单幅图像重建特定类别物体具有挑战性,但VRF框架能高效实现此任务。
- VRF通过全局潜在表示替换局部特征检索,提高效率和鲁棒性。
- VRF定义规范空间并引入类别特定形状模板,解决真实数据集坐标不一致问题。
- VRF使用超网络方法创建NeRF并增强重建性能通过对比学习预训练策略。
- VRF框架无需依赖已知相机参数,并对遮挡具有鲁棒性。
- 在CO3D数据集上的评估显示VRF达到最佳性能在重建质量和计算效率方面。
点此查看论文截图