⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-02-19 更新
A Survey on Bridging EEG Signals and Generative AI: From Image and Text to Beyond
Authors:Shreya Shukla, Jose Torres, Abhijit Mishra, Jacek Gwizdka, Shounak Roychowdhury
Integration of Brain-Computer Interfaces (BCIs) and Generative Artificial Intelligence (GenAI) has opened new frontiers in brain signal decoding, enabling assistive communication, neural representation learning, and multimodal integration. BCIs, particularly those leveraging Electroencephalography (EEG), provide a non-invasive means of translating neural activity into meaningful outputs. Recent advances in deep learning, including Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) and Transformer-based Large Language Models (LLMs), have significantly improved EEG-based generation of images, text, and speech. This paper provides a literature review of the state-of-the-art in EEG-based multimodal generation, focusing on (i) EEG-to-image generation through GANs, Variational Autoencoders (VAEs), and Diffusion Models, and (ii) EEG-to-text generation leveraging Transformer based language models and contrastive learning methods. Additionally, we discuss the emerging domain of EEG-to-speech synthesis, an evolving multimodal frontier. We highlight key datasets, use cases, challenges, and EEG feature encoding methods that underpin generative approaches. By providing a structured overview of EEG-based generative AI, this survey aims to equip researchers and practitioners with insights to advance neural decoding, enhance assistive technologies, and expand the frontiers of brain-computer interaction.
脑机接口(BCIs)与生成式人工智能(GenAI)的融合为脑信号解码开辟了新的领域,为实现辅助通信、神经表征学习和多模式融合提供了可能。脑机接口,特别是利用脑电图(EEG)的脑机接口,提供了一种非侵入性的方法,将神经活动转化为有意义的输出。深度学习领域的最新进展,包括生成对抗网络(GANs)和基于变压器的自然语言模型(LLMs),已经显著提高了基于EEG的图像、文本和语音生成。本文综述了基于EEG的多模态生成的最新研究状况,重点关注(i)通过GANs、变分自动编码器(VAEs)和扩散模型实现的EEG到图像生成,(ii)利用基于Transformer的自然语言模型和对比学习方法实现的EEG到文本生成。此外,我们还讨论了新兴的EEG到语音合成领域,这是一个不断发展的多模态前沿领域。我们重点介绍了关键数据集、用例、挑战以及支撑生成方法的EEG特征编码方法。通过对基于EEG的生成式人工智能进行结构化概述,本综述旨在为研究者和实践者提供洞察,以促进神经解码的发展,提升辅助技术的性能,并扩展脑机交互的边界。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
BCIs与GenAI的整合为脑信号解码打开了新领域,促进辅助交流、神经网络表示学习和多模式整合。通过脑电图(EEG)实现的BCIs为非侵入性地转化神经活动为有意义输出提供了手段。深度学习领域的最新进展,包括生成对抗网络(GANs)和基于Transformer的大型语言模型(LLMs),极大地改进了基于EEG的图像、文本和语音生成。本文综述了基于EEG的多模式生成的最新进展,包括EEG转图像生成和EEG转文本生成,并讨论了新兴的EEG转语音合成领域。通过提供对基于EEG的生成式AI的结构性概述,旨在为研究人员和实践者提供洞察,以推动神经解码的发展、增强辅助技术,并扩展脑机交互的边界。
Key Takeaways
- BCI与GenAI的整合推动了脑信号解码的新发展,助力辅助交流、神经网络表示学习和多模式整合。
- EEG-based BCIs为非侵入性地转化神经活动提供了手段。
- 深度学习领域的最新技术,如GANs和LLMs,大幅提升了基于EEG的图像、文本和语音生成能力。
- 基于EEG的多模式生成最新进展包括EEG转图像生成和EEG转文本生成。
- 新兴的EEG转语音合成领域成为多模态交互的新前沿。
- 文章综述了关键数据集、应用场景、挑战和EEG特征编码方法,这些都是生成式方法的基础。
点此查看论文截图

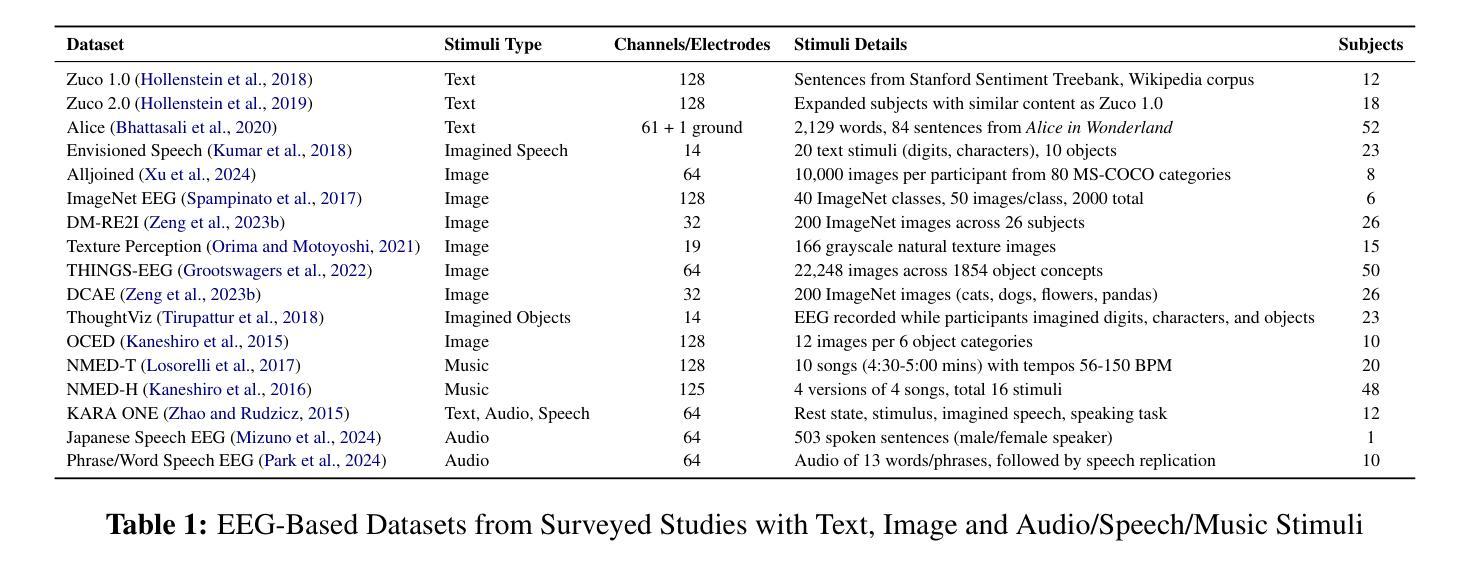
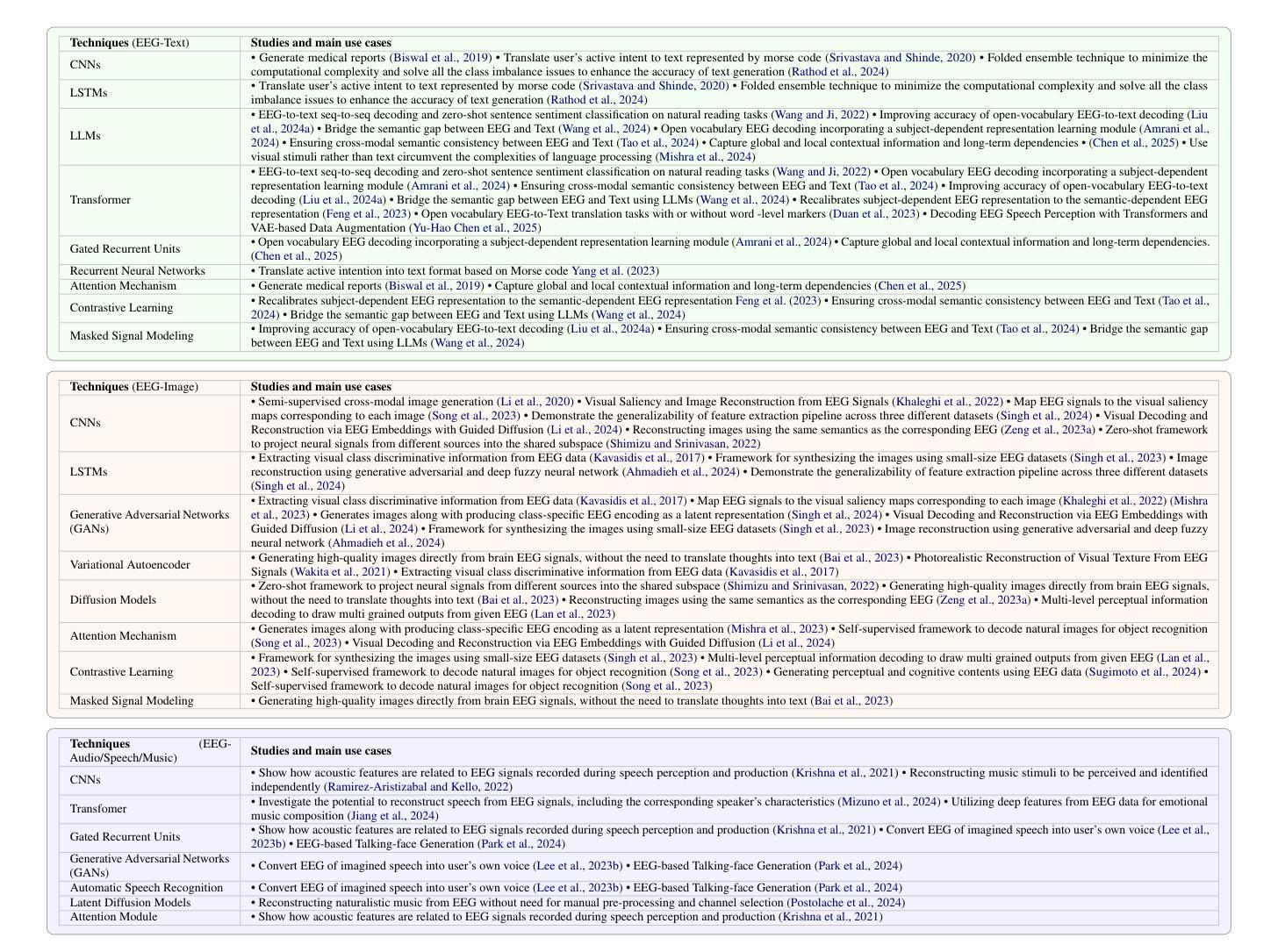
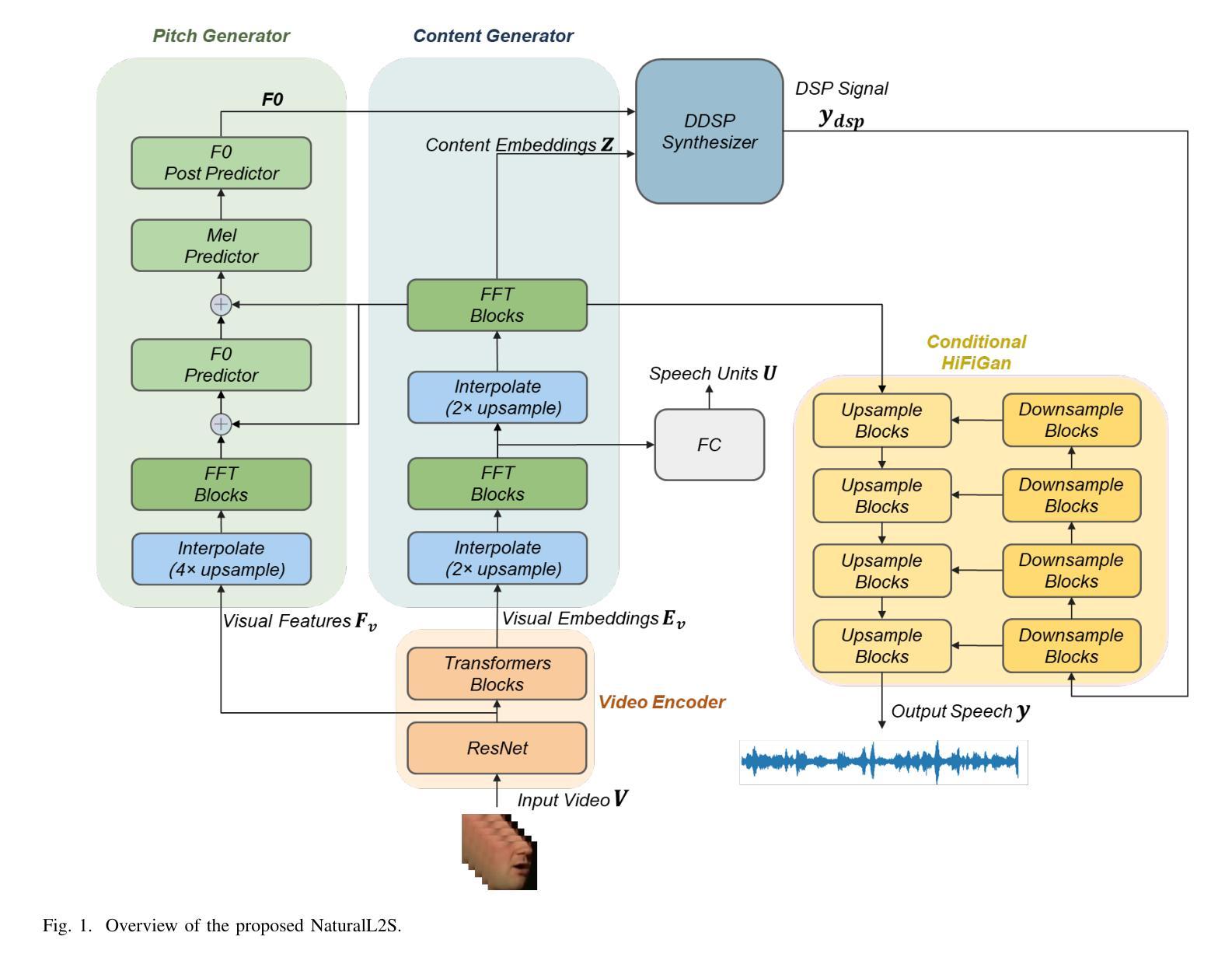
NaturalL2S: End-to-End High-quality Multispeaker Lip-to-Speech Synthesis with Differential Digital Signal Processing
Authors:Yifan Liang, Fangkun Liu, Andong Li, Xiaodong Li, Chengshi Zheng
Recent advancements in visual speech recognition (VSR) have promoted progress in lip-to-speech synthesis, where pre-trained VSR models enhance the intelligibility of synthesized speech by providing valuable semantic information. The success achieved by cascade frameworks, which combine pseudo-VSR with pseudo-text-to-speech (TTS) or implicitly utilize the transcribed text, highlights the benefits of leveraging VSR models. However, these methods typically rely on mel-spectrograms as an intermediate representation, which may introduce a key bottleneck: the domain gap between synthetic mel-spectrograms, generated from inherently error-prone lip-to-speech mappings, and real mel-spectrograms used to train vocoders. This mismatch inevitably degrades synthesis quality. To bridge this gap, we propose Natural Lip-to-Speech (NaturalL2S), an end-to-end framework integrating acoustic inductive biases with differentiable speech generation components. Specifically, we introduce a fundamental frequency (F0) predictor to capture prosodic variations in synthesized speech. The predicted F0 then drives a Differentiable Digital Signal Processing (DDSP) synthesizer to generate a coarse signal which serves as prior information for subsequent speech synthesis. Additionally, instead of relying on a reference speaker embedding as an auxiliary input, our approach achieves satisfactory performance on speaker similarity without explicitly modelling speaker characteristics. Both objective and subjective evaluation results demonstrate that NaturalL2S can effectively enhance the quality of the synthesized speech when compared to state-of-the-art methods. Our demonstration page is accessible at https://yifan-liang.github.io/NaturalL2S/.
近期视觉语音识别(VSR)的进展推动了唇音合成技术的进步。预训练的VSR模型通过提供有价值的语义信息,提高了合成语音的可识别性。级联框架结合伪VSR和伪文本到语音(TTS)或隐式利用转录文本的成功,突显了利用VSR模型的优势。然而,这些方法通常依赖于梅尔频谱图作为中间表示形式,这可能会引入一个关键瓶颈:由本质上是易出错的唇音映射生成的合成梅尔频谱图与用于训练vocoder的真实梅尔频谱图之间的领域差距。这种不匹配不可避免地会降低合成质量。为了弥补这一差距,我们提出了Natural Lip-to-Speech(NaturalL2S)框架,这是一个将声学归纳偏见与可微分的语音生成组件相结合端到端框架。具体来说,我们引入了一个基频(F0)预测器来捕捉合成语音中的韵律变化。预测的F0然后驱动一个可微分的数字信号处理(DDSP)合成器生成一个粗略的信号,该信号作为后续语音合成的先验信息。此外,我们的方法没有依靠参考说话人嵌入作为辅助输入来实现令人满意的说话人相似性表现,无需显式建模说话人的特点。客观和主观评估结果表明,与自然界的最新方法相比,NaturalL2S可以有效提高合成语音的质量。我们的演示页面可访问于:[https://yifan-liang.github.io/NaturalL2S/] 。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
视觉语音识别的最新进展促进了唇到语音合成的进步。预训练的视觉语音识别模型为合成语音提供了宝贵的语义信息,增强了语音的可识别性。级联框架的成功,结合伪视觉语音识别与伪文本到语音技术或隐含地使用转录文本,突显了利用视觉语音识别模型的优势。然而,这些方法通常依赖于梅尔频谱图作为中间表示形式,可能会引入一个关键瓶颈:由唇到语音映射本身存在的错误生成的合成梅尔频谱图与用于训练编码器的真实梅尔频谱图之间的域差距。这种不匹配不可避免地降低了合成质量。为了弥补这一差距,我们提出了端到端的自然唇到语音框架(NaturalL2S),该框架结合了声学诱导偏见与可微分的语音生成组件。具体来说,我们引入了一个基频预测器来捕捉合成语音中的韵律变化。预测的基频驱动可微分的数字信号处理合成器生成粗略信号,作为后续语音合成的先验信息。此外,我们的方法不需要依赖参考说话人嵌入作为辅助输入就能实现令人满意的说话人相似性建模。客观和主观评估结果均表明,与自然唇到语音框架相比,最新方法可以有效地提高合成语音的质量。我们的演示页面可在链接访问。
关键见解
- 视觉语音识别(VSR)的进展推动了唇到语音合成的进步。
- 预训练的VSR模型增强了合成语音的语义信息。
- 级联框架结合伪VSR与伪文本到语音技术显示了VSR模型的优势。
- 依赖梅尔频谱图作为中间表示形式可能会引入域差距问题。
- 合成梅尔频谱图与真实梅尔频谱图之间的域差距降低了合成质量。
- 提出的NaturalL2S框架结合了声学诱导偏见与可微分的语音生成组件。
点此查看论文截图

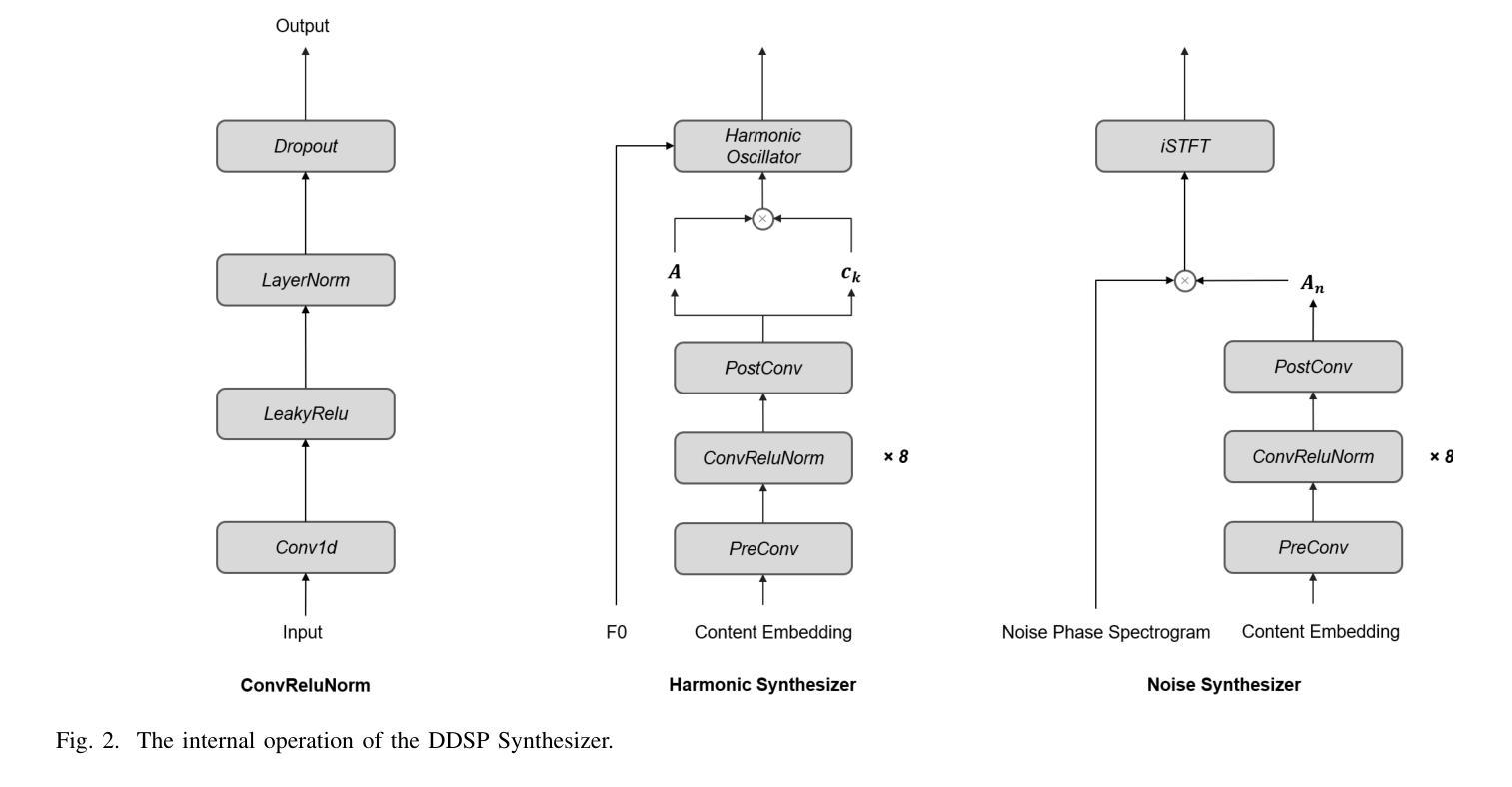
Step-Audio: Unified Understanding and Generation in Intelligent Speech Interaction
Authors:Ailin Huang, Boyong Wu, Bruce Wang, Chao Yan, Chen Hu, Chengli Feng, Fei Tian, Feiyu Shen, Jingbei Li, Mingrui Chen, Peng Liu, Ruihang Miao, Wang You, Xi Chen, Xuerui Yang, Yechang Huang, Yuxiang Zhang, Zheng Gong, Zixin Zhang, Brian Li, Changyi Wan, Hanpeng Hu, Ranchen Ming, Song Yuan, Xuelin Zhang, Yu Zhou, Bingxin Li, Buyun Ma, Kang An, Wei Ji, Wen Li, Xuan Wen, Yuankai Ma, Yuanwei Liang, Yun Mou, Bahtiyar Ahmidi, Bin Wang, Bo Li, Changxin Miao, Chen Xu, Chengting Feng, Chenrun Wang, Dapeng Shi, Deshan Sun, Dingyuan Hu, Dula Sai, Enle Liu, Guanzhe Huang, Gulin Yan, Heng Wang, Haonan Jia, Haoyang Zhang, Jiahao Gong, Jianchang Wu, Jiahong Liu, Jianjian Sun, Jiangjie Zhen, Jie Feng, Jie Wu, Jiaoren Wu, Jie Yang, Jinguo Wang, Jingyang Zhang, Junzhe Lin, Kaixiang Li, Lei Xia, Li Zhou, Longlong Gu, Mei Chen, Menglin Wu, Ming Li, Mingxiao Li, Mingyao Liang, Na Wang, Nie Hao, Qiling Wu, Qinyuan Tan, Shaoliang Pang, Shiliang Yang, Shuli Gao, Siqi Liu, Sitong Liu, Tiancheng Cao, Tianyu Wang, Wenjin Deng, Wenqing He, Wen Sun, Xin Han, Xiaomin Deng, Xiaojia Liu, Xu Zhao, Yanan Wei, Yanbo Yu, Yang Cao, Yangguang Li, Yangzhen Ma, Yanming Xu, Yaqiang Shi, Yilei Wang, Yinmin Zhong, Yu Luo, Yuanwei Lu, Yuhe Yin, Yuting Yan, Yuxiang Yang, Zhe Xie, Zheng Ge, Zheng Sun, Zhewei Huang, Zhichao Chang, Zidong Yang, Zili Zhang, Binxing Jiao, Daxin Jiang, Heung-Yeung Shum, Jiansheng Chen, Jing Li, Shuchang Zhou, Xiangyu Zhang, Xinhao Zhang, Yibo Zhu
Real-time speech interaction, serving as a fundamental interface for human-machine collaboration, holds immense potential. However, current open-source models face limitations such as high costs in voice data collection, weakness in dynamic control, and limited intelligence. To address these challenges, this paper introduces Step-Audio, the first production-ready open-source solution. Key contributions include: 1) a 130B-parameter unified speech-text multi-modal model that achieves unified understanding and generation, with the Step-Audio-Chat version open-sourced; 2) a generative speech data engine that establishes an affordable voice cloning framework and produces the open-sourced lightweight Step-Audio-TTS-3B model through distillation; 3) an instruction-driven fine control system enabling dynamic adjustments across dialects, emotions, singing, and RAP; 4) an enhanced cognitive architecture augmented with tool calling and role-playing abilities to manage complex tasks effectively. Based on our new StepEval-Audio-360 evaluation benchmark, Step-Audio achieves state-of-the-art performance in human evaluations, especially in terms of instruction following. On open-source benchmarks like LLaMA Question, shows 9.3% average performance improvement, demonstrating our commitment to advancing the development of open-source multi-modal language technologies. Our code and models are available at https://github.com/stepfun-ai/Step-Audio.
实时语音交互作为人机协作的基本接口,具有巨大的潜力。然而,当前的开源模型面临诸多挑战,如语音数据采集成本高昂、动态控制能力不足以及智能有限等。为了解决这些挑战,本文介绍了Step-Audio,这是一个准备投入生产的第一款开源解决方案。主要贡献包括:1)一个拥有130B参数的统一语音文本多模态模型,实现了统一的理解和生成能力,其中Step-Audio-Chat版本已开源;2)一个生成式语音数据引擎,建立了一个经济实惠的语音克隆框架,并通过蒸馏技术产生了开源的轻量级Step-Audio-TTS-3B模型;3)一个指令驱动的精细控制系统,能够实现不同方言、情感、歌唱和RAP的动态调整;4)一个增强型认知架构,通过增加工具调用和角色扮演能力,有效管理复杂任务。基于我们新的StepEval-Audio-360评估基准,Step-Audio在人体评估中达到了最先进的性能,特别是在指令遵循方面。在LLaMA Question等开源基准测试中,平均性能提高了9.3%,这证明了我们推动开源多模态语言技术发展的承诺。我们的代码和模型可在https://github.com/stepfun-ai/Step-Audio找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了一项名为Step-Audio的开放源代码解决方案,用于实时语音交互,解决了当前面临的数据收集成本高、动态控制弱和智能有限等挑战。它包含一系列关键贡献,如统一语音文本多模态模型、生成式语音数据引擎、指令驱动的精细控制系统和增强的认知架构等。基于StepEval-Audio-360评估基准,Step-Audio在人机评估中表现卓越,特别是在指令遵循方面。此外,它在开源基准测试中平均性能提升9.3%,显示出对推动开源多模态语言技术发展的承诺。
Key Takeaways
- Step-Audio是一种解决实时语音交互挑战的生产就绪开源解决方案。
- 它包含多模态统一语音文本模型,实现了理解和生成的统一。
- 通过蒸馏技术,Step-Audio能够生产轻量级的语音合成模型。
- 提供了指令驱动的精细控制系统,可实现跨方言、情感、歌唱和RAP的动态调整。
- 增强的认知架构使Step-Audio能够管理复杂任务,包括工具调用和角色扮演。
- 基于StepEval-Audio-360评估基准,Step-Audio在人机评估中表现优异。
点此查看论文截图

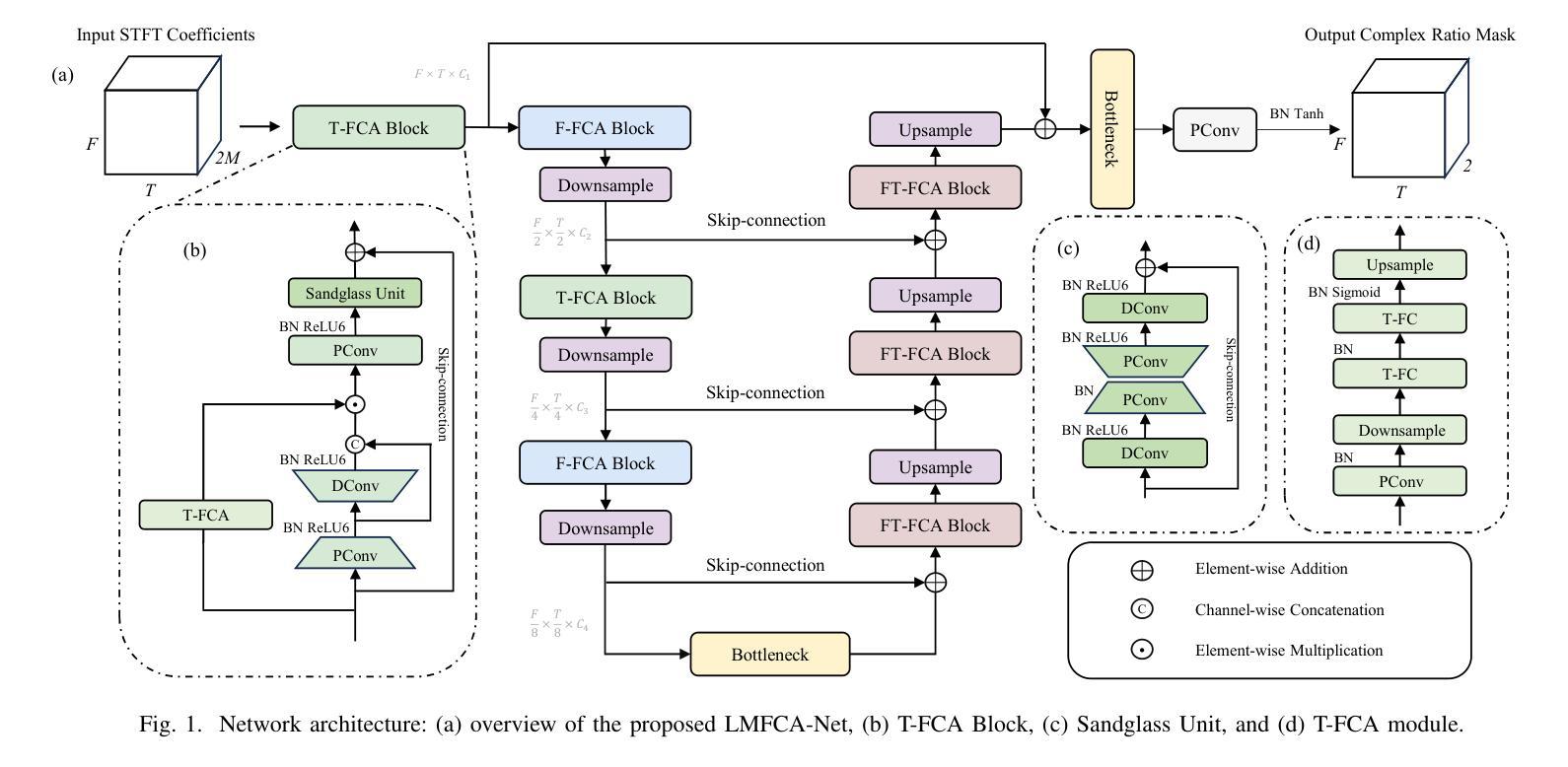
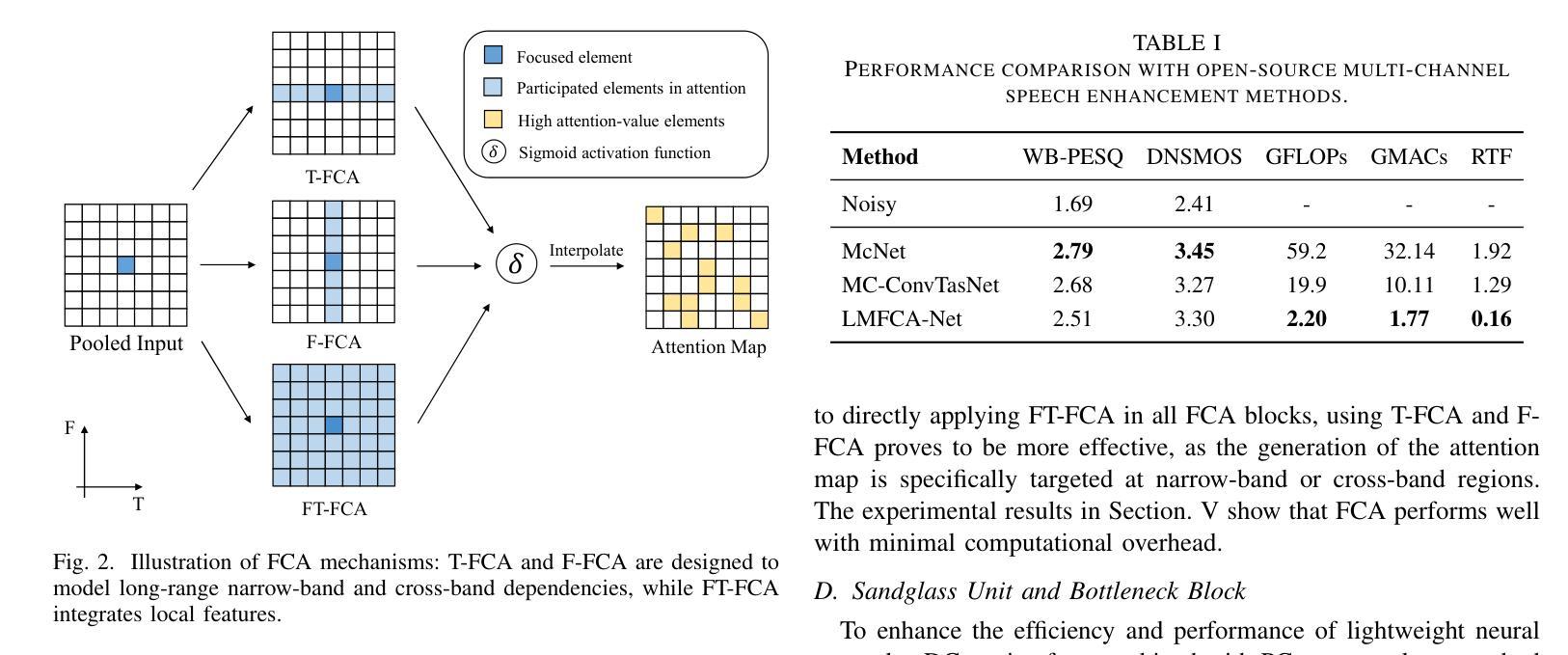
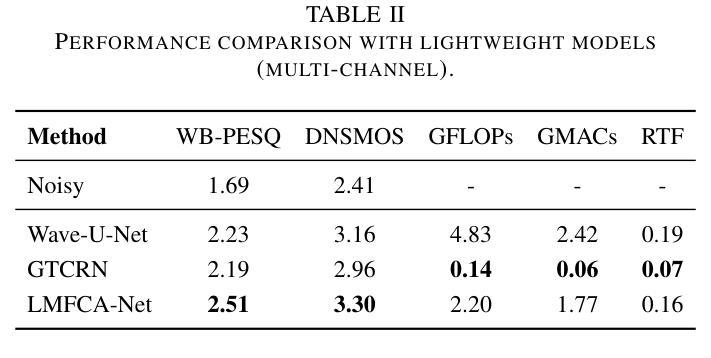
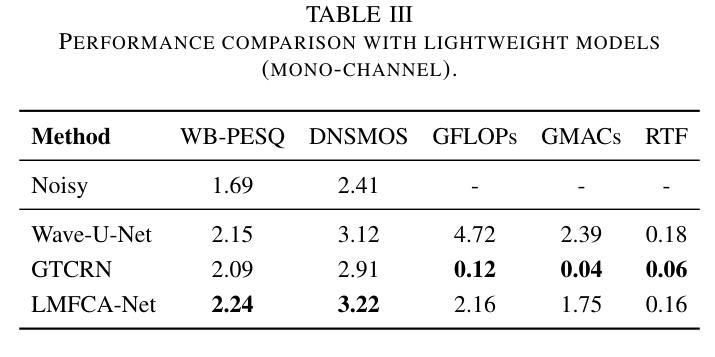
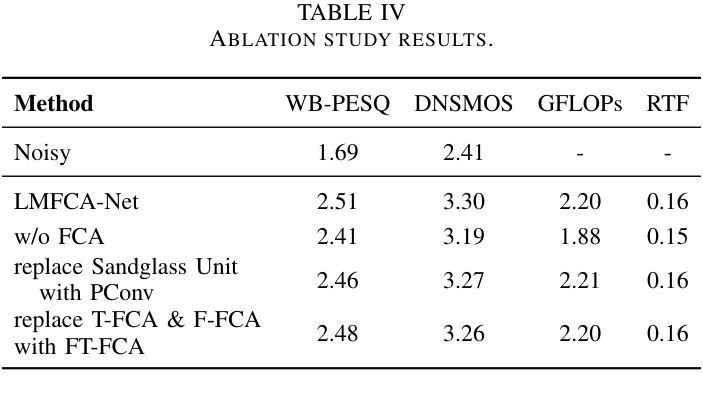
LMFCA-Net: A Lightweight Model for Multi-Channel Speech Enhancement with Efficient Narrow-Band and Cross-Band Attention
Authors:Yaokai Zhang, Hanchen Pei, Wanqi Wang, Gongping Huang
Deep learning based end-to-end multi-channel speech enhancement methods have achieved impressive performance by leveraging sub-band, cross-band, and spatial information. However, these methods often demand substantial computational resources, limiting their practicality on terminal devices. This paper presents a lightweight multi-channel speech enhancement network with decoupled fully connected attention (LMFCA-Net). The proposed LMFCA-Net introduces time-axis decoupled fully-connected attention (T-FCA) and frequency-axis decoupled fully-connected attention (F-FCA) mechanisms to effectively capture long-range narrow-band and cross-band information without recurrent units. Experimental results show that LMFCA-Net performs comparably to state-of-the-art methods while significantly reducing computational complexity and latency, making it a promising solution for practical applications.
基于深度学习的端到端多通道语音增强方法,通过利用子带、跨带和空间信息取得了令人印象深刻的性能。然而,这些方法通常需要大量的计算资源,在终端设备上实用性有限。本文提出了一种轻量级的多通道语音增强网络,具有解耦的全连接注意力(LMFCA-Net)。提出的LMFCA-Net引入了时间轴解耦的全连接注意力(T-FCA)和频率轴解耦的全连接注意力(F-FCA)机制,能够有效地捕捉长距离窄带和跨带信息,而无需循环单元。实验结果表明,LMFCA-Net与最新技术的方法相比表现相当,同时显著降低了计算复杂性和延迟,使其成为实际应用中很有前途的解决方案。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at ICASSP 2025
Summary
本文介绍了一种基于深度学习的轻量级多通道语音增强网络,称为LMFCA-Net。该网络引入了时间轴解耦全连接注意力(T-FCA)和频率轴解耦全连接注意力(F-FCA)机制,能有效捕捉长距离窄带和跨带信息,且无需递归单元。实验结果表明,LMFCA-Net与最先进的方法相比表现良好,同时大大降低了计算复杂性和延迟,为实际应用提供了有前景的解决方案。
Key Takeaways
- LMFCA-Net是一种轻量级的深度学习多通道语音增强网络。
- 该网络引入了时间轴解耦全连接注意力(T-FCA)和频率轴解耦全连接注意力(F-FCA)机制。
- LMFCA-Net能有效捕捉长距离窄带和跨带信息,而无需使用递归单元。
- 实验表明LMFCA-Net的性能与最先进的方法相当。
- LMFCA-Net显著降低了计算复杂性和延迟。
- LMFCA-Net为实际应用提供了有前景的解决方案。
点此查看论文截图

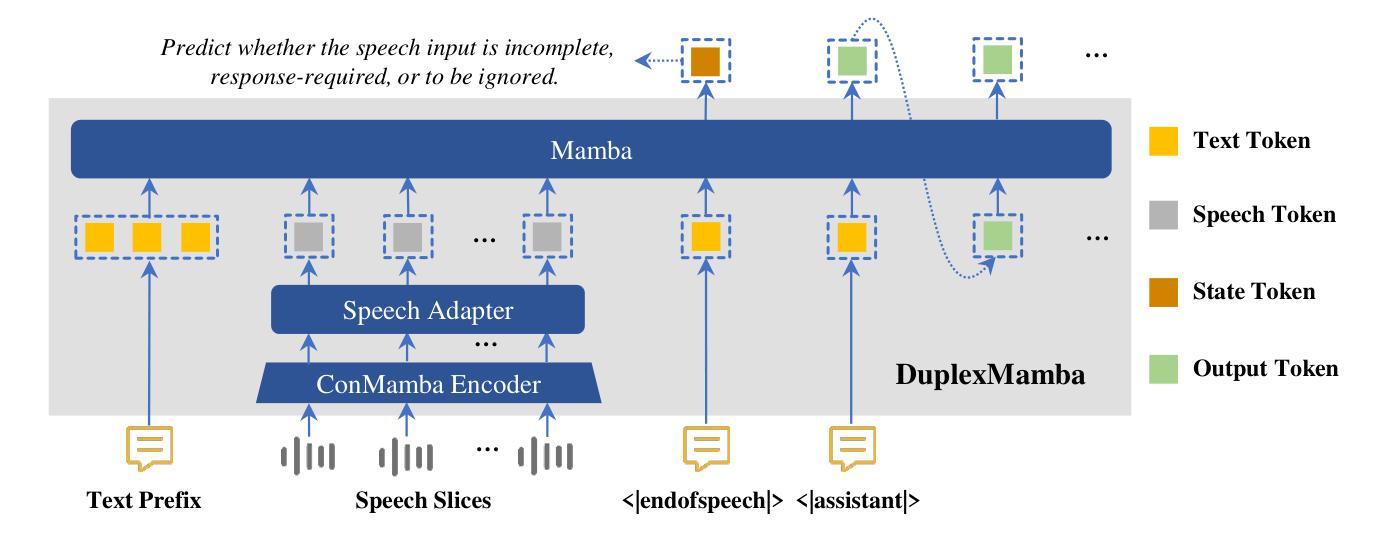
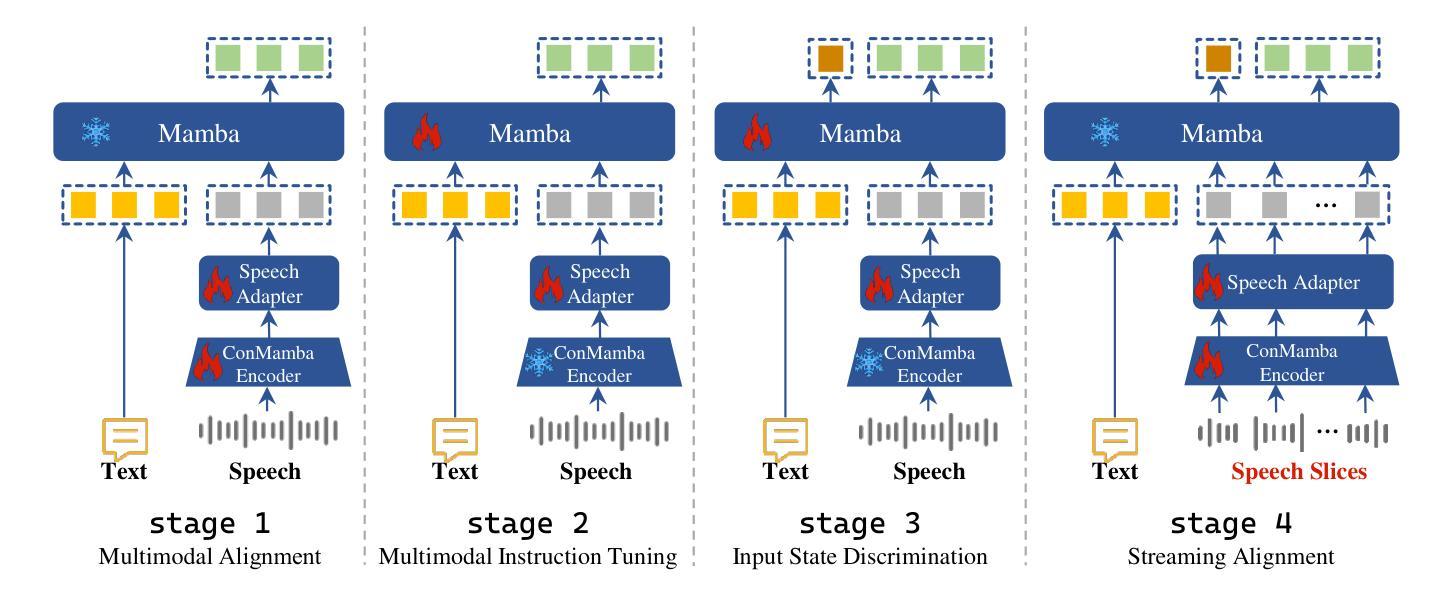
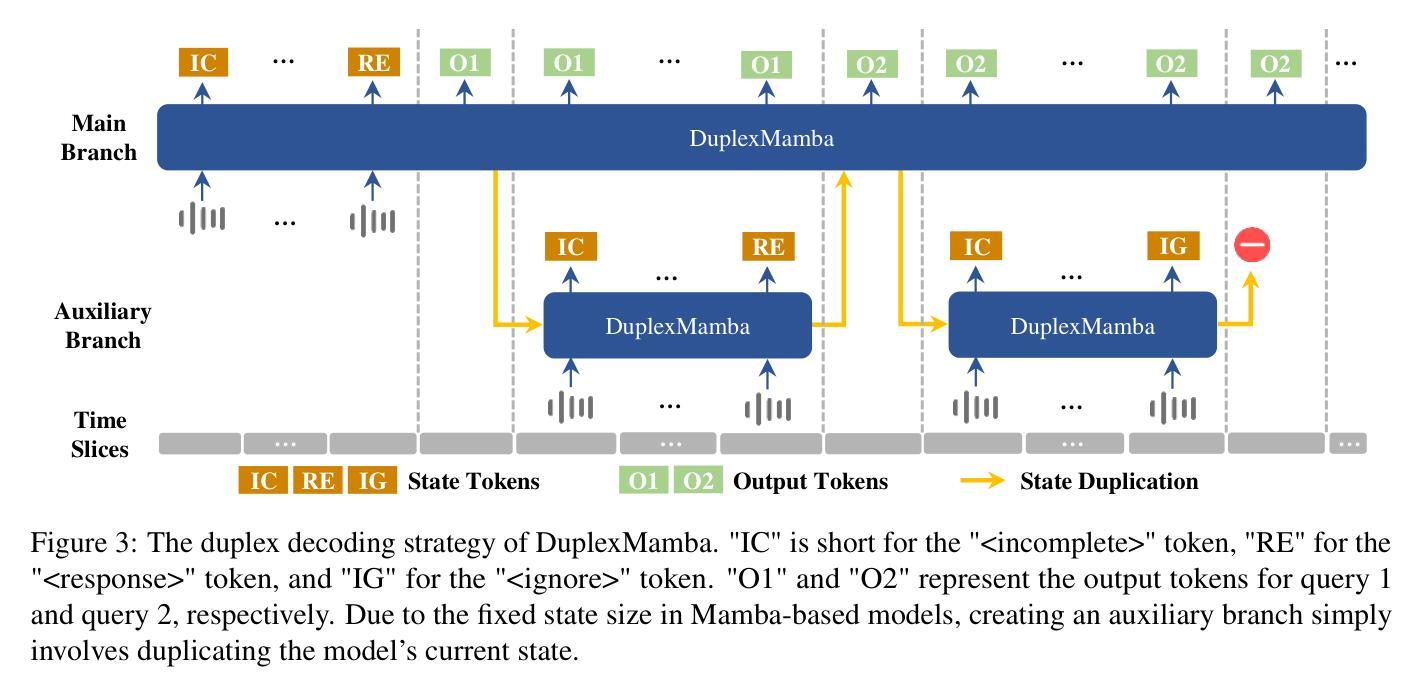
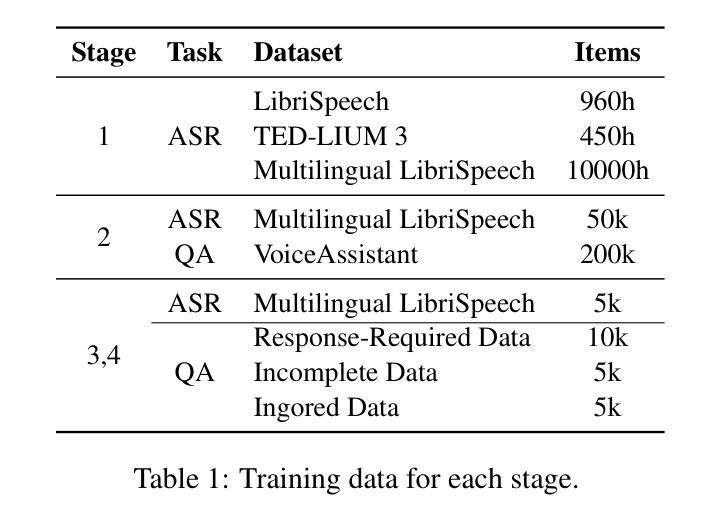
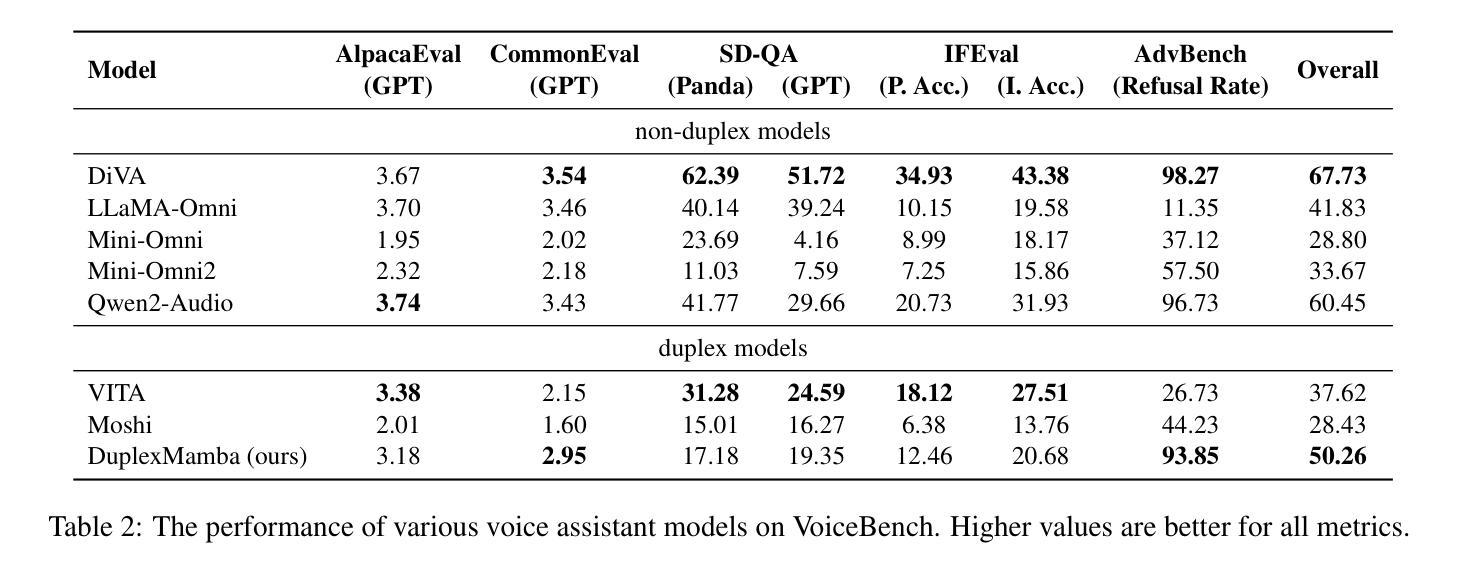
DuplexMamba: Enhancing Real-time Speech Conversations with Duplex and Streaming Capabilities
Authors:Xiangyu Lu, Wang Xu, Haoyu Wang, Hongyun Zhou, Haiyan Zhao, Conghui Zhu, Tiejun Zhao, Muyun Yang
Real-time speech conversation is essential for natural and efficient human-machine interactions, requiring duplex and streaming capabilities. Traditional Transformer-based conversational chatbots operate in a turn-based manner and exhibit quadratic computational complexity that grows as the input size increases. In this paper, we propose DuplexMamba, a Mamba-based end-to-end multimodal duplex model for speech-to-text conversation. DuplexMamba enables simultaneous input processing and output generation, dynamically adjusting to support real-time streaming. Specifically, we develop a Mamba-based speech encoder and adapt it with a Mamba-based language model. Furthermore, we introduce a novel duplex decoding strategy that enables DuplexMamba to process input and generate output simultaneously. Experimental results demonstrate that DuplexMamba successfully implements duplex and streaming capabilities while achieving performance comparable to several recently developed Transformer-based models in automatic speech recognition (ASR) tasks and voice assistant benchmark evaluations.
实时语音对话对于自然高效的人机交互至关重要,需要双向和流式处理能力。传统的基于Transformer的聊天机器人以轮次为基础进行操作,表现出随着输入大小增加而产生的二次计算复杂性。在本文中,我们提出了基于Mamba的端到端多模式双向对话模型DuplexMamba,用于语音到文本的对话。DuplexMamba能够同时处理输入和生成输出,动态调整以支持实时流式处理。具体来说,我们开发了一种基于Mamba的语音编码器,并将其与基于Mamba的语言模型相结合。此外,我们引入了一种新颖的双向解码策略,使DuplexMamba能够同时处理输入并生成输出。实验结果表明,DuplexMamba成功实现了双向和流式处理功能,同时在自动语音识别(ASR)任务和语音助手基准评估中实现了与最近开发的几个基于Transformer的模型相当的性能。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
本文提出一种基于Mamba的端到端多模态双向模型DuplexMamba,用于语音到文本的对话。该模型可实现实时流式处理,同时支持输入处理和输出生成。具体来说,我们开发了基于Mamba的语音编码器,并适配了基于Mamba的语言模型。此外,我们引入了一种新颖的双向解码策略,使DuplexMamba能够同时处理输入并生成输出。实验结果表明,DuplexMamba成功实现了双向和流式处理能力,同时在自动语音识别(ASR)任务和语音助手基准评估中取得了与最近开发的几种基于Transformer的模型相当的性能。
关键见解
1.DuplexMamba是基于Mamba的端到端多模态双向模型,用于实现语音到文本的实时对话。
2.DuplexMamba支持实时流式处理,实现输入处理和输出生成的同步进行。
3.通过开发基于Mamba的语音编码器和适配基于Mamba的语言模型,DuplexMamba可有效处理语音数据。
4.引入新颖的双向解码策略,使DuplexMamba能够同时处理输入并生成输出响应。
5.实验证实DuplexMamba在自动语音识别(ASR)任务中具有出色的性能。
6.DuplexMamba在语音助手基准评估中的表现与最新Transformer模型相当。
点此查看论文截图

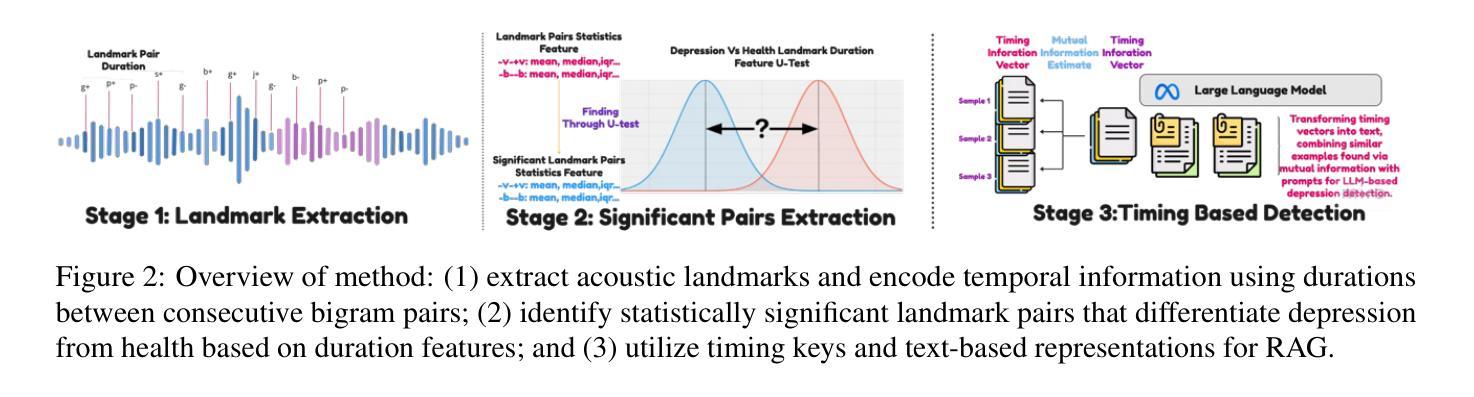
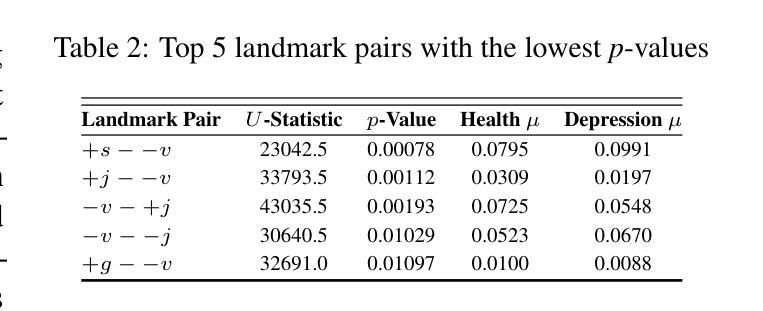
SpeechT-RAG: Reliable Depression Detection in LLMs with Retrieval-Augmented Generation Using Speech Timing Information
Authors:Xiangyu Zhang, Hexin Liu, Qiquan Zhang, Beena Ahmed, Julien Epps
Large Language Models (LLMs) have been increasingly adopted for health-related tasks, yet their performance in depression detection remains limited when relying solely on text input. While Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) typically enhances LLM capabilities, our experiments indicate that traditional text-based RAG systems struggle to significantly improve depression detection accuracy. This challenge stems partly from the rich depression-relevant information encoded in acoustic speech patterns information that current text-only approaches fail to capture effectively. To address this limitation, we conduct a systematic analysis of temporal speech patterns, comparing healthy individuals with those experiencing depression. Based on our findings, we introduce Speech Timing-based Retrieval-Augmented Generation, SpeechT-RAG, a novel system that leverages speech timing features for both accurate depression detection and reliable confidence estimation. This integrated approach not only outperforms traditional text-based RAG systems in detection accuracy but also enhances uncertainty quantification through a confidence scoring mechanism that naturally extends from the same temporal features. Our unified framework achieves comparable results to fine-tuned LLMs without additional training while simultaneously addressing the fundamental requirements for both accuracy and trustworthiness in mental health assessment.
大型语言模型(LLM)在健康相关任务中的应用越来越广泛,但在仅依赖文本输入的情况下,它们在抑郁症检测方面的表现仍然有限。虽然检索增强生成(RAG)通常可以增强LLM的能力,但我们的实验表明,传统的基于文本的RAG系统在提高抑郁症检测准确性方面遇到了困难。这一挑战部分源于编码在语音模式信息中的丰富抑郁症相关信息,而当前仅使用文本的方法无法有效地捕获这些信息。为了解决这个问题,我们对时间语音模式进行了系统分析,比较了健康个体和抑郁症患者的语音模式。基于我们的发现,我们引入了基于语音时序的检索增强生成(SpeechT-RAG)这一新型系统,该系统利用语音时序特征进行准确的抑郁症检测和可靠的可信度评估。这种综合方法不仅优于传统的基于文本的RAG系统在检测准确性方面,而且还通过信心评分机制增强了不确定性量化,该机制自然地来源于相同的时序特征。我们的统一框架在不进行额外训练的情况下实现了与微调LLM相当的结果,同时满足了心理健康评估中对准确性和可靠性的基本要求。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大型语言模型(LLMs)在健康相关任务中的应用日益广泛,但在仅依赖文本输入进行抑郁症检测时,其性能表现受限。尽管检索增强生成(RAG)技术通常能提升LLM的能力,但实验表明,传统文本为基础的RAG系统在提高抑郁症检测准确度方面效果有限。这部分挑战源于语音中的时序模式所蕴含丰富的抑郁症相关信息,而当前仅依赖文本的方法无法有效捕捉这些信息。为了应对这一挑战,本文进行了一系列针对健康个体和抑郁症患者之间语音时序模式的系统分析,并据此提出了基于语音时序特征的检索增强生成系统——SpeechT-RAG。该系统不仅提高了抑郁症检测的准确性,还通过信心评分机制增强了不确定性量化,该机制自然地扩展自相同的时序特征。在不进行额外训练的情况下,SpeechT-RAG取得了与微调LLM相当的结果,同时满足了精神健康评估对准确性和可靠性的基本要求。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLMs)在抑郁症检测方面的性能受限于仅使用文本输入。
- 检索增强生成(RAG)技术在提升LLM在抑郁症检测上的表现方面效果有限。
- 语音中的时序模式包含丰富的抑郁症相关信息,而传统文本方法无法有效捕捉。
- 通过对健康个体和抑郁症患者之间的语音时序模式进行系统分析,提出了SpeechT-RAG系统。
- SpeechT-RAG系统利用语音时序特征进行抑郁症检测和信心评估,提高了检测的准确性。
- SpeechT-RAG通过信心评分机制增强了不确定性量化,该机制自然地扩展自语音时序特征。
点此查看论文截图

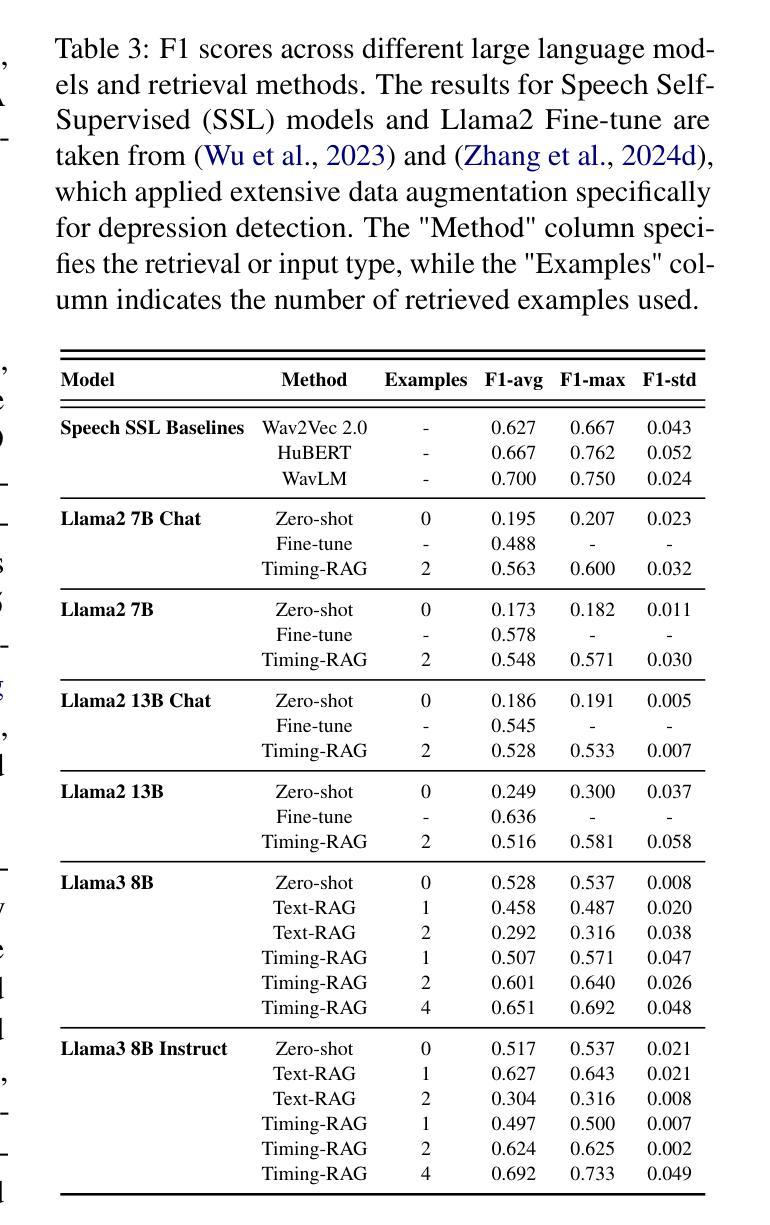
NeuroAMP: A Novel End-to-end General Purpose Deep Neural Amplifier for Personalized Hearing Aids
Authors:Shafique Ahmed, Ryandhimas E. Zezario, Hui-Guan Yuan, Amir Hussain, Hsin-Min Wang, Wei-Ho Chung, Yu Tsao
The prevalence of hearing aids is increasing. However, optimizing the amplification processes of hearing aids remains challenging due to the complexity of integrating multiple modular components in traditional methods. To address this challenge, we present NeuroAMP, a novel deep neural network designed for end-to-end, personalized amplification in hearing aids. NeuroAMP leverages both spectral features and the listener’s audiogram as inputs, and we investigate four architectures: Convolutional Neural Network (CNN), Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM), Convolutional Recurrent Neural Network (CRNN), and Transformer. We also introduce Denoising NeuroAMP, an extension that integrates noise reduction along with amplification capabilities for improved performance in real-world scenarios. To enhance generalization, a comprehensive data augmentation strategy was employed during training on diverse speech (TIMIT and TMHINT) and music (Cadenza Challenge MUSIC) datasets. Evaluation using the Hearing Aid Speech Perception Index (HASPI), Hearing Aid Speech Quality Index (HASQI), and Hearing Aid Audio Quality Index (HAAQI) demonstrates that the Transformer architecture within NeuroAMP achieves the best performance, with SRCC scores of 0.9927 (HASQI) and 0.9905 (HASPI) on TIMIT, and 0.9738 (HAAQI) on the Cadenza Challenge MUSIC dataset. Notably, our data augmentation strategy maintains high performance on unseen datasets (e.g., VCTK, MUSDB18-HQ). Furthermore, Denoising NeuroAMP outperforms both the conventional NAL-R+WDRC approach and a two-stage baseline on the VoiceBank+DEMAND dataset, achieving a 10% improvement in both HASPI (0.90) and HASQI (0.59) scores. These results highlight the potential of NeuroAMP and Denoising NeuroAMP to deliver notable improvements in personalized hearing aid amplification.
助听器的普及率正在不断提高。然而,由于传统方法中整合多个模块化组件的复杂性,优化助听器的放大过程仍然是一个挑战。为了解决这一挑战,我们提出了NeuroAMP,这是一种专为助听器端到端个性化放大而设计的新型深度神经网络。NeuroAMP利用频谱特征和听者的听力图作为输入,我们研究了四种架构:卷积神经网络(CNN)、长短期记忆网络(LSTM)、卷积循环神经网络(CRNN)和Transformer。我们还介绍了Denoising NeuroAMP,它是NeuroAMP的扩展,集成了降噪功能,以提高现实场景中的性能。为了增强泛化能力,我们在多样的语音(TIMIT和TMHINT)和音乐(Cadenza Challenge MUSIC)数据集上进行训练时,采用了一种全面的数据增强策略。使用助听语音感知指数(HASPI)、助听语音质量指数(HASQI)和助听音频质量指数(HAAQI)进行的评估表明,NeuroAMP中的Transformer架构表现最佳,在TIMIT上的HASQI和HASPI得分分别为0.9927和0.9905,在Cadenza Challenge MUSIC数据集上的HAAQI得分为0.9738。值得注意的是,我们的数据增强策略在未见过的数据集(例如VCTK、MUSDB18-HQ)上也能保持高性能。此外,Denoising NeuroAMP在VoiceBank+DEMAND数据集上的表现优于传统的NAL-R+WDRC方法和两阶段基线方法,HASPI和HASQI得分均提高了10%。这些结果突出了NeuroAMP和Denoising NeuroAMP在实现个性化助听器放大方面的潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
听力辅助设备的需求增长,但由于集成多个模块化组件的复杂性,优化听力辅助设备的放大过程仍然面临挑战。本研究提出了一种名为NeuroAMP的新型深度神经网络,用于听力辅助设备的端到端个性化放大。NeuroAMP利用频谱特征和听者的听力学检测作为输入,研究了四种架构。此外,还推出了集成降噪功能的Denoising NeuroAMP,以提高现实场景中的性能。评估结果表明,NeuroAMP中的Transformer架构表现最佳,Denoising NeuroAMP在未见数据集上的性能得到维持并超越了传统方法。这突显了NeuroAMP和Denoising NeuroAMP在个性化听力辅助设备放大方面的巨大潜力。
Key Takeaways
- 听力辅助设备需求增长,优化放大过程成为关键挑战。
- NeuroAMP是一种新型深度神经网络,用于听力辅助设备的端到端个性化放大。
- NeuroAMP利用频谱特征和听者的听力学检测作为输入,研究了CNN、LSTM、CRNN和Transformer四种架构。
- Denoising NeuroAMP集成了降噪功能,提高了现实场景中的性能。
- 评估结果表明Transformer架构在NeuroAMP中表现最佳。
- Denoising NeuroAMP在未见数据集上的性能得到维持,并超越了传统方法。
点此查看论文截图

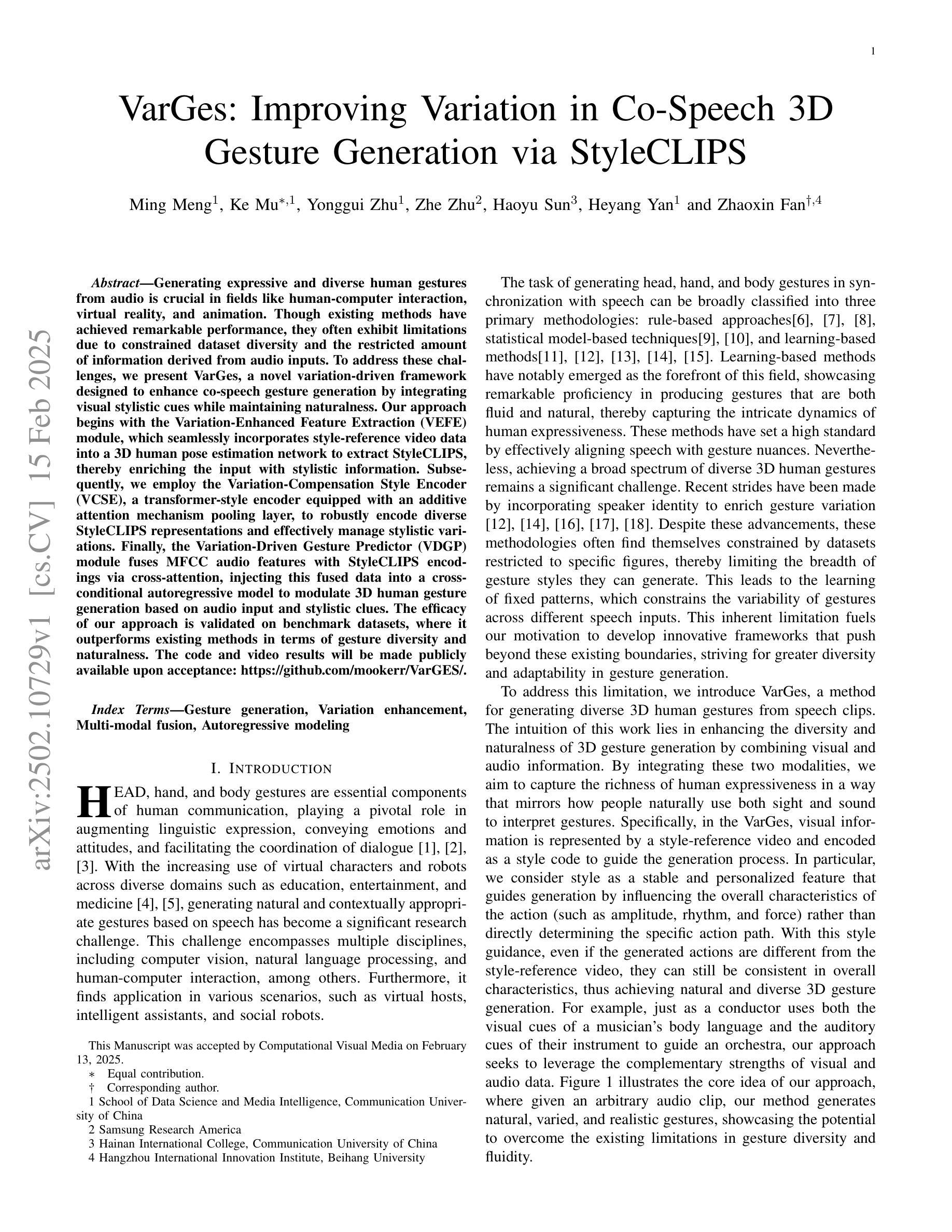
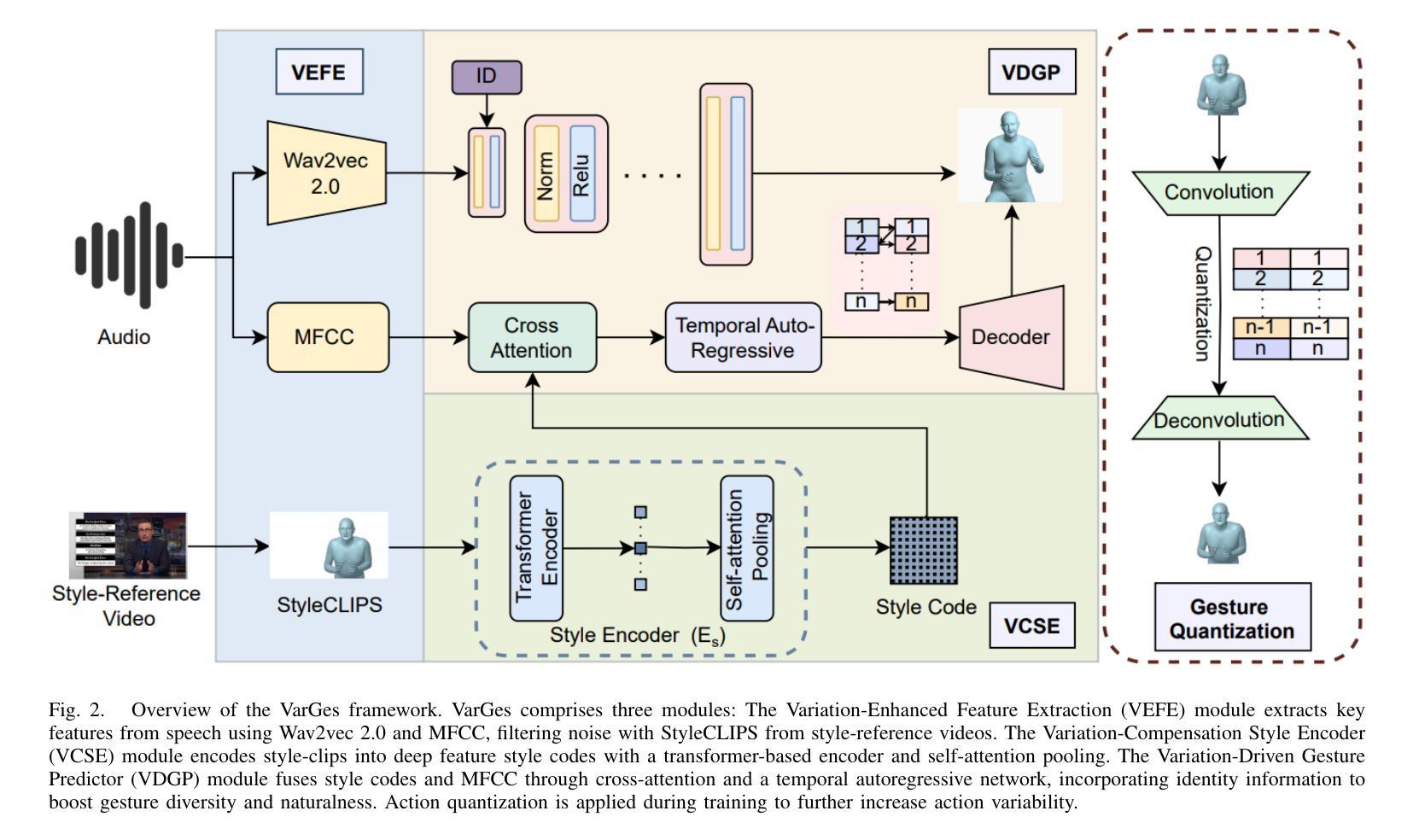
VarGes: Improving Variation in Co-Speech 3D Gesture Generation via StyleCLIPS
Authors:Ming Meng, Ke Mu, Yonggui Zhu, Zhe Zhu, Haoyu Sun, Heyang Yan, Zhaoxin Fan
Generating expressive and diverse human gestures from audio is crucial in fields like human-computer interaction, virtual reality, and animation. Though existing methods have achieved remarkable performance, they often exhibit limitations due to constrained dataset diversity and the restricted amount of information derived from audio inputs. To address these challenges, we present VarGes, a novel variation-driven framework designed to enhance co-speech gesture generation by integrating visual stylistic cues while maintaining naturalness. Our approach begins with the Variation-Enhanced Feature Extraction (VEFE) module, which seamlessly incorporates \textcolor{blue}{style-reference} video data into a 3D human pose estimation network to extract StyleCLIPS, thereby enriching the input with stylistic information. Subsequently, we employ the Variation-Compensation Style Encoder (VCSE), a transformer-style encoder equipped with an additive attention mechanism pooling layer, to robustly encode diverse StyleCLIPS representations and effectively manage stylistic variations. Finally, the Variation-Driven Gesture Predictor (VDGP) module fuses MFCC audio features with StyleCLIPS encodings via cross-attention, injecting this fused data into a cross-conditional autoregressive model to modulate 3D human gesture generation based on audio input and stylistic clues. The efficacy of our approach is validated on benchmark datasets, where it outperforms existing methods in terms of gesture diversity and naturalness. The code and video results will be made publicly available upon acceptance:https://github.com/mookerr/VarGES/ .
在人机交互、虚拟现实和动画等领域中,从音频生成表达丰富、多样化的手势至关重要。尽管现有方法已经取得了显著的成效,但由于数据集多样性的限制以及从音频输入中获取的有限信息,它们往往存在局限性。为了应对这些挑战,我们提出了VarGes,这是一个新的以变化驱动为核心的框架,旨在通过集成视觉风格线索来增强与语音同步的手势生成,同时保持自然性。我们的方法始于增强特征提取模块(VEFE),该模块无缝地结合了风格参考视频数据到一个3D人体姿态估计网络中,从而提取StyleCLIPS,使输入信息丰富并带有风格信息。随后,我们采用了配备附加注意力机制池层的变体补偿风格编码器(VCSE),以稳健地编码多样化的StyleCLIPS表示并有效地管理风格变化。最后,以变化驱动的手势预测器(VDGP)模块通过跨注意力融合MFCC音频特征与StyleCLIPS编码,将此融合数据注入跨条件自回归模型,以根据音频输入和风格线索调节3D手势生成。我们的方法已在基准数据集上进行了验证,在手势多样性和自然性方面优于现有方法。代码和视频结果将在接受后公开:https://github.com/mookerr/VarGES/。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
在人机交互、虚拟现实和动画等领域中,生成音频驱动的丰富多变的人类动作表情非常重要。现有的方法尽管已经取得了显著的效果,但由于数据集多样性受限以及从音频输入中获得的信息有限,仍存在一定的局限性。为此,我们提出了VarGes这一创新性的以变化驱动的方法框架,旨在通过整合视觉风格线索来增强语音动作表情的生成,同时保持自然性。该框架主要包含三个部分:Variation-Enhanced Feature Extraction模块用于融入风格参考视频数据,并提取StyleCLIPS信息丰富输入内容;Variation-Compensation Style Encoder模块负责使用带加法注意力机制pooling层的transformer风格的编码器进行稳健编码;最后,Variation-Driven Gesture Predictor模块通过跨注意力机制融合MFCC音频特征与StyleCLIPS编码信息,注入一个跨条件自回归模型中以根据音频输入和风格线索调整三维人类动作表情的生成。在基准数据集上的实验验证显示,我们的方法提高了动作表情的多样性和自然性。相关代码和视频结果将在接受后公开于https://github.com/mookerr/VarGES/。
Key Takeaways
- 生成音频驱动的人类动作表情在多个领域有广泛应用。
- 现有方法存在数据集多样性和信息提取的局限性。
- VarGes框架旨在增强语音动作表情的生成,结合视觉风格线索保持自然性。
- 包含三大核心模块:变化增强特征提取、补偿风格编码器和驱动动作表情预测器。
- StyleCLIPS信息融合丰富了输入内容,提高了动作表情的多样性。
- 通过跨注意力机制融合音频与视觉信息,增强了动作表情的自然性。
点此查看论文截图

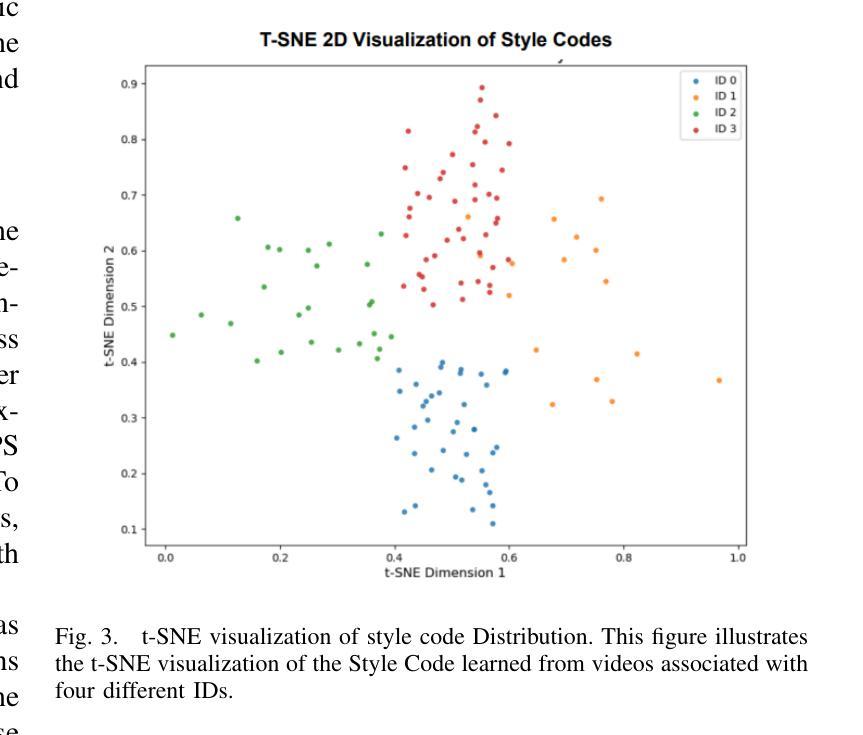
Enhancing Age-Related Robustness in Children Speaker Verification
Authors:Vishwas M. Shetty, Jiusi Zheng, Steven M. Lulich, Abeer Alwan
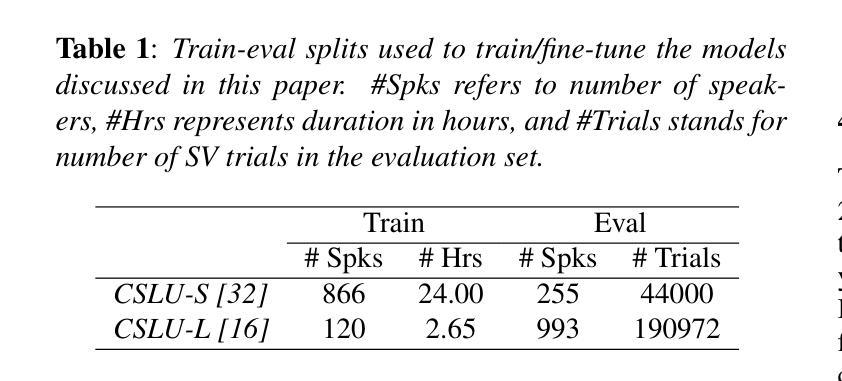
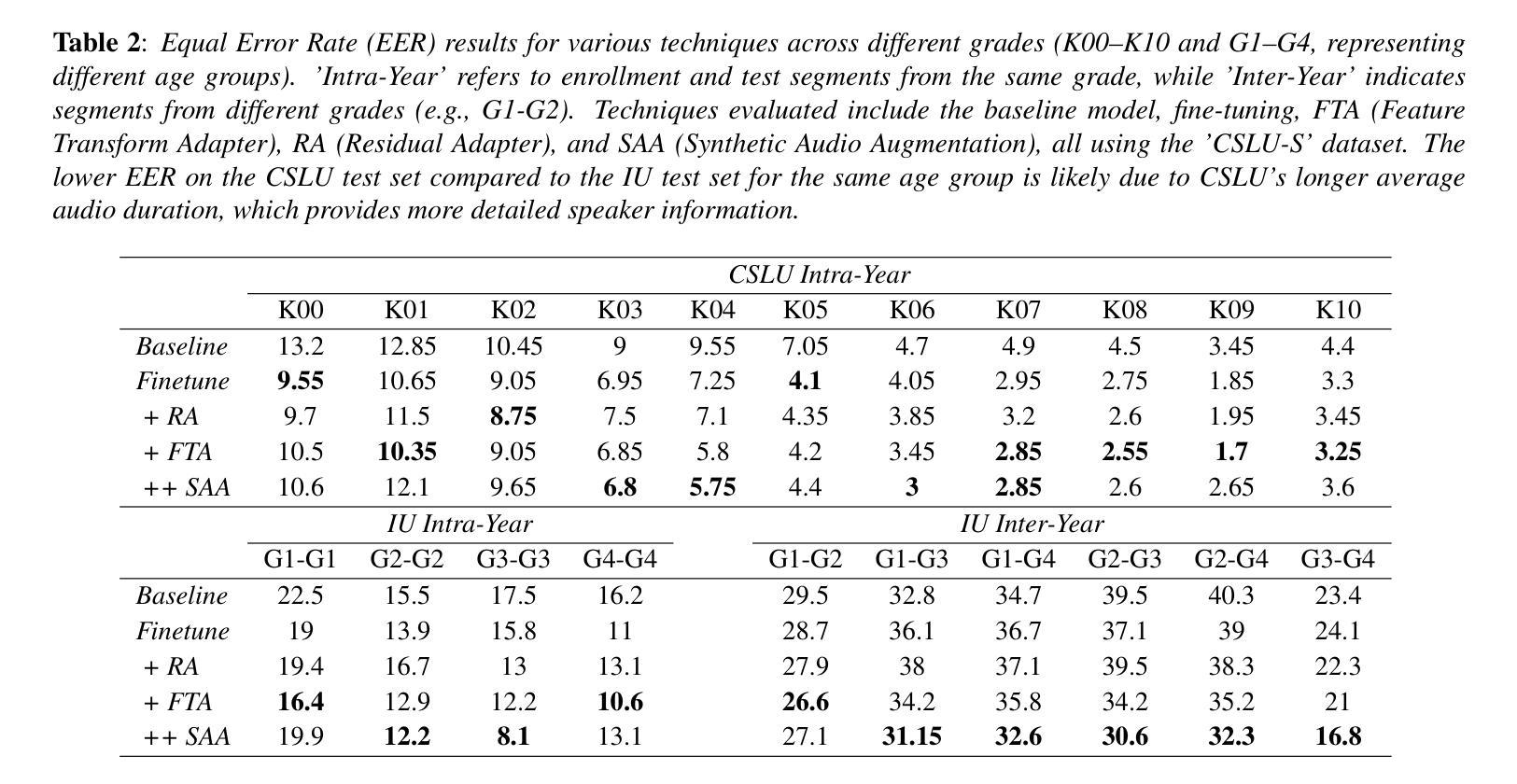
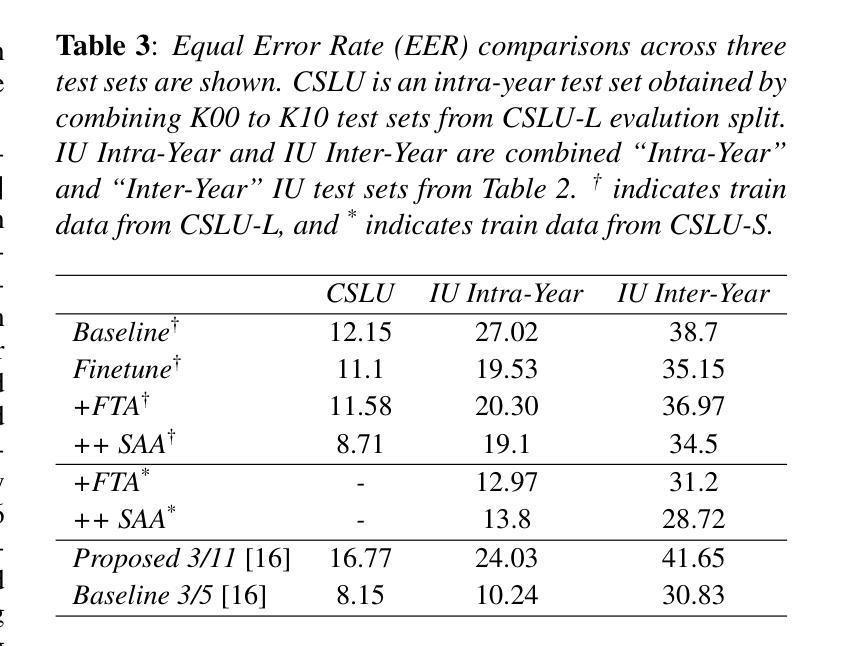
One of the main challenges in children’s speaker verification (C-SV) is the significant change in children’s voices as they grow. In this paper, we propose two approaches to improve age-related robustness in C-SV. We first introduce a Feature Transform Adapter (FTA) module that integrates local patterns into higher-level global representations, reducing overfitting to specific local features and improving the inter-year SV performance of the system. We then employ Synthetic Audio Augmentation (SAA) to increase data diversity and size, thereby improving robustness against age-related changes. Since the lack of longitudinal speech datasets makes it difficult to measure age-related robustness of C-SV systems, we introduce a longitudinal dataset to assess inter-year verification robustness of C-SV systems. By integrating both of our proposed methods, the average equal error rate was reduced by 19.4%, 13.0%, and 6.1% in the one-year, two-year, and three-year gap inter-year evaluation sets, respectively, compared to the baseline.
在儿童说话人验证(C-SV)中,主要挑战之一是儿童声音随年龄增长而发生的显著变化。在本文中,我们提出了两种方法来提高C-SV中与年龄相关的稳健性。首先,我们引入了一个特征转换适配器(FTA)模块,该模块将局部模式集成到高级全局表示中,减少了对特定局部特征的过度拟合,提高了系统的跨年度SV性能。然后,我们采用合成音频增强(SAA)来增加数据的多样性和规模,从而提高对与年龄相关的变化的稳健性。由于缺乏纵向语音数据集,使得难以衡量C-SV系统的与年龄相关的稳健性,因此我们引入了一个纵向数据集来评估C-SV系统的跨年度验证稳健性。通过整合我们提出的两种方法,与基线相比,在一年、两年和三年间隔的跨年度评估集中,平均等错误率分别降低了19.4%、13.0%和6.1%。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to ICASSP 2025
Summary
本文提出了两种方法来提高儿童说话者验证(C-SV)的年龄相关稳健性。首先引入特征转换适配器(FTA)模块,将局部模式集成到高级全局表示中,从而提高系统跨年龄段的稳健性。然后采用合成音频增强(SAA)来增加数据的多样性和规模,进一步提高对年龄相关变化的稳健性。由于缺乏纵向语音数据集来衡量C-SV系统的年龄相关稳健性,本文引入了一个纵向数据集来评估C-SV系统的跨年度验证稳健性。通过整合这两种方法,与基线相比,在一年、两年和三年间隔的跨年度评估集中,平均等误率分别降低了19.4%、13.0%和6.1%。
Key Takeaways
- 儿童说话者验证(C-SV)面临的主要挑战之一是儿童声音随年龄的重大变化。
- 特征转换适配器(FTA)模块被引入,以整合局部模式到高级全局表示,提高系统跨年龄段的稳健性。
- 合成音频增强(SAA)被用来增加数据的多样性和规模,进一步提高对年龄相关变化的稳健性。
- 缺乏纵向语音数据集来衡量C-SV系统的年龄相关稳健性,因此引入了一个纵向数据集。
- 通过整合FTA和SAA两种方法,在跨年度评估中,与基线相比,平均等误率显著降低。
- FTA和SAA的整合有助于改善系统在儿童成长过程中的声音变化方面的性能。
点此查看论文截图

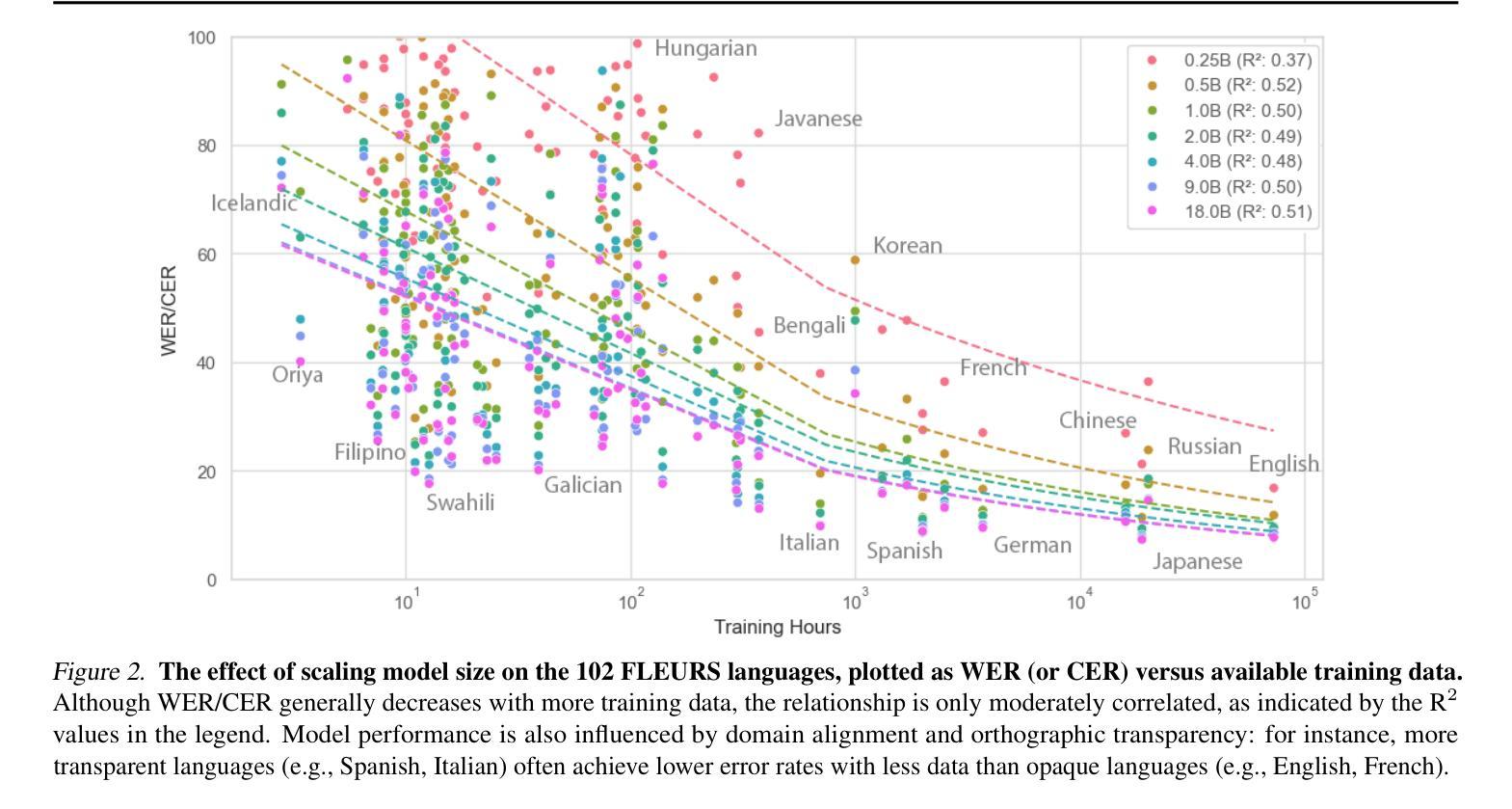
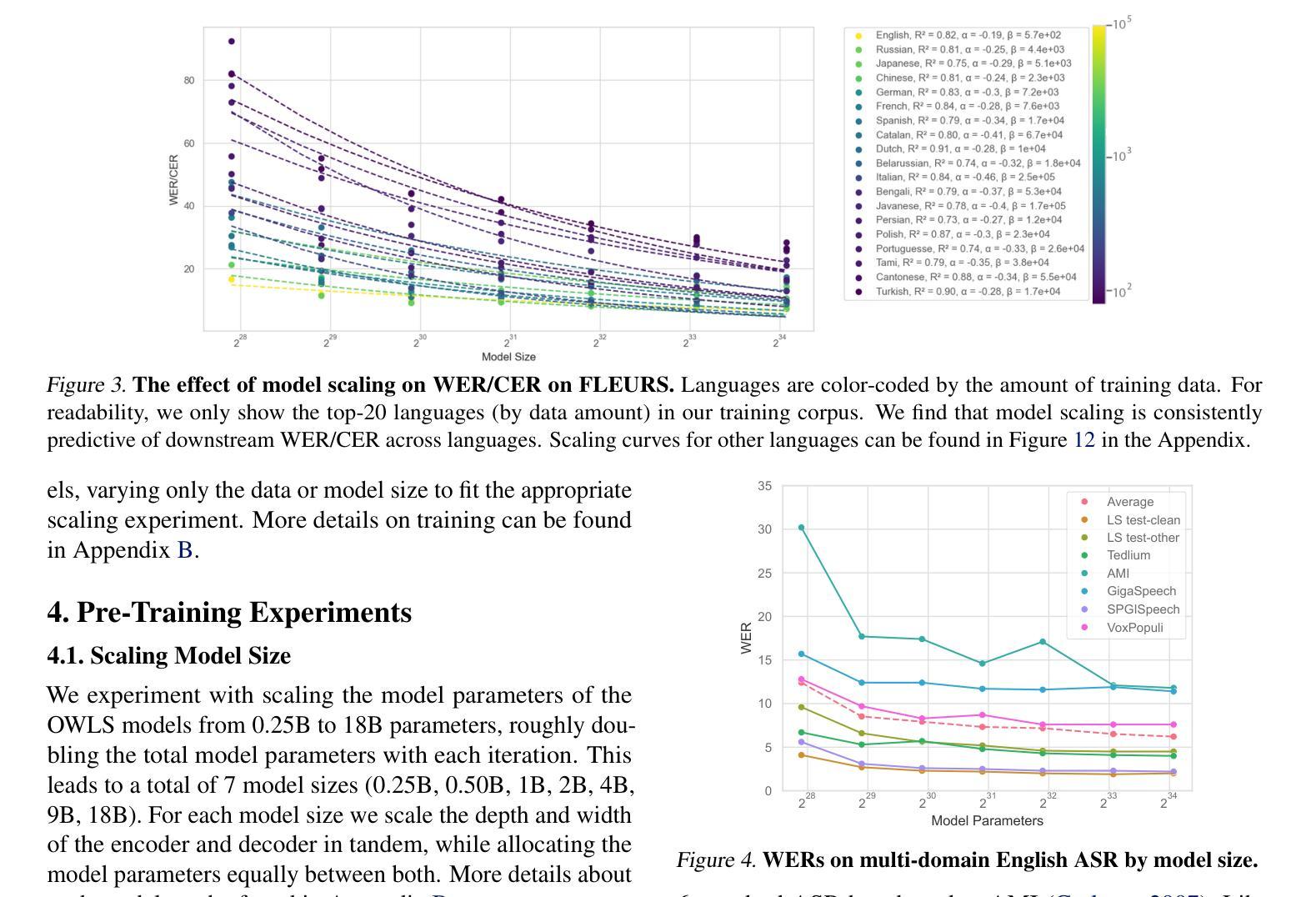
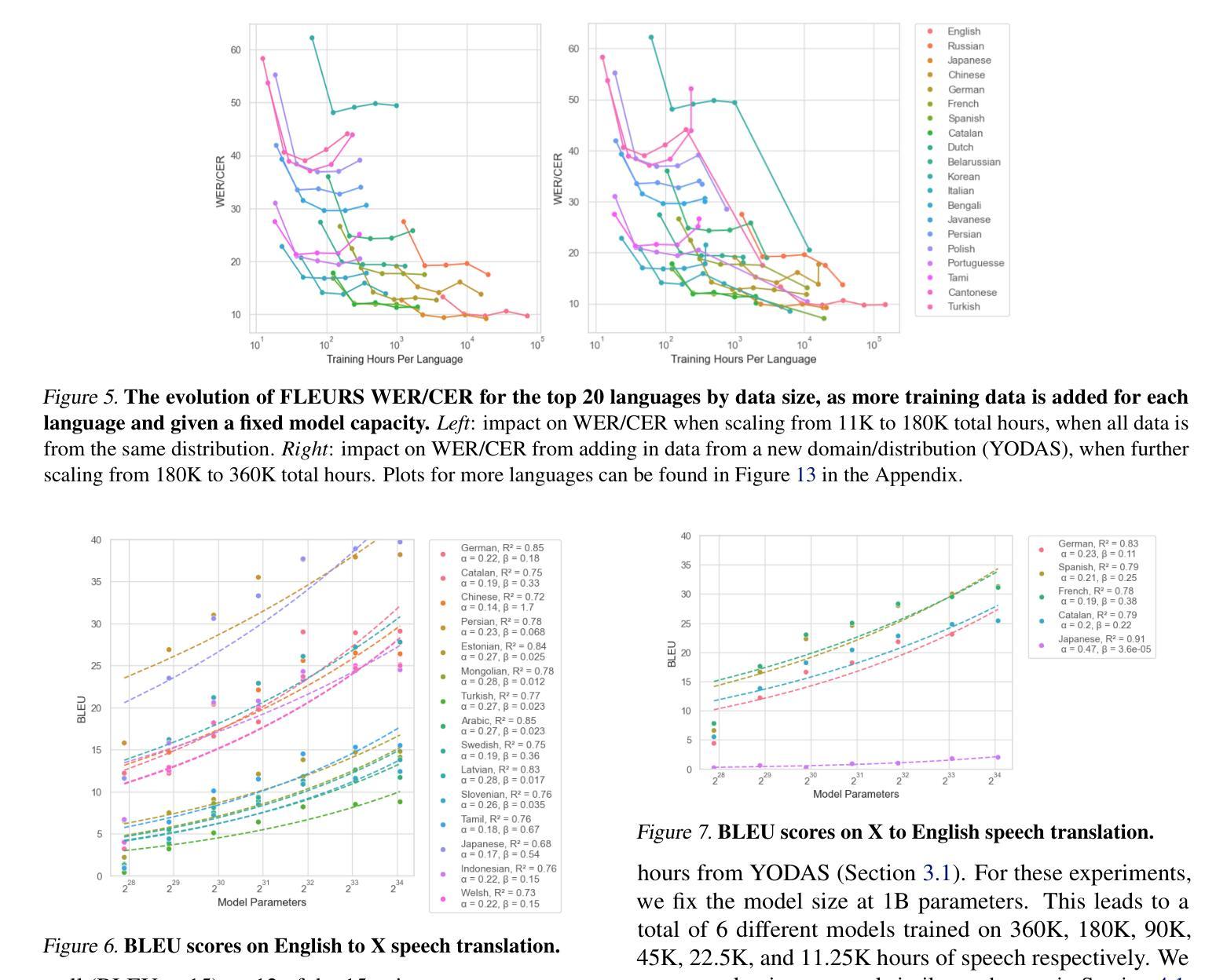
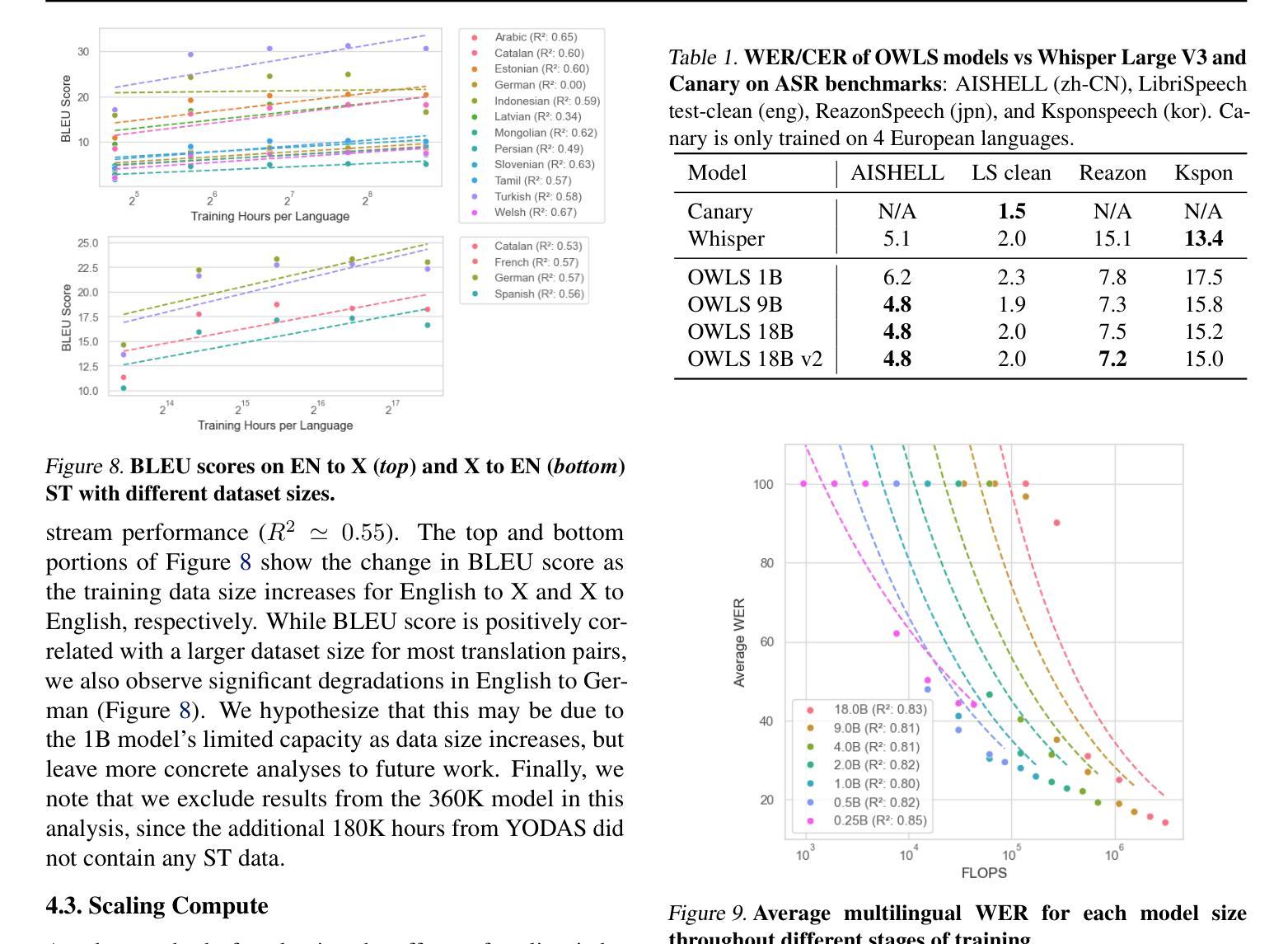
OWLS: Scaling Laws for Multilingual Speech Recognition and Translation Models
Authors:William Chen, Jinchuan Tian, Yifan Peng, Brian Yan, Chao-Han Huck Yang, Shinji Watanabe
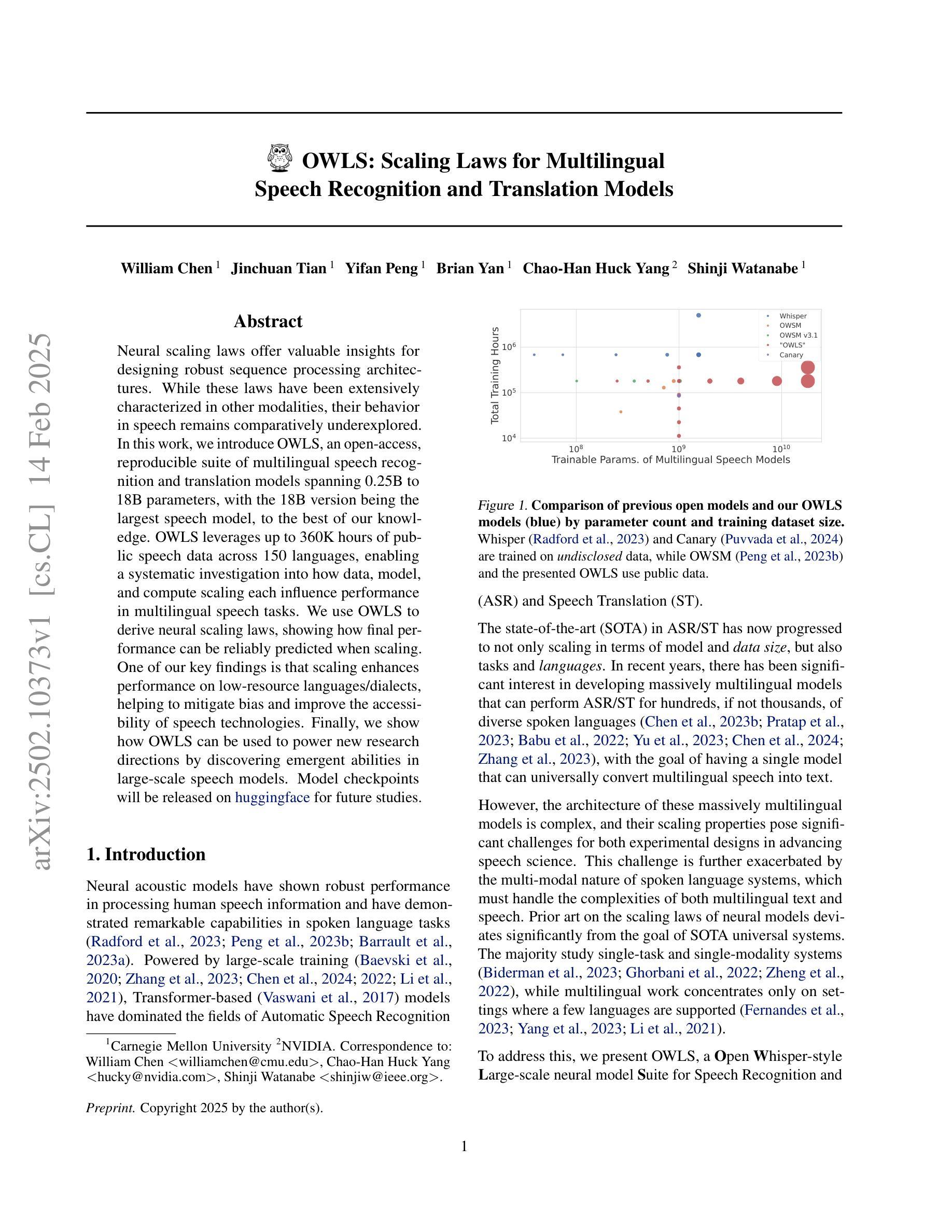
Neural scaling laws offer valuable insights for designing robust sequence processing architectures. While these laws have been extensively characterized in other modalities, their behavior in speech remains comparatively underexplored. In this work, we introduce OWLS, an open-access, reproducible suite of multilingual speech recognition and translation models spanning 0.25B to 18B parameters, with the 18B version being the largest speech model, to the best of our knowledge. OWLS leverages up to 360K hours of public speech data across 150 languages, enabling a systematic investigation into how data, model, and compute scaling each influence performance in multilingual speech tasks. We use OWLS to derive neural scaling laws, showing how final performance can be reliably predicted when scaling. One of our key findings is that scaling enhances performance on low-resource languages/dialects, helping to mitigate bias and improve the accessibility of speech technologies. Finally, we show how OWLS can be used to power new research directions by discovering emergent abilities in large-scale speech models. Model checkpoints will be released on https://huggingface.co/collections/espnet/owls-scaling-laws-for-speech-recognition-and-translation-67ab7f991c194065f057ce8d for future studies.
神经缩放定律为设计稳健的序列处理架构提供了宝贵的见解。虽然这些定律在其他模态上已经被广泛表征,但它们在语音中的行为仍然相对未被充分探索。在这项工作中,我们介绍了OWLS,这是一个开放访问的、可重复使用的多语言语音识别和翻译模型套件,涵盖0.25B到18B参数,据我们所知,18B版本是迄今为止最大的语音模型。OWLS利用跨越150种语言的36万小时公开语音数据,能够系统地研究数据、模型和计算缩放如何分别影响多语言语音任务中的性能。我们使用OWLS来推导神经缩放定律,展示在缩放时如何可靠地预测最终性能。我们的关键发现之一是,缩放增强了对低资源语言/方言的性能,有助于减轻偏见,提高语音技术的可及性。最后,我们展示了如何使用OWLS为新的研究方向提供动力,通过发现大规模语音模型的新兴能力。模型检查点将在https://huggingface.co/collections/espnet/owls-scaling-laws-for-speech-recognition-and-translation-67ab7f991c194065f057ce8d上发布,以供未来研究。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 23 pages, 13 figures
Summary
本文介绍了OWLS,一套涵盖多语种语音识别和翻译模型的开源套件,模型参数从数十亿到上百亿不等,其中最大的模型参数为18B。OWLS利用跨150种语言的公开语音数据,系统地研究了数据、模型和计算规模在多语种语音任务中的影响,并得出了神经规模定律。研究发现,规模扩大能提高低资源语言和方言的性能,有助于减少偏见并提高语音技术的普及性。模型检查点将发布在https://huggingface.co/collections/espnet/owls-scaling-laws-for-speech-recognition-and-translation-67ab7f991c194065f057ce8d上,以便未来研究使用。
Key Takeaways
- 介绍OWLS作为涵盖多语种语音识别和翻译模型的开源套件。
- OWLS模型参数范围广泛,从数十亿到上百亿不等,其中最大的模型参数为18B。
- 利用公开语音数据,系统地研究数据、模型和计算规模在多语种语音任务中的作用。
- 通过OWLS发现神经规模定律,揭示了如何预测最终的性能表现。
- 规模扩大能提高低资源语言和方言的性能,有助于减少偏见和提高语音技术的普及性。
- 通过OWLS的研究发现,大规模语音模型能够展现出新兴的能力。
点此查看论文截图
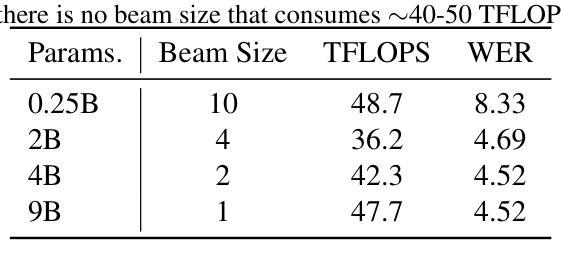
MTLM: an Innovative Language Model Training Paradigm for ASR
Authors:Qingliang Meng, Pengju Ren, Tian Li, Changsong Dai
Pre-training Transformer-based language models (LMs) on a large amount of text has proven crucial for improving automatic speech recognition (ASR) performance. Generally, traditional LMs are unidirectional and unable to access the context on the right. This paper proposes a method for training LMs that enable traditional unidirectional LMs to fully utilize left and right contexts. Compared with the unidirectional LMs, our LM facilitates ASR to transcribe hypotheses more consistently and in a more semantically unambiguous way, as it incorporates richer contextual representations. Finally, our experimental results on the LibriSpeech corpus demonstrate that our model outperforms traditional unidirectional LMs, whether n-best rescoring or shallow fusion is used as the decoding algorithm.
基于大量文本对Transformer语言模型进行预训练已经被证明对改善自动语音识别(ASR)性能至关重要。一般来说,传统的语言模型是单方向的,无法访问到右侧的内容。本文提出了一种训练语言模型的方法,使传统的单向语言模型能够充分利用左右上下文信息。与传统的单向语言模型相比,我们的语言模型可以促使自动语音识别更加一致且语义更加明确地转录假设,因为它融入了更丰富的上下文表示。最后,在LibriSpeech语料库上的实验结果表明,我们的模型无论是使用n-best重打分还是浅融合作为解码算法,都优于传统的单向语言模型。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
预训练Transformer基础的语言模型(LMs)在大量文本上对于提高自动语音识别(ASR)性能至关重要。传统LMs通常是单向的,无法获取右侧上下文。本文提出一种训练LMs的方法,使传统单向LMs能够充分利用左右上下文。与传统单向LMs相比,我们的LM促进ASR更一致且语义更明确地转录假设,因为它包含了更丰富的内容表示。在LibriSpeech语料库上的实验结果表明,无论使用n-best重评分还是浅融合作为解码算法,我们的模型都优于传统单向LMs。
Key Takeaways
- 预训练Transformer基础的语言模型对改善自动语音识别(ASR)性能至关重要。
- 传统LMs通常是单向的,无法获取右侧上下文信息。
- 本文提出一种方法,使传统LMs能够利用左右上下文,从而丰富其内容表示。
- 与传统单向LMs相比,该LM促进ASR更一致且语义更明确地转录假设。
- 该模型在LibriSpeech语料库上的实验表现优于传统单向LMs。
- 该论文研究的模型无论使用n-best重评分还是浅融合作为解码算法都有良好表现。
点此查看论文截图

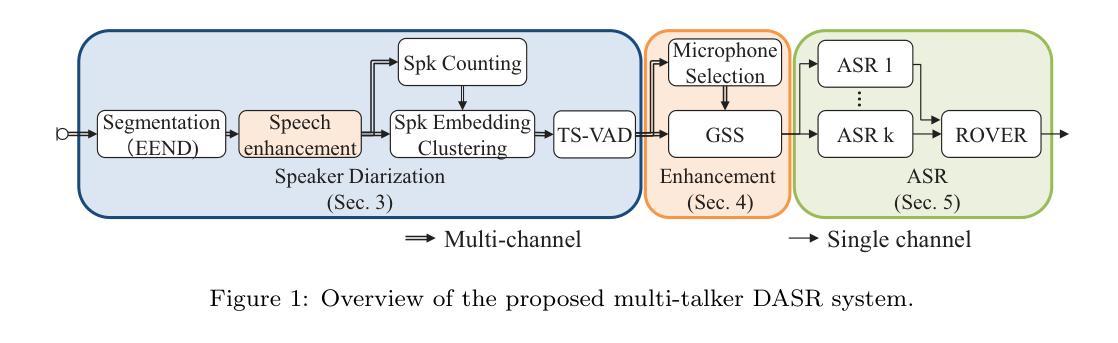
Microphone Array Geometry Independent Multi-Talker Distant ASR: NTT System for the DASR Task of the CHiME-8 Challenge
Authors:Naoyuki Kamo, Naohiro Tawara, Atsushi Ando, Takatomo Kano, Hiroshi Sato, Rintaro Ikeshita, Takafumi Moriya, Shota Horiguch, Kohei Matsuura, Atsunori Ogawa, Alexis Plaquet, Takanori Ashihara, Tsubasa Ochiai, Masato Mimura, Marc Delcroix, Tomohiro Nakatani, Taichi Asami, Shoko Araki
In this paper, we introduce a multi-talker distant automatic speech recognition (DASR) system we designed for the DASR task 1 of the CHiME-8 challenge. Our system performs speaker counting, diarization, and ASR. It handles various recording conditions, from diner parties to professional meetings and from two to eight speakers. We perform diarization first, followed by speech enhancement, and then ASR as the challenge baseline. However, we introduced several key refinements. First, we derived a powerful speaker diarization relying on end-to-end speaker diarization with vector clustering (EEND-VC), multi-channel speaker counting using enhanced embeddings from EEND-VC, and target-speaker voice activity detection (TS-VAD). For speech enhancement, we introduced a novel microphone selection rule to better select the most relevant microphones among the distributed microphones and investigated improvements to beamforming. Finally, for ASR, we developed several models exploiting Whisper and WavLM speech foundation models. We present the results we submitted to the challenge and updated results we obtained afterward. Our strongest system achieves a 63% relative macro tcpWER improvement over the baseline and outperforms the challenge best results on the NOTSOFAR-1 meeting evaluation data among geometry-independent systems.
在这篇论文中,我们介绍了一项针对CHiME-8挑战任务中的远距离自动语音识别(DASR)任务设计的多说话者远距离自动语音识别(DASR)系统。我们的系统可以进行说话人数统计、语音日记识别以及自动语音识别。该系统可以处理各种录音环境,无论是家庭聚会还是专业会议,从两人到八人的场景。我们首先进行语音日记识别,然后进行语音增强,最后进行自动语音识别作为挑战基线。然而,我们引入了几项关键改进。首先,我们依靠一种强大的语音日记识别方法实现端到端的语音日记识别,采用向量聚类(EEND-VC)、通过EEND-VC增强的嵌入实现多通道说话人数统计以及目标说话者语音活动检测(TS-VAD)。对于语音增强部分,我们引入了一种新的麦克风选择规则,以更好地选择分布麦克风中最相关的麦克风,并研究改进波束形成技术。最后,对于自动语音识别部分,我们开发了一些利用Whisper和WavLM语音基础模型的模型。我们展示了提交给挑战的结果以及之后获得的更新结果。我们最强大的系统在宏tcpWER上的相对改进率提高了63%,并优于在几何无关系统中针对NOTSOFAR-1会议评估数据的挑战最佳结果。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 55 pages, 12 figures
Summary
本文介绍了一种针对CHiME-8挑战DASR任务1的多说话人远距离自动语音识别(DASR)系统。该系统执行说话人计数、语音识别及自动语音识别(ASR)。它能应对从餐桌聚会到专业会议以及从两位到八位说话人的各种录音环境。首先进行说话人识别,然后进行语音增强,最后进行ASR作为基线挑战。同时,论文引入了多项关键技术改进,包括采用基于端对端说话人识别的向量聚类(EEND-VC)进行强大的说话人识别、使用EEND-VC增强嵌入的多通道说话人计数以及目标说话人的语音活动检测(TS-VAD)。在语音增强方面,论文引入了一种新的麦克风选择规则,以更好地选择分布式麦克风中最相关的麦克风,并对波束形成进行了改进。在ASR方面,论文开发了利用Whisper和WavLM语音基础模型的多个模型。论文展示了提交挑战的结果以及后续更新的结果。其最先进的系统相对于基线实现了63%的相对宏观tcpWER改进,并在几何无关系统中超越了挑战的最佳结果在NOTSOFAR-1会议评估数据上。
Key Takeaways
- 论文介绍了一种针对CHiME-8挑战的多说话人远距离自动语音识别(DASR)系统。
- 系统能应对不同场景和说话人数量的变化。
- 论文采用了基于端对端说话人识别的向量聚类的技术改进。
- 引入了新的麦克风选择规则用于语音增强。
- 在ASR方面,利用了Whisper和WavLM语音基础模型开发的多个模型。
- 最先进的系统相对于基线有显著的性能提升。
点此查看论文截图

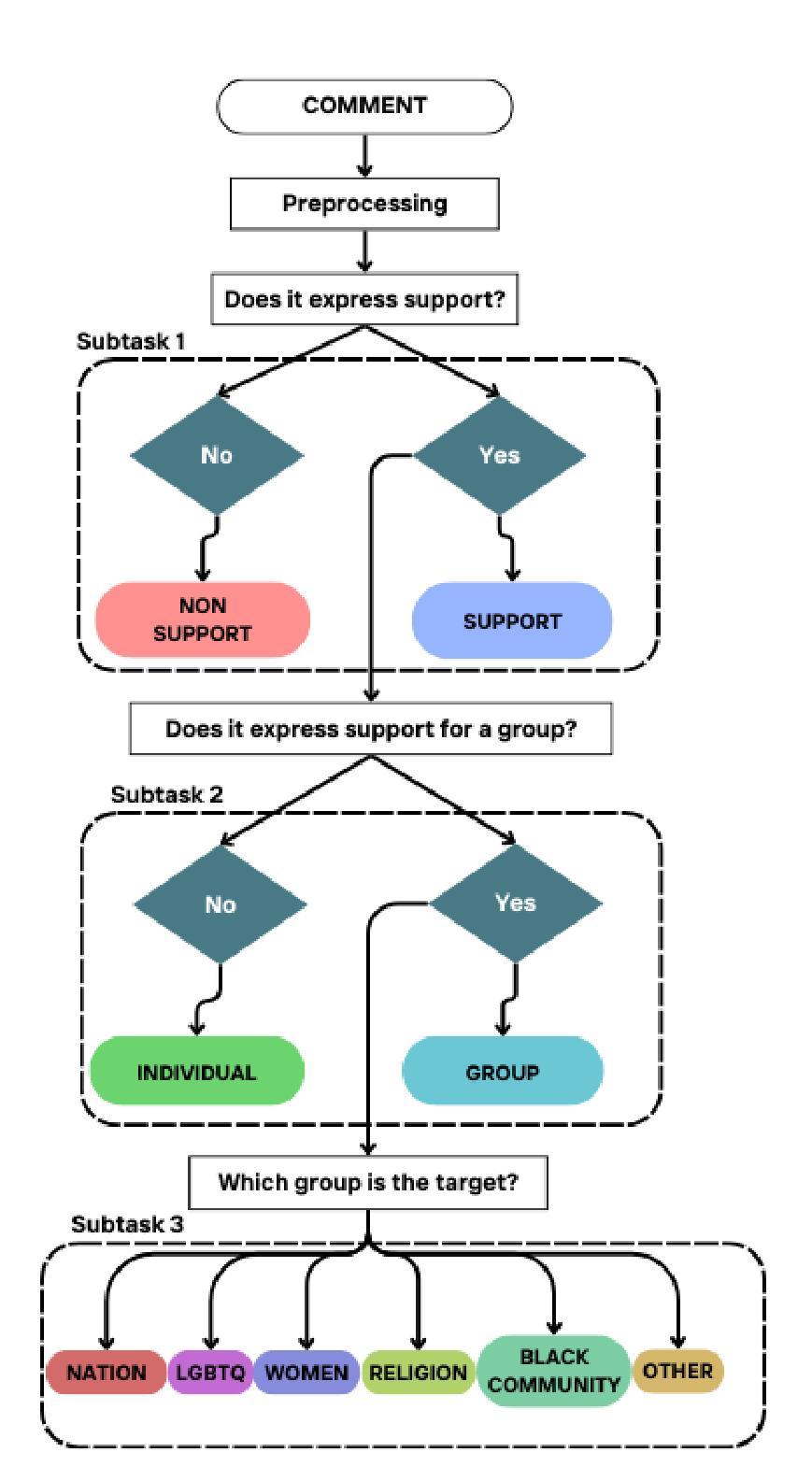
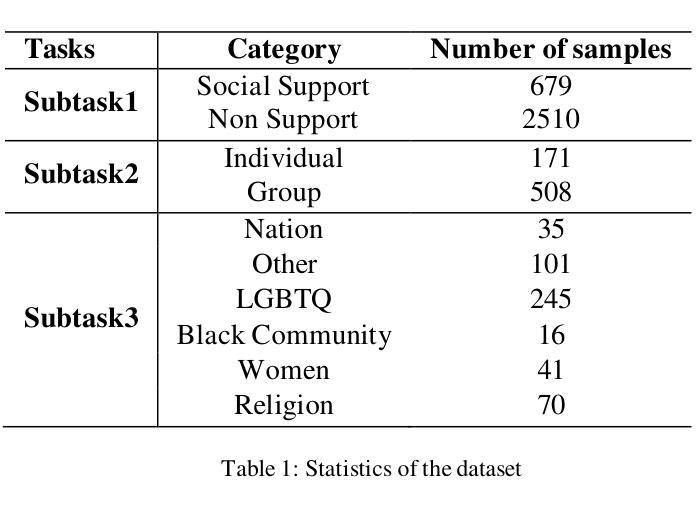
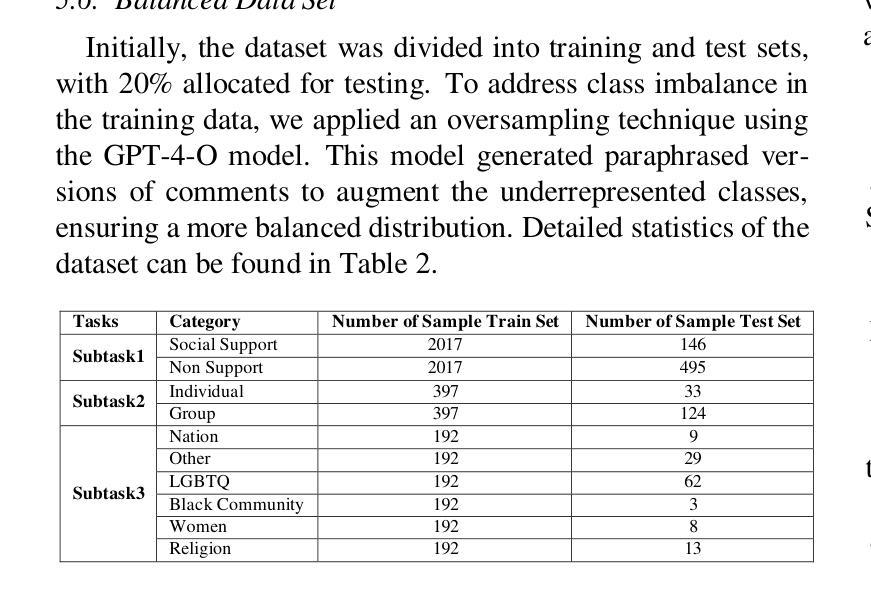
Online Social Support Detection in Spanish Social Media Texts
Authors:Moein Shahiki Tash, Luis Ramos, Zahra Ahani, Raul Monroy, Olga kolesnikova, Hiram Calvo, Grigori Sidorov
The advent of social media has transformed communication, enabling individuals to share their experiences, seek support, and participate in diverse discussions. While extensive research has focused on identifying harmful content like hate speech, the recognition and promotion of positive and supportive interactions remain largely unexplored. This study proposes an innovative approach to detecting online social support in Spanish-language social media texts. We introduce the first annotated dataset specifically created for this task, comprising 3,189 YouTube comments classified as supportive or non-supportive. To address data imbalance, we employed GPT-4o to generate paraphrased comments and create a balanced dataset. We then evaluated social support classification using traditional machine learning models, deep learning architectures, and transformer-based models, including GPT-4o, but only on the unbalanced dataset. Subsequently, we utilized a transformer model to compare the performance between the balanced and unbalanced datasets. Our findings indicate that the balanced dataset yielded improved results for Task 2 (Individual and Group) and Task 3 (Nation, Other, LGBTQ, Black Community, Women, Religion), whereas GPT-4o performed best for Task 1 (Social Support and Non-Support). This study highlights the significance of fostering a supportive online environment and lays the groundwork for future research in automated social support detection.
社交媒体的兴起已经改变了人们的交流方式,使得个人能够分享他们的经历、寻求支持,并参与各种讨论。虽然大量研究聚焦于识别有害内容,如仇恨言论,但对积极和支持性互动的认识和促进仍然未被充分探索。本研究提出了一种检测西班牙语文本中在线社会支持的创新方法。我们引入了专为这项任务创建的第一个注释数据集,包含3189条被分类为支持性或非支持性的YouTube评论。为了解决数据不平衡问题,我们采用GPT-4o生成了同义替换的评论,创建了平衡数据集。然后,我们使用传统的机器学习模型、深度学习架构和基于转换模型的GPT-4o评估社会支持分类的性能表现。此过程只在非平衡数据集上进行。随后,我们利用一个转换模型比较平衡和非平衡数据集的性能表现。我们的研究结果表明,在任务2(个人和团体)、任务3(国家、其他、LGBTQ、黑人社区、女性、宗教)中,平衡数据集的结果有所改善,而GPT-4o在任务1(社会支持和非支持)中的表现最佳。该研究强调了促进支持性在线环境的重要性,并为未来的自动化社会支持检测研究奠定了基础。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
社交媒体的出现改变了人们的交流方式,使得个人能够分享经历、寻求支持并参与各种讨论。本研究提出了一种检测在线社交支持的创新方法,并专门创建了首个用于此任务的注释数据集。研究包括创建平衡的数据集和评估不同类型的模型对在线社交支持分类的性能。研究表明,平衡数据集能够提高某些任务的性能,并且GPT-4o在特定任务上表现最佳。这为未来的在线支持检测研究奠定了基础。
Key Takeaways
- 社交媒体改变了人们的交流方式,促进个人分享经历、寻求支持和参与讨论。
- 本研究旨在检测在线社交支持,并创建了首个专门用于此任务的注释数据集。
- 研究中采用了多种技术来创建平衡数据集,以应对数据不平衡问题。
- 研究评估了不同类型的模型在在线社交支持分类方面的性能。
- GPT-4o在特定任务上的表现最佳。
- 平衡数据集在某些任务上的性能有所提高。
点此查看论文截图

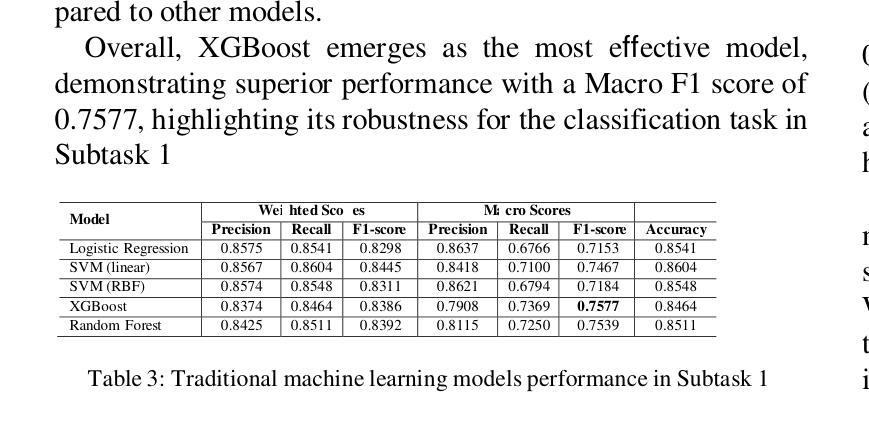
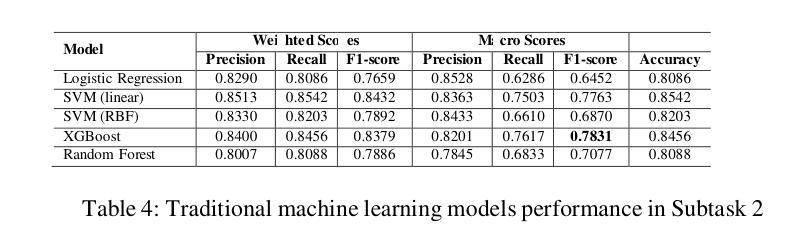
DiTAR: Diffusion Transformer Autoregressive Modeling for Speech Generation
Authors:Dongya Jia, Zhuo Chen, Jiawei Chen, Chenpeng Du, Jian Wu, Jian Cong, Xiaobin Zhuang, Chumin Li, Zhen Wei, Yuping Wang, Yuxuan Wang
Several recent studies have attempted to autoregressively generate continuous speech representations without discrete speech tokens by combining diffusion and autoregressive models, yet they often face challenges with excessive computational loads or suboptimal outcomes. In this work, we propose Diffusion Transformer Autoregressive Modeling (DiTAR), a patch-based autoregressive framework combining a language model with a diffusion transformer. This approach significantly enhances the efficacy of autoregressive models for continuous tokens and reduces computational demands. DiTAR utilizes a divide-and-conquer strategy for patch generation, where the language model processes aggregated patch embeddings and the diffusion transformer subsequently generates the next patch based on the output of the language model. For inference, we propose defining temperature as the time point of introducing noise during the reverse diffusion ODE to balance diversity and determinism. We also show in the extensive scaling analysis that DiTAR has superb scalability. In zero-shot speech generation, DiTAR achieves state-of-the-art performance in robustness, speaker similarity, and naturalness.
近期有几项研究尝试结合扩散模型和自回归模型,无离散语音标记地自动生成连续语音表示。然而,这些方法往往面临计算负载过大或结果不理想等挑战。在本研究中,我们提出了扩散变换自回归建模(DiTAR),这是一种结合语言模型和扩散变压器的基于补丁的自回归框架。该方法显著提高了自回归模型对连续标记的有效性,并降低了计算需求。DiTAR采用一种分而治之的补丁生成策略,其中语言模型处理聚合的补丁嵌入,然后扩散变压器根据语言模型的输出生成下一个补丁。对于推理,我们提议将温度定义为反向扩散ODE过程中引入噪声的时间点,以平衡多样性和确定性。在广泛的规模分析中,我们还表明DiTAR具有出色的可扩展性。在零样本语音生成中,DiTAR在稳健性、说话人相似性和自然性方面达到了最先进的性能。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 16 pages, 8 figures
Summary
本文提出一种名为Diffusion Transformer Autoregressive Modeling(DiTAR)的方法,结合语言模型和扩散变压器,以斑块为基础进行自回归建模,旨在更有效地生成连续语音表示。该方法采用分而治之的策略进行斑块生成,并通过调整反向扩散ODE中的温度来平衡多样性和确定性,从而实现更好的推理。DiTAR在零样本语音生成中取得了最先进的性能,具有出色的可扩展性。
Key Takeaways
- 结合扩散和自回归模型生成连续语音表示。
- 提出Diffusion Transformer Autoregressive Modeling(DiTAR)方法,有效增强自回归模型对连续标记的效力并降低计算需求。
- 采用分而治之的策略进行斑块生成,语言模型处理聚合斑块嵌入,扩散变压器根据语言模型的输出生成下一个斑块。
- 通过调整反向扩散ODE中的温度来平衡多样性和确定性,实现更好的推理。
- DiTAR具有出色的可扩展性,在零样本语音生成中表现出卓越的性能。
- 在鲁棒性、说话人相似性和自然性方面达到最新水平。
点此查看论文截图

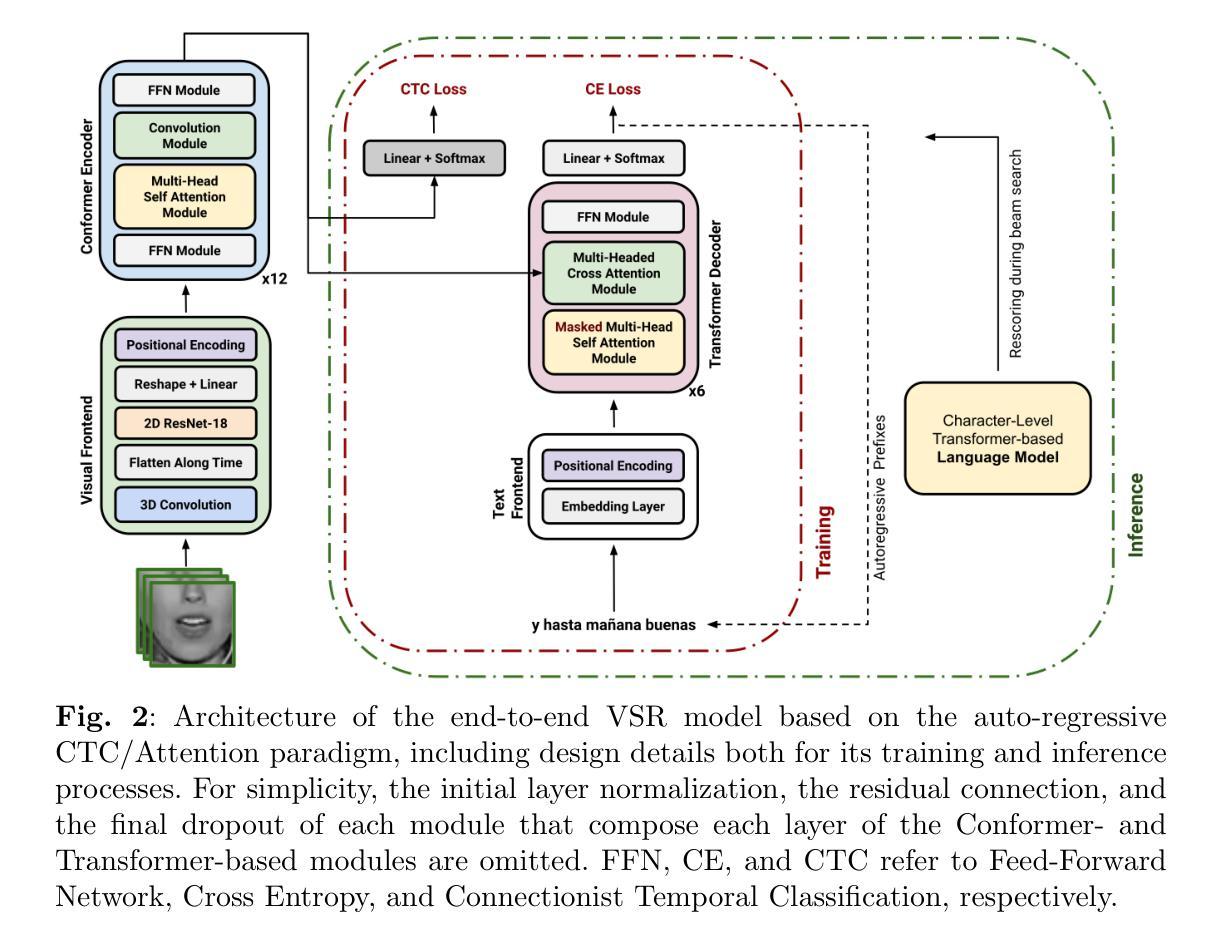
Evaluation of End-to-End Continuous Spanish Lipreading in Different Data Conditions
Authors:David Gimeno-Gómez, Carlos-D. Martínez-Hinarejos
Visual speech recognition remains an open research problem where different challenges must be considered by dispensing with the auditory sense, such as visual ambiguities, the inter-personal variability among speakers, and the complex modeling of silence. Nonetheless, recent remarkable results have been achieved in the field thanks to the availability of large-scale databases and the use of powerful attention mechanisms. Besides, multiple languages apart from English are nowadays a focus of interest. This paper presents noticeable advances in automatic continuous lipreading for Spanish. First, an end-to-end system based on the hybrid CTC/Attention architecture is presented. Experiments are conducted on two corpora of disparate nature, reaching state-of-the-art results that significantly improve the best performance obtained to date for both databases. In addition, a thorough ablation study is carried out, where it is studied how the different components that form the architecture influence the quality of speech recognition. Then, a rigorous error analysis is carried out to investigate the different factors that could affect the learning of the automatic system. Finally, a new Spanish lipreading benchmark is consolidated. Code and trained models are available at https://github.com/david-gimeno/evaluating-end2end-spanish-lipreading.
视觉语音识别仍然是一个开放的研究问题,必须考虑舍弃听觉所带来的不同挑战,例如视觉模糊、说话者之间的个体差异以及沉默的复杂建模。尽管如此,由于大规模数据库的可用性和强大注意力机制的使用,该领域已经取得了令人瞩目的最新成果。此外,如今除英语外的多种语言也成为关注的重点。本文介绍了西班牙语的自动连续唇读方面的显著进展。首先,介绍了一种基于混合CTC/注意力架构的端到端系统。实验在两个本质不同的语料库上进行,达到了最先进的成果,显著改进了迄今为止在这两个数据库上获得的最佳性能。此外,还进行了全面的消融研究,研究了构成架构的不同组件如何影响语音识别质量。然后,进行了严格的误差分析,以调查可能影响自动系统学习的不同因素。最后,巩固了一个新的西班牙语唇读基准测试。代码和训练模型可在https://github.com/david-gimeno/evaluating-end2end-spanish-lipreading找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted in the “Language Resources and Evaluation” journal, Springer Nature
Summary
视觉语音识别仍然是一个开放的研究问题,其挑战在于摒弃听觉,面临视觉模糊、不同个体之间的差异以及沉默的复杂建模等问题。近期由于大规模数据库和强大注意力机制的可用性,该领域取得了显著成果。本文介绍了西班牙语的自动连续唇读方面的显著进展。首先,提出了一种基于混合CTC/注意力架构的端到端系统。实验在两个性质不同的语料库上进行,达到了最新结果,显著提高了这两个数据库的最佳性能。此外,还进行了深入的分析研究,研究了构成架构的不同部分对语音识别质量的影响。然后进行了严格的误差分析,以调查可能影响自动系统学习的不同因素。最后巩固了一个新的西班牙语唇读基准测试。相关代码和训练好的模型可在https://github.com/david-gimeno/evaluating-end2end-spanish-lipreading 获取。
Key Takeaways
- 视觉语音识别是一个开放的研究问题,面临视觉模糊、个体差异和沉默建模等挑战。
- 近期由于大规模数据库和注意力机制的可用性,视觉语音识别领域取得显著进展。
- 本文介绍了基于混合CTC/注意力架构的端到端系统在自动连续唇读方面的应用。
- 实验在两个不同性质的语料库上进行,达到了最新结果,并显著提高了之前最佳性能。
- 进行了深入分析研究,探讨了架构的不同部分对语音识别质量的影响。
- 通过严格的误差分析,研究了影响自动系统学习的不同因素。
点此查看论文截图


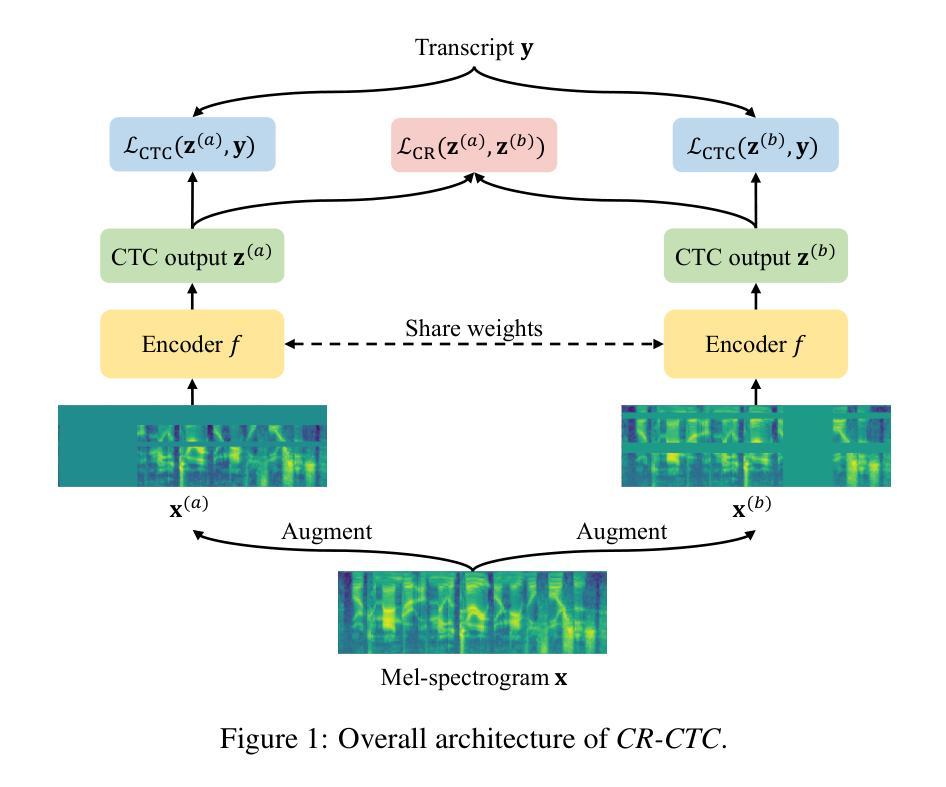
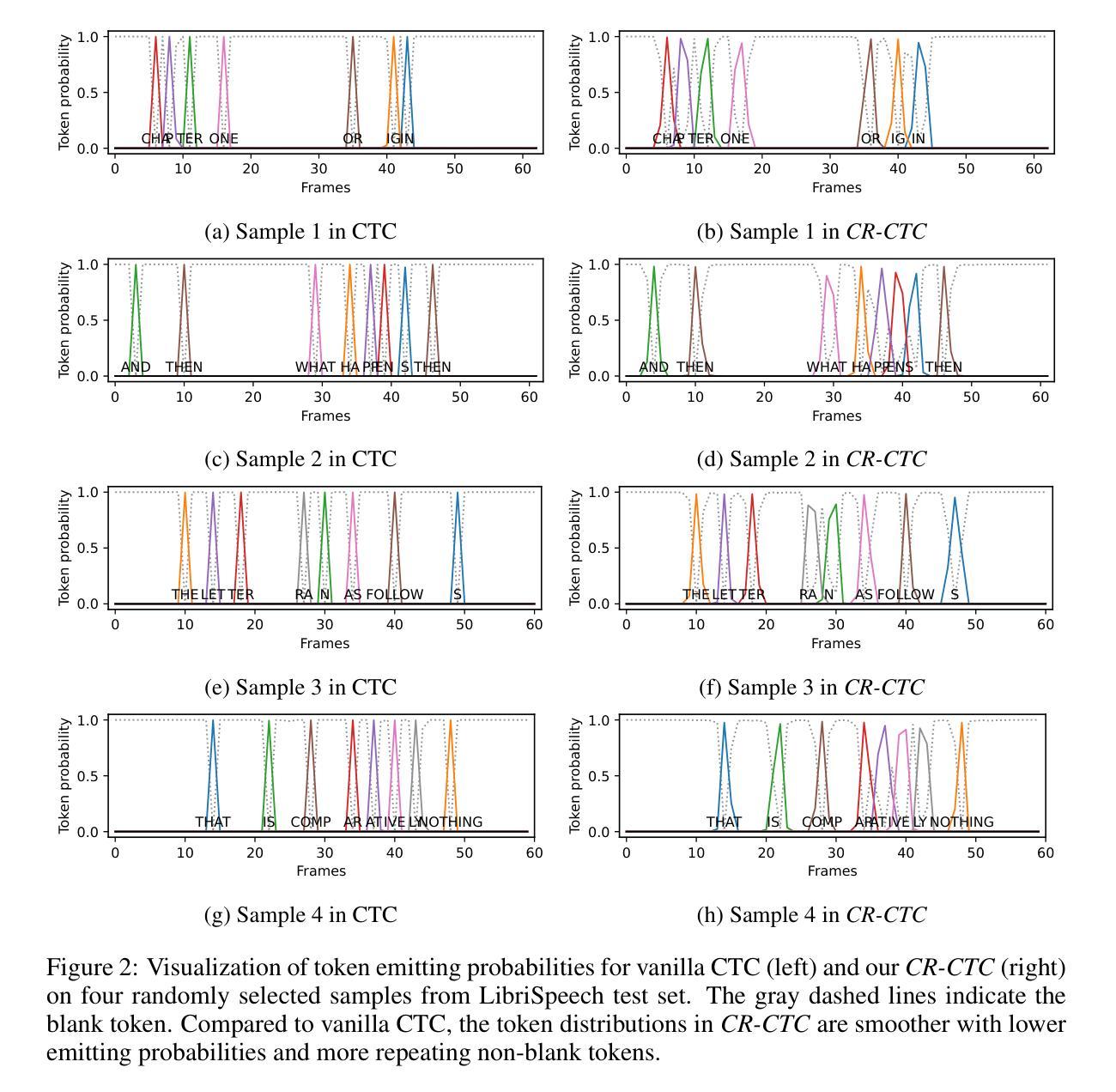
CR-CTC: Consistency regularization on CTC for improved speech recognition
Authors:Zengwei Yao, Wei Kang, Xiaoyu Yang, Fangjun Kuang, Liyong Guo, Han Zhu, Zengrui Jin, Zhaoqing Li, Long Lin, Daniel Povey
Connectionist Temporal Classification (CTC) is a widely used method for automatic speech recognition (ASR), renowned for its simplicity and computational efficiency. However, it often falls short in recognition performance. In this work, we propose the Consistency-Regularized CTC (CR-CTC), which enforces consistency between two CTC distributions obtained from different augmented views of the input speech mel-spectrogram. We provide in-depth insights into its essential behaviors from three perspectives: 1) it conducts self-distillation between random pairs of sub-models that process different augmented views; 2) it learns contextual representation through masked prediction for positions within time-masked regions, especially when we increase the amount of time masking; 3) it suppresses the extremely peaky CTC distributions, thereby reducing overfitting and improving the generalization ability. Extensive experiments on LibriSpeech, Aishell-1, and GigaSpeech datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of our CR-CTC. It significantly improves the CTC performance, achieving state-of-the-art results comparable to those attained by transducer or systems combining CTC and attention-based encoder-decoder (CTC/AED). We release our code at https://github.com/k2-fsa/icefall.
连接时序分类(CTC)是一种广泛应用于自动语音识别(ASR)的方法,以其简单性和计算效率而闻名。然而,它在识别性能上常常有所不足。在这项工作中,我们提出了一致性正则化CTC(CR-CTC),它强制输入语音梅尔频谱图的不同增强视图所获得的两个CTC分布之间的一致性。我们从以下三个角度对其核心行为进行了深入洞察:1)它在处理不同增强视图的随机子模型对之间进行自我蒸馏;2)它通过时间掩码区域内的位置进行掩码预测来学习上下文表示,尤其是当我们增加时间掩码的数量时;3)它抑制了极尖的CTC分布,从而减少过拟合,提高泛化能力。在LibriSpeech、Aishell-1和GigaSpeech数据集上的大量实验证明了我们的CR-CTC的有效性。它显著提高了CTC的性能,实现了与转换器或结合CTC和基于注意力的编码器解码器(CTC/AED)的系统所达到的最新技术成果相当的结果。我们在https://github.com/k2-fsa/icefall上发布了我们的代码。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Published as a conference paper at ICLR 2025
Summary
本文提出了一个名为Consistency-Regularized CTC(CR-CTC)的方法,用于改进自动语音识别(ASR)中的Connectionist Temporal Classification(CTC)方法的识别性能。该方法通过在不同增强视图下获取的两个CTC分布之间强制执行一致性,实现了自我蒸馏和上下文表示学习,并抑制了过于尖锐的CTC分布。实验表明,CR-CTC能显著提高CTC性能,达到与转换器或CTC与基于注意力的编码器解码器(CTC/AED)相结合的系统相当的水平。
Key Takeaways
- Consistency-Regularized CTC (CR-CTC) 是对自动语音识别(ASR)中广泛使用的Connectionist Temporal Classification(CTC)方法的改进。
- CR-CTC 通过在不同增强视图下获取的两个 CTC 分布之间强制执行一致性,实现了性能提升。
- CR-CTC 实现了自我蒸馏和上下文表示学习,通过随机子模型处理不同增强视图进行自我蒸馏,并学习时间遮挡区域内的上下文表示。
- CR-CTC 抑制了过于尖锐的 CTC 分布,从而减少过拟合并提高泛化能力。
- 实验表明,CR-CTC 在 LibriSpeech、Aishell-1 和 GigaSpeech 数据集上均能有效提高 CTC 性能。
- CR-CTC 达到与当前最佳水平相当的结果,如转换器或结合 CTC 和基于注意力的编码器解码器(CTC/AED)的系统。
点此查看论文截图

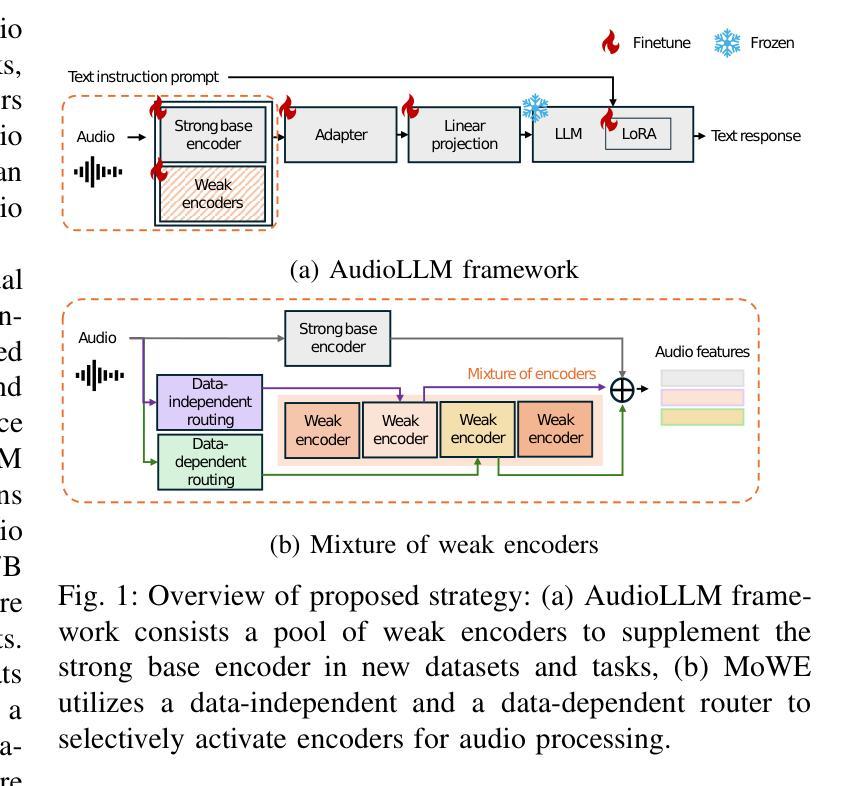
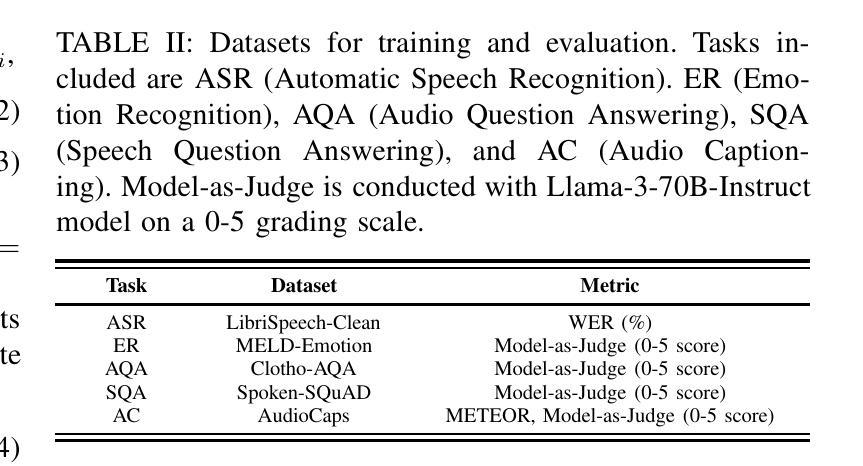
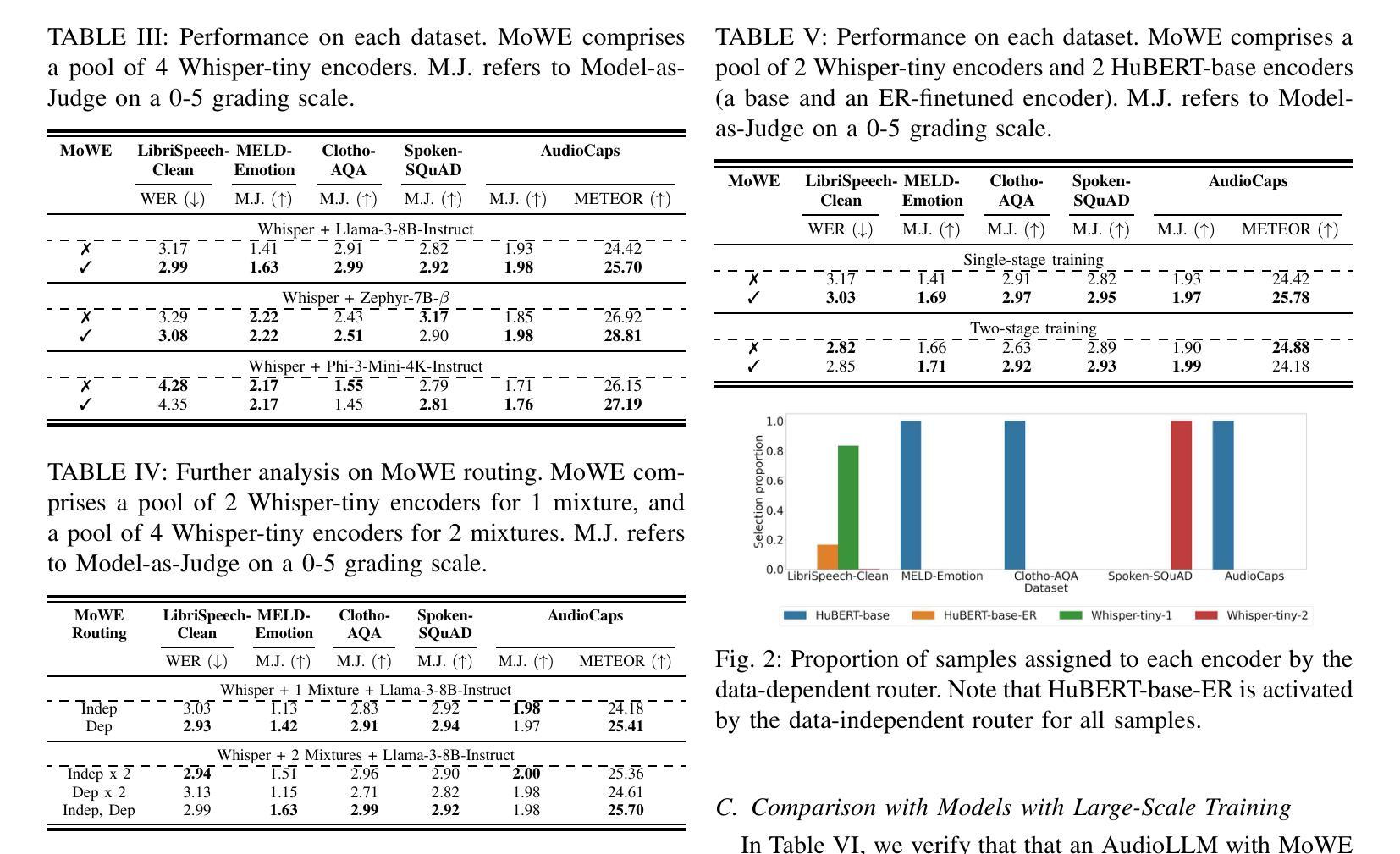
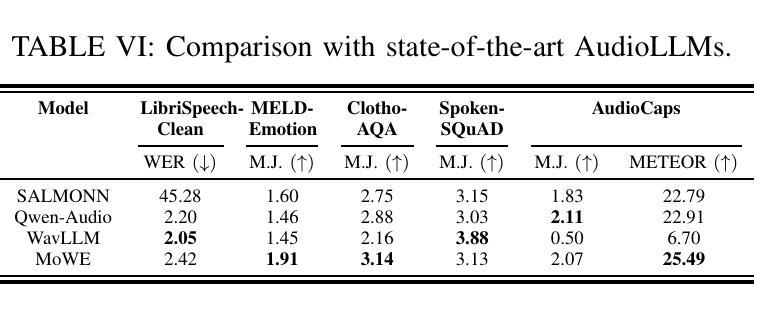
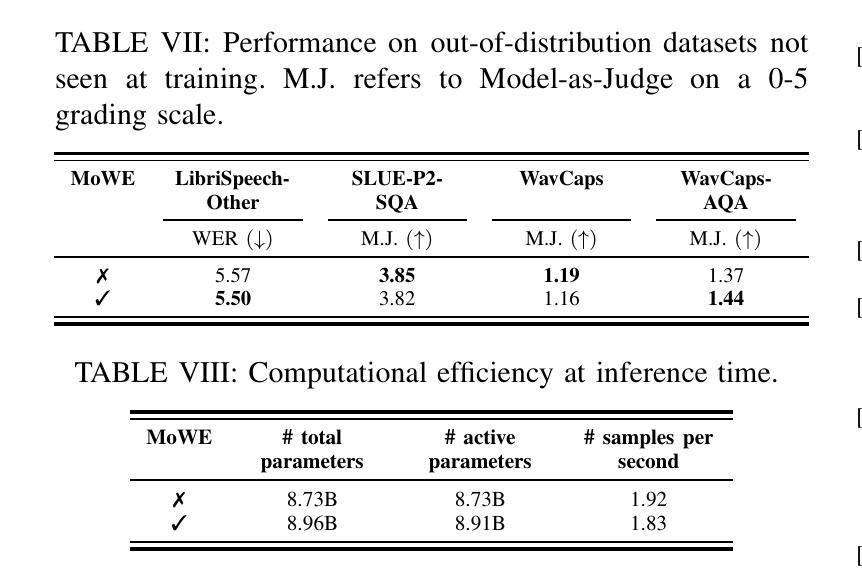
MoWE-Audio: Multitask AudioLLMs with Mixture of Weak Encoders
Authors:Wenyu Zhang, Shuo Sun, Bin Wang, Xunlong Zou, Zhuohan Liu, Yingxu He, Geyu Lin, Nancy F. Chen, Ai Ti Aw
The rapid advancements in large language models (LLMs) have significantly enhanced natural language processing capabilities, facilitating the development of AudioLLMs that process and understand speech and audio inputs alongside text. Existing AudioLLMs typically combine a pre-trained audio encoder with a pre-trained LLM, which are subsequently finetuned on specific audio tasks. However, the pre-trained audio encoder has constrained capacity to capture features for new tasks and datasets. To address this, we propose to incorporate mixtures of `weak’ encoders (MoWE) into the AudioLLM framework. MoWE supplements a base encoder with a pool of relatively light weight encoders, selectively activated based on the audio input to enhance feature extraction without significantly increasing model size. Our empirical results demonstrate that MoWE effectively improves multi-task performance, broadening the applicability of AudioLLMs to more diverse audio tasks.
随着大型语言模型(LLM)的快速发展,自然语言处理能力得到了极大的提升,推动了处理和理解语音和音频输入的AudioLLM的发展。现有的AudioLLM通常将预训练的音频编码器与预训练的LLM相结合,随后在特定的音频任务上进行微调。然而,预训练的音频编码器在捕获新任务和数据集的特征方面存在局限性。为了解决这一问题,我们提出在AudioLLM框架中融入“弱编码器混合物”(MoWE)。MoWE以基本编码器为基础,辅以一组相对轻量级的编码器池,根据音频输入进行选择激活,以增强特征提取能力,同时不会显著增加模型大小。我们的实证结果表明,MoWE有效提高多任务性能,拓宽了AudioLLM在更多不同音频任务中的应用范围。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to ICASSP 2025
Summary
大型语言模型(LLM)的快速发展显著提升了自然语言处理能力,促进了能够处理和理解语音和音频输入的AudioLLM的发展。针对现有AudioLLM中预训练音频编码器对新任务和数据集特征捕捉能力有限的问题,提出了混合弱编码器(MoWE)方法。MoWE以基本编码器为基础,辅以一组相对轻量级的编码器池,根据音频输入选择性激活,以增强特征提取能力,同时不显著增加模型大小。实验结果表明,MoWE有效提高多任务性能,拓宽AudioLLM在更多不同音频任务中的应用范围。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLM)提升自然语言处理能力。
- AudioLLM能够处理和理解语音和音频输入。
- 预训练音频编码器对新任务和数据集特征捕捉能力有限。
- MoWE方法通过混合弱编码器池提高AudioLLM性能。
- MoWE方法根据音频输入选择性激活编码器。
- MoWE有效增强特征提取能力,同时不显著增加模型大小。
点此查看论文截图

Wideband Relative Transfer Function (RTF) Estimation Exploiting Frequency Correlations
Authors:Giovanni Bologni, Richard C. Hendriks, Richard Heusdens
This article focuses on estimating relative transfer functions (RTFs) for beamforming applications. Traditional methods often assume that spectra are uncorrelated, an assumption that is often violated in practical scenarios due to factors such as time-domain windowing or the non-stationary nature of signals, as observed in speech. To overcome these limitations, we propose an RTF estimation technique that leverages spectral and spatial correlations through subspace analysis. Additionally, we derive Cram'er–Rao bounds (CRBs) for the RTF estimation task, providing theoretical insights into the achievable estimation accuracy. These bounds reveal that channel estimation can be performed more accurately if the noise or the target signal exhibits spectral correlations. Experiments with both real and synthetic data show that our technique outperforms the narrowband maximum-likelihood estimator, known as covariance whitening (CW), when the target exhibits spectral correlations. Although the proposed algorithm generally achieves accuracy close to the theoretical bound, there is potential for further improvement, especially in scenarios with highly spectrally correlated noise. While channel estimation has various applications, we demonstrate the method using a minimum variance distortionless (MVDR) beamformer for multichannel speech enhancement. A free Python implementation is also provided.
本文重点研究波束形成应用中相对传递函数(RTF)的估计。传统方法通常假设光谱不相关,但在实际场景中,由于时域窗口化或语音中的非平稳信号等因素,这一假设经常被违反。为了克服这些局限性,我们提出了一种利用子空间分析进行RTF估计的技术,该技术利用光谱和空间相关性。此外,我们还推导出了RTF估计任务的Cramér-Rao界(CRBs),为估计精度的可实现性提供了理论见解。这些界限表明,如果噪声或目标信号表现出光谱相关性,则可以进行更准确的信道估计。使用真实和合成数据的实验表明,当目标表现出光谱相关性时,我们的技术优于窄带最大似然估计器,称为协方差白化(CW)。虽然所提算法一般能达到接近理论界限的精度,但在光谱相关性高的噪声场景中仍有进一步改进的潜力。虽然信道估计有多种应用,但我们使用最小方差无失真(MVDR)波束形成器进行多通道语音增强来展示该方法。还提供了免费的Python实现。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted version
Summary
本文提出一种利用谱和空域相关性通过子空间分析估计相对传递函数(RTFs)的方法,用于波束形成应用。针对传统方法假设谱不相关在实际场景中经常失效的问题,我们提出一种新技术并推导出RTF估计任务的Cramér-Rao界(CRBs),为估计精度提供理论见解。实验表明,当目标表现出谱相关性时,我们的技术优于窄带最大似然估计器协方差白化(CW)。我们将该方法应用于多通道语音增强的最小方差无失真(MVDR)波束形成器进行演示。
Key Takeaways
- 文章聚焦于波束形成中的相对传递函数(RTFs)估计问题。
- 传统方法假设谱不相关,但在实际场景中这一假设经常不成立。
- 提出一种利用谱和空域相关性通过子空间分析的RTF估计技术。
- 推导了Cramér-Rao界(CRBs)以了解可达到的估计精度。
- 当目标信号表现出谱相关性时,新技术优于传统的协方差白化(CW)方法。
- 技术应用于多通道语音增强的最小方差无失真(MVDR)波束形成器进行演示。
点此查看论文截图

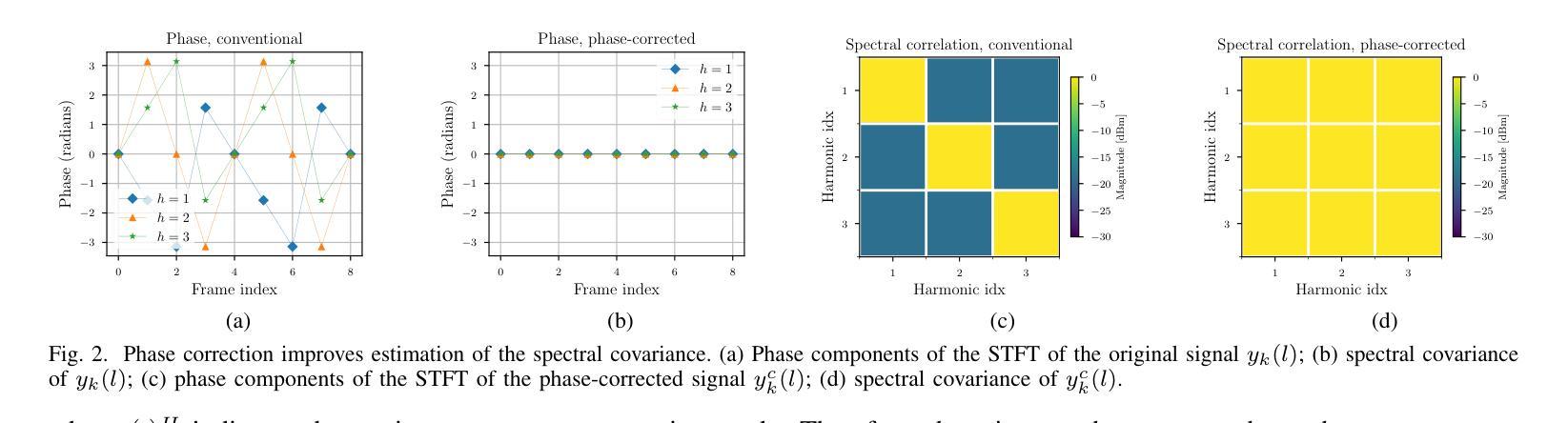
DiTTo-TTS: Diffusion Transformers for Scalable Text-to-Speech without Domain-Specific Factors
Authors:Keon Lee, Dong Won Kim, Jaehyeon Kim, Seungjun Chung, Jaewoong Cho
Large-scale latent diffusion models (LDMs) excel in content generation across various modalities, but their reliance on phonemes and durations in text-to-speech (TTS) limits scalability and access from other fields. While recent studies show potential in removing these domain-specific factors, performance remains suboptimal. In this work, we introduce DiTTo-TTS, a Diffusion Transformer (DiT)-based TTS model, to investigate whether LDM-based TTS can achieve state-of-the-art performance without domain-specific factors. Through rigorous analysis and empirical exploration, we find that (1) DiT with minimal modifications outperforms U-Net, (2) variable-length modeling with a speech length predictor significantly improves results over fixed-length approaches, and (3) conditions like semantic alignment in speech latent representations are key to further enhancement. By scaling our training data to 82K hours and the model size to 790M parameters, we achieve superior or comparable zero-shot performance to state-of-the-art TTS models in naturalness, intelligibility, and speaker similarity, all without relying on domain-specific factors. Speech samples are available at https://ditto-tts.github.io.
大规模潜在扩散模型(LDM)在多模态内容生成方面表现出色,但它们在文本到语音(TTS)中对音素和持续时间的依赖限制了其可扩展性和其他领域的访问。尽管最近的研究显示去除这些领域特定因素具有潜力,但性能仍然不尽人意。在这项工作中,我们引入了基于扩散变压器(DiT)的TTS模型DiTTo-TTS,旨在研究基于LDM的TTS是否能在不依赖领域特定因素的情况下达到最先进的性能。通过严格的分析和实证探索,我们发现(1)DiT在最小修改的情况下优于U-Net,(2)使用语音长度预测的可变长度建模显著改善了结果,优于固定长度的方法,(3)语音潜在表示中的语义对齐等条件是进一步改进的关键。通过将训练数据扩展到8.2万小时和模型大小扩展到7.9亿参数,我们在自然度、清晰度和说话人相似性方面达到了或超越了现有最先进的TTS模型的零样本性能,所有这些都不依赖于领域特定因素。语音样本可在https://ditto-tts.github.io上找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了基于Diffusion Transformer(DiT)的文本转语音(TTS)模型DiTTo-TTS,该模型在大规模潜在扩散模型(LDM)的基础上,实现了无需特定领域因素即可达到或超过现有TTS模型性能的效果。通过改进模型和扩大训练数据和模型规模,该模型在自然度、清晰度和说话人相似性方面表现优越。
Key Takeaways
- DiTTo-TTS模型基于Diffusion Transformer(DiT),旨在解决大规模潜在扩散模型在文本转语音(TTS)中的领域特定因素依赖问题。
- DiT模型在最小修改的情况下优于U-Net模型,验证了Diffusion Transformer在TTS任务中的有效性。
- 通过引入可变长度建模和语音长度预测器,显著提高了模型性能,优于固定长度方法。
- 语义对齐等条件在语音潜在表示中对于进一步提高性能至关重要。
- 通过扩大训练数据至82K小时和模型规模至790M参数,DiTTo-TTS实现了零样本性能,在自然度、清晰度和说话人相似性方面与最佳TTS模型相当或更优。
- 该模型的性能提升未依赖特定的领域因素,具有广泛的应用潜力。
点此查看论文截图

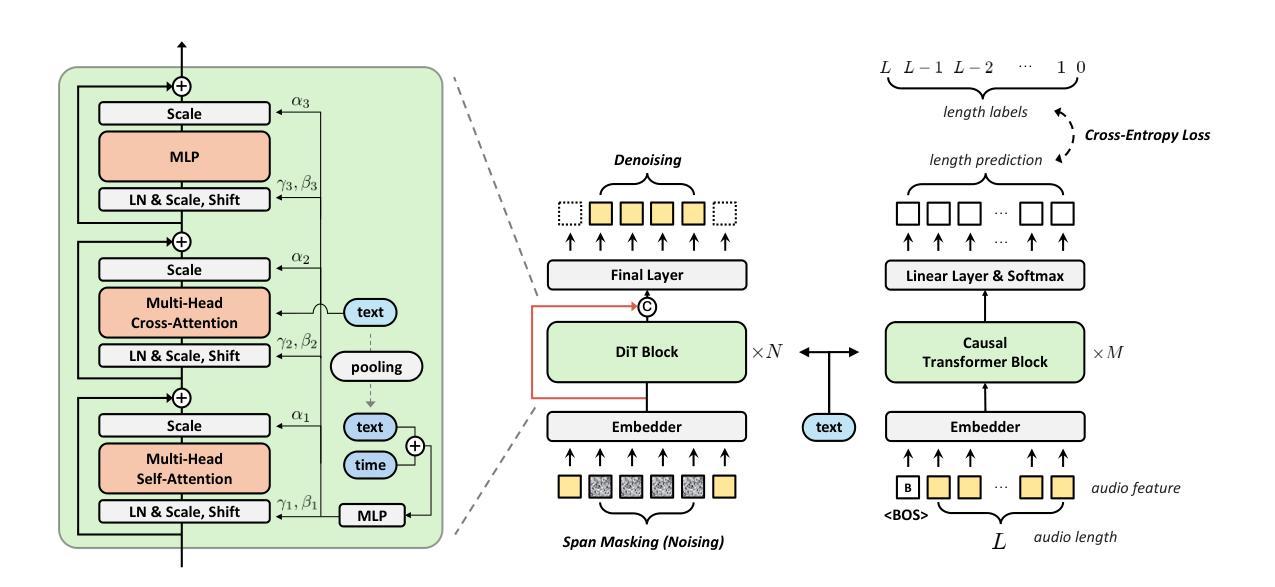
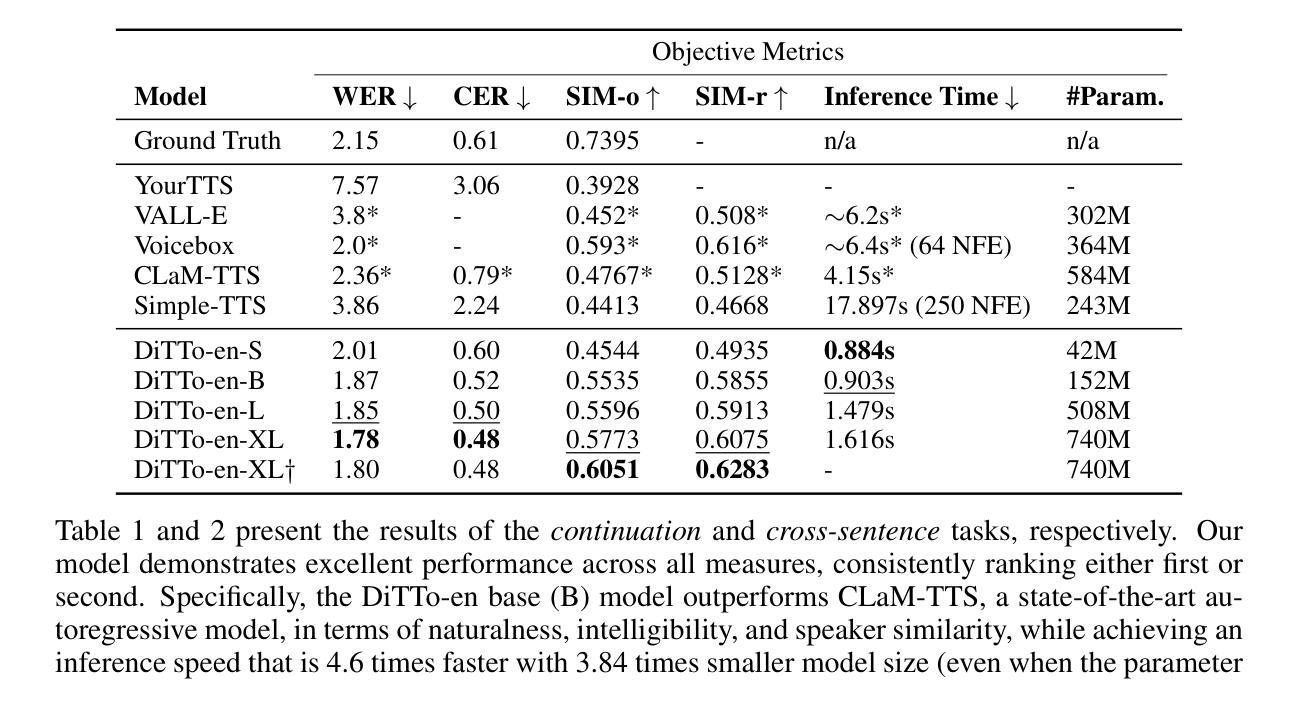
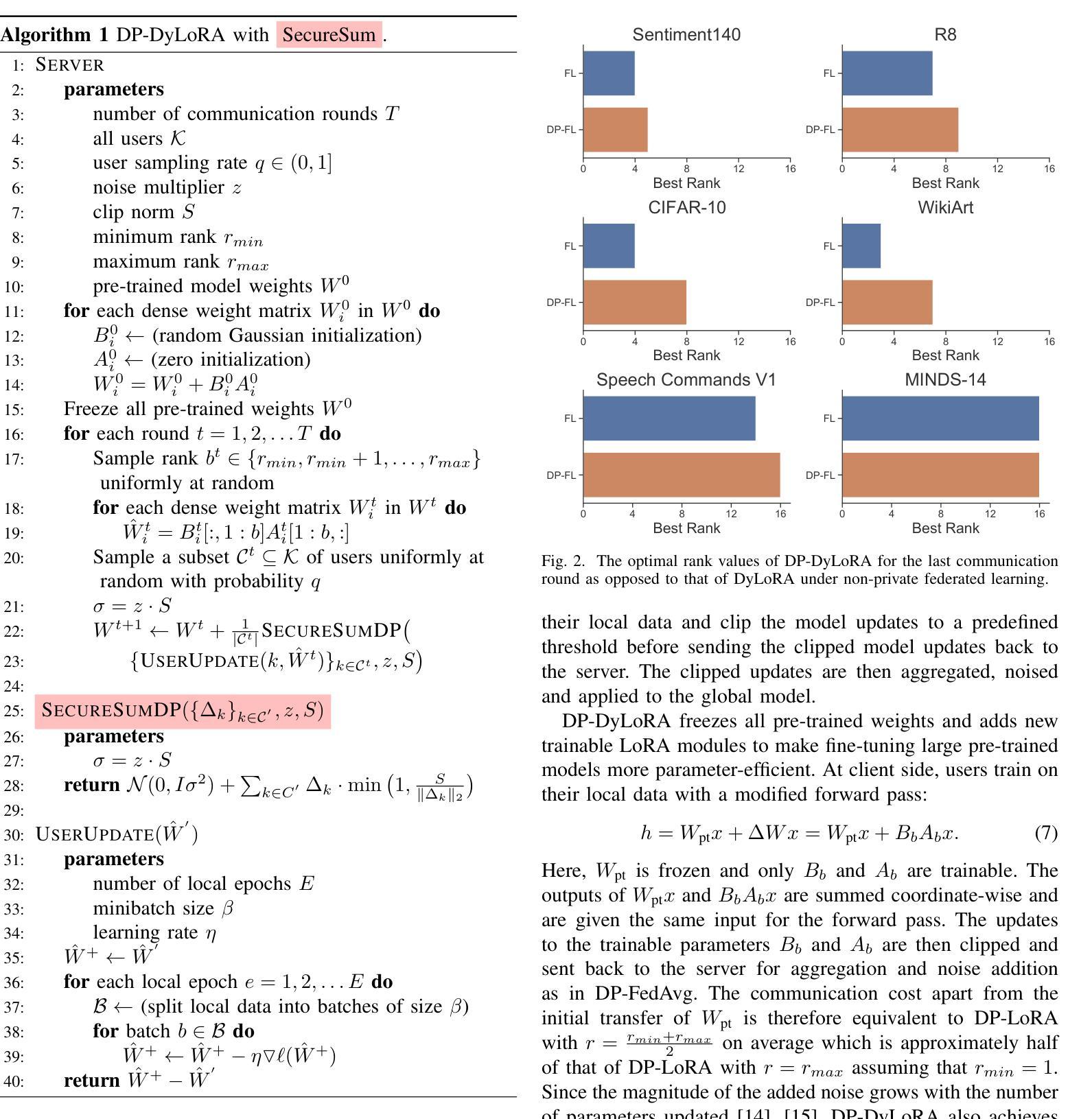
DP-DyLoRA: Fine-Tuning Transformer-Based Models On-Device under Differentially Private Federated Learning using Dynamic Low-Rank Adaptation
Authors:Jie Xu, Karthikeyan Saravanan, Rogier van Dalen, Haaris Mehmood, David Tuckey, Mete Ozay
Federated learning (FL) allows clients to collaboratively train a global model without sharing their local data with a server. However, clients’ contributions to the server can still leak sensitive information. Differential privacy (DP) addresses such leakage by providing formal privacy guarantees, with mechanisms that add randomness to the clients’ contributions. The randomness makes it infeasible to train large transformer-based models, common in modern federated learning systems. In this work, we empirically evaluate the practicality of fine-tuning large scale on-device transformer-based models with differential privacy in a federated learning system. We conduct comprehensive experiments on various system properties for tasks spanning a multitude of domains: speech recognition, computer vision (CV) and natural language understanding (NLU). Our results show that full fine-tuning under differentially private federated learning (DP-FL) generally leads to huge performance degradation which can be alleviated by reducing the dimensionality of contributions through parameter-efficient fine-tuning (PEFT). Our benchmarks of existing DP-PEFT methods show that DP-Low-Rank Adaptation (DP-LoRA) consistently outperforms other methods. An even more promising approach, DyLoRA, which makes the low rank variable, when naively combined with FL would straightforwardly break differential privacy. We therefore propose an adaptation method that can be combined with differential privacy and call it DP-DyLoRA. Finally, we are able to reduce the accuracy degradation and word error rate (WER) increase due to DP to less than 2% and 7% respectively with 1 million clients and a stringent privacy budget of $\epsilon=2$.
联邦学习(FL)允许客户端在无需将本地数据分享给服务器的情况下共同训练全球模型。然而,客户端对服务器的贡献仍然可能泄露敏感信息。差分隐私(DP)通过提供正式的隐私保证来解决此类泄露问题,其机制会为客户端的贡献增加随机性。这种随机性使得在联邦学习系统中训练基于大型变换模型的方案不可行,而这种模型在现代联邦学习系统中很常见。在这项工作中,我们从实证角度评估了在联邦学习系统中对基于大型变换模型的设备进行微调与差分隐私的实用性。我们在涵盖多个领域的任务上对各种系统属性进行了全面的实验,包括语音识别、计算机视觉(CV)和自然语言理解(NLU)。我们的结果表明,在差分私有联邦学习(DP-FL)下进行全面微调通常会导致巨大的性能下降,这可以通过通过参数高效微调(PEFT)减少贡献的维度来缓解。我们对现有的DP-PEFT方法的基准测试显示,DP-Low-Rank Adaptation(DP-LoRA)始终优于其他方法。一种更有前途的方法是将低等级变量DyLoRA化,但简单地与FL结合将直接破坏差分隐私。因此,我们提出了一种可以与差分隐私相结合的方法,称之为DP-DyLoRA。最后,在拥有1百万客户端和严格的隐私预算ε=2的情况下,我们能够将由于DP导致的准确性下降和单词错误率(WER)上升分别降低到不到2%和7%。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 16 pages, 10 figures, 5 tables
摘要
本文研究了在联邦学习系统中,对大规模设备上基于转换器的模型进行微调与差分隐私结合的实际应用。通过实验,发现差分私有联邦学习(DP-FL)下的全量微调会导致性能大幅下降,可通过参数高效的微调(PEFT)降低贡献的维度来缓解这一问题。文章评估了现有的DP-PEFT方法,发现DP-Low-Rank Adaptation(DP-LoRA)表现最佳。然而,当与联邦学习结合时,更先进的DyLoRA方法会破坏差分隐私。因此,本文提出了一种可以与差分隐私结合使用的适应方法,称为DP-DyLoRA。最终,在严格的隐私预算下,使用这种方法能将由于差分隐私导致的精度下降和词错误率(WER)增加减少到不到2%和7%。
关键见解
- 联邦学习允许客户端在没有将数据分享给服务器的情况下共同训练全局模型,但客户端对服务器的贡献仍然可能泄露敏感信息。
- 差分隐私通过为客户端的贡献增加随机性来解决此类泄露问题,但这对于现代联邦学习系统中常见的基于大型转换模型的训练来说并不实用。
- 全量微调在差分私有联邦学习(DP-FL)中会导致性能大幅下降,可通过参数高效的微调(PEFT)降低贡献的维度来缓解。
- DP-Low-Rank Adaptation(DP-LoRA)在现有的DP-PEFT方法中表现最佳。
- 更先进的DyLoRA方法若直接结合联邦学习会破坏差分隐私。
- 提出了一种新的方法DP-DyLoRA,旨在结合差分隐私,减少由于差分隐私导致的性能损失。
点此查看论文截图