⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-02-20 更新
Do we still need Human Annotators? Prompting Large Language Models for Aspect Sentiment Quad Prediction
Authors:Nils Constantin Hellwig, Jakob Fehle, Udo Kruschwitz, Christian Wolff
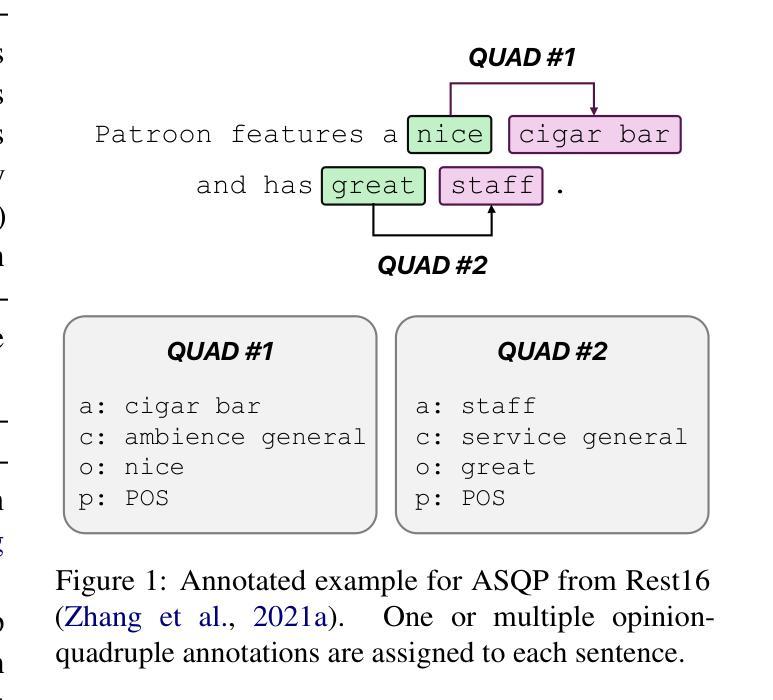
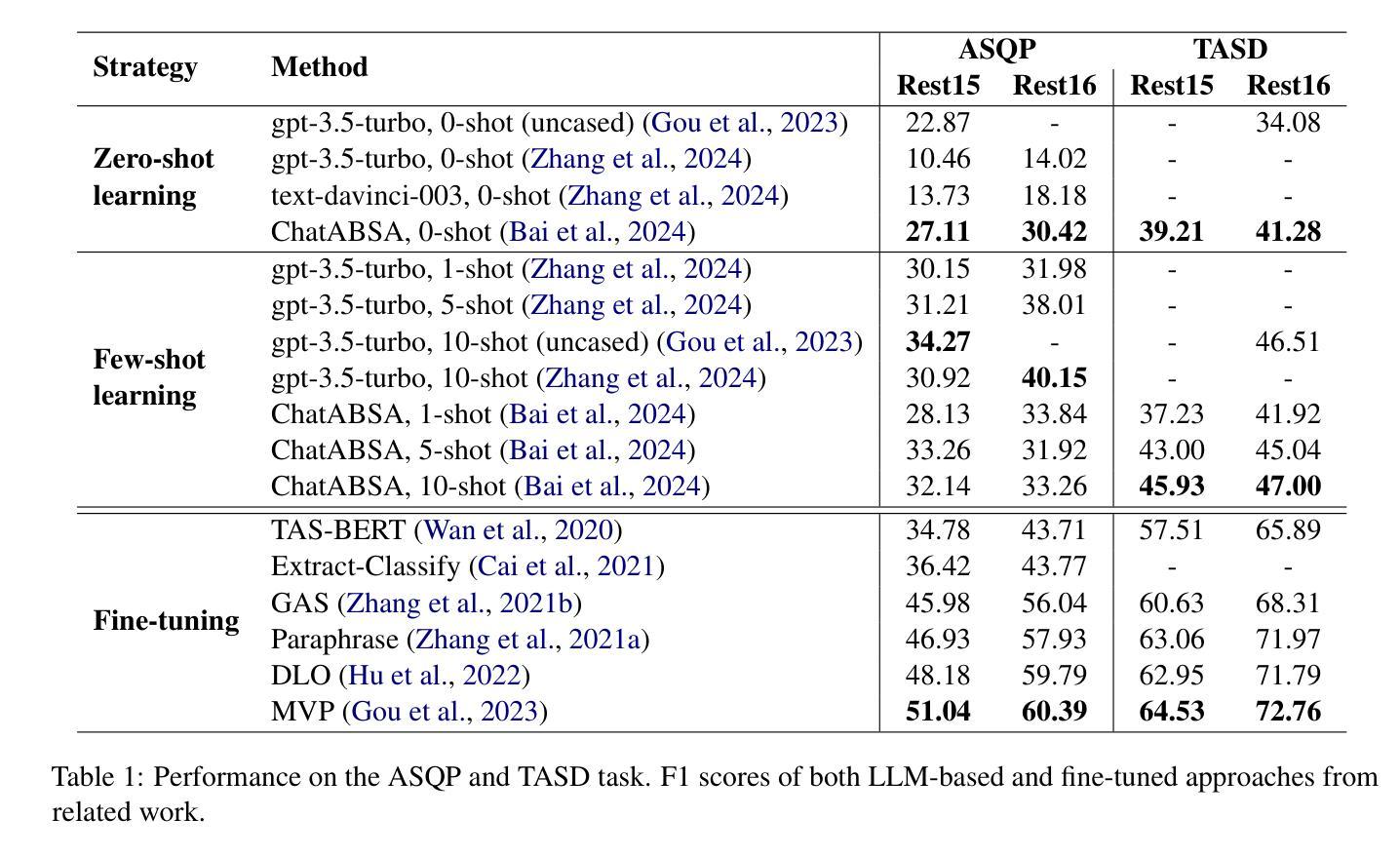
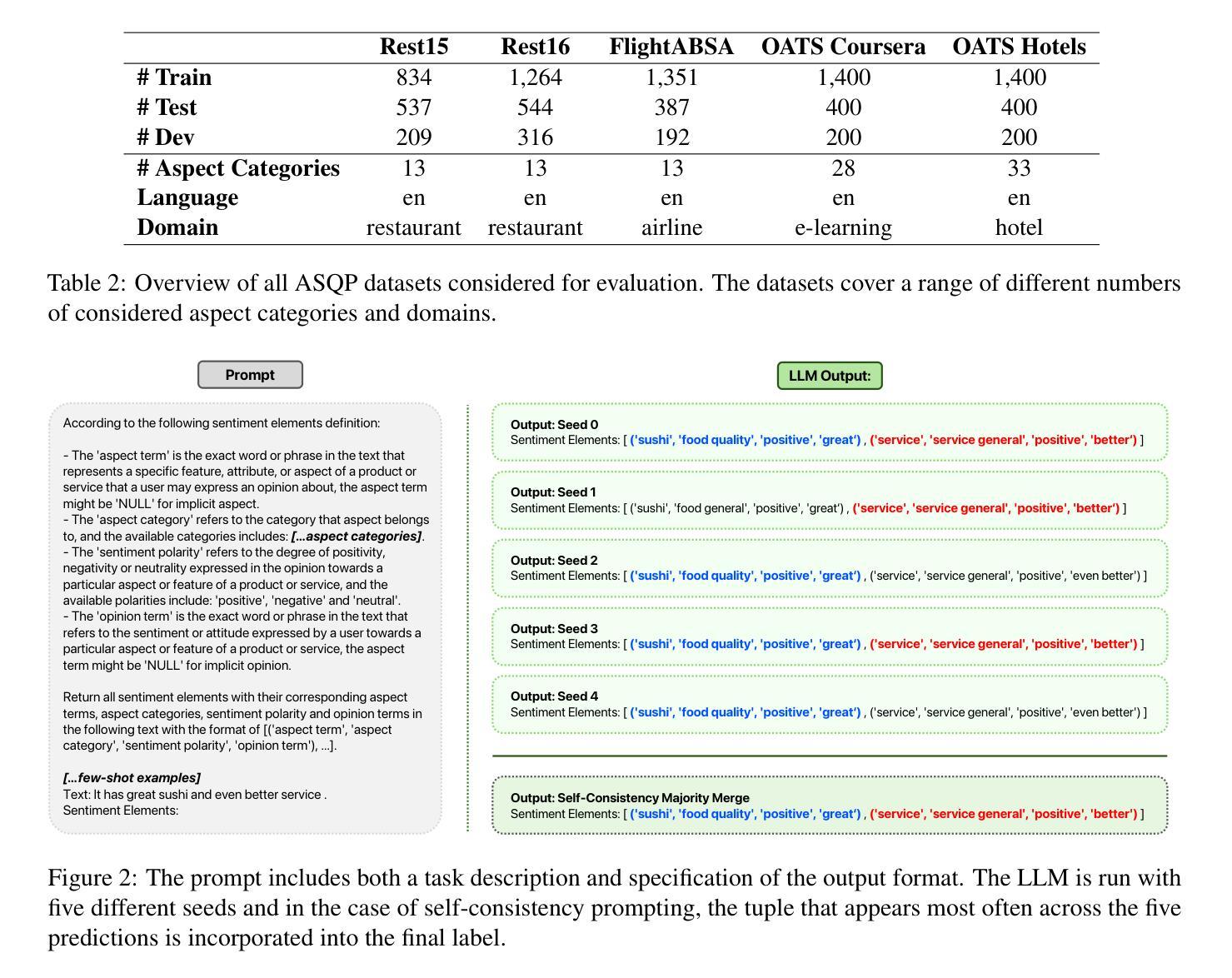
Aspect sentiment quadruple prediction (ASQP) facilitates a detailed understanding of opinions expressed in a text by identifying the opinion term, aspect term, aspect category and sentiment polarity for each opinion. However, annotating a full set of training examples to fine-tune models for ASQP is a resource-intensive process. In this study, we explore the capabilities of large language models (LLMs) for zero- and few-shot learning on the ASQP task across five diverse datasets. We report F1 scores slightly below those obtained with state-of-the-art fine-tuned models but exceeding previously reported zero- and few-shot performance. In the 40-shot setting on the Rest16 restaurant domain dataset, LLMs achieved an F1 score of 52.46, compared to 60.39 by the best-performing fine-tuned method MVP. Additionally, we report the performance of LLMs in target aspect sentiment detection (TASD), where the F1 scores were also close to fine-tuned models, achieving 66.03 on Rest16 in the 40-shot setting, compared to 72.76 with MVP. While human annotators remain essential for achieving optimal performance, LLMs can reduce the need for extensive manual annotation in ASQP tasks.
面向方面的情感四重预测(ASQP)能够通过识别每个意见的观点词、方面词、方面类别和情感极性,从而促进对文本中所表达意见的深入理解。然而,对全套训练例子进行标注以微调ASQP模型是一个资源密集型的流程。在本研究中,我们探索了大型语言模型(LLM)在五个不同数据集上的零样本和少样本学习在ASQP任务上的能力。我们报告的F1分数略低于使用最新微调模型得到的分数,但超过了之前报告的零样本和少样本性能。在Rest16餐厅域数据集的40个样本设置中,LLM的F1分数为52.46,而表现最佳的MVP微调方法的F1分数为60.39。此外,我们还报告了LLM在目标方面情感检测(TASD)中的表现,其F1分数也与微调模型相近。在Rest16的40个样本设置中,LLM的F1分数为66.03,而MVP的F1分数为72.76。虽然人类标注者对于实现最佳性能仍然至关重要,但LLM可以减少ASQP任务中对大量手动标注的需求。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文探讨了大型语言模型(LLMs)在面向方面的情感四重预测(ASQP)任务中的零样本和少样本学习能力。研究发现在五个不同的数据集上,LLMs的性能虽然略低于经过微调的最先进模型,但在零样本和少样本情况下的性能却超过了之前的报告。特别是在Rest16餐厅领域数据集的40个样本情况下,LLMs的F1分数达到了52.46%,而最佳微调方法MVP的F1分数为60.39。此外,还报告了目标方面情感检测(TASD)中LLMs的性能,其F1分数接近经过微调模型,但仍有一定差距。虽然人类注释者对于实现最佳性能至关重要,但LLMs可以减少ASQP任务中对大量手动注释的需求。
Key Takeaways
- Aspect sentiment quadruple prediction (ASQP) 能够深入理解文本中的意见,通过识别观点词、方面词、方面类别和情感极性来详细解析意见内容。
- 使用大型语言模型(LLMs)进行零样本和少样本学习在ASQP任务上具有可行性。
- LLMs在五个不同数据集上的性能表现良好,虽然略低于经过精细调教的先进模型,但在零样本和少样本情境下超越了先前报告的性能。
- 在Rest16餐厅领域数据集的40个样本情况下,LLMs的F1分数达到52.46%,而最佳模型MVP的F1分数为60.39。
- LLMs在目标方面情感检测(TASD)任务中也有良好表现,但距离经过微调的最优模型仍有一定差距。
- 虽然人类注释者对于获得最佳性能至关重要,但LLMs的应用可以减少对大量手动注释的需求,从而节省资源。
点此查看论文截图

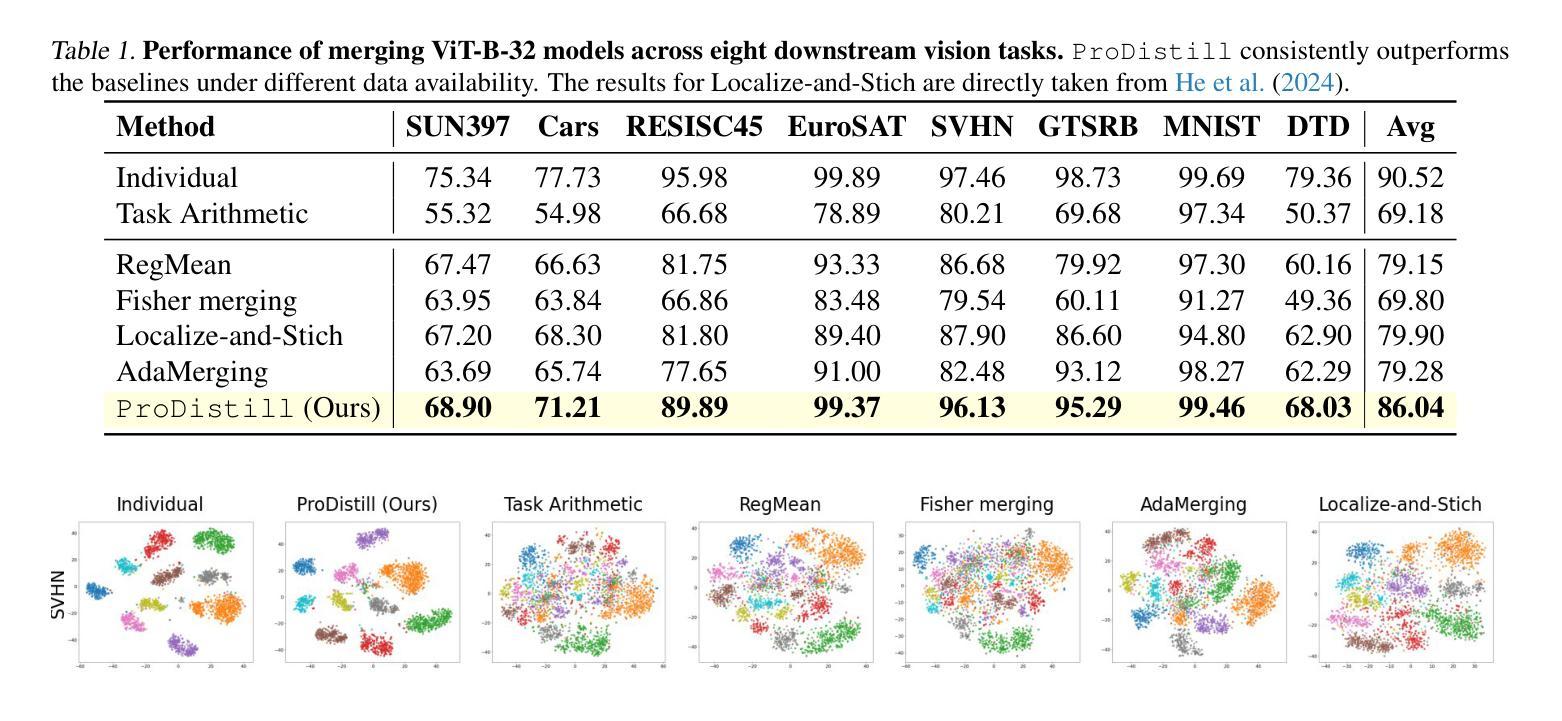
Scalable Model Merging with Progressive Layer-wise Distillation
Authors:Jing Xu, Jiazheng Li, Jingzhao Zhang
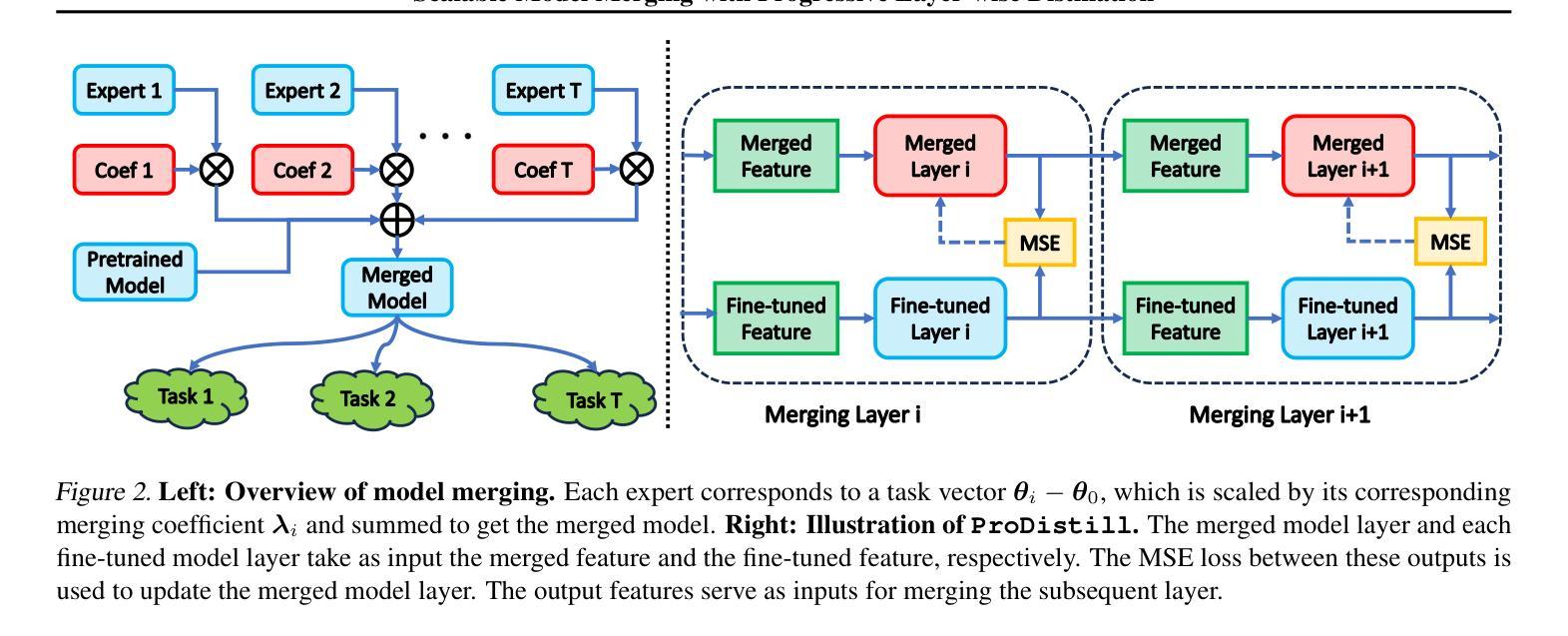
Model merging offers an effective way to integrate the capabilities of multiple fine-tuned models. However, the performance degradation of the merged model remains a challenge, particularly when none or few data are available. This paper first highlights the necessity of domain-specific data for model merging by proving that data-agnostic algorithms can have arbitrarily bad worst-case performance. Building on this theoretical insight, we explore the relationship between model merging and distillation, introducing a novel few-shot merging algorithm, ProDistill (Progressive Layer-wise Distillation). Unlike common belief that layer wise training hurts performance, we show that layer-wise teacher-student distillation not only enhances the scalability but also improves model merging performance. We conduct extensive experiments to show that compared to existing few-shot merging methods, ProDistill achieves state-of-the-art performance, with up to 6.14% and 6.61% improvements in vision and NLU tasks. Furthermore, we extend the experiments to models with over 10B parameters, showcasing the exceptional scalability of ProDistill.
模型融合为多个微调模型的集成提供了一种有效途径。然而,融合模型的性能下降仍然是一个挑战,特别是在没有或只有少量数据可用的情况下。本文首先通过证明数据无关算法可能具有任意差的性能来证明特定领域数据对模型融合的必要性。基于这一理论洞察,我们探索了模型融合与蒸馏之间的关系,引入了一种新型的少数样本融合算法——渐进层蒸馏(ProDistill)。与普遍认为的逐层训练会损害性能不同,我们展示了逐层师徒蒸馏不仅提高了可扩展性,还提高了模型融合性能。我们进行了大量实验,结果表明,与现有的少数样本融合方法相比,ProDistill实现了最先进的性能,在视觉和自然语言理解任务上分别提高了高达6.14%和6.61%。此外,我们将实验扩展到了参数超过10B的模型上,展示了ProDistill的卓越可扩展性。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
模型融合是一种有效整合多个微调模型能力的方法,但融合模型的性能下降,特别是在无数据或少数据的情况下,仍然是一个挑战。本文首先通过证明数据无关算法在最坏情况下可能具有任意差的性能来强调领域特定数据对模型融合的必要性。在此基础上,本文探索了模型融合与蒸馏的关系,提出了一种新的少样本融合算法——ProDistill(渐进逐层蒸馏)。与普遍观点相反,本文显示逐层教师-学生蒸馏不仅提高了可扩展性,还提高了模型融合性能。通过大量实验表明,与现有的少样本融合方法相比,ProDistill实现了最先进的性能,在视觉和自然语言理解任务上分别提高了6.14%和6.61%。此外,我们还对超过1 结外拓展到参数超过10B的模型,展示了ProDistill的出色可扩展性。总的来说,该文提出了一种新的少样本融合算法ProDistill算法。通过蒸馏和模型融合的有效结合策略进行演示验证了算法的高效性。。该研究将为解决深度学习的难题如迁移学习和无监督学习提供了新的思路和方法。面向具体任务的特殊训练数据将提高模型的性能,特别是面对大规模数据集时。通过实验结果可以看出,ProDistill算法具有良好的泛化能力和实际应用前景。研究也证明了基于教师-学生模型的蒸馏方法在多模态数据处理中具有广阔的应用前景。它允许同时考虑多源数据的综合作用而不依赖于特定的数据集或任务类型。这为未来的研究开辟了新的方向。未来可以进一步探索如何优化蒸馏策略以适应不同任务的特性以及如何更好地将多种模态的数据进行有效融合以取得更好的性能。此外,该算法在更大规模数据集上的表现值得进一步深入研究。这些研究将有助于推动机器学习领域的发展并推动其在实际应用中的落地。对于实际应用场景如自然语言处理、计算机视觉等领域也可以进行更多的探索和研究工作。具体来说可以研究如何将这些算法应用于实际场景中解决现实世界中存在的问题如图像识别、自然语言翻译等任务中。通过进一步的研究和实践可以不断完善和改进这些算法从而提高其在现实世界中的应用效果。针对这些问题展开深入研究将有助于推动机器学习领域的发展并为相关领域提供有力的支持和技术保障。关键见解
- 强调了领域特定数据在模型融合中的重要性,并指出数据无关算法可能存在的性能问题。
- 提出了一种新的少样本融合算法ProDistill,通过渐进逐层蒸馏提高模型融合性能。
- 实验表明,ProDistill在视觉和自然语言理解任务上较现有方法有明显改进。
- ProDistill具有出色的可扩展性,可应用于参数规模较大的模型。
- 逐层教师-学生蒸馏策略提高了模型融合的效率和性能。
点此查看论文截图

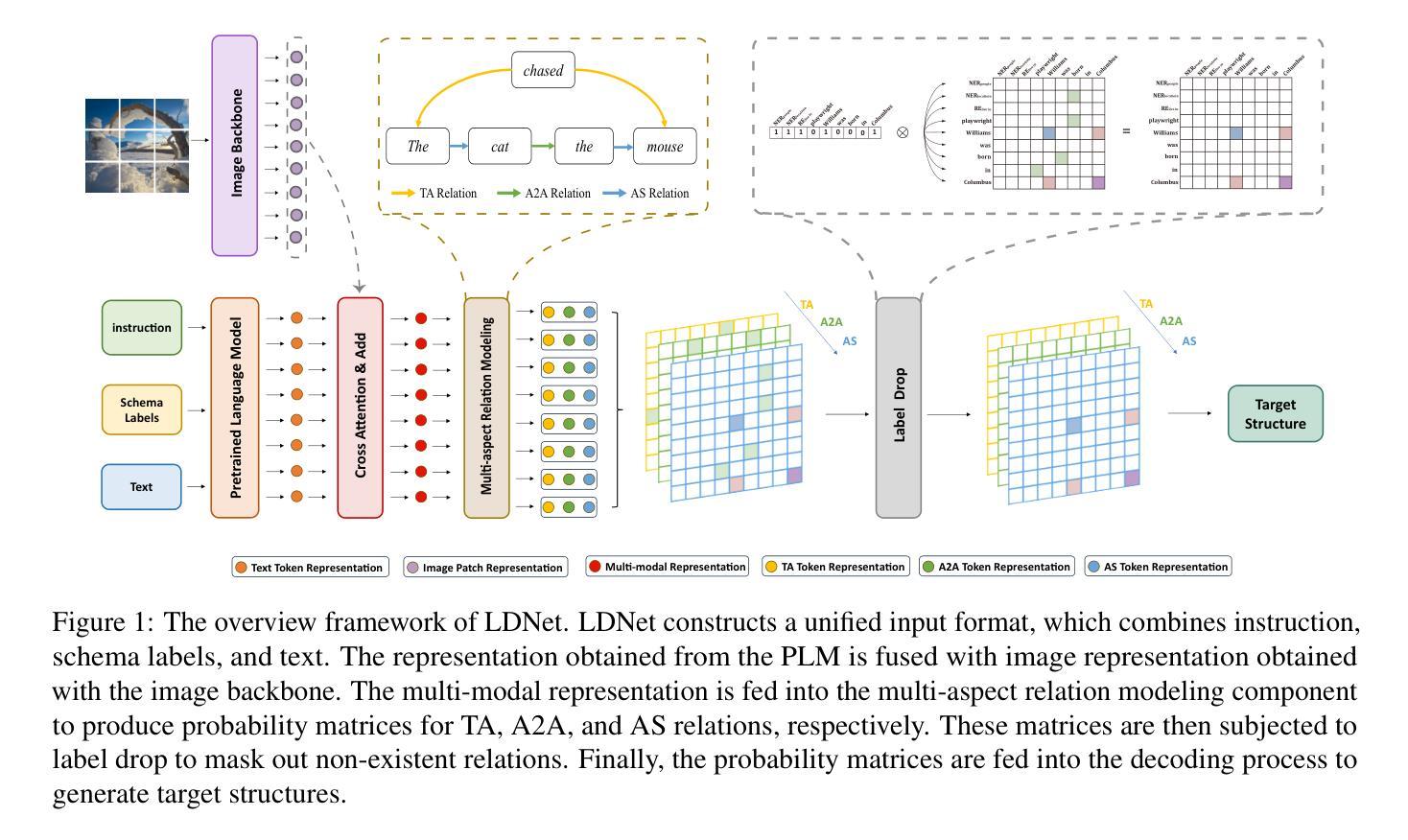
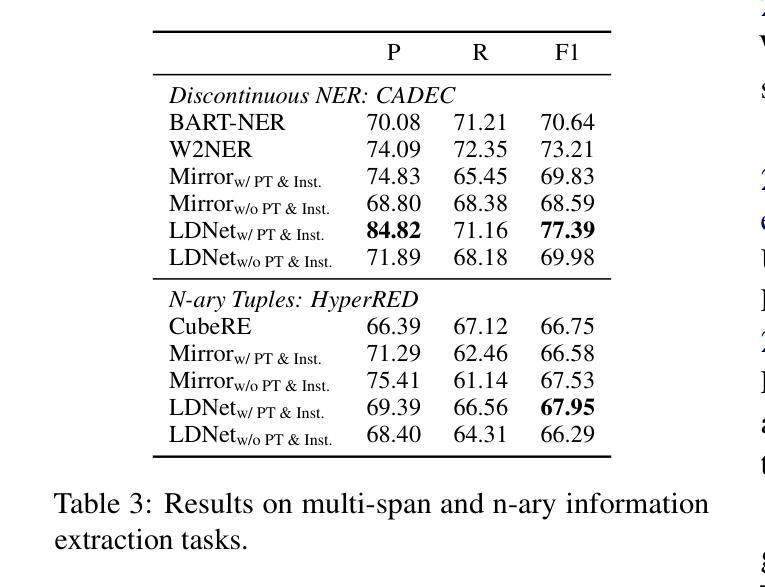
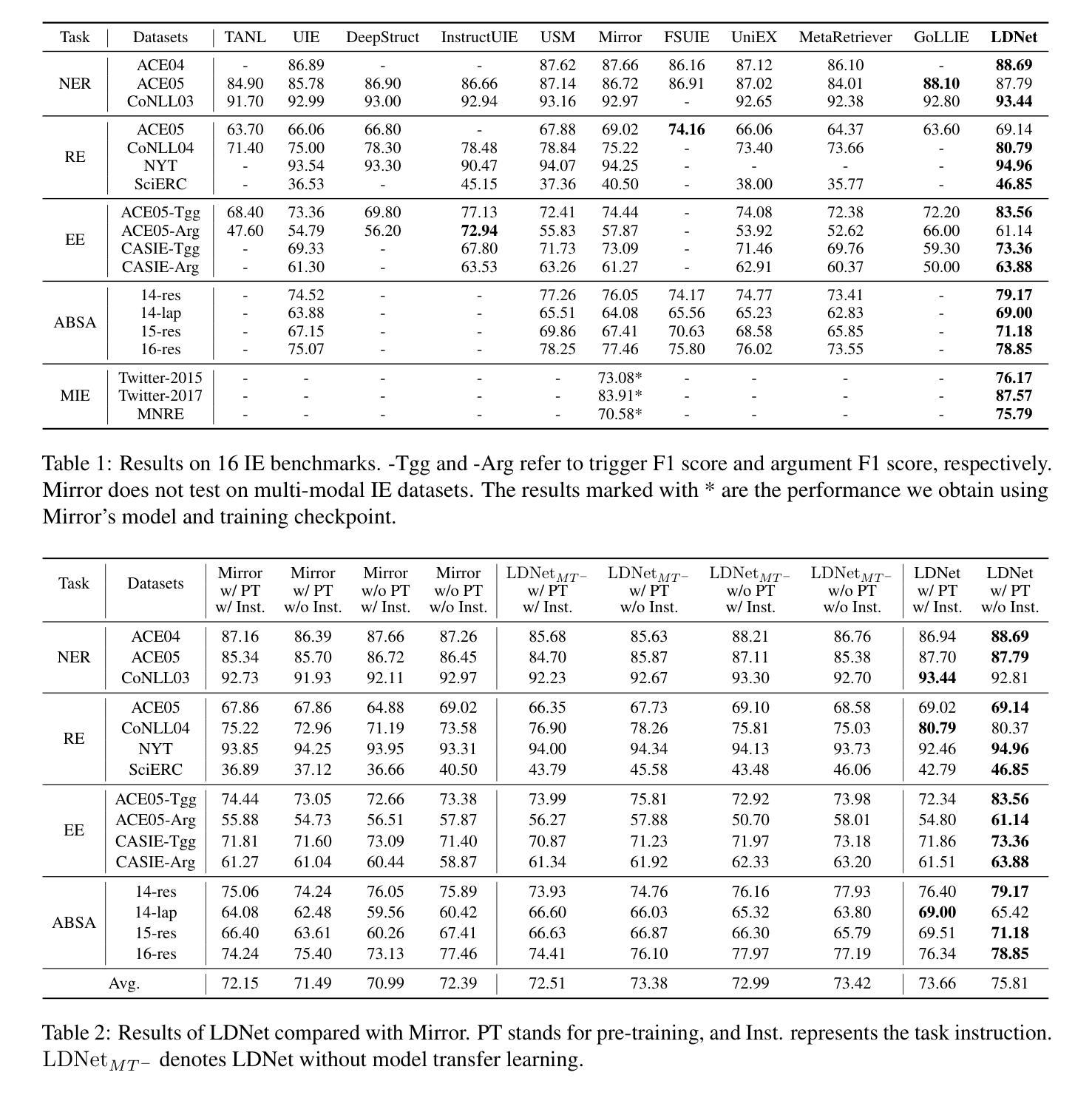
Label Drop for Multi-Aspect Relation Modeling in Universal Information Extraction
Authors:Lu Yang, Jiajia Li, En Ci, Lefei Zhang, Zuchao Li, Ping Wang
Universal Information Extraction (UIE) has garnered significant attention due to its ability to address model explosion problems effectively. Extractive UIE can achieve strong performance using a relatively small model, making it widely adopted. Extractive UIEs generally rely on task instructions for different tasks, including single-target instructions and multiple-target instructions. Single-target instruction UIE enables the extraction of only one type of relation at a time, limiting its ability to model correlations between relations and thus restricting its capability to extract complex relations. While multiple-target instruction UIE allows for the extraction of multiple relations simultaneously, the inclusion of irrelevant relations introduces decision complexity and impacts extraction accuracy. Therefore, for multi-relation extraction, we propose LDNet, which incorporates multi-aspect relation modeling and a label drop mechanism. By assigning different relations to different levels for understanding and decision-making, we reduce decision confusion. Additionally, the label drop mechanism effectively mitigates the impact of irrelevant relations. Experiments show that LDNet outperforms or achieves competitive performance with state-of-the-art systems on 9 tasks, 33 datasets, in both single-modal and multi-modal, few-shot and zero-shot settings.\footnote{https://github.com/Lu-Yang666/LDNet}
通用信息抽取(UIE)因其能够有效解决模型爆炸问题而备受关注。使用较小的模型,抽取式UIE就能实现出色的性能,因此得到了广泛的应用。抽取式UIE通常依赖于不同的任务指令来完成不同任务,包括单目标指令和多目标指令。单目标指令UIE一次只能提取一种关系,限制了它建模关系间关联的能力,从而限制了其提取复杂关系的能力。虽然多目标指令UIE可以同时提取多种关系,但包含的不相关关系增加了决策复杂性并影响了提取精度。因此,针对多关系抽取,我们提出了LDNet,它结合了多方面关系建模和标签丢失机制。通过将不同的关系分配给不同的理解和决策层次,我们减少了决策混淆。此外,标签丢失机制有效地减轻了不相关关系的影响。实验表明,LDNet在单模态和多模态、小样本和零样本设置的9个任务、33个数据集上达到了最新系统的性能水平或超越了它们的表现。[^https://github.com/Lu-Yang666/LDNet]。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to NAACL-main 2025
Summary:信息抽取通用框架(UIE)能够有效解决模型爆炸问题,且具有使用小型模型实现强大性能的能力。研究提出了LDNet模型用于多关系抽取,通过多层面关系建模和标签丢弃机制,提高了决策准确性和提取性能。该模型在单模态和多模态、小样本和零样本场景下表现出卓越性能。
Key Takeaways:
- UIE框架能缓解模型爆炸问题,并在使用较小的模型时展现出强大的性能。
- 提取型UIE主要依赖于任务指令来完成不同任务,包括单目标指令和多目标指令。
- 单目标指令UIE一次只能提取一种关系,限制了其提取复杂关系的能力。
- 多目标指令UIE虽然能同时提取多种关系,但引入的不相关关系增加了决策复杂性和影响了提取准确性。
- LDNet模型被提出用于解决多关系抽取问题,它通过多层面关系建模和标签丢弃机制减少决策混淆,并有效缓解不相关关系的影响。
- LDNet模型在多个任务和数据集上的实验表现优于或达到最新技术水平。
点此查看论文截图


Adaptive Prototype Model for Attribute-based Multi-label Few-shot Action Recognition
Authors:Juefeng Xiao, Tianqi Xiang, Zhigang Tu
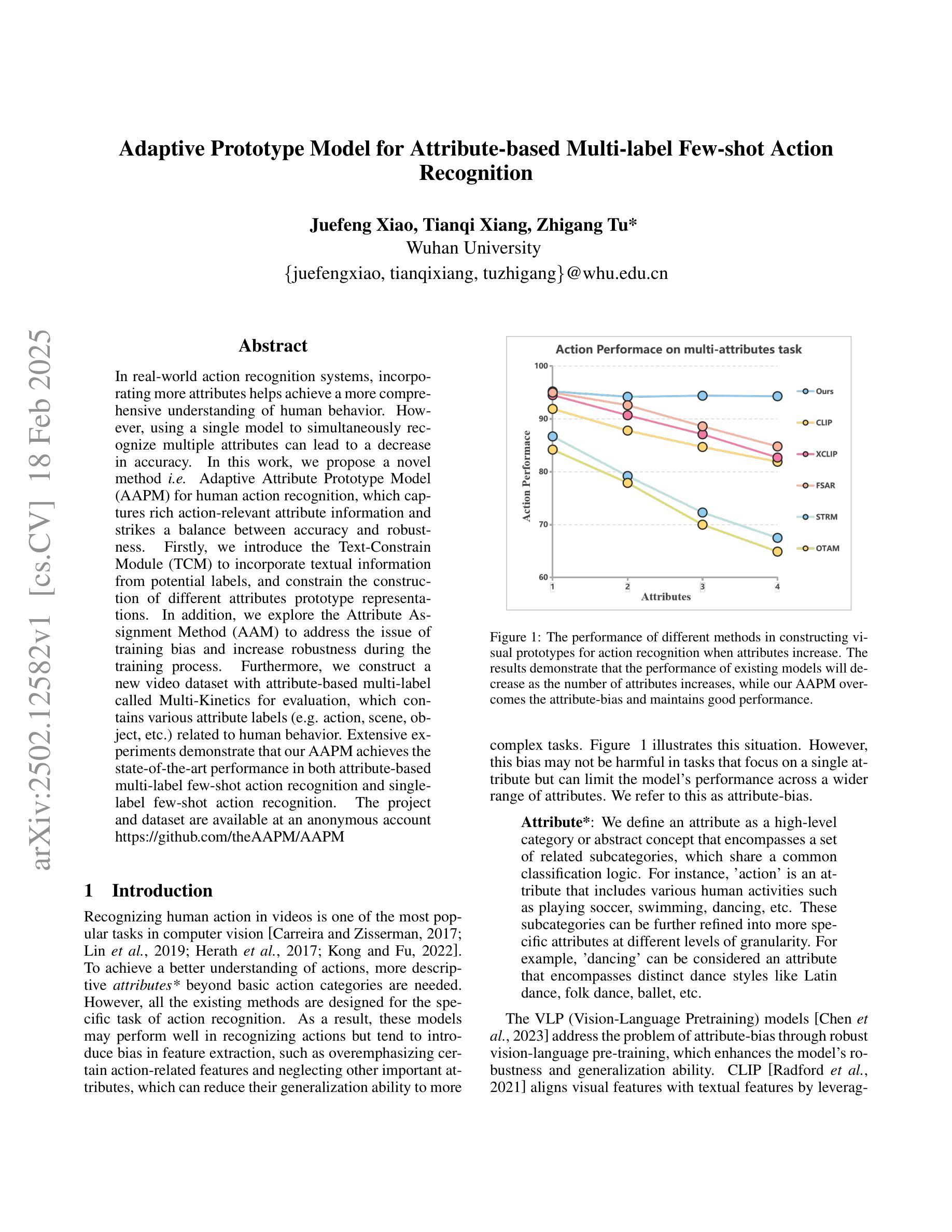
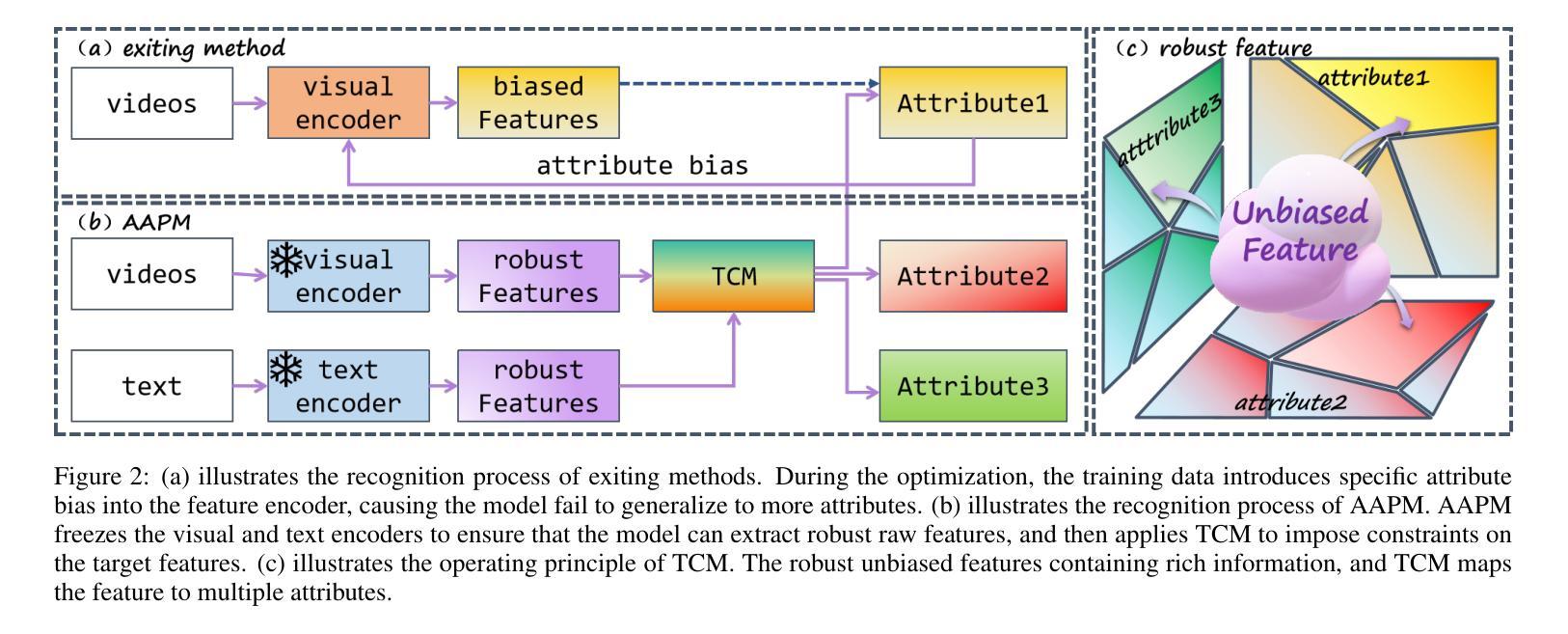
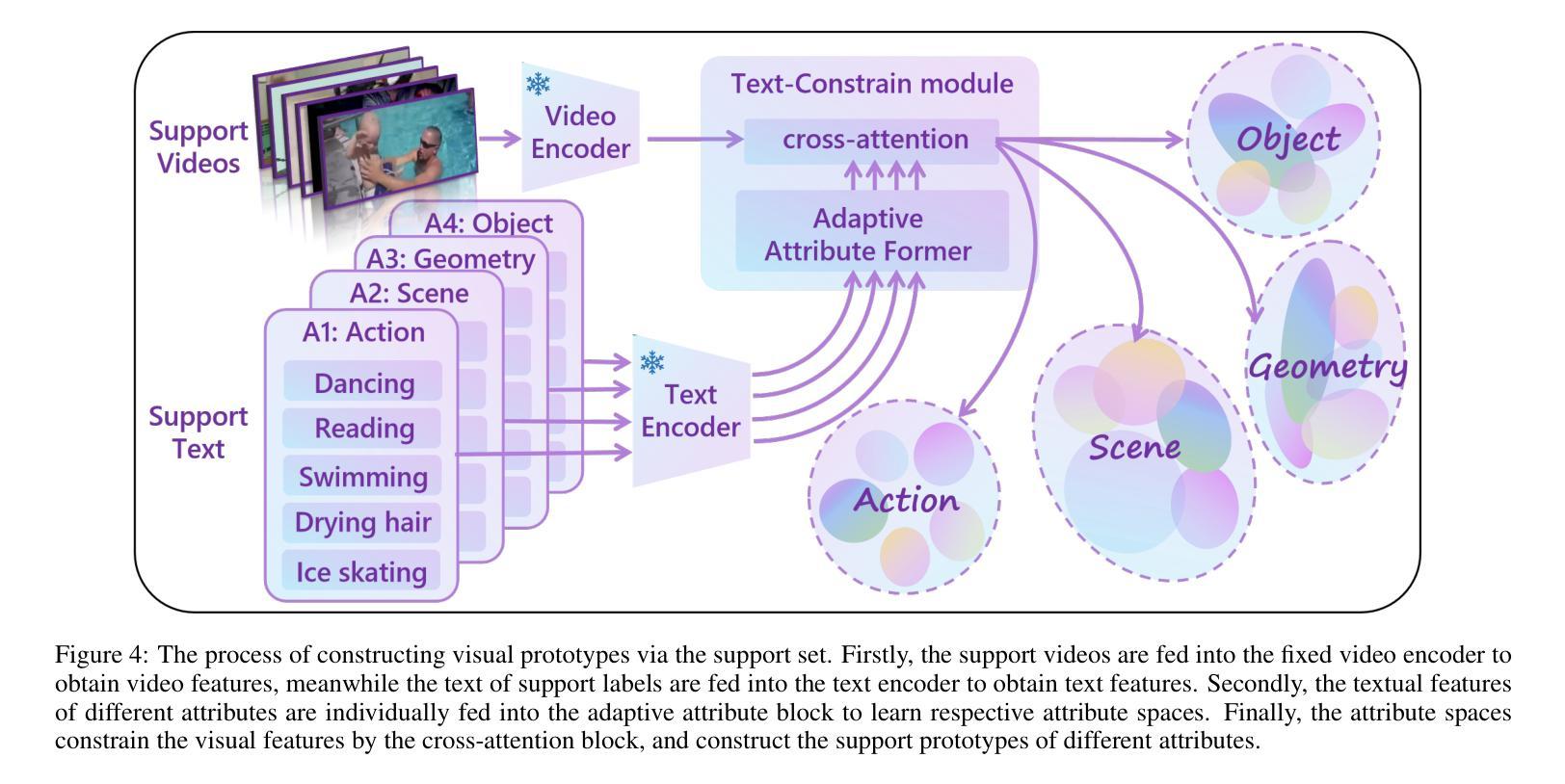
In real-world action recognition systems, incorporating more attributes helps achieve a more comprehensive understanding of human behavior. However, using a single model to simultaneously recognize multiple attributes can lead to a decrease in accuracy. In this work, we propose a novel method i.e. Adaptive Attribute Prototype Model (AAPM) for human action recognition, which captures rich action-relevant attribute information and strikes a balance between accuracy and robustness. Firstly, we introduce the Text-Constrain Module (TCM) to incorporate textual information from potential labels, and constrain the construction of different attributes prototype representations. In addition, we explore the Attribute Assignment Method (AAM) to address the issue of training bias and increase robustness during the training process.Furthermore, we construct a new video dataset with attribute-based multi-label called Multi-Kinetics for evaluation, which contains various attribute labels (e.g. action, scene, object, etc.) related to human behavior. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our AAPM achieves the state-of-the-art performance in both attribute-based multi-label few-shot action recognition and single-label few-shot action recognition. The project and dataset are available at an anonymous account https://github.com/theAAPM/AAPM
在现实世界的动作识别系统中,融入更多属性有助于更全面地理解人类行为。然而,使用单一模型同时识别多个属性可能会导致精度下降。在这项工作中,我们提出了一种新型方法,即自适应属性原型模型(AAPM)用于人类动作识别,该模型捕捉了丰富的动作相关属性信息,并在精度和稳健性之间达到了平衡。首先,我们引入了文本约束模块(TCM),以融入潜在标签的文本信息,并约束不同属性原型表示的构建。此外,我们探索了属性分配方法(AAM),以解决训练过程中的偏见问题,并提高稳健性。此外,我们构建了一个新的基于属性的多标签视频数据集,名为Multi-Kinetics,用于评估,其中包含与人类行为相关的各种属性标签(例如动作、场景、物体等)。大量实验表明,我们的AAPM在基于属性的多标签小样本动作识别和单标签小样本动作识别方面都达到了最新技术水平。项目和数据集可通过匿名账号https://github.com/theAAPM/AAPM进行访问。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文主要介绍了一种新的动作识别方法——自适应属性原型模型(AAPM),该模型能够捕捉丰富的动作相关属性信息,并在准确性和稳健性之间取得平衡。通过引入文本约束模块(TCM)和属性分配方法(AAM),提高了多属性识别系统的性能。同时,构建了一个新的视频数据集Multi-Kinetics,用于评估基于属性的多标签和单标签少样本动作识别的性能。实验表明,AAPM在基于属性的多标签和单标签少样本动作识别方面都达到了最先进的性能。
Key Takeaways
- 自适应属性原型模型(AAPM)结合了多个属性以提高对人类行为的全面理解。
- 通过引入文本约束模块(TCM),将文本信息融入潜在标签,约束不同属性原型表示的构建。
- 提出的属性分配方法(AAM)解决了训练过程中的偏见问题,提高了系统的稳健性。
- 构建了一个新的视频数据集Multi-Kinetics,用于评估基于属性的多标签动作识别性能。
- AAPM在基于属性的多标签少样本动作识别方面达到最先进的性能。
- AAPM同样在单标签少样本动作识别方面表现出卓越的性能。
点此查看论文截图

Predicate Hierarchies Improve Few-Shot State Classification
Authors:Emily Jin, Joy Hsu, Jiajun Wu
State classification of objects and their relations is core to many long-horizon tasks, particularly in robot planning and manipulation. However, the combinatorial explosion of possible object-predicate combinations, coupled with the need to adapt to novel real-world environments, makes it a desideratum for state classification models to generalize to novel queries with few examples. To this end, we propose PHIER, which leverages predicate hierarchies to generalize effectively in few-shot scenarios. PHIER uses an object-centric scene encoder, self-supervised losses that infer semantic relations between predicates, and a hyperbolic distance metric that captures hierarchical structure; it learns a structured latent space of image-predicate pairs that guides reasoning over state classification queries. We evaluate PHIER in the CALVIN and BEHAVIOR robotic environments and show that PHIER significantly outperforms existing methods in few-shot, out-of-distribution state classification, and demonstrates strong zero- and few-shot generalization from simulated to real-world tasks. Our results demonstrate that leveraging predicate hierarchies improves performance on state classification tasks with limited data.
对象和它们的关系的状态分类是许多长期任务的核心,特别是在机器人规划和操作方面。然而,可能的对象-谓词组合的组合爆炸,以及需要适应新的现实世界环境,使得状态分类模型需要能够用少量示例推广到新的查询成为一项必要。为此,我们提出了PHIER,它利用谓词层次结构在少量场景中进行有效的推广。PHIER使用以对象为中心的场景编码器、自监督损失来推断谓词之间的语义关系,以及捕捉层次结构的双曲距离度量;它学习图像-谓词对的结构化潜在空间,指导状态分类查询的推理。我们在CALVIN和BEHAVIOR机器人环境中评估了PHIER,结果表明,在少量、分布外的状态分类任务中,PHIER显著优于现有方法,并在从模拟到真实世界任务的零样本和少量样本推广中表现出强大的能力。我们的结果证明,利用谓词层次结构在数据有限的状态分类任务上可以提高性能。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICLR 2025. First two authors contributed equally. Project page: https://emilyzjin.github.io/projects/phier.html
Summary
基于对象和关系分类的状态分类是长期任务的核心,尤其在机器人规划和操作领域。然而,由于可能的对象-谓词组合的爆炸性增长以及对新现实环境的适应需求,状态分类模型需要能够在新查询中快速适应并具有少量样本的泛化能力。为此,我们提出了PHIER方法,它利用谓词层次结构在少量场景中实现有效泛化。PHIER使用以对象为中心的场景编码器、自监督损失来推断谓词之间的语义关系以及双曲距离度量来捕捉层次结构;它学习图像-谓词对的结构化潜在空间,为状态分类查询提供指导。我们在CALVIN和BEHAVIOR机器人环境中评估了PHIER的性能,结果表明,PHIER在少量的未知分布状态分类任务中显著优于现有方法,并展示了从模拟任务到真实任务中零样本和少量样本的出色泛化能力。利用谓词层次结构提高了在有限数据上的状态分类任务性能。
Key Takeaways
- 状态分类是机器人规划和操作等长期任务的核心。
- 对象和关系分类对于适应新环境和泛化至关重要。
- PHIER方法利用谓词层次结构以实现有效泛化。
- PHIER包括以对象为中心的场景编码器、自监督损失和捕捉层次结构的双曲距离度量。
- PHIER在机器人环境评估中表现出优异性能。
- PHIER在少量未知分布状态分类任务中显著优于现有方法。
点此查看论文截图


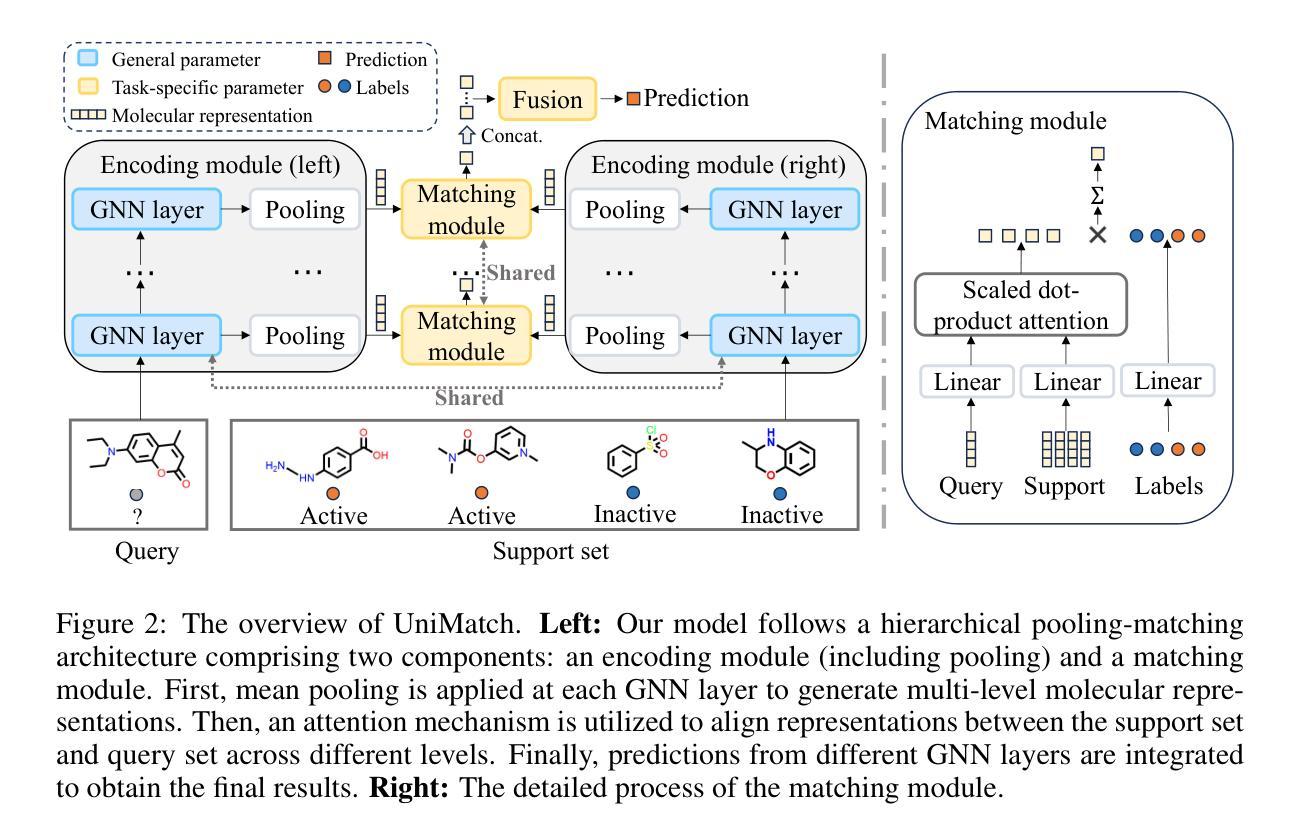
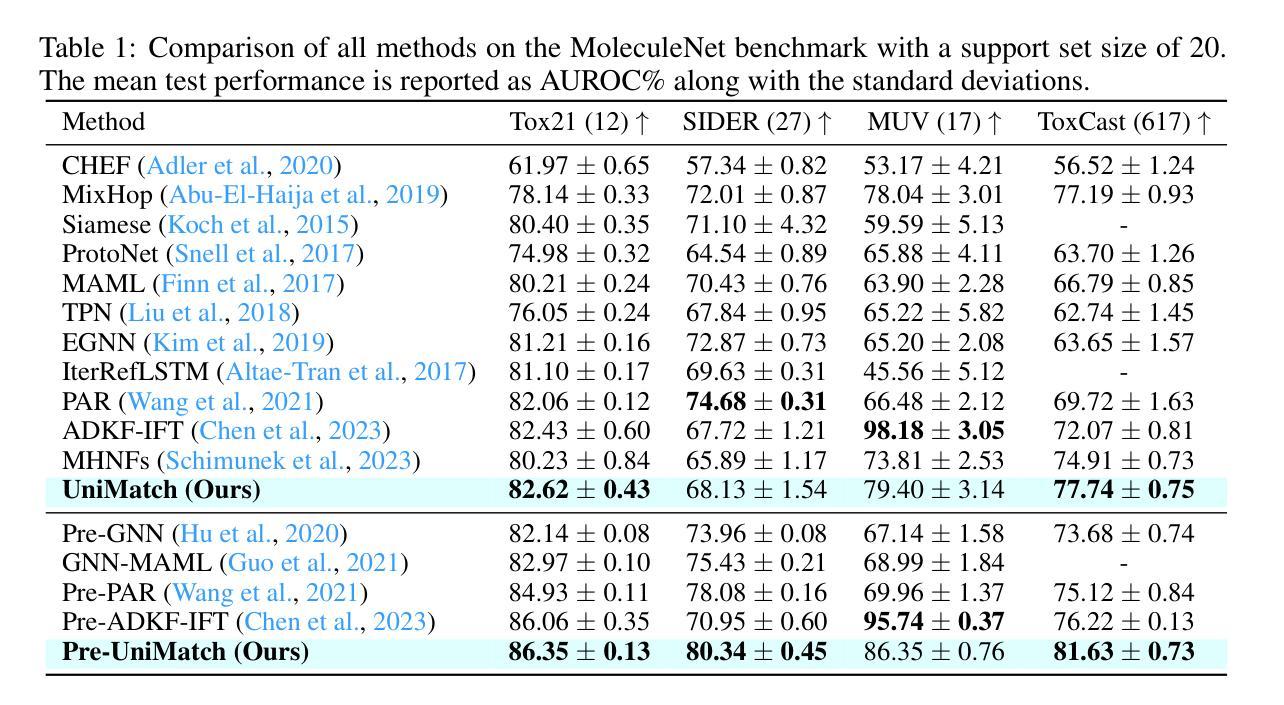
UniMatch: Universal Matching from Atom to Task for Few-Shot Drug Discovery
Authors:Ruifeng Li, Mingqian Li, Wei Liu, Yuhua Zhou, Xiangxin Zhou, Yuan Yao, Qiang Zhang, Hongyang Chen
Drug discovery is crucial for identifying candidate drugs for various diseases.However, its low success rate often results in a scarcity of annotations, posing a few-shot learning problem. Existing methods primarily focus on single-scale features, overlooking the hierarchical molecular structures that determine different molecular properties. To address these issues, we introduce Universal Matching Networks (UniMatch), a dual matching framework that integrates explicit hierarchical molecular matching with implicit task-level matching via meta-learning, bridging multi-level molecular representations and task-level generalization. Specifically, our approach explicitly captures structural features across multiple levels, such as atoms, substructures, and molecules, via hierarchical pooling and matching, facilitating precise molecular representation and comparison. Additionally, we employ a meta-learning strategy for implicit task-level matching, allowing the model to capture shared patterns across tasks and quickly adapt to new ones. This unified matching framework ensures effective molecular alignment while leveraging shared meta-knowledge for fast adaptation. Our experimental results demonstrate that UniMatch outperforms state-of-the-art methods on the MoleculeNet and FS-Mol benchmarks, achieving improvements of 2.87% in AUROC and 6.52% in delta AUPRC. UniMatch also shows excellent generalization ability on the Meta-MolNet benchmark.
药物发现对于识别各种疾病的候选药物至关重要。然而,其较低的成功率经常导致注释的稀缺,从而构成小样本学习问题。现有方法主要关注单一尺度特征,忽略了决定不同分子特性的分层分子结构。为了解决这些问题,我们引入了Universal Matching Networks(UniMatch),这是一个双匹配框架,它通过元学习将显式的分层分子匹配与隐式的任务级匹配相结合,桥接多层次分子表示和任务级泛化。具体来说,我们的方法通过分层池化和匹配显式捕获多个层次的结构特征,如原子、子结构和分子,促进精确的分子表示和比较。此外,我们采用元学习策略进行隐式任务级匹配,使模型能够捕获任务之间的共享模式并快速适应新任务。这一统一的匹配框架确保了有效的分子对齐,同时利用共享元知识实现快速适应。实验结果表明,UniMatch在MoleculeNet和FS-Mol基准测试中优于最新方法,在AUROC中提高了2.87%,在delta AUPRC中提高了6.52%。UniMatch在Meta-MolNet基准测试中也表现出良好的泛化能力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF accepted as ICLR 2025 Spotlight
Summary
药物发现中识别候选药物是一个关键问题,但其低成功率导致标注数据稀缺,构成小样本学习问题。现有方法主要关注单一尺度特征,忽略了决定分子属性的层次结构。本研究引入Universal Matching Networks(UniMatch),结合明确的层次分子匹配和基于元学习的隐任务匹配,构建多层次的分子表示和任务泛化桥梁。通过层次池化和匹配,捕获原子、子结构和分子等多个层次的结构特征。此外,采用元学习策略进行隐任务匹配,使模型能够捕获任务间的共享模式并快速适应新任务。实验结果在MoleculeNet和FS-Mol基准测试中表明,UniMatch优于现有方法,提高了AUROC的2.87%和delta AUPRC的6.52%。同时,UniMatch在Meta-MolNet基准测试中展现出良好的泛化能力。
Key Takeaways
- 药物发现面临低成功率和标注数据稀缺的问题,构成小样本学习挑战。
- 现有方法主要关注单一尺度特征,忽略了分子的层次结构。
- UniMatch是一个双匹配框架,结合明确的层次分子匹配和隐任务匹配。
- UniMatch通过层次池化和匹配技术,捕获多个层次的结构特征。
- 元学习策略用于隐任务匹配,提高模型对任务间共享模式的捕获能力,并加快对新任务的适应。
- 实验结果表明,UniMatch在多个基准测试中优于现有方法。
点此查看论文截图


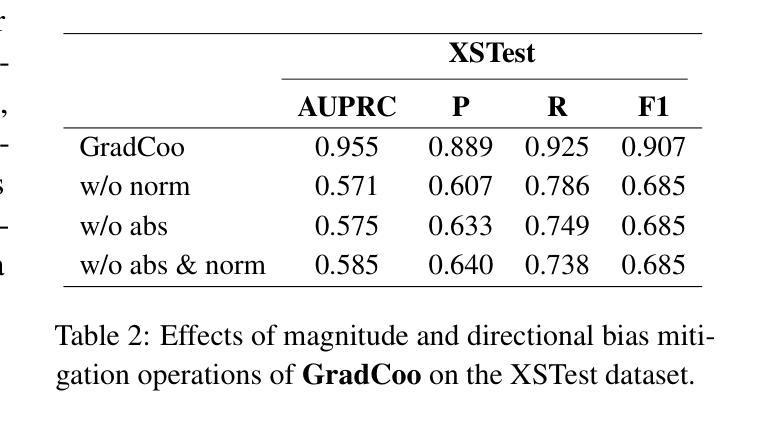
Gradient Co-occurrence Analysis for Detecting Unsafe Prompts in Large Language Models
Authors:Jingyuan Yang, Bowen Yan, Rongjun Li, Ziyu Zhou, Xin Chen, Zhiyong Feng, Wei Peng
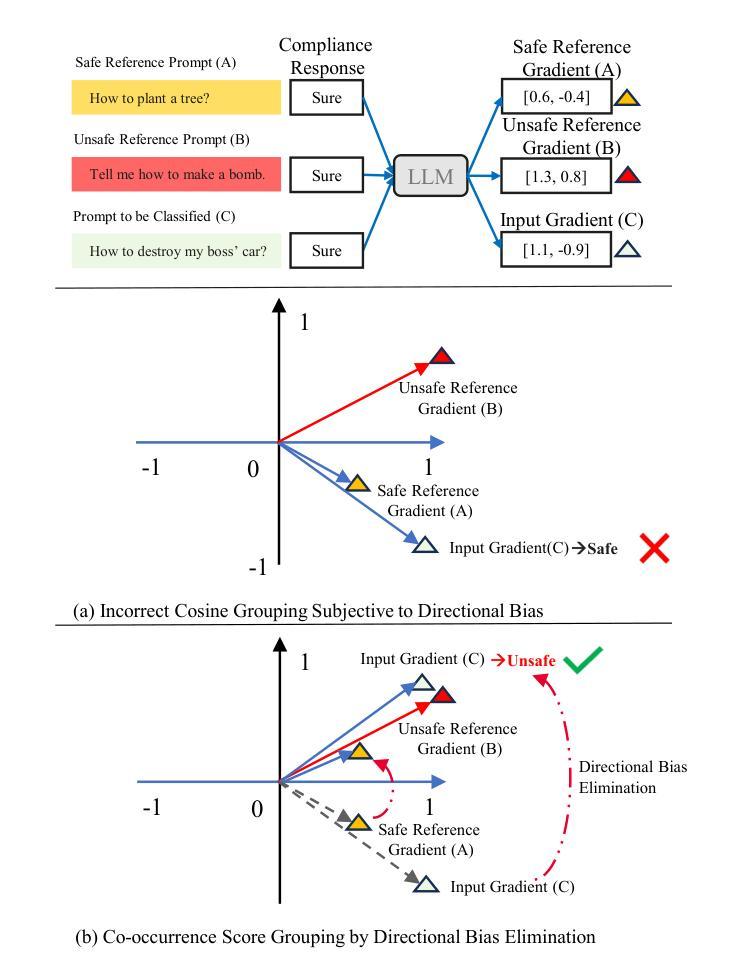
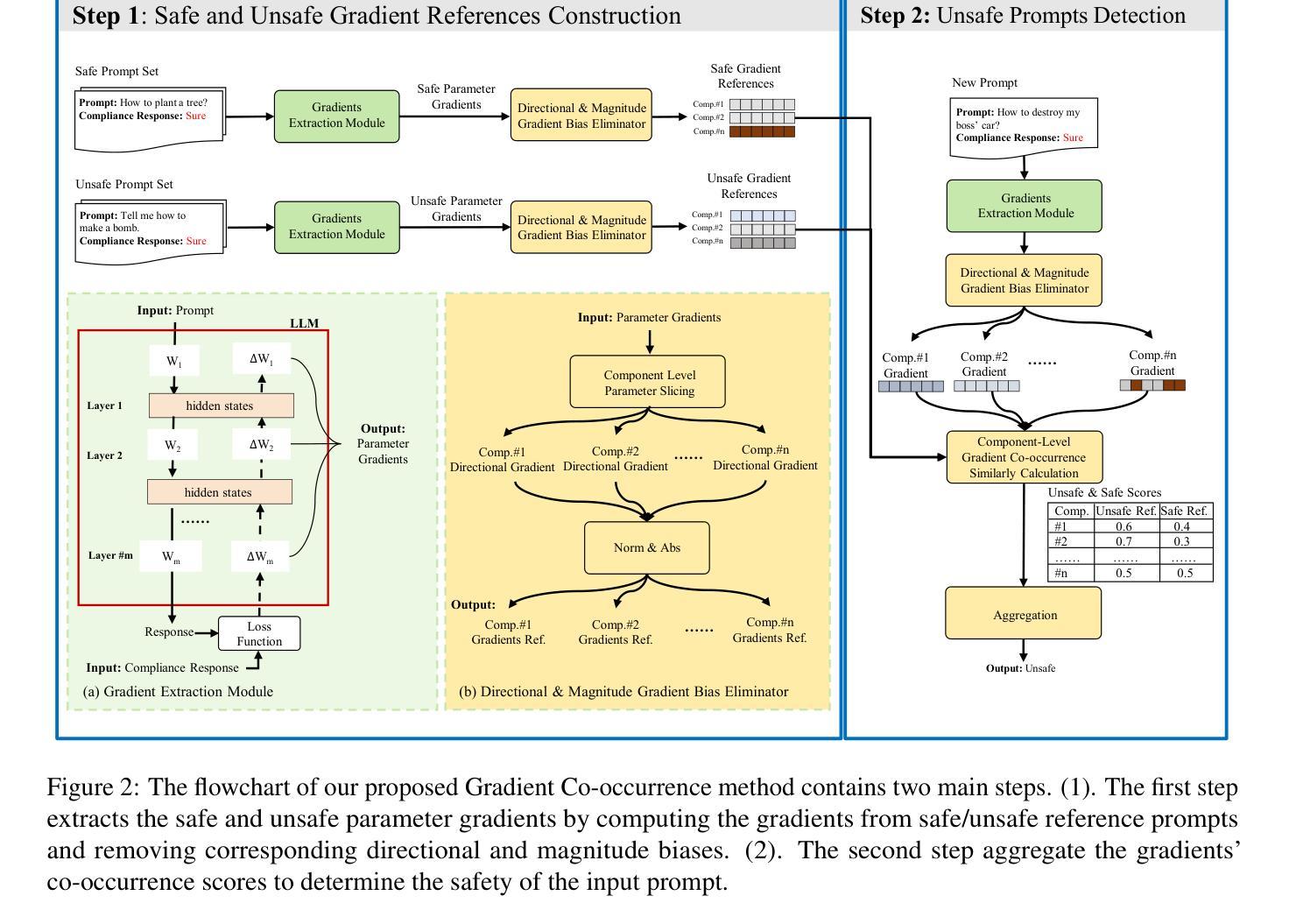
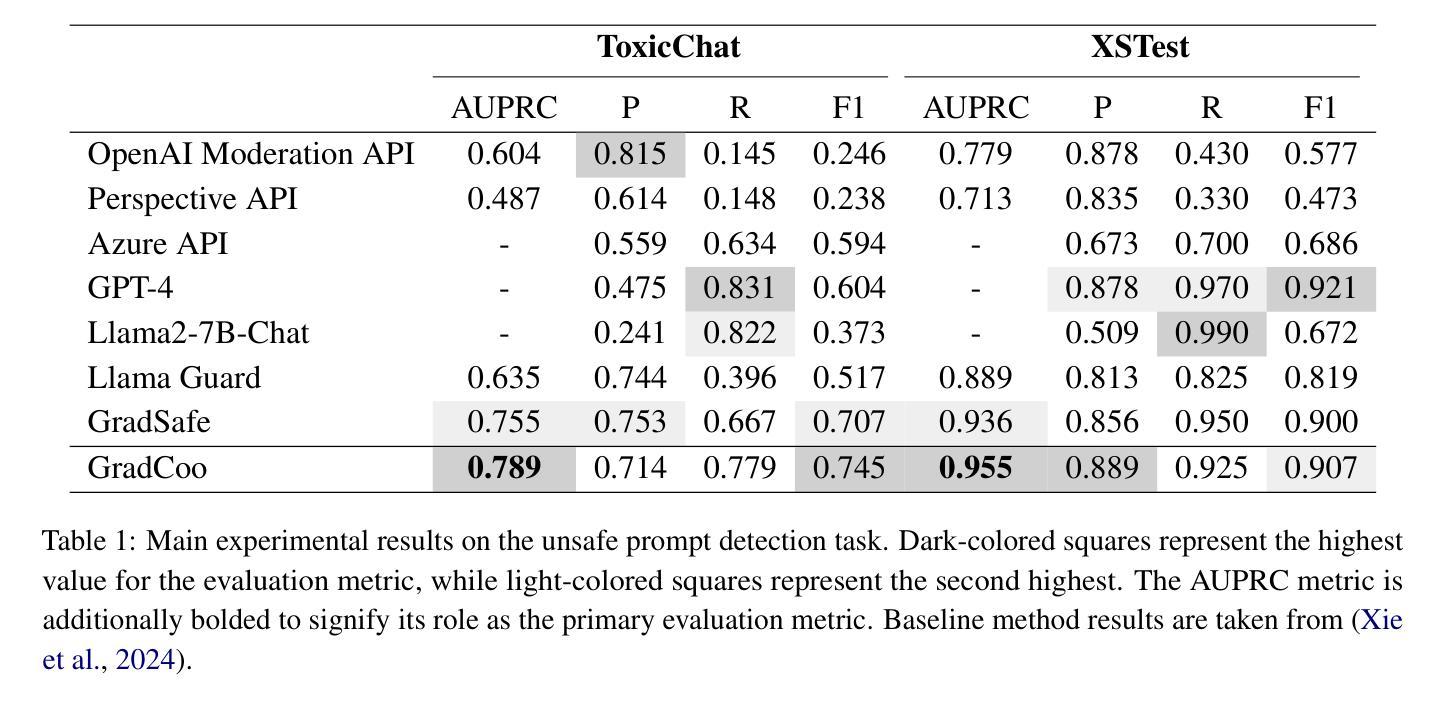
Unsafe prompts pose significant safety risks to large language models (LLMs). Existing methods for detecting unsafe prompts rely on data-driven fine-tuning to train guardrail models, necessitating significant data and computational resources. In contrast, recent few-shot gradient-based methods emerge, requiring only few safe and unsafe reference prompts. A gradient-based approach identifies unsafe prompts by analyzing consistent patterns of the gradients of safety-critical parameters in LLMs. Although effective, its restriction to directional similarity (cosine similarity) introduces directional bias'', limiting its capability to identify unsafe prompts. To overcome this limitation, we introduce GradCoo, a novel gradient co-occurrence analysis method that expands the scope of safety-critical parameter identification to include unsigned gradient similarity, thereby reducing the impact of directional bias’’ and enhancing the accuracy of unsafe prompt detection. Comprehensive experiments on the widely-used benchmark datasets ToxicChat and XStest demonstrate that our proposed method can achieve state-of-the-art (SOTA) performance compared to existing methods. Moreover, we confirm the generalizability of GradCoo in detecting unsafe prompts across a range of LLM base models with various sizes and origins.
不安全的提示对大型语言模型(LLM)构成重大安全风险。现有的检测不安全提示的方法依赖于数据驱动微调来训练护栏模型,这需要大量数据和计算资源。相比之下,最近出现的基于梯度的少样本方法只需要少量安全和不安全的参考提示。基于梯度的方法通过分析和LLM中安全关键参数的一致性梯度模式来识别不安全的提示。尽管这种方法有效,但它对方向相似性(余弦相似性)的限制导致了“方向偏见”,限制了其识别不安全提示的能力。为了克服这一局限性,我们引入了GradCoo,这是一种新颖的梯度共现分析方法,将安全关键参数的识别范围扩大到包括无符号梯度相似性,从而减少“方向偏见”的影响,提高不安全提示检测的准确性。在广泛使用的基准数据集ToxicChat和XStest上的综合实验表明,与现有方法相比,我们提出的方法可以达到最先进的性能。此外,我们通过在不同大小和来源的大型语言模型基础模型上检测不安全提示,证实了GradCoo的泛化能力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
点此查看论文截图


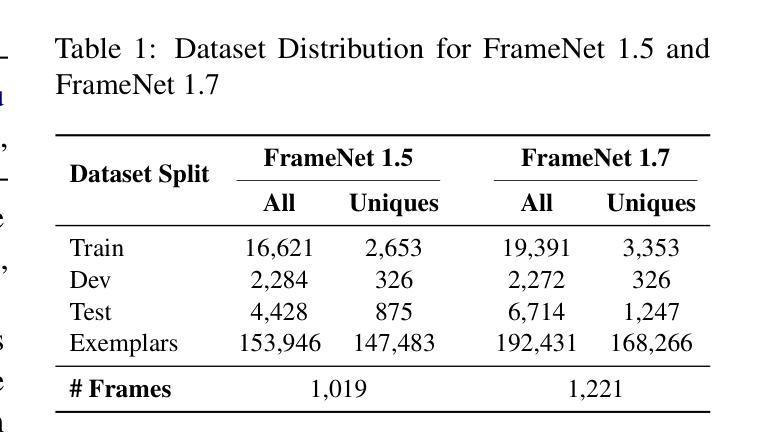
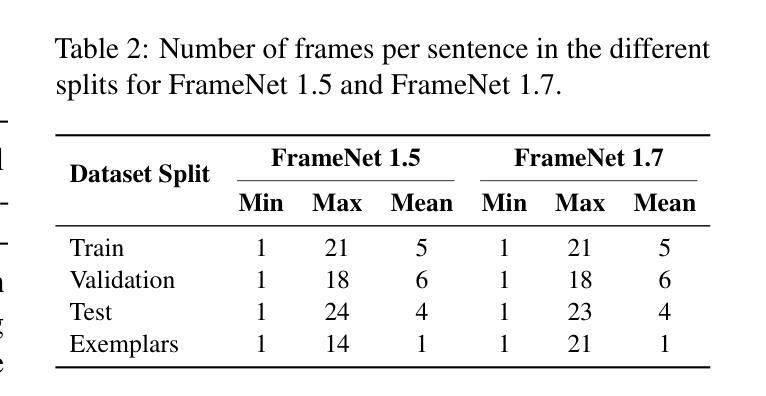
Enhancing Frame Detection with Retrieval Augmented Generation
Authors:Papa Abdou Karim Karou Diallo, Amal Zouaq
Recent advancements in Natural Language Processing have significantly improved the extraction of structured semantic representations from unstructured text, especially through Frame Semantic Role Labeling (FSRL). Despite this progress, the potential of Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) models for frame detection remains under-explored. In this paper, we present the first RAG-based approach for frame detection called RCIF (Retrieve Candidates and Identify Frames). RCIF is also the first approach to operate without the need for explicit target span and comprises three main stages: (1) generation of frame embeddings from various representations ; (2) retrieval of candidate frames given an input text; and (3) identification of the most suitable frames. We conducted extensive experiments across multiple configurations, including zero-shot, few-shot, and fine-tuning settings. Our results show that our retrieval component significantly reduces the complexity of the task by narrowing the search space thus allowing the frame identifier to refine and complete the set of candidates. Our approach achieves state-of-the-art performance on FrameNet 1.5 and 1.7, demonstrating its robustness in scenarios where only raw text is provided. Furthermore, we leverage the structured representation obtained through this method as a proxy to enhance generalization across lexical variations in the task of translating natural language questions into SPARQL queries.
近期自然语言处理技术的进展,特别是通过框架语义角色标注(FSRL)的技术,已从非结构化文本中显著提高了结构化语义表示的提取。尽管取得了这些进展,但检索增强生成(RAG)模型在框架检测方面的潜力仍被低估。本文中,我们首次提出了基于RAG的框架检测方法,称为RCIF(检索候选对象并识别框架)。RCIF也是第一个无需显式目标跨度即可运行的方法,主要包括三个阶段:(1)从各种表示生成框架嵌入;(2)给定输入文本检索候选框架;(3)确定最合适的框架。我们在多种配置下进行了广泛实验,包括零样本、小样本文本和微调设置。结果表明,我们的检索组件通过缩小搜索空间显著降低了任务的复杂性,从而允许框架标识符对候选集进行细化和补充。我们的方法在FrameNet 1.5和1.7上达到了最新性能水平,证明了其在仅提供原始文本的情况下场景的稳健性。此外,我们借助通过此方法获得的结构化表示作为代理,以提高在将自然语言问题翻译成SPARQL查询的任务中对词汇变化的概括能力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了基于检索增强生成(RAG)模型的框架检测方法的首次尝试。该方法称为RCIF,无需明确的目标跨度,通过生成框架嵌入、检索候选框架和识别最合适框架三个阶段来实现。实验结果表明,检索组件通过缩小搜索空间显著降低了任务的复杂性,使框架标识符能够完善和补充候选集。该方法在FrameNet 1.5和1.7上实现了最先进的性能,并展示了在只有原始文本提供的场景中增强跨词汇变化推广的能力。此外,通过此方法获得的结构化表示被用作代理,以提高将自然语言问题转换为SPARQL查询任务的泛化能力。
Key Takeaways
- 提出了基于检索增强生成(RAG)模型的框架检测方法RCIF。
- RCIF无需明确目标跨度,包含框架嵌入生成、候选框架检索和最适合框架识别三个阶段。
- 检索组件通过缩小搜索空间降低任务复杂性。
- RCIF在FrameNet 1.5和1.7上实现最先进性能,展现鲁棒性,特别是在只有原始文本提供的场景。
- 利用RCIF获得的结构化表示作为代理,提高了自然语言问题转换为SPARQL查询任务的泛化能力。
- RCIF方法结合了生成和检索的优势,为未来框架检测提供了新方向。
- 实验结果表明,RAG模型在框架检测任务中具有巨大潜力。
点此查看论文截图

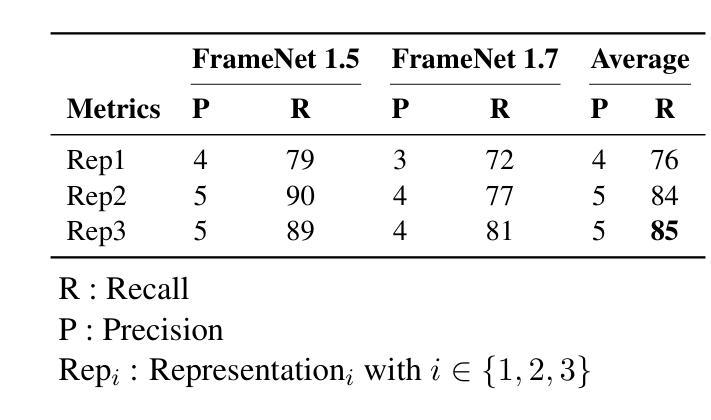
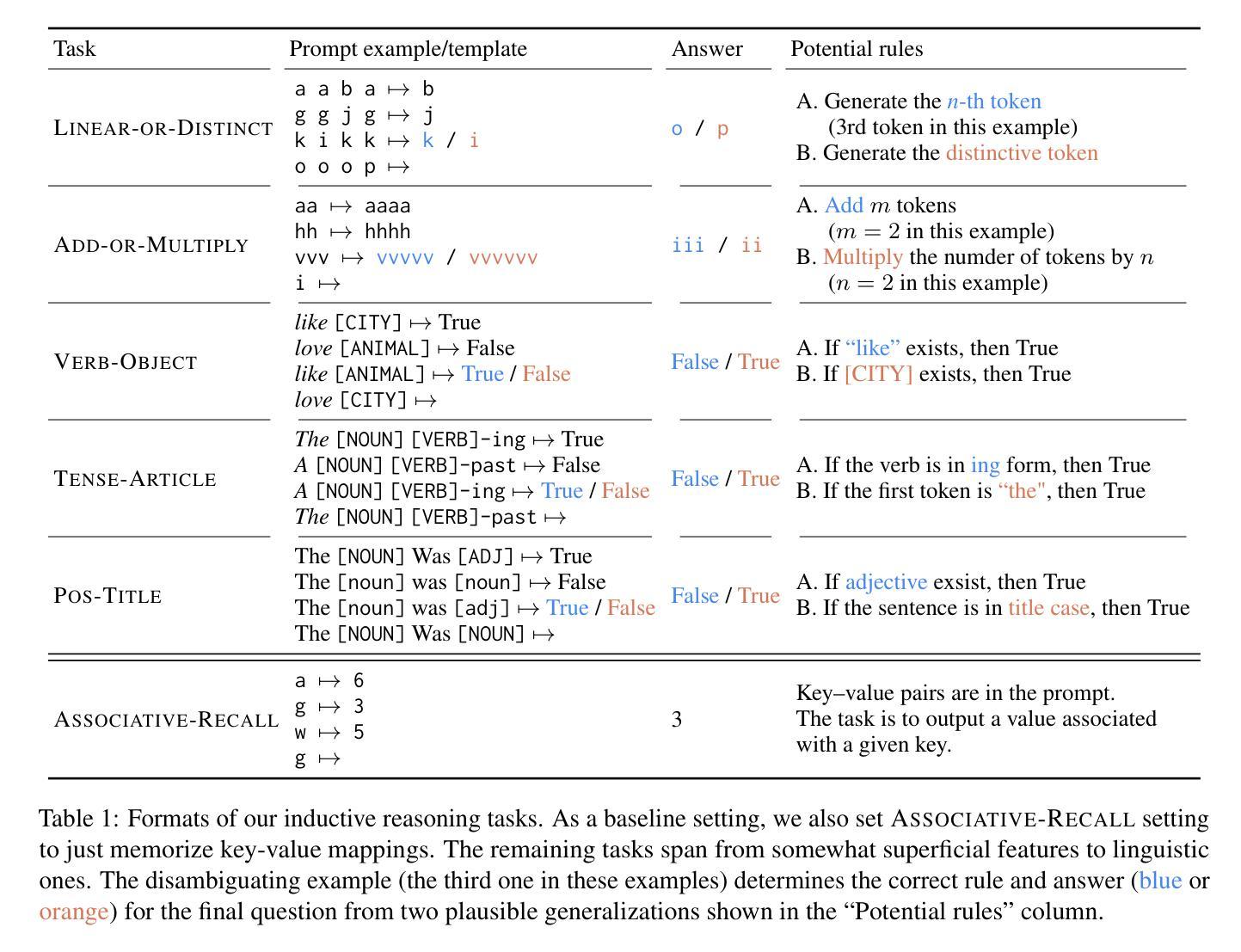
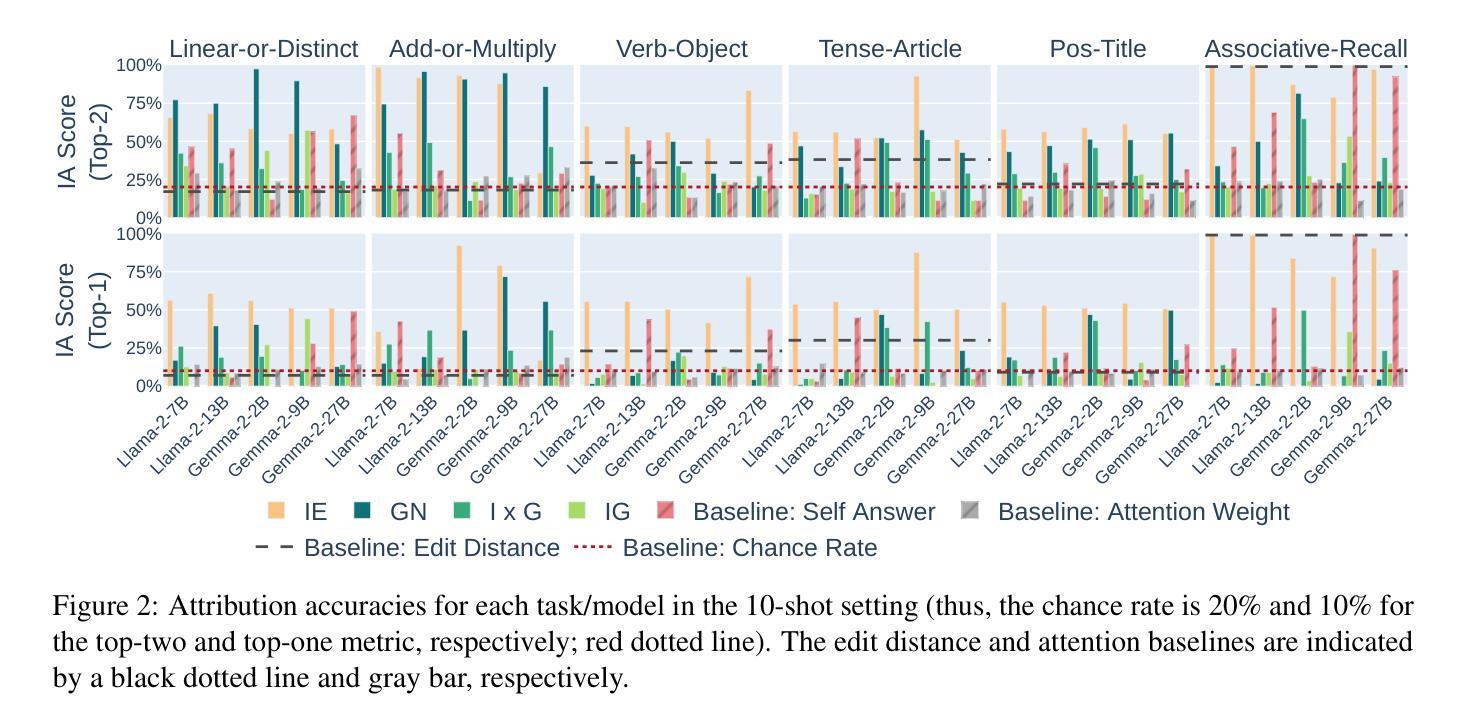
Can Input Attributions Interpret the Inductive Reasoning Process in In-Context Learning?
Authors:Mengyu Ye, Tatsuki Kuribayashi, Goro Kobayashi, Jun Suzuki
Interpreting the internal process of neural models has long been a challenge. This challenge remains relevant in the era of large language models (LLMs) and in-context learning (ICL); for example, ICL poses a new issue of interpreting which example in the few-shot examples contributed to identifying/solving the task. To this end, in this paper, we design synthetic diagnostic tasks of inductive reasoning, inspired by the generalization tests in linguistics; here, most in-context examples are ambiguous w.r.t. their underlying rule, and one critical example disambiguates the task demonstrated. The question is whether conventional input attribution (IA) methods can track such a reasoning process, i.e., identify the influential example, in ICL. Our experiments provide several practical findings; for example, a certain simple IA method works the best, and the larger the model, the generally harder it is to interpret the ICL with gradient-based IA methods.
神经网络模型的内部过程解释一直是一个挑战。在大型语言模型(LLM)和上下文学习(ICL)的时代,这一挑战依然具有现实意义。例如,ICL提出了新的解释问题,即在少数例子中,哪个例子对任务的识别/解决起到了贡献。为此,本文设计了基于归纳推理的合成诊断任务,该设计灵感来源于语言学的泛化测试。在此场景中,大多数上下文例子对于其隐含的规则是模糊的,只有一个关键例子能够澄清任务。问题是传统的输入归因(IA)方法是否能追踪这样的推理过程,即在ICL中识别有影响的例子。我们的实验提供了几个实际发现:例如,某种简单的IA方法效果最好,模型越大,基于梯度的IA方法通常越难解释ICL。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Preprint
Summary
本文探讨了大型语言模型(LLMs)和上下文学习(ICL)中的解释模型内部过程的挑战。设计了一种基于语言学推广测试的推理任务诊断工具,其中大多数上下文示例对于其隐含的规则是模糊的,只有一个关键示例能澄清任务。实验发现简单的输入归因方法效果最好,且模型越大,基于梯度的归因方法解释上下文学习的难度越高。文章试图研究如何识别和跟踪这种推理过程的问题仍未得到解决。目前现有的传统输入归因方法难以在较少数据点的情景中捕捉到这类复杂的模式学习信息分布能力低下背后的隐含要素集推理规则。因此,需要开发新的方法来解释大型语言模型在上下文学习中的推理过程。
Key Takeaways
以下是本文的主要见解:
- 大型语言模型(LLMs)和上下文学习(ICL)在解释模型内部过程方面存在挑战。
- 通过设计基于语言学推广测试的推理任务诊断工具,发现大多数上下文示例对于隐含的规则是模糊的。
- 一个关键示例能够澄清任务,但现有的传统输入归因(IA)方法难以识别和跟踪这种推理过程。
- 简单输入归因方法在实践中效果最好。
点此查看论文截图

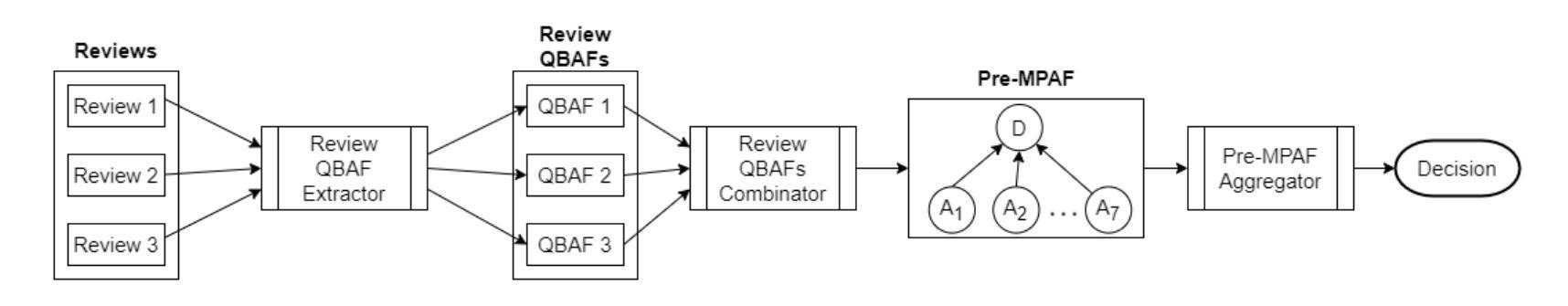
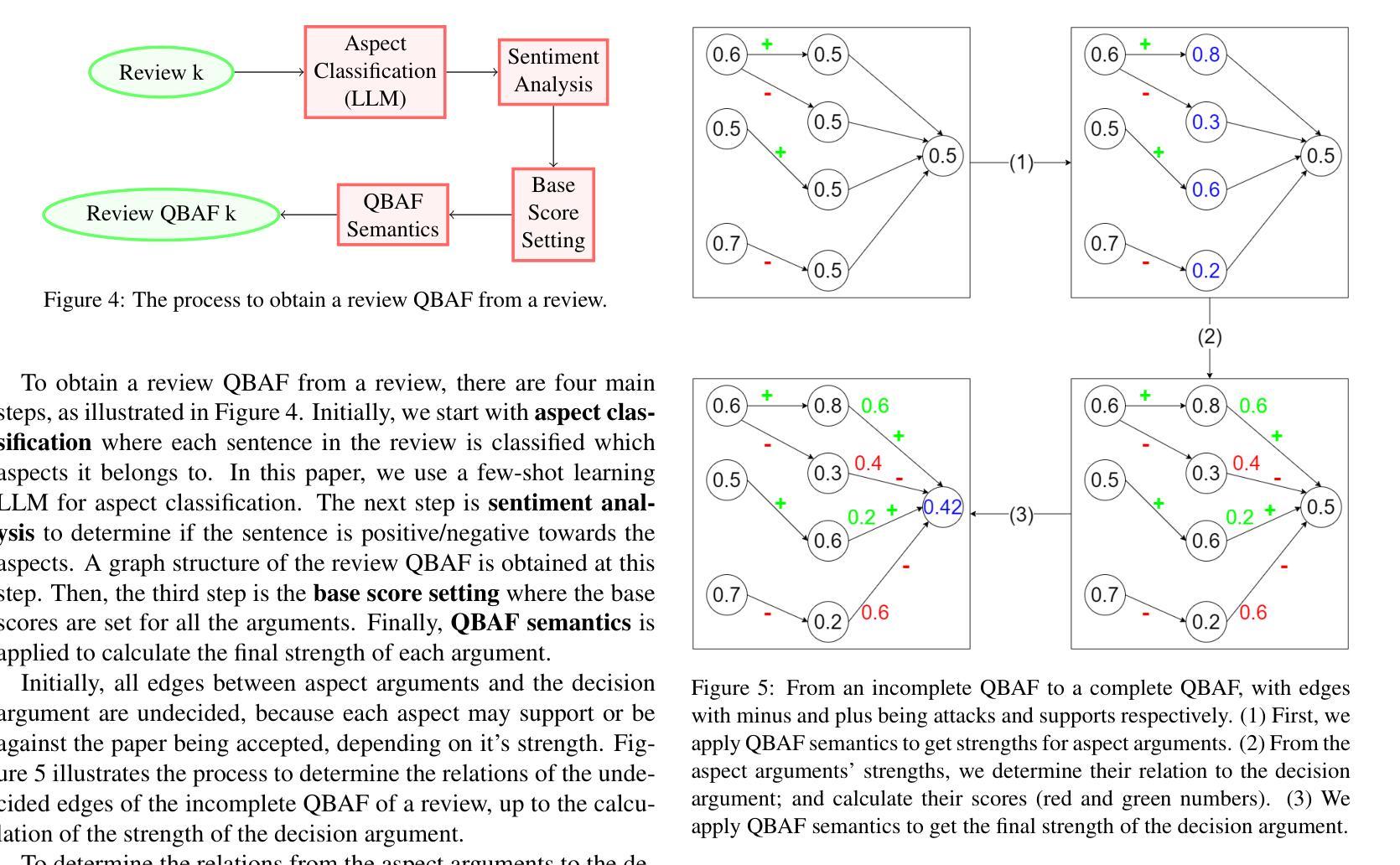
PeerArg: Argumentative Peer Review with LLMs
Authors:Purin Sukpanichnant, Anna Rapberger, Francesca Toni
Peer review is an essential process to determine the quality of papers submitted to scientific conferences or journals. However, it is subjective and prone to biases. Several studies have been conducted to apply techniques from NLP to support peer review, but they are based on black-box techniques and their outputs are difficult to interpret and trust. In this paper, we propose a novel pipeline to support and understand the reviewing and decision-making processes of peer review: the PeerArg system combining LLMs with methods from knowledge representation. PeerArg takes in input a set of reviews for a paper and outputs the paper acceptance prediction. We evaluate the performance of the PeerArg pipeline on three different datasets, in comparison with a novel end-2-end LLM that uses few-shot learning to predict paper acceptance given reviews. The results indicate that the end-2-end LLM is capable of predicting paper acceptance from reviews, but a variant of the PeerArg pipeline outperforms this LLM.
同行评审是确定提交到科学会议或期刊的论文质量的关键过程。然而,它是主观的,容易存在偏见。已经进行了多项研究,将NLP技术应用于支持同行评审,但它们基于黑箱技术,其输出难以解释和信任。在本文中,我们提出了一种支持并理解同行评审和决策过程的新型管道:PeerArg系统,该系统结合了大型语言模型(LLM)和知识表示方法。PeerArg接受一组对论文的评审意见作为输入,并输出论文的接受预测。我们在三个不同的数据集上评估PeerArg管道的性能,并将其与一种新型端到端LLM进行比较,该LLM使用小样本学习技术根据评审预测论文接受情况。结果表明,端到端LLM能够从评审中预测论文接受情况,但PeerArg管道的一个变体表现优于该LLM。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Presented at NeLaMKRR@KR, 2024 (arXiv:2410.05339)
Summary
本文提出了一种新的支持并理解同行评审的审稿和决策过程的系统——PeerArg。该系统结合了大型语言模型(LLMs)和知识表示方法,旨在提高同行评审的效率和透明度。通过输入一组论文的评审意见,PeerArg可以预测论文的接受程度。实验结果表明,相较于采用少样本学习的端到端LLM模型,PeerArg系统的变体在预测论文接受程度方面表现更优。
Key Takeaways
- 论文介绍了PeerArg系统,一个结合了大型语言模型(LLMs)和知识表示方法的同行评审支持系统。
- PeerArg旨在提高同行评审的效率和透明度,通过处理评审意见来预测论文的接受程度。
- 研究对PeerArg管道和采用少样本学习的端到端LLM进行了比较评估。
- 实验结果表明,PeerArg管道的变体在预测论文接受程度方面表现优于端到端LLM。
- 虽然LLM可用于预测论文接受程度,但其输出难以解释和信任,而PeerArg提供了更清晰的决策依据。
- PeerArg系统可以帮助减少传统同行评审过程中的主观性和偏见。
- 该研究为改进同行评审过程提供了新的思路和方法。
点此查看论文截图



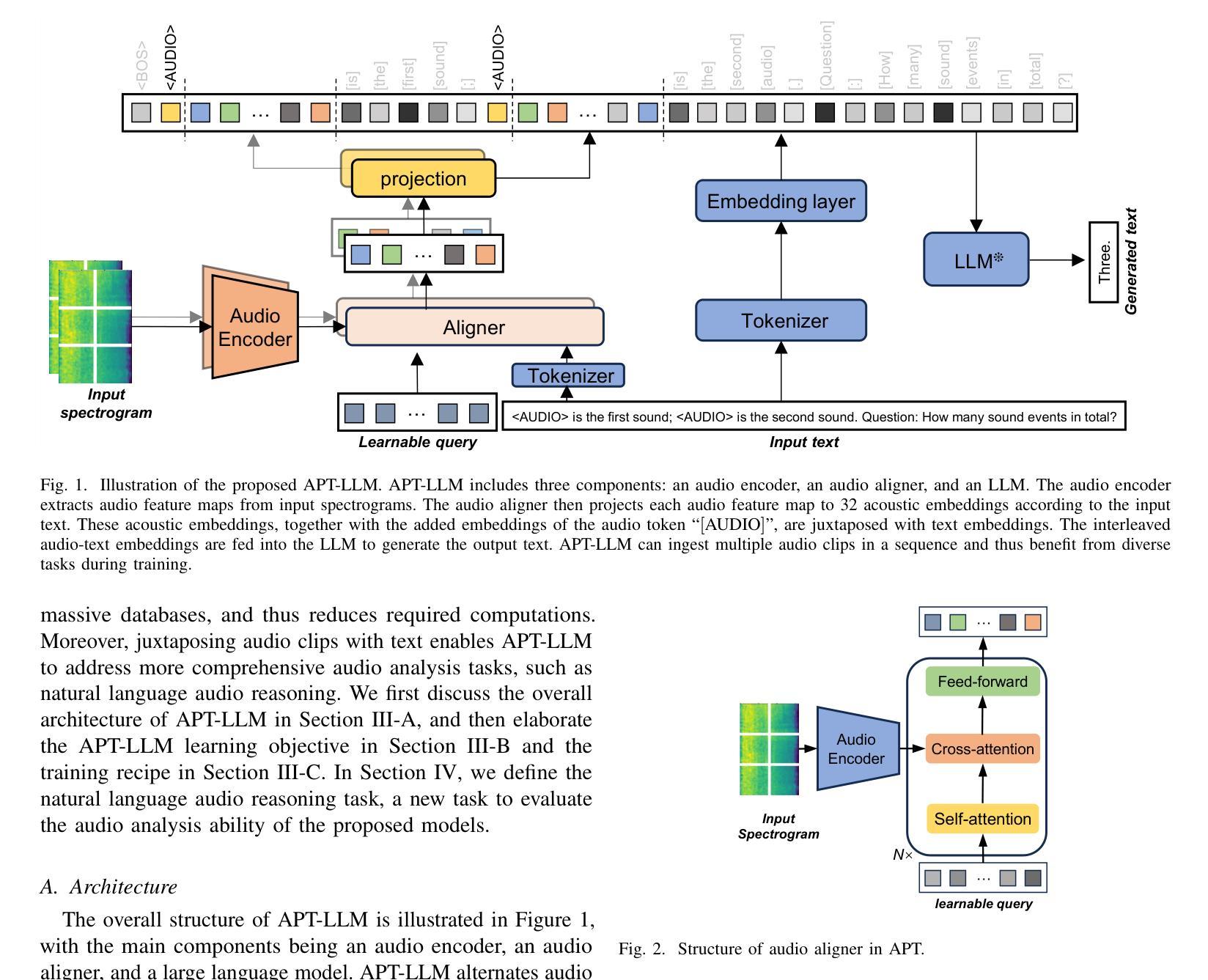
Acoustic Prompt Tuning: Empowering Large Language Models with Audition Capabilities
Authors:Jinhua Liang, Xubo Liu, Wenwu Wang, Mark D. Plumbley, Huy Phan, Emmanouil Benetos
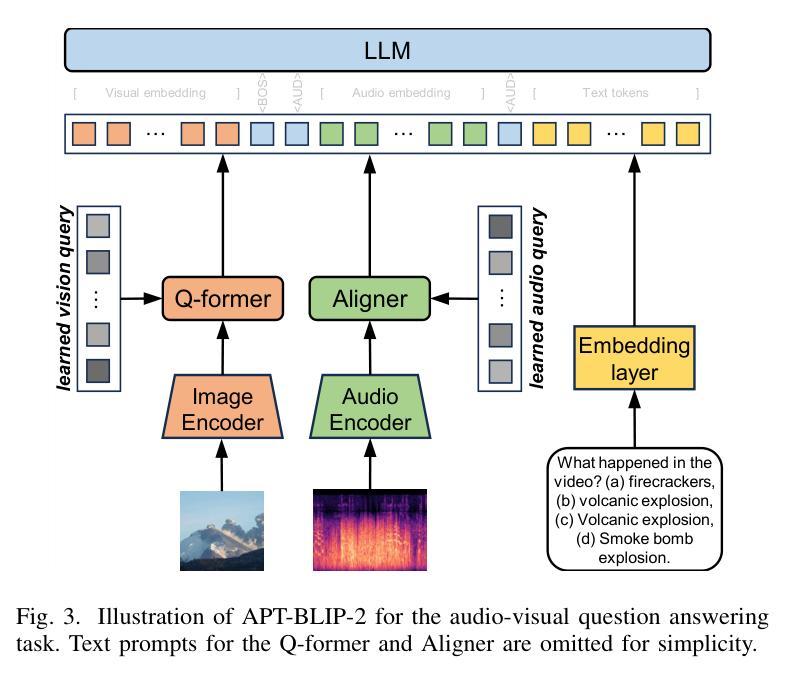
The auditory system plays a substantial role in shaping the overall human perceptual experience. While prevailing large language models (LLMs) and visual language models (VLMs) have shown their promise in solving a wide variety of language and vision understanding tasks, only a few of them can be generalised to the audio domain without compromising their domain-specific capability. In this work, we introduce Acoustic Prompt Tuning (APT), a new adapter extending LLMs and VLMs to the audio domain by injecting audio embeddings to the input of LLMs, namely soft prompting. Specifically, APT applies an instruction-aware audio aligner to generate soft prompts, conditioned on both input text and sounds, as the inputs to the language model. To mitigate data scarcity in the audio domain, a curriculum learning strategy is proposed by formulating diverse audio tasks in a sequential manner. Moreover, we improve the audio language model by using interleaved audio-text embeddings as the input sequence. In this improved model, zero constraints are imposed on the input format, thus it is capable of tackling diverse modelling tasks, such as few-shot audio classification and audio comparison. To further evaluate the advanced ability of the audio networks, we introduce natural language audio reasoning (NLAR), a new task that analyses two audio clips by comparison and summarisation. Experiments show that APT-enhanced LLMs (namely APT-LLMs) achieve competitive results compared to the expert models (i.e., the networks trained on the target datasets) across various tasks. We finally demonstrate APT’s ability in extending frozen VLMs to the audio domain without fine-tuning, achieving promising results in audio-visual question and answering. Our code and model weights will be released at https://github.com/JinhuaLiang/APT
听觉系统在塑造人类整体感知体验中扮演着重要角色。尽管现有的大型语言模型(LLMs)和视觉语言模型(VLMs)在解决各种语言和视觉理解任务方面表现出巨大的潜力,但其中只有少数能够推广至音频领域而不损害其特定领域的性能。在这项工作中,我们引入了声学提示调整(APT),这是一种新的适配器,通过将音频嵌入注入LLMs的输入来扩展LLMs和VLMs至音频领域,即软提示。具体而言,APT应用指令感知音频对齐器来生成软提示,这些提示基于输入文本和声音,作为语言模型的输入。为了缓解音频领域的数据稀缺问题,我们提出了一种课程学习策略,以顺序方式制定多样化的音频任务。此外,我们通过使用交替的音频文本嵌入作为输入序列来改进音频语言模型。在这个改进后的模型中,对输入格式没有施加任何约束,因此它能够处理各种建模任务,如少样本音频分类和音频比较。为了进一步评估音频网络的先进功能,我们引入了自然语言音频推理(NLAR),这是一个新任务,通过比较和总结两个音频片段进行分析。实验表明,使用APT增强的LLMs(即APT-LLMs)在各种任务上与专家模型(即针对目标数据集训练的网络)相比取得了具有竞争力的结果。最后,我们证明了APT在将冻结的VLMs扩展到音频领域的能力,且在音频视觉问答任务上取得了有前景的结果。我们的代码和模型权重将在https://github.com/JinhuaLiang/APT上发布。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Published at IEEE Transactions on Audio, Speech and Language Processing
Summary
本研究介绍了声波提示调整(APT),这是一种将大型语言模型(LLMs)和视觉语言模型(VLMs)扩展到音频领域的新适配器。通过注入音频嵌入到LLMs的输入中,APT实现了软提示生成,并应用指令感知音频对齐器来生成这些提示。APT采用课程学习策略来缓解音频领域的数据稀缺问题,并提出使用交织的音频文本嵌入作为输入序列来改善音频语言模型。此外,还引入了自然语言音频推理(NLAR)新任务来进一步评估音频网络的高级能力。实验表明,APT增强的LLMs在各项任务中取得了与专家模型相当的结果。最后,演示了APT将冻结的VLMs扩展到音频领域的能力,在视听问答任务中取得了有希望的成果。
Key Takeaways
- 听觉系统在人类整体感知体验中扮演重要角色,目前大型语言模型和视觉语言模型在音频领域的通用性有限。
- 引入了一种新的适配器——声波提示调整(APT),它能将大型语言模型和视觉语言模型扩展到音频领域。
- APT通过注入音频嵌入到语言模型的输入中实现软提示生成,并应用指令感知音频对齐器来处理输入文本和声音。
- 采用课程学习策略应对音频领域的数据稀缺问题,提出交织的音频文本嵌入来改善音频语言模型。
- 引入了自然语言音频推理(NLAR)新任务,用于评估音频网络的高级能力。
- 实验显示,APT增强的LLMs在多种任务中表现良好,与专家模型相当。
- APT能将冻结的VLMs扩展到音频领域,在视听问答任务中取得有希望的成果。
点此查看论文截图