⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-02-20 更新
Enhancing operational wind downscaling capabilities over Canada: Application of a Conditional Wasserstein GAN methodology
Authors:Jorge Guevara, Victor Nascimento, Johannes Schmude, Daniel Salles, Simon Corbeil-Létourneau, Madalina Surcel, Dominique Brunet
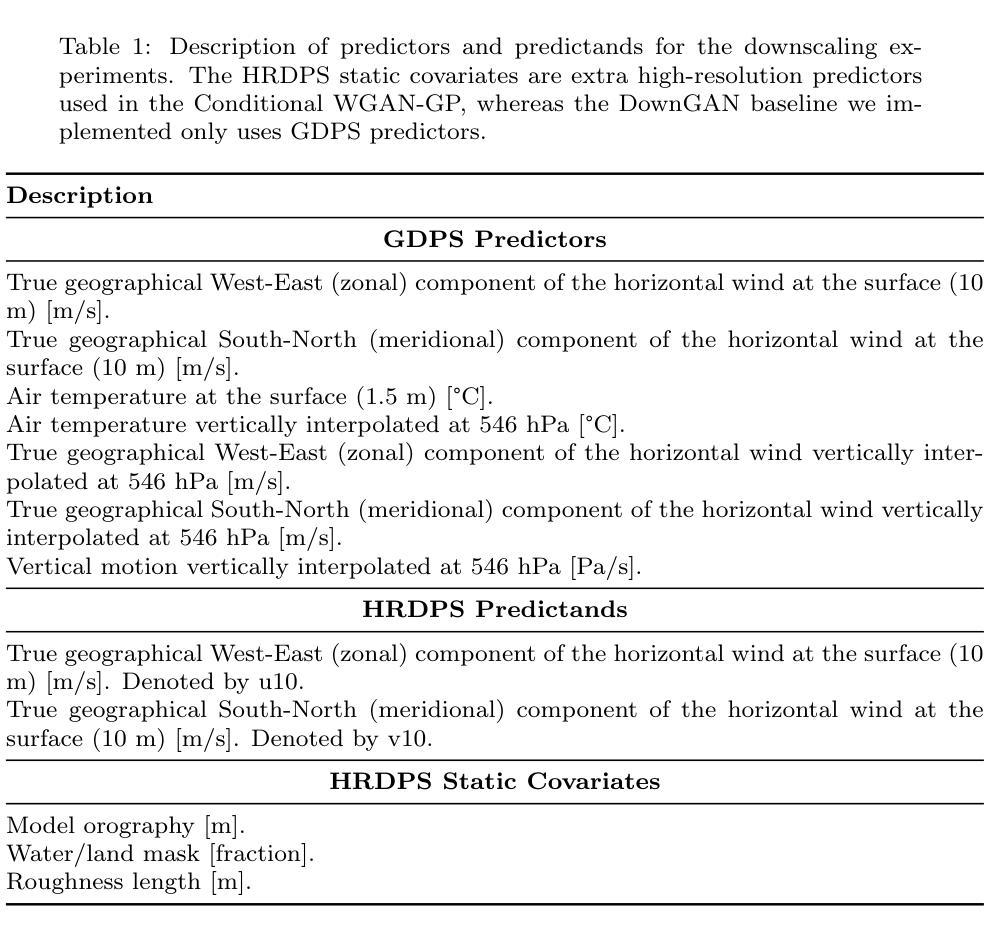
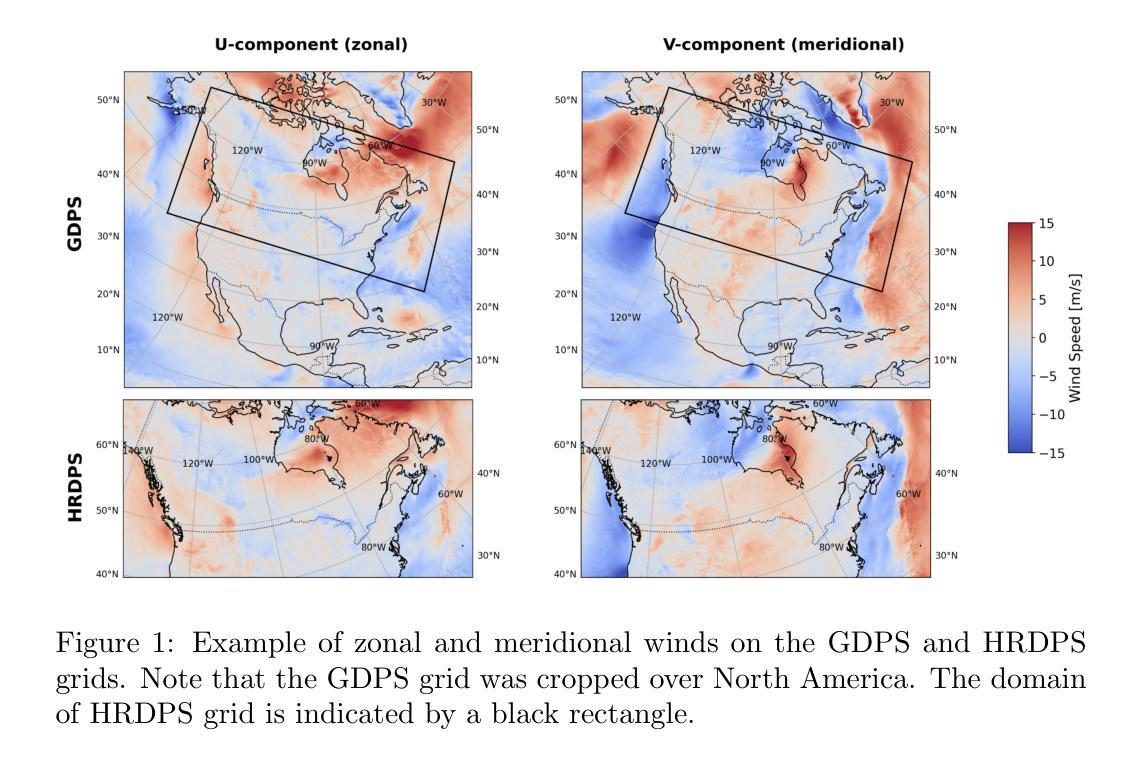
Wind downscaling is essential for improving the spatial resolution of weather forecasts, particularly in operational Numerical Weather Prediction (NWP). This study advances wind downscaling by extending the DownGAN framework introduced by Annau et al.,to operational datasets from the Global Deterministic Prediction System (GDPS) and High-Resolution Deterministic Prediction System (HRDPS), covering the entire Canadian domain. We enhance the model by incorporating high-resolution static covariates, such as HRDPS-derived topography, into a Conditional Wasserstein Generative Adversarial Network with Gradient Penalty, implemented using a UNET-based generator. Following the DownGAN framework, our methodology integrates low-resolution GDPS forecasts (15 km, 10-day horizon) and high-resolution HRDPS forecasts (2.5 km, 48-hour horizon) with Frequency Separation techniques adapted from computer vision. Through robust training and inference over the Canadian region, we demonstrate the operational scalability of our approach, achieving significant improvements in wind downscaling accuracy. Statistical validation highlights reductions in root mean square error (RMSE) and log spectral distance (LSD) metrics compared to the original DownGAN. High-resolution conditioning covariates and Frequency Separation strategies prove instrumental in enhancing model performance. This work underscores the potential for extending high-resolution wind forecasts beyond the 48-hour horizon, bridging the gap to the 10-day low resolution global forecast window.
风场降尺度化对于提高天气预报的空间分辨率至关重要,特别是在业务数值天气预报(NWP)中。本研究通过扩展Annau等人介绍的DownGAN框架,将风场降尺度化技术应用于全球确定性预测系统(GDPS)和高分辨率确定性预测系统(HRDPS)的业务数据集,覆盖整个加拿大区域。我们通过将高分辨率静态协变量(如由HRDPS派生的地形)纳入带有梯度惩罚的条件Wasserstein生成对抗网络(WGAN-GP),并使用基于UNET的生成器来实现模型的增强。遵循DownGAN框架,我们的方法融合了低分辨率GDPS预测(15公里,10天视野)和高分辨率HRDPS预测(2.5公里,48小时视野),并采用了计算机视觉中的频率分离技术。通过在加拿大地区的稳健训练和推理,我们证明了我们的方法具有业务可扩展性,在风场降尺度化精度方面取得了显著提高。统计验证显示,与原始DownGAN相比,我们的方法降低了均方根误差(RMSE)和对数谱距离(LSD)指标。高分辨率条件协变量和频率分离策略对增强模型性能起到了关键作用。这项工作强调了将高分辨率风场预测扩展到48小时视野之外,缩小与10天低分辨率全球预测窗口的差距的潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本研究利用DownGAN框架,将其扩展到全球确定性预测系统(GDPS)和高分辨率确定性预测系统(HRDPS)的操作数据集上,以改进气象预报的空间分辨率。通过融入高分辨率静态协变量和高频分离技术,提高了模型性能,实现了对加拿大整个区域的业务可扩展性,显著提高了风降尺度预报的准确性。
Key Takeaways
- 研究扩展了DownGAN框架至操作数据集,涵盖了整个加拿大区域。
- 融合了高分辨率静态协变量,如由HRDPS衍生的地形信息。
- 采用条件Wasserstein生成对抗网络,并结合梯度惩罚进行模型增强。
- 利用频率分离技术,整合了低分辨率和高分辨率的天气预报。
- 通过在加拿大区域的稳健训练和推理,实现了方法操作的可扩展性。
- 统计验证显示,与原始DownGAN相比,该方法在降低均方根误差和对数谱距离方面有所提高。
点此查看论文截图