⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-02-21 更新
Secure and Efficient Watermarking for Latent Diffusion Models in Model Distribution Scenarios
Authors:Liangqi Lei, Keke Gai, Jing Yu, Liehuang Zhu, Qi Wu
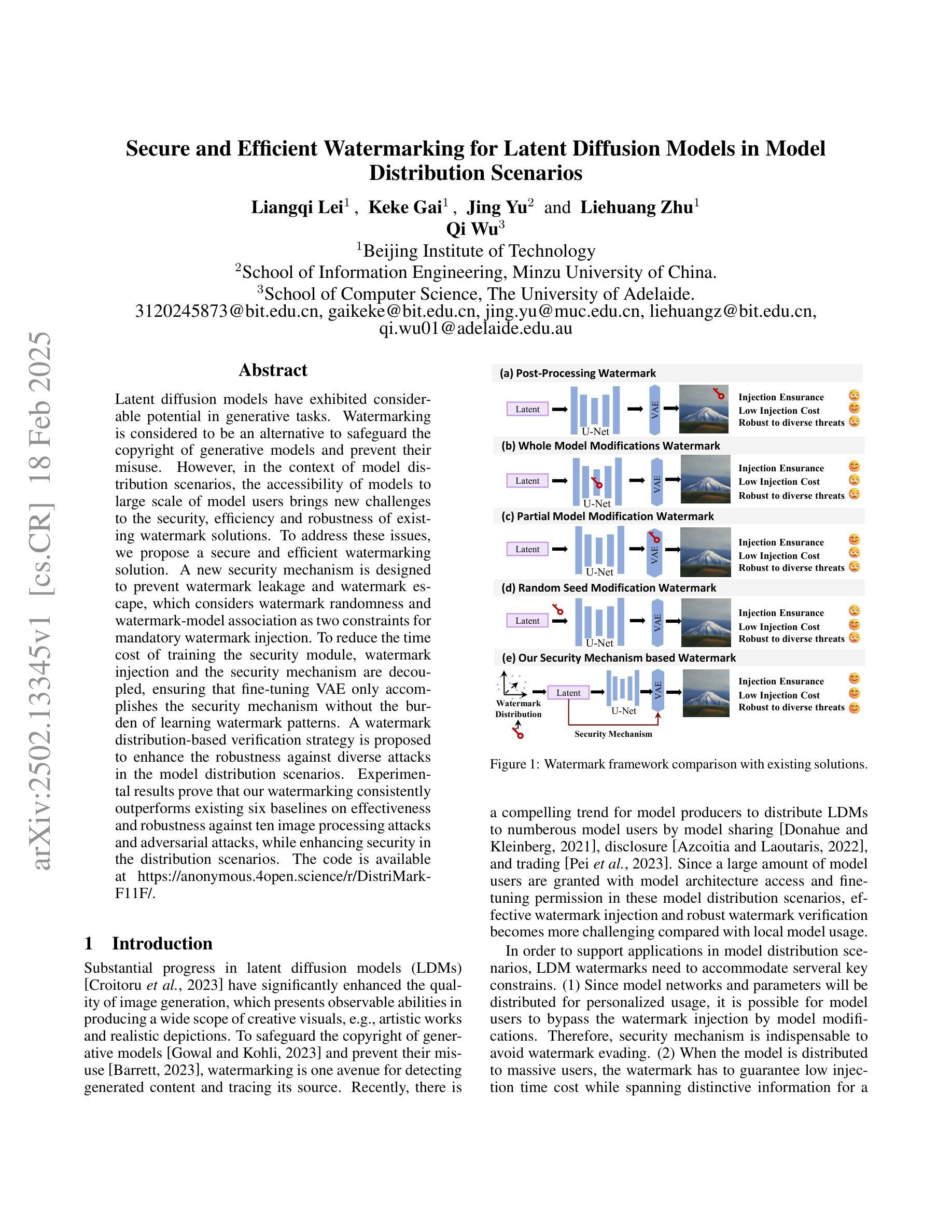
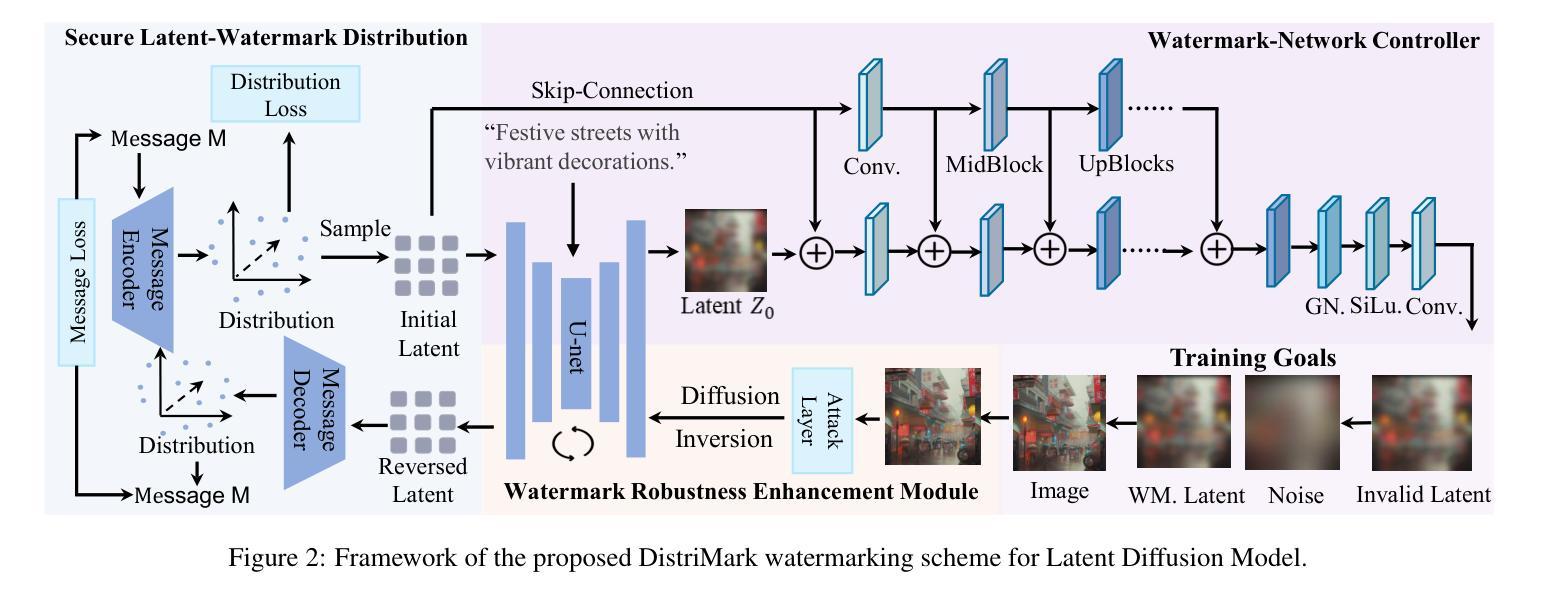
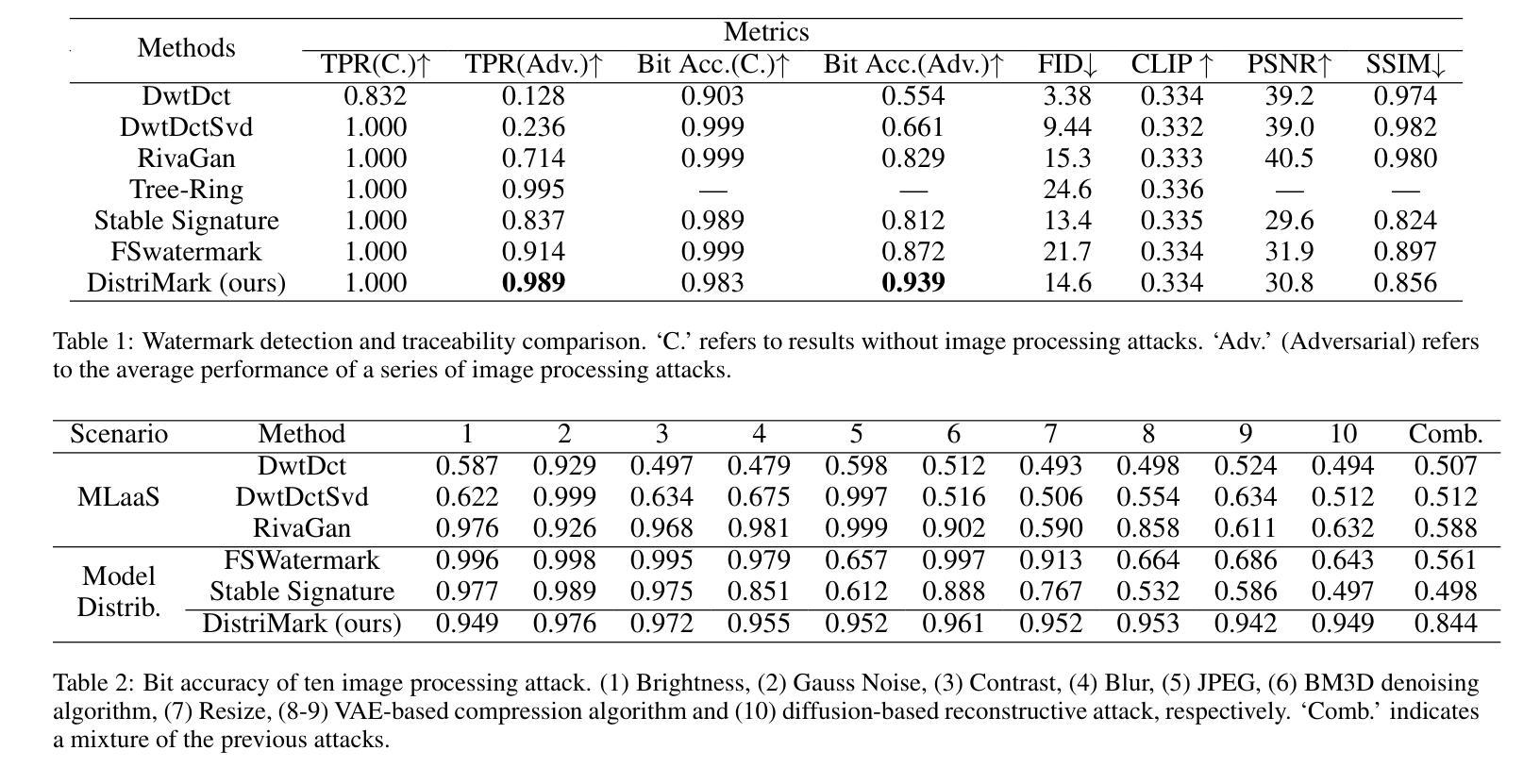
Latent diffusion models have exhibited considerable potential in generative tasks. Watermarking is considered to be an alternative to safeguard the copyright of generative models and prevent their misuse. However, in the context of model distribution scenarios, the accessibility of models to large scale of model users brings new challenges to the security, efficiency and robustness of existing watermark solutions. To address these issues, we propose a secure and efficient watermarking solution. A new security mechanism is designed to prevent watermark leakage and watermark escape, which considers watermark randomness and watermark-model association as two constraints for mandatory watermark injection. To reduce the time cost of training the security module, watermark injection and the security mechanism are decoupled, ensuring that fine-tuning VAE only accomplishes the security mechanism without the burden of learning watermark patterns. A watermark distribution-based verification strategy is proposed to enhance the robustness against diverse attacks in the model distribution scenarios. Experimental results prove that our watermarking consistently outperforms existing six baselines on effectiveness and robustness against ten image processing attacks and adversarial attacks, while enhancing security in the distribution scenarios.
潜在扩散模型在生成任务中展现出了巨大的潜力。水印被视为保护生成模型版权并防止其被滥用的替代方案。然而,在模型分发场景中,模型对大量用户的可访问性给现有水印解决方案的安全性、效率和稳健性带来了新的挑战。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了一种安全高效的水印解决方案。设计了一种新的安全机制,以防止水印泄露和水印逃逸,该机制将水印随机性和水印与模型的关联作为强制水印注入的两个约束条件。为了减少训练安全模块的时间成本,我们将水印注入与安全机制解耦,确保微调VAE只完成安全机制,而无需学习水印模式的负担。提出了一种基于水印分布的策略,以提高模型分发场景中各种攻击的稳健性。实验结果表明,我们的水印在有效性和对十种图像处理攻击和对抗性攻击的稳健性方面始终优于现有的六种基线方法,同时提高了分发场景中的安全性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
潜在扩散模型在生成任务中展现出巨大潜力,而水印技术用于保护生成模型的版权并防止滥用。但在模型分发场景下,模型的大规模用户访问给现有水印解决方案的安全性、效率和稳健性带来新挑战。为此,我们提出了一种安全高效的水印解决方案,设计新的安全机制防止水印泄露和逃逸,以水印随机性和水印与模型的关联为强制注入的两个约束。为提高安全模块训练的时间成本,将水印注入与安全机制解耦,确保微调VAE只实现安全机制,无需学习水印模式。提出基于水印分布的验证策略,提高模型分发场景中对抗各种攻击的稳健性。实验证明,我们的水印技术在有效性、对抗十种图像处理攻击和对抗攻击的稳健性方面优于现有六种基线技术,同时在分发场景中提高安全性。
Key Takeaways
- 潜在扩散模型在生成任务中有巨大潜力,但版权保护面临挑战。
- 水印技术用于保护生成模型的版权并防止滥用。
- 模型分发场景下,大规模用户访问给水印解决方案带来新挑战。
- 提出一种安全高效的水印解决方案,包括设计新的安全机制防止水印泄露和逃逸。
- 水印随机性和水印与模型的关联是强制水印注入的两个重要约束。
- 将水印注入与安全机制解耦,以提高训练效率。
点此查看论文截图

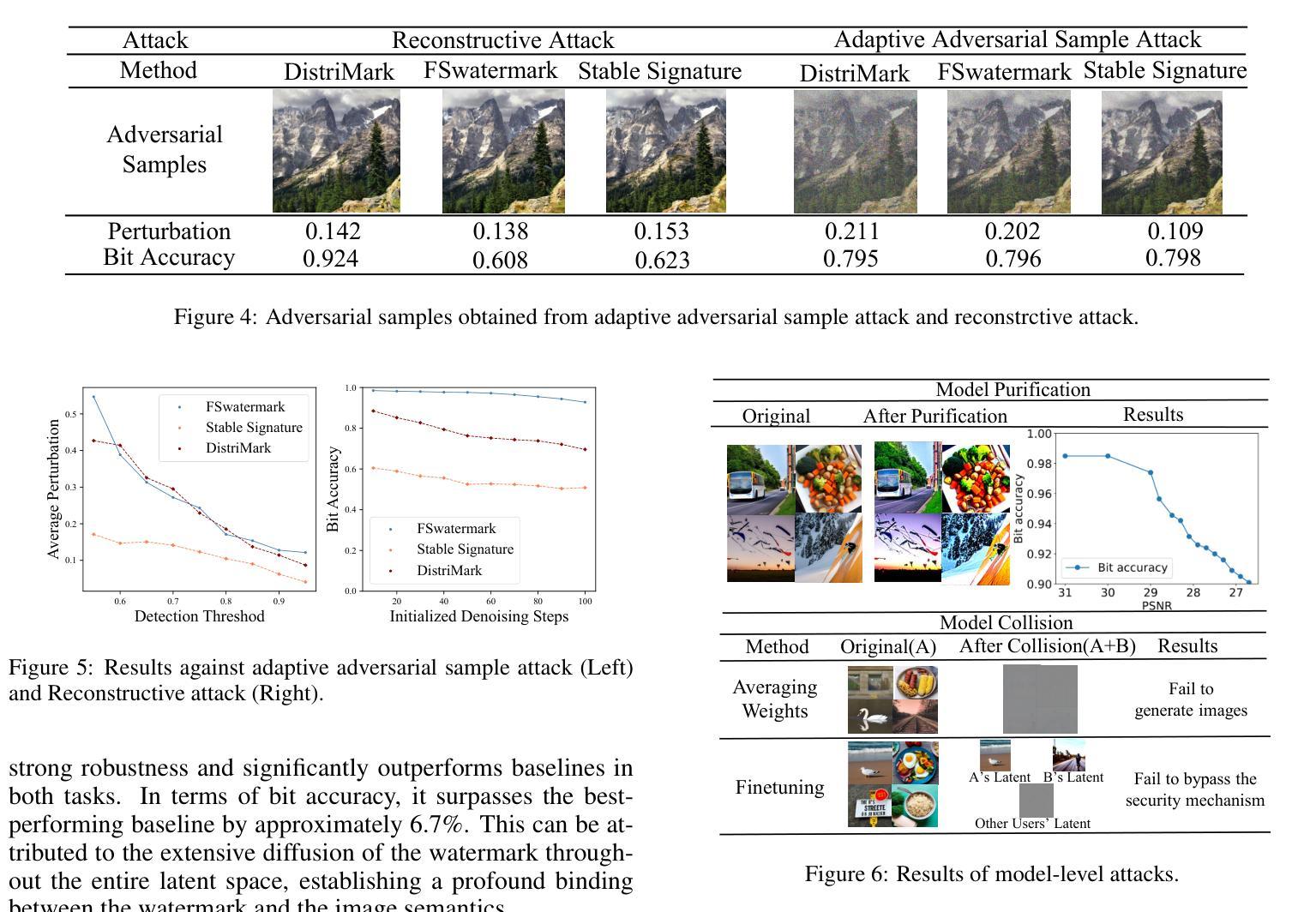
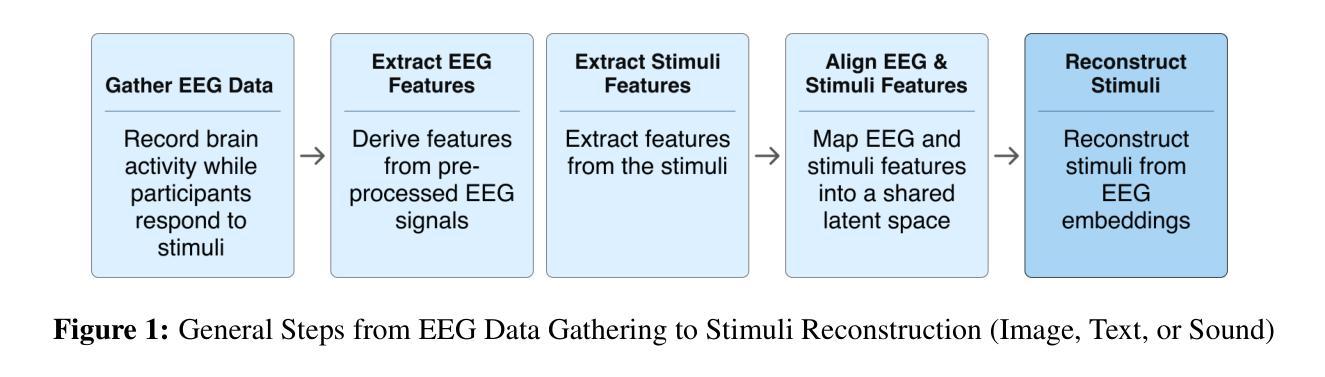
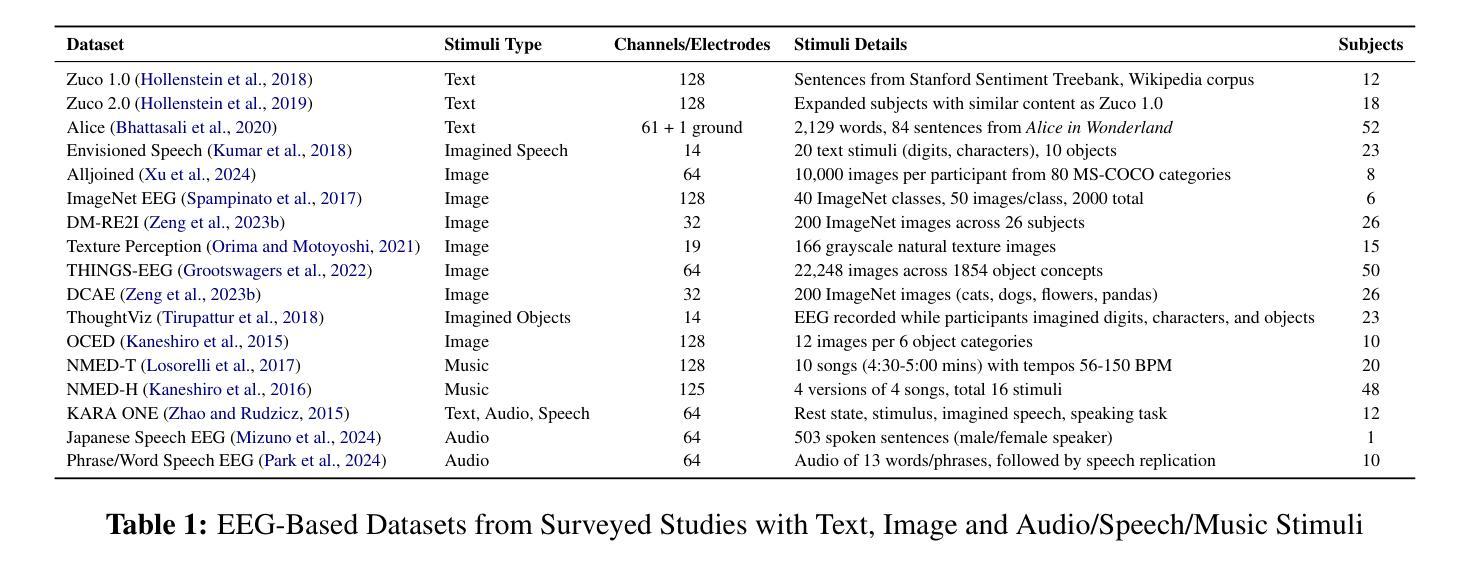
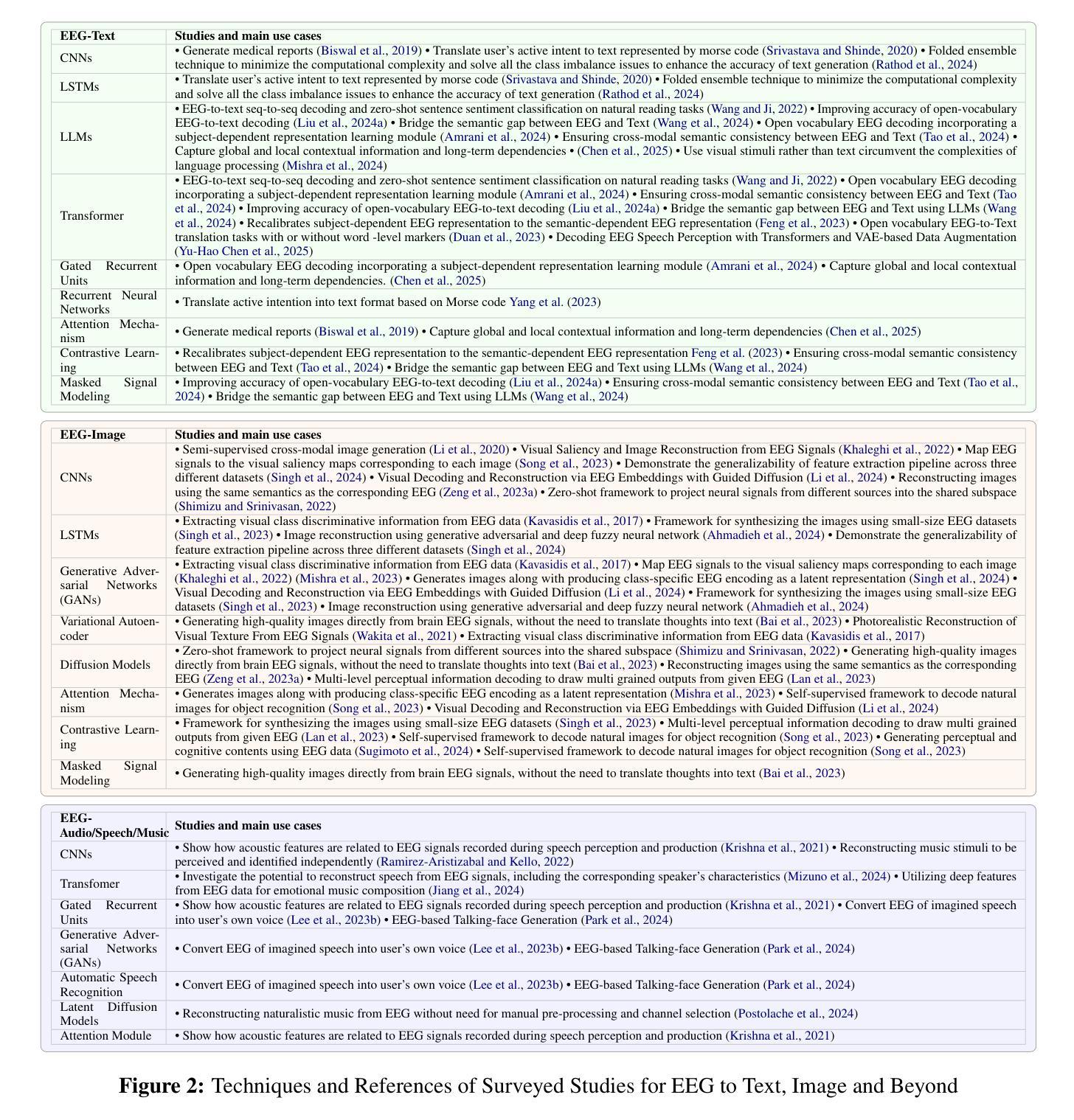
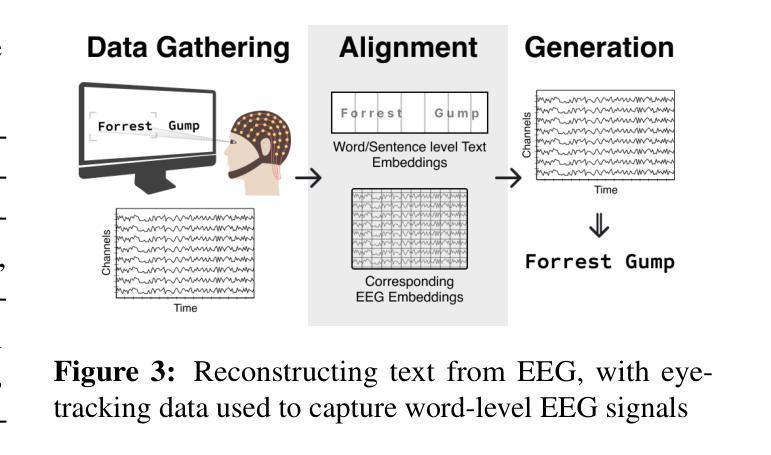
A Survey on Bridging EEG Signals and Generative AI: From Image and Text to Beyond
Authors:Shreya Shukla, Jose Torres, Abhijit Mishra, Jacek Gwizdka, Shounak Roychowdhury
Integration of Brain-Computer Interfaces (BCIs) and Generative Artificial Intelligence (GenAI) has opened new frontiers in brain signal decoding, enabling assistive communication, neural representation learning, and multimodal integration. BCIs, particularly those leveraging Electroencephalography (EEG), provide a non-invasive means of translating neural activity into meaningful outputs. Recent advances in deep learning, including Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) and Transformer-based Large Language Models (LLMs), have significantly improved EEG-based generation of images, text, and speech. This paper provides a literature review of the state-of-the-art in EEG-based multimodal generation, focusing on (i) EEG-to-image generation through GANs, Variational Autoencoders (VAEs), and Diffusion Models, and (ii) EEG-to-text generation leveraging Transformer based language models and contrastive learning methods. Additionally, we discuss the emerging domain of EEG-to-speech synthesis, an evolving multimodal frontier. We highlight key datasets, use cases, challenges, and EEG feature encoding methods that underpin generative approaches. By providing a structured overview of EEG-based generative AI, this survey aims to equip researchers and practitioners with insights to advance neural decoding, enhance assistive technologies, and expand the frontiers of brain-computer interaction.
脑机接口(BCI)与生成式人工智能(GenAI)的融合为脑信号解码开辟了新的领域,实现了辅助通信、神经表征学习和多模态融合。特别是利用脑电图(EEG)的脑机接口,提供了一种将神经活动转化为有意义输出的非侵入性手段。深度学习领域的最新进展,包括生成对抗网络(GANs)和基于Transformer的大型语言模型(LLMs),显著提高了基于EEG的图像、文本和语音生成能力。本文综述了基于EEG的多模态生成的最新进展,重点关注(i)通过GANs、变分自动编码器(VAEs)和扩散模型实现EEG到图像生成,以及(ii)利用基于Transformer的语言模型和对比学习方法实现EEG到文本生成。此外,我们还讨论了新兴的EEG到语音合成领域,这是一个不断发展的多模态前沿领域。本文重点介绍了关键数据集、用例、挑战和支撑生成方法的EEG特征编码方法。通过对基于EEG的生成式人工智能进行结构化概述,本综述旨在为研究人员和实践者提供洞察,以促进神经解码的发展,提高辅助技术的性能,并拓展脑机交互的边界。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
脑机接口(BCI)与生成式人工智能(GenAI)的融合为脑信号解码开创了新领域,推动了辅助通信、神经表征学习和多模式融合的发展。脑电图(EEG)为基础的BCI为非侵入式地转化神经活动为有意义输出提供了手段。深度学习领域的最新进展,包括生成对抗网络(GANs)、基于Transformer的大型语言模型(LLMs)等,已显著改善基于EEG的图像、文本和语音生成。本文综述了EEG基多模式生成的最新进展,包括EEG转图像生成和EEG转文本生成,并探讨了新兴的EEG语音合成领域。通过提供EEG基生成式AI的结构性概览,旨在为研究者和实践者提供洞察,以推动神经解码、辅助技术发展和拓展脑机交互的边界。
Key Takeaways
- BCI与GenAI的融合为脑信号解码带来新突破,促进辅助通信和神经表征学习的发展。
- EEG为非侵入式地转化神经活动提供手段,结合最新深度学习技术实现图像、文本和语音的生成。
- GANs、LLMs等深度学习技术在EEG基生成领域有显著改善。
- EEG转图像生成领域包括GANs、VAEs和Diffusion Models等技术。
- EEG转文本生成结合了基于Transformer的语言模型和对比学习方法。
- EEG语音合成是一个新兴且快速发展的多模式领域。
点此查看论文截图

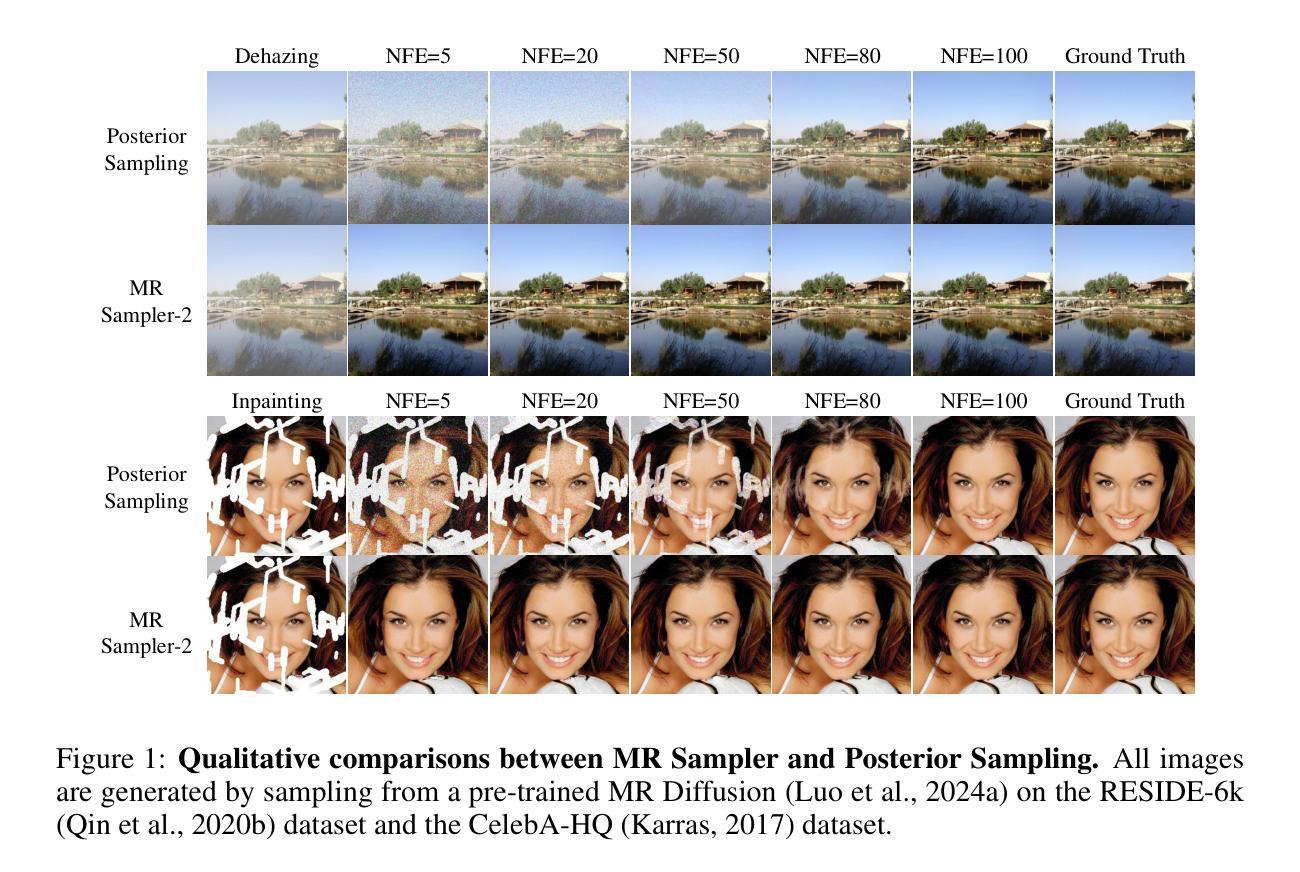
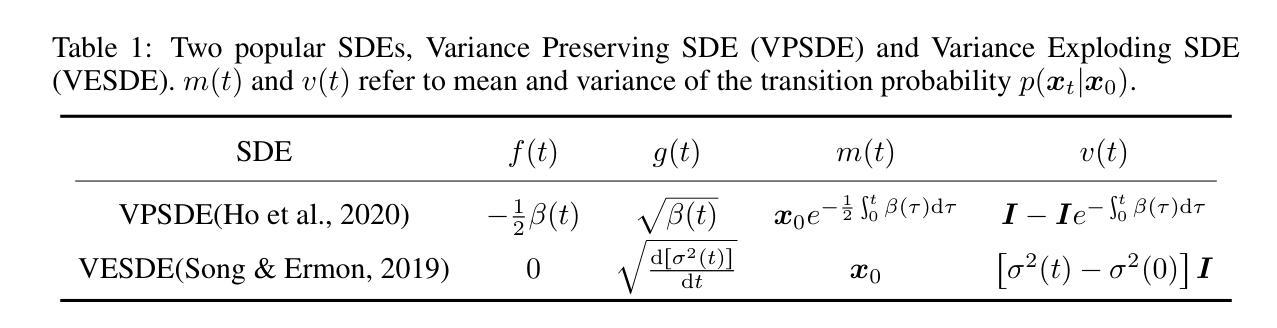
MRS: A Fast Sampler for Mean Reverting Diffusion based on ODE and SDE Solvers
Authors:Ao Li, Wei Fang, Hongbo Zhao, Le Lu, Ge Yang, Minfeng Xu
In applications of diffusion models, controllable generation is of practical significance, but is also challenging. Current methods for controllable generation primarily focus on modifying the score function of diffusion models, while Mean Reverting (MR) Diffusion directly modifies the structure of the stochastic differential equation (SDE), making the incorporation of image conditions simpler and more natural. However, current training-free fast samplers are not directly applicable to MR Diffusion. And thus MR Diffusion requires hundreds of NFEs (number of function evaluations) to obtain high-quality samples. In this paper, we propose a new algorithm named MRS (MR Sampler) to reduce the sampling NFEs of MR Diffusion. We solve the reverse-time SDE and the probability flow ordinary differential equation (PF-ODE) associated with MR Diffusion, and derive semi-analytical solutions. The solutions consist of an analytical function and an integral parameterized by a neural network. Based on this solution, we can generate high-quality samples in fewer steps. Our approach does not require training and supports all mainstream parameterizations, including noise prediction, data prediction and velocity prediction. Extensive experiments demonstrate that MR Sampler maintains high sampling quality with a speedup of 10 to 20 times across ten different image restoration tasks. Our algorithm accelerates the sampling procedure of MR Diffusion, making it more practical in controllable generation.
在扩散模型的应用中,可控生成具有实际意义,但也具有挑战性。当前的可控生成方法主要集中在修改扩散模型的评分函数,而均值回归(MR)扩散则直接修改随机微分方程(SDE)的结构,使得融入图像条件更加简单自然。然而,现有的无训练快速采样器并不直接适用于MR扩散。因此,MR扩散需要数百个功能评估(NFE)来获得高质量样本。在本文中,我们提出了一种名为MRS(MR采样器)的新算法,以减少MR扩散的采样NFE。我们解决了反向时间SDE和与MR扩散相关的概率流常微分方程(PF-ODE),并得出半解析解。这些解决方案由一个分析函数和一个由神经网络参数化的积分组成。基于这个解决方案,我们可以以更少的步骤生成高质量的样本。我们的方法不需要训练,支持包括噪声预测、数据预测和速度预测在内的所有主流参数化方法。大量实验表明,MR采样器在10个不同的图像恢复任务中保持了高采样质量,速度提升了10到20倍。我们的算法加速了MR扩散的采样过程,使其在可控生成中更加实用。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by ICLR 2025
Summary:本论文提出一种新的算法MRS来解决MR扩散模型中遇到的训练问题。通过对逆向时间随机微分方程和概率流常微分方程进行求解,得到半解析解,包括一个由神经网络参数化的积分。基于这个解,我们能够在较少的步骤内生成高质量样本,从而加速MR扩散模型的采样过程,使其在实际可控生成中更具实用性。
Key Takeaways:
- MR扩散模型通过直接修改随机微分方程的结构,简化了图像条件的引入。
- 当前的无训练快速采样器无法直接应用于MR扩散模型。
- MR采样器(MRS)被提出来解决MR扩散模型的采样问题,通过减少所需的函数评估次数(NFEs)来提高效率。
- MRS通过对逆向时间SDE和PF-ODE的解决,得到半解析解,该解包括一个解析函数和一个由神经网络参数化的积分。
- MRS算法无需训练,支持主流的参数化方法,包括噪声预测、数据预测和速度预测。
- 实验表明,MR采样器在10个不同的图像恢复任务中,保持高采样质量的同时实现了10到20倍的速度提升。
点此查看论文截图

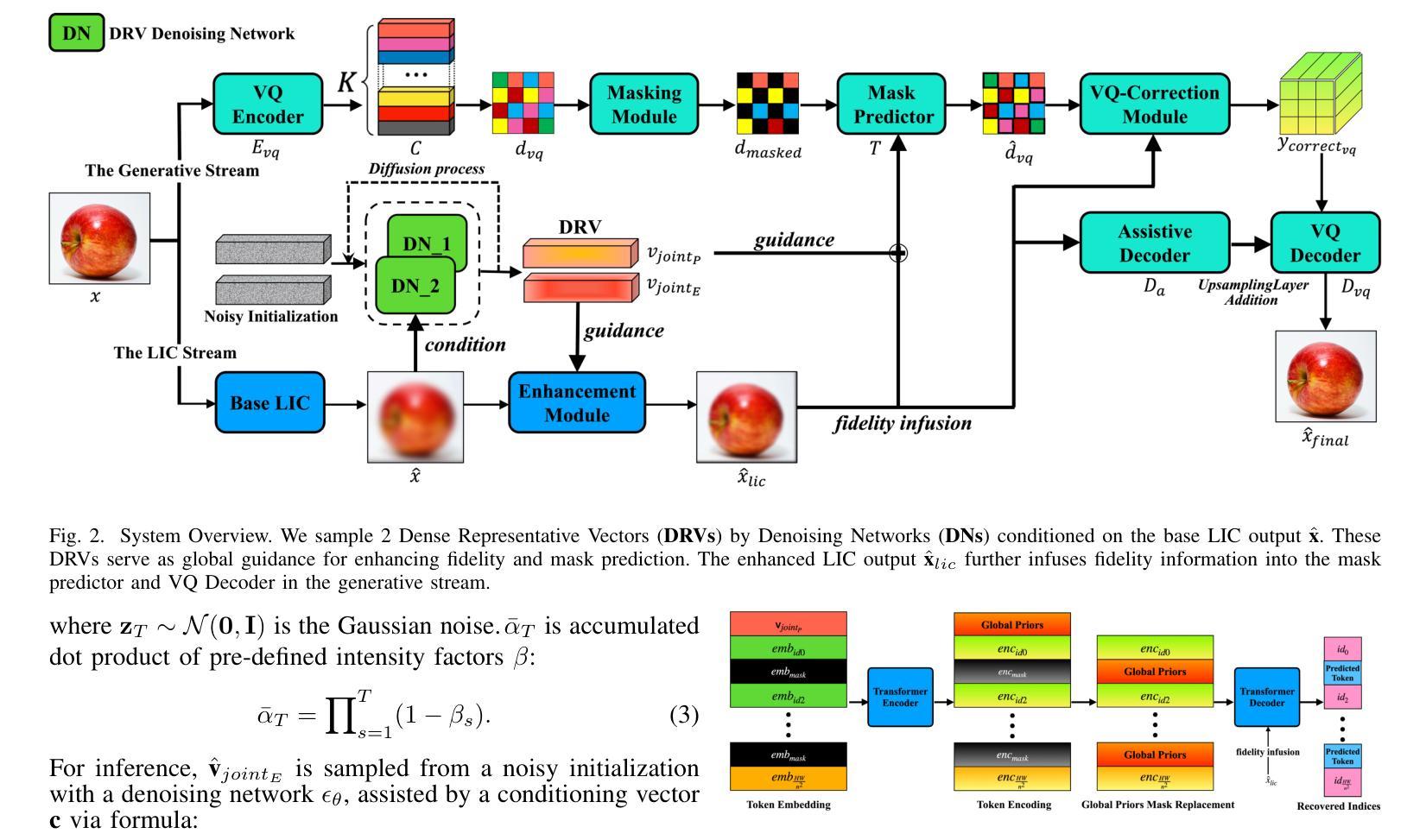
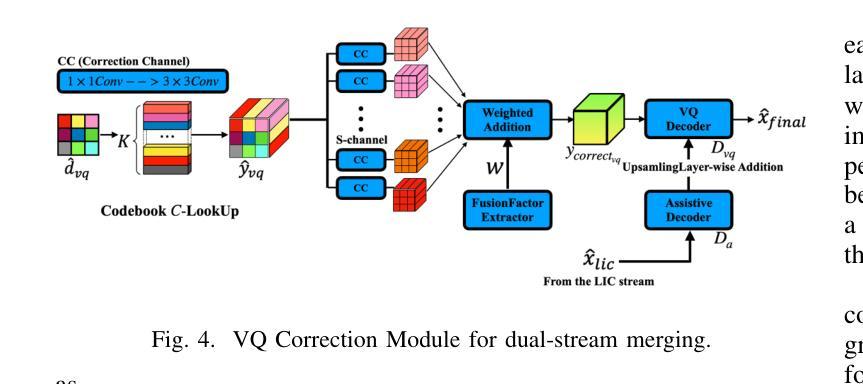
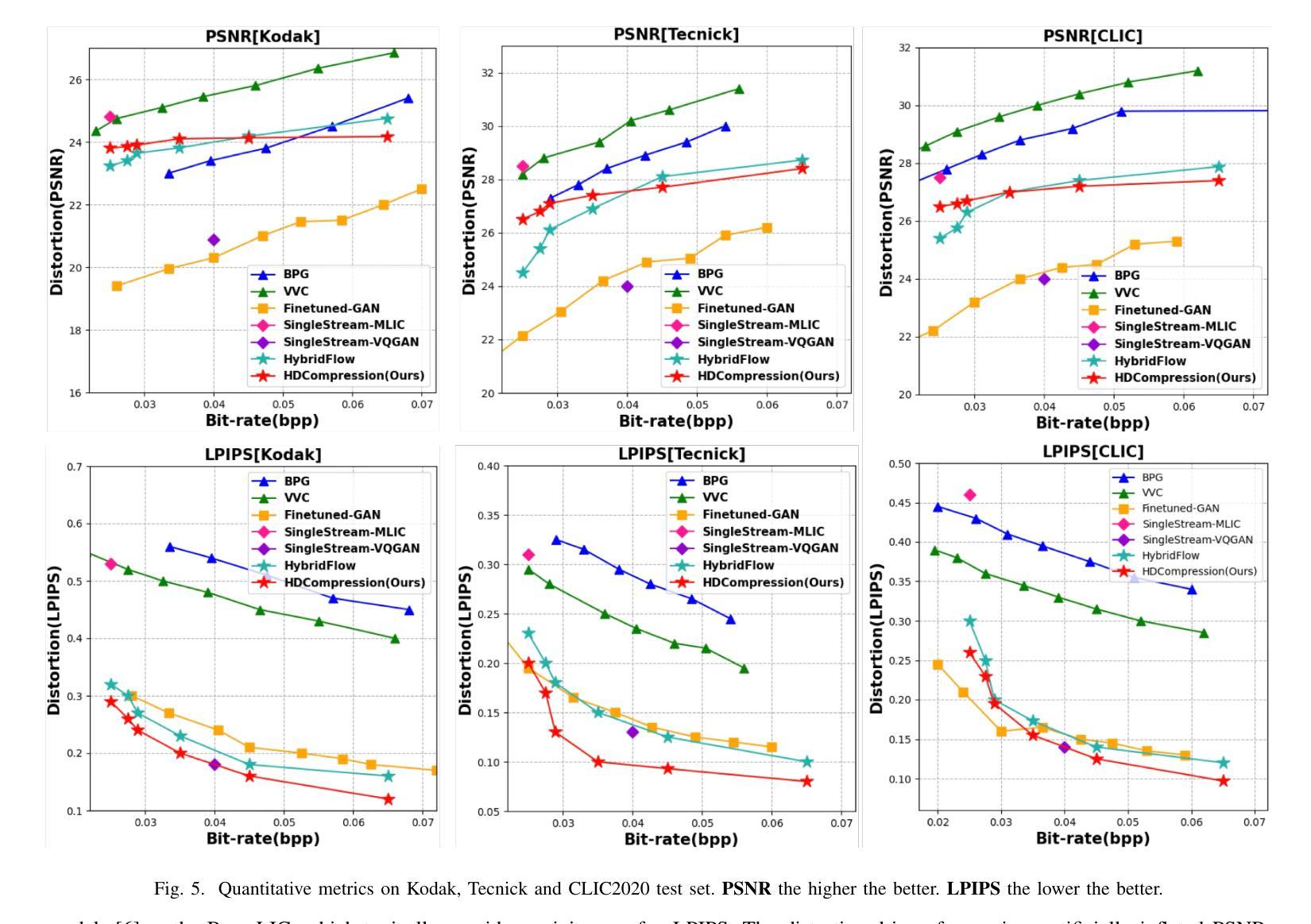
HDCompression: Hybrid-Diffusion Image Compression for Ultra-Low Bitrates
Authors:Lei Lu, Yize Li, Yanzhi Wang, Wei Wang, Wei Jiang
Image compression under ultra-low bitrates remains challenging for both conventional learned image compression (LIC) and generative vector-quantized (VQ) modeling. Conventional LIC suffers from severe artifacts due to heavy quantization, while generative VQ modeling gives poor fidelity due to the mismatch between learned generative priors and specific inputs. In this work, we propose Hybrid-Diffusion Image Compression (HDCompression), a dual-stream framework that utilizes both generative VQ-modeling and diffusion models, as well as conventional LIC, to achieve both high fidelity and high perceptual quality. Different from previous hybrid methods that directly use pre-trained LIC models to generate low-quality fidelity-preserving information from heavily quantized latent, we use diffusion models to extract high-quality complimentary fidelity information from the ground-truth input, which can enhance the system performance in several aspects: improving indices map prediction, enhancing the fidelity-preserving output of the LIC stream, and refining conditioned image reconstruction with VQ-latent correction. In addition, our diffusion model is based on a dense representative vector (DRV), which is lightweight with very simple sampling schedulers. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our HDCompression outperforms the previous conventional LIC, generative VQ-modeling, and hybrid frameworks in both quantitative metrics and qualitative visualization, providing balanced robust compression performance at ultra-low bitrates.
在超低比特率下,图像压缩对于传统的图像压缩(LIC)和生成向量量化(VQ)建模仍然具有挑战性。传统LIC由于重度量化而产生严重伪影,而生成VQ建模由于生成的先验知识和特定输入之间的不匹配而导致保真度低。在这项工作中,我们提出了混合扩散图像压缩(HDCompression),这是一个双流框架,利用生成VQ建模和扩散模型以及传统LIC,以实现高保真和高感知质量。不同于之前直接使用预训练的LIC模型从重度量化的潜在数据中生成低质量保真度保持信息的混合方法,我们使用扩散模型从原始真实输入中提取高质量补充保真信息,可以在以下几个方面增强系统性能:改善索引映射预测,提高LIC流的保真度保持输出,以及通过VQ潜在校正进行条件图像重建。此外,我们的扩散模型基于密集代表性向量(DRV),具有轻量级和非常简单的采样调度器。大量实验表明,我们的HDCompression在定量指标和定性可视化方面均优于以前的传统LIC、生成VQ建模和混合框架,在超低比特率下提供了平衡的稳健压缩性能。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Under Review
Summary
本文提出一种名为Hybrid-Diffusion Image Compression(HDCompression)的压缩方法,结合了传统图像压缩(LIC)、生成向量量化(VQ)建模和扩散模型。相较于以往直接使用预训练的LIC模型生成低质量保真度信息的方法,HDCompression利用扩散模型从原始图像中提取高质量互补的保真信息,从而提高了系统性能,包括改进索引映射预测、增强LIC流的保真度保留输出以及细化条件图像重建的VQ潜在校正。此外,该方法的扩散模型基于轻量级的密集代表性向量(DRV),采样调度器非常简单。实验表明,HDCompression在定量指标和定性可视化方面都优于传统的LIC、生成VQ建模和混合框架,在超低比特率下实现了平衡的稳健压缩性能。
Key Takeaways
- 面临超低比特率下图像压缩的挑战,传统LIC和生成VQ建模都存在局限性。
- HDCompression结合了多种技术,包括生成VQ建模、扩散模型和传统LIC。
- HDCompression利用扩散模型从原始图像中提取高质量互补的保真信息。
- 扩散模型能提高系统性能,改进索引映射预测、增强LIC流的保真度保留输出以及细化条件图像重建。
- HDCompression基于轻量级的密集代表性向量(DRV)的扩散模型设计。
- 实验结果显示HDCompression在定量和定性评估上都优于其他方法。
点此查看论文截图


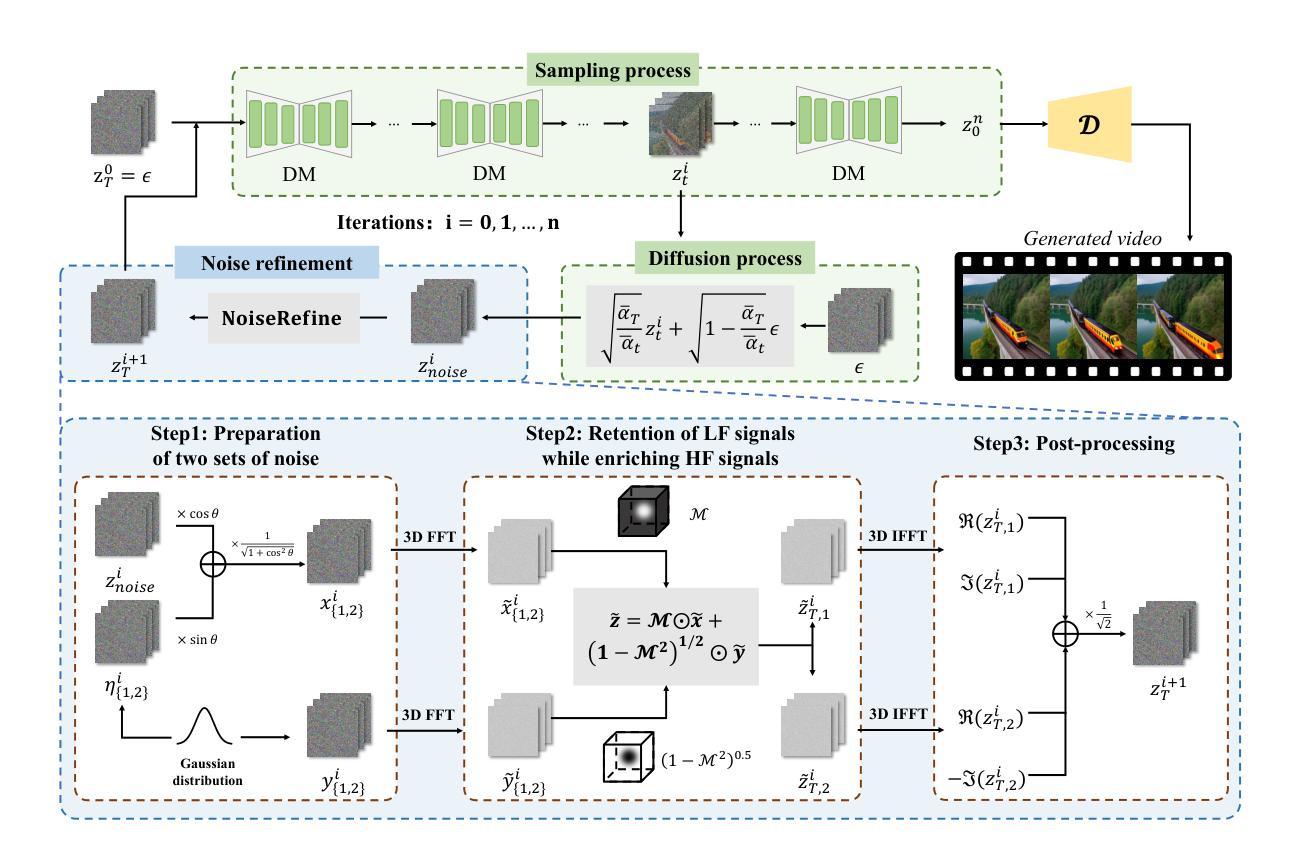
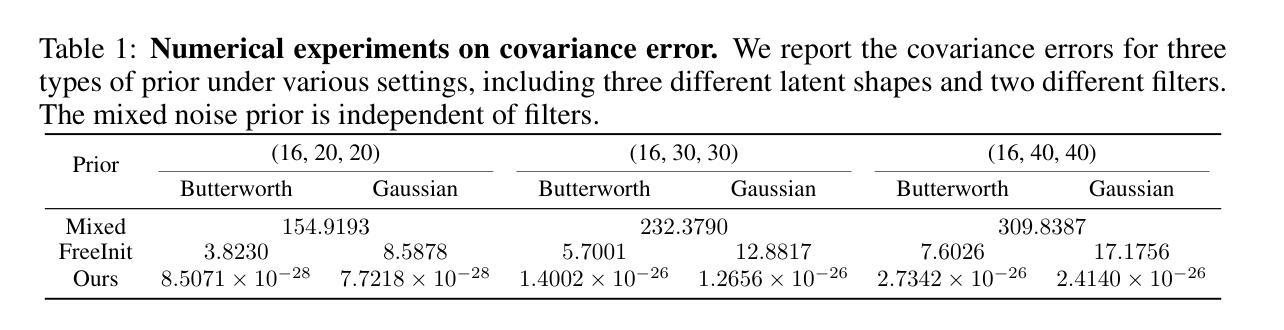
FreqPrior: Improving Video Diffusion Models with Frequency Filtering Gaussian Noise
Authors:Yunlong Yuan, Yuanfan Guo, Chunwei Wang, Wei Zhang, Hang Xu, Li Zhang
Text-driven video generation has advanced significantly due to developments in diffusion models. Beyond the training and sampling phases, recent studies have investigated noise priors of diffusion models, as improved noise priors yield better generation results. One recent approach employs the Fourier transform to manipulate noise, marking the initial exploration of frequency operations in this context. However, it often generates videos that lack motion dynamics and imaging details. In this work, we provide a comprehensive theoretical analysis of the variance decay issue present in existing methods, contributing to the loss of details and motion dynamics. Recognizing the critical impact of noise distribution on generation quality, we introduce FreqPrior, a novel noise initialization strategy that refines noise in the frequency domain. Our method features a novel filtering technique designed to address different frequency signals while maintaining the noise prior distribution that closely approximates a standard Gaussian distribution. Additionally, we propose a partial sampling process by perturbing the latent at an intermediate timestep during finding the noise prior, significantly reducing inference time without compromising quality. Extensive experiments on VBench demonstrate that our method achieves the highest scores in both quality and semantic assessments, resulting in the best overall total score. These results highlight the superiority of our proposed noise prior.
基于文本的视频生成由于扩散模型的发展而取得了显著的进步。除了训练和采样阶段,最近的研究还探索了扩散模型的噪声先验,因为改进的噪声先验会产生更好的生成结果。一种最近的方法使用傅里叶变换来操作噪声,标志着在此背景下对频率操作的初步探索。然而,它通常生成的视频缺乏运动动力和成像细节。在这项工作中,我们对现有方法中存在的方差衰减问题进行了全面的理论分析,这一问题导致了细节和运动动力的丧失。我们认识到噪声分布对生成质量的关键影响,因此引入了FreqPrior,这是一种新的噪声初始化策略,它在频率域中优化噪声。我们的方法采用了一种新型滤波技术,旨在处理不同的频率信号,同时保持噪声先验分布,紧密逼近标准高斯分布。此外,我们通过在中途寻找噪声先验时在潜在空间进行部分采样过程,扰动潜在空间,显著减少了推理时间,同时不妥协质量。在VBench上的广泛实验表明,我们的方法在质量和语义评估中都获得了最高分,总得分最高。这些结果凸显了我们所提出的噪声先验的优越性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICLR 2025
Summary
基于扩散模型的文本驱动视频生成技术取得显著进展。最新研究开始探索扩散模型的噪声先验,改进噪声先验可提升生成效果。本文提供了对现有的方差衰减问题的全面理论分析,影响了生成视频的细节和运动动力丢失问题。我们引入了FreqPrior,一种新颖的噪声初始化策略,在频率域对噪声进行精炼。此外,通过在寻找噪声先验过程中中间时刻扰动潜在变量,提出了部分采样过程,显著缩短了推理时间而不损失质量。实验证明,我们的方法在质量和语义评估上获得最高分,总体表现最佳。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型在文本驱动视频生成方面的显著进展得益于其噪声先验的研究和改进。
- 近期研究发现改进噪声先验有助于提高视频生成的品质。
- 现有方法存在方差衰减问题,导致生成视频缺乏运动动力学和成像细节。
- 本文全面分析了方差衰减问题,并指出噪声分布对生成质量的关键影响。
- 引入FreqPrior,一种新颖的噪声初始化策略,针对频率域进行噪声优化。
- 提出一种部分采样过程,通过中间时刻扰动潜在变量来缩短推理时间,同时保持高质量生成。
点此查看论文截图


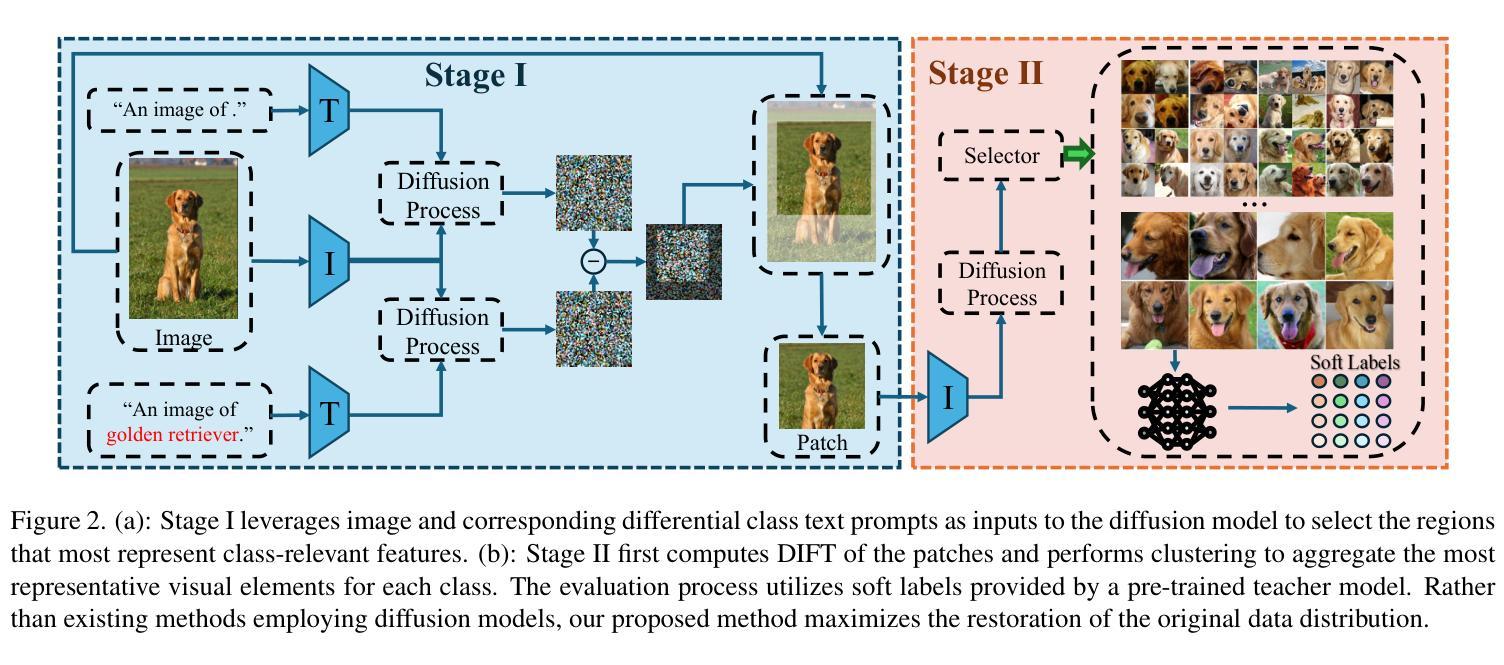
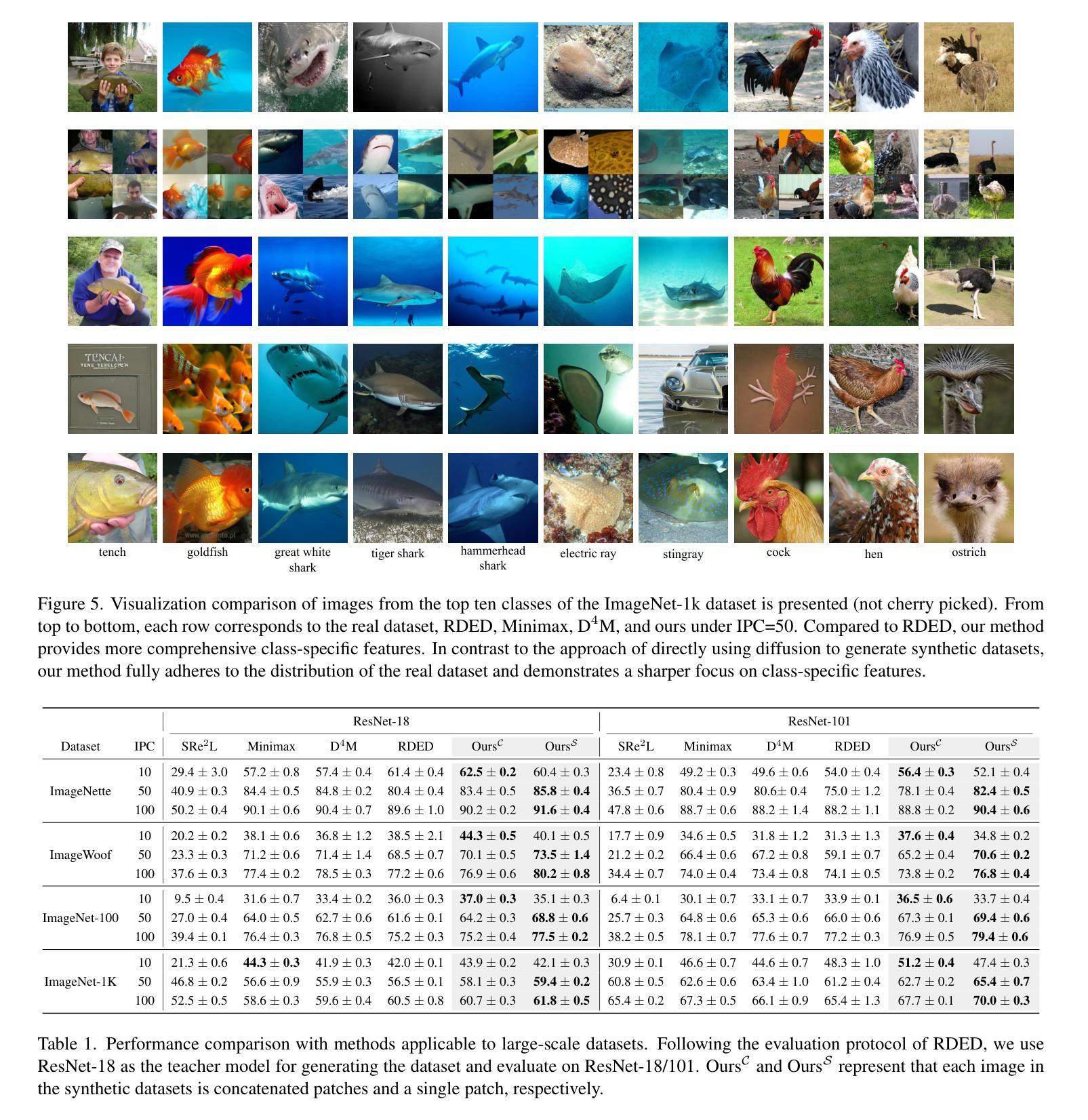
Efficient Dataset Distillation via Diffusion-Driven Patch Selection for Improved Generalization
Authors:Xinhao Zhong, Shuoyang Sun, Xulin Gu, Zhaoyang Xu, Yaowei Wang, Jianlong Wu, Bin Chen
Dataset distillation offers an efficient way to reduce memory and computational costs by optimizing a smaller dataset with performance comparable to the full-scale original. However, for large datasets and complex deep networks (e.g., ImageNet-1K with ResNet-101), the extensive optimization space limits performance, reducing its practicality. Recent approaches employ pre-trained diffusion models to generate informative images directly, avoiding pixel-level optimization and achieving notable results. However, these methods often face challenges due to distribution shifts between pre-trained models and target datasets, along with the need for multiple distillation steps across varying settings. To address these issues, we propose a novel framework orthogonal to existing diffusion-based distillation methods, leveraging diffusion models for selection rather than generation. Our method starts by predicting noise generated by the diffusion model based on input images and text prompts (with or without label text), then calculates the corresponding loss for each pair. With the loss differences, we identify distinctive regions of the original images. Additionally, we perform intra-class clustering and ranking on selected patches to maintain diversity constraints. This streamlined framework enables a single-step distillation process, and extensive experiments demonstrate that our approach outperforms state-of-the-art methods across various metrics.
数据集蒸馏提供了一种通过优化小型数据集来减少内存和计算成本的有效方法,其性能可与全尺寸原始数据集相当。然而,对于大型数据集和复杂的深度网络(例如,带有ResNet-101的ImageNet-1K),广泛的优化空间限制了性能,降低了其实用性。最近的方法采用预训练的扩散模型直接生成信息图像,避免了像素级的优化,并取得了显著的结果。然而,这些方法常常面临预训练模型和目标数据集之间分布转移的挑战,以及在不同设置下需要多次蒸馏步骤的问题。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了一种与现有基于扩散的蒸馏方法正交的新型框架,利用扩散模型进行选择而不是生成。我们的方法首先基于输入图像和文本提示(带有或不带标签文本)预测由扩散模型产生的噪声,然后计算每对相应的损失。通过损失差异,我们识别出原始图像的独特区域。此外,我们对选定的补丁进行类内聚类和排名,以保持多样性约束。这种简化的框架使单步蒸馏过程成为可能,大量实验表明,我们的方法在多种指标上超过了最先进的方法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Under Review
Summary
本文提出一种利用扩散模型进行选择而非生成的新框架,以解决现有蒸馏方法在处理大型数据集和复杂深度网络时的性能降低问题。该方法通过预测扩散模型生成的噪声来识别原始图像中的独特区域,并采用类内聚类与排名来保持多样性约束,实现单步蒸馏过程,并在各种指标上表现优异。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型在数据集蒸馏中的应用提供了新的优化思路。
- 传统蒸馏方法在处理大型数据集和复杂深度网络时存在性能限制。
- 本文提出的新框架利用扩散模型进行选择,而不是生成图像。
- 通过预测扩散模型生成的噪声和计算损失差异,识别原始图像中的独特区域。
- 框架采用类内聚类与排名来保持多样性约束。
- 实现了一种单步蒸馏过程,简化了流程并提高了效率。
点此查看论文截图



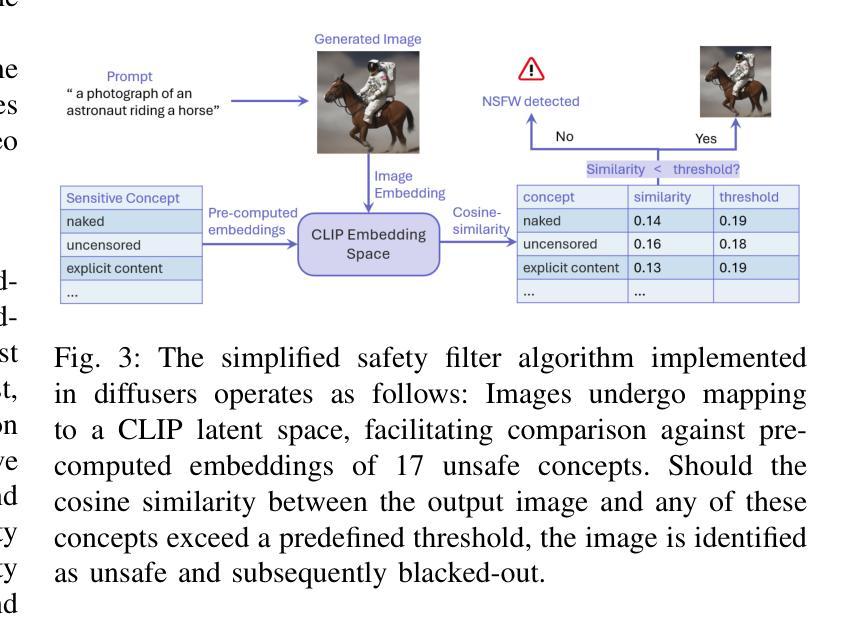
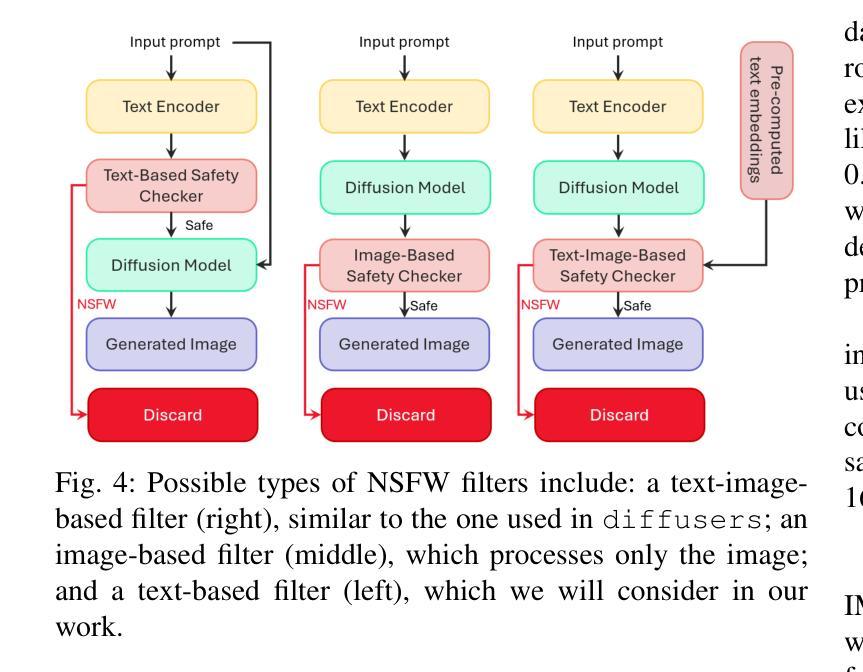
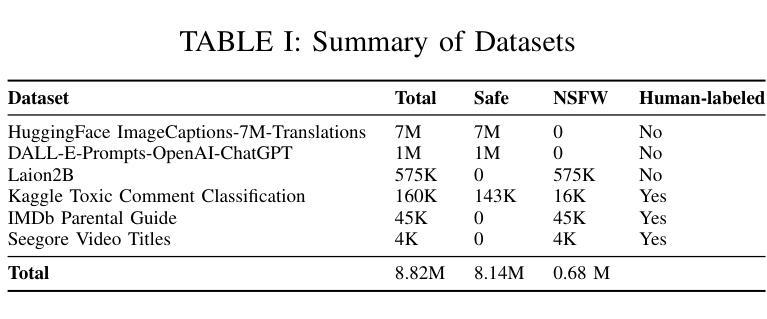
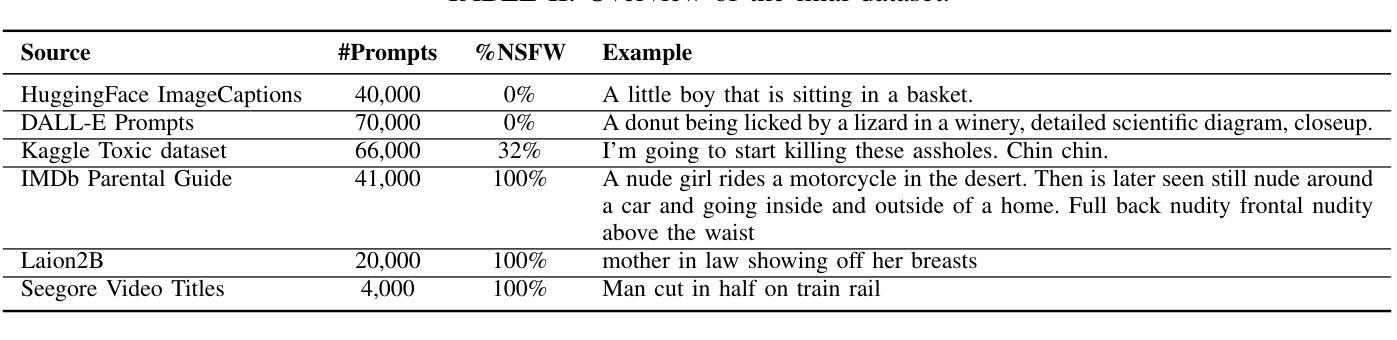
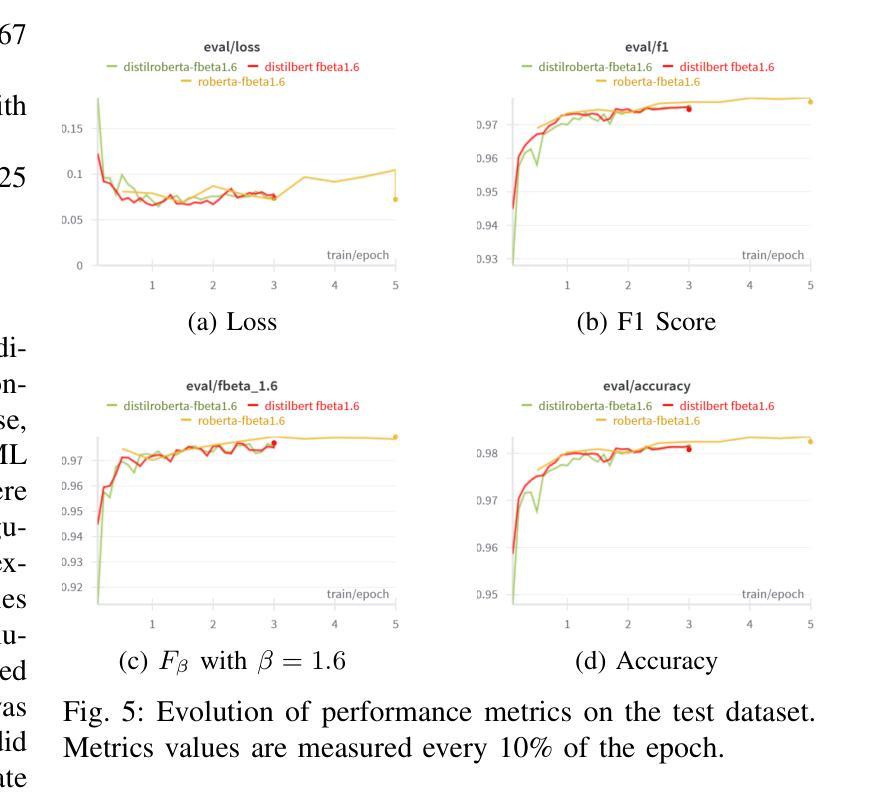
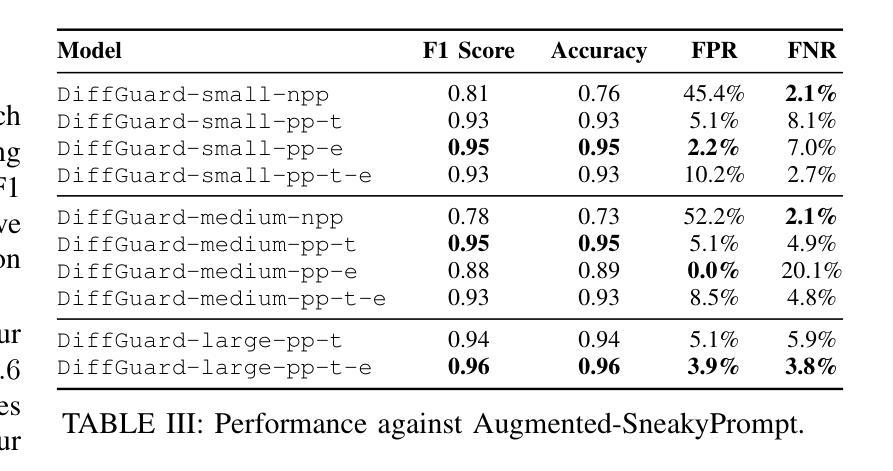
DiffGuard: Text-Based Safety Checker for Diffusion Models
Authors:Massine El Khader, Elias Al Bouzidi, Abdellah Oumida, Mohammed Sbaihi, Eliott Binard, Jean-Philippe Poli, Wassila Ouerdane, Boussad Addad, Katarzyna Kapusta
Recent advances in Diffusion Models have enabled the generation of images from text, with powerful closed-source models like DALL-E and Midjourney leading the way. However, open-source alternatives, such as StabilityAI’s Stable Diffusion, offer comparable capabilities. These open-source models, hosted on Hugging Face, come equipped with ethical filter protections designed to prevent the generation of explicit images. This paper reveals first their limitations and then presents a novel text-based safety filter that outperforms existing solutions. Our research is driven by the critical need to address the misuse of AI-generated content, especially in the context of information warfare. DiffGuard enhances filtering efficacy, achieving a performance that surpasses the best existing filters by over 14%.
扩散模型的最新进展使得从文本生成图像成为可能,强大的封闭源代码模型,如DALL-E和Midjourney,引领着这一趋势。然而,开源的替代品,如StabilityAI的稳定扩散,也提供了相当的能力。这些开源模型托管在Hugging Face上,配备了旨在防止生成明确图像的伦理过滤器保护。本文首先揭示了它们的局限性,然后提出了一种新型的基于文本的安全过滤器,它超越了现有的解决方案。我们的研究是由解决人工智能生成内容滥用问题的迫切需求所驱动的,特别是在信息战的大背景下。DiffGuard提高了过滤效率,性能超过了现有最佳过滤器超过14%。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
文本生成的新进展使得Diffusion Models能够实现文本驱动生成图像。闭源模型如DALL-E和Midjourney表现卓越,而开源模型如StabilityAI的Stable Diffusion也具备相当能力,并且加入了防止生成不当图像的伦理滤镜保护。本研究分析了这些模型的局限并提出一种新型的文本安全滤镜DiffGuard,其性能超越现有解决方案超过14%,旨在解决AI生成内容的滥用问题,尤其在信息战环境下。
Key Takeaways
- Diffusion Models能够实现文本驱动的图像生成。
- 闭源模型如DALL-E和Midjourney在图像生成方面表现出色。
- 开源模型如Stable Diffusion具备相似能力,并配备了防止生成不当图像的伦理滤镜。
- 现有模型存在局限性,需要改进。
- 提出了一种新型的文本安全滤镜DiffGuard。
- DiffGuard的性能超越了现有解决方案至少14%。
点此查看论文截图


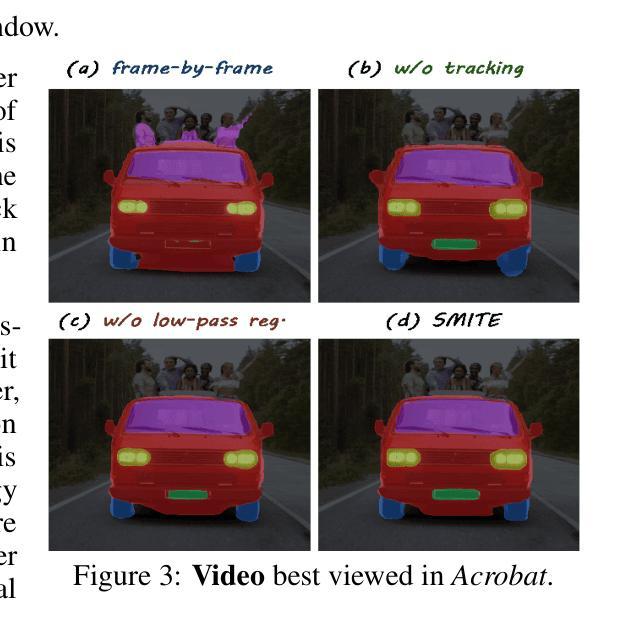
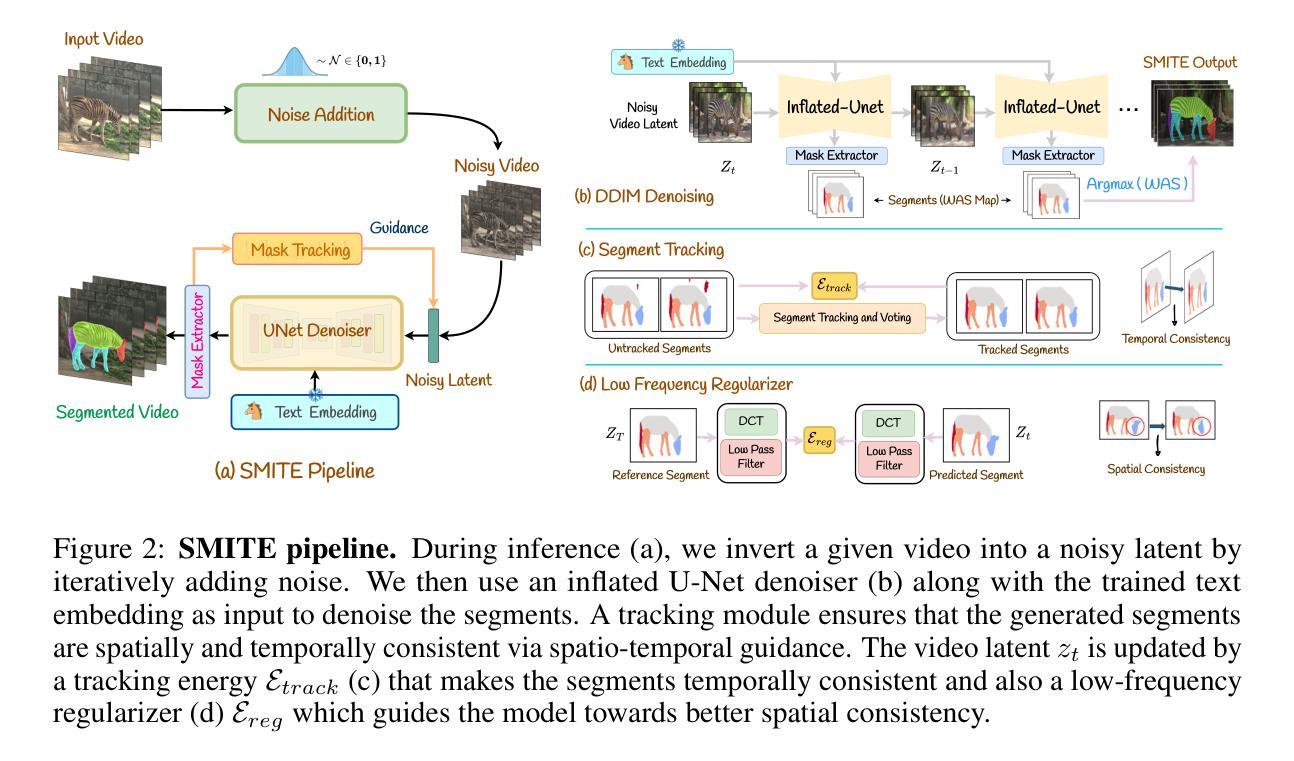
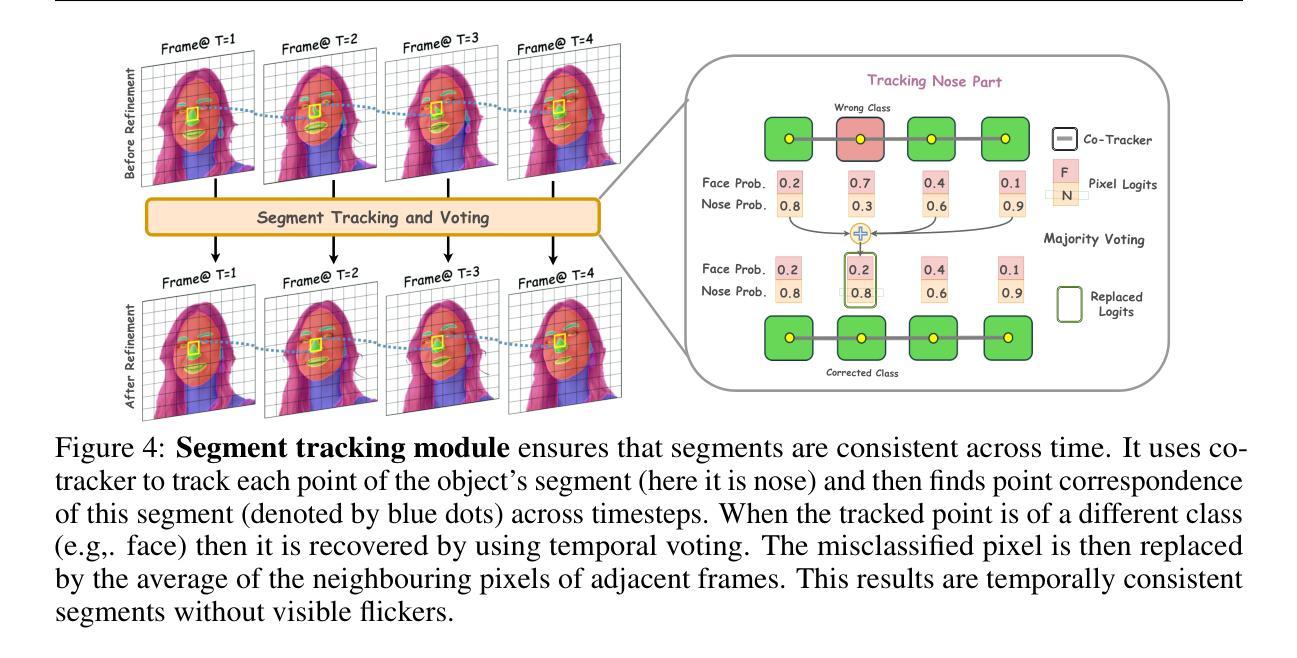
SMITE: Segment Me In TimE
Authors:Amirhossein Alimohammadi, Sauradip Nag, Saeid Asgari Taghanaki, Andrea Tagliasacchi, Ghassan Hamarneh, Ali Mahdavi Amiri
Segmenting an object in a video presents significant challenges. Each pixel must be accurately labelled, and these labels must remain consistent across frames. The difficulty increases when the segmentation is with arbitrary granularity, meaning the number of segments can vary arbitrarily, and masks are defined based on only one or a few sample images. In this paper, we address this issue by employing a pre-trained text to image diffusion model supplemented with an additional tracking mechanism. We demonstrate that our approach can effectively manage various segmentation scenarios and outperforms state-of-the-art alternatives.
在视频中分割对象存在重大挑战。每个像素都必须被精确标记,这些标签必须在各帧之间保持一致。当分割具有任意粒度时,难度会增加,意味着段落的数量可以任意变化,掩码仅基于一个或几个样本图像来定义。本文中,我们通过采用预训练的文本到图像扩散模型并辅以额外的跟踪机制来解决这个问题。我们证明我们的方法可以有效地管理各种分割场景并优于最先进的替代方案。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICLR 2025; Project page is at https://segment-me-in-time.github.io/
Summary:
本文解决了视频对象分割的问题,采用预训练的文本到图像扩散模型并辅以额外的跟踪机制,能有效处理各种分割场景,表现优于现有技术。
Key Takeaways:
- 视频对象分割面临重大挑战,需要准确标记每个像素,并且在各帧之间保持标签一致性。
- 当分割具有任意粒度时,挑战会加大,意味着片段数量可以任意变化,而掩模仅基于一个或少数样本图像定义。
- 本文采用预训练的文本到图像扩散模型来处理这个问题。
- 通过附加的跟踪机制,该方法能有效管理各种分割场景。
- 该方法表现优于现有技术。
- 本文提出的方法对于视频对象分割具有广泛的应用前景和实用价值。
点此查看论文截图


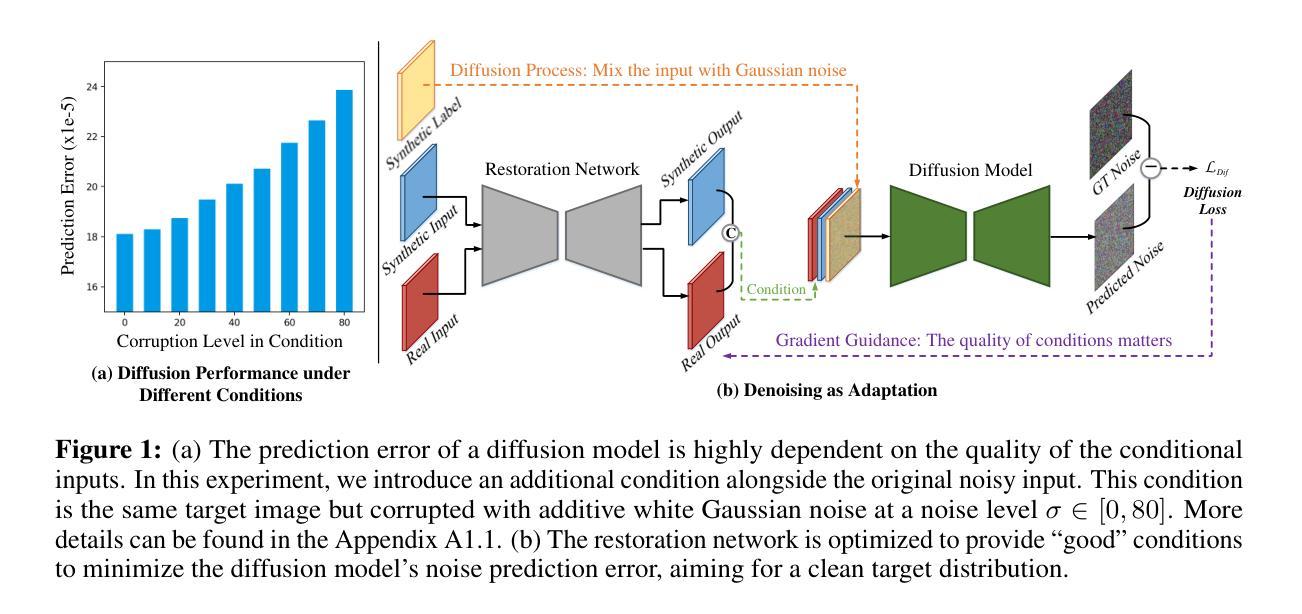
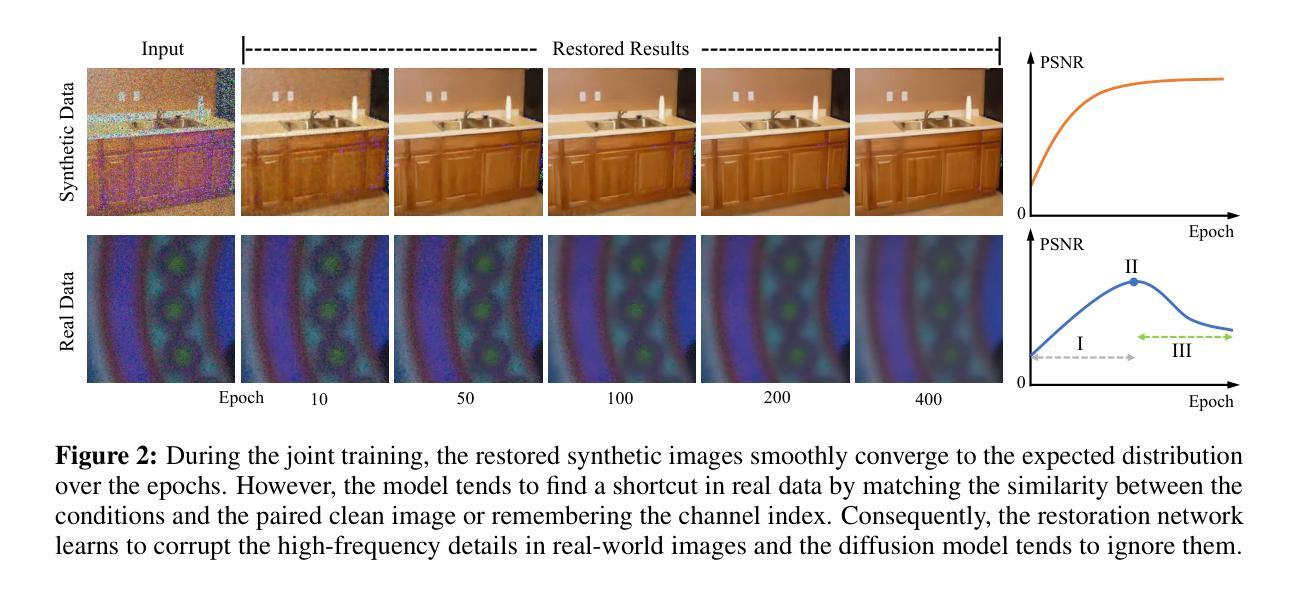
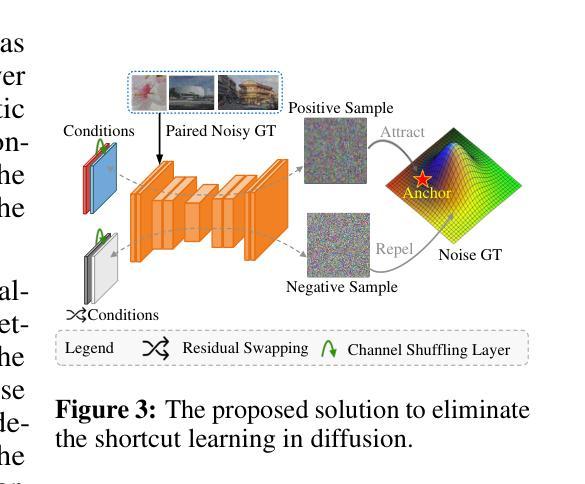
Denoising as Adaptation: Noise-Space Domain Adaptation for Image Restoration
Authors:Kang Liao, Zongsheng Yue, Zhouxia Wang, Chen Change Loy
Although learning-based image restoration methods have made significant progress, they still struggle with limited generalization to real-world scenarios due to the substantial domain gap caused by training on synthetic data. Existing methods address this issue by improving data synthesis pipelines, estimating degradation kernels, employing deep internal learning, and performing domain adaptation and regularization. Previous domain adaptation methods have sought to bridge the domain gap by learning domain-invariant knowledge in either feature or pixel space. However, these techniques often struggle to extend to low-level vision tasks within a stable and compact framework. In this paper, we show that it is possible to perform domain adaptation via the noise space using diffusion models. In particular, by leveraging the unique property of how auxiliary conditional inputs influence the multi-step denoising process, we derive a meaningful diffusion loss that guides the restoration model in progressively aligning both restored synthetic and real-world outputs with a target clean distribution. We refer to this method as denoising as adaptation. To prevent shortcuts during joint training, we present crucial strategies such as channel-shuffling layer and residual-swapping contrastive learning in the diffusion model. They implicitly blur the boundaries between conditioned synthetic and real data and prevent the reliance of the model on easily distinguishable features. Experimental results on three classical image restoration tasks, namely denoising, deblurring, and deraining, demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed method.
虽然基于学习的图像恢复方法已经取得了显著进展,但由于在合成数据上训练导致的域差距较大,它们仍然难以推广到现实场景。现有方法通过改进数据合成管道、估计退化核、采用深度内部学习以及执行域适应和正则化来解决这个问题。以前的域适应方法试图通过在学习特征或像素空间中的域不变知识来缩小域差距。然而,这些技术在稳定且紧凑的框架内往往难以扩展到低级视觉任务。在本文中,我们展示了可以通过使用扩散模型在噪声空间中进行域适应。特别是,通过利用辅助条件输入如何影响多步去噪过程的独特属性,我们推导出了一个有意义的扩散损失,该损失指导恢复模型逐步对齐恢复合成和真实世界输出与目标清洁分布。我们将这种方法称为去噪适应。为了防止联合训练过程中的捷径,我们在扩散模型中提出了关键策略,如通道混洗层和残差交换对比学习。它们隐含地模糊了受条件约束的合成数据和真实数据之间的边界,并防止模型依赖于容易区分的特征。在三个经典图像恢复任务——去噪、去模糊和去雨——上的实验结果证明了所提方法的有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by ICLR2025. Project Page: https://kangliao929.github.io/projects/noise-da/
Summary
本文提出了一种基于扩散模型的新型域自适应方法,通过在噪声空间利用辅助条件输入影响多步去噪过程,实现合成数据和真实世界输出与目标清洁分布的逐步对齐。通过通道混洗层和剩余交换对比学习等策略,防止联合训练中的捷径问题,模糊合成数据和真实数据之间的界限。实验结果表明,该方法在图像去噪、去模糊和去雨等三个经典任务中效果显著。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型被用于域自适应,通过在噪声空间利用辅助条件输入影响去噪过程,实现合成和真实世界数据之间的对齐。
- 提出了一种新的扩散损失函数,用于指导恢复模型逐步对齐恢复后的合成和真实世界输出与目标清洁分布。
- 通过通道混洗层和剩余交换对比学习等策略,防止模型在联合训练中出现捷径问题。
- 提出的方法在图像去噪、去模糊和去雨三个经典任务中取得了实验性的成功。
- 该方法能够在稳定且紧凑的框架内扩展至低层次视觉任务。
- 这种方法有助于缩小合成数据和真实世界场景之间的域差距。
点此查看论文截图