⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-02-20 更新
3D Shape-to-Image Brownian Bridge Diffusion for Brain MRI Synthesis from Cortical Surfaces
Authors:Fabian Bongratz, Yitong Li, Sama Elbaroudy, Christian Wachinger
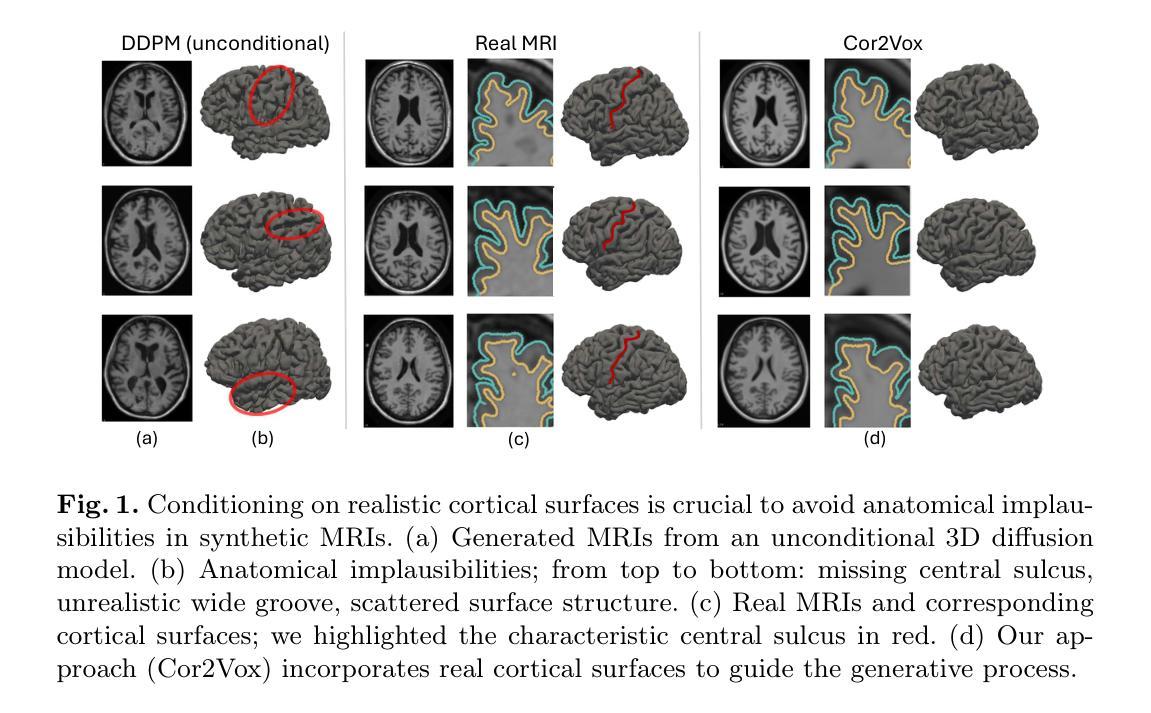
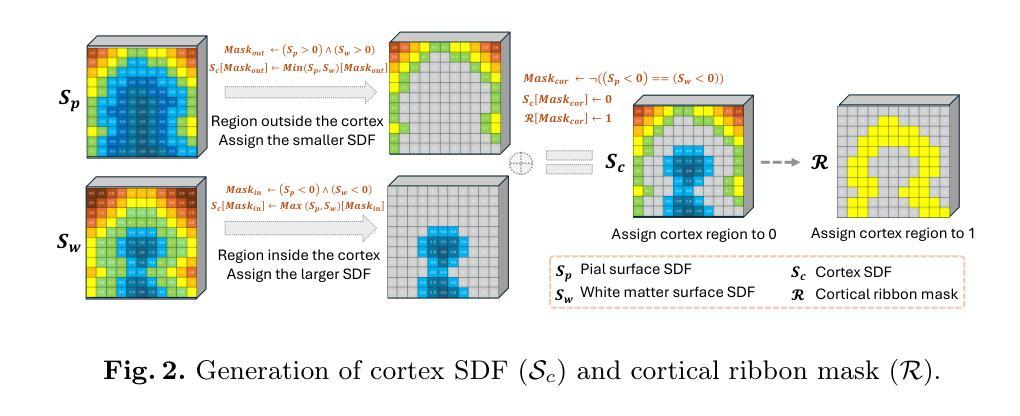
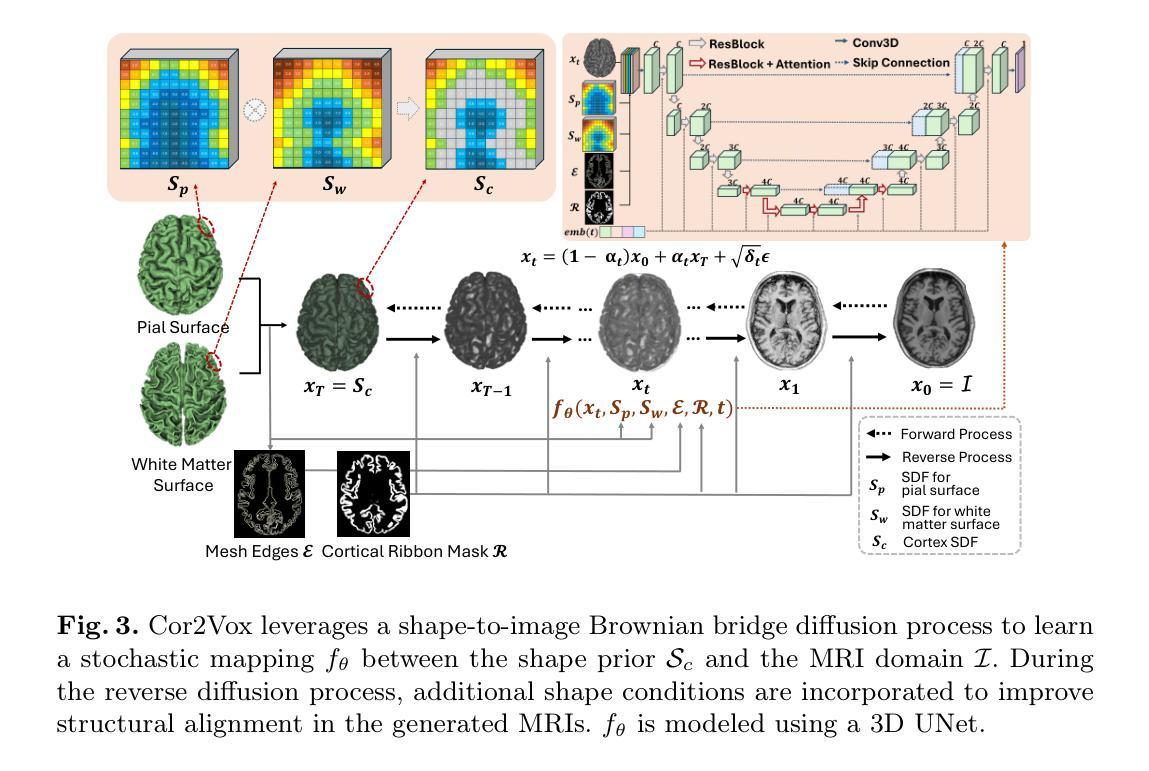
Despite recent advances in medical image generation, existing methods struggle to produce anatomically plausible 3D structures. In synthetic brain magnetic resonance images (MRIs), characteristic fissures are often missing, and reconstructed cortical surfaces appear scattered rather than densely convoluted. To address this issue, we introduce Cor2Vox, the first diffusion model-based method that translates continuous cortical shape priors to synthetic brain MRIs. To achieve this, we leverage a Brownian bridge process which allows for direct structured mapping between shape contours and medical images. Specifically, we adapt the concept of the Brownian bridge diffusion model to 3D and extend it to embrace various complementary shape representations. Our experiments demonstrate significant improvements in the geometric accuracy of reconstructed structures compared to previous voxel-based approaches. Moreover, Cor2Vox excels in image quality and diversity, yielding high variation in non-target structures like the skull. Finally, we highlight the capability of our approach to simulate cortical atrophy at the sub-voxel level. Our code is available at https://github.com/ai-med/Cor2Vox.
尽管最近医学影像生成领域有所进展,但现有方法仍难以生成解剖结构合理的3D结构。在合成的大脑磁共振成像(MRI)中,特征裂口往往缺失,重建的皮层表面看起来是散乱的,而不是密集卷曲的。为了解决这一问题,我们引入了Cor2Vox,这是基于扩散模型的方法,能够将连续的皮层形状先验知识转化为合成的大脑MRI。为实现这一目标,我们利用布朗桥过程,实现在形状轮廓和医学影像之间的直接结构映射。具体来说,我们将布朗桥扩散模型的概念适应到3D,并将其扩展到包含各种互补形状表示。我们的实验表明,与之前的体素化方法相比,重建结构的几何精度有了显著提高。此外,Cor= Vox在图像质量和多样性方面表现出色,非目标结构(如颅骨)的变异度较高。最后,我们强调了我们这种方法在亚体素层面模拟皮层萎缩的能力。我们的代码可在链接中找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by Information Processing in Medical Imaging (IPMI) 2025
Summary
Cor2Vox是一款基于扩散模型的方法,可将连续的皮质形状先验知识转化为合成脑MRI图像。该方法通过布朗桥过程实现形状轮廓与医学图像之间的直接结构映射,并在3D环境中适应布朗桥扩散模型的概念,同时扩展到各种互补形状表示。相比传统的体素方法,Cor2Vox在几何准确性上有显著提升,并在图像质量和多样性方面表现出色,还能模拟皮质萎缩。
Key Takeaways
- Cor2Vox是首款将连续皮质形状先验知识转化为合成脑MRI图像的扩散模型方法。
- 利用布朗桥过程实现形状轮廓与医学图像之间的直接结构映射。
- Cor2Vox将布朗桥扩散模型的概念适应到3D环境,并扩展到各种互补形状表示。
- 合成脑MRI图像中,现有方法常缺失特征裂隙,重建的皮质表面显得零散而非密集卷曲,Cor2Vox解决了这一问题。
- Cor2Vox在几何准确性上较传统体素方法有显著提升。
- Cor2Vox在图像质量和多样性方面表现出色,并能生成高变化的非目标结构,如颅骨。
点此查看论文截图

S2C: Learning Noise-Resistant Differences for Unsupervised Change Detection in Multimodal Remote Sensing Images
Authors:Lei Ding, Xibing Zuo, Danfeng Hong, Haitao Guo, Jun Lu, Zhihui Gong, Lorenzo Bruzzone
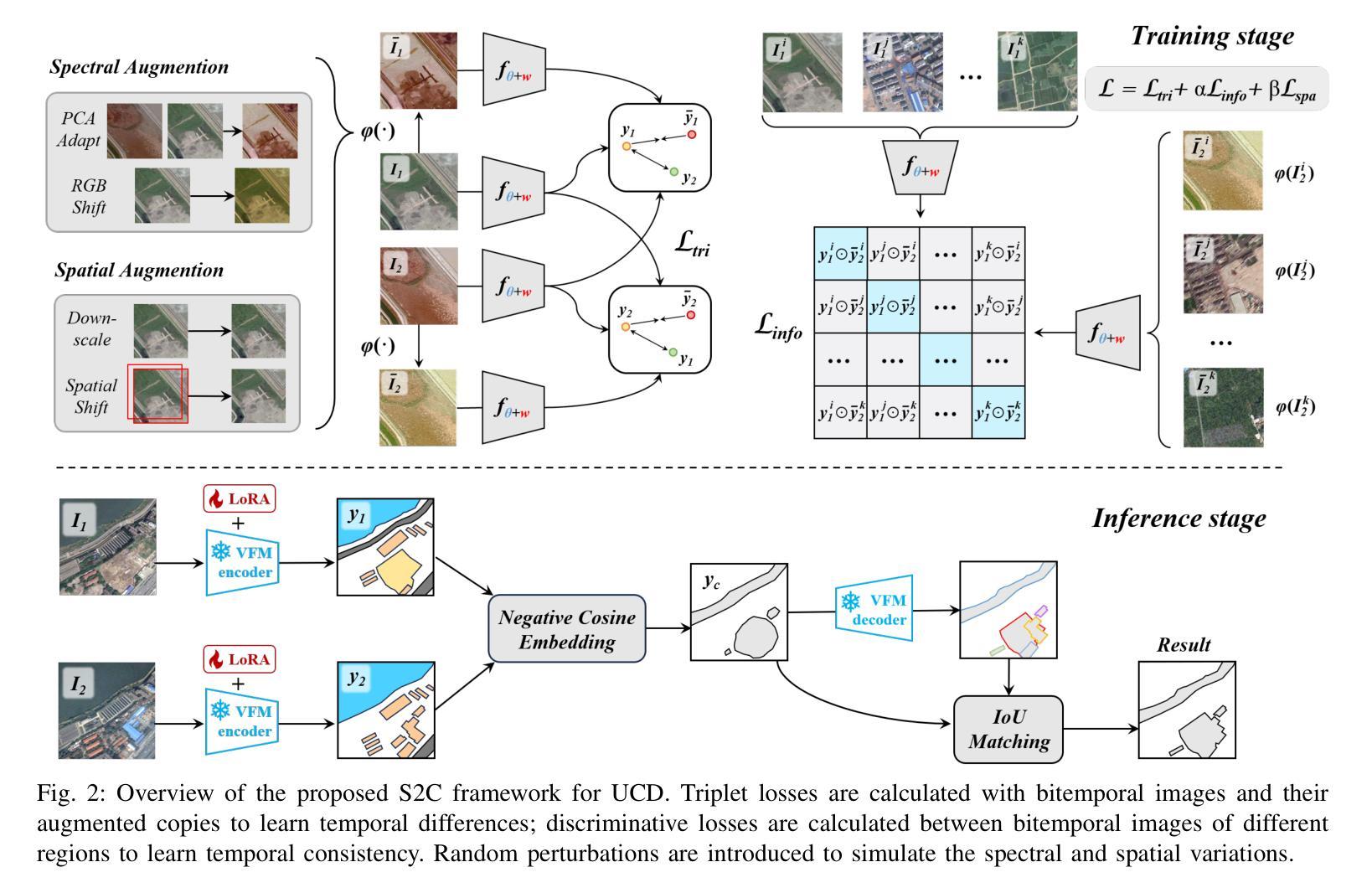
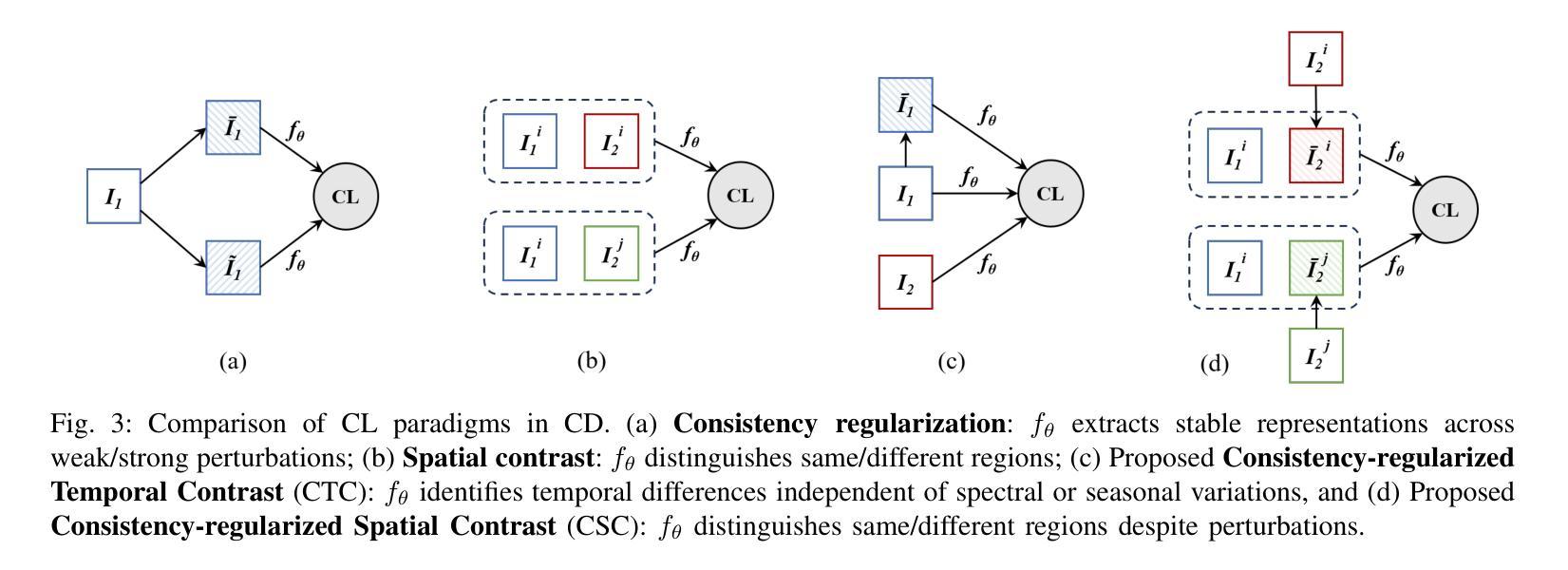
Unsupervised Change Detection (UCD) in multimodal Remote Sensing (RS) images remains a difficult challenge due to the inherent spatio-temporal complexity within data, and the heterogeneity arising from different imaging sensors. Inspired by recent advancements in Visual Foundation Models (VFMs) and Contrastive Learning (CL) methodologies, this research aims to develop CL methodologies to translate implicit knowledge in VFM into change representations, thus eliminating the need for explicit supervision. To this end, we introduce a Semantic-to-Change (S2C) learning framework for UCD in both homogeneous and multimodal RS images. Differently from existing CL methodologies that typically focus on learning multi-temporal similarities, we introduce a novel triplet learning strategy that explicitly models temporal differences, which are crucial to the CD task. Furthermore, random spatial and spectral perturbations are introduced during the training to enhance robustness to temporal noise. In addition, a grid sparsity regularization is defined to suppress insignificant changes, and an IoU-matching algorithm is developed to refine the CD results. Experiments on four benchmark CD datasets demonstrate that the proposed S2C learning framework achieves significant improvements in accuracy, surpassing current state-of-the-art by over 31%, 9%, 23%, and 15%, respectively. It also demonstrates robustness and sample efficiency, suitable for training and adaptation of various Visual Foundation Models (VFMs) or backbone neural networks. The relevant code will be available at: github.com/DingLei14/S2C.
无监督的多模态遥感图像变化检测(UCD)仍然存在很大的挑战,主要是由于数据内在的时空复杂性和来自不同成像传感器的异质性。受视觉基础模型(VFM)和对比学习(CL)方法最新进展的启发,本研究旨在开发CL方法,将VFM中的隐性知识转化为变化表示,从而无需显式监督。为此,我们引入了用于同质和多模态遥感图像UCD的语义到变化(S2C)学习框架。与通常关注多时相相似性学习的现有CL方法不同,我们引入了一种新的三元组学习策略,该策略显式地模拟了时间差异,这对于CD任务至关重要。此外,在训练过程中引入了随机空间和光谱扰动,以提高对时间噪声的鲁棒性。同时定义了一种网格稀疏正则化来抑制非显著变化,并开发了一种IoU匹配算法来完善CD结果。在四个基准CD数据集上的实验表明,所提出的S2C学习框架在准确性方面取得了显著改进,分别超过了当前最新技术超过31%、9%、23%和15%。它还表现出稳健性和样本效率,适用于各种视觉基础模型(VFM)或主干神经网络的学习和适应。相关代码将在github.com/DingLei14/S2C上提供。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
该研究利用视觉基础模型(VFM)和对比学习(CL)方法,提出一种语义到变化(S2C)学习框架,用于无监督多模态遥感图像变化检测(UCD)。该框架通过建模时间差异,引入新型的三元组学习策略,同时引入随机空间光谱扰动提高时间噪声的鲁棒性,并通过网格稀疏正则化和IoU匹配算法优化检测结果。在四个基准数据集上的实验表明,该框架准确性显著提高,超越现有技术水平,并展现出稳健性和样本效率。
Key Takeaways
- 研究针对无监督多模态遥感图像变化检测(UCD)的挑战,提出语义到变化(S2C)学习框架。
- 引入新型对比学习(CL)方法,将视觉基础模型(VFM)中的隐性知识转化为变化表示。
- 采用三元组学习策略,显式建模时间差异,这是变化检测任务的关键。
- 通过引入随机空间光谱扰动提高模型对时间噪声的鲁棒性。
- 采用网格稀疏正则化抑制非显著变化,并使用IoU匹配算法优化检测结果。
- 在四个基准数据集上的实验表明,S2C学习框架显著提高检测准确性,并超越现有技术。
点此查看论文截图
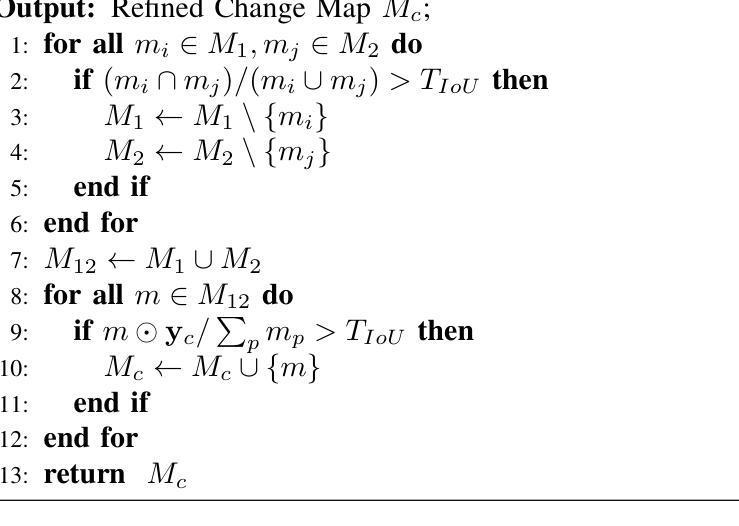
BenthicNet: A global compilation of seafloor images for deep learning applications
Authors:Scott C. Lowe, Benjamin Misiuk, Isaac Xu, Shakhboz Abdulazizov, Amit R. Baroi, Alex C. Bastos, Merlin Best, Vicki Ferrini, Ariell Friedman, Deborah Hart, Ove Hoegh-Guldberg, Daniel Ierodiaconou, Julia Mackin-McLaughlin, Kathryn Markey, Pedro S. Menandro, Jacquomo Monk, Shreya Nemani, John O’Brien, Elizabeth Oh, Luba Y. Reshitnyk, Katleen Robert, Chris M. Roelfsema, Jessica A. Sameoto, Alexandre C. G. Schimel, Jordan A. Thomson, Brittany R. Wilson, Melisa C. Wong, Craig J. Brown, Thomas Trappenberg
Advances in underwater imaging enable collection of extensive seafloor image datasets necessary for monitoring important benthic ecosystems. The ability to collect seafloor imagery has outpaced our capacity to analyze it, hindering mobilization of this crucial environmental information. Machine learning approaches provide opportunities to increase the efficiency with which seafloor imagery is analyzed, yet large and consistent datasets to support development of such approaches are scarce. Here we present BenthicNet: a global compilation of seafloor imagery designed to support the training and evaluation of large-scale image recognition models. An initial set of over 11.4 million images was collected and curated to represent a diversity of seafloor environments using a representative subset of 1.3 million images. These are accompanied by 3.1 million annotations translated to the CATAMI scheme, which span 190,000 of the images. A large deep learning model was trained on this compilation and preliminary results suggest it has utility for automating large and small-scale image analysis tasks. The compilation and model are made openly available for reuse at https://doi.org/10.20383/103.0614.
水下成像技术的进步使我们能够收集大量用于监测重要底栖生态系统的海底图像数据集。收集海底图像的能力已经超过了我们的分析能力,阻碍了调动这些重要的环境信息。机器学习的方法为提高海底图像分析效率提供了机会,但支持此类方法开发的大型且一致的数据集却十分稀缺。在这里,我们推出BenthicNet:一个支持大规模图像识别模型训练和评估的海底图像全球汇编。我们收集了超过1140万张图像作为初始数据集,并使用具有代表性的130万张图像来表示各种海底环境的多样性。这些数据集伴随有翻译成CATAMI方案的注释总计310万条,涵盖了其中的部分数据,包含总计有约十万张的图像。我们在此数据集上训练了一个大型深度学习模型,初步结果表明它在自动化大规模和小规模图像分析任务方面具有实用性。为了方便再次使用数据以及该模型,已在网站上公开可获取https://doi.org/10.20383/103.0614。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了水下成像技术的进展及其在监测海底生态系统方面的应用。尽管能够收集大量的海底图像数据,但分析这些数据的能力有限,这阻碍了重要环境信息的利用。机器学习方法的引入有望提高海底图像分析的效率,但缺乏大规模且一致的数据集来支持其发展。本文呈现了一个全球性的海底图像数据集BenthicNet,旨在支持大规模图像识别模型的开发与评估。该数据集收集了超过1140万张图像,使用具有代表性的子集对其进行整理与标注,并采用CATAMI方案将标注翻译。初步结果显示该数据集可以用于自动化大型和小型图像分析任务。该数据集与模型公开提供以供重用。
Key Takeaways
- 水下成像技术不断进步,为监测海底生态系统提供了广泛的图像数据集。
- 现有分析海底图像数据的能力不足,影响了环境信息的利用。
- 机器学习方法在海底图像分析中的应用有望提高效率。
- 缺乏用于支持机器学习模型开发的大规模且一致的海底图像数据集。
- BenthicNet是一个全球性的海底图像数据集,旨在支持大规模图像识别模型的开发与评估。
- BenthicNet包含了超过1140万张图像和采用CATAMI方案的标注信息。
点此查看论文截图