⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-02-20 更新
A Dual-Stage Time-Context Network for Speech-Based Alzheimer’s Disease Detection
Authors:Yifan Gao, Long Guo, Hong Liu
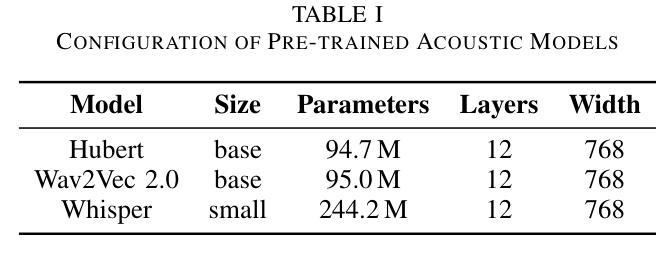
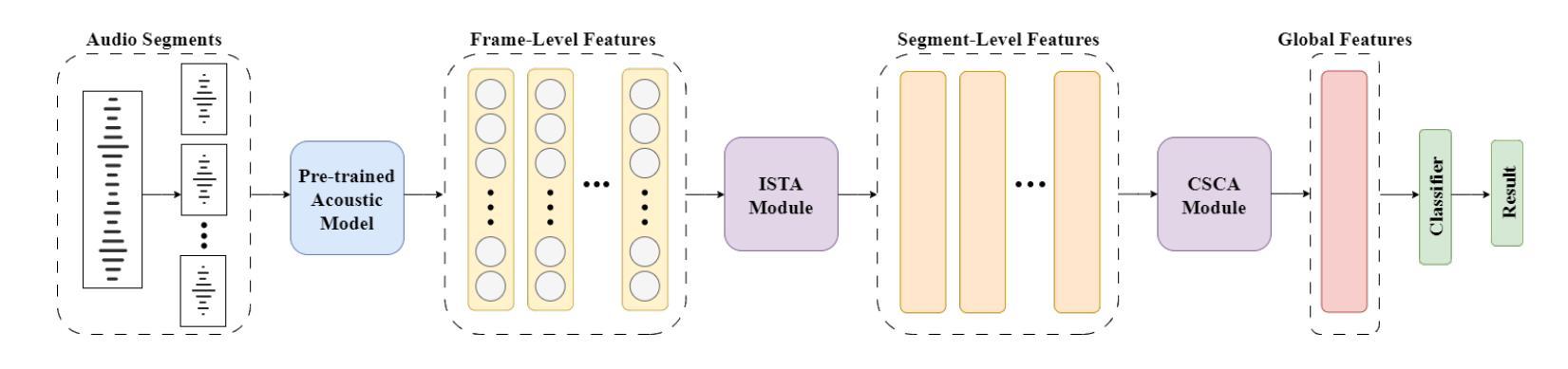
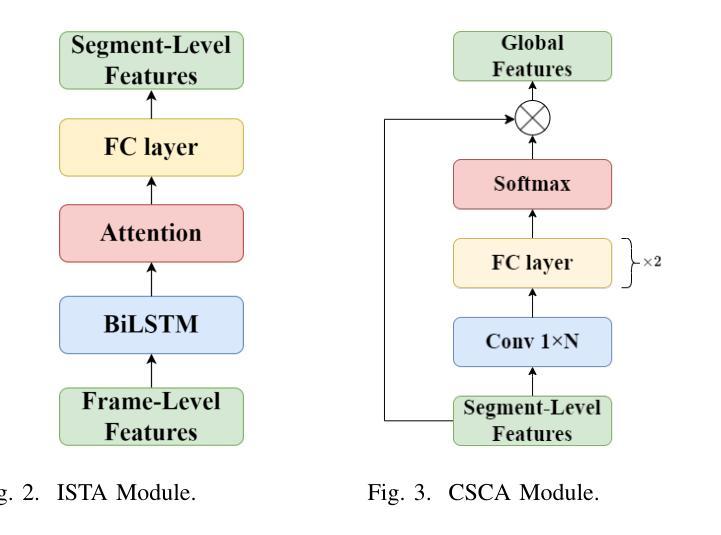
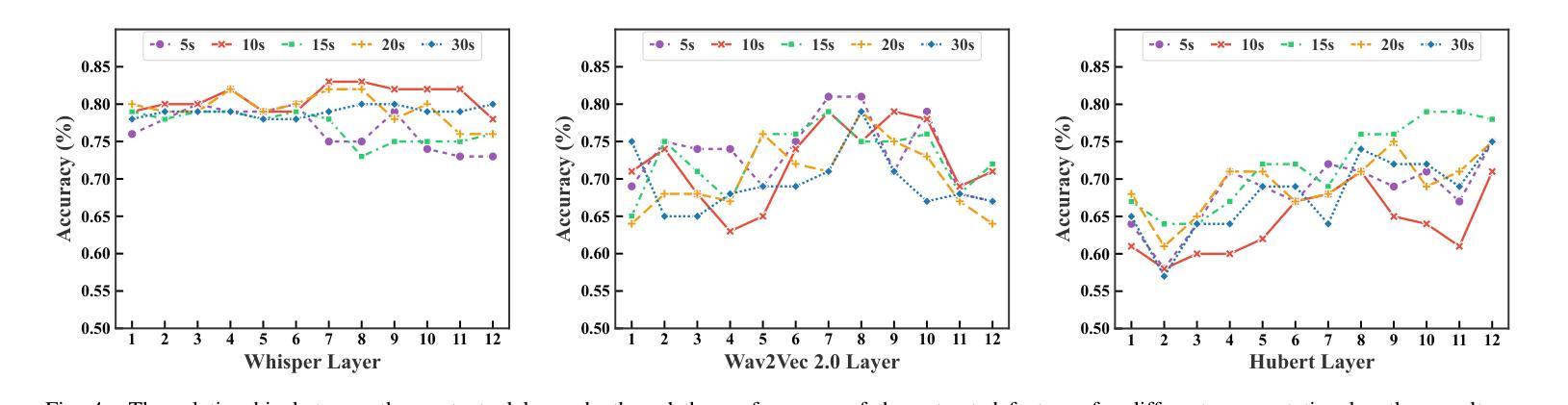
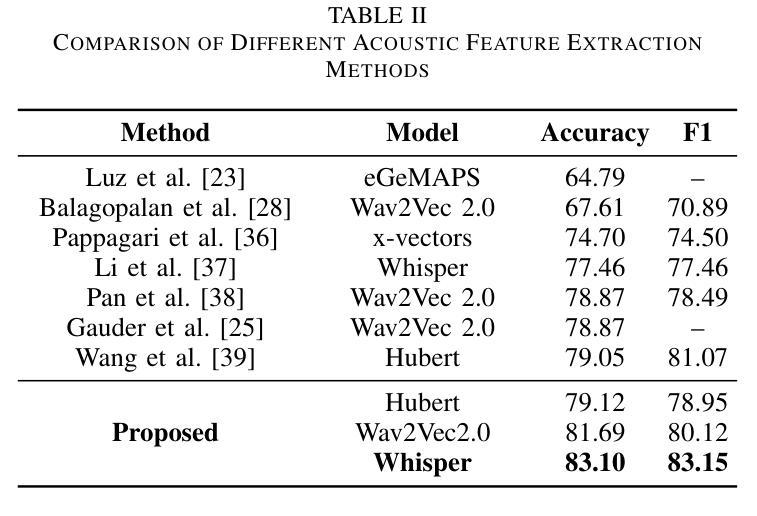
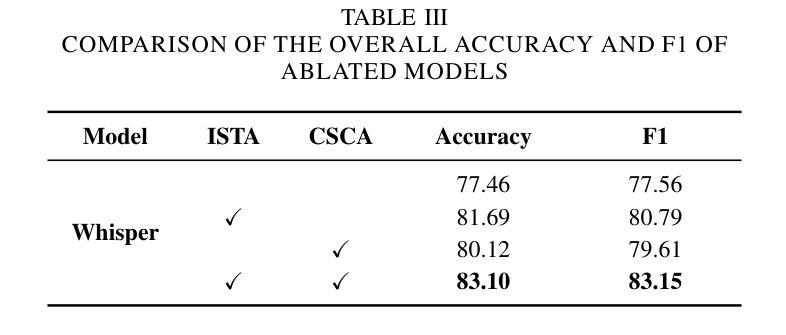
Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is a progressive neurodegenerative disorder that leads to irreversible cognitive decline in memory and communication. Early detection of AD through speech analysis is crucial for delaying disease progression. However, existing methods mainly use pre-trained acoustic models for feature extraction but have limited ability to model both local and global patterns in long-duration speech. In this letter, we introduce a Dual-Stage Time-Context Network (DSTC-Net) for speech-based AD detection, integrating local acoustic features with global conversational context in long-duration recordings.We first partition each long-duration recording into fixed-length segments to reduce computational overhead and preserve local temporal details.Next, we feed these segments into an Intra-Segment Temporal Attention (ISTA) module, where a bidirectional Long Short-Term Memory (BiLSTM) network with frame-level attention extracts enhanced local features.Subsequently, a Cross-Segment Context Attention (CSCA) module applies convolution-based context modeling and adaptive attention to unify global patterns across all segments.Extensive experiments on the ADReSSo dataset show that our DSTC-Net outperforms state-of-the-art models, reaching 83.10% accuracy and 83.15% F1.
阿尔茨海默病(AD)是一种进行性神经退行性疾病,会导致记忆和沟通能力的不可逆认知衰退。通过语音分析进行早期AD检测对于延缓疾病进展至关重要。然而,现有方法主要使用预训练的声学模型进行特征提取,但在长时语音中同时建模局部和全局模式的能力有限。在这封信中,我们介绍了一种用于基于语音的AD检测的Dual-Stage Time-Context网络(DSTC-Net),它将局部声学特征与长时录音中的全局对话上下文相结合。我们首先会将每个长时录音分成固定长度的片段,以减少计算开销并保留局部时间细节。接下来,我们将这些片段输入到Intra-Segment Temporal Attention(ISTA)模块中,其中使用带有帧级注意力的双向长短时记忆(BiLSTM)网络提取增强的局部特征。随后,Cross-Segment Context Attention(CSCA)模块采用基于卷积的上下文建模和自适应注意力,以统一所有片段中的全局模式。在ADReSSo数据集上的广泛实验表明,我们的DSTC-Net优于最新模型,达到83.10%的准确率和83.15%的F1分数。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:引入双阶段时间上下文网络(DSTC-Net)进行基于语音的阿尔茨海默病(AD)检测,结合长时录音中的局部声学特征和全局对话上下文。通过分段录音并应用双向LSTM网络和帧级注意力提取增强局部特征,再通过卷积上下文建模和自适应注意力统一全局模式。在ADReSSo数据集上的实验表明,该网络达到了较高的准确性和F1分数。
Key Takeaways:
- 阿尔茨海默病(AD)是一种导致不可逆记忆和沟通认知衰退的渐进性神经退行性疾病。
- 早期通过语音分析检测AD对于延缓疾病进展至关重要。
- 现有方法主要使用预训练的声学模型进行特征提取,但难以同时处理局部和全局模式的长时语音。
- 提出了一种名为Dual-Stage Time-Context Network(DSTC-Net)的模型,用于基于语音的AD检测。
- 该模型采用分段方法处理长时录音,旨在提取局部声学特征和全局对话上下文。
- 通过双向LSTM网络和帧级注意力增强局部特征提取,并通过卷积上下文建模和自适应注意力统一全局模式。
点此查看论文截图

Step-Audio: Unified Understanding and Generation in Intelligent Speech Interaction
Authors:Ailin Huang, Boyong Wu, Bruce Wang, Chao Yan, Chen Hu, Chengli Feng, Fei Tian, Feiyu Shen, Jingbei Li, Mingrui Chen, Peng Liu, Ruihang Miao, Wang You, Xi Chen, Xuerui Yang, Yechang Huang, Yuxiang Zhang, Zheng Gong, Zixin Zhang, Hongyu Zhou, Jianjian Sun, Brian Li, Chengting Feng, Changyi Wan, Hanpeng Hu, Jianchang Wu, Jiangjie Zhen, Ranchen Ming, Song Yuan, Xuelin Zhang, Yu Zhou, Bingxin Li, Buyun Ma, Hongyuan Wang, Kang An, Wei Ji, Wen Li, Xuan Wen, Xiangwen Kong, Yuankai Ma, Yuanwei Liang, Yun Mou, Bahtiyar Ahmidi, Bin Wang, Bo Li, Changxin Miao, Chen Xu, Chenrun Wang, Dapeng Shi, Deshan Sun, Dingyuan Hu, Dula Sai, Enle Liu, Guanzhe Huang, Gulin Yan, Heng Wang, Haonan Jia, Haoyang Zhang, Jiahao Gong, Junjing Guo, Jiashuai Liu, Jiahong Liu, Jie Feng, Jie Wu, Jiaoren Wu, Jie Yang, Jinguo Wang, Jingyang Zhang, Junzhe Lin, Kaixiang Li, Lei Xia, Li Zhou, Liang Zhao, Longlong Gu, Mei Chen, Menglin Wu, Ming Li, Mingxiao Li, Mingliang Li, Mingyao Liang, Na Wang, Nie Hao, Qiling Wu, Qinyuan Tan, Ran Sun, Shuai Shuai, Shaoliang Pang, Shiliang Yang, Shuli Gao, Shanshan Yuan, Siqi Liu, Shihong Deng, Shilei Jiang, Sitong Liu, Tiancheng Cao, Tianyu Wang, Wenjin Deng, Wuxun Xie, Weipeng Ming, Wenqing He, Wen Sun, Xin Han, Xin Huang, Xiaomin Deng, Xiaojia Liu, Xin Wu, Xu Zhao, Yanan Wei, Yanbo Yu, Yang Cao, Yangguang Li, Yangzhen Ma, Yanming Xu, Yaoyu Wang, Yaqiang Shi, Yilei Wang, Yizhuang Zhou, Yinmin Zhong, Yang Zhang, Yaoben Wei, Yu Luo, Yuanwei Lu, Yuhe Yin, Yuchu Luo, Yuanhao Ding, Yuting Yan, Yaqi Dai, Yuxiang Yang, Zhe Xie, Zheng Ge, Zheng Sun, Zhewei Huang, Zhichao Chang, Zhisheng Guan, Zidong Yang, Zili Zhang, Binxing Jiao, Daxin Jiang, Heung-Yeung Shum, Jiansheng Chen, Jing Li, Shuchang Zhou, Xiangyu Zhang, Xinhao Zhang, Yibo Zhu
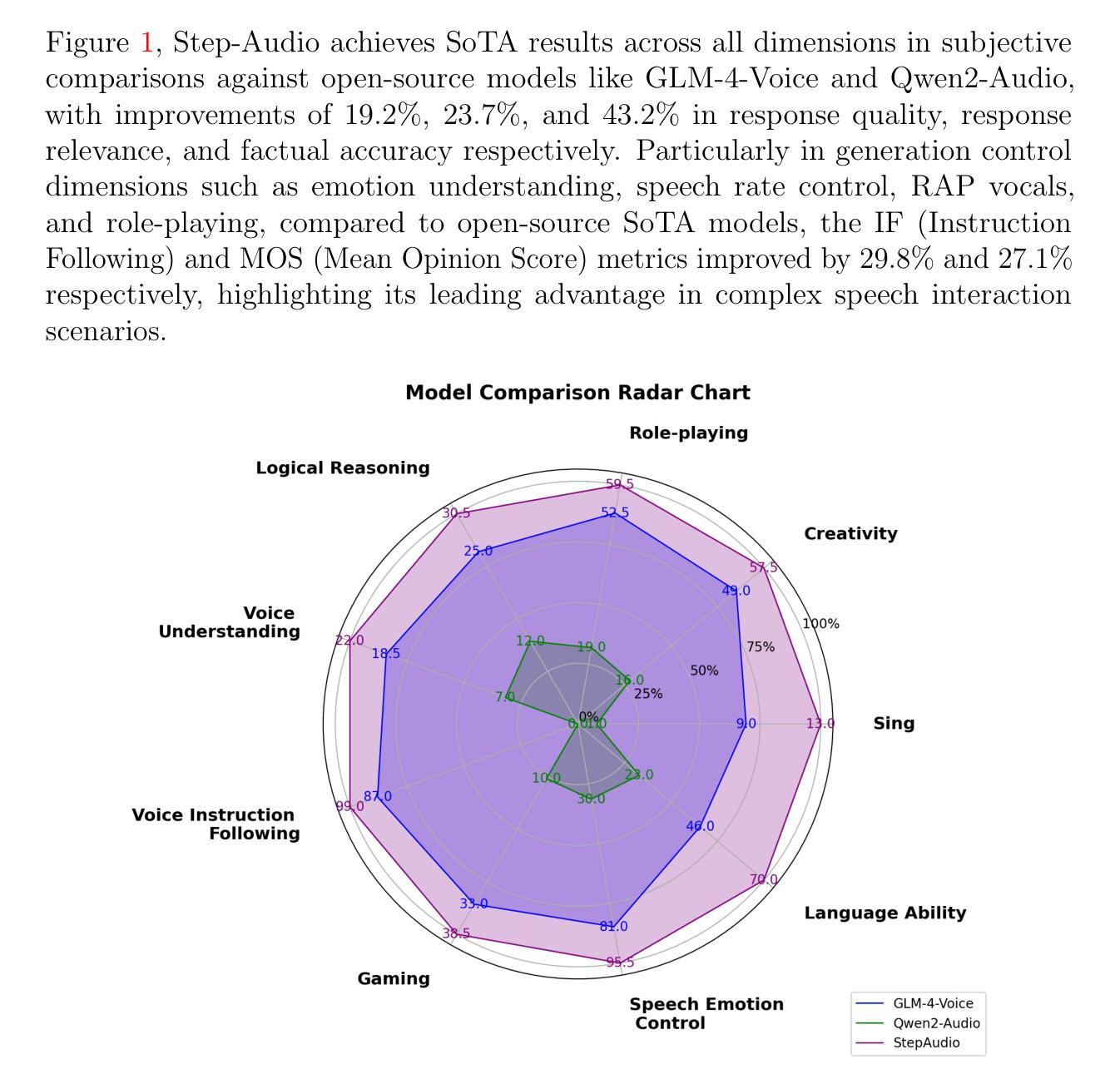
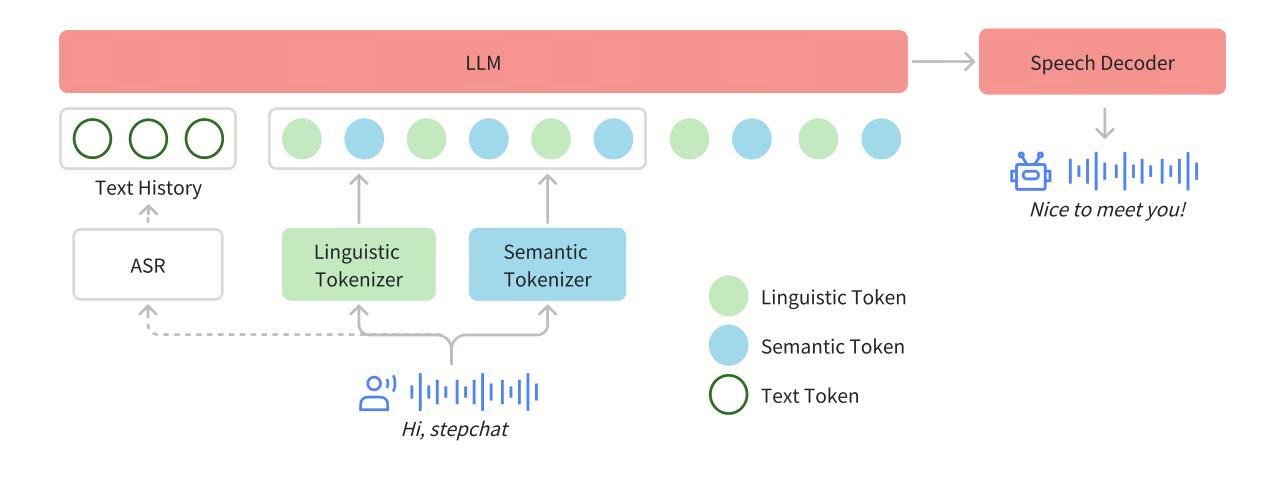
Real-time speech interaction, serving as a fundamental interface for human-machine collaboration, holds immense potential. However, current open-source models face limitations such as high costs in voice data collection, weakness in dynamic control, and limited intelligence. To address these challenges, this paper introduces Step-Audio, the first production-ready open-source solution. Key contributions include: 1) a 130B-parameter unified speech-text multi-modal model that achieves unified understanding and generation, with the Step-Audio-Chat version open-sourced; 2) a generative speech data engine that establishes an affordable voice cloning framework and produces the open-sourced lightweight Step-Audio-TTS-3B model through distillation; 3) an instruction-driven fine control system enabling dynamic adjustments across dialects, emotions, singing, and RAP; 4) an enhanced cognitive architecture augmented with tool calling and role-playing abilities to manage complex tasks effectively. Based on our new StepEval-Audio-360 evaluation benchmark, Step-Audio achieves state-of-the-art performance in human evaluations, especially in terms of instruction following. On open-source benchmarks like LLaMA Question, shows 9.3% average performance improvement, demonstrating our commitment to advancing the development of open-source multi-modal language technologies. Our code and models are available at https://github.com/stepfun-ai/Step-Audio.
实时语音交互作为人机交互的基本接口,具有巨大的潜力。然而,目前的开源模型面临诸多挑战,如语音数据采集成本高昂、动态控制薄弱以及智能有限等。为了应对这些挑战,本文介绍了Step-Audio,这是首个生产就绪的开源解决方案。主要贡献包括:1)一个拥有130B参数的统一语音文本多模态模型,实现了统一的理解和生成能力,其中Step-Audio-Chat版本已开源;2)一个生成式语音数据引擎,建立了一个经济实惠的语音克隆框架,并通过蒸馏技术推出了开源的轻量级Step-Audio-TTS-3B模型;3)一个指令驱动的精细控制系统,能够实现不同方言、情感、歌唱和RAP的动态调整;4)一个增强的认知架构,通过工具调用和角色扮演能力,有效管理复杂任务。基于我们新的StepEval-Audio-360评估基准,Step-Audio在人工评估中达到了最先进的性能,尤其在指令遵循方面。在LLaMA Question等开源基准测试中,平均性能提高了9.3%,这体现了我们推进开源多模态语言技术发展的承诺。我们的代码和模型可在https://github.com/stepfun-ai/Step-Audio获取。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了一项名为Step-Audio的创新技术,该技术为实时语音交互提供了新的生产就绪开源解决方案。通过引入统一语音文本多模态模型、生成式语音数据引擎、指令驱动精细控制系统以及增强认知架构,Step-Audio解决了现有开源模型在语音数据收集成本、动态控制能力以及智能程度上的局限性。其性能在StepEval-Audio-360评估基准上达到业界领先水平,特别是在指令遵循方面表现出色。此外,与开源基准相比,其在LLaMA Question上平均性能提升9.3%,展示了推进开源多模态语言技术发展的承诺。
Key Takeaways
- Step-Audio是一项创新的生产就绪开源解决方案,旨在改进实时语音交互技术。
- Step-Audio引入了多模态模型,实现了语音和文本的联合理解和生成。
- Step-Audio通过生成式语音数据引擎降低了语音克隆的成本,并开发了轻量级的语音合成模型。
- 指令驱动精细控制系统使得语音交互更加动态,可调整方言、情感、歌唱和RAP等元素。
- Step-Audio的认知架构得到了增强,具备工具调用和角色扮演能力,以更有效地管理复杂任务。
- Step-Audio的性能在StepEval-Audio-360评估基准上达到业界领先水平。
点此查看论文截图

VarGes: Improving Variation in Co-Speech 3D Gesture Generation via StyleCLIPS
Authors:Ming Meng, Ke Mu, Yonggui Zhu, Zhe Zhu, Haoyu Sun, Heyang Yan, Zhaoxin Fan
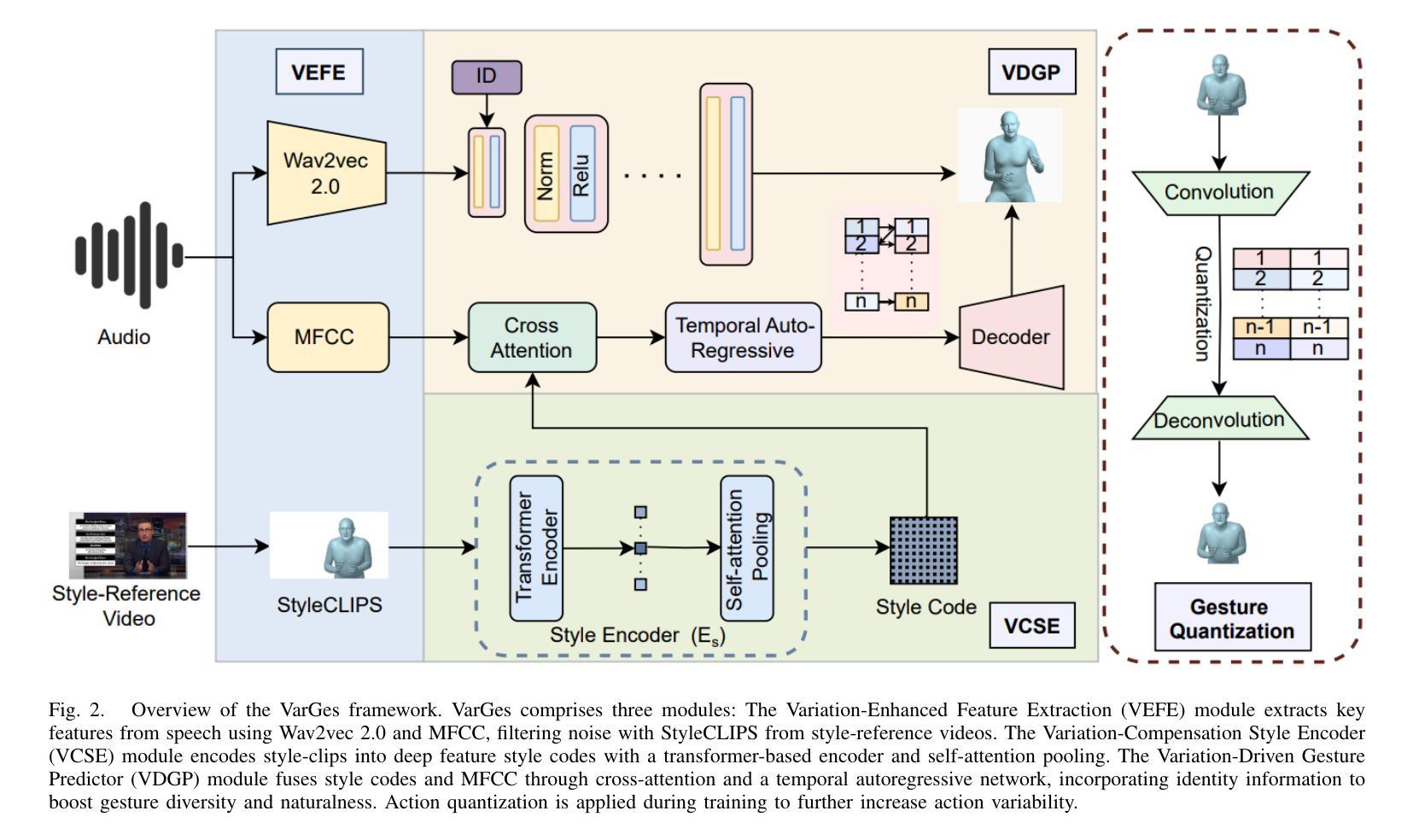
Generating expressive and diverse human gestures from audio is crucial in fields like human-computer interaction, virtual reality, and animation. Though existing methods have achieved remarkable performance, they often exhibit limitations due to constrained dataset diversity and the restricted amount of information derived from audio inputs. To address these challenges, we present VarGes, a novel variation-driven framework designed to enhance co-speech gesture generation by integrating visual stylistic cues while maintaining naturalness. Our approach begins with the Variation-Enhanced Feature Extraction (VEFE) module, which seamlessly incorporates \textcolor{blue}{style-reference} video data into a 3D human pose estimation network to extract StyleCLIPS, thereby enriching the input with stylistic information. Subsequently, we employ the Variation-Compensation Style Encoder (VCSE), a transformer-style encoder equipped with an additive attention mechanism pooling layer, to robustly encode diverse StyleCLIPS representations and effectively manage stylistic variations. Finally, the Variation-Driven Gesture Predictor (VDGP) module fuses MFCC audio features with StyleCLIPS encodings via cross-attention, injecting this fused data into a cross-conditional autoregressive model to modulate 3D human gesture generation based on audio input and stylistic clues. The efficacy of our approach is validated on benchmark datasets, where it outperforms existing methods in terms of gesture diversity and naturalness. The code and video results will be made publicly available upon acceptance:https://github.com/mookerr/VarGES/ .
音频生成的表情丰富且多样化的手势在人类与计算机交互、虚拟现实和动画等领域至关重要。尽管现有方法已经取得了显著的成效,但由于数据集多样性的限制以及从音频输入中获得的信息量有限,它们通常表现出局限性。为了应对这些挑战,我们提出了VarGes,这是一个新型的变化驱动框架,旨在通过整合视觉风格线索来增强与语音同步的手势生成,同时保持自然性。我们的方法始于增强特征提取模块(VEFE),该模块无缝地将风格参考视频数据融入3D人体姿态估计网络,从而提取StyleCLIPS,使输入信息丰富并带有风格信息。随后,我们采用了配备附加注意力机制池化层的变体补偿风格编码器(VCSE),这是一个变压器风格的编码器,能够稳健地编码各种StyleCLIPS表示并有效地管理风格变化。最后,变化驱动手势预测器(VDGP)模块通过跨注意力将MFCC音频特征与StyleCLIPS编码融合,将此融合数据注入跨条件自回归模型,根据音频输入和风格线索调制3D手势生成。我们的方法已在基准数据集上进行了验证,在手势多样性和自然性方面优于现有方法。代码和视频结果将在接受后公开:https://github.com/mookerr/VarGES/。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出了一种名为VarGes的新颖变化驱动框架,用于通过整合视觉风格线索增强音频驱动的手势生成。该框架通过引入变化增强特征提取模块(VEFE)、变化补偿风格编码器(VCSE)和变化驱动手势预测器(VDGP)等技术,解决了现有方法在数据集多样性和从音频输入中获取信息受限方面的局限性。实验结果表明,该方法在基准数据集上的手势多样性和自然度方面优于现有方法。
Key Takeaways
- VarGes是一个变化驱动框架,旨在通过集成视觉风格线索增强音频驱动的手势生成。
- 使用变化增强特征提取模块(VEFE)融入风格参考视频数据,丰富输入的风格信息。
- 变化补偿风格编码器(VCSE)能有效编码多样化的StyleCLIPS表示并管理风格变化。
- 变化驱动手势预测器(VDGP)结合音频特征和StyleCLIPS编码,通过交叉注意力注入数据,根据音频输入和风格线索调节3D手势生成。
- VarGes框架在基准数据集上实现了优于现有方法的手势多样性和自然度。
- 公开可用代码和视频结果:https://github.com/mookerr/VarGES/。
- 该框架在人机交互、虚拟现实和动画等领域具有潜在应用价值。
点此查看论文截图

VoxEval: Benchmarking the Knowledge Understanding Capabilities of End-to-End Spoken Language Models
Authors:Wenqian Cui, Xiaoqi Jiao, Ziqiao Meng, Irwin King
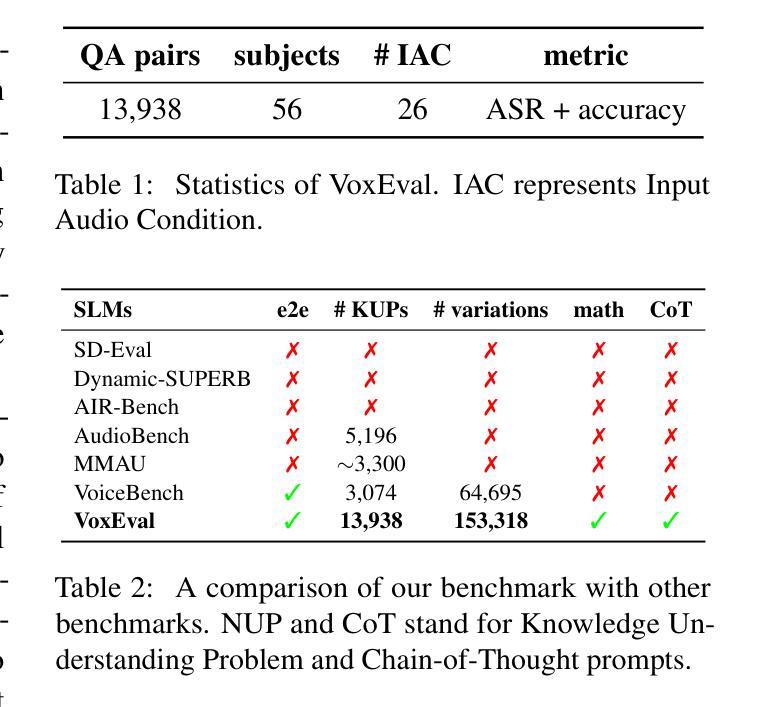
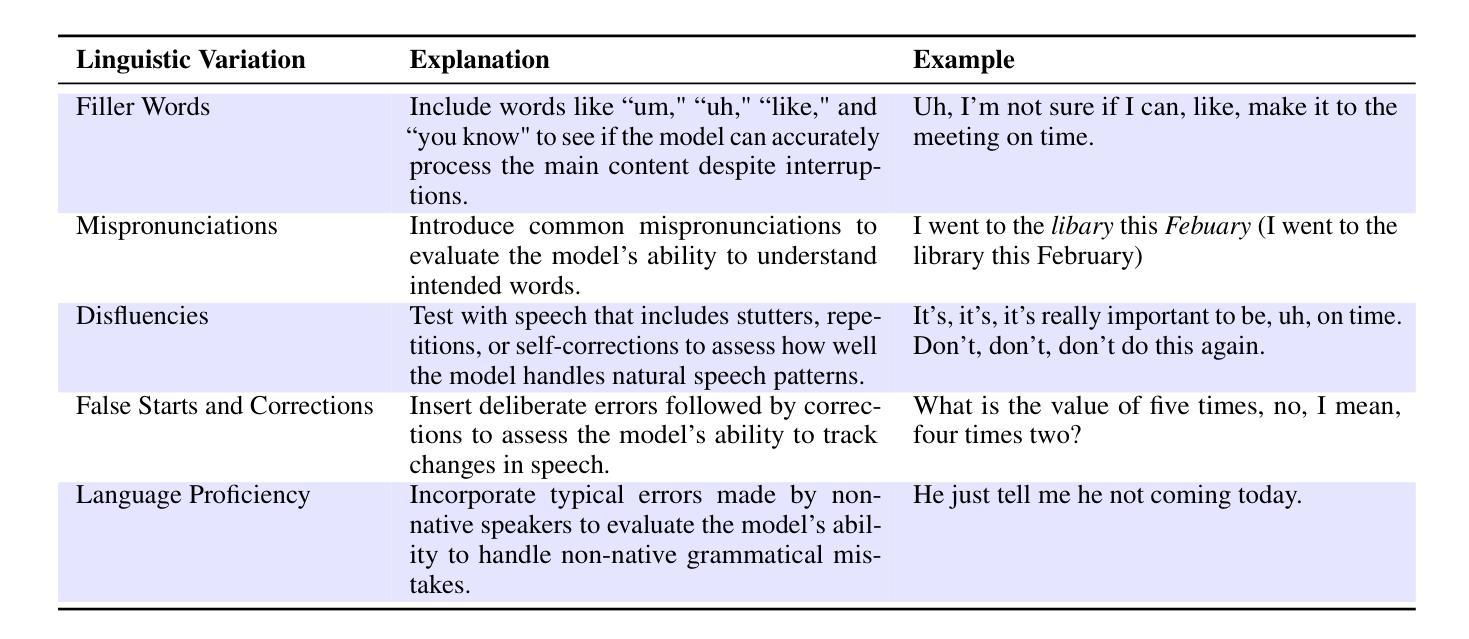
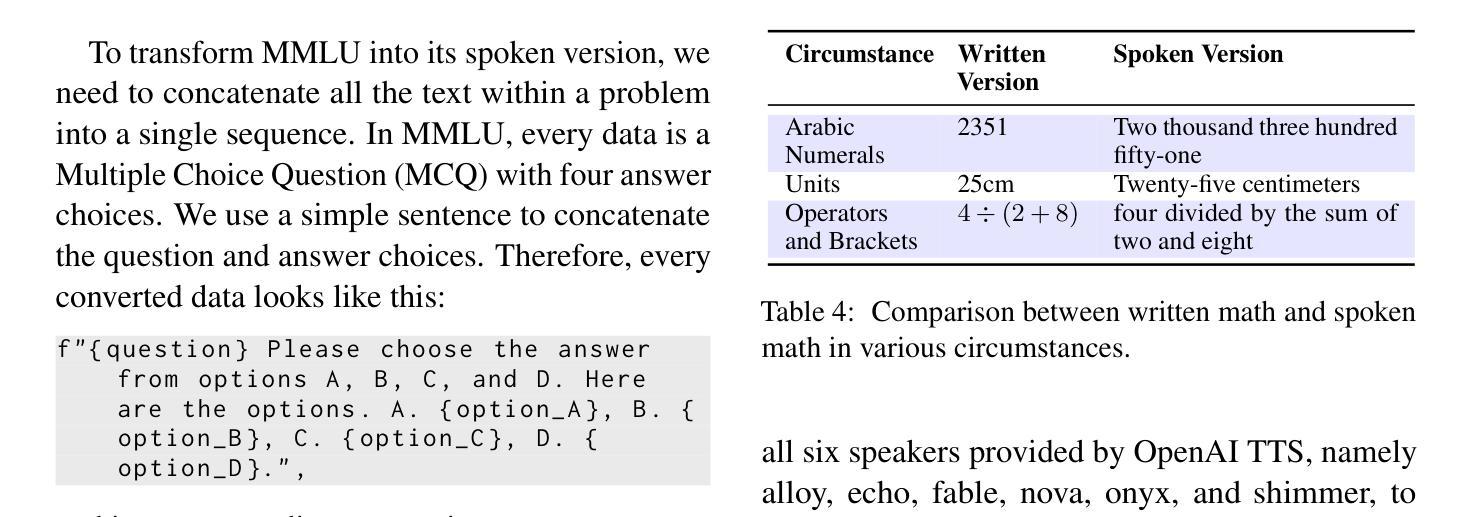
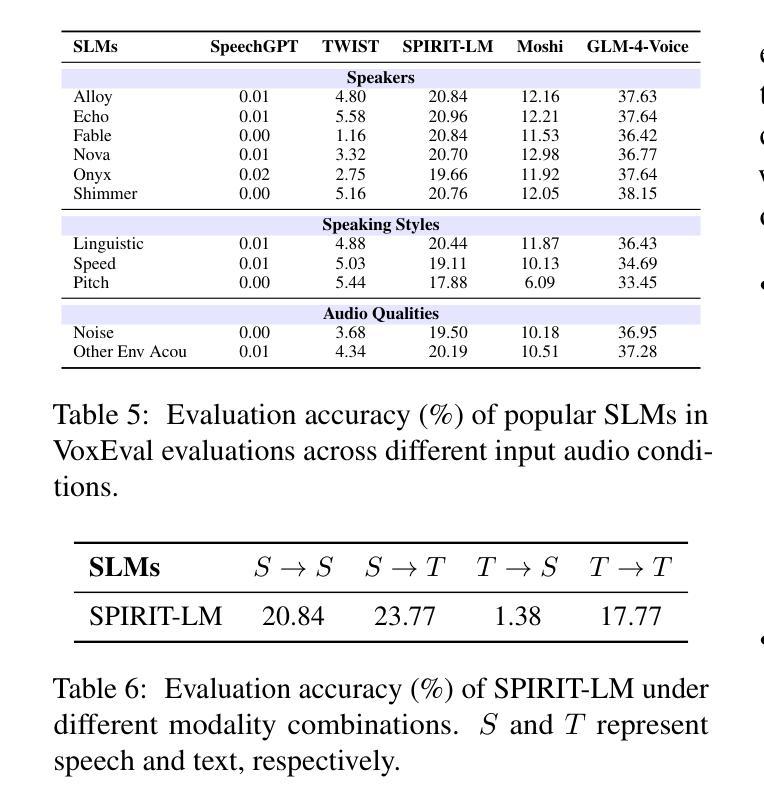
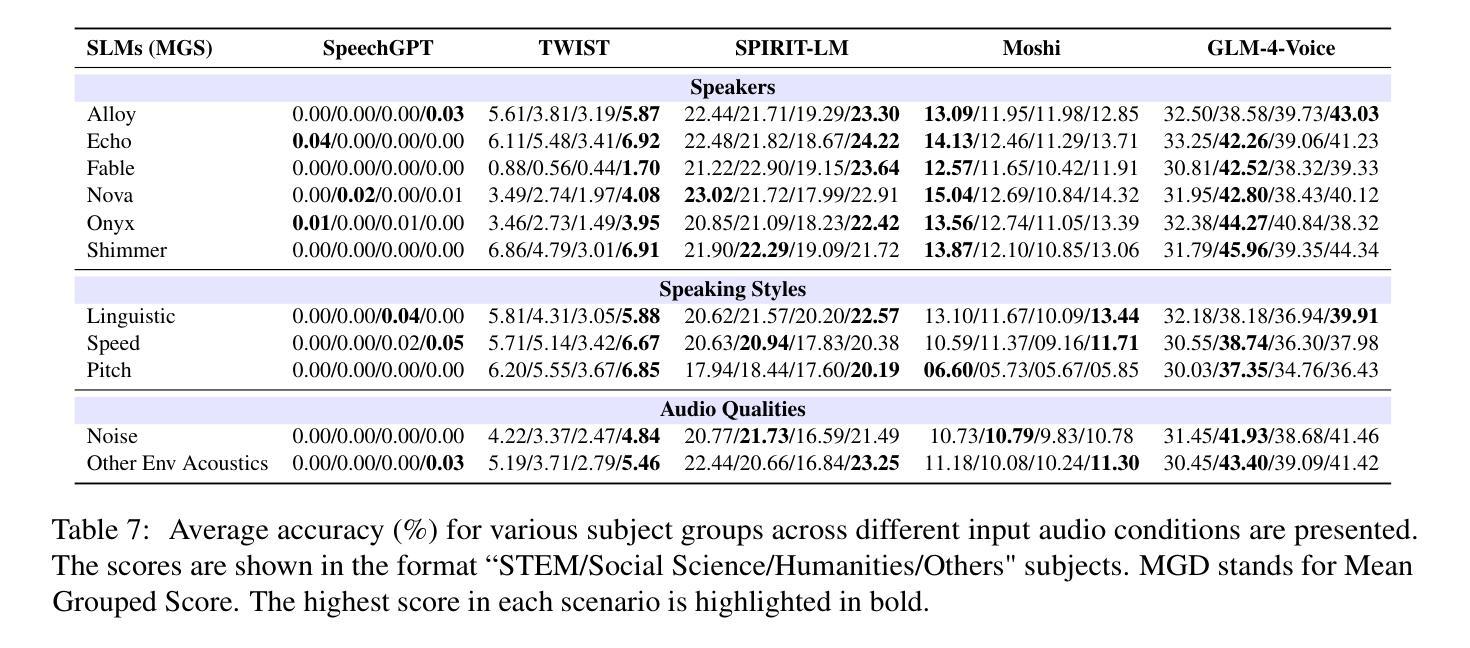
With the rising need for speech-based interaction models, end-to-end Spoken Language Models (SLMs) have emerged as a promising solution. While these models require comprehensive world knowledge for meaningful and reliable human interactions, existing question-answering (QA) benchmarks fall short in evaluating SLMs’ knowledge understanding due to their inability to support end-to-end speech evaluation and account for varied input audio conditions. To address these limitations, we present VoxEval, a novel SpeechQA benchmark that assesses SLMs’ knowledge understanding through pure speech interactions. Our benchmark 1) uniquely maintains speech format for both inputs and outputs, 2) evaluates model robustness across diverse input audio conditions, and 3) pioneers the assessment of complex tasks like mathematical reasoning in spoken format. Systematic evaluation demonstrates that VoxEval presents significant challenges to current SLMs, revealing their sensitivity to varying audio conditions and highlighting the need to enhance reasoning capabilities in future development. We hope this benchmark could guide the advancement of more sophisticated and reliable SLMs.\footnote{VoxEval dataset is available at: https://github.com/dreamtheater123/VoxEval
随着基于语音的交互模型的需不断求增长,端到端的口语模型(SLM)已成为一种前景广阔解决方案。虽然这些模型需要全面的世界知识来进行有意义和可靠的人类交互,但现有的问答(QA)基准测试在评估SLM的知识理解方面却显得不足,因为它们无法支持端到端的语音评估,也无法考虑到各种输入音频条件。为了解决这些局限性,我们推出了VoxEval,这是一个新的SpeechQA基准测试,它通过纯语音交互来评估SLM的知识理解。我们的基准测试1)独特地保持语音输入输出格式,2)评估模型在不同输入音频条件下的稳健性,3)率先评估口语形式的复杂任务,如数学推理。系统评估表明,VoxEval给当前的SLM带来了重大挑战,揭示了它们对各种音频条件的敏感性,并强调了未来开发时需要增强推理能力的必要性。我们希望这个基准测试能够引导更先进、更可靠的SLM的发展。VoxEval数据集可在:https://github.com/dreamtheater123/VoxEval找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
随着基于语音的交互模型需求的增加,端到端的口语模型(SLMs)展现出巨大的潜力。现有问答(QA)基准测试在评估SLM的知识理解方面存在不足,无法支持端到端的语音评估并考虑各种输入音频条件。为解决这些问题,我们提出了VoxEval这一新颖的SpeechQA基准测试,它通过纯语音交互评估SLM的知识理解。该基准测试具有以下特点:1)保持语音输入输出格式的独特性;2)评估模型在不同输入音频条件下的稳健性;3)率先评估口语形式的复杂任务,如数学推理等。系统评估表明,VoxEval对当前SLM提出了重大挑战,突显了它们对各种音频条件的敏感性,并强调未来发展中增强推理能力的必要性。我们期望此基准测试能推动更先进、更可靠的SLM的发展。
Key Takeaways
- 口语模型(SLMs)在基于语音的交互模型中表现出巨大潜力。
- 现有问答基准测试无法充分评估SLM的知识理解,尤其在端到端语音评估和不同输入音频条件下的表现。
- VoxEval是一个新颖的SpeechQA基准测试,以纯语音交互方式评估SLM的知识理解。
- VoxEval保持语音输入输出格式的独特性,并评估模型在不同输入音频条件下的稳健性。
- VoxEval率先评估口语形式的复杂任务,如数学推理。
- 系统评估显示,VoxEval对当前SLM提出了重大挑战,突显其音频条件敏感性和推理能力的不足。
点此查看论文截图

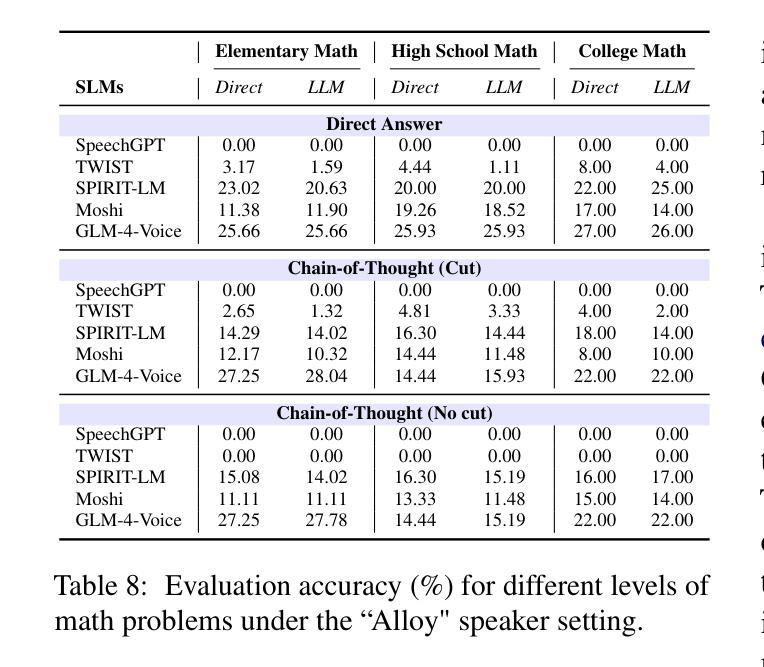
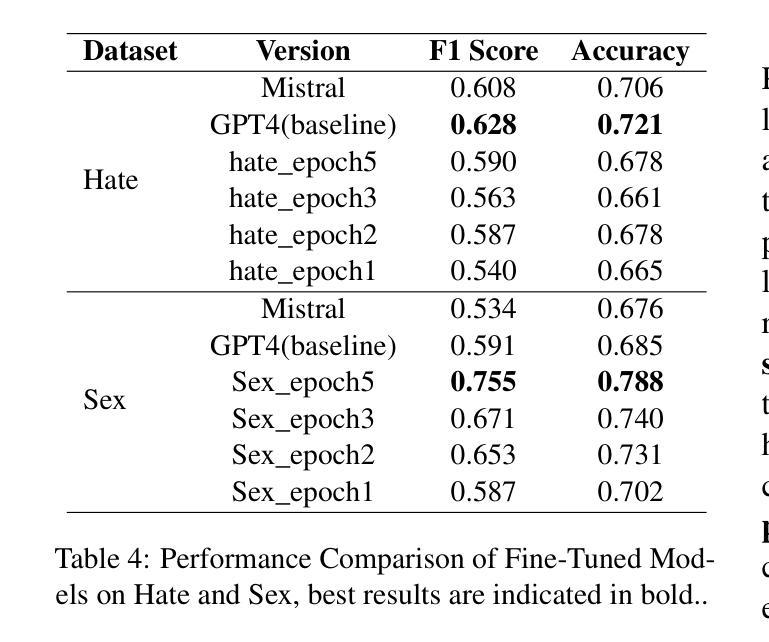
ToxiLab: How Well Do Open-Source LLMs Generate Synthetic Toxicity Data?
Authors:Zheng Hui, Zhaoxiao Guo, Hang Zhao, Juanyong Duan, Lin Ai, Yinheng Li, Julia Hirschberg, Congrui Huang
Effective toxic content detection relies heavily on high-quality and diverse data, which serve as the foundation for robust content moderation models. Synthetic data has become a common approach for training models across various NLP tasks. However, its effectiveness remains uncertain for highly subjective tasks like hate speech detection, with previous research yielding mixed results. This study explores the potential of open-source LLMs for harmful data synthesis, utilizing controlled prompting and supervised fine-tuning techniques to enhance data quality and diversity. We systematically evaluated 6 open source LLMs on 5 datasets, assessing their ability to generate diverse, high-quality harmful data while minimizing hallucination and duplication. Our results show that Mistral consistently outperforms other open models, and supervised fine-tuning significantly enhances data reliability and diversity. We further analyze the trade-offs between prompt-based vs. fine-tuned toxic data synthesis, discuss real-world deployment challenges, and highlight ethical considerations. Our findings demonstrate that fine-tuned open source LLMs provide scalable and cost-effective solutions to augment toxic content detection datasets, paving the way for more accessible and transparent content moderation tools.
有效的有毒内容检测在很大程度上依赖于高质量和多样化的数据,这些数据为构建稳健的内容管理模型提供了基础。合成数据已成为各种NLP任务中训练模型的常见方法。然而,对于像仇恨言论检测这样的高度主观任务,其有效性仍不确定,之前的研究结果喜忧参半。本研究探讨了开源大型语言模型在有害数据合成方面的潜力,利用受控提示和监督微调技术来提高数据的质量和多样性。我们在5个数据集上系统地评估了6个开源大型语言模型,评估它们生成多样化、高质量的有害数据的能力,同时尽量减少幻觉和重复。我们的结果表明,Mistral在各方面表现均优于其他开源模型,监督微调显著提高了数据的可靠性和多样性。我们进一步分析了基于提示与微调有毒数据合成的权衡,讨论了现实世界的部署挑战,并强调了伦理考量。我们的研究结果表明,经过微调后的开源大型语言模型为增强有毒内容检测数据集提供了可扩展和具有成本效益的解决方案,为更便捷和透明的内容管理工具的推广奠定了基础。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 14 pages
Summary
本研究探讨了开源大型语言模型(LLMs)在有害数据合成中的潜力,研究通过受控提示和监督微调技术提高数据质量和多样性。系统评估了6个开源LLMs在5个数据集上的表现,结果显示Mistral表现最佳,监督微调可显著提高数据可靠性和多样性。该研究为有毒内容检测数据集提供了可扩展和经济的解决方案。
Key Takeaways
- 有毒内容检测依赖于高质量和多样化的数据,这些数据是建立稳健内容管理模型的基础。
- 合成数据在多种NLP任务中常被用于模型训练,但对于高度主观的任务如仇恨言论检测,其效果尚不确定。
- 研究评估了六种开源LLMs在生成多样且高质量的有害数据方面的能力,并发现Mistral表现最佳。
- 监督微调技术显著提高了数据可靠性和多样性。
- 提示(prompt-based)与微调(fine-tuned)之间的权衡在有毒数据合成中存在。
- 研究讨论了实际部署挑战和伦理考量。
点此查看论文截图

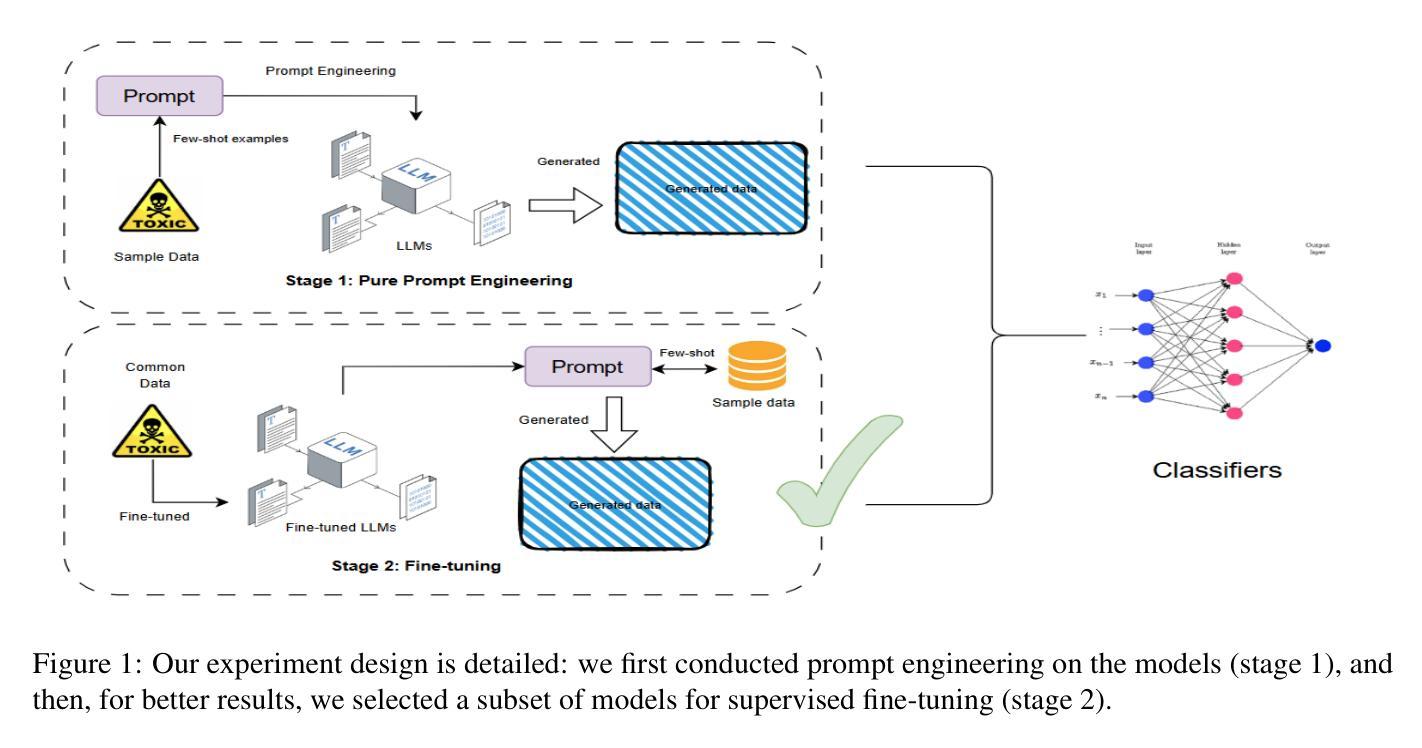
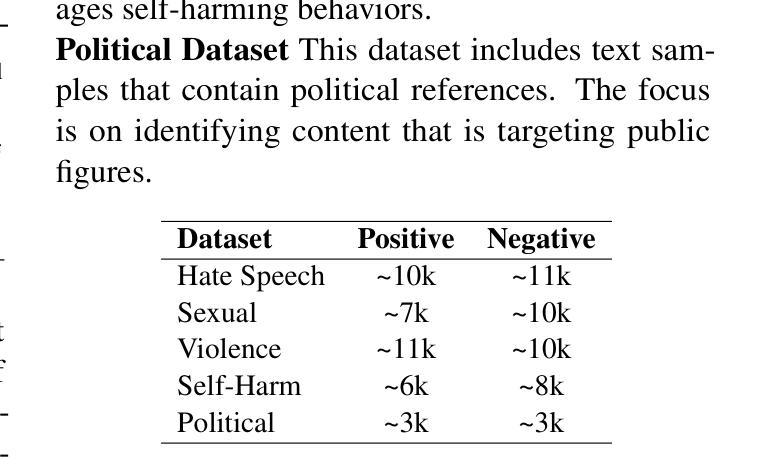
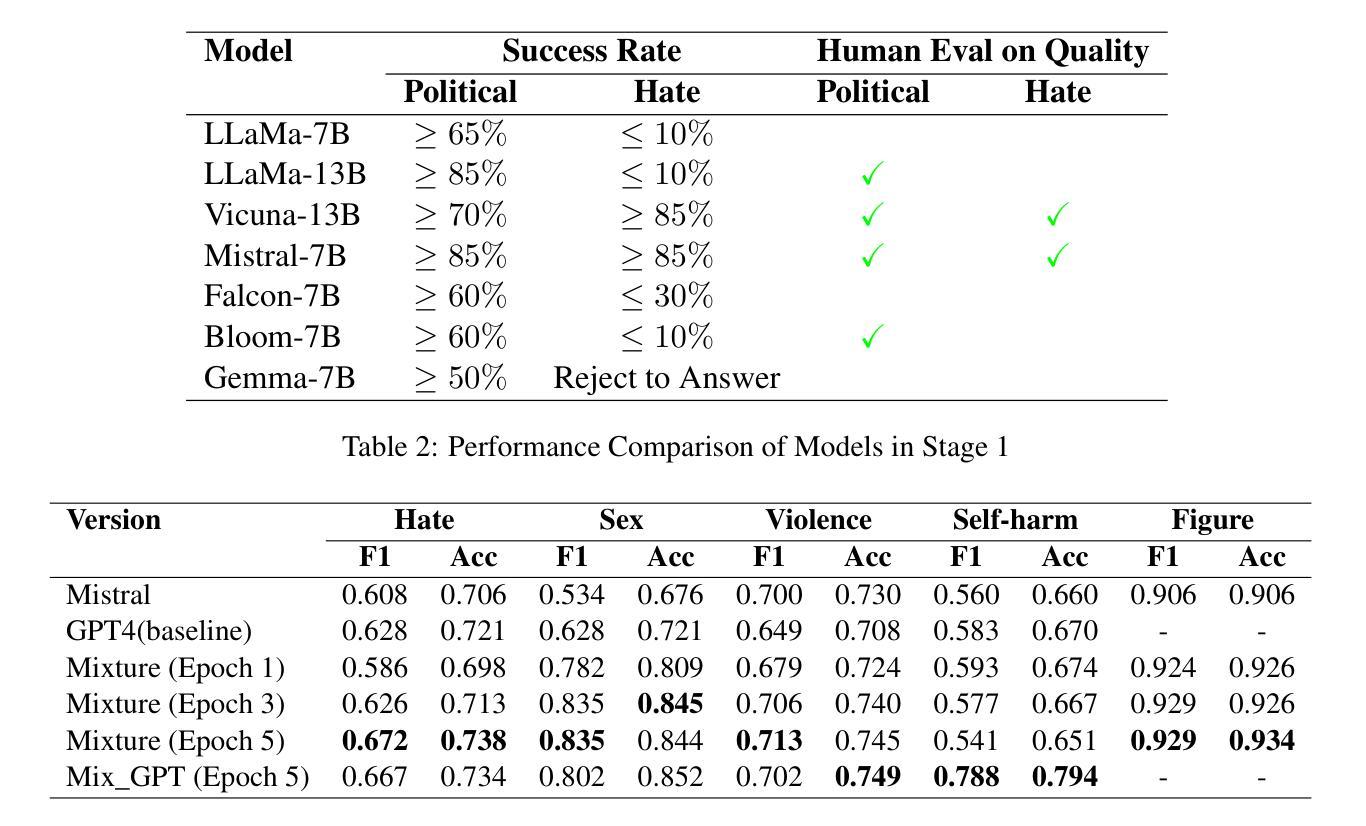
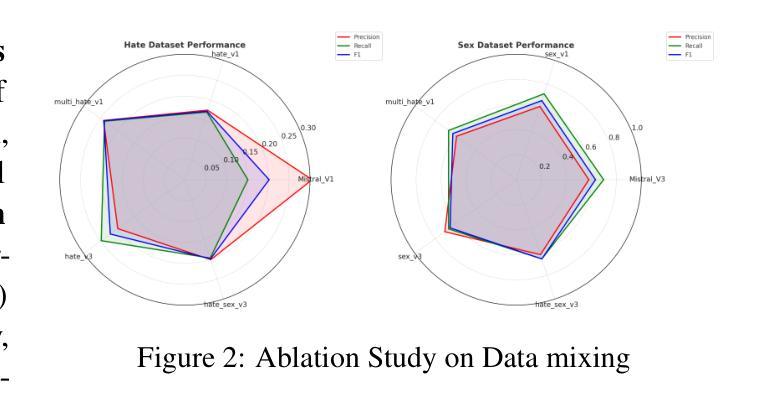
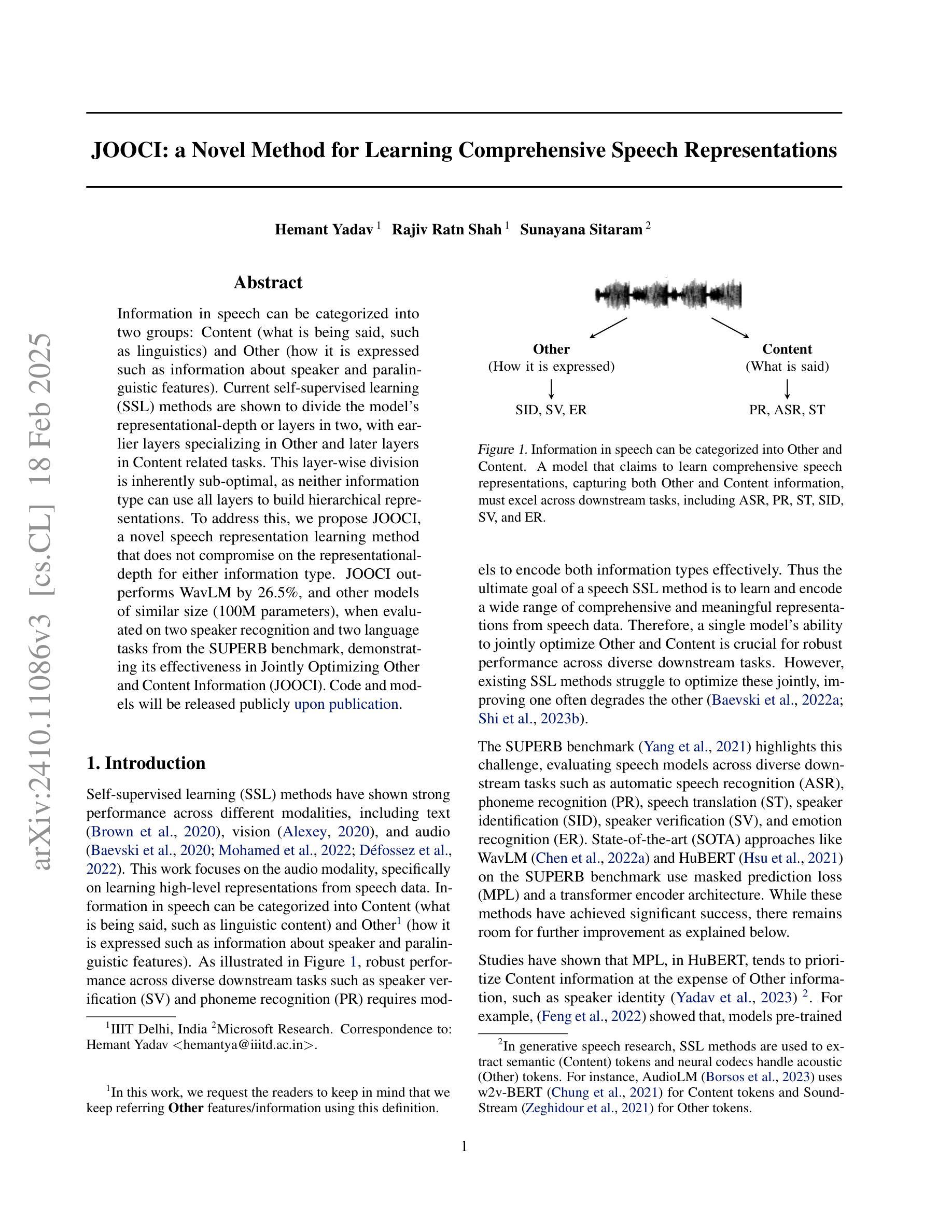
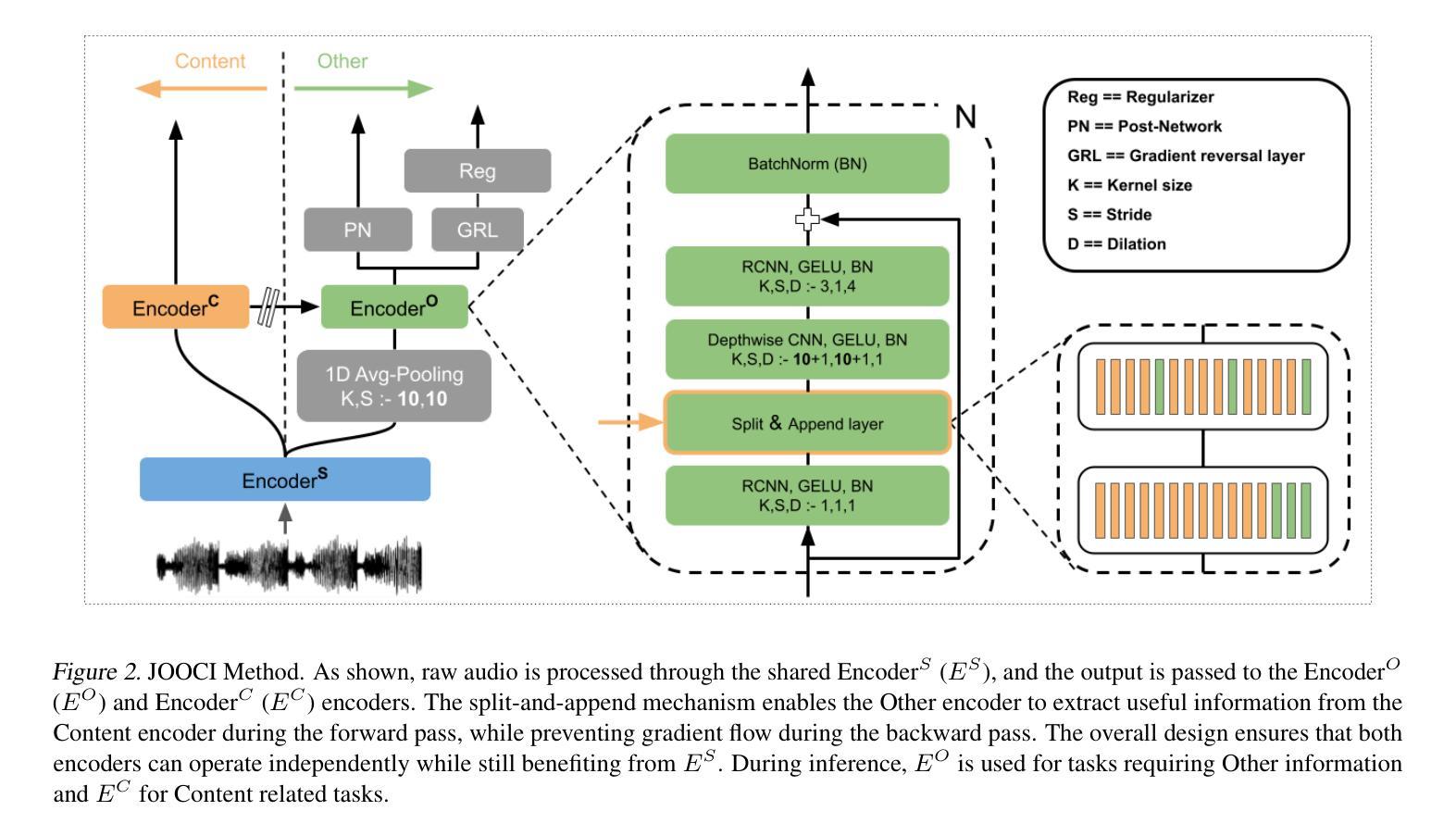
JOOCI: a Framework for Learning Comprehensive Speech Representations
Authors:Hemant Yadav, Rajiv Ratn Shah, Sunayana Sitaram
Information in speech can be categorized into two groups: Content (what is being said, such as linguistics) and Other (how it is expressed such as information about speaker and paralinguistic features). Current self-supervised learning (SSL) methods are shown to divide the model’s representational-depth or layers in two, with earlier layers specializing in Other and later layers in Content related tasks. This layer-wise division is inherently sub-optimal, as neither information type can use all layers to build hierarchical representations. To address this, we propose JOOCI, a novel speech representation learning method that does not compromise on the representational-depth for either information type. JOOCI outperforms WavLM by 26.5%, and other models of similar size (100M parameters), when evaluated on two speaker recognition and two language tasks from the SUPERB benchmark, demonstrating its effectiveness in Jointly Optimizing Other and Content Information (JOOCI).
语音中的信息可以分为两大类:内容(所说的内容,如语言学)和其他(如何表达,如关于说话人和副语言特征的信息)。现有的自监督学习方法被证明会将模型的表示深度或层次分为两部分,较早的层次专注于其他任务,而较后的层次专注于内容相关任务。这种逐层划分本质上是次优的,因为两种信息类型都无法使用所有层次来构建层次化表示。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了JOOCI,这是一种新的语音表示学习方法,不会损害两种信息类型的表示深度。在SUPERB基准测试的两个语音任务和两个语言任务中,JOOCI的性能优于WavLM 26.5%,以及其他类似规模的模型(1亿参数),证明了其在联合优化其他和内容信息方面的有效性(JOOCI)。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Submitted to ICLR 2025
Summary
本文介绍了当前自监督学习在语音识别中的局限性,并提出了一个新的语音表示学习方法JOOCI。该方法不妥协于内容和非语言信息的代表性深度,能够更有效地进行语音表示学习,并在SUPERB基准测试中表现出优异性能。
Key Takeaways
- 语音信息可以分为内容信息和其他信息两大类。
- 当前自监督学习方法在语音识别的模型层次深度上存在局限性,早期层次专注于其他信息,后期层次专注于内容信息。
- 这种层次划分是次优的,因为任何一种信息类型都无法利用所有层次来构建层次化的表示。
- JOOCI是一种新型的语音表示学习方法,旨在解决上述问题。
- JOOCI在SUPERB基准测试中的表现优于WavLM和其他类似规模的模型,显示出其优化内容和非语言信息的能力。
- JOOCI的优势在于不妥协于任何一类信息的代表性深度。
点此查看论文截图
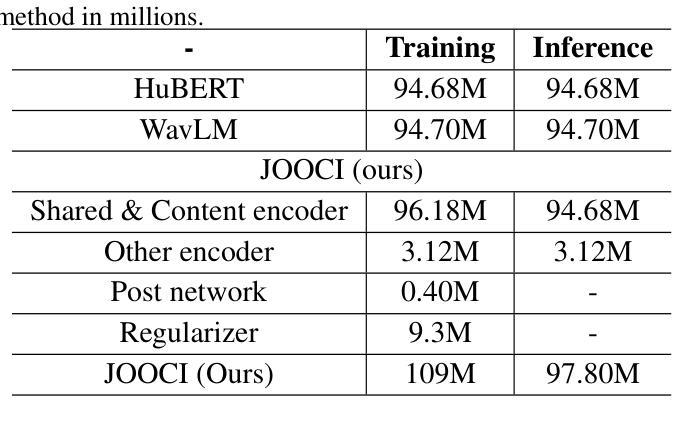
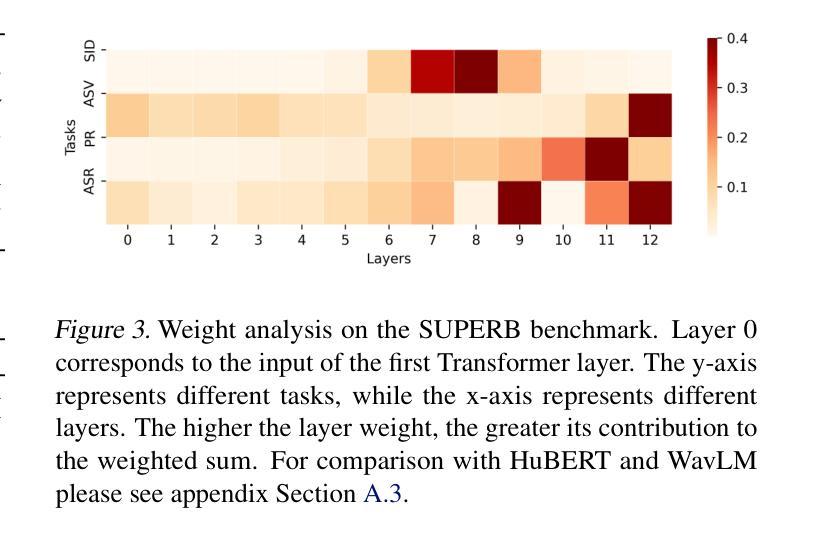
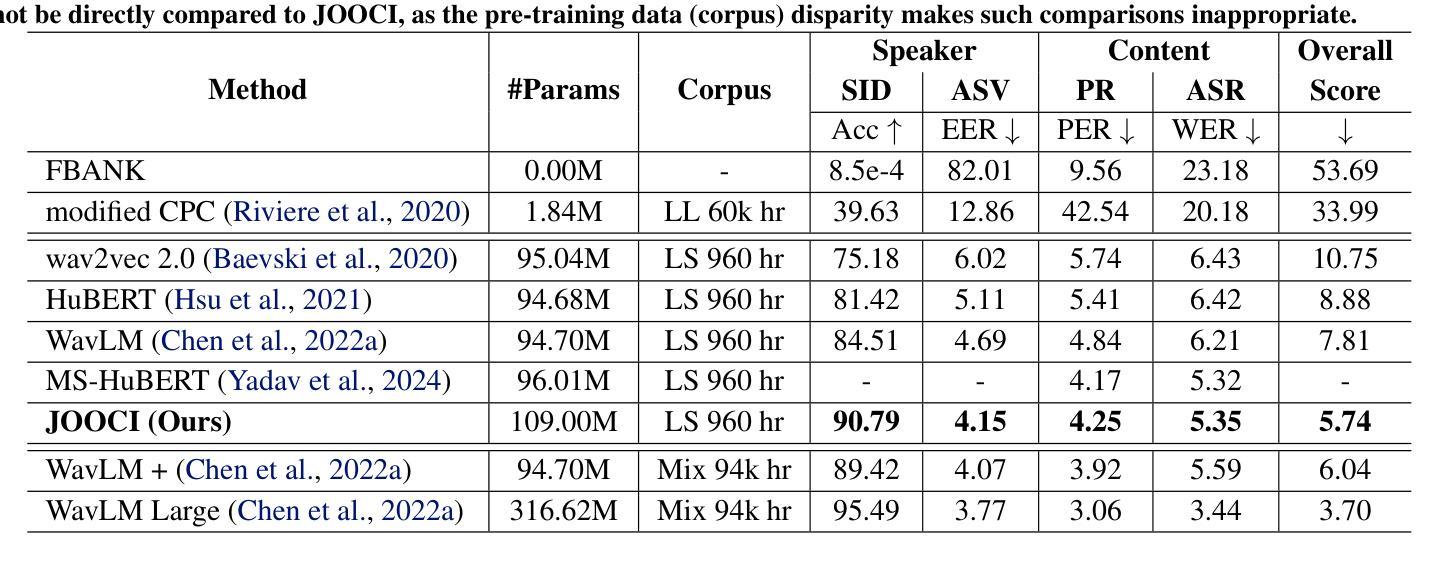
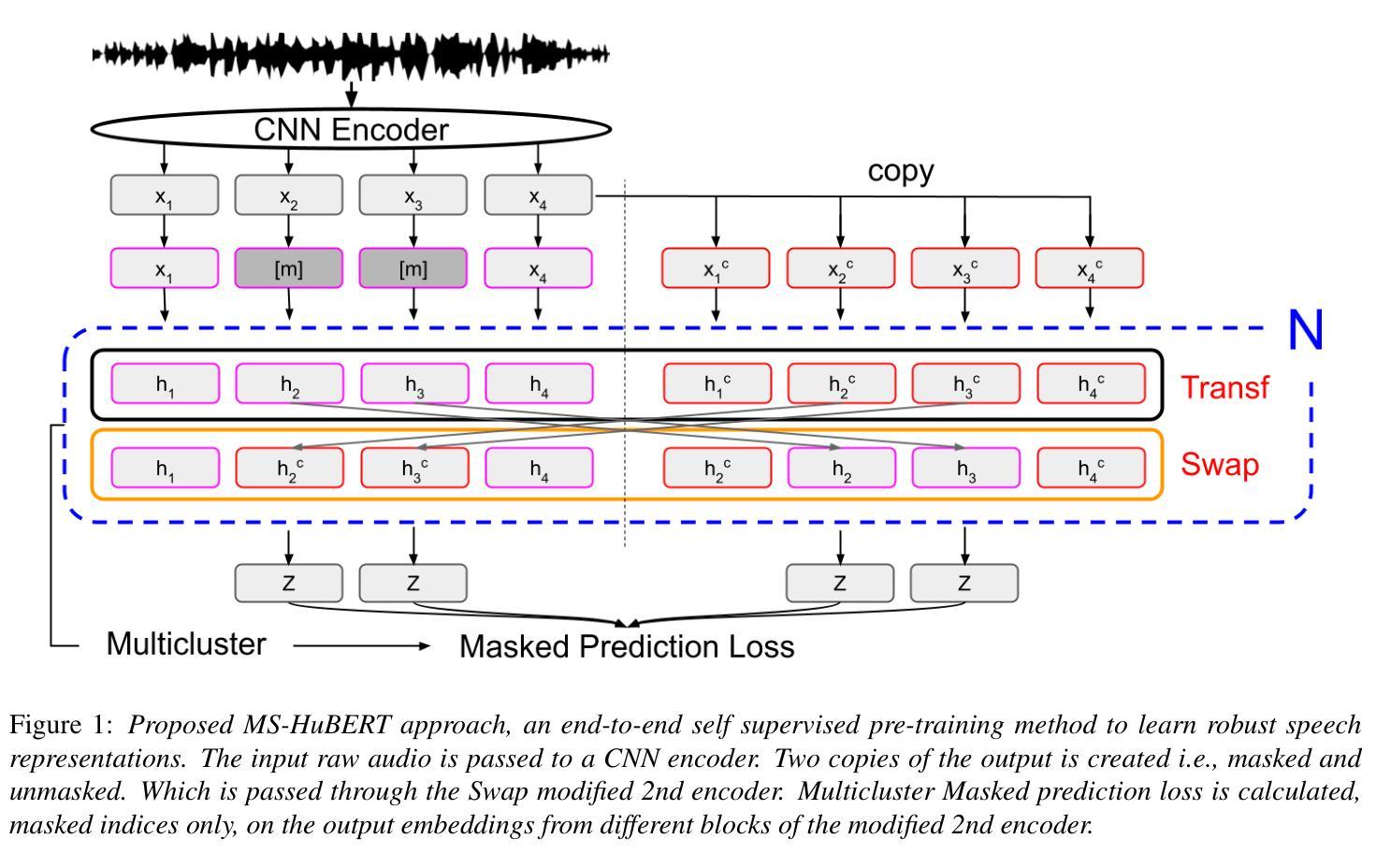
MS-HuBERT: Mitigating Pre-training and Inference Mismatch in Masked Language Modelling methods for learning Speech Representations
Authors:Hemant Yadav, Sunayana Sitaram, Rajiv Ratn Shah
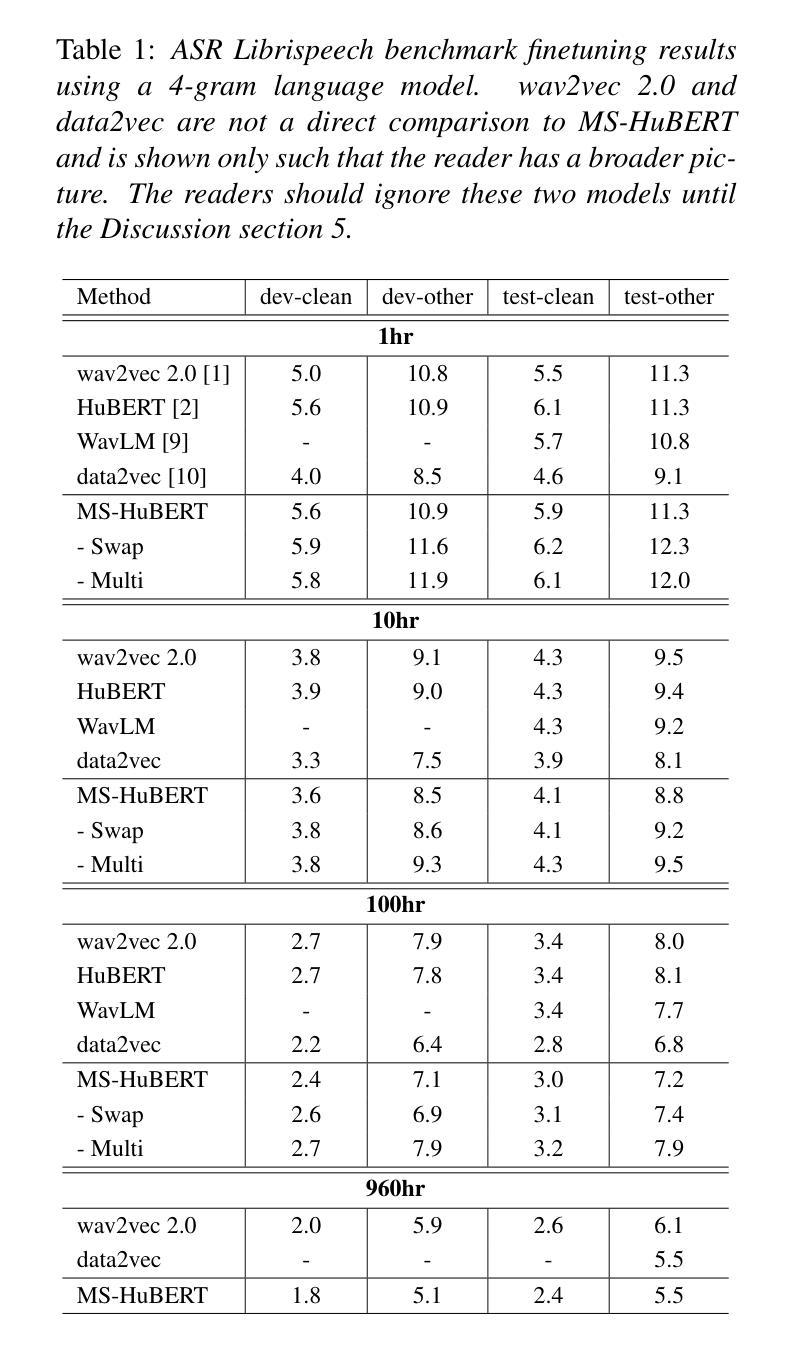
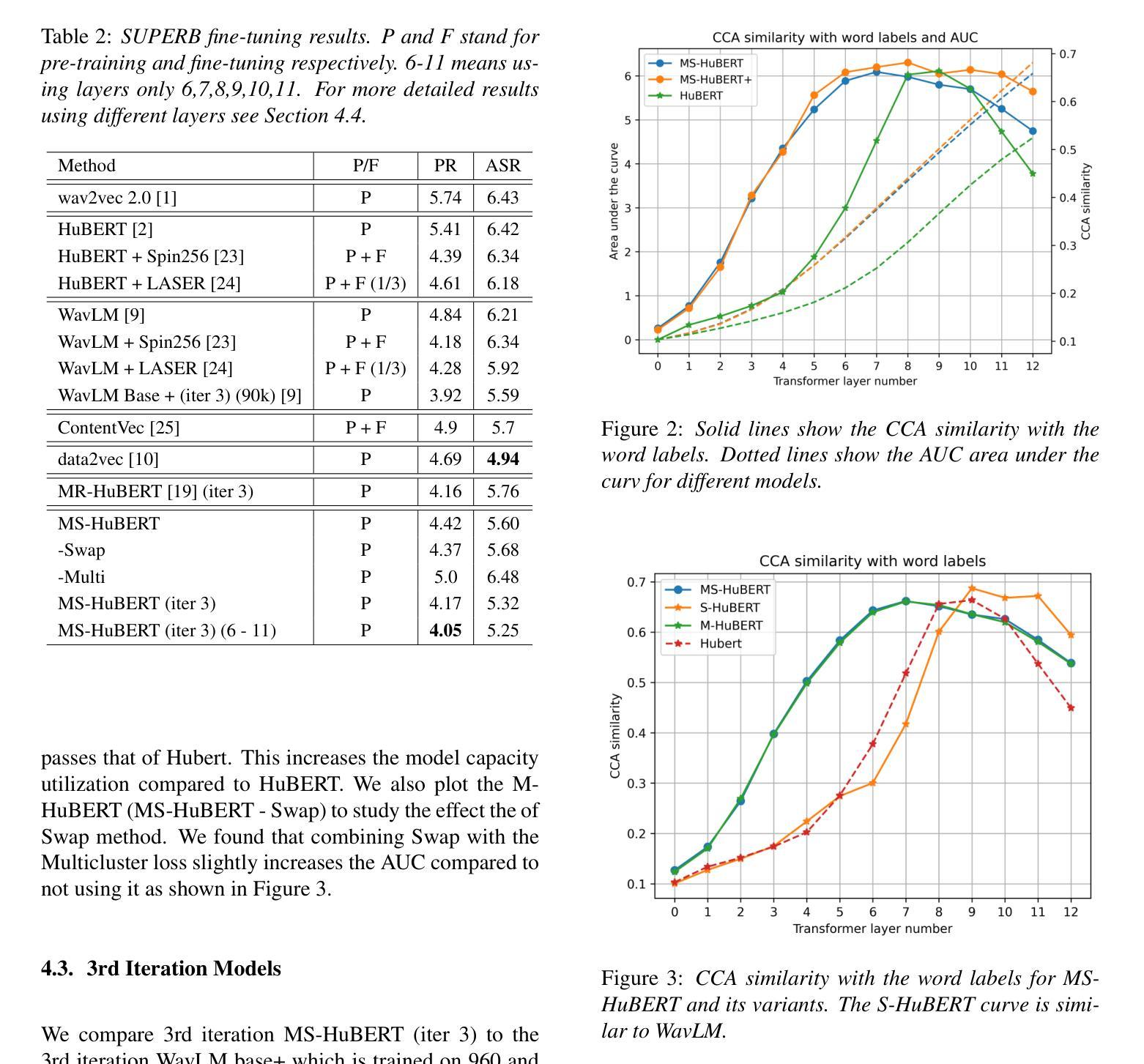
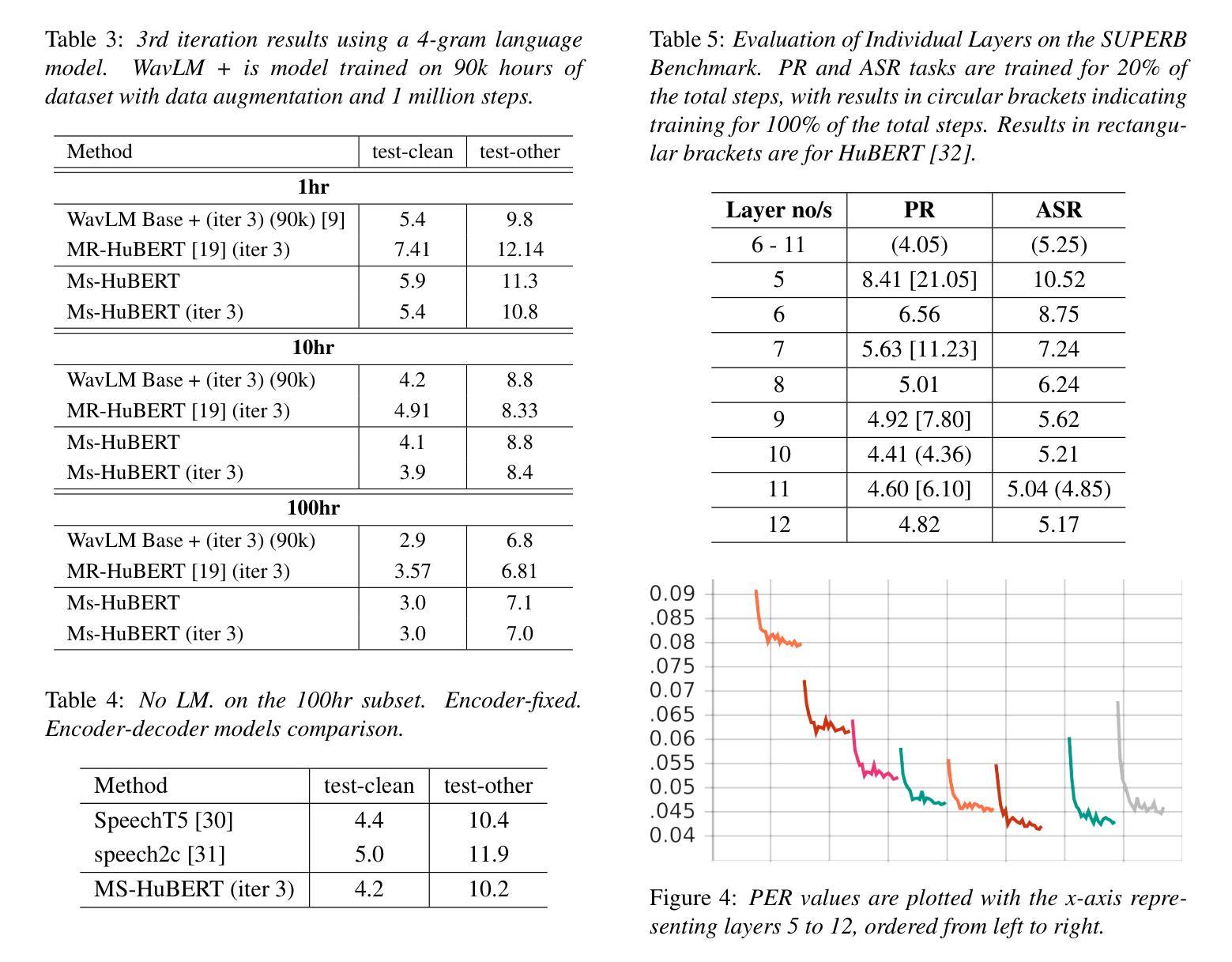
In recent years, self-supervised pre-training methods have gained significant traction in learning high-level information from raw speech. Among these methods, HuBERT has demonstrated SOTA performance in automatic speech recognition (ASR). However, HuBERT’s performance lags behind data2vec due to disparities in pre-training strategies. In this paper, we propose (i) a Swap method to address pre-training and inference mismatch observed in HuBERT and (ii) incorporates Multicluster masked prediction loss for more effective utilization of the models capacity. The resulting method is, MS-HuBERT, an end-to-end self-supervised pre-training method for learning robust speech representations. It beats vanilla HuBERT on the ASR Librispeech benchmark on average by a 5% margin when evaluated on different finetuning splits. Additionally, we demonstrate that the learned embeddings obtained during pre-training encode essential information for improving performance of content based tasks such as ASR.
近年来,自监督预训练方法在从原始语音中学习高级信息方面获得了很大的关注。在这些方法中,HuBERT在自动语音识别(ASR)方面表现出了顶尖的性能。然而,由于预训练策略的差异,HuBERT的性能落后于data2vec。在本文中,我们提出了(i)一种Swap方法,以解决HuBERT中观察到的预训练和推理不匹配的问题;(ii)并融合了多聚类掩码预测损失,以更有效地利用模型容量。由此产生的方法是MS-HuBERT,它是一种端到端的自监督预训练方法,用于学习稳健的语音表示。在针对不同微调分割的评估中,它在ASR Librispeech基准测试上平均击败了原版HuBERT,提升了5%的准确率。此外,我们还证明,在预训练过程中学到的嵌入编码包含重要信息,可改进基于内容的任务(如ASR)的性能。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 4 pages, submitted to interspeech2024
Summary
本文提出一种名为MS-HuBERT的端到端自监督预训练方法,用于学习稳健的语音表示。该方法通过解决HuBERT在预训练和推理过程中的不匹配问题,并结合多簇掩码预测损失,实现了对HuBERT模型的改进。在ASR Librispeech基准测试中,MS-HuBERT相较于原始HuBERT有5%的平均提升。同时,预训练过程中学到的嵌入信息对于提高基于内容的任务(如ASR)的性能至关重要。
Key Takeaways
- 自监督预训练方法在语音学习中受到广泛关注,其中HuBERT在语音识别方面表现出卓越性能。
- HuBERT在预训练和推理方面存在不匹配问题,导致性能下降。
- MS-HuBERT方法通过解决这种不匹配问题并结合多簇掩码预测损失,有效提升了HuBERT的性能。
- MS-HuBERT在ASR Librispeech基准测试中的表现优于原始HuBERT,平均提升5%。
- 预训练过程中学到的嵌入信息对于提高基于内容任务的性能至关重要。
- MS-HuBERT是一个端到端的自监督预训练方法,适用于学习稳健的语音表示。
点此查看论文截图