⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-02-19 更新
Adversarially Robust CLIP Models Can Induce Better (Robust) Perceptual Metrics
Authors:Francesco Croce, Christian Schlarmann, Naman Deep Singh, Matthias Hein
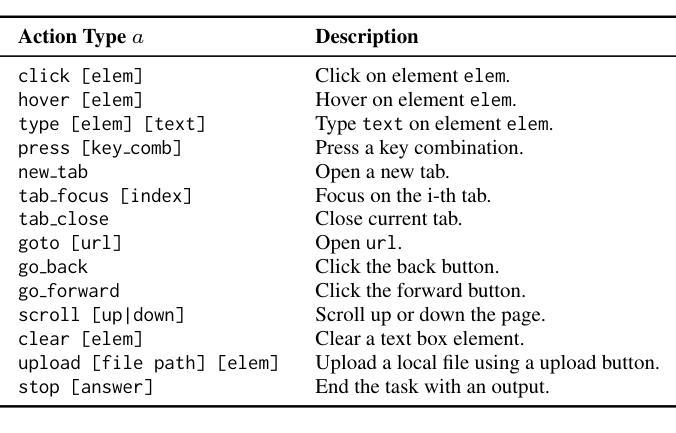
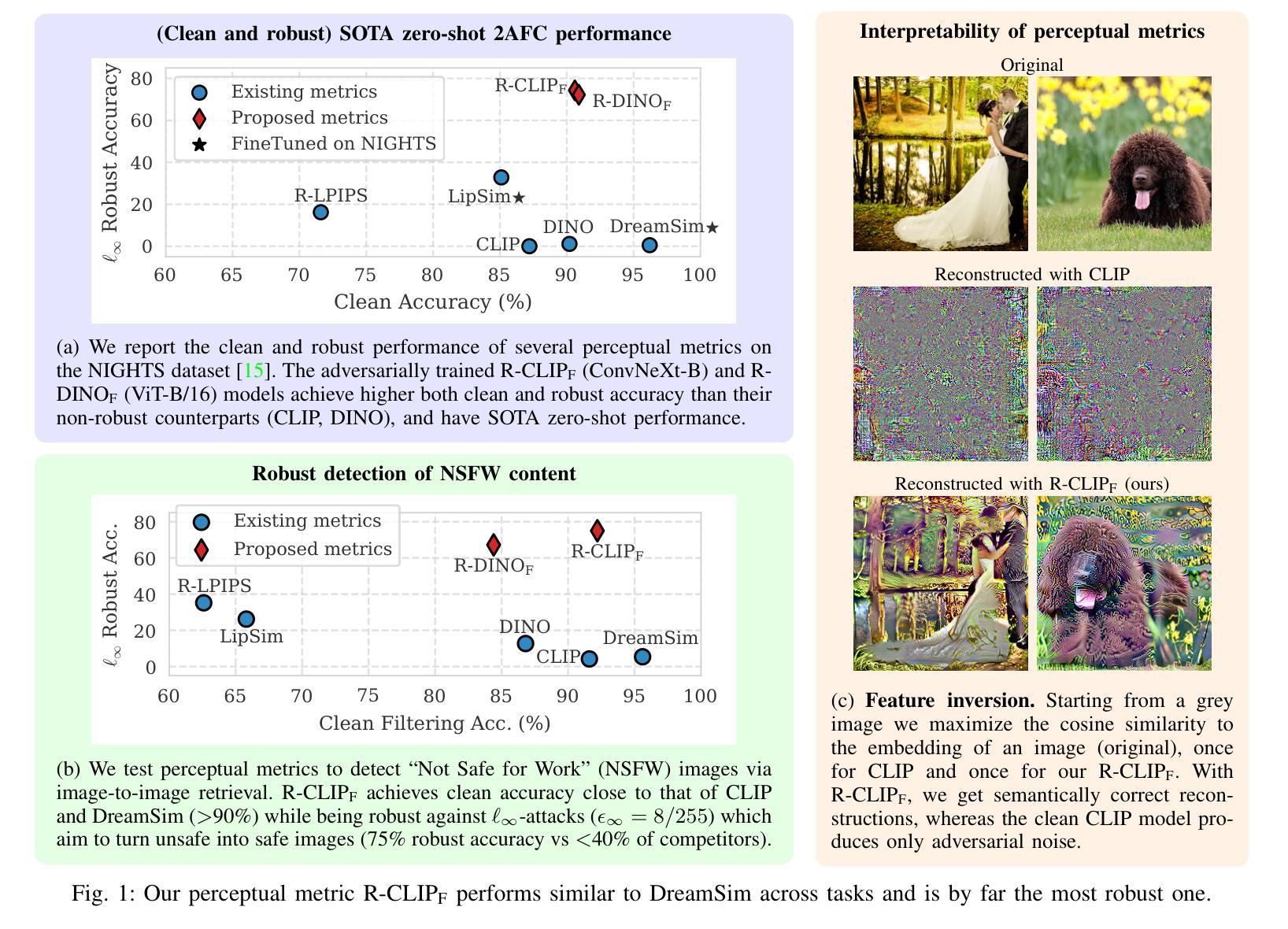
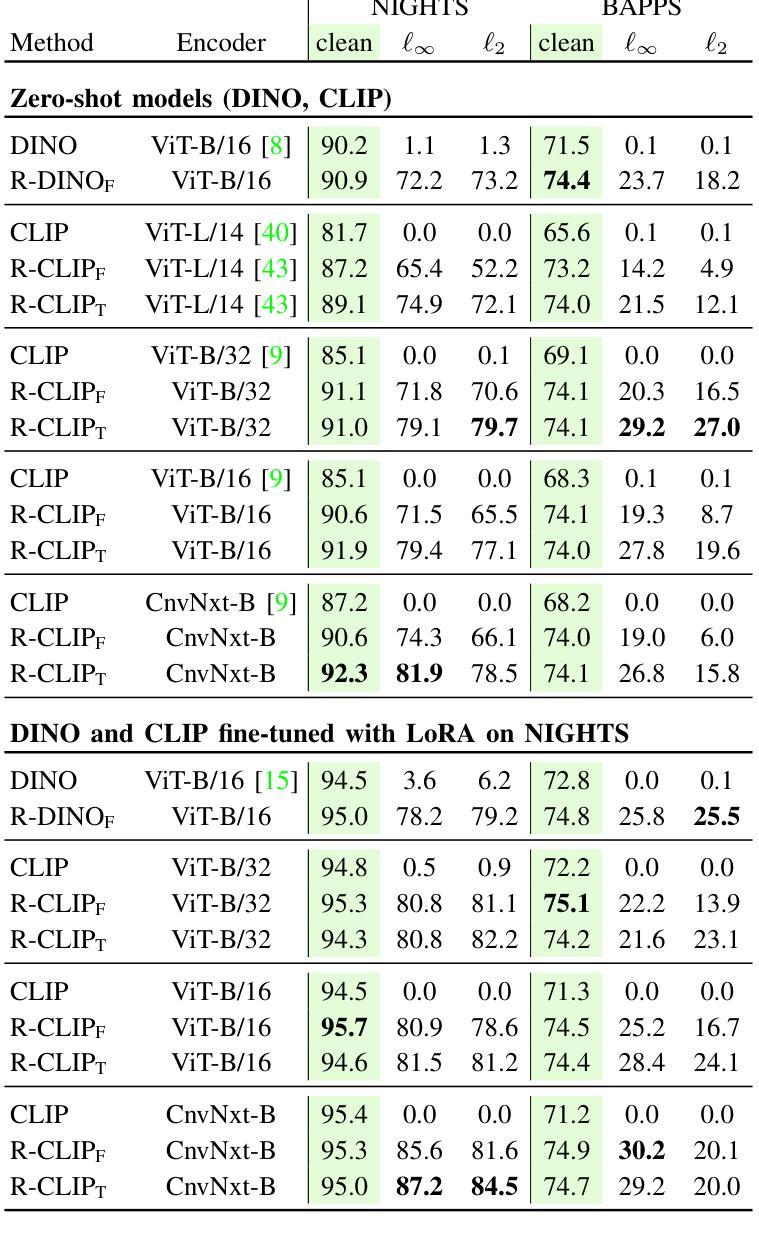
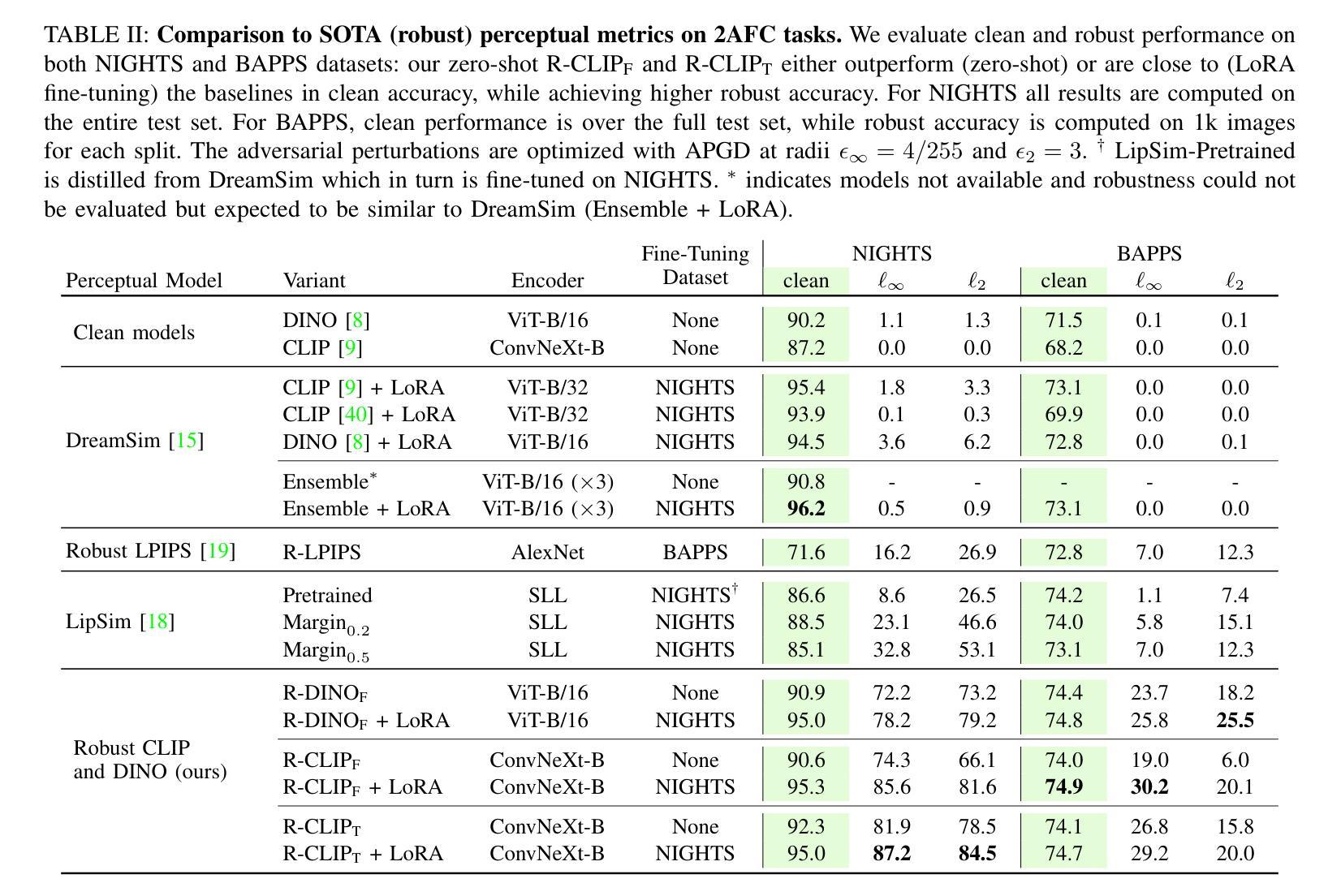
Measuring perceptual similarity is a key tool in computer vision. In recent years perceptual metrics based on features extracted from neural networks with large and diverse training sets, e.g. CLIP, have become popular. At the same time, the metrics extracted from features of neural networks are not adversarially robust. In this paper we show that adversarially robust CLIP models, called R-CLIP$_\textrm{F}$, obtained by unsupervised adversarial fine-tuning induce a better and adversarially robust perceptual metric that outperforms existing metrics in a zero-shot setting, and further matches the performance of state-of-the-art metrics while being robust after fine-tuning. Moreover, our perceptual metric achieves strong performance on related tasks such as robust image-to-image retrieval, which becomes especially relevant when applied to “Not Safe for Work” (NSFW) content detection and dataset filtering. While standard perceptual metrics can be easily attacked by a small perturbation completely degrading NSFW detection, our robust perceptual metric maintains high accuracy under an attack while having similar performance for unperturbed images. Finally, perceptual metrics induced by robust CLIP models have higher interpretability: feature inversion can show which images are considered similar, while text inversion can find what images are associated to a given prompt. This also allows us to visualize the very rich visual concepts learned by a CLIP model, including memorized persons, paintings and complex queries.
在计算机视觉中,衡量感知相似性是一项关键工具。近年来,基于从大型和多样化训练集中提取的特征的神经网络感知度量方法,例如CLIP,已经变得非常流行。然而同时,从神经网络特征中提取的指标并不具备对抗稳健性。本文中,我们展示了通过对抗性无监督微调获得的对抗性稳健CLIP模型(称为R-CLIPF)能够诱导出更好的对抗性稳健感知度量方法。在零样本设置下,该度量方法优于现有度量方法,并且在微调后匹配了最先进的度量方法的性能。此外,我们的感知度量在相关任务上表现强劲,如稳健的图像检索,这在应用于“不适合工作”(NSFW)内容检测和数据集过滤时尤其重要。虽然标准感知度量很容易受到微小扰动的影响而完全破坏NSFW检测,但我们的稳健感知度量在受到攻击时仍能维持高准确性,同时对未受扰动图像的性能相似。最后,由稳健CLIP模型诱导的感知度量具有更高的可解释性:特征反转可以显示哪些图像被视为相似,而文本反转可以找到与给定提示相关联的图像。这也让我们能够可视化CLIP模型学习的丰富视觉概念,包括记忆的人物、画作和复杂查询。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF This work has been accepted for publication in the IEEE Conference on Secure and Trustworthy Machine Learning (SaTML). The final version will be available on IEEE Xplore
Summary
基于神经网络的特征提取技术成为了计算机视觉中测量感知相似性的关键工具。最新研究表明,通过对抗鲁棒CLIP模型(称为R-CLIP$_F$)进行无监督对抗微调,可以得到更好的对抗鲁棒感知度量,它在零样本设置中的表现优于现有度量方法,并在微调后依然保持鲁棒性。此外,该感知度量在相关任务(如鲁棒图像到图像检索)上表现出色,特别是在“非安全工作环境”(NSFW)内容检测和筛选应用中尤为重要。相较于传统感知度量容易被攻击的问题,我们的鲁棒感知度量在被攻击时仍能维持高精确度,同时在不受干扰的图像上表现良好。最后,鲁棒CLIP模型诱导的感知度量具备更高的可解释性,通过特征反转可以展示哪些图像被视为相似,文本反转则能找到与给定提示相关的图像。这使我们能够可视化CLIP模型学到的丰富视觉概念。
Key Takeaways
- 对抗鲁棒CLIP模型(R-CLIP$_F$)通过无监督对抗微调提供更佳的感知度量。
- 该感知度量在零样本设置中具有优异表现,并能在微调后保持鲁棒性。
- 鲁棒感知度量在相关任务如图像检索中表现优越,特别是在NSFW内容检测和筛选方面更具实际意义。
- 对比传统感知度量,鲁棒感知度量在遭受攻击时仍能维持高精确度。
- 鲁棒CLIP模型诱导的感知度量具备高可解释性,能通过特征反转和文本反转展示模型的视觉概念学习。
- 该技术能可视化复杂查询和记忆中的图像概念,如人物、画作等。
点此查看论文截图

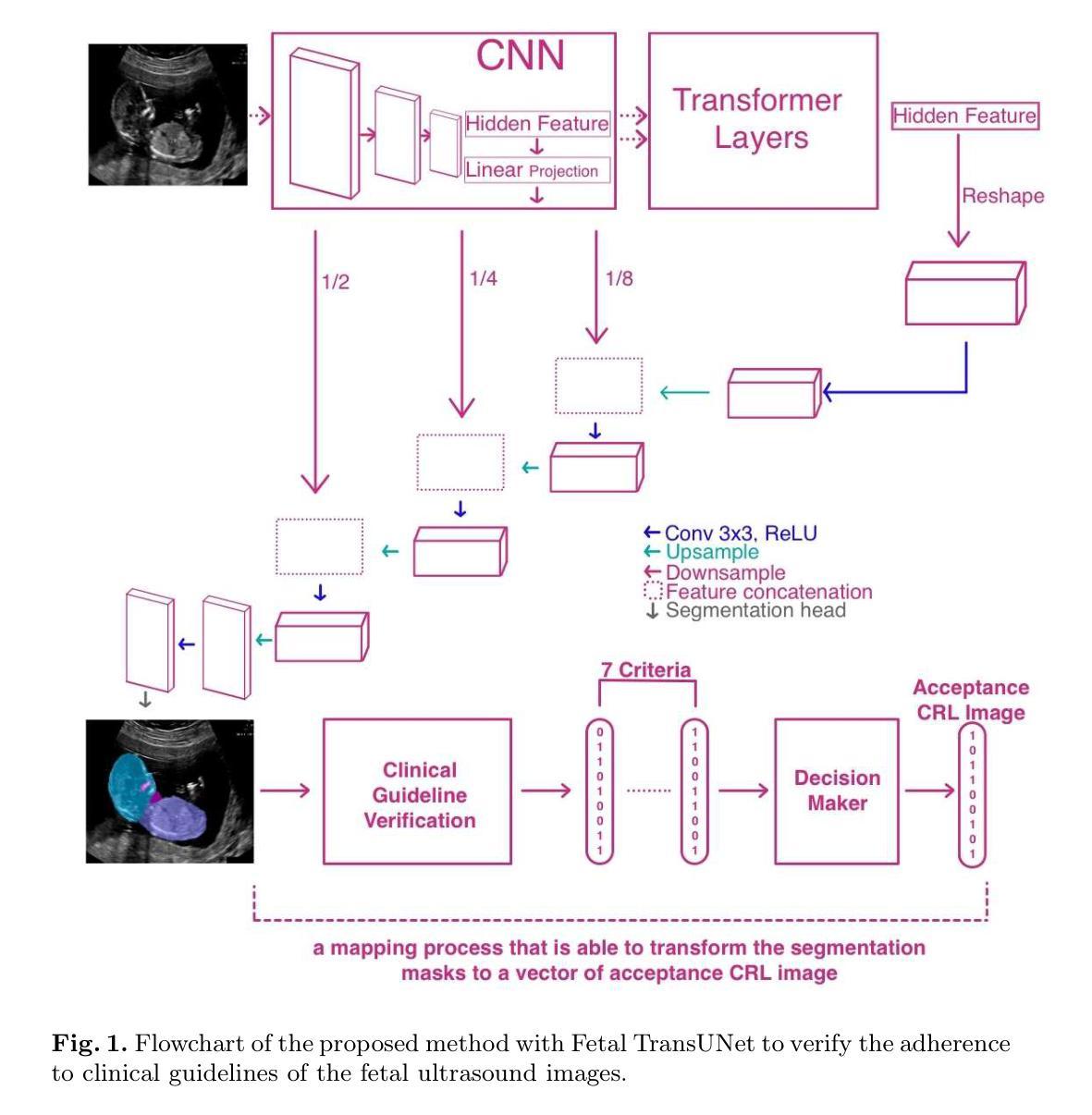
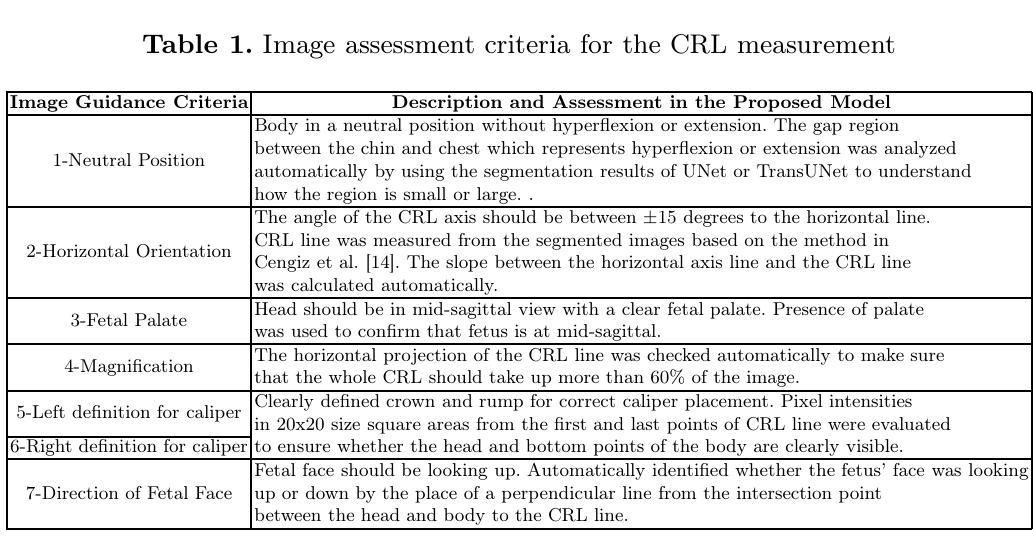
Automatic Quality Assessment of First Trimester Crown-Rump-Length Ultrasound Images
Authors:Sevim Cengiz, Ibraheem Hamdi, Mohammad Yaqub
Fetal gestational age (GA) is vital clinical information that is estimated during pregnancy in order to assess fetal growth. This is usually performed by measuring the crown-rump-length (CRL) on an ultrasound image in the Dating scan which is then correlated with fetal age and growth trajectory. A major issue when performing the CRL measurement is ensuring that the image is acquired at the correct view, otherwise it could be misleading. Although clinical guidelines specify the criteria for the correct CRL view, sonographers may not regularly adhere to such rules. In this paper, we propose a new deep learning-based solution that is able to verify the adherence of a CRL image to clinical guidelines in order to assess image quality and facilitate accurate estimation of GA. We first segment out important fetal structures then use the localized structures to perform a clinically-guided mapping that verifies the adherence of criteria. The segmentation method combines the benefits of Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) and the Vision Transformer (ViT) to segment fetal structures in ultrasound images and localize important fetal landmarks. For segmentation purposes, we compare our proposed work with UNet and show that our CNN/ViT-based method outperforms an optimized version of UNet. Furthermore, we compare the output of the mapping with classification CNNs when assessing the clinical criteria and the overall acceptability of CRL images. We show that the proposed mapping is not only explainable but also more accurate than the best performing classification CNNs.
胎儿胎龄(GA)是孕期评估胎儿生长的重要临床信息。这通常通过在超声检查时测量头臀长(CRL)来完成,然后将测量的结果与胎儿的年龄和生长轨迹进行关联。在进行CRL测量时面临的一个主要问题是确保获取的图像是符合标准的视角,否则可能会产生误导。虽然临床指南规定了正确的CRL视角的评估标准,但超声医生可能并不总是遵循这些规定。在本文中,我们提出了一种新的基于深度学习的解决方案,该方案能够验证CRL图像是否符合临床指南的规定,从而评估图像质量并有助于准确估算GA。我们首先对重要的胎儿结构进行分割,然后使用定位的结构进行临床指导映射,以验证是否满足标准。分割方法结合了卷积神经网络(CNN)和视觉转换器(ViT)的优点,用于分割超声图像中的胎儿结构并定位重要的胎儿地标。为了分割的目的,我们将所提出的工作与UNet进行了比较,并展示了我们的CNN/ViT方法优于优化后的UNet版本。此外,在评估临床标准和CRL图像的整体可接受性时,我们将映射的输出与分类CNN进行了比较。我们展示了所提出的映射不仅具有可解释性,而且比表现最佳的分类CNN更准确。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 9 pages, 2 figures
Summary
本文介绍了一种基于深度学习的解决方案,用于验证胎儿冠臀长(CRL)图像的采集是否符合临床指南规定,以提高图像质量并准确估计胎龄(GA)。该研究结合了卷积神经网络(CNN)和视觉转换器(ViT)对图像进行分割,识别重要胎儿结构并定位关键胎儿地标。研究发现,该方法在验证CRL图像是否符合临床指南方面表现出优异性能,相对于传统方法能提高估计GA的准确性。
Key Takeaways
- 胎龄(GA)的估计是孕期评估胎儿生长的重要临床信息。
2.CRL测量在评估胎龄中非常关键,但图像获取角度的正确性对测量结果的准确性至关重要。 - 虽然有临床指南规定CRL视图的标准,但超声医师可能并不总是遵循这些规则。
- 研究提出了一种基于深度学习的解决方案来验证CRL图像是否符合临床指南。
- 该方法结合了CNN和ViT进行图像分割,以识别和定位重要的胎儿结构和地标。
- 研究表明,该方法在验证CRL图像质量方面表现出卓越的性能。
点此查看论文截图

A CNN Approach to Automated Detection and Classification of Brain Tumors
Authors:Md. Zahid Hasan, Abdullah Tamim, D. M. Asadujjaman, Md. Mahfujur Rahman, Md. Abu Ahnaf Mollick, Nosin Anjum Dristi, Abdullah-Al-Noman
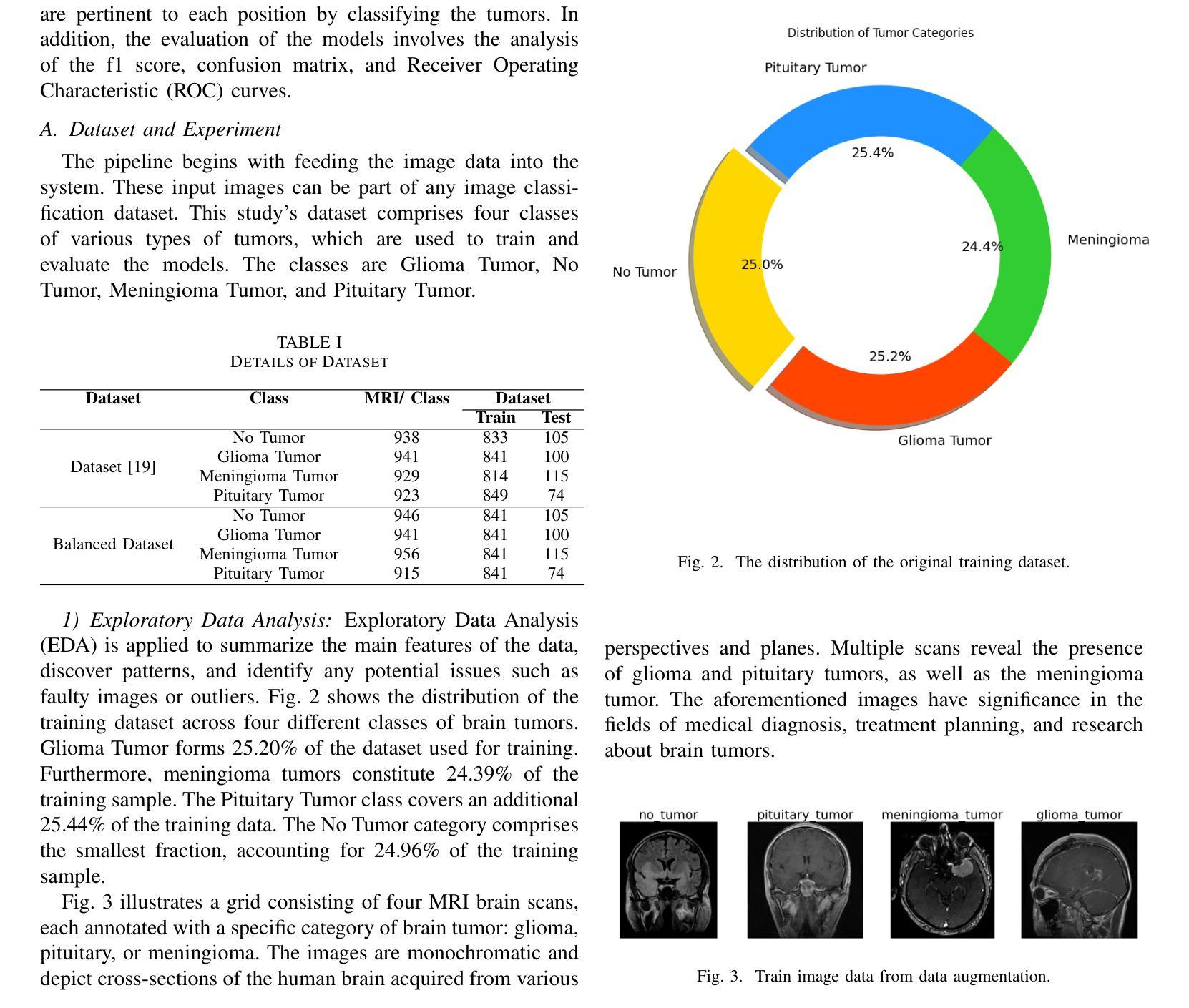
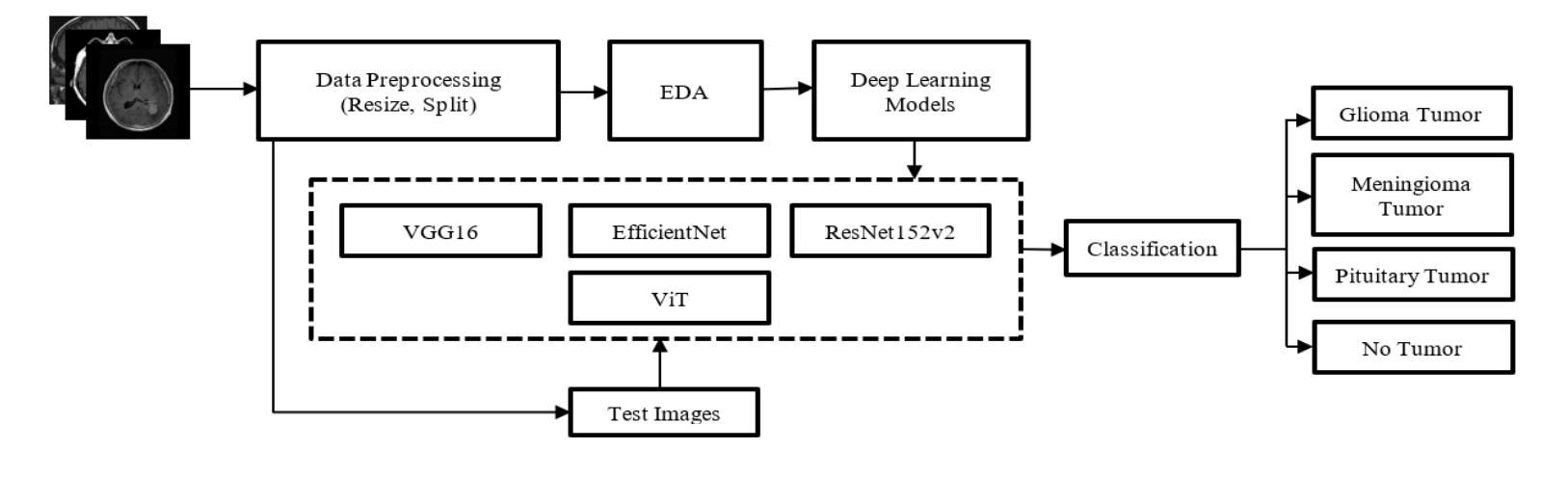
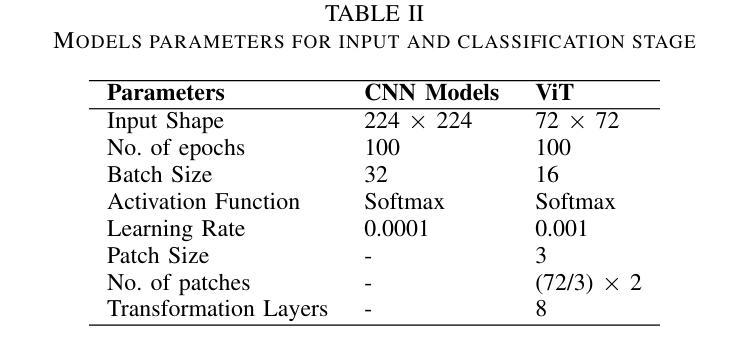
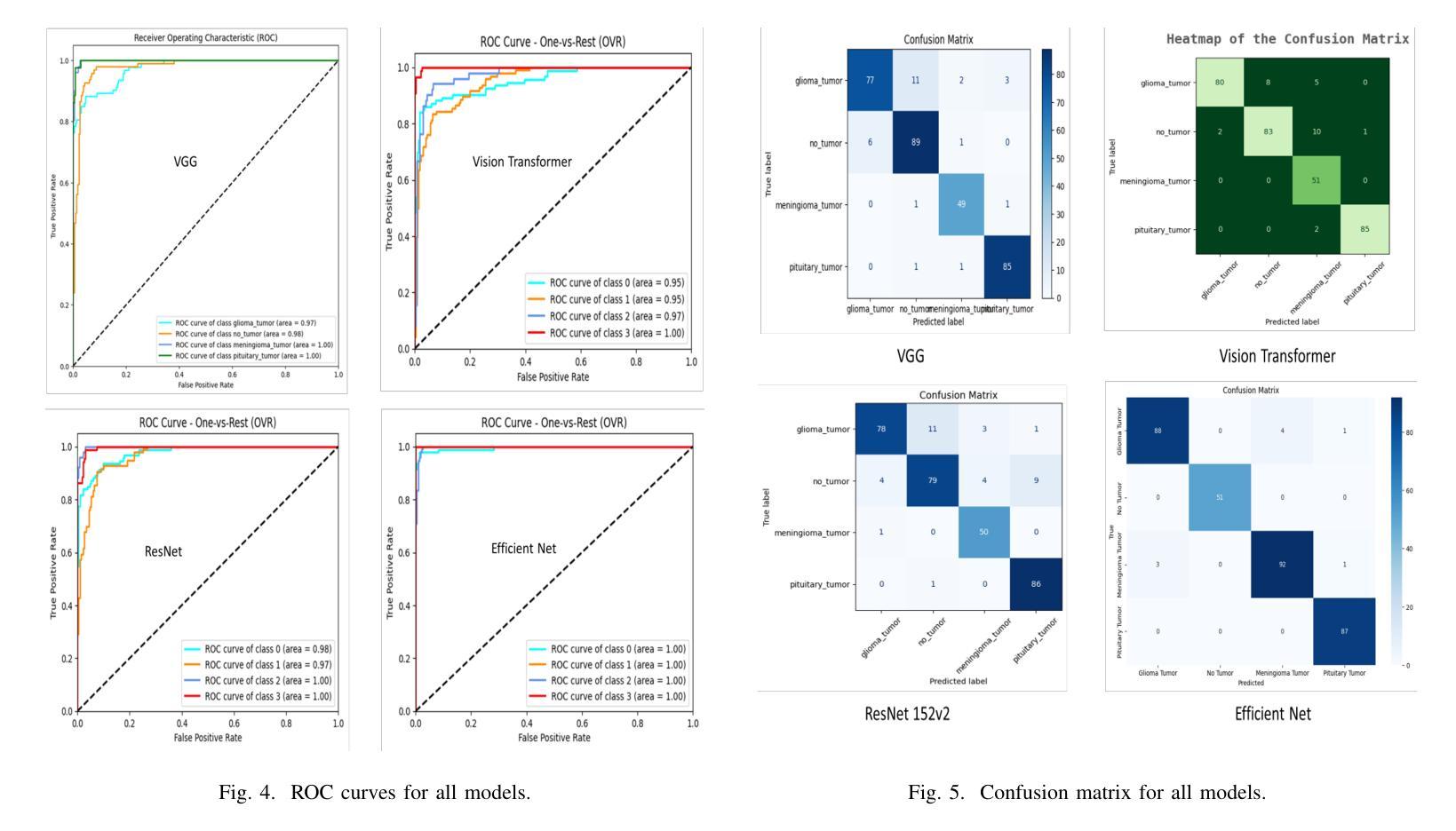
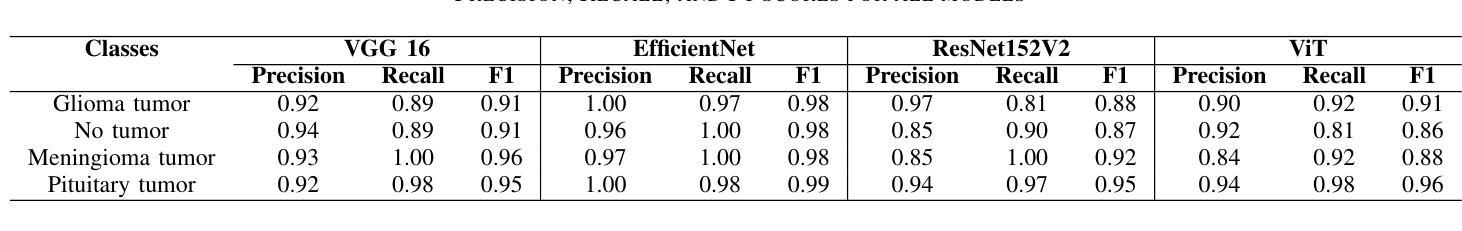
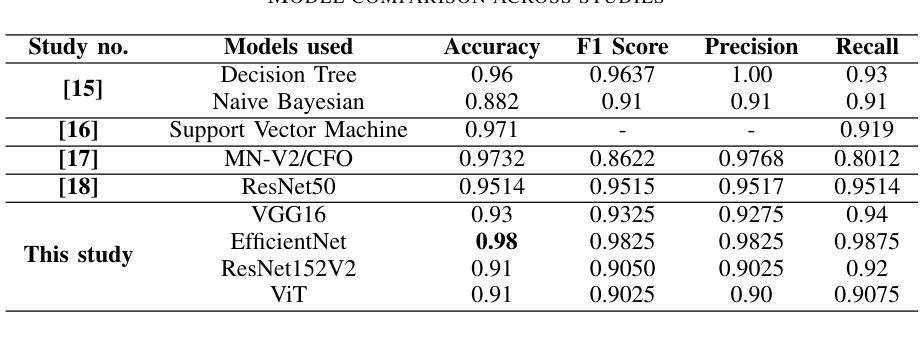
Brain tumors require an assessment to ensure timely diagnosis and effective patient treatment. Morphological factors such as size, location, texture, and variable appearance com- plicate tumor inspection. Medical imaging presents challenges, including noise and incomplete images. This research article presents a methodology for processing Magnetic Resonance Imag- ing (MRI) data, encompassing techniques for image classification and denoising. The effective use of MRI images allows medical professionals to detect brain disorders, including tumors. This research aims to categorize healthy brain tissue and brain tumors by analyzing the provided MRI data. Unlike alternative methods like Computed Tomography (CT), MRI technology offers a more detailed representation of internal anatomical components, mak- ing it a suitable option for studying data related to brain tumors. The MRI picture is first subjected to a denoising technique utilizing an Anisotropic diffusion filter. The dataset utilized for the models creation is a publicly accessible and validated Brain Tumour Classification (MRI) database, comprising 3,264 brain MRI scans. SMOTE was employed for data augmentation and dataset balancing. Convolutional Neural Networks(CNN) such as ResNet152V2, VGG, ViT, and EfficientNet were employed for the classification procedure. EfficientNet attained an accuracy of 98%, the highest recorded.
对脑肿瘤进行评估是确保及时诊断和治疗的关键。肿瘤的形态因素,如大小、位置、纹理和外观变化,使肿瘤检测变得复杂。医学成像面临噪声和图像不完整等挑战。这篇文章提出了一种处理磁共振成像(MRI)数据的方法,包括图像分类和去噪技术。有效地使用MRI图像可以让医疗专业人士检测包括肿瘤在内的脑部疾病。这项研究旨在通过分析提供的MRI数据来区分健康的大脑组织和脑肿瘤。与计算机断层扫描(CT)等替代方法不同,MRI技术提供更详细的内部解剖结构表示,使其成为研究脑肿瘤相关数据的理想选择。MRI图像首先采用各向异性扩散滤波器进行去噪处理。用于模型创建的数据集是公开可访问且经过验证的Brain Tumour Classification(MRI)数据库,包含3264个脑部MRI扫描。采用SMOTE进行数据增强和数据集平衡。卷积神经网络(CNN)如ResNet152V2、VGG、ViT和EfficientNet被用于分类过程。EfficientNet达到了98%的准确率,为目前记录的最高值。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了一种处理磁共振成像(MRI)数据的方法,旨在通过图像分类和去噪技术来检测脑部肿瘤。研究使用MRI图像来区分健康脑组织和脑部肿瘤,并使用公开验证的Brain Tumour Classification(MRI)数据库构建模型。采用卷积神经网络(CNN)进行分类,其中EfficientNet的准确率最高,达到98%。
Key Takeaways
- 研究关注于使用磁共振成像(MRI)数据处理方法,以检测并分类脑部肿瘤。
- 医学成像在肿瘤检测中面临噪声和图像不完整等挑战。
- 该研究使用了一种去噪技术,采用Anisotropic扩散滤波器处理MRI图像。
- 使用公开且经过验证的Brain Tumour Classification(MRI)数据库进行模型构建。
- 数据增强和平衡数据集采用了SMOTE方法。
- 研究采用了多种卷积神经网络(CNN)进行分类,包括ResNet152V2、VGG、ViT和EfficientNet。
点此查看论文截图

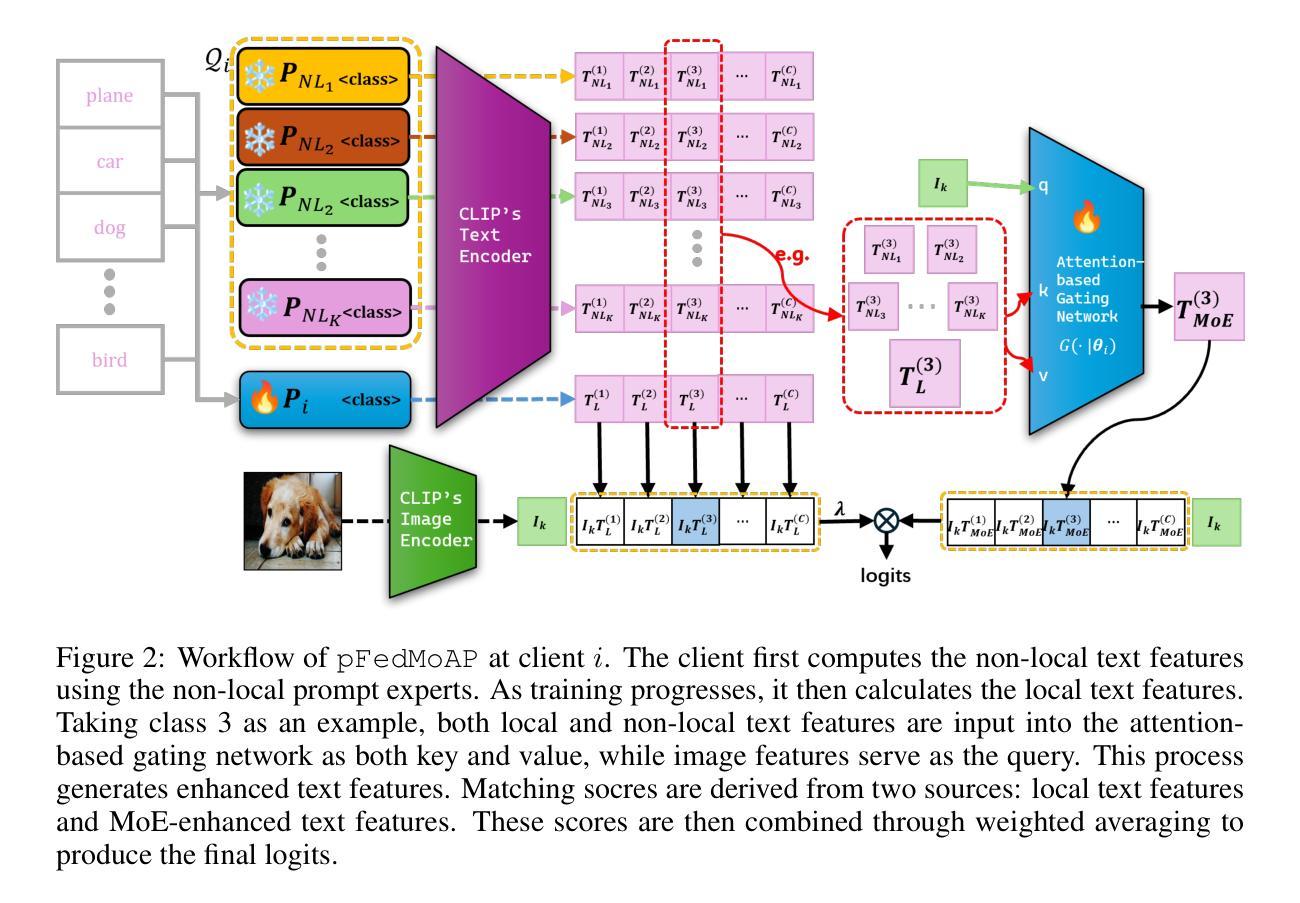
Mixture of Experts Made Personalized: Federated Prompt Learning for Vision-Language Models
Authors:Jun Luo, Chen Chen, Shandong Wu
Federated prompt learning benefits federated learning with CLIP-like Vision-Language Model’s (VLM’s) robust representation learning ability through prompt learning. However, current federated prompt learning methods are habitually restricted to the traditional FL paradigm, where the participating clients are generally only allowed to download a single globally aggregated model from the server. While justifiable for training full-sized models under federated settings, in this work, we argue that this paradigm is ill-suited for lightweight prompts. By facilitating the clients to download multiple pre-aggregated prompts as fixed non-local experts, we propose Personalized Federated Mixture of Adaptive Prompts (pFedMoAP), a novel FL framework that personalizes the prompt learning process through the lens of Mixture of Experts (MoE). pFedMoAP implements a local attention-based gating network that learns to generate enhanced text features for better alignment with local image data, benefiting from both local and downloaded non-local adaptive prompt experts. Extensive experiments on 9 datasets under various federated settings demonstrate the efficacy of the proposed pFedMoAP algorithm. The code is available at https://github.com/ljaiverson/pFedMoAP.
联邦提示学习通过提示学习能力提升了联邦学习与CLIP类似的视觉语言模型(VLM)的稳健表示学习能力。然而,当前的联邦提示学习方法通常受限于传统的联邦学习(FL)范式,在这种范式下,参与客户端通常只允许从服务器下载一个全局聚合模型。在联邦设置下训练全尺寸模型时这种做法是合理的,但在这项工作中,我们认为这种范式不适用于轻量级提示。通过促进客户端下载多个预先聚合的提示作为固定的非局部专家,我们提出了个性化联邦混合自适应提示(pFedMoAP),这是一种通过专家混合(MoE)视角个性化提示学习过程的新型联邦学习框架。pFedMoAP实现了一个基于本地注意力的门控网络,学习生成增强的文本特征,以更好地与本地图像数据对齐,受益于本地和下载的非局部自适应提示专家。在多种联邦设置下的9个数据集上进行的广泛实验证明了pFedMoAP算法的有效性。代码可在https://github.com/ljaiverson 访问到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICLR 2025
Summary
基于CLIP类似的视觉语言模型(VLM)的强大表示学习能力,联邦提示学习对联邦学习产生了积极影响。传统的联邦提示学习方法通常局限于传统的联邦学习模式,只允许客户端从服务器下载单一的全局聚合模型。然而,本文认为这种模式不适合轻量级提示。通过允许客户端下载多个预先聚合的提示作为固定的非本地专家,我们提出了个性化联邦混合自适应提示(pFedMoAP)这一新型联邦学习框架,它通过混合专家(MoE)的视角实现了个性化的提示学习过程。pFedMoAP采用基于本地注意力机制的门控网络,学习生成增强的文本特征,以便更好地与本地图像数据对齐,受益于本地和下载的非本地自适应提示专家。实验在九个数据集和各种联邦设置下验证了pFedMoAP算法的有效性。代码已公开在https://github.com/ljaiverson/pFedMoAP。
Key Takeaways
- 联邦提示学习通过结合视觉语言模型(VLM)在联邦学习中引入了一种新的学习模式。
- 传统联邦提示学习方法主要依赖于单一全局聚合模型,但这种方式在轻量级提示场景下可能不够灵活。
- pFedMoAP框架允许客户端下载多个预先聚合的提示作为非本地专家,实现了个性化的提示学习过程。
- pFedMoAP采用基于本地注意力机制的门控网络,以生成与本地图像数据对齐的增强文本特征。
- 该框架结合了本地和下载的非本地自适应提示专家的优势。
- 在多个数据集和不同的联邦设置下进行的实验验证了pFedMoAP算法的有效性。
点此查看论文截图

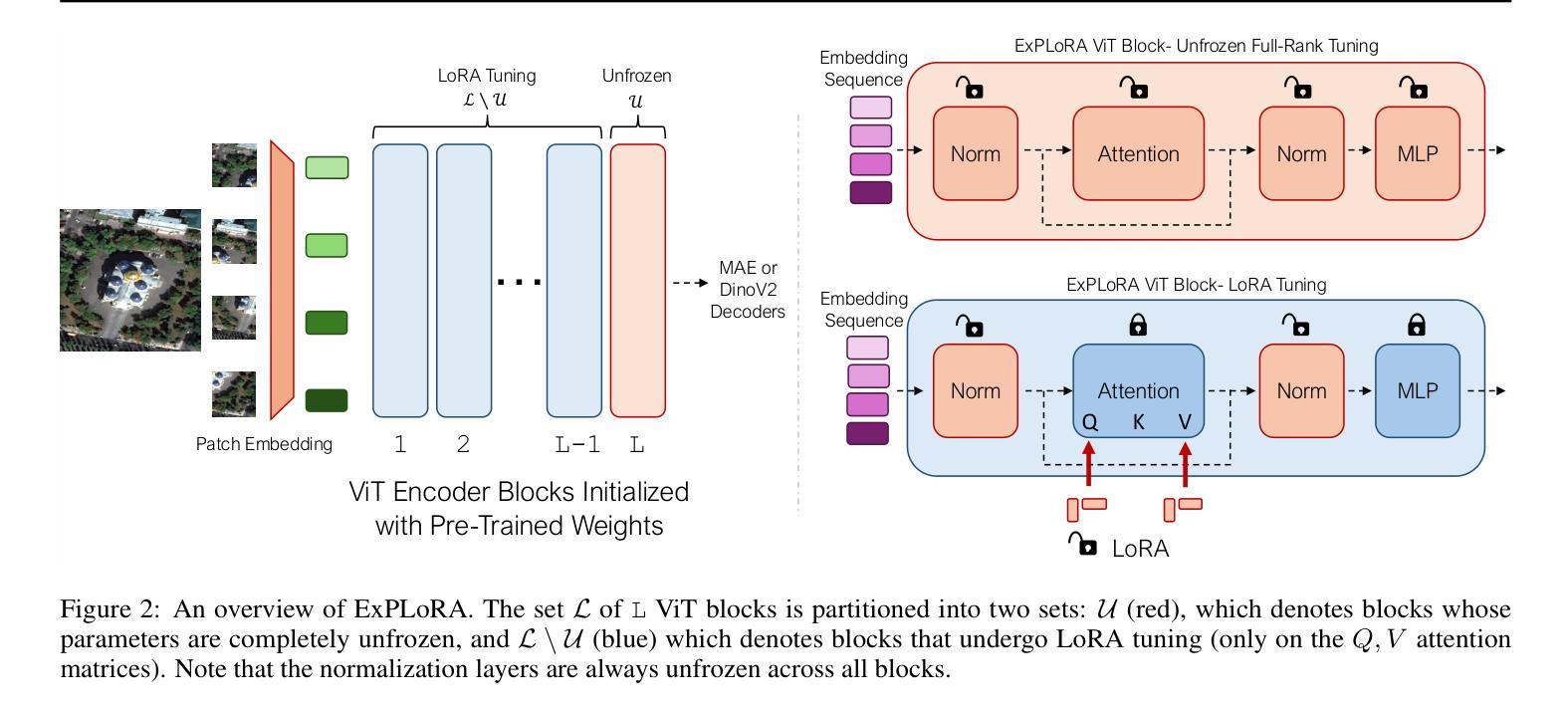
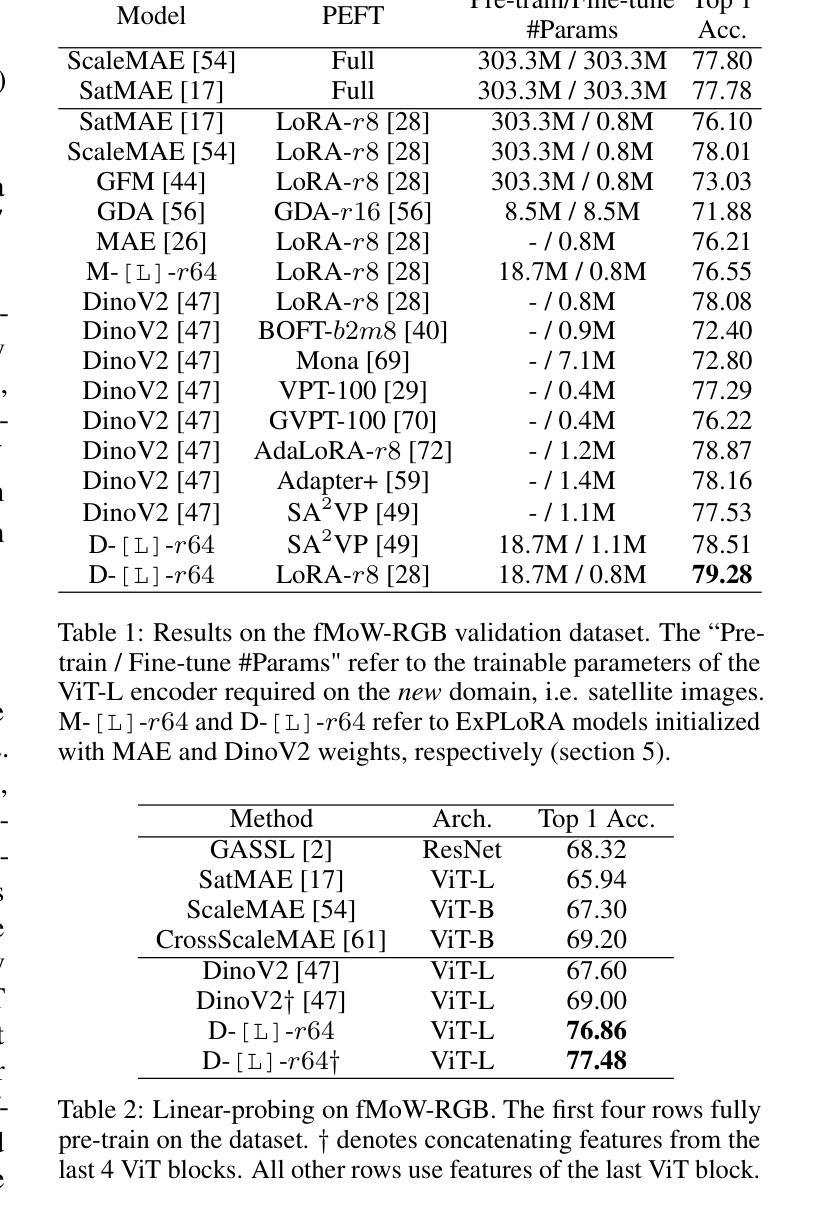
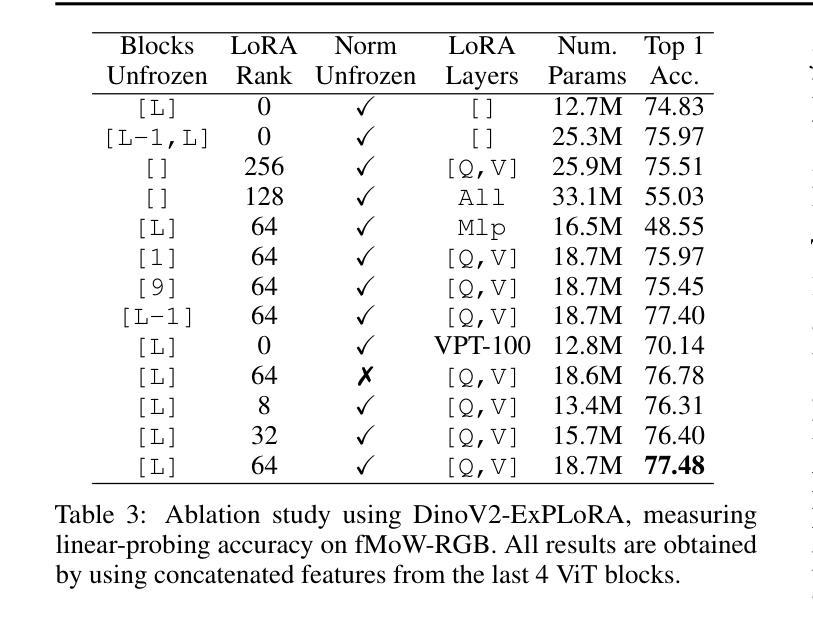
ExPLoRA: Parameter-Efficient Extended Pre-Training to Adapt Vision Transformers under Domain Shifts
Authors:Samar Khanna, Medhanie Irgau, David B. Lobell, Stefano Ermon
Parameter-efficient fine-tuning (PEFT) techniques such as low-rank adaptation (LoRA) can effectively adapt large pre-trained foundation models to downstream tasks using only a small fraction (0.1%-10%) of the original trainable weights. An under-explored question of PEFT is in extending the pre-training phase without supervised labels; that is, can we adapt a pre-trained foundation model to a new domain via efficient self-supervised pre-training on this new domain? In this work, we introduce ExPLoRA, a highly effective technique to improve transfer learning of pre-trained vision transformers (ViTs) under domain shifts. Initializing a ViT with pre-trained weights on large, natural-image datasets such as from DinoV2 or MAE, ExPLoRA continues the unsupervised pre-training objective on a new domain, unfreezing 1-2 pre-trained ViT blocks and tuning all other layers with LoRA. We then fine-tune the resulting model only with LoRA on this new domain for supervised learning. Our experiments demonstrate state-of-the-art results on satellite imagery, even outperforming fully pre-training and fine-tuning ViTs. Using the DinoV2 training objective, we demonstrate up to 8% improvement in linear probing top-1 accuracy on downstream tasks while using <10% of the number of parameters that are used in prior fully-tuned state-of-the art approaches. Our ablation studies confirm the efficacy of our approach over other baselines, including PEFT and unfreezing more ViT blocks. Code is available on the project website: https://samar-khanna.github.io/ExPLoRA/
参数高效微调(PEFT)技术,如低秩适应(LoRA),可以有效地使大型预训练基础模型适应下游任务,仅使用原始可训练权重的极小部分(0.1%-10%)。关于PEFT的一个尚未探索的问题是扩展预训练阶段而无需监督标签;也就是说,我们是否可以通过新领域上的高效自监督预训练,将预训练基础模型适应到新领域?在这项工作中,我们引入了ExPLoRA,这是一种有效提高预训练视觉转换器(ViTs)在领域转移中的迁移学习能力的高效技术。通过在大规模自然图像数据集(如DinoV2或MAE)上初始化的预训练权重来启动ViT,ExPLoRA继续在新领域上进行无监督的预训练目标,解冻1-2个预训练的ViT块并用LoRA调整所有其他层。然后,我们仅使用LoRA在此新领域上进行监督学习对模型进行微调。我们的实验表明,在卫星图像上取得了最新结果,甚至超过了完全预训练和微调ViTs。使用DinoV2训练目标,我们在下游任务的线性探测top-1准确率上提高了高达8%,同时使用的参数少于先前完全调整过的最新方法所使用的参数的10%。我们的消融研究证实了我们的方法相较于其他基准测试,包括PEFT和解冻更多ViT块的有效性。代码可在项目网站上找到:https://samar-khanna.github.io/ExPLoRA/
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
该文探讨了如何使用参数高效微调技术(PEFT)和低秩适应(LoRA)方法,在新领域上对预训练的视觉Transformer(ViT)进行转移学习。文章提出了ExPLoRA方法,该方法在继续无监督预训练目标的同时,只解冻1-2个预训练的ViT块,并使用LoRA调整所有其他层。实验表明,该方法在卫星图像等领域取得了最先进的成果,甚至超过了完全预训练和微调ViT的性能。
Key Takeaways
- ExPLoRA方法利用参数高效微调技术(PEFT)和低秩适应(LoRA)进行预训练视觉Transformer的转移学习。
- ExPLoRA方法可以在新领域上继续无监督预训练,同时只解冻部分预训练的ViT块。
- 使用LoRA对ViT的所有其他层进行调整,以提高模型的适应性。
- 实验结果表明,ExPLoRA方法在卫星图像等领域取得了最先进的成果。
- 与完全预训练和微调ViT相比,ExPLoRA方法在使用更少参数的情况下,仍然表现出更高的性能。
- 文章提供的网站链接包含相关代码。
点此查看论文截图

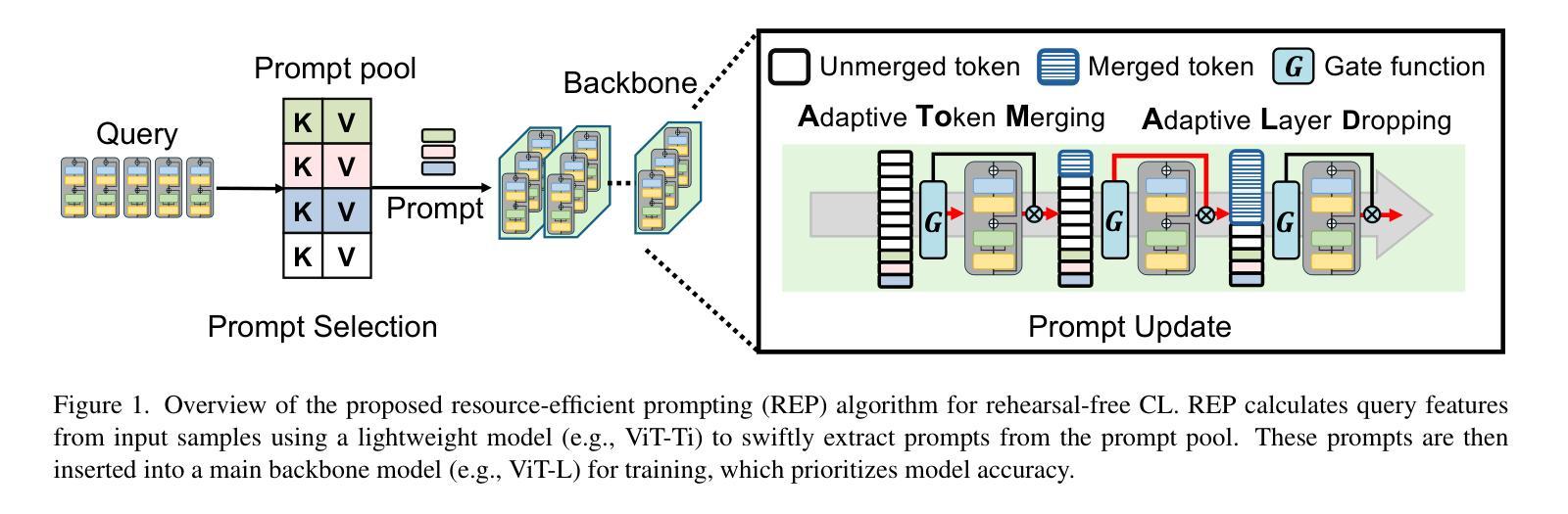
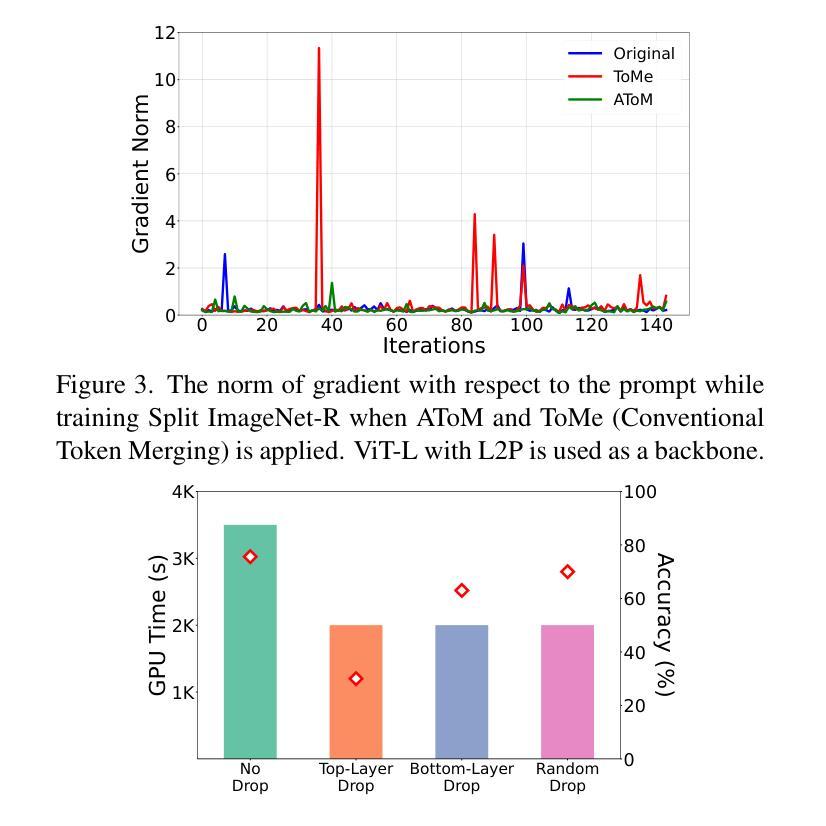
REP: Resource-Efficient Prompting for Rehearsal-Free Continual Learning
Authors:Sungho Jeon, Xinyue Ma, Kwang In Kim, Myeongjae Jeon
Recent rehearsal-free methods, guided by prompts, excel in vision-related continual learning (CL) with drifting data but lack resource efficiency, making real-world deployment challenging. In this paper, we introduce Resource-Efficient Prompting (REP), which improves the computational and memory efficiency of prompt-based rehearsal-free methods while minimizing accuracy trade-offs. Our approach employs swift prompt selection to refine input data using a carefully provisioned model and introduces adaptive token merging (AToM) and layer dropping (ALD) for efficient prompt updates. AToM and ALD selectively skip data and model layers while preserving task-specific features during new-task learning. Extensive experiments on multiple image classification datasets demonstrates REP’s superior resource efficiency over state-of-the-art ViT- and CNN-based methods.
最近的无复述方法,在提示的引导下,在数据漂移的情境下擅长视觉相关的持续学习(CL),但资源利用效率不足,给实际部署带来了挑战。在本文中,我们引入了资源高效提示(REP),它提高了基于提示的无复述方法的计算和内存效率,同时最小化了准确度的权衡。我们的方法采用快速提示选择,使用精心提供的模型对输入数据进行精细化处理,并引入了自适应令牌合并(AToM)和层丢弃(ALD)来进行高效的提示更新。AToM和ALD有选择地跳过数据和模型层,同时在新任务学习中保留任务特定的特征。在多个图像分类数据集上的广泛实验表明,REP在资源效率方面优于最新的ViT和CNN方法。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出了一种资源高效的提示方法(REP),用于改进基于提示的无排练方法在计算和内存效率方面的不足,同时尽量减少准确度的损失。REP采用快速提示选择来优化输入数据,并引入自适应令牌合并(AToM)和层丢弃(ALD)来进行高效的提示更新。在多个图像分类数据集上的实验表明,REP在资源效率上优于基于ViT和CNN的最新方法。
Key Takeaways
- 本文提出了一种新的方法——资源高效的提示方法(REP),旨在改进基于提示的无排练方法在视觉相关的持续学习中的计算与内存效率。
- REP通过使用快速提示选择来优化输入数据,提高模型的效率。
- REP引入了自适应令牌合并(AToM)和层丢弃(ALD)技术,以进行高效的提示更新。
- AToM和ALD能够选择性地跳过数据和模型层,同时保留任务特定的特征,有助于在新任务学习中提高效率。
- 实验表明,REP在多个图像分类数据集上的资源效率优于基于ViT和CNN的当前最先进的方法。
- REP在应对数据漂移问题方面表现出色,使得其在视觉相关的持续学习中具有优势。
点此查看论文截图

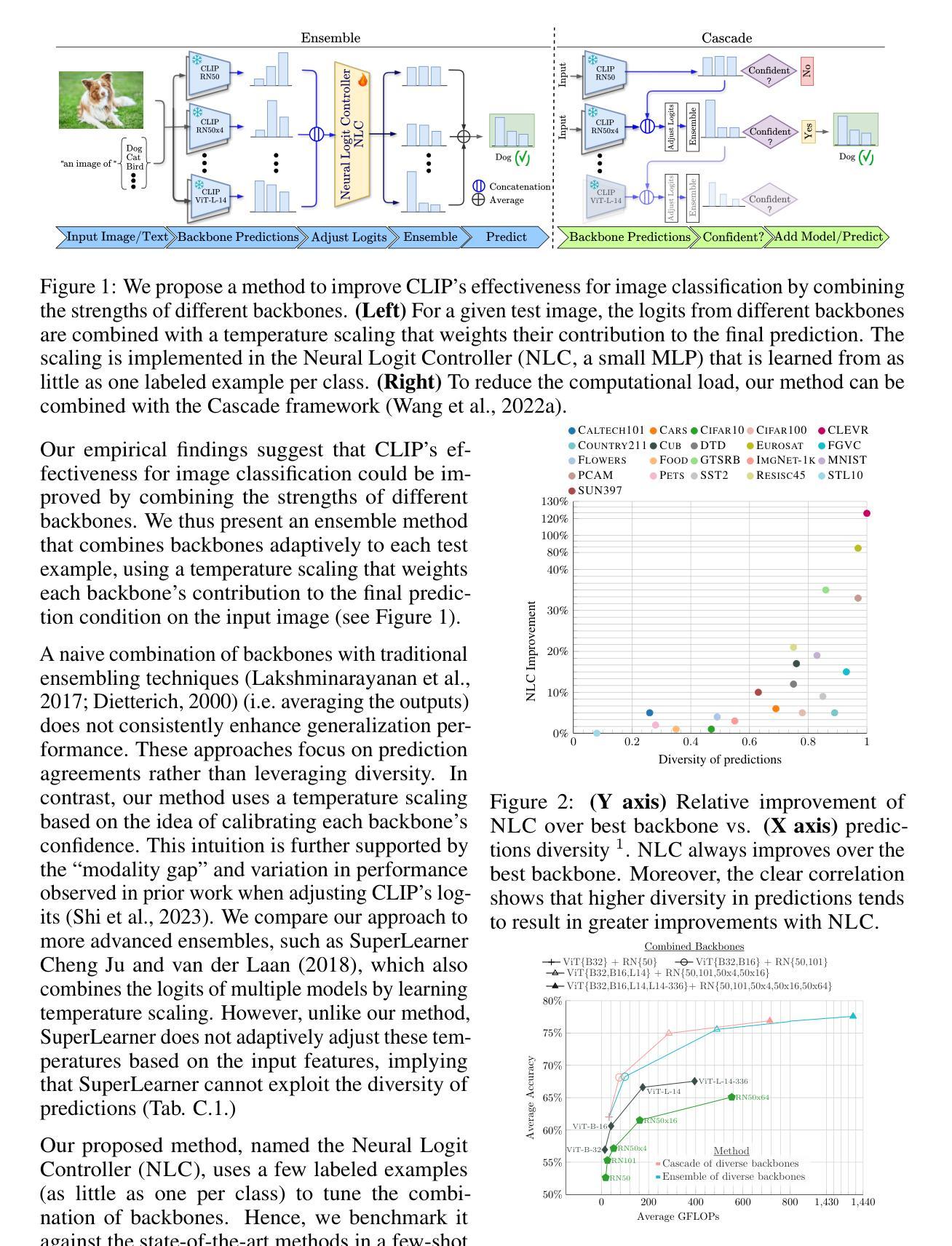
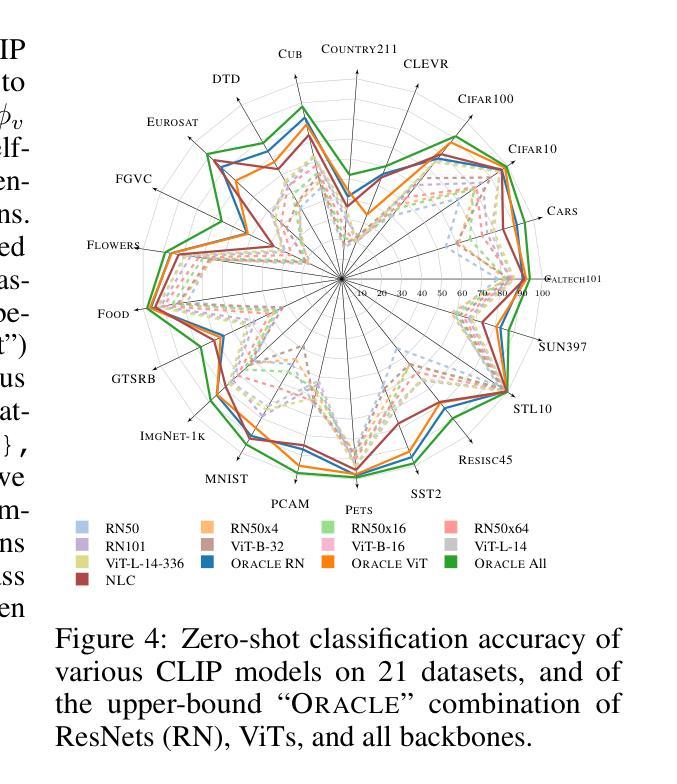
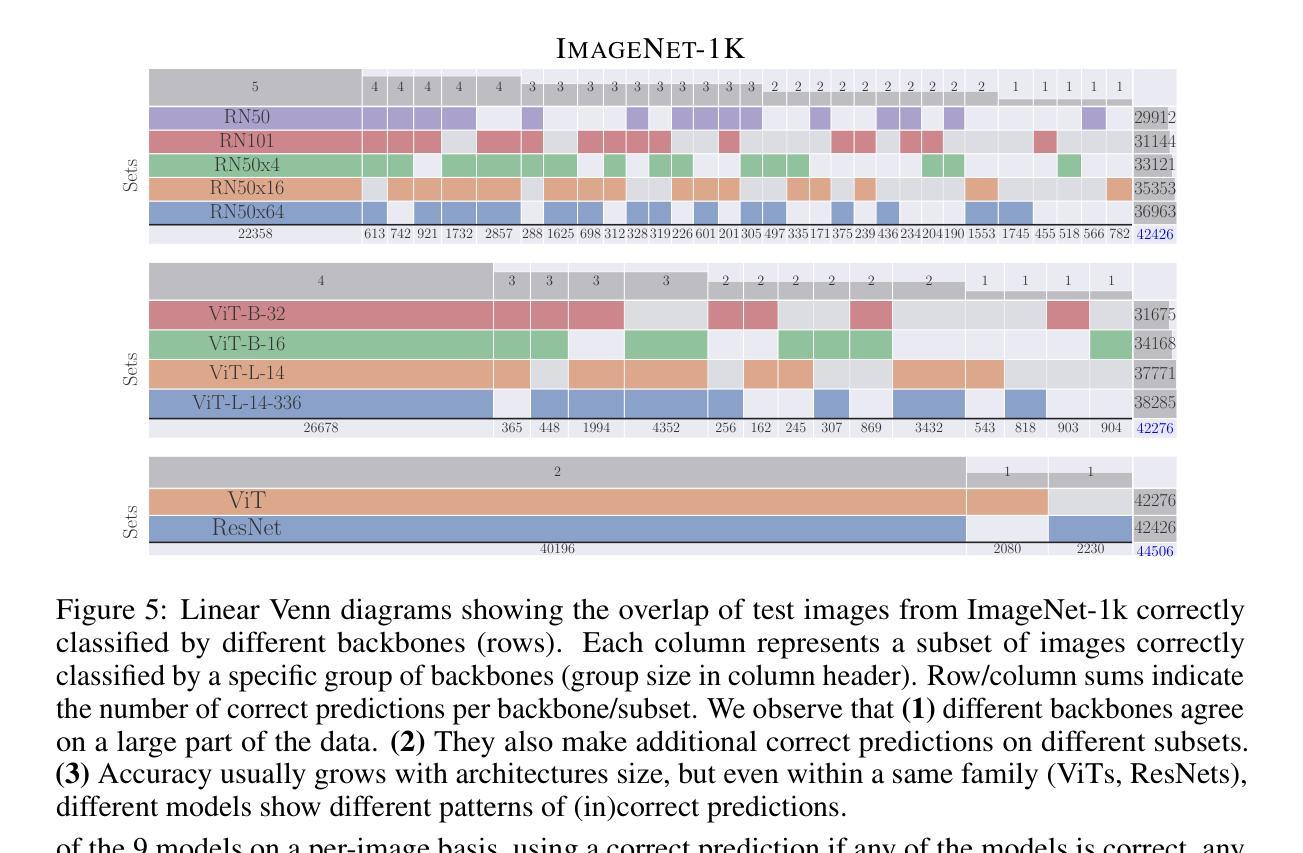
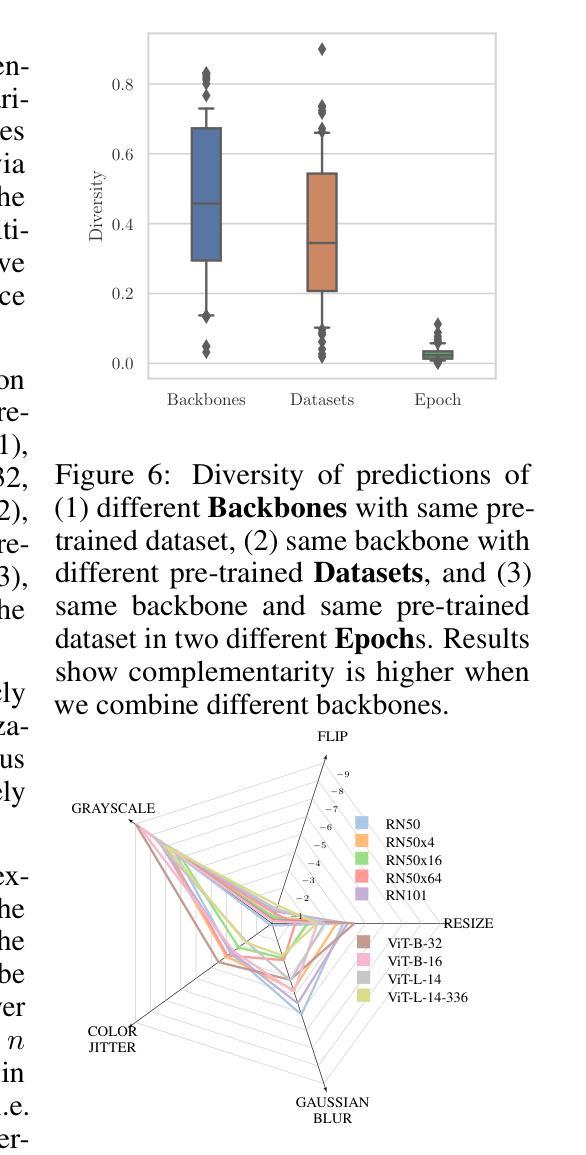
Synergy and Diversity in CLIP: Enhancing Performance Through Adaptive Backbone Ensembling
Authors:Cristian Rodriguez-Opazo, Ehsan Abbasnejad, Damien Teney, Hamed Damirchi, Edison Marrese-Taylor, Anton van den Hengel
Contrastive Language-Image Pretraining (CLIP) stands out as a prominent method for image representation learning. Various architectures, from vision transformers (ViTs) to convolutional networks (ResNets) have been trained with CLIP to serve as general solutions to diverse vision tasks. This paper explores the differences across various CLIP-trained vision backbones. Despite using the same data and training objective, we find that these architectures have notably different representations, different classification performance across datasets, and different robustness properties to certain types of image perturbations. Our findings indicate a remarkable possible synergy across backbones by leveraging their respective strengths. In principle, classification accuracy could be improved by over 40 percentage with an informed selection of the optimal backbone per test example.Using this insight, we develop a straightforward yet powerful approach to adaptively ensemble multiple backbones. The approach uses as few as one labeled example per class to tune the adaptive combination of backbones. On a large collection of datasets, the method achieves a remarkable increase in accuracy of up to 39.1% over the best single backbone, well beyond traditional ensembles
对比语言图像预训练(CLIP)作为图像表示学习的一种突出方法而备受关注。从视觉转换器(ViTs)到卷积网络(ResNets),各种架构都经过CLIP训练,作为解决各种视觉任务的一般解决方案。本文探讨了不同CLIP训练视觉骨架之间的差异。尽管使用了相同的数据和训练目标,但我们发现这些架构的表示法、不同数据集上的分类性能以及针对某些类型的图像扰动的稳健性属性都存在显著差异。我们的研究结果表明,通过利用各自的优点,可以在骨架之间实现显著的协同作用。原则上,通过针对每个测试样本选择最佳骨架的明智选择,分类精度可以提高40%以上。利用这一见解,我们开发了一种简单而强大的自适应集成多种骨架的方法。该方法仅使用每个类别的一个标记示例来调整骨架的自适应组合。在大量数据集上,该方法实现了相对于最佳单个骨架高达39.1%的准确度提升,远远超过了传统集成方法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICLR 2025. arXiv admin note: text overlap with arXiv:2312.14400
Summary
CLIP方法在图像表示学习领域表现突出,本文探讨了不同CLIP训练视觉骨架(如视觉变压器和卷积网络)之间的差异。尽管使用相同的数据和训练目标,但这些架构的表示、数据集上的分类性能和图像扰动的稳健性却大不相同。通过融合各种骨架的优势,分类精度可提高40%以上。此外,本文提出了一种简单而强大的自适应集成多种骨架的方法,仅使用一个类别标签的例子即可调整骨架的自适应组合,并在多个数据集上实现了相对于最佳单一骨架高达39.1%的准确度提升。
Key Takeaways
- CLIP是一种用于图像表示学习的主流方法,广泛应用于各种视觉任务。
- 不同CLIP训练的视觉骨架(如ViTs和ResNets)具有显著不同的表示、分类性能和稳健性。
- 通过对比各种骨架的特性,发现它们之间的协同作用潜力巨大。
- 选择适当的骨架可以显著提高分类精度,最高可提高40%以上。
- 提出了一种简单而强大的自适应集成多种骨架的方法,仅使用少量标签样本即可调整骨架组合。
- 该方法在多个数据集上实现了相对于单一最佳骨架高达39.1%的准确度提升。
点此查看论文截图

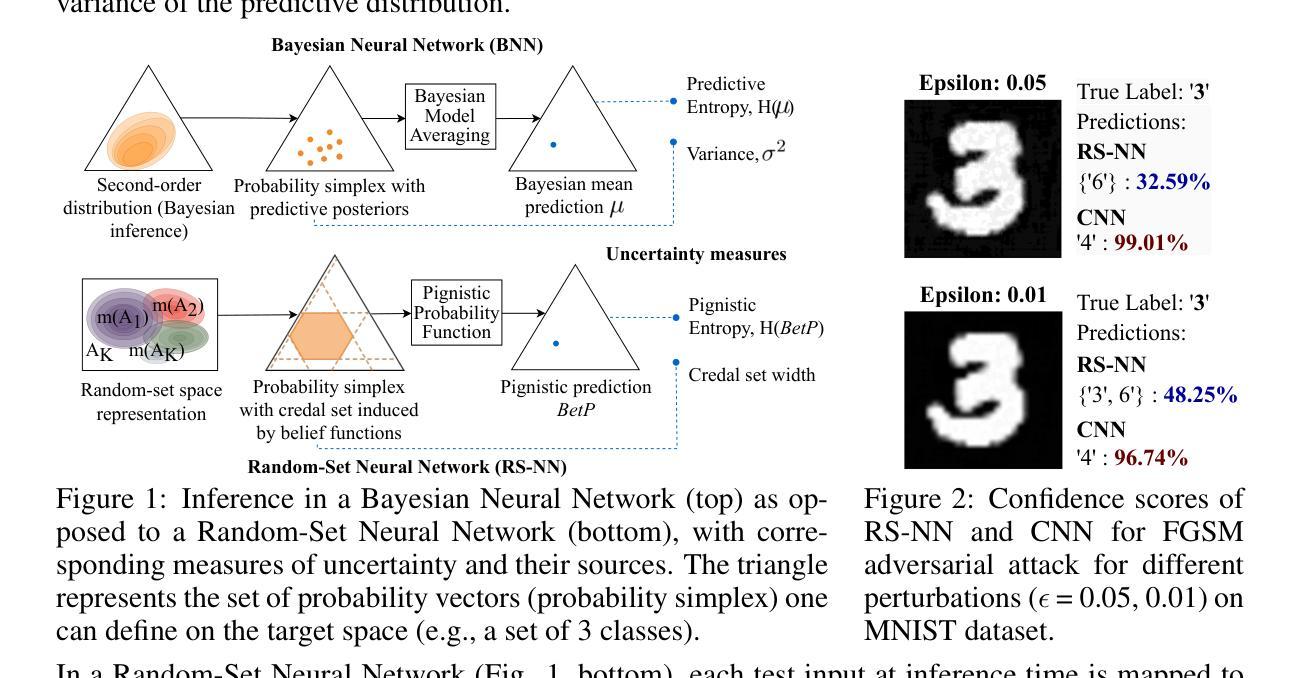
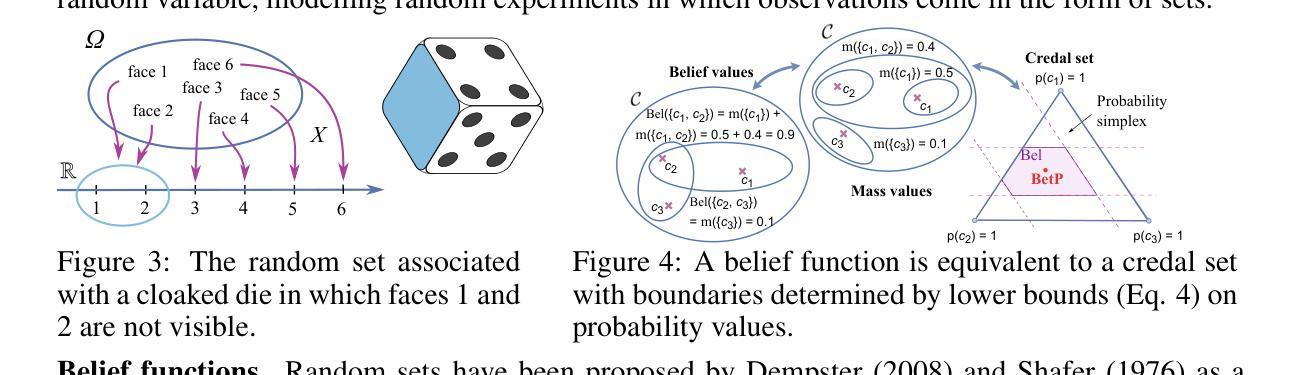
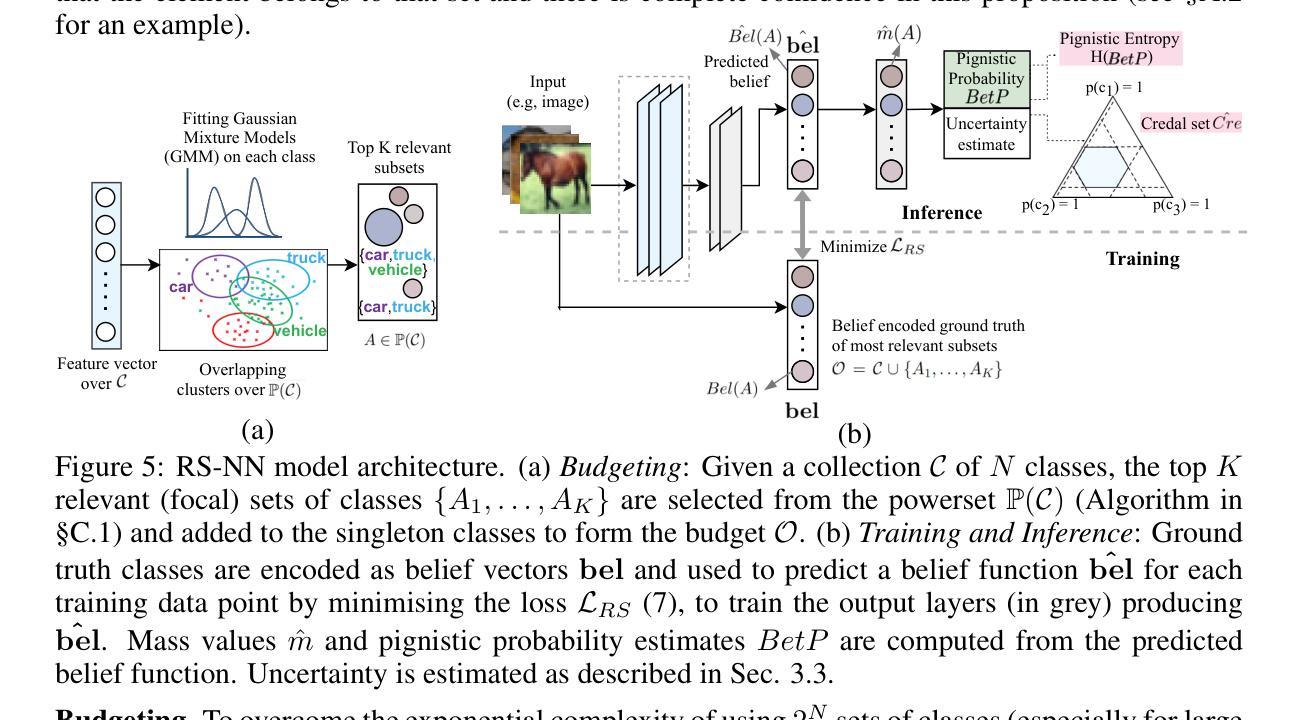
Random-Set Neural Networks (RS-NN)
Authors:Shireen Kudukkil Manchingal, Muhammad Mubashar, Kaizheng Wang, Keivan Shariatmadar, Fabio Cuzzolin
Machine learning is increasingly deployed in safety-critical domains where erroneous predictions may lead to potentially catastrophic consequences, highlighting the need for learning systems to be aware of how confident they are in their own predictions: in other words, ‘to know when they do not know’. In this paper, we propose a novel Random-Set Neural Network (RS-NN) approach to classification which predicts belief functions (rather than classical probability vectors) over the class list using the mathematics of random sets, i.e., distributions over the collection of sets of classes. RS-NN encodes the ‘epistemic’ uncertainty induced by training sets that are insufficiently representative or limited in size via the size of the convex set of probability vectors associated with a predicted belief function. Our approach outperforms state-of-the-art Bayesian and Ensemble methods in terms of accuracy, uncertainty estimation and out-of-distribution (OoD) detection on multiple benchmarks (CIFAR-10 vs SVHN/Intel-Image, MNIST vs FMNIST/KMNIST, ImageNet vs ImageNet-O). RS-NN also scales up effectively to large-scale architectures (e.g. WideResNet-28-10, VGG16, Inception V3, EfficientNetB2 and ViT-Base-16), exhibits remarkable robustness to adversarial attacks and can provide statistical guarantees in a conformal learning setting.
机器学习在安全性至关重要的领域得到了越来越广泛的应用,错误的预测可能导致灾难性的后果,这凸显了学习系统需要了解自己对预测的信心程度的重要性,换句话说,就是“要知道自己不知道”。在本文中,我们提出了一种新型的随机集神经网络(RS-NN)分类方法,该方法使用随机集的数学原理预测类列表上的信念函数(而不是传统的概率向量)。RS-NN通过预测的信仰函数关联的凸概率向量集合的大小,编码由训练集引起的“认识论”不确定性,这种不确定性可能是由于训练集代表性不足或规模有限造成的。我们的方法在多个基准测试(如CIFAR-10与SVHN/Intel-Image、MNIST与FMNIST/KMNIST、ImageNet与ImageNet-O)上的准确性、不确定性估计和离群检测方面均优于先进的贝叶斯和集成方法。RS-NN还能有效地扩展到大规模架构(如WideResNet-28-10、VGG16、Inception V3、EfficientNetB2和ViT-Base-16),对对抗性攻击表现出惊人的稳健性,并在符合学习的环境中提供统计保障。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Published as a conference paper at the Thirteenth International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR 2025)
Summary
本论文提出了一种名为RS-NN的随机集神经网络分类方法,它通过预测随机集上的信念函数而非传统的概率向量来表达模型的预测置信度。RS-NN通过编码训练集引起的知识不确定性,即由于数据集代表性不足或规模有限导致的凸概率向量集合的大小,以应对机器学习中日益增长的复杂性和不确定性问题。实验结果表明,RS-NN在多个基准测试上的准确性、不确定性估计和分布外检测方面优于现有最先进的贝叶斯和集成方法,并且在大型架构中也能有效扩展。此外,RS-NN还表现出对抗攻击的稳健性,并在合规学习环境中提供统计保证。
Key Takeaways
- RS-NN使用随机集神经网络预测信念函数来反映模型预测的置信度。
- RS-NN通过编码知识不确定性来应对数据集的不确定性和复杂性问题。知识不确定性是由于数据集代表性不足或规模有限所导致的。
- RS-NN在多个基准测试中展现出出色的准确性、不确定性估计和分布外检测性能。
- RS-NN在大型架构中也能有效扩展,如WideResNet-28-10、VGG16等。
- RS-NN展现出对抗攻击的稳健性。这对于在安全关键领域部署机器学习至关重要。
- RS-NN可以在合规学习环境中提供统计保证,确保模型的预测符合一定的可靠性标准。这对于机器学习模型的透明度和可信度至关重要。
点此查看论文截图