⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-02-22 更新
MedVAE: Efficient Automated Interpretation of Medical Images with Large-Scale Generalizable Autoencoders
Authors:Maya Varma, Ashwin Kumar, Rogier van der Sluijs, Sophie Ostmeier, Louis Blankemeier, Pierre Chambon, Christian Bluethgen, Jip Prince, Curtis Langlotz, Akshay Chaudhari
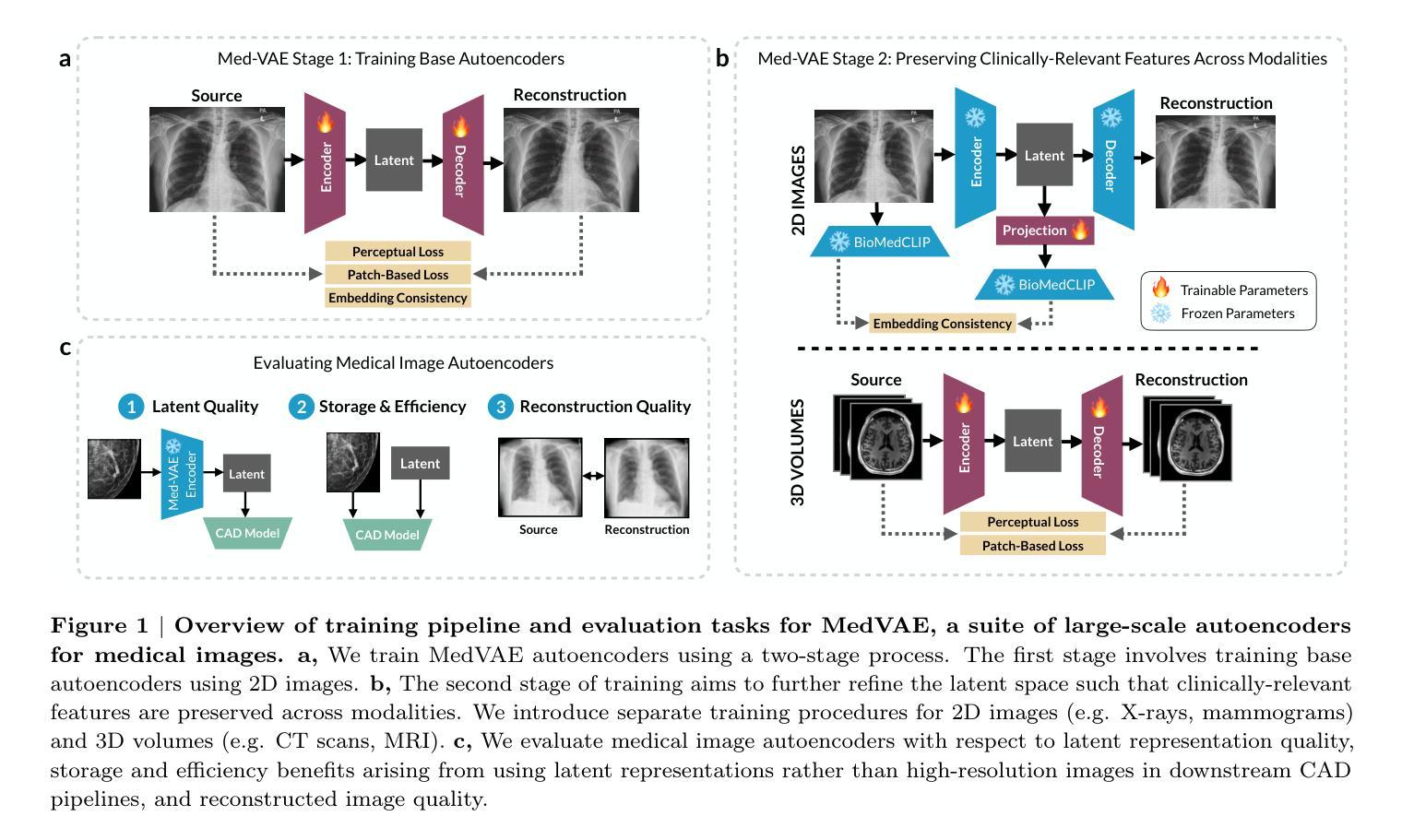
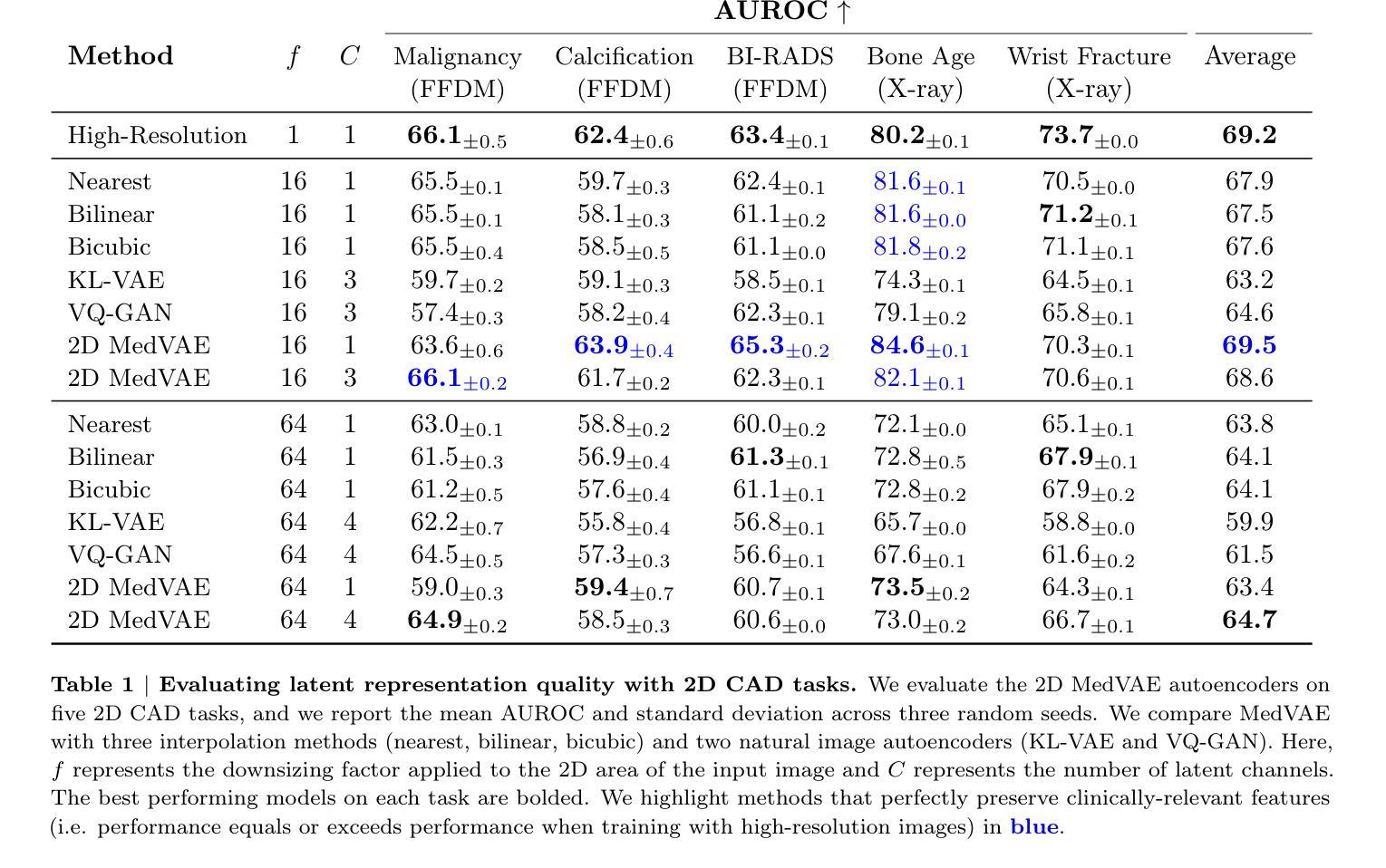
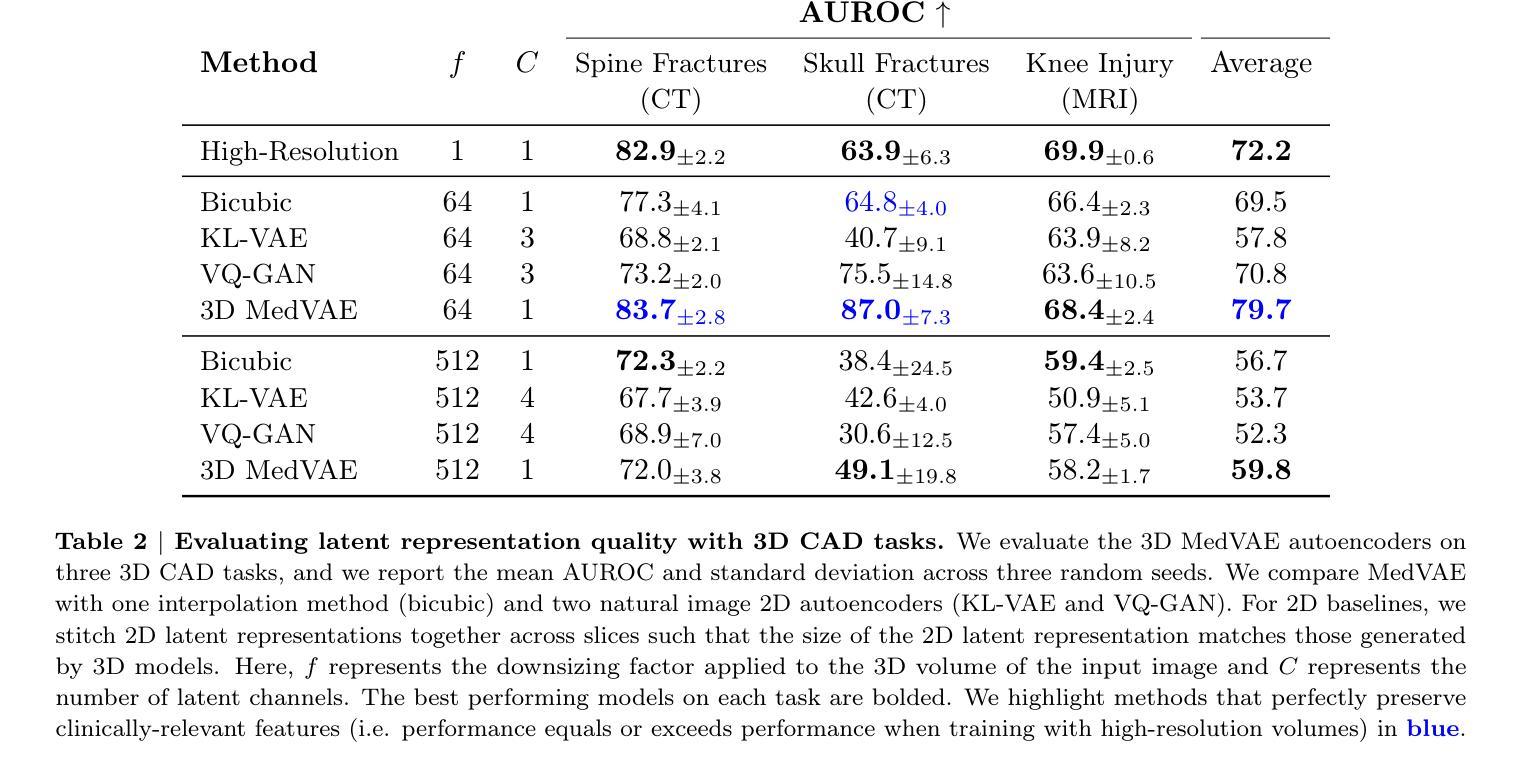
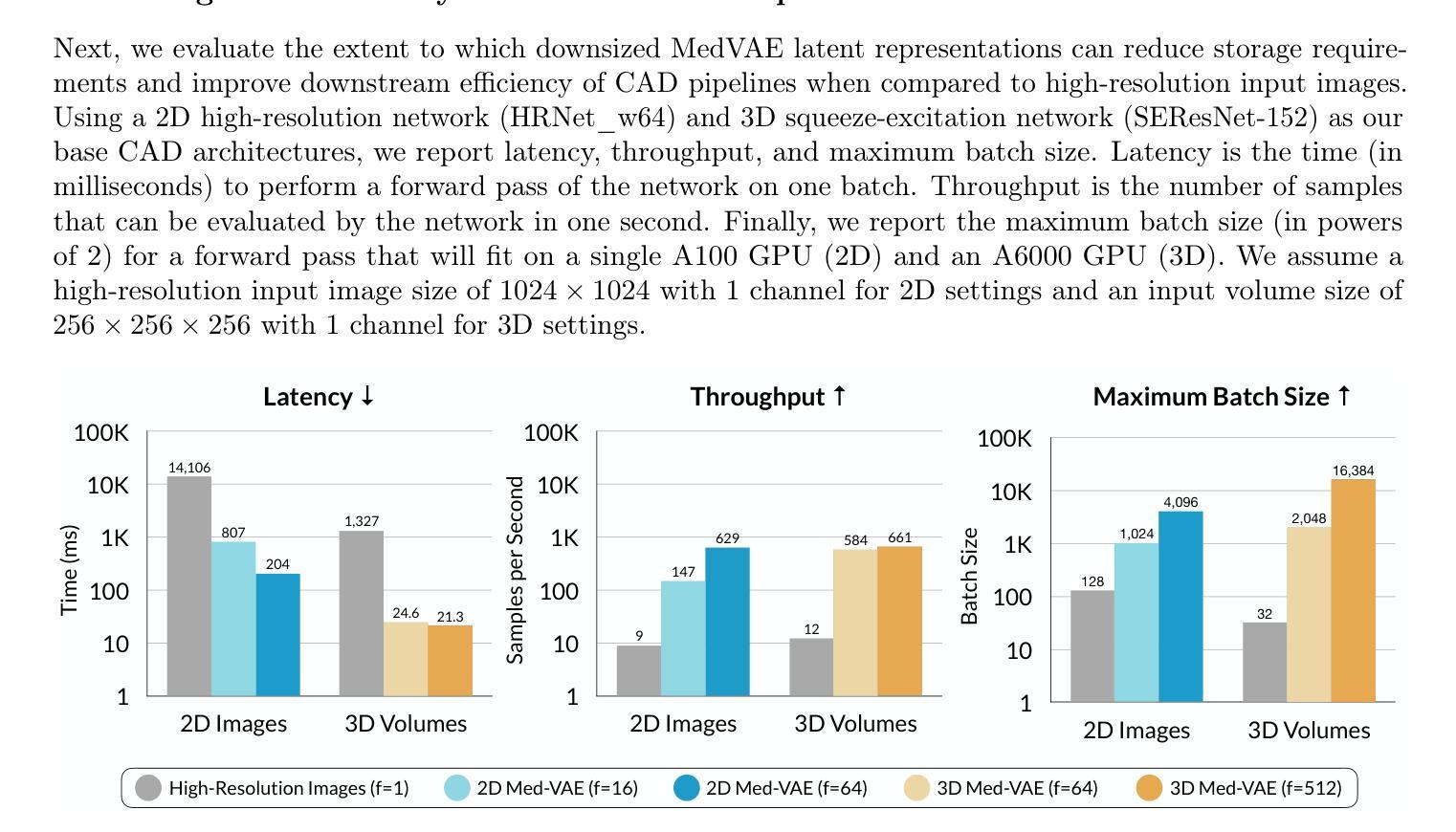
Medical images are acquired at high resolutions with large fields of view in order to capture fine-grained features necessary for clinical decision-making. Consequently, training deep learning models on medical images can incur large computational costs. In this work, we address the challenge of downsizing medical images in order to improve downstream computational efficiency while preserving clinically-relevant features. We introduce MedVAE, a family of six large-scale 2D and 3D autoencoders capable of encoding medical images as downsized latent representations and decoding latent representations back to high-resolution images. We train MedVAE autoencoders using a novel two-stage training approach with 1,052,730 medical images. Across diverse tasks obtained from 20 medical image datasets, we demonstrate that (1) utilizing MedVAE latent representations in place of high-resolution images when training downstream models can lead to efficiency benefits (up to 70x improvement in throughput) while simultaneously preserving clinically-relevant features and (2) MedVAE can decode latent representations back to high-resolution images with high fidelity. Our work demonstrates that large-scale, generalizable autoencoders can help address critical efficiency challenges in the medical domain. Our code is available at https://github.com/StanfordMIMI/MedVAE.
医学图像以高分辨率和大视野获取,以捕捉临床决策所需的小特征。因此,在医学图像上训练深度学习模型可能会产生巨大的计算成本。在这项工作中,我们解决了缩小医学图像尺寸的挑战,以提高下游计算效率,同时保留与临床相关的特征。我们介绍了MedVAE,这是一系列大型二维和三维自编码器家族,能够将医学图像编码为缩小的潜在表示形式,并将潜在表示形式解码回高分辨率图像。我们使用一种新型的两阶段训练方法和1052730张医学图像来训练MedVAE自编码器。从20个医学图像数据集中获得的各种任务表明:(1)在训练下游模型时使用MedVAE潜在表示形式代替高分辨率图像,可以在保留与临床相关特征的同时带来效率效益(吞吐量最多提高70倍);(2)MedVAE可以将潜在表示形式解码回高分辨率图像,保真度很高。我们的研究表明,大规模、可推广的自编码器有助于解决医学领域的关键效率挑战。我们的代码位于https://github.com/StanfordMIMI/MedVAE。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
医疗图像的高分辨率和大视野带来了庞大的计算成本,对深度学习模型的训练构成挑战。本研究提出MedVAE,一种能够编码医疗图像为缩小潜在表征并解码回高分辨率图像的二维和三维自编码器家族。通过采用新型两阶段训练方法和大量医疗图像数据,研究证明MedVAE在提高下游模型计算效率的同时,能保留临床相关特征,并实现高达70倍的性能提升。此外,MedVAE还能高质量地解码潜在表征至高分辨率图像。研究展示了大规模自编码器在医疗领域解决效率问题的潜力。
Key Takeaways
- 医疗图像的高分辨率和大视野带来计算成本挑战。
- MedVAE是一种用于医疗图像处理的自编码器家族,能编码图像为缩小潜在表征。
- MedVAE采用新型两阶段训练方法和大量医疗图像数据进行训练。
- MedVAE能提高下游模型的计算效率,同时保留临床相关特征。
- MedVAE能实现高达70倍的性能提升。
- MedVAE能将潜在表征解码回高分辨率图像,且质量高。
点此查看论文截图

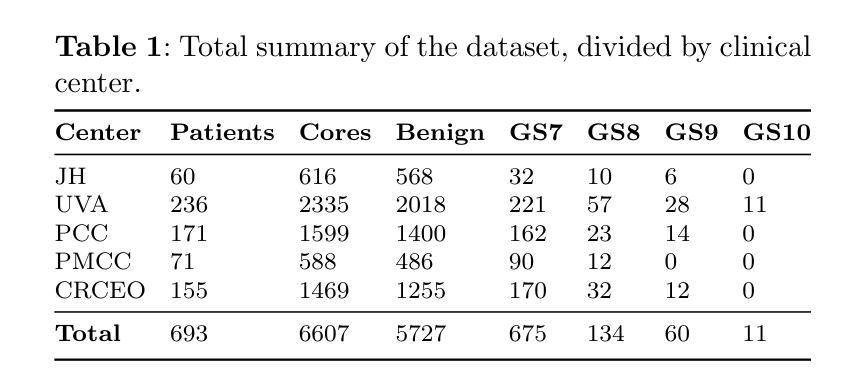
TRUSWorthy: Toward Clinically Applicable Deep Learning for Confident Detection of Prostate Cancer in Micro-Ultrasound
Authors:Mohamed Harmanani, Paul F. R. Wilson, Minh Nguyen Nhat To, Mahdi Gilany, Amoon Jamzad, Fahimeh Fooladgar, Brian Wodlinger, Purang Abolmaesumi, Parvin Mousavi
While deep learning methods have shown great promise in improving the effectiveness of prostate cancer (PCa) diagnosis by detecting suspicious lesions from trans-rectal ultrasound (TRUS), they must overcome multiple simultaneous challenges. There is high heterogeneity in tissue appearance, significant class imbalance in favor of benign examples, and scarcity in the number and quality of ground truth annotations available to train models. Failure to address even a single one of these problems can result in unacceptable clinical outcomes.We propose TRUSWorthy, a carefully designed, tuned, and integrated system for reliable PCa detection. Our pipeline integrates self-supervised learning, multiple-instance learning aggregation using transformers, random-undersampled boosting and ensembling: these address label scarcity, weak labels, class imbalance, and overconfidence, respectively. We train and rigorously evaluate our method using a large, multi-center dataset of micro-ultrasound data. Our method outperforms previous state-of-the-art deep learning methods in terms of accuracy and uncertainty calibration, with AUROC and balanced accuracy scores of 79.9% and 71.5%, respectively. On the top 20% of predictions with the highest confidence, we can achieve a balanced accuracy of up to 91%. The success of TRUSWorthy demonstrates the potential of integrated deep learning solutions to meet clinical needs in a highly challenging deployment setting, and is a significant step towards creating a trustworthy system for computer-assisted PCa diagnosis.
深度学习技术在通过经直肠超声(TRUS)检测前列腺癌(PCa)可疑病灶从而提高诊断效率方面显示出巨大潜力,但它们必须克服多个同时出现的挑战。组织外观存在高度异质性,良性样本的类别不平衡显著,用于训练模型的真实注释的数量和质量稀缺。即使不能解决其中任何一个问题,也可能会导致临床结果无法接受。我们提出了TRUSWorthy,这是一个精心设计、调整和集成的可靠PCa检测系统。我们的管道集成了自监督学习、使用变压器的多实例学习聚合、随机欠采样增强和集成:这些分别解决了标签稀缺、弱标签、类别不平衡和过度自信的问题。我们使用大规模多中心超声微数据集训和严格评估了我们的方法。我们的方法在准确度和不确定性校准方面超越了之前的最新深度学习技术,曲线下面积(AUROC)和平衡准确度分别为79.9%和71.5%。在预测置信度最高的前20%中,我们可以实现高达91%的平衡准确率。TRUSWorthy的成功展示了在高度挑战的部署环境中,集成深度学习解决方案满足临床需求的潜力,并且是朝着创建可信的计算机辅助PCa诊断系统迈出的重要一步。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF accepted to IJCARS. This preprint has not undergone post-submission improvements or corrections. To access the Version of Record of this article, see the journal reference below
Summary
在經直肠超聲波(TRUS)中檢測可疑病變以改善前列腺癌(PCa)診斷效果的深度學習方法展現出巨大潛力,但同時也需克服多重問題。本文提出TRUSWorthy系統,整合自監督學習、多實例學習聚合使用變換器、隨機欠樣本增強和集成等方法,解決標籤缺乏、弱標籤、類別不平衡和過度自信等問題。在大型多中心微超聲波數據集上進行訓練和嚴格評估,該方法性能優於先前最先進的深度學習方法,準確性和不確定度校正的AUROC和平衡準確度分別達到79.9%和71.5%,在預測置信度最高的前20%中可實現最高達91%的平衡準確度。TRUSWorthy的成功顯示出集成深度學習解決方案在高度挑戰性的部署環境中滿足診斷需求的潛力,是建立可信的電脈診斷系統的重要一步。
Key Takeaways
- 深度学习方法在前列腺癌诊断中具有巨大潜力,但面临组织外观高度异质性、良性示例显著类别不平衡和可用於训练模型的地面真相注释数量和質量稀缺等多重挑战。
- TRUSWorthy系统通过整合多种技术来解决这些挑战,包括自监督学习、多实例学习聚合使用变换器、随机欠采样增强和集成。
- TRUSWorthy系统在大型多中心微超声数据上进行训练和严格评估,性能优于先前的最先进深度学习方法。
- 该系统在准确度和不确定性校准方面的表现优异,AUROC和平衡准确度分别为79.9%和71.5%。
- 在高置信度预测的前20%中,平衡準確度可達到91%,顯示出該系統的可靠性。
- TRUSWorthy的成功证明了集成深度學習方案在极具挑战性的部署环境中满足临床诊断需求的潜力。
点此查看论文截图

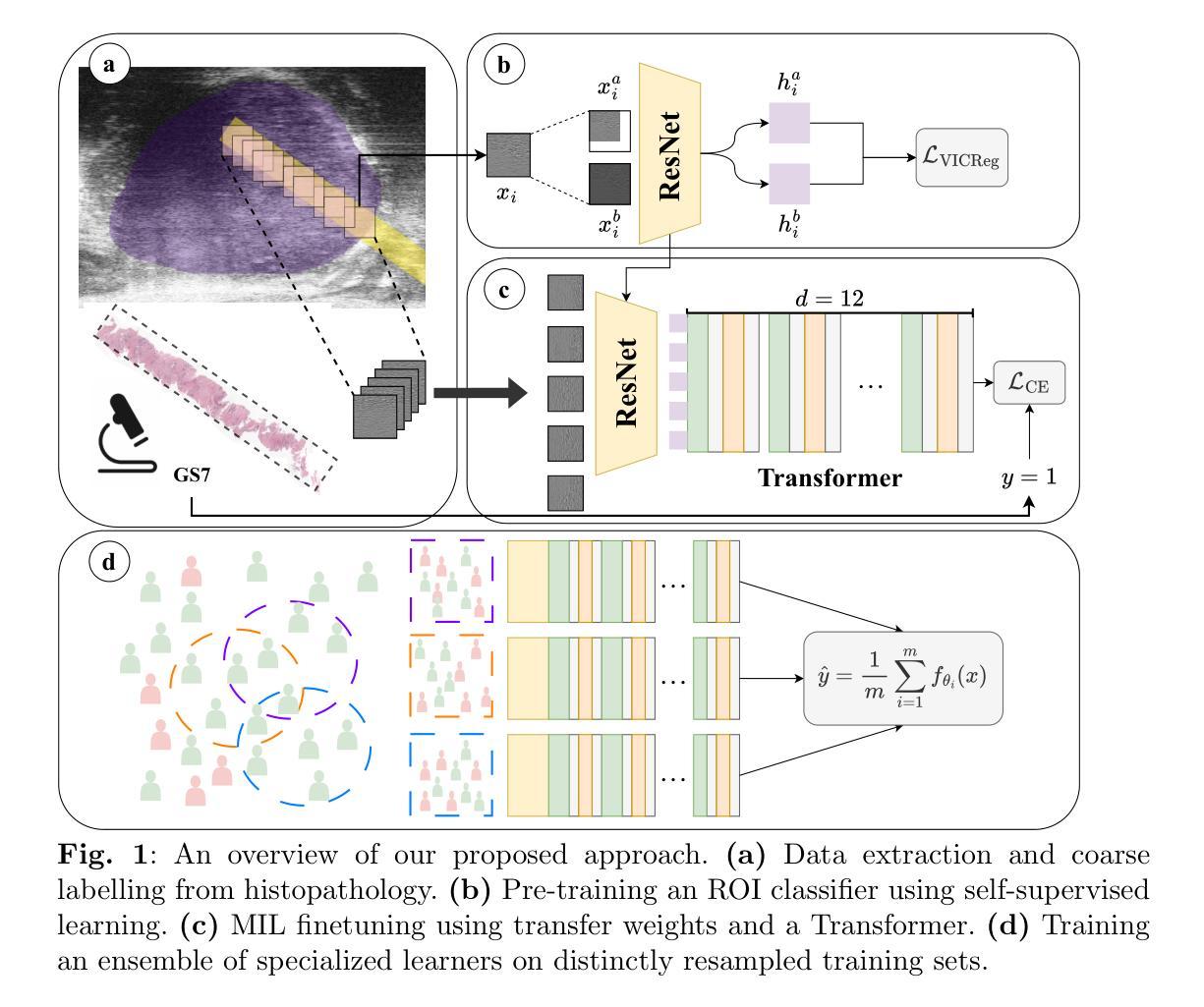
Vision Foundation Models in Medical Image Analysis: Advances and Challenges
Authors:Pengchen Liang, Bin Pu, Haishan Huang, Yiwei Li, Hualiang Wang, Weibo Ma, Qing Chang
The rapid development of Vision Foundation Models (VFMs), particularly Vision Transformers (ViT) and Segment Anything Model (SAM), has sparked significant advances in the field of medical image analysis. These models have demonstrated exceptional capabilities in capturing long-range dependencies and achieving high generalization in segmentation tasks. However, adapting these large models to medical image analysis presents several challenges, including domain differences between medical and natural images, the need for efficient model adaptation strategies, and the limitations of small-scale medical datasets. This paper reviews the state-of-the-art research on the adaptation of VFMs to medical image segmentation, focusing on the challenges of domain adaptation, model compression, and federated learning. We discuss the latest developments in adapter-based improvements, knowledge distillation techniques, and multi-scale contextual feature modeling, and propose future directions to overcome these bottlenecks. Our analysis highlights the potential of VFMs, along with emerging methodologies such as federated learning and model compression, to revolutionize medical image analysis and enhance clinical applications. The goal of this work is to provide a comprehensive overview of current approaches and suggest key areas for future research that can drive the next wave of innovation in medical image segmentation.
视觉基础模型(VFMs)的快速发展,特别是视觉转换器(ViT)和分段任何模型(SAM),在医学图像分析领域引发了重大突破。这些模型在捕捉长期依赖关系和实现分割任务的高泛化方面表现出卓越的能力。然而,将这些大型模型适应医学图像分析面临几个挑战,包括医学图像和自然图像领域之间的差异、需要有效的模型适应策略以及小规模医学数据集的局限性。本文综述了将VFMs适应医学图像分割的最新研究,重点关注领域适应、模型压缩和联邦学习的挑战。我们讨论了基于适配器的改进、知识蒸馏技术和多尺度上下文特征建模的最新发展,并提出了克服这些瓶颈的未来发展方向。我们的分析强调了VFMs的潜力,以及与联邦学习和模型压缩等新兴方法相结合,将革命医学图像分析并增强临床应用。本工作的目标是提供当前方法论的全面概述,并为未来的研究提出关键领域,以推动医学图像分割领域的下一波创新。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 17 pages, 1 figure
Summary
医学图像分析领域因Vision Foundation Models(VFMs)的快速发展,尤其是Vision Transformers(ViT)和Segment Anything Model(SAM)的崛起而取得显著进步。这些模型在捕捉长程依赖性和实现高泛化分割任务方面表现出卓越的能力。然而,将这些大型模型应用于医学图像分析面临诸多挑战,包括医学与自然图像领域之间的差异、对高效模型适配策略的需求以及小规模医学数据集的局限性。本文综述了VFMs在医学图像分割中的最新研究,重点关注领域适配、模型压缩和联邦学习的挑战。通过讨论基于适配器的改进、知识蒸馏技术和多尺度上下文特征建模的最新进展,提出了克服这些瓶颈的未来方向。本文强调了VFMs的潜力,以及联邦学习和模型压缩等新兴方法,这些有望革新医学图像分析,提高临床应用。
Key Takeaways
- Vision Foundation Models (VFMs) 在医学图像分析领域取得显著进展,特别是Vision Transformers (ViT) 和 Segment Anything Model (SAM)。
- VFMs 在捕捉长程依赖性和实现高泛化分割任务方面表现出卓越能力。
- 将VFMs应用于医学图像分析面临诸多挑战,包括领域差异、模型适配策略需求和医学数据集局限性。
- 论文综述了VFMs在医学图像分割中的最新研究,关注领域适配、模型压缩和联邦学习的挑战。
- 适配器改进、知识蒸馏技术和多尺度上下文特征建模是克服挑战的最新进展。
- VFMs 的潜力巨大,与新兴方法如联邦学习和模型压缩结合,有望革新医学图像分析,提高临床应用。
点此查看论文截图

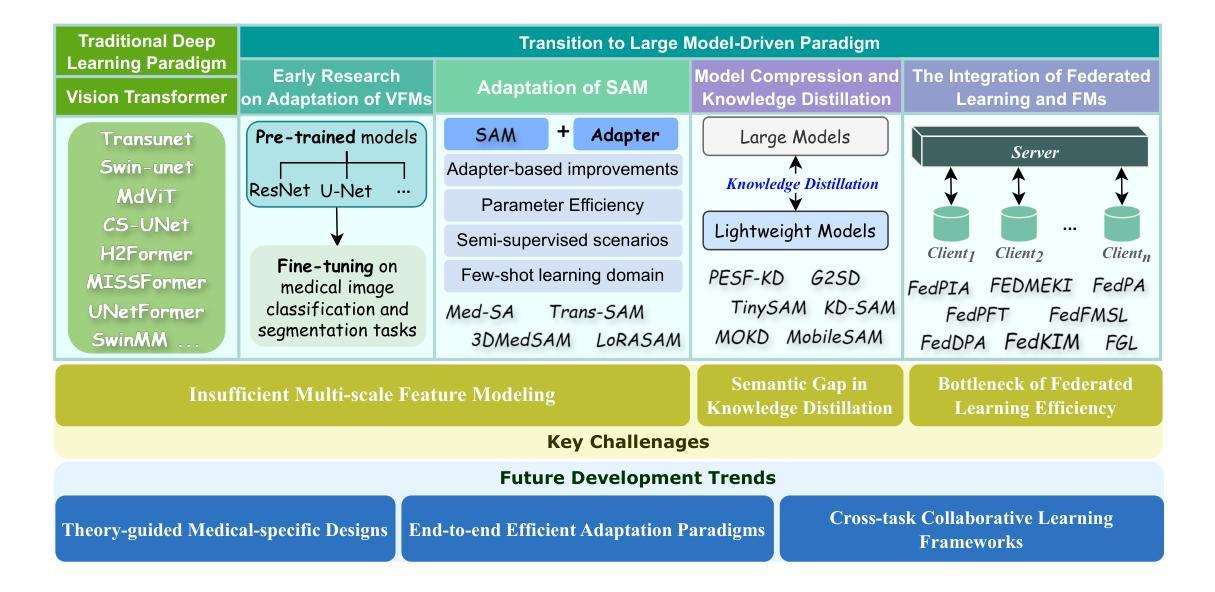
A Mobile Robotic Approach to Autonomous Surface Scanning in Legal Medicine
Authors:Sarah Grube, Sarah Latus, Martin Fischer, Vidas Raudonis, Axel Heinemann, Benjamin Ondruschka, Alexander Schlaefer
Purpose: Comprehensive legal medicine documentation includes both an internal but also an external examination of the corpse. Typically, this documentation is conducted manually during conventional autopsy. A systematic digital documentation would be desirable, especially for the external examination of wounds, which is becoming more relevant for legal medicine analysis. For this purpose, RGB surface scanning has been introduced. While a manual full surface scan using a handheld camera is timeconsuming and operator dependent, floor or ceiling mounted robotic systems require substantial space and a dedicated room. Hence, we consider whether a mobile robotic system can be used for external documentation. Methods: We develop a mobile robotic system that enables full-body RGB-D surface scanning. Our work includes a detailed configuration space analysis to identify the environmental parameters that need to be considered to successfully perform a surface scan. We validate our findings through an experimental study in the lab and demonstrate the system’s application in a legal medicine environment. Results: Our configuration space analysis shows that a good trade-off between coverage and time is reached with three robot base positions, leading to a coverage of 94.96 %. Experiments validate the effectiveness of the system in accurately capturing body surface geometry with an average surface coverage of 96.90 +- 3.16 % and 92.45 +- 1.43 % for a body phantom and actual corpses, respectively. Conclusion: This work demonstrates the potential of a mobile robotic system to automate RGB-D surface scanning in legal medicine, complementing the use of post-mortem CT scans for inner documentation. Our results indicate that the proposed system can contribute to more efficient and autonomous legal medicine documentation, reducing the need for manual intervention.
目的:全面的法律医学文档记录包括内部和外部的尸体检查。通常,这种文档记录是在传统尸检过程中手动进行的。对于伤口的外部检查,尤其需要系统的数字化记录,这在法律医学分析中具有越来越重要的意义。为此,已经引入了RGB表面扫描技术。使用手持相机进行手动全面表面扫描既耗时又依赖于操作人员,而地面或天花板安装的机器人系统则需要大量空间和一个专门的房间。因此,我们考虑是否可以使用移动机器人系统进行外部记录。方法:我们开发了一种移动机器人系统,能够进行全身RGB-D表面扫描。我们的工作包括详细的配置空间分析,以识别成功执行表面扫描需要考虑的环境参数。我们通过实验室的实验研究验证了我们的发现,并展示了该系统在法律医学环境中的实际应用。结果:我们的配置空间分析表明,通过三个机器人基座位置可以达到覆盖率和时间之间的良好平衡,覆盖率为94.96%。实验验证了该系统在准确捕捉人体表面几何结构方面的有效性,对于人体假体和实际尸体,平均表面覆盖率分别为96.90 ± 3.16%和92.45 ± 1.43%。结论:这项工作证明了移动机器人系统在法律医学中自动进行RGB-D表面扫描的潜力,可以配合死后CT扫描用于内部记录。我们的结果表明,所提出的系统可以提高法律医学记录的效率和自主性,减少人工干预的需求。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Submitted and accepted for presentation at CARS 2025. This preprint has not undergone peer review or post-submission revisions. The final version of this work will appear in the official CARS 2025 proceedings
Summary
本文介绍了一种用于法律医学文档记录的移动机器人系统,该系统能够进行全身RGB-D表面扫描。通过配置空间分析,确定了成功进行表面扫描所需考虑的环境参数。实验验证表明,该系统能够准确捕捉人体表面几何结构,对尸体进行自动RGB表面扫描具有潜力,有助于更有效率且自主的医学文档记录。
Key Takeaways
- 移动机器人系统被开发用于法律医学中的全身RGB-D表面扫描。
- 配置空间分析确定了成功进行表面扫描所需考虑的环境参数。
- 实验验证表明,该系统能够准确捕捉人体表面几何结构。
- 系统在尸体表面扫描的覆盖率高,为94.96%。
- 与尸体幻影和真实尸体的实验表明,系统表面覆盖率为96.90%±3.16%和92.45%±1.43%。
- 该系统有助于更有效率且自主的医学文档记录,减少人工干预的需求。
点此查看论文截图

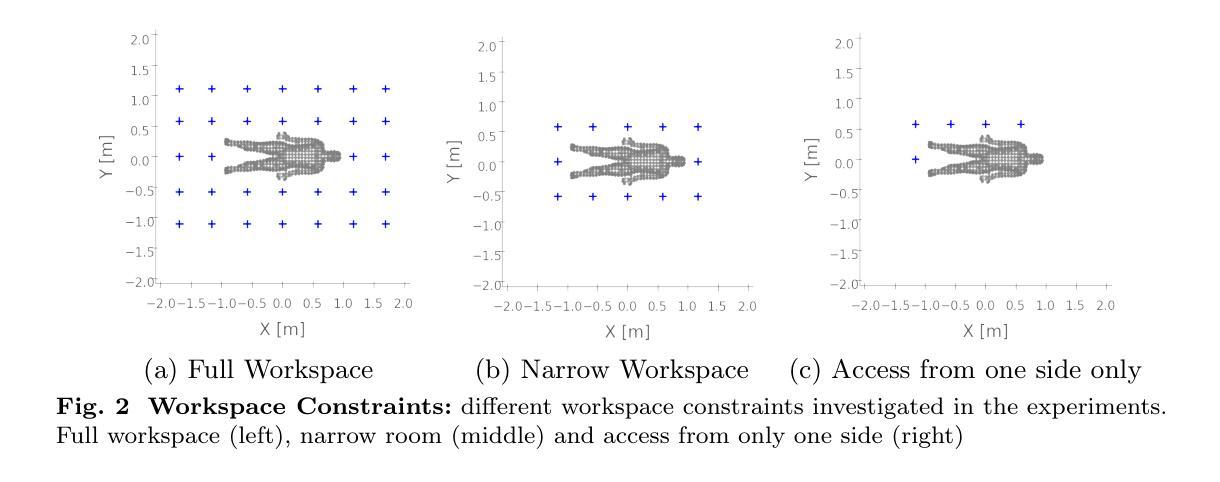
Role of the Pretraining and the Adaptation data sizes for low-resource real-time MRI video segmentation
Authors:Masoud Thajudeen Tholan, Vinayaka Hegde, Chetan Sharma, Prasanta Kumar Ghosh
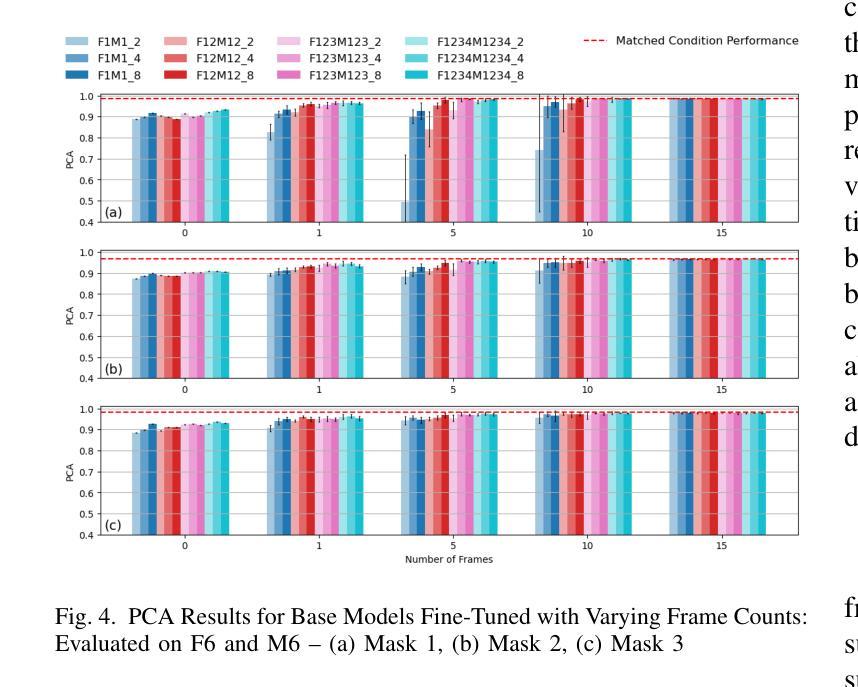
Real-time Magnetic Resonance Imaging (rtMRI) is frequently used in speech production studies as it provides a complete view of the vocal tract during articulation. This study investigates the effectiveness of rtMRI in analyzing vocal tract movements by employing the SegNet and UNet models for Air-Tissue Boundary (ATB)segmentation tasks. We conducted pretraining of a few base models using increasing numbers of subjects and videos, to assess performance on two datasets. First, consisting of unseen subjects with unseen videos from the same data source, achieving 0.33% and 0.91% (Pixel-wise Classification Accuracy (PCA) and Dice Coefficient respectively) better than its matched condition. Second, comprising unseen videos from a new data source, where we obtained an accuracy of 99.63% and 98.09% (PCA and Dice Coefficient respectively) of its matched condition performance. Here, matched condition performance refers to the performance of a model trained only on the test subjects which was set as a benchmark for the other models. Our findings highlight the significance of fine-tuning and adapting models with limited data. Notably, we demonstrated that effective model adaptation can be achieved with as few as 15 rtMRI frames from any new dataset.
实时磁共振成像(rtMRI)在语音生产研究中经常被使用,因为它能提供发音时整个声道的视图。本研究探讨了rtMRI在分析声道运动中的有效性,采用SegNet和UNet模型进行空气-组织边界(ATB)分割任务。我们通过对多个基础模型进行预训练,并使用不断增加的受试者和视频数量来评估两个数据集上的性能。首先,我们使用了来自同一数据源的未见过的受试者及其视频,相较于匹配条件下的性能,取得了0.33%(像素级分类准确度)和0.91%(Dice系数)的改进。其次,我们使用了来自新数据源的未见过的视频,相较于匹配条件下的性能,我们获得了99.63%(PCA)和98.09%(Dice系数)的准确率。这里,匹配条件下的性能是指仅对测试受试者进行训练的模型的表现,它被设定为其他模型性能的基准。我们的研究结果表明了微调并适应有限数据的模型的重要性。值得注意的是,我们证明仅使用任何新数据集的15个rtMRI帧即可实现有效的模型适应。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to ICASSP 2025
Summary
本研究利用rtMRI实时磁共振成像技术,通过SegNet和UNet模型对空气组织边界(ATB)分割任务进行分析,探讨其在研究语音产生过程中声带运动的有效性。研究通过在不同数据集上预训练基础模型并增加受试者和视频数量来评估性能。在未见受试者和未见视频的数据集上取得了优异的表现,且在新数据源未见视频的测试中,模型性能达到了很高的准确率。此外,研究发现精细调整模型并适应有限数据至关重要,仅使用新数据集的少量rtMRI帧即可实现有效的模型适应。
Key Takeaways
- rtMRI在语音产生研究中被广泛应用于观察声带运动。
- SegNet和UNet模型被用于进行空气组织边界(ATB)分割任务的分析。
- 通过预训练基础模型并增加受试者和视频数量来评估模型性能。
- 在未见受试者和未见视频的数据集上取得了优异表现。
- 在新数据源未见视频的测试中,模型性能达到了很高的准确率。
- 精细调整模型并适应有限数据至关重要。
点此查看论文截图

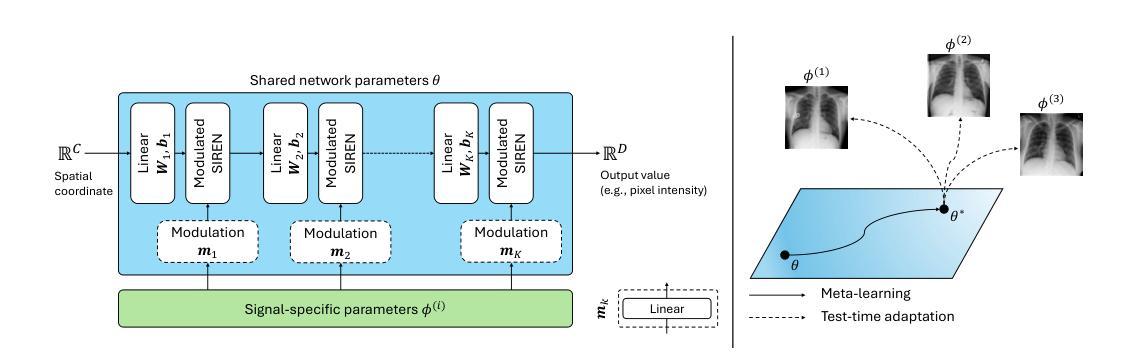
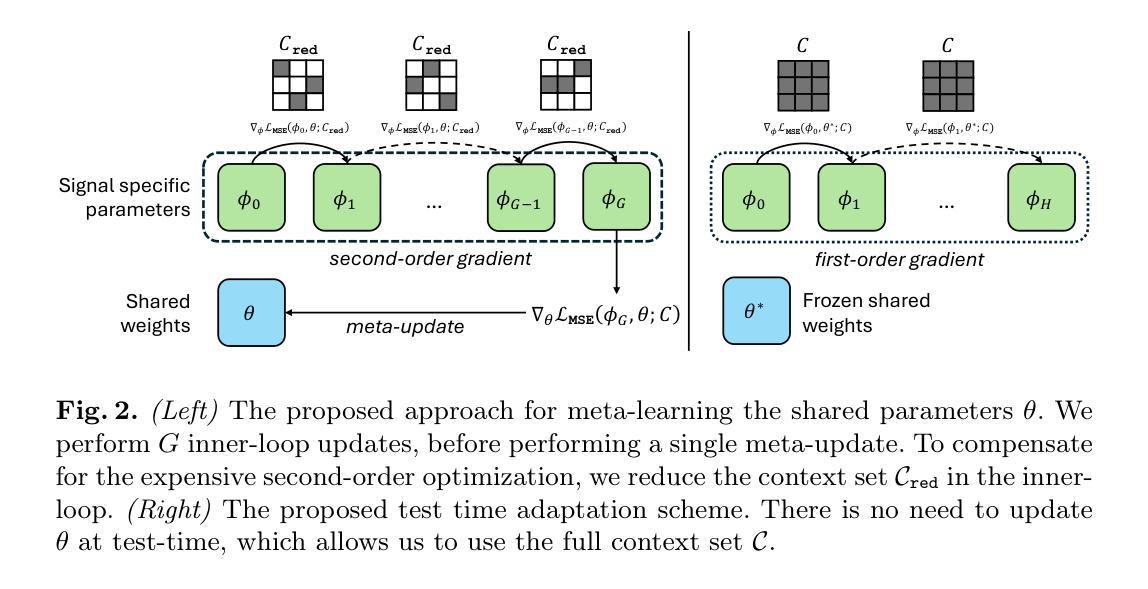
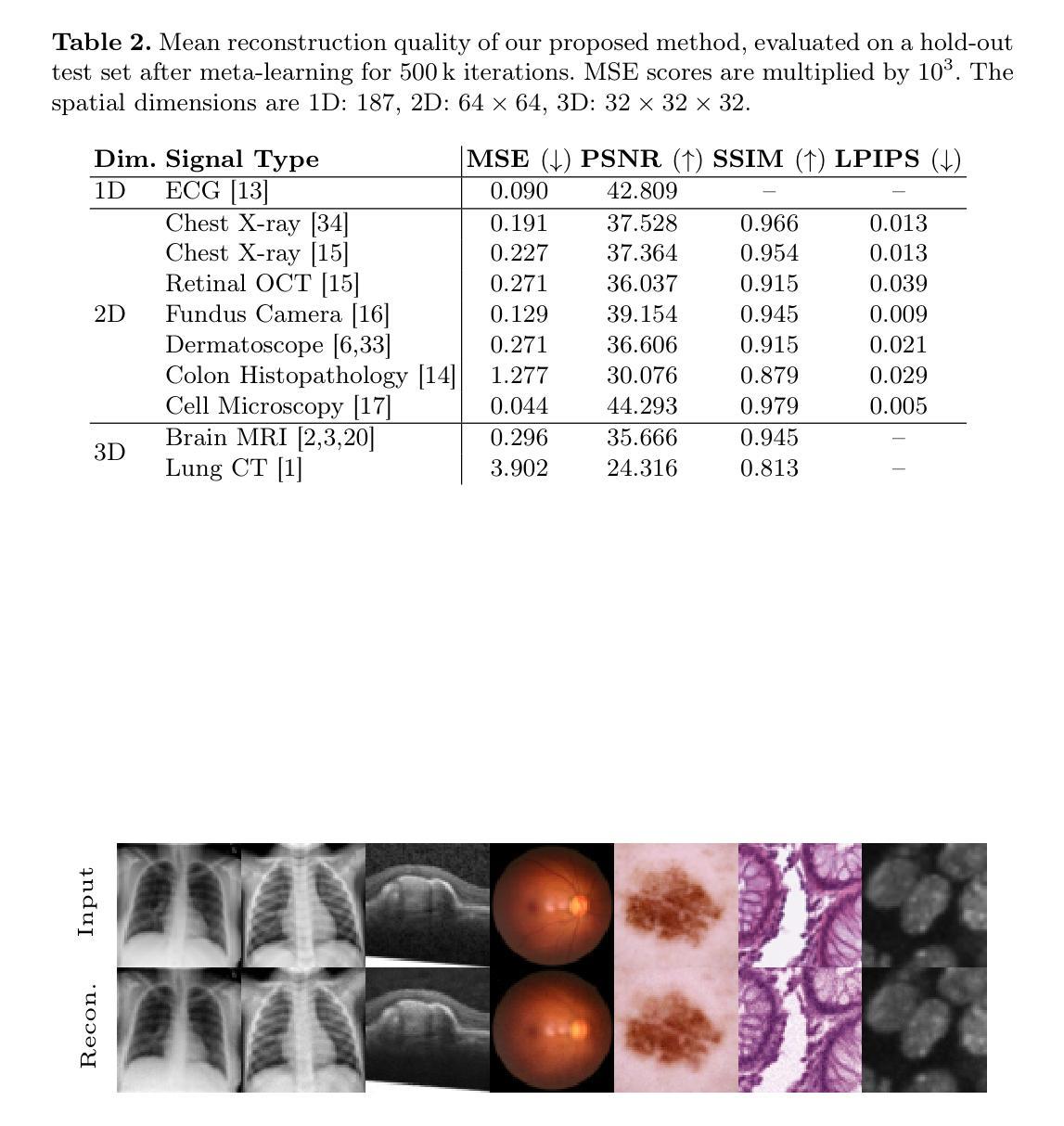
MedFuncta: Modality-Agnostic Representations Based on Efficient Neural Fields
Authors:Paul Friedrich, Florentin Bieder, Phlippe C. Cattin
Recent research in medical image analysis with deep learning almost exclusively focuses on grid- or voxel-based data representations. We challenge this common choice by introducing MedFuncta, a modality-agnostic continuous data representation based on neural fields. We demonstrate how to scale neural fields from single instances to large datasets by exploiting redundancy in medical signals and by applying an efficient meta-learning approach with a context reduction scheme. We further address the spectral bias in commonly used SIREN activations, by introducing an $\omega_0$-schedule, improving reconstruction quality and convergence speed. We validate our proposed approach on a large variety of medical signals of different dimensions and modalities (1D: ECG; 2D: Chest X-ray, Retinal OCT, Fundus Camera, Dermatoscope, Colon Histopathology, Cell Microscopy; 3D: Brain MRI, Lung CT) and successfully demonstrate that we can solve relevant downstream tasks on these representations. We additionally release a large-scale dataset of > 550k annotated neural fields to promote research in this direction.
近期深度学习在医学图像分析领域的研究几乎完全集中在基于网格或体素的数据表示上。我们通过引入MedFuncta这一基于神经场的模态无关连续数据表示方式,对这一常见选择提出了挑战。我们展示了如何利用医学信号中的冗余信息,通过采用带有上下文缩减方案的高效元学习方法,将神经场从单个实例扩展到大型数据集。此外,我们通过引入ω0调度方法解决了常用SIREN激活函数中的频谱偏差问题,提高了重建质量和收敛速度。我们在多种不同维度和模态的医学信号(1D:心电图;2D:胸部X射线、视网膜OCT、眼底相机、皮肤显微镜、结肠组织病理学、细胞显微镜;3D:脑部MRI、肺部CT)上验证了我们的方法,并成功证明我们能够在这些表示上解决相关的下游任务。此外,我们还发布了一个包含超过55万个注释神经场的大型数据集,以促进这一方向的研究。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Code and Dataset: https://github.com/pfriedri/medfuncta
Summary
基于深度学习在医学图像分析领域的研究主要聚焦于网格或体素数据表示。本研究通过引入MedFuncta这一模态无关的连续数据表示方法,对这一现象提出挑战。该研究通过利用医学信号的冗余信息和采用一种带有上下文缩减方案的高效元学习方法实现了神经网络从单一实例到大数据集的扩展。同时,该研究针对常用SIREN激活函数中的频谱偏差问题,通过引入ω0调度方案,提高了重建质量和收敛速度。本研究在不同维度和模态的医学信号上验证了所提出方法的有效性,并成功展示了其在相关下游任务中的应用潜力。此外,该研究还发布了一个大规模神经场数据集,以促进该方向的研究发展。
Key Takeaways
- 研究挑战了深度学习在医学图像分析中的主流数据表示方法,引入了模态无关的连续数据表示方法MedFuncta。
- 通过利用医学信号的冗余信息和高效元学习方法,实现了神经网络在大数据集上的应用。
- 针对SIREN激活函数的频谱偏差问题,提出了ω0调度方案,提高了模型性能。
- 在多种维度和模态的医学信号上验证了所提出方法的有效性。
- 成功展示了方法在相关下游任务中的应用潜力。
- 发布了大规模神经场数据集,促进研究方向的发展。
点此查看论文截图


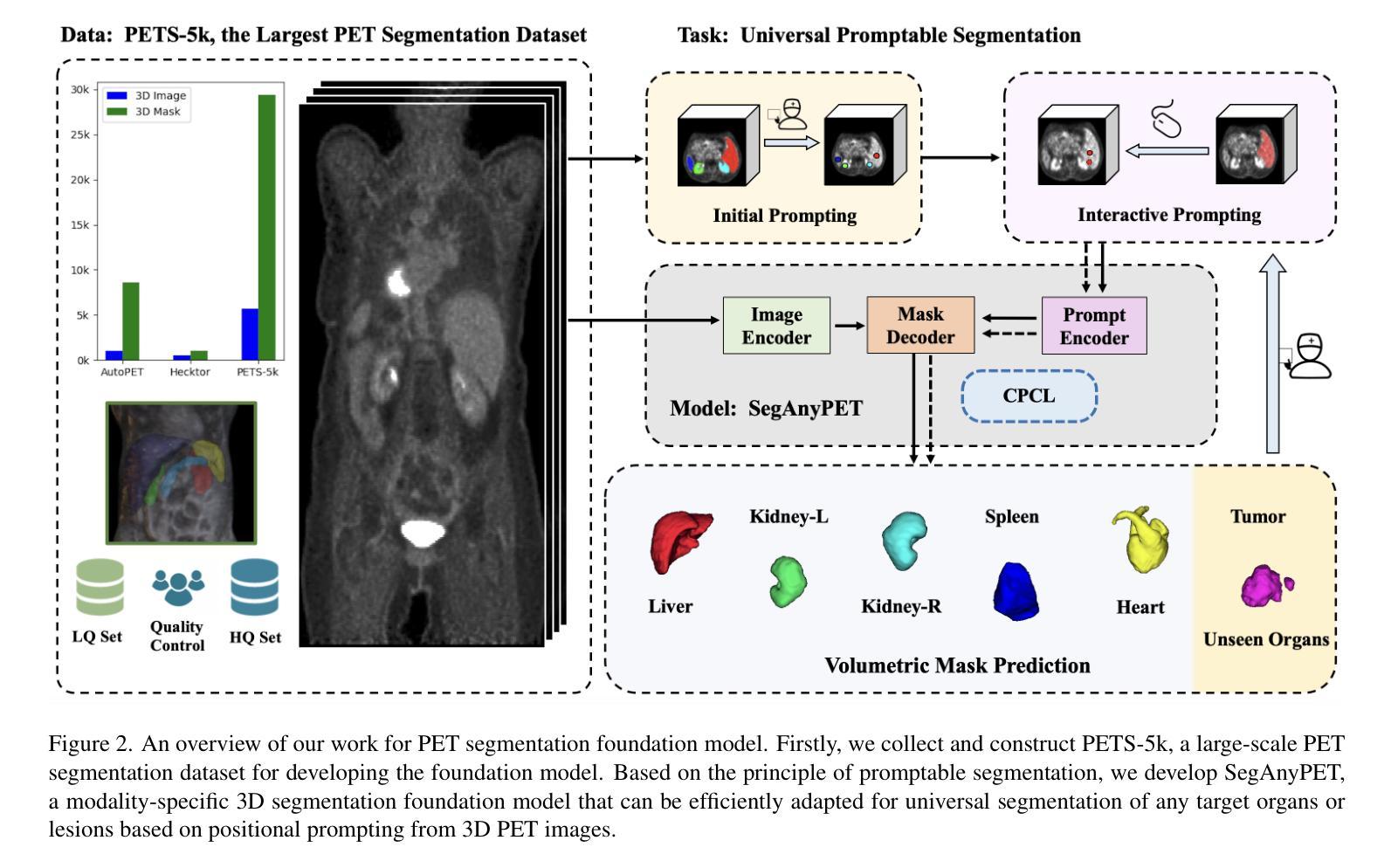
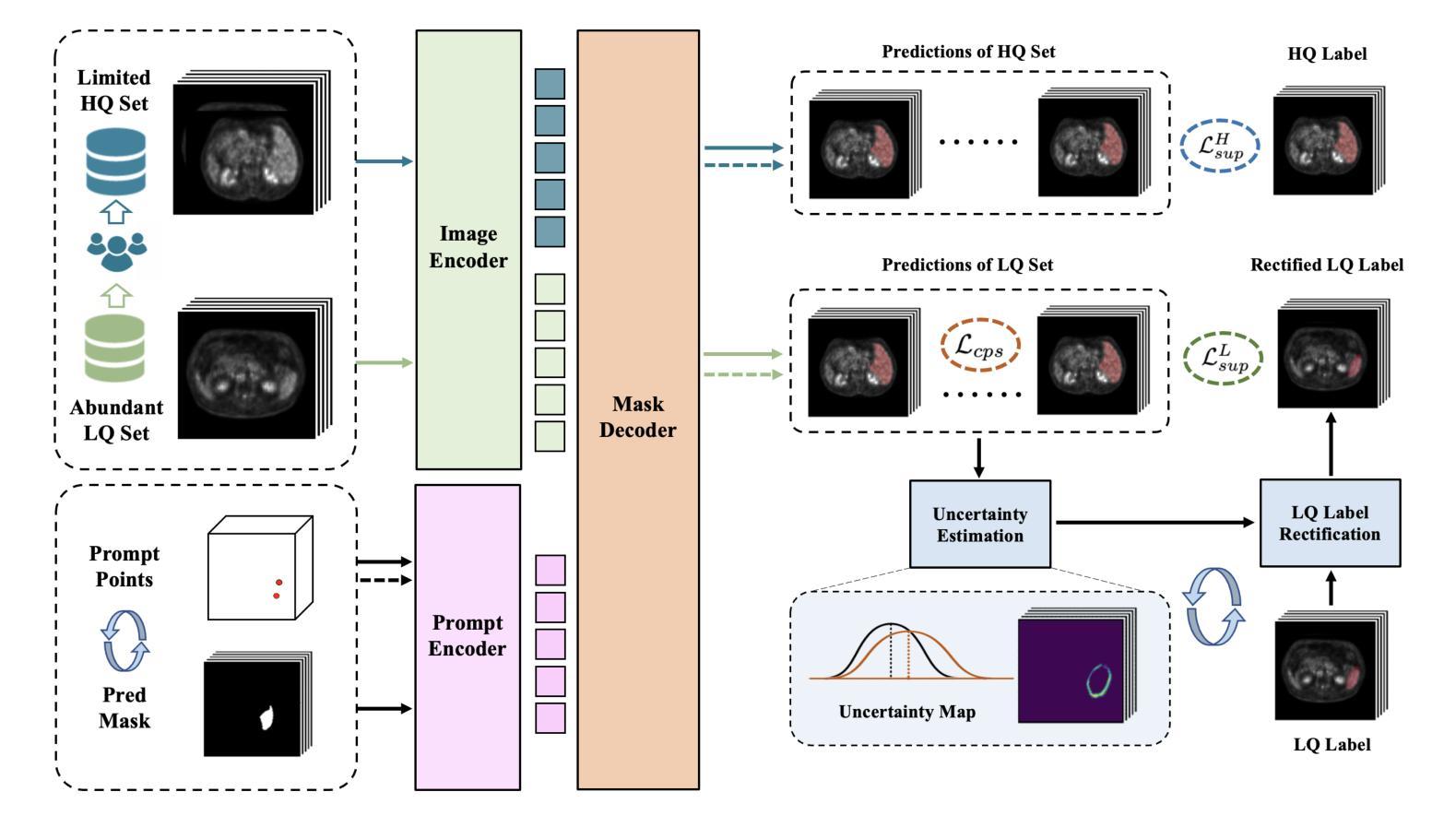
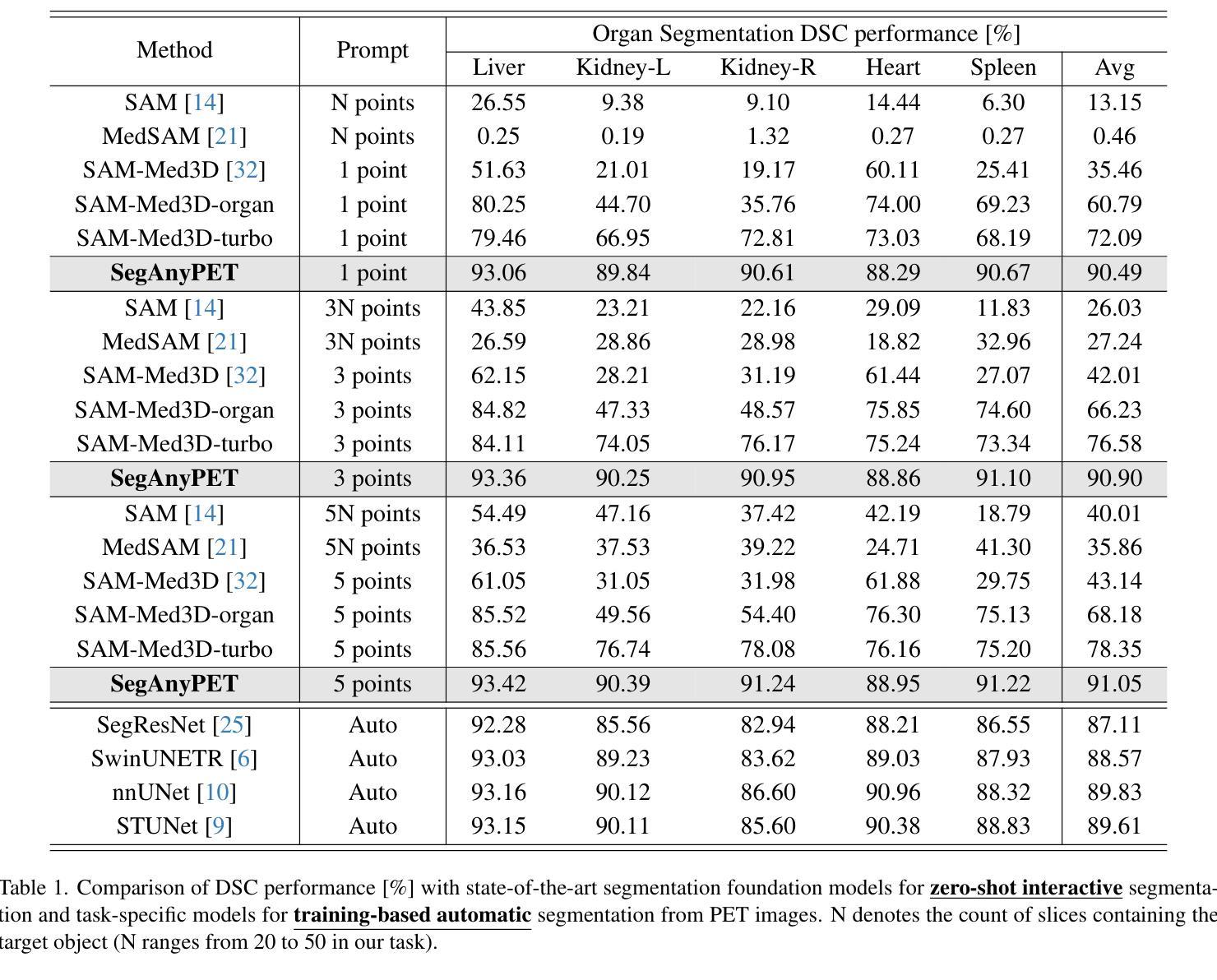
SegAnyPET: Universal Promptable Segmentation from Positron Emission Tomography Images
Authors:Yichi Zhang, Le Xue, Wenbo Zhang, Lanlan Li, Yuchen Liu, Chen Jiang, Yuan Cheng, Yuan Qi
Positron Emission Tomography (PET) imaging plays a crucial role in modern medical diagnostics by revealing the metabolic processes within a patient’s body, which is essential for quantification of therapy response and monitoring treatment progress. However, the segmentation of PET images presents unique challenges due to their lower contrast and less distinct boundaries compared to other structural medical modalities. Recent developments in segmentation foundation models have shown superior versatility across diverse natural image segmentation tasks. Despite the efforts of medical adaptations, these works primarily focus on structural medical images with detailed physiological structural information and exhibit poor generalization ability when adapted to molecular PET imaging. In this paper, we collect and construct PETS-5k, the largest PET segmentation dataset to date, comprising 5,731 three-dimensional whole-body PET images and encompassing over 1.3M 2D images. Based on the established dataset, we develop SegAnyPET, a modality-specific 3D foundation model for universal promptable segmentation from PET images. To issue the challenge of discrepant annotation quality of PET images, we adopt a cross prompting confident learning (CPCL) strategy with an uncertainty-guided self-rectification process to robustly learn segmentation from high-quality labeled data and low-quality noisy labeled data. Experimental results demonstrate that SegAnyPET can correctly segment seen and unseen targets using only one or a few prompt points, outperforming state-of-the-art foundation models and task-specific fully supervised models with higher accuracy and strong generalization ability for universal segmentation. As the first foundation model for PET images, we believe that SegAnyPET will advance the applications to various downstream tasks for molecular imaging.
正电子发射断层扫描(PET)成像在现代医学诊断中发挥着关键作用,它能够揭示患者体内的代谢过程,这对于量化治疗反应和监测治疗进展至关重要。然而,由于PET图像的对比度较低,边界不够清晰,与其他结构医学图像相比,其分割面临独特挑战。最近的分割基础模型的发展表明,它们在各种自然图像分割任务中具有出色的多功能性。尽管进行了医学适应性的努力,但这些工作主要集中在具有详细生理结构信息的结构医学图像上,而在适应分子PET成像时表现出较差的泛化能力。在本文中,我们收集和构建了迄今为止最大的PET分割数据集PETS-5k,包含5731个三维全身PET图像和超过130万个二维图像。基于建立的数据集,我们开发了一种特定模态的三维基础模型SegAnyPET,用于从PET图像进行通用即时分割。为了解决PET图像标注质量不一致的问题,我们采用带有不确定性引导的自我修正过程的交叉提示置信学习(CPCL)策略,以稳健地从高质量标注数据和低质量噪声标注数据中学习分割。实验结果表明,SegAnyPET仅使用一个或少数提示点就能正确分割已知和未知目标,优于最新的基础模型和任务特定全监督模型,具有更高的准确性和强大的泛化能力进行通用分割。作为第一个用于PET图像的基础模型,我们相信SegAnyPET将推动其在分子成像的各种下游任务中的应用。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了正电子发射断层扫描(PET)成像在现代医学诊断中的重要性,并指出了PET图像分割面临的挑战。为此,作者构建了迄今为止最大的PET分割数据集PETS-5k,并在此基础上开发了一种适用于PET图像的通用即时分割模型SegAnyPET。该模型采用跨提示置信学习(CPCL)策略,可稳健地从高质量标注数据和低质量噪声标注数据中学习分割。实验结果表明,SegAnyPET能够正确分割已见和未见目标,优于最先进的基础模型和特定任务的完全监督模型,具有更高的准确性和强大的通用分割能力。
Key Takeaways
- PET成像在现代医学诊断中起关键作用,能揭示患者体内的代谢过程,对治疗反应的量化和治疗进展的监测至关重要。
- PET图像分割面临挑战,因其对比度较低,边界较模糊。
- 构建了迄今为止最大的PET分割数据集PETS-5k,包含5731个三维全身PET图像和超过130万个二维图像。
- 开发了适用于PET图像的通用即时分割模型SegAnyPET。
- SegAnyPET采用跨提示置信学习(CPCL)策略,可从不同质量标注数据中稳健学习分割。
- 实验结果表明SegAnyPET性能优越,能够正确分割已见和未见目标,并具备强大的通用分割能力。
点此查看论文截图

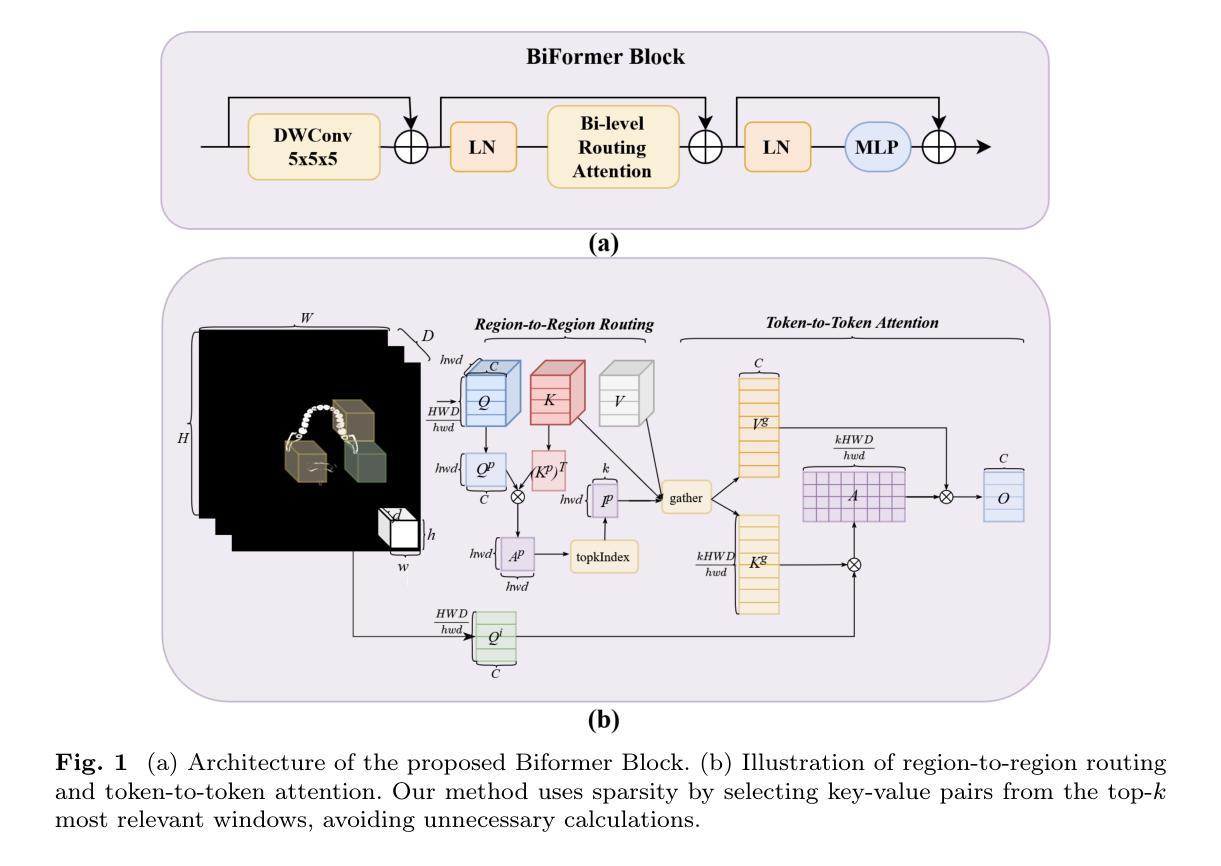
H3DE-Net: Efficient and Accurate 3D Landmark Detection in Medical Imaging
Authors:Zhen Huang, Ronghao Xu, Xiaoqian Zhou, Yangbo Wei, Suhua Wang, Xiaoxin Sun, Han Li, Qingsong Yao
3D landmark detection is a critical task in medical image analysis, and accurately detecting anatomical landmarks is essential for subsequent medical imaging tasks. However, mainstream deep learning methods in this field struggle to simultaneously capture fine-grained local features and model global spatial relationships, while maintaining a balance between accuracy and computational efficiency. Local feature extraction requires capturing fine-grained anatomical details, while global modeling requires understanding the spatial relationships within complex anatomical structures. The high-dimensional nature of 3D volume further exacerbates these challenges, as landmarks are sparsely distributed, leading to significant computational costs. Therefore, achieving efficient and precise 3D landmark detection remains a pressing challenge in medical image analysis. In this work, We propose a \textbf{H}ybrid \textbf{3}D \textbf{DE}tection \textbf{Net}(H3DE-Net), a novel framework that combines CNNs for local feature extraction with a lightweight attention mechanism designed to efficiently capture global dependencies in 3D volumetric data. This mechanism employs a hierarchical routing strategy to reduce computational cost while maintaining global context modeling. To our knowledge, H3DE-Net is the first 3D landmark detection model that integrates such a lightweight attention mechanism with CNNs. Additionally, integrating multi-scale feature fusion further enhances detection accuracy and robustness. Experimental results on a public CT dataset demonstrate that H3DE-Net achieves state-of-the-art(SOTA) performance, significantly improving accuracy and robustness, particularly in scenarios with missing landmarks or complex anatomical variations. We aready open-source our project, including code, data and model weights.
三维(3D)地标检测是医学图像分析中的一项关键任务,而准确检测解剖地标对于后续医学成像任务至关重要。然而,该领域的主流深度学习方法难以在捕捉精细局部特征、对全局空间关系进行建模的同时,保持准确性和计算效率之间的平衡。局部特征提取需要捕捉精细的解剖细节,而全局建模则需要理解复杂解剖结构内的空间关系。由于地标分布稀疏,三维体积的高维性质进一步加剧了这些挑战,导致计算成本显著增加。因此,实现高效且精确的3D地标检测仍然是医学图像分析领域的一个紧迫挑战。在本研究中,我们提出了一种混合三维检测网络(Hybrid 3D Detection Net,简称H3DE-Net),这是一个新颖框架,结合了卷积神经网络(CNN)用于局部特征提取和一个轻量级注意力机制,旨在高效捕捉三维体积数据中的全局依赖关系。该机制采用分层路由策略来降低计算成本,同时保持全局上下文建模。据我们所知,H3DE-Net是首个将轻量级注意力机制与CNN结合用于三维地标检测的模型。此外,多尺度特征融合技术进一步提高了检测精度和鲁棒性。在公共CT数据集上的实验结果表明,H3DE-Net达到了最新的性能水平,特别是在地标缺失或解剖结构复杂的场景中,显著提高了准确性和鲁棒性。我们已经开源了我们的项目,包括代码、数据和模型权重。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种混合三维检测网络(H3DE-Net),结合卷积神经网络(CNN)进行局部特征提取,并设计了一种轻量级注意力机制以高效捕捉三维体积数据中的全局依赖关系。该方法采用分层路由策略降低计算成本,同时保持全局上下文建模。在公开CT数据集上的实验结果表明,H3DE-Net达到最先进的性能,特别是在缺失地标或复杂解剖变异情况下,显著提高了准确性和鲁棒性。
Key Takeaways
- 3D landmark detection在医学图像分析中是关键任务。
- 主流深度学习方法难以在捕捉局部精细特征和建模全局空间关系之间保持平衡。
- H3DE-Net结合CNN进行局部特征提取,并采用轻量级注意力机制捕捉全局依赖。
- 分层路由策略降低计算成本,同时保持全局上下文建模。
- H3DE-Net是首个结合轻量级注意力机制和CNN的3D地标检测模型。
- 多尺度特征融合进一步提高检测准确性和鲁棒性。
点此查看论文截图

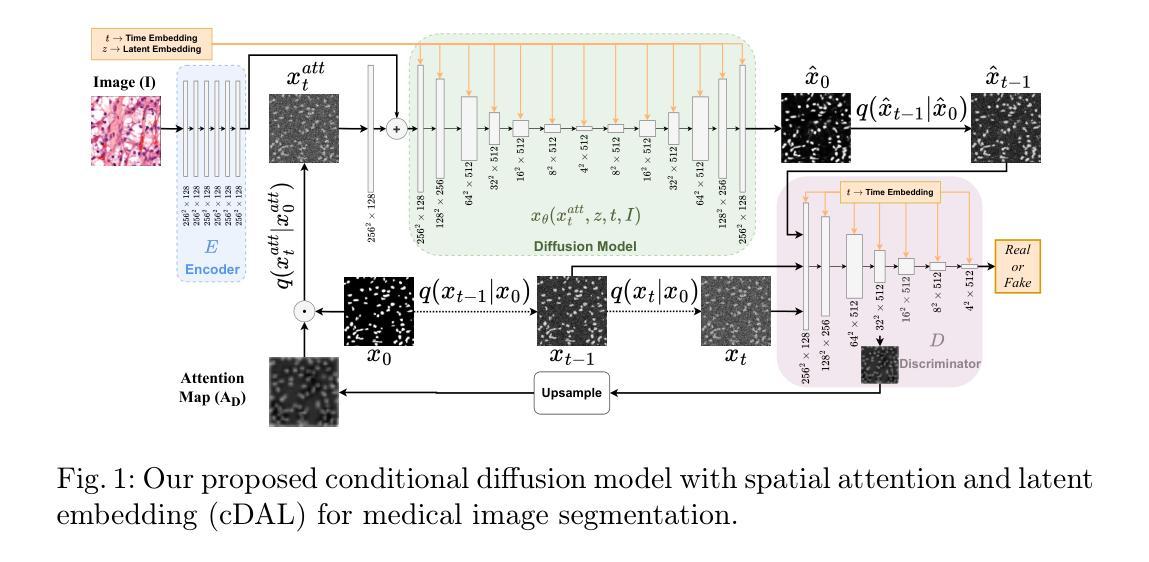
Conditional diffusion model with spatial attention and latent embedding for medical image segmentation
Authors:Behzad Hejrati, Soumyanil Banerjee, Carri Glide-Hurst, Ming Dong
Diffusion models have been used extensively for high quality image and video generation tasks. In this paper, we propose a novel conditional diffusion model with spatial attention and latent embedding (cDAL) for medical image segmentation. In cDAL, a convolutional neural network (CNN) based discriminator is used at every time-step of the diffusion process to distinguish between the generated labels and the real ones. A spatial attention map is computed based on the features learned by the discriminator to help cDAL generate more accurate segmentation of discriminative regions in an input image. Additionally, we incorporated a random latent embedding into each layer of our model to significantly reduce the number of training and sampling time-steps, thereby making it much faster than other diffusion models for image segmentation. We applied cDAL on 3 publicly available medical image segmentation datasets (MoNuSeg, Chest X-ray and Hippocampus) and observed significant qualitative and quantitative improvements with higher Dice scores and mIoU over the state-of-the-art algorithms. The source code is publicly available at https://github.com/Hejrati/cDAL/.
扩散模型已被广泛应用于高质量图像和视频生成任务。在本文中,我们提出了一种具有空间注意力和潜在嵌入(cDAL)的新型条件扩散模型,用于医学图像分割。在cDAL中,扩散过程的每个时间步都使用基于卷积神经网络(CNN)的判别器来区分生成的标签和真实的标签。基于判别器学习的特征计算空间注意力图,以帮助cDAL生成输入图像中判别区域的更准确分割。此外,我们将随机潜在嵌入融入模型中的每一层,以大大减少训练和采样时间步的数量,从而使它比其他图像分割扩散模型更快。我们在3个公开可用的医学图像分割数据集(MoNuSeg、Chest X-ray和Hippocampus)上应用了cDAL,并在最先进的算法上观察到显著的定性和定量改进,具有更高的Dice分数和mIoU。源代码可在https://github.com/Hejrati/cDAL/处获得。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 13 pages, 5 figures, 3 tables, Accepted in MICCAI 2024
Summary
医学图像分割中,提出一种新型的条件扩散模型cDAL,结合空间注意力和潜在嵌入。使用CNN判别器区分生成标签和真实标签,计算空间注意图以提高输入图像中判别区域的分割准确性。融入随机潜在嵌入,减少训练和采样时间步数,较其他图像分割扩散模型更快。在三个公开医学图像分割数据集上应用,获得较高的Dice分数和mIoU,优于现有算法。
Key Takeaways
- 提出新型条件扩散模型cDAL用于医学图像分割。
- 结合空间注意力和潜在嵌入技术。
- 使用CNN判别器以提高分割准确性。
- 空间注意图可帮助cDAL生成更准确的结果。
- 融入随机潜在嵌入以加速训练和采样过程。
- 在三个公开医学图像分割数据集上实现显著效果。
点此查看论文截图

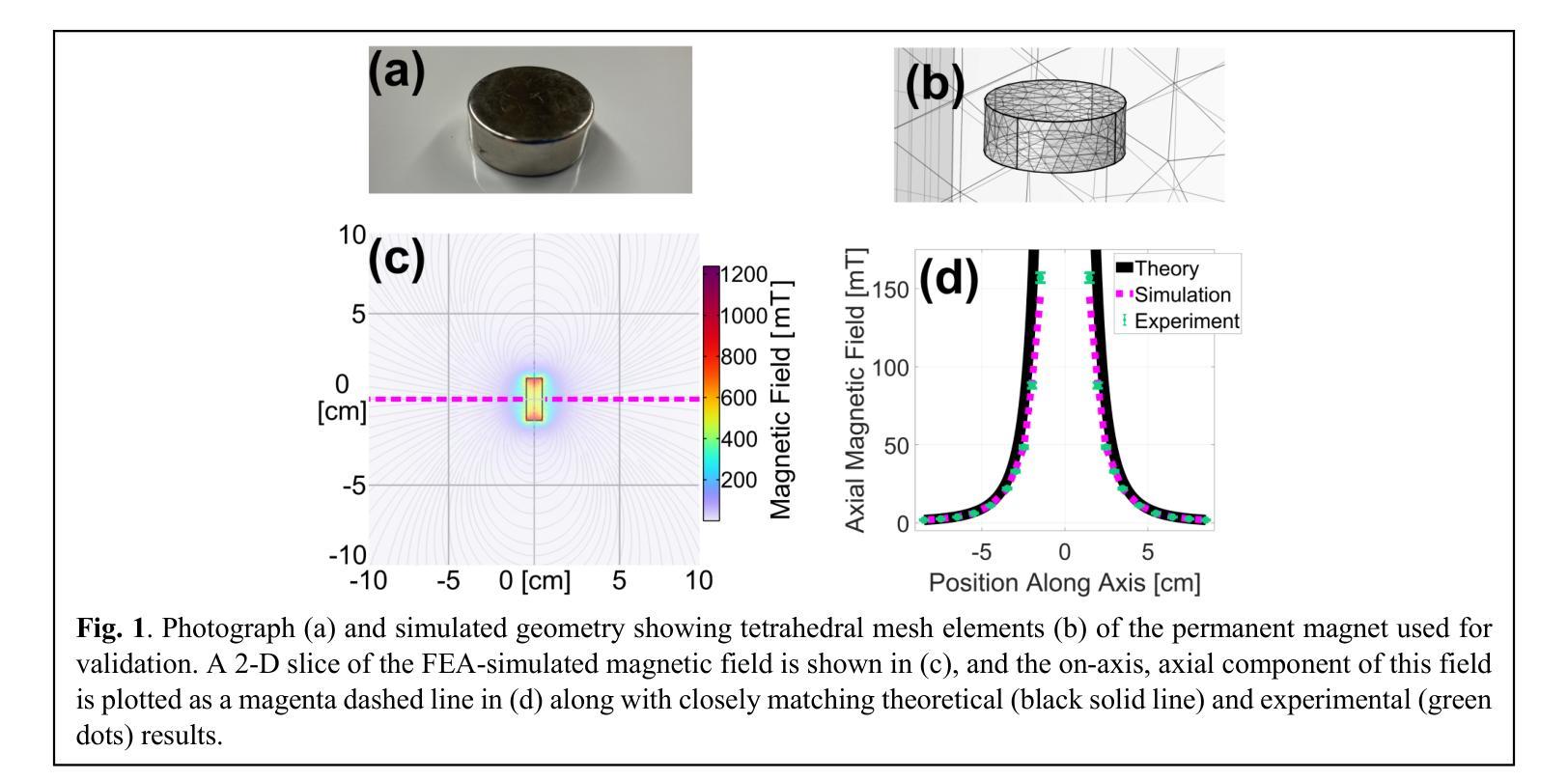
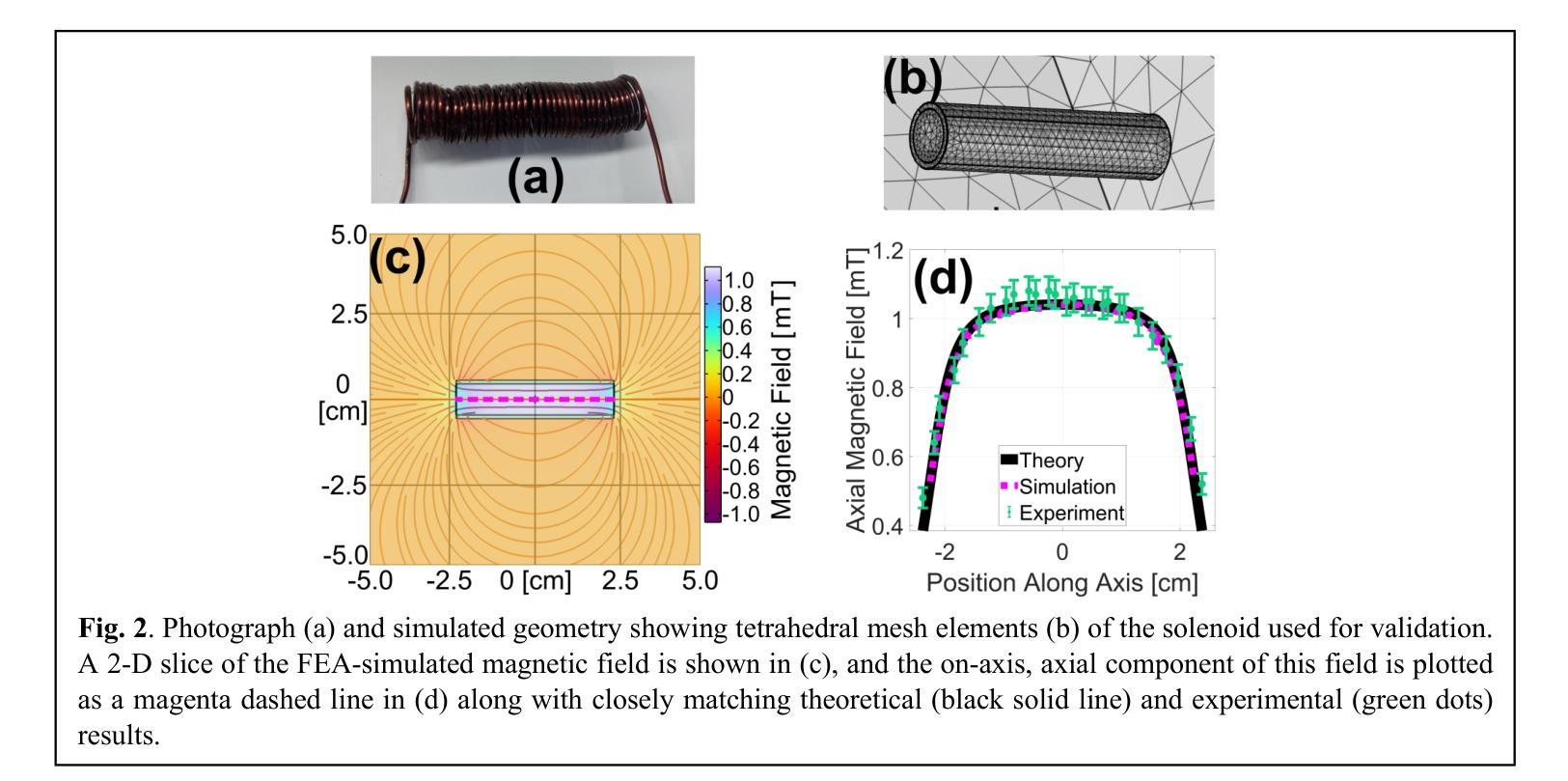
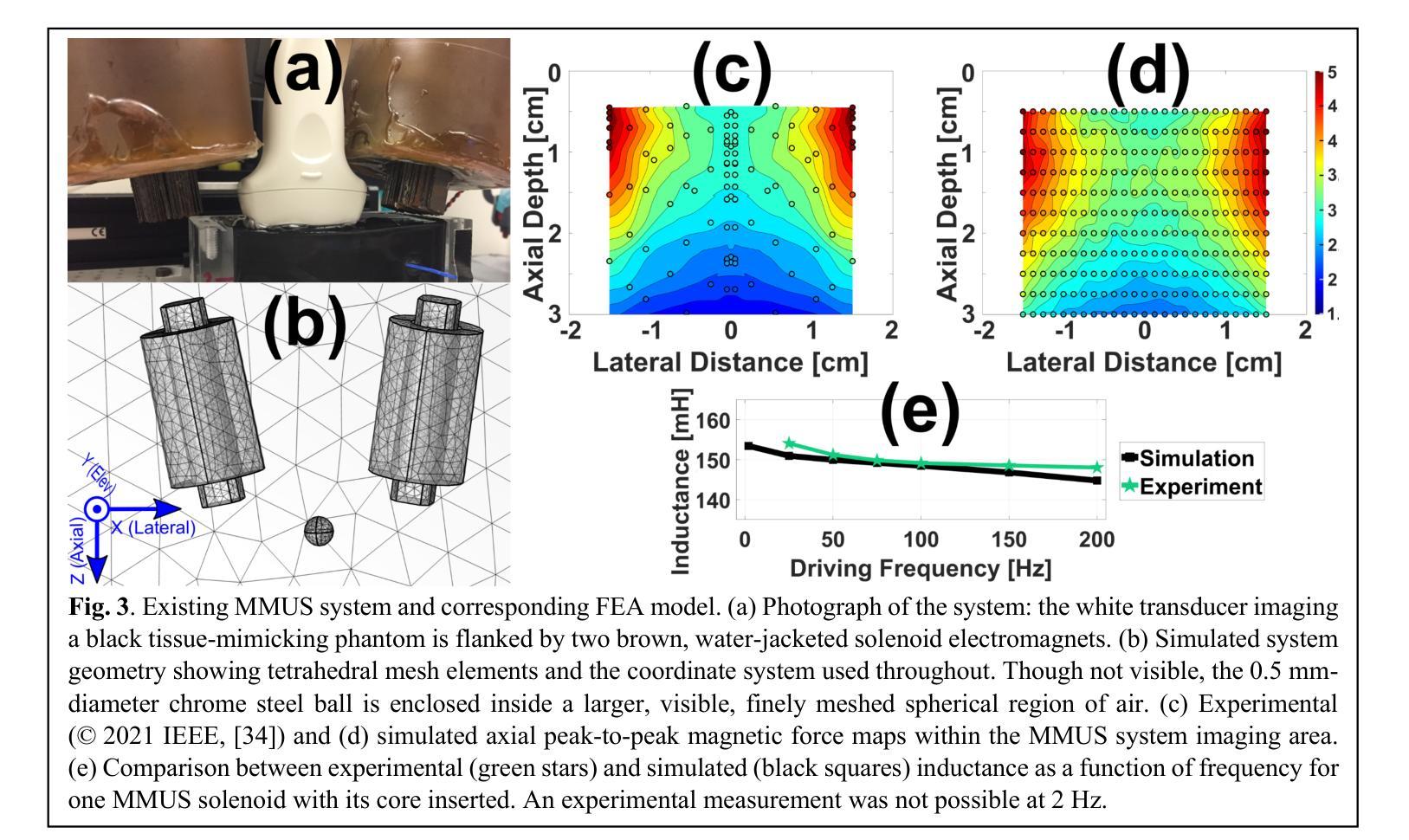
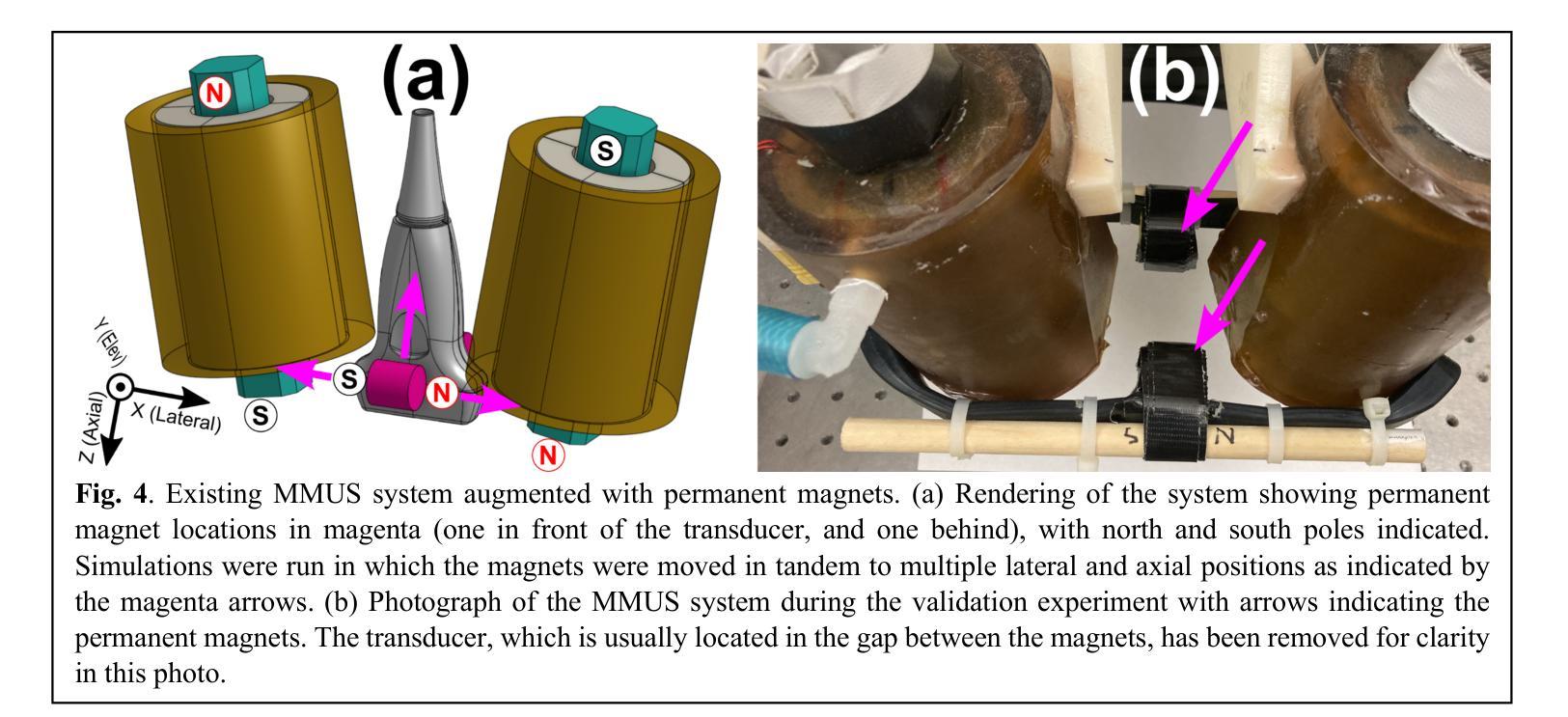
A Finite Element Analysis Model for Magnetomotive Ultrasound Elastometry Magnet Design with Experimental Validation
Authors:Jacquelline Nyakunu, Christopher T. Piatnichouk, Henry C. Russell, Niels J. van Duijnhoven, Benjamin E. Levy
Magnetomotive ultrasound (MMUS) using magnetic nanoparticle contrast agents has shown promise for thrombosis imaging and quantitative elastometry via magnetomotive resonant acoustic spectroscopy (MRAS). Young’s modulus measurements of smaller, stiffer thrombi require an MRAS system capable of generating forces at higher temporal frequencies. Solenoids with fewer turns, and thus less inductance, could improve high frequency performance, but the reduced force may compromise results. In this work, a computational model capable of assessing the effectiveness of MRAS elastometry magnet configurations is presented and validated. Finite element analysis (FEA) was used to model the force and inductance of MRAS systems. The simulations incorporated both solenoid electromagnets and permanent magnets in three-dimensional steady-state, frequency domain, and time domain studies. The model successfully predicted that a configuration in which permanent magnets were added to an existing MRAS system could be used to increase the force supplied. Accordingly, the displacement measured in a magnetically labeled validation phantom increased by a factor of $2.2 \pm 0.3$ when the force was predicted to increase by a factor of $2.2 \pm 0.2$. The model additionally identified a new solenoid configuration consisting of four smaller coils capable of providing sufficient force at higher driving frequencies. These results indicate two methods by which MRAS systems could be designed to deliver higher frequency magnetic forces without the need for experimental trial and error. Either the number of turns within each solenoid could be reduced while permanent magnets are added at precise locations, or a larger number of smaller solenoids could be used. These findings overcome a key challenge toward the goal of MMUS thrombosis elastometry, and simulation files are provided online for broader experimentation.
磁动超声(MMUS)利用磁性纳米粒子造影剂在血栓成像和定量弹性测量方面表现出巨大潜力,这通过磁动共振声学光谱法(MRAS)实现。对较小、较硬的血栓的杨氏模量测量需要一种能够在较高时间频率下产生力的MRAS系统。具有较少匝数、因此电感较小的螺线管可以提高高频性能,但减小的作用力可能会损害结果。在这项工作中,提出了一种能够评估MRAS弹性测量磁构型的有效性的计算模型,并进行验证。有限元分析(FEA)用于模拟MRAS系统的力和电感。模拟结合了螺线管电磁铁和永久磁铁的三维稳态、频域和时域研究。该模型成功预测,向现有MRAS系统添加永久磁铁的配置可用于增加所提供的力。因此,在预测力增加了一个因子$2.2±0.2$的情况下,磁性标记验证模型中的位移增加了$2.2±0.3$倍。此外,该模型还确定了一种新的螺线管配置,由四个较小的线圈组成,能够在较高的驱动频率下提供足够的力。这些结果表明,可以通过两种方法设计MRAS系统以产生较高频率的磁力,无需通过实验反复试错。一种方法是减少每个螺线管中的匝数,同时在精确位置添加永久磁铁;另一种方法是使用更多较小的螺线管。这些发现为实现MMUS血栓弹性测量的目标克服了关键挑战,并且仿真文件已在线提供供进一步实验使用。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 12 pages, 8 figures. This manuscript has been revised from version v1 via the peer review process. It has been accepted in its current form and is awaiting publication at Biomedical Physics and Engineering Express
Summary
本文介绍了磁动机超声(MMUS)利用磁性纳米粒子造影剂在血栓成像和定量弹性测量方面的潜力。为提高对较小、较硬血栓的杨氏模量测量能力,需要能在更高时间频率下产生力的MRAS系统。研究提出了一种能够评估MRAS弹性测量磁配置的有效性的计算模型,并通过有限元分析(FEA)进行模拟验证。模型成功预测了添加永久磁铁到现有MRAS系统中可增加提供的力的配置。此外,模型还识别了一种新的由四个小型线圈组成的天线配置,能够在较高的驱动频率下提供足够的力量。这标志着解决MRAS系统在设计上朝着更高频率磁场力发展的两大突破,无需实验性的反复试错。这些发现克服了实现MMUS血栓弹性测量的关键挑战,且模拟文件已在线提供以供更广泛的实验使用。
Key Takeaways
- MMUS使用磁性纳米粒子造影剂在血栓成像和定量弹性测量方面展现潜力。
- 高频性能提升需要能在更高时间频率下产生力的MRAS系统。
- 计算模型通过有限元分析评估不同磁配置的有效性。
- 添加永久磁铁到MRAS系统中可增加提供的力。
- 新识别的一种由四个小型线圈组成的配置能在高驱动频率下提供足够力量。
- 这些发现解决了设计MRAS系统以实现更高频率磁场力的关键挑战。
点此查看论文截图

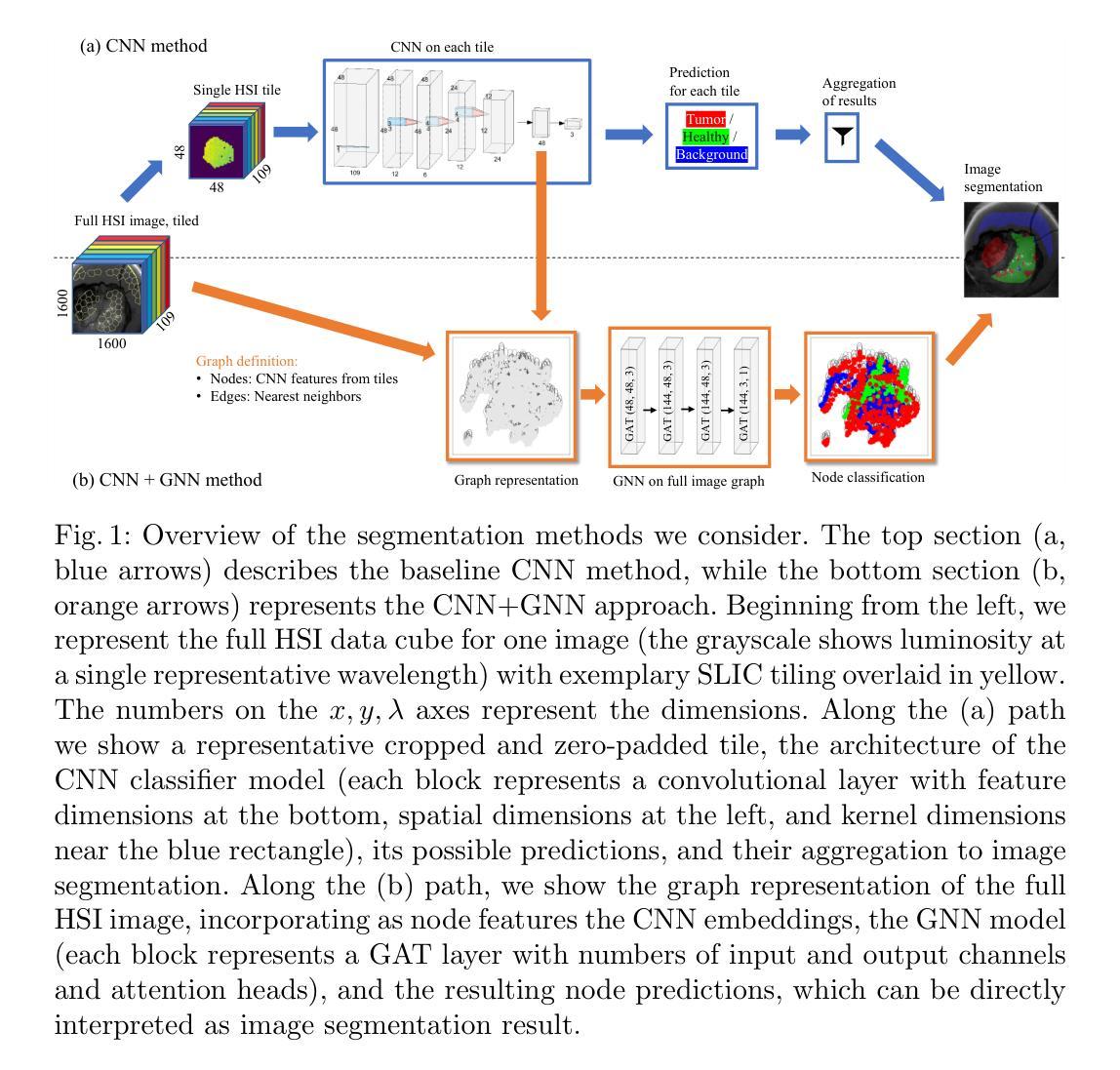
Robust Tumor Segmentation with Hyperspectral Imaging and Graph Neural Networks
Authors:Mayar Lotfy Mostafa, Anna Alperovich, Tommaso Giannantonio, Bjorn Barz, Xiaohan Zhang, Felix Holm, Nassir Navab, Felix Boehm, Carolin Schwamborn, Thomas K. Hoffmann, Patrick J. Schuler
Segmenting the boundary between tumor and healthy tissue during surgical cancer resection poses a significant challenge. In recent years, Hyperspectral Imaging (HSI) combined with Machine Learning (ML) has emerged as a promising solution. However, due to the extensive information contained within the spectral domain, most ML approaches primarily classify individual HSI (super-)pixels, or tiles, without taking into account their spatial context. In this paper, we propose an improved methodology that leverages the spatial context of tiles for more robust and smoother segmentation. To address the irregular shapes of tiles, we utilize Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) to propagate context information across neighboring regions. The features for each tile within the graph are extracted using a Convolutional Neural Network (CNN), which is trained simultaneously with the subsequent GNN. Moreover, we incorporate local image quality metrics into the loss function to enhance the training procedure’s robustness against low-quality regions in the training images. We demonstrate the superiority of our proposed method using a clinical ex vivo dataset consisting of 51 HSI images from 30 patients. Despite the limited dataset, the GNN-based model significantly outperforms context-agnostic approaches, accurately distinguishing between healthy and tumor tissues, even in images from previously unseen patients. Furthermore, we show that our carefully designed loss function, accounting for local image quality, results in additional improvements. Our findings demonstrate that context-aware GNN algorithms can robustly find tumor demarcations on HSI images, ultimately contributing to better surgery success and patient outcome.
在手术切除癌症的过程中,区分肿瘤和健康组织的边界是一个巨大的挑战。近年来,高光谱成像(HSI)结合机器学习(ML)已成为一种前景广阔的解决方案。然而,由于光谱域内包含的大量信息,大多数机器学习的方法主要对单个HSI(超级)像素或瓦片进行分类,而没有考虑到它们的空间上下文。在本文中,我们提出了一种改进的方法,该方法利用瓦片的空间上下文来实现更稳健、更平滑的分割。为了解决瓦片形状不规则的问题,我们利用图神经网络(GNNs)在邻近区域之间传播上下文信息。图中每个瓦片的特征是使用卷积神经网络(CNN)提取的,该网络是与随后的GNN同时训练的。此外,我们将局部图像质量指标纳入损失函数中,以提高训练过程对训练图像中低质量区域的稳健性。我们使用由30名患者的51张HSI图像组成的临床离体数据集来证明我们提出的方法的优越性。尽管数据集有限,但基于GNN的模型显著优于上下文无关的方法,能够准确区分健康组织和肿瘤组织,即使在以前未见过的患者的图像中也是如此。此外,我们表明,我们精心设计的考虑局部图像质量的损失函数会导致额外的改进。我们的研究结果表明,上下文感知的GNN算法可以稳健地在HSI图像上找到肿瘤边界,最终有助于提高手术成功率和患者治疗效果。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 18 pages, 5 figures, The German Conference on Pattern Recognition (GCPR) 2024
Summary
本论文提出了一种利用图神经网络(GNN)结合卷积神经网络(CNN)的方法,通过考虑超光谱成像(HSI)中像素的空间上下文信息,实现对肿瘤与健康组织的更稳健、平滑的分割。该方法在有限的临床离体数据集上表现出显著优势,能准确区分健康组织和肿瘤组织,甚至在对未见患者的新图像上也有良好表现。同时,考虑到局部图像质量的损失函数设计进一步提高模型的稳健性。
Key Takeaways
- 超光谱成像(HSI)结合机器学习(ML)在肿瘤切除手术中区分肿瘤和健康组织方面具有潜力。
- 大多数ML方法主要对HSI像素或瓦片进行分类,忽略了其空间上下文信息。
- 本研究提出了一种利用图神经网络(GNN)的方法,考虑瓦片的空间上下文信息,实现更稳健和平滑的分割。
- 通过卷积神经网络(CNN)提取瓦片特征,并与随后的图神经网络(GNN)一起进行训练。
- 纳入局部图像质量指标,增强训练程序对低质量区域的稳健性。
- 在包含51张HSI图像的临床离体数据集上验证了所提出方法的优越性,该数据集来自30名患者。
点此查看论文截图