⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-02-20 更新
A Dual-Stage Time-Context Network for Speech-Based Alzheimer’s Disease Detection
Authors:Yifan Gao, Long Guo, Hong Liu
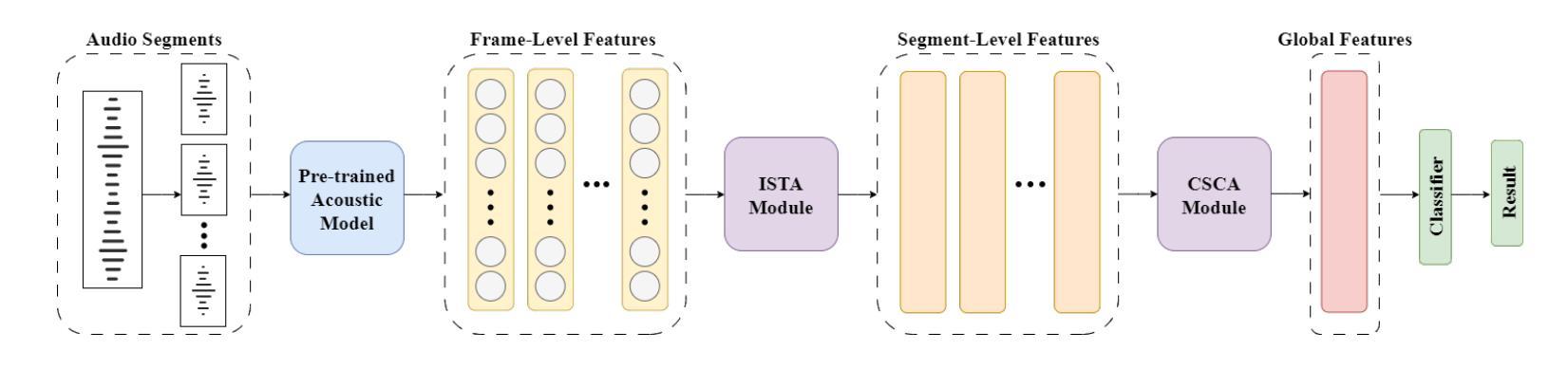
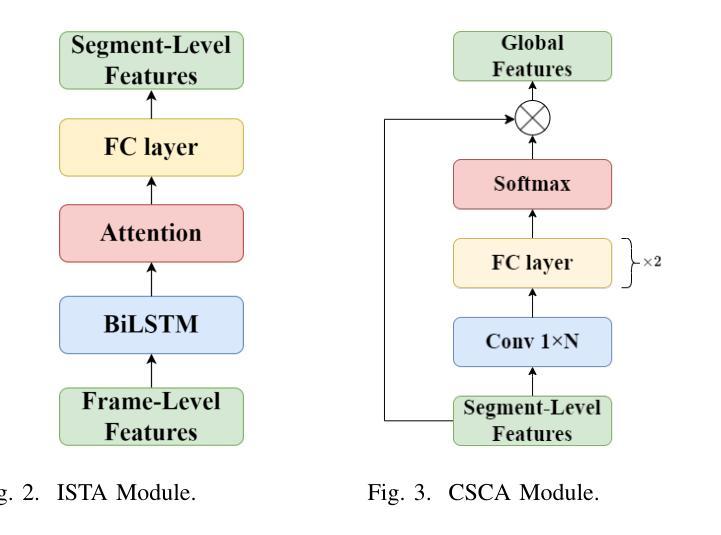
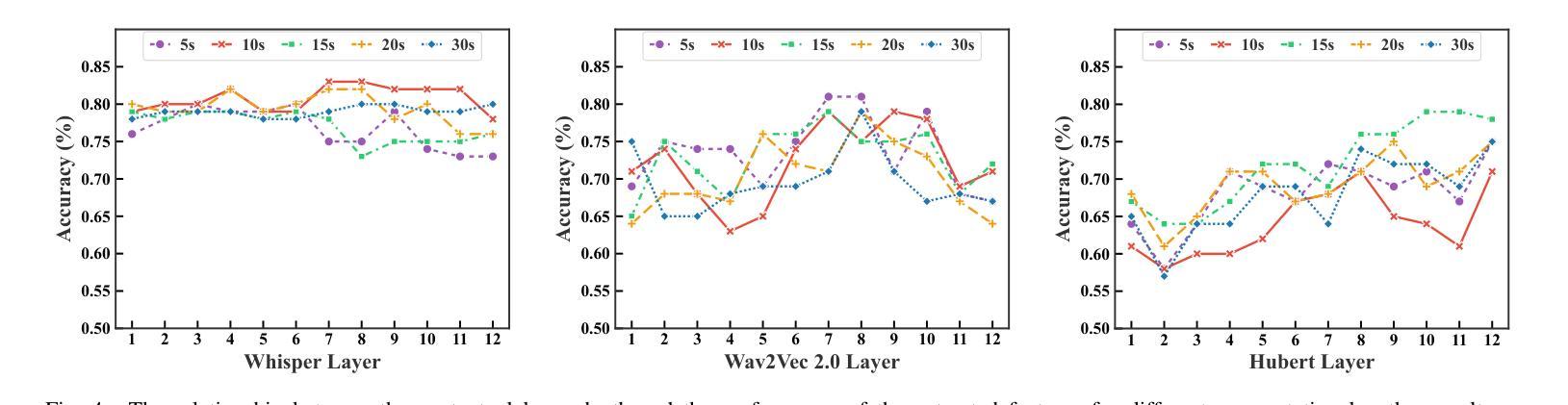
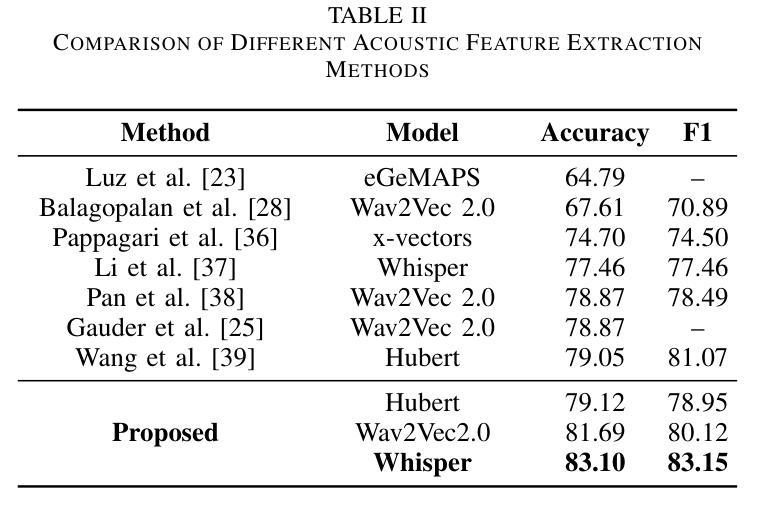
Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is a progressive neurodegenerative disorder that leads to irreversible cognitive decline in memory and communication. Early detection of AD through speech analysis is crucial for delaying disease progression. However, existing methods mainly use pre-trained acoustic models for feature extraction but have limited ability to model both local and global patterns in long-duration speech. In this letter, we introduce a Dual-Stage Time-Context Network (DSTC-Net) for speech-based AD detection, integrating local acoustic features with global conversational context in long-duration recordings.We first partition each long-duration recording into fixed-length segments to reduce computational overhead and preserve local temporal details.Next, we feed these segments into an Intra-Segment Temporal Attention (ISTA) module, where a bidirectional Long Short-Term Memory (BiLSTM) network with frame-level attention extracts enhanced local features.Subsequently, a Cross-Segment Context Attention (CSCA) module applies convolution-based context modeling and adaptive attention to unify global patterns across all segments.Extensive experiments on the ADReSSo dataset show that our DSTC-Net outperforms state-of-the-art models, reaching 83.10% accuracy and 83.15% F1.
阿尔茨海默病(AD)是一种进行性神经退行性疾病,会导致记忆和沟通的认知能力不可逆地下降。通过语音分析早期检测AD对于延缓疾病进展至关重要。然而,现有方法主要使用预训练的声学模型进行特征提取,但在长时语音中同时建模局部和全局模式的能力有限。
在这篇文章中,我们介绍了一种用于基于语音的AD检测的双阶段时间上下文网络(DSTC-Net),该网络将局部声学特征与长时录音中的全局对话上下文相结合。我们首先将所有长时录音划分为固定长度的片段,以减少计算开销并保留局部时间细节。然后,我们将这些片段输入到Intra-Segment Temporal Attention(ISTA)模块中,其中具有帧级注意力的双向长短时记忆(BiLSTM)网络提取增强的局部特征。接下来,Cross-Segment Context Attention(CSCA)模块应用基于卷积的上下文建模和自适应注意力,以统一所有片段中的全局模式。在ADReSSo数据集上的大量实验表明,我们的DSTC-Net优于最新模型,达到了83.10%的准确率和83.15%的F1值。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出了一种名为Dual-Stage Time-Context Network(DSTC-Net)的模型,用于基于语音的阿尔茨海默病(AD)检测。该模型结合了局部声学特征和全局对话上下文,以在长时长录音中实现更好的检测效果。通过分段处理长录音、强化局部特征和捕捉全局模式,DSTC-Net在ADReSSo数据集上的表现优于现有模型,达到83.10%的准确率和83.15%的F1值。
Key Takeaways
- 阿尔茨海默病(AD)是一种导致不可逆记忆和沟通认知衰退的进展性神经退行性疾病。
- 早期检测AD对延缓疾病进展至关重要。
- 现有方法主要通过预训练的声学模型进行特征提取,但难以在长时长语音中同时建模局部和全局模式。
- 本文提出了Dual-Stage Time-Context Network(DSTC-Net)模型,整合局部声学特征和全局对话上下文。
- DSTC-Net通过分段处理长录音、强化局部特征和捕捉全局模式实现更好的检测效果。
- DSTC-Net在ADReSSo数据集上的表现优于现有模型,达到较高的准确率和F1值。
点此查看论文截图

A deep learning framework for efficient pathology image analysis
Authors:Peter Neidlinger, Tim Lenz, Sebastian Foersch, Chiara M. L. Loeffler, Jan Clusmann, Marco Gustav, Lawrence A. Shaktah, Rupert Langer, Bastian Dislich, Lisa A. Boardman, Amy J. French, Ellen L. Goode, Andrea Gsur, Stefanie Brezina, Marc J. Gunter, Robert Steinfelder, Hans-Michael Behrens, Christoph Röcken, Tabitha Harrison, Ulrike Peters, Amanda I. Phipps, Giuseppe Curigliano, Nicola Fusco, Antonio Marra, Michael Hoffmeister, Hermann Brenner, Jakob Nikolas Kather
Artificial intelligence (AI) has transformed digital pathology by enabling biomarker prediction from high-resolution whole slide images (WSIs). However, current methods are computationally inefficient, processing thousands of redundant tiles per WSI and requiring complex aggregator models. We introduce EAGLE (Efficient Approach for Guided Local Examination), a deep learning framework that emulates pathologists by selectively analyzing informative regions. EAGLE incorporates two foundation models: CHIEF for efficient tile selection and Virchow2 for extracting high-quality features. Benchmarking was conducted against leading slide- and tile-level foundation models across 31 tasks from four cancer types, spanning morphology, biomarker prediction and prognosis. EAGLE outperformed state-of-the-art foundation models by up to 23% and achieved the highest AUROC overall. It processed a slide in 2.27 seconds, reducing computational time by more than 99% compared to existing models. This efficiency enables real-time workflows, allows pathologists to validate all tiles which are used by the model during analysis, and eliminates dependence on high-performance computing, making AI-powered pathology more accessible. By reliably identifying meaningful regions and minimizing artifacts, EAGLE provides robust and interpretable outputs, supporting rapid slide searches, integration into multi-omics pipelines and emerging clinical foundation models.
人工智能(AI)已经通过从高分辨率全切片图像(WSI)进行生物标志物预测,从而彻底改变了数字病理学。然而,当前的方法计算效率低下,每张WSI需要处理数千个冗余瓦片,并且需要复杂的聚合模型。我们引入了EAGLE(用于引导局部检查的高效方法),这是一个深度学习框架,通过选择性分析信息区域来模拟病理学家。EAGLE结合了两种基础模型:用于高效瓦片选择的CHIEF和用于提取高质量特征的Virchow2。我们在来自四种癌症类型、涵盖形态学、生物标志物预测和预后的31项任务上,与领先的幻灯片及瓦片级别的基础模型进行了基准测试。EAGLE在最高标准上超越了高达23%的现有先进基础模型,并获得了最高的AUROC值。它可以在2.27秒内处理一张幻灯片,与现有模型相比,计算时间减少了99%以上。这种效率实现了实时工作流程,允许病理学家验证模型在分析过程中使用的所有瓦片,并消除了对高性能计算的依赖,使AI驱动的病理学更加易于访问。通过可靠地识别有意义区域并尽量减少伪影,EAGLE提供了稳健和可解释的输出结果,支持快速幻灯片搜索、多组学管道集成和新兴的临床基础模型。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
人工智能通过高效地从高分辨率全切片图像(WSIs)预测生物标志物,实现了数字病理学领域的变革。然而,当前方法计算效率低下,处理大量冗余切片,并需要复杂的聚合模型。我们引入了EAGLE(用于引导局部检查的效率方法),这是一个深度学习框架,通过选择性分析信息区域来模拟病理医师的行为。EAGLE包含两个基础模型:用于高效切片选择的CHIEF和用于提取高质量特征的Virchow2。跨四种癌症类型中的31个任务进行的基准测试表明,EAGLE在形态学、生物标志物预测和预后评估方面优于其他领先的切片级和基础模型级技术,其AUROC值最高。同时,它可以在实际应用中大幅度减少计算时间并提高诊断效率。因此,通过准确识别有意义区域并最小化伪影,EAGLE能够提供稳健和可解释的输出来支持快速切片搜索和多组学管道集成等应用。这一技术的出现使得人工智能赋能的病理学更加实用和便捷。
Key Takeaways
- AI在数字病理学领域中实现了从高分辨率全切片图像预测生物标志物的高效化变革。然而,当前方法存在计算效率低下的问题。
点此查看论文截图

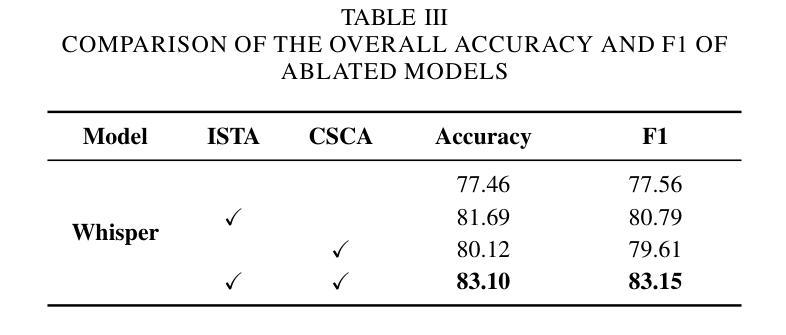
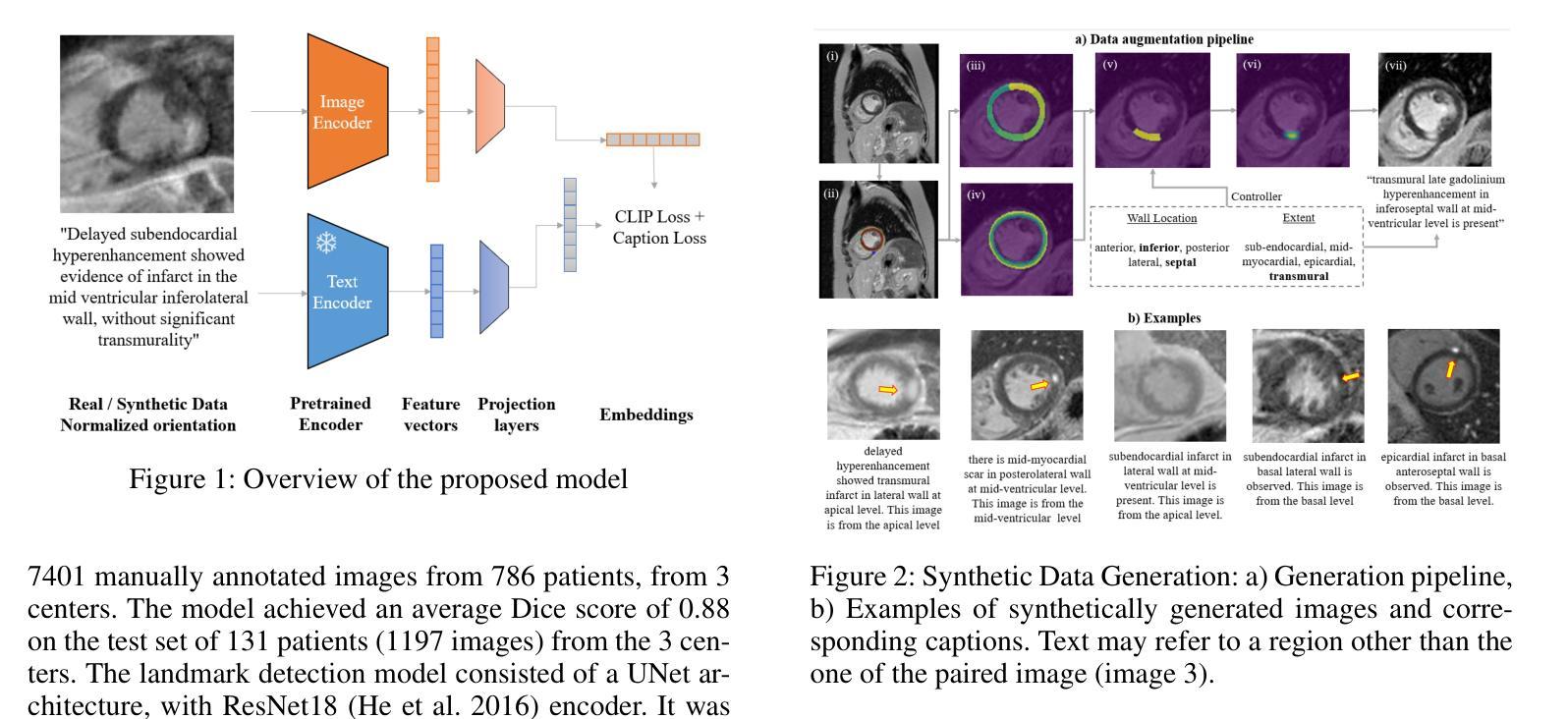
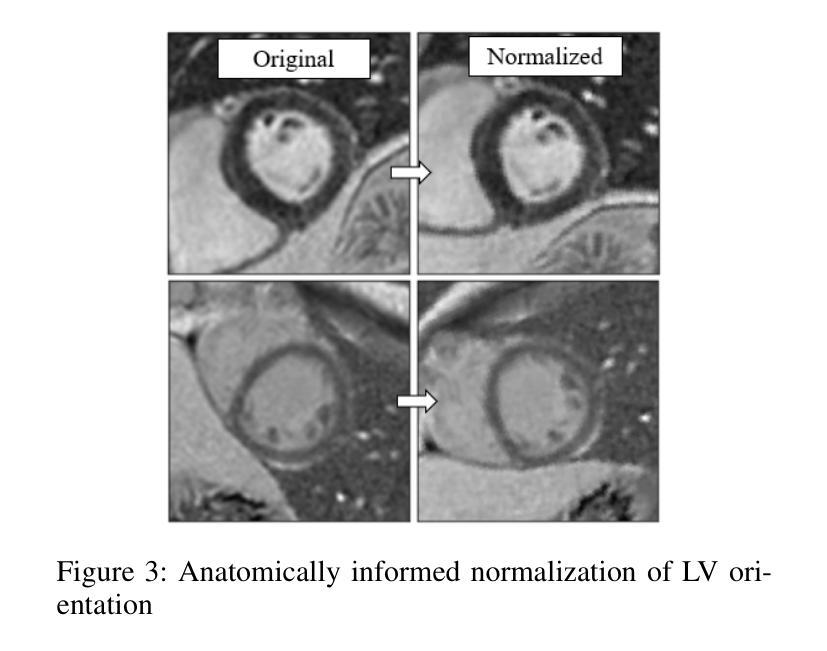
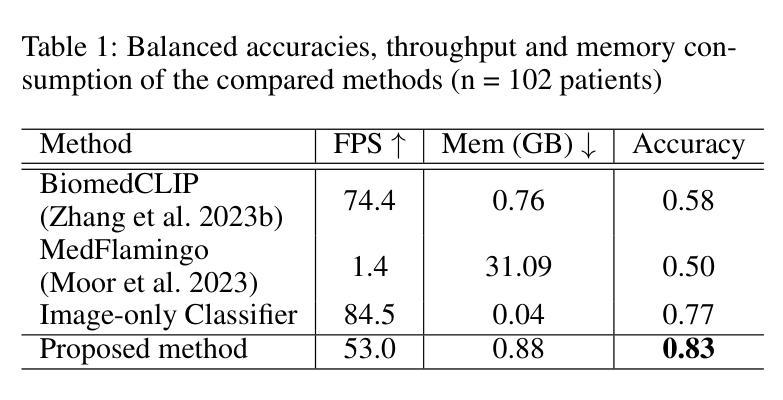
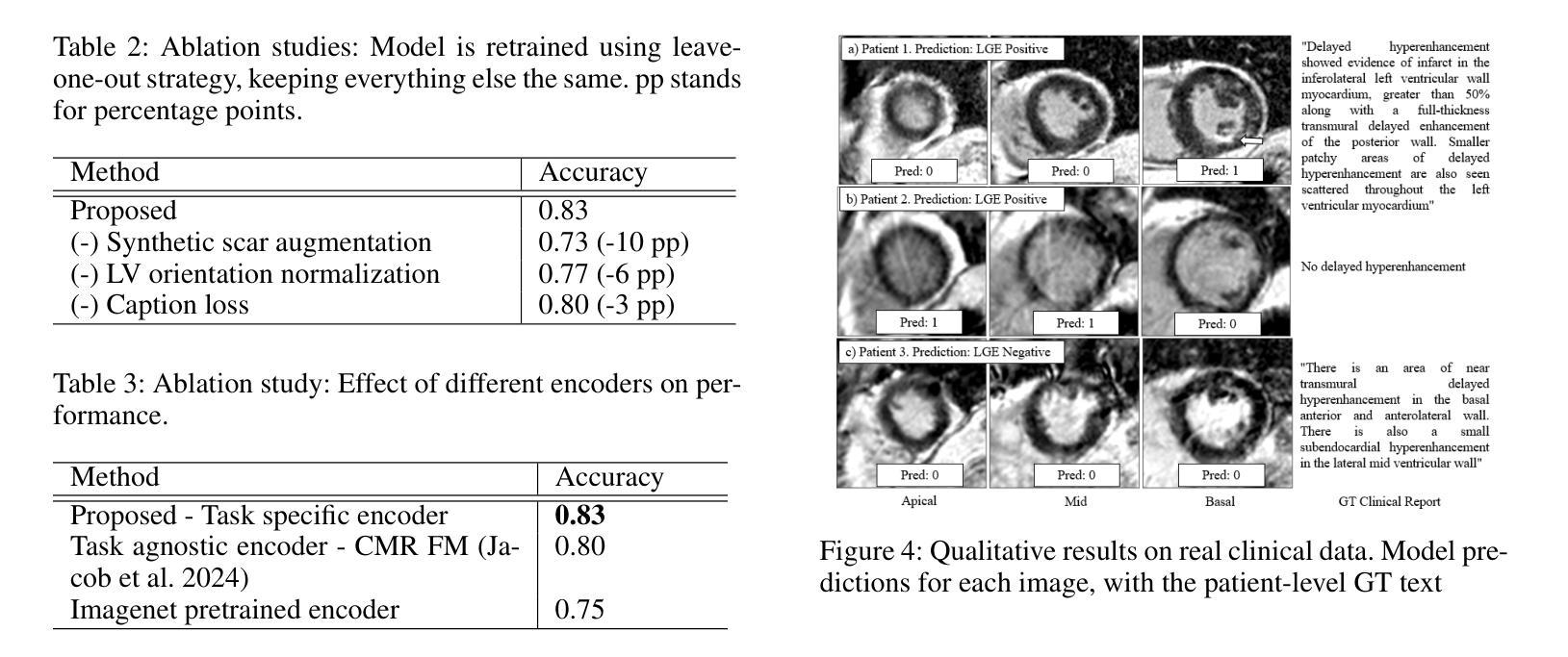
Fake It Till You Make It: Using Synthetic Data and Domain Knowledge for Improved Text-Based Learning for LGE Detection
Authors:Athira J Jacob, Puneet Sharma, Daniel Rueckert
Detection of hyperenhancement from cardiac LGE MRI images is a complex task requiring significant clinical expertise. Although deep learning-based models have shown promising results for the task, they require large amounts of data with fine-grained annotations. Clinical reports generated for cardiac MR studies contain rich, clinically relevant information, including the location, extent and etiology of any scars present. Although recently developed CLIP-based training enables pretraining models with image-text pairs, it requires large amounts of data and further finetuning strategies on downstream tasks. In this study, we use various strategies rooted in domain knowledge to train a model for LGE detection solely using text from clinical reports, on a relatively small clinical cohort of 965 patients. We improve performance through the use of synthetic data augmentation, by systematically creating scar images and associated text. In addition, we standardize the orientation of the images in an anatomy-informed way to enable better alignment of spatial and text features. We also use a captioning loss to enable fine-grained supervision and explore the effect of pretraining of the vision encoder on performance. Finally, ablation studies are carried out to elucidate the contributions of each design component to the overall performance of the model.
从心脏LGE MRI图像中检测超增强是一个复杂的任务,需要丰富的临床经验。尽管基于深度学习的模型在该任务中显示出有希望的结果,但它们需要大量的精细标注数据。为心脏MR研究生成的临床报告包含丰富的与临床相关的信息,包括任何疤痕的位置、程度和病因。虽然最近开发的基于CLIP的训练方法能够实现图像文本对的预训练模型,但它需要大量数据,并且需要在下游任务上进一步微调策略。在这项研究中,我们利用基于领域知识的各种策略,仅使用来自965名患者临床报告的文本,对LGE检测模型进行训练。我们通过系统地创建疤痕图像和相关文本,提高通过合成数据增强性能。此外,我们以解剖信息的方式标准化图像方向,以实现空间特征和文本特征的更好对齐。我们还使用描述性损失来实现精细监督,并探索视觉编码器预训练对性能的影响。最后,进行消融研究以阐明每个设计组件对模型总体性能的贡献。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Poster at Workshop on Large Language Models and Generative AI for Health at AAAI 2025
Summary
本研究利用临床报告中的文本数据,结合领域知识和多种策略,如合成数据增强、图像标准化、精细监督的标注损失和视觉编码器的预训练,训练了一个仅使用文本数据的LGE MRI图像超增强检测模型。在较小的965例患者队列中取得了良好性能。
Key Takeaways
- 心脏LGE MRI图像的超增强检测是一项需要临床专家经验的复杂任务。
- 深度学习模型在该任务中显示出潜力,但需要大量精细标注的数据。
- 临床报告包含关于心脏MR研究的重要临床信息,可用于训练检测模型。
- 本研究使用基于领域知识的策略,仅使用临床报告的文本数据来训练模型。
- 通过合成数据增强、图像标准化和精细监督的标注损失等方法提高了模型性能。
- 通过对视觉编码器进行预训练,进一步提升了模型性能。
点此查看论文截图

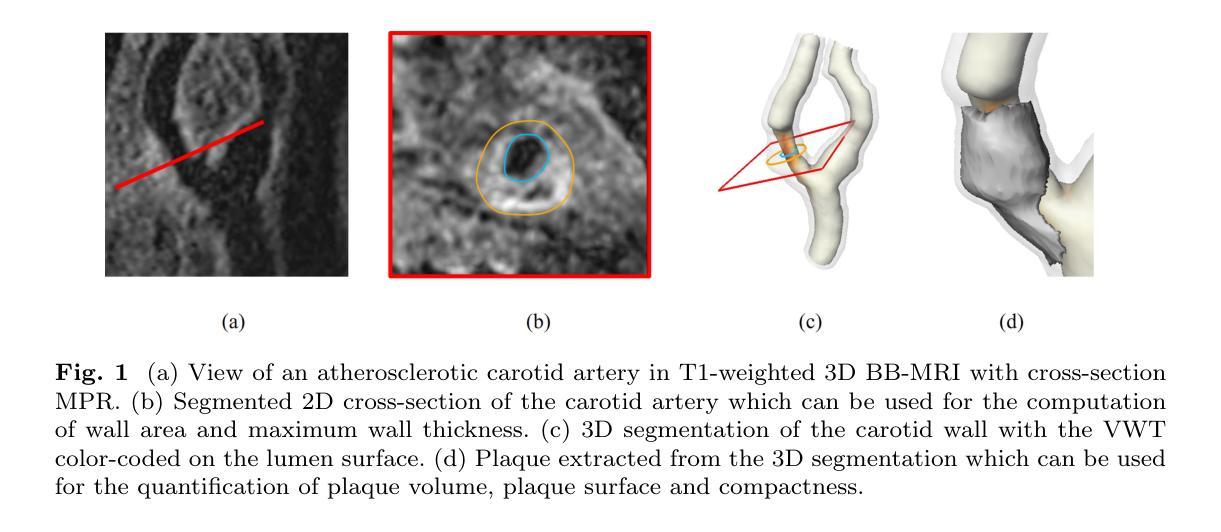
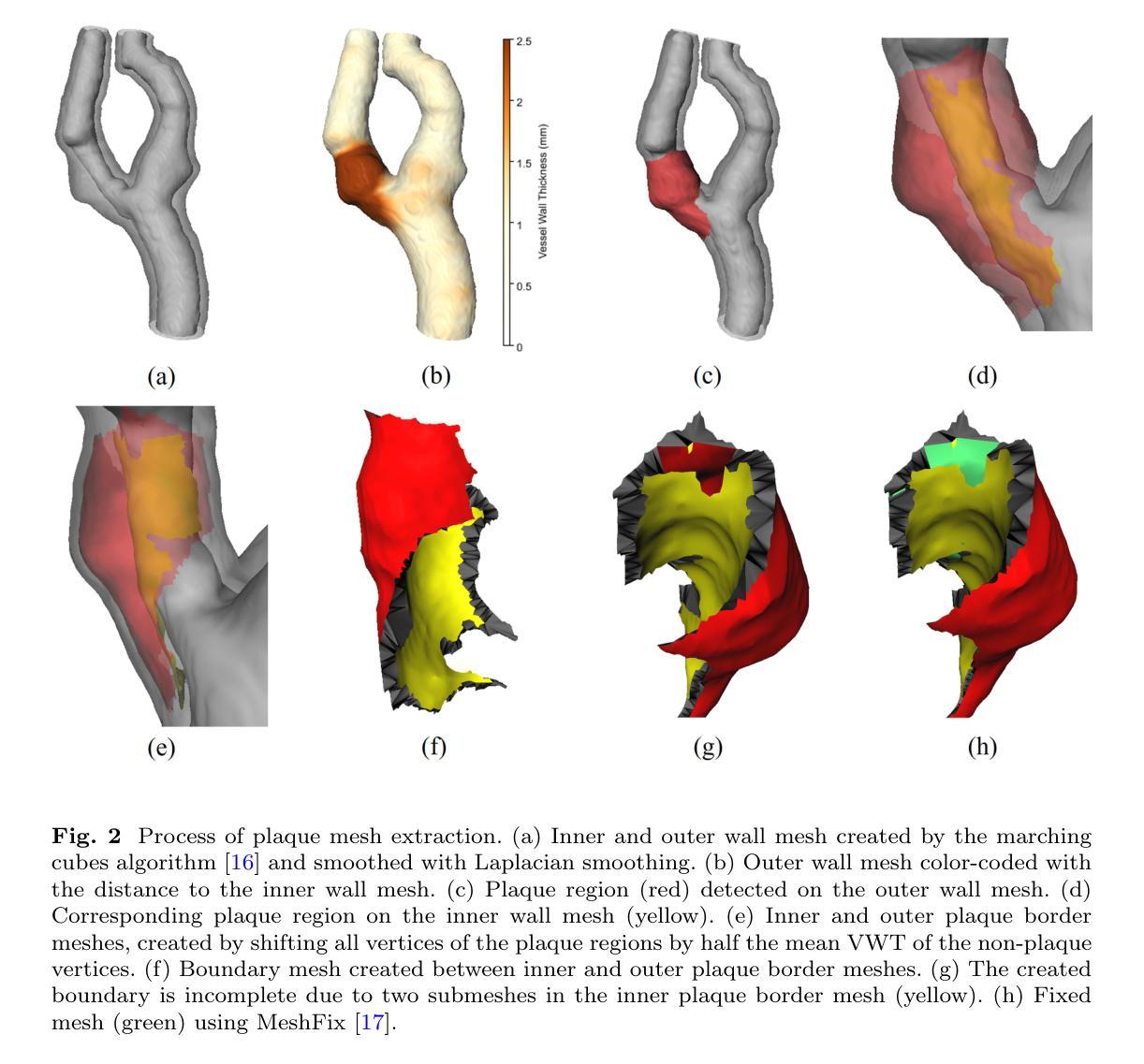
Carotid Artery Plaque Analysis in 3D Based on Distance Encoding in Mesh Representations
Authors:Hinrich Rahlfs, Markus Hüllebrand, Sebastian Schmitter, Christoph Strecker, Andreas Harloff, Anja Hennemuth
Purpose: Enabling a comprehensive and robust assessment of carotid artery plaques in 3D through extraction and visualization of quantitative plaque parameters. These parameters have potential applications in stroke risk analysis, evaluation of therapy effectiveness, and plaque progression prediction. Methods: We propose a novel method for extracting a plaque mesh from 3D vessel wall segmentation using distance encoding on the inner and outer wall mesh for precise plaque structure analysis. A case-specific threshold, derived from the normal vessel wall thickness, was applied to extract plaques from a dataset of 202 T1-weighted black-blood MRI scans of subjects with up to 50% stenosis. Applied to baseline and one-year follow-up data, the method supports detailed plaque morphology analysis over time, including plaque volume quantification, aided by improved visualization via mesh unfolding. Results: We successfully extracted plaque meshes from 341 carotid arteries, capturing a wide range of plaque shapes with volumes ranging from 2.69{\mu}l to 847.7{\mu}l. The use of a case-specific threshold effectively eliminated false positives in young, healthy subjects. Conclusion: The proposed method enables precise extraction of plaque meshes from 3D vessel wall segmentation masks enabling a correspondence between baseline and one-year follow-up examinations. Unfolding the plaque meshes enhances visualization, while the mesh-based analysis allows quantification of plaque parameters independent of voxel resolution.
目的:通过提取和可视化定量斑块参数,实现对颈动脉斑块在3D中的全面和稳健评估。这些参数在脑卒中风险分析、疗效评估以及斑块进展预测中具有潜在应用价值。方法:我们提出了一种新方法,通过距离编码内、外壁网格从3D血管壁分割中提取斑块网格,用于精确分析斑块结构。应用由正常血管壁厚推导出的针对特定病例的阈值,从一组包含高达50%狭窄的202例T1加权黑血MRI扫描数据集中提取斑块。该方法应用于基线数据以及一年后的随访数据,支持随时间变化的详细斑块形态分析,包括斑块体积量化,辅以网格展开改进的可视化。结果:我们成功地从341个颈动脉中提取了斑块网格,捕捉到了各种斑块形状,体积范围从2.69μl到847.7μl。使用特定病例的阈值有效地消除了年轻健康人群中的假阳性结果。结论:所提出的方法能够精确地从3D血管壁分割蒙版中提取斑块网格,实现基线检查和一年后的随访检查之间的对应关系。展开斑块网格增强了可视化效果,而基于网格的分析允许独立于体素分辨率的斑块参数量化。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 13 pages, 5 Figures, Submitted to the International Journal of Computer Assisted Radiology and Surgery
Summary
本文提出了一种基于三维血管壁分割的新型斑块提取方法,该方法可通过距离编码确定内外壁网格进行精确斑块结构分析。应用于基于T1加权黑血MRI扫描的数据集,该方法可从基准线和一年的随访数据中分析斑块形态,包括量化斑块体积等。本文成功的从341个颈动脉中提取了斑块网格,捕捉到了广泛的斑块形态和体积范围。此方法利用特定的阈值有效地消除了年轻健康人群中的假阳性结果。这种方法使得精确提取斑块网格成为可能,为斑块参数量化提供了基础,有助于评估中风风险、评估治疗效果和预测斑块进展。
Key Takeaways
- 提出了一种基于三维血管壁分割的新型斑块提取方法,用于精确分析斑块结构。
- 利用距离编码确定内外壁网格进行斑块提取和可视化。
- 通过应用特定的阈值,成功从数据集中提取了斑块网格,捕捉到了广泛的斑块形态和体积范围。
- 该方法可以应用于基准线和一年的随访数据,进行详细的斑块形态分析,包括量化斑块体积。
- 展开网格增强了斑块的可视化效果。
点此查看论文截图

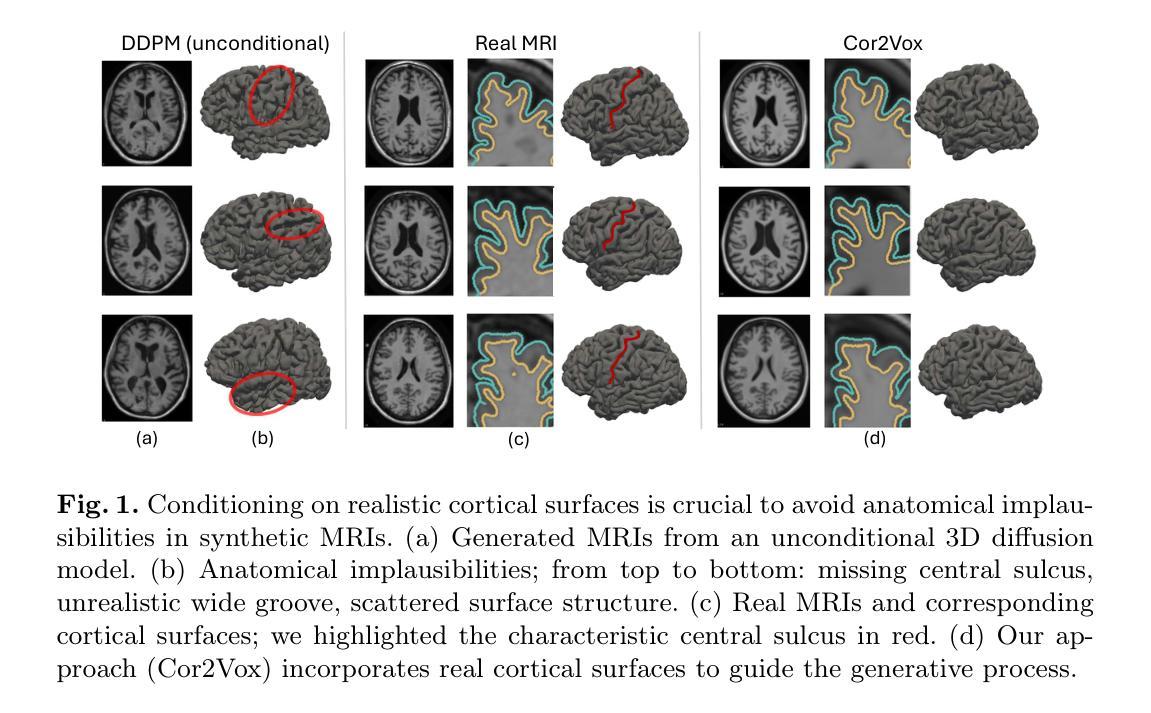
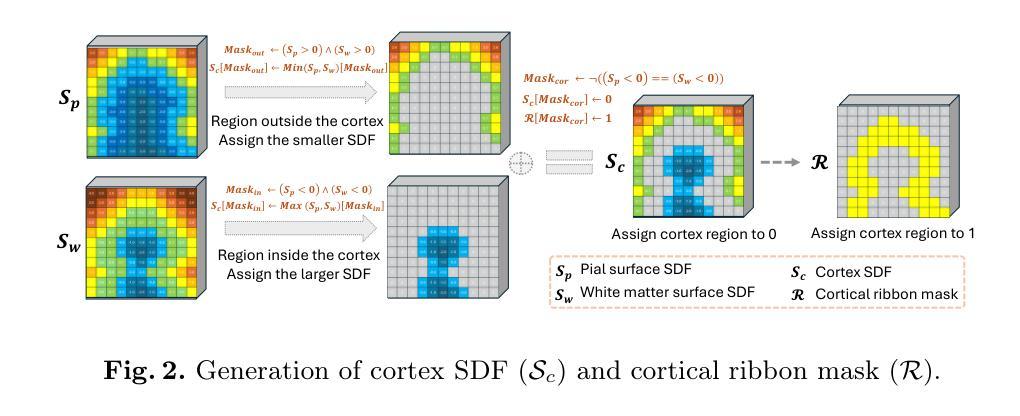
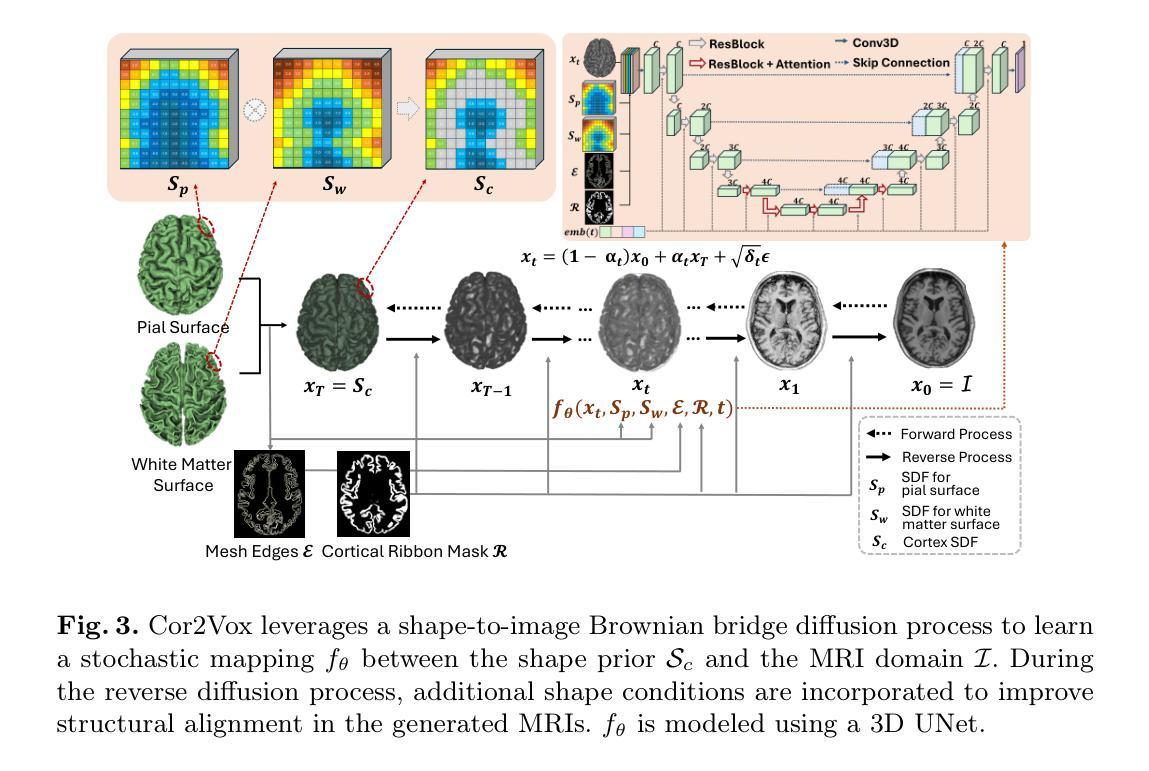
3D Shape-to-Image Brownian Bridge Diffusion for Brain MRI Synthesis from Cortical Surfaces
Authors:Fabian Bongratz, Yitong Li, Sama Elbaroudy, Christian Wachinger
Despite recent advances in medical image generation, existing methods struggle to produce anatomically plausible 3D structures. In synthetic brain magnetic resonance images (MRIs), characteristic fissures are often missing, and reconstructed cortical surfaces appear scattered rather than densely convoluted. To address this issue, we introduce Cor2Vox, the first diffusion model-based method that translates continuous cortical shape priors to synthetic brain MRIs. To achieve this, we leverage a Brownian bridge process which allows for direct structured mapping between shape contours and medical images. Specifically, we adapt the concept of the Brownian bridge diffusion model to 3D and extend it to embrace various complementary shape representations. Our experiments demonstrate significant improvements in the geometric accuracy of reconstructed structures compared to previous voxel-based approaches. Moreover, Cor2Vox excels in image quality and diversity, yielding high variation in non-target structures like the skull. Finally, we highlight the capability of our approach to simulate cortical atrophy at the sub-voxel level. Our code is available at https://github.com/ai-med/Cor2Vox.
尽管最近在医学图像生成方面取得了进展,但现有方法仍然难以生成解剖上合理的3D结构。在合成的大脑磁共振成像(MRI)中,特征裂往往缺失,重建的皮层表面看起来是散乱的,而不是密集卷曲的。为了解决这个问题,我们引入了Cor2Vox,这是基于扩散模型的方法,首次将连续的皮质形状先验知识转化为合成的大脑MRI。为了实现这一点,我们利用布朗桥过程,允许形状轮廓和医学图像之间的直接结构化映射。具体来说,我们将布朗桥扩散模型的概念适应到3D,并将其扩展到包含各种互补形状表示。我们的实验表明,与先前的基于体素的方法相比,重建结构的几何精度有了显着提高。此外,Cor2Vox在图像质量和多样性方面表现出色,在非目标结构(如颅骨)上产生了较高的变化。最后,我们强调了我们的方法在亚体素级别模拟皮质萎缩的能力。我们的代码可在https://github.com/ai-med/Cor2Vox获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by Information Processing in Medical Imaging (IPMI) 2025
Summary
本文介绍了Cor2Vox,首个基于扩散模型的方法,能将连续的皮质形状先验转化为合成的大脑MRI图像。通过采用布朗桥过程,实现了形状轮廓与医学图像之间的直接结构化映射,并在3D环境中对布朗桥扩散模型进行了适应和扩展,以容纳各种互补形状表示。相较于传统的体素方法,Cor2Vox在几何准确性上有了显著提升,同时图像质量和多样性也有所提高,特别是在非目标结构如颅骨上表现出高变异性。此外,Cor2Vox还能模拟子体素级别的皮质萎缩。
Key Takeaways
- Cor2Vox是首个基于扩散模型的医学图像生成方法,专注于合成大脑MRI。
- 通过布朗桥过程实现形状轮廓与医学图像之间的直接结构化映射。
- Cor2Vox将连续的皮质形状先验转化为合成的大脑MRI。
- 该方法在3D环境中对布朗桥扩散模型进行了适应和扩展。
- Cor2Vox在几何准确性上相较于传统体素方法有所提升。
- Cor2Vox能提高图像质量和多样性,特别是在非目标结构上。
- Cor2Vox能模拟子体素级别的皮质萎缩。
点此查看论文截图

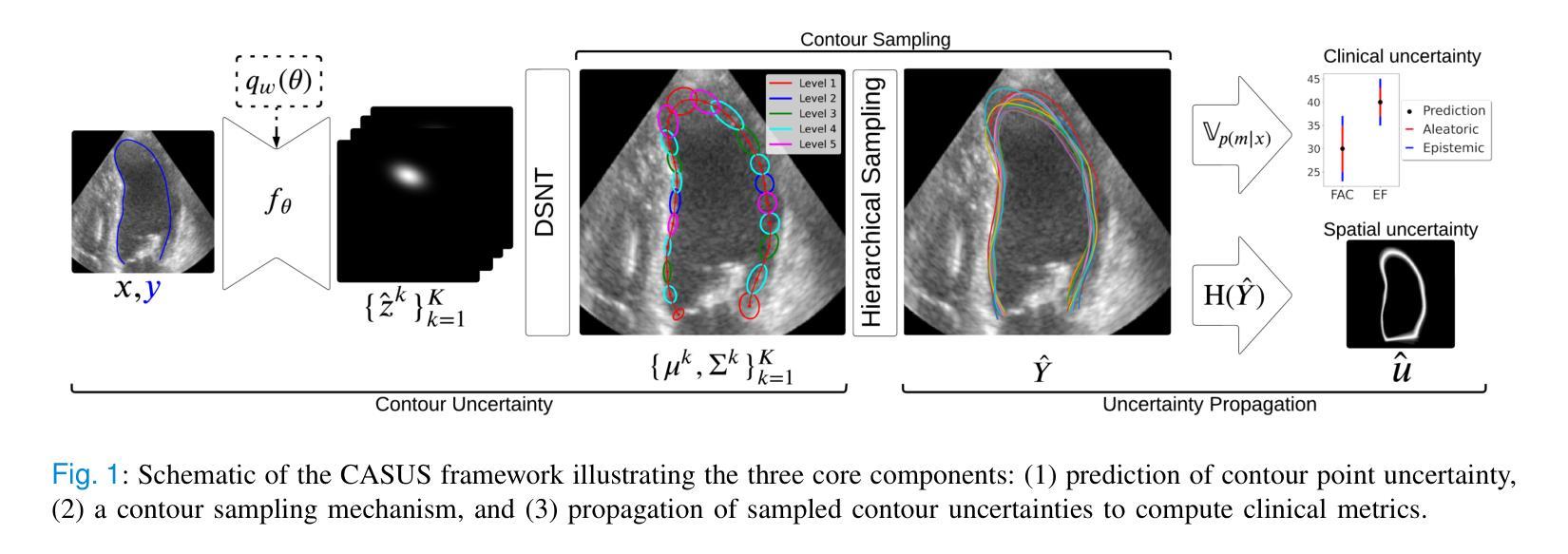
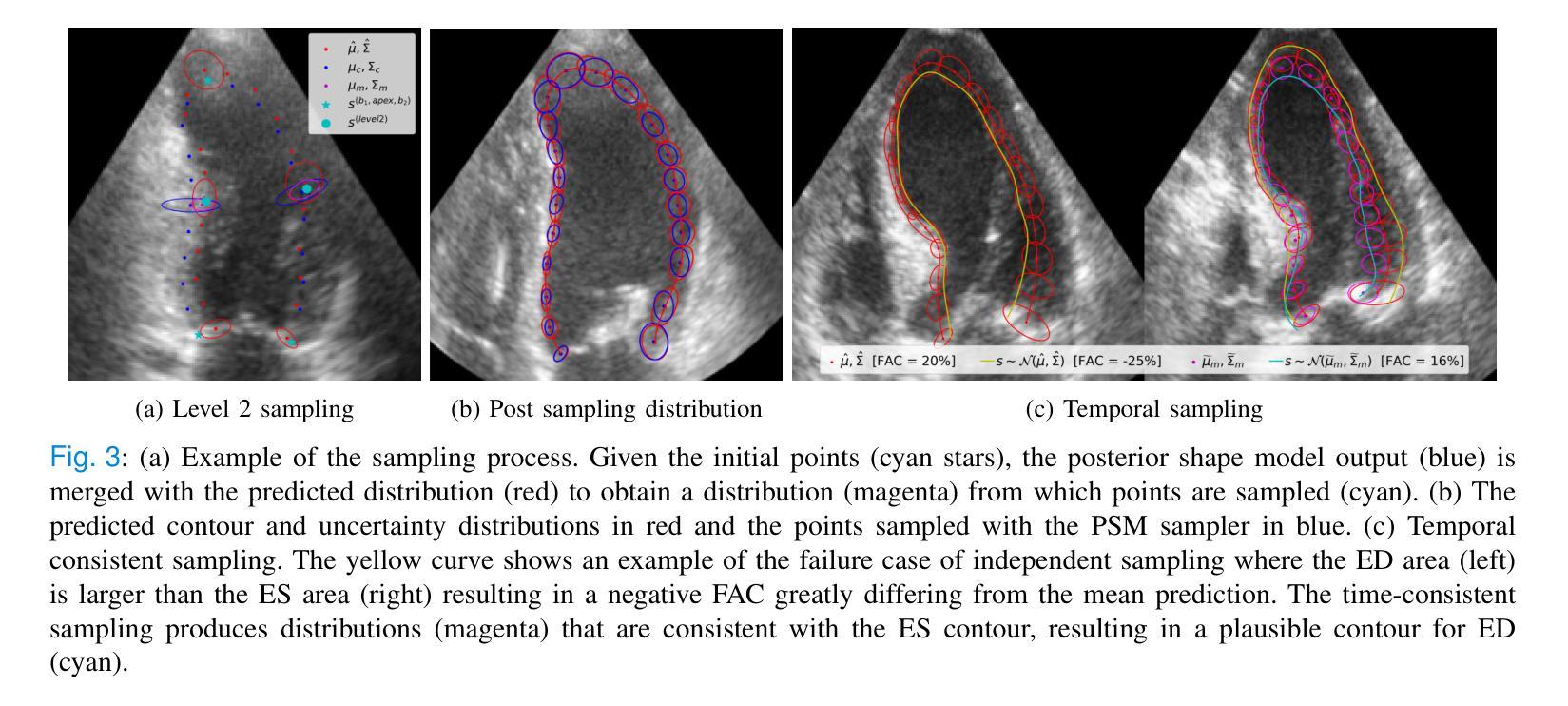
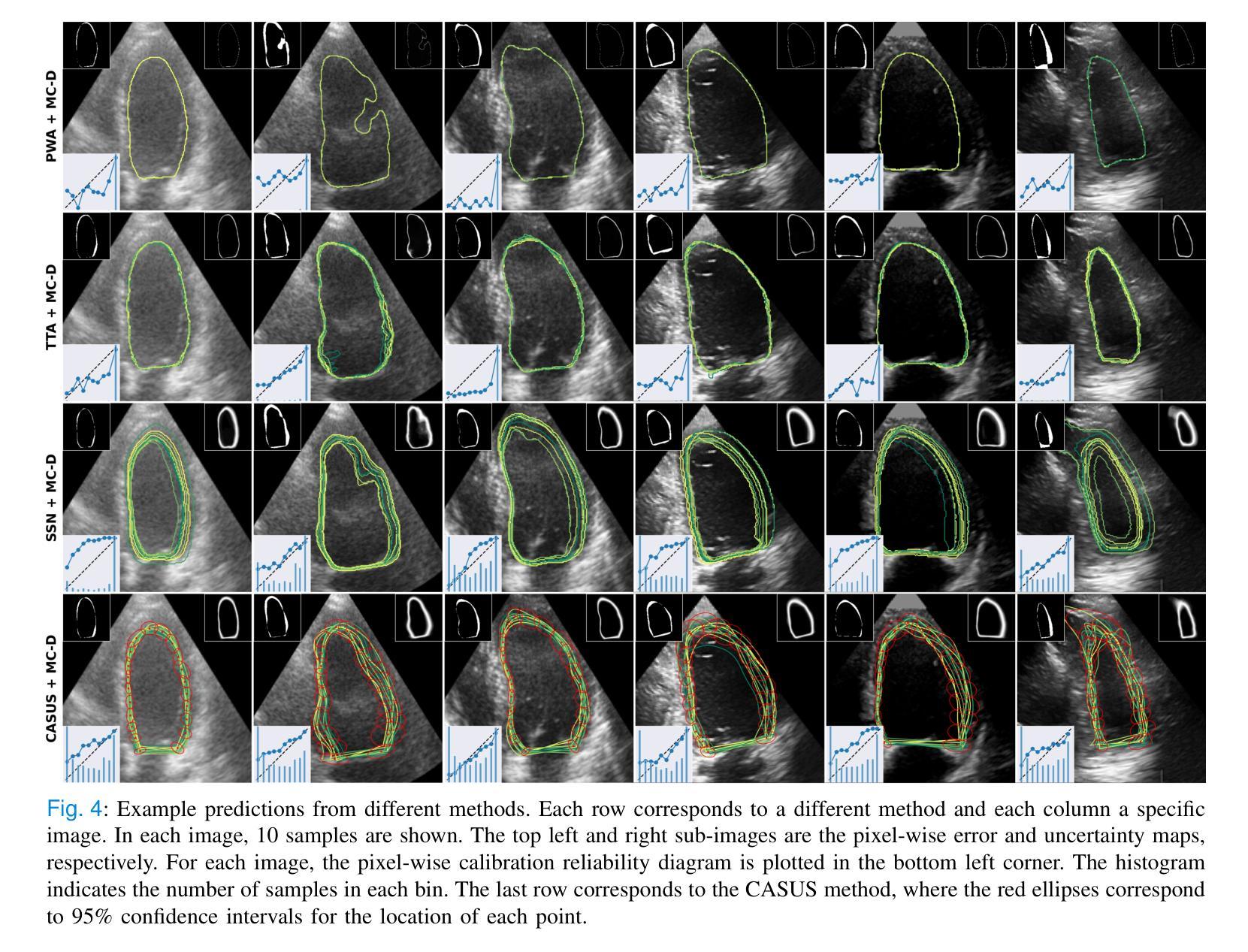
Uncertainty Propagation for Echocardiography Clinical Metric Estimation via Contour Sampling
Authors:Thierry Judge, Olivier Bernard, Woo-Jin Cho Kim, Alberto Gomez, Arian Beqiri, Agisilaos Chartsias, Pierre-Marc Jodoin
Echocardiography plays a fundamental role in the extraction of important clinical parameters (e.g. left ventricular volume and ejection fraction) required to determine the presence and severity of heart-related conditions. When deploying automated techniques for computing these parameters, uncertainty estimation is crucial for assessing their utility. Since clinical parameters are usually derived from segmentation maps, there is no clear path for converting pixel-wise uncertainty values into uncertainty estimates in the downstream clinical metric calculation. In this work, we propose a novel uncertainty estimation method based on contouring rather than segmentation. Our method explicitly predicts contour location uncertainty from which contour samples can be drawn. Finally, the sampled contours can be used to propagate uncertainty to clinical metrics. Our proposed method not only provides accurate uncertainty estimations for the task of contouring but also for the downstream clinical metrics on two cardiac ultrasound datasets. Code is available at: https://github.com/ThierryJudge/contouring-uncertainty.
超声心动术在提取确定心脏状况存在与否及其严重程度所需的重要临床参数(例如左心室容积和射血分数)方面起着至关重要的作用。当应用自动化技术来计算这些参数时,对不确定性的评估是至关重要的。由于临床参数通常来自分割图,因此没有明确的途径将像素级的不确定性值转换为下游临床指标计算中的不确定性估计。在这项工作中,我们提出了一种基于轮廓而不是分割的不确定性估计新方法。我们的方法可以明确地预测轮廓位置的不确定性,从而可以从中绘制轮廓样本。最后,这些采样轮廓可用于将不确定性传播到临床指标。我们提出的方法不仅为轮廓任务提供了准确的不确定性估计,而且在两个心脏超声数据集上对下游临床指标也提供了准确的不确定性估计。相关代码可在以下网址找到:https://github.com/ThierryJudge/contouring-uncertainty 。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 10 pages, submitted to IEEE TMI
Summary
超声心动图在提取重要临床参数(如左心室容积和射血分数)以判断心脏相关疾病的存在和严重程度方面发挥着重要作用。当使用自动化技术计算这些参数时,对不确定性进行估计是评估其效用的关键。本研究提出了一种基于轮廓而非分割的不确定性估计新方法,该方法能够明确预测轮廓位置的不确定性,从而绘制轮廓样本。最后,这些样本可用于将不确定性传播到临床指标。该方法不仅为轮廓任务提供了准确的不确定性估计,而且在两个心脏超声数据集上对下游临床指标也提供了准确的不确定性估计。
Key Takeaways
- 超声心动图在诊断心脏相关疾病中扮演重要角色,能提取关键临床参数。
- 自动化技术在计算临床参数时,不确定性估计是评估其效用的关键。
- 本研究提出了一种基于轮廓的不确定性估计新方法,该方法优于传统的分割方法。
- 该方法能明确预测轮廓位置的不确定性,并绘制轮廓样本。
- 轮廓样本可用于将不确定性传播到临床指标。
- 该方法在两个心脏超声数据集上表现出对临床指标准确的不确定性估计。
点此查看论文截图

VLBI Imaging of Parsec-scale Radio Structures in Nearby Low-luminosity AGN
Authors:Xiaopeng Cheng, Tao An, Willem Baan, Raneri D. Baldi, David R. A. Williams-Baldwin, Bong Won Sohn, Robert Beswick, Ian M. Mchardy
We report the results of high-resolution 5 GHz Very Long Baseline Array and European VLBI Network observations of 36 nearby galaxies, an extension of the Legacy e-MERLIN Multi-band Imaging of Nearby Galaxies (LeMMINGs) survey. Our sample includes 21 low ionization nuclear emission regions (LINERs), 4 Seyferts, 3 absorption line galaxies (ALGs), and 8 HII galaxies. We achieved an unprecedented detection rate, successfully imaging 23 out of 36 sources with a detection threshold of $\sim$20 $\mu$Jy beam$^{-1}$. The radio sizes are typically of $\leq$ 5 pc. Core identification was achieved in 16 sources, while 7 others were identified as core candidates. Radio luminosities of the sample range from 10$\rm ^{34}$ to 10$\rm ^{38}$ erg s$^{-1}$. Our analysis reveals a predominance of compact core structures, with ten sources exhibiting a one-sided core jet morphology and NGC 2146 exhibiting a rare two-sided jet structure. The study advances our understanding of the compactness of radio sources at various scales, indicating a core-dominated nature in all but one galaxy NGC2655. We find moderate to strong correlations between radio luminosity, black hole mass, optical [O III] line luminosity, and hard X-ray luminosity, suggesting a common active galactic nucleus (AGN) core origin. These results provide new insights into the fundamental plane of black hole activity and support the role of the synchrotron process in Low-luminosity AGN (LLAGN) radio emission.
我们报告了使用高解析度5 GHz超长基线阵列和欧洲VLBI网络对附近36个星系进行观测的结果,这是对遗留e-MERLIN邻近星系多波段成像(LeMMINGs)调查的扩展。我们的样本包括21个低电离核发射区(LINERs)、4个塞弗里特星系、3个吸收线星系(ALGs)和8个HII星系。我们取得了前所未有的检测率,成功地对其中23个源进行了成像,检测阈值约为$\sim$20 $\mu$Jy beam$^{-1}$。射电大小通常小于或等于5 pc。核心识别在16个源上实现,而其他7个被识别为核心候选者。样本的射电光度范围从10$^{34}$到10$^{38}$ erg s$^{-1}$。我们的分析显示紧凑的核心结构占主导地位,有十个源呈现单边核心喷射形态,而NGC 2146呈现罕见的双边喷射结构。该研究推进了对不同尺度上射电源紧凑性的理解,除了一个星系NGC2655之外,其他所有星系都显示出核心主导的特征。我们发现射电光度与黑洞质量、光学[O III]线光度和硬X射线光度之间存在中度到强度的相关性,这表明它们都来自活跃的星系核(AGN)核心。这些结果提供了关于黑洞活动基本平面的新见解,并支持同步辐射过程在低光度活动星系核(LLAGN)射电发射中的作用。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 25 pages, 6 figures, 4 tables, accepted for publication in ApJS
摘要
报告了使用高分辨率5 GHz超长基线阵列和欧洲VLBI网络对附近星系进行观测的结果,这是Legacy e-MERLIN对附近星系的多波段成像(LeMMINGs)调查的延伸。样本包括低电离核发射区(LINERs)的21个星系,赛弗特星系(Seyferts)的4个星系,吸收线星系(ALGs)的3个星系和HII星系的8个星系。在约20微吉束的灵敏度极限下成功检测了超过三分之二的星系。核结构明显并且小型紧凑,长度一般不超过≤五千兆秒的距离尺度。核心鉴定成功完成在十六个星系中,而另外七个星系被确认为核心候选者。样本的射电光度介于每平方秒千兆瓦特(erg s-²)之间。我们的分析揭示了紧凑核心结构占主导地位,有十个星系呈现单边核心喷射形态,而NGC 2146呈现罕见的双边喷射结构。研究推进了对不同尺度上射电源紧凑性的理解,揭示了除NGC 2655外所有星系的以核心为主的特点。我们发现射电光度与黑洞质量、光学氧III线光度以及硬X射线光度之间存在中度至强相关性,暗示着活动星系核(AGNs)核心的常见起源。这些结果提供了关于黑洞活动基本平面的新见解,并支持同步辐射过程在低光度活动星系核(LLAGNs)射电发射中的作用。
关键发现列表
- 利用高分辨阵列观测技术对附近星系进行了广泛的射电观测。
- 成功检测到超过三分之二的观测目标,揭示了射电源的高检测率。
- 观测到的射电源核心结构显著且规模较小,主要呈现紧凑的核心形态。
- 在部分星系中发现单边核心喷射形态,并在NGC 2146中发现罕见的双边喷射结构。
- 除NGC 2655外,所有观测的星系均表现出以核心为主的特点。
点此查看论文截图

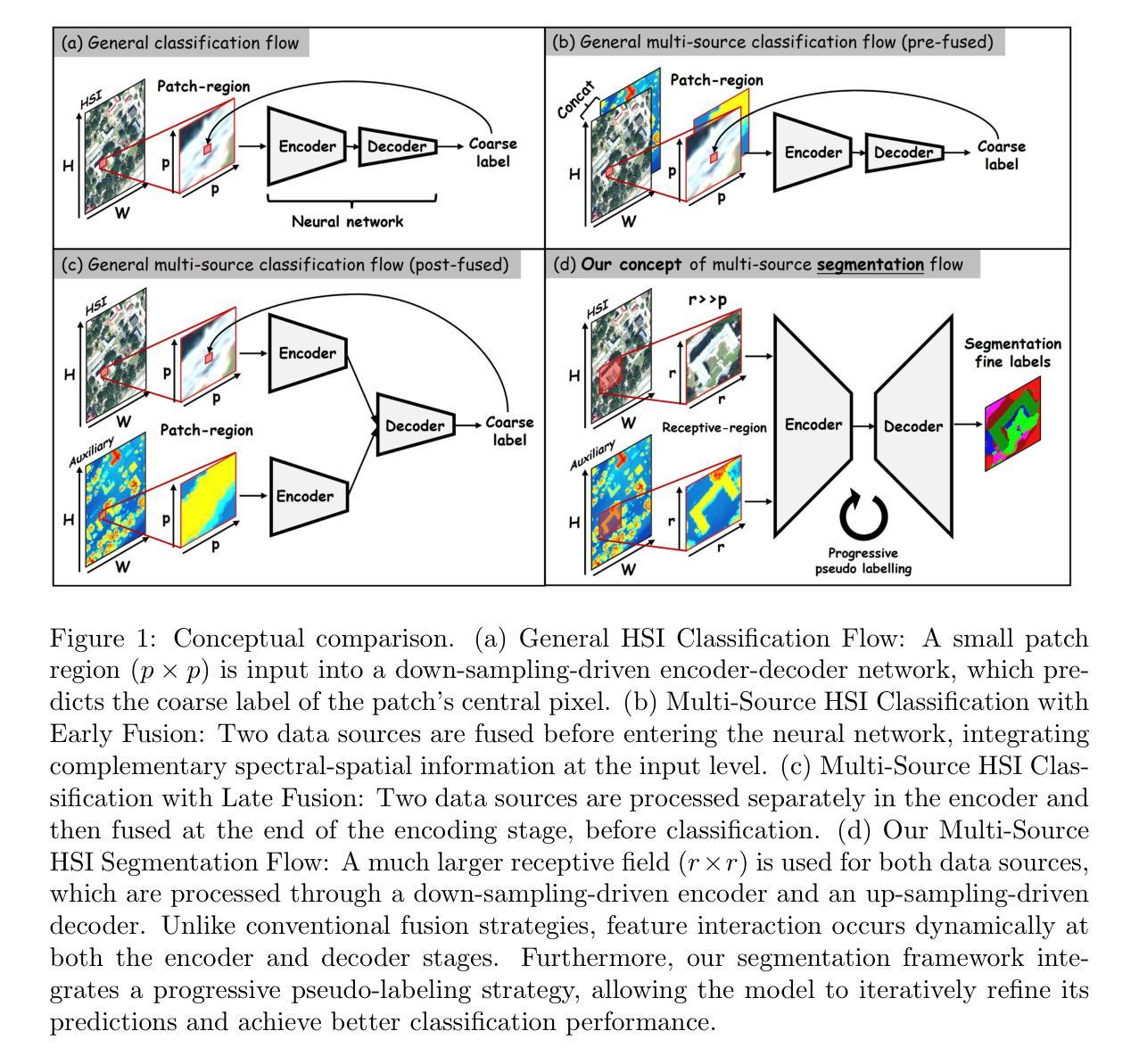
When Segmentation Meets Hyperspectral Image: New Paradigm for Hyperspectral Image Classification
Authors:Weilian Zhou, Weixuan Xie, Sei-ichiro Kamata, Man Sing Wong, Huiying, Hou, Haipeng Wang
Hyperspectral image (HSI) classification is a cornerstone of remote sensing, enabling precise material and land-cover identification through rich spectral information. While deep learning has driven significant progress in this task, small patch-based classifiers, which account for over 90% of the progress, face limitations: (1) the small patch (e.g., 7x7, 9x9)-based sampling approach considers a limited receptive field, resulting in insufficient spatial structural information critical for object-level identification and noise-like misclassifications even within uniform regions; (2) undefined optimal patch sizes lead to coarse label predictions, which degrade performance; and (3) a lack of multi-shape awareness around objects. To address these challenges, we draw inspiration from large-scale image segmentation techniques, which excel at handling object boundaries-a capability essential for semantic labeling in HSI classification. However, their application remains under-explored in this task due to (1) the prevailing notion that larger patch sizes degrade performance, (2) the extensive unlabeled regions in HSI groundtruth, and (3) the misalignment of input shapes between HSI data and segmentation models. Thus, in this study, we propose a novel paradigm and baseline, HSIseg, for HSI classification that leverages segmentation techniques combined with a novel Dynamic Shifted Regional Transformer (DSRT) to overcome these challenges. We also introduce an intuitive progressive learning framework with adaptive pseudo-labeling to iteratively incorporate unlabeled regions into the training process, thereby advancing the application of segmentation techniques. Additionally, we incorporate auxiliary data through multi-source data collaboration, promoting better feature interaction. Validated on five public HSI datasets, our proposal outperforms state-of-the-art methods.
高光谱图像(HSI)分类是遥感的核心,它通过丰富的光谱信息实现精确的材料和土地覆盖物识别。虽然深度学习在此任务中取得了显著进展,但基于小块的分类器占据了超过90%的进展,仍面临一些局限性:(1)基于小块(例如7x7、9x9)的采样方法考虑了一个有限的感受野,导致缺乏对于对象级别识别至关重要的空间结构信息,甚至在均匀区域内出现类似噪声的误分类;(2)不确定的最佳块大小导致标签预测粗糙,从而降低了性能;(3)缺乏对象周围的多形状意识。为了应对这些挑战,我们从大规模图像分割技术中汲取灵感,它们擅长处理对象边界——这是HSI分类中语义标记所必需的能力。然而,它们在此任务中的应用仍然未被充分探索,因为(1)普遍认为较大的块大小会降低性能,(2)HSI基准图像中存在大量未标记区域,以及(3)HSI数据与分割模型之间输入形状的不匹配。因此,本研究提出了一种新的范式和基线方法HSIseg,用于HSI分类,它结合了分割技术与一种新的动态移位区域转换器(DSRT)来克服这些挑战。我们还介绍了一种直观的渐进学习框架,具有自适应伪标签,可以逐步将未标记区域纳入训练过程,从而促进分割技术的应用。此外,我们通过多源数据协作融入辅助数据,促进更好的特征交互。在五个公共HSI数据集上进行验证,我们的提案优于最先进的方法。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了高光谱图像分类中的挑战,包括小补丁分类器在空间结构信息上的不足、标签预测粗糙和缺乏多形状感知能力。为此,借鉴大规模图像分割技术,结合动态平移区域变换器(DSRT)和自适应伪标签的渐进学习框架,提出了HSIseg这一新的高光谱图像分类范式和基线方法。同时引入多源数据协作来提高特征交互效果,在五个公开的高光谱数据集上的验证显示该方法优于现有技术。
Key Takeaways
- 高光谱图像分类面临挑战:小补丁分类器在空间结构信息上的不足导致噪声干扰和误分类。
- 借鉴大规模图像分割技术来处理对象边界问题,有助于解决语义标注问题。
- 动态平移区域变换器(DSRT)在分割技术的整合中发挥关键作用。
- 提出渐进学习框架和自适应伪标签方法,将未标记区域纳入训练过程。
点此查看论文截图

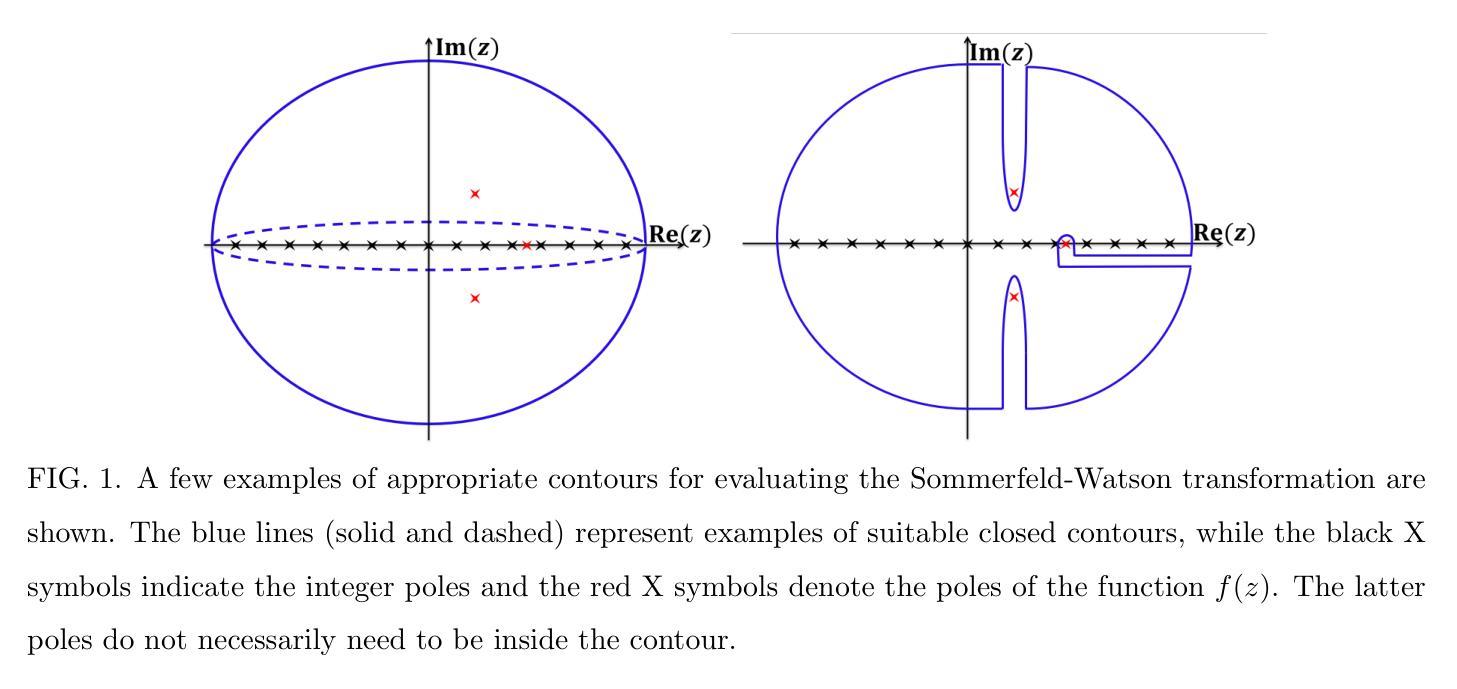
Analytical Diagonalization of Fermi Gas-like Hamiltonians using the Sommerfeld-Watson Transformation
Authors:G. Diniz, F. D. Picoli, M. P. Lenzarini
The Sommerfeld-Watson transformation is a powerful mathematical technique widely used in physics to simplify summations over discrete quantum numbers by converting them into contour integrals in the complex plane. This method has applications in scattering theory, high-energy physics, quantum field theory, and electrostatics. A lesser-known but significant use is in the analytical diagonalization of specific Hamiltonians in condensed matter physics, such as the Fermi gas Hamiltonian and the single-impurity Anderson model with vanishing Coulomb repulsion. These models are used to describe important phenomena like conductance in metals, x-ray photoemission, and aspects of the Kondo problem. In this work, we provide a comprehensive explanation of the Sommerfeld-Watson transformation and its application in diagonalization procedures for these models, using modern notation to enhance clarity for new students. The analytical results were validated against the numerical diagonalization, showing excellent agreement. Furthermore, we extend the presented method to a more generalized non-interacting single-impurity Anderson model with variable couplings and arbitrary band dispersion. The procedure presented here successfully achieved the analytical diagonalization of this more complex model, providing a unified solution that encompasses simpler cases. To our knowledge, this general solution has not been previously reported.
Sommerfeld-Watson转换是一种强大的数学技术,在物理学中广泛应用,通过将其转换为复平面上的轮廓积分来简化离散量子数的求和。该方法在散射理论、高能物理、量子场论和静电学等领域有应用。其较少为人知但重要的应用是在凝聚态物理学中对特定哈密顿量的分析对角化,例如费米气体哈密顿量和无库仑排斥的单杂质安德森模型。这些模型用于描述金属中的电导、X射线光电子发射和康多问题的某些方面等重要现象。在这项工作中,我们使用现代符号体系,为新的学生提供更清晰的解释,全面解释了Sommerfeld-Watson转换及其在这些模型对角化程序中的应用。分析的结果经过与数值对角化的验证,显示出极好的一致性。此外,我们将所介绍的方法扩展到了具有可变耦合和任意带散射的更通用的非相互作用单杂质安德森模型。这里介绍的程序成功地实现了这个更复杂模型的分析对角化,提供了一个涵盖简单情况的综合解决方案。据我们所知,这一通用解决方案尚未有报道过。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
索末菲尔德-沃森变换是一种强大的数学技巧,广泛应用于物理学中,通过将其转换为复平面上的轮廓积分来简化离散量子数的求和。此方法在散射理论、高能物理、量子场论和静电学中都有应用。它在凝聚态物理中对特定哈密顿量的解析对角化方面的应用虽然鲜为人知,但也是重要的应用之一,如费米气体哈密顿量和无库仑排斥的单杂质安德森模型。这些模型被用来描述金属中的导电现象、X射线光电子发射和康多问题的某些方面。本文提供了索末菲尔德-沃森变换及其在这些模型对角化程序中的应用的综合解释,并使用现代符号来提高新学生的清晰度。解析结果与数值对角化的验证结果吻合良好。此外,我们将所介绍的方法扩展到了更通用的具有可变耦合和任意带色散的非相互作用单杂质安德森模型。本文所介绍的程序成功地实现了这一更复杂模型的解析对角化,提供了一个涵盖简单情况的综合解决方案。据我们所知,这种一般解决方案以前尚未报道。
Key Takeaways
* 索末菲尔德-沃森变换是一种强大的数学技巧,广泛应用于物理学中的多个领域。
* 此方法能够简化离散量子数的求和,通过将它们转换为复平面上的轮廓积分。
* 索末菲尔德-沃森变换在凝聚态物理中对特定哈密顿量的解析对角化方面有重要应用。
* 文章提到了两个具体的模型:费米气体哈密顿量和单杂质安德森模型,这些模型在描述物理现象方面具有重要的应用价值。
* 文章提供了索末菲尔德-沃森变换的综合解释,并展示了其在对角化程序中的应用。
* 解析结果与数值对角化的验证结果一致,证明了方法的可靠性。
点此查看论文截图

Modelling the impact of Multi Cancer Early Detection tests: a review of natural history of disease models
Authors:O Mandrik, S Whyte, N Kunst, A Rayner, M Harden, S Dias, K Payne, S Palmer, MO Soares
Introduction: The potential for multi-cancer early detection (MCED) tests to detect cancer at earlier stages is currently being evaluated in screening clinical trials. Once trial evidence becomes available, modelling will be necessary to predict impacts on final outcomes (benefits and harms), account for heterogeneity in determining clinical and cost-effectiveness, and explore alternative screening programme specifications. The natural history of disease (NHD) component of a MCED model will use statistical, mathematical or calibration methods. Methods: Modelling approaches for MCED screening that include an NHD component were identified from the literature, reviewed and critically appraised. Purposively selected (non-MCED) cancer screening models were also reviewed. The appraisal focussed on the scope, data sources, evaluation approaches and the structure and parameterisation of the models. Results: Five different MCED NHD models were identified and reviewed, alongside four additional (non-MCED) models. The critical appraisal highlighted several features of this literature. In the absence of trial evidence, MCED effects are based on predictions derived from test accuracy. These predictions rely on simplifying assumptions with unknown impacts, such as the stage-shift assumption used to estimate mortality impacts from predicted stage-shifts. None of the MCED models fully characterised uncertainty in the NHD or examined uncertainty in the stage-shift assumption. Conclusion: MCED technologies are developing rapidly, and large and costly clinical studies are being designed and implemented across the globe. Currently there is no modelling approach that can integrate clinical study evidence and therefore, in support of policy, it is important that similar efforts are made in the development of MCED models that make best use of the available data on benefits and harms.
引言:多癌早期检测(MCED)试验在筛查临床试验中评估检测癌症早期阶段的可能性。一旦试验证据可用,建模将必不可少,以预测对最终结果(利益和危害)的影响,考虑临床和成本效益的异质性,并探索替代筛查方案规格。MCED模型的疾病自然史(NHD)部分将使用统计、数学或校准方法。方法:从文献中确定了包含NHD部分的MCED筛查建模方法,并对其进行了评论和批判性评估。还审查了有意选择的(非MCED)癌症筛查模型。评估的重点是模型的范围、数据来源、评估方法以及模型和参数的结构。结果:识别并审查了5种不同的MCED NHD模型以及4种额外的(非MCED)模型。批判性评估突出了这篇文献的几个特点。在没有试验证据的情况下,MCED的效果是基于测试准确度的预测。这些预测依赖于简化假设,其影响未知,例如用于估计预期阶段转变对死亡率影响的阶段转变假设。没有一个MCED模型能完全刻画NHD中的不确定性,也没有一个模型能检验阶段转变假设中的不确定性。结论:MCED技术正在迅速发展,全球范围内正在设计和实施大规模且昂贵的临床研究。目前尚无建模方法能够整合临床研究证据,因此,为了支持政策制定,在开发MCED模型方面做出类似努力至关重要,这些模型应最大限度地利用关于利益和危害的可用数据。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了多癌症早期检测(MCED)试验在筛查临床试验中检测癌症早期阶段的潜力。文章指出,在试验证据可用后,建模是必要的,以预测对最终结局的影响(包括利益和危害),并探讨了不同筛查方案规格的问题。文章通过文献综述和评估了MCED筛查的建模方法,重点关注了模型的范围、数据来源、评估方法等。然而,当前MCED模型存在不确定性,特别是在自然病史(NHD)方面,并且缺乏对阶段转移假设的考察。因此,需要发展能更好地利用可用数据的MCED模型。
Key Takeaways
- MCED试验具有在较早阶段检测癌症的潜力,目前正在筛选临床试验中进行评估。
- 在试验证据可用后,建模是必要的,以预测对最终结局的影响,并考虑临床和成本效益的异质性。
- MCED模型的自然病史(NHD)部分将使用统计、数学或校准方法。
- 文献综述和评估发现MCED筛查的建模方法存在不确定性,特别是在自然病史方面。
- MCED效应基于测试准确性的预测,这些预测依赖于未知影响的简化假设,如阶段转移假设。
- 目前的MCED模型未能充分刻画自然病史的不确定性,也未考察阶段转移假设的不确定性。
点此查看论文截图

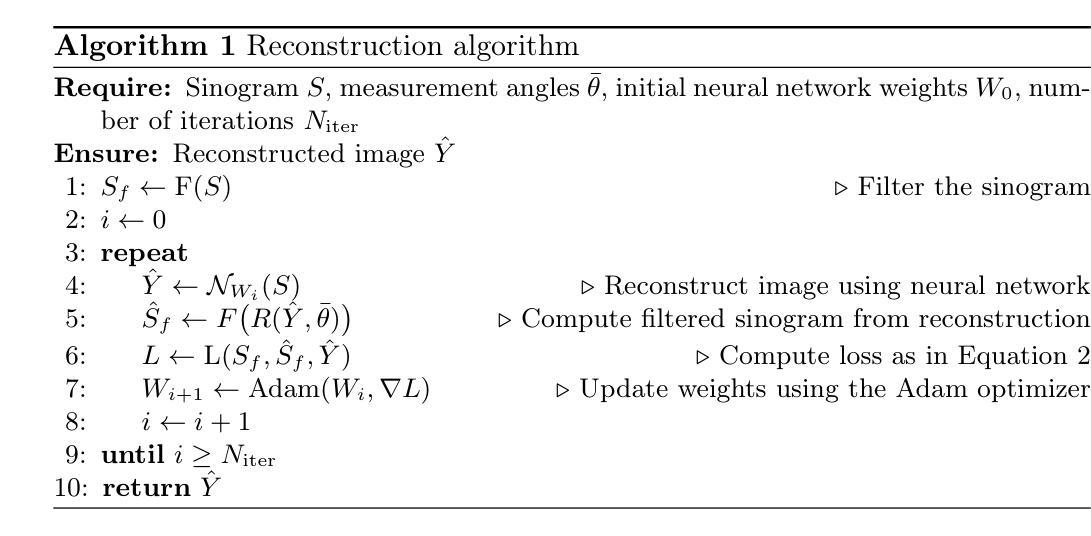
Data-Efficient Limited-Angle CT Using Deep Priors and Regularization
Authors:Ilmari Vahteristo, Zhi-Song Liu, Andreas Rupp
Reconstructing an image from its Radon transform is a fundamental computed tomography (CT) task arising in applications such as X-ray scans. In many practical scenarios, a full 180-degree scan is not feasible, or there is a desire to reduce radiation exposure. In these limited-angle settings, the problem becomes ill-posed, and methods designed for full-view data often leave significant artifacts. We propose a very low-data approach to reconstruct the original image from its Radon transform under severe angle limitations. Because the inverse problem is ill-posed, we combine multiple regularization methods, including Total Variation, a sinogram filter, Deep Image Prior, and a patch-level autoencoder. We use a differentiable implementation of the Radon transform, which allows us to use gradient-based techniques to solve the inverse problem. Our method is evaluated on a dataset from the Helsinki Tomography Challenge 2022, where the goal is to reconstruct a binary disk from its limited-angle sinogram. We only use a total of 12 data points–eight for learning a prior and four for hyperparameter selection–and achieve results comparable to the best synthetic data-driven approaches.
从Radon变换重建图像是计算机断层扫描(CT)中的一个基本任务,出现在X射线扫描等应用中。在许多实际场景中,完整的180度扫描并不可行,或者存在减少辐射暴露的需求。在这些有限角度的设置下,问题变得不适定,专为全视角数据设计的方法通常会产生明显的伪影。我们提出了一种在严重角度限制下从Radon变换重建原始图像的低数据方法。由于反问题是适定的,我们结合了多种正则化方法,包括全变差、辛图滤波器、深度图像先验和补丁级别的自动编码器。我们使用Radon变换的可微实现,这使我们能够使用基于梯度的方法来解决反问题。我们的方法在赫尔辛基断层扫描挑战赛2022的数据集上进行了评估,该数据集的目标是从其有限的角辛图重建一个二进制磁盘。我们只使用了总共12个数据点——8个用于学习先验知识,4个用于超参数选择——并取得了与最佳合成数据驱动方法相当的结果。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 12 pages, 2 reference pages, 5 figures, submitted to SCIA 2024
Summary
该文本介绍了在CT扫描(计算机断层扫描)中,如何从Radon变换重建图像的问题。在实际应用中,由于角度限制或辐射暴露问题,通常无法完成完整的180度扫描。作者提出了一种在严重角度限制下,利用极少量数据从Radon变换重建原始图像的方法。该方法结合了多种正则化方法,并使用可微分的Radon变换实现,以梯度为基础解决反问题。在Helsinki Tomography Challenge 2022的数据集上进行的评估表明,仅使用总计12个数据点(8个用于学习先验知识,4个用于选择超参数)即可获得与最佳合成数据驱动方法相当的结果。
Key Takeaways
- 该文本讨论了CT扫描中从Radon变换重建图像的问题,特别是在有限角度下的挑战。
- 作者提出了一种在严重角度限制下,利用非常有限的数据进行图像重建的方法。
- 该方法结合了多种正则化技术,以改善在有限角度下的图像重建质量。
- 使用可微分的Radon变换实现,便于使用梯度下降法进行优化。
- 仅在Helsinki Tomography Challenge 2022的数据集上,使用少量数据点(总计12个)即可实现与最佳方法相当的性能。
- 该方法不仅用于学习先验知识,还用于超参数的选择。
点此查看论文截图

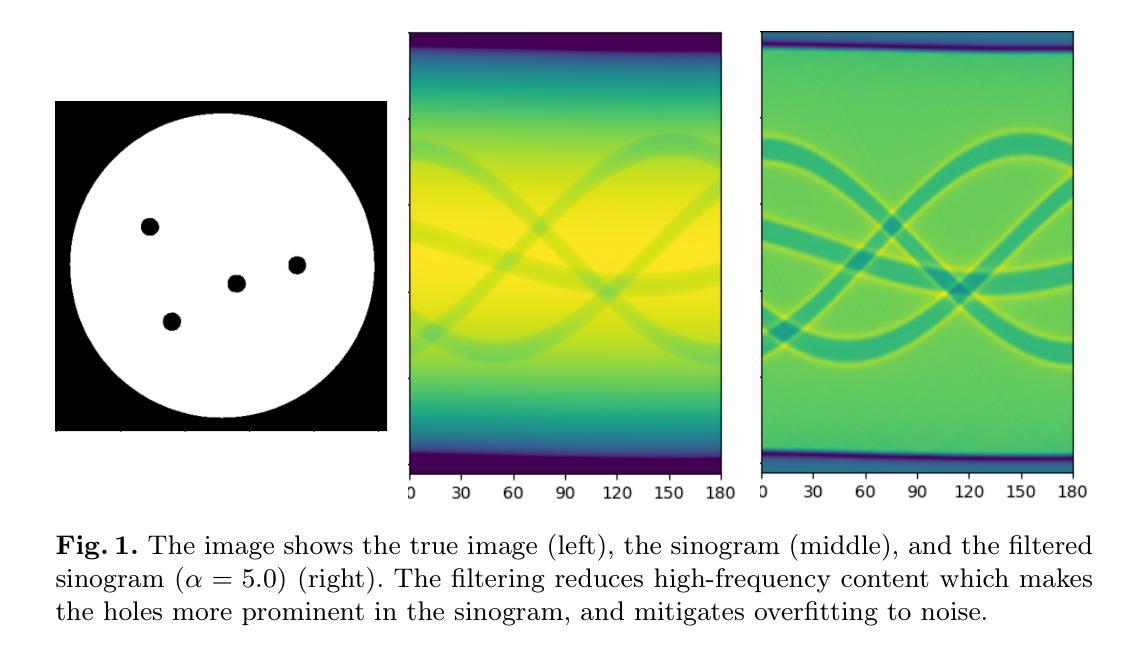
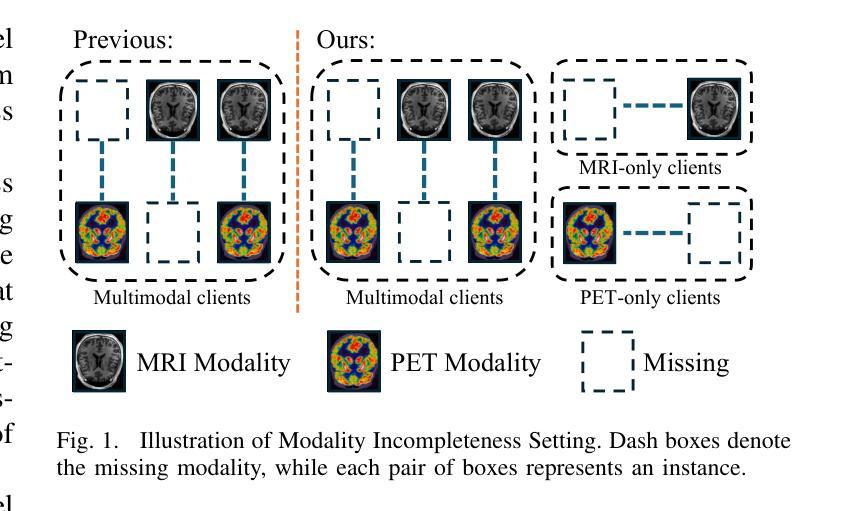
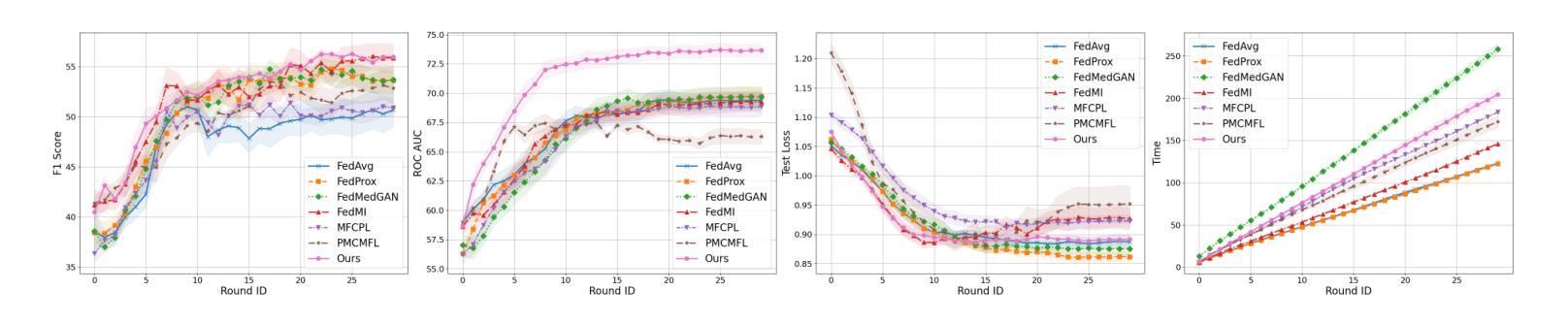
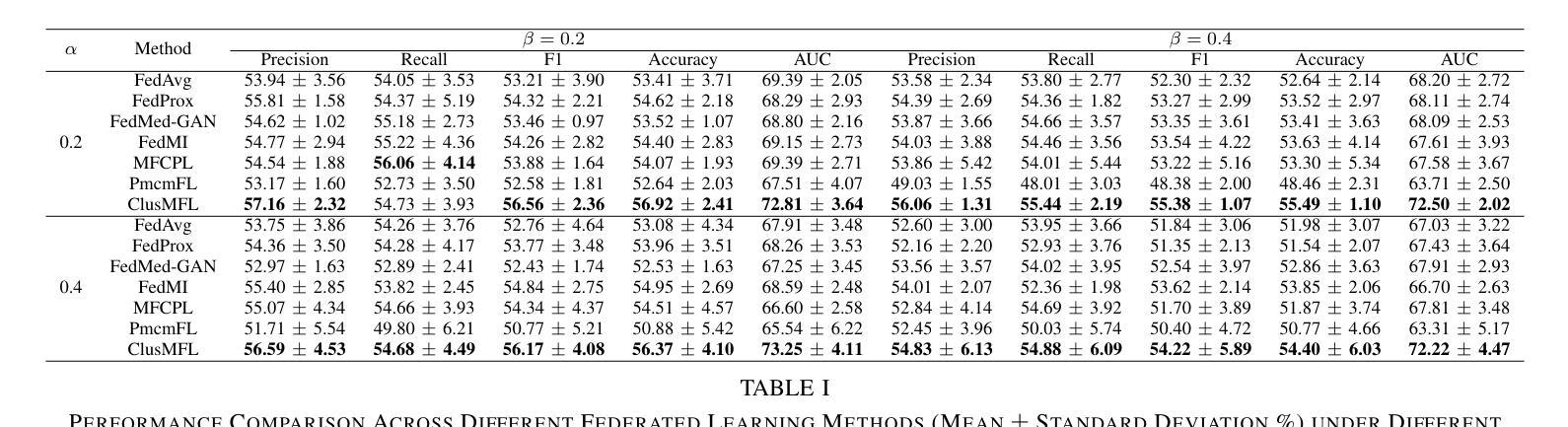
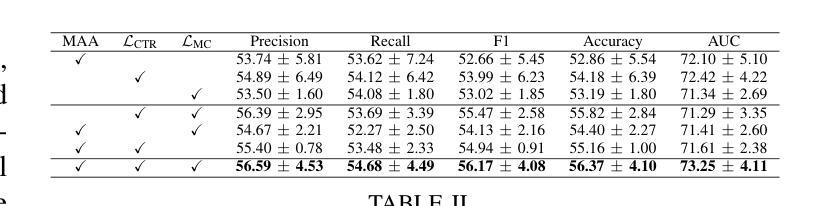
ClusMFL: A Cluster-Enhanced Framework for Modality-Incomplete Multimodal Federated Learning in Brain Imaging Analysis
Authors:Xinpeng Wang, Rong Zhou, Han Xie, Xiaoying Tang, Lifang He, Carl Yang
Multimodal Federated Learning (MFL) has emerged as a promising approach for collaboratively training multimodal models across distributed clients, particularly in healthcare domains. In the context of brain imaging analysis, modality incompleteness presents a significant challenge, where some institutions may lack specific imaging modalities (e.g., PET, MRI, or CT) due to privacy concerns, device limitations, or data availability issues. While existing work typically assumes modality completeness or oversimplifies missing-modality scenarios, we simulate a more realistic setting by considering both client-level and instance-level modality incompleteness in this study. Building on this realistic simulation, we propose ClusMFL, a novel MFL framework that leverages feature clustering for cross-institutional brain imaging analysis under modality incompleteness. Specifically, ClusMFL utilizes the FINCH algorithm to construct a pool of cluster centers for the feature embeddings of each modality-label pair, effectively capturing fine-grained data distributions. These cluster centers are then used for feature alignment within each modality through supervised contrastive learning, while also acting as proxies for missing modalities, allowing cross-modal knowledge transfer. Furthermore, ClusMFL employs a modality-aware aggregation strategy, further enhancing the model’s performance in scenarios with severe modality incompleteness. We evaluate the proposed framework on the ADNI dataset, utilizing structural MRI and PET scans. Extensive experimental results demonstrate that ClusMFL achieves state-of-the-art performance compared to various baseline methods across varying levels of modality incompleteness, providing a scalable solution for cross-institutional brain imaging analysis.
多模态联邦学习(MFL)已成为一种有前途的方法,用于在分布式客户端上协同训练多模态模型,特别是在医疗领域。在脑成像分析的背景下,模态不完整性问题是一个巨大的挑战,一些机构可能会因隐私担忧、设备限制或数据可用性等问题而缺少特定的成像模态(例如PET、MRI或CT)。虽然现有工作通常假设模态完整性或过于简化缺失模态场景,本研究在考虑客户端和实例级模态不完整性的情况下,模拟了一个更现实的环境。基于这种现实模拟,我们提出了ClusMFL,这是一种新的MFL框架,它利用特征聚类在模态不完整的情况下进行跨机构脑成像分析。具体来说,ClusMFL使用FINCH算法为每种模态标签对构建特征嵌入的簇中心池,有效捕获细粒度数据分布。这些簇中心随后用于通过监督对比学习进行每种模态内的特征对齐,同时作为缺失模态的代理,实现跨模态知识转移。此外,ClusMFL采用了一种模态感知聚合策略,进一步提高了在严重模态不完整场景中的模型性能。我们在ADNI数据集上评估了所提出的框架,利用结构MRI和PET扫描。大量的实验结果表明,与各种基线方法相比,ClusMFL在不同程度的模态不完整性上达到了最先进的性能,为跨机构脑成像分析提供了可伸缩的解决方案。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本研究考虑了在医疗领域尤其是脑成像分析中面临的多模态数据缺失问题,提出了基于特征聚类的多模态联邦学习框架ClusMFL。针对客户端和实例级别的模态缺失问题,ClusMFL通过利用FINCH算法构建模态标签对的特征嵌入簇中心池,实现跨机构脑成像分析在模态缺失下的精细粒度数据处理。此外,通过监督对比学习进行特征对齐,并采用模态感知聚合策略,提高在严重模态缺失场景下的模型性能。在ADNI数据集上的实验表明,ClusMFL在不同水平的模态缺失情况下均达到最佳性能。
Key Takeaways
- 多模态联邦学习(MFL)是处理分布式客户端上的多模态模型的有效方法,特别是在医疗领域。
- 现实情况下存在模态缺失问题,本研究考虑了客户端和实例级别的模态缺失。
- ClusMFL利用特征聚类解决模态缺失问题,通过构建模态标签对的特征嵌入簇中心池来捕捉精细粒度的数据分布。
- ClusMFL采用监督对比学习进行特征对齐,并使用这些簇中心作为缺失模态的代理,实现跨模态知识转移。
- ClusMFL采用模态感知聚合策略,增强在严重模态缺失情况下的模型性能。
- 在ADNI数据集上的实验验证了ClusMFL的有效性,其在不同水平的模态缺失情况下均表现最佳。
点此查看论文截图

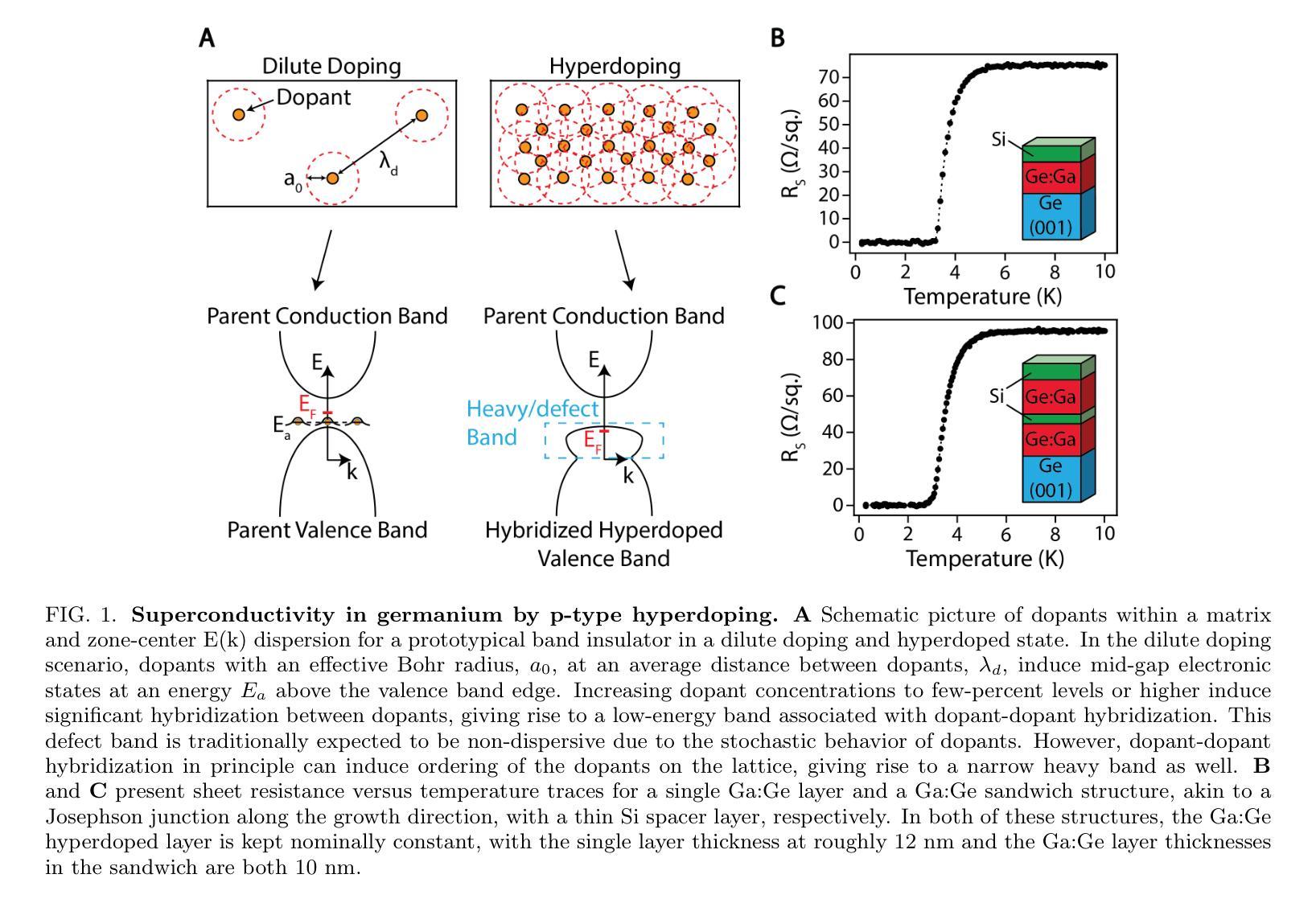
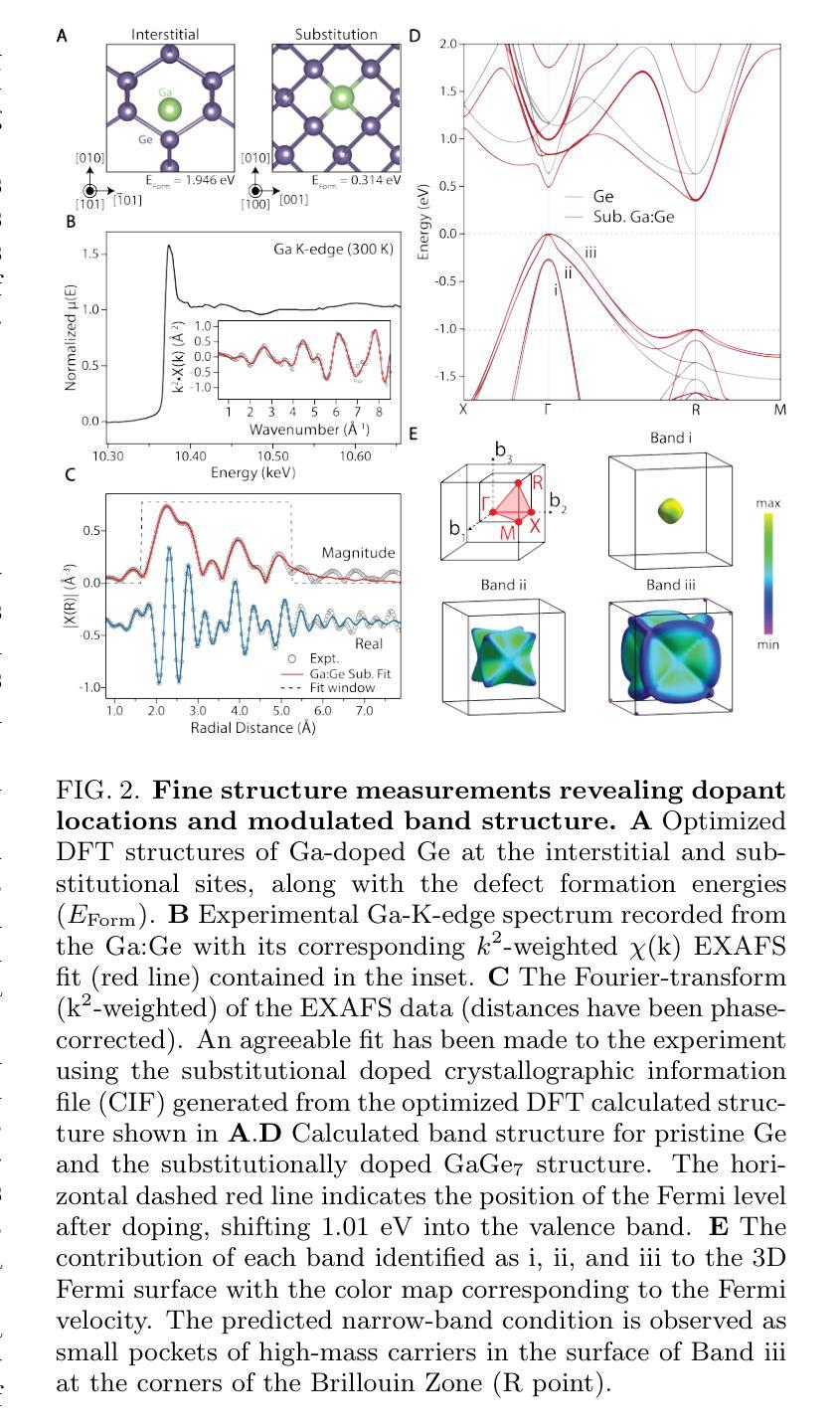
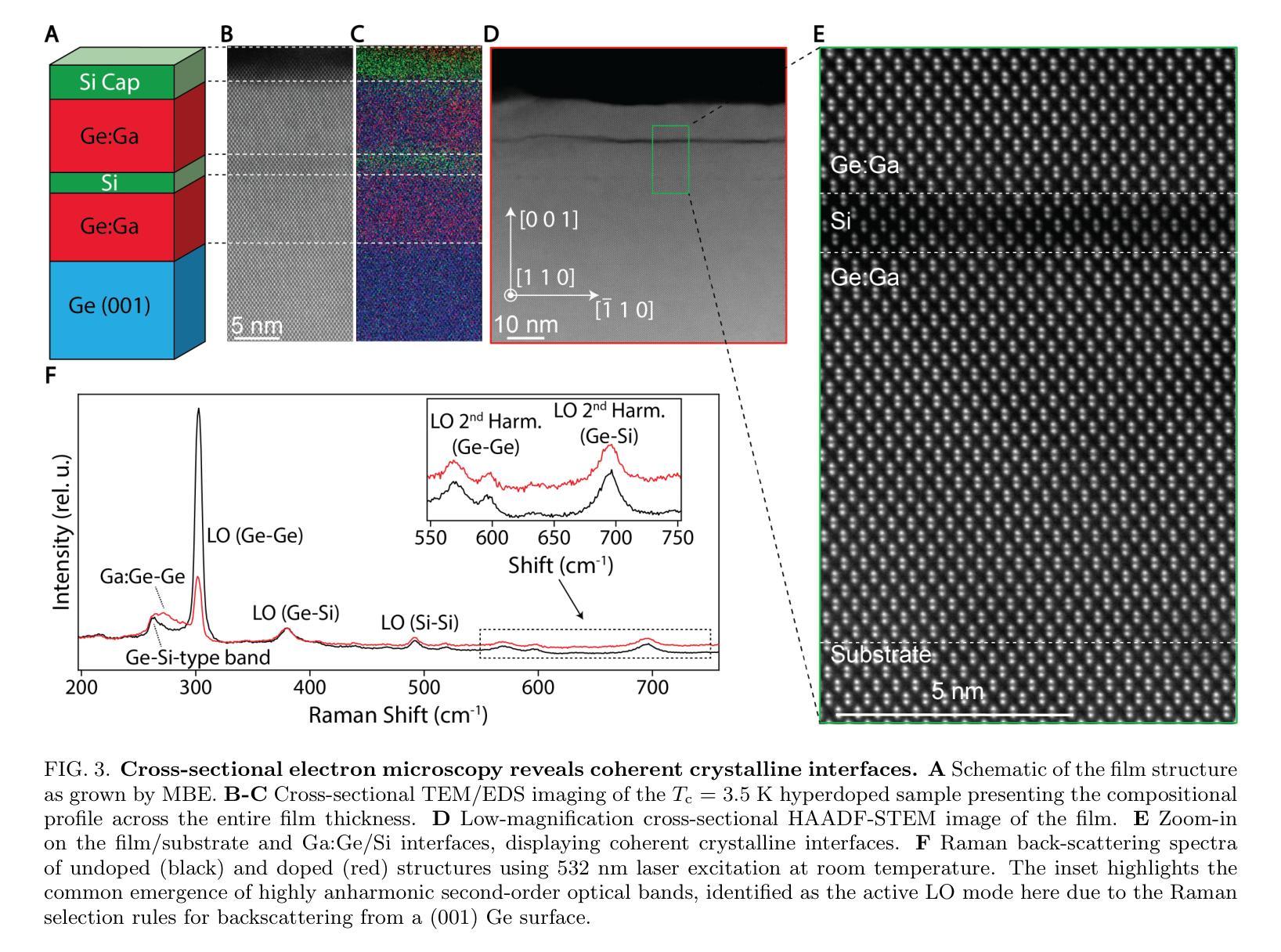
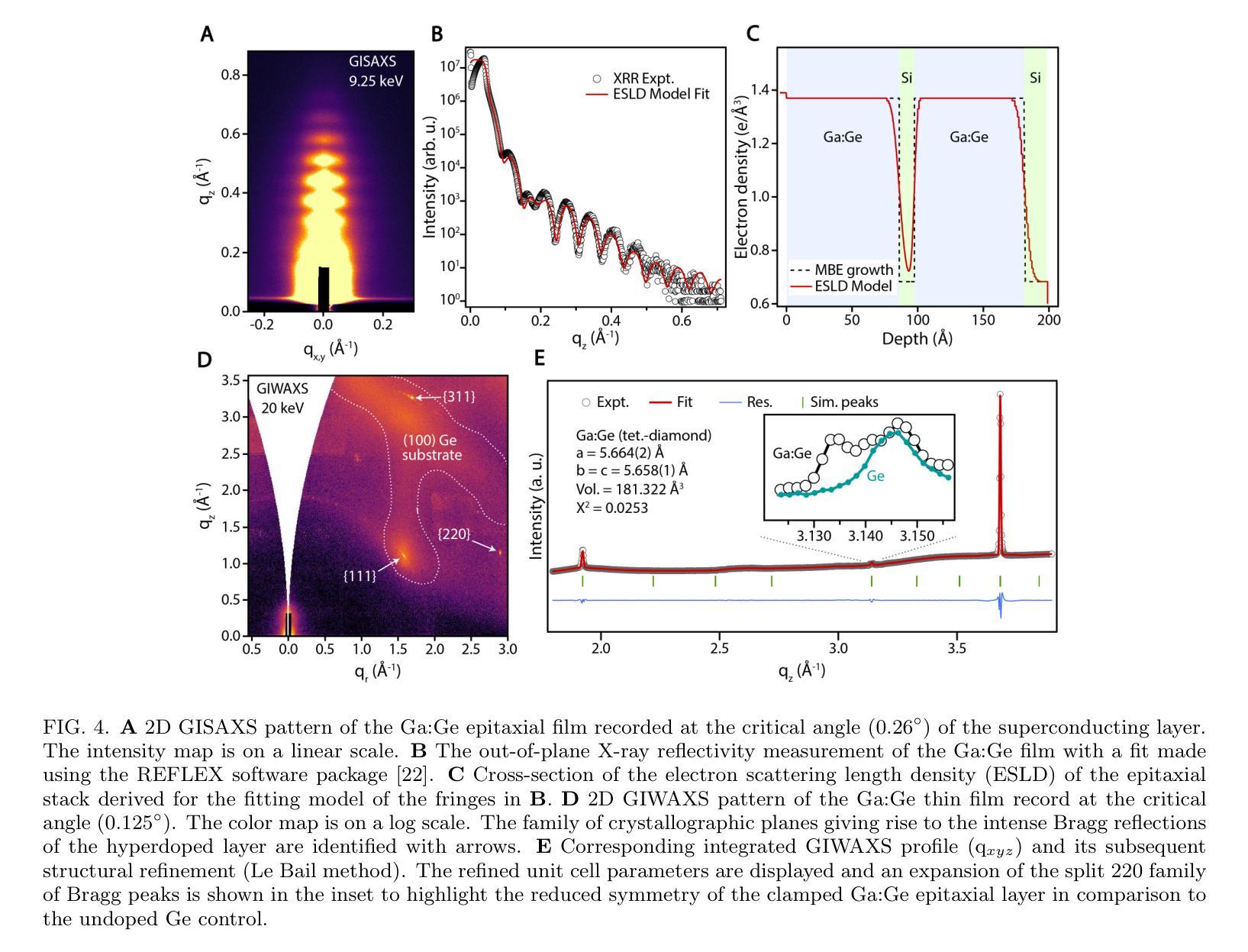
Coherent Superconductor-Semiconductor Epitaxy for Integrated Quantum Electronics
Authors:Julian A. Steele, Patrick J. Strohbeen, Carla Verdi, Ardeshir Baktash, Alisa Danilenko, Yi-Hsun Chen, Jechiel van Dijk, Lianzhou Wang, Eugene Demler, Salva Salmani-Rezaie, Peter Jacobson, Javad Shabani
Introducing superconductivity into group IV elements by doping has long promised a pathway to introduce quantum functionalities into well-established semiconductor technologies. The non-equilibrium hyperdoping of group III atoms into Si or Ge has successfully shown superconductivity can be achieved, however, the origin of superconductivity has been obscured by structural disorder and dopant clustering. Here, we report the epitaxial growth of hyperdoped Ga:Ge films by molecular beam epitaxy with extreme hole concentrations ($n_\textup{h} = 4.15 \times 10^{21}$cm$^{-3}$, ~17.9% Ga substitution) that yield superconductivity with a critical temperature of $T_{\textup{c}} = 3.5$K and an out-of-plane critical field of 1T at 270mK. Synchrotron-based X-ray absorption and scattering methods reveal that Ga dopants are substitutionally incorporated within the Ge lattice, introducing a tetragonal distortion to the crystal unit cell. Our findings, corroborated by first-principles calculations, suggest that the structural order of Ga dopants creates a narrow band for the emergence of superconductivity in Ge, establishing hyperdoped Ga:Ge as a low-disorder, epitaxial superconductor-semiconductor platform.
将超导性引入第四族元素通过掺杂长期以来为将量子功能引入成熟的半导体技术中开辟了一条道路。第三族原子对Si或Ge的非平衡超掺杂已成功证明可以实现超导性。然而,由于结构无序和掺杂剂聚集,超导性的起源变得模糊不清。在这里,我们报告了通过分子束外延方法实现超掺杂Ga:Ge薄膜的外延生长,具有极高的空穴浓度(nh= 4.15×10^21 cm^-3,约17.9%的Ga替代),产生超导性,临界温度Tc= 3.5 K,在270 mK时的面外临界场为1 T。基于同步辐射的X射线吸收和散射方法显示,Ga掺杂剂被替代性地掺入Ge晶格中,为晶胞引入了四方畸变。我们的发现得到了第一性原理计算的证实,表明Ga掺杂剂的结构顺序为Ge中出现超导性开辟了一个狭窄的通道,确立了超掺杂Ga:Ge作为低无序、外延的超导体-半导体平台。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
掺杂III族原子进入硅或锗的非平衡超掺杂已成功实现超导性,但结构无序和掺杂剂聚集使得超导性的起源变得模糊。本研究报告通过分子束外延技术外延生长超掺杂Ga:Ge薄膜,实现了极端空穴浓度下的超导性,关键温度达到3.5K,并在极低温度下具有临界场强度。同步辐射X射线吸收和散射方法揭示Ga掺杂剂在Ge晶格中的替代位置,引入了四方晶胞畸变。本研究建立超掺杂Ga:Ge作为低无序、外延超导半导体平台。
Key Takeaways
- 通过掺杂III族原子进入集团IV元素(如Si或Ge)可以实现超导性。
- 超掺杂技术成功在Ga:Ge薄膜中实现超导性,关键温度达到3.5K。
- Ga掺杂剂在Ge晶格中的位置对超导性的出现有重要影响,引入四方晶胞畸变。
- 高浓度的Ga掺杂剂($n_\text{h} = 4.15 \times 10^{21}$ cm$^{-3}$)对超导性能的提升起到关键作用。
- 通过分子束外延技术实现了极端空穴浓度下的Ga:Ge薄膜的外延生长。
- 同步辐射X射线吸收和散射方法被用来揭示Ga掺杂剂在Ge晶格中的结构位置。
点此查看论文截图

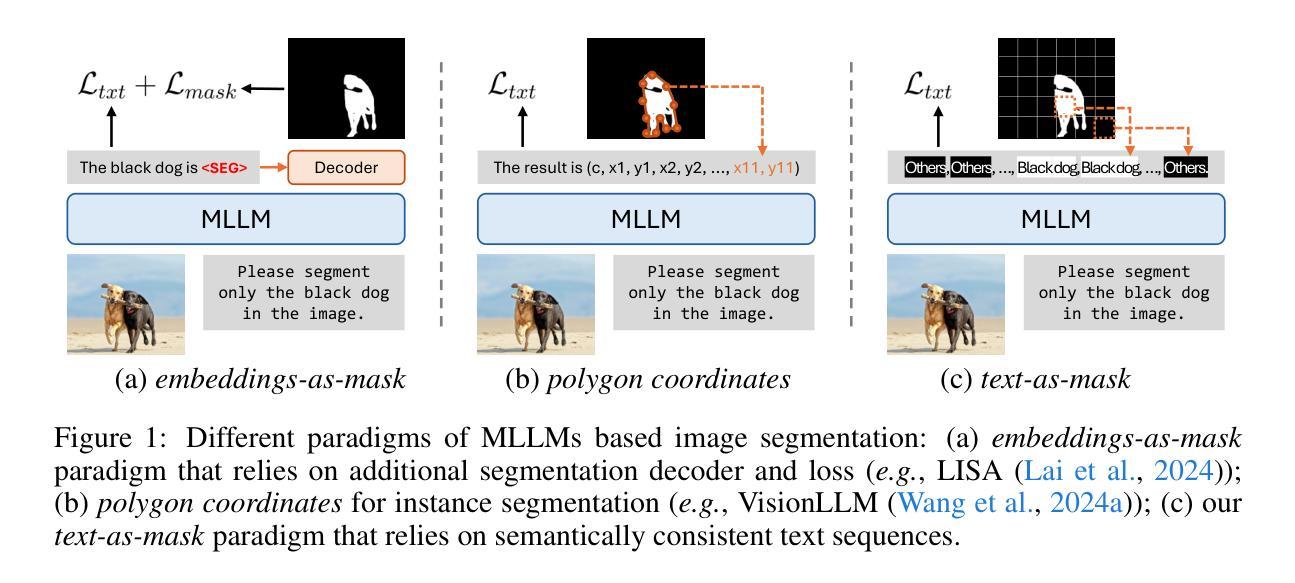
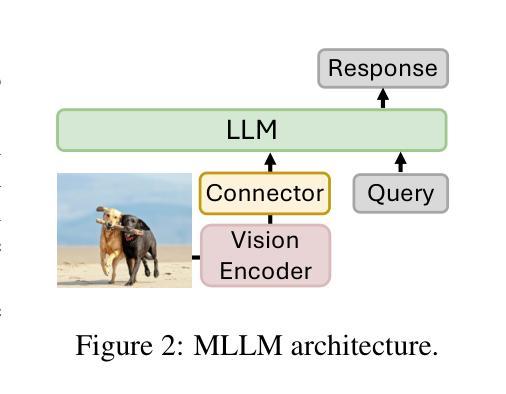
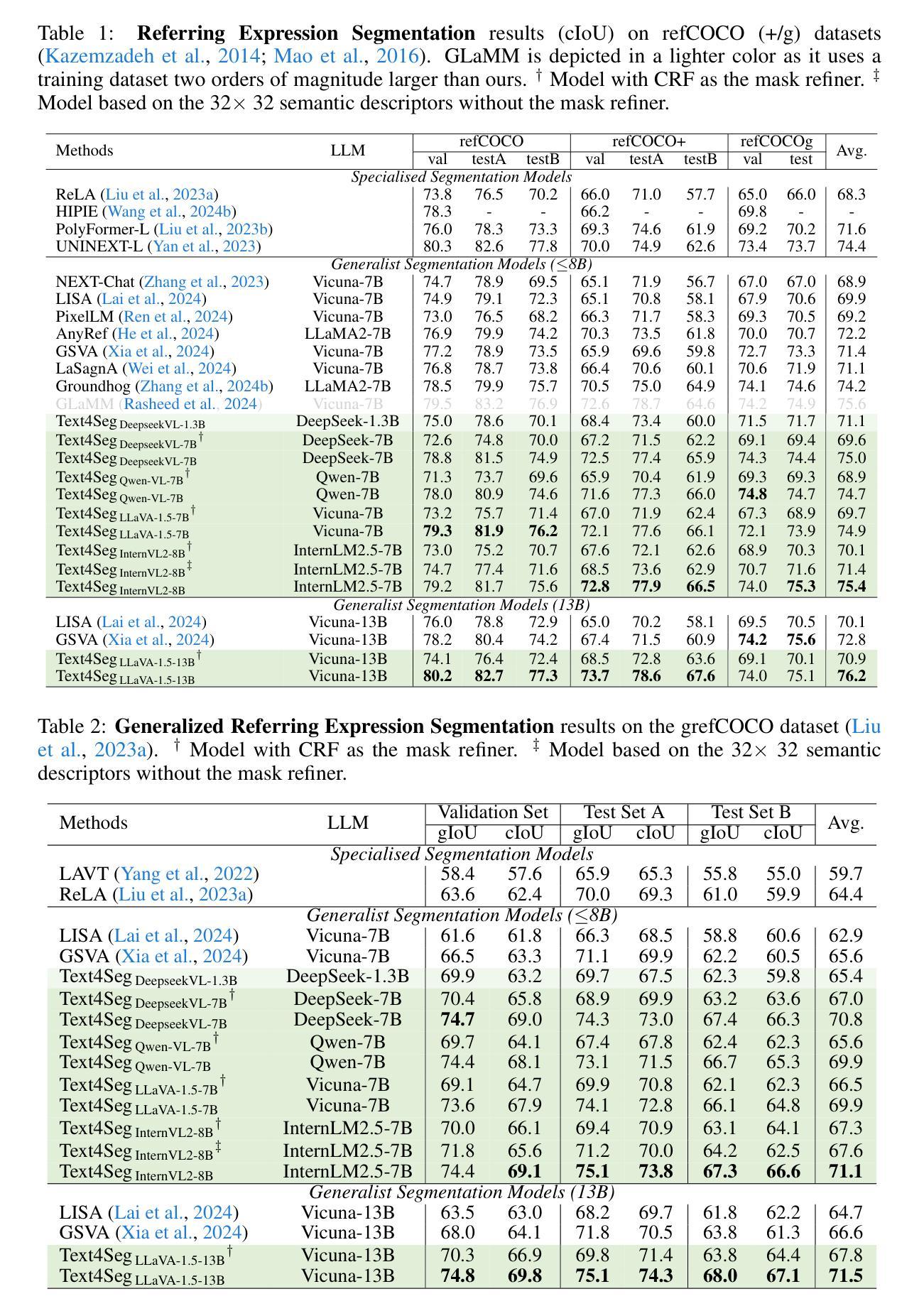
Text4Seg: Reimagining Image Segmentation as Text Generation
Authors:Mengcheng Lan, Chaofeng Chen, Yue Zhou, Jiaxing Xu, Yiping Ke, Xinjiang Wang, Litong Feng, Wayne Zhang
Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) have shown exceptional capabilities in vision-language tasks; however, effectively integrating image segmentation into these models remains a significant challenge. In this paper, we introduce Text4Seg, a novel text-as-mask paradigm that casts image segmentation as a text generation problem, eliminating the need for additional decoders and significantly simplifying the segmentation process. Our key innovation is semantic descriptors, a new textual representation of segmentation masks where each image patch is mapped to its corresponding text label. This unified representation allows seamless integration into the auto-regressive training pipeline of MLLMs for easier optimization. We demonstrate that representing an image with $16\times16$ semantic descriptors yields competitive segmentation performance. To enhance efficiency, we introduce the Row-wise Run-Length Encoding (R-RLE), which compresses redundant text sequences, reducing the length of semantic descriptors by 74% and accelerating inference by $3\times$, without compromising performance. Extensive experiments across various vision tasks, such as referring expression segmentation and comprehension, show that Text4Seg achieves state-of-the-art performance on multiple datasets by fine-tuning different MLLM backbones. Our approach provides an efficient, scalable solution for vision-centric tasks within the MLLM framework.
多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)在视觉语言任务中表现出了卓越的能力;然而,有效地将图像分割集成到这些模型中仍然是一个巨大的挑战。在本文中,我们介绍了Text4Seg,这是一种新的文本作为掩膜范式,它将图像分割转化为文本生成问题,无需额外的解码器,从而极大地简化了分割过程。我们的关键创新之处在于语义描述符,这是一种新的分割掩膜文本表示,其中每个图像块都映射到其相应的文本标签。这种统一表示允许无缝集成到MLLMs的自回归训练管道中,更易于优化。我们证明,使用$16\times16$语义描述符表示图像可以获得具有竞争力的分割性能。为了提高效率,我们引入了行运行长度编码(R-RLE),它压缩了冗余的文本序列,将语义描述符的长度减少了74%,推理速度提高了3倍,同时不损害性能。在各种视觉任务上的大量实验,如指代表达式分割和理解,表明Text4Seg通过微调不同的MLLM主干在多个数据集上实现了最先进的性能。我们的方法为MLLM框架内的以视觉为中心的任务提供了高效、可伸缩的解决方案。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICLR 2025. Project page: https://mc-lan.github.io/Text4Seg/
Summary
本文提出一种名为Text4Seg的新方法,将图像分割转化为文本生成问题,通过语义描述符这一新的文本表示方式,实现了与多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)的紧密集成。此方法消除了对额外解码器的需求,简化了分割过程。通过引入行级运行长度编码(R-RLE),提高了效率,同时保持了在多种视觉任务上的卓越性能。
Key Takeaways
- Text4Seg将图像分割转化为文本生成问题,简化了分割过程。
- 语义描述符是Text4Seg的关键创新,它将图像补丁映射到相应的文本标签,实现了统一表示。
- 语义描述符的应用使得图像能以更紧凑的方式表示,提高了计算效率。
- Row-wise Run-Length Encoding(R-RLE)技术减少了文本序列的冗余,降低了语义描述符的长度,并加速了推理过程。
- Text4Seg在多种视觉任务上实现了最先进的性能,如指代表达式分割和理解。
- Text4Seg方法可以通过微调不同的MLLM主干来实现高效、可扩展的解决方案。
点此查看论文截图



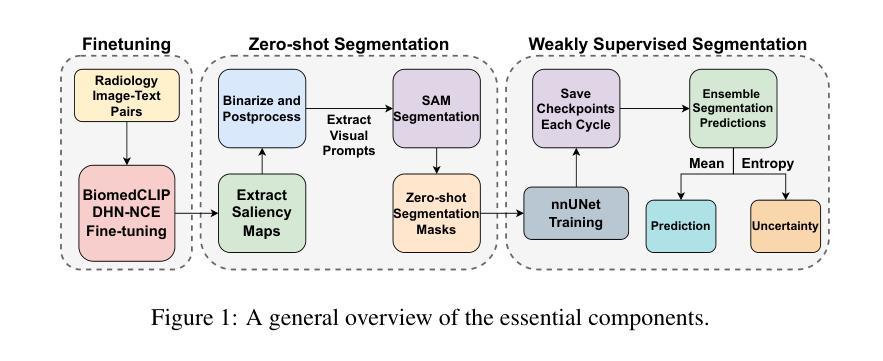
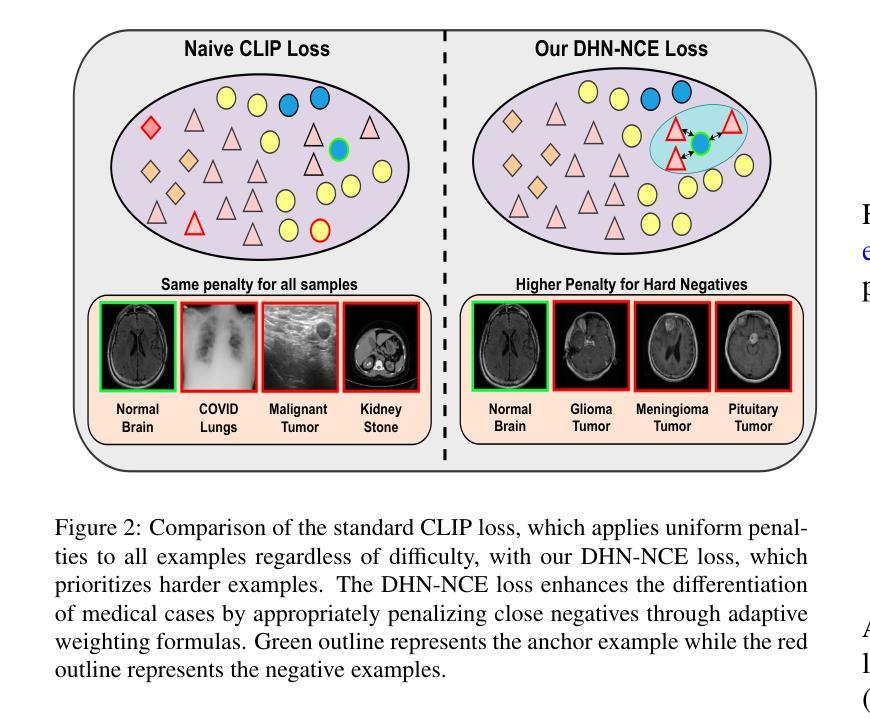
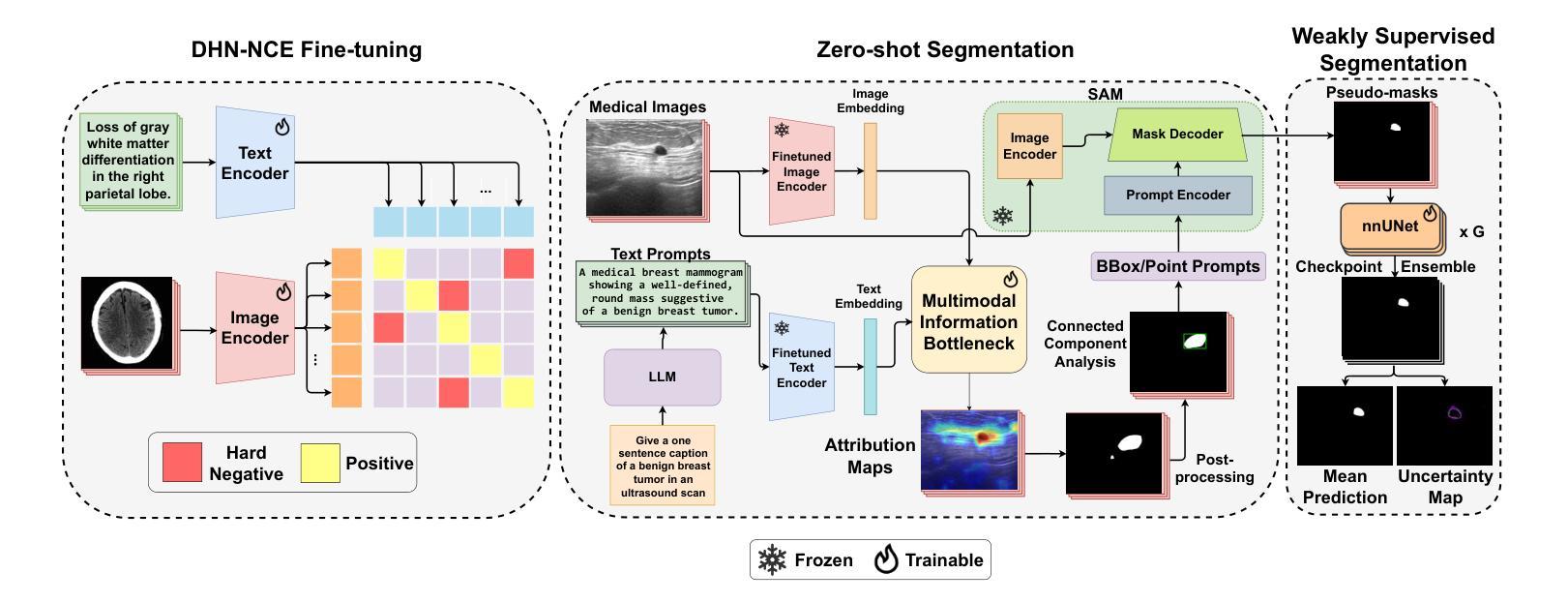
MedCLIP-SAMv2: Towards Universal Text-Driven Medical Image Segmentation
Authors:Taha Koleilat, Hojat Asgariandehkordi, Hassan Rivaz, Yiming Xiao
Segmentation of anatomical structures and pathological regions in medical images is essential for modern clinical diagnosis, disease research, and treatment planning. While significant advancements have been made in deep learning-based segmentation techniques, many of these methods still suffer from limitations in data efficiency, generalizability, and interactivity. As a result, developing precise segmentation methods that require fewer labeled datasets remains a critical challenge in medical image analysis. Recently, the introduction of foundation models like CLIP and Segment-Anything-Model (SAM), with robust cross-domain representations, has paved the way for interactive and universal image segmentation. However, further exploration of these models for data-efficient segmentation in medical imaging is still needed and highly relevant. In this paper, we introduce MedCLIP-SAMv2, a novel framework that integrates the CLIP and SAM models to perform segmentation on clinical scans using text prompts, in both zero-shot and weakly supervised settings. Our approach includes fine-tuning the BiomedCLIP model with a new Decoupled Hard Negative Noise Contrastive Estimation (DHN-NCE) loss, and leveraging the Multi-modal Information Bottleneck (M2IB) to create visual prompts for generating segmentation masks from SAM in the zero-shot setting. We also investigate using zero-shot segmentation labels within a weakly supervised paradigm to enhance segmentation quality further. Extensive testing across four diverse segmentation tasks and medical imaging modalities (breast tumor ultrasound, brain tumor MRI, lung X-ray, and lung CT) demonstrates the high accuracy of our proposed framework. Our code is available at https://github.com/HealthX-Lab/MedCLIP-SAMv2.
医学图像中的解剖结构和病理区域的分割对于现代临床诊断、疾病研究和治疗计划制定至关重要。虽然基于深度学习的分割技术已经取得了重大进展,但这些方法中的许多在数据效率、通用性和交互性方面仍存在局限性。因此,开发需要较少标注数据集的精确分割方法仍然是医学图像分析中的一个关键挑战。最近,引入具有稳健跨域表示能力的CLIP和Segment-Anything-Model(SAM)等基础模型,为交互式和通用图像分割铺平了道路。然而,针对医学成像中的数据高效分割,这些模型的进一步探索仍然是需要且高度相关的。在本文中,我们介绍了MedCLIP-SAMv2,这是一个结合CLIP和SAM模型的新框架,可以使用文本提示对临床扫描进行零样本和弱监督环境下的分割。我们的方法包括使用新的解耦硬负噪声对比估计(DHN-NCE)损失对BiomedCLIP模型进行微调,并利用多模式信息瓶颈(M2IB)创建视觉提示,以便在零样本环境中从SAM生成分割掩膜。我们还研究在弱监督范式中使用零样本分割标签,以进一步提高分割质量。在四个不同的分割任务和医学成像模式(乳腺肿瘤超声、脑肿瘤MRI、肺部X射线和肺部CT)的广泛测试表明,我们提出的框架具有很高的准确性。我们的代码可在https://github.com/HealthX-Lab/MedCLIP-SAMv2找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 10 pages, 2 figures, 6 tables
Summary
本文提出MedCLIP-SAMv2框架,结合CLIP和SAM模型,利用文本提示进行医学图像分割,涉及零样本和弱监督设置。通过微调BiomedCLIP模型并应用DHN-NCE损失和M2IB方法,实现在多种医学图像模态和分割任务上的高准确性。
Key Takeaways
- 医学图像分割对于现代临床诊断、疾病研究和治疗计划至关重要。
- 虽然深度学习在医学图像分割上取得显著进展,但仍存在数据效率、通用性和交互性的挑战。
- MedCLIP-SAMv2框架结合了CLIP和SAM模型,用于医学图像分割。
- MedCLIP-SAMv2通过文本提示进行分割,适用于零样本和弱监督设置。
- 框架通过微调BiomedCLIP模型并应用DHN-NCE损失提高分割准确性。
- M2IB方法用于创建视觉提示,生成SAM的分割掩膜。
- 在多种医学图像模态和分割任务上的测试证明了该框架的高准确性。
点此查看论文截图

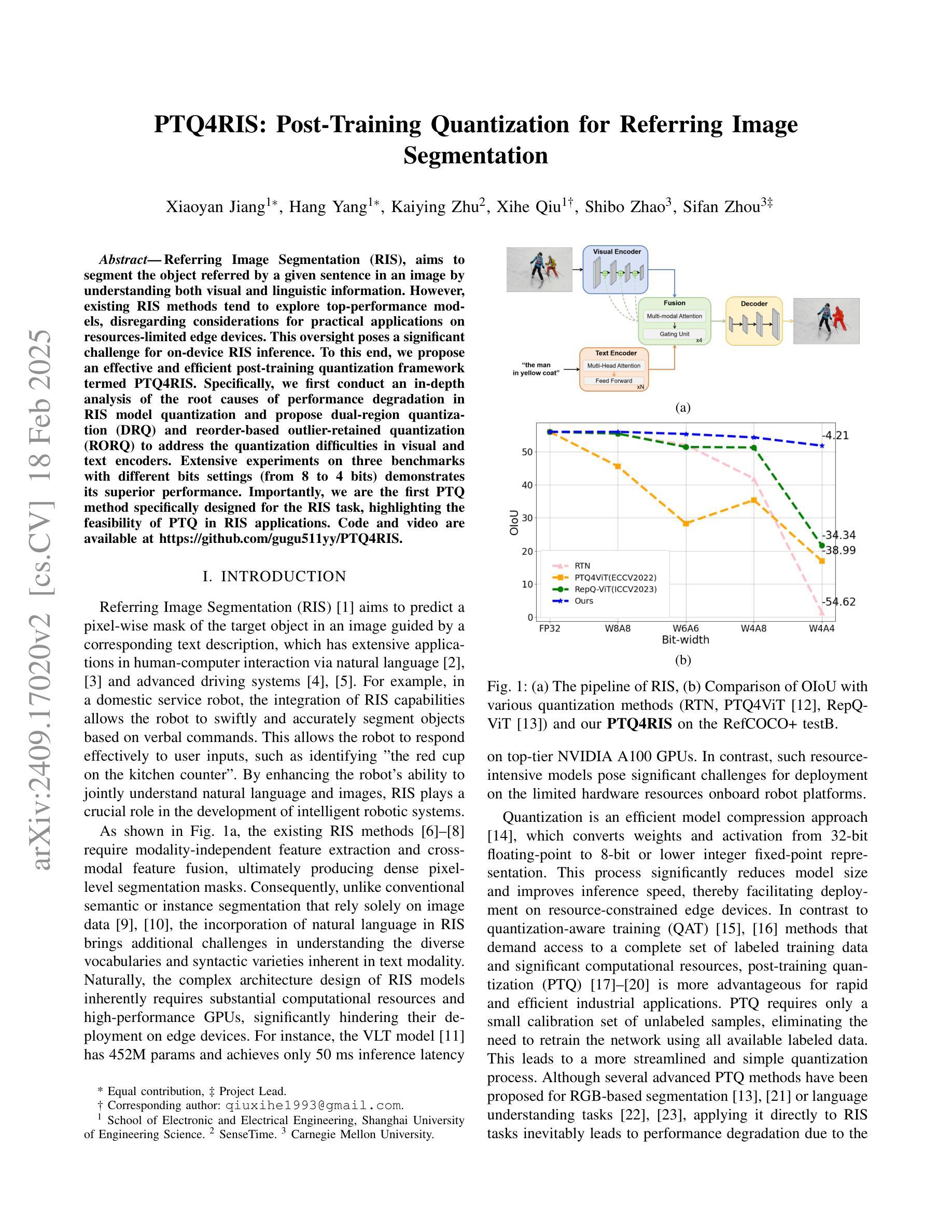
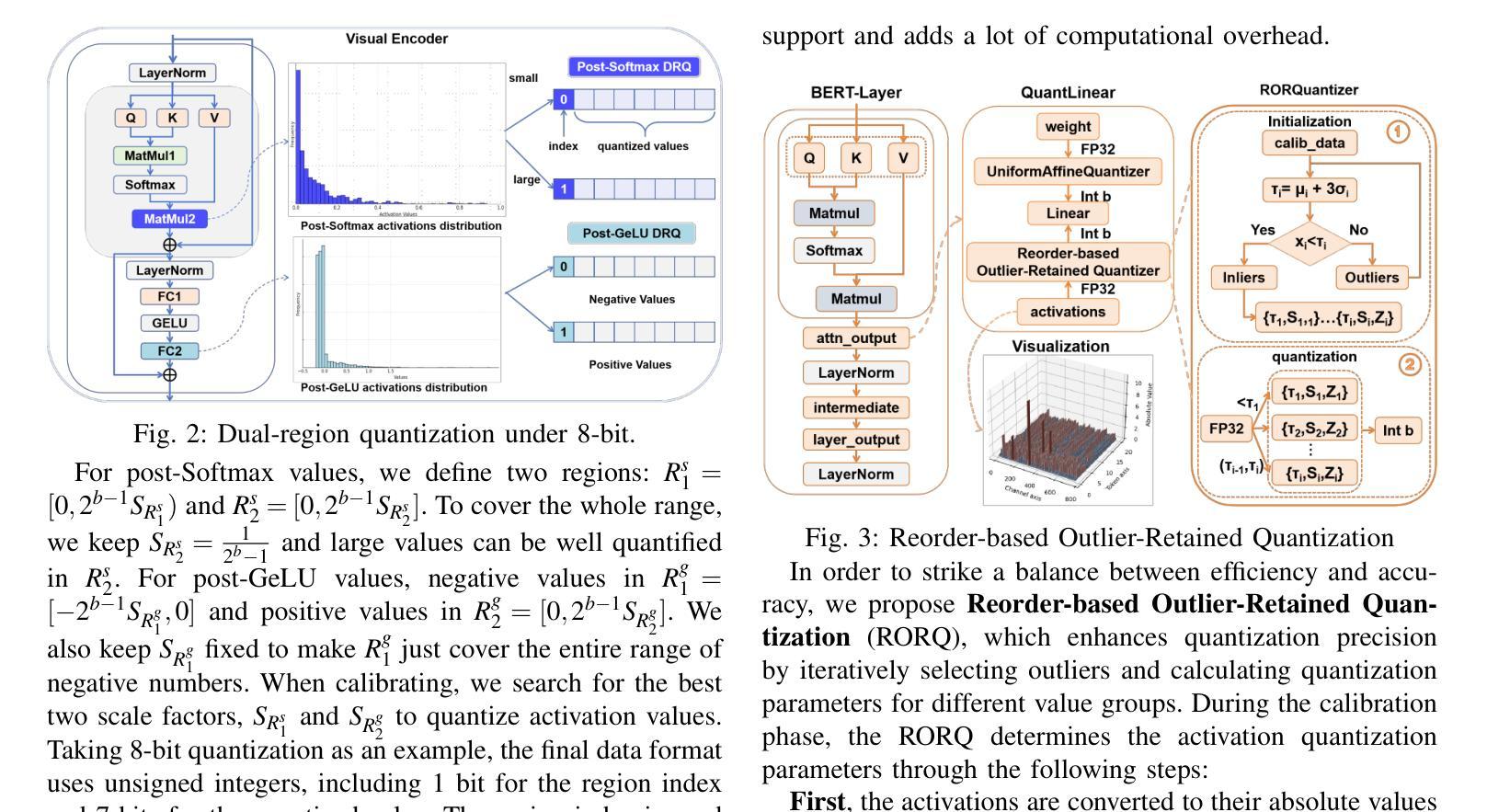
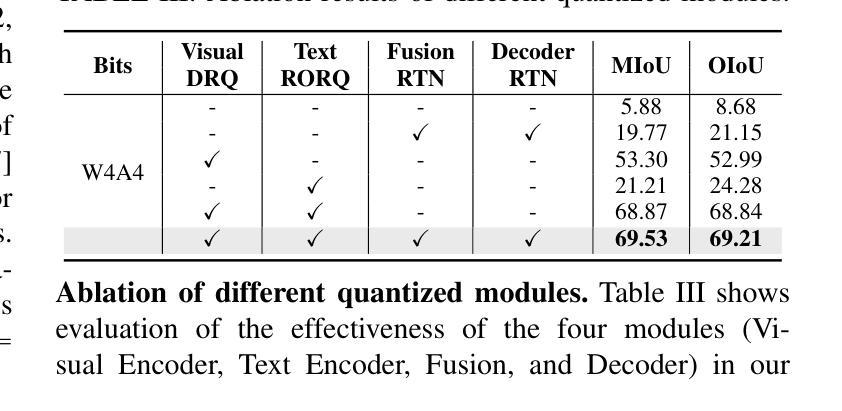
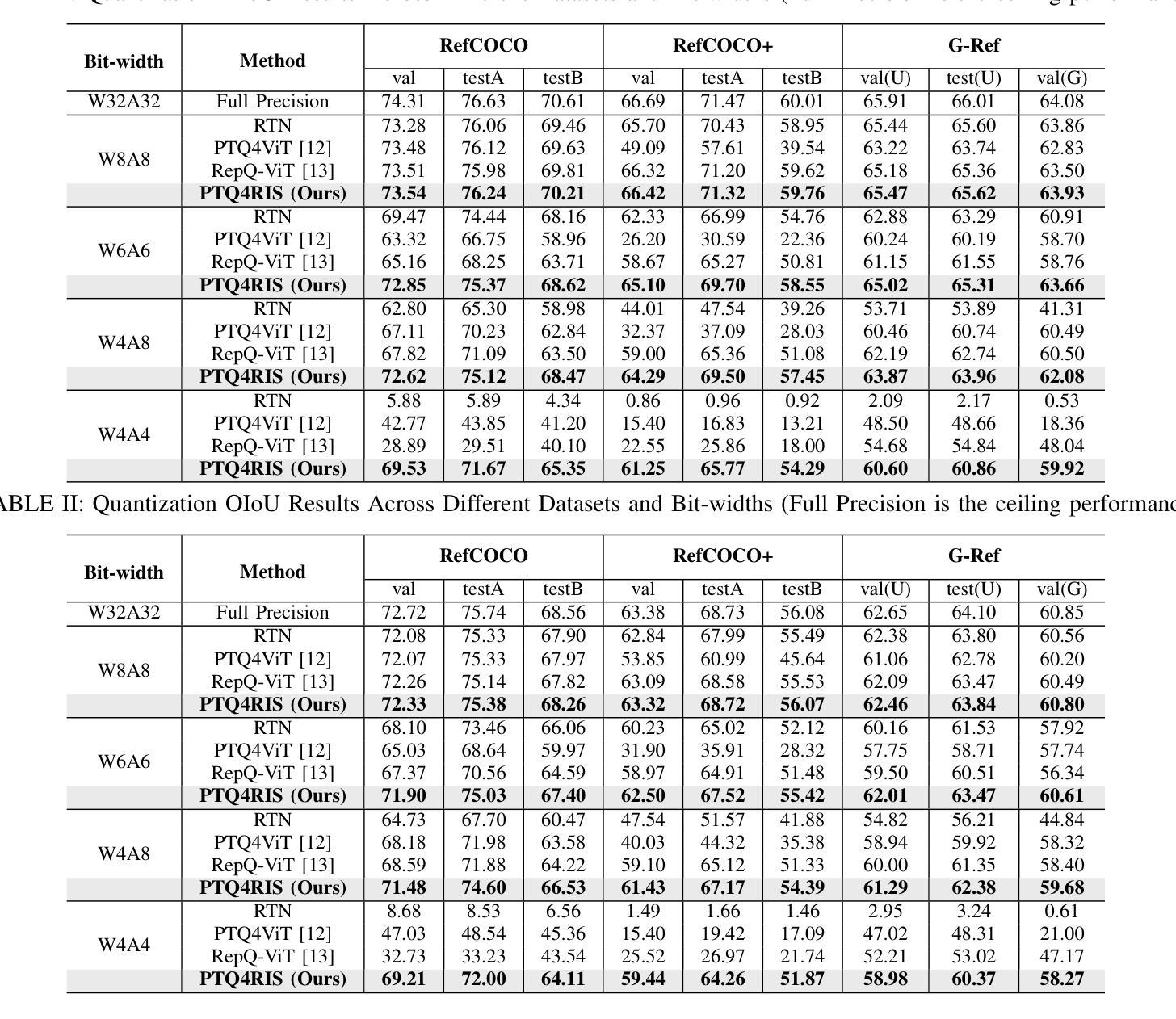
PTQ4RIS: Post-Training Quantization for Referring Image Segmentation
Authors:Xiaoyan Jiang, Hang Yang, Kaiying Zhu, Xihe Qiu, Shibo Zhao, Sifan Zhou
Referring Image Segmentation (RIS), aims to segment the object referred by a given sentence in an image by understanding both visual and linguistic information. However, existing RIS methods tend to explore top-performance models, disregarding considerations for practical applications on resources-limited edge devices. This oversight poses a significant challenge for on-device RIS inference. To this end, we propose an effective and efficient post-training quantization framework termed PTQ4RIS. Specifically, we first conduct an in-depth analysis of the root causes of performance degradation in RIS model quantization and propose dual-region quantization (DRQ) and reorder-based outlier-retained quantization (RORQ) to address the quantization difficulties in visual and text encoders. Extensive experiments on three benchmarks with different bits settings (from 8 to 4 bits) demonstrates its superior performance. Importantly, we are the first PTQ method specifically designed for the RIS task, highlighting the feasibility of PTQ in RIS applications. Code and video are available at {https://github.com/gugu511yy/PTQ4RIS}.
参照图像分割(RIS)旨在通过理解视觉和语言信息,对给定句子中提及的对象进行图像分割。然而,现有的RIS方法往往探索性能优越模型,却忽视了在资源有限的边缘设备上实际应用的问题。这一疏忽给设备上的RIS推理带来了重大挑战。为此,我们提出了一种有效且高效的训练后量化框架,称为PTQ4RIS。具体来说,我们首先深入分析了RIS模型量化中性能下降的根本原因,并提出了双区域量化(DRQ)和基于重排的保留异常值量化(RORQ)来解决视觉和文本编码器的量化难题。在三个基准数据集上的实验,采用不同的比特设置(从8位到4位)证明了其卓越的性能。重要的是,我们是第一个专门针对RIS任务设计的PTQ方法,突显了PTQ在RIS应用中的可行性。代码和视频可在[https://github.com/gugu511yy/PTQ4RIS]查看。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by ICRA 2025.(Update the code link.)
Summary
提出一种针对图像分割的新方法——引用图像分割(RIS),综合考虑视觉和语言信息,但在实际应用于资源有限的边缘设备时面临挑战。为此,研究团队提出了一个高效且实用的后训练量化框架PTQ4RIS,深入分析了量化过程中性能下降的根本原因,并针对性地提出了双区域量化(DRQ)和基于重排序的异常保留量化(RORQ)方法来解决视觉和文本编码器的量化难题。在三个不同比特设置(从8位到4位)下的广泛实验证明其性能优越。此方法旨在为RIS任务进行特定设计的PTQ方法,突显PTQ在RIS应用中的可行性。
Key Takeaways
- 引用图像分割(RIS)结合了视觉和语言信息,旨在根据句子中的描述在图像中分割目标对象。
- 现存的RIS方法更注重高性能模型,忽略了在资源受限的边缘设备上的实际应用考虑。
- 为解决这一问题,提出了后训练量化框架PTQ4RIS,以提高模型在边缘设备的效率和实用性。
- PTQ4RIS通过深入分析发现,性能下降的主要原因是量化过程中的问题,特别是视觉和文本编码器的量化难题。
- 研究团队提出了双区域量化(DRQ)和基于重排序的异常保留量化(RORQ)方法来应对这些挑战。
- 在三个不同比特设置下的广泛实验证明了PTQ4RIS的优越性能。
点此查看论文截图

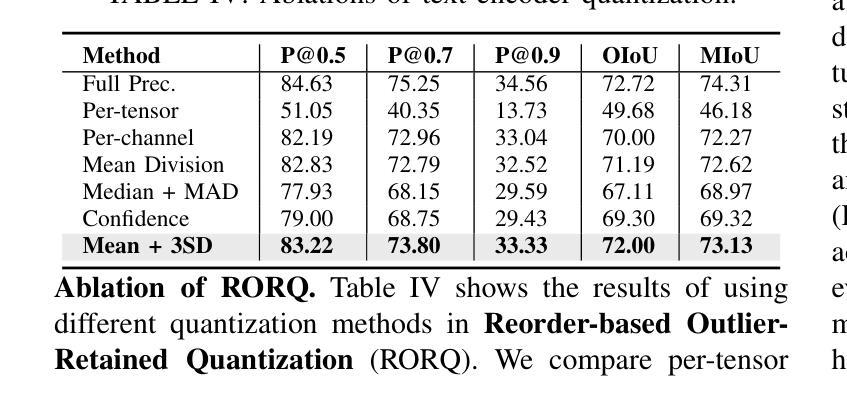
IRSRMamba: Infrared Image Super-Resolution via Mamba-based Wavelet Transform Feature Modulation Model
Authors:Yongsong Huang, Tomo Miyazaki, Xiaofeng Liu, Shinichiro Omachi
Infrared image super-resolution demands long-range dependency modeling and multi-scale feature extraction to address challenges such as homogeneous backgrounds, weak edges, and sparse textures. While Mamba-based state-space models (SSMs) excel in global dependency modeling with linear complexity, their block-wise processing disrupts spatial consistency, limiting their effectiveness for IR image reconstruction. We propose IRSRMamba, a novel framework integrating wavelet transform feature modulation for multi-scale adaptation and an SSMs-based semantic consistency loss to restore fragmented contextual information. This design enhances global-local feature fusion, structural coherence, and fine-detail preservation while mitigating block-induced artifacts. Experiments on benchmark datasets demonstrate that IRSRMamba outperforms state-of-the-art methods in PSNR, SSIM, and perceptual quality. This work establishes Mamba-based architectures as a promising direction for high-fidelity IR image enhancement. Code are available at https://github.com/yongsongH/IRSRMamba.
红外图像超分辨率处理需要建立长期依赖关系模型和多尺度特征提取,以解决背景均匀、边缘模糊和纹理稀疏等挑战。虽然基于Mamba的状态空间模型(SSMs)在线性复杂度下擅长全局依赖关系建模,但其分块处理会破坏空间一致性,限制了其在红外图像重建中的有效性。我们提出了IRSRMamba这一新型框架,它结合了基于小波变换的特征调制进行多尺度适配,以及基于SSMs的语义一致性损失来恢复分散的上下文信息。这种设计增强了全局和局部特征的融合、结构连贯性和细节保留性,同时减轻了因分块引起的伪影。在基准数据集上的实验表明,IRSRMamba在峰值信噪比(PSNR)、结构相似性(SSIM)和感知质量上均优于现有先进方法。本研究确立了基于Mamba的架构在高保真红外图像增强中的研究前景。代码可通过https://github.com/yongsongH/IRSRMamba获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF This work has been submitted to the IEEE for possible publication
Summary
医学红外图像超分辨率需要长程依赖建模和多尺度特征提取,以应对均匀背景、弱边缘和稀疏纹理等挑战。Mamba基状态空间模型虽擅长全局依赖建模,但其块状处理破坏了空间一致性,限制了红外图像重建的效果。本研究提出IRSRMamba框架,集成小波变换特征调制实现多尺度自适应,并引入SSM语义一致性损失恢复断裂的上下文信息。此设计提高了全局局部特征融合、结构连贯性和细节保留能力,同时减少了块状引起的伪影。实验表明,IRSRMamba在PSNR、SSIM和感知质量方面优于先进方法,确立了Mamba基架构在高保真红外图像增强中的潜力。
Key Takeaways
- 医学红外图像超分辨率面临的挑战包括均匀背景、弱边缘和稀疏纹理。
- Mamba基状态空间模型在全局依赖建模方面具有优势,但块状处理会导致空间一致性问题。
- IRSRMamba框架通过集成小波变换特征调制实现多尺度自适应。
- SSMs语义一致性损失用于恢复断裂的上下文信息。
- IRSRMamba提高了全局局部特征融合、结构连贯性和细节保留能力。
- 该框架减少了因块状处理引起的伪影。
点此查看论文截图

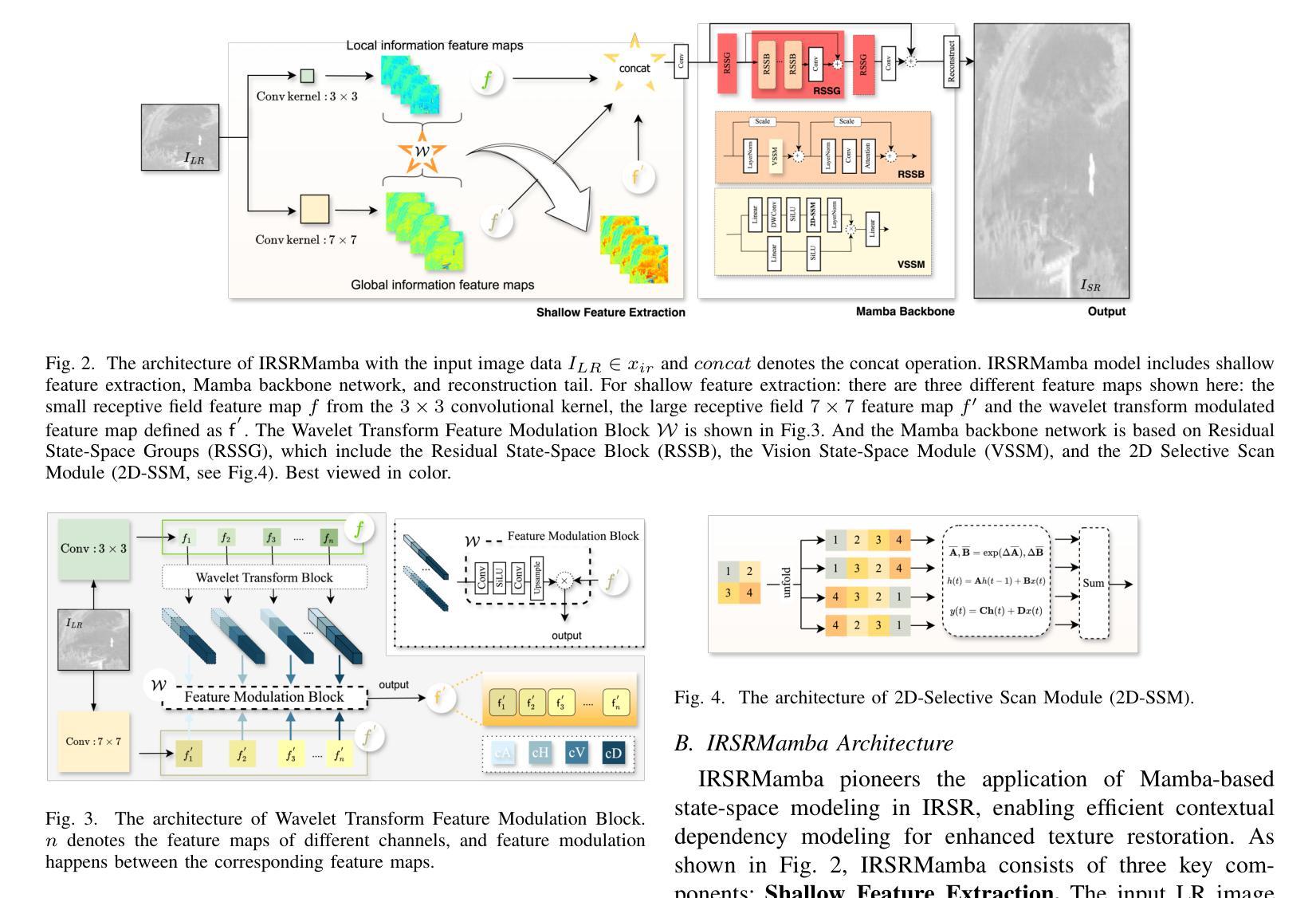

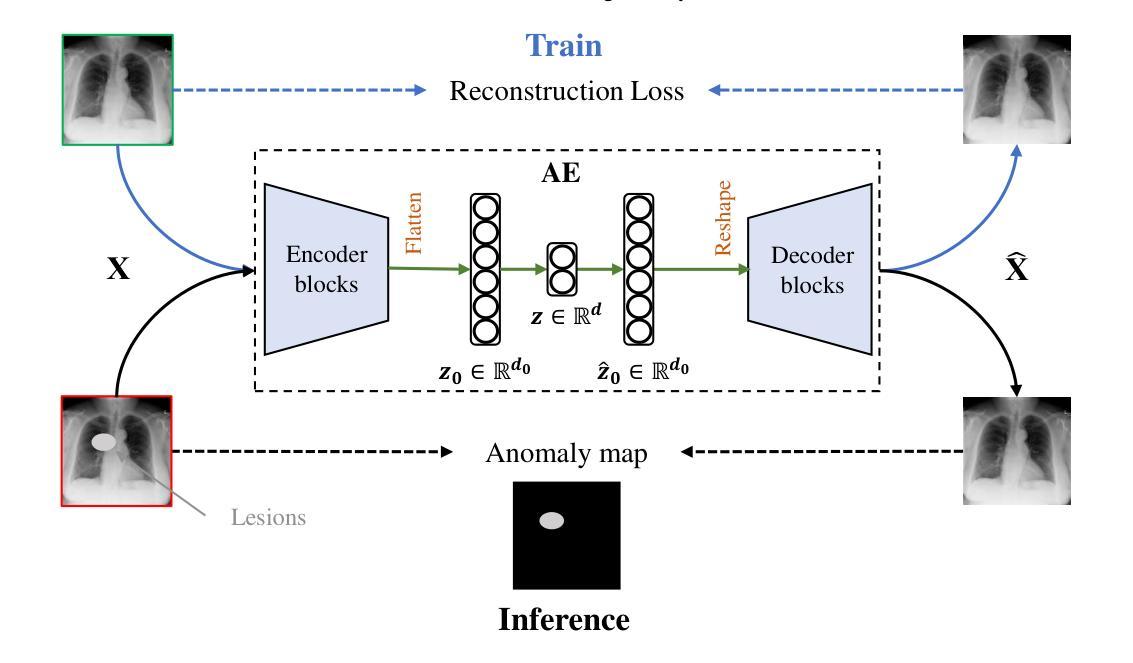
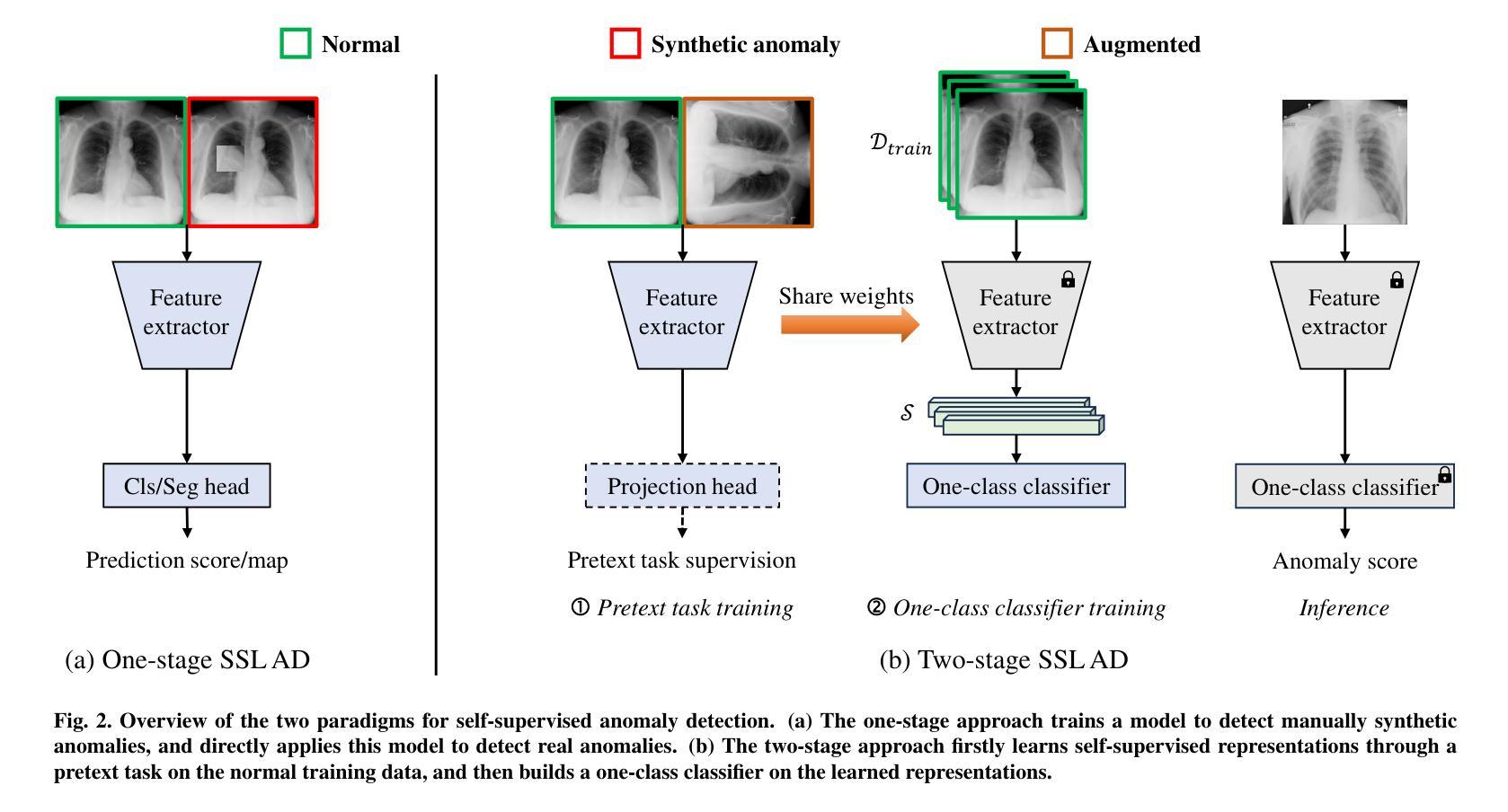
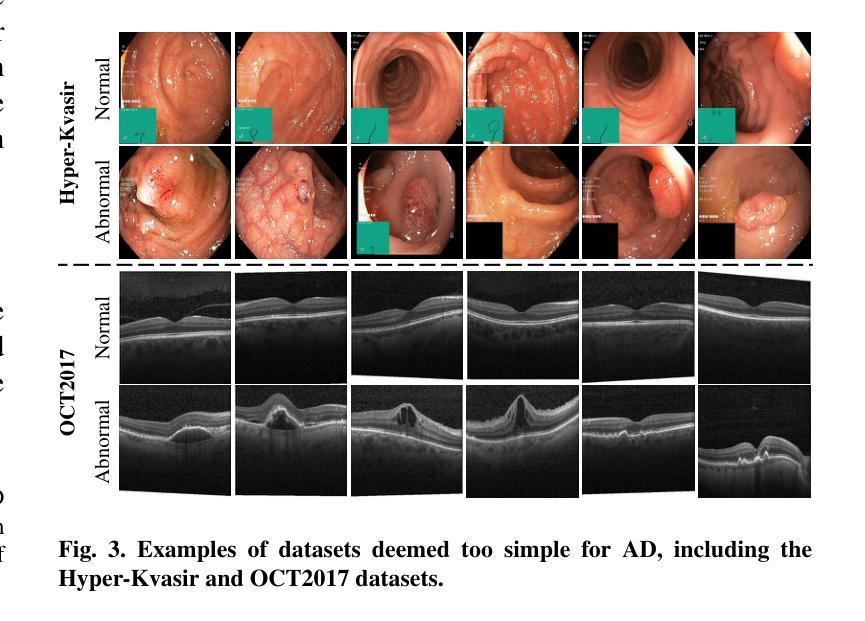
MedIAnomaly: A comparative study of anomaly detection in medical images
Authors:Yu Cai, Weiwen Zhang, Hao Chen, Kwang-Ting Cheng
Anomaly detection (AD) aims at detecting abnormal samples that deviate from the expected normal patterns. Generally, it can be trained merely on normal data, without a requirement for abnormal samples, and thereby plays an important role in the recognition of rare diseases and health screening in the medical domain. Despite the emergence of numerous methods for medical AD, we observe a lack of a fair and comprehensive evaluation, which causes ambiguous conclusions and hinders the development of this field. To address this problem, this paper builds a benchmark with unified comparison. Seven medical datasets with five image modalities, including chest X-rays, brain MRIs, retinal fundus images, dermatoscopic images, and histopathology whole slide images, are curated for extensive evaluation. Thirty typical AD methods, including reconstruction and self-supervised learning-based methods, are involved in comparison of image-level anomaly classification and pixel-level anomaly segmentation. Furthermore, for the first time, we formally explore the effect of key components in existing methods, clearly revealing unresolved challenges and potential future directions. The datasets and code are available at https://github.com/caiyu6666/MedIAnomaly.
异常检测(AD)旨在检测与预期正常模式偏离的异常样本。通常,它仅能在正常数据上进行训练,无需异常样本,因此在医学领域的罕见疾病识别和健康筛查中发挥着重要作用。尽管出现了许多医学异常检测方法,但我们发现缺乏公平而全面的评估,这导致结论模糊并阻碍了该领域的发展。针对这一问题,本文建立了一个统一的比较基准。我们精心挑选了七个医学数据集,包含五种图像模态,包括胸部X射线、脑部MRI、眼底视网膜图像、皮肤镜图像和病理全切片图像,进行了广泛评估。本文比较了30种典型的异常检测方法,包括重建和基于自监督学习的方法,涉及图像级异常分类和像素级异常分割。此外,我们首次正式探讨了现有方法中的关键组件的影响,清晰地揭示了未解决的挑战和潜在的未来方向。数据集和代码可在https://github.com/caiyu6666/MedIAnomaly上找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to Medical Image Analysis, 2025
Summary
医学图像异常检测(AD)旨在发现偏离预期正常模式的异常样本,对于识别罕见疾病和健康筛查具有重要意义。本文建立了一个统一的基准测试平台,用于评估不同的医学图像AD方法。该平台涵盖了七种医学数据集和五种图像模态,包括胸部X射线、脑部MRI、眼底图像、皮肤镜图像和病理全切片图像等。此外,本文首次正式探讨了现有方法中的关键组件的影响,揭示了未解决的挑战和潜在的未来方向。数据集和代码可在GitHub上找到。
Key Takeaways
- 异常检测(AD)在医学图像领域具有重要意义,用于识别罕见疾病和健康筛查。
- 医学图像AD方法的评估缺乏公平性和综合性,导致结论模糊,阻碍该领域的发展。
- 为解决这一问题,本文建立了一个统一的基准测试平台,包括七个医学数据集和五种图像模态。
- 平台涵盖了多种典型的AD方法,包括重建和自监督学习方法,用于比较图像级别的异常分类和像素级别的异常分割。
- 本文首次探讨了现有方法中的关键组件的影响,包括对异常检测性能的具体作用。
- 文章揭示了该领域的未解决挑战和潜在未来方向。
点此查看论文截图

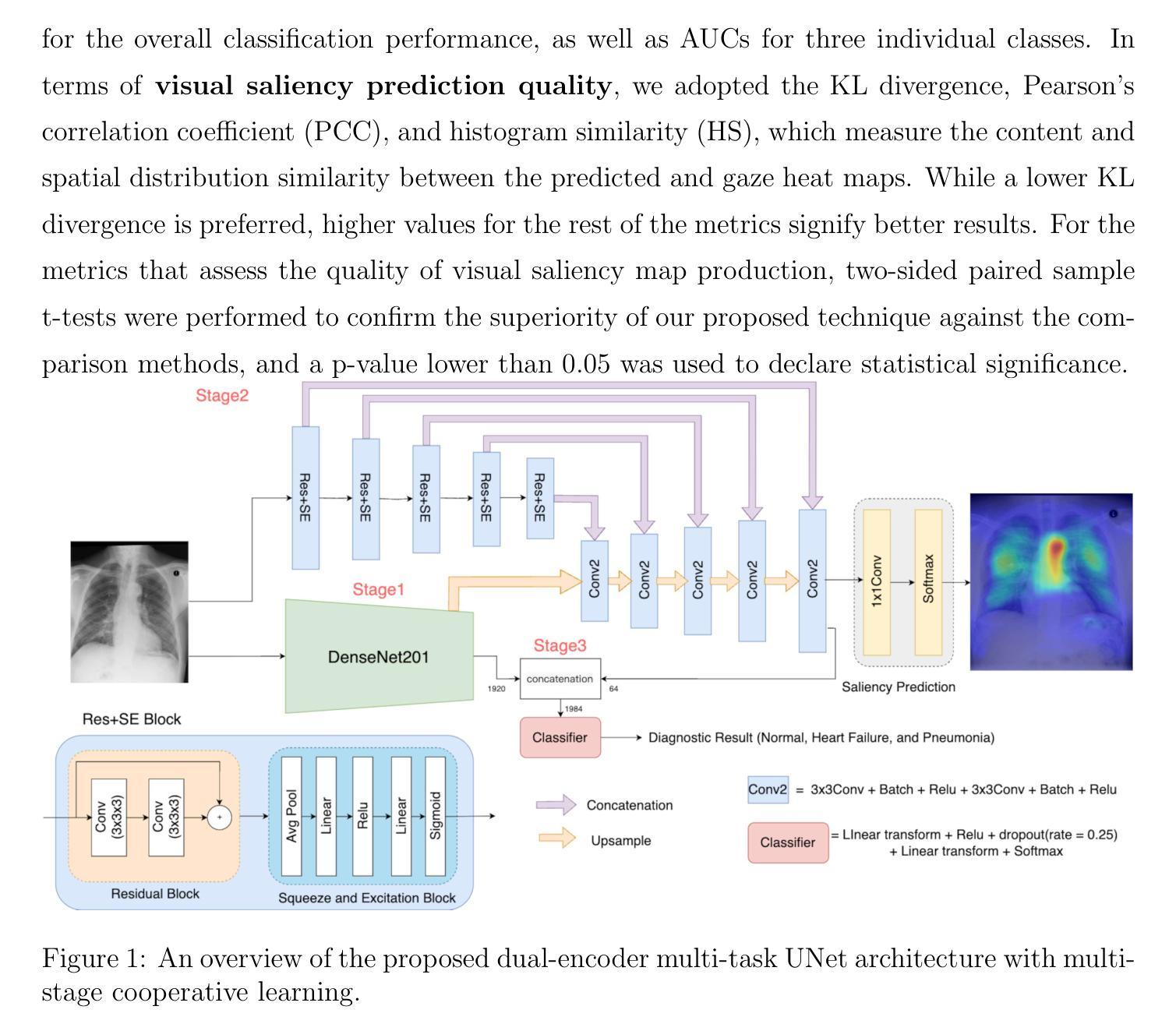
Joint enhancement of automatic chest X-ray diagnosis and radiological gaze prediction with multi-stage cooperative learning
Authors:Zirui Qiu, Hassan Rivaz, Yiming Xiao
Purpose: As visual inspection is an inherent process during radiological screening, the associated eye gaze data can provide valuable insights into relevant clinical decisions. As deep learning has become the state-of-the-art for computer-assisted diagnosis, integrating human behavior, such as eye gaze data, into these systems is instrumental to help align machine predictions with clinical diagnostic criteria, thus enhancing the quality of automatic radiological diagnosis. Methods: We propose a novel deep learning framework for joint disease diagnosis and prediction of corresponding clinical visual attention maps for chest X-ray scans. Specifically, we introduce a new dual-encoder multi-task UNet, which leverages both a DenseNet201 backbone and a Residual and Squeeze-and-Excitation block-based encoder to extract diverse features for visual attention map prediction, and a multi-scale feature-fusion classifier to perform disease classification. To tackle the issue of asynchronous training schedules of individual tasks in multi-task learning, we proposed a multi-stage cooperative learning strategy, with contrastive learning for feature encoder pretraining to boost performance. Results: Our proposed method is shown to significantly outperform existing techniques for chest X-ray diagnosis (AUC=0.93) and the quality of visual attention map prediction (Correlation coefficient=0.58). Conclusion: Benefiting from the proposed multi-task multi-stage cooperative learning, our technique demonstrates the benefit of integrating clinicians’ eye gaze into clinical AI systems to boost performance and potentially explainability.
目的:视觉检查是放射学筛查过程中的固有过程,相关的眼动数据可以为相关的临床决策提供有价值的见解。随着深度学习成为计算机辅助诊断的最新技术,将人类行为(如眼动数据)整合到这些系统中,有助于使机器预测与临床诊断标准保持一致,从而提高自动放射学诊断的质量。方法:我们提出了一种新型的深度学习框架,用于联合疾病诊断和预测胸部X射线扫描对应的临床视觉注意力图。具体来说,我们引入了一种新的双编码器多任务UNet,它利用DenseNet201主干和基于残差和挤压激励块编码器来预测视觉注意力图特征,以及多尺度特征融合分类器进行疾病分类。为了解决多任务学习中单个任务异步训练日程的问题,我们提出了一种多阶段合作学习策略,使用对比学习对特征编码器进行预训练以提高性能。结果:所提出的方法在胸部X光诊断(AUC=0.93)和视觉注意力图预测质量(相关系数=0.58)方面显著优于现有技术。结论:得益于所提出的多任务多阶段合作学习,我们的技术证明了将临床医生眼动数据整合到临床人工智能系统中的好处,可以提高性能和潜在的解释性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种新型深度学习框架,用于联合诊断关节疾病并预测对应的临床视觉注意力地图。通过引入双编码器多任务UNet网络,结合DenseNet201骨干网络和基于残差与挤压激励块的编码器,以提取多样化的特征用于视觉注意力地图预测和多尺度特征融合分类器进行疾病分类。为解决多任务学习中单个任务训练安排不同步的问题,本文提出了一种多阶段协作学习策略,并利用对比学习对特征编码器进行预训练以提高性能。实验结果表明,该方法在胸部X光诊断上显著优于现有技术,且视觉注意力地图预测质量较高。整合医生视线数据有助于提高临床AI系统的性能和解释性。
Key Takeaways
- 视觉检查是放射学筛查中的固有过程,相关的眼动数据能为临床决策提供宝贵见解。
- 深度学习已成为计算机辅助诊断的尖端技术,整合人类行为(如眼动数据)有助于使机器预测与临床诊断标准对齐,从而提高自动放射学诊断的质量。
- 本文提出一种新型深度学习框架,结合双编码器多任务UNet网络进行疾病诊断和视觉注意力地图预测。
- 该框架利用DenseNet201和基于残差与挤压激励块的编码器提取多样化特征,并采用多尺度特征融合分类器进行疾病分类。
- 为解决多任务学习中任务训练安排不同步的问题,采用多阶段协作学习策略。
- 对比学习用于特征编码器的预训练,以提升性能。
点此查看论文截图
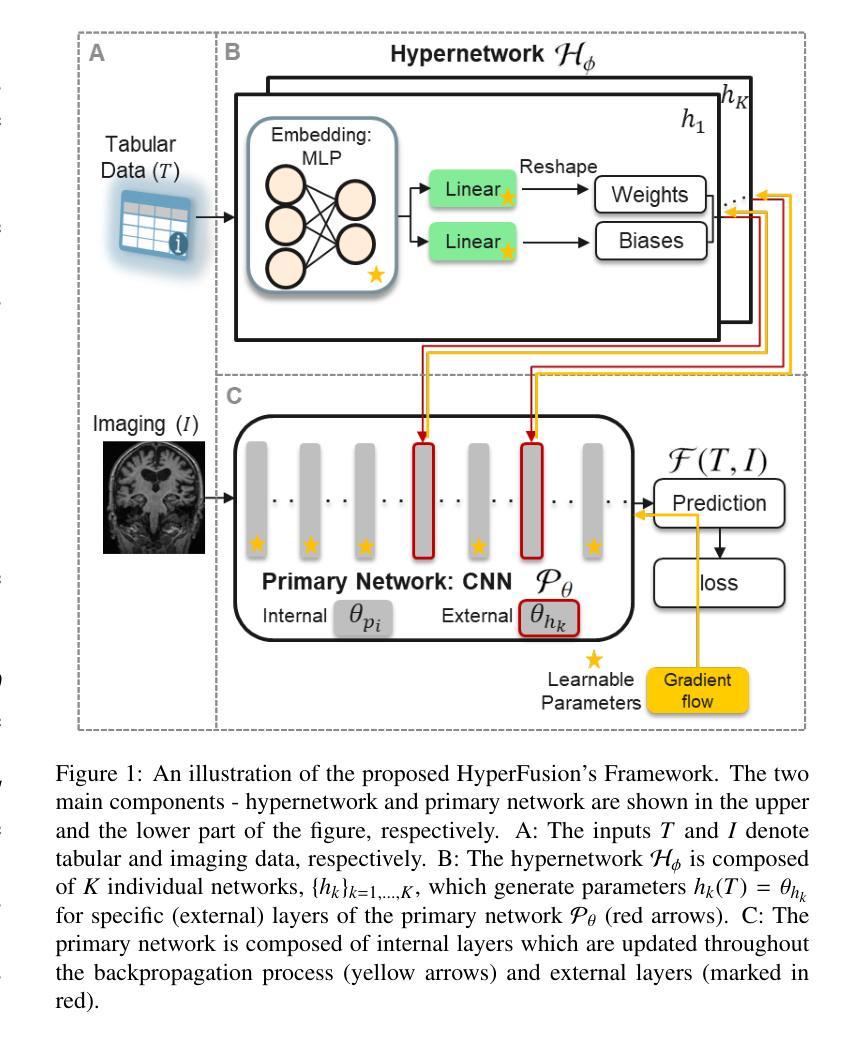
HyperFusion: A Hypernetwork Approach to Multimodal Integration of Tabular and Medical Imaging Data for Predictive Modeling
Authors:Daniel Duenias, Brennan Nichyporuk, Tal Arbel, Tammy Riklin Raviv
The integration of diverse clinical modalities such as medical imaging and the tabular data extracted from patients’ Electronic Health Records (EHRs) is a crucial aspect of modern healthcare. Integrative analysis of multiple sources can provide a comprehensive understanding of the clinical condition of a patient, improving diagnosis and treatment decision. Deep Neural Networks (DNNs) consistently demonstrate outstanding performance in a wide range of multimodal tasks in the medical domain. However, the complex endeavor of effectively merging medical imaging with clinical, demographic and genetic information represented as numerical tabular data remains a highly active and ongoing research pursuit. We present a novel framework based on hypernetworks to fuse clinical imaging and tabular data by conditioning the image processing on the EHR’s values and measurements. This approach aims to leverage the complementary information present in these modalities to enhance the accuracy of various medical applications. We demonstrate the strength and generality of our method on two different brain Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) analysis tasks, namely, brain age prediction conditioned by subject’s sex and multi-class Alzheimer’s Disease (AD) classification conditioned by tabular data. We show that our framework outperforms both single-modality models and state-of-the-art MRI tabular data fusion methods. A link to our code can be found at https://github.com/daniel4725/HyperFusion
多样临床模式如医学成像与从患者电子健康记录(EHRs)中提取的表格数据的融合是现代医疗保健的重要组成部分。对多个来源的综合分析可以提供对患者临床状况的全面了解,从而提高诊断和治疗决策。深度神经网络(DNNs)在医疗领域的多模式任务中始终表现出卓越的性能。然而,有效地将医学成像与临床、人口统计学和遗传信息融合,这些以数值表格数据的形式呈现,仍然是一项活跃而持续的研究追求。我们提出了一种基于超网络的新型框架,通过以电子健康记录的数值为条件来融合临床成像和表格数据。该方法旨在利用这些模式中的互补信息,以提高各种医疗应用的准确性。我们在两个不同的脑部磁共振成像(MRI)分析任务上展示了我们的方法的优势和通用性,即根据受试者性别进行脑龄预测和根据表格数据进行的多类阿尔茨海默病(AD)分类。我们显示,我们的框架优于单模态模型和最先进的MRI表格数据融合方法。我们的代码链接为:https://github.com/daniel4725/HyperFusion 。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 20 pages, 11 figures
Summary
医学成像与电子健康记录(EHRs)表格数据的融合是现代医疗的重要方向。本文提出一种基于超网络的新框架,旨在通过以EHR的数值数据和测量结果为条件进行图像处理,利用两种模态的互补信息提升医疗应用的准确性。框架在大脑核磁共振成像的两个任务上表现出卓越性能:以性别为条件的脑龄预测和以表格数据为条件的阿尔茨海默病多类别分类。
Key Takeaways
- 医学成像与电子健康记录(EHRs)表格数据的融合是现代医疗的关键需求。
- 深神经网络在多模态医学任务中表现优异。
- 新框架基于超网络,旨在融合医学成像和表格数据。
- 框架以EHR的数值数据和测量结果为条件进行图像处理。
- 框架在大脑核磁共振成像的脑龄预测和阿尔茨海默病分类任务上表现优越。
- 新框架优于单模态模型和先进的MRI表格数据融合方法。
点此查看论文截图