⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-02-21 更新
STaR-SQL: Self-Taught Reasoner for Text-to-SQL
Authors:Mingqian He, Yongliang Shen, Wenqi Zhang, Qiuying Peng, Jun Wang, Weiming Lu
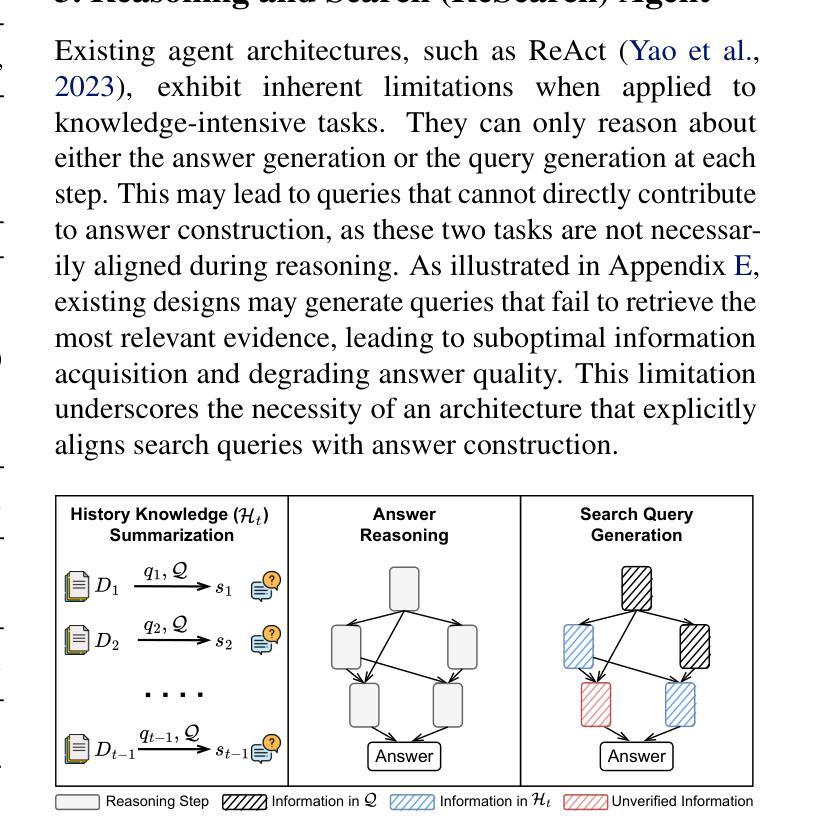
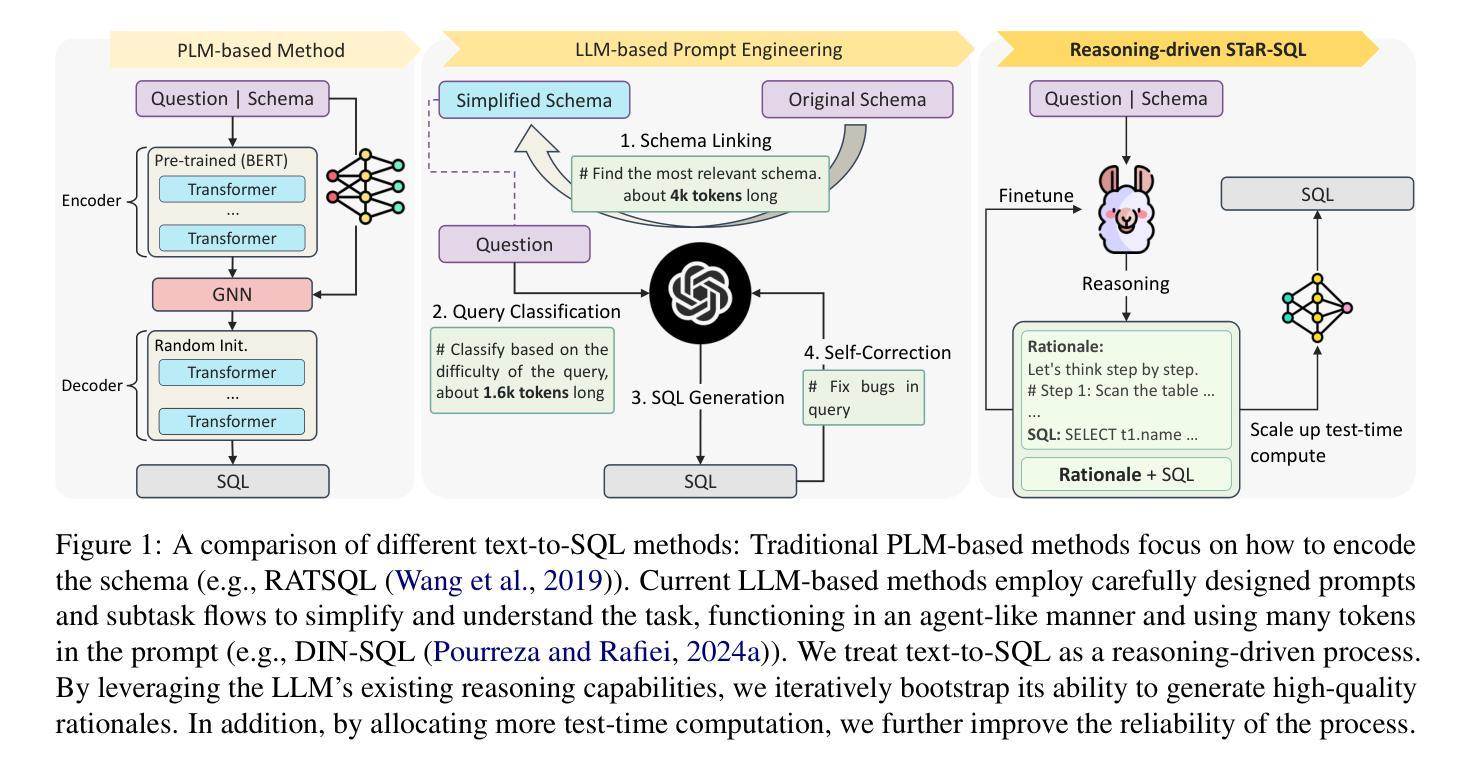
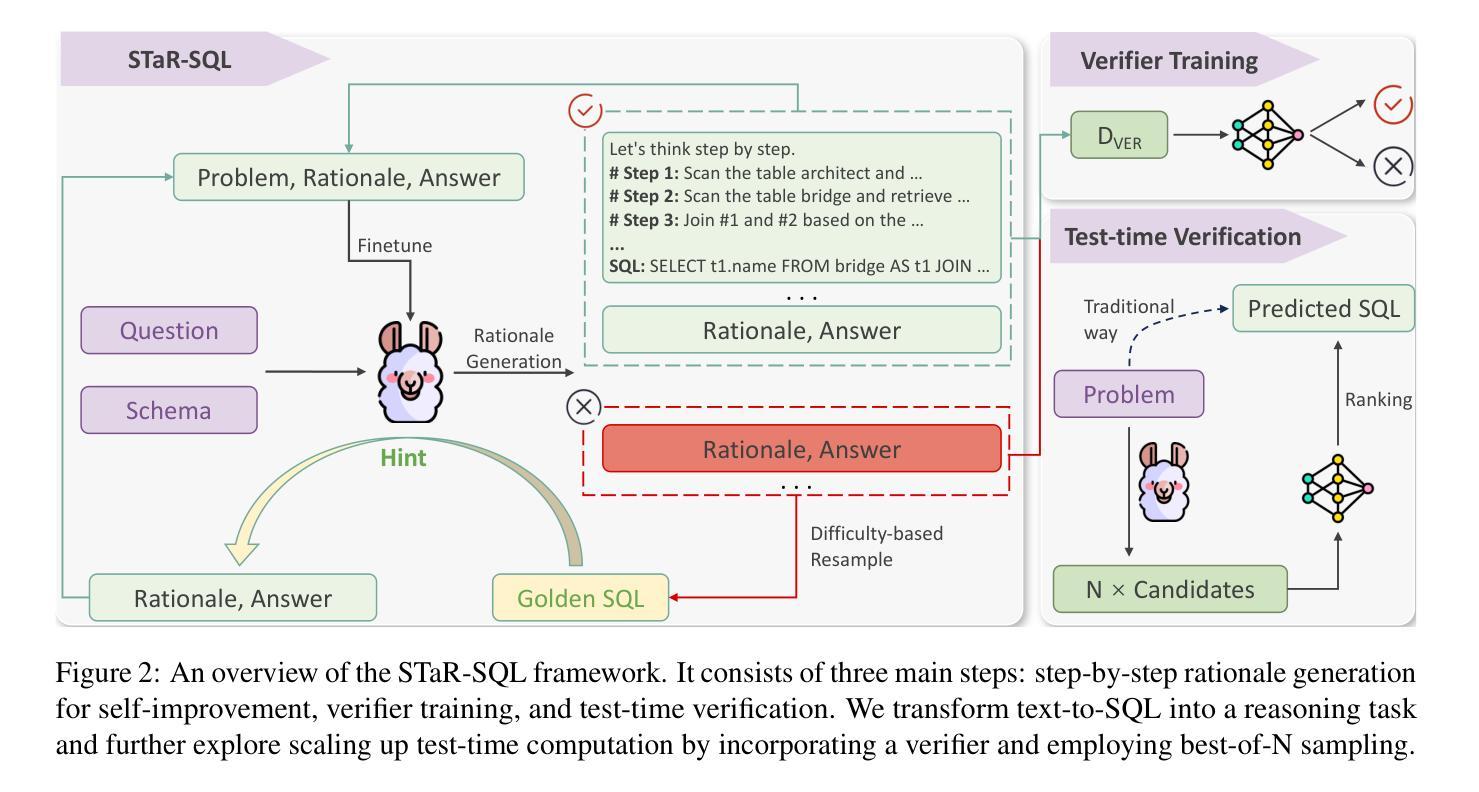
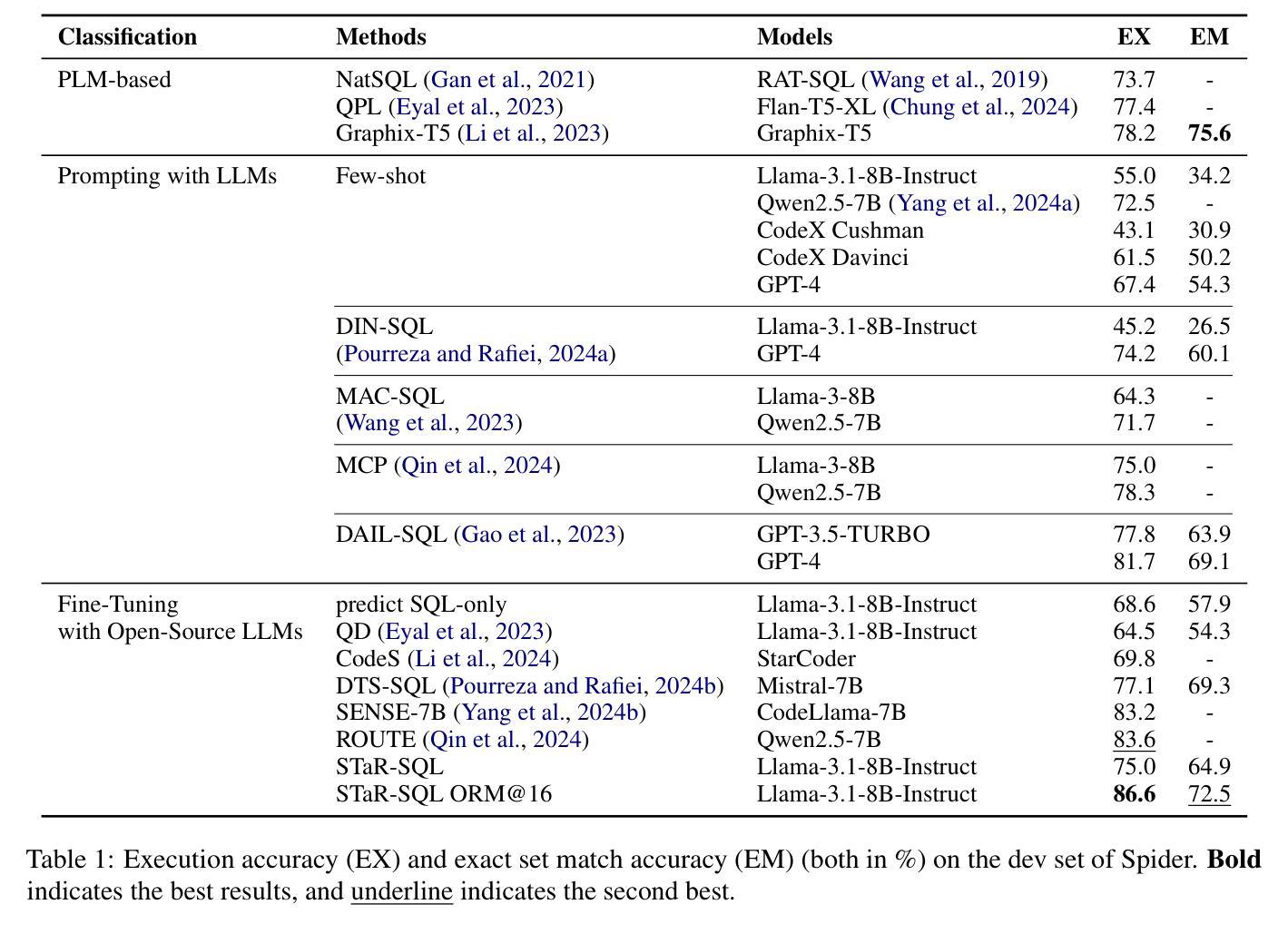
Generating step-by-step “chain-of-thought” rationales has proven effective for improving the performance of large language models on complex reasoning tasks. However, applying such techniques to structured tasks, such as text-to-SQL, remains largely unexplored. In this paper, we introduce Self-Taught Reasoner for text-to-SQL (STaR-SQL), a novel approach that reframes SQL query generation as a reasoning-driven process. Our method prompts the LLM to produce detailed reasoning steps for SQL queries and fine-tunes it on rationales that lead to correct outcomes. Unlike traditional methods, STaR-SQL dedicates additional test-time computation to reasoning, thereby positioning LLMs as spontaneous reasoners rather than mere prompt-based agents. To further scale the inference process, we incorporate an outcome-supervised reward model (ORM) as a verifier, which enhances SQL query accuracy. Experimental results on the challenging Spider benchmark demonstrate that STaR-SQL significantly improves text-to-SQL performance, achieving an execution accuracy of 86.6%. This surpasses a few-shot baseline by 31.6% and a baseline fine-tuned to predict answers directly by 18.0%. Additionally, STaR-SQL outperforms agent-like prompting methods that leverage more powerful yet closed-source models such as GPT-4. These findings underscore the potential of reasoning-augmented training for structured tasks and open the door to extending self-improving reasoning models to text-to-SQL generation and beyond.
生成逐步的”思维链”推理已被证明在提高大型语言模型在复杂推理任务上的性能方面非常有效。然而,将这种技术应用于结构化的任务,如文本到SQL的转换,仍然在很大程度上未被探索。在本文中,我们介绍了Self-Taught Reasoner for text-to-SQL(STaR-SQL),这是一种将SQL查询生成重新构建为受推理驱动的过程的新方法。我们的方法提示大型语言模型(LLM)为SQL查询生成详细的推理步骤,并根据导致正确结果的推理对其进行微调。与传统的不同,STaR-SQL在测试时增加了额外的计算用于推理,从而将LLM定位为自主的推理者,而不仅仅是基于提示的代理。为了进一步扩展推理过程,我们引入了结果监督奖励模型(ORM)作为验证器,提高了SQL查询的准确性。在具有挑战性的Spider基准测试上的实验结果表明,STaR-SQL显著提高了文本到SQL的转换性能,执行准确率达到了86.6%。这超过了少样本基准的31.6%,并超越了直接预测答案的基准的18.0%。此外,STaR-SQL还优于利用更强大但封闭模型的代理式提示方法,如GPT-4。这些发现强调了推理增强训练在结构化任务中的潜力,并为自我改进推理模型在文本到SQL生成及其他领域的应用打开了大门。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种名为STaR-SQL的新方法,用于文本到SQL的查询生成。该方法将SQL查询生成重新构建为推理驱动的过程,促使大型语言模型(LLM)产生详细的推理步骤,并通过正确的推理结果进行微调。实验结果表明,STaR-SQL在文本到SQL任务上显著提高性能,达到执行准确率86.6%,显著超越了几种基准方法。
Key Takeaways
- STaR-SQL将文本到SQL查询生成重新定位为推理驱动的过程。
- LLM通过产生详细的推理步骤来进行SQL查询,并通过正确的推理结果进行微调。
- STaR-SQL在Spider基准测试上表现出卓越性能,执行准确率高达86.6%。
- 与几种基准方法和直接预测答案的模型相比,STaR-SQL表现出显著优势。
- STaR-SQL甚至超越了使用更强大但封闭模型的代理提示方法,如GPT-4。
- 实验结果强调了推理增强训练在结构化任务中的潜力。
点此查看论文截图

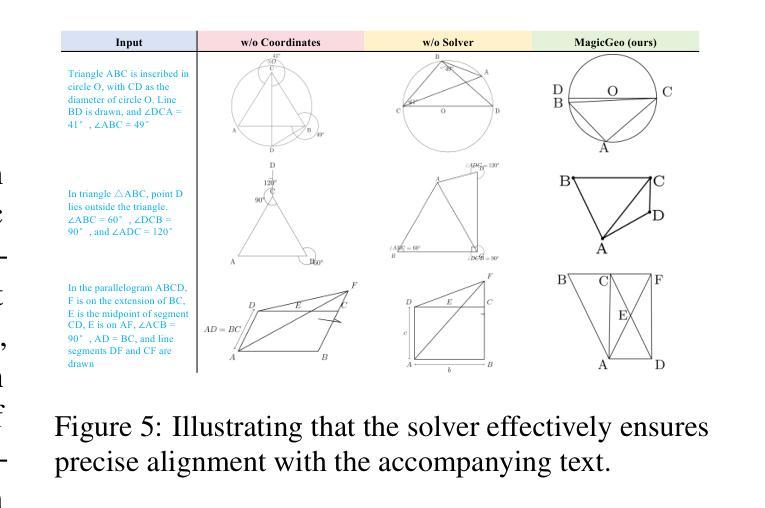
Language Models are Few-Shot Graders
Authors:Chenyan Zhao, Mariana Silva, Seth Poulsen
Providing evaluations to student work is a critical component of effective student learning, and automating its process can significantly reduce the workload on human graders. Automatic Short Answer Grading (ASAG) systems, enabled by advancements in Large Language Models (LLMs), offer a promising solution for assessing and providing instant feedback for open-ended student responses. In this paper, we present an ASAG pipeline leveraging state-of-the-art LLMs. Our new LLM-based ASAG pipeline achieves better performances than existing custom-built models on the same datasets. We also compare the grading performance of three OpenAI models: GPT-4, GPT-4o, and o1-preview. Our results demonstrate that GPT-4o achieves the best balance between accuracy and cost-effectiveness. On the other hand, o1-preview, despite higher accuracy, exhibits a larger variance in error that makes it less practical for classroom use. We investigate the effects of incorporating instructor-graded examples into prompts using no examples, random selection, and Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG)-based selection strategies. Our findings indicate that providing graded examples enhances grading accuracy, with RAG-based selection outperforming random selection. Additionally, integrating grading rubrics improves accuracy by offering a structured standard for evaluation.
为学生提供作品评价是有效学习的重要组成部分,自动化该过程可以显著减少人工评分员的工作量。借助大型语言模型(LLM)的进步,自动简答评分(ASAG)系统为评估和为学生提供开放式回答的即时反馈提供了有前景的解决方案。在本文中,我们介绍了一个利用最新LLM的ASAG管道。我们新的基于LLM的ASAG管道在相同数据集上实现了比现有自定义模型更好的性能。我们还比较了三个OpenAI模型的评分性能:GPT-4、GPT-4o和o1-preview。我们的结果表明,GPT-4o在准确性和成本效益之间达到了最佳平衡。另一方面,尽管o1-preview的准确率更高,但其误差变化较大,不太适合课堂使用。我们研究了将教师评分示例纳入提示的影响,使用无示例、随机选择和基于检索增强生成(RAG)的选择策略。我们的研究结果表明,提供评分示例可以提高评分准确性,其中基于RAG的选择策略表现优于随机选择。此外,通过整合评分量表,提供结构化的评价标提高了评价的准确性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于大型语言模型(LLM)的自动短答评分(ASAG)系统为学生开放答案的即时反馈提供了有前景的解决方案。本文介绍了一个新型的ASAG流程,它比现有自定义模型有更好的性能。比较了GPT-4、GPT-4o和o1-preview三种OpenAI模型的评分性能,发现GPT-4o在准确性和成本效益之间取得了最佳平衡。此外,研究还表明,将教师评分示例纳入提示可提升评分准确性,其中基于RAG的选择策略表现最佳。整合评分规范也能提高准确性,为评价提供结构化标准。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLM)为自动短答评分(ASAG)提供了技术基础。
- 新型的ASAG流程相比现有自定义模型有更好的性能。
- GPT-4o在评分准确性和成本效益之间达到了最佳平衡。
- o1-preview虽然准确率较高,但误差变化较大,不太适合课堂教学使用。
- 将教师评分示例纳入提示可以提高评分准确性。
- 基于RAG的选择策略在提供教师评分示例时表现最佳。
点此查看论文截图

Task Shift: From Classification to Regression in Overparameterized Linear Models
Authors:Tyler LaBonte, Kuo-Wei Lai, Vidya Muthukumar
Modern machine learning methods have recently demonstrated remarkable capability to generalize under task shift, where latent knowledge is transferred to a different, often more difficult, task under a similar data distribution. We investigate this phenomenon in an overparameterized linear regression setting where the task shifts from classification during training to regression during evaluation. In the zero-shot case, wherein no regression data is available, we prove that task shift is impossible in both sparse signal and random signal models for any Gaussian covariate distribution. In the few-shot case, wherein limited regression data is available, we propose a simple postprocessing algorithm which asymptotically recovers the ground-truth predictor. Our analysis leverages a fine-grained characterization of individual parameters arising from minimum-norm interpolation which may be of independent interest. Our results show that while minimum-norm interpolators for classification cannot transfer to regression a priori, they experience surprisingly structured attenuation which enables successful task shift with limited additional data.
最近,现代机器学习的方法在任务迁移中展示出了显著的泛化能力,其中潜在的知识被迁移到一个不同的任务上,通常这个任务更加困难,但数据分布是相似的。我们在一个过度参数化的线性回归环境中研究这一现象,其中任务从训练期间的分类转变为评估期间的回归。在零样本情况下(没有回归数据可用),我们证明了在任何高斯协变量分布下,稀疏信号模型和随机信号模型中任务迁移是不可能的。在有限回归数据可用的情况下,我们提出了一种简单的后处理算法,该算法可以渐近地恢复基础真实预测器。我们的分析利用了最小范数插值产生的单个参数的精细特征刻画,这可能具有独立的兴趣。我们的结果表明,虽然分类的最小范数插值器不能先验地转移到回归任务,但它们会出现结构化的衰减现象,这使得使用有限附加数据成功进行任务迁移成为可能。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF AISTATS 2025
摘要
最新机器学习技术在任务转换中表现出卓越泛化能力,能将潜在知识转移到类似数据分布的不同任务中,即使这些任务更具挑战性。本研究在参数过多的线性回归环境中探究这一现象,训练任务从分类转变为评估时的回归。在零样本情况下(即无法使用回归数据),我们证明在稀疏信号和随机信号模型中,任何高斯协变量分布的任务转换都不可能实现。在少样本情况下(即有限回归数据可用),我们提出了一种简单的后处理算法,该算法可渐近恢复真实预测器。我们的分析基于最小范数插值产生的个别参数的精细特征刻画,这可能对独立研究有兴趣。结果表明,虽然用于分类的最小范数插值器不能先验地转移到回归任务,但它们会经历令人惊讶的结构衰减,这使得它们在有限的数据补充下成功实现任务转换。
关键见解
- 现代机器学习技术在任务转换中展现出卓越泛化能力,特别是在类似数据分布的不同任务间转移潜在知识。
- 在参数过多的线性回归环境中,当任务从分类转变为回归时,本研究进行了探究。
- 在零样本情况下,任务转换在稀疏信号和随机信号模型中无法实现。
- 在少样本情况下,提出了一种简单的后处理算法,可渐近恢复真实预测器。
- 本研究分析基于最小范数插值的个别参数的精细刻画。
- 最小范数插值器虽然在分类任务中表现出色,但不一定能先验地转移到回归任务。
点此查看论文截图

CLIP-RT: Learning Language-Conditioned Robotic Policies from Natural Language Supervision
Authors:Gi-Cheon Kang, Junghyun Kim, Kyuhwan Shim, Jun Ki Lee, Byoung-Tak Zhang
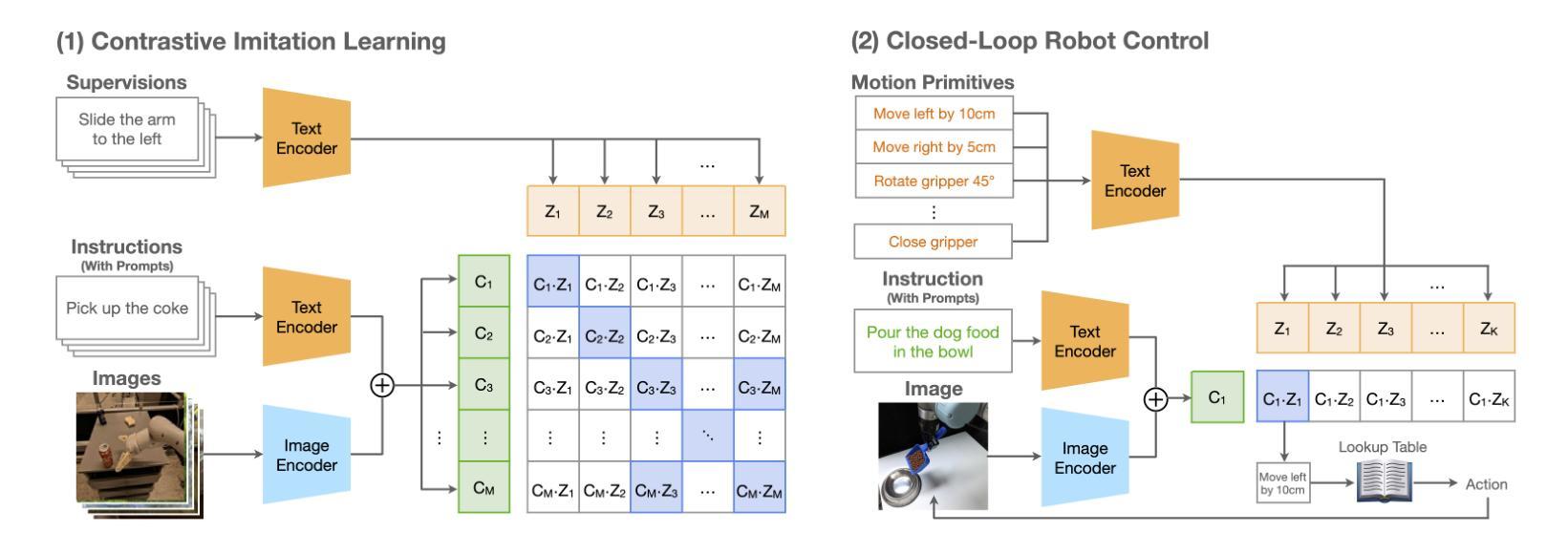
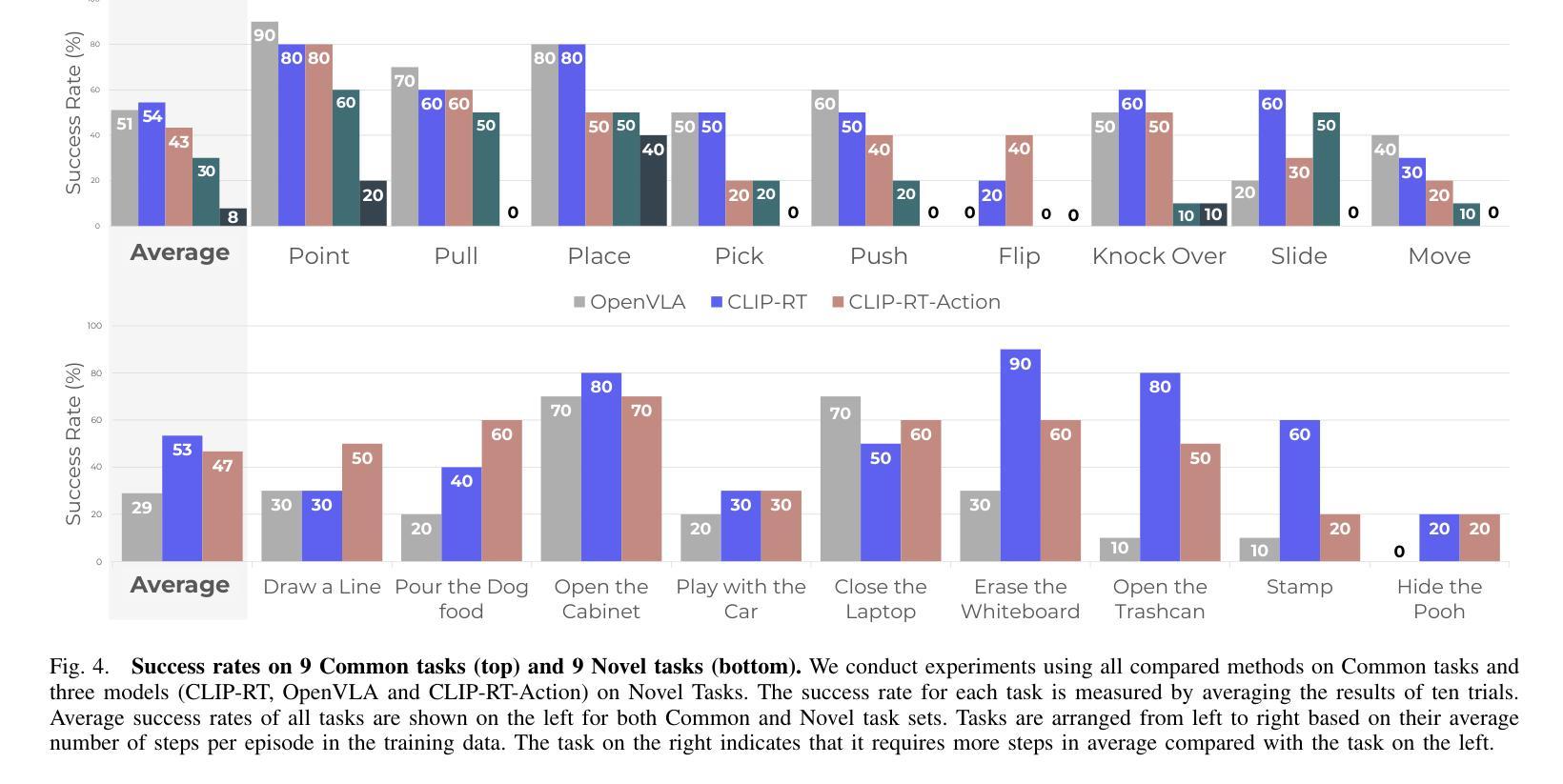
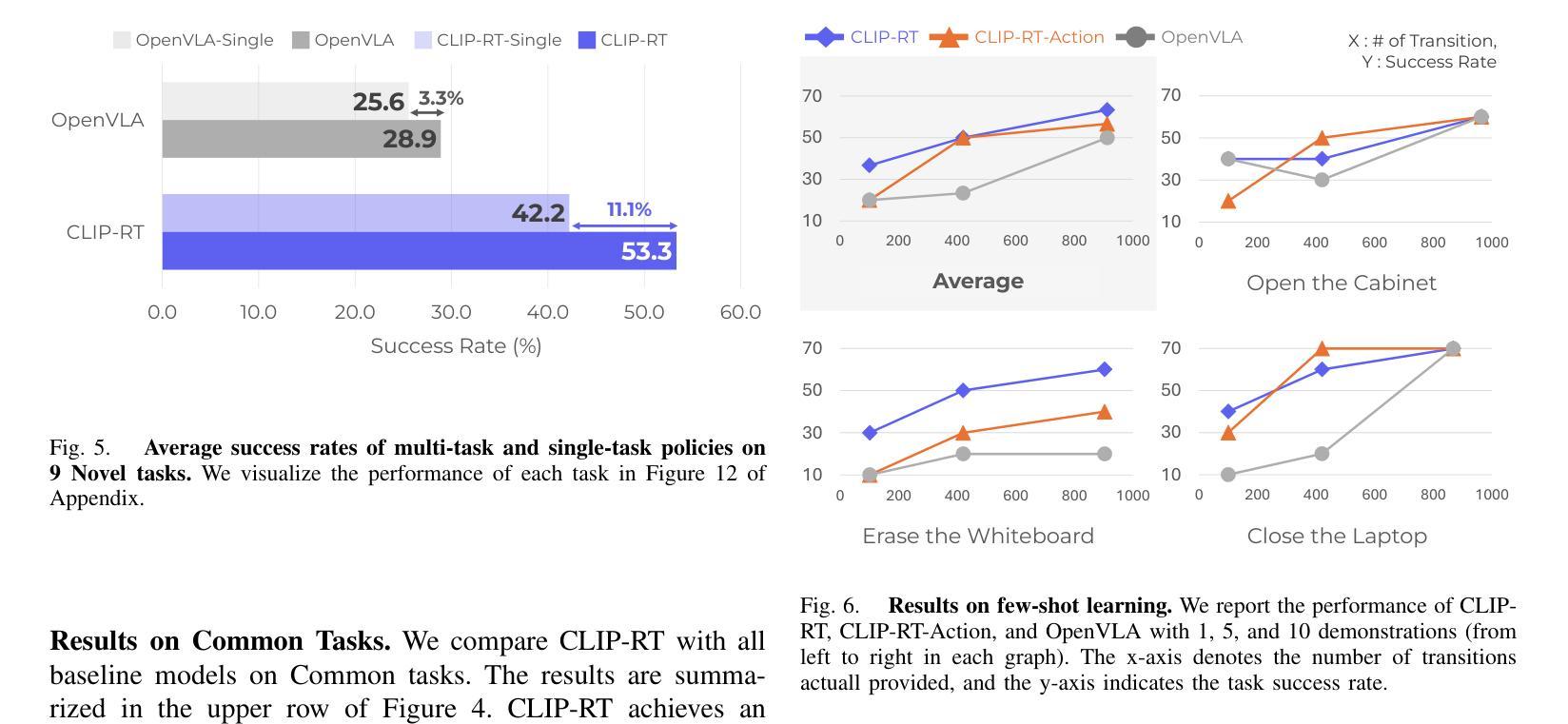
Teaching robots desired skills in real-world environments remains challenging, especially for non-experts. The reliance on specialized expertise in robot control and teleoperation systems often limits accessibility to non-experts. We posit that natural language offers an intuitive and accessible interface for robot learning. To this end, we study two aspects: (1) enabling non-experts to collect robotic data through natural language supervision (e.g., “move the arm to the right”) and (2) learning robotic policies directly from this supervision. Specifically, we introduce a data collection framework that collects robot demonstrations based on natural language supervision and further augments these demonstrations. We then present CLIP-RT, a vision-language-action (VLA) model that learns language-conditioned visuomotor policies from this supervision. CLIP-RT adapts the pretrained CLIP models and learns to predict language-based motion primitives via contrastive imitation learning. We train CLIP-RT on the Open X-Embodiment dataset and finetune it on in-domain data collected by our framework to learn diverse skills. CLIP-RT demonstrates strong capabilities in learning novel manipulation skills, outperforming the state-of-the-art model, OpenVLA (7B parameters), by 24% in average success rates, while using 7x fewer parameters (1B). We further observe that CLIP-RT shows significant improvements in few-shot generalization. Finally, through collaboration with humans or large pretrained models, we demonstrate that CLIP-RT can further improve its generalization on challenging tasks.
教授机器人在真实世界环境中所需的技能仍然是一个挑战,尤其对于非专业人士来说。对机器人控制和遥操作系统的专业知识的依赖往往限制了非专业人士的可达性。我们认为自然语言为机器人学习提供了一个直观和可访问的界面。为此,我们研究了两个方面:(1)通过自然语言监督(例如,“把胳膊移到右边”)使非专业人士能够收集机器人数据;(2)直接从这种监督中学习机器人策略。具体来说,我们引入了一个数据收集框架,该框架基于自然语言监督收集机器人演示,并进一步增强了这些演示。然后,我们提出了CLIP-RT,这是一种视觉语言动作(VLA)模型,它可以从这种监督中学习语言调节的视运动策略。CLIP-RT适应了预训练的CLIP模型,并学习通过对比模仿学习预测基于语言的运动原始数据。我们在Open X-Embodiment数据集上训练CLIP-RT,并通过我们的框架收集的领域内数据进行微调,以学习各种技能。CLIP-RT在学习新型操作技能方面表现出强大的能力,在平均成功率方面超过了最先进的模型OpenVLA(70亿参数),同时使用更少的参数(10亿),提高了24%。我们进一步观察到CLIP-RT在少量场景中的泛化能力显著提高。最后,通过与人类或大型预训练模型的合作,我们证明CLIP-RT可以在具有挑战性的任务上进一步改善其泛化能力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 27 pages
Summary
本文研究利用自然语言作为机器人学习的接口,让非专家能够通过自然语言监督来收集机器人数据,并直接从此监督中学习机器人策略。通过引入一个基于自然语言监督的机器人演示收集框架和CLIP-RT模型,实现在Open X-Embodiment数据集上的高效学习,并在少样本情况下表现出良好的泛化能力。相较于现有模型OpenVLA,CLIP-RT在平均成功率上提高了24%,同时参数使用减少了7倍。通过人类合作或与大型预训练模型的合作,CLIP-RT在挑战性任务上的泛化能力得到进一步提升。
Key Takeaways
- 自然语言作为机器人学习的接口,使非专家能够更方便地教授机器人技能。
- 引入了一个基于自然语言监督的机器人演示收集框架。
- CLIP-RT模型能够从自然语言监督中学习语言条件下的视觉运动策略。
- CLIP-RT在Open X-Embodiment数据集上的表现优于现有模型OpenVLA,平均成功率提高24%。
- CLIP-RT具有优秀的少样本泛化能力。
- CLIP-RT通过与人类或大型预训练模型的合作,进一步提升了在挑战性任务上的泛化能力。
点此查看论文截图

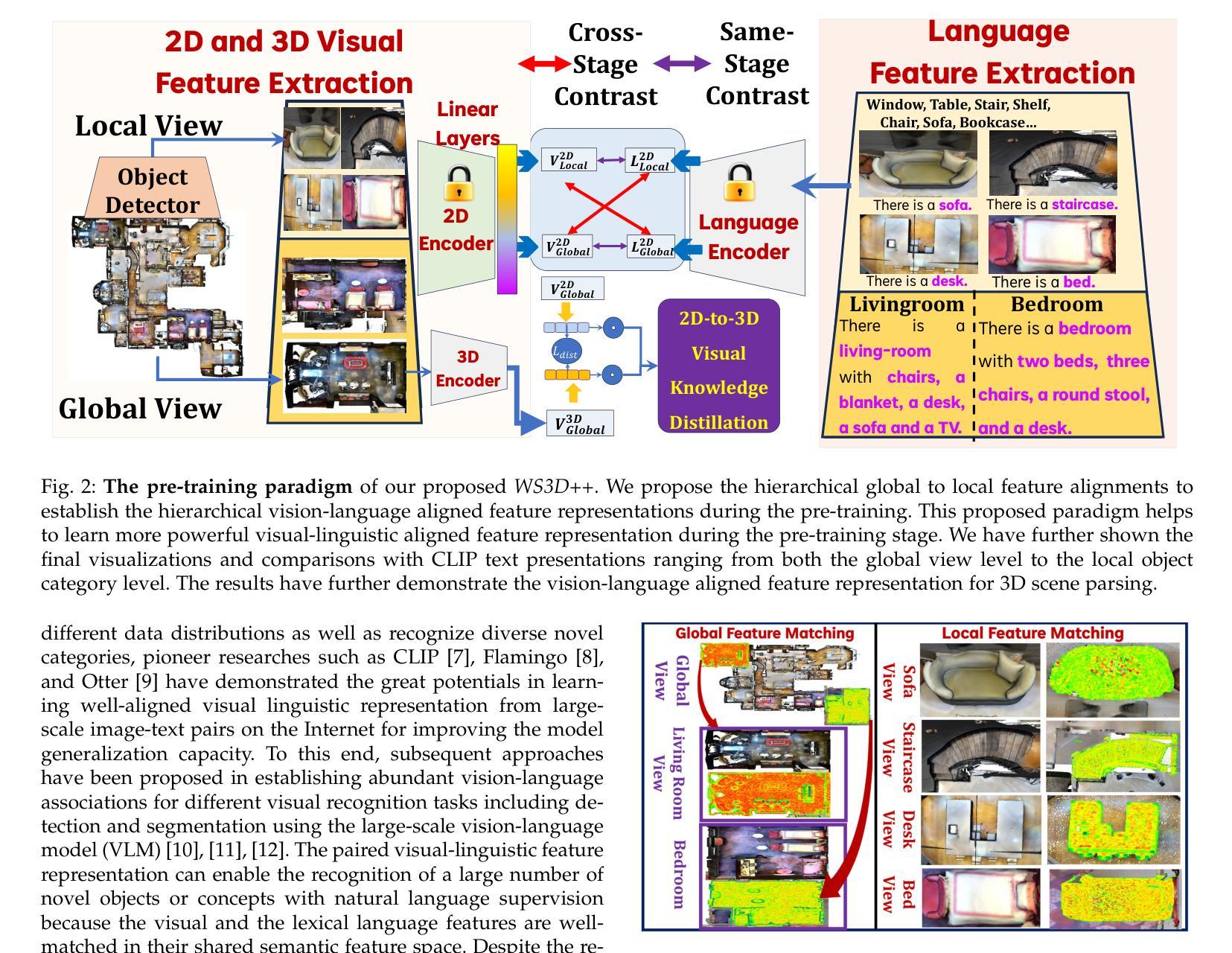
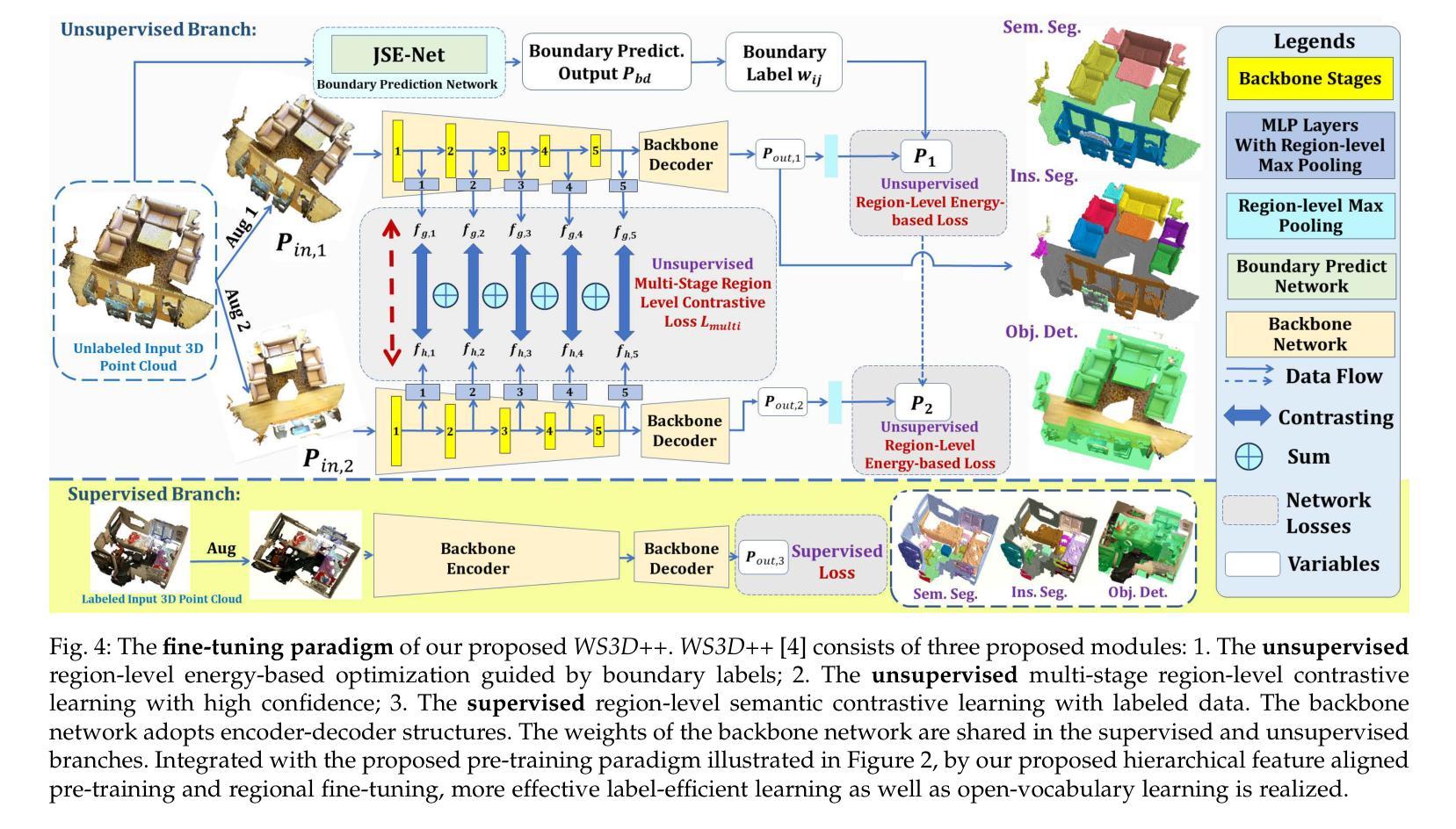
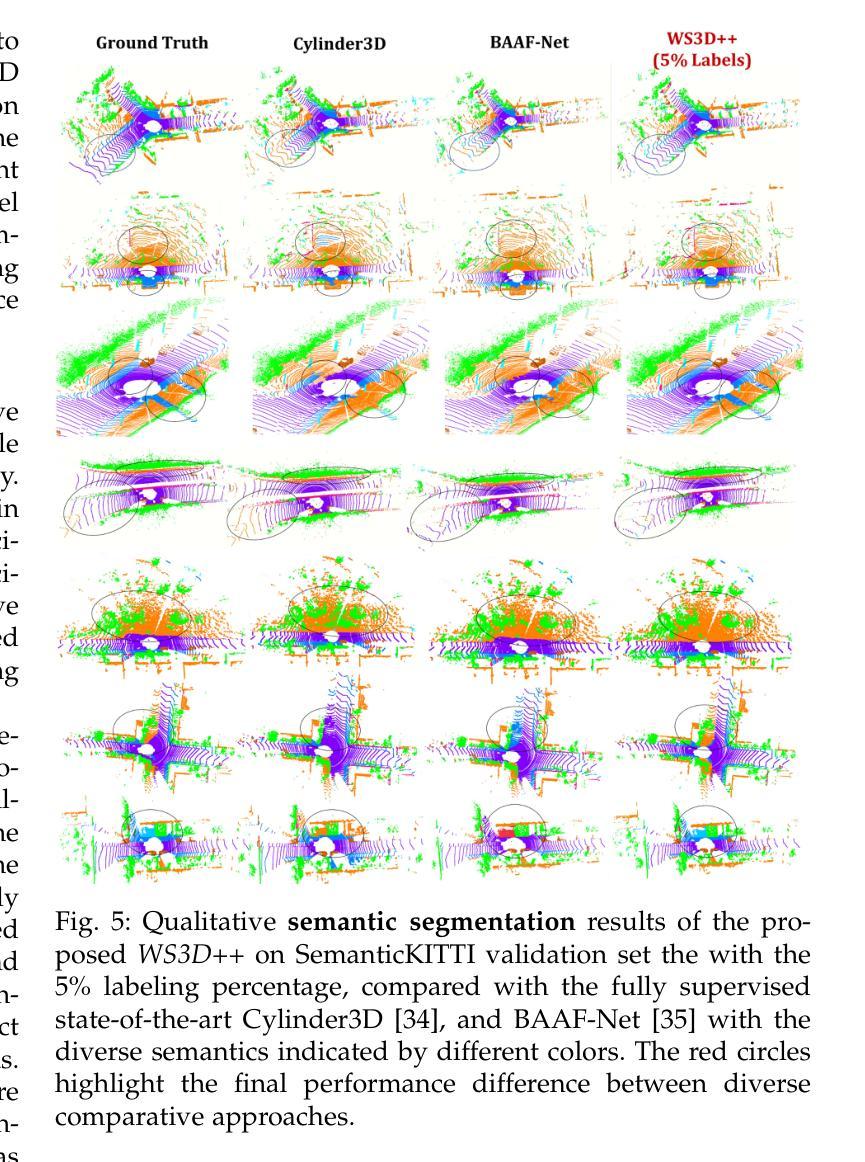
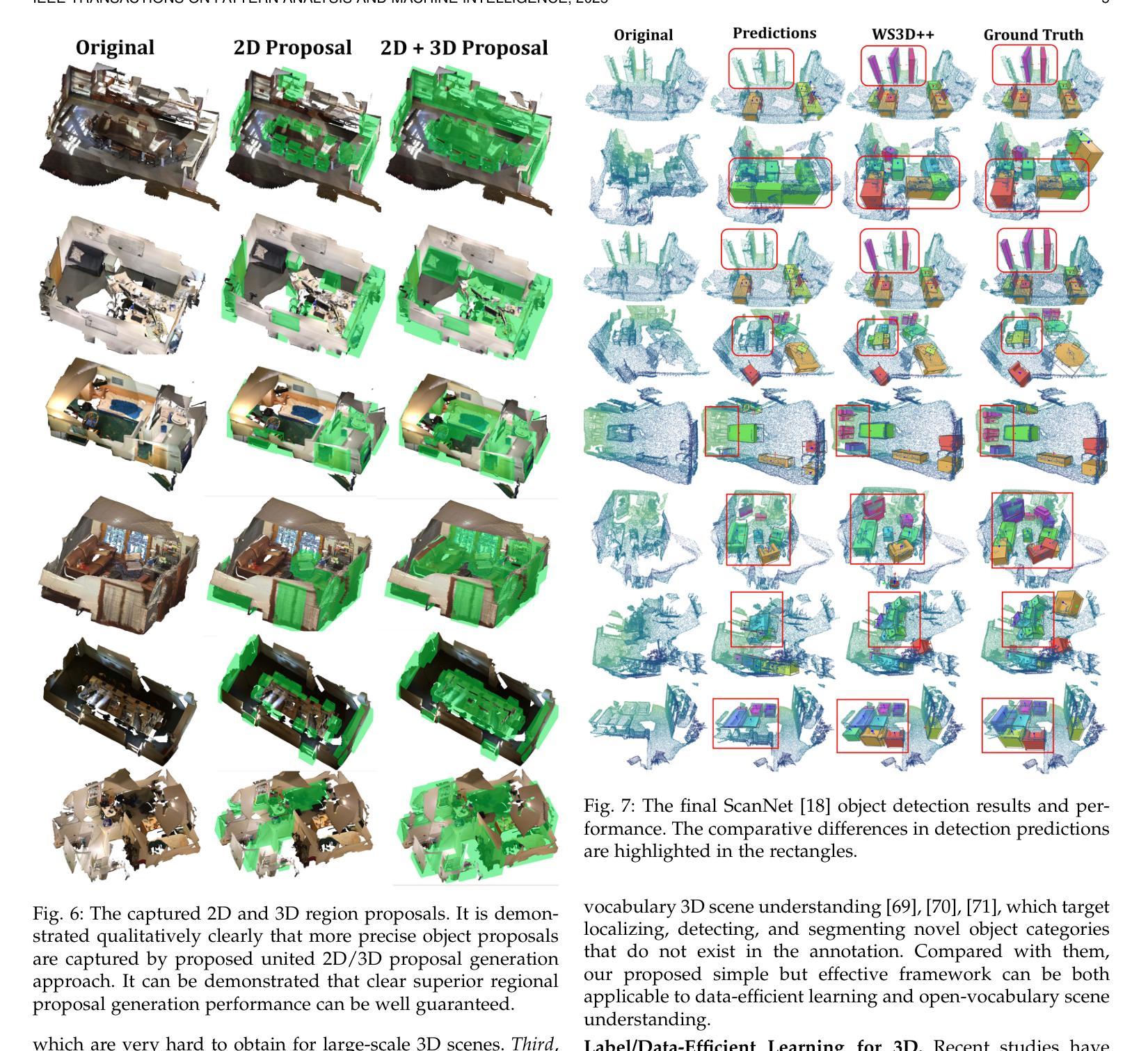
Generalized Robot 3D Vision-Language Model with Fast Rendering and Pre-Training Vision-Language Alignment
Authors:Kangcheng Liu, Yong-Jin Liu, Baoquan Chen
Deep neural network models have achieved remarkable progress in 3D scene understanding while trained in the closed-set setting and with full labels. However, the major bottleneck is that these models do not have the capacity to recognize any unseen novel classes beyond the training categories in diverse real-world applications. Therefore, we are in urgent need of a framework that can simultaneously be applicable to both 3D point cloud segmentation and detection, particularly in the circumstances where the labels are rather scarce. This work presents a generalized and straightforward framework for dealing with 3D scene understanding when the labeled scenes are quite limited. To extract knowledge for novel categories from the pre-trained vision-language models, we propose a hierarchical feature-aligned pre-training and knowledge distillation strategy to extract and distill meaningful information from large-scale vision-language models, which helps benefit the open-vocabulary scene understanding tasks. To encourage latent instance discrimination and to guarantee efficiency, we propose the unsupervised region-level semantic contrastive learning scheme for point clouds, using confident predictions of the neural network to discriminate the intermediate feature embeddings at multiple stages. In the limited reconstruction case, our proposed approach, termed WS3D++, ranks 1st on the large-scale ScanNet benchmark on both the task of semantic segmentation and instance segmentation. Extensive experiments with both indoor and outdoor scenes demonstrated the effectiveness of our approach in both data-efficient learning and open-world few-shot learning. The code is made publicly available at: https://drive.google.com/drive/folders/1M58V-PtR8DBEwD296zJkNg_m2qq-MTAP?usp=sharing.
深度神经网络模型在封闭集设置和完全标签训练下,在3D场景理解方面取得了显著的进步。然而,主要瓶颈在于这些模型无法识别训练类别之外未见的新类别,在多样化的现实世界应用中无法适应。因此,我们急需一个能同时应用于3D点云分割和检测的框架,特别是在标签稀缺的情况下。这项工作提出了一个通用且直接的框架,用于处理标签有限的3D场景理解问题。为了从预训练的视觉语言模型中提取新类别的知识,我们提出了一种分层特征对齐的预训练和知识蒸馏策略,从大规模视觉语言模型中提取和蒸馏有意义的信息,这有助于开放词汇场景理解任务。为了鼓励潜在实例鉴别并保证效率,我们为点云提出了无监督区域级语义对比学习方案,利用神经网络的有信心预测来鉴别多个阶段的中间特征嵌入。在有限的重建情况下,我们提出的方法——WS3D++,在大型ScanNet基准测试中都获得了第一名,无论是语义分割任务还是实例分割任务。室内外场景的广泛实验证明了我们方法在数据高效学习和开放世界小样本学习中的有效性。代码已公开提供在:链接地址。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, Manuscript Info: 17 Pages, 13 Figures, and 6 Tables
Summary
本文提出了一种用于处理3D场景理解的通用框架,适用于标签有限的场景。通过预训练的视觉语言模型和分层特征对齐预训练及知识蒸馏策略,从大型视觉语言模型中提取新知识以应对开放词汇场景理解任务。同时,通过神经网络自信预测进行区域级别的语义对比学习,以鼓励潜在实例的辨别和提高效率。此方法在大型ScanNet基准测试中表现优秀,荣获第一名,同时在室内和室外场景的实验也证明了其在数据高效学习和开放世界小样本学习中的有效性。相关代码已公开分享。
Key Takeaways
- 框架适用于处理标签有限的场景下的3D点云分割和检测问题。
- 通过视觉语言模型预训练结合知识蒸馏策略来应对开放词汇场景理解任务。
- 利用神经网络自信预测进行区域级别的语义对比学习,提高实例辨别效率。
- 方法在ScanNet基准测试中排名第一,验证了其有效性。
- 方法在室内外场景实验表现出良好的数据高效学习和小样本学习能力。
点此查看论文截图