⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-02-20 更新
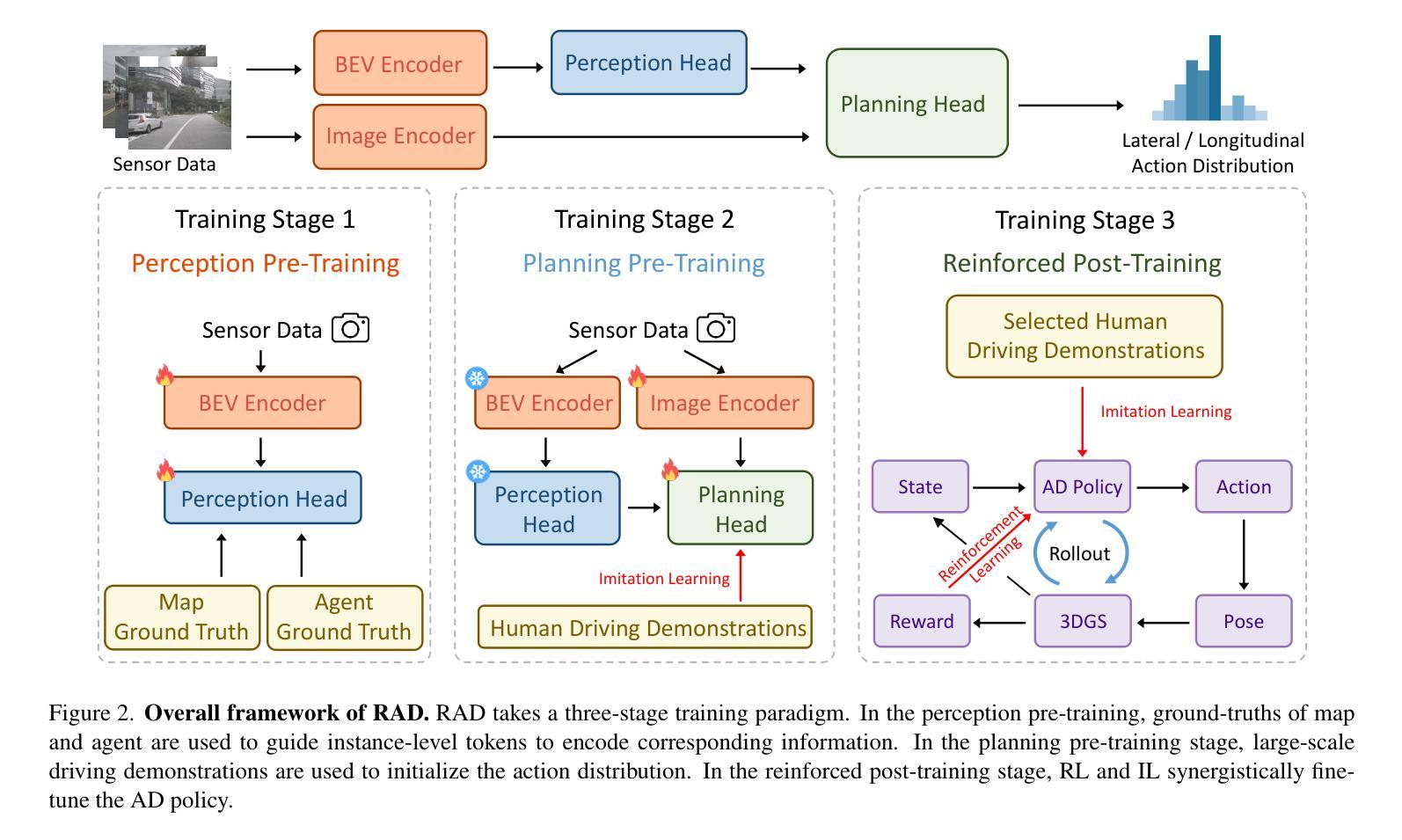
RAD: Training an End-to-End Driving Policy via Large-Scale 3DGS-based Reinforcement Learning
Authors:Hao Gao, Shaoyu Chen, Bo Jiang, Bencheng Liao, Yiang Shi, Xiaoyang Guo, Yuechuan Pu, Haoran Yin, Xiangyu Li, Xinbang Zhang, Ying Zhang, Wenyu Liu, Qian Zhang, Xinggang Wang
Existing end-to-end autonomous driving (AD) algorithms typically follow the Imitation Learning (IL) paradigm, which faces challenges such as causal confusion and the open-loop gap. In this work, we establish a 3DGS-based closed-loop Reinforcement Learning (RL) training paradigm. By leveraging 3DGS techniques, we construct a photorealistic digital replica of the real physical world, enabling the AD policy to extensively explore the state space and learn to handle out-of-distribution scenarios through large-scale trial and error. To enhance safety, we design specialized rewards that guide the policy to effectively respond to safety-critical events and understand real-world causal relationships. For better alignment with human driving behavior, IL is incorporated into RL training as a regularization term. We introduce a closed-loop evaluation benchmark consisting of diverse, previously unseen 3DGS environments. Compared to IL-based methods, RAD achieves stronger performance in most closed-loop metrics, especially 3x lower collision rate. Abundant closed-loop results are presented at https://hgao-cv.github.io/RAD.
当前端到端的自动驾驶(AD)算法通常遵循模仿学习(IL)范式,这面临着因果混淆和开环间隙等挑战。在这项工作中,我们建立了基于3DGS的闭环强化学习(RL)训练范式。通过利用3DGS技术,我们构建了真实物理世界的照片级数字副本,使AD策略能够广泛探索状态空间,并通过大规模试错学习处理超出分布范围的情况。为了提高安全性,我们设计了专门的奖励,以指导策略有效应对安全关键事件并理解真实世界的因果关系。为了更好地与人类驾驶行为对齐,将IL纳入RL训练中作为正则化项。我们引入了一个闭环评估基准,包括多样化且之前未见的3DGS环境。与基于IL的方法相比,RAD在大多数闭环指标上表现更出色,尤其是碰撞率降低了三倍。丰富的闭环结果请参阅:https://hgao-cv.github.io/RAD。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project Page: https://hgao-cv.github.io/RAD
Summary
本文提出了一种基于3DGS的闭环强化学习(RL)训练范式,用于解决自主驾驶(AD)的挑战。通过利用3DGS技术,构建真实世界的数字副本,使AD策略能够广泛探索状态空间,并通过大规模试错学习处理异常情况。设计专项奖励以提高安全性,并引入模仿学习(IL)以增强与人类驾驶行为的契合度。在封闭循环评估基准上,相比基于IL的方法,该策略在大多数封闭循环指标上表现更强,尤其是碰撞率降低了三倍。
Key Takeaways
- 采用基于3DGS的闭环强化学习训练范式,解决自主驾驶面临的挑战。
- 利用3DGS技术创建真实世界的数字副本,使AD策略能够广泛探索状态空间并学习处理异常情况。
- 设计专项奖励以提高安全性并响应安全关键事件。
- 结合IL和RL训练,增强与人类驾驶行为的契合度。
- 引入封闭循环评估基准,以测试自主驾驶系统的性能。
- 该方法在封闭循环评估基准上的表现优于基于IL的方法,特别是在碰撞率方面。
点此查看论文截图



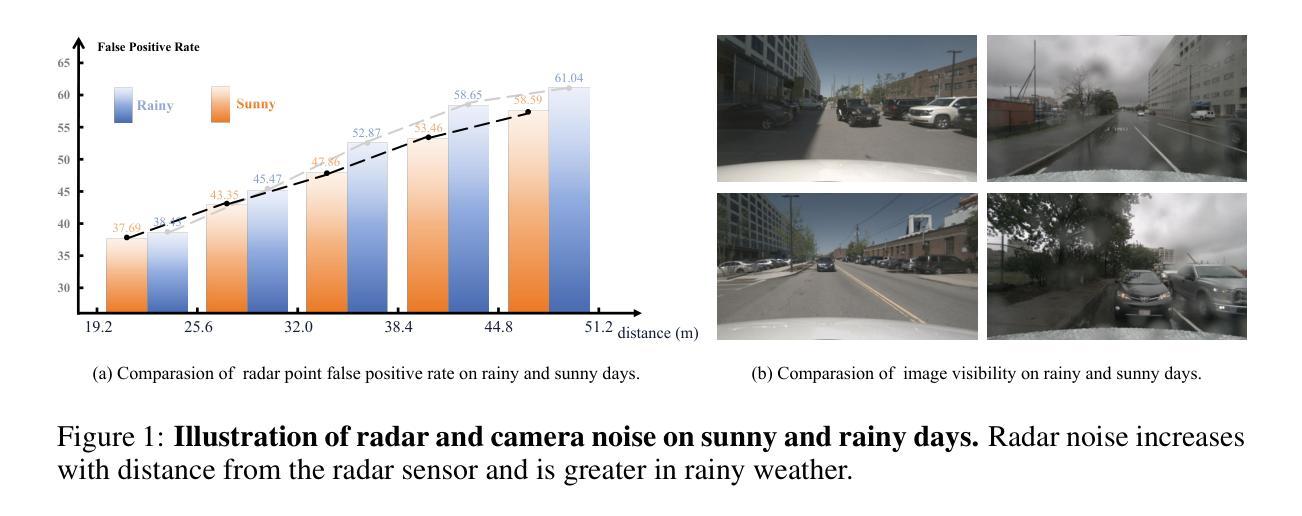
RobuRCDet: Enhancing Robustness of Radar-Camera Fusion in Bird’s Eye View for 3D Object Detection
Authors:Jingtong Yue, Zhiwei Lin, Xin Lin, Xiaoyu Zhou, Xiangtai Li, Lu Qi, Yongtao Wang, Ming-Hsuan Yang
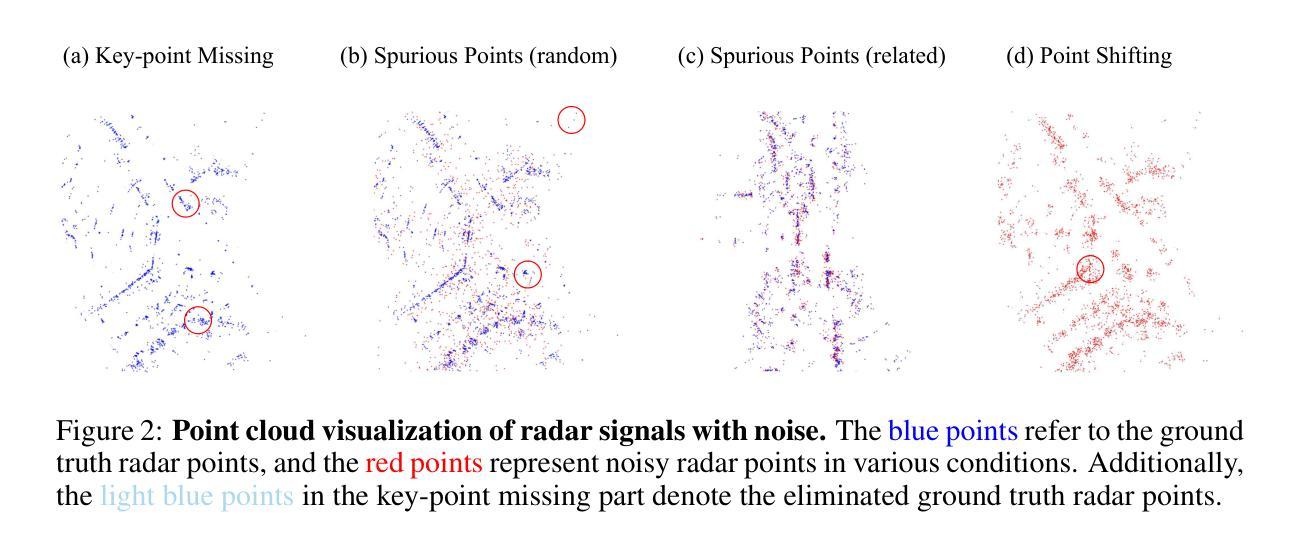
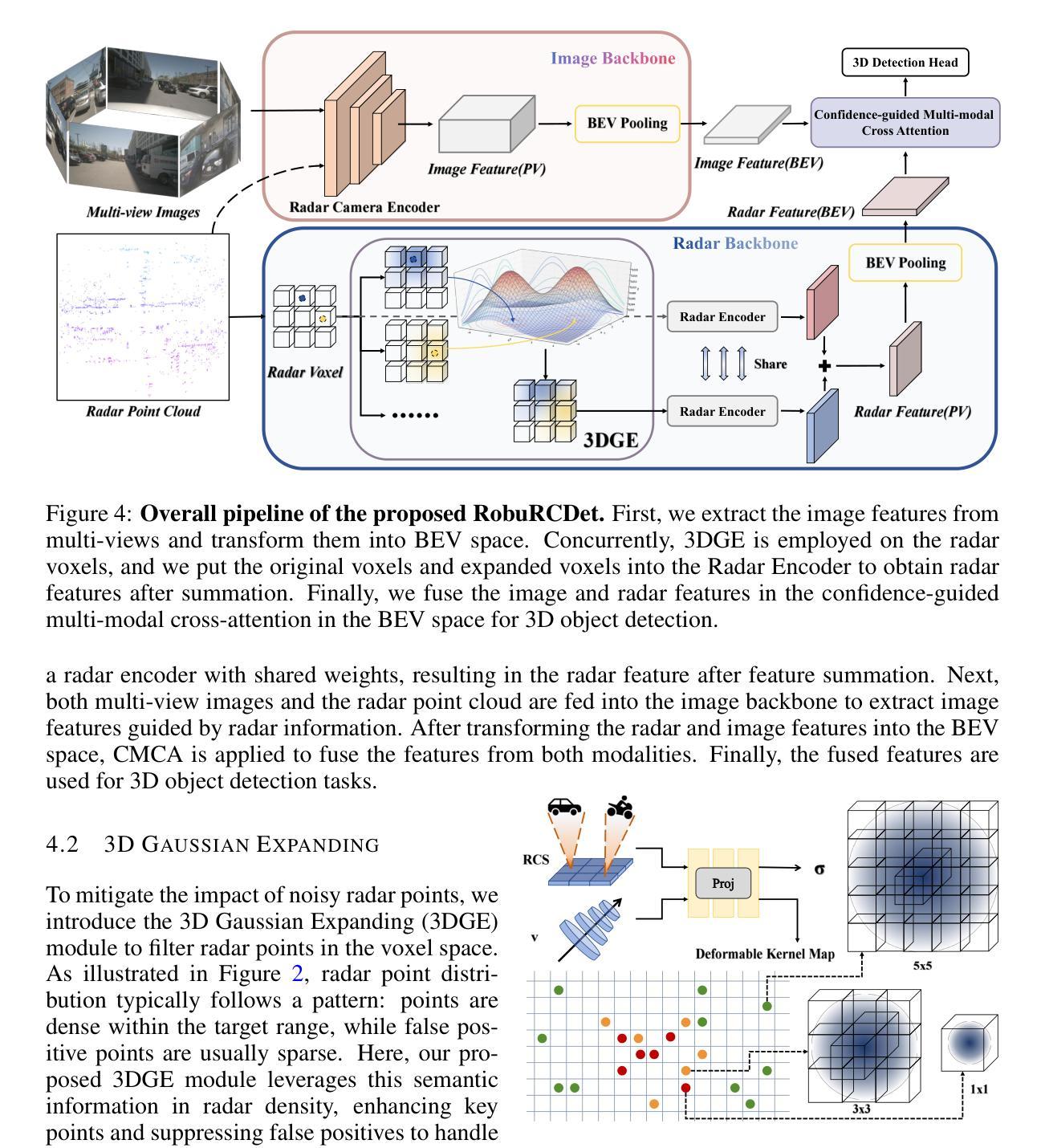
While recent low-cost radar-camera approaches have shown promising results in multi-modal 3D object detection, both sensors face challenges from environmental and intrinsic disturbances. Poor lighting or adverse weather conditions degrade camera performance, while radar suffers from noise and positional ambiguity. Achieving robust radar-camera 3D object detection requires consistent performance across varying conditions, a topic that has not yet been fully explored. In this work, we first conduct a systematic analysis of robustness in radar-camera detection on five kinds of noises and propose RobuRCDet, a robust object detection model in BEV. Specifically, we design a 3D Gaussian Expansion (3DGE) module to mitigate inaccuracies in radar points, including position, Radar Cross-Section (RCS), and velocity. The 3DGE uses RCS and velocity priors to generate a deformable kernel map and variance for kernel size adjustment and value distribution. Additionally, we introduce a weather-adaptive fusion module, which adaptively fuses radar and camera features based on camera signal confidence. Extensive experiments on the popular benchmark, nuScenes, show that our model achieves competitive results in regular and noisy conditions.
虽然最近低成本雷达相机方法在多模态三维物体检测方面取得了有前景的结果,但两种传感器都面临来自环境和内在干扰的挑战。光照不足或恶劣天气条件会降低相机性能,而雷达则受到噪声和位置不确定性的困扰。实现稳健的雷达相机三维物体检测需要在各种条件下保持性能一致性,这一话题尚未得到充分探索。在这项工作中,我们首先对雷达相机检测的鲁棒性进行了五种噪声的系统分析,并提出了RobuRCDet,一个稳健的三维物体检测模型。具体来说,我们设计了一个三维高斯扩展(3DGE)模块,以缓解雷达点的不准确性,包括位置、雷达截面(RCS)和速度。3DGE使用RCS和速度先验值生成可变形内核图以及内核大小调整和值分布的方差。此外,我们引入了一个自适应天气融合模块,该模块基于相机信号置信度自适应地融合雷达和相机特征。在流行基准nuScenes上的广泛实验表明,我们的模型在常规和噪声条件下都取得了有竞争力的结果。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by ICLR2025
Summary
雷达与摄像头结合的多模态三维物体检测虽已有成果,但仍面临环境与自身干扰的挑战。恶劣天气或光线不足会影响摄像头性能,雷达则易受噪声与定位模糊的影响。为实现稳健的雷达-摄像头三维物体检测,需要针对多种条件保持性能稳定,这一议题尚未被完全探索。本研究首先对雷达-摄像头检测的稳健性进行了系统分析,并针对五种噪声提出了RobuRCDet模型。设计3D高斯扩展模块缓解雷达点的误差,并引入天气自适应融合模块,基于摄像头信号置信度自适应融合雷达与摄像头特征。在流行基准nuScenes上的广泛实验表明,该模型在常规与噪声条件下均取得有竞争力的结果。
Key Takeaways
- 雷达与摄像头结合的多模态三维物体检测虽具前景,但仍面临环境与自身干扰的挑战。
- 恶劣天气和光线不足会影响摄像头性能,雷达则易受噪声和定位模糊困扰。
- 实现稳健的雷达-摄像头三维物体检测需在不同条件下保持性能稳定,此议题尚未被完全探索。
- 研究者对雷达-摄像头检测的稳健性进行了系统分析,并提出了RobuRCDet模型以应对五种常见噪声。
- 3D高斯扩展模块设计用于缓解雷达点的误差,包括位置、雷达散射截面和速度。
- 天气自适应融合模块能根据摄像头信号置信度自适应融合雷达与摄像头特征。
点此查看论文截图


RadSplatter: Extending 3D Gaussian Splatting to Radio Frequencies for Wireless Radiomap Extrapolation
Authors:Yiheng Wang, Ye Xue, Shutao Zhang, Tsung-Hui Chang
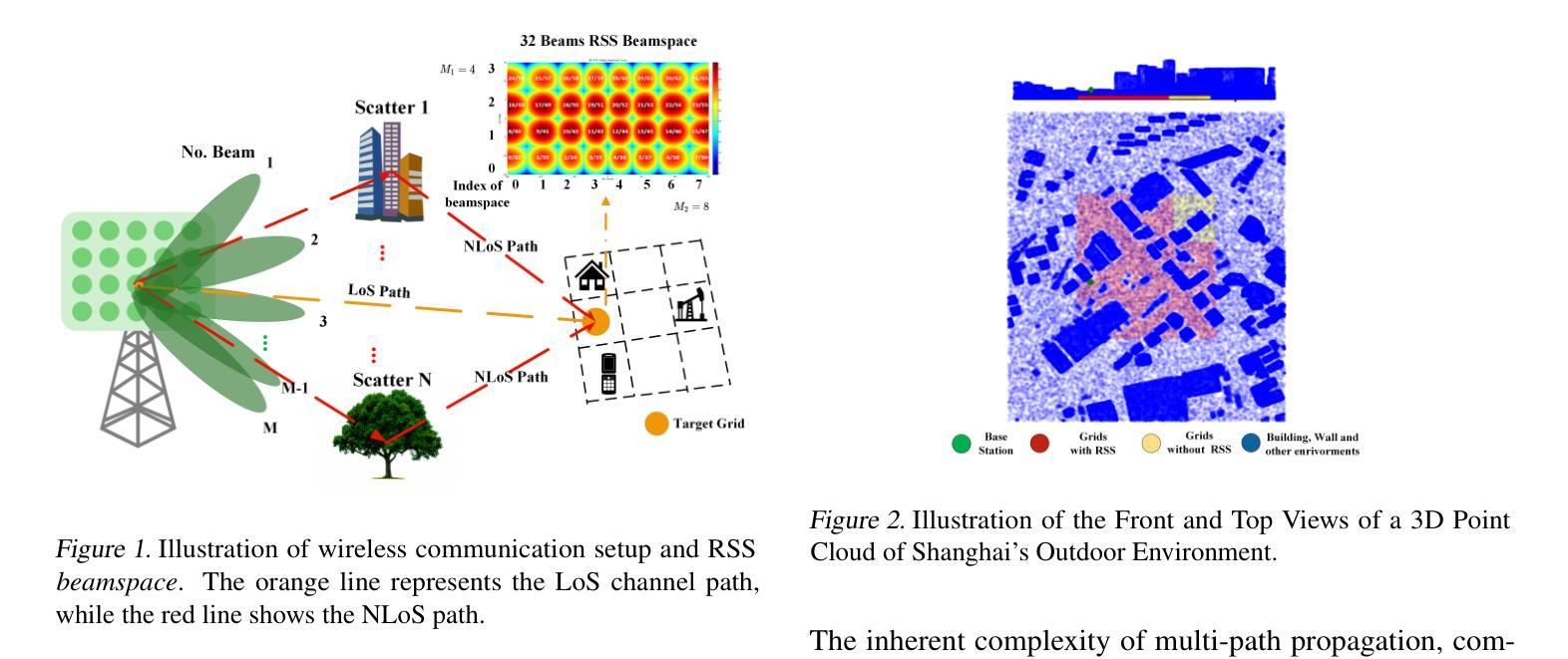
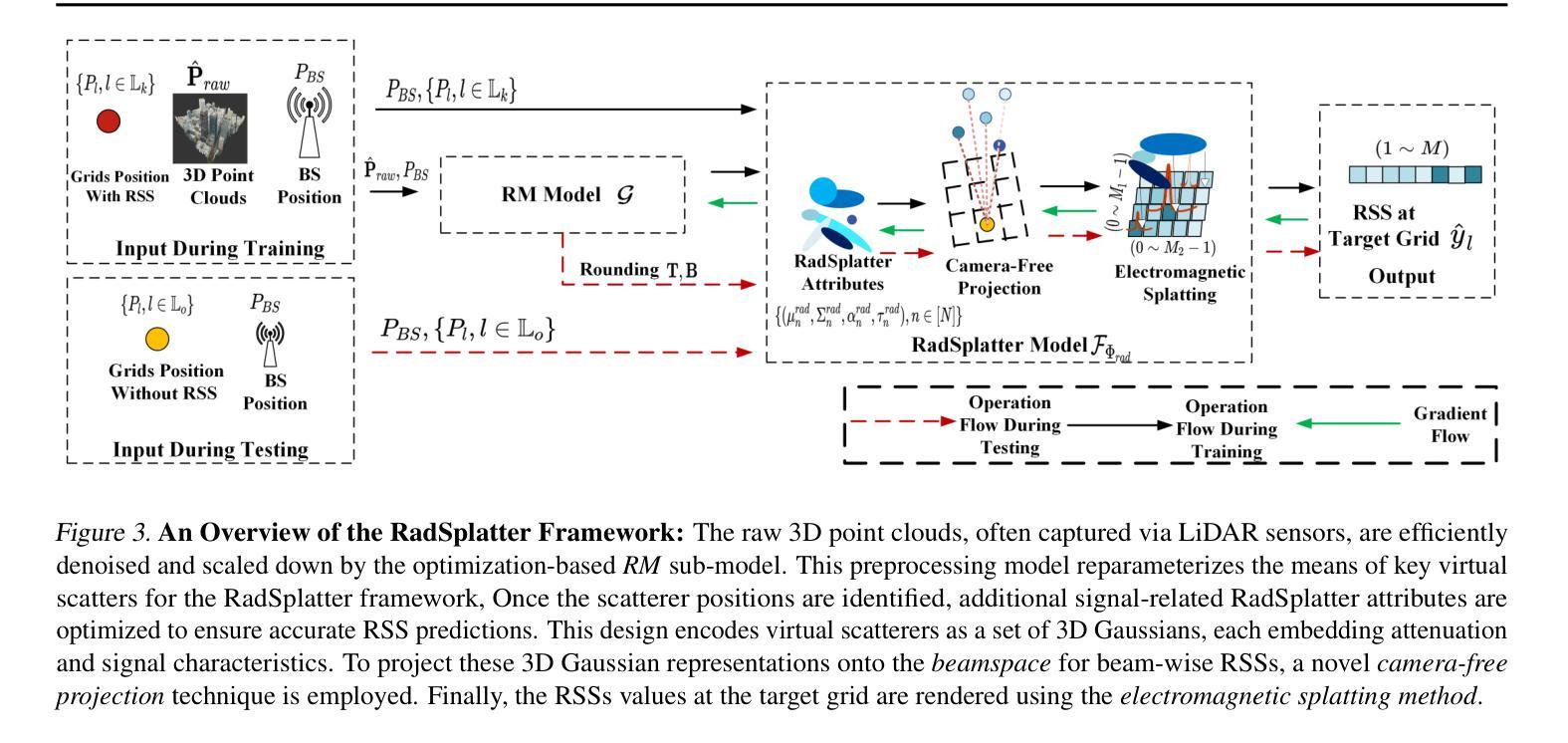
A radiomap represents the spatial distribution of wireless signal strength, critical for applications like network optimization and autonomous driving. However, constructing radiomap relies on measuring radio signal power across the entire system, which is costly in outdoor environments due to large network scales. We present RadSplatter, a framework that extends 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) to radio frequencies for efficient and accurate radiomap extrapolation from sparse measurements. RadSplatter models environmental scatterers and radio paths using 3D Gaussians, capturing key factors of radio wave propagation. It employs a relaxed-mean (RM) scheme to reparameterize the positions of 3D Gaussians from noisy and dense 3D point clouds. A camera-free 3DGS-based projection is proposed to map 3D Gaussians onto 2D radio beam patterns. Furthermore, a regularized loss function and recursive fine-tuning using highly structured sparse measurements in real-world settings are applied to ensure robust generalization. Experiments on synthetic and real-world data show state-of-the-art extrapolation accuracy and execution speed.
辐射图代表了无线信号强度的空间分布,对网络优化和自动驾驶等应用至关重要。然而,构建辐射图需要测量整个系统的无线电信号功率,由于网络规模庞大,在室外环境中成本高昂。我们提出了RadSplatter框架,它将3D高斯摊铺(3DGS)扩展到无线电频率,以从稀疏测量中进行高效且准确的辐射图外推。RadSplatter使用3D高斯对环境散射器和无线电路径进行建模,捕捉电波传播的关键因素。它采用松弛均值(RM)方案对来自噪声和密集3D点云的3D高斯位置进行重新参数化。提出了一种基于无相机3DGS的投影方法,将3D高斯映射到2D无线电波束模式上。此外,通过应用结构化的稀疏测量和真实环境中的递归微调,使用正则化损失函数确保了稳健的泛化能力。在合成和真实世界数据上的实验显示出最新的外推精度和执行速度。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
该文本介绍了一种基于三维高斯散斑(3DGS)技术的新框架RadSplatter,用于从稀疏测量中有效且准确地推断出无线信号强度的空间分布图(radiomap)。该框架通过模拟环境散射体和无线电路径的三维高斯模型,并采用一种无摄像头的投影方法,将三维高斯映射到二维无线电波束模式上。通过采用正则化损失函数和基于真实世界环境中结构化稀疏测量的递归微调,确保了其在真实环境中的稳健性和泛化能力。实验结果表明,该框架在合成数据和真实数据上均达到了最先进的推断精度和执行速度。
Key Takeaways
- RadSplatter是一个基于三维高斯散斑(3DGS)技术的框架,用于从稀疏测量中推断无线信号强度的空间分布图(radiomap)。
- 该框架对无线电信号传播的关键因素进行建模,包括环境散射体和无线路径。
- 采用无摄像头3DGS投影方法,将三维高斯映射到二维无线电波束模式上。
- 通过采用正则化损失函数和递归微调技术,确保在真实环境中的稳健性和泛化能力。
- RadSplatter可以从稀疏的测量数据中提取高度结构化的信息,用于精确推断radiomap。
- 实验结果表明,RadSplatter在合成数据和真实数据上的推断精度和执行速度均达到最新水平。
点此查看论文截图

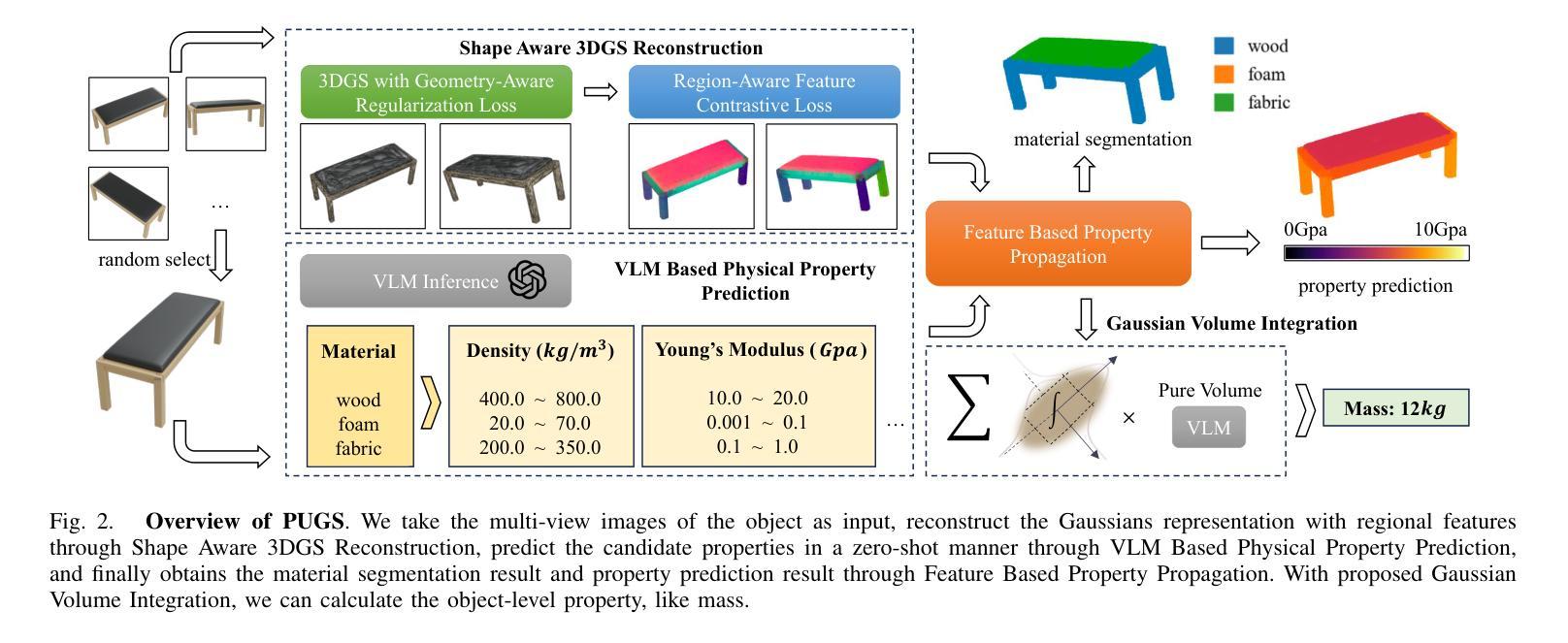
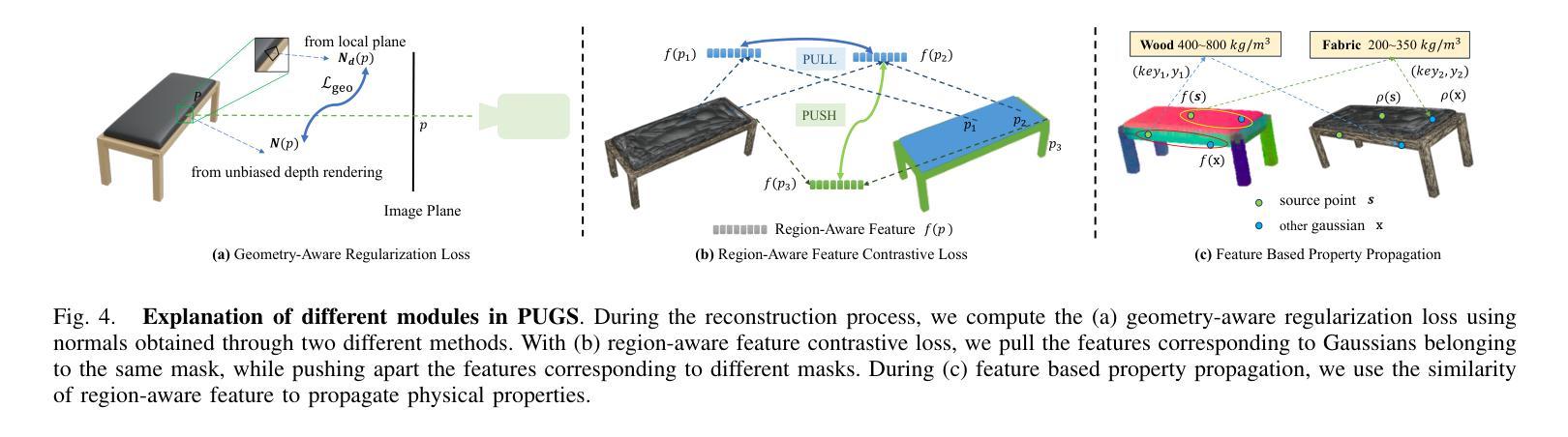
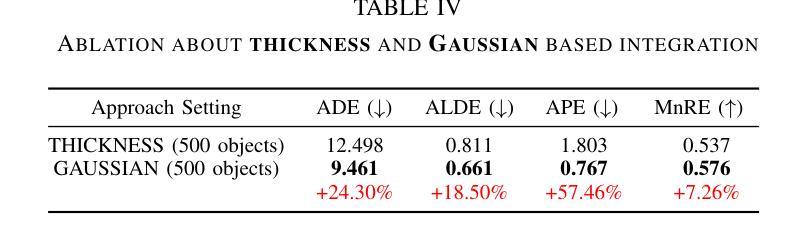
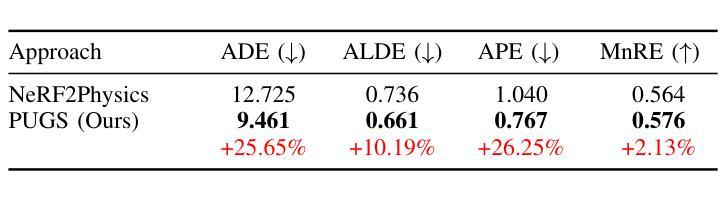
PUGS: Zero-shot Physical Understanding with Gaussian Splatting
Authors:Yinghao Shuai, Ran Yu, Yuantao Chen, Zijian Jiang, Xiaowei Song, Nan Wang, Jv Zheng, Jianzhu Ma, Meng Yang, Zhicheng Wang, Wenbo Ding, Hao Zhao
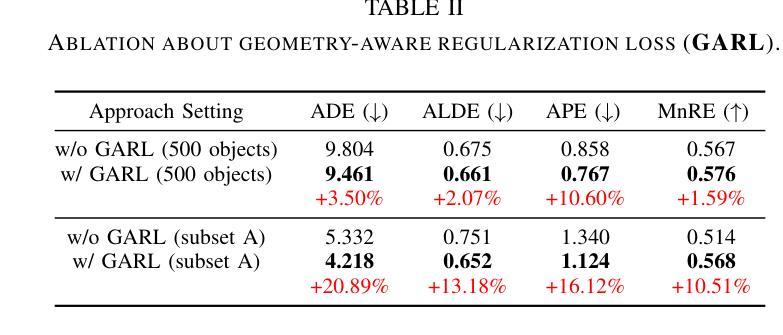
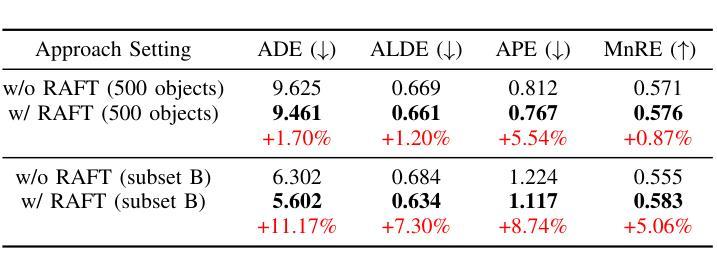
Current robotic systems can understand the categories and poses of objects well. But understanding physical properties like mass, friction, and hardness, in the wild, remains challenging. We propose a new method that reconstructs 3D objects using the Gaussian splatting representation and predicts various physical properties in a zero-shot manner. We propose two techniques during the reconstruction phase: a geometry-aware regularization loss function to improve the shape quality and a region-aware feature contrastive loss function to promote region affinity. Two other new techniques are designed during inference: a feature-based property propagation module and a volume integration module tailored for the Gaussian representation. Our framework is named as zero-shot physical understanding with Gaussian splatting, or PUGS. PUGS achieves new state-of-the-art results on the standard benchmark of ABO-500 mass prediction. We provide extensive quantitative ablations and qualitative visualization to demonstrate the mechanism of our designs. We show the proposed methodology can help address challenging real-world grasping tasks. Our codes, data, and models are available at https://github.com/EverNorif/PUGS
当前机器人系统可以很好地理解物体的类别和姿态。但在野外理解物理属性,如质量、摩擦和硬度,仍然具有挑战性。我们提出了一种使用高斯溅射表示法重建3D物体并零样本预测各种物理属性的新方法。在重建阶段,我们提出了两种技术:一种用于改进形状质量的几何感知正则化损失函数,以及一种促进区域亲和力的区域感知特征对比损失函数。在推理阶段,我们设计另外两个新技术:基于特征的属性传播模块和针对高斯表示的体积集成模块。我们的框架被命名为基于高斯溅射的零样本物理理解(PUGS)。PUGS在ABO-500质量预测的标准基准测试中实现了最新结果。我们通过广泛的定量分析和定性可视化来展示我们设计的机制。我们展示了所提出的方法可以帮助解决具有挑战性的真实世界抓取任务。我们的代码、数据和模型可在https://github.com/EverNorif/PUGS找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICRA 2025, Project page: https://evernorif.github.io/PUGS/
Summary
本文提出了一种名为PUGS的新框架,用于重建三维物体并预测其物理属性,如质量、摩擦和硬度等。框架采用高斯贴图表示法,并在重建过程中引入了几项新技术,包括几何感知正则化损失函数和区域感知特征对比损失函数,以提高形状质量和区域亲和力。在推理阶段,还设计了两个新模块:基于特征的性质传播模块和针对高斯表示的体积集成模块。该框架在ABO-500质量预测标准上取得了最新成果。
Key Takeaways
- 当前机器人系统对物体的类别和姿态有良好理解,但理解物体的物理属性(如质量、摩擦和硬度)仍然具有挑战性。
- 提出了一种新的三维物体重建方法,使用高斯贴图表示法预测物体的物理属性。
- 在重建过程中引入了几项新技术,包括几何感知正则化损失函数和区域感知特征对比损失函数,以提高形状质量和区域亲和力。
- 推出两个新模块:基于特征的性质传播模块和体积集成模块,这两个模块针对高斯表示设计,以提高预测性能。
- 所提出的框架被称为PUGS(零样本物理理解与高斯贴图),在ABO-500质量预测标准上达到了最新成果。
- PUGS框架可以通过解决具有挑战性的现实抓取任务来实际应用。
点此查看论文截图